Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 12: Respiration in Plants
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
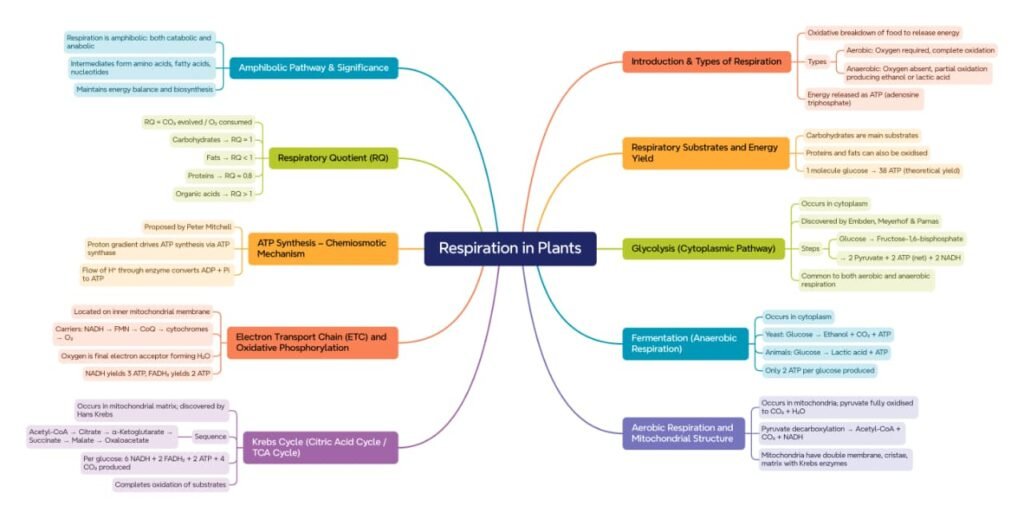
🌱✨ Introduction
🧠 Respiration is a vital catabolic process in which food molecules (mainly glucose) are broken down to release energy for cellular activities.
🌿 Unlike photosynthesis, which stores energy, respiration releases energy in the form of ATP ⚡ — the energy currency of cells.
💡 Concept:
➡️ Photosynthesis: Anabolic (builds food)
➡️ Respiration: Catabolic (breaks food)
🧬 Equation:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + Energy (≈ 686 kcal)
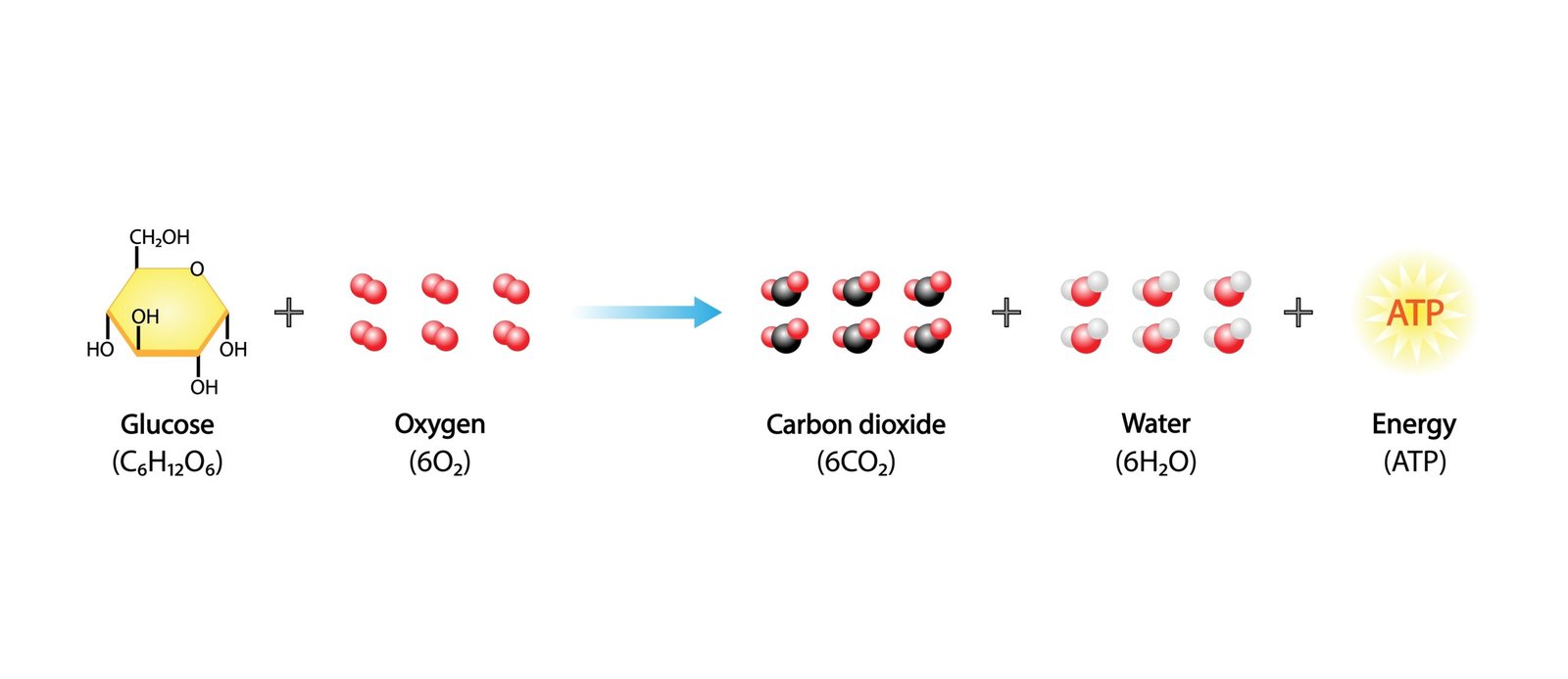
🌍 This process occurs in all living cells — including plants — continuously, both day and night.
🌾 Importance of Respiration
🍃 Provides ATP for growth, repair, and absorption
🌸 Maintains metabolic balance
🧪 Breaks complex compounds into simpler ones
⚡ Supports biosynthesis, transport, active absorption
✏️ Note: Though plants photosynthesize, they also respire continuously to meet energy demands.
🧬 Types of Respiration
🟢 1. Aerobic Respiration
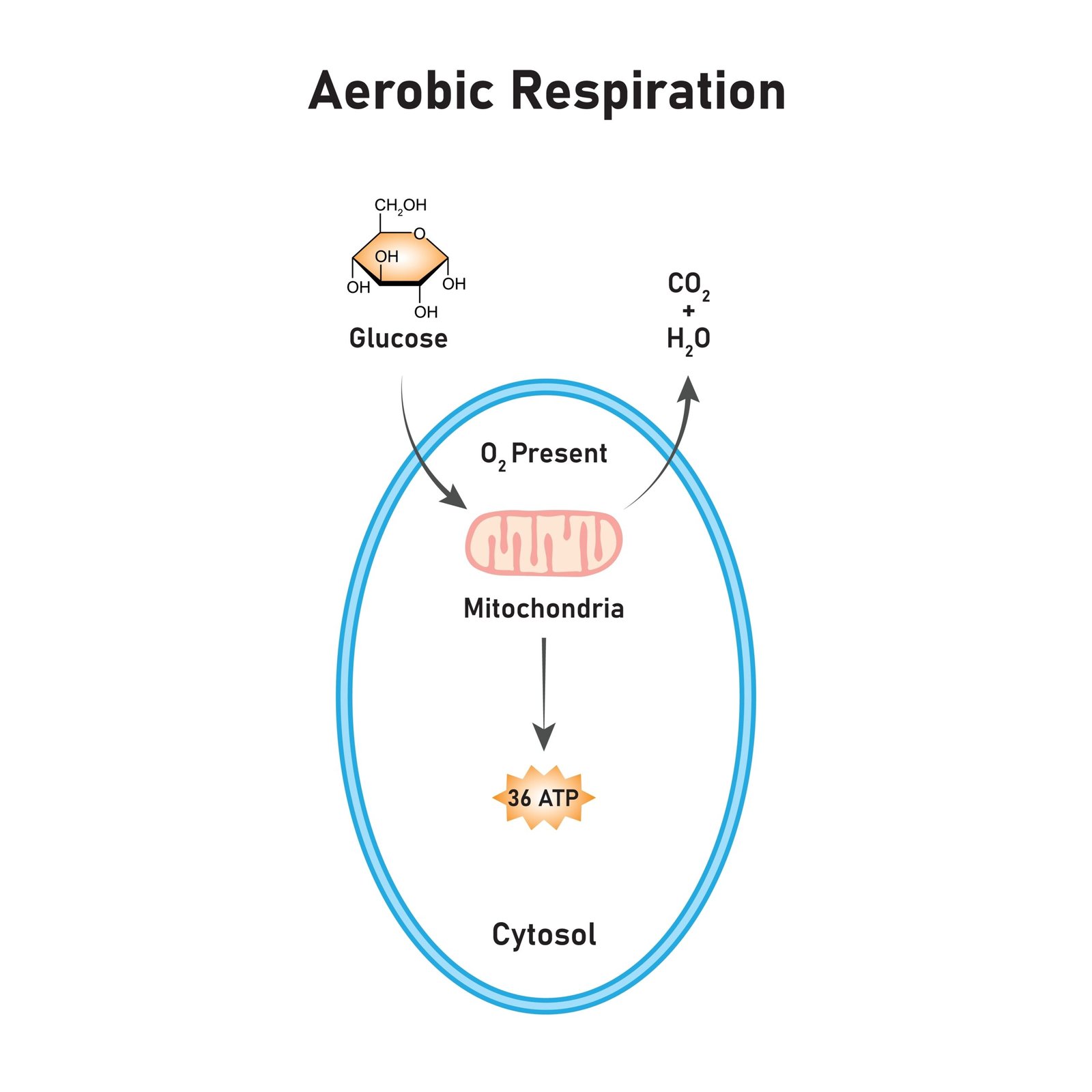
Occurs in presence of oxygen
💨 End products: CO₂ + H₂O + Energy
🧠 Complete oxidation of glucose
🔴 2. Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs without oxygen
💨 End products: Ethanol + CO₂ + Energy (in plants)
⚡ Less energy released (2 ATP per glucose)
💡 Concept:
🌾 Yeast undergoes alcoholic fermentation, forming ethanol (used in brewing).
🌱 Plant roots in waterlogged soils may temporarily switch to anaerobic mode.
🌸 Steps of Aerobic Respiration
Occurs in multiple steps — each in a specific site of the cell:
Step Process Site Key Products
1️⃣ Glycolysis Cytoplasm 2 ATP, 2 NADH
2️⃣ Pyruvate Oxidation Mitochondrial matrix 2 Acetyl-CoA, 2 NADH
3️⃣ Krebs Cycle Mitochondrial matrix 6 NADH, 2 FADH₂, 2 ATP
4️⃣ Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Inner mitochondrial membrane ~34 ATP
Total yield ≈ 38 ATP per glucose (in theory).
🌿 Step-by-Step Explanation
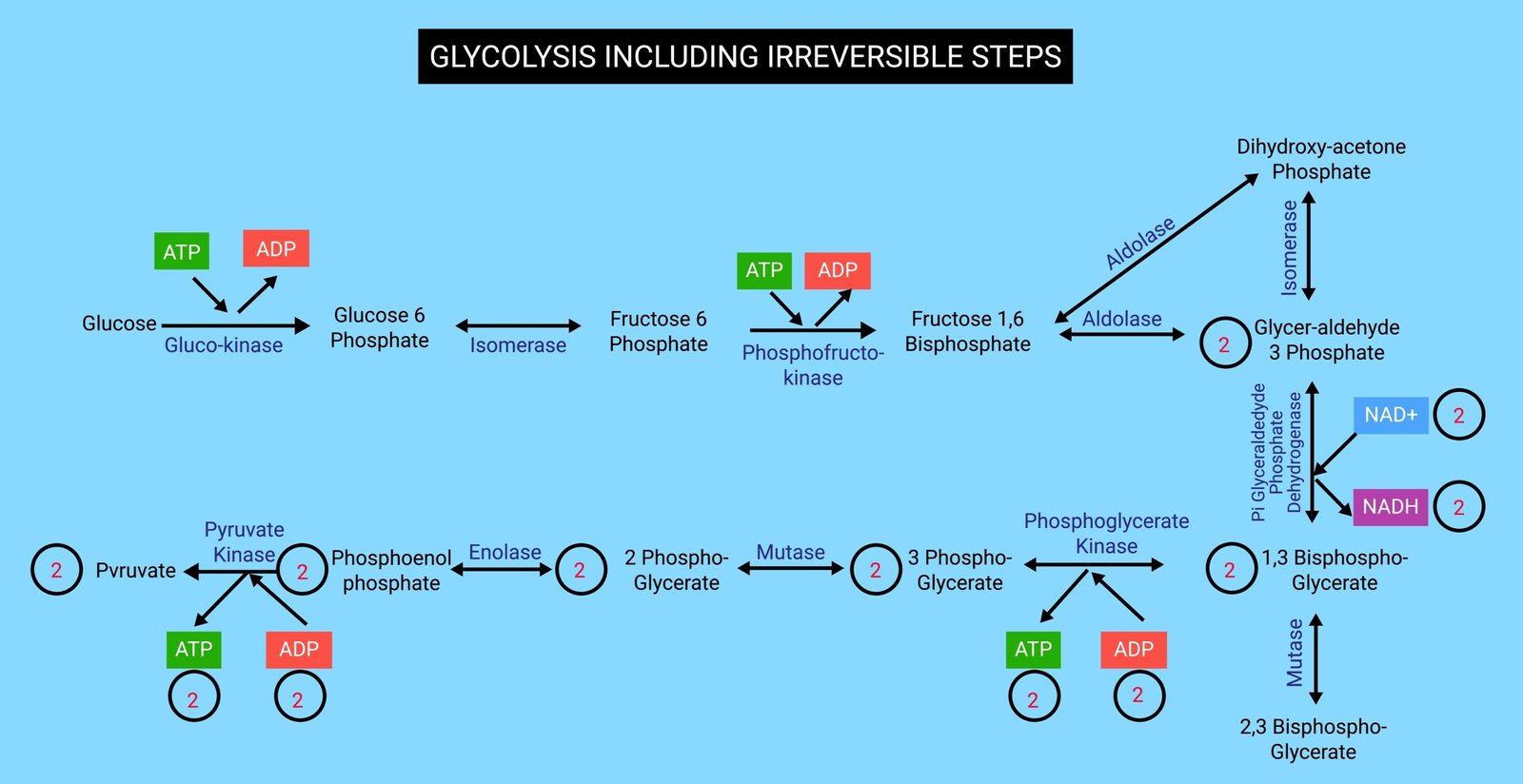
🧪 Step 1: Glycolysis
🧠 Meaning “splitting of sugar”
📍 Site: Cytoplasm
🔬 Occurs in both aerobic & anaerobic respiration
🌀 Steps:
1️⃣ Glucose (6C) phosphorylated → Glucose-6-phosphate
2️⃣ Converted → Fructose-6-phosphate
3️⃣ → Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate → splits into 3C units
4️⃣ Forms 2 molecules of pyruvate
⚡ Products:
2 Pyruvate
2 ATP (net)
2 NADH
💡 Concept: Universal pathway present in all living cells.
🔥 Step 2: Oxidative Decarboxylation of Pyruvate
📍 Site: Mitochondrial matrix
🎯 Pyruvate (3C) → Acetyl-CoA (2C) + CO₂
🧪 Enzyme: Pyruvate dehydrogenase
🧠 NAD⁺ reduced to NADH
✏️ Note: This links glycolysis and Krebs cycle.
🌿 Step 3: Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
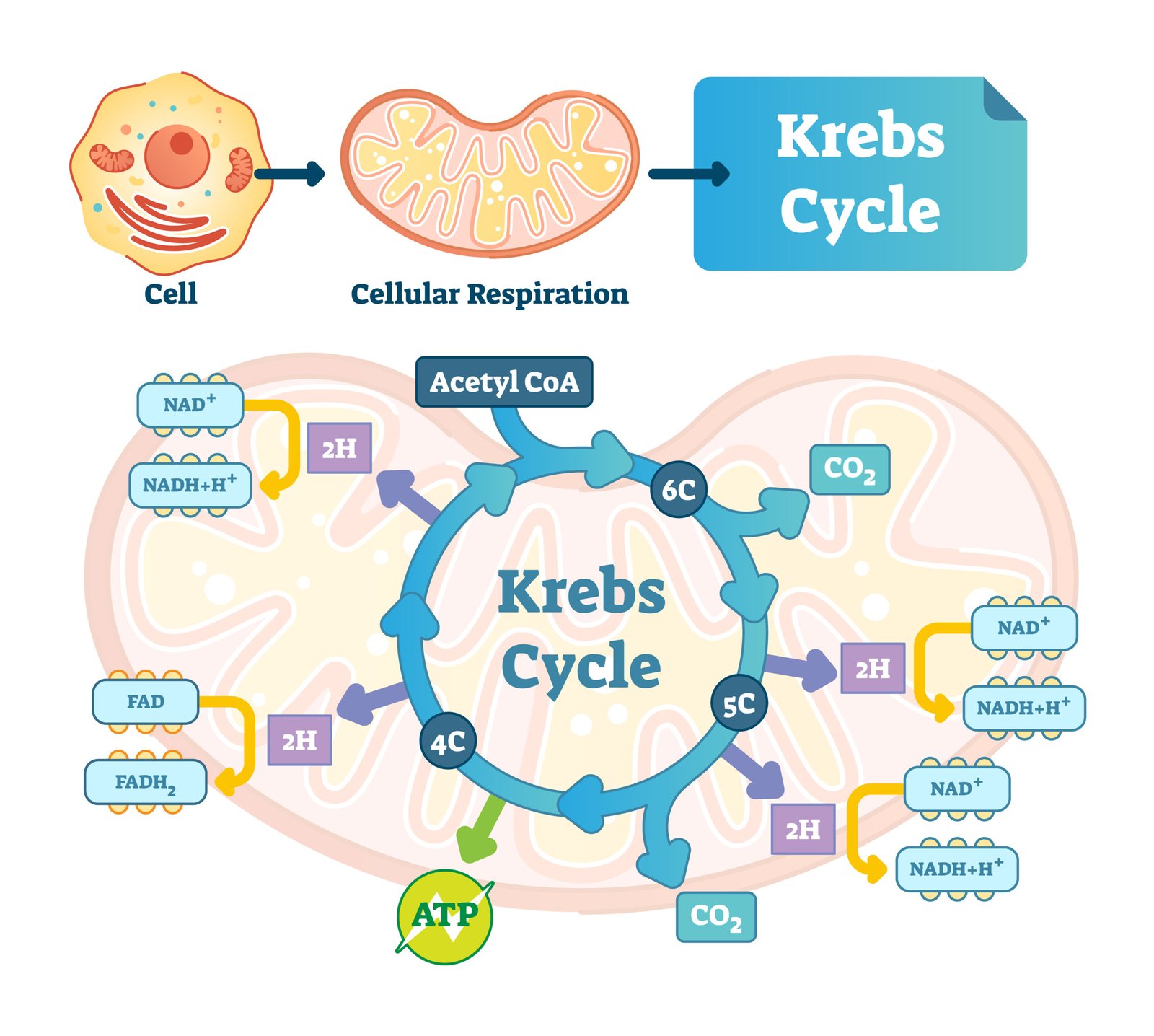
🧬 Discovered by Hans Krebs
📍 Site: Mitochondrial matrix
🎯 Acetyl-CoA + Oxaloacetate (4C) → Citrate (6C) → undergoes series of reactions → regenerates oxaloacetate
🧠 Products per glucose:
6 NADH
2 FADH₂
2 ATP
4 CO₂
💡 Concept: Central metabolic hub — provides intermediates for biosynthesis.
⚡ Step 4: Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
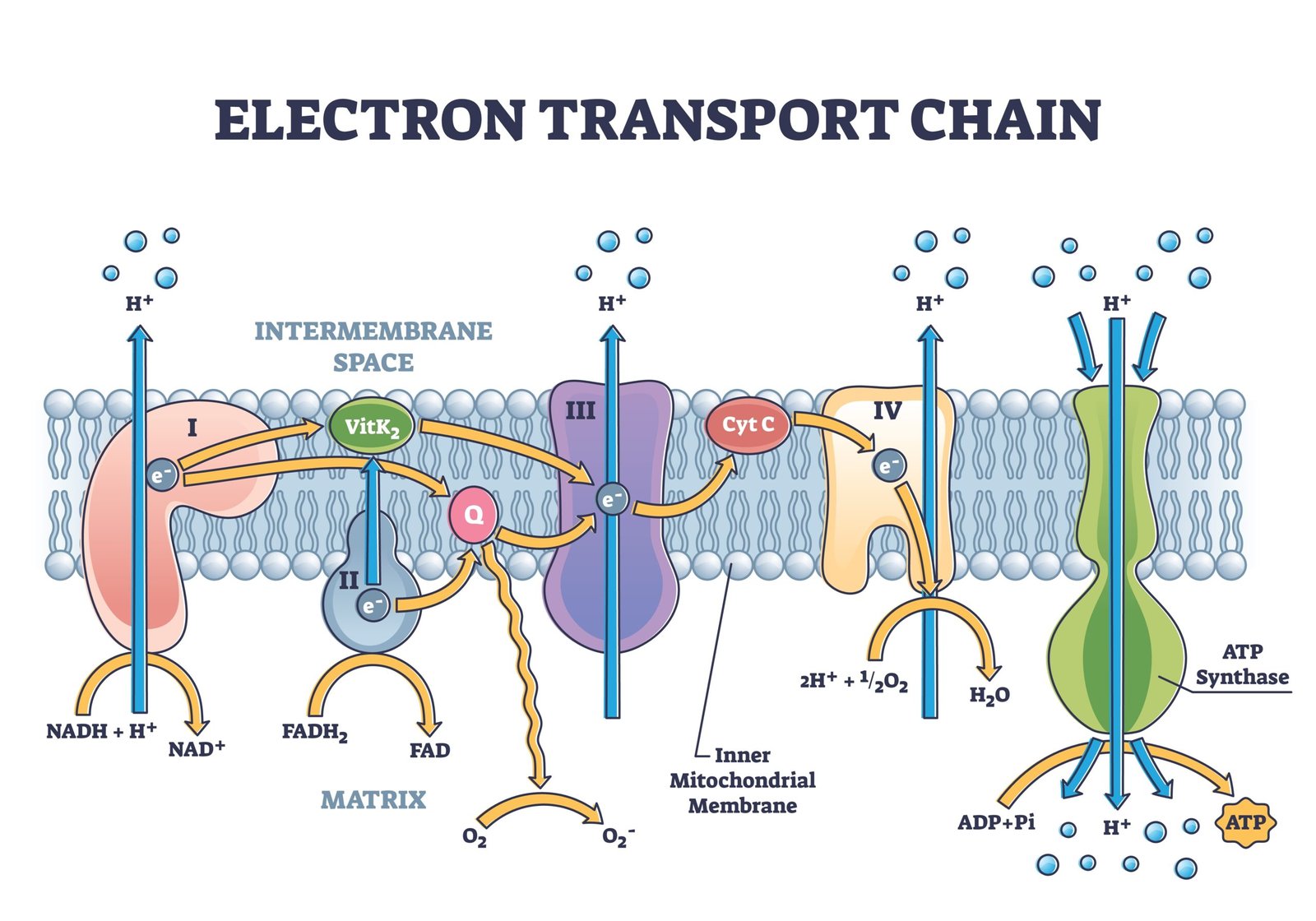
📍 Site: Inner mitochondrial membrane
🧬 NADH & FADH₂ donate electrons → pass through complexes (I–IV)
💧 Oxygen = final electron acceptor → forms H₂O
🧠 Chemiosmotic Theory (Mitchell): Proton gradient across membrane drives ATP synthesis through ATP synthase.
⚡ ATP Yield: ~34 ATP
💡 Total Aerobic Gain: ≈ 38 ATP/glucose
🍃 Anaerobic Respiration
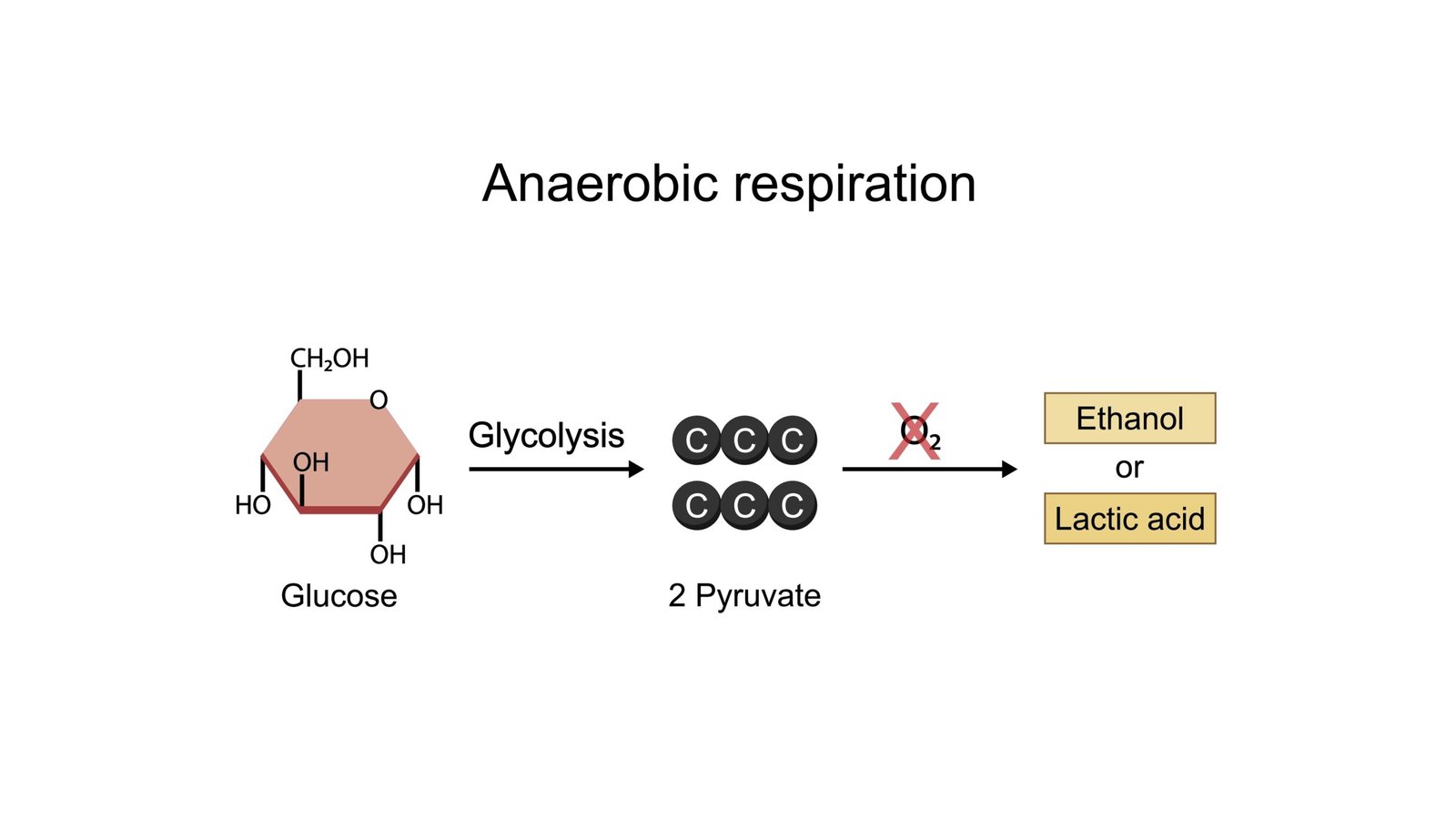
🧠 Occurs when O₂ absent
📍 Site: Cytoplasm
🌾 Common in yeast, germinating seeds, waterlogged roots
Pathway:
Glucose → Pyruvate (via glycolysis) → Ethanol + CO₂ + ATP
⚡ Net energy: 2 ATP
✏️ Note: Less efficient, but essential under hypoxic conditions.
🧪 Fermentation in Plants
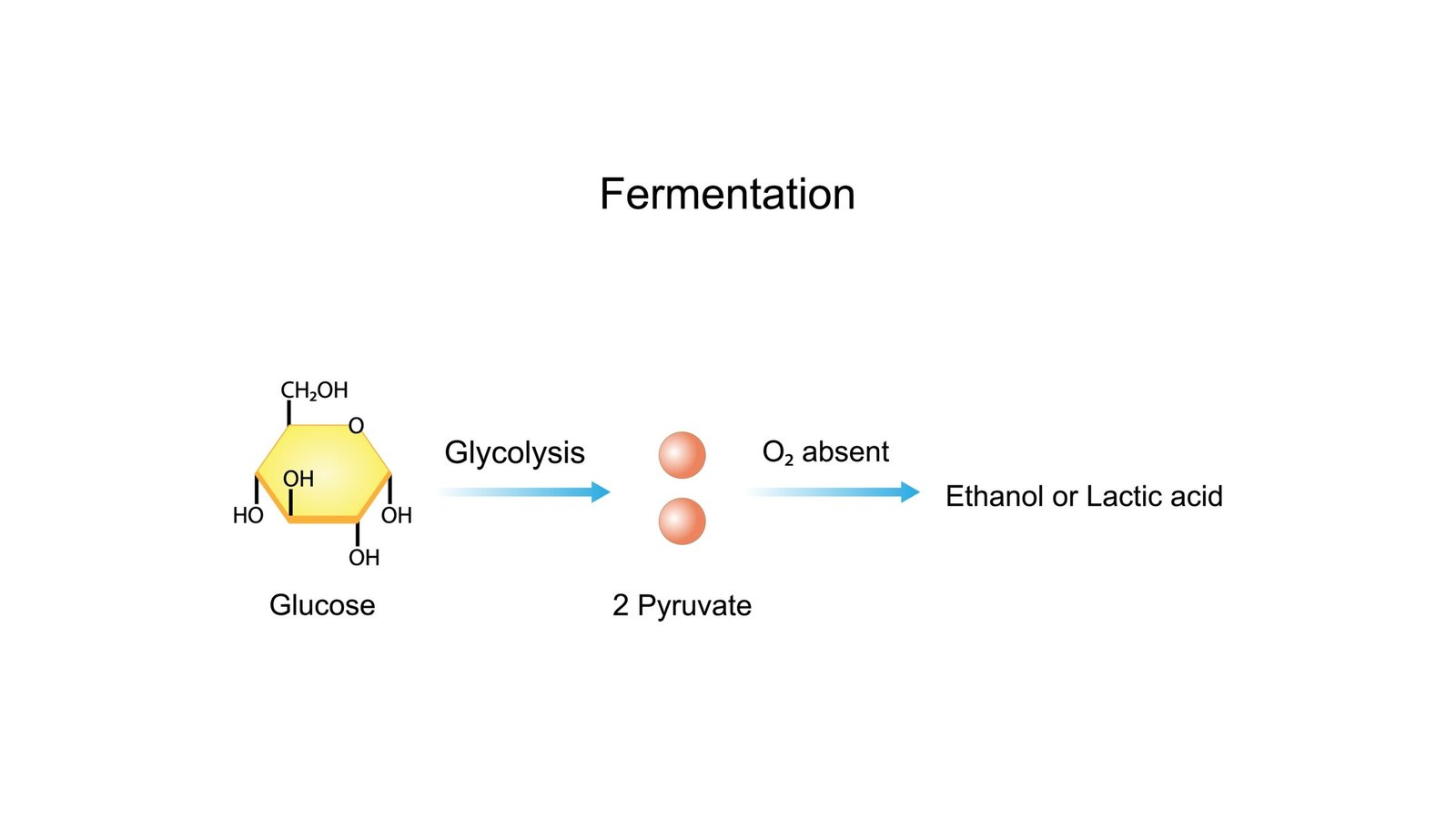
🌱 In yeast: Pyruvate → Ethanol + CO₂
🧫 Enzymes: Pyruvate decarboxylase, Alcohol dehydrogenase
🍺 Used in brewing, baking
💡 Concept: Fermentation regenerates NAD⁺ to continue glycolysis.
🌾 Amphibolic Pathway
🧠 Respiration serves as catabolic + anabolic process
➡️ Provides intermediates for amino acid, lipid, nucleic acid synthesis
⚙️ Example: Acetyl-CoA → fatty acids; α-ketoglutarate → amino acids
💡 Amphibolic = dual role of degradation & biosynthesis.
🌿 Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
🧪 RQ = CO₂ produced / O₂ consumed
Substrate RQ Value
Carbohydrates 1
Fats <1 Proteins <1 Organic acids >1
💡 Indicates substrate being respired and metabolic balance.
✏️ Example:
Glucose → RQ = 1
Fat → RQ = 0.7
Succinate → RQ > 1
🌱 Respiratory Substrates
1️⃣ Carbohydrates: primary
2️⃣ Fats: yield more energy
3️⃣ Proteins: used under starvation
⚡ All eventually enter Krebs cycle as intermediates.
🌸 Energy Yield Summary
Step ATP Yield
Glycolysis 2 ATP + 2 NADH
Pyruvate Oxidation 2 NADH
Krebs Cycle 2 ATP + 6 NADH + 2 FADH₂
ETC ~34 ATP
Total ≈ 38 ATP
🧠 Actual yield may be lower (~30–32) due to transport losses.
🌍 Factors Affecting Respiration
1️⃣ Temperature: increases rate up to optimum
2️⃣ Oxygen: required for aerobic phase
3️⃣ Substrate type: carbohydrate vs fat
4️⃣ Tissue type: active meristems > storage tissues
5️⃣ Age: younger tissues respire more
💡 Concept: Respiration adapts to plant needs and environment.
🌿 Respiration vs Combustion
Feature Respiration Combustion
Nature Enzymatic Non-enzymatic
Control Stepwise Uncontrolled
Energy Stored in ATP Lost as heat
Site Living cells Outside cells
🧠 Respiration is controlled biological oxidation.
🌳 Significance
🌾 Provides ATP for vital activities
🧬 Supplies intermediates for biosynthesis
💨 Maintains CO₂-O₂ balance
🧠 Integrates catabolism with anabolism
🌍 Essential for growth and survival
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🌿 Explains how plants extract energy from food
🧠 Links metabolism, biosynthesis, and growth
⚙️ Foundation for biochemistry and ecology
💨 Highlights balance between photosynthesis and respiration
📝 Quick Recap
🧠 Respiration = breakdown of food to release energy
🌱 Aerobic: O₂ present → CO₂ + H₂O + ATP (~38)
🌾 Anaerobic: no O₂ → Ethanol + CO₂ + ATP (2)
⚙️ Steps: Glycolysis → Pyruvate Oxidation → Krebs → ETC
💡 Fermentation: regenerates NAD⁺
🧬 Amphibolic = catabolic + anabolic
🧪 RQ indicates substrate used
🌍 Provides energy, intermediates, and balance
📘 Summary
Respiration in plants is a vital energy-releasing process involving the oxidation of organic compounds. The aerobic pathway yields maximum ATP through glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport. Anaerobic respiration or fermentation operates without oxygen, releasing less energy. The process is amphibolic, integrating breakdown and biosynthesis. Factors like oxygen, temperature, and substrate influence the rate. Through respiration, plants obtain ATP and essential intermediates for various metabolic functions, maintaining cellular energy balance and sustaining life processes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. Differentiate between:
🟢 Answer:
(a) 🌿 Respiration and Combustion
Feature Respiration Combustion
Nature Biological, enzymatic Non-biological, rapid
Energy release Step-wise, controlled Sudden, uncontrolled
Temperature Occurs at body temperature High temperature
Intermediate formation Several intermediates formed None
Example Cellular respiration Burning of fuels
(b) 🌸 Glycolysis and Krebs’ Cycle
Feature Glycolysis Krebs’ Cycle
Site Cytoplasm Mitochondrial matrix
Oxygen requirement Anaerobic phase Aerobic phase
Substrate Glucose Pyruvic acid
Products 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH CO₂, NADH, FADH₂, ATP
Occurs in All cells Only aerobic cells
(c) 🧪 Aerobic Respiration and Fermentation
Feature Aerobic Respiration Fermentation
Oxygen Required Absent
End products CO₂ + H₂O Alcohol / Lactic acid
ATP yield 36–38 ATP 2 ATP
Site Mitochondria Cytoplasm
Efficiency High Low
🔵 Question 2. What are respiratory substrates? Name the most common respiratory substrate.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Respiratory substrates are organic compounds oxidised during respiration to release energy.
💡 Types:
Carbohydrates: e.g. glucose (most common)
Fats
Proteins
✔️ Most common: Glucose
🔵 Question 3. Give the schematic representation of glycolysis.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Glycolysis: Conversion of glucose (6C) → 2 Pyruvate (3C)
✏️ Steps description:
Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate (uses 1 ATP)
→ Fructose-6-phosphate
→ Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (uses 1 ATP)
→ Splits into two 3C compounds
→ Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate → Pyruvic acid
✔️ Net products: 2 ATP (net gain), 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate
🔵 Question 4. What are the main steps in aerobic respiration? Where does it take place?
🟢 Answer:
🧠 Main steps:
Glycolysis – cytoplasm
Oxidative decarboxylation – mitochondria
Krebs’ cycle – mitochondrial matrix
Electron Transport System (ETS) – inner mitochondrial membrane
✔️ End products: CO₂ + H₂O + 38 ATP
🔵 Question 5. Give the schematic representation of an overall view of Krebs’ cycle.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Cycle description:
Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetic acid → Citric acid
Citric acid → α-Ketoglutaric acid → Succinic acid → Malic acid → Oxaloacetic acid
✔️ Products per cycle:
3 NADH, 1 FADH₂, 1 ATP (via GTP), 2 CO₂
✏️ Cycle regenerates oxaloacetic acid each turn.
🔵 Question 6. Explain ETS.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Electron Transport System (ETS):
Located in inner mitochondrial membrane
Consists of four complexes (I–IV) with electron carriers (FMN, Fe-S, cytochromes)
➡️ NADH/FADH₂ donate electrons → move through complexes → O₂ is final acceptor → H₂O formed
✔️ Energy released used to pump protons → ATP formed by ATP synthase = Oxidative phosphorylation
🔵 Question 7. Distinguish between:
(a) 🌸 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Feature Aerobic Anaerobic
Oxygen Present Absent
End product CO₂, H₂O Alcohol or Lactic acid
ATP yield 36–38 2
Site Mitochondria Cytoplasm
(b) 🧪 Glycolysis and Fermentation
Feature Glycolysis Fermentation
Process Breakdown of glucose to pyruvate Conversion of pyruvate to ethanol/lactate
Oxygen Independent Anaerobic
ATP 2 2
Location Cytoplasm Cytoplasm
(c) ⚗️ Glycolysis and Citric Acid Cycle
Feature Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle
Site Cytoplasm Mitochondria
O₂ requirement Not required Requires O₂
Product Pyruvate CO₂, NADH, FADH₂, ATP
Type Linear pathway Cyclic pathway
🔵 Question 8. What are the assumptions made during the calculation of net gain of ATP?
🟢 Answer:
🧠 Assumptions:
Complete oxidation of glucose.
NADH from cytoplasm enters mitochondria efficiently.
ATP yield: 3 per NADH, 2 per FADH₂.
No energy loss.
✔️ Net gain: ~36 ATP per glucose molecule (theoretical).
🔵 Question 9. Discuss “The respiratory pathway is an amphibolic pathway.”
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Amphibolic = both catabolic + anabolic
🌿 Catabolic: Breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, proteins → energy.
🌸 Anabolic: Intermediates used for synthesis (amino acids, lipids).
✔️ Thus, respiratory pathway serves dual role.
🔵 Question 10. Define RQ. What is its value for fats?
🟢 Answer:
🧪 Respiratory Quotient (RQ) = CO₂ produced / O₂ consumed
➡️ For fats (e.g. tripalmitin): RQ = 0.7
💡 Because fats require more oxygen for oxidation.
🔵 Question 11. What is oxidative phosphorylation?
🟢 Answer:
⚡ Process of ATP synthesis using energy released by electron transport through ETS.
➡️ O₂ = final electron acceptor → H₂O formed
➡️ ATP synthase utilizes proton gradient → ATP
✔️ Coupled with aerobic respiration.
🔵 Question 12. What is the significance of step-wise release of energy in respiration?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Significance:
Prevents energy loss as heat.
Allows controlled release for ATP synthesis.
Enables regulation via enzymes.
Ensures efficient energy utilisation.
✔️ Maintains metabolic balance in cell.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
Respiration in plants is a —
🔴1️⃣ Catabolic process
🟢2️⃣ Anabolic process
🟡3️⃣ Both
🔵4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Catabolic process
🔴 Question 2:
Which of the following is a common substrate for respiration?
🔴1️⃣ Protein
🟢2️⃣ Glucose
🟡3️⃣ Fat
🔵4️⃣ Organic acid
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Glucose
🔴 Question 3:
Where does glycolysis occur in a cell?
🔴1️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢2️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟡3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵4️⃣ Chloroplast
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔴 Question 4:
The end products of aerobic respiration are —
🔴1️⃣ CO₂ + H₂O + ATP
🟢2️⃣ Alcohol + CO₂
🟡3️⃣ Lactic acid + ATP
🔵4️⃣ Only ATP
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ CO₂ + H₂O + ATP
🔴 Question 5:
In which organelle does Krebs cycle occur?
🔴1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟢2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🟡3️⃣ Inner membrane
🔵4️⃣ Chloroplast
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🔴 Question 6:
Which enzyme converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
🔴1️⃣ Dehydrogenase
🟢2️⃣ Pyruvate dehydrogenase
🟡3️⃣ Decarboxylase
🔵4️⃣ Oxidase
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Pyruvate dehydrogenase
🔴 Question 7:
Number of ATP molecules produced from one glucose molecule in aerobic respiration is —
🔴1️⃣ 2
🟢2️⃣ 36
🟡3️⃣ 4
🔵4️⃣ 8
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 36
🔴 Question 8:
Which of the following processes does not require oxygen?
🔴1️⃣ Krebs cycle
🟢2️⃣ Glycolysis
🟡3️⃣ ETS
🔵4️⃣ Oxidative phosphorylation
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🔴 Question 9:
The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is —
🔴1️⃣ NAD⁺
🟢2️⃣ Oxygen
🟡3️⃣ ATP
🔵4️⃣ Cytochrome
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Oxygen
🔴 Question 10:
Fermentation takes place in the —
🔴1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟢2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡3️⃣ Chloroplast
🔵4️⃣ Nucleus
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔴 Question 11:
Define glycolysis.
🟢 Answer:
Stepwise breakdown of glucose (6C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C) in cytoplasm, releasing 2 ATP and 2 NADH ⚡
🔴 Question 12:
Write two end products of alcoholic fermentation.
🟢 Answer:
Ethyl alcohol (C₂H₅OH) 🍶
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) 💨
🔴 Question 13:
What is respiration? Write its overall equation.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Biochemical process where food molecules are broken down to release energy (ATP).
Overall Equation:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy (ATP) ⚡
Significance: Energy released is used for all cellular activities.
🔴 Question 14:
Describe the main stages of aerobic respiration.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Glycolysis – In cytoplasm; glucose → pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH.
2️⃣ Krebs Cycle – In mitochondria; acetyl CoA oxidized to CO₂ + NADH + FADH₂ + ATP.
3️⃣ Electron Transport System – Inner mitochondrial membrane; NADH/FADH₂ oxidized → ATP + H₂O.
🔴 Question 15:
Explain the process of glycolysis.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Cytoplasm.
Steps:
1️⃣ Glucose phosphorylated → fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
2️⃣ Split into 2 triose phosphates.
3️⃣ Oxidation → 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP (net), 2 NADH.
Products: 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH.
🔴 Question 16:
Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Aerobic Anaerobic
Oxygen Required Not required
End products CO₂ + H₂O Alcohol / Lactic acid
ATP yield 36 ATP 2 ATP
Site Mitochondria Cytoplasm
💡 Aerobic is more efficient.
🔴 Question 17:
Describe the link reaction.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Mitochondrial matrix.
Reaction: Pyruvate (3C) → Acetyl CoA (2C) + CO₂ + NADH.
Enzyme: Pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Purpose: Connects glycolysis and Krebs cycle 🔗.
🔴 Question 18:
Explain the Krebs cycle.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Mitochondrial matrix.
Steps:
1️⃣ Acetyl CoA + OAA → Citrate (6C).
2️⃣ Series of oxidation and decarboxylation.
3️⃣ Products per turn: 3 NADH, 1 FADH₂, 1 ATP, 2 CO₂.
Significance: Produces high-energy carriers.
🔴 Question 19:
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Formation of ATP using energy released by electron transport through ETC.
Site: Inner mitochondrial membrane.
Process: NADH & FADH₂ donate e⁻ → proton gradient → ATP formed by ATP synthase. ⚡
Product: 34 ATP approx.
🔴 Question 20:
Explain electron transport system (ETS).
🟢 Answer:
Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane.
Carriers: NADH → FMN → CoQ → Cytochromes → O₂.
Function:
1️⃣ Transfers electrons from NADH/FADH₂.
2️⃣ Creates proton gradient.
3️⃣ ATP formed by ATP synthase.
✅ O₂ is final acceptor → H₂O formed.
🔴 Question 21:
What are respiratory substrates? Name their types.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Compounds oxidized during respiration to release energy.
Types:
1️⃣ Carbohydrates (e.g. glucose) – main substrate.
2️⃣ Fats – yield more energy.
3️⃣ Proteins – used in starvation.
💡 Preference order: Carbohydrates > Fats > Proteins.
🔴 Question 22:
Mention factors affecting rate of respiration.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Temperature: Optimum ~30°C; low temp slows rate. 🌡️
2️⃣ Oxygen: Needed for aerobic respiration.
3️⃣ Substrate concentration: More substrate → higher rate till saturation.
4️⃣ Protoplasmic condition: Active cells respire faster.
🔴 Question 23:
Explain the steps of aerobic respiration in detail.
🟢 Answer:
Step 1️⃣ — Glycolysis:
Occurs in cytoplasm; glucose (6C) → 2 pyruvate (3C) + 2 ATP + 2 NADH.
Step 2️⃣ — Link Reaction:
In mitochondria; pyruvate → acetyl CoA + CO₂ + NADH.
Step 3️⃣ — Krebs Cycle:
Acetyl CoA oxidized → CO₂ + NADH + FADH₂ + ATP.
Step 4️⃣ — Electron Transport System:
Electrons from NADH/FADH₂ → ETC → ATP by oxidative phosphorylation; O₂ final acceptor.
✅ Products per glucose: 36 ATP + 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O ⚡
🔴 Question 24:
Describe glycolysis with schematic flow.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Cytoplasm.
Stages:
1️⃣ Phosphorylation: Glucose → Glucose-6-P → Fructose-1,6-bisP.
2️⃣ Cleavage: Splits into 2 triose phosphates.
3️⃣ Oxidation: Forms pyruvate, 4 ATP (gross), 2 ATP (net), 2 NADH.
Equation:
Glucose + 2 NAD⁺ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H₂O.
💡 Result: Energy captured in ATP and NADH for next steps.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain the Krebs cycle with major products and significance.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Mitochondrial matrix.
Steps:
1️⃣ Acetyl CoA + OAA → Citrate.
2️⃣ Series of oxidation & decarboxylation reactions.
3️⃣ Regeneration of OAA.
Products (per turn): 3 NADH, 1 FADH₂, 1 ATP, 2 CO₂.
Significance:
✔️ Major source of NADH & FADH₂.
✔️ Connects anabolic & catabolic pathways.
✔️ Provides intermediates for biosynthesis.
🔴 Question 26:
Explain the mechanism of electron transport system (ETS) and oxidative phosphorylation.
🟢 Answer:
Location: Inner mitochondrial membrane.
Carriers: NADH → FMN → CoQ → Cyt b → Cyt c → Cyt a/a₃ → O₂.
Process:
1️⃣ Electrons flow → energy released pumps H⁺ into intermembrane space.
2️⃣ Gradient drives ATP synthase → ATP formed (chemiosmosis).
3️⃣ O₂ accepts electrons → H₂O.
Result: ~34 ATP generated.
✅ This is oxidative phosphorylation. ⚡
🔴 Question 27:
Differentiate between aerobic respiration, anaerobic respiration, and fermentation.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Aerobic Anaerobic Fermentation
O₂ requirement Present Absent Absent
Site Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cytoplasm
End products CO₂ + H₂O Lactic acid Alcohol + CO₂
ATP yield 36 2 2
Organisms Higher plants Muscle cells Yeast 🍞
💡 Fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration.
🔴 Question 28:
Explain respiratory quotient (RQ) and write its values for different substrates.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Ratio of CO₂ evolved to O₂ consumed.
RQ = CO₂ / O₂
Substrate Equation RQ
Carbohydrate C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O 1
Fat 2C₅₇H₁₁₀O₆ + 163O₂ → 114CO₂ + 110H₂O <1 Protein Variable <1 Organic acid C₄H₆O₅ + 3O₂ → 4CO₂ + 3H₂O >1
💡 RQ indicates type of substrate used.
🔴 Question 29:
Discuss amphibolic nature of respiration.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Acts as both catabolic (breakdown) and anabolic (synthesis) pathway.
Catabolic: Glucose oxidized to CO₂ + H₂O.
Anabolic: Intermediates used to synthesize amino acids, fats, nucleotides.
💡 Hence, respiration is amphibolic — center of metabolism.
🔴 Question 30:
Write short notes on fermentation and its economic importance.
🟢 Answer:
Fermentation: Incomplete oxidation of glucose in absence of O₂ by microbes.
Glucose → Alcohol + CO₂ + 2 ATP.
Types:
1️⃣ Alcoholic (Yeast) 🍶
2️⃣ Lactic acid (Bacteria) 🧀
Uses:
✔️ Brewing and baking industries.
✔️ Dairy products (curd, cheese).
✔️ Production of biofuels.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The common pathway for aerobic and anaerobic respiration is
🟡 A. Krebs cycle
🟡 B. Glycolysis
🟡 C. Electron transport chain
🟡 D. Oxidative phosphorylation
🟢 Answer: B. Glycolysis
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q2. The end product of glycolysis is
🟡 A. Acetyl-CoA
🟡 B. Pyruvate
🟡 C. Lactate
🟡 D. Ethanol
🟢 Answer: B. Pyruvate
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q3. The link reaction connects
🟡 A. Glycolysis and Calvin cycle
🟡 B. Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
🟡 C. Glycolysis and Electron transport chain
🟡 D. Krebs cycle and Photosynthesis
🟢 Answer: B. Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q4. The number of ATP molecules produced during complete oxidation of one glucose molecule in aerobic respiration is
🟡 A. 34
🟡 B. 36
🟡 C. 38
🟡 D. 40
🟢 Answer: C. 38
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q5. The site of glycolysis in a cell is
🟡 A. Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 B. Cytoplasm
🟡 C. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 D. Thylakoid lumen
🟢 Answer: B. Cytoplasm
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q6. During anaerobic respiration in plants, pyruvate is converted into
🟡 A. Acetyl-CoA
🟡 B. Ethanol and CO₂
🟡 C. Lactate and ATP
🟡 D. Malate and NADPH
🟢 Answer: B. Ethanol and CO₂
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q7. The enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction of glycolysis is
🟡 A. Phosphofructokinase
🟡 B. Hexokinase
🟡 C. Pyruvate kinase
🟡 D. Aldolase
🟢 Answer: B. Hexokinase
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q8. The terminal electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is
🟡 A. NAD⁺
🟡 B. Oxygen
🟡 C. FAD
🟡 D. Water
🟢 Answer: B. Oxygen
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q9. Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in
🟡 A. Cytosol
🟡 B. Outer mitochondrial membrane
🟡 C. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 D. Chloroplast stroma
🟢 Answer: C. Inner mitochondrial membrane
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q10. The main respiratory substrate in plants is
🟡 A. Proteins
🟡 B. Lipids
🟡 C. Carbohydrates
🟡 D. Organic acids
🟢 Answer: C. Carbohydrates
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q11. The respiratory quotient (RQ) of glucose is
🟡 A. 1
🟡 B. <1 🟡 C. >1
🟡 D. Zero
🟢 Answer: A. 1
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q12. Link reaction occurs in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 C. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 D. Chloroplast stroma
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondrial matrix
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q13. In plants, anaerobic respiration occurs in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Mitochondria
🟡 C. Endoplasmic reticulum
🟡 D. Golgi bodies
🟢 Answer: A. Cytoplasm
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q14. Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs in
🟡 A. Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
🟡 B. Calvin cycle and Glycolysis
🟡 C. Krebs cycle and ETS
🟡 D. Oxidative phosphorylation
🟢 Answer: A. Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q15. The enzymes of the Krebs cycle are present in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Outer mitochondrial membrane
🟡 C. Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 D. Chloroplast stroma
🟢 Answer: C. Mitochondrial matrix
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q16. The RQ of fats is usually
🟡 A. 1
🟡 B. >1
🟡 C. <1
🟡 D. Zero
🟢 Answer: C. <1
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q17. The first step in aerobic respiration is
🟡 A. Oxidative phosphorylation
🟡 B. Glycolysis
🟡 C. Krebs cycle
🟡 D. Link reaction
🟢 Answer: B. Glycolysis
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q18. Decarboxylation of pyruvic acid occurs in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 C. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 D. Intermembrane space
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondrial matrix
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q19. The electron transport system is located in
🟡 A. Outer mitochondrial membrane
🟡 B. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 C. Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 D. Cytoplasm
🟢 Answer: B. Inner mitochondrial membrane
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q20. The first molecule to enter the Krebs cycle is
🟡 A. Oxaloacetic acid
🟡 B. Pyruvic acid
🟡 C. Acetyl-CoA
🟡 D. Citrate
🟢 Answer: C. Acetyl-CoA
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q21. The ATP yield from oxidative phosphorylation per NADH is
🟡 A. 2
🟡 B. 3
🟡 C. 4
🟡 D. 1
🟢 Answer: B. 3
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q22. The enzyme phosphofructokinase acts in
🟡 A. Krebs cycle
🟡 B. Glycolysis
🟡 C. Calvin cycle
🟡 D. Photorespiration
🟢 Answer: B. Glycolysis
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q23. The net gain of ATP in glycolysis is
🟡 A. 2
🟡 B. 4
🟡 C. 6
🟡 D. 8
🟢 Answer: A. 2
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q24. Which one is not an intermediate of Krebs cycle?
🟡 A. Citrate
🟡 B. Malate
🟡 C. Oxaloacetate
🟡 D. Lactate
🟢 Answer: D. Lactate
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q25. The energy released in respiration is used to produce
🟡 A. Glucose
🟡 B. ATP
🟡 C. Starch
🟡 D. Pyruvate
🟢 Answer: B. ATP
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q26. The first stable product of Krebs cycle is
🟡 A. Malate
🟡 B. Citrate
🟡 C. Oxaloacetate
🟡 D. Fumarate
🟢 Answer: B. Citrate
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q27. The electron transport chain is located in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Mitochondrial inner membrane
🟡 C. Chloroplast stroma
🟡 D. Golgi membrane
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondrial inner membrane
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q28. The terminal step of aerobic respiration produces
🟡 A. CO₂
🟡 B. O₂
🟡 C. Water
🟡 D. Pyruvate
🟢 Answer: C. Water
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q29. The coenzyme that carries electrons from glycolysis to the ETC is
🟡 A. FADH₂
🟡 B. NADH
🟡 C. NADPH
🟡 D. ATP
🟢 Answer: B. NADH
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q30. Oxidative phosphorylation occurs due to
🟡 A. Electron transport and proton gradient
🟡 B. Substrate-level phosphorylation
🟡 C. Photolysis
🟡 D. Glycolysis
🟢 Answer: A. Electron transport and proton gradient
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q31. During anaerobic respiration in animals, pyruvate is converted into
🟡 A. Ethanol
🟡 B. Lactate
🟡 C. Acetyl-CoA
🟡 D. Citrate
🟢 Answer: B. Lactate
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q32. The number of ATP produced from one FADH₂ in ETC is
🟡 A. 1
🟡 B. 2
🟡 C. 3
🟡 D. 4
🟢 Answer: B. 2
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q33. The decarboxylation of pyruvate is catalyzed by
🟡 A. Pyruvate decarboxylase
🟡 B. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
🟡 C. Aldolase
🟡 D. Phosphofructokinase
🟢 Answer: B. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q34. The enzyme that converts glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate is
🟡 A. Phosphoglucoisomerase
🟡 B. Hexokinase
🟡 C. Aldolase
🟡 D. Enolase
🟢 Answer: A. Phosphoglucoisomerase
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q35. The process of conversion of pyruvate into ethanol and CO₂ is called
🟡 A. Lactic acid fermentation
🟡 B. Alcoholic fermentation
🟡 C. Glycolysis
🟡 D. Krebs cycle
🟢 Answer: B. Alcoholic fermentation
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q36. The number of ATP molecules produced by substrate-level phosphorylation in Krebs cycle per glucose molecule is
🟡 A. 1
🟡 B. 2
🟡 C. 3
🟡 D. 4
🟢 Answer: B. 2
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q37. The respiratory quotient (RQ) of fats is approximately
🟡 A. 1.0
🟡 B. 0.7
🟡 C. 1.3
🟡 D. 0
🟢 Answer: B. 0.7
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q38. The respiratory quotient of proteins is
🟡 A. 1.0
🟡 B. 0.7
🟡 C. 0.9
🟡 D. 0.5
🟢 Answer: C. 0.9
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q39. During glycolysis, ATP is formed by
🟡 A. Chemiosmosis
🟡 B. Substrate-level phosphorylation
🟡 C. Oxidative phosphorylation
🟡 D. Photophosphorylation
🟢 Answer: B. Substrate-level phosphorylation
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q40. Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate consumes
🟡 A. 1 ATP
🟡 B. 2 ATP
🟡 C. 1 NADH
🟡 D. 2 NADH
🟢 Answer: A. 1 ATP
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q41. Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate yields
🟡 A. Acetyl-CoA, CO₂, and NADH
🟡 B. Ethanol and CO₂
🟡 C. Lactate and ATP
🟡 D. Citrate and NADH
🟢 Answer: A. Acetyl-CoA, CO₂, and NADH
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q42. The net gain of ATP from one glucose molecule in glycolysis under anaerobic conditions is
🟡 A. 4
🟡 B. 2
🟡 C. 6
🟡 D. 8
🟢 Answer: B. 2
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q43. In aerobic respiration, electrons are finally transferred to
🟡 A. CO₂
🟡 B. Oxygen
🟡 C. Water
🟡 D. NADH
🟢 Answer: B. Oxygen
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q44. The enzyme fumarase acts on
🟡 A. Fumarate
🟡 B. Malate
🟡 C. Succinate
🟡 D. Oxaloacetate
🟢 Answer: B. Malate
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q45. In the electron transport chain, ATP synthase is located in
🟡 A. Outer mitochondrial membrane
🟡 B. Inner mitochondrial membrane
🟡 C. Intermembrane space
🟡 D. Matrix
🟢 Answer: B. Inner mitochondrial membrane
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q46. The connecting link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle is
🟡 A. Pyruvate
🟡 B. Acetyl-CoA
🟡 C. Citrate
🟡 D. Malate
🟢 Answer: B. Acetyl-CoA
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q47. The Krebs cycle is also known as
🟡 A. Calvin cycle
🟡 B. Citric acid cycle
🟡 C. Hatch–Slack pathway
🟡 D. Oxidative cycle
🟢 Answer: B. Citric acid cycle
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q48. The respiratory substrate that yields the highest RQ is
🟡 A. Carbohydrates
🟡 B. Proteins
🟡 C. Lipids
🟡 D. Organic acids
🟢 Answer: D. Organic acids
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q49. Malate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of
🟡 A. Malate to Oxaloacetate
🟡 B. Oxaloacetate to Citrate
🟡 C. Succinate to Fumarate
🟡 D. Pyruvate to Lactate
🟢 Answer: A. Malate to Oxaloacetate
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q50. The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is
🟡 A. NADH
🟡 B. ATP
🟡 C. Pyruvate
🟡 D. Citrate
🟢 Answer: B. ATP
📅 NEET 2015
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Respiration is a process of:
🔴 1️⃣ Energy utilization
🟢 2️⃣ Energy release
🟡 3️⃣ Energy storage
🔵 4️⃣ Energy loss
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Energy release
🔵 Question 2:
Respiration occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Only green cells
🟢 2️⃣ All living cells
🟡 3️⃣ Only animal cells
🔵 4️⃣ Only root cells
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ All living cells
🔵 Question 3:
Which of the following is the site of glycolysis?
🔴 1️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢 2️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟡 3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 4️⃣ Chloroplast
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔵 Question 4:
Glycolysis was discovered by:
🔴 1️⃣ Calvin
🟢 2️⃣ Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas
🟡 3️⃣ Krebs
🔵 4️⃣ Blackman
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas
🔵 Question 5:
The end product of glycolysis is:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ Pyruvic acid
🟡 3️⃣ Lactic acid
🔵 4️⃣ Acetyl CoA
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pyruvic acid
🔵 Question 6:
The process of conversion of glucose into pyruvic acid is known as:
🔴 1️⃣ Glycogenesis
🟢 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🟡 3️⃣ Gluconeogenesis
🔵 4️⃣ Fermentation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🔵 Question 7:
Number of ATP molecules formed in glycolysis (net gain) is:
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 4
🟡 3️⃣ 6
🔵 4️⃣ 8
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 8:
Which is the common step in aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
🔴 1️⃣ Krebs cycle
🟢 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🟡 3️⃣ ETS
🔵 4️⃣ Oxidative phosphorylation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🔵 Question 9:
Pyruvic acid is converted into ethanol in:
🔴 1️⃣ Yeast
🟢 2️⃣ Muscle cells
🟡 3️⃣ Plant roots
🔵 4️⃣ Animal tissues
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Yeast
🔵 Question 10:
Krebs cycle occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 4️⃣ Stroma
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🔵 Question 11:
Link between glycolysis and Krebs cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Pyruvate
🟢 2️⃣ Acetyl CoA
🟡 3️⃣ Citric acid
🔵 4️⃣ Glucose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Acetyl CoA
🔵 Question 12:
Krebs cycle was discovered by:
🔴 1️⃣ Calvin
🟢 2️⃣ Krebs
🟡 3️⃣ Hill
🔵 4️⃣ Blackman
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Krebs
🔵 Question 13:
Which is the first stable product of Krebs cycle?
🔴 1️⃣ Citric acid
🟢 2️⃣ Oxaloacetic acid
🟡 3️⃣ Succinic acid
🔵 4️⃣ Malic acid
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Citric acid
🔵 Question 14:
Krebs cycle is also known as:
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolytic pathway
🟢 2️⃣ Citric acid cycle
🟡 3️⃣ Oxidative pathway
🔵 4️⃣ Electron transport system
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Citric acid cycle
🔵 Question 15:
Which of the following is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ O₂
🟡 3️⃣ H₂O
🔵 4️⃣ NAD⁺
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ O₂
🔵 Question 16:
The number of ATPs produced in complete oxidation of one glucose molecule is:
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 36
🟡 3️⃣ 38
🔵 4️⃣ 40
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 38
🔵 Question 17:
The process of breaking down glucose in absence of oxygen is:
🔴 1️⃣ Aerobic respiration
🟢 2️⃣ Anaerobic respiration
🟡 3️⃣ Photorespiration
🔵 4️⃣ Combustion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Anaerobic respiration
🔵 Question 18:
Which step of respiration does not release CO₂?
🔴 1️⃣ Link reaction
🟢 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🟡 3️⃣ Krebs cycle
🔵 4️⃣ Pyruvate oxidation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🔵 Question 19:
Decarboxylation means:
🔴 1️⃣ Removal of oxygen
🟢 2️⃣ Removal of CO₂
🟡 3️⃣ Removal of hydrogen
🔵 4️⃣ Addition of oxygen
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Removal of CO₂
🔵 Question 20:
Which of the following is produced during aerobic respiration?
🔴 1️⃣ Lactic acid
🟢 2️⃣ CO₂ and H₂O
🟡 3️⃣ Ethanol
🔵 4️⃣ Acetaldehyde
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ CO₂ and H₂O
🔵 Question 21:
In which step of aerobic respiration is maximum ATP produced?
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolysis
🟢 2️⃣ Electron transport system (ETS)
🟡 3️⃣ Krebs cycle
🔵 4️⃣ Link reaction
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Electron transport system (ETS)
🔵 Question 22:
Respiratory quotient (RQ) for carbohydrate is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ <1 🟡 3️⃣ >1
🔵 4️⃣ 0
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1
🔵 Question 23:
RQ for fat is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ <1 🟡 3️⃣ >1
🔵 4️⃣ 0
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ <1
🔵 Question 24:
RQ for organic acids is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ >1
🟡 3️⃣ <1 🔵 4️⃣ 0 ✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ >1
🔵 Question 25:
The respiratory substrate in plants is usually:
🔴 1️⃣ Fats
🟢 2️⃣ Carbohydrates
🟡 3️⃣ Proteins
🔵 4️⃣ Organic acids
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Carbohydrates
🔵 Question 26:
The number of CO₂ molecules released in one turn of Krebs cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ 2
🟡 3️⃣ 3
🔵 4️⃣ 4
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 27:
Which enzyme converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
🔴 1️⃣ Pyruvate carboxylase
🟢 2️⃣ Pyruvate dehydrogenase
🟡 3️⃣ Pyruvate kinase
🔵 4️⃣ Decarboxylase
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pyruvate dehydrogenase
🔵 Question 28:
The link reaction occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🟡 3️⃣ Inner membrane
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleus
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondrial matrix
🔵 Question 29:
Which of the following is not a product of Krebs cycle?
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ ATP
🟡 3️⃣ NADH
🔵 4️⃣ Oxygen
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Oxygen
🔵 Question 30:
The number of NADH produced in one turn of Krebs cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ 3
🟡 3️⃣ 4
🔵 4️⃣ 2
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 3
🔵 Question 31:
The number of FADH₂ molecules produced per glucose in Krebs cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ 2
🟡 3️⃣ 3
🔵 4️⃣ 4
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 32:
Each NADH yields how many ATP molecules in ETS?
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 3
🟡 3️⃣ 4
🔵 4️⃣ 1
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 3
🔵 Question 33:
Each FADH₂ yields how many ATP molecules in ETS?
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ 2
🟡 3️⃣ 3
🔵 4️⃣ 4
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 34:
Chemiosmotic theory was proposed by:
🔴 1️⃣ Hill
🟢 2️⃣ Peter Mitchell
🟡 3️⃣ Calvin
🔵 4️⃣ Krebs
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Peter Mitchell
🔵 Question 35:
In ETS, ATP is synthesized by:
🔴 1️⃣ Photophosphorylation
🟢 2️⃣ Oxidative phosphorylation
🟡 3️⃣ Substrate-level phosphorylation
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Oxidative phosphorylation
🔵 Question 36:
Substrate-level phosphorylation occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
🟢 2️⃣ ETS only
🟡 3️⃣ Glycolysis only
🔵 4️⃣ Krebs cycle only
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
🔵 Question 37:
Which compound enters the Krebs cycle?
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Acetyl CoA
🟡 3️⃣ Pyruvate
🔵 4️⃣ OAA
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Acetyl CoA
🔵 Question 38:
Which compound combines with acetyl CoA to form citric acid?
🔴 1️⃣ Malate
🟢 2️⃣ Oxaloacetic acid
🟡 3️⃣ Fumarate
🔵 4️⃣ Succinic acid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Oxaloacetic acid
🔵 Question 39:
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate produces:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂, ATP
🟢 2️⃣ CO₂, NADH, Acetyl CoA
🟡 3️⃣ CO₂, FADH₂
🔵 4️⃣ Only CO₂
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ CO₂, NADH, Acetyl CoA
🔵 Question 40:
Anaerobic respiration in plants leads to formation of:
🔴 1️⃣ Lactic acid
🟢 2️⃣ Ethanol and CO₂
🟡 3️⃣ CO₂ and H₂O
🔵 4️⃣ Pyruvate
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ethanol and CO₂
🔵 Question 41:
In aerobic respiration, the final acceptor of electrons is:
🔴 1️⃣ NAD⁺
🟢 2️⃣ O₂
🟡 3️⃣ CO₂
🔵 4️⃣ FAD
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ O₂
🔵 Question 42:
Which step produces maximum ATP in aerobic respiration?
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolysis
🟢 2️⃣ ETS
🟡 3️⃣ Krebs cycle
🔵 4️⃣ Link reaction
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ ETS
🔵 Question 43:
Which intermediate is common to aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Pyruvate
🟡 3️⃣ Acetyl CoA
🔵 4️⃣ Citric acid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pyruvate
🔵 Question 44:
Which enzyme is responsible for substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis?
🔴 1️⃣ Hexokinase
🟢 2️⃣ Pyruvate kinase
🟡 3️⃣ Phosphofructokinase
🔵 4️⃣ Enolase
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pyruvate kinase
🔵 Question 45:
During anaerobic respiration, the number of ATP molecules produced is:
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 4
🟡 3️⃣ 8
🔵 4️⃣ 38
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 46:
Which compound acts as hydrogen carrier in ETS?
🔴 1️⃣ Cytochrome
🟢 2️⃣ NADH
🟡 3️⃣ Oxygen
🔵 4️⃣ CO₂
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ NADH
🔵 Question 47:
In plant respiration, the RQ of protein is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ <1 🟡 3️⃣ >1
🔵 4️⃣ 0
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ <1
🔵 Question 48:
In respiration, which step releases CO₂?
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolysis
🟢 2️⃣ Link reaction and Krebs cycle
🟡 3️⃣ ETS
🔵 4️⃣ ATP synthesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Link reaction and Krebs cycle
🔵 Question 49:
The total number of NADH produced in complete oxidation of one glucose is:
🔴 1️⃣ 8
🟢 2️⃣ 10
🟡 3️⃣ 12
🔵 4️⃣ 14
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 10
🔵 Question 50:
Which of the following processes does not require oxygen?
🔴 1️⃣ ETS
🟢 2️⃣ Glycolysis
🟡 3️⃣ Krebs cycle
🔵 4️⃣ Oxidative phosphorylation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycolysis
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
