Class 12 : Physics (English) – Chapter 13: Nuclei
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction to the Nucleus
The atom, once thought to be indivisible, is now understood as a system with a tiny but massive nucleus at its centre.
This nucleus contains protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral), collectively called nucleons.
➡️ The size of the nucleus is about 10⁻¹⁵ m, whereas the size of the atom is about 10⁻¹⁰ m.
✔️ This means that if an atom were a stadium, the nucleus would be like a marble at the centre, yet carrying nearly all the mass.
🟢 Atomic Mass and Composition
Atomic number (Z): Number of protons.
Mass number (A): Total number of protons + neutrons.
Neutron number (N): N = A – Z.
💡 Concept:
Isotopes → Same Z, different N.
Isobars → Same A, different Z.
Isotones → Same N, different Z.
✏️ Note: Atomic masses are measured in u (atomic mass unit), where 1 u = 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
🔴 Size of the Nucleus
Nuclear radius formula:
R = R₀ A^(1/3), with R₀ ≈ 1.2 × 10⁻¹⁵ m.
➡️ Since radius grows only as cube root of A:
✔️ Larger nuclei are not proportionally much bigger than lighter nuclei.
Volume ∝ A
Mass ∝ A
Hence, nuclear density ≈ constant ≈ 2.3 × 10¹⁷ kg/m³.
🌿 This density is unimaginably high: A sugar cube of nuclear matter would weigh billions of tonnes!
🟡 Mass Defect and Binding Energy
The actual mass of a nucleus is less than the sum of masses of its nucleons.
This difference = Mass defect (Δm).
Formula:
Δm = [Z m_p + N m_n] – m_nucleus
➡️ Binding energy (B) is energy equivalent of Δm:
B = Δm c²
Binding energy per nucleon (B/A): A measure of nuclear stability.
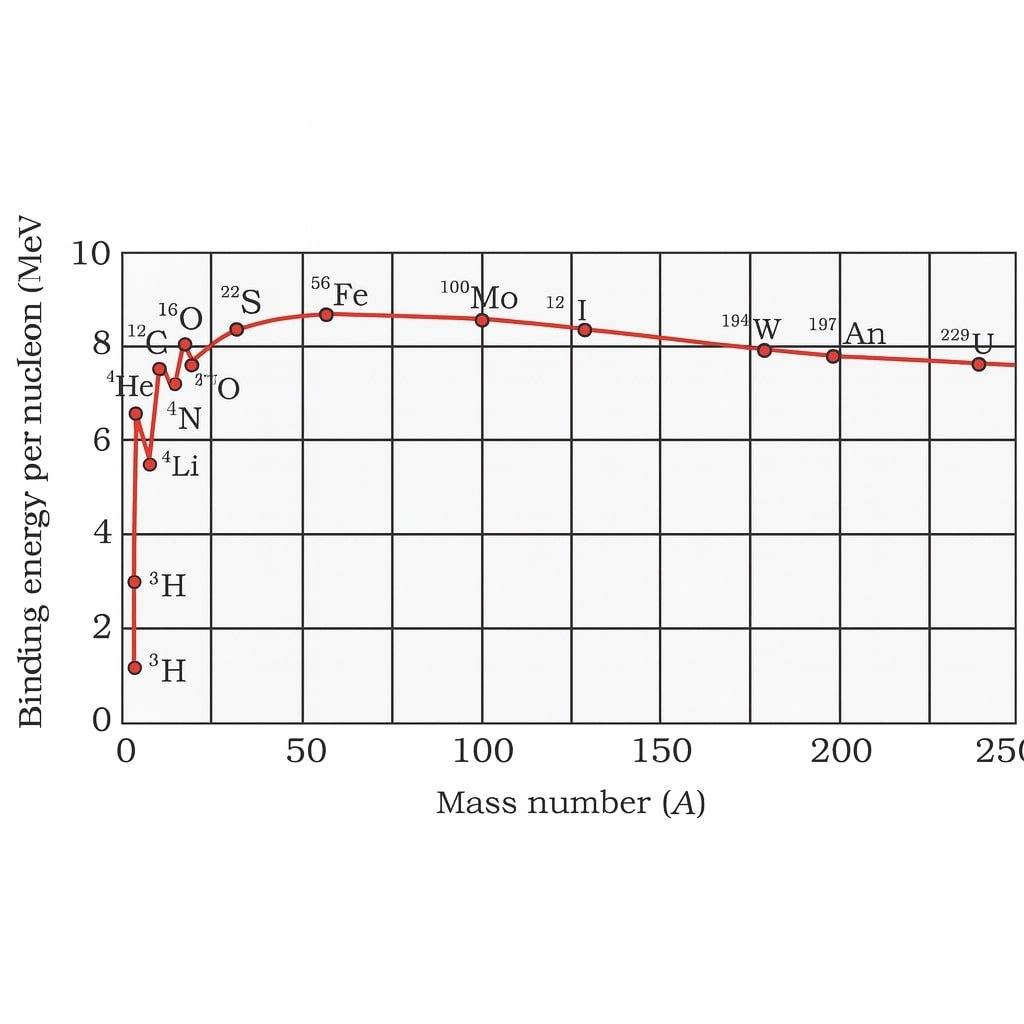
✔️ Curve of B/A vs A shows:
🔵 Light nuclei have small B/A.
🟢 Maximum stability at iron (A ≈ 56).
🔴 Very heavy nuclei have smaller B/A.
💡 This explains:
Fusion of light nuclei → energy release.
Fission of heavy nuclei → energy release.
🔵 Nuclear Force

Nucleons are held together by the nuclear force.
Properties:
✔️ Extremely strong (much stronger than electrostatic force).
✔️ Short range (works within ~2–3 femtometres).
✔️ Charge independent (acts same between p–p, n–n, p–n).
✔️ Saturation → each nucleon interacts only with nearest neighbours.
✏️ Note: Despite protons repelling by Coulomb’s law, nuclear force keeps them bound.
🟢 Radioactivity
Unstable nuclei undergo radioactive decay spontaneously.
Types:
Alpha decay (α): Nucleus emits a helium nucleus (2p + 2n).
Z decreases by 2, A decreases by 4.
Beta minus decay (β⁻): Neutron → Proton + electron + antineutrino.
Z increases by 1, A unchanged.
Beta plus decay (β⁺): Proton → Neutron + positron + neutrino.
Z decreases by 1, A unchanged.
Gamma decay (γ): Excited nucleus emits a photon; A and Z unchanged.
🔴 Law of Radioactive Decay
If N(t) is the number of undecayed nuclei at time t:
N(t) = N₀ e^(−λt)
where λ = decay constant.
Activity A(t) = λN(t).
Half-life T₁/₂ = (ln 2)/λ.
Mean life τ = 1/λ = 1.44 T₁/₂.
✔️ The law is exponential and universal.
💡 Example: If activity drops to 1/16th, 4 half-lives have passed.
🟡 Nuclear Energy
(a) Fission
➡️ A heavy nucleus like U-235 splits into two smaller nuclei when struck by a neutron.
Releases ~200 MeV per fission.
Used in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
✔️ In reactors, control rods regulate neutron supply to keep reaction steady.
(b) Fusion
➡️ Two light nuclei combine, e.g.:
²H + ³H → ⁴He + n + 17.6 MeV
Source of energy in stars.
Requires very high temperature (~10⁷ K).
Promising for future energy (hydrogen bomb, fusion reactors).
🔵 Applications of Radioactivity
Carbon dating: C-14 (half-life 5730 years) helps determine age of fossils.
Medical use: I-131 for thyroid, Co-60 for cancer therapy.
Industrial use: Tracers in pipelines, thickness gauges.
🟢 Environmental Concerns
Fission reactors produce radioactive waste.
Accidents (Chernobyl, Fukushima) highlight risks.
Fusion is cleaner but technologically challenging.
✨ Summary Section (~300 words)
🔵 Overview
The nucleus is a tiny, dense core with protons and neutrons.
Mass number (A) = Z + N.
Nuclear radius ∝ A^(1/3); density nearly constant.
🟢 Key Concepts
Mass defect arises because the nucleus is lighter than its nucleons’ sum.
This lost mass = binding energy, showing stability.
Binding energy per nucleon peaks at iron (A ≈ 56).
🔴 Forces
Nuclear force: short-ranged, very strong, charge-independent, saturating.
🟡 Radioactivity
Decay follows exponential law.
Half-life T₁/₂ = ln 2 / λ.
Mean life τ = 1.44 T₁/₂.
α decay → Z–2, A–4.
β⁻ decay → Z+1.
β⁺ decay → Z–1.
γ decay → Z, A unchanged.
🔵 Nuclear Energy
Fission: Heavy nucleus splits → 200 MeV energy.
Fusion: Light nuclei fuse → immense energy (sun, hydrogen bomb).
🟢 Applications
Archaeology (carbon dating).
Medicine (diagnosis, therapy).
Industry (tracers, thickness control).
🔴 Concerns
Fission → radioactive waste.
Fusion → promising but challenging.
📝 Quick Recap
✔️ Nucleus = protons + neutrons; tiny but massive.
✔️ Nuclear radius ∝ A^(1/3); density constant.
✔️ Mass defect → binding energy; stability peaks at Fe.
✔️ Radioactive decay follows N(t) = N₀ e^(−λt).
✔️ Fission (heavy nuclei split) and fusion (light nuclei join) release huge energy.
✔️ Uses: dating, medicine, industry; concerns: waste, safety, environment.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 13.1
Obtain the binding energy (in MeV) of a nitrogen nucleus (₇¹⁴N).
Given: m(₇¹⁴N) = 14.00307 u, mₚ = 1.007825 u, mₙ = 1.008665 u.
Answer 13.1
🔵 Step 1: Identify Z and N
Z = 7, A = 14 ⇒ N = 14 − 7 = 7
🟢 Step 2: Mass defect
Δm = [Z mₚ + N mₙ] − m(nucleus)
= [7(1.007825) + 7(1.008665)] − 14.00307
= 14.11543 − 14.00307 = 0.11236 u
🟠 Step 3: Binding energy
B = Δm × 931.5 = 0.11236 × 931.5 ≈ 104.66 MeV
🔴 Step 4: Binding energy per nucleon
B/A = 104.66 / 14 ≈ 7.48 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: Binding energy ≈ 104.66 MeV
Question 13.2
Obtain the binding energy of the nuclei ₂₆⁵⁶Fe and ₈₃²⁰⁸Bi.
Given: m(₂₆⁵⁶Fe) = 55.934939 u, m(₈₃²⁰⁸Bi) = 208.980388 u.
Answer 13.2
🔵 For ₂₆⁵⁶Fe: Z = 26, N = 30
Δm = [26(1.007825) + 30(1.008665)] − 55.934939
= 56.46340 − 55.934939 = 0.528461 u
B = 0.528461 × 931.5 ≈ 492.26 MeV
B/A = 492.26 / 56 ≈ 8.79 MeV
🟢 For ₈₃²⁰⁸Bi: Z = 83, N = 125
Δm = [83(1.007825) + 125(1.008665)] − 208.980388
= 209.732600 − 208.980388 = 0.752212 u
B = 0.752212 × 931.5 ≈ 700.69 MeV
B/A = 700.69 / 208 ≈ 3.37 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: Fe-56 = 492.26 MeV (8.79 MeV/nucleon); Bi-208 = 700.69 MeV (3.37 MeV/nucleon)
Question 13.3
A coin of mass 3.0 g is entirely made of ₂₉⁶³Cu (m = 62.92960 u). Calculate the nuclear energy required to separate all the neutrons and protons.
Answer 13.3
🔵 Step 1: Number of atoms
Moles = 3 / 63 = 0.04762 mol
Atoms = 0.04762 × 6.023×10²³ ≈ 2.87×10²² nuclei
🟢 Step 2: Mass defect for ₂₉⁶³Cu
Z = 29, N = 34
Δm = [29(1.007825) + 34(1.008665)] − 62.92960
= 63.521535 − 62.92960 = 0.591935 u
🟠 Step 3: Binding energy per nucleus
B = 0.591935 × 931.5 ≈ 551.39 MeV
🔴 Step 4: Total energy
E(MeV) = 551.39 × 2.87×10²² ≈ 1.58×10²⁵ MeV
E(J) = 1.58×10²⁵ × 1.6×10⁻¹³ ≈ 2.53×10¹² J
✔️ Final Answer: ≈ 2.53×10¹² J
Question 13.4
Obtain approximately the ratio of the nuclear radii of ₇₉¹⁹⁷Au and ₄₇¹⁰⁷Ag.
Answer 13.4
🔵 Formula: R ∝ A^(1/3)
🟢 Ratio = (197/107)^(1/3) ≈ 1.226
✔️ Final Answer: R(Au)/R(Ag) ≈ 1.23
Question 13.5
Calculate Q-value of the reactions:
(i) ²H + ²H → ³He + ¹n
(ii) ¹²C + ²H → ²⁰Ne + ⁴He
Given: m(²H) = 2.014102 u, m(³He) = 3.016049 u, m(¹²C) = 12.000000 u, m(²⁰Ne) = 19.992439 u, m(⁴He) = 4.002603 u, mₙ = 1.008665 u.
Answer 13.5
🔹 For (i):
Δm = [2×2.014102] − [3.016049 + 1.008665] = 0.003490 u
Q = 0.003490 × 931.5 ≈ 3.25 MeV (positive)
✔️ Exothermic
🔹 For (ii):
Δm = [12.000000 + 2.014102] − [19.992439 + 4.002603] = −9.98094 u
Q = −9.98094 × 931.5 ≈ −9.30×10³ MeV (negative)
✔️ Endothermic
Question 13.6
Check whether fission of ₂₆⁵⁶Fe → 2(₁₃²⁸Al) is energetically possible.
Given: m(₂₆⁵⁶Fe) = 55.93494 u, m(₁₃²⁸Al) = 27.98191 u.
Answer 13.6
🔵 Mass defect: Δm = 55.93494 − 2(27.98191) = −0.02888 u
🟢 Q = −0.02888 × 931.5 ≈ −26.90 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: Q < 0 ⇒ Fission is not energetically possible
Question 13.7
The fission properties of ₉₄²³⁹Pu are very similar to those of ₉₂²³⁵U. The average energy released per fission is 180 MeV. How much energy, in MeV, is released if all the atoms in 1 kg of ₉₄²³⁹Pu undergo fission?
Answer 13.7
🔵 Step 1: Moles of ₂³⁹Pu
molar mass ≈ 239 g/mol → moles = 1000 g / 239 g/mol ≈ 4.184 mol
🟢 Step 2: Number of atoms
atoms = 4.184 × 6.023×10²³ ≈ 2.52×10²⁴
🟠 Step 3: Total fission energy
E = (number of fissions) × (energy per fission)
E ≈ 2.52×10²⁴ × 180 MeV ≈ 4.54×10²⁶ MeV
✔️ Final Answer: ≈ 4.54×10²⁶ MeV
Question 13.8
How long can an electric lamp of 100 W be kept glowing by fusion of 2.0 kg of deuterium?
Take the fusion reaction as: ²H + ²H → ³He + n + 3.27 MeV.
Answer 13.8
🔵 Step 1: Amount of deuterium atoms
molar mass of D ≈ 2 g/mol → moles = 2000 g / 2 g/mol = 1000 mol
atoms = 1000 × 6.023×10²³ = 6.023×10²⁶
🟢 Step 2: Number of fusion reactions (2 D per reaction)
reactions = 6.023×10²⁶ / 2 = 3.012×10²⁶
🟠 Step 3: Total energy released
E(MeV) = 3.012×10²⁶ × 3.27 ≈ 9.85×10²⁶ MeV
convert to joules: E(J) = 9.85×10²⁶ × 1.6×10⁻¹³ ≈ 1.58×10¹⁴ J
🔴 Step 4: Time for a 100 W lamp (P = 100 J s⁻¹)
t = E / P = 1.58×10¹⁴ / 100 = 1.58×10¹² s
in years: t ≈ 1.58×10¹² / 3.154×10⁷ ≈ 5.0×10⁴ years
✔️ Final Answer: ≈ 5.0×10⁴ years
Question 13.9
Calculate the height of the potential barrier for a head-on collision of two deuterons. (Hint: Treat deuterons as hard spheres of radius 2.0 fm that just touch each other.)
Answer 13.9
🔵 Step 1: Separation at contact
each radius = 2.0 fm → centre-to-centre r = 4.0 fm = 4.0×10⁻¹⁵ m
🟢 Step 2: Coulomb potential energy
U = (1 / 4πϵ₀) (e² / r)
≈ (9.0×10⁹) × (1.6×10⁻¹⁹)² / (4.0×10⁻¹⁵) J
🟠 Step 3: Compute
(1.6×10⁻¹⁹)² = 2.56×10⁻³⁸
U ≈ 9.0×10⁹ × (2.56×10⁻³⁸ / 4.0×10⁻¹⁵)
= 9.0×10⁹ × 6.4×10⁻²⁴ = 5.76×10⁻¹⁴ J
🔴 Step 4: Convert to MeV (1 MeV = 1.6×10⁻¹³ J)
U ≈ 5.76×10⁻¹⁴ / 1.6×10⁻¹³ ≈ 0.36 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: ≈ 0.36 MeV
Question 13.10
From R = R₀ A^(1/3), where R₀ is a constant and A is the mass number of a nucleus, show that the nuclear matter density is nearly constant (independent of A).
Answer 13.10
🔵 Step 1: Nuclear mass
M ≈ A m_N, where m_N is average nucleon mass (≈ constant)
🟢 Step 2: Nuclear volume
V = (4/3)πR³ = (4/3)π (R₀ A^(1/3))³ = (4/3)π R₀³ A
🟠 Step 3: Density
ρ = M / V = (A m_N) / ((4/3)π R₀³ A) = m_N / ((4/3)π R₀³)
🔴 Step 4: Conclusion
A cancels out; ρ depends only on constants m_N and R₀ → independent of A
✔️ Final Answer: Nuclear density is nearly constant for all nuclei
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Section A (Q1–Q18: MCQs)
Question 1
Which of the following correctly represents the relation between A, Z, and N?
🔵 (A) A = Z – N
🟢 (B) A = Z + N
🟠 (C) A = Z × N
🔴 (D) A = Z/N
Answer: (B) A = Z + N
✔️ Final Answer: A = Z + N
Question 2
The radius of a nucleus varies with mass number as:
🔵 (A) R ∝ A
🟢 (B) R ∝ A^(1/2)
🟠 (C) R ∝ A^(1/3)
🔴 (D) R ∝ A^(2/3)
Answer: (C) R ∝ A^(1/3)
✔️ Final Answer: R ∝ A^(1/3)
Question 3
The approximate nuclear density is:
🔵 (A) 10^3 kg/m^3
🟢 (B) 10^6 kg/m^3
🟠 (C) 10^12 kg/m^3
🔴 (D) 10^17 kg/m^3
Answer: (D) 10^17 kg/m^3
✔️ Final Answer: 10^17 kg/m^3
Question 4
Which force binds protons and neutrons inside the nucleus?
🔵 (A) Gravitational force
🟢 (B) Coulomb force
🟠 (C) Strong nuclear force
🔴 (D) Weak nuclear force
Answer: (C) Strong nuclear force
✔️ Final Answer: Strong nuclear force
Question 5
In beta-minus (β⁻) decay, the atomic number:
🔵 (A) decreases by 1
🟢 (B) increases by 1
🟠 (C) remains unchanged
🔴 (D) decreases by 2
Answer: (B) increases by 1
✔️ Final Answer: Increases by 1
Question 6
The half-life of a radioactive sample is 10 days. In 30 days, its activity will reduce to:
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
✔️ Final Answer: 1/8
Question 7
The maximum binding energy per nucleon is observed for nuclei around:
🔵 (A) Hydrogen
🟢 (B) Helium
🟠 (C) Iron
🔴 (D) Uranium
Answer: (C) Iron
✔️ Final Answer: Iron (A ≈ 56)
Question 8
If Q-value of a reaction is positive, the reaction is:
🔵 (A) Endothermic
🟢 (B) Exothermic
🟠 (C) Forbidden
🔴 (D) Impossible
Answer: (B) Exothermic
✔️ Final Answer: Exothermic
Question 9
Mean life τ and half-life T1/2 are related as:
🔵 (A) τ = T1/2
🟢 (B) τ = T1/2 / ln2
🟠 (C) τ = T1/2 × ln2
🔴 (D) τ = (T1/2)^2
Answer: (B) τ = T1/2 / ln2
✔️ Final Answer: τ = T1/2 / ln2
Question 10
Carbon dating is based on isotope:
🔵 (A) C-12
🟢 (B) C-13
🟠 (C) C-14
🔴 (D) C-11
Answer: (C) C-14
✔️ Final Answer: C-14
Question 11
Which of the following statements is correct for gamma (γ) emission?
🔵 (A) A decreases, Z decreases
🟢 (B) A unchanged, Z unchanged
🟠 (C) A increases, Z decreases
🔴 (D) A unchanged, Z increases
Answer: (B) A unchanged, Z unchanged
✔️ Final Answer: A and Z unchanged
Question 12
The SI unit of radioactivity is:
🔵 (A) Curie (Ci)
🟢 (B) Becquerel (Bq)
🟠 (C) Tesla (T)
🔴 (D) Weber (Wb)
Answer: (B) Becquerel (Bq)
✔️ Final Answer: Becquerel (Bq)
Question 13
Which of the following has the least penetration power?
🔵 (A) α-particle
🟢 (B) β-particle
🟠 (C) γ-ray
🔴 (D) Neutrino
Answer: (A) α-particle
✔️ Final Answer: α-particle
Question 14
The equation of radioactive decay is:
🔵 (A) N = N0 e^(λt)
🟢 (B) N = N0 e^(−λt)
🟠 (C) N = N0 (1 − λt)
🔴 (D) N = N0 λt
Answer: (B) N = N0 e^(−λt)
✔️ Final Answer: N = N0 e^(−λt)
Question 15
Which conservation law explains neutrino emission in β-decay?
🔵 (A) Conservation of momentum
🟢 (B) Conservation of lepton number
🟠 (C) Conservation of charge
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
✔️ Final Answer: All of these
Question 16
Binding energy per nucleon decreases for very heavy nuclei because:
🔵 (A) Coulomb repulsion increases
🟢 (B) Nuclear force becomes weak
🟠 (C) Electrons dominate
🔴 (D) Protons escape
Answer: (A) Coulomb repulsion increases
✔️ Final Answer: Coulomb repulsion increases
Question 17
If activity becomes 1/16 of initial, number of elapsed half-lives is:
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 3
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 5
Answer: (C) 4
✔️ Final Answer: 4 half-lives
Question 18
The mass defect Δm of a nucleus leads to binding energy B according to:
🔵 (A) B = Δm × g
🟢 (B) B = Δm × c^2
🟠 (C) B = Δm × h
🔴 (D) B = Δm / c^2
Answer: (B) B = Δm × c^2
✔️ Final Answer: B = Δm × c^2
Section B (Q19–Q23: Very Short Answer)
Question 19
Define binding energy per nucleon. Why is it a measure of stability?
Answer:
🔵 B/A = total binding energy ÷ A.
🟢 Higher B/A ⇒ nucleons more tightly bound.
✔️ Final Answer: Binding energy per nucleon is stability index
Question 20
State two properties of nuclear force.
Answer:
🔵 Very strong but short-ranged (~2–3 fm).
🟢 Saturating nature – each nucleon interacts with nearby nucleons only.
✔️ Final Answer: Strong, short-ranged, saturating
Question 21
Write the relation between half-life and decay constant.
Answer:
🔵 N = N0 e^(−λt).
🟢 At t = T1/2, N = N0/2.
🟠 ⇒ e^(−λT1/2) = 1/2 → λT1/2 = ln2.
✔️ Final Answer: T1/2 = ln2 / λ
Question 22
What is Q-value of a nuclear reaction? When is it exothermic?
Answer:
🔵 Q = [m(initial) − m(final)] c^2.
🟢 If Q > 0, exothermic.
✔️ Final Answer: Q > 0 → exothermic
Question 23
Why is U-235 used as fuel in reactors instead of U-238?
Answer:
🔵 U-235 undergoes fission with thermal neutrons.
🟢 U-238 requires fast neutrons.
✔️ Final Answer: U-235 is fissionable with slow neutrons
Section C (Q24–Q28: Mid-length Numericals/Theory)
Question 24
A nucleus has A = 64. Calculate its radius using R0 = 1.2×10^−15 m.
Answer:
🔵 Formula: R = R0 A^(1/3).
🟢 64^(1/3) = 4.
🟠 R = 1.2×10^−15 × 4 = 4.8×10^−15 m.
✔️ Final Answer: 4.8×10^−15 m
Question 25
The activity of a sample drops from 8000/s to 1000/s. How many half-lives have elapsed?
Answer:
🔵 Ratio = 1000/8000 = 1/8 = (1/2)^3.
🟢 Elapsed half-lives = 3.
✔️ Final Answer: 3 half-lives
Question 26
A radionuclide has mean life 10 h. Calculate half-life.
Answer:
🔵 Relation: τ = T1/2 / ln2.
🟢 T1/2 = τ ln2 = 10 × 0.693 = 6.93 h.
✔️ Final Answer: 6.93 h
Question 27
Explain why α-decay occurs in heavy nuclei.
Answer:
🔵 Coulomb repulsion is very high in heavy nuclei.
🟢 α-emission reduces Z and A, lowering Coulomb energy.
✔️ Final Answer: α-decay reduces repulsion, giving stability
Question 28
Show that nuclear density is independent of A.
Answer:
🔵 R = R0 A^(1/3).
🟢 V ∝ A, M ∝ A.
🟠 ρ = M/V = constant.
✔️ Final Answer: Nuclear density constant, independent of A
Section D (Q29–Q31: Long Answer)
Question 29
Derive the law of radioactive decay.
Answer:
🔵 dN/dt = −λN.
🟢 ∫ dN/N = −λ ∫ dt.
🟠 lnN = −λt + C.
🔴 N = N0 e^(−λt).
🟣 T1/2 = ln2 / λ.
✔️ Final Answer: N = N0 e^(−λt), T1/2 = ln2 / λ
Question 30
Explain binding energy and its relation with mass defect.
Answer:
🔵 Δm = Zmp + Nmn − Mnucleus.
🟢 Binding energy B = Δm c^2.
🟠 B/A measures stability.
✔️ Final Answer: B = Δm c^2, B/A = stability index
Question 31
Discuss α, β, and γ decays in terms of A and Z.
Answer:
🔵 α: ΔA = −4, ΔZ = −2.
🟢 β⁻: ΔA = 0, ΔZ = +1.
🟠 β⁺: ΔA = 0, ΔZ = −1.
🔴 γ: ΔA = 0, ΔZ = 0.
✔️ Final Answer: α changes A,Z; β changes Z; γ leaves A,Z same
Section E (Q32–Q33: Case/Application)
Question 32
A radioactive sample has N0 nuclei. Write the expression for total decays recorded by a detector of efficiency η in time T.
Answer:
🔵 N(t) = N0 e^(−λt).
🟢 A(t) = λN0 e^(−λt).
🟠 R(t) = ηA(t).
🔴 C = ηN0 (1 − e^(−λT)).
✔️ Final Answer: C = ηN0 (1 − e^(−λT))
Question 33
An α-decay has Q = 5.3 MeV. If daughter mass ≈ 56 times α, find K of α-particle.
Answer:
🔵 Kd/Kα = mα/md = 1/56.
🟢 Q = Kα (1 + 1/56).
🟠 Kα = 5.3 × 56/57 ≈ 5.21 MeV.
🔴 Kd ≈ 0.09 MeV.
✔️ Final Answer: Kα ≈ 5.21 MeV, Kd ≈ 0.09 MeV
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question 1: The binding energy per nucleon is maximum for
🔵 (A) Hydrogen
🟢 (B) Helium
🟠 (C) Iron
🔴 (D) Uranium
Answer: (C) Iron
Year: 2025
Question 2: The energy released in nuclear fission is due to
🔵 (A) loss of neutrons
🟢 (B) loss of protons
🟠 (C) mass defect
🔴 (D) conversion of charge
Answer: (C) mass defect
Year: 2025
Question 3: Which of the following is a nuclear fusion reaction?
🔵 (A) Splitting of uranium nucleus
🟢 (B) Combining two hydrogen nuclei to form helium
🟠 (C) Disintegration of radium
🔴 (D) Neutron emission
Answer: (B) Combining two hydrogen nuclei to form helium
Year: 2025
Question 4: The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time in which
🔵 (A) half atoms decay
🟢 (B) activity becomes half
🟠 (C) mass becomes half
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2024
Question 5: A radioactive element has half-life T. The fraction left after 2T is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 3/4
Answer: (B) 1/4
Year: 2024
Question 6: The activity of a radioactive sample is proportional to
🔵 (A) number of undecayed nuclei
🟢 (B) square of number of nuclei
🟠 (C) half-life
🔴 (D) energy released
Answer: (A) number of undecayed nuclei
Year: 2024
Question 7: If a radioactive isotope has half-life of 10 hours, then in 30 hours the fraction remaining undecayed is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2024
Question 8: Which particle has highest penetrating power?
🔵 (A) α-particles
🟢 (B) β-particles
🟠 (C) γ-rays
🔴 (D) protons
Answer: (C) γ-rays
Year: 2023
Question 9: Which radiation is deflected by both electric and magnetic fields?
🔵 (A) α-particles
🟢 (B) β-particles
🟠 (C) γ-rays
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) β-particles
Year: 2023
Question 10: In nuclear fission, the total mass of products is
🔵 (A) more than reactants
🟢 (B) less than reactants
🟠 (C) equal to reactants
🔴 (D) zero
Answer: (B) less than reactants
Year: 2023
Question 11: The SI unit of radioactivity is
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Becquerel
🟠 (C) Rutherford
🔴 (D) Joule
Answer: (B) Becquerel
Year: 2022
Question 12: A radioactive isotope has half-life of 5 days. The fraction remaining after 15 days is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2022
Question 13: Nuclear force is
🔵 (A) short-range and charge-independent
🟢 (B) long-range and charge-dependent
🟠 (C) short-range and charge-dependent
🔴 (D) long-range and charge-independent
Answer: (A) short-range and charge-independent
Year: 2022
Question 14: The energy released in fission of one U-235 nucleus is about
🔵 (A) 200 MeV
🟢 (B) 2 MeV
🟠 (C) 20 MeV
🔴 (D) 2 GeV
Answer: (A) 200 MeV
Year: 2022
Question 15: Half-life and decay constant are related as
🔵 (A) T½ = 0.693/λ
🟢 (B) T½ = λ/0.693
🟠 (C) T½ = 1/λ
🔴 (D) T½ = λ
Answer: (A) T½ = 0.693/λ
Year: 2021
Question 16: In β⁻ decay,
🔵 (A) neutron → proton + electron + antineutrino
🟢 (B) proton → neutron + electron + neutrino
🟠 (C) neutron → proton + positron + neutrino
🔴 (D) proton → neutron + positron + antineutrino
Answer: (A) neutron → proton + electron + antineutrino
Year: 2021
Question 17: A sample has activity 8000 disintegrations/s. After 3 half-lives, activity becomes
🔵 (A) 4000
🟢 (B) 2000
🟠 (C) 1000
🔴 (D) 500
Answer: (C) 1000
Year: 2021
Question 18: The number of neutrons in U-235 is
🔵 (A) 92
🟢 (B) 143
🟠 (C) 146
🔴 (D) 235
Answer: (B) 143
Year: 2021
Question 19: The phenomenon of radioactivity was discovered by
🔵 (A) Becquerel
🟢 (B) Rutherford
🟠 (C) Marie Curie
🔴 (D) Chadwick
Answer: (A) Becquerel
Year: 2020
Question 20: The half-life of a radioactive element is 20 days. After 60 days, the remaining undecayed fraction is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2020
Question 21: In a nuclear reactor, the moderator is used to
🔵 (A) absorb neutrons
🟢 (B) slow down neutrons
🟠 (C) speed up neutrons
🔴 (D) cool reactor
Answer: (B) slow down neutrons
Year: 2020
Question 22: Which of the following is used as moderator in nuclear reactor?
🔵 (A) Heavy water
🟢 (B) Sodium
🟠 (C) Graphite
🔴 (D) Both A and C
Answer: (D) Both A and C
Year: 2019
Question 23: The relation between decay constant and mean life is
🔵 (A) τ = 1/λ
🟢 (B) τ = λ
🟠 (C) τ = 0.693/λ
🔴 (D) τ = log 2/λ
Answer: (A) τ = 1/λ
Year: 2019
Question 24: In α-decay,
🔵 (A) Z decreases by 2 and A decreases by 4
🟢 (B) Z increases by 2 and A increases by 4
🟠 (C) Z increases by 2 and A unchanged
🔴 (D) Z unchanged and A decreases by 4
Answer: (A) Z decreases by 2 and A decreases by 4
Year: 2019
Question 25: If a radioactive element has decay constant λ, the mean life is
🔵 (A) λ
🟢 (B) 1/λ
🟠 (C) 0.693/λ
🔴 (D) log 2/λ
Answer: (B) 1/λ
Year: 2019
Question 26: Which nuclear reaction is responsible for the energy production in the sun?
🔵 (A) Fission of uranium
🟢 (B) Fusion of hydrogen nuclei
🟠 (C) Fission of thorium
🔴 (D) Radioactive decay
Answer: (B) Fusion of hydrogen nuclei
Year: 2018
Question 27: Which of the following is not a unit of radioactivity?
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Rutherford
🟠 (C) Becquerel
🔴 (D) Tesla
Answer: (D) Tesla
Year: 2018
Question 28: The disintegration constant of a radioactive element is 0.001 s⁻¹. Its half-life is approximately
🔵 (A) 693 s
🟢 (B) 69.3 s
🟠 (C) 0.693 s
🔴 (D) 6.93 s
Answer: (A) 693 s
Year: 2018
Question 29: In nuclear fission, the average energy released per nucleon is about
🔵 (A) 0.9 MeV
🟢 (B) 200 MeV
🟠 (C) 8 MeV
🔴 (D) 20 MeV
Answer: (A) 0.9 MeV
Year: 2017
Question 30: The half-life of a radioactive sample is 10 min. Its mean life is
🔵 (A) 14.4 min
🟢 (B) 10 min
🟠 (C) 7.2 min
🔴 (D) 20 min
Answer: (A) 14.4 min
Year: 2017
Question 31: In β⁺ decay,
🔵 (A) proton → neutron + positron + neutrino
🟢 (B) neutron → proton + positron + neutrino
🟠 (C) neutron → proton + electron + antineutrino
🔴 (D) proton → neutron + electron + neutrino
Answer: (A) proton → neutron + positron + neutrino
Year: 2017
Question 32: If N₀ is the initial number of nuclei and N is the number at time t, then
🔵 (A) N = N₀e^λt
🟢 (B) N = N₀e^−λt
🟠 (C) N = N₀λt
🔴 (D) N = N₀/t
Answer: (B) N = N₀e^−λt
Year: 2016
Question 33: The ratio of activities of two samples with half-lives T and 2T, taken in equal number of atoms, is
🔵 (A) 2:1
🟢 (B) 1:2
🟠 (C) 1:√2
🔴 (D) √2:1
Answer: (A) 2:1
Year: 2016
Question 34: The half-life of radium is 1600 years. Its decay constant is
🔵 (A) 1.37 × 10⁻⁴ yr⁻¹
🟢 (B) 4.33 × 10⁻⁴ yr⁻¹
🟠 (C) 6.25 × 10⁻⁴ yr⁻¹
🔴 (D) 2.31 × 10⁻⁴ yr⁻¹
Answer: (A) 1.37 × 10⁻⁴ yr⁻¹
Year: 2016
Question 35: Which one is not a constituent of an atomic nucleus?
🔵 (A) Electron
🟢 (B) Proton
🟠 (C) Neutron
🔴 (D) Nucleon
Answer: (A) Electron
Year: 2015
Question 36: The stability of nucleus is determined by
🔵 (A) Mass number
🟢 (B) Binding energy per nucleon
🟠 (C) Neutron number
🔴 (D) Proton number
Answer: (B) Binding energy per nucleon
Year: 2015
Question 37: Which decay does not change mass number of nucleus?
🔵 (A) α-decay
🟢 (B) β-decay
🟠 (C) γ-decay
🔴 (D) both B and C
Answer: (D) both B and C
Year: 2015
Question 38: A radioactive isotope has mean life τ. Its half-life is
🔵 (A) τ/2
🟢 (B) τ ln 2
🟠 (C) τ/ln 2
🔴 (D) 1/τ
Answer: (B) τ ln 2
Year: 2014
Question 39: The time in which a radioactive sample reduces to 1/16 of initial is
🔵 (A) 2 half-lives
🟢 (B) 3 half-lives
🟠 (C) 4 half-lives
🔴 (D) 5 half-lives
Answer: (C) 4 half-lives
Year: 2014
Question 40: Which force is responsible for stability of nucleus?
🔵 (A) Gravitational
🟢 (B) Coulomb
🟠 (C) Nuclear force
🔴 (D) Weak force
Answer: (C) Nuclear force
Year: 2014
Question 41: The SI unit of half-life is
🔵 (A) second
🟢 (B) curie
🟠 (C) becquerel
🔴 (D) mole
Answer: (A) second
Year: 2013
Question 42: When a nucleus emits α-particle, its atomic number and mass number change as
🔵 (A) Z → Z+2, A → A+4
🟢 (B) Z → Z−2, A → A−4
🟠 (C) Z → Z+1, A unchanged
🔴 (D) Z → Z−1, A unchanged
Answer: (B) Z → Z−2, A → A−4
Year: 2013
Question 43: The activity of a radioactive sample is measured in
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Becquerel
🟠 (C) Joule
🔴 (D) Watt
Answer: (B) Becquerel
Year: 2012
Question 44: The half-life of a sample is 1 hour. In 3 hours, the fraction of atoms left is
🔵 (A) 1/8
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/2
🔴 (D) 3/4
Answer: (A) 1/8
Year: 2012
Question 45: Which decay decreases Z but not A?
🔵 (A) α-decay
🟢 (B) β⁻-decay
🟠 (C) β⁺-decay
🔴 (D) γ-decay
Answer: (C) β⁺-decay
Year: 2011
Question 46: In β⁻ emission,
🔵 (A) proton converts into neutron
🟢 (B) neutron converts into proton
🟠 (C) electron converts into proton
🔴 (D) neutrino converts into proton
Answer: (B) neutron converts into proton
Year: 2010
Question 47: The half-life of C-14 is about
🔵 (A) 1600 years
🟢 (B) 5568 years
🟠 (C) 3730 years
🔴 (D) 2000 years
Answer: (B) 5568 years
Year: 2010
Question 48: The element used as fuel in nuclear reactors is
🔵 (A) Thorium-232
🟢 (B) Uranium-235
🟠 (C) Plutonium-239
🔴 (D) Both B and C
Answer: (D) Both B and C
Year: 2009
Question 49: In nuclear fusion,
🔵 (A) energy is absorbed
🟢 (B) energy is released
🟠 (C) neutrons are absorbed
🔴 (D) protons are absorbed
Answer: (B) energy is released
Year: 2008
Question 50: Which of the following is used for nuclear fusion on earth?
🔵 (A) Deuterium and Tritium
🟢 (B) U-235
🟠 (C) Th-232
🔴 (D) Pu-239
Answer: (A) Deuterium and Tritium
Year: 2006
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question 1: The binding energy per nucleon is maximum for
🔵 (A) Uranium
🟢 (B) Iron
🟠 (C) Deuterium
🔴 (D) Helium
Answer: (B) Iron
Year: 2025 | Shift 1
Question 2: Energy released in nuclear fission is due to
🔵 (A) conservation of charge
🟢 (B) mass defect
🟠 (C) emission of neutrons
🔴 (D) binding energy decrease
Answer: (B) mass defect
Year: 2025 | Shift 2
Question 3: Half-life of a radioactive isotope is 30 min. The fraction remaining after 2 hours is
🔵 (A) 1/16
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/2
Answer: (A) 1/16
Year: 2024 | Jan Shift 1
Question 4: The activity of a radioactive sample is proportional to
🔵 (A) mass
🟢 (B) number of undecayed nuclei
🟠 (C) square of mass
🔴 (D) volume
Answer: (B) number of undecayed nuclei
Year: 2024 | Apr Shift 1
Question 5: A nucleus of mass number A has binding energy BE. Its binding energy per nucleon is
🔵 (A) A × BE
🟢 (B) BE/A
🟠 (C) BE²/A
🔴 (D) BE/A²
Answer: (B) BE/A
Year: 2024 | Jan Shift 2
Question 6: The half-life of a substance is related to decay constant λ by
🔵 (A) T½ = ln 2 / λ
🟢 (B) T½ = λ / ln 2
🟠 (C) T½ = 1/λ
🔴 (D) T½ = 2/λ
Answer: (A) T½ = ln 2 / λ
Year: 2024 | Apr Shift 2
Question 7: If N₀ nuclei are present initially, the number left after n half-lives is
🔵 (A) N₀/2ⁿ
🟢 (B) 2ⁿ/N₀
🟠 (C) N₀ × 2ⁿ
🔴 (D) 2N₀
Answer: (A) N₀/2ⁿ
Year: 2023 | Jan Shift 1
Question 8: The dimension of decay constant λ is
🔵 (A) T
🟢 (B) 1/T
🟠 (C) L/T
🔴 (D) none
Answer: (B) 1/T
Year: 2023 | Apr Shift 1
Question 9: The activity of a radioactive sample is measured in
🔵 (A) Coulomb
🟢 (B) Curie
🟠 (C) Ohm
🔴 (D) Watt
Answer: (B) Curie
Year: 2023 | Apr Shift 2
Question 10: In a radioactive decay, emission of β⁻ particle results in
🔵 (A) Z → Z−1
🟢 (B) Z → Z+1
🟠 (C) A → A−1
🔴 (D) A → A+2
Answer: (B) Z → Z+1
Year: 2022 | Jun Shift 1
Question 11: The SI unit of activity is
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Becquerel
🟠 (C) Rutherford
🔴 (D) erg/sec
Answer: (B) Becquerel
Year: 2022 | Jul Shift 1
Question 12: For a radioactive sample, activity R is related to number of nuclei N as
🔵 (A) R = λN
🟢 (B) R = N/λ
🟠 (C) R = Nλ²
🔴 (D) R = λ/N
Answer: (A) R = λN
Year: 2022 | Jun Shift 2
Question 13: Radioactive decay law is
🔵 (A) N = N₀e^(λt)
🟢 (B) N = N₀e^(−λt)
🟠 (C) N = N₀/λt
🔴 (D) N = N₀ − λt
Answer: (B) N = N₀e^(−λt)
Year: 2021 | Feb Shift 1
Question 14: Half-life is the time in which
🔵 (A) half nuclei decay
🟢 (B) half activity decreases
🟠 (C) half mass reduces
🔴 (D) all of these
Answer: (D) all of these
Year: 2021 | Mar Shift 1
Question 15: The sum of decay constants for parallel radioactive decays is
🔵 (A) λ
🟢 (B) Σλ
🟠 (C) λ/2
🔴 (D) λ²
Answer: (B) Σλ
Year: 2021 | Jul Shift 1
Question 16: Which particle has maximum penetrating power?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β
🟠 (C) γ
🔴 (D) proton
Answer: (C) γ
Year: 2021 | Mar Shift 2
Question 17: A radioactive isotope has half-life T. The time taken to reduce activity to 1/8 is
🔵 (A) T
🟢 (B) 2T
🟠 (C) 3T
🔴 (D) 4T
Answer: (C) 3T
Year: 2020 | Jan Shift 1
Question 18: The mass defect of a nucleus is directly related to its
🔵 (A) charge
🟢 (B) binding energy
🟠 (C) atomic number
🔴 (D) volume
Answer: (B) binding energy
Year: 2020 | Sept Shift 1
Question 19: The half-life of a substance is 140 days. Its mean life is
🔵 (A) 140 days
🟢 (B) 200 days
🟠 (C) 100 days
🔴 (D) 280 days
Answer: (B) 200 days
Year: 2020 | Sept Shift 2
Question 20: If 25% of a radioactive sample remains, the number of half-lives passed is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Year: 2019 | Jan Shift 1
Question 21: In α-decay, the change in Z and A is
🔵 (A) ΔZ = −2, ΔA = −4
🟢 (B) ΔZ = −1, ΔA = 0
🟠 (C) ΔZ = +1, ΔA = 0
🔴 (D) ΔZ = +2, ΔA = +4
Answer: (A) ΔZ = −2, ΔA = −4
Year: 2019 | Apr Shift 1
Question 22: The energy released in nuclear reaction is calculated from
🔵 (A) E = mc²
🟢 (B) E = mv²
🟠 (C) E = ma²
🔴 (D) E = mh²
Answer: (A) E = mc²
Year: 2019 | Apr Shift 2
Question 23: The unit of half-life is
🔵 (A) same as time
🟢 (B) same as mass
🟠 (C) same as volume
🔴 (D) same as decay constant
Answer: (A) same as time
Year: 2018
Question 24: For a radioactive sample, the ratio of number of nuclei decayed in equal successive intervals is
🔵 (A) constant
🟢 (B) increasing
🟠 (C) decreasing
🔴 (D) unpredictable
Answer: (C) decreasing
Year: 2018
Question 25: The ratio of decay constant to half-life is
🔵 (A) λ/T½
🟢 (B) T½/λ
🟠 (C) 1/ln2
🔴 (D) ln2
Answer: (D) ln2
Year: 2018
Question 26: In β⁺ decay, the change in Z and A is
🔵 (A) ΔZ = −1, ΔA = 0
🟢 (B) ΔZ = +1, ΔA = 0
🟠 (C) ΔZ = 0, ΔA = −1
🔴 (D) ΔZ = −2, ΔA = −4
Answer: (A) ΔZ = −1, ΔA = 0
Year: 2017
Question 27: Which radiation has the least penetrating power?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β
🟠 (C) γ
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) α
Year: 2017
Question 28: Mean life τ is related to half-life T½ as
🔵 (A) τ = T½ / ln 2
🟢 (B) τ = T½ × ln 2
🟠 (C) τ = λ / ln 2
🔴 (D) τ = 1/λ²
Answer: (A) τ = T½ / ln 2
Year: 2017
Question 29: The energy released in the fusion of four protons into one helium nucleus is approximately
🔵 (A) 26.7 MeV
🟢 (B) 13.6 MeV
🟠 (C) 6.8 MeV
🔴 (D) 54.2 MeV
Answer: (A) 26.7 MeV
Year: 2016
Question 30: The parent nucleus in α-decay loses
🔵 (A) 2 protons only
🟢 (B) 2 protons and 2 neutrons
🟠 (C) 2 neutrons only
🔴 (D) 4 protons
Answer: (B) 2 protons and 2 neutrons
Year: 2016
Question 31: The half-life of a radioactive element is 1 hour. The fraction decayed in 2 hours is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 3/4
🟠 (C) 7/8
🔴 (D) 1/4
Answer: (B) 3/4
Year: 2016
Question 32: In a radioactive decay series, the end product of uranium-238 is
🔵 (A) Lead-206
🟢 (B) Thorium-232
🟠 (C) Uranium-235
🔴 (D) Radium-226
Answer: (A) Lead-206
Year: 2015
Question 33: The mass defect of a nucleus is 0.1 u. The binding energy is (1 u = 931 MeV)
🔵 (A) 93.1 MeV
🟢 (B) 931 MeV
🟠 (C) 9.31 MeV
🔴 (D) 186 MeV
Answer: (A) 93.1 MeV
Year: 2015
Question 34: The disintegration constant λ has dimension
🔵 (A) [M⁰L⁰T⁻¹]
🟢 (B) [M¹L¹T⁻¹]
🟠 (C) [M⁰L¹T⁰]
🔴 (D) [M⁻¹L⁰T¹]
Answer: (A) [M⁰L⁰T⁻¹]
Year: 2015
Question 35: In a nuclear reactor, chain reaction is controlled by
🔵 (A) cadmium rods
🟢 (B) graphite
🟠 (C) heavy water
🔴 (D) concrete shield
Answer: (A) cadmium rods
Year: 2014
Question 36: The decay constant λ and mean life τ are related as
🔵 (A) τ = 1/λ
🟢 (B) τ = λ
🟠 (C) τ = ln 2/λ
🔴 (D) τ = λ²
Answer: (A) τ = 1/λ
Year: 2014
Question 37: Which conservation law is not obeyed in nuclear reaction?
🔵 (A) Energy
🟢 (B) Linear momentum
🟠 (C) Angular momentum
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (D) None
Year: 2014
Question 38: The radius of nucleus is proportional to
🔵 (A) A
🟢 (B) A^(1/3)
🟠 (C) √A
🔴 (D) 1/A
Answer: (B) A^(1/3)
Year: 2013
Question 39: The relation between decay constant and half-life is
🔵 (A) λ = ln2 / T½
🟢 (B) λ = T½ / ln2
🟠 (C) λ = 1/T½
🔴 (D) λ = (T½)²
Answer: (A) λ = ln2 / T½
Year: 2013
Question 40: In a chain reaction, the average number of neutrons produced per fission must be
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) >1
🟠 (C) <1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 1
Year: 2013
Question 41: Which decay increases atomic number by 1?
🔵 (A) α-decay
🟢 (B) β⁻-decay
🟠 (C) β⁺-decay
🔴 (D) γ-decay
Answer: (B) β⁻-decay
Year: 2012 (AIEEE)
Question 42: The unit of radioactivity Curie corresponds to
🔵 (A) 3.7 × 10¹⁰ disintegrations/sec
🟢 (B) 3.7 × 10¹⁰ disintegrations/min
🟠 (C) 37 disintegrations/sec
🔴 (D) 37 × 10¹⁰ disintegrations/sec
Answer: (A) 3.7 × 10¹⁰ disintegrations/sec
Year: 2012 (AIEEE)
Question 43: The energy equivalent of 1 u is
🔵 (A) 931 MeV
🟢 (B) 1 MeV
🟠 (C) 9.31 MeV
🔴 (D) 186 MeV
Answer: (A) 931 MeV
Year: 2011 (AIEEE)
Question 44: Which particle is emitted in natural radioactivity?
🔵 (A) α, β, γ
🟢 (B) neutrons only
🟠 (C) protons only
🔴 (D) neutrinos only
Answer: (A) α, β, γ
Year: 2011 (AIEEE)
Question 45: The number of neutrons in U-235 is
🔵 (A) 92
🟢 (B) 143
🟠 (C) 235
🔴 (D) 146
Answer: (B) 143
Year: 2011 (AIEEE)
Question 46: The half-life of a sample is 2 hours. Its decay constant is
🔵 (A) 0.693 h⁻¹
🟢 (B) 0.346 h⁻¹
🟠 (C) 1.386 h⁻¹
🔴 (D) 2 h⁻¹
Answer: (B) 0.346 h⁻¹
Year: 2010 (AIEEE)
Question 47: The half-life of radium is 1600 years. Its decay constant is approximately
🔵 (A) 1.37 × 10⁻¹¹ s⁻¹
🟢 (B) 1.37 × 10⁻⁴ s⁻¹
🟠 (C) 1.37 × 10⁻¹⁰ s⁻¹
🔴 (D) 1.37 × 10⁻¹² s⁻¹
Answer: (A) 1.37 × 10⁻¹¹ s⁻¹
Year: 2010 (AIEEE)
Question 48: The mass number of a nucleus changes in
🔵 (A) α-decay
🟢 (B) β-decay
🟠 (C) γ-decay
🔴 (D) none
Answer: (A) α-decay
Year: 2009 (AIEEE)
Question 49: The ratio of nuclear densities of two nuclei having mass numbers in ratio 1:8 is
🔵 (A) 1:1
🟢 (B) 1:2
🟠 (C) 1:8
🔴 (D) 8:1
Answer: (A) 1:1
Year: 2009 (AIEEE)
Question 50: The half-life of a radioactive substance is 1 day. The fraction of substance left after 3 days is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2008 (AIEEE)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. The binding energy per nucleon is maximum for
🔵 (A) Hydrogen
🟢 (B) Uranium
🟠 (C) Iron
🔴 (D) Helium
Answer: (C) Iron
Year: 2023 | Paper 1
Q2. In nuclear fission of U-235, the energy released per fission is approximately
🔵 (A) 200 MeV
🟢 (B) 2 MeV
🟠 (C) 20 MeV
🔴 (D) 0.2 MeV
Answer: (A) 200 MeV
Year: 2023 | Paper 1
Q3. Nuclear radius is proportional to
🔵 (A) A^1/3
🟢 (B) A^1/2
🟠 (C) A
🔴 (D) A^2/3
Answer: (A) A^1/3
Year: 2022 | Paper 1
Q4. Half-life of a radioactive substance is the time in which
🔵 (A) half nuclei decay
🟢 (B) activity becomes half
🟠 (C) both A and B
🔴 (D) activity becomes zero
Answer: (C) both A and B
Year: 2022 | Paper 1
Q5. The mass defect in nucleus is due to
🔵 (A) Coulomb energy
🟢 (B) nuclear binding energy
🟠 (C) proton mass difference
🔴 (D) electron screening
Answer: (B) nuclear binding energy
Year: 2021 | Paper 1
Q6. The energy equivalent of 1 amu is
🔵 (A) 931 MeV
🟢 (B) 9.31 MeV
🟠 (C) 93.1 MeV
🔴 (D) 931 keV
Answer: (A) 931 MeV
Year: 2021 | Paper 1
Q7. The decay constant λ is related to half-life T1/2 as
🔵 (A) λ = ln2 / T1/2
🟢 (B) λ = 1/T1/2
🟠 (C) λ = T1/2 / ln2
🔴 (D) λ = (ln2)^2 / T1/2
Answer: (A) λ = ln2 / T1/2
Year: 2020 | Paper 1
Q8. A radioactive nucleus has half-life 10 days. Fraction of activity left after 30 days is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2020 | Paper 1
Q9. The unit of activity of radioactive substance is
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Becquerel
🟠 (C) Rutherford
🔴 (D) all of these
Answer: (D) all of these
Year: 2019 | Paper 1
Q10. The energy released in nuclear fusion of 4 protons into He nucleus is about
🔵 (A) 26 MeV
🟢 (B) 2.6 MeV
🟠 (C) 260 MeV
🔴 (D) 0.26 MeV
Answer: (A) 26 MeV
Year: 2019 | Paper 1
Q11. The number of α and β particles emitted in conversion of U-238 to Pb-206 are
🔵 (A) 8α, 6β
🟢 (B) 6α, 4β
🟠 (C) 7α, 4β
🔴 (D) 8α, 4β
Answer: (A) 8α, 6β
Year: 2018 | Paper 1
Q12. The mean life τ of a radioactive sample is related to half-life as
🔵 (A) τ = T1/2 / ln2
🟢 (B) τ = (ln2) T1/2
🟠 (C) τ = 1/ T1/2
🔴 (D) τ = T1/2^2
Answer: (A) τ = T1/2 / ln2
Year: 2018 | Paper 1
Q13. The activity of a radioactive sample at time t is A = A0 e^(−λt). The unit of λ is
🔵 (A) s^−1
🟢 (B) s
🟠 (C) dimensionless
🔴 (D) J
Answer: (A) s^−1
Year: 2017 | Paper 1
Q14. Which radiation has maximum penetrating power?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β
🟠 (C) γ
🔴 (D) neutron
Answer: (C) γ
Year: 2017 | Paper 1
Q15. The disintegration energy Q in nuclear reaction is
🔵 (A) difference in rest mass energies
🟢 (B) sum of rest mass energies
🟠 (C) product of rest mass energies
🔴 (D) independent of rest mass
Answer: (A) difference in rest mass energies
Year: 2016 | Paper 1
Q16. A sample has half-life 20 min. After 1 hr, fraction of undecayed nuclei left is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2016 | Paper 1
Q17. The energy released in fusion is due to
🔵 (A) decrease in binding energy per nucleon
🟢 (B) increase in binding energy per nucleon
🟠 (C) decrease in total mass
🔴 (D) both B and C
Answer: (D) both B and C
Year: 2015 | Paper 1
Q18. Radioactivity is a
🔵 (A) nuclear phenomenon
🟢 (B) atomic phenomenon
🟠 (C) molecular phenomenon
🔴 (D) chemical phenomenon
Answer: (A) nuclear phenomenon
Year: 2023 | Paper 2
Q19. The half-life of C-14 is 5730 years. The mean life is approximately
🔵 (A) 4930 years
🟢 (B) 8260 years
🟠 (C) 5730 years
🔴 (D) 6930 years
Answer: (B) 8260 years
Year: 2023 | Paper 2
Q20. The number of protons and neutrons in 92U^238 are
🔵 (A) 92, 146
🟢 (B) 146, 92
🟠 (C) 92, 238
🔴 (D) 238, 92
Answer: (A) 92, 146
Year: 2022 | Paper 2
Q21. The disintegration constant λ of a radioactive substance having half-life 10 hr is
🔵 (A) 0.069 hr^−1
🟢 (B) 0.693 hr^−1
🟠 (C) 6.93 hr^−1
🔴 (D) 0.00693 hr^−1
Answer: (A) 0.069 hr^−1
Year: 2022 | Paper 2
Q22. Tritium has half-life of 12.3 years. After 36.9 years the fraction of undecayed nuclei is
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
Year: 2021 | Paper 2
Q23. Which of the following is used in nuclear fusion reaction in stars?
🔵 (A) Deuterium and tritium
🟢 (B) U-235
🟠 (C) Th-232
🔴 (D) Pu-239
Answer: (A) Deuterium and tritium
Year: 2021 | Paper 2
Q24. In a nuclear reactor, the function of moderator is to
🔵 (A) absorb neutrons
🟢 (B) slow down neutrons
🟠 (C) stop chain reaction
🔴 (D) provide neutrons
Answer: (B) slow down neutrons
Year: 2020 | Paper 2
Q25. The average binding energy per nucleon of deuteron is about
🔵 (A) 1.1 MeV
🟢 (B) 7 MeV
🟠 (C) 2.2 MeV
🔴 (D) 8.8 MeV
Answer: (A) 1.1 MeV
Year: 2020 | Paper 2
Q26. The half-life of a substance is 5 hr. Its activity falls to 1/16th in
🔵 (A) 10 hr
🟢 (B) 15 hr
🟠 (C) 20 hr
🔴 (D) 25 hr
Answer: (B) 20 hr
Year: 2019 | Paper 2
Q27. If N is number of nuclei and λ is decay constant, then rate of disintegration is
🔵 (A) λ
🟢 (B) λN
🟠 (C) N/λ
🔴 (D) N^2λ
Answer: (B) λN
Year: 2019 | Paper 2
Q28. The penetrating power is maximum for
🔵 (A) α-particles
🟢 (B) β-particles
🟠 (C) γ-rays
🔴 (D) protons
Answer: (C) γ-rays
Year: 2018 | Paper 2
Q29. Uranium-235 is used as fuel in
🔵 (A) fusion reactor
🟢 (B) fission reactor
🟠 (C) breeder reactor only
🔴 (D) solar reactor
Answer: (B) fission reactor
Year: 2018 | Paper 2
Q30. If a radioactive sample has mean life 100 s, its half-life is approximately
🔵 (A) 69.3 s
🟢 (B) 50 s
🟠 (C) 100 s
🔴 (D) 138.6 s
Answer: (A) 69.3 s
Year: 2017 | Paper 2
Q31. The law governing radioactive decay is
🔵 (A) exponential law
🟢 (B) inverse square law
🟠 (C) Newton’s law
🔴 (D) Boyle’s law
Answer: (A) exponential law
Year: 2017 | Paper 2
Q32. Which particle has highest ionising power?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β
🟠 (C) γ
🔴 (D) neutron
Answer: (A) α
Year: 2016 | Paper 2
Q33. A radioactive element has atomic number Z and mass number A. After emission of 2 α and 1 β particles, new Z and A are
🔵 (A) Z−3, A−8
🟢 (B) Z−4, A−8
🟠 (C) Z−3, A−4
🔴 (D) Z−4, A−4
Answer: (A) Z−3, A−8
Year: 2016 | Paper 2
Q34. Which among the following has the least binding energy per nucleon?
🔵 (A) Deuteron
🟢 (B) Helium
🟠 (C) Iron
🔴 (D) Uranium
Answer: (A) Deuteron
Year: 2015 | Paper 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
NEET Level (Q1–Q20)
Q1.
Which symbol denotes the decay constant?
🔵 (A) λ
🟢 (B) τ
🟠 (C) T
🔴 (D) N
Answer: (A) λ
✔️ Final Answer: λ
Q2.
The half-life of a radioactive substance is the time in which:
🔵 (A) N reduces to 1/e of N0
🟢 (B) N reduces to half of N0
🟠 (C) Activity becomes zero
🔴 (D) Energy becomes zero
Answer: (B) N reduces to half of N0
✔️ Final Answer: Half of N0
Q3.
Which quantity remains unchanged during α-decay?
🔵 (A) Mass number
🟢 (B) Proton number
🟠 (C) Neutron number
🔴 (D) Nuclear density
Answer: (D) Nuclear density
✔️ Final Answer: Nuclear density
Q4.
Binding energy per nucleon is maximum for:
🔵 (A) Uranium
🟢 (B) Iron
🟠 (C) Hydrogen
🔴 (D) Helium
Answer: (B) Iron
✔️ Final Answer: Iron
Q5.
Which emission has the highest penetration power?
🔵 (A) α-particle
🟢 (B) β-particle
🟠 (C) γ-ray
🔴 (D) Proton
Answer: (C) γ-ray
✔️ Final Answer: γ-ray
Q6.
The SI unit of activity is:
🔵 (A) Curie
🟢 (B) Becquerel
🟠 (C) Joule
🔴 (D) Watt
Answer: (B) Becquerel
✔️ Final Answer: Becquerel (Bq)
Q7.
If N0 is the initial nuclei, number left after 2 half-lives is:
🔵 (A) N0/2
🟢 (B) N0/4
🟠 (C) N0/8
🔴 (D) N0/16
Answer: (B) N0/4
✔️ Final Answer: N0/4
Q8.
The mean life τ is related to half-life T1/2 as:
🔵 (A) τ = T1/2
🟢 (B) τ = T1/2 × ln2
🟠 (C) τ = T1/2 / ln2
🔴 (D) τ = (T1/2)^2
Answer: (C) τ = T1/2 / ln2
✔️ Final Answer: τ = T1/2 / ln2
Q9.
Which decay conserves both A and Z?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β⁻
🟠 (C) β⁺
🔴 (D) γ
Answer: (D) γ
✔️ Final Answer: γ-decay
Q10.
What particle is emitted in β⁻-decay?
🔵 (A) Electron
🟢 (B) Positron
🟠 (C) Proton
🔴 (D) Neutron
Answer: (A) Electron
✔️ Final Answer: Electron
Q11.
Which law is obeyed by radioactive decay?
🔵 (A) Linear
🟢 (B) Exponential
🟠 (C) Parabolic
🔴 (D) Harmonic
Answer: (B) Exponential
✔️ Final Answer: Exponential law
Q12.
In β⁻-decay, what happens to atomic number?
🔵 (A) Increases by 1
🟢 (B) Decreases by 1
🟠 (C) No change
🔴 (D) Increases by 2
Answer: (A) Increases by 1
✔️ Final Answer: Increases by 1
Q13.
Which particle ensures conservation of energy and lepton number in β-decay?
🔵 (A) Proton
🟢 (B) Neutrino/Antineutrino
🟠 (C) Photon
🔴 (D) Electron
Answer: (B) Neutrino/Antineutrino
✔️ Final Answer: Neutrino/Antineutrino
Q14.
The average life of a radioactive substance is:
🔵 (A) Longer than half-life
🟢 (B) Shorter than half-life
🟠 (C) Equal to half-life
🔴 (D) Infinite
Answer: (A) Longer than half-life
✔️ Final Answer: Longer than half-life
Q15.
Nuclear density is independent of:
🔵 (A) Z
🟢 (B) N
🟠 (C) A
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
✔️ Final Answer: Independent of A, Z, N
Q16.
Which of the following is correct for nuclear forces?
🔵 (A) Long-ranged and weak
🟢 (B) Short-ranged and strong
🟠 (C) Repulsive always
🔴 (D) Acts only on protons
Answer: (B) Short-ranged and strong
✔️ Final Answer: Short-ranged and strong
Q17.
Which process is the source of stellar energy?
🔵 (A) Nuclear fission
🟢 (B) Nuclear fusion
🟠 (C) Radioactive decay
🔴 (D) Chemical reaction
Answer: (B) Nuclear fusion
✔️ Final Answer: Fusion
Q18.
The curve of B/A vs A has a maximum at:
🔵 (A) U-238
🟢 (B) Fe-56
🟠 (C) H-1
🔴 (D) He-4
Answer: (B) Fe-56
✔️ Final Answer: Fe-56
Q19.
What happens to stability when binding energy per nucleon increases?
🔵 (A) Stability decreases
🟢 (B) Stability increases
🟠 (C) Stability remains same
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) Stability increases
✔️ Final Answer: Increases
Q20.
Which of the following statements is correct about α-particles?
🔵 (A) High penetration
🟢 (B) Helium nuclei
🟠 (C) Negative charge
🔴 (D) Very light
Answer: (B) Helium nuclei
✔️ Final Answer: Helium nuclei
JEE Main Level (Q21–Q40)
Q21.
If activity becomes 1/32 of initial, number of half-lives passed = ?
🔵 (A) 3
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 5
🔴 (D) 6
Answer: (C) 5
✔️ Final Answer: 5 half-lives
Q22.
For a nucleus of radius R = 7.2×10^−15 m and R0 = 1.2×10^−15 m, find A.
🔵 (A) 250
🟢 (B) 150
🟠 (C) 200
🔴 (D) 300
Answer: (C) 200
✔️ Final Answer: A = 200
Q23.
A radioactive isotope has half-life 2 h. Fraction left after 6 h is:
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1/4
🟠 (C) 1/8
🔴 (D) 1/16
Answer: (C) 1/8
✔️ Final Answer: 1/8
Q24.
For α-decay, change in A and Z is:
🔵 (A) ΔA = −2, ΔZ = −4
🟢 (B) ΔA = −4, ΔZ = −2
🟠 (C) ΔA = −4, ΔZ = 0
🔴 (D) ΔA = −2, ΔZ = −1
Answer: (B) ΔA = −4, ΔZ = −2
✔️ Final Answer: ΔA = −4, ΔZ = −2
Q25.
A sample has activity 2000 s^−1. After 3 half-lives, activity = ?
🔵 (A) 250
🟢 (B) 500
🟠 (C) 1000
🔴 (D) 125
Answer: (A) 250
✔️ Final Answer: 250 s^−1
Q26.
Mass defect of He nucleus is 0.030 u. Find binding energy (1 u = 931 MeV/c^2).
🔵 (A) 27.9 MeV
🟢 (B) 28.0 MeV
🟠 (C) 29.3 MeV
🔴 (D) 27.0 MeV
Answer: (B) 28.0 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: 28.0 MeV
Q27.
In β⁺-decay, what particle is emitted along with positron?
🔵 (A) Antineutrino
🟢 (B) Neutrino
🟠 (C) Photon
🔴 (D) Proton
Answer: (B) Neutrino
✔️ Final Answer: Neutrino
Q28.
A nucleus of mass M splits into two equal nuclei of mass M/2 each. Which is true?
🔵 (A) Mass of products < M 🟢 (B) Mass of products > M
🟠 (C) Mass of products = M
🔴 (D) Cannot say
Answer: (A) Mass of products < M
✔️ Final Answer: Mass of products < M
Q29.
If half-life of isotope = 5 days, activity after 15 days = ? (A0 = 1600).
🔵 (A) 200
🟢 (B) 400
🟠 (C) 100
🔴 (D) 50
Answer: (A) 200
✔️ Final Answer: 200 s^−1
Q30.
Which of the following decays increases neutron number by 1?
🔵 (A) α
🟢 (B) β⁻
🟠 (C) β⁺
🔴 (D) γ
Answer: (C) β⁺
✔️ Final Answer: β⁺-decay
Q31.
Activity A is related to N and λ by:
🔵 (A) A = N/λ
🟢 (B) A = λN
🟠 (C) A = Nλ^2
🔴 (D) A = N/τ
Answer: (B) A = λN
✔️ Final Answer: A = λN
Q32.
Energy released per fission of U-235 nucleus is about:
🔵 (A) 100 MeV
🟢 (B) 200 MeV
🟠 (C) 50 MeV
🔴 (D) 500 MeV
Answer: (B) 200 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: 200 MeV
Q33.
In carbon dating, half-life of C-14 is about:
🔵 (A) 5730 years
🟢 (B) 573 years
🟠 (C) 5000 years
🔴 (D) 1000 years
Answer: (A) 5730 years
✔️ Final Answer: 5730 years
Q34.
Mean life of isotope = 5 h. Find λ.
🔵 (A) 0.1 h^−1
🟢 (B) 0.2 h^−1
🟠 (C) 0.3 h^−1
🔴 (D) 0.4 h^−1
Answer: (B) 0.2 h^−1
✔️ Final Answer: 0.2 h^−1
Q35.
Which is conserved in all nuclear reactions?
🔵 (A) Energy and momentum
🟢 (B) Charge
🟠 (C) Baryon number
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
✔️ Final Answer: All of these
Q36.
The saturation property of nuclear force means:
🔵 (A) Each nucleon interacts with all others
🟢 (B) Each nucleon interacts with few neighbors
🟠 (C) No interaction
🔴 (D) Infinite interaction
Answer: (B) Each nucleon interacts with few neighbors
✔️ Final Answer: Few neighbors only
Q37.
The fission chain reaction is controlled using:
🔵 (A) Graphite rods
🟢 (B) Cadmium rods
🟠 (C) Water
🔴 (D) Neutrons
Answer: (B) Cadmium rods
✔️ Final Answer: Cadmium rods
Q38.
If activity halves in 2 h, mean life τ = ?
🔵 (A) 2.88 h
🟢 (B) 3.00 h
🟠 (C) 1.44 h
🔴 (D) 0.72 h
Answer: (A) 2.88 h
✔️ Final Answer: 2.88 h
Q39.
In a nuclear reactor, moderator is used to:
🔵 (A) Absorb neutrons
🟢 (B) Slow down neutrons
🟠 (C) Increase temperature
🔴 (D) Control rods
Answer: (B) Slow down neutrons
✔️ Final Answer: Slow down neutrons
Q40.
Fusion is possible only at very high temperature due to:
🔵 (A) Nuclear force
🟢 (B) Coulomb barrier
🟠 (C) Gravitational force
🔴 (D) Binding energy
Answer: (B) Coulomb barrier
✔️ Final Answer: Coulomb barrier
JEE Advanced Level (Q41–Q50)
Q41.
A sample has N0 nuclei, decay constant λ. Fraction decayed in time T = ?
🔵 (A) 1 − e^(−λT)
🟢 (B) e^(−λT)
🟠 (C) λT
🔴 (D) 1/(1+λT)
Answer: (A) 1 − e^(−λT)
✔️ Final Answer: 1 − e^(−λT)
Q42.
For two isotopes with half-lives 2 h and 4 h, ratio of activities after 8 h?
🔵 (A) 1:1
🟢 (B) 1:2
🟠 (C) 1:4
🔴 (D) 1:8
Answer: (C) 1:4
✔️ Final Answer: 1:4
Q43.
If Δm = 0.2 u, calculate binding energy (1 u = 931 MeV/c^2).
🔵 (A) 150 MeV
🟢 (B) 186 MeV
🟠 (C) 200 MeV
🔴 (D) 100 MeV
Answer: (B) 186 MeV
✔️ Final Answer: 186 MeV
Q44.
Decay constant λ = 0.001 s^−1. Half-life T1/2 = ?
🔵 (A) 1000 s
🟢 (B) 693 s
🟠 (C) 500 s
🔴 (D) 100 s
Answer: (B) 693 s
✔️ Final Answer: 693 s
Q45.
Why does spontaneous fission not occur in medium nuclei?
🔵 (A) Too much Coulomb repulsion
🟢 (B) Too little binding energy difference
🟠 (C) No neutrons present
🔴 (D) Fusion dominates
Answer: (B) Too little binding energy difference
✔️ Final Answer: Too little binding energy difference
Q46.
For a decay chain A→B→C, condition for secular equilibrium is:
🔵 (A) T1/2 of parent ≫ daughter
🟢 (B) T1/2 of parent ≪ daughter
🟠 (C) Both equal
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) T1/2 of parent ≫ daughter
✔️ Final Answer: Parent half-life ≫ daughter
Q47.
Binding energy per nucleon decreases for A > 56 mainly due to:
🔵 (A) Nuclear force stronger
🟢 (B) Coulomb repulsion stronger
🟠 (C) Weak interaction
🔴 (D) Mass defect increases
Answer: (B) Coulomb repulsion stronger
✔️ Final Answer: Coulomb repulsion
Q48.
If half-life of isotope is 1 day, mean life = ?
🔵 (A) 1.44 days
🟢 (B) 0.693 days
🟠 (C) 2 days
🔴 (D) 0.5 days
Answer: (A) 1.44 days
✔️ Final Answer: 1.44 days
Q49.
Why are heavy nuclei unstable against α-emission?
🔵 (A) Coulomb repulsion high
🟢 (B) Weak nuclear force
🟠 (C) Proton-proton attraction
🔴 (D) Lack of neutrons
Answer: (A) Coulomb repulsion high
✔️ Final Answer: Coulomb repulsion high
Q50.
Fusion of light nuclei is energetically favorable because:
🔵 (A) Mass defect decreases
🟢 (B) Binding energy per nucleon increases
🟠 (C) Density decreases
🔴 (D) Coulomb force weaker
Answer: (B) Binding energy per nucleon increases
✔️ Final Answer: B/A increases
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
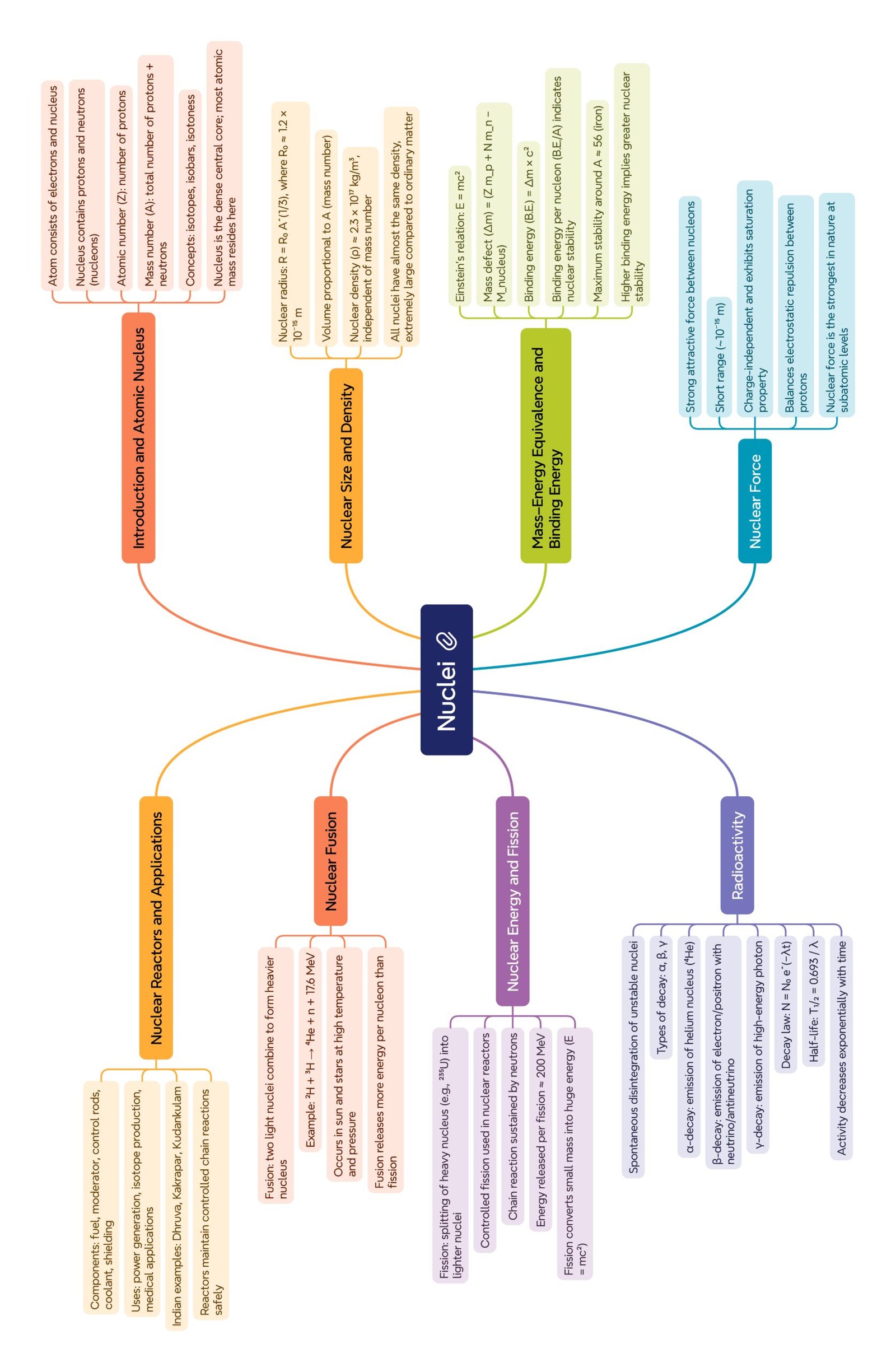
MIND MAP
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
