Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 13: Biodiversity and Conservation
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
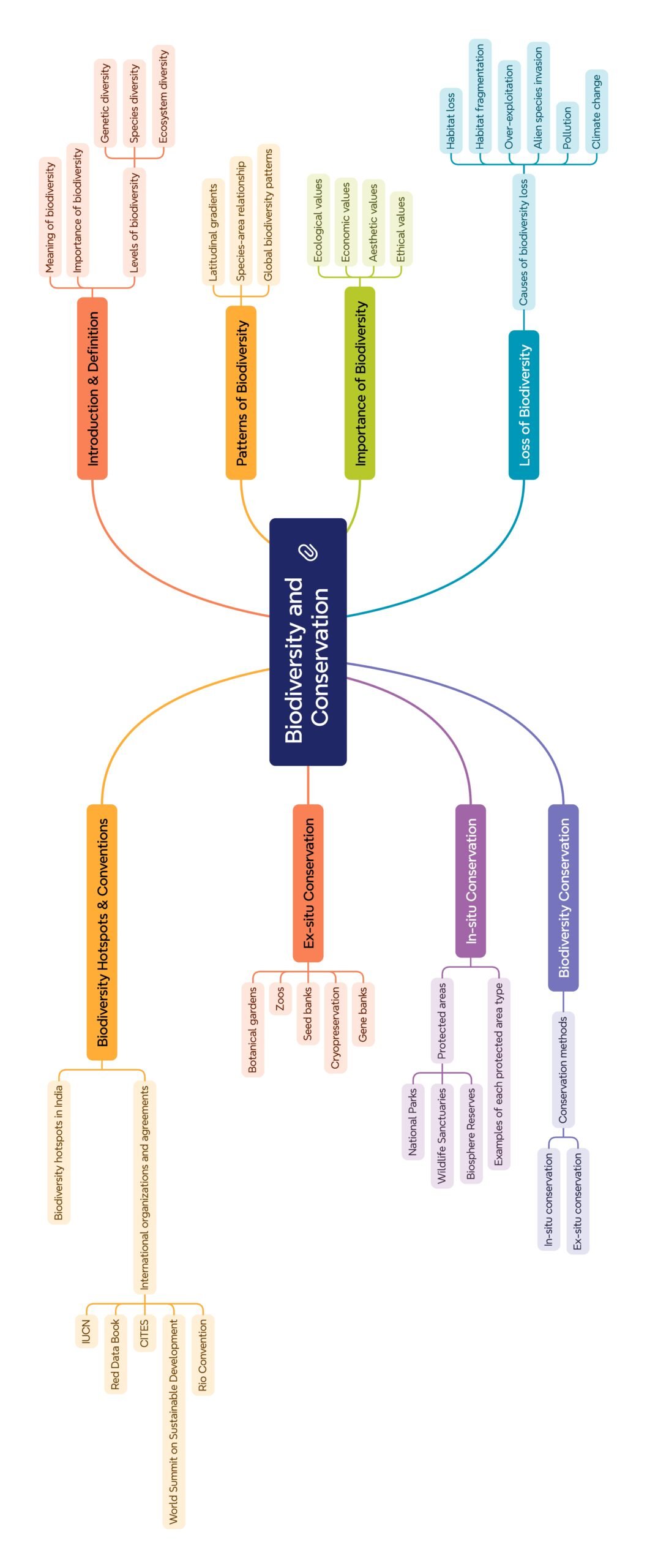
🌿 Introduction to Biodiversity
🔵 Definition:
Biodiversity = variety of life at all levels of biological organisation 🌱🦋🦜🐟.
🟢 Levels of Biodiversity:
✨ Genetic diversity — variation of genes within species (e.g., rice varieties 🍚, mango varieties 🥭).
🌳 Species diversity — variety of species in an area (e.g., Western Ghats 🐸🌴 > Gangetic plains).
🌏 Ecological/Ecosystem diversity — variety of habitats, ecosystems, landscapes (forests 🌲, deserts 🏜️, wetlands 🐊).
🟠 Global Biodiversity:
Identified species ≈ 1.7–1.8 million 🌍.
India = megadiverse country (2.4% land area but 8.1% species 🌸🦚🐅).
🌍 Patterns of Biodiversity
🔹 Latitudinal gradients:
🌴 Species richness higher in tropics (Amazon rainforest = “lungs of the planet”).
🌡️ Stable climate + productivity → greater diversity.
🔹 Species–area relationship (SAR):
📈 Alexander von Humboldt → larger area = more species.
Formula: S = C·A^Z
S = species richness
A = area
Z = slope (0.1–0.2 generally, 0.6–1.2 for islands 🏝️).
⚠️ Threats to Biodiversity
🔴 HIPPO mnemonic (E.O. Wilson):
H — Habitat loss & fragmentation (deforestation 🌳✂️, Amazon rainforest burning 🔥).
I — Invasive species (Lantana, Parthenium 🌿, African catfish 🐟).
P — Population explosion 👥 (resource overuse).
P — Pollution ☠️ (industrial effluents, biomagnification 🐟→🦅).
O — Overexploitation 🐅🐚 (hunting, poaching).
➡️ Global concern: 🌡️ Climate change, ozone depletion, acid rain.
💡 Importance of Biodiversity
🟡 Ecosystem services (R. Costanza study, 1997):
🌬️ Gas regulation (O₂–CO₂ balance).
💧 Water purification, soil formation, pollination 🐝.
🌾 Provision of food, fibres, medicines 💊.
💰 Estimated value = US $33 trillion/year.
🟢 Direct benefits:
Food crops 🍚, medicinal plants 🌿, fibre crops, fuelwood, rubber.
Drugs: morphine (Papaver), quinine (Cinchona), taxol (Taxus).
🛡️ Conservation of Biodiversity
In situ (on-site):
🌳 Protected areas:
Biosphere reserves (Nilgiri, Nanda Devi).
National parks (Kaziranga 🦏, Gir 🦁).
Wildlife sanctuaries (Keoladeo 🐦).
🌱 Sacred groves (Meghalaya, Western Ghats).
Ex situ (off-site):
🧬 Seed banks 🌾, cryopreservation ❄️, tissue culture.
🦓 Zoological parks, botanical gardens 🌼.
📊 India’s Biodiversity Profile
34 global biodiversity hotspots → India has 4 (Himalaya, Indo-Burma, Indo-Malayan, Western Ghats).
104 national parks, 566 wildlife sanctuaries 🦌, 18 biosphere reserves.
Endangered species: Lion-tailed macaque 🐒, Sangai deer 🦌, Great Indian bustard 🦅.
📝 Summary (≈300 words)
Biodiversity is the variety of life forms on Earth, expressed at three levels: genetic, species, and ecological diversity. It sustains life and maintains ecosystem balance. Global biodiversity counts about 1.7 million described species, with India ranked among the 17 megadiverse nations, harbouring 8.1% of global species.
Patterns of biodiversity include latitudinal gradients—tropical forests like Amazon having the highest richness—and species–area relationships, where larger areas support more species (S = C·A^Z).
Biodiversity faces serious threats due to HIPPO factors: habitat loss, invasive species, population growth, pollution, and overexploitation. Examples include deforestation, alien weeds like Parthenium, and poaching of tigers and elephants. Climate change and pollution worsen the crisis.
Biodiversity is vital for ecosystem services such as oxygen production, water purification, pollination, and nutrient cycling. R. Costanza’s 1997 study estimated its economic worth at US $33 trillion/year. Humans derive direct benefits as well: food, fibre, fuel, and medicines (e.g., quinine, morphine, taxol).
To conserve biodiversity, two strategies are adopted: in situ conservation (protecting species in natural habitats, e.g., biosphere reserves, national parks, sanctuaries, sacred groves) and ex situ conservation (protecting outside natural habitats, e.g., zoological parks, seed banks, cryopreservation). India has 4 biodiversity hotspots and extensive protected area networks.
Conservation of biodiversity is crucial to ensure sustainability of ecosystems, secure natural resources, and preserve heritage for future generations.
🎯 Quick Recap
🟢 Levels: Genetic, Species, Ecological.
🔵 Patterns: Latitudinal gradient, SAR (S = C·A^Z).
🔴 Threats: HIPPO (Habitat loss, Invasives, Population, Pollution, Overexploitation).
🟠 Values: Food, medicines, ecosystem services.
🟡 Conservation: In situ (parks, reserves, sacred groves) & Ex situ (zoos, seed banks).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
❓ Q1. Name the three important components of biodiversity.
✅ Answer:
🌱 Genetic diversity — variation of genes within species (e.g., rice varieties 🍚).
🦋 Species diversity — variety of species in a region (e.g., birds 🐦, mammals 🐘).
🌳 Ecosystem diversity — variety of ecosystems (forests 🌲, wetlands 🐊, deserts 🏜️).
❓ Q2. How do ecologists estimate the total number of species present in the world?
✅ Answer:
🔬 Ecologists use statistical models & extrapolations:
Known species described scientifically (~1.7 million).
Ratios between studied and unexplored groups (e.g., insects 🐞).
Sampling in small regions → extrapolated to global scale.
🌍 Thus, estimates suggest 8.1 million eukaryotic species globally.
❓ Q3. Give three hypotheses for explaining why tropics show greatest levels of species richness.
✅ Answer:
1️⃣ Stable climate — less seasonal variation → long periods for speciation 🌴.
2️⃣ High productivity due to more sunlight & rainfall 🌞🌧️.
3️⃣ Larger geographical area of tropics → promotes diversity.
❓ Q4. What is the significance of the slope of regression in a species–area relationship?
✅ Answer:
📈 The slope Z indicates rate of species richness with area.
Normal areas: Z = 0.1–0.2.
Islands & isolated habitats 🏝️: Z = 0.6–1.2 (steeper slope due to isolation).
❓ Q5. What are the major causes of species losses in a geographical region?
✅ Answer (HIPPO):
H — Habitat loss & fragmentation 🌳✂️.
I — Invasive species (Parthenium, Lantana 🌿).
P — Population pressure 👥.
P — Pollution ☠️.
O — Overexploitation (poaching 🦏, hunting 🐅).
❓ Q6. How is biodiversity important for ecosystem functioning?
✅ Answer:
Ensures stability & resilience of ecosystems.
Provides ecosystem services (pollination 🐝, nutrient cycling ♻️, soil fertility 🌱).
Experiments show plots with higher biodiversity have greater productivity & sustainability.
❓ Q7. What are sacred groves? What is their role in conservation?
✅ Answer:
🌿 Sacred groves = patches of forests protected due to cultural/religious beliefs (e.g., Meghalaya, Western Ghats).
🌳 Role:
Preserve rare & endemic species.
Act as biodiversity reservoirs.
Provide habitat for endangered flora & fauna.
❓ Q8. Among ecosystem services are control of floods and soil erosion. How is this achieved by the biotic components of the ecosystem?
✅ Answer:
🌱 Forests & vegetation cover:
Roots bind soil → prevent erosion.
Plants slow water flow → reduce floods.
Forests regulate water cycle 💧 → maintain groundwater.
❓ Q9. The species diversity of plants (22%) is less than animals (72%). What could be the explanations to how animals achieved greater diversification?
✅ Answer:
Animals show greater mobility → adapt to diverse habitats 🐒🐦.
Faster speciation & adaptation due to mobility and varied diets 🍃🍖.
Occupy wider ecological niches compared to plants.
❓ Q10. Can you think of a situation where we deliberately want to make a species extinct? How would you justify it?
✅ Answer:
⚠️ Yes — species harmful to humans/environment:
Example: Smallpox virus 🦠 — eradicated by vaccination.
Justification: Prevents disease spread, protects health, ensures survival of humans and livestock.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🟢 Section A — MCQs (Q1–Q12)
🔸 Q1. 🌱 Which of the following is not a standard level of biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Genetic diversity
🟢 (B) Species diversity
🟠 (C) Ecosystem diversity
🔴 (D) Biochemical diversity
✅ Answer: (D) Biochemical diversity
🔸 Q2. 📈 In the species–area relationship S = C·A^Z, the slope Z for most continental habitats typically lies between
🔵 (A) 0.1–0.2
🟢 (B) 0.6–1.2
🟠 (C) 1.5–2.0
🔴 (D) 2.0–3.0
✅ Answer: (A) 0.1–0.2
🔸 Q3. 🏝️ Island communities commonly have a steeper species–area curve because
🔵 (A) Lower immigration and higher extinction
🟢 (B) Higher productivity always
🟠 (C) Absence of predators
🔴 (D) Only endemic plants occur
✅ Answer: (A) Lower immigration and higher extinction
🔸 Q4. 🌴 The tropics harbour higher species richness mainly due to
🔵 (A) High climatic stability over long periods
🟢 (B) Frequent glaciations
🟠 (C) Uniform day length at poles
🔴 (D) Lower productivity
✅ Answer: (A) High climatic stability over long periods
🔸 Q5. 🌿 Which is the correct in situ conservation measure?
🔵 (A) Seed bank
🟢 (B) Botanical garden
🟠 (C) National park
🔴 (D) Cryopreservation
✅ Answer: (C) National park
🔸 Q6. ❄️ Cryopreservation is best described as
🔵 (A) Storage of seeds at room temperature
🟢 (B) Storage at very low temperature in liquid nitrogen
🟠 (C) Drying of seeds by desiccation
🔴 (D) In vitro micropropagation at 25°C
✅ Answer: (B) Storage at very low temperature in liquid nitrogen
🔸 Q7. 🌾 Sacred groves primarily help in conserving
🔵 (A) Soil microbes only
🟢 (B) Rare and endemic plant species
🟠 (C) Only large mammals
🔴 (D) Marine algae
✅ Answer: (B) Rare and endemic plant species
🔸 Q8. 🚫 Which pair shows alien invasive species in India?
🔵 (A) Lantana camara and Parthenium
🟢 (B) Azadirachta and Mangifera
🟠 (C) Shorea and Dalbergia
🔴 (D) Ficus and Ficus religiosa
✅ Answer: (A) Lantana camara and Parthenium
🔸 Q9. 📕 The IUCN Red List provides
🔵 (A) Techniques of herbarium preparation
🟢 (B) Status of threatened species
🟠 (C) Keys for plant identification only
🔴 (D) Zoogeographical maps only
✅ Answer: (B) Status of threatened species
🔸 Q10. 🦊 Keystone species are those that
🔵 (A) Are always the most abundant
🟢 (B) Exert disproportionate influence on community stability
🟠 (C) Occupy the largest habitat area
🔴 (D) Are always producers
✅ Answer: (B) Exert disproportionate influence on community stability
🔸 Q11. ♻️ An ecosystem service that directly supports agriculture is
🔵 (A) Ozone formation
🟢 (B) Pollination
🟠 (C) Seafloor spreading
🔴 (D) Plate tectonics
✅ Answer: (B) Pollination
🔸 Q12. 🐟 Biomagnification is the
🔵 (A) Increase of nutrient concentration along food chain
🟢 (B) Decrease of pollutant concentration at higher trophic levels
🟠 (C) Increase of pollutant concentration at higher trophic levels
🔴 (D) Dilution of toxins in producers
✅ Answer: (C) Increase of pollutant concentration at higher trophic levels
🟠 Section B — Very Short Answer (Q13–Q15)
🔸 Q13. ✍️ Define biodiversity and list its three components with one example each.
✅ Answer: Biodiversity = variety of life at genetic, species, and ecosystem levels.
Genetic: rice varieties
Species: birds of Western Ghats
Ecosystem: forests, deserts, wetlands
🔸 Q14. 🧭 Give three causes for biodiversity loss (HIPPO).
✅ Answer: Habitat loss, Invasive species, Population pressure, Pollution, Overexploitation.
🔸 Q15. 🧪 Differentiate: In situ vs Ex situ conservation with one example each.
✅ Answer:
In situ: conservation in natural habitats (e.g., Kaziranga National Park).
Ex situ: conservation outside natural habitats (e.g., seed banks, zoos).
🔴 Section C — Short Answer (Q16–Q17)
🔸 Q16. 🔬 What does species richness measure? How is it different from evenness?
✅ Answer: Richness = number of species present.
Evenness = distribution of individuals across species.
🔸 Q17. Numerical — Species–Area relationship
A reserve of area A1 = 100 km² has S1 = 200 species. If Z = 0.2, predict species in a proposed reserve A2 = 400 km² (assume same C).
✅ Answer (step by step):
Step 1: Formula → S2 / S1 = (A2 / A1)^Z
Step 2: Substitute → S2 / 200 = (400 / 100)^0.2
Step 3: (400 / 100) = 4 → 4^0.2
Step 4: 4^0.2 = e^(0.2 × ln4) ≈ e^0.2773 ≈ 1.319
Step 5: S2 = 200 × 1.319 = 263.8
Final Answer: ≈ 264 species
🟢 Section D — Short Answer (Q18–Q24)
🔸 Q18. 🌍 Explain the role of biodiversity in providing ecosystem services.
✅ Answer:
Provisioning: food, fuel, fibre, medicine 🌾💊
Regulating: climate control, flood control 🌧️
Supporting: nutrient cycling, soil formation ♻️
Cultural: aesthetic, spiritual, recreation 🎨
🔸 Q19. 🧬 Define endemic species with an example.
✅ Answer: Species confined to a specific geographical area.
Example: Nicobar megapode bird 🐦 in Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
🔸 Q20. 🦏 Give two examples of Indian animals included in the Red Data Book.
✅ Answer: Indian rhinoceros, Lion-tailed macaque.
🔸 Q21. 🌳 How are biosphere reserves different from wildlife sanctuaries?
✅ Answer:
Biosphere reserve: large area, multiple levels of protection (core, buffer, transition).
Wildlife sanctuary: smaller area, only faunal protection.
🔸 Q22. 🚨 State two consequences of habitat loss and fragmentation.
✅ Answer:
Decline in population sizes.
Local extinction of species.
🔸 Q23. 🌲 Define hotspots of biodiversity and name two in India.
✅ Answer:
Hotspots = regions rich in endemic species but under threat.
India: Himalaya and Indo-Burma regions.
🔸 Q24. 🔬 Write a note on IUCN categories of threat.
✅ Answer:
Extinct (EX)
Critically Endangered (CR)
Endangered (EN)
Vulnerable (VU)
Near Threatened (NT)
Least Concern (LC)
🟠 Section E — Long Answer (Q25–Q29)
🔸 Q25. 📈 Explain the species–area relationship and its ecological importance.
✅ Answer:
Described by Alexander von Humboldt.
Larger areas harbour more species.
Expressed as S = C·A^Z (S = species, A = area, Z = slope, C = constant).
Important in reserve design and island biogeography.
🔸 Q26. 🧭 Discuss the HIPPO causes of biodiversity loss with suitable examples.
✅ Answer:
Habitat loss (deforestation 🌳).
Invasive alien species (Parthenium 🌿).
Population explosion 👥.
Pollution (DDT biomagnification 🐟).
Overexploitation (overfishing 🐠, poaching 🦏).
🔸 Q27. 🏞️ Explain in situ conservation strategies in India.
✅ Answer:
National Parks (e.g., Gir NP).
Wildlife Sanctuaries (e.g., Bharatpur).
Biosphere Reserves (e.g., Nilgiri).
Sacred groves (Meghalaya).
🔸 Q28. 🧪 Describe ex situ conservation with examples.
✅ Answer:
Seed banks, cryopreservation ❄️
Tissue culture labs
Zoological parks 🦁
Botanical gardens 🌱
🔸 Q29. 🌐 Explain the role of conventions and acts in biodiversity conservation.
✅ Answer:
CBD (Convention on Biological Diversity, 1992).
CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species).
Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India).
🔴 Section F — Case Study + Application (Q30–Q33)
🔸 Q30. MCQ Case Study 🦋
A lake ecosystem is polluted with pesticide residues. Zooplankton → Small fish → Large fish → Birds.
Which trophic level will have maximum pesticide concentration?
🔵 (A) Zooplankton
🟢 (B) Small fish
🟠 (C) Large fish
🔴 (D) Birds
✅ Answer: (D) Birds
🔸 Q31. MCQ Case Study 🌳
In an island of 500 km², researchers find 800 species. Using species–area curve with Z = 0.2, predict species richness if area increases to 2000 km².
🔵 (A) 1200
🟢 (B) 1320
🟠 (C) 1600
🔴 (D) 2000
✅ Answer: (B) 1320
🔸 Q32. 🧭 Justify why tropical rainforests are called “cradles of biodiversity.”
✅ Answer:
High productivity due to year-round warmth and moisture.
Stable climate over millions of years.
Greater opportunities for speciation.
🔸 Q33. 🦏 Write an essay on the importance of biodiversity conservation for sustainable development.
✅ Answer:
Provides food, medicine, fuel, fibre.
Maintains ecological balance.
Supports ecosystem services.
Ensures long-term sustainability of human society.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. The most important reason for the loss of biodiversity is
🔵 (A) Habitat loss
🟢 (B) Overexploitation
🟠 (C) Deforestation
🔴 (D) Alien species invasion
✅ Answer: (A) Habitat loss
Year: NEET 2024
🔹 Q2. Which of the following is not a cause of biodiversity loss?
🔵 (A) Habitat loss
🟢 (B) Overexploitation
🟠 (C) Sustainable harvesting
🔴 (D) Alien species invasion
✅ Answer: (C) Sustainable harvesting
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q3. Alexander von Humboldt described species–area relationship as
🔵 (A) Rectangular hyperbola
🟢 (B) Exponential
🟠 (C) Logarithmic
🔴 (D) Linear
✅ Answer: (D) Linear
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q4. The species–area relationship curve becomes a straight line on
🔵 (A) Arithmetic scale
🟢 (B) Semi-log scale
🟠 (C) Log–log scale
🔴 (D) Linear scale
✅ Answer: (C) Log–log scale
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q5. The most species-rich taxonomic group of organisms is
🔵 (A) Mammals
🟢 (B) Insects
🟠 (C) Birds
🔴 (D) Angiosperms
✅ Answer: (B) Insects
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q6. India is one of the megadiversity countries because it has
🔵 (A) >8% of global species
🟢 (B) 2% of world’s land area
🟠 (C) Large forest area
🔴 (D) Himalayan ranges
✅ Answer: (A) >8% of global species
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q7. Which region of India is not a biodiversity hotspot?
🔵 (A) Himalaya
🟢 (B) Indo-Burma
🟠 (C) Indo-Gangetic plain
🔴 (D) Indo-Malayan
✅ Answer: (C) Indo-Gangetic plain
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q8. Latitudinal gradient of biodiversity means
🔵 (A) More species towards poles
🟢 (B) More species towards tropics
🟠 (C) Equal species distribution
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (B) More species towards tropics
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q9. Hotspots are identified on the basis of
🔵 (A) Endemism and threat perception
🟢 (B) Productivity
🟠 (C) Density
🔴 (D) Latitude
✅ Answer: (A) Endemism and threat perception
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q10. According to Paul Ehrlich, the rivet popper hypothesis is related to
🔵 (A) Stability of ecosystem
🟢 (B) Evolution of species
🟠 (C) Extinction of dinosaurs
🔴 (D) Origin of biodiversity
✅ Answer: (A) Stability of ecosystem
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q11. Which conservation strategy maintains species in their natural habitats?
🔵 (A) Ex situ
🟢 (B) In situ
🟠 (C) Cryopreservation
🔴 (D) Tissue culture
✅ Answer: (B) In situ
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q12. Sacred groves help in
🔵 (A) Industrial growth
🟢 (B) Protection of biodiversity
🟠 (C) Agriculture
🔴 (D) Food storage
✅ Answer: (B) Protection of biodiversity
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q13. Which one is ex situ conservation method?
🔵 (A) Sacred groves
🟢 (B) National parks
🟠 (C) Seed banks
🔴 (D) Biosphere reserves
✅ Answer: (C) Seed banks
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q14. Biodiversity provides ecosystem services valued at about
🔵 (A) US $33 trillion per year
🟢 (B) US $3 trillion per year
🟠 (C) US $30 billion per year
🔴 (D) US $330 trillion per year
✅ Answer: (A) US $33 trillion per year
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q15. The major cause of extinction of species is
🔵 (A) Habitat loss
🟢 (B) Overhunting
🟠 (C) Pollution
🔴 (D) Population pressure
✅ Answer: (A) Habitat loss
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q16. Which one is an alien invasive weed in India?
🔵 (A) Rauwolfia
🟢 (B) Parthenium
🟠 (C) Cycas
🔴 (D) Mango
✅ Answer: (B) Parthenium
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q17. Which conservation approach protects entire ecosystems?
🔵 (A) Species-centric
🟢 (B) In situ
🟠 (C) Ex situ
🔴 (D) Captive breeding
✅ Answer: (B) In situ
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q18. Which Indian state has the maximum number of sacred groves?
🔵 (A) Rajasthan
🟢 (B) Meghalaya
🟠 (C) Kerala
🔴 (D) Odisha
✅ Answer: (B) Meghalaya
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q19. Alien species invasion has caused extinction of
🔵 (A) Cichlid fish in Lake Victoria
🟢 (B) Dinosaurs
🟠 (C) Passenger pigeon
🔴 (D) Dodo
✅ Answer: (A) Cichlid fish in Lake Victoria
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q20. Which is not an in situ method?
🔵 (A) Biosphere reserves
🟢 (B) Zoological park
🟠 (C) National park
🔴 (D) Wildlife sanctuary
✅ Answer: (B) Zoological park
Year: NEET 2014
🔹 Q21. The term biodiversity hotspot was coined by
🔵 (A) Norman Myers
🟢 (B) Paul Ehrlich
🟠 (C) E.O. Wilson
🔴 (D) Humboldt
✅ Answer: (A) Norman Myers
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q22. Which is the richest region of the world in terms of biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Temperate forests
🟢 (B) Tundra
🟠 (C) Tropical forests
🔴 (D) Mangroves
✅ Answer: (C) Tropical forests
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q23. The extinction of passenger pigeon was due to
🔵 (A) Habitat destruction
🟢 (B) Overexploitation
🟠 (C) Pollution
🔴 (D) Alien species
✅ Answer: (B) Overexploitation
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q24. Which of the following is not a threat to biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Climate change
🟢 (B) Pollution
🟠 (C) Genetic diversity
🔴 (D) Overexploitation
✅ Answer: (C) Genetic diversity
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q25. Which of the following is a megadiverse country?
🔵 (A) India
🟢 (B) Canada
🟠 (C) Russia
🔴 (D) UK
✅ Answer: (A) India
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q26. Which is the most important cause for biodiversity loss?
🔵 (A) Overexploitation
🟢 (B) Habitat loss and fragmentation
🟠 (C) Pollution
🔴 (D) Alien species invasion
✅ Answer: (B) Habitat loss and fragmentation
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q27. In India, the first national park established was
🔵 (A) Gir
🟢 (B) Jim Corbett
🟠 (C) Kaziranga
🔴 (D) Keoladeo
✅ Answer: (B) Jim Corbett
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q28. The primary producers in a forest ecosystem are
🔵 (A) Phytoplankton
🟢 (B) Shrubs and trees
🟠 (C) Herbivores
🔴 (D) Decomposers
✅ Answer: (B) Shrubs and trees
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q29. Extinction of a species in a given area leading to loss of biodiversity is called
🔵 (A) Ex situ extinction
🟢 (B) Local extinction
🟠 (C) Global extinction
🔴 (D) Endemism
✅ Answer: (B) Local extinction
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q30. Which of the following is not a cause of global biodiversity decline?
🔵 (A) Deforestation
🟢 (B) Overharvesting
🟠 (C) Afforestation
🔴 (D) Pollution
✅ Answer: (C) Afforestation
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q31. Which one of the following is not included under in situ conservation?
🔵 (A) National park
🟢 (B) Sanctuary
🟠 (C) Zoological garden
🔴 (D) Biosphere reserve
✅ Answer: (C) Zoological garden
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q32. Which of the following ecosystems has maximum primary productivity?
🔵 (A) Coral reefs
🟢 (B) Tropical rain forests
🟠 (C) Deserts
🔴 (D) Oceans
✅ Answer: (B) Tropical rain forests
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q33. The most important human activity causing extinction of wildlife is
🔵 (A) Alteration and destruction of natural habitats
🟢 (B) Hunting
🟠 (C) Pollution
🔴 (D) Introducing alien species
✅ Answer: (A) Alteration and destruction of natural habitats
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q34. In India, biodiversity is protected by
🔵 (A) National parks
🟢 (B) Sanctuaries
🟠 (C) Biosphere reserves
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q35. Which is not an ex situ conservation method?
🔵 (A) Botanical garden
🟢 (B) Tissue culture
🟠 (C) Cryopreservation
🔴 (D) National park
✅ Answer: (D) National park
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q36. Which Indian bird was recently extinct due to hunting and habitat loss?
🔵 (A) Peacock
🟢 (B) Passenger pigeon
🟠 (C) Pink-headed duck
🔴 (D) Sparrow
✅ Answer: (C) Pink-headed duck
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q37. The IUCN Red Data Book contains data on
🔵 (A) Endangered species
🟢 (B) Fossils
🟠 (C) Marine fishes
🔴 (D) Exotic plants
✅ Answer: (A) Endangered species
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q38. Which one of the following is an example of in situ conservation?
🔵 (A) Seed bank
🟢 (B) Zoological park
🟠 (C) Sacred grove
🔴 (D) Cryopreservation
✅ Answer: (C) Sacred grove
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q39. Biodiversity of a geographical region represents
🔵 (A) Genetic diversity in the dominant species
🟢 (B) Variety of organisms
🟠 (C) Endangered species only
🔴 (D) Ecological niches
✅ Answer: (B) Variety of organisms
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q40. Which is not a feature of biodiversity hotspot?
🔵 (A) High endemism
🟢 (B) High species richness
🟠 (C) Low degree of threat
🔴 (D) High habitat loss
✅ Answer: (C) Low degree of threat
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q41. Sacred groves are specially useful in
🔵 (A) Generating environmental awareness
🟢 (B) Preventing soil erosion
🟠 (C) Conserving rare plants
🔴 (D) Conserving water
✅ Answer: (C) Conserving rare plants
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q42. Which one of the following is the most important human-caused factor for loss of biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Pollution
🟢 (B) Habitat destruction
🟠 (C) Introduction of exotic species
🔴 (D) Over-hunting
✅ Answer: (B) Habitat destruction
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q43. Which one of the following forests is known as “lungs of the planet”?
🔵 (A) Taiga
🟢 (B) Amazon rain forest
🟠 (C) Alpine forest
🔴 (D) Deciduous forest
✅ Answer: (B) Amazon rain forest
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q44. Which group of vertebrates shows maximum species diversity?
🔵 (A) Fishes
🟢 (B) Amphibians
🟠 (C) Birds
🔴 (D) Mammals
✅ Answer: (A) Fishes
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q45. Which one is not an ex situ conservation strategy?
🔵 (A) Seed bank
🟢 (B) Sacred grove
🟠 (C) Botanical garden
🔴 (D) Cryopreservation
✅ Answer: (B) Sacred grove
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q46. The most important cause of extinction of animals and plants at present is
🔵 (A) Habitat loss
🟢 (B) Deforestation
🟠 (C) Overhunting
🔴 (D) Pollution
✅ Answer: (A) Habitat loss
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q47. Which one of the following is considered a “biodiversity hotspot” in India?
🔵 (A) Indo-Gangetic plain
🟢 (B) Western Ghats
🟠 (C) Deccan plateau
🔴 (D) Eastern Rajasthan
✅ Answer: (B) Western Ghats
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q48. The term “biodiversity” was popularised by
🔵 (A) Edward Wilson
🟢 (B) Humboldt
🟠 (C) Norman Myers
🔴 (D) Paul Ehrlich
✅ Answer: (A) Edward Wilson
Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q49. Which of the following is a mega-diverse country?
🔵 (A) Iceland
🟢 (B) India
🟠 (C) Greenland
🔴 (D) Finland
✅ Answer: (B) India
Year: PMT 1996
🔹 Q50. The extinction of dodo was due to
🔵 (A) Alien species invasion
🟢 (B) Overexploitation
🟠 (C) Habitat loss
🔴 (D) Competition
✅ Answer: (B) Overexploitation
Year: PMT 1993
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20 (NEET-Level, Moderate)
🔹 Q1. Which of the following is not a component of biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Genetic diversity
🟢 (B) Species diversity
🟠 (C) Ecosystem diversity
🔴 (D) Climatic diversity
✅ Answer: (D) Climatic diversity
🔹 Q2. India is considered a megadiverse country because
🔵 (A) It has deserts, mountains, and plains
🟢 (B) It possesses >8% of world’s species
🟠 (C) It has a high human population
🔴 (D) It has many rivers
✅ Answer: (B) It possesses >8% of world’s species
🔹 Q3. The species–area relationship is mathematically expressed as
🔵 (A) S = Z·A^C
🟢 (B) S = C·A^Z
🟠 (C) S = A + C + Z
🔴 (D) S = A^Z / C
✅ Answer: (B) S = C·A^Z
🔹 Q4. Biodiversity is richest in
🔵 (A) Temperate forests
🟢 (B) Tropical rainforests
🟠 (C) Polar regions
🔴 (D) Alpine ecosystems
✅ Answer: (B) Tropical rainforests
🔹 Q5. Which is the most species-rich group of animals?
🔵 (A) Birds
🟢 (B) Insects
🟠 (C) Mammals
🔴 (D) Reptiles
✅ Answer: (B) Insects
🔹 Q6. Which of the following is a biodiversity hotspot in India?
🔵 (A) Deccan plateau
🟢 (B) Indo-Gangetic plain
🟠 (C) Indo-Burma region
🔴 (D) Rajasthan desert
✅ Answer: (C) Indo-Burma region
🔹 Q7. Which one is an in situ conservation method?
🔵 (A) Seed bank
🟢 (B) Zoological park
🟠 (C) National park
🔴 (D) Botanical garden
✅ Answer: (C) National park
🔹 Q8. Which one is an ex situ conservation method?
🔵 (A) Biosphere reserve
🟢 (B) Wildlife sanctuary
🟠 (C) Cryopreservation
🔴 (D) National park
✅ Answer: (C) Cryopreservation
🔹 Q9. The Amazon rainforest is referred to as the “lungs of the planet” because
🔵 (A) It regulates rainfall
🟢 (B) It contributes major oxygen to the atmosphere
🟠 (C) It has maximum biodiversity
🔴 (D) It prevents soil erosion
✅ Answer: (B) It contributes major oxygen to the atmosphere
🔹 Q10. The rivet popper hypothesis relates to
🔵 (A) Climate change
🟢 (B) Species extinction and ecosystem stability
🟠 (C) Photosynthesis efficiency
🔴 (D) Gene diversity
✅ Answer: (B) Species extinction and ecosystem stability
🔹 Q11. Which of the following is an invasive alien species?
🔵 (A) Rauwolfia serpentina
🟢 (B) Parthenium hysterophorus
🟠 (C) Shorea robusta
🔴 (D) Mangifera indica
✅ Answer: (B) Parthenium hysterophorus
🔹 Q12. The major cause of extinction of passenger pigeon was
🔵 (A) Pollution
🟢 (B) Overexploitation
🟠 (C) Alien species invasion
🔴 (D) Habitat loss
✅ Answer: (B) Overexploitation
🔹 Q13. The slope (Z) of species–area curve for large islands is generally
🔵 (A) 0.01–0.05
🟢 (B) 0.1–0.2
🟠 (C) 0.6–1.2
🔴 (D) >2.0
✅ Answer: (C) 0.6–1.2
🔹 Q14. Sacred groves of Meghalaya are examples of
🔵 (A) Ex situ conservation
🟢 (B) In situ conservation
🟠 (C) Species extinction
🔴 (D) Cryopreservation
✅ Answer: (B) In situ conservation
🔹 Q15. Which of the following is not an ecosystem service?
🔵 (A) Soil formation
🟢 (B) Climate regulation
🟠 (C) Water purification
🔴 (D) Mining of fossil fuels
✅ Answer: (D) Mining of fossil fuels
🔹 Q16. The most important human activity causing extinction of species is
🔵 (A) Pollution
🟢 (B) Habitat destruction
🟠 (C) Hunting
🔴 (D) Alien species introduction
✅ Answer: (B) Habitat destruction
🔹 Q17. The IUCN Red List provides information about
🔵 (A) Endangered species
🟢 (B) Zoological gardens
🟠 (C) Botanical gardens
🔴 (D) National parks
✅ Answer: (A) Endangered species
🔹 Q18. The term biodiversity hotspot was coined by
🔵 (A) E.O. Wilson
🟢 (B) Norman Myers
🟠 (C) Alexander von Humboldt
🔴 (D) Paul Ehrlich
✅ Answer: (B) Norman Myers
🔹 Q19. Which one is a critically endangered species of India?
🔵 (A) Peacock
🟢 (B) Lion-tailed macaque
🟠 (C) Tiger
🔴 (D) House sparrow
✅ Answer: (B) Lion-tailed macaque
🔹 Q20. Which region shows the latitudinal gradient of biodiversity most clearly?
🔵 (A) Polar regions
🟢 (B) Temperate forests
🟠 (C) Tropics
🔴 (D) Deserts
✅ Answer: (C) Tropics
🟠 Q21–Q40 (Enhanced NEET-Level, Higher Thinking)
🔹 Q21. Which of the following correctly explains species richness?
🔵 (A) Number of individuals in a population
🟢 (B) Number of species in a given area
🟠 (C) Genetic variability within species
🔴 (D) Balance among trophic levels
✅ Answer: (B) Number of species in a given area
🔹 Q22. Which value of Z in the species–area curve indicates greater isolation (as in islands)?
🔵 (A) 0.1
🟢 (B) 0.2
🟠 (C) 0.6
🔴 (D) 0.01
✅ Answer: (C) 0.6
🔹 Q23. Which of the following represents ecosystem diversity?
🔵 (A) Variety of DNA sequences
🟢 (B) Tropical forests, wetlands, deserts, mangroves
🟠 (C) Variations in genes of rice
🔴 (D) Number of bird species in a forest
✅ Answer: (B) Tropical forests, wetlands, deserts, mangroves
🔹 Q24. A critically endangered species from India is
🔵 (A) House sparrow
🟢 (B) Sangai deer
🟠 (C) Tiger
🔴 (D) Asiatic lion
✅ Answer: (B) Sangai deer
🔹 Q25. Which is not an invasive alien species?
🔵 (A) Lantana
🟢 (B) Parthenium
🟠 (C) Rauwolfia
🔴 (D) Eichhornia
✅ Answer: (C) Rauwolfia
🔹 Q26. Which is not a HIPPO cause?
🔵 (A) Habitat loss
🟢 (B) Industrialisation
🟠 (C) Overexploitation
🔴 (D) Alien species
✅ Answer: (B) Industrialisation
🔹 Q27. Which of the following is an in situ method?
🔵 (A) Seed bank
🟢 (B) Botanical garden
🟠 (C) National park
🔴 (D) Cryopreservation
✅ Answer: (C) National park
🔹 Q28. Which Indian biodiversity hotspot is home to the lion-tailed macaque?
🔵 (A) Indo-Burma
🟢 (B) Western Ghats
🟠 (C) Himalaya
🔴 (D) Indo-Malayan
✅ Answer: (B) Western Ghats
🔹 Q29. The economic value of ecosystem services was estimated as US $33 trillion/year by
🔵 (A) E.O. Wilson
🟢 (B) R. Costanza
🟠 (C) Norman Myers
🔴 (D) Humboldt
✅ Answer: (B) R. Costanza
🔹 Q30. The Red Data Book provides
🔵 (A) Agricultural statistics
🟢 (B) List of threatened species
🟠 (C) Medicinal plants only
🔴 (D) Biodiversity hotspots
✅ Answer: (B) List of threatened species
🔹 Q31. Which one is ex situ conservation?
🔵 (A) Sacred grove
🟢 (B) National park
🟠 (C) Zoological park
🔴 (D) Biosphere reserve
✅ Answer: (C) Zoological park
🔹 Q32. Which biome is expected to have lowest biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Tropical rain forest
🟢 (B) Desert
🟠 (C) Temperate forest
🔴 (D) Coral reef
✅ Answer: (B) Desert
🔹 Q33. Which conservation strategy ensures long-term survival of a species?
🔵 (A) Captive breeding
🟢 (B) In situ conservation
🟠 (C) Tissue culture
🔴 (D) Seed storage
✅ Answer: (B) In situ conservation
🔹 Q34. Which ecosystem service is provisioning?
🔵 (A) Climate regulation
🟢 (B) Food and fuel
🟠 (C) Soil fertility
🔴 (D) Water cycling
✅ Answer: (B) Food and fuel
🔹 Q35. Which factor is the largest driver of present-day species extinction?
🔵 (A) Overgrazing
🟢 (B) Habitat destruction
🟠 (C) Climate change
🔴 (D) Poaching
✅ Answer: (B) Habitat destruction
🔹 Q36. Which category in IUCN Red List indicates species facing highest risk?
🔵 (A) Endangered
🟢 (B) Vulnerable
🟠 (C) Critically endangered
🔴 (D) Near threatened
✅ Answer: (C) Critically endangered
🔹 Q37. Which is not an Indian biosphere reserve?
🔵 (A) Nanda Devi
🟢 (B) Kaziranga
🟠 (C) Nilgiri
🔴 (D) Gulf of Mannar
✅ Answer: (B) Kaziranga
🔹 Q38. Which of the following best explains ecosystem resilience?
🔵 (A) Ability to produce more energy
🟢 (B) Ability to recover after disturbance
🟠 (C) Ability to resist invasive species
🔴 (D) Ability to form new habitats
✅ Answer: (B) Ability to recover after disturbance
🔹 Q39. Which one of the following is not a benefit of biodiversity?
🔵 (A) Source of food
🟢 (B) Oxygen generation
🟠 (C) Pollination
🔴 (D) Global warming
✅ Answer: (D) Global warming
🔹 Q40. Which one is not part of India’s four biodiversity hotspots?
🔵 (A) Himalaya
🟢 (B) Indo-Burma
🟠 (C) Western Ghats
🔴 (D) Deccan plateau
✅ Answer: (D) Deccan plateau
🔴 Q41–Q50 (Advanced NEET-Level, Higher-Order Thinking)
🔹 Q41. The species richness of an area depends mainly on
🔵 (A) Productivity and time
🟢 (B) Latitude and altitude
🟠 (C) Isolation and immigration rate
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
🔹 Q42. The most accurate method to conserve plant genetic resources is
🔵 (A) Botanical gardens
🟢 (B) Tissue culture
🟠 (C) Cryopreservation
🔴 (D) Field gene banks
✅ Answer: (C) Cryopreservation
🔹 Q43. Which biome contributes maximum to global primary productivity?
🔵 (A) Oceans
🟢 (B) Tropical rainforests
🟠 (C) Deserts
🔴 (D) Tundra
✅ Answer: (A) Oceans
🔹 Q44. The slope (Z) of the species–area curve is highest for
🔵 (A) Large islands
🟢 (B) Small islands
🟠 (C) Continental areas
🔴 (D) Polar regions
✅ Answer: (A) Large islands
🔹 Q45. Which is not a service of ecosystems?
🔵 (A) Soil formation
🟢 (B) Climate regulation
🟠 (C) Nutrient cycling
🔴 (D) Industrial mining
✅ Answer: (D) Industrial mining
🔹 Q46. Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
🔵 (A) IUCN — Endangered species list
🟢 (B) CITES — Trade of endangered species
🟠 (C) CBD — Conservation of biodiversity
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
🔹 Q47. The most species-rich phylum in the animal kingdom is
🔵 (A) Arthropoda
🟢 (B) Mollusca
🟠 (C) Chordata
🔴 (D) Annelida
✅ Answer: (A) Arthropoda
🔹 Q48. Which one is an example of flagship species conservation in India?
🔵 (A) Tiger in Project Tiger
🟢 (B) Vulture in Vulture project
🟠 (C) Crocodile in Crocodile project
🔴 (D) Asiatic lion in Gir project
✅ Answer: (A) Tiger in Project Tiger
🔹 Q49. Which conservation method preserves both species and ecosystem together?
🔵 (A) Gene banks
🟢 (B) In situ conservation
🟠 (C) Botanical gardens
🔴 (D) Zoological parks
✅ Answer: (B) In situ conservation
🔹 Q50. Which factor explains why tropical forests are called “cradles of biodiversity”?
🔵 (A) High productivity
🟢 (B) Climatic stability
🟠 (C) Absence of glaciations
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
