Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 6: Evolution
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌟 Introduction
🔵 Evolution is the study of how life forms have changed over time.
🟢 It explains diversity of life, origin of species, and adaptations.
🟠 Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection is the cornerstone of modern evolutionary biology.
🔴 The NCERT chapter covers concepts from origin of life to molecular evidence of evolution.
🌍 Origin of Life
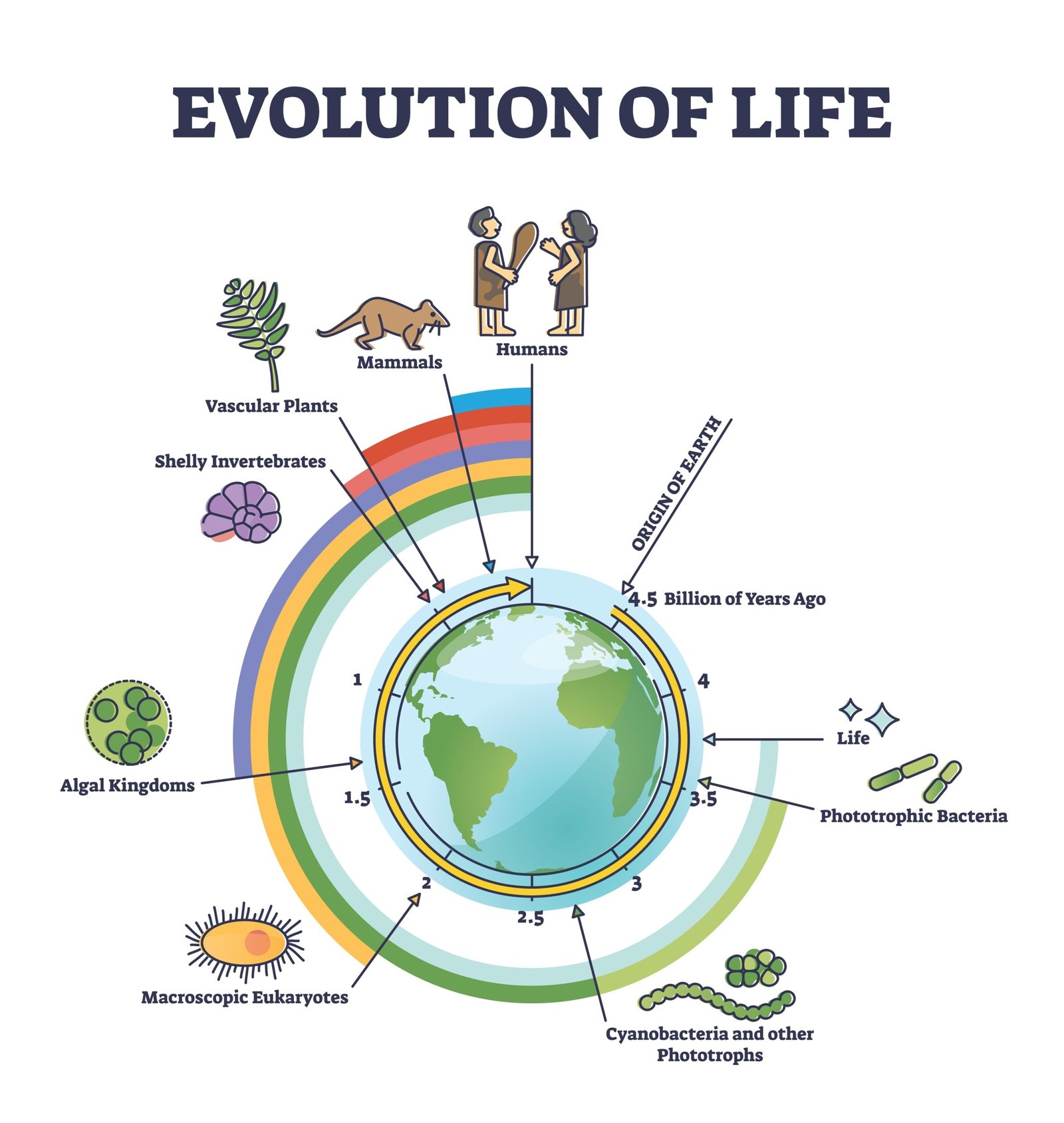
✨ Abiogenesis Hypothesis
Early Greek philosophers suggested life originated spontaneously from non-living matter.
✨ Oparin–Haldane Theory
Primitive Earth had reducing atmosphere: CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapour.
Energy from UV rays, lightning → organic molecules.
✨ Miller–Urey Experiment (1953)
Created conditions of primitive Earth in lab.
Mixture of CH₄, NH₃, H₂, water vapour + electric discharge → amino acids formed.
✔️ Proved organic molecules could form under primitive Earth conditions.
🦠 Theories of Evolution
🔹 Lamarckism (Inheritance of Acquired Characters)
✏️ Example: Giraffe’s neck elongation due to stretching.
⚠️ Rejected due to lack of experimental evidence.
🔹 Darwinism (Natural Selection)
✔️ Variations exist among organisms.
✔️ Struggle for existence leads to survival of the fittest.
✔️ Favourable variations inherited → new species.
🔹 Mutation Theory (de Vries)
✔️ Sudden, large variations (mutations) cause evolution.
🧬 Evidences of Evolution


🔵 Morphological & Anatomical
Homologous organs (e.g., forelimbs of man, whale, bat).
Analogous organs (e.g., wings of butterfly vs. bird).


🟢 Palaeontological
Fossils show gradual changes (e.g., horse evolution).
🟠 Embryological
Early embryos of vertebrates resemble each other.
🔴 Molecular Biology
Similarities in DNA, RNA, proteins among species indicate common ancestry.

🐒 Human Evolution
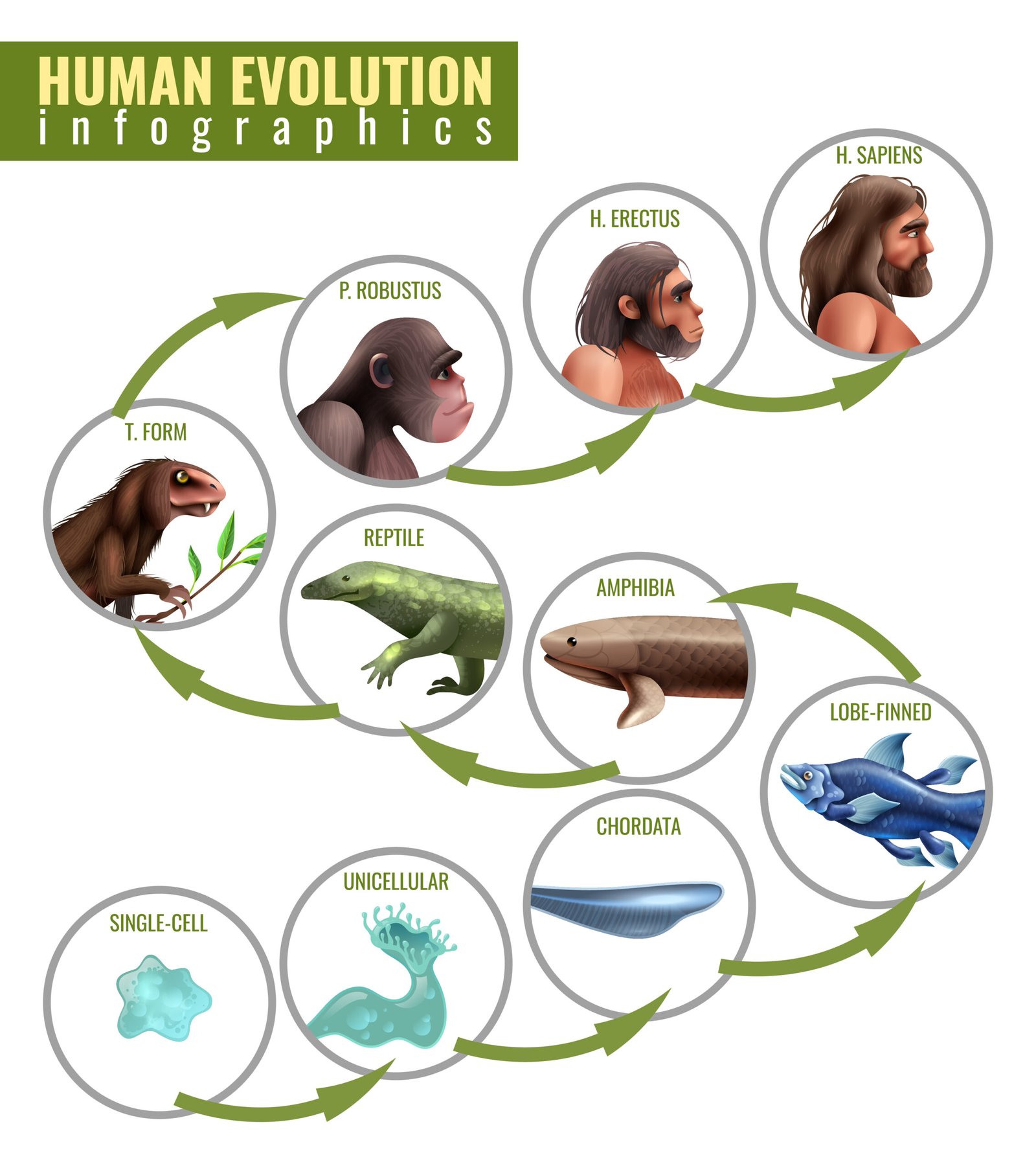
Dryopithecus & Ramapithecus: earliest primates.
Australopithecus: ape-like + human-like features.
Homo habilis: first tool maker.
Homo erectus: discovered fire.
Homo sapiens: modern humans, appeared ~75,000–10,000 years ago.

📊 Hardy–Weinberg Principle
💡 States: Gene frequencies in a population remain constant if no evolutionary forces act.
Formula: p² + 2pq + q² = 1
p = frequency of dominant allele
q = frequency of recessive allele
Conditions:
✔️ No mutation
✔️ Random mating
✔️ Large population
✔️ No migration
✔️ No selection
Deviation from principle = evolutionary change.
🌿 Factors Affecting Evolution
🔹 Mutation
🔹 Genetic drift
🔹 Gene flow (migration)
🔹 Natural selection
🔹 Recombination
📝 Summary (~300 words)
Evolution explains the diversity of life and its gradual transformation. Early theories like Lamarckism suggested acquired traits could be inherited, but Darwin’s theory of natural selection provided a scientific basis. De Vries highlighted the role of mutations in evolution.
Evidences of evolution come from comparative anatomy (homologous and analogous organs), fossils, embryology, and molecular studies. Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium mathematically explains genetic stability in populations, with deviations indicating evolutionary change. Factors like mutation, selection, genetic drift, and gene flow drive this change.
The origin of life is explained by Oparin–Haldane theory and supported experimentally by Miller–Urey. Human evolution traces a gradual lineage from Dryopithecus to Homo sapiens, with adaptations like bipedalism, larger brain, and cultural development.
Thus, evolution integrates multiple evidences and principles, forming the foundation of modern biology.
🎯 Quick Recap
🟦 Origin of life → Oparin–Haldane, Miller–Urey
🟩 Theories → Lamarckism, Darwinism, Mutation theory
🟨 Evidences → Anatomy, fossils, embryology, molecular
🟧 Human evolution → Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
🟪 Hardy–Weinberg → p² + 2pq + q² = 1
🟫 Factors → Mutation, drift, gene flow, selection
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔬🦠 Q1. Explain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinian selection theory.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🔵 Random mutations occur naturally in bacterial populations.
🟢 Some mutations confer antibiotic resistance.
🧬 When antibiotic is applied → 💀 sensitive bacteria die.
🦠 Resistant bacteria survive ➡️ multiply ➡️ pass on resistance genes.
🌍 This is natural selection in action: “Survival of the fittest”.
📜🦴 Q2. Find out from newspapers and popular science articles any new fossil discoveries or controversies about evolution.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🟢 New fossils like feathered dinosaurs in China support link between reptiles & birds.
🟡 Fossil Homo naledi discovered in South Africa enriched human lineage knowledge.
🦕 Controversies exist regarding the exact ancestor of modern humans.
💡 Science evolves with new discoveries, refining evolutionary theories.
🌳🐒 Q3. Attempt giving a clear definition of the term species.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🔵 Species: A group of organisms capable of interbreeding naturally and producing fertile offspring.
🦓 Example: Horse × Donkey → Mule (sterile), showing they are separate species.
🧬 Species represent the basic unit of evolution.
🧠👣 Q4. Trace the various components of human evolution.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🧬 Brain size & function: from ~600 cc (Australopithecus) ➡️ ~1450 cc (Homo sapiens).
🦴 Skeletal structure: pelvis broad, limbs adapted to bipedalism.
🥩 Diet: shift from plant-based → omnivorous, tool-based food gathering.
🔥 Culture & tools: Homo habilis (stone tools), Homo erectus (fire), Homo sapiens (art, culture).
🐬🐘 Q5. Find out whether animals other than man have self-consciousness.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🟢 Mirror test studies show dolphins, apes, elephants, magpies have self-recognition.
🧠 However, complex self-consciousness (language, abstract thought, morals) ➡️ unique to humans.
🦖🦒 Q6. List 10 modern-day animals and link them with corresponding fossils.
🌱✔️ Answer:
1️⃣ 🐎 Horse — Eohippus
2️⃣ 🐘 Elephant — Mastodon
3️⃣ 🐪 Camel — Protylopus
4️⃣ 🐋 Whale — Ambulocetus
5️⃣ 👨 Human — Australopithecus
6️⃣ 🐦 Bird — Archaeopteryx
7️⃣ 🐅 Tiger — Smilodon (Saber-toothed cat)
8️⃣ 🐕 Dog — Leptocyon
9️⃣ 🐊 Crocodile — Deinosuchus
🔟 🐟 Coelacanth (living fossil)
✏️🌿 Q7. Practise drawing various animals and plants.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🎨 Draw horse evolution stages, 🦕 dinosaurs, 🐦 Archaeopteryx, 🌱 plant fossils.
📚 Helps compare modern forms vs. ancient fossils.
🌈🦜 Q8. Describe one example of adaptive radiation.
🌱✔️ Answer:
🟢 Darwin’s finches (Galápagos Islands):
🌾 Different beaks adapted for seeds.
🐛 Others for insects.
🌸 Some for nectar.
➡️ One ancestor diversified → many species in different niches.
🧬👨 Q9. Can we call human evolution adaptive radiation?
🌱✔️ Answer:
🟢 Yes: Within genus Homo, multiple species (habilis, erectus, sapiens) arose.
🦴 Each adapted to different environments, diets, tools.
⚠️ But extent is less dramatic than finches or marsupials.
🐎⏳ Q10. Trace evolutionary stages of horse.
🌱✔️ Answer:
1️⃣ Eohippus (Hyracotherium): 🌳 Small, 4 toes, lived in forests.
2️⃣ Mesohippus: 🌾 3 toes, larger, adapted to grasslands.
3️⃣ Merychippus: 🐎 Middle toe dominant, grazing teeth.
4️⃣ Pliohippus: 🚀 Single strong toe, fast runner.
5️⃣ Equus (modern horse): 🐎 One hoof, long limbs, advanced grazers.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔹 Q1. 🧬🌍 Which set best represents primitive Earth’s reducing atmosphere in Oparin–Haldane theory?
🔵 (A) CO₂, O₂, N₂
🟢 (B) CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapour
🟠 (C) O₂, O₃, N₂
🔴 (D) CO₂, O₂, H₂O
✔️ Answer: (B) CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapour
🔹 Q2. 🧪⚡ Miller–Urey apparatus simulated early Earth. The first organic compounds detected were mainly:
🔵 (A) Polysaccharides
🟢 (B) Amino acids
🟠 (C) DNA
🔴 (D) Triglycerides
✔️ Answer: (B) Amino acids
🔹 Q3. 🦋🌳 Wings of a butterfly and a bird are:
🔵 (A) Homologous
🟢 (B) Analogous
🟠 (C) Vestigial
🔴 (D) Atavistic
✔️ Answer: (B) Analogous
🔹 Q4. 🐳🖐 Forelimbs of whale, bat and human are:
🔵 (A) Analogous
🟢 (B) Homologous
🟠 (C) Vestigial
🔴 (D) Convergent traits
✔️ Answer: (B) Homologous
🔹 Q5. 🌫️🦋 Industrial melanism in peppered moths supports:
🔵 (A) Lamarckism
🟢 (B) Natural selection
🟠 (C) Neutral evolution
🔴 (D) Catastrophism
✔️ Answer: (B) Natural selection
🔹 Q6. 🧮 Gene-pool stability in a large randomly mating population is expressed by:
🔵 (A) p + q = 1
🟢 (B) p² + 2pq + q² = 1
🟠 (C) p² − q² = 1
🔴 (D) 2p + q = 1
✔️ Answer: (B) p² + 2pq + q² = 1
🔹 Q7. 🧊➡️🌱 The first life forms (prokaryotes) are thought to have appeared in:
🔵 (A) Ozone-rich atmosphere
🟢 (B) Reducing atmosphere
🟠 (C) Oxygenic atmosphere
🔴 (D) Indoor lab settings only
✔️ Answer: (B) Reducing atmosphere
🔹 Q8. 🧬 Genetic drift (founder effect) is most pronounced in:
🔵 (A) Very large populations
🟢 (B) Small isolated populations
🟠 (C) Panmictic continental populations
🔴 (D) Only asexual populations
✔️ Answer: (B) Small isolated populations
🔹 Q9. 🐦🌋 Adaptive radiation is best illustrated by:
🔵 (A) Darwin’s finches
🟢 (B) Hydra budding
🟠 (C) Binary fission in E. coli
🔴 (D) Parthenogenesis in aphids
✔️ Answer: (A) Darwin’s finches
🔹 Q10. 🧠🔥 In human evolution, the first confirmed tool-maker was:
🔵 (A) Homo erectus
🟢 (B) Homo habilis
🟠 (C) Australopithecus afarensis
🔴 (D) Homo sapiens sapiens
✔️ Answer: (B) Homo habilis
🔹 Q11. 🦖🕊 Archaeopteryx is considered a “connecting link” because it has:
🔵 (A) Only reptilian features
🟢 (B) Only avian features
🟠 (C) Both reptilian (teeth, tail) and avian (feathers) traits
🔴 (D) Only mammalian traits
✔️ Answer: (C) Both reptilian (teeth, tail) and avian (feathers) traits
🔹 Q12. 🧪🧬 “Use and disuse” of organs and inheritance of acquired characters was proposed by:
🔵 (A) Darwin
🟢 (B) Lamarck
🟠 (C) de Vries
🔴 (D) Wallace
✔️ Answer: (B) Lamarck
🔹 Q13. 🦋🌫️ Assertion (A): Industrial melanism is evidence for natural selection.
Reason (R): Dark moths had higher survival on soot-darkened trees due to reduced predation.
🔵 (1)
🟢 (2)
🟠 (3)
🔴 (4)
✔️ Answer: (1)
🔹 Q14. 🧬📊 Assertion (A): Evolution is a change in allele frequencies across generations.
Reason (R): Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium describes conditions under which allele frequencies remain constant.
🔵 (1)
🟢 (2)
🟠 (3)
🔴 (4)
✔️ Answer: (2)
🔹 Q15. 🐒🌍 Define speciation.
✔️ Answer: Formation of new species from ancestral populations through reproductive isolation and divergence.
🔹 Q16. 🧬🧠 Differentiate (one point each): Homology vs Analogy.
✔️ Answer: Homology = common ancestry with divergent functions (human arm vs whale flipper); Analogy = convergent function with different ancestry (bird wing vs insect wing).
🔹 Q17. 🧮🧬 In a population, recessive phenotype frequency (q²) = 0.16. Calculate q and p (Hardy–Weinberg).
✔️ Answer (step-by-step):
q² = 0.16
q = sqrt(0.16) = 0.4
p = 1 − q = 1 − 0.4 = 0.6
🔹 Q18. 🧬🌱 Which one of the following is a vestigial organ in humans?
🔵 (A) Kidney
🟢 (B) Appendix
🟠 (C) Pancreas
🔴 (D) Liver
✔️ Answer: (B) Appendix
🔹 Q19. 🦠🧪 Which process introduces new alleles into a population gene pool?
🔵 (A) Genetic drift
🟢 (B) Mutation
🟠 (C) Natural selection
🔴 (D) Recombination
✔️ Answer: (B) Mutation
🔹 Q20. 🧮 If in a Hardy–Weinberg population, p = 0.7 and q = 0.3, what is the frequency of heterozygotes (2pq)?
🔵 (A) 0.21
🟢 (B) 0.42
🟠 (C) 0.49
🔴 (D) 0.09
✔️ Answer: (B) 0.42
🔹 Q21. 🌍🦕 Fossils provide which type of evidence for evolution?
🔵 (A) Comparative anatomy
🟢 (B) Biochemical
🟠 (C) Palaeontological
🔴 (D) Embryological
✔️ Answer: (C) Palaeontological
🔹 Q22. 🦋🌸 Natural selection is based on:
🔵 (A) Variations present in a population
🟢 (B) Absence of competition
🟠 (C) Occurrence of acquired characters
🔴 (D) Lack of mutations
✔️ Answer: (A) Variations present in a population
🔹 Q23. 🧠🐒 Arrange in correct sequence: Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo sapiens.
🔵 (A) Homo erectus → Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo sapiens
🟢 (B) Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
🟠 (C) Australopithecus → Homo erectus → Homo habilis → Homo sapiens
🔴 (D) Homo habilis → Australopithecus → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
✔️ Answer: (B) Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
🔹 Q24. 🐦🦖 Archaeopteryx shows evolutionary relationship between:
🔵 (A) Mammals and birds
🟢 (B) Reptiles and birds
🟠 (C) Amphibians and reptiles
🔴 (D) Fish and amphibians
✔️ Answer: (B) Reptiles and birds
🔹 Q25. 🧬 Which scientist gave mutation theory of evolution?
🔵 (A) Hugo de Vries
🟢 (B) Lamarck
🟠 (C) Darwin
🔴 (D) Wallace
✔️ Answer: (A) Hugo de Vries
🔹 Q26. 🌱🧪 Which experiment demonstrated DNA as genetic material?
🔵 (A) Hershey and Chase
🟢 (B) Griffith
🟠 (C) Meselson and Stahl
🔴 (D) Miller–Urey
✔️ Answer: (A) Hershey and Chase
🔹 Q27. 🦋🌳 Which is NOT a postulate of Darwin’s theory?
🔵 (A) Variations are heritable
🟢 (B) More individuals produced than survive
🟠 (C) Variations arise due to acquired characters
🔴 (D) Fittest survive
✔️ Answer: (C) Variations arise due to acquired characters
🔹 Q28. 🦠🧬 Which type of selection maintains polymorphism in a population?
🔵 (A) Stabilising selection
🟢 (B) Directional selection
🟠 (C) Disruptive selection
🔴 (D) Artificial selection
✔️ Answer: (C) Disruptive selection
🔹 Q29. 🐒🧠 Which hominid first used fire?
🔵 (A) Australopithecus
🟢 (B) Homo erectus
🟠 (C) Homo habilis
🔴 (D) Homo sapiens
✔️ Answer: (B) Homo erectus
🔹 Q30. 🌊🦠 According to Oparin and Haldane, first life arose in:
🔵 (A) Land surface
🟢 (B) Primitive oceans (soup of molecules)
🟠 (C) Atmosphere
🔴 (D) Volcanoes
✔️ Answer: (B) Primitive oceans (soup of molecules)
🔹 Q31. 🧬🦋 Which phenomenon best explains “microevolution”?
🔵 (A) Change in allele frequency within populations
🟢 (B) Origin of eukaryotic cells
🟠 (C) Evolution of whales from land mammals
🔴 (D) Evolution of Homo sapiens
✔️ Answer: (A) Change in allele frequency within populations
🔹 Q32. 🐘🦣 Fossil of “woolly mammoth” is evidence for:
🔵 (A) Coevolution
🟢 (B) Extinction
🟠 (C) Divergent evolution
🔴 (D) Vestigiality
✔️ Answer: (B) Extinction
🔹 Q33. 🧪🦠 Who disproved spontaneous generation of life by experiment with sterilised flasks?
🔵 (A) Louis Pasteur
🟢 (B) Darwin
🟠 (C) Lamarck
🔴 (D) Oparin
✔️ Answer: (A) Louis Pasteur
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Match List-I with List-II:
List–I: (A) Gene pool (B) Genetic drift (C) Gene flow (D) Gene frequency
List–II: (I) Stable within a generation (II) Change in gene frequency by chance (III) Transfer of genes into or out of population (IV) Total number of genes and their alleles
🔵 (A) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
🟢 (B) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
🟠 (C) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
🔴 (D) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
✅ Answer: (B) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
Year: 2024 | Exam: NEET (Re-Examination)
🔹 Q2. Arrange the following in correct order during human evolution:
(i) Homo habilis (ii) Homo neanderthalensis (iii) Homo erectus (iv) Homo sapiens
🔵 (A) i → iii → ii → iv
🟢 (B) i → ii → iii → iv
🟠 (C) iii → i → ii → iv
🔴 (D) ii → iii → i → iv
✅ Answer: (A) i → iii → ii → iv
Year: 2024 | Exam: NEET (Re-Examination)
🔹 Q3. Select the correct group of Australian marsupials exhibiting adaptive radiation.
🔵 (A) Lemur, Anteater, Wolf
🟢 (B) Tasmanian wolf, Bobcat, Marsupial mole
🟠 (C) Numbat, Spotted cuscus, Flying phalanger
🔴 (D) Mole, Flying squirrel, Tasmanian tiger cat
✅ Answer: (C) Numbat, Spotted cuscus, Flying phalanger
Year: 2023 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q4. Given below are two statements:
I. RNA mutates at a faster rate.
II. Viruses with RNA genomes and shorter life span mutate and evolve faster.
Choose the correct option.
🔵 (A) Both I and II are false
🟢 (B) I is true but II is false
🟠 (C) I is false but II is true
🔴 (D) Both I and II are true
✅ Answer: (D) Both I and II are true
Year: 2023 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q5. Natural selection where more individuals acquire specific character value other than the mean character value leads to
🔵 (A) Directional change
🟢 (B) Stabilising change
🟠 (C) Disruptive change
🔴 (D) Random change
✅ Answer: (A) Directional change
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q6. Select the correct statement regarding mutation theory of evolution.
🔵 (A) Large differences due to mutations arise gradually in a population
🟢 (B) This theory was proposed by Alfred Wallace
🟠 (C) Variations are small directional changes
🔴 (D) Single-step large mutation is a cause of speciation
✅ Answer: (D) Single-step large mutation is a cause of speciation
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q7. The factor that leads to Founder effect in a population is
🔵 (A) Natural selection
🟢 (B) Genetic recombination
🟠 (C) Mutation
🔴 (D) Genetic drift
✅ Answer: (D) Genetic drift
Year: 2021 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q8. Match List-I with List-II.
List–I: (A) Adaptive radiation (B) Convergent evolution (C) Divergent evolution (D) Evolution by anthropogenic action
List–II: (I) Selection of resistant varieties due to excessive use of herbicides/pesticides (II) Bones of forelimbs in Man and Whale (III) Wings of Butterfly and Bird (IV) Darwin’s finches
🔵 (A) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-II
🟢 (B) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
🟠 (C) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
🔴 (D) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
✅ Answer: (D) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Year: 2021 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q9. Embryological support for evolution was disapproved by
🔵 (A) Oparin
🟢 (B) Alfred Wallace
🟠 (C) Karl Ernst von Baer
🔴 (D) Charles Darwin
✅ Answer: (C) Karl Ernst von Baer
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q10. From his experiments, S. L. Miller produced amino acids by mixing, in a closed flask,
🔵 (A) CH₄, H₂, NH₃ and water vapour at 800°C
🟢 (B) CH₃, H₂, NH₄ and water vapour at 800°C
🟠 (C) CH₄, H₂, NH₃ and water vapour at 600°C
🔴 (D) CH₃, H₂, NH₃ and water vapour at 600°C
✅ Answer: (A) CH₄, H₂, NH₃ and water vapour at 800°C
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q11. Flippers of Penguins and Dolphins are examples of
🔵 (A) Adaptive radiation
🟢 (B) Natural selection
🟠 (C) Industrial melanism
🔴 (D) Convergent evolution
✅ Answer: (D) Convergent evolution
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q12. Which of the following refer to organisms evolved due to anthropogenic action?
(a) Herbicide-resistant weeds (b) Drug-resistant microbes (c) Man-created breeds of dogs (d) Darwin’s finches
🔵 (A) (b), (c), (d)
🟢 (B) only (a)
🟠 (C) (a) and (c)
🔴 (D) (a), (b) and (c)
✅ Answer: (D) (a), (b) and (c)
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q13. In a species, newborn weights range from 2–5 kg. About 97% of infants between 3–3.3 kg survive; ~99% of infants at 2–2.5 kg or 4.5–5 kg die. Which selection operates?
🔵 (A) Disruptive selection
🟢 (B) Cyclical selection
🟠 (C) Directional selection
🔴 (D) Stabilizing selection
✅ Answer: (D) Stabilizing selection
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET (05-05-2019)
🔹 Q14. A population will NOT exist in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium if
🔵 (A) There are no mutations
🟢 (B) Population is large
🟠 (C) Individuals mate selectively
🔴 (D) Population has not migrated
✅ Answer: (C) Individuals mate selectively
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q15. Industrial melanism in peppered moth is an example of
🔵 (A) Natural selection
🟢 (B) Mutation
🟠 (C) Neo-Lamarckism
🔴 (D) None of the above
✅ Answer: (A) Natural selection
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q16. The wings of a bird and the wings of an insect are
🔵 (A) Analogous structures
🟢 (B) Homologous structures
🟠 (C) Phylogenetic structures
🔴 (D) None of the above
✅ Answer: (A) Analogous structures
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q17. What is common to a Whale, Shark and Seal?
🔵 (A) Seasonal migration
🟢 (B) Homeothermy
🟠 (C) Subcutaneous fat
🔴 (D) Convergent evolution
✅ Answer: (D) Convergent evolution
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q18. In a population of 1000, 360 = AA, 480 = Aa, 160 = aa. The frequency of allele A is
🔵 (A) 0.4
🟢 (B) 0.5
🟠 (C) 0.6
🔴 (D) 0.7
✅ Answer: (C) 0.6
Year: 2014 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q19. The forelimbs of cat, lizard (walking), whale (swimming) and bat (flying) exemplify
🔵 (A) Analogous organs
🟢 (B) Adaptive radiation
🟠 (C) Homologous organs
🔴 (D) Convergent evolution
✅ Answer: (C) Homologous organs
Year: 2014 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q20. Which are analogous structures?
🔵 (A) Gills of prawn and lungs of cow
🟢 (B) Wings of pigeon and wings of bat
🟠 (C) Flippers of dolphin and legs of rabbit
🔴 (D) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
✅ Answer: (B) Wings of pigeon and wings of bat
Year: 2014 | Exam: AIPMT/NEET
🔹 Q21. Darwin’s finches are a good example of
🔵 (A) Convergent evolution
🟢 (B) Adaptive radiation
🟠 (C) Connecting link
🔴 (D) Industrial melanism
✅ Answer: (B) Adaptive radiation
Year: 2010 | Exam: AIPMT (Prelims)
🔹 Q22. In Biston betularia, the melanic form dominated during the Industrial Revolution. This illustrates
🔵 (A) Natural selection favouring darker forms
🟢 (B) Protective mimicry
🟠 (C) Inheritance of acquired characters
🔴 (D) Effect of poor sunlight
✅ Answer: (A) Natural selection favouring darker forms
Year: 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q23. Peripatus is a connecting link between
🔵 (A) Ctenophora and Platyhelminthes
🟢 (B) Mollusca and Echinodermata
🟠 (C) Coelenterata and Porifera
🔴 (D) Annelida and Arthropoda
✅ Answer: (D) Annelida and Arthropoda
Year: 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q24. Darwin’s finches provide evidence in favour of
🔵 (A) Special Creation
🟢 (B) Biogeographical evolution
🟠 (C) Evolution due to mutation
🔴 (D) Retrogressive evolution
✅ Answer: (B) Biogeographical evolution
Year: 2007 | Exam: AIPMT (Screening)
🔹 Q25. Thorn of Bougainvillea and tendril of Cucurbita are examples of
🔵 (A) Analogous organs
🟢 (B) Homologous organs
🟠 (C) Vestigial organs
🔴 (D) Retrogressive evolution
✅ Answer: (B) Homologous organs
Year: 2008 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q26. Industrial melanism is an example of
🔵 (A) Disruptive selection
🟢 (B) Natural selection
🟠 (C) Mutation
🔴 (D) Balanced polymorphism
✅ Answer: (B) Natural selection
Year: 2007 | Exam: AIPMT (Prelims)
🔹 Q27. Which is NOT a vestigial organ in humans?
🔵 (A) Nictitating membrane
🟢 (B) Appendix
🟠 (C) Wisdom teeth
🔴 (D) Kidney
✅ Answer: (D) Kidney
Year: 2007 | Exam: AIPMT (Mains)
🔹 Q28. Which set represents homologous organs?
🔵 (A) Forelimb of man and wing of bat
🟢 (B) Flippers of penguin and dolphin
🟠 (C) Eye of octopus and eye of human
🔴 (D) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
✅ Answer: (A) Forelimb of man and wing of bat
Year: 2006 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q29. The wings of butterfly and bat show:
🔵 (A) Divergent evolution
🟢 (B) Convergent evolution
🟠 (C) Adaptive radiation
🔴 (D) Atavism
✅ Answer: (B) Convergent evolution
Year: 2006 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q30. Which of the following is an example of atavism in man?
🔵 (A) Vermiform appendix
🟢 (B) Thick body hair
🟠 (C) Presence of tail
🔴 (D) Wisdom teeth
✅ Answer: (C) Presence of tail
Year: 2005 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q31. Which evidence does NOT support evolution?
🔵 (A) Fossil record
🟢 (B) Homology of organs
🟠 (C) Vestigial organs
🔴 (D) Use and disuse of organs
✅ Answer: (D) Use and disuse of organs
Year: 2005 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q32. Fossil of Archaeopteryx is a connecting link between:
🔵 (A) Amphibia and Reptilia
🟢 (B) Pisces and Amphibia
🟠 (C) Reptilia and Aves
🔴 (D) Reptilia and Mammalia
✅ Answer: (C) Reptilia and Aves
Year: 2004 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q33. Which scientist rejected embryological evidence for evolution?
🔵 (A) Ernst Haeckel
🟢 (B) Karl Ernst von Baer
🟠 (C) Lamarck
🔴 (D) Wallace
✅ Answer: (B) Karl Ernst von Baer
Year: 2004 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q34. Which concept explains the origin of life?
🔵 (A) Big bang theory
🟢 (B) Oparin–Haldane hypothesis
🟠 (C) Cell theory
🔴 (D) Spontaneous generation
✅ Answer: (B) Oparin–Haldane hypothesis
Year: 2003 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q35. Which phenomenon maintains genetic variation in a population?
🔵 (A) Mutation
🟢 (B) Gene flow
🟠 (C) Sexual reproduction
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: 2003 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q36. Which type of evolution is represented by Darwin’s finches?
🔵 (A) Convergent evolution
🟢 (B) Adaptive radiation
🟠 (C) Divergent evolution
🔴 (D) Artificial selection
✅ Answer: (B) Adaptive radiation
Year: 2002 | Exam: AIEEE Biology Section
🔹 Q37. Which of the following is a vestigial organ in man?
🔵 (A) Coccyx
🟢 (B) Pancreas
🟠 (C) Liver
🔴 (D) Kidney
✅ Answer: (A) Coccyx
Year: 2002 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q38. Which evolutionary force reduces genetic diversity within a population?
🔵 (A) Gene flow
🟢 (B) Natural selection
🟠 (C) Genetic drift
🔴 (D) Mutations
✅ Answer: (C) Genetic drift
Year: 2001 | Exam: AIEEE Biology Section
🔹 Q39. The term “survival of the fittest” was given by:
🔵 (A) Charles Darwin
🟢 (B) Herbert Spencer
🟠 (C) Alfred Wallace
🔴 (D) Hugo de Vries
✅ Answer: (B) Herbert Spencer
Year: 2001 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q40. Darwin got an idea of organic evolution after visiting:
🔵 (A) Java Islands
🟢 (B) Galápagos Islands
🟠 (C) Madagascar
🔴 (D) Himalayas
✅ Answer: (B) Galápagos Islands
Year: 2000 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q41. Which one of the following is the oldest hominid?
🔵 (A) Australopithecus
🟢 (B) Homo erectus
🟠 (C) Homo habilis
🔴 (D) Homo sapiens
✅ Answer: (A) Australopithecus
Year: 1999 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q42. Which concept deals with genetic equilibrium?
🔵 (A) Darwinism
🟢 (B) Hardy–Weinberg law
🟠 (C) Mutation theory
🔴 (D) Natural selection
✅ Answer: (B) Hardy–Weinberg law
Year: 1999 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q43. Which is an example of adaptive radiation in mammals?
🔵 (A) Placental and marsupial mammals
🟢 (B) Man and Gorilla
🟠 (C) Whale and Shark
🔴 (D) Cow and Buffalo
✅ Answer: (A) Placental and marsupial mammals
Year: 1998 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q44. Who proposed the mutation theory of evolution?
🔵 (A) Hugo de Vries
🟢 (B) Charles Darwin
🟠 (C) Lamarck
🔴 (D) Wallace
✅ Answer: (A) Hugo de Vries
Year: 1998 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q45. Which is the connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda?
🔵 (A) Peripatus
🟢 (B) Limulus
🟠 (C) Neopilina
🔴 (D) Balanoglossus
✅ Answer: (A) Peripatus
Year: 1997 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q46. Which scientist gave the “Biogenetic Law”?
🔵 (A) Haeckel
🟢 (B) von Baer
🟠 (C) Darwin
🔴 (D) Wallace
✅ Answer: (A) Haeckel
Year: 1997 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q47. “Use and disuse” theory of organs is associated with:
🔵 (A) Lamarck
🟢 (B) Darwin
🟠 (C) Wallace
🔴 (D) Hugo de Vries
✅ Answer: (A) Lamarck
Year: 1996 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q48. Which is considered the “living fossil”?
🔵 (A) Peripatus
🟢 (B) Limulus
🟠 (C) Archaeopteryx
🔴 (D) Neopilina
✅ Answer: (B) Limulus
Year: 1996 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q49. Who conducted experiments to disprove spontaneous generation?
🔵 (A) Louis Pasteur
🟢 (B) Darwin
🟠 (C) Lamarck
🔴 (D) Wallace
✅ Answer: (A) Louis Pasteur
Year: 1995 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q50. Which is the “connecting link” between reptiles and birds?
🔵 (A) Archaeopteryx
🟢 (B) Peripatus
🟠 (C) Neopilina
🔴 (D) Limulus
✅ Answer: (A) Archaeopteryx
Year: 1994 | Exam: PMT
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20: NEET-Level (Moderate Difficulty)
🔹 Q1. 🌍 Which gases were used by Miller–Urey to simulate primitive Earth?
🔵 (A) CO₂, O₂, N₂
🟢 (B) CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapour
🟠 (C) CO₂, H₂, O₂
🔴 (D) CO, CH₄, NH₄
✔️ Answer: (B) CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapour
🔹 Q2. 🦠 The earliest organisms on Earth were:
🔵 (A) Autotrophic eukaryotes
🟢 (B) Heterotrophic prokaryotes
🟠 (C) Autotrophic prokaryotes
🔴 (D) Multicellular organisms
✔️ Answer: (B) Heterotrophic prokaryotes
🔹 Q3. 🧬 Which one is a vestigial organ in humans?
🔵 (A) Appendix
🟢 (B) Liver
🟠 (C) Kidney
🔴 (D) Pancreas
✔️ Answer: (A) Appendix
🔹 Q4. 🦖 Archaeopteryx provides evolutionary link between:
🔵 (A) Amphibians and reptiles
🟢 (B) Reptiles and birds
🟠 (C) Mammals and reptiles
🔴 (D) Fish and amphibians
✔️ Answer: (B) Reptiles and birds
🔹 Q5. 🌱 Which is an example of adaptive radiation?
🔵 (A) Human races
🟢 (B) Darwin’s finches
🟠 (C) Whale and Shark resemblance
🔴 (D) Wisdom teeth in humans
✔️ Answer: (B) Darwin’s finches
🔹 Q6. 🧪 Which scientist disproved spontaneous generation by swan-neck flask experiment?
🔵 (A) Oparin
🟢 (B) Louis Pasteur
🟠 (C) Darwin
🔴 (D) Lamarck
✔️ Answer: (B) Louis Pasteur
🔹 Q7. 🦋 Industrial melanism in peppered moths is an example of:
🔵 (A) Mutation
🟢 (B) Natural selection
🟠 (C) Artificial selection
🔴 (D) Genetic drift
✔️ Answer: (B) Natural selection
🔹 Q8. 🧮 According to Hardy–Weinberg principle, deviation from equilibrium indicates:
🔵 (A) Random mating
🟢 (B) Evolution
🟠 (C) Equilibrium
🔴 (D) Mutation absent
✔️ Answer: (B) Evolution
🔹 Q9. 🐒 Arrange in sequence: Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens.
🔵 (A) Correct evolutionary order
🟢 (B) Reverse order
🟠 (C) Mixed order
🔴 (D) Not related
✔️ Answer: (A) Correct evolutionary order
🔹 Q10. 🦠 The phenomenon where small isolated populations develop distinct allelic frequencies is:
🔵 (A) Natural selection
🟢 (B) Genetic drift
🟠 (C) Mutation
🔴 (D) Gene flow
✔️ Answer: (B) Genetic drift
🔹 Q11. 🐦 Convergent evolution is exhibited by:
🔵 (A) Flippers of penguin and dolphin
🟢 (B) Forelimb of whale and human
🟠 (C) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
🔴 (D) Darwin’s finches
✔️ Answer: (A) Flippers of penguin and dolphin
🔹 Q12. 🧬 Mutations that bring sudden large variations were proposed to be the cause of evolution by:
🔵 (A) Darwin
🟢 (B) Hugo de Vries
🟠 (C) Lamarck
🔴 (D) Wallace
✔️ Answer: (B) Hugo de Vries
🔹 Q13. 🧪 Which is a molecular evidence of evolution?
🔵 (A) Fossils
🟢 (B) DNA sequence similarity
🟠 (C) Homologous organs
🔴 (D) Vestigial organs
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA sequence similarity
🔹 Q14. 🌍 The adaptive significance of Darwin’s finches lies in:
🔵 (A) Size of feathers
🟢 (B) Shape of beak
🟠 (C) Colour of body
🔴 (D) Nesting habit
✔️ Answer: (B) Shape of beak
🔹 Q15. 🦖 Which one is NOT a direct evidence of evolution?
🔵 (A) Fossils
🟢 (B) Vestigial organs
🟠 (C) Molecular homology
🔴 (D) Direct observation of speciation
✔️ Answer: (D) Direct observation of speciation
🔹 Q16. 🐕 “Artificial selection” was used by Darwin to explain:
🔵 (A) Origin of humans
🟢 (B) Domestication of dogs and pigeons
🟠 (C) Vestigial organs
🔴 (D) Fossil evidence
✔️ Answer: (B) Domestication of dogs and pigeons
🔹 Q17. 🧬 Which one of the following is NOT a force disrupting Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium?
🔵 (A) Large population size
🟢 (B) Gene flow
🟠 (C) Mutation
🔴 (D) Natural selection
✔️ Answer: (A) Large population size
🔹 Q18. 🐘 Which one is a connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda?
🔵 (A) Archaeopteryx
🟢 (B) Peripatus
🟠 (C) Limulus
🔴 (D) Neopilina
✔️ Answer: (B) Peripatus
🔹 Q19. 🦠 Evolutionary convergence is shown by:
🔵 (A) Sweet potato and potato
🟢 (B) Eyes of octopus and mammals
🟠 (C) Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita
🔴 (D) Whale and shark
✔️ Answer: (B) Eyes of octopus and mammals
🔹 Q20. 🧠 In human evolution, increase in cranial capacity is seen from:
🔵 (A) Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
🟢 (B) Homo erectus → Australopithecus → Homo sapiens
🟠 (C) Homo habilis → Australopithecus → Homo sapiens
🔴 (D) Homo sapiens → Homo erectus → Australopithecus
✔️ Answer: (A) Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens
🔹 Q21. 🧬 Which statement about Hardy–Weinberg principle is correct?
🔵 (A) It explains evolution in all conditions
🟢 (B) It applies when evolutionary forces are absent
🟠 (C) It is invalid for diploid populations
🔴 (D) It applies only in small populations
✔️ Answer: (B) It applies when evolutionary forces are absent
🔹 Q22. 🦠 Which condition disrupts genetic equilibrium?
🔵 (A) Random mating
🟢 (B) Large population size
🟠 (C) Migration of individuals
🔴 (D) Absence of mutation
✔️ Answer: (C) Migration of individuals
🔹 Q23. 🦖 The fossil Archaeopteryx is important because it shows:
🔵 (A) Transitional form between reptiles and birds
🟢 (B) Direct ancestor of mammals
🟠 (C) Evolution of amphibians
🔴 (D) A purely reptilian species
✔️ Answer: (A) Transitional form between reptiles and birds
🔹 Q24. 🦋 Which type of natural selection favours extreme phenotypes?
🔵 (A) Stabilising
🟢 (B) Disruptive
🟠 (C) Directional
🔴 (D) Artificial
✔️ Answer: (B) Disruptive
🔹 Q25. 🌍 Which one is a connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda?
🔵 (A) Limulus
🟢 (B) Peripatus
🟠 (C) Neopilina
🔴 (D) Balanoglossus
✔️ Answer: (B) Peripatus
🔹 Q26. 🧪 In Miller–Urey experiment, which compound was NOT added?
🔵 (A) Methane
🟢 (B) Ammonia
🟠 (C) Oxygen
🔴 (D) Hydrogen
✔️ Answer: (C) Oxygen
🔹 Q27. 🧬 Which is a molecular evidence of evolution?
🔵 (A) Homologous structures
🟢 (B) Analogous structures
🟠 (C) Cytochrome c similarity
🔴 (D) Fossils
✔️ Answer: (C) Cytochrome c similarity
🔹 Q28. 🐦 Darwin’s finches represent:
🔵 (A) Convergent evolution
🟢 (B) Adaptive radiation
🟠 (C) Genetic drift
🔴 (D) Mutation theory
✔️ Answer: (B) Adaptive radiation
🔹 Q29. 🐳 Which is an example of convergent evolution?
🔵 (A) Whale and shark
🟢 (B) Whale and bat
🟠 (C) Bat and human
🔴 (D) Darwin’s finches
✔️ Answer: (A) Whale and shark
🔹 Q30. 🐒 Arrange in order: Australopithecus → Homo habilis → Homo erectus → Homo sapiens.
🔵 (A) Correct evolutionary order
🟢 (B) Reverse order
🟠 (C) Mixed order
🔴 (D) Random
✔️ Answer: (A) Correct evolutionary order
🔹 Q31. 🦋 Which type of evolution gives rise to analogous organs?
🔵 (A) Convergent
🟢 (B) Divergent
🟠 (C) Adaptive radiation
🔴 (D) Mutation
✔️ Answer: (A) Convergent
🔹 Q32. 🦖 Fossils of horse evolution show:
🔵 (A) Adaptive radiation
🟢 (B) Gradual evolution
🟠 (C) Convergent evolution
🔴 (D) Atavism
✔️ Answer: (B) Gradual evolution
🔹 Q33. 🧠 Which hominid first used fire?
🔵 (A) Homo habilis
🟢 (B) Homo erectus
🟠 (C) Homo sapiens
🔴 (D) Australopithecus
✔️ Answer: (B) Homo erectus
🔹 Q34. 🧬 Which factor is NOT a cause of evolution?
🔵 (A) Mutation
🟢 (B) Recombination
🟠 (C) Natural selection
🔴 (D) Stability of allelic frequency
✔️ Answer: (D) Stability of allelic frequency
🔹 Q35. 🦠 Who proposed mutation theory of evolution?
🔵 (A) Darwin
🟢 (B) Lamarck
🟠 (C) Hugo de Vries
🔴 (D) Wallace
✔️ Answer: (C) Hugo de Vries
🔹 Q36. 🌱 Thorns of Bougainvillea and tendrils of Cucurbita are:
🔵 (A) Analogous organs
🟢 (B) Homologous organs
🟠 (C) Vestigial organs
🔴 (D) Atavistic traits
✔️ Answer: (B) Homologous organs
🔹 Q37. 🧮 In Hardy–Weinberg, if p = 0.8, q = ?
🔵 (A) 0.1
🟢 (B) 0.2
🟠 (C) 0.8
🔴 (D) 0.5
✔️ Answer: (B) 0.2
🔹 Q38. 🧬 Genetic drift is also called:
🔵 (A) Founder effect
🟢 (B) Artificial selection
🟠 (C) Mutation
🔴 (D) Gene flow
✔️ Answer: (A) Founder effect
🔹 Q39. 🦖 Which is a living fossil?
🔵 (A) Archaeopteryx
🟢 (B) Limulus
🟠 (C) Peripatus
🔴 (D) Homo erectus
✔️ Answer: (B) Limulus
🔹 Q40. 🐦 Which type of selection reduces variation and favours average phenotype?
🔵 (A) Stabilising
🟢 (B) Directional
🟠 (C) Disruptive
🔴 (D) Artificial
✔️ Answer: (A) Stabilising
🔹 Q41. 🧪 The term “use and disuse” was given by:
🔵 (A) Lamarck
🟢 (B) Darwin
🟠 (C) Hugo de Vries
🔴 (D) Wallace
✔️ Answer: (A) Lamarck
🔹 Q42. 🐕 Artificial selection is responsible for:
🔵 (A) Industrial melanism
🟢 (B) Varieties of domestic dogs
🟠 (C) Resistance to antibiotics
🔴 (D) Natural speciation
✔️ Answer: (B) Varieties of domestic dogs
🔹 Q43. 🧬 Which type of evidence is provided by comparative embryology?
🔵 (A) Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny
🟢 (B) Homologous structures
🟠 (C) Convergent evolution
🔴 (D) Fossil dating
✔️ Answer: (A) Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny
🔹 Q44. 🌱 Which of the following is a vestigial organ in humans?
🔵 (A) Wisdom teeth
🟢 (B) Kidney
🟠 (C) Heart
🔴 (D) Liver
✔️ Answer: (A) Wisdom teeth
🔹 Q45. 🦕 Fossils are most commonly found in:
🔵 (A) Igneous rocks
🟢 (B) Sedimentary rocks
🟠 (C) Metamorphic rocks
🔴 (D) Granite
✔️ Answer: (B) Sedimentary rocks
🔹 Q46. 🐦 Which feature is unique to humans compared to other primates?
🔵 (A) Bipedal locomotion
🟢 (B) Binocular vision
🟠 (C) Opposable thumb
🔴 (D) Mammary glands
✔️ Answer: (A) Bipedal locomotion
🔹 Q47. 🧬 Which is an example of atavism?
🔵 (A) Presence of tail in some human babies
🟢 (B) Appendix in humans
🟠 (C) Coccyx in humans
🔴 (D) Body hair in humans
✔️ Answer: (A) Presence of tail in some human babies
🔹 Q48. 🦠 Which was the first hominid to bury its dead?
🔵 (A) Homo erectus
🟢 (B) Homo sapiens
🟠 (C) Homo neanderthalensis
🔴 (D) Australopithecus
✔️ Answer: (C) Homo neanderthalensis
🔹 Q49. 🧬 Which concept suggests that allele frequency may change by chance in small populations?
🔵 (A) Genetic drift
🟢 (B) Mutation theory
🟠 (C) Adaptive radiation
🔴 (D) Natural selection
✔️ Answer: (A) Genetic drift
🔹 Q50. 🦕 The correct sequence in horse evolution is:
🔵 (A) Eohippus → Mesohippus → Merychippus → Pliohippus → Equus
🟢 (B) Mesohippus → Eohippus → Pliohippus → Equus → Merychippus
🟠 (C) Equus → Merychippus → Mesohippus → Eohippus → Pliohippus
🔴 (D) Eohippus → Pliohippus → Mesohippus → Equus → Merychippus
✔️ Answer: (A) Eohippus → Mesohippus → Merychippus → Pliohippus → Equus
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
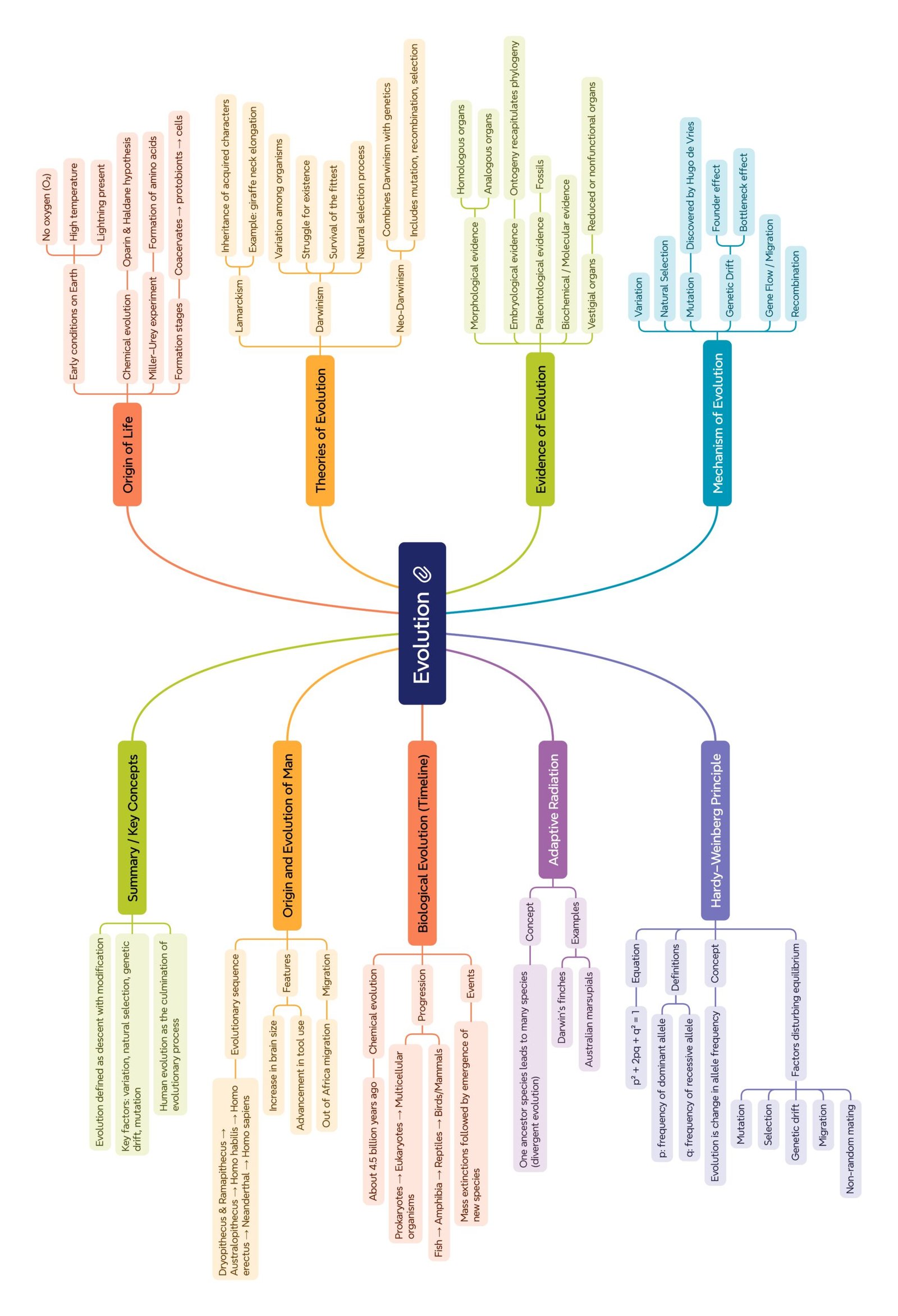
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
