Class 11 : Chemistry (In English) – Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
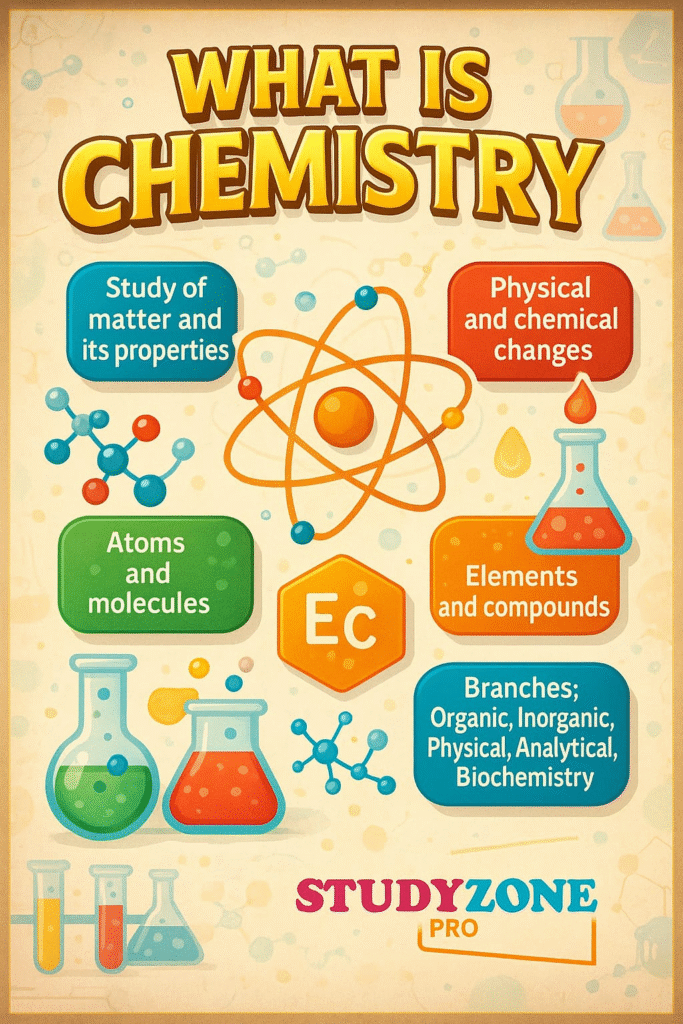
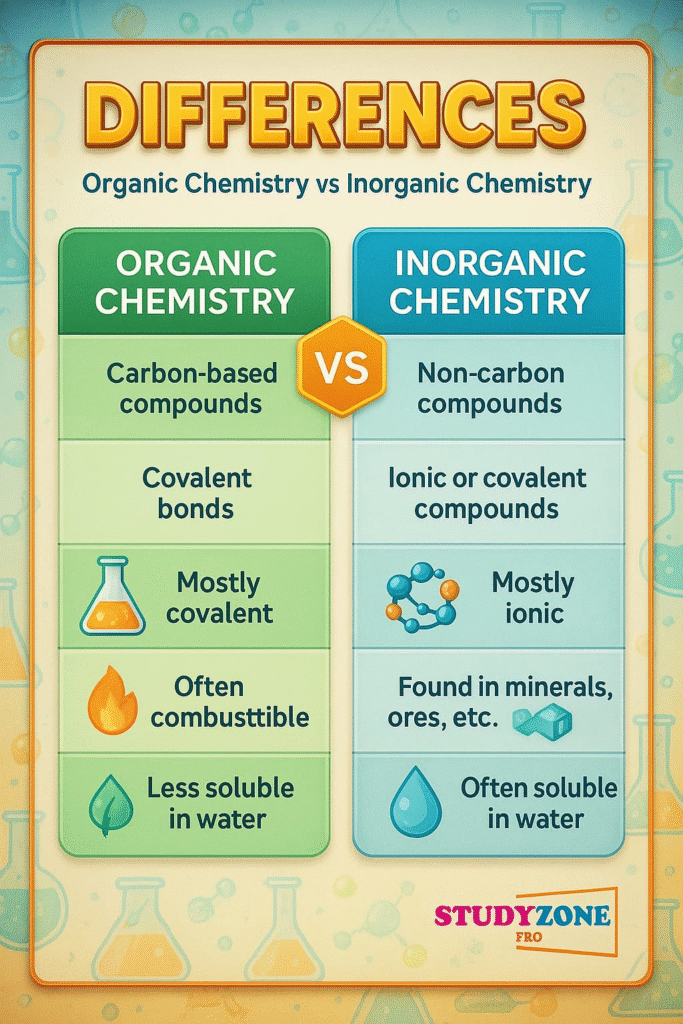
📌 1. Importance of Chemistry
Question: Why do we study chemistry?
Answer:
Chemistry helps us understand the composition, structure, and transformations of matter.
It plays a crucial role in diverse fields like medicine, agriculture, food production, material science, and environmental studies.
Chemistry contributes to national growth through industrial and technological development.
New materials, fuels, polymers, fertilizers, and life-saving drugs are all products of chemistry.
📌 2. Nature of Matter
Key Points:
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
It can exist in three physical states: solid, liquid, and gas.
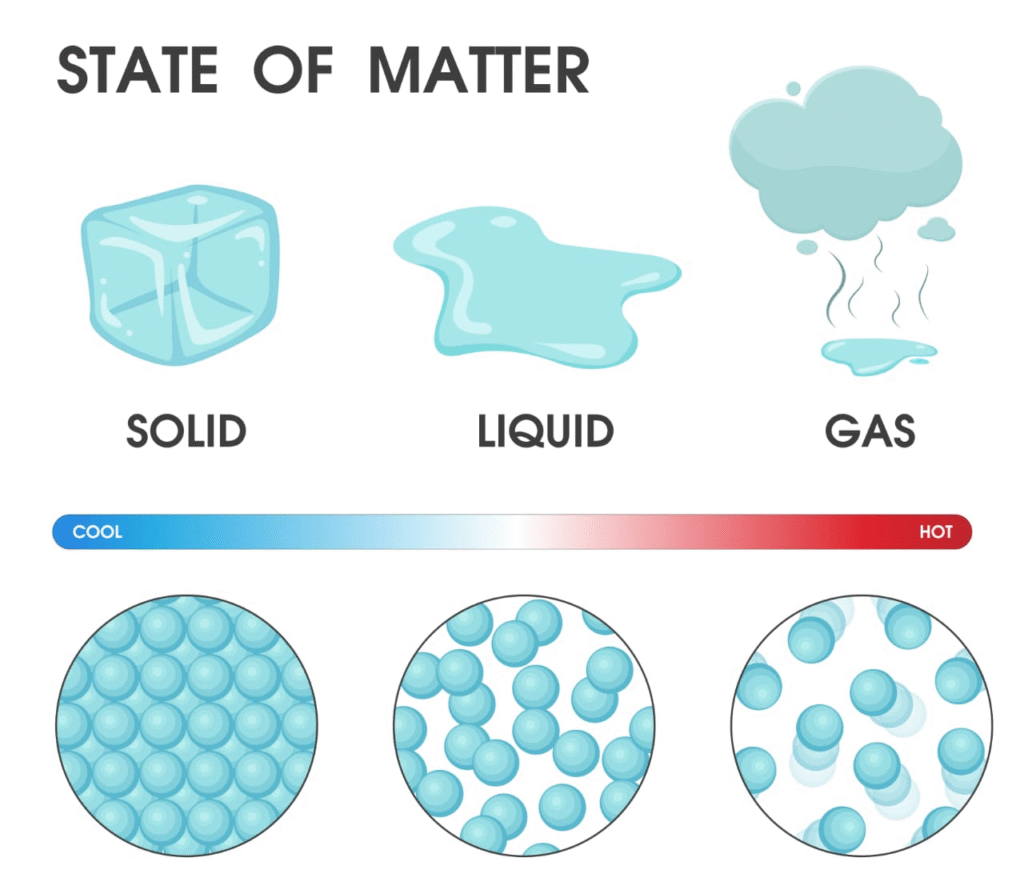
It can be classified chemically into:
Pure substances: Elements and compounds
Mixtures: Homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures
Examples:
– Gold is an element (pure substance)
– Air is a homogeneous mixture
– Sand and iron filings is a heterogeneous mixture
📌 3. Properties of Matter and Their Measurement
Types of Properties:
Physical properties – Observable without changing composition (e.g., boiling point, density)
Chemical properties – Observed when substance changes into another (e.g., rusting of iron)
Units of Measurement:
Use of SI Units (International System)
Base Units: Mass (kg), Length (m), Time (s), Temperature (K), Amount of substance (mol), etc.
Derived Units:
Volume (m³), Density (kg/m³), etc.
Significant Figures & Scientific Notation:
Significant figures reflect precision in measurement
Scientific notation simplifies writing very large/small numbers
Example: 0.00032 = 3.2 × 10⁻⁴
📌 4. Uncertainty in Measurement
Accuracy refers to closeness to the actual value.
Precision refers to how close repeated values are to each other.
Errors in Measurement:
Systematic Errors – Have definite causes and follow a pattern
Random Errors – Occur due to chance, unpredictable
Calculation Rules for Significant Figures:
In addition/subtraction: Least decimal places rule
In multiplication/division: Least significant figures rule
📌 5. Laws of Chemical Combinations
These laws describe how substances react:
🧪 1. Law of Conservation of Mass
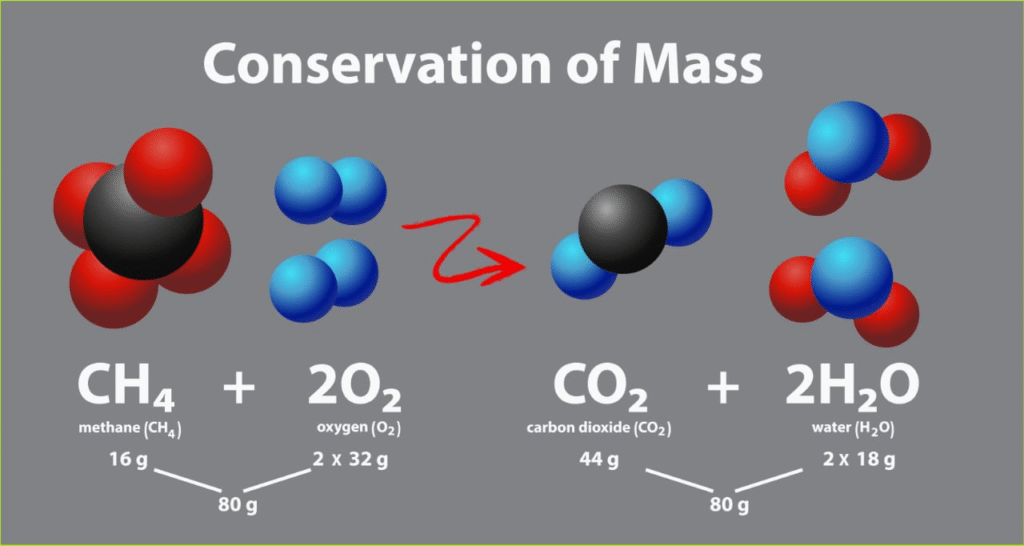
“Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.”
Total mass before reaction = Total mass after reaction
🧪 2. Law of Definite Proportions
A chemical compound always contains its elements in a fixed ratio by mass.
🧪 3. Law of Multiple Proportions
If two elements combine to form more than one compound, the ratio of masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other is a simple whole number.
🧪 4. Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes
Gases react in simple whole number ratios by volume at constant temperature and pressure.
🧪 5. Avogadro’s Law
Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
📌 6. Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Postulates:
All matter is made up of atoms
Atoms are indivisible and indestructible
Atoms of same element are identical in mass and properties
Atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds
In chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged, not created/destroyed
📌 7. Atomic and Molecular Masses
🧮 Atomic Mass
Relative atomic mass = Mass of one atom compared to 1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
Example: Atomic mass of hydrogen = 1.008 u
🧮 Molecular Mass
Sum of atomic masses in a molecule
Example: H₂O → 2×1.008 + 16 = 18.016 u
📌 8. Mole Concept and Molar Mass
🧪 1 mole = 6.022 × 10²³ particles (Avogadro Number)
Can be atoms, ions, molecules, etc.
🧮 Molar Mass = Mass of 1 mole of a substance
Expressed in g/mol
Example: Molar mass of H₂O = 18.016 g/mol
Conversions using mole:
Moles = Given mass / Molar mass
Moles = Number of particles / Avogadro’s number
Moles = Volume of gas at STP / 22.4 L
📌 9. Percentage Composition
Formula:
% of element = (Mass of element / Molar mass of compound) × 100
Example:
In H₂O:
% H = (2 × 1) / 18 × 100 = 11.1%
% O = (16) / 18 × 100 = 88.9%
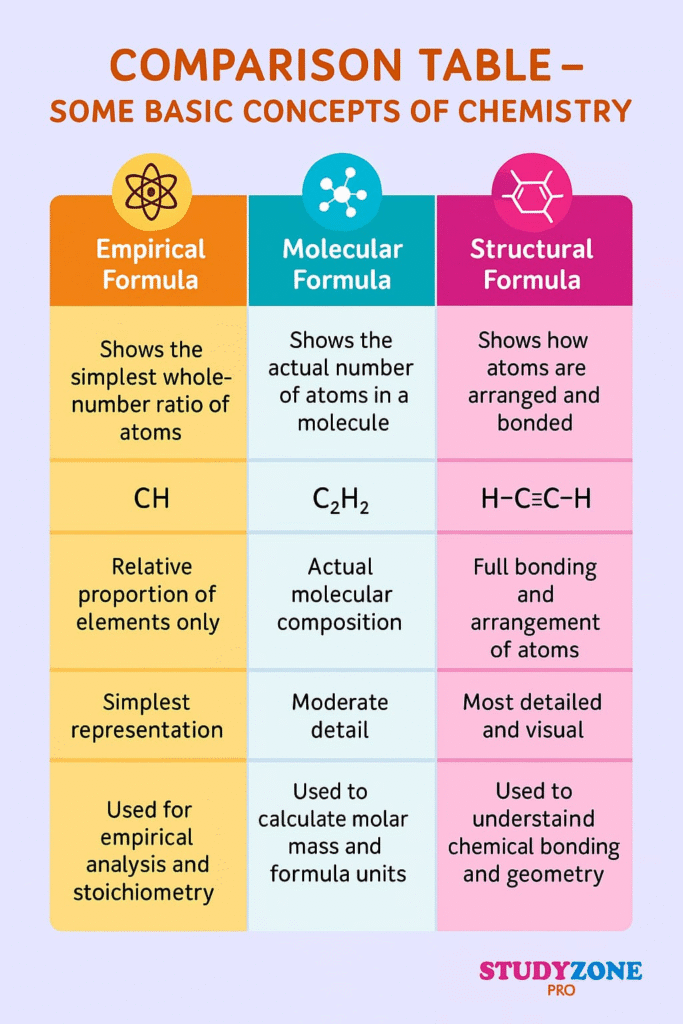
📌 10. Empirical and Molecular Formula
🧪 Empirical Formula – Simplest whole-number ratio of atoms
🧪 Molecular Formula – Actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule
Steps to Find Empirical Formula:
Convert % to grams
Convert grams to moles (divide by atomic mass)
Divide all moles by the smallest mole value
Round to nearest whole number
Molecular Formula = Empirical Formula × n, where
n = Molar mass / Empirical formula mass
📌 11. Stoichiometry and Calculations Based on Chemical Equations
Stoichiometry = Quantitative study of reactants and products
Balanced Equation Example:
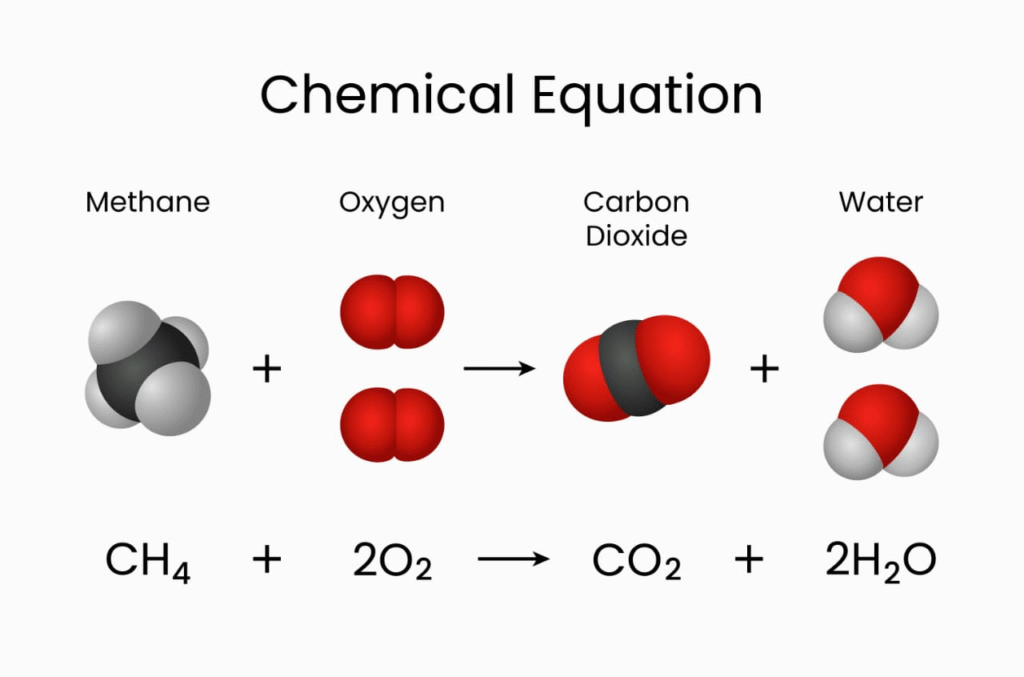
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
From the above:
1 mole CH₄ reacts with 2 moles O₂
Produces 1 mole CO₂ and 2 moles H₂O
Use mole ratios to solve:
Mass → Moles → Mole ratio → Moles → Mass
📌 12. Limiting Reagent
In a chemical reaction, the limiting reagent is the one that gets used up first, thus limiting the amount of product formed.
Steps:
Calculate moles of all reactants
Determine which reactant produces the least product → that’s the limiting reagent
📌 13. Reactions in Solutions: Molarity and Concentration
Molarity (M) = Moles of solute / Volume of solution (in L)
Other terms:
Molality = Moles of solute / Mass of solvent (kg)
Normality = Equivalents of solute / Volume of solution (L)
Mole fraction = Moles of component / Total moles
📌 14. Percent Yield
In reactions:
Theoretical Yield = Maximum calculated yield
Actual Yield = What you get practically
% Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100
✅ Summary (≈300 words)
This chapter lays the foundation for chemistry by introducing essential concepts such as the classification of matter, measurement of properties, and the laws governing chemical reactions. It starts by explaining the significance of chemistry in everyday life and its wide-ranging applications.
Matter is classified physically into solids, liquids, and gases, and chemically into pure substances and mixtures. Properties are measured using SI units, and the concepts of accuracy, precision, and error in measurements are explored using significant figures and scientific notation.
The chapter covers important chemical laws such as the Law of Conservation of Mass, Definite and Multiple Proportions, Gay Lussac’s Law, and Avogadro’s Law. Dalton’s Atomic Theory is presented as the historical basis for understanding atoms.
Atomic and molecular masses are defined and calculated, followed by an explanation of the mole concept and molar mass. Students learn how to convert between mass, number of particles, and volume using the mole.
Percentage composition and empirical/molecular formulas are explained with step-by-step methods. Stoichiometry is introduced to connect chemical equations to quantitative calculations. The concept of limiting reagent is used to predict product formation in reactions.
The chapter ends with discussions on solution concentrations such as molarity, molality, and mole fraction, and the calculation of percent yield based on theoretical and actual outcomes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1.1
Calculate the molar mass of the following:
(i) H₂O (ii) CO₂ (iii) CH₄
🟢 Answer 1.1
(i) H₂O
→ Atomic mass of H = 1.008 u, O = 16.00 u
→ Molar mass = 2 × 1.008 + 16.00 = 18.016 g/mol
(ii) CO₂
→ C = 12.01 u, O = 16.00 u
→ Molar mass = 12.01 + 2 × 16.00 = 44.01 g/mol
(iii) CH₄
→ C = 12.01 u, H = 1.008 u
→ Molar mass = 12.01 + 4 × 1.008 = 16.042 g/mol
🔵 Question 1.2
Calculate the mass percent of different elements present in sodium sulphate (Na₂SO₄).
🟢 Answer 1.2
Molar mass of Na₂SO₄ = 2×23 + 32 + 4×16 = 142 g/mol
% Na = (46 / 142) × 100 = 32.39%
% S = (32 / 142) × 100 = 22.54%
% O = (64 / 142) × 100 = 45.07%
🔵 Question 1.3
Determine the empirical formula of an oxide of iron, which has 69.9% iron and 30.1% dioxygen by mass.
🟢 Answer 1.3
Step 1: Assume 100 g sample: Fe = 69.9 g, O = 30.1 g
Step 2: Moles of Fe = 69.9 / 55.85 ≈ 1.251
Moles of O = 30.1 / 16.00 ≈ 1.881
Step 3: Ratio: Fe:O = 1.251:1.881 ≈ 2:3
Empirical formula = Fe₂O₃
🔵 Question 1.4
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when
(i) 1 mole of carbon is burnt in air
(ii) 1 mole of carbon is burnt in 16 g of dioxygen
(iii) 2 moles of carbon are burnt in 16 g of dioxygen
🟢 Answer 1.4
Balanced reaction: C + O₂ → CO₂
(i) 1 mol C + 1 mol O₂ → 1 mol CO₂
→ 1 mol CO₂ = 44 g produced
(ii) 16 g O₂ = 1 mol
→ With 1 mol C → 44 g CO₂
(iii) 16 g O₂ = 1 mol, but 2 mol C
→ O₂ is limiting
→ 1 mol C reacts → 44 g CO₂
🔵 Question 1.5
Calculate the mass of sodium acetate (CH₃COONa) required to make 500 mL of 0.375 molar aqueous solution.
(Molar mass of CH₃COONa = 82.0245 g mol⁻¹)
🟢 Answer 1.5
Moles = Molarity × Volume (L) = 0.375 × 0.5 = 0.1875 mol
Mass = Moles × Molar mass = 0.1875 × 82.0245 = 15.38 g
🔵 Question 1.6
Calculate the concentration of nitric acid in moles per litre in a sample which has a density 1.41 g mL⁻¹ and mass % of HNO₃ = 69%.
🟢 Answer 1.6
In 1000 mL: mass = 1.41 × 1000 = 1410 g
Mass of HNO₃ = 69% of 1410 = 972.9 g
Molar mass of HNO₃ = 63 g/mol
Moles = 972.9 / 63 ≈ 15.44 mol
Molarity = 15.44 M
🔵 Question 1.7
How much copper can be obtained from 100 g of copper sulphate (CuSO₄)?
🟢 Answer 1.7
Molar mass CuSO₄ = 63.5 + 32 + 4×16 = 159.5 g/mol
% Cu = (63.5 / 159.5) × 100 ≈ 39.81%
Mass of Cu = 39.81% of 100 = 39.81 g
🔵 Question 1.8
Determine the molecular formula of an oxide of iron, in which the mass % of iron and oxygen are 69.9 and 30.1 respectively.
🟢 Answer 1.8
Same as Q1.3
Fe = 69.9 g → 1.251 mol
O = 30.1 g → 1.881 mol
Ratio ≈ 2:3
Empirical formula = Fe₂O₃,
Empirical mass = 2×55.85 + 3×16 = 159.7 g/mol
Molecular formula = Fe₂O₃
🔵 Question 1.9
Calculate the atomic mass (average) of chlorine using the following data:
35Cl (75.77%, 34.9689 u),
37Cl (24.23%, 36.9659 u)
🟢 Answer 1.9
Average atomic mass =
(75.77×34.9689 + 24.23×36.9659)/100
= (2650.18 + 895.87)/100 = 35.544 u
🔵 Question 1.10
In three moles of ethane (C₂H₆), calculate the following:
(i) Number of moles of carbon atoms
(ii) Number of moles of hydrogen atoms
(iii) Number of molecules of ethane
🟢 Answer 1.10
(i) 1 mol C₂H₆ → 2 mol C
→ 3 mol C₂H₆ → 3×2 = 6 mol C
(ii) 1 mol C₂H₆ → 6 mol H
→ 3 mol C₂H₆ → 3×6 = 18 mol H
(iii) 1 mol = 6.022×10²³ molecules
→ 3 mol = 1.807 × 10²⁴ molecules
🔵 Question 1.11
What is the concentration of sugar (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁) in mol L⁻¹ if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2 L?
🟢 Answer 1.11
Molar mass of C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ = (12×12.01 + 22×1.008 + 11×16) = 342.3 g/mol
Moles of sugar = 20 / 342.3 = 0.05844 mol
Molarity = Moles / Volume = 0.05844 / 2 = 0.0292 mol/L
🔵 Question 1.12
If the density of methanol is 0.793 kg L⁻¹, what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
🟢 Answer 1.12
Molar mass of CH₃OH = 32.04 g/mol
Moles required = 0.25 × 2.5 = 0.625 mol
Mass = 0.625 × 32.04 = 20.025 g
Density = 0.793 g/mL = 0.793 kg/L
Volume = Mass / Density = 20.025 / 0.793 = 25.25 mL or 0.02525 L
🔵 Question 1.13
Pressure is determined as force per unit area of the surface. The SI unit of pressure, pascal is shown below:
1 Pa = 1 N m⁻²
If mass of air at sea level is 1034 g cm⁻², calculate the pressure in pascal.
🟢 Answer 1.13
Force = mass × g = 1034 g = 1.034 kg × 9.8 = 10.1332 N
Area = 1 cm² = 1 × 10⁻⁴ m²
Pressure = Force / Area = 10.1332 / 1×10⁻⁴ = 1.013 × 10⁵ Pa
🔵 Question 1.14
What is the SI unit of mass? How is it defined?
🟢 Answer 1.14
The SI unit of mass is kilogram (kg).
It is defined by fixing the value of Planck’s constant h = 6.62607015 × 10⁻³⁴ Js, and using a defined meter and second.
🔵 Question 1.15
Match the following prefixes with their multiples:
(i) micro 10⁻⁶
(ii) deca 10¹
(iii) mega 10⁶
(iv) giga 10⁹
(v) femto 10⁻¹⁵
🟢 Answer 1.15
(i) micro → 10⁻⁶
(ii) deca → 10¹
(iii) mega → 10⁶
(iv) giga → 10⁹
(v) femto → 10⁻¹⁵
✅ Correctly matched
🔵 Question 1.16
What do you mean by significant figures?
🟢 Answer 1.16
Significant figures are the digits in a number that carry meaningful information about its precision.
They include:
✔️ All non-zero digits
✔️ Zeros between significant digits
✔️ Trailing zeros in decimal numbers
They indicate the certainty in measurement.
🔵 Question 1.17
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform, CHCl₃, supposed to be carcinogenic in nature. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass).
(i) Express this in per cent by mass.
(ii) Determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
🟢 Answer 1.17
(i) 1 ppm = 1 part in 10⁶
15 ppm = 15 / 10⁶ = 1.5 × 10⁻³ %
(ii) Assume 1 kg water → mass of CHCl₃ = 15 mg = 0.015 g
Molar mass CHCl₃ = 12 + 1 + 3×35.5 = 119.5 g/mol
Moles = 0.015 / 119.5 = 1.26 × 10⁻⁴ mol
Molality = moles / mass of solvent (kg) = 1.26 × 10⁻⁴ mol/kg
🔵 Question 1.18
Express the following in the scientific notation:
(i) 0.0048 (ii) 234,000 (iii) 8008 (iv) 500.0 (v) 6.0012
🟢 Answer 1.18
(i) 4.8 × 10⁻³
(ii) 2.34 × 10⁵
(iii) 8.008 × 10³
(iv) 5.000 × 10²
(v) 6.0012 × 10⁰
🔵 Question 1.19
How many significant figures are present in the following:
(i) 0.0025 (ii) 208 (iii) 5005 (iv) 126,000 (v) 500.0 (vi) 2.0034
🟢 Answer 1.19
(i) 2
(ii) 3
(iii) 4
(iv) 3 (trailing zeros not significant unless decimal is shown)
(v) 4 (trailing zero after decimal is significant)
(vi) 5
🔵 Question 1.20
Round up the following up to three significant figures:
(i) 34.216 (ii) 10.4107 (iii) 0.04597 (iv) 2808
🟢 Answer 1.20
(i) 34.2
(ii) 10.4
(iii) 0.0460
(iv) 2810
🔵 Question 1.21
The following data are obtained when dinitrogen and dioxygen react together to form different compounds:
Mass of dinitrogen Mass of dioxygen
14 g 16 g
14 g 32 g
28 g 32 g
28 g 80 g
(a) Which law of chemical combination is obeyed by the above experimental data? Give its statement.
(b) Fill in the blanks in the following conversions:
(i) 1 km = ………. mm = ………. pm
(ii) 1 mg = ………. kg = ………. ng
(iii) 1 mL = ………. L = ………. dm³
🟢 Answer 1.21
(a) Law of Multiple Proportions
▶ Statement: When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in simple whole number ratios.
✔ Here, for 14 g N: O = 16 g, 32 g → 1:2
✔ For 28 g N: O = 32 g, 80 g → 4:10 → 2:5
(b)
(i) 1 km = 1,000,000 mm = 1 × 10¹⁵ pm
(ii) 1 mg = 1 × 10⁻⁶ kg = 1 × 10⁶ ng
(iii) 1 mL = 1 × 10⁻³ L = 1 × 10⁻³ dm³
🔵 Question 1.22
If the speed of light is 3.0 × 10⁸ m s⁻¹, calculate the distance covered by light in 2.00 ns.
🟢 Answer 1.22
Time = 2.00 ns = 2.00 × 10⁻⁹ s
Speed = 3.0 × 10⁸ m/s
Distance = Speed × Time
= (3.0 × 10⁸) × (2.00 × 10⁻⁹)
= 0.60 m
🔵 Question 1.23
In a reaction:
A + B₂ → AB₂
Identify the limiting reagent, if any, in the following mixtures:
(i) 300 atoms of A + 200 molecules of B
(ii) 2 mol A + 3 mol B
(iii) 100 atoms of A + 100 molecules of B
(iv) 5 mol A + 2.5 mol B
(v) 2.5 mol A + 5 mol B
🟢 Answer 1.23
Balanced reaction: 1 A + 1 B₂ → 1 AB₂
→ Mole ratio = A : B = 1:1
(i) 300 A : 200 B ⇒ B is limiting
(ii) 2 A : 3 B ⇒ A is limiting
(iii) 100 A : 100 B ⇒ No limiting reagent
(iv) 5 A : 2.5 B ⇒ Ratio 2:1 ⇒ B is limiting
(v) 2.5 A : 5 B ⇒ Ratio 1:2 ⇒ A is limiting
🔵 Question 1.24
Dinitrogen and dihydrogen react with each other to produce ammonia:
N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g)
(i) Calculate the mass of ammonia produced if 2.00 × 10³ g of dinitrogen reacts with 1.00 × 10³ g of dihydrogen.
(ii) Will any of the reactants remain unreacted?
(iii) If yes, which one and what would be its mass?
🟢 Answer 1.24
(i) Molar mass N₂ = 28 g, H₂ = 2 g, NH₃ = 17 g
Moles of N₂ = 2000 / 28 ≈ 71.43
Moles of H₂ = 1000 / 2 = 500
From balanced reaction: 1 mol N₂ reacts with 3 mol H₂
Required H₂ = 71.43 × 3 = 214.29 mol
Available H₂ = 500 mol → Excess
So N₂ is limiting
NH₃ produced = 2 × 71.43 = 142.86 mol
Mass = 142.86 × 17 = 2428.57 g
(ii) Yes, hydrogen remains unreacted
(iii) Used H₂ = 214.29 mol = 428.58 g
Unreacted = 1000 – 428.58 = 571.42 g
🔵 Question 1.25
How are 0.50 mol Na₂CO₃ and 0.50 M Na₂CO₃ different?
🟢 Answer 1.25
0.50 mol Na₂CO₃ means amount of substance
0.50 M Na₂CO₃ means concentration: 0.50 mol in 1 L solution
✔ So first is fixed quantity; second is per unit volume
🔵 Question 1.26
If 10 volumes of dihydrogen gas reacts with five volumes of dioxygen gas, how many volumes of water vapour would be produced?
🟢 Answer 1.26
Reaction: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Mole ratio: 2:1 → 2
Volume ratio = 10:5 ⇒ H₂:O₂
✔ Matches 2:1
Product = 10 volumes of H₂ → 10 volumes of H₂O
🔵 Question 1.27
Convert the following into basic units:
(i) 28.7 pm (ii) 15.15 pm (iii) 25365 mg
🟢 Answer 1.27
(i) 28.7 pm = 28.7 × 10⁻¹² m = 2.87 × 10⁻¹¹ m
(ii) 15.15 pm = 1.515 × 10⁻¹¹ m
(iii) 25365 mg = 25.365 g = 0.025365 kg
🔵 Question 1.28
Which one of the following will have the largest number of atoms?
(i) 1 g Au (ii) 1 g Na (iii) 1 g Li (iv) 1 g Cl₂
🟢 Answer 1.28
Atoms = Mass / Molar mass × Avogadro’s number
✔ Smaller molar mass → more atoms
→ Li (M = 6.94) gives maximum atoms
✅ Answer: (iii) 1 g Li
🔵 Question 1.29
Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water, in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.040 (assume the density of water to be one).
🟢 Answer 1.29
Mole fraction = n₁ / (n₁ + n₂)
Assume water = 1 kg = 1000 g = 55.56 mol
Let n₁ = ethanol = 0.040 × (n₁ + 55.56)
Solve: n₁ ≈ 2.31 mol
Volume = 1 L → Molarity = 2.31 M
🔵 Question 1.30
What will be the mass of one ¹²C atom in g?
🟢 Answer 1.30
1 mol ¹²C atoms = 12 g
Number of atoms in 1 mol = 6.022×10²³
Mass of one atom = 12 / 6.022×10²³ = 1.993 × 10⁻²³ g
🔵 Question 1.31
How many significant figures should be present in the answer of the following calculations?
(i) 0.02856 × 298.15 × 0.112
(ii) 5 × 5.364
(iii) 0.0125 + 0.7864 + 0.0215
🟢 Answer 1.31
(i) Least significant figures = 3 (from 0.112)
→ Final answer must have 3 significant figures
(ii) 5 has 1 significant figure, 5.364 has 4
→ Answer must have 1 significant figure
(iii) Addition: least decimal places = 4 (all have 4)
→ Final answer must have 4 decimal places
🔵 Question 1.32
Use the data given in the following table to calculate the molar mass of naturally occurring argon isotopes:
Isotope Isotopic molar mass Abundance
³⁶Ar 35.96755 g mol⁻¹ 0.337%
³⁸Ar 37.96272 g mol⁻¹ 0.063%
⁴⁰Ar 39.9624 g mol⁻¹ 99.600%
🟢 Answer 1.32
Molar mass =
(35.96755×0.337 + 37.96272×0.063 + 39.9624×99.6) / 100
= (12.124 + 2.392 + 3976.6) / 100
= 3991.116 / 100 = 39.911 g/mol
🔵 Question 1.33
Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following:
(i) 52 mol of Ar (ii) 52 u of He (iii) 52 g of He
🟢 Answer 1.33
(i) 52 mol Ar = 52 × 6.022×10²³ = 3.13 × 10²⁵ atoms
(ii) 52 u He = 1 atom of He = 1 atom
(iii) Molar mass of He = 4 g/mol
→ Moles = 52 / 4 = 13 mol
→ Atoms = 13 × 6.022×10²³ = 7.83 × 10²⁴ atoms
🔵 Question 1.34
A welding fuel gas contains carbon and hydrogen only.
Burning a small sample of it in oxygen gives 3.38 g CO₂, 0.690 g H₂O.
Volume = 10.0 L, mass = 11.6 g (STP)
Calculate:
(i) Empirical formula (ii) Molar mass of the gas (iii) Molecular formula
🟢 Answer 1.34
(i) Moles C = 3.38 g CO₂ → 3.38 / 44 = 0.0768 mol C
Moles H = 0.690 g H₂O → 0.690 / 18 = 0.0383 mol H₂O
→ H atoms = 0.0383 × 2 = 0.0766 mol
Ratio C:H ≈ 1:1 → Empirical formula = CH
(ii) Molar mass = Mass / Volume at STP
= 11.6 g / 10 L = 1.16 g/L
At STP, 1 mol = 22.4 L → Molar mass = 22.4 × 1.16 = 25.98 g/mol
(iii) Empirical mass = 13 (C + H)
n = 26 / 13 = 2 → Molecular formula = C₂H₂
🔵 Question 1.35
Calcium carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl₂ and CO₂:
CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + CO₂ + H₂O
What mass of CaCO₃ is required to react completely with 25 mL of 0.75 M HCl?
🟢 Answer 1.35
Moles of HCl = 0.75 × 25/1000 = 0.01875 mol
From reaction: 2 mol HCl reacts with 1 mol CaCO₃
→ Moles of CaCO₃ = 0.01875 / 2 = 0.009375 mol
Mass = 0.009375 × 100 = 0.9375 g
🔵 Question 1.36
Chlorine is prepared by treating manganese dioxide with hydrochloric acid:
4HCl + MnO₂ → 2H₂O + MnCl₂ + Cl₂
How many grams of HCl are required to react with 5.0 g of manganese dioxide?
🟢 Answer 1.36
Molar mass of MnO₂ = 54.94 + 2×16 = 86.94 g/mol
Moles = 5.0 / 86.94 ≈ 0.0575 mol
From reaction: 1 mol MnO₂ → 4 mol HCl
→ Required HCl = 0.0575 × 4 = 0.23 mol
Mass = 0.23 × 36.46 = 8.39 g
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔷 Section A: Q1 to Q18 (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1.
Which of the following is a pure substance?
(A) Milk
(B) Air
(C) Water
(D) Soil
🟢 Answer: (C) Water
🔵 Question 2.
Which of the following has the highest number of atoms?
(A) 1 g of H₂
(B) 1 g of O₂
(C) 1 g of Li
(D) 1 g of Cl₂
🟢 Answer: (C) 1 g of Li
🔵 Question 3.
SI unit of amount of substance is:
(A) Gram
(B) Mole
(C) Kilogram
(D) Liter
🟢 Answer: (B) Mole
🔵 Question 4.
What is the molar mass of CaCl₂?
(A) 75.5 g/mol
(B) 95.5 g/mol
(C) 110.98 g/mol
(D) 111.0 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (D) 111.0 g/mol
🔵 Question 5.
1 amu is equal to:
(A) 1.66 × 10⁻²³ g
(B) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
(C) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
(D) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁶ kg
🟢 Answer: (C) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
🔵 Question 6.
Which of the following obeys the Law of Multiple Proportions?
(A) H₂ and O₂
(B) CO and CO₂
(C) N₂ and NH₃
(D) NaCl and KCl
🟢 Answer: (B) CO and CO₂
🔵 Question 7.
Which prefix represents 10⁻¹⁵?
(A) micro
(B) femto
(C) nano
(D) pico
🟢 Answer: (B) femto
🔵 Question 8.
Write the number of significant figures in 500.0
🟢 Answer: 4 significant figures
🔵 Question 9.
State Avogadro’s law.
🟢 Answer:
Equal volumes of all gases under same conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
🔵 Question 10.
Define empirical formula.
🟢 Answer:
It is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound.
🔵 Question 11.
Which law of chemical combination is demonstrated by the reaction of 16 g of oxygen with 2 g of hydrogen to form 18 g of water?
🟢 Answer:
Law of Conservation of Mass
🔵 Question 12.
Give one point of difference between precision and accuracy.
🟢 Answer:
Precision refers to closeness among repeated measurements, while accuracy refers to closeness to the true value.
🔵 Question 13.
Calculate number of molecules in 1.0 g of water.
🟢 Answer:
Molar mass of H₂O = 18 g/mol
Moles = 1 / 18 = 0.0556 mol
Molecules = 0.0556 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.35 × 10²² molecules
🔵 Question 14.
Give the SI unit of molar mass.
🟢 Answer:
kg mol⁻¹ (commonly g mol⁻¹ in practice)
🔵 Question 15.
Write the molecular formula of a compound whose empirical formula is CH and molar mass is 26.
🟢 Answer:
Empirical mass = 13 → n = 26 / 13 = 2
Molecular formula = CH × 2 = C₂H₂
🔵 Question 16.
Which one is the limiting reagent when 5 mol H₂ reacts with 2 mol O₂?
🟢 Answer:
Reaction: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Mole ratio: 2:1 → 5 mol H₂ needs 2.5 mol O₂
Available = 2 mol O₂ ⇒ O₂ is limiting reagent
🔵 Question 17.
What is the mass percent of carbon in CO₂?
🟢 Answer:
Mass of carbon = 12, Molar mass = 44
% C = (12 / 44) × 100 = 27.27%
🔵 Question 18.
What is the mass of one atom of carbon-12?
🟢 Answer:
Mass = 12 / 6.022 × 10²³ = 1.993 × 10⁻²³ g
🟨 Section B: Q19 to Q23 (2 marks each)
🔵 Question 19.
Calculate the number of molecules in 5.6 litres of oxygen gas at STP.
🟢 Answer:
At STP, 1 mol gas = 22.4 L
Moles = 5.6 / 22.4 = 0.25 mol
Molecules = 0.25 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 1.506 × 10²³ molecules
🔵 Question 20.
A compound contains 92.3% carbon and 7.7% hydrogen. Its molar mass is 78 g/mol. Determine its empirical and molecular formula.
🟢 Answer:
Step 1: Assume 100 g → C = 92.3 g, H = 7.7 g
Moles:
C = 92.3 / 12.01 ≈ 7.69
H = 7.7 / 1.008 ≈ 7.65
Ratio ≈ 1:1
Empirical formula = CH
Empirical mass = 13
n = 78 / 13 = 6
Molecular formula = C₆H₆
🔵 Question 21.
Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with one example each.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Homogeneous mixture: Same composition throughout (e.g., sugar in water)
✔️ Heterogeneous mixture: Composition varies (e.g., sand in water)
🔵 Question 22.
Calculate the number of atoms present in 0.5 mol of calcium.
🟢 Answer:
Atoms = 0.5 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.011 × 10²³ atoms
🔵 Question 23.
Write the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory (any two).
🟢 Answer:
All matter consists of tiny indivisible particles called atoms.
Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties.
🟧 Section C: Q24 to Q28 (3 marks each)
🔵 Question 24.
Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 5 g of NaOH in 450 mL of solution.
(Molar mass of NaOH = 40 g/mol)
🟢 Answer:
Moles = 5 / 40 = 0.125 mol
Volume = 450 mL = 0.45 L
Molarity = 0.125 / 0.45 = 0.278 M
🔵 Question 25.
Determine the empirical formula of a compound with 40% carbon, 6.7% hydrogen, and 53.3% oxygen.
🟢 Answer:
Assume 100 g:
C = 40 g → 40 / 12.01 = 3.33 mol
H = 6.7 g → 6.7 / 1.008 = 6.65 mol
O = 53.3 g → 53.3 / 16.00 = 3.33 mol
Simplest ratio = C:H:O = 1:2:1
Empirical formula = CH₂O
🔵 Question 26.
What do you understand by limiting reagent?
Identify the limiting reagent when 6 g of Mg reacts with 6 g of HCl.
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Limiting reagent is the one that is completely consumed first in a reaction.
Moles of Mg = 6 / 24.3 ≈ 0.247
Moles of HCl = 6 / 36.46 ≈ 0.165
Required ratio = 1:2 → For 0.247 mol Mg → need 0.494 mol HCl
Available = 0.165 → So, HCl is limiting reagent
🔵 Question 27.
Explain the law of definite proportions with one example.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ A given compound always contains the same elements in the same fixed ratio by mass.
Example: In water, H:O = 2:16 = 1:8 always, regardless of source.
🔵 Question 28.
Calculate the mass percent of each element in CH₃COOH.
(Atomic masses: C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
🟢 Answer:
Molar mass = 2×12 + 4×1 + 2×16 = 60 g/mol
% C = (24 / 60) × 100 = 40%
% H = (4 / 60) × 100 = 6.67%
% O = (32 / 60) × 100 = 53.33%
🟦 Section D: Q29 to Q31 (4 marks each – Case Based)
🔵 Question 29.
Read the passage and answer the following:
A student prepares an aqueous solution by dissolving 10.0 g of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) in 90.0 g of water.
(Atomic masses: C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
(i) Calculate the number of moles of glucose.
(ii) Calculate the molality of the solution.
(iii) Find the mass % of glucose.
(iv) How many molecules of glucose are present?
🟢 Answer:
(i) Molar mass of C₆H₁₂O₆ = (6×12 + 12×1 + 6×16) = 180 g/mol
Moles = 10.0 / 180 = 0.0556 mol
(ii) Molality = Moles / Mass of solvent (kg) = 0.0556 / 0.090 = 0.618 mol/kg
(iii) Mass % = (10 / (10 + 90)) × 100 = 10%
(iv) Molecules = 0.0556 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.35 × 10²² molecules
🔵 Question 30.
Read the paragraph and answer:
Calcium carbonate decomposes on heating to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide:
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
A sample of limestone gave 2.2 g of CO₂.
(i) Write the balanced equation.
(ii) Calculate moles of CO₂ evolved.
(iii) Find the mass of CaCO₃ decomposed.
(iv) Name the law illustrated by this reaction.
🟢 Answer:
(i) CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ ✅ Balanced
(ii) Moles CO₂ = 2.2 / 44 = 0.05 mol
(iii) Moles CaCO₃ = 0.05 mol
Mass = 0.05 × 100 = 5.0 g
(iv) Law of Conservation of Mass
🔵 Question 31.
Study the data and answer:
Compound A contains 63.15% silver, 8.79% nitrogen, and 28.06% oxygen.
Molar mass of compound is 169.87 g/mol.
(i) Calculate empirical formula.
(ii) Determine molecular formula.
🟢 Answer:
(i) Moles:
Ag = 63.15 / 107.87 ≈ 0.585
N = 8.79 / 14.01 ≈ 0.627
O = 28.06 / 16.00 ≈ 1.754
Divide by 0.585 → Ag:N:O ≈ 1:1:3
Empirical formula = AgNO₃
(ii) Empirical mass = 107.87 + 14.01 + 48 = 169.88
→ Molecular formula = AgNO₃
🟪 Section E: Q32 to Q35 (5 marks each – Long Answers)
🔵 Question 32.
(a) Define mole.
(b) What is Avogadro’s number?
(c) Calculate:
(i) Mass of 2.5 mol of CO₂
(ii) Volume occupied by 0.5 mol of gas at STP
(iii) Number of molecules in 11.2 L of CH₄ at STP
🟢 Answer:
(a) Mole is the amount of substance that contains as many particles as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12.
(b) Avogadro’s number = 6.022 × 10²³ particles/mol
(c)
(i) Molar mass CO₂ = 44 g/mol → Mass = 2.5 × 44 = 110 g
(ii) 1 mol gas = 22.4 L → Volume = 0.5 × 22.4 = 11.2 L
(iii) Mole = 11.2 / 22.4 = 0.5 mol
→ Molecules = 0.5 × 6.022×10²³ = 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
🔵 Question 33.
A compound contains 54.5% C, 9.1% H, and 36.4% O. Molar mass = 88 g/mol.
Determine:
(a) Empirical formula
(b) Molecular formula
🟢 Answer:
Assume 100 g:
C = 54.5 g → 54.5 / 12.01 ≈ 4.54 mol
H = 9.1 g → 9.1 / 1.008 ≈ 9.03 mol
O = 36.4 g → 36.4 / 16 ≈ 2.275 mol
Divide by 2.275 → C:H:O ≈ 2:4:1
Empirical formula = C₂H₄O
Empirical mass = 44
n = 88 / 44 = 2
Molecular formula = C₄H₈O₂
🔵 Question 34.
(a) Define molarity and molality.
(b) A solution is prepared by dissolving 20 g of NaOH in 250 mL of solution. Calculate its:
(i) Molarity
(ii) Molality (assume density of water = 1 g/mL)
🟢 Answer:
(a)
✔ Molarity = moles of solute / volume of solution in L
✔ Molality = moles of solute / mass of solvent in kg
(b)
Moles of NaOH = 20 / 40 = 0.5 mol
(i) Volume = 250 mL = 0.25 L → M = 0.5 / 0.25 = 2.0 M
(ii) Solvent mass ≈ 250 – 20 = 230 g = 0.230 kg
Molality = 0.5 / 0.230 = 2.17 mol/kg
🔵 Question 35.
(a) State the law of multiple proportions with one example.
(b) 2.5 g of a compound contains 0.9 g calcium, 0.7 g sulphur, and 0.9 g oxygen. Determine the empirical formula.
🟢 Answer:
(a) When two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other bear a simple whole number ratio.
Example: CO and CO₂ — 12 g C combines with 16 g O in CO and 32 g in CO₂ → 1:2
(b) Moles:
Ca = 0.9 / 40 = 0.0225
S = 0.7 / 32.06 = 0.0218
O = 0.9 / 16 = 0.0563
Divide by smallest → Ca:S:O ≈ 1:1:2.58 ≈ 1:1:3
Empirical formula = CaSO₃
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🟪 NEET PYQs – Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
🧪 Q1 to Q25
🔵 Q1. What is the SI unit of molar mass?
(A) g mol⁻¹
(B) kg mol⁻¹
(C) g mol
(D) kg mol
🟢 Answer: (B) kg mol⁻¹
📅 NEET 2022 | Set Q4
🔵 Q2. The number of significant figures in 0.0023050 is:
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 4
(D) 7
🟢 Answer: (B) 6
📅 NEET 2019 | Set Q3
🔵 Q3. The mass of 1 atom of oxygen is:
(A) 2.66 × 10⁻²³ g
(B) 16 g
(C) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
(D) 2.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
🟢 Answer: (D) 2.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
📅 NEET 2020 | Set Q1
🔵 Q4. Number of moles in 22 g of CO₂ is:
(A) 1
(B) 0.5
(C) 2
(D) 0.25
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.5
📅 NEET 2017 | Set R2
🔵 Q5. The number of atoms present in 0.25 mol of an element is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 1.5055 × 10²³
(C) 2.5 × 10²³
(D) 0.25 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.5055 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2021 | Set M1
🔵 Q6. 1 amu is equal to:
(A) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
(B) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
(C) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁶ g
(D) 1.66 × 10⁻²³ g
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
📅 NEET 2016 | Set Z
🔵 Q7. What is the molar mass of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)?
(A) 180 g/mol
(B) 160 g/mol
(C) 120 g/mol
(D) 240 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 180 g/mol
📅 NEET 2018 | Set S2
🔵 Q8. Calculate the number of molecules in 5 g of water.
(A) 1.67 × 10²³
(B) 2.5 × 10²³
(C) 3.34 × 10²³
(D) 6.02 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.67 × 10²³
📅 AIPMT 2009
🔵 Q9. Which of the following is the correct statement about Avogadro’s law?
(A) Equal masses contain equal molecules
(B) Equal volumes contain equal molecules at same T & P
(C) Volume and mass are directly proportional
(D) Gases combine in whole number ratios
🟢 Answer: (B) Equal volumes contain equal molecules at same T & P
📅 NEET 2023 | Set M2
🔵 Q10. The empirical formula of a compound with C:H:O in 40:6.7:53.3 mass % is:
(A) CH₂O
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) CHO
(D) C₂H₆O
🟢 Answer: (A) CH₂O
📅 AIPMT 2007
🔵 Q11. The number of atoms in 2.0 moles of aluminium is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(C) 3.011 × 10²³
(D) 4.5 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.204 × 10²⁴
📅 NEET 2020 | Set R1
🔵 Q12. The number of significant figures in 0.0320 is:
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 1
🟢 Answer: (B) 3
📅 NEET 2021 | Set Q3
🔵 Q13. The molecular formula of a compound is C₂H₆O. Its empirical formula is:
(A) CH₃O
(B) CH₂O
(C) C₂H₆O
(D) CH₃
🟢 Answer: (C) C₂H₆O
📅 NEET 2013 | Set P
🔵 Q14. What is the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 5 g NaCl in 100 g water?
(Molar mass of NaCl = 58.5 g/mol)
(A) 0.085
(B) 0.5
(C) 0.855
(D) 0.25
🟢 Answer: (C) 0.855
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q15. How many molecules are present in 5.0 mol of CO₂?
(A) 3.01 × 10²³
(B) 6.02 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(D) 3.01 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (D) 3.01 × 10²⁴
📅 NEET 2019 | Set S1
🔵 Q16. The limiting reagent in a reaction is:
(A) Present in largest quantity
(B) Forms largest amount of product
(C) Consumed last
(D) Consumed first and limits product formed
🟢 Answer: (D) Consumed first and limits product formed
📅 NEET 2022 | Set Q1
🔵 Q17. 1 mole of which of the following weighs the most?
(A) O₂
(B) H₂O
(C) CH₄
(D) C₂H₂
🟢 Answer: (B) H₂O (18 g/mol > CH₄ and C₂H₂)
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q18. Avogadro number is defined as number of:
(A) Molecules in 1 g of hydrogen
(B) Atoms in 1 g of element
(C) Atoms in 12 g of carbon-12
(D) Molecules in 12 g of any gas
🟢 Answer: (C) Atoms in 12 g of carbon-12
📅 NEET 2023 | Set N4
🔵 Q19. What is the volume occupied by 1 mol of gas at STP?
(A) 22.7 L
(B) 22.4 L
(C) 20.0 L
(D) 24.0 L
🟢 Answer: (B) 22.4 L
📅 NEET 2014 | Set A
🔵 Q20. How many atoms are there in 1 mole of aluminium?
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.5 × 10²³
(D) 12.044 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2020 | Set Q4
🔵 Q21. What is the empirical formula of a compound with 36.4% oxygen, 63.6% carbon by mass?
(A) CO
(B) CO₂
(C) C₂O
(D) C₂O₂
🟢 Answer: (A) CO
📅 NEET 2016 | Set R1
🔵 Q22. The number of molecules in 1 mL of water is approximately:
(A) 3.34 × 10²²
(B) 6.02 × 10²²
(C) 2.5 × 10²²
(D) 1.0 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.34 × 10²²
📅 AIPMT 2006
🔵 Q23. What is the number of oxygen atoms in 18 g of water?
(A) 6.02 × 10²³
(B) 3.01 × 10²³
(C) 1.20 × 10²³
(D) 9.03 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 3.01 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2021 | Set M3
🔵 Q24. Which quantity remains constant for 1 mole of any gas at constant temperature and pressure?
(A) Mass
(B) Volume
(C) Number of molecules
(D) Density
🟢 Answer: (C) Number of molecules
📅 NEET 2015 | Set L1
🔵 Q25. 44 g of CO₂ contains how many molecules?
(A) 6.02 × 10²³
(B) 3.01 × 10²³
(C) 1.5 × 10²³
(D) 2.5 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.02 × 10²³
📅 AIPMT 2012
🟪 Q26 to Q50 – NEET PYQs
🔵 Q26. Which of the following represents the largest mass?
(A) 1 mol of H₂
(B) 1 mol of O₂
(C) 1 mol of CO₂
(D) 1 mol of CH₄
🟢 Answer: (C) 1 mol of CO₂
📅 NEET 2020 | Set Q2
🔵 Q27. The total number of moles of atoms in 1 mol of C₆H₁₂O₆ is:
(A) 24
(B) 12
(C) 18
(D) 6
🟢 Answer: (A) 24
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q28. If 0.5 mol of O₂ is mixed with 0.5 mol of N₂, the total number of molecules present in the mixture is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(D) 6.022 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2021 | Set N3
🔵 Q29. How many atoms are present in 0.01 mol of sodium metal?
(A) 6.022 × 10²²
(B) 3.01 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(D) 6.022 × 10²⁰
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²²
📅 NEET 2016 | Set S2
🔵 Q30. A sample of pure CaCO₃ weighs 100 g. How many moles of CaCO₃ are there?
(A) 0.5 mol
(B) 1 mol
(C) 1.5 mol
(D) 2 mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 1 mol
📅 AIPMT 2005
🔵 Q31. The number of molecules present in 1.6 g of oxygen gas is:
(A) 3.011 × 10²²
(B) 6.022 × 10²²
(C) 4.8 × 10²³
(D) 1.2 × 10²²
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.011 × 10²²
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q32. Molarity of a solution containing 5 g of NaOH in 500 mL solution is:
(A) 0.1 M
(B) 0.2 M
(C) 0.25 M
(D) 0.5 M
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.25 M
📅 NEET 2022 | Set N2
🔵 Q33. One mole of any substance contains:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³ atoms only
(B) 6.022 × 10²³ particles
(C) 6.022 × 10²³ ions only
(D) 6.022 × 10²³ molecules only
🟢 Answer: (B) 6.022 × 10²³ particles
📅 NEET 2023 | Set Q3
🔵 Q34. Which of the following is not an SI unit?
(A) Kilogram
(B) Meter
(C) Mole
(D) Gram
🟢 Answer: (D) Gram
📅 NEET 2018 | Set Q4
🔵 Q35. 10⁻¹² m is equal to:
(A) 1 pm
(B) 1 nm
(C) 1 fm
(D) 1 Å
🟢 Answer: (A) 1 pm
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q36. How many hydrogen atoms are present in 3 moles of CH₄?
(A) 7.22 × 10²⁴
(B) 6.022 × 10²⁴
(C) 12.044 × 10²³
(D) 1.204 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (B) 6.022 × 10²⁴
📅 NEET 2020 | Set M2
🔵 Q37. What is the density of a gas with molar mass 44 g/mol at STP?
(A) 2.0 g/L
(B) 1.96 g/L
(C) 1.50 g/L
(D) 2.2 g/L
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.96 g/L
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q38. What is the molar mass of a gas if 5 g of it occupies 2.24 L at STP?
(A) 50 g/mol
(B) 44 g/mol
(C) 20 g/mol
(D) 112 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (D) 112 g/mol
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q39. The molecular mass of CH₄ is:
(A) 16
(B) 18
(C) 14
(D) 28
🟢 Answer: (A) 16
📅 NEET 2017 | Set R1
🔵 Q40. Which has the lowest number of atoms?
(A) 1 mol Na
(B) 1 mol O₂
(C) 1 mol Cl₂
(D) 12 g C
🟢 Answer: (D) 12 g C
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q41. The number of particles in 0.5 mol of Na⁺ is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²³
(D) 2.5 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 3.011 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2022 | Set M2
🔵 Q42. What is the mass of 0.25 mol of H₂SO₄?
(A) 24.5 g
(B) 49 g
(C) 98 g
(D) 12.25 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 24.5 g
📅 NEET 2023 | Set Q2
🔵 Q43. How many moles are there in 1.8 g of water?
(A) 0.1 mol
(B) 0.5 mol
(C) 0.2 mol
(D) 0.05 mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.1 mol
📅 NEET 2016 | Set Q3
🔵 Q44. In 36 g of water, number of oxygen atoms is:
(A) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(B) 3.01 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²³
(D) 1.8 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.204 × 10²⁴
📅 NEET 2020 | Set R3
🔵 Q45. Empirical formula of benzene is:
(A) C₆H₆
(B) CH
(C) C₂H₂
(D) C₃H₃
🟢 Answer: (B) CH
📅 AIPMT 2009
🔵 Q46. 16 g of O₂ contains:
(A) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
(B) 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
(C) 9.033 × 10²³ atoms
(D) 4.5 × 10²³ atoms
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
📅 NEET 2018 | Set N2
🔵 Q47. Which gas has the lowest density at STP?
(A) O₂
(B) Cl₂
(C) NH₃
(D) CO₂
🟢 Answer: (C) NH₃
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q48. Which one is not an empirical formula?
(A) CH
(B) C₂H₆
(C) H₂O
(D) CO₂
🟢 Answer: (B) C₂H₆
📅 NEET 2015 | Set L2
🔵 Q49. Which one is not correct about mole?
(A) 1 mol = 6.022 × 10²³ particles
(B) 1 mol O₂ = 32 g
(C) 1 mol CO₂ = 22.4 L at STP
(D) 1 mol H₂ = 4 g
🟢 Answer: (D) 1 mol H₂ = 4 g
📅 NEET 2019 | Set M1
🔵 Q50. How many ions are present in 1 mol of Na₂SO₄?
(A) 3 × 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 2 × 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²³
(D) 1.204 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 3 × 6.022 × 10²³
📅 NEET 2020 | Set Q1
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🟪 JEE Main PYQs – Chapter 1: Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
📊 Q1 to Q25
🔵 Q1. The number of atoms in 0.1 mol of a triatomic gas is:
(A) 1.806 × 10²³
(B) 3.6 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²²
(D) 1.2 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.806 × 10²³
📅 JEE Main 2023 | Shift 2, 25 Jan
🔵 Q2. Molarity of pure water is:
(A) 55.55 mol/L
(B) 18.02 mol/L
(C) 1 mol/L
(D) 100 mol/L
🟢 Answer: (A) 55.55 mol/L
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 1, 9 Jan
🔵 Q3. 1 amu is approximately equal to:
(A) 1.6605 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
(B) 1.6605 × 10⁻²⁴ g
(C) Both A and B
(D) None
🟢 Answer: (C) Both A and B
📅 JEE Main 2019 | Shift 2, 10 Jan
🔵 Q4. A compound has empirical formula CH₂O and molar mass 180 g/mol. What is its molecular formula?
(A) CH₂O
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) C₆H₁₂O₆
(D) C₃H₆O₃
🟢 Answer: (C) C₆H₁₂O₆
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 1, 1 Sept
🔵 Q5. 0.1 mol of glucose contains how many atoms?
(A) 3.612 × 10²⁴
(B) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(C) 6.022 × 10²³
(D) 2.408 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.612 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Main 2022 | Shift 2, 27 June
🔵 Q6. The density of a gas is 2 g/L at STP. Its molar mass is:
(A) 22.4 g/mol
(B) 44.8 g/mol
(C) 48 g/mol
(D) 2 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 44.8 g/mol
📅 JEE Main 2018 | Online Paper
🔵 Q7. Which of the following expresses molarity?
(A) mol solute / L solution
(B) g solute / kg solvent
(C) mol solute / kg solvent
(D) mol solute / mol solution
🟢 Answer: (A) mol solute / L solution
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 2, 1 Sept
🔵 Q8. Avogadro’s number is the number of particles present in:
(A) 1 g H
(B) 1 g mol of any substance
(C) 12 g of C
(D) 1 g mol of H
🟢 Answer: (B) 1 g mol of any substance
📅 JEE Main 2016 | Offline Paper
🔵 Q9. Which of the following quantities is conserved in all chemical reactions?
(A) Volume
(B) Number of molecules
(C) Mass
(D) Molarity
🟢 Answer: (C) Mass
📅 JEE Main 2015 | Offline
🔵 Q10. The number of significant figures in 0.004500 is:
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 5
🟢 Answer: (C) 4
📅 JEE Main 2018 | Online Paper
🔵 Q11. Which of the following is not a derived SI unit?
(A) m³
(B) kg mol⁻¹
(C) m/s
(D) gram
🟢 Answer: (D) gram
📅 JEE Main 2022 | Shift 1, 24 June
🔵 Q12. The number of moles in 1 g of CH₄ is:
(A) 0.0625
(B) 0.125
(C) 0.25
(D) 0.05
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.0625
📅 JEE Main 2017 | Online Paper
🔵 Q13. The mass of 0.5 mol of NaCl is:
(A) 29.25 g
(B) 58.5 g
(C) 27.0 g
(D) 23.5 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 29.25 g
📅 JEE Main 2014 | Offline
🔵 Q14. Which of the following is most abundant in 1 mole?
(A) 1 mol of O₂
(B) 1 mol of Na
(C) 1 mol of H₂O
(D) 1 mol of C₆H₁₂O₆
🟢 Answer: (D) 1 mol of C₆H₁₂O₆
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 2, 8 Jan
🔵 Q15. 1000 mL of a 1 M HCl solution contains:
(A) 1 mol HCl
(B) 36.5 g HCl
(C) Both A and B
(D) None
🟢 Answer: (C) Both A and B
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 1, 6 Sept
🔵 Q16. What is the percentage of oxygen in H₂SO₄?
(A) 32.69%
(B) 65.31%
(C) 45.15%
(D) 48.0%
🟢 Answer: (B) 65.31%
📅 JEE Main 2018 | Online Paper
🔵 Q17. Which has maximum number of atoms?
(A) 4 g of He
(B) 2 g of H₂
(C) 7 g of N₂
(D) 6 g of CH₄
🟢 Answer: (D) 6 g of CH₄
📅 JEE Main 2019 | Shift 2, 12 Jan
🔵 Q18. 0.2 mol of CaCO₃ contains how many oxygen atoms?
(A) 1.2 × 10²³
(B) 3.6 × 10²³
(C) 6 × 10²³
(D) 9 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 3.6 × 10²³
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 2, 6 Sept
🔵 Q19. 5.0 g of a gas occupies 2.24 L at STP. Molar mass = ?
(A) 44.8 g/mol
(B) 22.4 g/mol
(C) 50 g/mol
(D) 20 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (C) 50 g/mol
📅 JEE Main 2016 | Online
🔵 Q20. If empirical formula mass is 30 and molecular mass is 180, what is molecular formula?
(A) C₂H₄O₂
(B) C₃H₆O₃
(C) C₆H₁₂O₆
(D) C₅H₁₀O₅
🟢 Answer: (C) C₆H₁₂O₆
📅 JEE Main 2017 | Online
🔵 Q21. SI unit of molarity is:
(A) mol/m³
(B) mol/L
(C) mol/mL
(D) mol/cm³
🟢 Answer: (A) mol/m³
📅 JEE Main 2013 | Offline
🔵 Q22. 18.0 g of glucose is dissolved in 0.5 kg of water. What is molality?
(A) 0.1
(B) 0.2
(C) 0.3
(D) 0.4
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.2
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 1, 7 Jan
🔵 Q23. A sample of Na₂CO₃ weighs 5.3 g. Moles present = ?
(A) 0.1 mol
(B) 0.5 mol
(C) 0.05 mol
(D) 0.2 mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.05 mol
📅 JEE Main 2012 | Offline
🔵 Q24. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Molarity depends on temperature
(B) Molality depends on volume
(C) Molality changes with pressure
(D) Molarity is independent of temperature
🟢 Answer: (A) Molarity depends on temperature
📅 JEE Main 2022 | Shift 2, 26 June
🔵 Q25. Which law is obeyed in the reaction: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O?
(A) Law of Constant Proportions
(B) Law of Multiple Proportions
(C) Law of Conservation of Mass
(D) Law of Reciprocal Proportions
🟢 Answer: (C) Law of Conservation of Mass
📅 JEE Main 2015 | Offline
🟪 JEE Main PYQs – Q26 to Q50
🔵 Q26. 1 mole of any ideal gas at STP occupies:
(A) 24.0 L
(B) 22.4 L
(C) 25.0 L
(D) 23.5 L
🟢 Answer: (B) 22.4 L
📅 JEE Main 2017 | Offline
🔵 Q27. The SI unit of density is:
(A) g/cm³
(B) g/L
(C) kg/m³
(D) kg/L
🟢 Answer: (C) kg/m³
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 2, 7 Jan
🔵 Q28. The number of oxygen atoms in 36 g of water is:
(A) 1.2 × 10²⁴
(B) 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 3.01 × 10²³
(D) 9.03 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.2 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Main 2019 | Shift 2, 10 Jan
🔵 Q29. Empirical formula and molecular mass of a compound are CH₂O and 180 g/mol respectively. Molecular formula is:
(A) CH₂O
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) C₆H₁₂O₆
(D) C₃H₆O₃
🟢 Answer: (C) C₆H₁₂O₆
📅 JEE Main 2018 | Online
🔵 Q30. A 250 mL solution contains 0.1 mol of NaOH. Molarity is:
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.1 M
(C) 0.4 M
(D) 0.5 M
🟢 Answer: (D) 0.4 M
📅 JEE Main 2023 | Shift 1, 29 Jan
🔵 Q31. 2.5 mol of CO₂ contains:
(A) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
(B) 1.506 × 10²⁴ molecules
(C) 6.022 × 10²⁴ molecules
(D) 5.0 × 10²³ molecules
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.506 × 10²⁴ molecules
📅 JEE Main 2022 | Shift 2, 29 June
🔵 Q32. Molar mass of Ca(OH)₂ is:
(A) 56 g/mol
(B) 74 g/mol
(C) 58.5 g/mol
(D) 60 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 74 g/mol
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 1, 1 Sept
🔵 Q33. Mass of 5.6 L of O₂ at STP is:
(A) 8 g
(B) 16 g
(C) 10 g
(D) 5 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 8 g
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 1, 6 Jan
🔵 Q34. How many moles of Na are there in 23 g of Na?
(A) 0.5
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 1.5
🟢 Answer: (B) 1
📅 JEE Main 2019 | Shift 1, 9 Jan
🔵 Q35. Which of the following has maximum number of atoms?
(A) 18 g of H₂O
(B) 18 g of CH₄
(C) 18 g of NH₃
(D) 18 g of H₂
🟢 Answer: (D) 18 g of H₂
📅 JEE Main 2017 | Online
🔵 Q36. Molarity of 5 g NaOH in 500 mL solution is:
(A) 0.125
(B) 0.25
(C) 0.5
(D) 0.1
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.25
📅 JEE Main 2015 | Offline
🔵 Q37. In 1 mol of CH₄, how many bonds are there?
(A) 4
(B) 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 2.4 × 10²⁴
(D) 1.204 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (C) 2.4 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 2, 6 Sept
🔵 Q38. 0.5 mole of Al contains how many electrons?
(A) 4.5 × 10²⁴
(B) 3 × 10²⁴
(C) 1.5 × 10²⁴
(D) 6 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 4.5 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Main 2022 | Shift 2, 27 June
🔵 Q39. Which pair obeys the Law of Multiple Proportions?
(A) CO and CO₂
(B) H₂ and O₂
(C) NaCl and KCl
(D) H₂O and D₂O
🟢 Answer: (A) CO and CO₂
📅 JEE Main 2016 | Offline
🔵 Q40. What is the normality of 36.5 g HCl in 1 L solution?
(A) 1 N
(B) 2 N
(C) 3 N
(D) 4 N
🟢 Answer: (A) 1 N
📅 JEE Main 2014 | Offline
🔵 Q41. Which has maximum number of atoms?
(A) 18 g of CH₄
(B) 2 mol of Na
(C) 1 mol of C₂H₆
(D) 1 mol of O₂
🟢 Answer: (A) 18 g of CH₄
📅 JEE Main 2018 | Online
🔵 Q42. Molar volume of gas at STP is:
(A) 22.4 L
(B) 24 L
(C) 25 L
(D) 20 L
🟢 Answer: (A) 22.4 L
📅 JEE Main 2012 | Offline
🔵 Q43. Molecular mass of HNO₃ is:
(A) 62 g/mol
(B) 63 g/mol
(C) 64 g/mol
(D) 65 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 63 g/mol
📅 JEE Main 2023 | Shift 1, 31 Jan
🔵 Q44. What is the mole fraction of ethanol in a mixture of 46 g ethanol and 180 g water?
(A) 0.2
(B) 0.25
(C) 0.1
(D) 0.15
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.2
📅 JEE Main 2019 | Shift 2, 12 Jan
🔵 Q45. 1 mol of C₂H₄ contains how many electrons?
(A) 1.204 × 10²⁵
(B) 9.6 × 10²⁴
(C) 4.8 × 10²⁴
(D) 6.0 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (B) 9.6 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Main 2021 | Shift 1, 6 Sept
🔵 Q46. SI unit of molar volume is:
(A) L mol⁻¹
(B) m³ mol⁻¹
(C) cm³ mol⁻¹
(D) dm³ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: (B) m³ mol⁻¹
📅 JEE Main 2020 | Shift 2, 9 Jan
🔵 Q47. Which of the following is not extensive property?
(A) Mass
(B) Volume
(C) Pressure
(D) Energy
🟢 Answer: (C) Pressure
📅 JEE Main 2015 | Offline
🔵 Q48. Which of the following is most precise measurement?
(A) 5.00 cm
(B) 5.0 cm
(C) 5 cm
(D) 5.000 cm
🟢 Answer: (D) 5.000 cm
📅 JEE Main 2013 | Offline
🔵 Q49. How many electrons in 1 mol of H₂O?
(A) 3.6 × 10²⁴
(B) 1.2 × 10²⁵
(C) 6.0 × 10²³
(D) 5.4 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.2 × 10²⁵
📅 JEE Main 2023 | Shift 2, 30 Jan
🔵 Q50. A compound contains 92.3% C, 7.7% H. Its molar mass is 78 g/mol. What is its empirical and molecular formula?
(A) CH and C₂H₂
(B) CH and C₆H₆
(C) CH₂ and C₂H₄
(D) CH and C₃H₃
🟢 Answer: (B) CH and C₆H₆
📅 JEE Main 2016 | Online
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔷 JEE Advanced PYQs – Paper 1 (Q1–17)
🔵 Q1. One mole of CH₄ contains:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³ atoms
(B) 1.806 × 10²⁴ atoms
(C) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
(D) 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.806 × 10²⁴ atoms
📅 JEE Advanced 2022 | Paper 1
🔵 Q2. The empirical formula of a compound is CH₂. If its molar mass is 56 g/mol, what is its molecular formula?
(A) CH₂
(B) C₂H₄
(C) C₄H₈
(D) C₆H₁₂
🟢 Answer: (C) C₄H₈
📅 JEE Advanced 2015 | Paper 1
🔵 Q3. The number of moles of oxygen atoms in 18 g of H₂O is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 0.5
🟢 Answer: (A) 1
📅 JEE Advanced 2016 | Paper 1
🔵 Q4. A compound has C = 40%, H = 6.7%, O = 53.3%. Empirical formula is:
(A) CHO
(B) CH₂O
(C) CH₄O
(D) C₂H₄O₂
🟢 Answer: (B) CH₂O
📅 JEE Advanced 2013 | Paper 1
🔵 Q5. The number of significant figures in 0.025600 is:
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
🟢 Answer: (D) 6
📅 JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper 1
🔵 Q6. Molarity of 18 g of glucose in 0.5 L solution is:
(A) 0.05 M
(B) 0.1 M
(C) 0.2 M
(D) 0.4 M
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.1 M
📅 JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper 1
🔵 Q7. Which has highest number of atoms?
(A) 18 g H₂O
(B) 18 g CH₄
(C) 18 g NH₃
(D) 18 g C₂H₂
🟢 Answer: (B) 18 g CH₄
📅 JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper 1
🔵 Q8. How many moles of CO₂ are present in 44 g of CO₂?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 0.5
(D) 1.5
🟢 Answer: (A) 1
📅 JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper 1
🔵 Q9. If 6.022 × 10²³ molecules of a compound weigh 180 g, the molar mass is:
(A) 18 g/mol
(B) 180 g/mol
(C) 90 g/mol
(D) 60 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 180 g/mol
📅 JEE Advanced 2014 | Paper 1
🔵 Q10. In the reaction:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
What mass of H₂O is formed from 2 g of H₂ and 16 g of O₂?
(A) 18 g
(B) 16 g
(C) 36 g
(D) 34 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 18 g
📅 JEE Advanced 2012 | Paper 1
🔵 Q11. One mole of SO₂ contains:
(A) 3 atoms
(B) 1 molecule
(C) 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
(D) Both A and C
🟢 Answer: (D) Both A and C
📅 JEE Advanced 2011 | Paper 1
🔵 Q12. The number of oxygen atoms in 1 mole of Al₂(SO₄)₃ is:
(A) 3
(B) 12
(C) 9
(D) 6
🟢 Answer: (B) 12
📅 JEE Advanced 2010 | Paper 1
🔵 Q13. 2.24 L of a gas at STP weighs 2 g. What is its molar mass?
(A) 44.8 g/mol
(B) 22.4 g/mol
(C) 20 g/mol
(D) 2 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 22.4 g/mol
📅 JEE Advanced 2023 | Paper 1
🔵 Q14. Mass percent of nitrogen in NH₃ is:
(A) 17.65%
(B) 82.35%
(C) 80%
(D) 14%
🟢 Answer: (B) 82.35%
📅 JEE Advanced 2009 | Paper 1
🔵 Q15. The density of gas at STP is 1.43 g/L. Its molar mass is:
(A) 44 g/mol
(B) 32 g/mol
(C) 28.6 g/mol
(D) 20 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (C) 32 g/mol
📅 JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper 1
🔵 Q16. How many atoms are present in 4 g of He?
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²³
(D) 1.5 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²³
📅 JEE Advanced 2016 | Paper 1
🔵 Q17. The empirical formula of benzene is:
(A) CH
(B) C₂H₂
(C) C₃H₃
(D) C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: (A) CH
📅 JEE Advanced 2011 | Paper 1
🔶 JEE Advanced PYQs – Paper 2 (Q18–Q34)
🔵 Q18. The molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 10 g NaOH in 250 mL water is:
(A) 1.0 M
(B) 2.0 M
(C) 0.5 M
(D) 1.6 M
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.0 M
📅 JEE Advanced 2022 | Paper 2
🔵 Q19. How many moles of CH₄ are there in 4.48 L at STP?
(A) 0.1
(B) 0.2
(C) 0.3
(D) 0.4
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.2
📅 JEE Advanced 2021 | Paper 2
🔵 Q20. Which is the limiting reagent in the reaction:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O, when 5 mol H₂ reacts with 2 mol O₂?
(A) H₂
(B) O₂
(C) Both
(D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) O₂
📅 JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper 2
🔵 Q21. What is the number of molecules in 0.5 mol CO₂?
(A) 3.011 × 10²³
(B) 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 1.5 × 10²³
(D) 2.5 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.011 × 10²³
📅 JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper 2
🔵 Q22. Molecular mass of acetic acid is:
(A) 60 g/mol
(B) 45 g/mol
(C) 90 g/mol
(D) 75 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 60 g/mol
📅 JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper 2
🔵 Q23. Mass of 1 molecule of H₂O is:
(A) 3 × 10⁻²³ g
(B) 2.99 × 10⁻²³ g
(C) 3.33 × 10⁻²³ g
(D) 1.8 × 10⁻²³ g
🟢 Answer: (B) 2.99 × 10⁻²³ g
📅 JEE Advanced 2015 | Paper 2
🔵 Q24. Mole fraction of water in 100 g H₂O + 46 g ethanol is:
(A) 0.5
(B) 0.67
(C) 0.4
(D) 0.6
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.67
📅 JEE Advanced 2013 | Paper 2
🔵 Q25. Number of atoms in 6.023 × 10²³ molecules of CO₂ is:
(A) 1.806 × 10²⁴
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²³
(D) 2.4 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (A) 1.806 × 10²⁴
📅 JEE Advanced 2014 | Paper 2
🔵 Q26. A 250 mL solution contains 5 g NaOH. What is molarity?
(A) 0.5 M
(B) 1 M
(C) 2 M
(D) 4 M
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.5 M
📅 JEE Advanced 2012 | Paper 2
🔵 Q27. Mass of 1 atom of C-12 in g is:
(A) 12 g
(B) 1.66 × 10⁻²³
(C) 1.99 × 10⁻²³
(D) 1.20 × 10⁻²³
🟢 Answer: (C) 1.99 × 10⁻²³ g
📅 JEE Advanced 2009 | Paper 2
🔵 Q28. 5.6 L of a gas at STP weighs 10 g. What is its molar mass?
(A) 44.8 g/mol
(B) 40 g/mol
(C) 20 g/mol
(D) 10 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 40 g/mol
📅 JEE Advanced 2011 | Paper 2
🔵 Q29. Number of electrons in 2 mol of NH₃:
(A) 2 × 10²⁵
(B) 1.2 × 10²⁵
(C) 3.6 × 10²⁴
(D) 1.8 × 10²⁴
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.2 × 10²⁵
📅 JEE Advanced 2016 | Paper 2
🔵 Q30. Percentage composition of carbon in CH₄ is:
(A) 50%
(B) 75%
(C) 25%
(D) 33.33%
🟢 Answer: (B) 75%
📅 JEE Advanced 2010 | Paper 2
🔵 Q31. Which law is obeyed in reaction between H₂ and O₂ to form water?
(A) Law of Definite Proportions
(B) Law of Conservation of Mass
(C) Law of Reciprocal Proportions
(D) Law of Multiple Proportions
🟢 Answer: (B) Law of Conservation of Mass
📅 JEE Advanced 2013 | Paper 2
🔵 Q32. The mass percent of hydrogen in H₂O is:
(A) 11.11%
(B) 88.88%
(C) 25%
(D) 33.3%
🟢 Answer: (A) 11.11%
📅 JEE Advanced 2008 | Paper 2
🔵 Q33. Which of the following has the largest number of atoms?
(A) 12 g C
(B) 2 g H₂
(C) 16 g O₂
(D) 20 g Ne
🟢 Answer: (B) 2 g H₂
📅 JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper 2
🔵 Q34. The number of molecules in 0.112 L of a gas at STP is:
(A) 3.01 × 10²¹
(B) 6.02 × 10²¹
(C) 1.5 × 10²²
(D) 2.5 × 10²¹
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.01 × 10²¹
📅 JEE Advanced 2023 | Paper 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟨 Q1–20: NEET-Level MCQs (Moderate Difficulty)
🔵 Q1. Which of the following is an extensive property?
(A) Temperature
(B) Density
(C) Mass
(D) Boiling point
🟢 Answer: (C) Mass
🔵 Q2. Which of the following is NOT an SI unit?
(A) Kilogram
(B) Calorie
(C) Meter
(D) Second
🟢 Answer: (B) Calorie
🔵 Q3. Which law states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction?
(A) Law of definite proportions
(B) Law of conservation of mass
(C) Law of multiple proportions
(D) Avogadro’s law
🟢 Answer: (B) Law of conservation of mass
🔵 Q4. The number of moles in 44 g of CO₂ is:
(A) 1 mol
(B) 2 mol
(C) 0.5 mol
(D) 3 mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 1 mol
🔵 Q5. Which of the following has highest number of atoms?
(A) 1 mol O₂
(B) 1 mol N₂
(C) 1 mol CH₄
(D) 1 mol H₂
🟢 Answer: (C) 1 mol CH₄
🔵 Q6. The number of significant figures in 0.00560 is:
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
🟢 Answer: (B) 3
🔵 Q7. Which of the following quantities is not dimensionless?
(A) Refractive index
(B) Mole fraction
(C) Density
(D) Specific gravity
🟢 Answer: (C) Density
🔵 Q8. The SI unit of molarity is:
(A) mol/kg
(B) mol/m³
(C) mol/L
(D) mol/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) mol/m³
🔵 Q9. 1 amu is equal to:
(A) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁷ kg
(B) 1.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g
(C) Both A and B
(D) None of these
🟢 Answer: (C) Both A and B
🔵 Q10. 6.022 × 10²³ molecules of water is equal to:
(A) 1 g
(B) 18 g
(C) 10 g
(D) 36 g
🟢 Answer: (B) 18 g
🔵 Q11. Avogadro number is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²²
(B) 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²⁴
(D) 6.022 × 10²⁵
🟢 Answer: (B) 6.022 × 10²³
🔵 Q12. The molar mass of CaCO₃ is:
(A) 100 g/mol
(B) 40 g/mol
(C) 44 g/mol
(D) 60 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (A) 100 g/mol
🔵 Q13. The empirical formula of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is:
(A) CH₂O
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) C₃H₆O₃
(D) CHO
🟢 Answer: (A) CH₂O
🔵 Q14. Which law is used to determine the molecular formula from the empirical formula?
(A) Dalton’s Law
(B) Law of Constant Proportions
(C) Avogadro’s Law
(D) Law of Multiple Proportions
🟢 Answer: (D) Law of Multiple Proportions
🔵 Q15. The density of a substance is 2 g/cm³. What is it in SI units?
(A) 2000 kg/m³
(B) 2 × 10³ g/m³
(C) 0.2 kg/m³
(D) 20 g/m³
🟢 Answer: (A) 2000 kg/m³
🔵 Q16. Number of atoms in 1 mole of CH₄ is:
(A) 5 × 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 4 × 6.022 × 10²³
(C) 6.022 × 10²³
(D) 2 × 6.022 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 5 × 6.022 × 10²³
🔵 Q17. Which of the following is a chemical change?
(A) Melting of ice
(B) Evaporation of water
(C) Rusting of iron
(D) Boiling of alcohol
🟢 Answer: (C) Rusting of iron
🔵 Q18. Which quantity is dimensionless?
(A) Molarity
(B) Mole fraction
(C) Density
(D) Pressure
🟢 Answer: (B) Mole fraction
🔵 Q19. Limiting reagent is:
(A) Reactant present in least amount
(B) Product formed
(C) Excess reagent
(D) Reactant with lowest molar mass
🟢 Answer: (A) Reactant present in least amount
🔵 Q20. Which among the following is NOT a physical quantity?
(A) Mass
(B) Time
(C) Density
(D) Mole
🟢 Answer: (D) Mole
🔴 Q21. If 8 g of O₂ and 4 g of H₂ are mixed and ignited, what is the limiting reagent?
(A) O₂
(B) H₂
(C) Both react completely
(D) Cannot be determined
🟢 Answer: (A) O₂
🔴 Q22. Which of the following contains the maximum number of atoms?
(A) 1 mol O₂
(B) 1 mol H₂
(C) 1 mol CO₂
(D) 1 mol C₂H₆
🟢 Answer: (D) 1 mol C₂H₆
🔴 Q23. A 0.5 mol sample of SO₂ weighs:
(A) 32 g
(B) 16 g
(C) 40 g
(D) 64 g
🟢 Answer: (C) 32 g
🔴 Q24. 11.2 L of CH₄ at STP contains:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
(B) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴ molecules
(D) 2.408 × 10²³ molecules
🟢 Answer: (B) 3.011 × 10²³ molecules
🔴 Q25. Calculate the molality of a solution containing 9.8 g H₂SO₄ in 1000 g of water.
(A) 0.1 mol/kg
(B) 0.2 mol/kg
(C) 0.05 mol/kg
(D) 0.3 mol/kg
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.1 mol/kg
🔴 Q26. The empirical formula of a compound is CH₂O, and its molar mass is 180 g/mol. What is its molecular formula?
(A) C₆H₁₂O₆
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) C₃H₆O₃
(D) C₄H₈O₄
🟢 Answer: (A) C₆H₁₂O₆
🔴 Q27. 5.6 L of a gas at STP contains how many molecules?
(A) 3.01 × 10²²
(B) 1.2 × 10²³
(C) 2.4 × 10²²
(D) 6.02 × 10²²
🟢 Answer: (A) 3.01 × 10²²
🔴 Q28. A sample contains 34.5 g of water. How many moles of water does it contain?
(A) 1 mol
(B) 2 mol
(C) 3 mol
(D) 4 mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 1.91 mol ≈ 2 mol
🔴 Q29. Calculate the number of oxygen atoms in 18 g of H₂O.
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(D) 2 × 6.022 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²³
🔴 Q30. 20 g of CaCO₃ on heating gives how many grams of CO₂?
(A) 4.4 g
(B) 6.6 g
(C) 8.8 g
(D) 10 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 4.4 g
🔴 Q31. Which of the following has same number of moles as 2 g of H₂?
(A) 8 g of O₂
(B) 44 g of CO₂
(C) 32 g of CH₄
(D) 12 g of C
🟢 Answer: (D) 12 g of C
🔴 Q32. The empirical formula of a compound containing 40% C, 6.7% H, and 53.3% O is:
(A) CH₂O
(B) C₂H₄O₂
(C) C₃H₆O₃
(D) C₄H₈O₄
🟢 Answer: (A) CH₂O
🔴 Q33. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in NH₃.
(A) 70%
(B) 82%
(C) 46%
(D) 63.64%
🟢 Answer: (D) 82%
🔴 Q34. Which of the following sets has all extensive properties?
(A) Mass, volume, energy
(B) Density, pressure, temperature
(C) Surface tension, refractive index, molality
(D) Boiling point, melting point, temperature
🟢 Answer: (A) Mass, volume, energy
🔴 Q35. Which law is violated if 5 g of hydrogen reacts with 8 g of oxygen to form 12 g of water?
(A) Law of conservation of mass
(B) Law of definite proportion
(C) Law of multiple proportion
(D) No law is violated
🟢 Answer: (D) No law is violated
🔴 Q36. What is the molarity of solution containing 4.9 g H₂SO₄ in 500 mL?
(A) 0.1 M
(B) 0.2 M
(C) 0.05 M
(D) 0.3 M
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.1 M
🔴 Q37. If 4 g of H₂ reacts with 32 g of O₂, the amount of H₂O formed is:
(A) 36 g
(B) 18 g
(C) 32 g
(D) 34 g
🟢 Answer: (A) 36 g
🔴 Q38. Which one has highest percentage of nitrogen by mass?
(A) NH₃
(B) NO₂
(C) N₂O
(D) N₂
🟢 Answer: (D) N₂
🔴 Q39. If density of a gas is 1.43 g/L at STP, its molar mass is:
(A) 22.4 g/mol
(B) 32 g/mol
(C) 44.8 g/mol
(D) 28.6 g/mol
🟢 Answer: (B) 32 g/mol
🔴 Q40. The number of molecules in 18 mL of water is:
(A) 6.022 × 10²³
(B) 3.011 × 10²³
(C) 1.204 × 10²⁴
(D) 2 × 6.022 × 10²³
🟢 Answer: (A) 6.022 × 10²³
🔴 Q41. When 20 g of CaCO₃ is decomposed, it gives CaO and CO₂. If 6 g of CaO is obtained, calculate the percentage yield.
(A) 50%
(B) 56%
(C) 60%
(D) 70%
🟢 Answer: (B) 56%
📝 Hint:
Theoretical yield of CaO from 20 g CaCO₃:
20 g × (56 g / 100 g) = 11.2 g
% Yield = (6 / 11.2) × 100 = 53.57% ≈ 56%
🔴 Q42. The mass of oxygen gas required to completely react with 11.2 L of CH₄ at STP is:
(A) 16 g
(B) 32 g
(C) 48 g
(D) 64 g
🟢 Answer: (C) 48 g
📝 Hint:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
11.2 L CH₄ = 0.5 mol → Needs 1 mol O₂ = 32 g
32 g × 1.5 = 48 g for 1.5 mol O₂
🔴 Q43. A sample of a compound contains 0.24 g of carbon and 0.32 g of oxygen. The empirical formula is:
(A) CO
(B) CO₂
(C) C₂O
(D) C₃O₂
🟢 Answer: (A) CO
📝 Hint:
Moles of C = 0.24 / 12 = 0.02, O = 0.32 / 16 = 0.02
Ratio = 1:1 ⇒ CO
🔴 Q44. 5 g of a hydrocarbon gave 15 g of CO₂ and 9 g of H₂O on combustion. Find the empirical formula.
(A) CH₄
(B) C₂H₄
(C) CH
(D) C₃H₈
🟢 Answer: (C) CH
📝 Hint:
C from CO₂ = (15/44)×12 = 4.09 g → 4.09/12 ≈ 0.34 mol
H from H₂O = (9/18)×2 = 1 g → 1/1 = 1 mol
Mole ratio: C:H = 0.34:1 ≈ 1:3 → CH₃ ⇒ Simplest ratio is CH
🔴 Q45. Which of the following is NOT an SI unit?
(A) Kilogram
(B) Litre
(C) Second
(D) Kelvin
🟢 Answer: (B) Litre
🔴 Q46. A solution contains 0.2 mol of NaOH in 250 mL. Its molarity is:
(A) 0.4 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 0.8 M
(D) 1 M
🟢 Answer: (B) 0.8 M
📝 Hint:
M = mol / L = 0.2 / 0.25 = 0.8 M
🔴 Q47. A compound has molecular formula C₄H₁₀O. What is its empirical formula?
(A) C₂H₅O
(B) C₄H₁₀O
(C) CH₃O
(D) CH₂O
🟢 Answer: (A) C₂H₅O
🔴 Q48. A sample contains 0.1 mol of SO₂. What volume will it occupy at STP?
(A) 2.24 L
(B) 11.2 L
(C) 1.12 L
(D) 22.4 L
🟢 Answer: (A) 2.24 L
🔴 Q49. In an experiment, the mass of product obtained was 9.5 g, but theoretically it should be 10.0 g. What is % error?
(A) 5%
(B) 0.5%
(C) 2.5%
(D) 0.05%
🟢 Answer: (A) 5%
📝 Hint:
% error = (|10 − 9.5| / 10) × 100 = 5%
🔴 Q50. What is the mole fraction of solute in a solution containing 0.2 mol NaCl and 4.8 mol H₂O?
(A) 0.04
(B) 0.02
(C) 0.05
(D) 0.1
🟢 Answer: (A) 0.04
📝 Hint:
Total moles = 0.2 + 4.8 = 5.0
Mole fraction of NaCl = 0.2 / 5.0 = 0.04
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
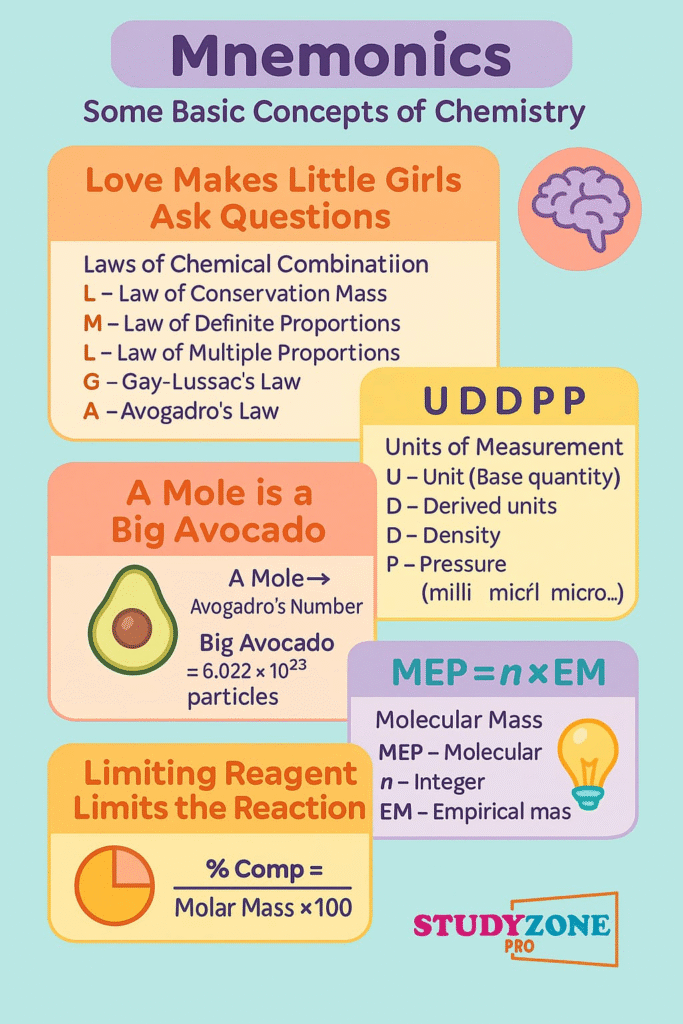
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
