Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 11: Organisms and Populations
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌱 Introduction
🔵 Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and their environment.
🟢 The chapter Organisms and Populations is the foundation of ecology in NCERT Class 12.
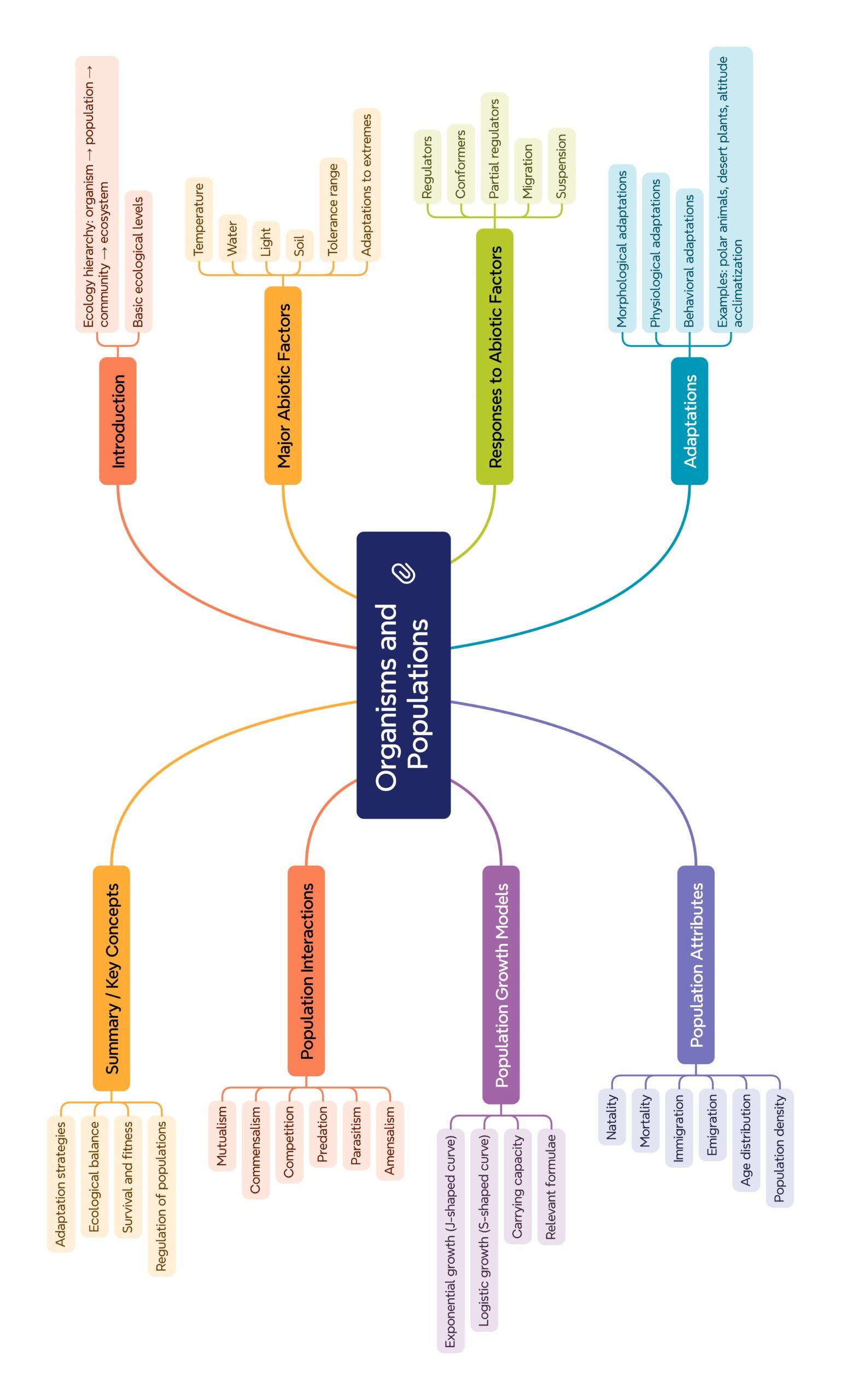
🟠 It deals with levels of organization: organism → population → community → ecosystem.
🔴 The focus is on adaptations, population dynamics, and interactions among organisms.
🌍 Major Abiotic Factors Affecting Organisms
☀️ Temperature
Most important ecological factor.
Influences metabolism, growth, reproduction, distribution of organisms.
Ranges:
🔵 Psychrophiles (cold-loving) → thrive at <20°C. 🟢 Mesophiles (moderate) → thrive at 20–45°C. 🟠 Thermophiles → thrive at >45°C.
Examples: Mango trees cannot grow in temperate countries.
💧 Water
Essential for life processes.
Availability affects productivity and distribution of plants and animals.
Freshwater vs. marine organisms differ in osmoregulation.
Examples: Desert animals (camel 🐪) conserve water.
☀️ Light
Determines photosynthesis in plants 🌿.
Affects photoperiodism, reproduction, and migration in animals (e.g., birds 🕊️).
Plants: Heliophytes (sun-loving) vs. Sciophytes (shade-loving).
⛰️ Soil
Determines vegetation type → affects animal life indirectly.
Properties: texture, pH, water-holding capacity, nutrients.
Example: Mangroves in saline soils.
🧬 Responses of Organisms to Environment
Regulation
Some organisms maintain homeostasis.
Example: Humans maintain 37°C by sweating or shivering.
Conformation
Majority conform → internal environment changes with external.
Example: Ectotherms like reptiles 🦎.
Migration
Temporary escape from stressful conditions.
Example: Birds migrate during winter.
Suspension
Dormancy or hibernation.
Examples:
🔵 Bears hibernate 🐻.
🟢 Seeds enter dormancy.
🟠 Some microbes form spores.
🐾 Adaptations
Morphological, physiological, behavioural traits that help survival.
Examples:
🔵 Polar bears → thick fur, fat insulation.

🟢 Desert plants → CAM photosynthesis, reduced leaves (spines 🌵).

🟠 Kangaroo rat → water from metabolic fat oxidation.

🔴 Altitude adaptation → humans produce more RBCs at high altitude.
👥 Populations
Population = group of interbreeding individuals in a defined area.
Attributes beyond individual:
Population density (no. per unit area).
Birth rate (no. of births per capita per unit time).
Death rate (no. of deaths per capita per unit time).
Age distribution (pre-reproductive, reproductive, post-reproductive).
Sex ratio.
📈 Population Growth
Exponential Growth
When resources are unlimited.
Equation:
dN/dt = rN
where r = intrinsic growth rate, N = population size.
Graph: J-shaped curve.
Logistic Growth
When resources become limiting.
Equation:
dN/dt = rN (K–N)/K
where K = carrying capacity.
Graph: S-shaped curve.
🔗 Population Interactions
Positive (+) and Negative (–) Interactions
🔵 Predation (+/–)
Predator benefits, prey harmed.
Examples: Tiger–deer 🐅🦌.
Biological control of pests.
🟢 Parasitism (+/–)
Parasite benefits, host harmed.
Examples: Plasmodium → malaria, lice on humans.
🟠 Commensalism (+/0)
One benefits, other unaffected.
Example: Barnacles on whales 🐋.
🔴 Mutualism (+/+)
Both benefit.
Examples: Lichens (algae + fungi), pollination.
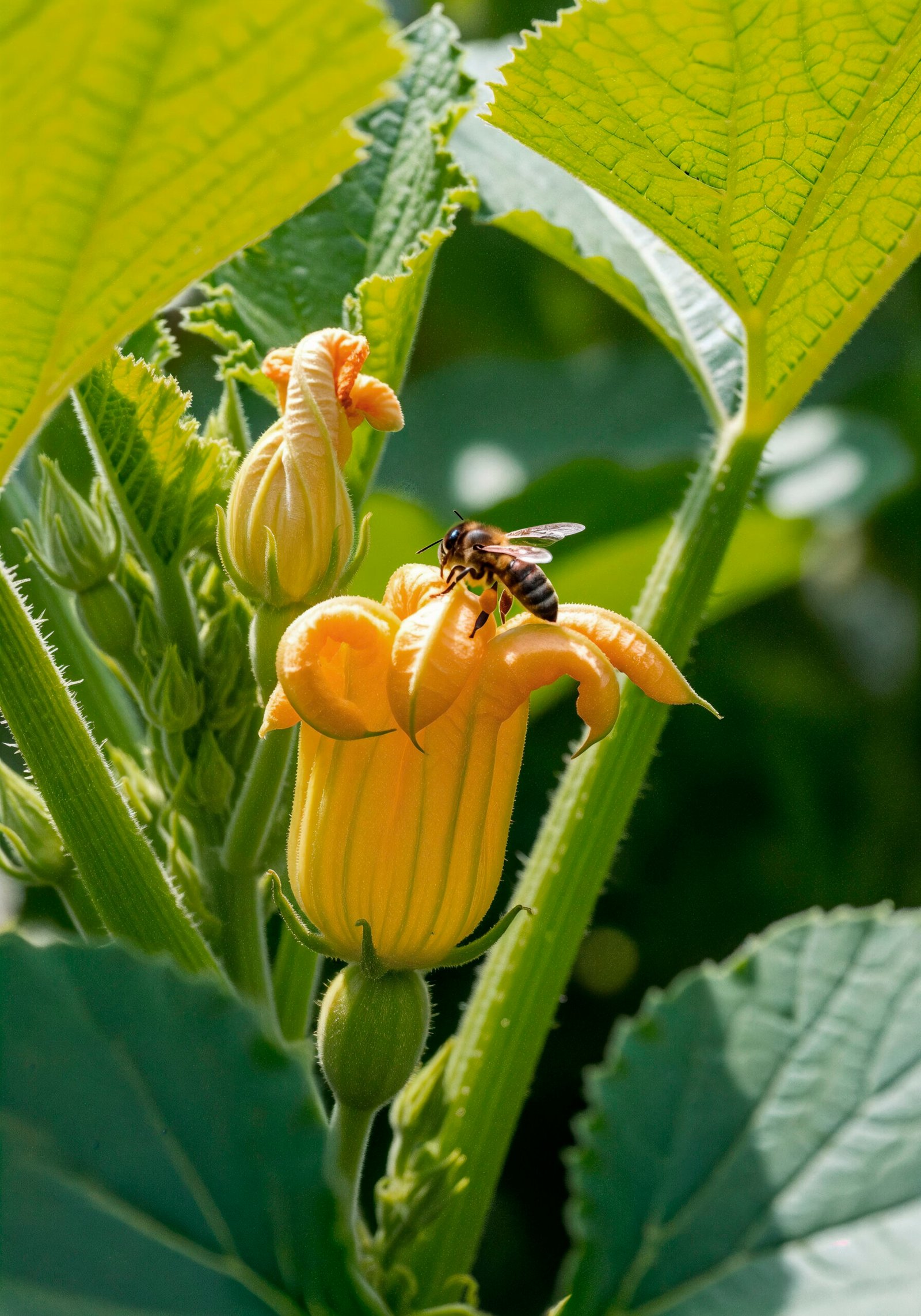

Fig.-Pollination.
🟡 Competition (–/–)
Both species harmed due to shared resources.
Example: Flamingoes vs. fishes compete for zooplankton.

📝 Summary (~300 words)
The chapter Organisms and Populations explores how organisms interact with their environment and with each other. Abiotic factors like temperature, water, light, and soil determine the distribution and survival of species. Organisms respond by regulation, conformation, migration, or suspension. Adaptations such as CAM photosynthesis in desert plants, hibernation in bears, and high-altitude RBC production in humans illustrate survival strategies.
Populations are studied in terms of attributes such as density, growth rate, age distribution, and sex ratio. Population growth follows two models: exponential (J-curve) when resources are unlimited, and logistic (S-curve) under resource-limited conditions with carrying capacity (K).
Interactions among species include predation, parasitism, competition, commensalism, and mutualism. These interactions maintain ecological balance, regulate populations, and drive evolution. The chapter lays the groundwork for advanced ecological concepts, preparing students for understanding ecosystems and biodiversity in later lessons.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
❓ Q1. List the attributes that populations possess but not individuals.
✅ Answer:
Populations show features that an individual organism cannot:
🔵 Natality (birth rate): Number of births per individual per unit time.
🟢 Mortality (death rate): Number of deaths per individual per unit time.
🟠 Population density: Number of individuals per unit area/volume.
🔴 Age distribution: Ratio of individuals in pre-reproductive, reproductive, and post-reproductive stages.
🟡 Sex ratio: Proportion of males and females in a population.
❓ Q2. If a population growing exponentially double in size in 3 years, what is the intrinsic rate of increase (r) of the population?
✅ Answer (Step by step):
Formula for exponential growth:
N(t) = N₀ eʳᵗ
Step 1: Here, N(t) = 2N₀ (since the population doubles).
Step 2: Substitute → 2N₀ = N₀ eʳ³
Step 3: Cancel N₀ → 2 = e³ʳ
Step 4: Take natural log → ln(2) = 3r
Step 5: r = ln(2)/3
Step 6: Value → r = 0.693 / 3 = 0.231 per year
💡 Final Answer: r = 0.231 per year
❓ Q3. Name important defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory.
✅ Answer:
Plants have evolved structural, chemical, and ecological defences:
🌵 Morphological defences: Thorns in cactus, spines in Acacia.
🧪 Chemical defences:
Alkaloids (morphine, nicotine, quinine).
Tannins (make plant tissues indigestible).
Latex (milky sap in Calotropis).
🐜 Indirect defence: Acacia provides shelter to ants → ants protect it from herbivores.
❓ Q4. An orchid plant is growing on the branch of mango tree. How do you describe this interaction between the orchid and the mango tree?
✅ Answer:
🌱 Orchid = epiphyte, grows on mango branches.
🌳 Mango = host, provides only support, not nutrients.
🟢 Orchid benefits (gains space, light).
🔵 Mango neither benefits nor harmed.
💡 This is an example of Commensalism (one benefits, other unaffected).
❓ Q5. What is the ecological principle behind the biological control method of managing with pest insects?
✅ Answer:
Biological control is based on Predator–prey interaction.
🐞 Ladybird beetle feeds on aphids.
🦋 Dragonfly feeds on mosquito larvae.
By releasing predators/parasitoids, pest population is controlled naturally.
💡 Principle: Using natural enemies (predators/parasitoids) of pests to control them.
❓ Q6. Define population and community.
✅ Answer:
👥 Population: A group of individuals of the same species, living in a defined geographical area, interbreeding and sharing a common gene pool.
➡️ Example: All tigers in Sundarbans.
🌍 Community: A group of populations of different species living together in a particular area and interacting with each other.
➡️ Example: Grass + deer + tiger + microbes in a forest ecosystem.
❓ Q7. Define the following terms and give one example for each:
🔵 Commensalism (+/0): One benefits, other unaffected.
➡️ Example: Orchid on mango tree 🌳.
🟢 Parasitism (+/–): Parasite benefits, host harmed.
➡️ Example: Plasmodium in humans (malaria).
🟠 Camouflage: Organisms blend with surroundings to escape predators.
➡️ Example: Green leaf insect 🪲.
🔴 Mutualism (+/+): Both partners benefit.
➡️ Example: Lichens (algae + fungi).
🟡 Interspecific competition (–/–): Both species harmed due to limited resources.
➡️ Example: Flamingos and fish competing for zooplankton.
❓ Q8. With the help of suitable diagram describe the logistic population growth curve.
✅ Answer:
Logistic growth occurs when resources are limited.
Equation:
dN/dt = rN (K–N)/K
where:
🔵 N = population size
🟢 r = intrinsic growth rate
🟠 K = carrying capacity
Shape: S-shaped (sigmoid) curve
Lag phase → slow growth.
Exponential phase → rapid growth.
Deceleration → growth slows.
Steady state → population stabilises at K.
❓ Q9. Select the statement which explains best parasitism.
🔵 (A) One organism is benefited.
🟢 (B) Both organisms are benefited.
🟠 (C) One organism is benefited, other is not affected.
🔴 (D) One organism is benefited, other is affected.
✅ Answer: (D) One organism is benefited, other is affected.
❓ Q10. List any three important characteristics of a population and explain.
✅ Answer:
👥 Population density:
Number of individuals per unit area/volume.
Example: Number of deer per km² in a forest.
👶 Birth rate (Natality):
Number of births per individual per unit time.
Determines growth capacity of population.
⚰️ Death rate (Mortality):
Number of deaths per individual per unit time.
Indicates population decline or pressure.
💡 Other important attributes: Age distribution, Sex ratio, Growth models.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
Section A — Objective (Q1–Q10)
Q1. The single most important abiotic factor deciding species distribution is 🌡️
🔵 (A) Light
🟢 (B) Temperature
🟠 (C) Soil pH
🔴 (D) Wind
Answer: (B) Temperature
Q2. A true population attribute (not shown by an individual) is 👥
🔵 (A) Height
🟢 (B) Age pyramid
🟠 (C) Body mass
🔴 (D) Blood group
Answer: (B) Age pyramid
Q3. Choose the correct regulator–conformer pair ♨️🦎
🔵 (A) Human–Regulator, Lizard–Conformer
🟢 (B) Human–Conformer, Lizard–Regulator
🟠 (C) Both regulators
🔴 (D) Both conformers
Answer: (A) Human–Regulator, Lizard–Conformer
Q4. A typical desert plant adaptation is 🌵
🔵 (A) Broad leaves
🟢 (B) CAM metabolism with stomata open at night
🟠 (C) Thin cuticle
🔴 (D) Shallow roots only
Answer: (B) CAM metabolism with stomata open at night
Q5. A J-shaped curve represents 📈
🔵 (A) Logistic growth
🟢 (B) Exponential growth
🟠 (C) Zero growth
🔴 (D) Declining growth
Answer: (B) Exponential growth
Q6. In logistic growth, population stabilises at ⚖️
🔵 (A) r
🟢 (B) K (carrying capacity)
🟠 (C) N₀
🔴 (D) 2K
Answer: (B) K (carrying capacity)
Q7. A population doubles in 3 years. Intrinsic rate of increase r is (per year) 🧮
(Use N = N₀e^{rt})
🔵 (A) 0.115
🟢 (B) 0.231
🟠 (C) 0.462
🔴 (D) 0.693
Answer: (B) 0.231
Q8. Orchid growing on mango branch shows 🌱🌳
🔵 (A) Mutualism
🟢 (B) Parasitism
🟠 (C) Commensalism
🔴 (D) Amensalism
Answer: (C) Commensalism
Q9. Biological control of pests is based mainly on 🐞🦟
🔵 (A) Competition
🟢 (B) Predation/Parasitism
🟠 (C) Mutualism
🔴 (D) Commensalism
Answer: (B) Predation/Parasitism
Q10. An expanding (growing) population has an age pyramid that is 🔺
🔵 (A) Urn-shaped
🟢 (B) Bell-shaped
🟠 (C) Triangular
🔴 (D) Inverted
Answer: (C) Triangular
Q12. Differentiate: Regulators, Conformers, Partial regulators (with one example each).
Answer:
♨️ Regulators: maintain homeostasis (humans—thermoregulation).
🦎 Conformers: internal conditions follow environment (fishes, reptiles).
🌿 Partial/behavioural regulators: regulate within limits via behaviour (desert lizard basking/shuttling shade).
Q13. High-altitude adaptation in humans (acute to chronic).
Answer:
⬆️ Short term: hyperventilation, ↑ heart rate.
🩸 Long term: ↑ RBC count & haemoglobin, ↑ 2,3-BPG, increased capillary density.
Q14. r-selected vs K-selected species (any three points).
Answer:
r: small size, early maturity, many offspring, little parental care (weeds, rodents).
K: large size, late maturity, few offspring, high parental care (elephants, humans).
Q15. State Allen’s rule and one ecological example.
Answer:
🐰 Allen’s rule: endotherms in cold climates have shorter extremities to reduce heat loss.
Example: Arctic fox has shorter ears/limbs than desert fox.
Section C — Short Answer II (Q16–Q17)
Q16. Write the equations for exponential and logistic growth and label terms.
Answer:
📈 Exponential: dN/dt = rN (N = population size, r = intrinsic rate).
⚖️ Logistic: dN/dt = rN( K−N )/K (K = carrying capacity).
Q17. Processes changing population density other than birth & death; explain in one line each.
Answer:
🔼 Immigration (I): individuals enter a population → D increases.
🔽 Emigration (E): individuals leave a population → D decreases.
Section D — Long Answer Questions (Q18–Q25)
Q18. Explain logistic growth curve with diagram.
Answer:
⚖️ Logistic growth: when resources are limited, growth slows & stabilises.
📊 Equation: dN/dt = rN( K−N )/K.
🌀 Phases: lag → exponential → deceleration → stationary (at K).
🔴 Shape: S-shaped (sigmoid curve).
Q19. Write a note on predator–prey interactions with two examples.
Answer:
🐅 Tiger–deer: predator controls prey population.
🐞 Ladybird beetle–aphids: used in pest control.
✅ Maintains ecological balance & drives evolution (coevolution).
Q20. Describe three defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory.
Answer:
🌵 Morphological: thorns in cactus, spines in Acacia.
🧪 Chemical: alkaloids (nicotine, quinine), tannins.
🐜 Indirect: Acacia shelters ants → ants defend plant.
Q21. Differentiate parasitism, mutualism, commensalism (with one example each).
Answer:
🦠 Parasitism (+/–): Plasmodium in humans.
🌸🐝 Mutualism (+/+): Pollination (bee & flower).
🌱🌳 Commensalism (+/0): Orchid on mango tree.
Q22. Explain competitive exclusion principle. Give one example.
Answer:
🟠 Principle: No two species can coexist for long if they compete for same resources.
Example: Paramecium aurelia outcompetes Paramecium caudatum.
Q23. Write a note on adaptations of desert animals.
Answer:
🐪 Camels conserve water, tolerate dehydration.
🐭 Kangaroo rat: water via fat oxidation.
🌙 Many are nocturnal to avoid heat.
Q24. Explain population age pyramids with diagrams.
Answer:
🔺 Expanding: broad base (India).
🔔 Stable: uniform width (France).
🏺 Declining: narrow base, broad top (Japan).
Q25. Write three differences between commensalism and mutualism.
Answer:
Commensalism: one benefits, other unaffected.
Mutualism: both benefit.
Example: Orchid–mango vs. Pollination.
Section E — Case Study / Application-based MCQs (Q26–Q33)
Q26. In a grassland, rabbits (herbivores) increase in population. Which of the following happens first?
🔵 (A) Grass decreases
🟢 (B) Tiger population decreases
🟠 (C) Deer population increases
🔴 (D) Eagle population decreases
Answer: (A) Grass decreases
Q27. If a fish species survives only in narrow temperature range, it is called
🔵 (A) Eurythermal
🟢 (B) Stenothermal
🟠 (C) Euryhaline
🔴 (D) Stenohaline
Answer: (B) Stenothermal
Q28. A population of 100 becomes 200 in 10 years. Birth = 80, Death = 20. Net Immigration = 40. What is population size after 10 years?
🔵 (A) 200
🟢 (B) 240
🟠 (C) 220
🔴 (D) 260
Answer: (B) 240
Q29. Which of the following is NOT a density-dependent factor?
🔵 (A) Competition
🟢 (B) Predation
🟠 (C) Flood
🔴 (D) Parasitism
Answer: (C) Flood
Q30. A predator controlling the population of prey is an example of
🔵 (A) Negative feedback
🟢 (B) Positive feedback
🟠 (C) Mutualism
🔴 (D) Amensalism
Answer: (A) Negative feedback
Q31. Barnacles growing on the back of whales show
🔵 (A) Parasitism
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Commensalism
🔴 (D) Predation
Answer: (C) Commensalism
Q32. Which statement best describes competition?
🔵 (A) Both species benefit
🟢 (B) One benefits, other unaffected
🟠 (C) Both harmed
🔴 (D) One harmed, one benefits
Answer: (C) Both harmed
Q33. Logistic growth curve is sigmoidal because
🔵 (A) Growth unlimited
🟢 (B) Carrying capacity limits growth
🟠 (C) Mortality absent
🔴 (D) Natality always increases
Answer: (B) Carrying capacity limits growth
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Which of the following is a characteristic of a population, not an individual?
🔵 (A) Birth rate
🟢 (B) Height
🟠 (C) Weight
🔴 (D) Age
✅ Answer: (A) Birth rate
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q2. In logistic growth, the population growth is fastest at:
🔵 (A) Initial lag phase
🟢 (B) Exponential phase
🟠 (C) At carrying capacity
🔴 (D) Decline phase
✅ Answer: (B) Exponential phase
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q3. Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
🔵 (A) Orchid–Mango tree → Parasitism
🟢 (B) Cuckoo–Crow → Brood parasitism
🟠 (C) Lichen → Commensalism
🔴 (D) Tiger–Deer → Mutualism
✅ Answer: (B) Cuckoo–Crow → Brood parasitism
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q4. Which population growth curve is more realistic?
🔵 (A) Exponential growth curve
🟢 (B) Logistic growth curve
🟠 (C) Both exponential and logistic
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (B) Logistic growth curve
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q5. In mutualism:
🔵 (A) One benefits, other harmed
🟢 (B) Both benefit
🟠 (C) One benefits, other unaffected
🔴 (D) Both harmed
✅ Answer: (B) Both benefit
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q6. Which of the following is an example of commensalism?
🔵 (A) Cuscuta on hibiscus
🟢 (B) Orchid on mango tree
🟠 (C) Lichen
🔴 (D) Mycorrhiza
✅ Answer: (B) Orchid on mango tree
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q7. Which of the following equations represents logistic growth?
🔵 (A) dN/dt = rN
🟢 (B) dN/dt = rN(K–N)/K
🟠 (C) dN/dt = r/K
🔴 (D) dN/dt = K/r
✅ Answer: (B) dN/dt = rN(K–N)/K
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q8. Which of the following is a regulator?
🔵 (A) Fishes
🟢 (B) Amphibians
🟠 (C) Birds
🔴 (D) Reptiles
✅ Answer: (C) Birds
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q9. Which of the following explains better the survivorship curve of humans?
🔵 (A) Type I
🟢 (B) Type II
🟠 (C) Type III
🔴 (D) All types
✅ Answer: (A) Type I
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q10. Logistic growth curve is also called:
🔵 (A) J-curve
🟢 (B) S-curve
🟠 (C) U-curve
🔴 (D) V-curve
✅ Answer: (B) S-curve
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q11. Which of the following interactions is negative for both partners?
🔵 (A) Parasitism
🟢 (B) Competition
🟠 (C) Commensalism
🔴 (D) Mutualism
✅ Answer: (B) Competition
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q12. Which of the following is an adaptation in desert animals?
🔵 (A) Sweat glands
🟢 (B) Estivation
🟠 (C) Hibernation
🔴 (D) Thick fur
✅ Answer: (B) Estivation
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q13. What does K represent in logistic growth equation?
🔵 (A) Growth rate
🟢 (B) Carrying capacity
🟠 (C) Mortality
🔴 (D) Natality
✅ Answer: (B) Carrying capacity
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q14. Which of the following is an example of brood parasitism?
🔵 (A) Crow and cuckoo
🟢 (B) Tiger and deer
🟠 (C) Barnacle and whale
🔴 (D) Algae and fungi
✅ Answer: (A) Crow and cuckoo
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q15. The pyramids of number and biomass in a pond ecosystem are:
🔵 (A) Both upright
🟢 (B) Both inverted
🟠 (C) Number upright, biomass inverted
🔴 (D) Number inverted, biomass upright
✅ Answer: (A) Both upright
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q16. Which of the following is a density-independent factor?
🔵 (A) Predation
🟢 (B) Competition
🟠 (C) Flood
🔴 (D) Parasitism
✅ Answer: (C) Flood
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q17. Which one is not a population interaction?
🔵 (A) Mutualism
🟢 (B) Commensalism
🟠 (C) Amensalism
🔴 (D) Stratification
✅ Answer: (D) Stratification
Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q18. Which of the following has highest intrinsic growth rate?
🔵 (A) Bacteria
🟢 (B) Humans
🟠 (C) Elephants
🔴 (D) Oak tree
✅ Answer: (A) Bacteria
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q19. Carrying capacity is determined by:
🔵 (A) Natality
🟢 (B) Limiting resources
🟠 (C) Immigration
🔴 (D) Mortality
✅ Answer: (B) Limiting resources
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q20. Which of the following organisms is a conformer?
🔵 (A) Mammals
🟢 (B) Birds
🟠 (C) Reptiles
🔴 (D) Humans
✅ Answer: (C) Reptiles
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q21. When two species compete, one is eliminated. This is:
🔵 (A) Resource partitioning
🟢 (B) Competitive exclusion
🟠 (C) Predation
🔴 (D) Amensalism
✅ Answer: (B) Competitive exclusion
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q22. In a stable population, age pyramid is:
🔵 (A) Bell-shaped
🟢 (B) Urn-shaped
🟠 (C) Triangular
🔴 (D) Inverted
✅ Answer: (A) Bell-shaped
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q23. Which of the following is an example of amensalism?
🔵 (A) Algae and fungi
🟢 (B) Penicillium and bacteria
🟠 (C) Tiger and deer
🔴 (D) Crow and cuckoo
✅ Answer: (B) Penicillium and bacteria
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q24. Population density is measured in terms of:
🔵 (A) Number of organisms per unit area/volume
🟢 (B) Birth rate
🟠 (C) Mortality
🔴 (D) Growth rate
✅ Answer: (A) Number of organisms per unit area/volume
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q25. Which one is an example of parasitism?
🔵 (A) Ficus and wasp
🟢 (B) Orchid and mango
🟠 (C) Plasmodium in humans
🔴 (D) Lichen
✅ Answer: (C) Plasmodium in humans
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q26. Which survivorship curve shows high mortality in early life stages?
🔵 (A) Type I
🟢 (B) Type II
🟠 (C) Type III
🔴 (D) All types
✅ Answer: (C) Type III
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q27. Which of the following is the best example of mutualism?
🔵 (A) Lichen
🟢 (B) Orchid on mango
🟠 (C) Crow and cuckoo
🔴 (D) Penicillium and bacteria
✅ Answer: (A) Lichen
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q28. The intrinsic rate of increase (r) depends on:
🔵 (A) Age distribution only
🟢 (B) Natality and mortality
🟠 (C) Immigration only
🔴 (D) Emigration only
✅ Answer: (B) Natality and mortality
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q29. Which of the following shows brood parasitism?
🔵 (A) Cuscuta on hibiscus
🟢 (B) Koel in crow’s nest
🟠 (C) Orchid on mango
🔴 (D) Penicillium on bacteria
✅ Answer: (B) Koel in crow’s nest
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q30. Carrying capacity is defined as:
🔵 (A) Maximum birth rate
🟢 (B) Maximum individuals an environment can support
🟠 (C) Minimum mortality rate
🔴 (D) Zero growth point
✅ Answer: (B) Maximum individuals an environment can support
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q31. Organisms blending with environment to escape predators exhibit:
🔵 (A) Mutualism
🟢 (B) Camouflage
🟠 (C) Mimicry
🔴 (D) Parasitism
✅ Answer: (B) Camouflage
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q32. Which one is a density-dependent factor regulating population?
🔵 (A) Rainfall
🟢 (B) Flood
🟠 (C) Predation
🔴 (D) Drought
✅ Answer: (C) Predation
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q33. Which of the following is an example of amensalism?
🔵 (A) Cuscuta on hibiscus
🟢 (B) Orchid on mango
🟠 (C) Penicillium secreting antibiotic killing bacteria
🔴 (D) Lichen
✅ Answer: (C) Penicillium secreting antibiotic killing bacteria
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q34. Which of the following interactions is not interspecific?
🔵 (A) Competition
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Amensalism
🔴 (D) Cannibalism
✅ Answer: (D) Cannibalism
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q35. Which ecological rule states that mammals in colder regions have shorter extremities?
🔵 (A) Bergmann’s rule
🟢 (B) Allen’s rule
🟠 (C) Gloger’s rule
🔴 (D) Jordan’s rule
✅ Answer: (B) Allen’s rule
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q36. Which curve represents exponential growth?
🔵 (A) S-curve
🟢 (B) J-curve
🟠 (C) Bell-shaped curve
🔴 (D) U-shaped curve
✅ Answer: (B) J-curve
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q37. Natality is defined as:
🔵 (A) Number of births per individual per unit time
🟢 (B) Number of deaths per individual per unit time
🟠 (C) Number of immigrants
🔴 (D) Number of emigrants
✅ Answer: (A) Number of births per individual per unit time
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q38. Which of the following is a r-strategist?
🔵 (A) Elephant
🟢 (B) Human
🟠 (C) Rodent
🔴 (D) Tiger
✅ Answer: (C) Rodent
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q39. Which one is a K-selected species?
🔵 (A) Bacteria
🟢 (B) Human
🟠 (C) Weeds
🔴 (D) Insects
✅ Answer: (B) Human
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q40. If N = population size and K = carrying capacity, logistic growth rate is maximum when:
🔵 (A) N = 0
🟢 (B) N = K
🟠 (C) N = K/2
🔴 (D) N = 2K
✅ Answer: (C) N = K/2
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q41. When prey population increases, predator population also increases. This shows:
🔵 (A) Positive feedback
🟢 (B) Negative feedback
🟠 (C) Competition
🔴 (D) Commensalism
✅ Answer: (A) Positive feedback
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q42. Which interaction is shown by barnacles growing on whale?
🔵 (A) Parasitism
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Commensalism
🔴 (D) Amensalism
✅ Answer: (C) Commensalism
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q43. Which of the following is NOT density dependent?
🔵 (A) Predation
🟢 (B) Competition
🟠 (C) Rainfall
🔴 (D) Parasitism
✅ Answer: (C) Rainfall
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q44. In logistic growth, growth is zero at:
🔵 (A) Beginning
🟢 (B) Carrying capacity
🟠 (C) N = K/2
🔴 (D) Declining phase
✅ Answer: (B) Carrying capacity
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q45. Which of the following represents resource partitioning?
🔵 (A) Species coexisting by utilising different resources
🟢 (B) Elimination of one species
🟠 (C) Mimicry
🔴 (D) Camouflage
✅ Answer: (A) Species coexisting by utilising different resources
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q46. Which type of population pyramid shows declining population?
🔵 (A) Bell-shaped
🟢 (B) Urn-shaped
🟠 (C) Triangular
🔴 (D) Rectangular
✅ Answer: (B) Urn-shaped
Year: PMT 2000
🔹 Q47. Which of the following pairs is NOT correct?
🔵 (A) Predator–prey → Tiger–deer
🟢 (B) Parasitism → Plasmodium–Human
🟠 (C) Commensalism → Orchid–Mango
🔴 (D) Mutualism → Crow–Cuckoo
✅ Answer: (D) Mutualism → Crow–Cuckoo
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q48. A stable population with equal birth and death rate shows which age pyramid?
🔵 (A) Triangular
🟢 (B) Bell-shaped
🟠 (C) Urn-shaped
🔴 (D) Inverted
✅ Answer: (B) Bell-shaped
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q49. Which of the following best explains amensalism?
🔵 (A) One benefits, other harmed
🟢 (B) Both benefit
🟠 (C) One unaffected, other harmed
🔴 (D) Both harmed
✅ Answer: (C) One unaffected, other harmed
Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q50. Which of the following is a K-strategy feature?
🔵 (A) Large number of offspring, little parental care
🟢 (B) Small size, short life span
🟠 (C) Late maturity, high parental care
🔴 (D) Early maturity, rapid reproduction
✅ Answer: (C) Late maturity, high parental care
Year: PMT 1998
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20 (NEET-Level, Moderate Difficulty)
🔹 Q1. Which is the most significant ecological factor controlling distribution of organisms?
🔵 (A) Light
🟢 (B) Temperature
🟠 (C) Soil type
🔴 (D) Rainfall
✅ Answer: (B) Temperature
🔹 Q2. Which group belongs to conformers?
🔵 (A) Mammals
🟢 (B) Birds
🟠 (C) Reptiles
🔴 (D) Humans
✅ Answer: (C) Reptiles
🔹 Q3. Which interaction describes orchid on mango tree?
🔵 (A) Commensalism
🟢 (B) Parasitism
🟠 (C) Mutualism
🔴 (D) Competition
✅ Answer: (A) Commensalism
🔹 Q4. Which is an adaptation in desert plants?
🔵 (A) Broad leaves
🟢 (B) CAM photosynthesis
🟠 (C) Thin cuticle
🔴 (D) Shallow roots
✅ Answer: (B) CAM photosynthesis
🔹 Q5. Which population growth curve is more realistic?
🔵 (A) J-shaped
🟢 (B) S-shaped
🟠 (C) Bell-shaped
🔴 (D) U-shaped
✅ Answer: (B) S-shaped
🔹 Q6. A pyramid with broad base and narrow apex indicates
🔵 (A) Stable population
🟢 (B) Declining population
🟠 (C) Expanding population
🔴 (D) Zero growth population
✅ Answer: (C) Expanding population
🔹 Q7. Which is not a population attribute?
🔵 (A) Sex ratio
🟢 (B) Birth rate
🟠 (C) Age distribution
🔴 (D) Height of individual
✅ Answer: (D) Height of individual
🔹 Q8. In logistic growth, population stabilises when
🔵 (A) N = 0
🟢 (B) N = K
🟠 (C) N = K/2
🔴 (D) N = r
✅ Answer: (B) N = K
🔹 Q9. Which of the following represents parasitism?
🔵 (A) Lichen
🟢 (B) Plasmodium in human
🟠 (C) Orchid on mango
🔴 (D) Barnacle on whale
✅ Answer: (B) Plasmodium in human
🔹 Q10. Which one is density-independent factor?
🔵 (A) Predation
🟢 (B) Parasitism
🟠 (C) Competition
🔴 (D) Flood
✅ Answer: (D) Flood
🔹 Q11. In predation, the predator is
🔵 (A) Harmed
🟢 (B) Benefited
🟠 (C) Unaffected
🔴 (D) Neutral
✅ Answer: (B) Benefited
🔹 Q12. Which of the following is not a regulator?
🔵 (A) Birds
🟢 (B) Mammals
🟠 (C) Amphibians
🔴 (D) Humans
✅ Answer: (C) Amphibians
🔹 Q13. The principle stating that two species competing for the same resource cannot coexist indefinitely is
🔵 (A) Resource partitioning
🟢 (B) Competitive exclusion principle
🟠 (C) Law of tolerance
🔴 (D) Allen’s rule
✅ Answer: (B) Competitive exclusion principle
🔹 Q14. Carrying capacity (K) of a population means
🔵 (A) Minimum population size
🟢 (B) Maximum population size supported by environment
🟠 (C) Maximum growth rate
🔴 (D) Zero population growth
✅ Answer: (B) Maximum population size supported by environment
🔹 Q15. In logistic growth, growth rate is maximum when
🔵 (A) N = 0
🟢 (B) N = K
🟠 (C) N = K/2
🔴 (D) N = 2K
✅ Answer: (C) N = K/2
🔹 Q16. A survivorship curve with high death rate in early stages is
🔵 (A) Type I
🟢 (B) Type II
🟠 (C) Type III
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (C) Type III
🔹 Q17. An example of mutualism is
🔵 (A) Orchid on mango
🟢 (B) Koel in crow’s nest
🟠 (C) Lichen
🔴 (D) Penicillium secreting antibiotics
✅ Answer: (C) Lichen
🔹 Q18. Which is an example of amensalism?
🔵 (A) Penicillium killing bacteria
🟢 (B) Orchid on mango
🟠 (C) Algae and fungi
🔴 (D) Tiger and deer
✅ Answer: (A) Penicillium killing bacteria
🔹 Q19. Allen’s rule is related to
🔵 (A) Body colour in different climates
🟢 (B) Extremity size in cold vs warm regions
🟠 (C) Reproductive strategy
🔴 (D) Population density
✅ Answer: (B) Extremity size in cold vs warm regions
🔹 Q20. Which of the following is a r-strategist?
🔵 (A) Elephant
🟢 (B) Rodent
🟠 (C) Human
🔴 (D) Tiger
✅ Answer: (B) Rodent
🔵 Q21–Q25 (NEET-Level, More Challenging)
🔹 Q21. In logistic growth, initial slow growth is due to
🔵 (A) Abundant resources
🟢 (B) Lag phase
🟠 (C) Maximum growth rate
🔴 (D) K = N
✅ Answer: (B) Lag phase
🔹 Q22. Which interaction shows both species harmed?
🔵 (A) Competition
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Commensalism
🔴 (D) Predation
✅ Answer: (A) Competition
🔹 Q23. In high altitude areas, people show increase in
🔵 (A) WBC count
🟢 (B) RBC count and haemoglobin
🟠 (C) Platelets
🔴 (D) Plasma volume
✅ Answer: (B) RBC count and haemoglobin
🔹 Q24. Which pyramid represents a stable population?
🔵 (A) Triangular
🟢 (B) Bell-shaped
🟠 (C) Urn-shaped
🔴 (D) Inverted
✅ Answer: (B) Bell-shaped
🔹 Q25. Which of the following is density-dependent?
🔵 (A) Earthquake
🟢 (B) Flood
🟠 (C) Parasitism
🔴 (D) Temperature
✅ Answer: (C) Parasitism
🔵 Q26–Q40 (NEET-Level, Enhanced Difficulty)
🔹 Q26. Which curve best represents population growth in a resource-limited environment?
🔵 (A) J-shaped
🟢 (B) S-shaped
🟠 (C) Bell-shaped
🔴 (D) U-shaped
✅ Answer: (B) S-shaped
🔹 Q27. Which of the following is not a density-dependent factor?
🔵 (A) Predation
🟢 (B) Competition
🟠 (C) Flood
🔴 (D) Parasitism
✅ Answer: (C) Flood
🔹 Q28. Which ecological principle explains the elimination of one species by another due to competition?
🔵 (A) Allen’s rule
🟢 (B) Bergmann’s rule
🟠 (C) Competitive exclusion principle
🔴 (D) Resource partitioning
✅ Answer: (C) Competitive exclusion principle
🔹 Q29. Which of the following interactions is positive for one and neutral for the other?
🔵 (A) Commensalism
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Parasitism
🔴 (D) Competition
✅ Answer: (A) Commensalism
🔹 Q30. A population that has more individuals in pre-reproductive age than in reproductive age is
🔵 (A) Stable
🟢 (B) Expanding
🟠 (C) Declining
🔴 (D) Zero growth
✅ Answer: (B) Expanding
🔹 Q31. Which survivorship curve represents constant death rate across all ages?
🔵 (A) Type I
🟢 (B) Type II
🟠 (C) Type III
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (B) Type II
🔹 Q32. If N = 1000, r = 0.1, K = 2000, then logistic growth rate (dN/dt) is
🔵 (A) 50
🟢 (B) 100
🟠 (C) 200
🔴 (D) 400
✅ Answer: (B) 100
🔹 Q33. Which is a K-selected species?
🔵 (A) Bacteria
🟢 (B) Human
🟠 (C) Weeds
🔴 (D) Insects
✅ Answer: (B) Human
🔹 Q34. Which is an r-selected species?
🔵 (A) Elephant
🟢 (B) Oak tree
🟠 (C) Rodent
🔴 (D) Human
✅ Answer: (C) Rodent
🔹 Q35. Which of the following shows brood parasitism?
🔵 (A) Crow and Koel
🟢 (B) Deer and Tiger
🟠 (C) Barnacle and Whale
🔴 (D) Penicillium and Bacteria
✅ Answer: (A) Crow and Koel
🔹 Q36. Which is a correct pair of regulator and conformer?
🔵 (A) Mammal–Regulator, Fish–Conformer
🟢 (B) Reptile–Regulator, Bird–Conformer
🟠 (C) Both regulators
🔴 (D) Both conformers
✅ Answer: (A) Mammal–Regulator, Fish–Conformer
🔹 Q37. Which ecological rule explains darker pigmentation in animals of humid regions?
🔵 (A) Allen’s rule
🟢 (B) Bergmann’s rule
🟠 (C) Gloger’s rule
🔴 (D) Jordan’s rule
✅ Answer: (C) Gloger’s rule
🔹 Q38. The equation dN/dt = rN represents
🔵 (A) Logistic growth
🟢 (B) Exponential growth
🟠 (C) Declining population
🔴 (D) Zero growth
✅ Answer: (B) Exponential growth
🔹 Q39. Which interaction is represented by Acacia and ants?
🔵 (A) Commensalism
🟢 (B) Parasitism
🟠 (C) Mutualism
🔴 (D) Competition
✅ Answer: (C) Mutualism
🔹 Q40. Which is the correct sequence of ecological levels of organisation?
🔵 (A) Population → Organism → Community → Ecosystem
🟢 (B) Organism → Population → Community → Ecosystem
🟠 (C) Community → Population → Ecosystem → Organism
🔴 (D) Ecosystem → Organism → Community → Population
✅ Answer: (B) Organism → Population → Community → Ecosystem
🔴 Q41–Q50 (NEET-Level, Higher Difficulty)
🔹 Q41. Which pyramid is always upright?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of biomass
🟢 (B) Pyramid of energy
🟠 (C) Pyramid of number
🔴 (D) Age pyramid
✅ Answer: (B) Pyramid of energy
🔹 Q42. Which is the best strategy for survival in unpredictable environments?
🔵 (A) K-strategy
🟢 (B) r-strategy
🟠 (C) Both strategies
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (B) r-strategy
🔹 Q43. A species restricted to narrow salinity tolerance is
🔵 (A) Euryhaline
🟢 (B) Stenohaline
🟠 (C) Stenothermal
🔴 (D) Eurythermal
✅ Answer: (B) Stenohaline
🔹 Q44. Which age pyramid represents declining population?
🔵 (A) Triangular
🟢 (B) Bell-shaped
🟠 (C) Urn-shaped
🔴 (D) Inverted
✅ Answer: (C) Urn-shaped
🔹 Q45. Which type of interaction is Penicillium secreting antibiotics against bacteria?
🔵 (A) Amensalism
🟢 (B) Mutualism
🟠 (C) Parasitism
🔴 (D) Competition
✅ Answer: (A) Amensalism
🔹 Q46. Which is an example of migration as a response to environment?
🔵 (A) Hibernation in bears
🟢 (B) Birds flying to warmer regions in winter
🟠 (C) CAM pathway in plants
🔴 (D) Spore formation in microbes
✅ Answer: (B) Birds flying to warmer regions in winter
🔹 Q47. Which survivorship curve is typical for oysters?
🔵 (A) Type I
🟢 (B) Type II
🟠 (C) Type III
🔴 (D) Type IV
✅ Answer: (C) Type III
🔹 Q48. Which factor is most critical for plants in aquatic environments?
🔵 (A) Temperature
🟢 (B) Light penetration
🟠 (C) Soil type
🔴 (D) Humidity
✅ Answer: (B) Light penetration
🔹 Q49. A stable population shows which age pyramid?
🔵 (A) Triangular
🟢 (B) Bell-shaped
🟠 (C) Urn-shaped
🔴 (D) Rectangular
✅ Answer: (B) Bell-shaped
🔹 Q50. Which of the following shows both benefit?
🔵 (A) Commensalism
🟢 (B) Parasitism
🟠 (C) Mutualism
🔴 (D) Amensalism
✅ Answer: (C) Mutualism
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
