Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 13. Our Environment
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
🌍 Introduction
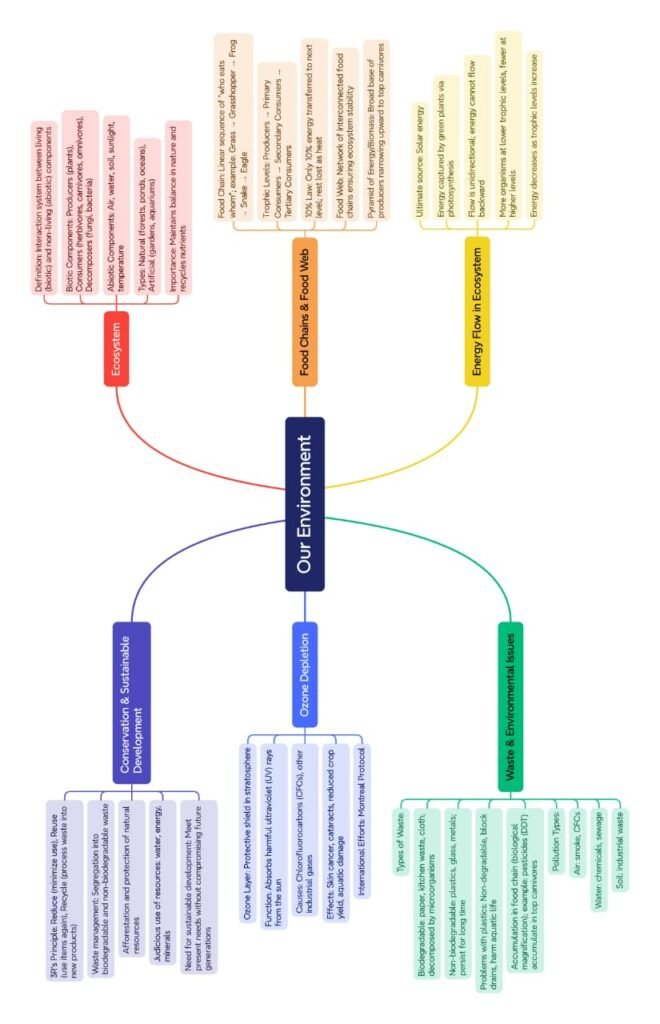
🔵 The environment is the sum of all external conditions and influences affecting living organisms.
🟢 It consists of biotic components (plants, animals, microorganisms) and abiotic components (air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature).
🟡 Human activities like industrialisation, urbanisation, deforestation, and overuse of resources disturb natural balance.
🌿 Ecosystem
🔵 Definition: A functional unit of nature where living beings interact with each other and with their physical surroundings.
🟢 Two main components:
Biotic: producers (plants), consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores), decomposers (fungi, bacteria).
Abiotic: soil, water, air, sunlight.
🟡 Types of ecosystem: Natural (forest, pond, lake, desert, grassland) and artificial (crop field, aquarium).
💡 Example: Pond ecosystem → producers (algae, plants), primary consumers (insects, fish), secondary consumers (bigger fish), decomposers (fungi, bacteria).
🔴 Food Chain and Food Web
🌿 Food chain: Linear sequence of who eats whom.

Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle.
🟢 Food web: Interconnection of multiple food chains; more stable.
🟡 Trophic levels: Each step in food chain is a trophic level.
Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers.

✏️ Note: Energy flow is unidirectional.
⚡ Energy Flow in Ecosystem
🔵 Energy enters ecosystem through sunlight → captured by producers (photosynthesis).
🟢 Only 10% of energy at one trophic level is transferred to next (10% law).
🟡 Remaining energy lost as heat or used for life processes.
🔴 Pyramid of energy is always upright.
💡 Example: Grass (1000 J) → Grasshopper (100 J) → Frog (10 J) → Snake (1 J).
🟣 Ozone Layer and its Depletion
🌍 Ozone (O₃): Found in stratosphere; protects from harmful UV radiation.
🟢 Depletion: Caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigerators, ACs, aerosol sprays.
🟡 Effects: skin cancer, eye cataract, reduced immunity, harm to plants and animals.
🔴 Global efforts: Montreal Protocol (1987) to reduce CFCs.
🟠 Waste Generation and Management
🌿 Human activities produce biodegradable waste (food, paper, wood) and non-biodegradable waste (plastics, glass, metals).
🟢 Non-biodegradable wastes accumulate → pollute soil, water, harm organisms.
🟡 Methods of management:
Reduce → minimise waste.
Reuse → use same item again (bottles, containers).
Recycle → convert waste to usable form (plastic, paper, metal).
💡 Example: Carry cloth/jute bags instead of plastic bags.
🔵 Environmental Issues
🌍 Air pollution: Due to vehicles, industries, burning fossil fuels → respiratory issues, global warming.
🟢 Water pollution: Due to sewage, industrial effluents, plastics → waterborne diseases.
🟡 Soil pollution: Excess fertilisers, pesticides, plastics → reduces fertility.
🔴 Deforestation: Loss of biodiversity, climate imbalance.
🟢 Summary
Ecosystem = interaction of living + non-living.
Food chain and food web → transfer of energy.
Only 10% energy transferred between trophic levels.
Ozone protects from UV, CFCs cause depletion.
Waste management: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
Environmental problems: pollution, deforestation.
📝 Quick Recap
🌿 Ecosystem = biotic + abiotic.
🍃 Food chain = linear, Food web = interconnected.
⚡ 10% law of energy transfer.
🛡️ Ozone = protective shield.
♻️ Waste management → 3Rs.
🌍 Pollution = global concern.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
➡️Question 1
Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
(a) Grass, flowers and leather
(b) Grass, wood and plastic
(c) Fruit-peels, cake and lime-juice
(d) Cake, wood and grass
Answer
🔵 Biodegradable = decomposable by microorganisms.
🟢 Plastic is not biodegradable.
🟡 Correct set: fruit-peels, cake, lime-juice.
✔️ Correct option: (c)
➡️Question 2
Which of the following constitute a food-chain?
(a) Grass, wheat and mango
(b) Grass, goat and human
(c) Goat, cow and elephant
(d) Grass, fish and goat
Answer
🌿 Food chain must show producer → consumer → higher consumer.
🟢 (b) Grass → goat → human forms valid chain.
✔️ Correct option: (b)
➡️Question 3
Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
(a) Carrying cloth-bags while shopping
(b) Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
(c) Walking to school instead of using scooter
(d) All of the above
Answer
🔵 All three reduce pollution, save energy, reduce plastic use.
✔️ Correct option: (d) All of the above
➡️Question 4
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer
🌍 Balance of ecosystem breaks.
🔴 Previous level organisms (prey) multiply unchecked.
🟢 Next level organisms (predators) starve and die.
⚡ Whole food web collapses.
➡️Question 5
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing damage?
Answer
🟢 Yes, impact differs by level.
If producers removed → entire chain breaks.
If herbivores removed → carnivores die, plants overgrow.
If carnivores removed → herbivores multiply, plants depleted.
🔴 No trophic level can be removed without causing harm.
➡️Question 6
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer
🔵 Definition: Increase in concentration of harmful non-biodegradable chemicals (like pesticides, DDT, heavy metals) as we move up the food chain.
🟢 Higher trophic levels accumulate more toxins.
🌿 Example: pesticides in plants → cow → humans (highest effect).
➡️Question 7
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer
🔴 Accumulate in environment → soil/water pollution.
🟡 Cause biological magnification in food chains.
🌍 Block drains, harm aquatic life.
🟢 Non-decomposable, persist for long time.
➡️Question 8
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer
🌿 Even biodegradable waste in excess causes harm.
🔵 Produces foul smell, releases methane.
🟡 Excess waste may choke drains, affect soil fertility.
✔️ So, it will still impact environment unless managed properly.
➡️Question 9
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer
🔴 Ozone absorbs harmful UV rays.
🟢 Depletion → skin cancer, cataract, immune damage, harm to crops and animals.
🌍 Steps taken:
Ban on CFCs under Montreal Protocol.
Use eco-friendly coolants, refrigerants, sprays.
Awareness campaigns to reduce ozone-depleting substances.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
SECTION A — (Q1–Q18 : MCQs, 1 Mark Each)
Q1. The physical components of the environment are called
🔵 (A) Biotic components
🟢 (B) Abiotic components
🟠 (C) Producers
🔴 (D) Consumers
✔️ Answer: (B) Abiotic components
Q2. Which of the following is an abiotic component?
🔵 (A) Plants
🟢 (B) Animals
🟠 (C) Bacteria
🔴 (D) Water
✔️ Answer: (D) Water
Q3. The pyramid of energy in an ecosystem is always
🔵 (A) Inverted
🟢 (B) Straight
🟠 (C) Irregular
🔴 (D) Upright
✔️ Answer: (D) Upright
Q4. In a food chain, energy flow is
🔵 (A) Unidirectional
🟢 (B) Bidirectional
🟠 (C) Multidirectional
🔴 (D) Circular
✔️ Answer: (A) Unidirectional
Q5. Which of the following is a producer?
🔵 (A) Deer
🟢 (B) Grass
🟠 (C) Lion
🔴 (D) Tiger
✔️ Answer: (B) Grass
Q6. The highest trophic level is occupied by
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Decomposers
🟠 (C) Herbivores
🔴 (D) Top carnivores
✔️ Answer: (D) Top carnivores
Q7. The percentage of solar energy captured by green plants is about
🔵 (A) 1%
🟢 (B) 10%
🟠 (C) 20%
🔴 (D) 50%
✔️ Answer: (A) 1%
Q8. Which one of the following organisms is a decomposer?
🔵 (A) Earthworm
🟢 (B) Mushroom
🟠 (C) Cat
🔴 (D) Crow
✔️ Answer: (B) Mushroom
Q9. The 10% law of energy transfer was given by
🔵 (A) Charles Darwin
🟢 (B) Lindeman
🟠 (C) Stanley Miller
🔴 (D) Joseph Priestley
✔️ Answer: (B) Lindeman
Q10. Which of the following gases damages the ozone layer?
🔵 (A) CO₂
🟢 (B) SO₂
🟠 (C) CFCs
🔴 (D) O₂
✔️ Answer: (C) CFCs
Q11. Which of the following is biodegradable?
🔵 (A) Plastic cup
🟢 (B) Polythene bag
🟠 (C) Paper
🔴 (D) Aluminium foil
✔️ Answer: (C) Paper
Q12. The correct sequence of food chain is
🔵 (A) Grass → Deer → Tiger
🟢 (B) Tiger → Deer → Grass
🟠 (C) Grass → Tiger → Deer
🔴 (D) Deer → Grass → Tiger
✔️ Answer: (A) Grass → Deer → Tiger
Q13. The energy flow in ecosystem follows
🔵 (A) 10% law
🟢 (B) 100% law
🟠 (C) 25% law
🔴 (D) None
✔️ Answer: (A) 10% law
Q14. Ozone layer protects us from
🔵 (A) Infrared rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet rays
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) X-rays
✔️ Answer: (B) Ultraviolet rays
Q15. Which of the following represents a correct food chain?
🔵 (A) Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake → Hawk
🟢 (B) Grass → Frog → Snake → Insect → Hawk
🟠 (C) Grass → Snake → Insect → Hawk
🔴 (D) Insect → Grass → Snake
✔️ Answer: (A) Grass → Insect → Frog → Snake → Hawk
Q16. The main reason for the depletion of ozone layer is
🔵 (A) Excess CO₂
🟢 (B) Excess O₂
🟠 (C) Use of CFCs
🔴 (D) Acid rain
✔️ Answer: (C) Use of CFCs
Q17. Which of the following is not a component of the food chain?
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Decomposers
🟠 (C) Detritivores
🔴 (D) Wind
✔️ Answer: (D) Wind
Q18. Which of the following is a non-biodegradable waste?
🔵 (A) Wood
🟢 (B) Cotton
🟠 (C) Glass
🔴 (D) Vegetable peels
✔️ Answer: (C) Glass
SECTION B — (Q19–Q27 : Short and Mid-Length Answers)
Q19. Define ecosystem.
💡 An ecosystem is the interaction between all living organisms (biotic) and non-living components (abiotic) of an environment, functioning as a unit.
Q20. What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
✔️ Decomposers (bacteria, fungi) break down dead matter into simple substances, recycling nutrients back to the soil for producers.
Q21. Explain the flow of energy in an ecosystem.
➡️ Energy from sunlight → captured by producers → transferred to consumers → decomposers.
💡 Energy flow is unidirectional, and only 10% energy passes to next level.
Q22. State two differences between biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes.
✔️ Biodegradable: decomposed naturally (e.g., paper).
✔️ Non-biodegradable: cannot be decomposed (e.g., plastics).
Q23. What will happen if all decomposers are eliminated from the Earth?
💡 Dead matter will accumulate, nutrients won’t recycle, and ecosystem balance will be lost.
Q24. What is the function of ozone in the atmosphere?
✔️ Ozone absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun, protecting living organisms.
Q25. State two harmful effects of CFCs.
✔️ Depletion of ozone layer.
✔️ Increase in harmful UV radiation → skin cancer and eye cataract.
Q26. Define trophic level. Give one example.
💡 A trophic level represents each step in the food chain.
Example: Grass (1st trophic level) → Deer (2nd) → Tiger (3rd).
Q27. What are food chains and food webs?
✔️ A food chain shows a linear sequence of energy transfer.
✔️ A food web is interconnected food chains showing complex feeding relationships.
SECTION C — (Q28–Q30 : Long and Case-Based Answers)
Q28. Explain the phenomenon of biological magnification with an example.
💡 Non-biodegradable substances (like DDT) accumulate in organisms and increase in concentration at higher trophic levels.
Example: DDT sprayed on crops → enters water → fish → birds → human.
✔️ Top-level consumers suffer maximum harm.
Q29. Describe the various steps involved in waste management.
➡️ (i) Segregation: Separate biodegradable & non-biodegradable waste.
➡️ (ii) Collection & Recycling: Proper collection and recycling of plastics, metals.
➡️ (iii) Composting: Biodegradable waste converted to manure.
➡️ (iv) Reduction at Source: Minimize use of disposables.
Q30. Case Study:
A factory releases harmful chemicals into a nearby water body.
(a) Which trophic level is most affected?
(b) Which law of energy flow is followed?
(c) Suggest two preventive steps.
✔️ (a) Top consumers (humans, birds) due to biological magnification.
✔️ (b) 10% law of energy flow.
✔️ (c) Avoid chemical disposal; encourage treatment before release.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
