Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 9: Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌟 Introduction
🧬 Biotechnology = application of biological organisms, systems, and processes for human welfare.
🔬 This chapter explains the principles (tools & techniques of genetic engineering) and processes (steps in recombinant DNA technology).
🔧 Principles of Biotechnology
Modern Definition
✔️ Biotechnology = genetic engineering + maintenance of sterile conditions + large-scale cultivation.
Core Techniques
🧪 Genetic Engineering — direct manipulation of DNA, e.g.:
Recombinant DNA technology
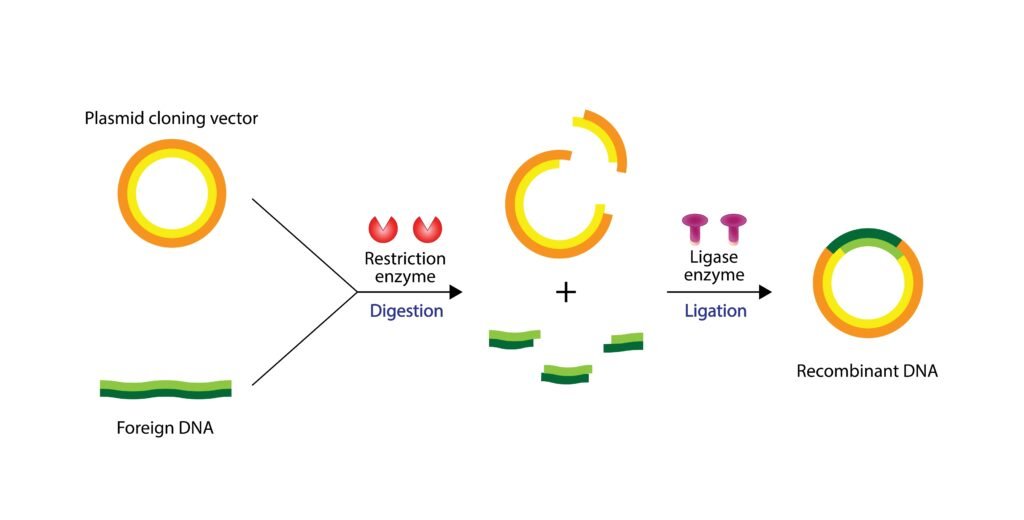
Gene transfer methods
Cloning
🧫 Tissue Culture — growth of isolated plant/animal cells under sterile, nutrient-rich conditions.
🛠️ Tools of Recombinant DNA Technology
Restriction Enzymes (Molecular Scissors ✂️)
Recognise specific DNA sequences (palindromes).
Types:
🔹 Exonucleases → cut ends of DNA.
🔹 Endonucleases → cut within DNA.
Example: EcoRI (cuts between G and A in GAATTC).
DNA Ligase (Molecular Glue 🧩)
Joins DNA fragments → seals “nicks”.
Vectors 🚚
DNA molecules used to carry foreign DNA into host.
Common vectors:

🟢 Plasmids (E. coli)
🔵 Bacteriophages (virus-based)
Good vector properties: origin of replication, selectable markers, cloning sites.
Competent Host Cells 🦠
E. coli often used.
DNA introduced via:
➡️ Transformation
➡️ Electroporation
➡️ Microinjection
➡️ Gene gun
🧪 Processes in Recombinant DNA Technology
Step 1: Isolation of DNA 🧬
Cells broken open → DNA separated from RNA, proteins, polysaccharides.
Step 2: Cutting DNA at Specific Sites ✂️
Restriction enzymes generate sticky ends.
Step 3: Amplification of Gene of Interest (GOI) 🔄
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):

Denaturation (DNA strands separate).
Annealing (primers bind).
Extension (Taq polymerase synthesises DNA).
Step 4: Insertion of DNA into Vector 🧩
GOI ligated into plasmid/phage vector.
Step 5: Introduction of Recombinant DNA into Host Cell 🦠
Techniques: microinjection, electroporation, gene gun.
Step 6: Selection of Recombinants ✅
Markers used (antibiotic resistance, colour change).
Step 7: Downstream Processing 🏭
Large-scale production in bioreactors.
Purification of product → packaging.
🏭 Bioreactors (Large-Scale Production)
Fermenters for growth of cells and production of metabolites.
Types:
🔵 Stirred-tank bioreactor (mechanical stirrer).
🟢 Air-lift bioreactor.
Conditions controlled: pH, temperature, O₂, nutrients.
🌍 Applications
Production of insulin, interferons, growth hormones.
Transgenic plants (pest resistance, nutritional enhancement).
Gene therapy.

📝 Summary (~300 words)
Biotechnology integrates genetic engineering and bioprocess engineering. Its foundation lies in restriction enzymes, vectors, DNA ligases, and competent hosts.
The process involves isolation of DNA, cutting by restriction enzymes, amplification via PCR, ligation into vectors, and transfer into host cells. Recombinant organisms are screened with selectable markers.
At industrial level, bioreactors produce large-scale metabolites like antibiotics, hormones, enzymes, vaccines. Applications span medicine, agriculture, and industry, such as insulin production, biofortification, and transgenics.
🎯 Quick Recap
🧬 Principles: Genetic engineering + tissue culture.
✂️ Tools: Restriction enzymes, ligase, vectors, host cells.
🔄 Process: DNA isolation → cutting → PCR amplification → ligation → transformation → selection → large-scale production.
🏭 Bioreactors: Controlled vessels for industrial production.
💉 Applications: Medicines, vaccines, transgenics, therapy.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔹 Q1. Can you list 10 recombinant proteins which are used in medical practice? Find out where they are used as therapeutics.
✨ Answer:
🧬 Some important recombinant proteins used in therapy:
💉 Insulin → Diabetes mellitus treatment.
🧪 Human Growth Hormone (hGH) → Pituitary dwarfism.
🛡️ Interferons → Viral infections and cancer therapy.
🩸 Factor VIII → Treatment of Haemophilia A.
🩺 Erythropoietin (EPO) → Stimulates RBC formation in anaemia.
🧬 tPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator) → Dissolves blood clots (thrombolysis).
🦠 Hepatitis B Vaccine → Prevention of hepatitis B infection.
🧩 Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) → Cancer, autoimmune diseases (like trastuzumab).
💊 Interleukins → Stimulate immune response.
🧪 DNase enzyme → Cystic fibrosis treatment (clears mucus).
🔹 Q2. Make a chart (with diagrammatic representation) showing a restriction enzyme, the substrate DNA on which it acts, the site at which it cuts DNA and the product it produces.
✨ Answer:
✔️ Example: EcoRI (restriction endonuclease)
Recognition sequence: 5′-GAATTC-3′
Cuts between G and A → produces sticky ends.
📊 Representation:
5′—GAATTC—3′
3′—CTTAAG—5′
✂️ Cut →
5′—G AATTC—3′
3′—CTTAA G—5′
Product → sticky ends, useful for recombinant DNA formation.
🔹 Q3. From what you have learnt, can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How did you know?
✨ Answer:
DNA molecules are much larger compared to enzymes.
Example: Human DNA = billions of base pairs.
Enzymes = proteins of a few thousand amino acids.
➡️ Thus, DNA >> enzymes in size.
🔹 Q4. What would be the molar concentration of human DNA in a human cell?
✨ Answer:
Haploid human genome: ~3.3 × 10⁹ bp.
Diploid genome (in one somatic cell): 6.6 × 10⁹ bp.
Since DNA is present as two sets of chromosomes, molar concentration per cell ≈ 2.2 picograms of DNA per haploid genome.
Hence, a diploid cell has about 6.6 picograms DNA.
🔹 Q5. Do eukaryotic cells have restriction endonucleases? Justify your answer.
✨ Answer:
❌ No, eukaryotic cells do not have restriction endonucleases.
✔️ These enzymes are found in bacteria (where they act as a defence mechanism against bacteriophage DNA).
Eukaryotes lack such restriction-modification systems.
🔹 Q6. Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred-tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
✨ Answer:
🏭 Advantages of Stirred-Tank Bioreactors:
✔️ Continuous monitoring of pH, oxygen, temperature, nutrients.
✔️ Better sterility maintenance.
✔️ Large-scale production possible.
✔️ More uniform distribution of cells, gases, and nutrients.
✔️ Downstream processing easier.
🔹 Q7. Collect 5 examples of palindromic DNA sequences.
✨ Answer:
✔️ Palindromic sequences read the same in both directions (5′→3′ and 3′→5′). Examples:
5′-GAATTC-3′ / 3′-CTTAAG-5′ (EcoRI)
5′-GGATCC-3′ / 3′-CCTAGG-5′ (BamHI)
5′-AAGCTT-3′ / 3′-TTCGAA-5′ (HindIII)
5′-GTCGAC-3′ / 3′-CAGCTG-5′ (SalI)
5′-CCCGGG-3′ / 3′-GGGCCC-5′ (SmaI)
🔹 Q8. Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA is made?
✨ Answer:
During meiosis, crossing over occurs in prophase I (pachytene stage).
Exchange of chromosomal segments between homologous chromosomes → recombinant DNA in gametes.
🔹 Q9. How can a reporter enzyme be used to monitor transformation of host cells by foreign DNA in addition to a selectable marker?
✨ Answer:
Reporter enzymes (e.g., β-galactosidase, luciferase, GFP) produce visible signals.
If host cells take up recombinant DNA:
Colonies show colour/fluorescence/light emission.
Example: lacZ reporter gene → blue/white colony selection in E. coli.
🔹 Q10. Describe briefly:
(a) Origin of replication
(b) Bioreactors
(c) Downstream processing
✨ Answer:
(a) Origin of replication (Ori): Specific DNA sequence where replication begins; ensures vector DNA multiplies inside host.
(b) Bioreactors: Large fermentation vessels with controlled conditions (pH, O₂, nutrients) for mass production of proteins/enzymes.
(c) Downstream processing: Purification and recovery of biotechnological products → includes separation, purification, formulation, and quality testing.
🔹 Q11. Explain briefly:
(a) PCR
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA
(c) Chitinase
✨ Answer:
(a) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Technique to amplify DNA using denaturation, annealing, and extension steps.
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA: Enzymes that cut DNA at palindromic sequences → generate sticky/blunt ends for cloning.
(c) Chitinase: Enzyme that digests chitin (present in fungal cell walls); used to isolate DNA from fungi.
🔹 Q12. Distinguish between:
(a) Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA
(b) RNA and DNA
(c) Exonuclease and Endonuclease
✨ Answer:
(a) Plasmid DNA: Small, circular, extrachromosomal; Chromosomal DNA: large, linear, carries essential genes.
(b) RNA: Single-stranded, ribose sugar, uracil; DNA: double-stranded, deoxyribose, thymine.
(c) Exonuclease: Removes nucleotides from ends; Endonuclease: cuts within DNA.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🟢 Section A — Very Short Answer / MCQs (Q1–Q6)
🔹 Q1. Which enzyme is called the “molecular scissors” in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) RNA polymerase
🔴 (D) DNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q2. The function of DNA ligase is to:
🔵 (A) Cut DNA at palindromic sites
🟢 (B) Join DNA fragments
🟠 (C) Replicate DNA
🔴 (D) Denature DNA
✅ Answer: (B) Join DNA fragments
🔹 Q3. Which organism is widely used to produce insulin by recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Rhizopus
🔴 (D) Penicillium
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
🔹 Q4. PCR is used for:
🔵 (A) Protein purification
🟢 (B) DNA amplification
🟠 (C) RNA translation
🔴 (D) Gene silencing
✅ Answer: (B) DNA amplification
🔹 Q5. Name the specific site on plasmid DNA where replication begins.
✅ Answer: Origin of replication (Ori).
🔹 Q6. Which enzyme is required to digest fungal cell walls during DNA isolation?
✅ Answer: Chitinase.
🟡 Section B — Short Answer (Q7–Q12)
🔹 Q7. What are palindromic sequences? Give one example.
✅ Answer: Palindromic sequences are DNA sequences that read the same in 5′→3′ and 3′→5′ directions.
Example: 5′-GAATTC-3′ / 3′-CTTAAG-5′ (recognized by EcoRI).
🔹 Q8. Why are bioreactors preferred over shake flasks for large-scale production?
✅ Answer: Bioreactors maintain sterility, monitor pH, O₂, and temperature, allow better aeration, nutrient mixing, and large-scale production of recombinant proteins.
🔹 Q9. Differentiate between exonuclease and endonuclease.
✅ Answer:
Exonuclease: Removes nucleotides from DNA ends.
Endonuclease: Cuts DNA within the strand at specific sites.
🔹 Q10. What is downstream processing?
✅ Answer: Series of processes for purification and formulation of the recombinant product, including separation, quality control, and packaging.
🔹 Q11. Give two uses of recombinant human insulin.
✅ Answer:
Treatment of Type 1 diabetes.
Management of Type 2 diabetes in severe cases.
🔹 Q12. Mention the three steps of PCR in correct order.
✅ Answer:
Denaturation (DNA strands separate)
Annealing (primers attach)
Extension (Taq polymerase synthesises DNA)
🔴 Section C — Short Answer II (Q13–Q22)
🔹 Q13. How are selectable markers useful in rDNA technology?
✅ Answer: Selectable markers (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes) help distinguish recombinants from non-recombinants, as only recombinants grow on selective medium.
🔹 Q14. Explain the role of ori site in cloning vectors.
✅ Answer: Ori site initiates replication, controls copy number of plasmid, and ensures propagation of inserted gene.
🔹 Q15. Give one difference between plasmid DNA and chromosomal DNA.
✅ Answer: Plasmid: Small, circular, non-essential, extrachromosomal. Chromosomal: Large, linear, essential genes.
🔹 Q16. What is meant by competent host cells? How are E. coli cells made competent?
✅ Answer: Cells capable of taking up foreign DNA are competent. E. coli is made competent by treating with divalent cations (Ca²⁺) and heat shock.
🔹 Q17. Explain the principle of gel electrophoresis.
✅ Answer: DNA fragments migrate in an electric field through agarose gel; smaller fragments move faster towards the positive electrode.
🔹 Q18. What are cloning vectors? Mention two desirable features.
✅ Answer: DNA molecules that transfer foreign DNA into host. Features: Ori site, selectable markers, unique cloning sites, small size.
🔹 Q19. What is the use of biocontrol agents like Trichoderma in biotechnology?
✅ Answer: Trichoderma acts as a biocontrol fungus against plant pathogens, reducing chemical pesticide use.
🔹 Q20. Differentiate between RNA and DNA.
✅ Answer: RNA: Single-stranded, ribose sugar, uracil. DNA: Double-stranded, deoxyribose, thymine.
🔹 Q21. Why are sticky ends better than blunt ends in recombinant DNA technology?
✅ Answer: Sticky ends allow complementary base pairing, making ligation easier and more specific.
🔹 Q22. Write one application of recombinant DNA technology in agriculture.
✅ Answer: Development of pest-resistant Bt cotton.
🟣 Section D — Long Answer (Q23–Q30)
🔹 Q23. Explain the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
✅ Answer:
Isolation of DNA.
Cutting with restriction enzymes.
Amplification of gene (PCR).
Ligation of DNA fragment into vector.
Transfer into host (transformation).
Selection of recombinants using markers.
Large-scale production and downstream processing.
🔹 Q24. What is PCR? Explain its steps and applications.
✅ Answer:
Definition: Technique to amplify DNA.
Steps:
Denaturation (strand separation at ~95°C).
Annealing (primer binding at ~55°C).
Extension (DNA synthesis by Taq polymerase at ~72°C).
Applications: DNA fingerprinting, diagnosis, gene cloning, forensics.
🔹 Q25. Discuss the role of restriction enzymes in genetic engineering.
✅ Answer:
Cut DNA at specific palindromic sequences.
Produce sticky/blunt ends useful for cloning.
Essential for recombinant DNA technology.
Examples: EcoRI, BamHI, HindIII.
🔹 Q26. Describe bioreactors and their advantages in biotechnology.
✅ Answer:
Bioreactors: Vessels for large-scale cultivation of microbes/animal cells.
Types: Stirred-tank, air-lift.
Advantages: Controlled environment, large yield, continuous monitoring, sterile conditions, cost-efficient.
🔹 Q27. What is downstream processing? Mention its importance.
✅ Answer:
Series of steps for recovery and purification of recombinant products.
Includes: separation, purification, quality control, formulation, and packaging.
Importance: Ensures product safety, efficacy, and usability (e.g., insulin, vaccines).
🔹 Q28. Describe the process of producing recombinant human insulin.
✅ Answer:
Gene for insulin (A & B chains) inserted into E. coli plasmids.
Separate expression of A and B chains.
Chains purified and chemically combined to form functional insulin.
Marketed as Humulin.
🔹 Q29. Explain the principle and applications of gel electrophoresis.
✅ Answer:
DNA fragments separated based on size through agarose gel under electric field.
Smaller fragments move faster toward positive electrode.
Applications: DNA fingerprinting, gene cloning, genetic diagnosis, sequencing.
🔹 Q30. How are competent cells prepared and why are they important?
✅ Answer:
Preparation: Treating cells with Ca²⁺ ions and subjecting to heat shock to make cell walls permeable.
Importance: Allows uptake of foreign DNA → transformation → recombinant production.
🔵 Section E — Case Study Based Questions (Q31–Q33 with MCQs)
📌 Case Study: A scientist is working on producing recombinant human growth hormone (hGH). He uses E. coli as the host, a plasmid as the vector, restriction enzymes to cut the DNA, ligase to join the DNA, and selectable markers for screening.
🔹 Q31. Which enzyme is essential to cut the hGH gene and plasmid at the same site?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q32. Which selectable marker would best help in identifying recombinant colonies?
🔵 (A) Origin of replication
🟢 (B) Antibiotic resistance gene
🟠 (C) Promoter sequence
🔴 (D) Restriction site
✅ Answer: (B) Antibiotic resistance gene
🔹 Q33. Which step ensures large-scale production of hGH after transformation?
🔵 (A) Downstream processing
🟢 (B) Bioreactor cultivation
🟠 (C) Gel electrophoresis
🔴 (D) PCR amplification
✅ Answer: (B) Bioreactor cultivation
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Which enzyme is known as “molecular glue” in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase
🟠 (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (A) DNA ligase
Year: NEET 2024
🔹 Q2. Which of the following is used to cut DNA at specific sites?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q3. Which host organism is commonly used in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Rhizobium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🔴 (D) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q4. The recognition sequence for EcoRI is:
🔵 (A) GAATTC
🟢 (B) GGATCC
🟠 (C) AAGCTT
🔴 (D) CCTAGG
✅ Answer: (A) GAATTC
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q5. Which enzyme is thermostable and used in PCR?
🔵 (A) Taq DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (A) Taq DNA polymerase
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q6. Which of the following is not a feature of a plasmid vector?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable marker
🟠 (C) Reporter gene
🔴 (D) Telomere
✅ Answer: (D) Telomere
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q7. The first clinical use of recombinant DNA technology was in the production of:
🔵 (A) Recombinant insulin
🟢 (B) Hepatitis B vaccine
🟠 (C) Interferons
🔴 (D) Growth hormone
✅ Answer: (A) Recombinant insulin
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q8. In blue-white colony selection, white colonies indicate:
🔵 (A) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) Plasmids without Ori
🔴 (D) Dead bacteria
✅ Answer: (B) Recombinant plasmids
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q9. Which method is used to introduce foreign DNA into plant cells?
🔵 (A) Microinjection
🟢 (B) Biolistic gene gun
🟠 (C) Electroporation
🔴 (D) Heat shock
✅ Answer: (B) Biolistic gene gun
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q10. In genetic engineering, selectable markers are:
🔵 (A) Ori sequences
🟢 (B) Antibiotic resistance genes
🟠 (C) Promoter sequences
🔴 (D) Terminator sequences
✅ Answer: (B) Antibiotic resistance genes
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q11. Which of the following enzymes removes RNA primer during DNA replication?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase I
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase III
🔴 (D) Primase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA polymerase I
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q12. The principle of gel electrophoresis is separation of DNA fragments based on:
🔵 (A) Charge
🟢 (B) Size
🟠 (C) Density
🔴 (D) Base composition
✅ Answer: (B) Size
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q13. Agrobacterium tumefaciens is used in biotechnology because:
🔵 (A) It fixes nitrogen
🟢 (B) It is a source of restriction enzymes
🟠 (C) It transfers T-DNA into plant genome
🔴 (D) It produces antibiotics
✅ Answer: (C) It transfers T-DNA into plant genome
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q14. The most commonly used bioreactor in rDNA technology is:
🔵 (A) Air-lift bioreactor
🟢 (B) Stirred-tank bioreactor
🟠 (C) Shake flask
🔴 (D) Bubble column
✅ Answer: (B) Stirred-tank bioreactor
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q15. Which of the following is not required in PCR?
🔵 (A) Primers
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Template DNA
🔴 (D) Taq polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q16. The function of ori site in a plasmid is:
🔵 (A) Marker gene expression
🟢 (B) Initiation of replication
🟠 (C) Restriction enzyme site
🔴 (D) Protein synthesis
✅ Answer: (B) Initiation of replication
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q17. Which enzyme is used to break open bacterial cell wall during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Cellulase
🔴 (D) Lipase
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q18. Which step in PCR involves extension of primers?
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Annealing
🟠 (C) Extension
🔴 (D) Replication
✅ Answer: (C) Extension
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q19. Chitinase enzyme is used in genetic engineering to:
🔵 (A) Cut DNA
🟢 (B) Break fungal cell wall
🟠 (C) Ligate DNA
🔴 (D) Synthesize primers
✅ Answer: (B) Break fungal cell wall
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q20. The thermostable DNA polymerase used in PCR is obtained from:
🔵 (A) Thermus aquaticus
🟢 (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟠 (C) E. coli
🔴 (D) Rhizobium
✅ Answer: (A) Thermus aquaticus
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q21. Which enzyme seals nicks in DNA?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) Polymerase
🟠 (C) Helicase
🔴 (D) Topoisomerase
✅ Answer: (A) Ligase
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q22. Which of the following is a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) Plasmid
🟠 (C) rRNA
🔴 (D) Ribosome
✅ Answer: (B) Plasmid
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q23. The selectable markers in plasmid pBR322 are:
🔵 (A) Genes for tetracycline and ampicillin resistance
🟢 (B) Genes for kanamycin and chloramphenicol resistance
🟠 (C) Genes for rifampicin and streptomycin resistance
🔴 (D) Genes for erythromycin and penicillin resistance
✅ Answer: (A) Genes for tetracycline and ampicillin resistance
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q24. Palindromic sequence is:
🔵 (A) Same sequence in one direction
🟢 (B) Same sequence when read from both ends
🟠 (C) Sequence repeated many times
🔴 (D) Random nucleotide sequence
✅ Answer: (B) Same sequence when read from both ends
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q25. Which enzyme is used to degrade bacterial cell wall for DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) DNase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q26. Which of the following enzymes is not used in genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) Lipase
✅ Answer: (D) Lipase
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q27. Which one is not a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Plasmid
🟢 (B) Bacteriophage
🟠 (C) Cosmid
🔴 (D) Ribosome
✅ Answer: (D) Ribosome
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q28. Which of the following is used in recombinant DNA technology as a vector in plants?
🔵 (A) E. coli plasmid
🟢 (B) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟠 (C) λ phage
🔴 (D) F plasmid
✅ Answer: (B) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q29. Which of the following is required for PCR?
🔵 (A) RNA primer
🟢 (B) DNA primer
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA primer
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q30. Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
🔵 (A) EcoRI — Restriction enzyme
🟢 (B) Taq polymerase — Thermostable enzyme
🟠 (C) Ori — Initiation of transcription
🔴 (D) pBR322 — Cloning vector
✅ Answer: (C) Ori — Initiation of transcription
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q31. What is the function of bioreactors in biotechnology?
🔵 (A) Isolation of DNA
🟢 (B) Large-scale production of biomolecules
🟠 (C) Gene transfer
🔴 (D) DNA cutting
✅ Answer: (B) Large-scale production of biomolecules
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q32. Which of the following enzymes is used to cut DNA at specific recognition sites?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNase
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) DNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q33. Which bacteria produce restriction enzymes?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Streptococcus
🔴 (D) Rhizobium
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q34. Which of the following is used in rDNA technology to introduce DNA into host cells?
🔵 (A) Helicase
🟢 (B) Vectors
🟠 (C) RNase
🔴 (D) Protease
✅ Answer: (B) Vectors
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q35. In blue-white colony selection, blue colonies indicate:
🔵 (A) Recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) Dead bacteria
🔴 (D) No plasmid
✅ Answer: (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q36. Which of the following enzymes is used in PCR for DNA amplification?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Taq DNA polymerase
🟠 (C) RNA polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (B) Taq DNA polymerase
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q37. Which of the following is not an essential feature of a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable marker
🟠 (C) Reporter gene
🔴 (D) Introns
✅ Answer: (D) Introns
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q38. Which enzyme is used to cut and paste DNA segments in genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease and ligase
🟢 (B) Polymerase and ligase
🟠 (C) Lysozyme and ligase
🔴 (D) DNase and ligase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease and ligase
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q39. Which of the following is used to amplify DNA in vitro?
🔵 (A) PCR
🟢 (B) Gel electrophoresis
🟠 (C) Restriction digestion
🔴 (D) Hybridisation
✅ Answer: (A) PCR
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q40. Which of the following is a palindromic sequence?
🔵 (A) ATGCAT
🟢 (B) AGCTAG
🟠 (C) AAAAGG
🔴 (D) TTTTAA
✅ Answer: (A) ATGCAT
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q41. Which of the following organisms is the source of Taq polymerase?
🔵 (A) Thermus aquaticus
🟢 (B) Rhizobium
🟠 (C) Streptomyces
🔴 (D) Agrobacterium
✅ Answer: (A) Thermus aquaticus
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q42. Which step is not part of PCR?
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Annealing
🟠 (C) Extension
🔴 (D) Transcription
✅ Answer: (D) Transcription
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q43. Which of the following enzymes joins DNA fragments together?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Restriction enzyme
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q44. The plasmid widely used as a cloning vector is:
🔵 (A) pBR322
🟢 (B) pUC18
🟠 (C) Ti plasmid
🔴 (D) F plasmid
✅ Answer: (A) pBR322
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q45. Which enzyme is used to digest bacterial cell wall during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) DNase
🟠 (C) Protease
🔴 (D) Ligase
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q46. Which of the following steps is not required in genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Isolation of DNA
🟢 (B) Cutting DNA at specific sites
🟠 (C) Selection of recombinants
🔴 (D) Protein denaturation
✅ Answer: (D) Protein denaturation
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q47. Which is the first step in rDNA technology?
🔵 (A) Amplification of gene
🟢 (B) Isolation of DNA
🟠 (C) Ligation of DNA
🔴 (D) Transformation
✅ Answer: (B) Isolation of DNA
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q48. Which of the following organisms is not used as host in biotechnology?
🔵 (A) E. coli
🟢 (B) Yeast
🟠 (C) Bacteriophage
🔴 (D) Amoeba
✅ Answer: (D) Amoeba
Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q49. Which method is used for introducing recombinant DNA into animal cells?
🔵 (A) Microinjection
🟢 (B) Biolistics
🟠 (C) Heat shock
🔴 (D) Conjugation
✅ Answer: (A) Microinjection
Year: PMT 1997
🔹 Q50. Which enzyme is used to cut plasmid DNA in recombinant technology?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
Year: PMT 1996
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20 (Moderate, NEET-level)
🔹 Q1. Which enzyme helps in joining DNA fragments during recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔴 (D) Primase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
🔹 Q2. The recognition sequence of HindIII is:
🔵 (A) GAATTC
🟢 (B) AAGCTT
🟠 (C) GGATCC
🔴 (D) CCTAGG
✅ Answer: (B) AAGCTT
🔹 Q3. Which organism is most commonly used as a host in recombinant DNA experiments?
🔵 (A) Rhizobium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Saccharomyces cerevisiae
🔴 (D) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
🔹 Q4. Which is called the “molecular scissors”?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) Taq polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q5. Which of the following is thermostable and used in PCR?
🔵 (A) Taq DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) RNA polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (A) Taq DNA polymerase
🔹 Q6. Which enzyme is required to digest bacterial cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Pectinase
🔴 (D) Lipase
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
🔹 Q7. Which one is a selectable marker in plasmid pBR322?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Ampicillin resistance gene
🟠 (C) Promoter sequence
🔴 (D) Termination codon
✅ Answer: (B) Ampicillin resistance gene
🔹 Q8. Which technique separates DNA fragments based on size?
🔵 (A) Electrophoresis
🟢 (B) Chromatography
🟠 (C) Centrifugation
🔴 (D) Precipitation
✅ Answer: (A) Electrophoresis
🔹 Q9. Which step in PCR comes first?
🔵 (A) Annealing
🟢 (B) Denaturation
🟠 (C) Extension
🔴 (D) Replication
✅ Answer: (B) Denaturation
🔹 Q10. Blue colonies in blue-white selection contain:
🔵 (A) Recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) No plasmid
🔴 (D) Dead cells
✅ Answer: (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
🔹 Q11. Which vector is commonly used in plant genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟢 (B) λ phage
🟠 (C) F plasmid
🔴 (D) Cosmid
✅ Answer: (A) Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🔹 Q12. Which enzyme is required to isolate DNA from fungi?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Cellulase
🔴 (D) Pectinase
✅ Answer: (B) Chitinase
🔹 Q13. Ori site in a plasmid helps in:
🔵 (A) Ligation
🟢 (B) Replication initiation
🟠 (C) Antibiotic resistance
🔴 (D) Transcription termination
✅ Answer: (B) Replication initiation
🔹 Q14. In PCR, primers are required for:
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Initiating DNA synthesis
🟠 (C) Ligating DNA
🔴 (D) Cutting DNA
✅ Answer: (B) Initiating DNA synthesis
🔹 Q15. Which of the following is not used in genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Restriction enzymes
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) DNase
🔴 (D) Vectors
✅ Answer: (C) DNase
🔹 Q16. The plasmid used as a cloning vector in early experiments was:
🔵 (A) pBR322
🟢 (B) F plasmid
🟠 (C) Ti plasmid
🔴 (D) pUC18
✅ Answer: (A) pBR322
🔹 Q17. Which of the following is a palindromic sequence?
🔵 (A) GAATTC
🟢 (B) CGATCG
🟠 (C) AGTCGA
🔴 (D) ATGCTA
✅ Answer: (A) GAATTC
🔹 Q18. Which one is not a step in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Isolation of DNA
🟢 (B) Protein denaturation
🟠 (C) DNA ligation
🔴 (D) Transformation
✅ Answer: (B) Protein denaturation
🔹 Q19. In rDNA technology, foreign DNA is introduced into host cells by:
🔵 (A) Transformation
🟢 (B) Transduction
🟠 (C) Conjugation
🔴 (D) Binary fission
✅ Answer: (A) Transformation
🔹 Q20. Which of the following organisms is not used as host in biotechnology?
🔵 (A) E. coli
🟢 (B) Yeast
🟠 (C) Amoeba
🔴 (D) Bacteriophage
✅ Answer: (C) Amoeba
🟡 Q21–Q50 (Enhanced NEET-level, original)
🔹 Q21. Which of the following is used to transfer foreign DNA into plant cells?
🔵 (A) Ti plasmid
🟢 (B) λ phage
🟠 (C) F plasmid
🔴 (D) pUC18
✅ Answer: (A) Ti plasmid
🔹 Q22. Which enzyme unwinds DNA strands during replication?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) Helicase
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) Restriction enzyme
✅ Answer: (B) Helicase
🔹 Q23. Which enzyme seals nicks in the DNA backbone?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) Polymerase
🟠 (C) DNase
🔴 (D) Exonuclease
✅ Answer: (A) Ligase
🔹 Q24. In PCR, annealing step occurs at approximately:
🔵 (A) 94°C
🟢 (B) 55°C
🟠 (C) 72°C
🔴 (D) 37°C
✅ Answer: (B) 55°C
🔹 Q25. Which of the following is a palindrome sequence?
🔵 (A) 5′-GAATTC-3′
🟢 (B) 5′-AAGCTA-3′
🟠 (C) 5′-TACGGT-3′
🔴 (D) 5′-CCGGGA-3′
✅ Answer: (A) 5′-GAATTC-3′
🔹 Q26. Which bacterium provides Taq polymerase?
🔵 (A) Thermus aquaticus
🟢 (B) Rhizobium
🟠 (C) Agrobacterium
🔴 (D) E. coli
✅ Answer: (A) Thermus aquaticus
🔹 Q27. The function of primers in PCR is:
🔵 (A) To ligate DNA
🟢 (B) To initiate DNA synthesis
🟠 (C) To denature DNA
🔴 (D) To cut DNA
✅ Answer: (B) To initiate DNA synthesis
🔹 Q28. Which of the following is a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Plasmid
🟢 (B) Ribosome
🟠 (C) mRNA
🔴 (D) tRNA
✅ Answer: (A) Plasmid
🔹 Q29. Which method introduces DNA directly into animal cells?
🔵 (A) Microinjection
🟢 (B) Biolistics
🟠 (C) Electroporation
🔴 (D) Heat shock
✅ Answer: (A) Microinjection
🔹 Q30. Which enzyme is used to remove RNA primers?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase I
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (A) DNA polymerase I
🔹 Q31. What is the role of Ori in a plasmid?
🔵 (A) Initiates replication
🟢 (B) Terminates replication
🟠 (C) Acts as a marker
🔴 (D) Cuts DNA
✅ Answer: (A) Initiates replication
🔹 Q32. Recombinant insulin was first produced in:
🔵 (A) Rhizobium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Agrobacterium
🔴 (D) Saccharomyces
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
🔹 Q33. Which enzyme is used to cut plasmid DNA?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q34. Which one of the following is a reporter gene?
🔵 (A) lacZ
🟢 (B) Ori
🟠 (C) Ligase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (A) lacZ
🔹 Q35. Which of the following enzymes is required in downstream processing?
🔵 (A) Protease
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) Ligase
✅ Answer: (A) Protease
🔹 Q36. Which of these is not a feature of a vector?
🔵 (A) Ori
🟢 (B) Selectable marker
🟠 (C) Promoter
🔴 (D) Introns
✅ Answer: (D) Introns
🔹 Q37. Blue colonies in blue-white selection represent:
🔵 (A) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) No plasmid
🔴 (D) Dead cells
✅ Answer: (A) Non-recombinant plasmids
🔹 Q38. Which technique is used to produce multiple DNA copies in vitro?
🔵 (A) PCR
🟢 (B) Gel electrophoresis
🟠 (C) Restriction digestion
🔴 (D) Centrifugation
✅ Answer: (A) PCR
🔹 Q39. Which enzyme adds nucleotides during PCR extension?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Taq polymerase
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (B) Taq polymerase
🔹 Q40. Which step is not a part of PCR?
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Annealing
🟠 (C) Extension
🔴 (D) Translation
✅ Answer: (D) Translation
🔹 Q41. Which enzyme is used to digest fungal cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Chitinase
🟢 (B) Lysozyme
🟠 (C) Cellulase
🔴 (D) Pectinase
✅ Answer: (A) Chitinase
🔹 Q42. Which plasmid is commonly used as a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) pBR322
🟢 (B) F plasmid
🟠 (C) Cosmid
🔴 (D) Ribosome
✅ Answer: (A) pBR322
🔹 Q43. Which enzyme separates DNA fragments in electrophoresis?
🔵 (A) None
🟢 (B) Restriction enzyme
🟠 (C) DNase
🔴 (D) Ligase
✅ Answer: (A) None (movement is due to electric field, not enzyme)
🔹 Q44. Which bacterium is used to transfer genes into plants?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟢 (B) Rhizobium
🟠 (C) Streptococcus
🔴 (D) Clostridium
✅ Answer: (A) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🔹 Q45. Which enzyme is absent in eukaryotes but present in bacteria for protection?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Helicase
🔴 (D) Topoisomerase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q46. Which step follows ligation in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Transformation into host
🟢 (B) Electrophoresis
🟠 (C) Downstream processing
🔴 (D) PCR amplification
✅ Answer: (A) Transformation into host
🔹 Q47. Which enzyme is used to digest plant cell wall?
🔵 (A) Cellulase
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Lysozyme
🔴 (D) Pectinase
✅ Answer: (A) Cellulase
🔹 Q48. Which enzyme catalyses the synthesis of DNA during replication?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) Helicase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (A) DNA polymerase
🔹 Q49. Which bioreactor is most widely used?
🔵 (A) Stirred-tank bioreactor
🟢 (B) Air-lift bioreactor
🟠 (C) Bubble column
🔴 (D) Shake flask
✅ Answer: (A) Stirred-tank bioreactor
🔹 Q50. Which enzyme is used to cut DNA at specific palindromic sequences?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
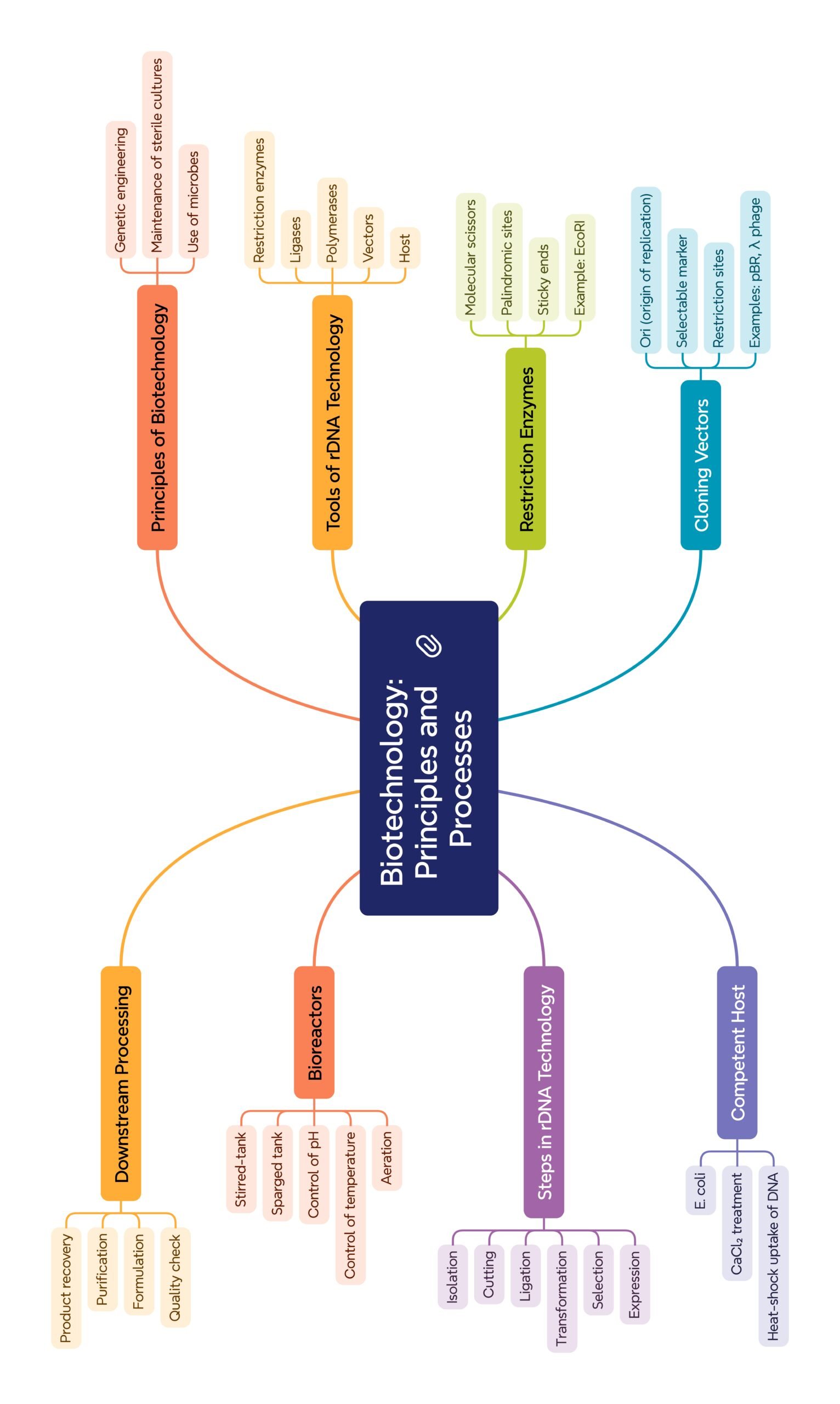
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
