Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 4. Animal Kingdom
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
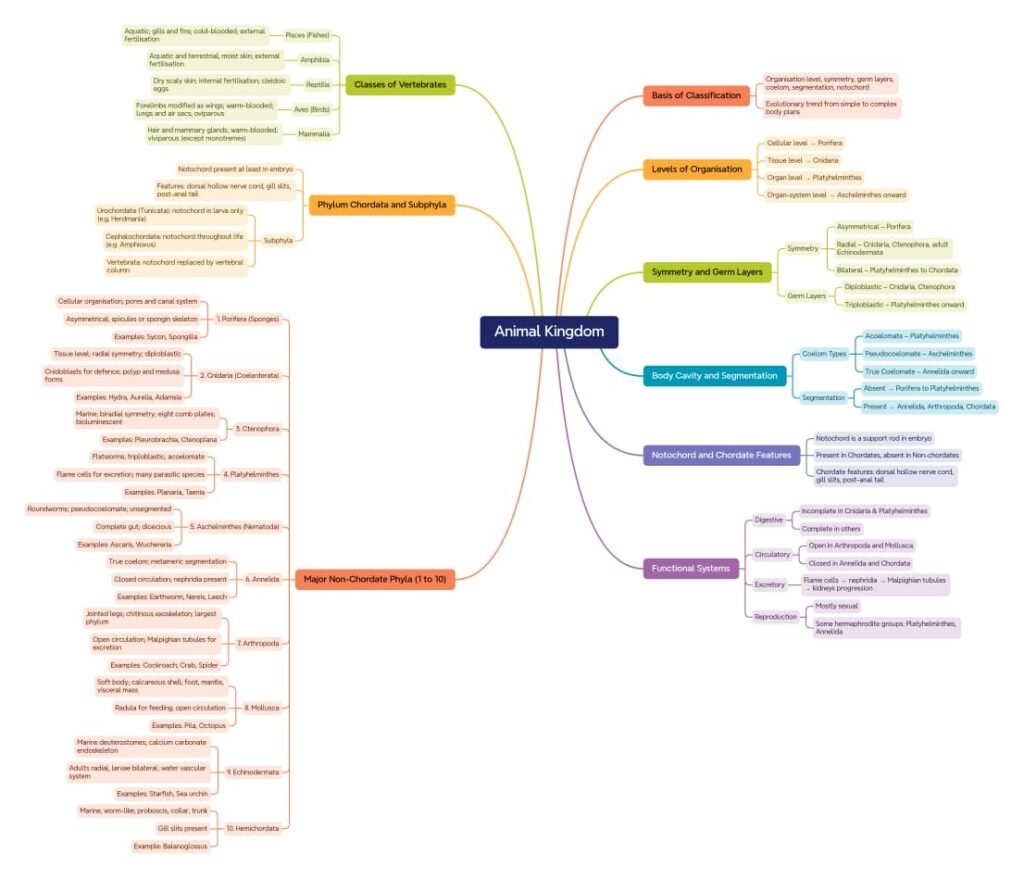
🔵 Introduction to Animal Kingdom
The animal kingdom includes multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms. These organisms show tissue differentiation, body organization, and diverse modes of reproduction and development.
🟢 Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia:
Multicellular and eukaryotic.
Heterotrophic (obtain food by ingestion).
Lack cell walls (unlike plants).
Show locomotion at some stage.
Possess nervous and muscle tissues (except a few lower forms).
Store carbohydrates as glycogen.
✏️ Note: Classification is based on features like body symmetry, coelom, germ layers, segmentation, notochord, and level of organization.
🔴 Basis of Classification
🟡 1. Levels of Organization
➡️ Animals show increasing complexity:
Cellular level: Cells are loosely arranged (e.g., sponges).
Tissue level: Similar cells form tissues (e.g., cnidarians).
Organ level: Tissues form organs (e.g., Platyhelminthes).
Organ system level: Organ systems (e.g., annelids, vertebrates).
🟡 2. Body Symmetry
➡️ Symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts.
Asymmetrical: Cannot divide equally (e.g., sponges).
Radial symmetry: Can be divided into equal halves along many planes (e.g., cnidarians, echinoderms in larval stage).
Bilateral symmetry: Divided into mirror halves in one plane (e.g., humans, arthropods).
💡 Concept: Bilateral symmetry is linked with cephalization (head development).
🟡 3. Germ Layers
➡️ Layers formed during embryonic development.
Diploblastic: Two layers – ectoderm and endoderm (e.g., cnidarians).
Triploblastic: Three layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm (e.g., annelids to chordates).
🟡 4. Coelom
➡️ Fluid-filled body cavity between body wall and gut.
Acoelomate: No body cavity (e.g., flatworms).
Pseudocoelomate: Body cavity not lined with mesoderm (e.g., roundworms).
Coelomate (Eucoelomate): True coelom (e.g., annelids, vertebrates).
✔️ True coelom arises from the mesoderm.
🟡 5. Segmentation
➡️ Division of body into repetitive units.
Unsegmented: No repetition (e.g., platyhelminthes).
Segmented: Repetition of body units (e.g., annelids, arthropods).
🟡 6. Notochord
➡️ A flexible rod-like structure supporting the body.
Present in chordates (at least in embryonic stage).
Absent in non-chordates.
🧠 Chordates = animals with notochord
🧠 Non-chordates = animals without notochord
🔵 Classification of Animals (Based on Phyla)
There are broad phyla under Kingdom Animalia:
🟣 1. Phylum – Porifera (Sponges)
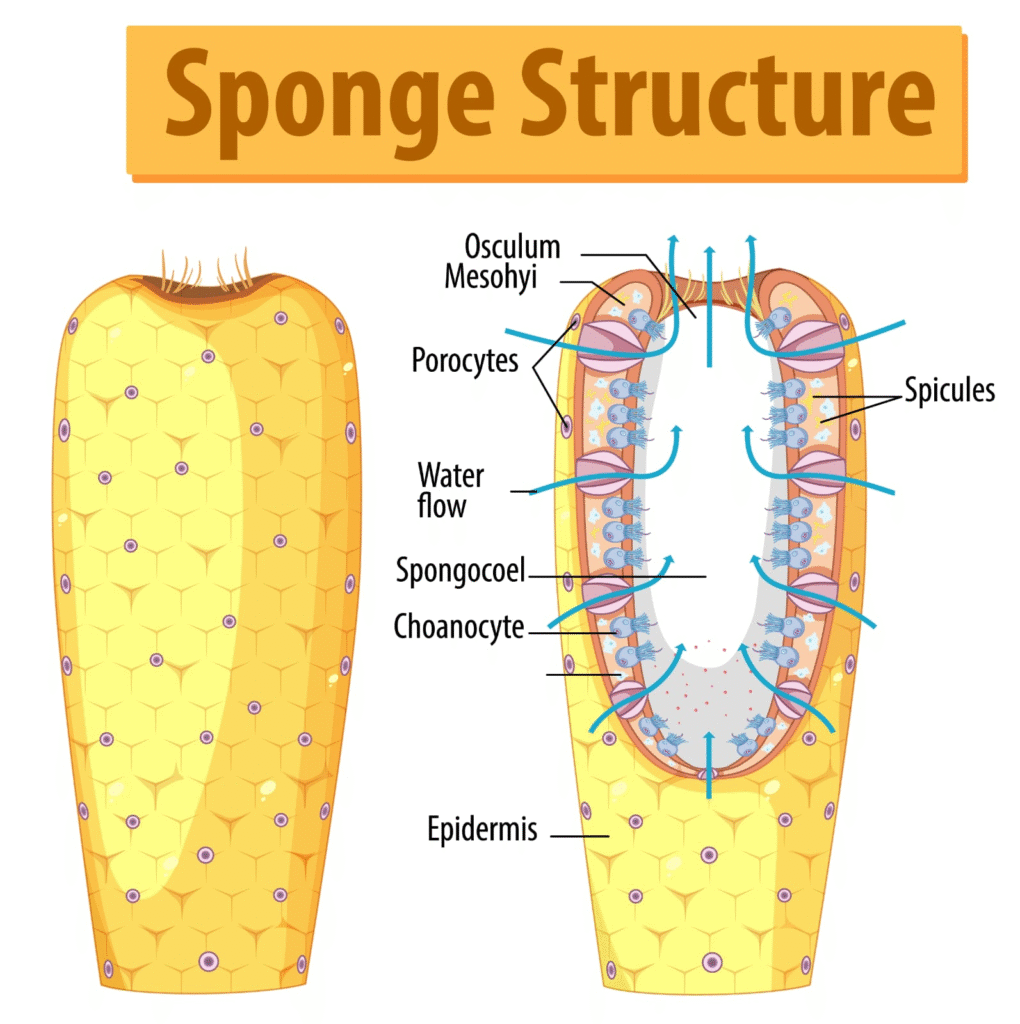
✔️ Simplest animals
✔️ Cellular level organization
✔️ Asymmetrical
✔️ Water canal system (for circulation)
✔️ Internal skeleton of spicules
🌿 Examples: Sycon, Spongilla, Euspongia
🟣 2. Phylum – Cnidaria (Coelenterata)
✔️ Tissue level of organization
✔️ Radial symmetry
✔️ Diploblastic
✔️ Body forms: polyp and medusa
✔️ Cnidoblasts for defense and capturing prey
🌿 Examples: Hydra, Jellyfish, Sea anemone

Jellyfish
🟣 3. Phylum – Ctenophora
✔️ Commonly called sea walnuts
✔️ Radially symmetrical, diploblastic
✔️ Tissue level organization
✔️ Eight comb plates for locomotion
✔️ Bioluminescent
🌿 Examples: Pleurobrachia, Ctenoplana
🟣 4. Phylum – Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
✔️ Triploblastic, acoelomate
✔️ Bilateral symmetry
✔️ Organ level of organization
✔️ Flame cells for excretion
🌿 Examples: Planaria, Liver fluke, Tapeworm
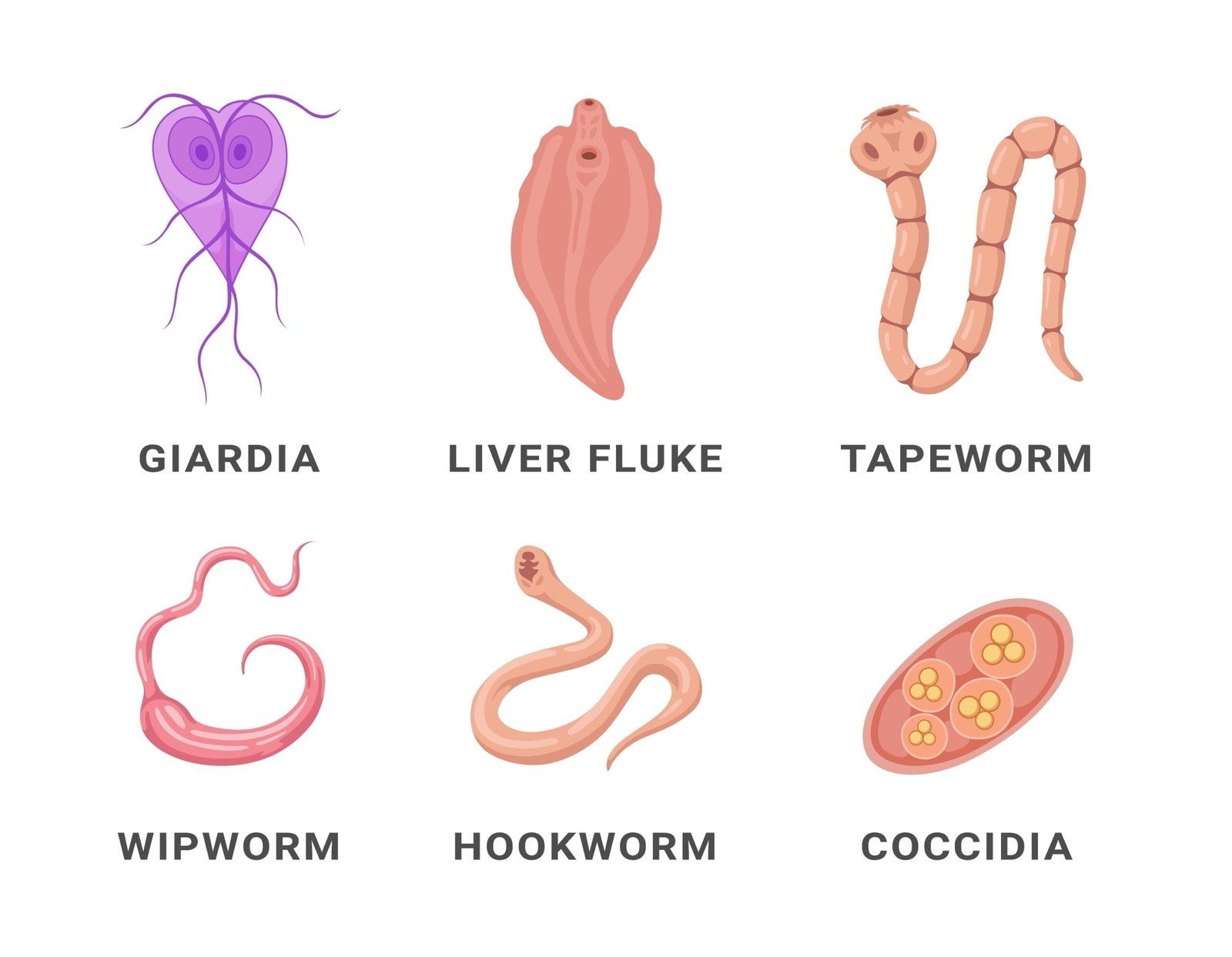
🟣 5. Phylum – Nematoda (Roundworms)
✔️ Pseudocoelomate
✔️ Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic
✔️ Organ system level
✔️ Complete digestive system
🌿 Examples: Ascaris, Wuchereria, Ancylostoma
🟣 6. Phylum – Annelida
✔️ Triploblastic, coelomate
✔️ Metameric segmentation
✔️ Closed circulatory system
✔️ Nephridia for excretion
🌿 Examples: Earthworm, Leeches, Nereis
🟣 7. Phylum – Arthropoda
✔️ Largest phylum
✔️ Jointed appendages
✔️ Chitinous exoskeleton
✔️ Open circulatory system
🌿 Examples: Insects, Prawns, Spiders, Scorpions

🟣 8. Phylum – Mollusca
✔️ Second largest phylum
✔️ Body soft, unsegmented
✔️ Muscular foot, visceral mass, mantle
✔️ Calcareous shell
🌿 Examples: Snail, Octopus, Mussel, Pila

Octopus

🟣 9. Phylum – Echinodermata
✔️ Exclusively marine
✔️ Radial symmetry (adult), bilateral (larva)
✔️ Water vascular system
✔️ Calcareous endoskeleton
🌿 Examples: Starfish, Sea urchin, Sea cucumber
🟣 10. Phylum – Hemichordata
✔️ Previously considered chordates
✔️ Stomochord (rudimentary notochord)
✔️ Vermiform body
✔️ Marine habitat
🌿 Example: Balanoglossus
🟣 11. Phylum – Chordata
🧠 Key feature: presence of notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, and pharyngeal slits at some stage
✔️ Triploblastic, bilateral, coelomate
✔️ Closed circulatory system
✔️ Post-anal tail (present in many)
🧪 Subphyla:
🔵 Urochordata: Notochord in larval tail (e.g., Ascidia)
🔵 Cephalochordata: Notochord throughout life (e.g., Amphioxus)
🔵 Vertebrata: Notochord replaced by vertebral column
🟡 Vertebrates – Further Division
🔶 1. Cyclostomata
✔️ Jawless vertebrates
✔️ Circular mouth
✔️ Cartilaginous body
🌿 Examples: Petromyzon, Myxine
🔶 2. Pisces (Fishes)
✔️ Gills, fins, scales
✔️ Two-chambered heart
✔️ External fertilization
🌿 Examples: Shark, Rohu, Catla
🔶 3. Amphibia
✔️ Moist skin, no scales
✔️ Three-chambered heart
✔️ Both aquatic and terrestrial life
🌿 Examples: Frog, Toad, Salamander
🔶 4. Reptilia
✔️ Dry skin with scales
✔️ Three-chambered heart (except crocodiles – four)
✔️ Internal fertilization, shelled eggs
🌿 Examples: Lizard, Snake, Crocodile
🔶 5. Aves (Birds)
✔️ Feathers, forelimbs as wings
✔️ Four-chambered heart
✔️ Warm-blooded
✔️ Oviparous
🌿 Examples: Pigeon, Ostrich, Crow

🔶 6. Mammalia
✔️ Hair, mammary glands
✔️ Four-chambered heart
✔️ Most are viviparous
✔️ External ears (pinnae)
🌿 Examples: Human, Whale, Lion, Bat
🧩 Why This Lesson Matters
📌 Understanding classification helps:
Grasp structural and evolutionary diversity
Appreciate ecological roles of animals
Build foundation for advanced zoology, biodiversity, and medical studies
📝 Quick Recap:
🔹 Levels: Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ system
🔹 Symmetry: Asymmetrical → Radial → Bilateral
🔹 Germ layers: Diploblastic / Triploblastic
🔹 Coelom: Acoelomate / Pseudocoelomate / Coelomate
🔹 Segmentation: Present in annelids, arthropods
🔹 Notochord: Present in chordates only
🔹 Eleven major phyla
🔹 Vertebrates: Cyclostomes → Fishes → Amphibians → Reptiles → Birds → Mammals
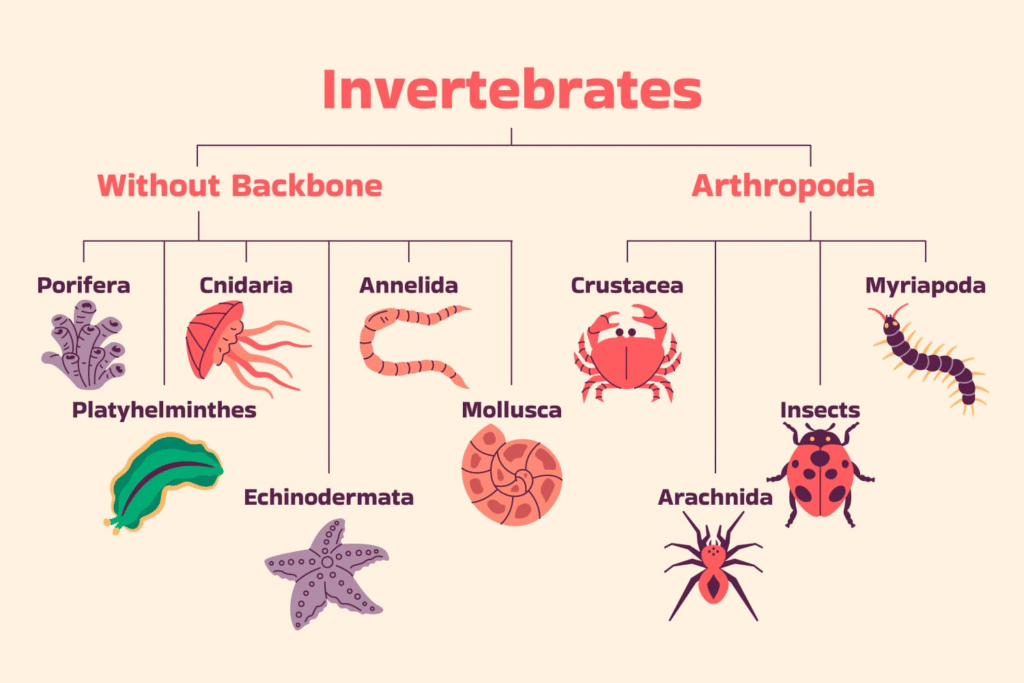
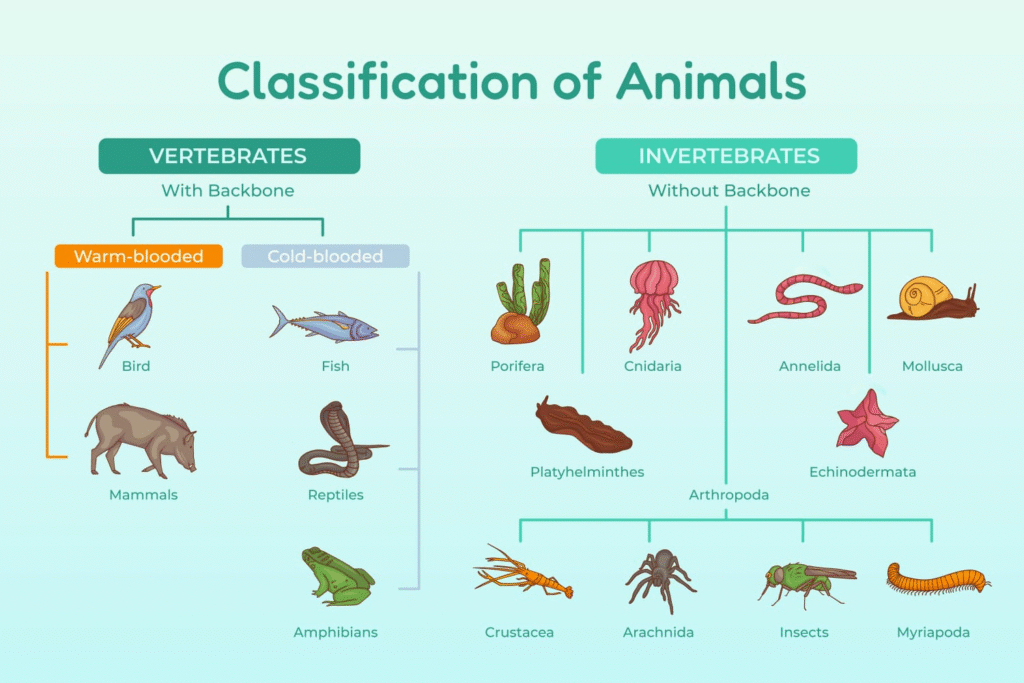
📚 Summary (300 Words)
🔹 The Animal Kingdom includes all multicellular, eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms with complex body organization.
🔹 Classification is based on:
Body organization (cell, tissue, organ, organ system)
Body symmetry (asymmetrical, radial, bilateral)
Germ layers (diploblastic or triploblastic)
Coelom (true, false, absent)
Segmentation
Presence or absence of notochord
🔹 Non-chordates include:
Porifera – cellular level, sponges
Cnidaria – diploblastic, cnidoblasts
Ctenophora – comb plates, bioluminescent
Platyhelminthes – flatworms, flame cells
Nematoda – roundworms, pseudocoel
Annelida – segmented worms, nephridia
Arthropoda – jointed appendages, largest phylum
Mollusca – soft-bodied, shell, second largest
Echinodermata – water vascular system, radial symmetry
Hemichordata – stomochord, marine
🔹 Chordates have a notochord and include:
Urochordata (notochord in tail of larva)
Cephalochordata (notochord throughout life)
Vertebrata (notochord replaced by vertebral column)
🔹 Vertebrates include:
Cyclostomes – jawless fishes
Pisces – true fishes
Amphibians – moist-skinned, dual life
Reptiles – dry skin, shelled eggs
Birds – feathers, warm-blooded, oviparous
Mammals – hair, mammary glands, mostly viviparous
✅ This lesson is foundational to all future study in zoology and environmental science.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🟦 Q1. What are the modifications that are observed in birds that help them fly?
✅ Answer:
Birds have evolved special adaptations for flight:
🪽 1. Hollow bones: Light-weight skeleton reduces body mass
🪶 2. Feathers: Provide lift and streamline the body
💪 3. Powerful flight muscles: Especially the pectoral muscles
💨 4. Air sacs: Enhance oxygen supply during flight
💓 5. High metabolic rate: Supports high energy demand
🪶 6. Forelimbs modified into wings
🟦 Q2. Could the number of eggs or young ones produced by an oviparous and viviparous mother be equal? Why?
✅ Answer:
❌ Not necessarily equal. Here’s why:
🐣 Oviparous animals (e.g., frogs, birds):
🔸 Lay more eggs due to higher mortality
🔸 External fertilization – less protection
👶 Viviparous animals (e.g., mammals):
🔹 Produce fewer young
🔹 Internal fertilization – better nourishment and protection
📌 Hence, viviparous species don’t need to produce many offspring.
🟦 Q3. Segmentation in the body is first observed in which of the following:
(a) Platyhelminthes (b) Aschelminthes (c) Annelida (d) Arthropoda
✅ Answer: ✔️ (c) Annelida
📌 Annelids (like earthworms) are the first animals to show true segmentation (metamerism).
🟦 Q4. Match the following:
🅰️ Column A 🅱️ Column B
(a) Operculum (viii) Osteichthyes
(b) Parapodia (v) Annelida
(c) Scales (iv) Reptilia
(d) Comb plates (i) Ctenophora
(e) Radula (ii) Mollusca
(f) Hairs (vii) Mammalia
(g) Choanocytes (iii) Porifera
(h) Gill slits (vi) Cyclostomata and Chondrichthyes
✔️ Matching done based on defining features of each group.
🟦 Q5. Prepare a list of some animals that are found parasitic on human beings.
✅ Answer:
🔹 Ascaris lumbricoides – Roundworm (intestinal parasite)
🔹 Taenia solium – Pork tapeworm (intestinal)
🔹 Entamoeba histolytica – Causes amoebic dysentery
🔹 Plasmodium spp. – Causes malaria (via mosquito)
🔹 Wuchereria bancrofti – Filarial worm (causes elephantiasis)
🔹 Pediculus humanus – Head louse (ectoparasite)
🔹 Ancylostoma – Hookworm (feeds on blood in intestine)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔷 Section A – MCQs + Assertion & Reason (Q1–Q16)
(Each question carries 1 mark)
Q1. Which of the following animals belongs to phylum Ctenophora?
(A) Physalia
(B) Pleurobrachia
(C) Aurelia
(D) Adamsia
Answer: (B)
Q2. Notochord is present in:
(A) All non-chordates
(B) Some invertebrates
(C) All chordates at some stage
(D) Only vertebrates
Answer: (C)
Q3. In which of the following phyla is the water vascular system present?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Echinodermata
(D) Coelenterata
Answer: (C)
Q4. Which one of the following features is NOT present in the members of phylum Mollusca?
(A) Muscular foot
(B) Radula
(C) Closed circulatory system
(D) Mantle
Answer: (C)
Q5. Which animal is a diploblastic organism?
(A) Ascaris
(B) Hydra
(C) Planaria
(D) Earthworm
Answer: (B)
Q6. Assertion (A): All vertebrates are chordates.
Reason (R): All chordates possess notochord throughout life.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false but R is true
Answer: (C)
Q7. The excretory structures in Annelids are called:
(A) Flame cells
(B) Malpighian tubules
(C) Nephridia
(D) Protonephridia
Answer: (C)
Q8. The characteristic of radial symmetry is seen in which of the following groups?
(A) Annelida and Arthropoda
(B) Coelenterata and Ctenophora
(C) Mollusca and Annelida
(D) Arthropoda and Mollusca
Answer: (B)
Q9. Which of the following animal is a pseudocoelomate?
(A) Ascaris
(B) Pheretima
(C) Sycon
(D) Taenia
Answer: (A)
Q10. Assertion (A): Echinoderms have bilateral symmetry in larval stages.
Reason (R): They show organ system level of organization.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true but R is false
(D) A is false but R is true
Answer: (B)
Q11. Which of the following organisms exhibit metameric segmentation?
(A) Earthworm, Leech
(B) Tapeworm, Ascaris
(C) Cockroach, Pila
(D) Hydra, Aurelia
Answer: (A)
Q12. Which is the largest phylum in the animal kingdom?
(A) Annelida
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Mollusca
(D) Chordata
Answer: (B)
Q13. Which of the following organisms has a true coelom?
(A) Planaria
(B) Ascaris
(C) Pheretima
(D) Taenia
Answer: (C)
Q14. In which of the following organisms does the circulatory system remain open?
(A) Pheretima
(B) Octopus
(C) Cockroach
(D) Leech
Answer: (C)
Q15. Which animal has a canal system for water transport?
(A) Leech
(B) Sycon
(C) Hydra
(D) Starfish
Answer: (B)
Q16. Which of the following structures is not associated with molluscs?
(A) Mantle
(B) Proboscis
(C) Foot
(D) Shell
Answer: (B)
🔷 Section B – Very Short Answer Questions (Q17–Q18)
(Each question carries 2 marks)
Q17. Write any two characteristic features of phylum Platyhelminthes.
🟢 Answer:
🔹 They are dorsoventrally flattened, triploblastic and acoelomate animals.
🔹 They exhibit bilateral symmetry and organ-level body organization.
Q18. Differentiate between diploblastic and triploblastic animals.
🟣 Answer:
🔸 Diploblastic animals: Have two germ layers — ectoderm and endoderm (e.g., Hydra).
🔸 Triploblastic animals: Have three germ layers — ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm (e.g., Earthworm).
🔷 Section B – Very Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
(Questions Q19 to Q21)
Q19. Why are echinoderms considered closer to chordates than to other non-chordates?
🟢 Answer:
🔸 Both echinoderms and chordates are deuterostomes, i.e., their blastopore develops into anus during embryonic development.
🔸 Both groups exhibit radial cleavage and have coelomic pouches formed from the archenteron.
Q20. What is metameric segmentation? Name two phyla in which it is found.
🔹 Answer:
✔️ Metameric segmentation is the serial repetition of similar body segments along the body length.
✔️ It is found in Annelida (e.g., Earthworm) and Arthropoda (e.g., Cockroach).
Q21. Define canal system. In which phylum is it found?
🔸 Answer:
✔️ Canal system is a network of water channels through which water enters the body, facilitates food and oxygen intake, and removes waste.
✔️ It is a characteristic feature of phylum Porifera (e.g., Sycon).
🔶 Section C – Short Answer Questions (3 Marks Each)
(Questions Q22 to Q28)
Q22. State three differences between non-chordates and chordates.
🧬 Answer:
🔹 Notochord: Absent in non-chordates; present in chordates.
🔹 Nervous system: Ventral, solid, and paired in non-chordates; dorsal, hollow, and single in chordates.
🔹 Heart: If present, is ventral in non-chordates; dorsal in chordates.
Q23. Differentiate between acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, and coelomate animals.
🟢 Answer:
🔸 Acoelomate: No body cavity (e.g., Platyhelminthes)
🔸 Pseudocoelomate: Body cavity not lined by mesoderm (e.g., Nematoda)
🔸 Coelomate: True body cavity lined by mesoderm (e.g., Annelida, Chordata)
Q24. Describe the structure and function of the water vascular system in echinoderms.
🔹 Answer:
✔️ The water vascular system is a network of fluid-filled canals used for locomotion, food capture, respiration, and excretion.
✔️ It includes madreporite, stone canal, ring canal, radial canals, and tube feet.
✔️ Unique to echinoderms like starfish.
Q25. List three adaptive features of arthropods that make them the most successful phylum.
🧠 Answer:
🔸 Presence of jointed appendages for varied functions
🔸 Chitinous exoskeleton for protection and support
🔸 Segmented body allowing specialization of body parts
Q26. Mention three distinguishing features of phylum Mollusca.
🟣 Answer:
🔹 Muscular foot for movement
🔹 Visceral hump with internal organs
🔹 Mantle secretes a calcareous shell
Q27. What are the key characteristics of phylum Platyhelminthes? Give one example.
🧬 Answer:
✔️ Dorsoventrally flattened body
✔️ Triploblastic and acoelomate
✔️ Show bilateral symmetry and organ-level organization
🌿 Example: Taenia solium (Tapeworm)
Q28. Give three reasons why vertebrates are more advanced than non-chordates.
🟢 Answer:
🔸 Presence of vertebral column and internal skeleton
🔸 Highly developed brain and sensory organs
🔸 Advanced closed circulatory system and efficient respiration
🔷 Section D – Case-Based Questions (4 Marks Each)
(Questions Q29 to Q30)
Q29. Read the passage and answer the following questions:
Earthworms belong to phylum Annelida. They are segmented worms showing metamerism and a true coelom. They possess nephridia for excretion, and their circulatory system is closed type. Locomotion is achieved with the help of setae and body muscles.
(a) Identify the level of body organization in earthworms.
(b) Name the type of symmetry and coelom they possess.
(c) What is the significance of nephridia?
(d) Mention two adaptive features of earthworms.
🟢 Answer:
🔹 (a) Organ system level of organization
🔹 (b) Bilateral symmetry; true coelom (coelomate)
🔹 (c) Nephridia help in osmoregulation and excretion of nitrogenous wastes.
🔹 (d) Adaptive features:
✅ Metameric segmentation (body flexibility)
✅ Setae and body muscles for locomotion
Q30. Read the passage and answer the following questions:
Members of phylum Echinodermata are exclusively marine animals. They possess a unique water vascular system and exhibit radial symmetry in adults. Their larval stages show bilateral symmetry. The body has a calcareous endoskeleton made of ossicles.
(a) Why are echinoderms considered closer to chordates?
(b) What kind of symmetry is present in adult echinoderms?
(c) What is the function of the water vascular system?
(d) Mention two examples of echinoderms.
🧬 Answer:
🔹 (a) Both are deuterostomes and share embryonic developmental similarities.
🔹 (b) Radial symmetry in adults
🔹 (c) Water vascular system helps in locomotion, feeding, respiration, and excretion.
🔹 (d) Asterias (starfish), Echinus (sea urchin)
🔷 Section E – Long Answer Questions (5 Marks Each)
(Questions Q31 to Q33)
Q31. Describe the general characteristics of phylum Arthropoda. Mention two examples from different arthropod groups.
🟣 Answer:
✔️ Arthropoda is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom.
🔸 Body Segmentation: Divided into head, thorax, and abdomen.
🔸 Exoskeleton: Made of chitin; provides protection and structure.
🔸 Jointed Appendages: Modified for walking, feeding, or sensing.
🔸 Open Circulatory System: Blood flows into body cavity (haemocoel).
🔸 Respiration: Through gills (aquatic), tracheae or book lungs (terrestrial).
🔸 Malpighian tubules: For excretion and osmoregulation.
🔸 Sense Organs: Compound eyes, antennae.
🔸 Reproduction: Mostly sexual with internal fertilization.
🌿 Examples:
🧬 Palaemon (Prawn – Crustacea)
🧬 Periplaneta americana (Cockroach – Insecta)
Q32. Classify animals based on germ layers, body symmetry, and coelom. Give examples.
🧠 Answer:
📌 Based on Germ Layers:
🔸 Diploblastic – Animals with two germ layers (ectoderm and endoderm)
✔️ Example: Hydra (Cnidaria)
🔸 Triploblastic – Animals with three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
✔️ Example: Earthworm (Annelida)
📌 Based on Body Symmetry:
🔸 Asymmetrical – No definite body axis (e.g., Sponges)
🔸 Radial symmetry – Divided into equal halves along multiple planes (e.g., Jellyfish)
🔸 Bilateral symmetry – Single plane divides into two mirror halves (e.g., Human)
📌 Based on Coelom:
🔸 Acoelomate – No body cavity (e.g., Planaria)
🔸 Pseudocoelomate – Body cavity not lined by mesoderm (e.g., Ascaris)
🔸 Coelomate – True body cavity lined by mesoderm (e.g., Annelida, Chordata)
Q33. Compare any five fundamental features of Chordates and Non-Chordates.
🔹 Answer:
Feature Chordates Non-Chordates
Notochord Present Absent
Nervous system Dorsal, hollow, single Ventral, solid, double
Pharyngeal slits Present at some stage Absent
Heart position Ventral Dorsal or absent
Post-anal tail Present (at least in embryo) Absent
✔️ Example of chordate: Frog
✔️ Example of non-chordate: Earthworm
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following organisms are hermaphrodites?
(A) Earthworm and Leech
(B) Cockroach and Earthworm
(C) Housefly and Frog
(D) Frog and Leech
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Set: Z
Q2. Which phylum is characterized by the presence of cnidoblasts?
(A) Annelida
(B) Ctenophora
(C) Cnidaria
(D) Porifera
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 | Set: 1
Q3. Which one of the following organisms belongs to phylum Mollusca?
(A) Octopus
(B) Earthworm
(C) Ascaris
(D) Starfish
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024 | Set: Z
Q4. Metameric segmentation is a characteristic feature of which of the following groups?
(A) Platyhelminthes and Arthropoda
(B) Annelida and Arthropoda
(C) Annelida and Mollusca
(D) Ctenophora and Annelida
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Set: 2
Q5. Which of the following phyla possesses a water vascular system?
(A) Porifera
(B) Echinodermata
(C) Mollusca
(D) Arthropoda
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Set: 1
Q6. Which animal group has open circulatory system?
(A) Annelida
(B) Mollusca
(C) Arthropoda
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Year: 2022 | Set: Q
Q7. Which of the following shows indirect development?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Frog
(C) Hydra
(D) Leech
Answer: (B)
Year: 2022 | Set: R
Q8. In which group of animals, segmentation is both internal and external?
(A) Annelida
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Mollusca
(D) Platyhelminthes
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Set: S
Q9. Presence of flame cells is a feature of:
(A) Annelida
(B) Platyhelminthes
(C) Mollusca
(D) Cnidaria
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021 | Set: M
Q10. Which of the following features is common to birds and mammals?
(A) Scales
(B) Oviparity
(C) Warm-blooded nature
(D) Nucleated RBCs
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020 | Set: N
Q11. Which of the following is radially symmetrical?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Starfish
(C) Cockroach
(D) Leech
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 | Set: M
Q12. Which one is not a characteristic of chordates?
(A) Notochord
(B) Dorsal nerve cord
(C) Pharyngeal slits
(D) Ventral heart
Answer: (D)
Year: 2019 | Set: P
Q13. Which phylum has pseudocoelom?
(A) Annelida
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Nematoda
(D) Mollusca
Answer: (C)
Year: 2019 | Set: R
Q14. Which of these is not correctly matched?
(A) Balanoglossus – Hemichordata
(B) Pila – Mollusca
(C) Sea Urchin – Echinodermata
(D) Nereis – Mollusca
Answer: (D)
Year: 2018 | Set: 1
Q15. Which organism shows alternation of generations?
(A) Obelia
(B) Hydra
(C) Ascaris
(D) Pheretima
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Set: Z
Q16. Which animal phylum lacks true tissues and organs?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Cnidaria
(C) Porifera
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Year: 2017 | Set: Q
Q17. Which animal phylum shows radial symmetry in adults but bilateral in larvae?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Echinodermata
(D) Ctenophora
Answer: (C)
Year: 2017 | Set: R
Q18. Which is the second largest phylum after Arthropoda?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Echinodermata
(C) Annelida
(D) Chordata
Answer: (A)
Year: 2016 | Set: 3
Q19. In which animal group is the notochord present only in larval stage?
(A) Hemichordata
(B) Urochordata
(C) Cephalochordata
(D) Vertebrata
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016 | Set: Q
Q20. Which feature is not found in a cockroach?
(A) Open circulatory system
(B) Compound eyes
(C) Jointed legs
(D) Ciliated epithelium
Answer: (D)
Year: 2015 | Set: A
Q21. Excretion in Planaria occurs through:
(A) Flame cells
(B) Nephridia
(C) Kidneys
(D) Contractile vacuole
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015 | Set: Z
Q22. Which of the following has a calcareous endoskeleton?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Cockroach
(C) Starfish
(D) Leech
Answer: (C)
Year: 2014 | Set: R
Q23. Which one is a non-chordate with bilateral symmetry and triploblastic organization?
(A) Starfish
(B) Hydra
(C) Tapeworm
(D) Octopus
Answer: (D)
Year: 2013 | Set: S
Q24. Which of the following is a connecting link between annelida and mollusca?
(A) Neopilina
(B) Nereis
(C) Pila
(D) Octopus
Answer: (A)
Year: 2012 | Set: X
Q25. Which one of the following groups contains only radially symmetrical animals?
(A) Coelenterata, Ctenophora, Echinodermata
(B) Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Arthropoda
(C) Annelida, Mollusca, Arthropoda
(D) Porifera, Echinodermata, Mollusca
Answer: (A)
Year: 2011 | Set: Z
Q26. Which of the following shows a closed circulatory system?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Prawn
(C) Cockroach
(D) Ascaris
Answer: (A)
Year: 2010 | Set: 3
Q27. A true coelom is lined by
(A) Endoderm
(B) Mesoderm
(C) Ectoderm
(D) None of these
Answer: (B)
Year: 2010 | Set: 2
Q28. Which one of the following animals has non-glandular skin?
(A) Frog
(B) Lizard
(C) Snake
(D) Bird
Answer: (B)
Year: 2009 | Set: Z
Q29. Which of the following groups of animals is triploblastic and acoelomate?
(A) Ctenophora
(B) Platyhelminthes
(C) Aschelminthes
(D) Annelida
Answer: (B)
Year: 2009 | Set: 1
Q30. Flame cells are specialized for
(A) Digestion
(B) Circulation
(C) Respiration
(D) Excretion
Answer: (D)
Year: 2008 | Set: 2
Q31. Which phylum includes animals with jointed appendages?
(A) Annelida
(B) Mollusca
(C) Arthropoda
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Year: 2008 | Set: 1
Q32. The radula is a structure used for feeding by
(A) Arthropods
(B) Molluscs
(C) Echinoderms
(D) Coelenterates
Answer: (B)
Year: 2007 | Set: M
Q33. Which group of animals possesses endoskeleton made of calcareous plates?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Echinodermata
(C) Arthropoda
(D) Coelenterata
Answer: (B)
Year: 2007 | Set: S
Q34. Which animal phylum does not exhibit tissue level organization?
(A) Porifera
(B) Cnidaria
(C) Mollusca
(D) Annelida
Answer: (A)
Year: 2006 | Set: 2
Q35. Which of these is correctly matched?
(A) Starfish – Bilateral symmetry
(B) Octopus – Radial symmetry
(C) Earthworm – Bilateral symmetry
(D) Hydra – Triploblastic
Answer: (C)
Year: 2006 | Set: 1
Q36. Which one of the following animals is not a deuterostome?
(A) Starfish
(B) Amphioxus
(C) Earthworm
(D) Bird
Answer: (C)
Year: 2005 | Set: B
Q37. Which of these is a connecting link between chordates and non-chordates?
(A) Balanoglossus
(B) Amphioxus
(C) Ascidia
(D) Salpa
Answer: (A)
Year: 2005 | Set: A
Q38. Which of the following is not a feature of phylum Annelida?
(A) Closed circulatory system
(B) Pseudocoelom
(C) Nephridia
(D) Metamerism
Answer: (B)
Year: 2004 | Set: Q
Q39. Which of the following is not a chordate character?
(A) Notochord
(B) Dorsal nerve cord
(C) Paired appendages
(D) Pharyngeal slits
Answer: (C)
Year: 2004 | Set: Z
Q40. The correct sequence of taxonomic hierarchy in descending order is:
(A) Kingdom – Class – Phylum – Order – Family
(B) Kingdom – Phylum – Class – Order – Family
(C) Phylum – Kingdom – Class – Order – Family
(D) Class – Kingdom – Phylum – Family – Order
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003 | Set: 1
Q41. Which of the following is not a function of water vascular system in echinoderms?
(A) Locomotion
(B) Circulation
(C) Excretion
(D) Digestion
Answer: (D)
Year: 2003 | Set: 3
Q42. Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
(A) Cnidaria – Flame cells
(B) Echinodermata – Calcareous endoskeleton
(C) Mollusca – Open circulatory system in all
(D) Arthropoda – Nephridia
Answer: (B)
Year: 2002 | Set: 2
Q43. Nereis belongs to phylum:
(A) Mollusca
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Annelida
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Year: 2002 | Set: 1
Q44. Which of the following animals is triploblastic and bilaterally symmetrical?
(A) Hydra
(B) Starfish
(C) Planaria
(D) Sea anemone
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001 | Set: A
Q45. Body of sponges is supported by skeleton made up of:
(A) Chitin
(B) Spicules or spongin
(C) Cartilage
(D) Calcareous shell
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: Z
Q46. Which of the following is not related to molluscs?
(A) Radula
(B) Mantle
(C) Proboscis
(D) Foot
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001 | Set: R
Q47. Cephalization is first observed in:
(A) Cnidaria
(B) Platyhelminthes
(C) Echinodermata
(D) Mollusca
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: Y
Q48. Which of these is segmented both internally and externally?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Starfish
(C) Tapeworm
(D) Hydra
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001 | Set: Q
Q49. One of the characteristics of chordates is:
(A) Ventral heart and dorsal nerve cord
(B) Pharyngeal gill slits at some stage
(C) Exoskeleton of chitin
(D) Presence of compound eyes
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: S
Q50. Which of the following is a characteristic of phylum Ctenophora?
(A) Bioluminescence
(B) Nematocysts
(C) Flame cells
(D) Compound eyes
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001 | Set: T
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following animal groups exhibits diploblastic organization?
(A) Annelida
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Cnidaria
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Q2. Metamerism is the characteristic feature of which phylum?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Annelida
(C) Platyhelminthes
(D) Cnidaria
Answer: (B)
Q3. Which animal shows bilateral symmetry and a pseudocoelom?
(A) Pheretima
(B) Ascaris
(C) Sycon
(D) Hydra
Answer: (B)
Q4. Which of the following animals is correctly matched with its phylum?
(A) Octopus – Arthropoda
(B) Starfish – Mollusca
(C) Leech – Annelida
(D) Jellyfish – Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Q5. Which one of the following groups is exclusively marine?
(A) Echinodermata
(B) Mollusca
(C) Annelida
(D) Arthropoda
Answer: (A)
Q6. Flame cells function in:
(A) Digestion
(B) Respiration
(C) Circulation
(D) Excretion
Answer: (D)
Q7. Which of the following is a triploblastic and acoelomate organism?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Planaria
(C) Ascaris
(D) Pila
Answer: (B)
Q8. In which group of animals does the body exhibit radial symmetry in adults but bilateral in larvae?
(A) Mollusca
(B) Echinodermata
(C) Cnidaria
(D) Arthropoda
Answer: (B)
Q9. Which of the following has a complete digestive tract?
(A) Hydra
(B) Ascaris
(C) Planaria
(D) Spongilla
Answer: (B)
Q10. Which one is a feature of phylum Porifera?
(A) Organ system level of organization
(B) Bilateral symmetry
(C) Water canal system
(D) Closed circulatory system
Answer: (C)
Q11. Presence of cnidoblasts is a unique feature of:
(A) Ctenophora
(B) Coelenterata
(C) Annelida
(D) Mollusca
Answer: (B)
Q12. Which of the following is not a characteristic of arthropods?
(A) Jointed legs
(B) Chitinous exoskeleton
(C) Closed circulation
(D) Segmented body
Answer: (C)
Q13. Which of the following animals is unsegmented and soft-bodied?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Tapeworm
(C) Snail
(D) Cockroach
Answer: (C)
Q14. Which phylum includes animals with a mantle and radula?
(A) Echinodermata
(B) Arthropoda
(C) Mollusca
(D) Hemichordata
Answer: (C)
Q15. Which of these is a non-chordate with bilateral symmetry and triploblastic organization?
(A) Hydra
(B) Ascaris
(C) Starfish
(D) Spongilla
Answer: (B)
Q16. Which one of the following characteristics is not found in chordates?
(A) Dorsal hollow nerve cord
(B) Post-anal tail
(C) Notochord
(D) Ventral heart
Answer: (D)
Q17. The larval form of echinoderms shows:
(A) Radial symmetry
(B) No symmetry
(C) Bilateral symmetry
(D) Spherical symmetry
Answer: (C)
Q18. Which feature is common in annelids and arthropods?
(A) Coelom formation
(B) Closed circulation
(C) Segmented body
(D) Jointed legs
Answer: (C)
Q19. A muscular foot is used for movement in which group?
(A) Echinodermata
(B) Mollusca
(C) Annelida
(D) Arthropoda
Answer: (B)
Q20. Which of the following animals is a diploblastic marine organism with bioluminescence?
(A) Hydra
(B) Pleurobrachia
(C) Octopus
(D) Starfish
Answer: (B)
Q21. Which of the following features is found only in phylum Annelida?
(A) Cnidoblasts
(B) Nephridia
(C) Radula
(D) Tube feet
Answer: (B)
Q22. Which of these animals is correctly classified under Hemichordata?
(A) Amphioxus
(B) Balanoglossus
(C) Salpa
(D) Sea urchin
Answer: (B)
Q23. Which feature is common in molluscs and echinoderms?
(A) Radula
(B) Water vascular system
(C) Coelom
(D) Segmentation
Answer: (C)
Q24. What is the type of coelom found in roundworms?
(A) Acoelom
(B) True coelom
(C) Pseudocoelom
(D) Enterocoelom
Answer: (C)
Q25. Which of the following is used for osmoregulation in earthworms?
(A) Malpighian tubules
(B) Flame cells
(C) Nephridia
(D) Green glands
Answer: (C)
Q26. Which one of the following animals possesses a true coelom derived from mesoderm?
(A) Earthworm
(B) Planaria
(C) Ascaris
(D) Hydra
Answer: (A)
Q27. In which group does the notochord get replaced by vertebral column during development?
(A) Urochordata
(B) Vertebrata
(C) Cephalochordata
(D) Hemichordata
Answer: (B)
Q28. Which of the following statements is correct regarding symmetry and level of organization?
(A) Radial symmetry – Organ system level
(B) Bilateral symmetry – Cellular level
(C) Asymmetry – Tissue level
(D) Bilateral symmetry – Organ system level
Answer: (D)
Q29. Which of the following organisms exhibits the phenomenon of alternation of generation?
(A) Obelia
(B) Pheretima
(C) Hydra
(D) Leech
Answer: (A)
Q30. Which of the following phyla has mesoglea between ectoderm and endoderm?
(A) Annelida
(B) Platyhelminthes
(C) Mollusca
(D) Cnidaria
Answer: (D)
Q31. In echinoderms, the embryonic development is similar to chordates in all except:
(A) Radial cleavage
(B) Blastopore becoming anus
(C) Enterocoelous coelom
(D) Presence of notochord
Answer: (D)
Q32. Which animal shows internal fertilization and is ovoviviparous?
(A) Frog
(B) Pigeon
(C) Shark
(D) Rabbit
Answer: (C)
Q33. Choose the correct ascending order of body organization:
(A) Tissue → Organ → Cellular → Organ system
(B) Cellular → Tissue → Organ system → Organ
(C) Cellular → Tissue → Organ → Organ system
(D) Tissue → Cellular → Organ → Organ system
Answer: (C)
Q34. Which of the following animals exhibits segmentation, coelom, and nephridia?
(A) Pila
(B) Ascaris
(C) Nereis
(D) Starfish
Answer: (C)
Q35. Identify the incorrect match:
(A) Planaria – Flame cells
(B) Prawn – Antennae
(C) Earthworm – Gills
(D) Starfish – Tube feet
Answer: (C)
Q36. In which of the following animals is the body divided into head, thorax and abdomen?
(A) Octopus
(B) Earthworm
(C) Cockroach
(D) Leech
Answer: (C)
Q37. Which of the following statements is true for Balanoglossus?
(A) Has true notochord
(B) Has gill slits but no notochord
(C) Has a dorsal hollow nerve cord
(D) Belongs to vertebrata
Answer: (B)
Q38. Which of the following possesses flame cells and is hermaphroditic?
(A) Taenia
(B) Ascaris
(C) Leech
(D) Cockroach
Answer: (A)
Q39. Which of the following features are common to all chordates at some stage?
(A) Notochord, dorsal tubular nerve cord, pharyngeal slits
(B) Ventral nerve cord, post-anal tail, cilia
(C) Closed circulatory system, compound eyes
(D) Chitinous exoskeleton, notochord
Answer: (A)
Q40. Which of the following is a marine echinoderm with tube feet but no arms?
(A) Sea urchin
(B) Starfish
(C) Brittle star
(D) Sea lily
Answer: (A)
Q41. If an unknown animal shows bilateral symmetry, triploblastic organization, a true coelom, and segmentation, it likely belongs to:
(A) Mollusca
(B) Annelida
(C) Cnidaria
(D) Platyhelminthes
Answer: (B)
**Q42. Match the following and choose the correct combination:
Column I:
a. Earthworm
b. Cockroach
c. Starfish
d. Ascaris
Column II:
Pseudocoelomate
Coelomate with open circulatory system
Radial symmetry in adult
Nephridia for excretion**
(A) a–4, b–2, c–3, d–1
(B) a–1, b–3, c–2, d–4
(C) a–2, b–1, c–4, d–3
(D) a–4, b–3, c–1, d–2
Answer: (A)
Q43. Which group of animals exhibits enterocoelous coelom, radial indeterminate cleavage, and deuterostomic development?
(A) Arthropoda
(B) Echinodermata
(C) Mollusca
(D) Annelida
Answer: (B)
Q44. Which of the following represents a correct example of a triploblastic, acoelomate and dorsoventrally flattened animal?
(A) Taenia
(B) Hydra
(C) Obelia
(D) Amphioxus
Answer: (A)
Q45. What is the correct taxonomic position of Amphioxus?
(A) Hemichordata – Cephalochordata – Chordata
(B) Chordata – Cephalochordata – Protochordata
(C) Urochordata – Vertebrata – Chordata
(D) Vertebrata – Cyclostomata – Chordata
Answer: (B)
Q46. Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
(A) Pheretima – Closed circulatory system
(B) Pila – Radula
(C) Sycon – Cnidoblasts
(D) Pleurobrachia – Bioluminescence
Answer: (C)
Q47. A marine animal with ciliary locomotion, diploblastic body, and eight comb plates belongs to:
(A) Cnidaria
(B) Mollusca
(C) Ctenophora
(D) Echinodermata
Answer: (C)
Q48. Which of the following organisms lacks a true body cavity but has organ level organization?
(A) Hydra
(B) Planaria
(C) Ascaris
(D) Earthworm
Answer: (B)
Q49. Identify the animal with closed blood circulation, true coelom, nephridia, and metameric segmentation.
(A) Nereis
(B) Ascaris
(C) Prawn
(D) Snail
Answer: (A)
Q50. Which statement is true regarding starfish?
(A) Bilateral symmetry in both adult and larva
(B) Larva is triploblastic and pseudocoelomate
(C) Adult has radial symmetry; larva has bilateral symmetry
(D) Coelom originates from ectoderm
Answer: (C)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
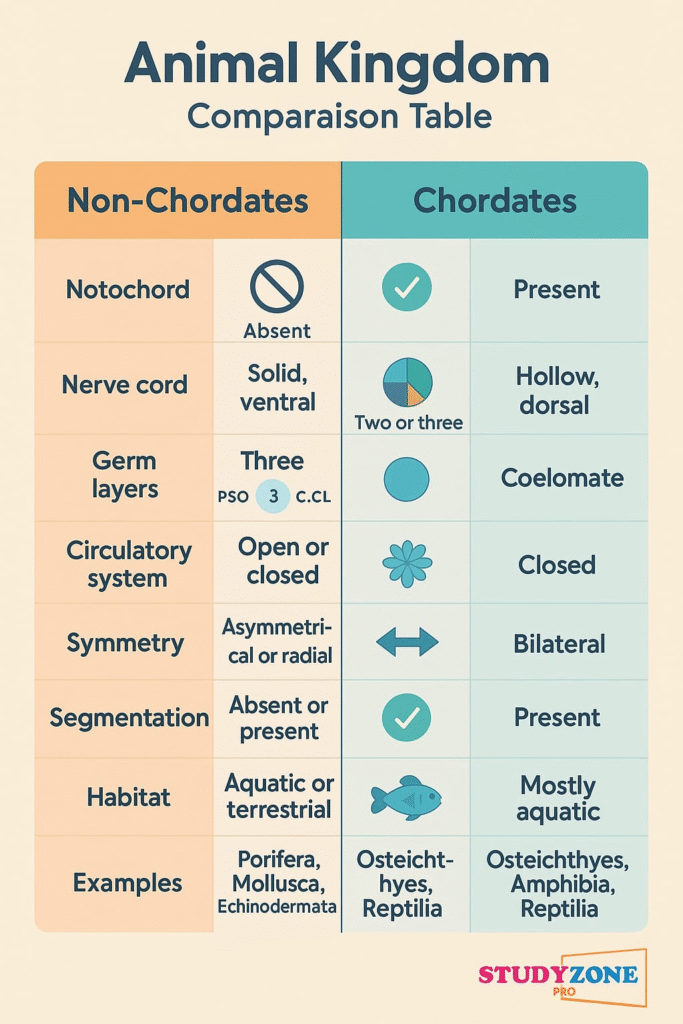
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MINDMAPS