Class 11 : Chemistry (In English) – Chapter 5: Thermodynamics
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction
Thermodynamics is the branch of science dealing with the study of energy changes 🔥 in physical and chemical processes. Every reaction around us involves energy — burning fuel 🚗, boiling water 💧, photosynthesis 🌱, respiration in our body 🫁. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but it can change from one form to another. Thermodynamics helps us understand how energy is transferred, in what direction it flows, and whether a process is possible or not.
Chemistry uses thermodynamics mainly to study the heat changes (enthalpy) accompanying chemical reactions and the feasibility of processes.
🟢 Basic Terms in Thermodynamics
1️⃣ System and Surroundings
System: Part of universe under study (reaction mixture, vessel).
Surroundings: Everything outside the system.
Universe = System + Surroundings.
2️⃣ Types of Systems
Open system: exchange of matter + energy (boiling water in open pot).
Closed system: exchange of energy only, not matter (sealed vessel).
Isolated system: no exchange of matter or energy (thermos flask).
3️⃣ State of System
Defined by properties like pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), composition.
4️⃣ State Functions
Properties that depend only on state, not path taken. Examples: P, V, T, U (internal energy), H (enthalpy), G (Gibbs free energy).
5️⃣ Intensive vs Extensive Properties
Intensive: independent of mass (temperature, pressure).
Extensive: depend on mass (volume, enthalpy).
🔵 Internal Energy (U)
Total energy of system = kinetic + potential energy of particles.
Change in internal energy (ΔU) occurs due to heat (q) absorbed or work (w) done.
Equation:
ΔU = q + w
✔ Work done at constant pressure: w = −PΔV
(negative when system expands, positive when compressed).
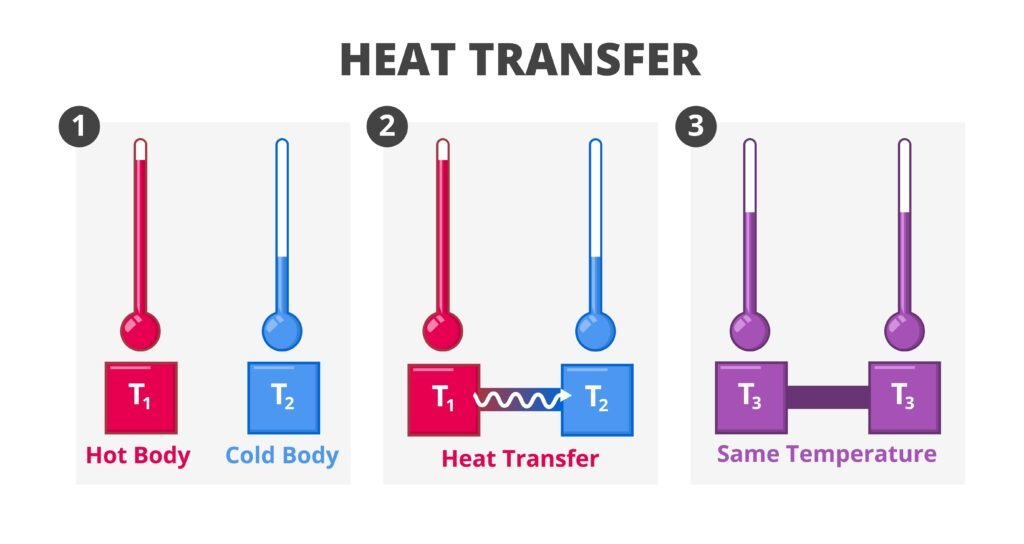
🟢 First Law of Thermodynamics
✨ Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it only changes form.
Equation:
ΔU = q + w
At constant volume (ΔV=0), ΔU = qᵥ.
At constant pressure, heat absorbed = enthalpy change (ΔH).
🔴 Enthalpy (H)
H = U + PV
Change in enthalpy (ΔH) = qₚ (heat at constant pressure).
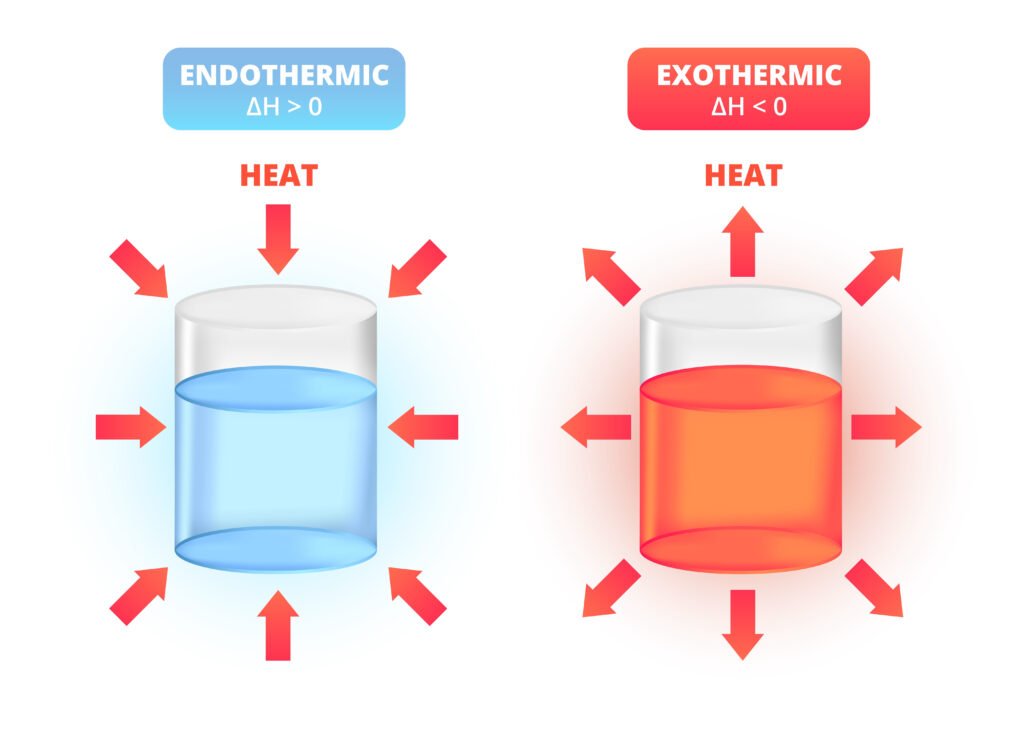
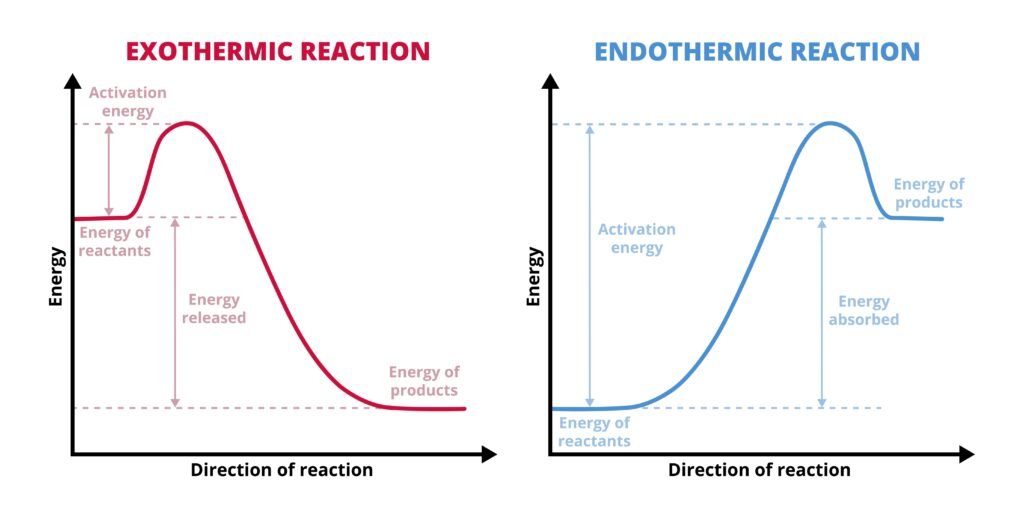
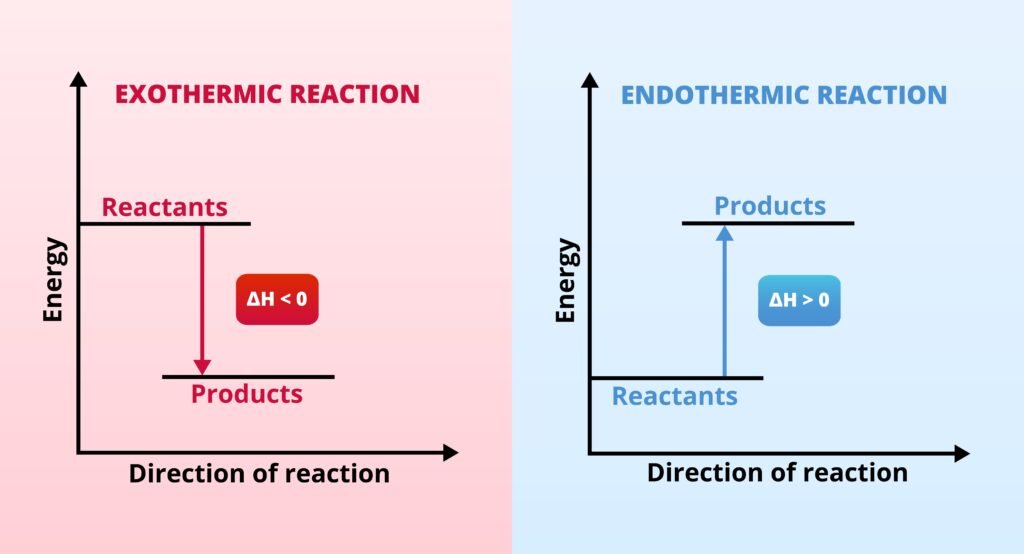
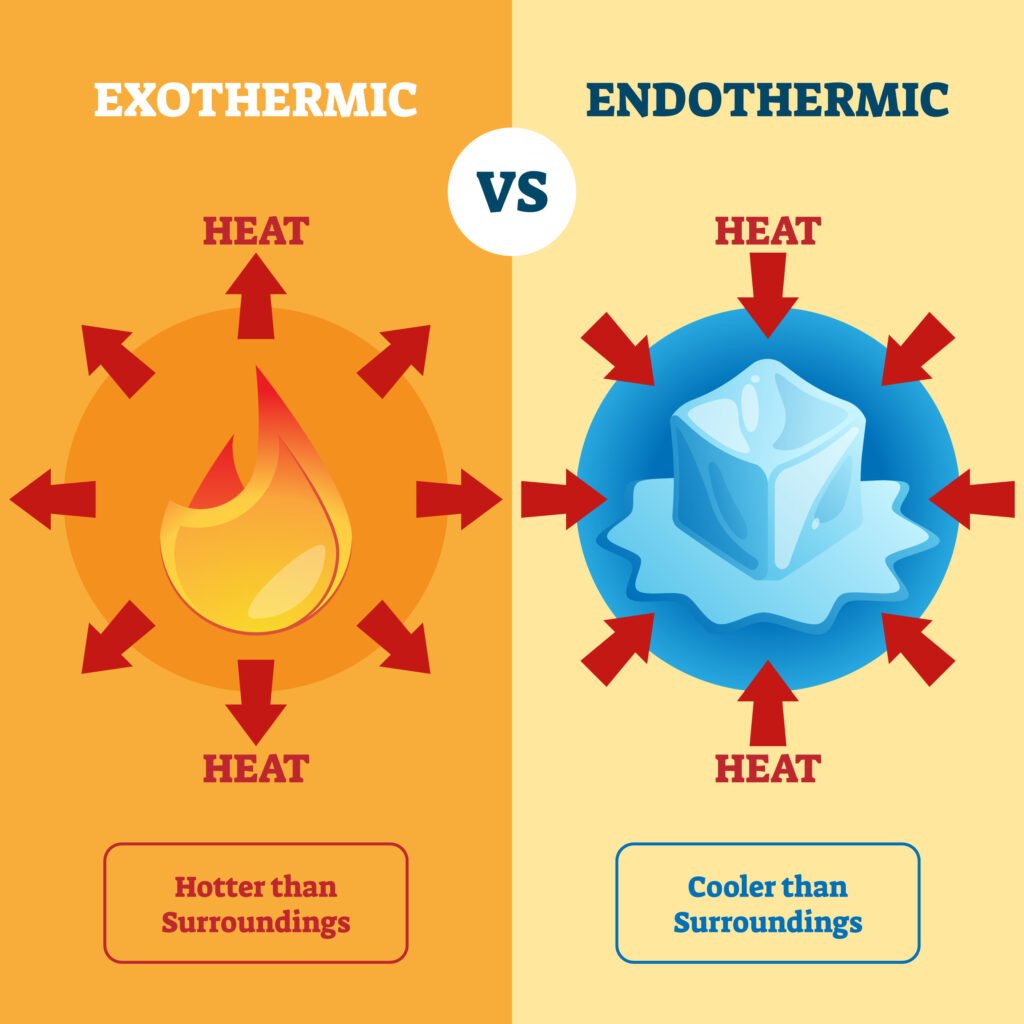
Endothermic process: ΔH > 0 (absorbs heat, e.g., melting ice ❄).
Exothermic process: ΔH < 0 (releases heat, e.g., combustion 🔥).
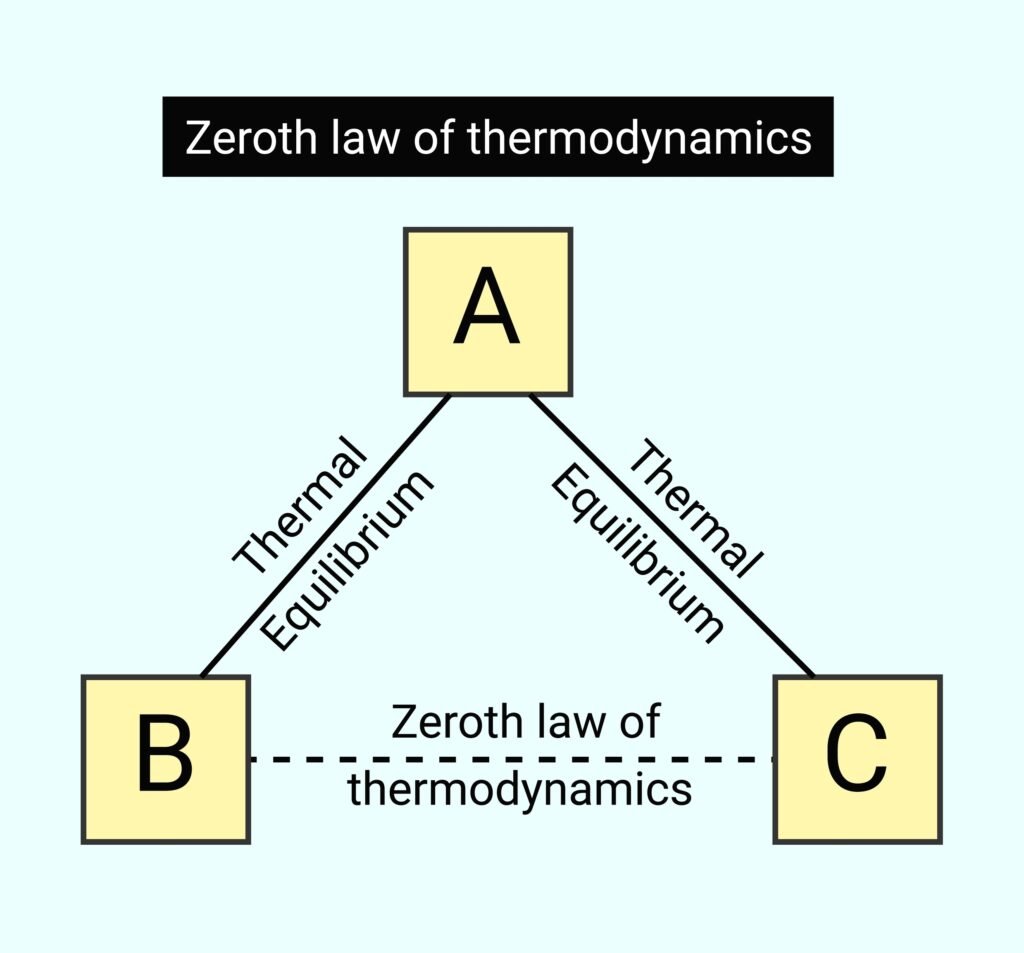
🟡 Second Law of Thermodynamics
Focuses on spontaneity. Some processes occur naturally (ice melts at 25°C, gas diffuses), others don’t (heat doesn’t flow cold → hot).
Important statements:
Clausius Statement: Heat cannot flow from cold body to hot body without external work.
Kelvin–Planck Statement: It is impossible to convert all heat into work.
Introduces entropy (S): measure of disorder/randomness.
ΔS > 0 → disorder increases (spontaneous tendency).
ΔS < 0 → disorder decreases.
🟢 Third Law of Thermodynamics
At absolute zero (0 K), entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance = 0.
This provides reference point for entropy values.
🔵 Applications of First Law
✔ Heat capacity (C): quantity of heat required to raise temperature by 1 K.
C = q / ΔT.
Molar heat capacity: per mole of substance.
✔ Relation between Cp and Cv:
Cp − Cv = R (ideal gas).
🟡 Standard Enthalpy Changes
Enthalpy of Formation
Heat change when 1 mole of compound forms from elements in standard state.
Example: ΔHf° of H₂O = −286 kJ/mol.
Enthalpy of Combustion
Heat released on complete combustion of 1 mole.
Example: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O, ΔH = −890 kJ.
Enthalpy of Neutralization
Heat change when 1 mole of H⁺ neutralizes 1 mole OH⁻.
Strong acid + strong base → always −57.1 kJ/mol.
Enthalpy of Atomization
Heat change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms formed from element.
Enthalpy of Sublimation, Fusion, Vaporization
Heat change for phase transitions.
🔴 Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation
If a reaction occurs in several steps, total enthalpy change = sum of enthalpy changes of steps.
Example:
C (diamond) → C (graphite), ΔH = −1.9 kJ
C (graphite) + O₂ → CO₂, ΔH = −393.5 kJ
Total: C (diamond) + O₂ → CO₂, ΔH = −395.4 kJ
Applications:
Calculate ΔH when direct measurement not possible.
Useful for lattice enthalpies, bond enthalpies.
🟢 Bond Enthalpy
Energy required to break 1 mole of bonds in gaseous molecules.
For polyatomic molecules, average bond enthalpy is used.
Example: Bond enthalpy of H–H = 436 kJ/mol.
🔵 Spontaneity of Reactions
Why does ice melt at room temperature but not freeze? Thermodynamics answers this using Gibbs Free Energy (G).
Equation:
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
ΔG < 0 → spontaneous.
ΔG > 0 → non-spontaneous.
ΔG = 0 → equilibrium.
🟡 Important Relationships
✔ ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT (for gaseous reactions).
✔ ΔG° = −RT ln K (relation with equilibrium constant).
✔ ΔG = wmax (maximum non-expansion work possible).
🔴 Applications of Thermodynamics in Chemistry
Predicts feasibility of reactions.
Explains why combustion is exothermic and spontaneous.
Determines enthalpies for industrial processes (Haber, Contact process).
Basis for energy cycles in biology (ATP hydrolysis).
Explains solubility, phase changes, spontaneity of diffusion.
✨ Conclusion
Thermodynamics is a guiding principle of chemistry 🔥🌊. It explains why reactions occur, how much heat is released or absorbed, and whether processes are feasible. It connects chemistry to physics, biology, and engineering, making it a universal science of energy and matter.
📌 Thermodynamics – Key Takeaways
🔵 Basic Concepts
System, surroundings, universe.
Types: open, closed, isolated.
State functions (P, V, T, U, H, G, S).
Intensive vs extensive properties.
🟢 First Law
ΔU = q + w.
Energy conserved.
Enthalpy H = U + PV, ΔH = qₚ.
Exothermic (−ΔH), endothermic (+ΔH).
🔴 Second Law
Spontaneous processes increase entropy.
Heat doesn’t flow cold → hot naturally.
Efficiency always less than 100%.
🟡 Third Law
Entropy of perfect crystal at 0 K = 0.
🌟 Enthalpy Changes
Formation, combustion, neutralization, atomization, fusion, vaporization, sublimation.
📚 Important Laws & Concepts
Hess’s Law: ΔH is additive.
Bond enthalpy: average energy to break bonds.
Heat capacities: Cp, Cv; Cp − Cv = R.
💡 Spontaneity
Gibbs Free Energy: ΔG = ΔH − TΔS.
ΔG < 0 → spontaneous.
Relation to equilibrium constant: ΔG° = −RT ln K.
✨ Applications
Predict feasibility of reactions.
Industrial processes (Haber, Contact).
Biological energy (ATP hydrolysis).
Explains combustion, phase changes, solubility.
📝 Quick Recap:
✔ Thermodynamics studies energy changes in chemical/physical processes.
✔ First Law: energy conserved (ΔU = q + w).
✔ Enthalpy (ΔH): heat at constant pressure; exothermic vs endothermic.
✔ Second Law: entropy (S) increases in spontaneous processes.
✔ Third Law: entropy of perfect crystal at 0 K = 0.
✔ Key tools: Hess’s Law, bond enthalpies, Gibbs Free Energy.
✔ ΔG = ΔH − TΔS decides spontaneity.
✔ Basis for industrial, biological, and natural processes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 5.1
A thermodynamic state function is a quantity
(i) used to determine heat changes
(ii) whose value is independent of path
(iii) used to determine pressure–volume work
(iv) whose value depends on temperature only
🟢 Answer: ✅ (ii) — whose value is independent of path
✏ Explanation:
A state function depends only on the initial and final states, not on the path.
Examples: Internal energy (U), Enthalpy (H), Entropy (S), Pressure (P), Volume (V), Temperature (T).
In contrast, heat (q) and work (w) are path functions.
🔵 Question 5.2
For a process to occur under adiabatic conditions, the correct condition is
(i) ΔT = 0 (ii) Δp = 0 (iii) q = 0 (iv) w = 0
🟢 Answer: ✅ (iii) q = 0
✏ Explanation:
Adiabatic process means no heat exchange with surroundings.
So q = 0, but temperature and pressure can change as work is done.
🔵 Question 5.3
The enthalpies of all elements in their standard states are
(i) unity (ii) zero (iii) < 0 (iv) different
🟢 Answer: ✅ (ii) zero
✏ Explanation:
By convention, standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of an element in its standard state (298 K, 1 bar) is zero.
Example: ΔHf°(O₂, g) = 0; ΔHf°(N₂, g) = 0.
🔵 Question 5.4
If ΔU° = −X kJ mol⁻¹ for combustion of CH₄, the relation is
🟢 Answer: ✅ ΔH° < ΔU°
✏ Explanation:
Relation: ΔH = ΔU + Δn₍gas₎ × R × T
Reaction: CH₄(g) + 2 O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2 H₂O(l)
Δn₍gas₎ = 1 − 3 = −2
⇒ ΔH = ΔU − 2RT → ΔH° < ΔU°
🔵 Question 5.5
Find ΔHf° of CH₄(g) from data (kJ mol⁻¹):
ΔHcomb(CH₄) = −890.3
ΔHcomb(C) = −393.5
ΔHcomb(H₂) = −285.8
🟢 Answer:
✏ Step 1: Formation reaction:
C(s) + 2 H₂(g) → CH₄(g)
✏ Step 2: Use Hess’s Law:
ΔHf°(CH₄) = [ΔHcomb(C) + 2 × ΔHcomb(H₂)] − ΔHcomb(CH₄)
✏ Step 3: Substitute values:
= [ (−393.5) + 2(−285.8) ] − (−890.3)
= (−393.5 − 571.6) + 890.3
= −965.1 + 890.3 = −74.8 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔHf°(CH₄) = −74.8 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.6
Reaction: A + B → C + D + q, with ΔS > 0
🟢 Answer: ✅ Possible at any temperature
✏ Explanation:
Exothermic ⇒ ΔH < 0; also ΔS > 0
Gibbs equation: ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
Both terms favour spontaneity ⇒ ΔG < 0 at all T ⇒ spontaneous always.
🔵 Question 5.7
System absorbs q = 701 J, does w = 394 J.
🟢 Answer:
ΔU = q − w = 701 − 394 = +307 J
✔ Internal energy increases by 307 J.
🔵 Question 5.8
NH₂CN(s) + 3/2 O₂(g) → N₂(g) + CO₂(g) + H₂O(l), ΔU = −742.7 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer:
✏ Step 1: Find Δn₍gas₎ = (1 + 1) − 1.5 = 0.5
✏ Step 2: Use relation: ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
= −742.7 + 0.5 × 8.314 × 298 / 1000
= −742.7 + 1.24 = −741.5 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔH = −741.5 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.9
Heat to raise 60 g Al from 35 °C to 55 °C (Cₘ = 24 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹)
🟢 Answer:
✏ Step 1: moles, n = 60 / 27 = 2.22 mol
✏ Step 2: ΔT = 55 − 35 = 20 K
✏ Step 3: q = n × Cₘ × ΔT = 2.22 × 24 × 20 = 1065.6 J ≈ 1.07 kJ
✔ q = +1.07 kJ absorbed by Al.
🔵 Question 5.10
Find ΔH for freezing 1 mol H₂O (10 °C → ice 0 °C)
Data: ΔHfusion = 6.03 kJ mol⁻¹; Cp(liq) = 75.3 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 Answer:
✏ Step 1: Cool water: q₁ = 75.3 × (−10)/1000 = −0.753 kJ
✏ Step 2: Freeze: q₂ = −6.03 kJ
✏ Step 3: Total ΔH = q₁ + q₂ = −6.78 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔH = −6.78 kJ mol⁻¹ (exothermic)
🔵 Question 5.11
ΔHcomb(C) = −393.5 kJ mol⁻¹. Heat evolved for 35.2 g CO₂?
🟢 Answer:
✏ Step 1: n = 35.2 / 44 = 0.8 mol
✏ Step 2: q = n × ΔH = 0.8 × (−393.5) = −314.8 kJ
✔ Heat released = 314.8 kJ
🔵 Question 5.12
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
N₂O(g) + 3 CO(g) → N₂(g) + 3 CO₂(g)
Given enthalpies of formation (kJ mol⁻¹):
CO = −110.5, CO₂ = −393.5, N₂O = +81, N₂ = 0
🟢 Answer:
✏ Formula: ΔH = ΣΔHf(products) − ΣΔHf(reactants)
= [0 + 3(−393.5)] − [81 + 3(−110.5)]
= (−1180.5) − (−250.5) = −930.0 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ Reaction is exothermic; ΔH = −930 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.13
Given: N₂ + 3 H₂ → 2 NH₃, ΔH = −92.4 kJ mol⁻¹
Find ΔHf° of NH₃
🟢 Answer:
The equation forms 2 mol NH₃,
So enthalpy per mole = (−92.4) / 2 = −46.2 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔHf°(NH₃,g) = −46.2 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.14
Find ΔHf°(CH₃OH,l) from:
CH₃OH(l)+ 3/2 O₂ → CO₂ + 2 H₂O(l), ΔH = −726 kJ
ΔHf°(CO₂)=−393.5, ΔHf°(H₂O)=−286 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer:
ΔHf°(CH₃OH) = [ΔHf(CO₂)+2ΔHf(H₂O)] − ΔH
= [−393.5 + 2(−286)] − (−726)
= (−965.5) + 726 = −239.5 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔHf°(CH₃OH,l) = −239.5 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.15
Find bond enthalpy of C–Cl in CCl₄(l) using:
ΔvapH = +30.5, ΔatH(C) = +715, ΔdissH(Cl₂) = +242 kJ mol⁻¹,
ΔHf(CCl₄,l) = −135.5 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer:
To break into atoms:
CCl₄(l) → C(g) + 4 Cl(g)
ΔH = ΔvapH + ΔatH(C) + 2ΔdissH(Cl₂) − ΔHf(CCl₄)
= 30.5 + 715 + 484 + 135.5 = 1365 kJ
Bond enthalpy = 1365 / 4 = 341 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ E(C–Cl) = 341 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.16
In an isolated system, ΔU = 0. What about ΔS?
🟢 Answer:
No energy or matter exchange; but entropy increases for spontaneous change.
✔ ΔS > 0 for spontaneous processes.
🔵 Question 5.17
At 298 K: 2A + B → C, ΔH = 400 kJ, ΔS = +0.2 kJ K⁻¹
Find T where reaction becomes spontaneous.
🟢 Answer:
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
Spontaneous when ΔG < 0 ⇒ T > ΔH / ΔS
= 400 / 0.2 = 2000 K
✔ Reaction spontaneous at T > 2000 K.
🔵 Question 5.18
2 Cl(g) → Cl₂(g): predict signs of ΔH and ΔS.
🟢 Answer:
Bond formation releases energy ⇒ ΔH < 0
2 mol → 1 mol ⇒ disorder decreases ⇒ ΔS < 0
✔ ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
🔵 Question 5.19
2 A(g)+B(g) → 2 D(g); ΔU = −10.5 kJ, ΔS = −44.1 J K⁻¹.
Find ΔG at 298 K and spontaneity.
🟢 Answer:
Convert ΔS = −0.0441 kJ K⁻¹
Δn = 2 − 3 = −1 ⇒ ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT = −10.5 − 2.48 = −12.98 kJ
ΔG = ΔH − TΔS = −12.98 − 298(−0.0441) = +0.17 kJ
✔ ΔG = +0.17 kJ > 0, reaction non-spontaneous.
🔵 Question 5.20
K = 10, T = 300 K, R = 8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹.
Find ΔG°.
🟢 Answer:
ΔG° = −RT ln K
= −8.314 × 300 × 2.303 × 1 = −5.74 kJ mol⁻¹
✔ ΔG° = −5.74 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 Question 5.21
Thermodynamic stability of NO(g):
½ N₂ + ½ O₂ → NO, ΔH = +90 kJ
NO + ½ O₂ → NO₂, ΔH = −74 kJ
🟢 Answer:
Formation of NO is endothermic ⇒ less stable
Converts exothermically to NO₂ ⇒ NO₂ more stable
✔ NO is thermodynamically unstable.
🔵 Question 5.22
Entropy change in surroundings for
H₂(g) + ½ O₂(g) → H₂O(l), ΔH = −286 kJ at 298 K.
🟢 Answer:
ΔS₍surr₎ = −ΔH / T = −(−286) / 298 = +0.96 kJ K⁻¹ = +960 J K⁻¹
✔ ΔS₍surr₎ = +960 J K⁻¹
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
✳ Section A (Q1–Q16) – MCQs (1 mark each, 16 × 1 = 16 marks)
Options:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
A is true, but R is false
A is false, but R is true
Question 1. Thermodynamics is concerned with:
Rate of reactions
Heat and work
Mechanism of reactions
Atomic structure
Answer: 2
Question 2. Which of the following is a state function?
Work
Heat
Enthalpy
Path
Answer: 3
Question 3. The internal energy of a system is denoted by:
H
U
S
G
Answer: 2
Question 4. Which law states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed?
Zeroth law
First law
Second law
Third law
Answer: 2
Question 5. Work done at constant pressure is related to:
ΔU
ΔH
q_v
q_p
Answer: 4
Question 6. ΔH – ΔU = nRΔT is valid for:
Constant temperature
Gaseous reactions
Reversible reactions
Ionic reactions
Answer: 2
Question 7. The enthalpy of neutralization of strong acid and strong base is approximately:
–57 kJ mol⁻¹
–117 kJ mol⁻¹
–100 kJ mol⁻¹
–34 kJ mol⁻¹
Answer: 1
Question 8. Hess’s law is based on:
First law of thermodynamics
Second law of thermodynamics
Third law of thermodynamics
Zeroth law
Answer: 1
Question 9. Entropy is a measure of:
Heat content
Work capacity
Randomness
Free energy
Answer: 3
Question 10. Which process has ΔS < 0?
Melting of ice
Vaporization of water
Condensation of steam
Dissolution of salt
Answer: 3
Question 11. Gibbs free energy is represented by:
G = H + TS
G = H – TS
G = U + PV
G = U – TS
Answer: 2
Question 12. At equilibrium ΔG is:
Positive
Negative
Zero
Infinite
Answer: 3
Question 13. Which law defines temperature?
Zeroth law
First law
Second law
Third law
Answer: 1
Question 14. (Assertion–Reason)
Assertion (A): Heat is a path function.
Reason (R): Heat depends on path taken, not on initial and final states.
Answer: 1
Question 15. (Assertion–Reason)
Assertion (A): Enthalpy is a state function.
Reason (R): Its value depends only on initial and final states.
Answer: 1
Question 16. Standard enthalpy of formation of an element in its standard state is:
Zero
Positive
Negative
One
Answer: 1
⚡ Section B (Q17–Q21) – Very Short Answer (2 marks each, 5 × 2 = 10 marks)
Q17. Define system and surroundings.
🟦 System → part of universe under study.
🟩 Surroundings → rest of the universe that interacts with system.
Q18. Write first law of thermodynamics in mathematical form.
🟦 ΔU = q + w
🟩 Where ΔU = change in internal energy, q = heat supplied, w = work done.
Q19. State Hess’s law.
🟦 The enthalpy change of a reaction is the same, whether reaction occurs in one step or in multiple steps.
🟩 It depends only on initial and final states.
Q20. Calculate ΔH if ΔU = 50 J, Δn = 2 mol, R = 8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹, T = 300 K.
➤ Formula: ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT
➤ Substitution: = 50 + (2 × 8.314 × 300)
➤ Calculation: = 50 + 4988.4 = 5038.4 J
✅ Final Answer: ΔH = 5038.4 J
Q21. Why entropy increases when ice melts?
🟦 Ice → ordered solid, water → disordered liquid.
🟩 Increase in randomness → ΔS > 0.
🧪 Section C (Q22–Q28) – Short Answer (3 marks each, 7 × 3 = 21 marks)
Q22. State three limitations of first law of thermodynamics.
🟦 It does not indicate feasibility of process.
🟨 It does not predict direction of process.
🟩 It does not give information about rate of process.
Q23. Differentiate between extensive and intensive properties with examples.
🟦 Extensive → depend on amount of substance (mass, volume, enthalpy).
🟨 Intensive → independent of amount (temperature, pressure, density).
🟩 Examples: Heat capacity (extensive), specific heat (intensive).
Q24. Explain standard enthalpy of formation with example.
🟦 Heat change when 1 mol of compound is formed from its elements in standard state.
🟨 Example: C(graphite) + O₂(g) → CO₂(g), ΔH = –393.5 kJ mol⁻¹.
🟩 Standard state = 298 K, 1 bar pressure.
Q25. Derive relation between ΔH and ΔU.
➤ At constant pressure: ΔH = ΔU + pΔV.
➤ For gases, pΔV = ΔnRT.
✅ Final: ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT.
Q26. State second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy.
🟦 For a spontaneous process, total entropy of system and surroundings increases.
🟩 ΔS_universe = ΔS_system + ΔS_surroundings > 0.
Q27. Define Gibbs free energy. Give criterion for spontaneity.
🟦 G = H – TS.
🟨 ΔG < 0 → process spontaneous. 🟩 ΔG = 0 → equilibrium; ΔG > 0 → non-spontaneous.
Q28. Explain enthalpy of neutralization with example.
🟦 Heat change when 1 mol of H⁺ reacts with 1 mol of OH⁻ to form water.
🟨 Strong acid + strong base → ΔH = –57 kJ mol⁻¹.
🟩 Example: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O.
🧭 Section D (Q29–Q30) – Case-Based Questions (4 marks each, 2 × 4 = 8 marks)
Q29. Read the passage and answer the questions:
The combustion of methane is highly exothermic. The enthalpy change depends on whether the process is carried out directly or in steps, but the overall enthalpy remains the same. This demonstrates Hess’s law.
(a) Write the chemical equation for combustion of methane. (1 mark)
(b) State Hess’s law. (1 mark)
(c) Explain why enthalpy change remains the same for direct and indirect routes. (2 marks)
🧪 Answer:
(a) CH₄(g) + 2O₂(g) → CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(l), ΔH = –890 kJ mol⁻¹
(b) Hess’s law: Enthalpy change is independent of path, depends only on initial and final states.
(c) Because enthalpy is a state function, it depends only on states, not on process steps.
Q30. Read the passage and answer the questions:
Entropy is a measure of disorder. For spontaneous processes such as melting of ice or expansion of gas, entropy increases. According to the second law of thermodynamics, ΔS_universe > 0 for spontaneity.
(a) Define entropy. (1 mark)
(b) What happens to entropy during freezing of water? (1 mark)
(c) State second law of thermodynamics in terms of entropy. (2 marks)
🧪 Answer:
(a) Entropy is a measure of randomness/disorder of a system.
(b) Entropy decreases because order increases when liquid turns into solid.
(c) For spontaneous process: ΔS_universe = ΔS_system + ΔS_surroundings > 0.
⚡ Section E (Q31–Q33) – Long Answer (5 marks each, 3 × 5 = 15 marks)
Q31. (a) Derive the relation between ΔH and ΔU for a gaseous reaction.
OR
(b) Calculate ΔH for the reaction: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g), given ΔU = –92 kJ, Δn = –2, T = 298 K, R = 8.314 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹.
🧪 Answer (a):
➤ By definition: H = U + pV → ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV).
➤ For gases: Δ(pV) = ΔnRT.
➤ So, ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT.
✅ Relation derived: ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT.
Answer (b):
➤ Formula: ΔH = ΔU + ΔnRT.
➤ Substitution: ΔU = –92 kJ, Δn = (2 – 4) = –2, T = 298 K.
➤ ΔH = –92 kJ + (–2 × 8.314 × 298)/1000 kJ.
➤ ΔH = –92 kJ – 4.95 kJ = –96.95 kJ.
✅ Final Answer: ΔH = –96.95 kJ.
Q32. (a) State and explain the second law of thermodynamics using Gibbs free energy.
OR
(b) Calculate ΔG for a reaction at 298 K if ΔH = –40 kJ mol⁻¹ and ΔS = –100 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹. Comment on spontaneity.
🧪 Answer (a):
🟦 Second law: Natural processes tend to occur spontaneously.
🟨 In terms of Gibbs energy: ΔG = ΔH – TΔS.
🟩 If ΔG < 0 → process spontaneous. 🧪 ΔG = 0 → equilibrium, ΔG > 0 → non-spontaneous.
🎯 Thus Gibbs energy criterion predicts spontaneity.
Answer (b):
➤ Formula: ΔG = ΔH – TΔS.
➤ Convert ΔS: –100 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹ = –0.100 kJ mol⁻¹ K⁻¹.
➤ ΔG = –40 – (298 × –0.100).
➤ ΔG = –40 + 29.8 = –10.2 kJ mol⁻¹.
✅ Final Answer: ΔG = –10.2 kJ mol⁻¹ → reaction is spontaneous.
Q33. (a) State and explain the third law of thermodynamics. Mention its significance.
OR
(b) Define enthalpy of formation, enthalpy of combustion, and enthalpy of neutralization with examples.
🧪 Answer (a):
🟦 Third law: Entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance is zero at 0 K.
🟨 Significance: Provides absolute scale of entropy values.
🟩 Used to calculate standard entropy changes and predict spontaneity of reactions.
🎯 Helps in determination of equilibrium constants.
Answer (b):
🟦 Enthalpy of formation: Heat change when 1 mol compound formed from elements (C + O₂ → CO₂, ΔH = –393.5 kJ mol⁻¹).
🟨 Enthalpy of combustion: Heat change when 1 mol substance completely burns (CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O, ΔH = –890 kJ mol⁻¹).
🟩 Enthalpy of neutralization: Heat change when 1 mol H⁺ reacts with 1 mol OH⁻ (HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O, ΔH = –57 kJ mol⁻¹).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is a state function?
🔴 ① Work
🟢 ② Heat
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Path length
🟢 Answer: ③ Internal energy
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: O
🔵 Question 2:
The enthalpy change for neutralisation of a strong acid with a strong base is always:
🔴 ① –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② –34.5 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –100 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ –10 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ① –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: B
🔵 Question 3:
ΔH is equal to ΔU when:
🔴 ① Pressure is constant
🟢 ② Volume is constant
🟡 ③ No work is done
🔵 ④ Reaction is isothermal
🟢 Answer: ② Volume is constant
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: M
🔵 Question 4:
Which law of thermodynamics is also known as the law of conservation of energy?
🔴 ① Zeroth
🟢 ② First
🟡 ③ Second
🔵 ④ Third
🟢 Answer: ② First
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: C
🔵 Question 5:
The enthalpy of an element in its standard state is taken as:
🔴 ① 0 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② 1 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –1 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ Depends on element
🟢 Answer: ① 0 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: P2
🔵 Question 6:
For an ideal gas, ΔH – ΔU =
🔴 ① ΔnRT
🟢 ② –ΔnRT
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ nRT
🟢 Answer: ① ΔnRT
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 7:
The heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a substance by 1°C is called:
🔴 ① Molar heat capacity
🟢 ② Specific heat
🟡 ③ Latent heat
🔵 ④ Enthalpy
🟢 Answer: ① Molar heat capacity
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2008 | Set: C
🔵 Question 8:
The entropy change for a reversible process is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: Q2
🔵 Question 9:
The enthalpy change for conversion of ice to water at 0°C is called:
🔴 ① Heat of combustion
🟢 ② Heat of vaporisation
🟡 ③ Heat of fusion
🔵 ④ Heat of sublimation
🟢 Answer: ③ Heat of fusion
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: B
🔵 Question 10:
The entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance at 0 K is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Positive
🟡 ③ Negative
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2020 | Set: R2
🔵 Question 11:
In an isothermal reversible expansion of an ideal gas:
🔴 ① ΔU = 0
🟢 ② ΔH ≠ 0
🟡 ③ q = 0
🔵 ④ w = 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔU = 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 12:
The work done in an isothermal reversible expansion of an ideal gas is given by:
🔴 ① –nRT ln(V₂/V₁)
🟢 ② –ΔnRT
🟡 ③ PΔV
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ① –nRT ln(V₂/V₁)
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: C
🔵 Question 13:
Which process is always spontaneous?
🔴 ① ΔG > 0
🟢 ② ΔG < 0
🟡 ③ ΔG = 0
🔵 ④ ΔH = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: M
🔵 Question 14:
Which one is intensive property?
🔴 ① Enthalpy
🟢 ② Internal energy
🟡 ③ Heat capacity
🔵 ④ Temperature
🟢 Answer: ④ Temperature
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: A
🔵 Question 15:
The condition for spontaneity of a process at constant T and P is:
🔴 ① ΔH < 0 🟢 ② ΔG < 0 🟡 ③ ΔS > 0
🔵 ④ ΔU < 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 16:
Which is true for a spontaneous reaction?
🔴 ① ΔS < 0, ΔG < 0 🟢 ② ΔS > 0, ΔG < 0 🟡 ③ ΔS = 0, ΔG = 0 🔵 ④ ΔS > 0, ΔG > 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔS > 0, ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: P
🔵 Question 17:
The heat change at constant pressure is equal to:
🔴 ① ΔU
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ qv
🔵 ④ w
🟢 Answer: ② ΔH
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: C
🔵 Question 18:
Which of the following expressions is correct?
🔴 ① ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
🟢 ② ΔG = ΔH + TΔS
🟡 ③ ΔG = ΔU + PΔV
🔵 ④ ΔH = ΔU – PΔV
🟢 Answer: ① ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: O
🔵 Question 19:
Work done in reversible expansion of gas is maximum because:
🔴 ① Pext > Pint
🟢 ② Pext < Pint
🟡 ③ Pext = Pint (infinitesimally less)
🔵 ④ Temperature is variable
🟢 Answer: ③ Pext = Pint (infinitesimally less)
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: A
🔵 Question 20:
Which of the following is not a state function?
🔴 ① Enthalpy
🟢 ② Work
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Entropy
🟢 Answer: ② Work
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: R1
🔵 Question 21:
If ΔH = –ve and ΔS = –ve, the reaction is spontaneous at:
🔴 ① High temperature
🟢 ② Low temperature
🟡 ③ All temperatures
🔵 ④ Never spontaneous
🟢 Answer: ② Low temperature
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: S1
🔵 Question 22:
The relation between Cp and Cv is:
🔴 ① Cp – Cv = R
🟢 ② Cp – Cv = nR
🟡 ③ Cp + Cv = R
🔵 ④ Cp/Cv = R
🟢 Answer: ② Cp – Cv = nR
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2001 | Set: B
🔵 Question 23:
Which process is accompanied by decrease in entropy?
🔴 ① Evaporation of water
🟢 ② Dissolution of salt in water
🟡 ③ Condensation of steam
🔵 ④ Expansion of gas
🟢 Answer: ③ Condensation of steam
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 24:
Which one is not an extensive property?
🔴 ① Heat capacity
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Temperature
🟢 Answer: ④ Temperature
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2020 | Set: P1
🔵 Question 25:
ΔU = q – w is an expression of:
🔴 ① Second law
🟢 ② First law
🟡 ③ Third law
🔵 ④ Zeroth law
🟢 Answer: ② First law
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: C
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following processes is non-spontaneous?
🔴 ① Flow of heat from hot to cold body
🟢 ② Expansion of gas into vacuum
🟡 ③ Electrolysis of water
🔵 ④ Dissolution of NaCl in water
🟢 Answer: ③ Electrolysis of water
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: M
🔵 Question 27:
Which of the following has highest entropy?
🔴 ① Ice
🟢 ② Water
🟡 ③ Steam
🔵 ④ Diamond
🟢 Answer: ③ Steam
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: A
🔵 Question 28:
The entropy change when 2 moles of an ideal gas expands isothermally and reversibly from V to 2V is:
🔴 ① 2R ln 2
🟢 ② R ln 2
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ –2R ln 2
🟢 Answer: ① 2R ln 2
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 29:
At equilibrium ΔG is:
🔴 ① > 0
🟢 ② < 0
🟡 ③ = 0
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ③ = 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: R2
🔵 Question 30:
The entropy of the universe:
🔴 ① Always decreases
🟢 ② Always increases
🟡 ③ Remains constant
🔵 ④ Becomes zero
🟢 Answer: ② Always increases
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: B
🔵 Question 31:
For a spontaneous process, which condition is correct?
🔴 ① ΔG > 0
🟢 ② ΔG < 0
🟡 ③ ΔS = 0
🔵 ④ ΔH = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: P
🔵 Question 32:
The enthalpy of neutralisation of strong acid and strong base is:
🔴 ① –13.6 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –273 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ② –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: A
🔵 Question 33:
The second law of thermodynamics introduces the concept of:
🔴 ① Internal energy
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Entropy
🔵 ④ Heat capacity
🟢 Answer: ③ Entropy
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 34:
The unit of entropy is:
🔴 ① J K⁻¹ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ J mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ kJ K mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ① J K⁻¹ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: C
🔵 Question 35:
If ΔH = –40 kJ and ΔS = –100 J K⁻¹, then ΔG at 300 K is:
🔴 ① –10 kJ
🟢 ② –70 kJ
🟡 ③ –30 kJ
🔵 ④ –100 kJ
🟢 Answer: ① –10 kJ
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: C
🔵 Question 36:
The internal energy change for isothermal expansion of ideal gas is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: S2
🔵 Question 37:
The work done when one mole of an ideal gas expands reversibly at temperature T from V₁ to V₂ is:
🔴 ① –RT ln(V₂/V₁)
🟢 ② –nRT ln(P₂/P₁)
🟡 ③ –ΔnRT
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ① –RT ln(V₂/V₁)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: P
🔵 Question 38:
At absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Infinity
🟡 ③ Constant
🔵 ④ Cannot be determined
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: M
🔵 Question 39:
The work done during free expansion of an ideal gas is:
🔴 ① Maximum
🟢 ② Minimum
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Positive
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: A
🔵 Question 40:
Enthalpy is equal to:
🔴 ① U + PV
🟢 ② U – PV
🟡 ③ q – w
🔵 ④ TS
🟢 Answer: ① U + PV
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2020 | Set: Q2
🔵 Question 41:
Which of the following is an extensive property?
🔴 ① Temperature
🟢 ② Pressure
🟡 ③ Heat capacity
🔵 ④ Density
🟢 Answer: ③ Heat capacity
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: B
🔵 Question 42:
If ΔH = +ve and ΔS = +ve, the reaction will be spontaneous at:
🔴 ① High temperature
🟢 ② Low temperature
🟡 ③ All temperatures
🔵 ④ Never spontaneous
🟢 Answer: ① High temperature
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: P
🔵 Question 43:
The expression ΔH = ΔU + PΔV is valid at:
🔴 ① Constant volume
🟢 ② Constant pressure
🟡 ③ Constant temperature
🔵 ④ Constant entropy
🟢 Answer: ② Constant pressure
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: M
🔵 Question 44:
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, which quantity remains constant?
🔴 ① ΔU
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ Temperature
🔵 ④ All of these
🟢 Answer: ④ All of these
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2010 | Set: C
🔵 Question 45:
If a process is endothermic and accompanied by decrease in entropy, it will be:
🔴 ① Spontaneous at all T
🟢 ② Non-spontaneous at all T
🟡 ③ Spontaneous at high T
🔵 ④ Spontaneous at low T
🟢 Answer: ② Non-spontaneous at all T
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: S
🔵 Question 46:
For a spontaneous process, the total entropy change is:
🔴 ① ΔStotal > 0
🟢 ② ΔStotal < 0
🟡 ③ ΔStotal = 0
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ① ΔStotal > 0
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: O
🔵 Question 47:
The value of work done in free expansion of an ideal gas is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Positive
🟡 ③ Negative
🔵 ④ Maximum
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: A
🔵 Question 48:
In thermodynamics, work done by the system is taken as:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Depends on process
🟢 Answer: ① Positive
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 49:
At constant temperature and pressure, Gibbs free energy change is equal to:
🔴 ① Maximum work other than PV work
🟢 ② Heat absorbed
🟡 ③ Change in enthalpy
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ① Maximum work other than PV work
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: M
🔵 Question 50:
A process is spontaneous if:
🔴 ① ΔG > 0
🟢 ② ΔG < 0 🟡 ③ ΔS < 0 🔵 ④ ΔH > 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: B
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
For an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, which of the following is correct?
🔴 ① ΔU = 0, q = w
🟢 ② ΔU ≠ 0, q = –w
🟡 ③ ΔU = q + w
🔵 ④ ΔU > 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔU = 0, q = w
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 2
Which of the following is a state function?
🔴 ① Work
🟢 ② Heat
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Path length
🟢 Answer: ③ Internal energy
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 3
The enthalpy of neutralisation of strong acid and strong base is:
🔴 ① –13.7 kJ/mol
🟢 ② –57.1 kJ/mol
🟡 ③ –100 kJ/mol
🔵 ④ –120 kJ/mol
🟢 Answer: ② –57.1 kJ/mol
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 4
The internal energy of an ideal gas decreases by 200 J when it does 500 J of work. The heat absorbed is:
🔴 ① 300 J
🟢 ② 700 J
🟡 ③ –300 J
🔵 ④ –700 J
🟢 Answer: ③ –300 J
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 5
Which one of the following is an extensive property?
🔴 ① Pressure
🟢 ② Temperature
🟡 ③ Volume
🔵 ④ Density
🟢 Answer: ③ Volume
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 6
The heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) is related to Cp as:
🔴 ① Cp – Cv = R
🟢 ② Cp – Cv = 0
🟡 ③ Cp + Cv = R
🔵 ④ Cp = Cv
🟢 Answer: ① Cp – Cv = R
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 7
Which of the following is correct for enthalpy (H)?
🔴 ① H = U – PV
🟢 ② H = U + PV
🟡 ③ H = U × PV
🔵 ④ H = U / PV
🟢 Answer: ② H = U + PV
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 8
If ΔH = –ve and ΔS = –ve, then reaction will be spontaneous at:
🔴 ① High T
🟢 ② Low T
🟡 ③ All T
🔵 ④ Never
🟢 Answer: ② Low T
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 9
The work done in reversible isothermal expansion of one mole of ideal gas is:
🔴 ① w = –nRT ln(Vf/Vi)
🟢 ② w = –PΔV
🟡 ③ w = ΔU
🔵 ④ w = q
🟢 Answer: ① w = –nRT ln(Vf/Vi)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 10
Which of the following processes is endothermic?
🔴 ① Freezing of ice
🟢 ② Combustion of fuel
🟡 ③ Dissolution of NH₄Cl in water
🔵 ④ Condensation of steam
🟢 Answer: ③ Dissolution of NH₄Cl in water
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 11
For an isobaric process:
🔴 ① ΔH = ΔU + PΔV
🟢 ② ΔH = ΔU – PΔV
🟡 ③ ΔH = ΔU
🔵 ④ ΔU = 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔH = ΔU + PΔV
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 12
In an adiabatic process:
🔴 ① q = 0
🟢 ② ΔU = 0
🟡 ③ w = 0
🔵 ④ ΔH = 0
🟢 Answer: ① q = 0
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 13
If ΔG = 0, the reaction is:
🔴 ① Spontaneous
🟢 ② Non-spontaneous
🟡 ③ At equilibrium
🔵 ④ Impossible
🟢 Answer: ③ At equilibrium
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 14
Which has highest entropy?
🔴 ① Ice
🟢 ② Liquid water
🟡 ③ Steam
🔵 ④ All equal
🟢 Answer: ③ Steam
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 15
In which case is ΔU = ΔH?
🔴 ① Constant pressure
🟢 ② Constant volume
🟡 ③ No work of expansion
🔵 ④ All processes
🟢 Answer: ③ No work of expansion (ΔV=0)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 16
If a system absorbs 200 J heat and does 50 J work, ΔU is:
🔴 ① 150 J
🟢 ② 250 J
🟡 ③ –150 J
🔵 ④ –250 J
🟢 Answer: ① 150 J
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 17
Standard enthalpy of formation of an element in its reference state is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Positive
🟡 ③ Negative
🔵 ④ Cannot be defined
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 18
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS. If ΔH = +ve and ΔS = +ve, reaction is:
🔴 ① Spontaneous at low T
🟢 ② Spontaneous at high T
🟡 ③ Non-spontaneous at all T
🔵 ④ Equilibrium only
🟢 Answer: ② Spontaneous at high T
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 19
Which of the following statements is correct?
🔴 ① Work is a state function
🟢 ② Heat is a state function
🟡 ③ Internal energy is a state function
🔵 ④ Path length is a state function
🟢 Answer: ③ Internal energy is a state function
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 20
The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure is approximately:
🔴 ① 4.18 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 ② 75 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟡 ③ 42 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🔵 ④ 25 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ② 75 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 21
Which law is the basis of calorimetry?
🔴 ① First law of thermodynamics
🟢 ② Second law
🟡 ③ Zeroth law
🔵 ④ Hess’s law
🟢 Answer: ④ Hess’s law
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 22
The entropy of a perfect crystal at 0 K is:
🔴 ① 0
🟢 ② 1
🟡 ③ Infinite
🔵 ④ Cannot be determined
🟢 Answer: ① 0 (Third law)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 23
When ice melts into water, entropy:
🔴 ① Decreases
🟢 ② Increases
🟡 ③ Remains same
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ② Increases
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 24
Enthalpy of neutralisation of weak acid with strong base is less than –57.1 kJ/mol because:
🔴 ① Heat lost
🟢 ② Weak acid partially ionised
🟡 ③ Weak base partially ionised
🔵 ④ Heat absorbed
🟢 Answer: ② Weak acid partially ionised
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 25
Which of the following is true for free expansion of an ideal gas?
🔴 ① q = 0, w = 0, ΔU = 0
🟢 ② q = 0, w ≠ 0, ΔU ≠ 0
🟡 ③ q ≠ 0, w = 0, ΔU ≠ 0
🔵 ④ q = w
🟢 Answer: ① q = 0, w = 0, ΔU = 0
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 26
If a system absorbs 500 J heat and work done on system is 300 J, ΔU is:
🔴 ① 200 J
🟢 ② 800 J
🟡 ③ –200 J
🔵 ④ –800 J
🟢 Answer: ② 800 J
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 27
For a spontaneous process, which of the following is true?
🔴 ① ΔG > 0
🟢 ② ΔG < 0
🟡 ③ ΔG = 0
🔵 ④ ΔH = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 28
The value of ΔU for cyclic process is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Positive
🟡 ③ Negative
🔵 ④ Cannot be predicted
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 29
At constant temperature and pressure, spontaneity depends on:
🔴 ① ΔU
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ ΔS
🔵 ④ ΔG
🟢 Answer: ④ ΔG
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 30
The entropy change for evaporation of one mole of water at 373 K and ΔHvap = 40.8 kJ/mol is:
🔴 ① 40.8 J/K
🟢 ② 109 J/K
🟡 ③ 81.6 J/K
🔵 ④ 218 J/K
🟢 Answer: ② 109 J/K (ΔS = ΔH/T)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 31
The relation between ΔG and equilibrium constant K is:
🔴 ① ΔG = RT ln K
🟢 ② ΔG° = –RT ln K
🟡 ③ ΔG = –RT ln K
🔵 ④ ΔG° = RT ln K
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG° = –RT ln K
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 32
Which one of the following is always correct?
🔴 ① ΔS universe = ΔS system
🟢 ② ΔS universe = ΔS system + ΔS surroundings
🟡 ③ ΔS system = 0
🔵 ④ ΔS surroundings = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔS universe = ΔS system + ΔS surroundings
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 33
The maximum work obtained from a system at constant temperature and pressure is equal to:
🔴 ① ΔH
🟢 ② ΔU
🟡 ③ ΔG
🔵 ④ ΔS
🟢 Answer: ③ ΔG
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 34
If ΔH = –ve and ΔS = +ve, the reaction is:
🔴 ① Always spontaneous
🟢 ② Never spontaneous
🟡 ③ Spontaneous at high T only
🔵 ④ Spontaneous at low T only
🟢 Answer: ① Always spontaneous
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 35
The enthalpy of combustion of methane is –890 kJ/mol. This means:
🔴 ① 890 kJ absorbed
🟢 ② 890 kJ released
🟡 ③ 445 kJ absorbed
🔵 ④ 445 kJ released
🟢 Answer: ② 890 kJ released
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 36
For an ideal gas, the difference Cp – Cv equals:
🔴 ① γ
🟢 ② R
🟡 ③ nR
🔵 ④ 1
🟢 Answer: ② R
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 37
Which one is not a thermodynamic state function?
🔴 ① Internal energy
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Work
🔵 ④ Entropy
🟢 Answer: ③ Work
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 38
In which of the following processes entropy decreases?
🔴 ① Evaporation of liquid
🟢 ② Freezing of liquid water
🟡 ③ Melting of ice
🔵 ④ Expansion of gas
🟢 Answer: ② Freezing of liquid water
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 39
The heat change at constant volume is measured by:
🔴 ① Calorimeter
🟢 ② Bomb calorimeter
🟡 ③ Thermometer
🔵 ④ Barometer
🟢 Answer: ② Bomb calorimeter
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 40
The efficiency of Carnot engine depends on:
🔴 ① Working substance
🟢 ② Temperature of source and sink
🟡 ③ Pressure of gas
🔵 ④ Heat capacity
🟢 Answer: ② Temperature of source and sink
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 41
Work done in an isochoric process is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Cannot be determined
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 42
The free energy change for a reversible process is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Cannot be defined
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 43
ΔH < ΔU when:
🔴 ① Number of moles of gas increases
🟢 ② Number of moles of gas decreases
🟡 ③ ΔV = 0
🔵 ④ T constant
🟢 Answer: ② Number of moles of gas decreases
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 44
The spontaneity of a process depends on:
🔴 ① Only enthalpy
🟢 ② Only entropy
🟡 ③ Both enthalpy and entropy
🔵 ④ Pressure
🟢 Answer: ③ Both enthalpy and entropy
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 45
Which law states “energy can neither be created nor destroyed”?
🔴 ① Zeroth law
🟢 ② First law
🟡 ③ Second law
🔵 ④ Third law
🟢 Answer: ② First law
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 46
Entropy change for an isothermal reversible expansion of an ideal gas is:
🔴 ① ΔS = nR ln(Vf/Vi)
🟢 ② ΔS = ΔU/T
🟡 ③ ΔS = qrev
🔵 ④ ΔS = 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔS = nR ln(Vf/Vi)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 47
The entropy of universe increases in:
🔴 ① Irreversible process
🟢 ② Reversible process
🟡 ③ At equilibrium
🔵 ④ Isochoric process
🟢 Answer: ① Irreversible process
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 48
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS. For a reaction endothermic in nature and ΔS < 0:
🔴 ① Always spontaneous
🟢 ② Never spontaneous
🟡 ③ Spontaneous at low T
🔵 ④ Spontaneous at high T
🟢 Answer: ② Never spontaneous
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 49
The standard enthalpy of formation of H₂O(l) is –286 kJ/mol. This refers to:
🔴 ① Heat absorbed when 1 mol water formed
🟢 ② Heat released when 1 mol water formed
🟡 ③ Heat absorbed when 1 mol H₂ formed
🔵 ④ Heat released when 1 mol H₂ formed
🟢 Answer: ② Heat released when 1 mol water formed
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 50
For an endothermic reaction to be spontaneous:
🔴 ① ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0 🟢 ② ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0
🟡 ③ ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0 🔵 ④ ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0 (at high T)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
For an ideal gas, which of the following quantities is path dependent?
🔴 ① ΔU
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ q
🔵 ④ ΔG
🟢 Answer: ③ q
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 2:
The enthalpy change for the reaction H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g) is –184 kJ mol⁻¹. The bond energy of HCl is:
🔴 ① 92 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② 184 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ 368 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ 436 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ④ 436 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 3:
The internal energy change in the isothermal expansion of 2 moles of an ideal gas is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 4:
Which one of the following reactions is exothermic?
🔴 ① Evaporation of water
🟢 ② Combustion of methane
🟡 ③ Fusion of ice
🔵 ④ Vaporisation of ethanol
🟢 Answer: ② Combustion of methane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 5:
The ΔU for vaporisation of 1 mole of liquid water at 373 K and 1 atm is 40.7 kJ mol⁻¹. The work done against atmospheric pressure is approximately:
🔴 ① 1.2 kJ
🟢 ② 3.0 kJ
🟡 ③ 2.5 kJ
🔵 ④ 0.5 kJ
🟢 Answer: ② 3.0 kJ
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 6:
For a spontaneous process at constant temperature and pressure, the condition is:
🔴 ① ΔH > 0
🟢 ② ΔG < 0 🟡 ③ ΔS < 0 🔵 ④ ΔU > 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG < 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 7:
If the enthalpy of formation of CO₂ is –393.5 kJ mol⁻¹ and that of H₂O is –285.8 kJ mol⁻¹, the enthalpy of combustion of CH₄ is:
🔴 ① –890.3 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② –740.0 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –1000.0 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ –1200.0 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ① –890.3 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 8:
Which of the following statements is correct?
🔴 ① Heat is a state function
🟢 ② Work done in adiabatic reversible expansion is maximum
🟡 ③ Internal energy depends on path
🔵 ④ Entropy of universe decreases in spontaneous process
🟢 Answer: ② Work done in adiabatic reversible expansion is maximum
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 9:
The value of ΔG for a reaction at equilibrium is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 10:
Which of the following is always positive?
🔴 ① ΔG
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ ΔS for universe
🔵 ④ q
🟢 Answer: ③ ΔS for universe
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 11:
For an isothermal process, which of the following is true?
🔴 ① ΔU = 0
🟢 ② ΔH = 0
🟡 ③ ΔS = 0
🔵 ④ q = 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔU = 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 12:
The efficiency of a Carnot engine working between 400 K and 300 K is:
🔴 ① 25%
🟢 ② 50%
🟡 ③ 75%
🔵 ④ 33%
🟢 Answer: ④ 33%
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 13:
The relation between ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS at constant temperature is:
🔴 ① ΔG = ΔH + TΔS
🟢 ② ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
🟡 ③ ΔG = ΔU – PΔV
🔵 ④ ΔG = ΔS – ΔH/T
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 14:
Which one of the following processes is endothermic?
🔴 ① Combustion of carbon
🟢 ② Dissolution of NH₄Cl in water
🟡 ③ Condensation of steam
🔵 ④ Freezing of water
🟢 Answer: ② Dissolution of NH₄Cl in water
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 15:
The work done when one mole of an ideal gas expands reversibly and isothermally from volume V to 2V at temperature T is:
🔴 ① –RT ln 2
🟢 ② RT ln 2
🟡 ③ 2RT ln 2
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ① –RT ln 2
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2008 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 16:
The entropy change for the reversible melting of one mole of ice at 0 °C (ΔHfus = 6.0 kJ mol⁻¹) is:
🔴 ① 6.0 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 ② 22 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟡 ③ 6000 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🔵 ④ 273 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ② 22 J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 17:
Which of the following statements is true for a spontaneous process?
🔴 ① ΔSsys < 0 and ΔSuniverse < 0 🟢 ② ΔSuniverse > 0
🟡 ③ ΔSsys > 0 always
🔵 ④ ΔH = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔSuniverse > 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 18:
The enthalpy change for the reaction N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH₃ is –92 kJ mol⁻¹. The enthalpy of formation of NH₃ is:
🔴 ① –92 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② –46 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –23 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ –184 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ② –46 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 19:
Which of the following is true for an adiabatic process?
🔴 ① q = 0
🟢 ② ΔU = 0
🟡 ③ ΔH = 0
🔵 ④ ΔS = 0 always
🟢 Answer: ① q = 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 20:
At constant temperature and pressure, a process will be spontaneous if:
🔴 ① ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0 🟢 ② ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
🟡 ③ ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0
🔵 ④ ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 21:
Which of the following processes has ΔH = ΔU?
🔴 ① Heating at constant pressure
🟢 ② Heating at constant volume
🟡 ③ Isothermal expansion
🔵 ④ Adiabatic compression
🟢 Answer: ② Heating at constant volume
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 22:
The entropy change in the universe for a reversible process is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② Positive
🟡 ③ Negative
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 23:
For a chemical reaction at equilibrium, which of the following is true?
🔴 ① ΔH = 0
🟢 ② ΔG = 0
🟡 ③ ΔS = 0
🔵 ④ ΔU = 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG = 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 24:
Which of the following statements is correct for exothermic reactions?
🔴 ① ΔH > 0
🟢 ② ΔH < 0 🟡 ③ ΔG > 0
🔵 ④ ΔS > 0 always
🟢 Answer: ② ΔH < 0
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 25:
The work done in a free expansion of an ideal gas is:
🔴 ① Maximum
🟢 ② Zero
🟡 ③ Positive
🔵 ④ Negative
🟢 Answer: ② Zero
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 26:
For which of the following processes is ΔS negative?
🔴 ① Melting of ice
🟢 ② Freezing of water
🟡 ③ Vaporisation of liquid
🔵 ④ Mixing of gases
🟢 Answer: ② Freezing of water
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 27:
Which of the following is a state function?
🔴 ① Heat
🟢 ② Work
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Path
🟢 Answer: ③ Internal energy
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 28:
The second law of thermodynamics introduces the concept of:
🔴 ① Work
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Entropy
🔵 ④ Internal energy
🟢 Answer: ③ Entropy
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 29:
The enthalpy of neutralisation of a strong acid and strong base is approximately:
🔴 ① –13.6 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 ② –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ –100 kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ –120 kJ mol⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ② –57.1 kJ mol⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 30:
In an isochoric process, which of the following is true?
🔴 ① ΔU = q
🟢 ② ΔU = w
🟡 ③ ΔH = 0
🔵 ④ ΔS = 0
🟢 Answer: ① ΔU = q
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 31:
Which of the following is not a state function?
🔴 ① Enthalpy
🟢 ② Internal energy
🟡 ③ Work
🔵 ④ Entropy
🟢 Answer: ③ Work
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 32:
The unit of entropy is:
🔴 ① J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
🟢 ② J mol⁻¹
🟡 ③ kJ mol⁻¹
🔵 ④ J K⁻¹
🟢 Answer: ① J mol⁻¹ K⁻¹
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 33:
Which one of the following reactions has ΔH ≈ ΔU?
🔴 ① Combustion of glucose
🟢 ② H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g)
🟡 ③ N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2NH₃(g)
🔵 ④ CaCO₃(s) → CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
🟢 Answer: ② H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g)
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2008 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 34:
The maximum possible work that can be obtained from a system in a given process is equal to:
🔴 ① ΔH
🟢 ② ΔU
🟡 ③ ΔG
🔵 ④ ΔS
🟢 Answer: ③ ΔG
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
The branch of chemistry which deals with energy changes during chemical reactions is:
🔴 ① Electrochemistry
🟢 ② Thermodynamics
🟡 ③ Chemical kinetics
🔵 ④ Photochemistry
🟢 Answer: ② Thermodynamics
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 2:
The first law of thermodynamics is a statement of:
🔴 ① Conservation of mass
🟢 ② Conservation of energy
🟡 ③ Conservation of momentum
🔵 ④ Conservation of entropy
🟢 Answer: ② Conservation of energy
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 3:
The SI unit of heat is:
🔴 ① Calorie
🟢 ② Joule
🟡 ③ Erg
🔵 ④ Kilocalorie
🟢 Answer: ② Joule
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 4:
Internal energy is a:
🔴 ① Path function
🟢 ② State function
🟡 ③ Work function
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ② State function
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 5:
The enthalpy of elements in their standard states is taken as:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② One
🟡 ③ Positive
🔵 ④ Negative
🟢 Answer: ① Zero
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 6:
Work done in isothermal reversible expansion of an ideal gas is given by:
🔴 ① W = nRT ln(V₂/V₁)
🟢 ② W = –PΔV
🟡 ③ W = ΔE
🔵 ④ W = q
🟢 Answer: ① W = nRT ln(V₂/V₁)
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 7:
Which process occurs at constant pressure?
🔴 ① Isochoric
🟢 ② Isobaric
🟡 ③ Isothermal
🔵 ④ Adiabatic
🟢 Answer: ② Isobaric
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 8:
The heat change at constant pressure is equal to change in:
🔴 ① Internal energy
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Entropy
🔵 ④ Work
🟢 Answer: ② Enthalpy
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 9:
Which one is an extensive property?
🔴 ① Pressure
🟢 ② Temperature
🟡 ③ Volume
🔵 ④ Density
🟢 Answer: ③ Volume
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 10:
Which one is an intensive property?
🔴 ① Heat capacity
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Density
🔵 ④ Internal energy
🟢 Answer: ③ Density
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 11:
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mol of a substance by 1 K is:
🔴 ① Specific heat
🟢 ② Molar heat capacity
🟡 ③ Latent heat
🔵 ④ Enthalpy
🟢 Answer: ② Molar heat capacity
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 12:
In adiabatic process, exchange of heat is:
🔴 ① Maximum
🟢 ② Zero
🟡 ③ Minimum
🔵 ④ Positive
🟢 Answer: ② Zero
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 13:
The entropy of a perfectly crystalline substance at absolute zero is:
🔴 ① Infinite
🟢 ② Zero
🟡 ③ One
🔵 ④ Cannot be defined
🟢 Answer: ② Zero
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 14:
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS is the equation of:
🔴 ① First law of thermodynamics
🟢 ② Gibbs free energy
🟡 ③ Work function
🔵 ④ Helmholtz energy
🟢 Answer: ② Gibbs free energy
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 15:
In an isothermal process of an ideal gas:
🔴 ① ΔE = 0
🟢 ② ΔH = 0
🟡 ③ ΔE = ΔH = 0
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ③ ΔE = ΔH = 0
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 16:
Which law is also called the “law of constant heat summation”?
🔴 ① Hess’s law
🟢 ② First law of thermodynamics
🟡 ③ Zeroth law
🔵 ④ Second law
🟢 Answer: ① Hess’s law
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 17:
Which property determines the spontaneity of a process?
🔴 ① ΔH
🟢 ② ΔG
🟡 ③ ΔS
🔵 ④ ΔE
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 18:
For a spontaneous reaction at constant T and P, ΔG is:
🔴 ① Positive
🟢 ② Negative
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ② Negative
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 19:
Which one is a state function?
🔴 ① Work
🟢 ② Heat
🟡 ③ Enthalpy
🔵 ④ Path
🟢 Answer: ③ Enthalpy
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 20:
The condition for equilibrium in terms of Gibbs free energy is:
🔴 ① ΔG > 0
🟢 ② ΔG = 0
🟡 ③ ΔG < 0
🔵 ④ ΔG = –TΔS
🟢 Answer: ② ΔG = 0
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 21:
The latent heat of fusion of ice at 0°C is:
🔴 ① 3.36 kJ/mol
🟢 ② 6.01 kJ/mol
🟡 ③ 40.7 kJ/mol
🔵 ④ 1.0 kJ/mol
🟢 Answer: ② 6.01 kJ/mol
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 22:
Which law of thermodynamics defines temperature?
🔴 ① Zeroth law
🟢 ② First law
🟡 ③ Second law
🔵 ④ Third law
🟢 Answer: ① Zeroth law
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 23:
The heat absorbed by a system at constant volume is equal to:
🔴 ① ΔH
🟢 ② ΔE
🟡 ③ qₚ
🔵 ④ Work
🟢 Answer: ② ΔE
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 24:
In which type of process ΔH = ΔE?
🔴 ① Isothermal
🟢 ② Isochoric
🟡 ③ Isobaric
🔵 ④ Adiabatic
🟢 Answer: ② Isochoric
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 25:
The free expansion of an ideal gas is an example of:
🔴 ① Irreversible process
🟢 ② Reversible process
🟡 ③ Isothermal work
🔵 ④ Adiabatic reversible
🟢 Answer: ① Irreversible process
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 26:
For an isothermal reversible expansion of an ideal gas, work done depends on:
🔴 ① Initial and final pressure/volume
🟢 ② Path followed
🟡 ③ Temperature change
🔵 ④ Heat capacity
🟢 Answer: ① Initial and final pressure/volume
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 27:
If ΔH = –100 kJ and ΔS = –200 J/K, the reaction is spontaneous at:
🔴 ① Low temperature
🟢 ② High temperature
🟡 ③ All temperatures
🔵 ④ Never spontaneous
🟢 Answer: ① Low temperature
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 28:
The maximum work done by a system in a reversible isothermal expansion is equal to:
🔴 ① ΔE
🟢 ② ΔH
🟡 ③ q
🔵 ④ ΔG
🟢 Answer: ④ ΔG
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 29:
If ΔU = +20 J and W = –15 J, then q = ?
🔴 ① +35 J
🟢 ② +5 J
🟡 ③ –5 J
🔵 ④ –35 J
🟢 Answer: ② +5 J
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 30:
The enthalpy change for the reaction C(graphite) → C(diamond) is positive. This indicates:
🔴 ① Diamond is more stable
🟢 ② Graphite is more stable
🟡 ③ Both equally stable
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ② Graphite is more stable
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 31:
If ΔH = 50 kJ and ΔS = 100 J/K, at what minimum temperature will the reaction become spontaneous?
🔴 ① 100 K
🟢 ② 200 K
🟡 ③ 300 K
🔵 ④ 500 K
🟢 Answer: ② 200 K
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 32:
In an isobaric process, heat supplied is used for:
🔴 ① Only increasing internal energy
🟢 ② Only work done
🟡 ③ Both ΔE and work
🔵 ④ Only ΔH
🟢 Answer: ③ Both ΔE and work
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 33:
A reaction is endothermic and has positive entropy change. It will be:
🔴 ① Always spontaneous
🟢 ② Spontaneous at high T
🟡 ③ Spontaneous at low T
🔵 ④ Non-spontaneous
🟢 Answer: ② Spontaneous at high T
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 34:
Which property is NOT a state function?
🔴 ① Heat
🟢 ② Enthalpy
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Entropy
🟢 Answer: ① Heat
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 35:
During an adiabatic reversible expansion of an ideal gas:
🔴 ① q = 0
🟢 ② ΔE = –W
🟡 ③ ΔH = ΔE
🔵 ④ All of these
🟢 Answer: ④ All of these
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 36:
ΔU of a system can be calculated from:
🔴 ① q + W
🟢 ② q – W
🟡 ③ q/W
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ① q + W
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 37:
The efficiency of a Carnot engine depends upon:
🔴 ① Nature of working substance
🟢 ② Temperature of source and sink
🟡 ③ Pressure of system
🔵 ④ Volume of system
🟢 Answer: ② Temperature of source and sink
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 38:
Which process has ΔE = ΔH = 0?
🔴 ① Isothermal expansion of an ideal gas
🟢 ② Cooling of a solid
🟡 ③ Melting of ice
🔵 ④ Freezing of water
🟢 Answer: ① Isothermal expansion of an ideal gas
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 39:
ΔH is less than ΔU when:
🔴 ① Reaction produces more moles of gases
🟢 ② Reaction consumes moles of gases
🟡 ③ No gases involved
🔵 ④ Reaction is exothermic
🟢 Answer: ② Reaction consumes moles of gases
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 40:
In a cyclic process:
🔴 ① ΔE = 0
🟢 ② ΔH = 0
🟡 ③ ΔS = 0
🔵 ④ All of these
🟢 Answer: ④ All of these
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🚀 Advanced-level (Q41–Q50):
🔵 Question 41:
If an ideal gas expands isothermally and reversibly, entropy change of the system is:
🔴 ① Zero
🟢 ② nR ln(V₂/V₁)
🟡 ③ ΔH/T
🔵 ④ ΔE/T
🟢 Answer: ② nR ln(V₂/V₁)
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 42:
The efficiency of a Carnot engine operating between 500 K and 300 K is:
🔴 ① 0.2
🟢 ② 0.3
🟡 ③ 0.4
🔵 ④ 0.5
🟢 Answer: ③ 0.4
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 43:
If ΔH = 100 kJ and ΔE = 80 kJ, the work done by the system at 300 K is:
🔴 ① 20 kJ
🟢 ② 100 kJ
🟡 ③ 80 kJ
🔵 ④ Zero
🟢 Answer: ① 20 kJ
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 44:
Entropy is a measure of:
🔴 ① Heat content
🟢 ② Disorder of a system
🟡 ③ Internal energy
🔵 ④ Work function
🟢 Answer: ② Disorder of a system
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 45:
For a spontaneous endothermic reaction:
🔴 ① ΔH < 0, ΔS < 0 🟢 ② ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0
🟡 ③ ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0
🔵 ④ ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0
🟢 Answer: ② ΔH > 0, ΔS > 0
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 46:
The second law of thermodynamics introduces the concept of:
🔴 ① Enthalpy
🟢 ② Entropy
🟡 ③ Gibbs energy
🔵 ④ Internal energy
🟢 Answer: ② Entropy
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 47:
If ΔS(universe) > 0, the process is:
🔴 ① Non-spontaneous
🟢 ② Spontaneous
🟡 ③ At equilibrium
🔵 ④ Impossible
🟢 Answer: ② Spontaneous
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 48:
The entropy change in reversible adiabatic process is:
🔴 ① Maximum
🟢 ② Minimum
🟡 ③ Zero
🔵 ④ Infinite
🟢 Answer: ③ Zero
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 49:
If one mole of an ideal gas expands isothermally at 300 K from 10 L to 20 L, the work done is (R = 8.314 J/mol·K):
🔴 ① 1.73 kJ
🟢 ② 1.73 J
🟡 ③ 17.3 J
🔵 ④ 173 J
🟢 Answer: ① 1.73 kJ
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 50:
According to the third law of thermodynamics, entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is:
🔴 ① Infinite
🟢 ② Zero
🟡 ③ One
🔵 ④ Cannot be defined
🟢 Answer: ② Zero
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
