Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 5: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
🧬 The molecular basis of inheritance explains how DNA acts as the genetic material, its structure, replication, transcription, translation, regulation of gene expression, and human genome mapping.
🌱 This chapter connects genetics with molecular biology and is key to understanding heredity at the biochemical level.
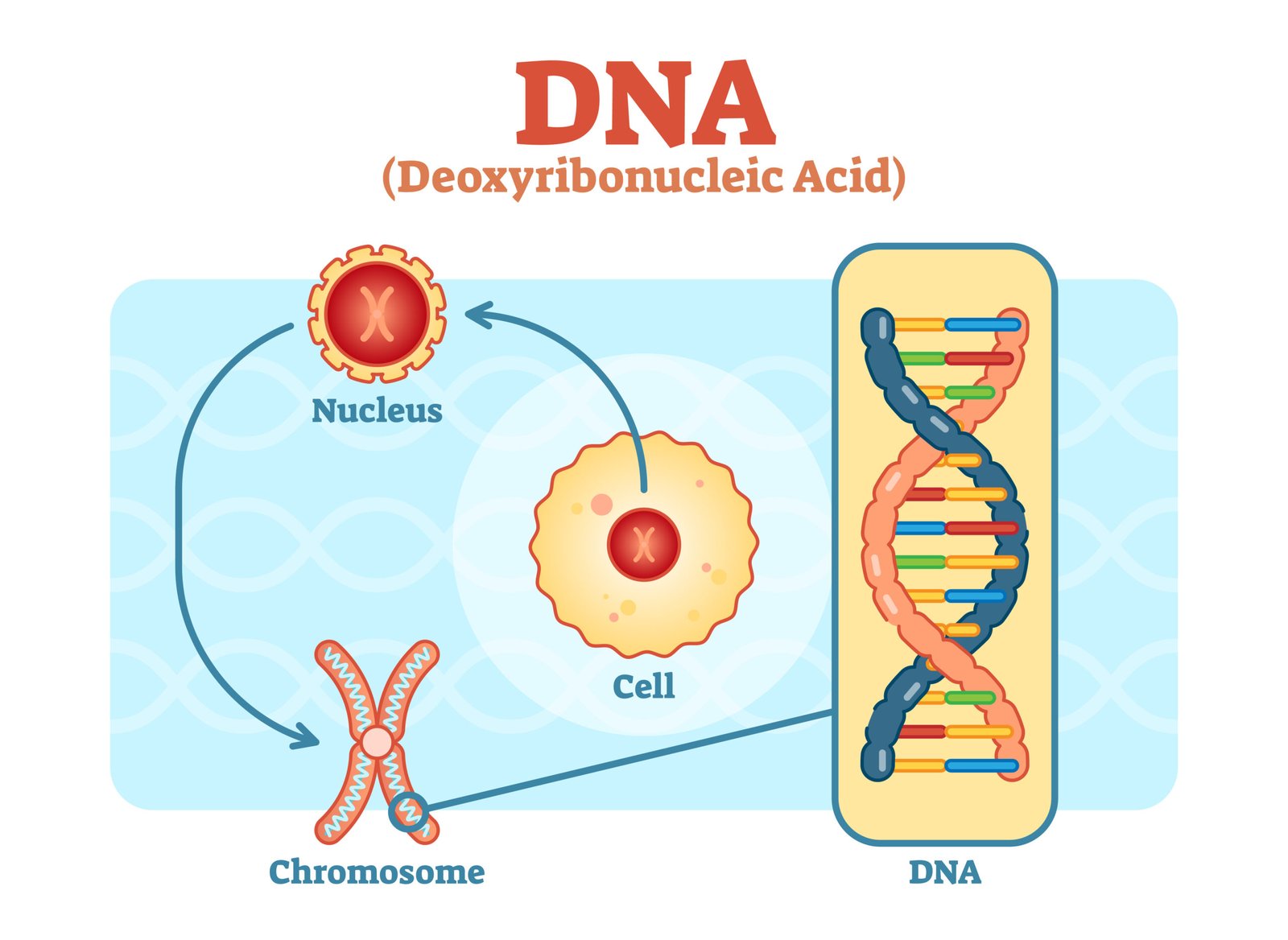
🧬 DNA — The Genetic Material
💡 Griffith’s Experiment (1928): Transformation principle in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
🧪 Avery, MacLeod & McCarty (1944): Proved DNA is the genetic material.
🧪 Hershey–Chase Experiment (1952): Blender experiment with T2 phage confirmed DNA is genetic material.
🧬 Structure of DNA
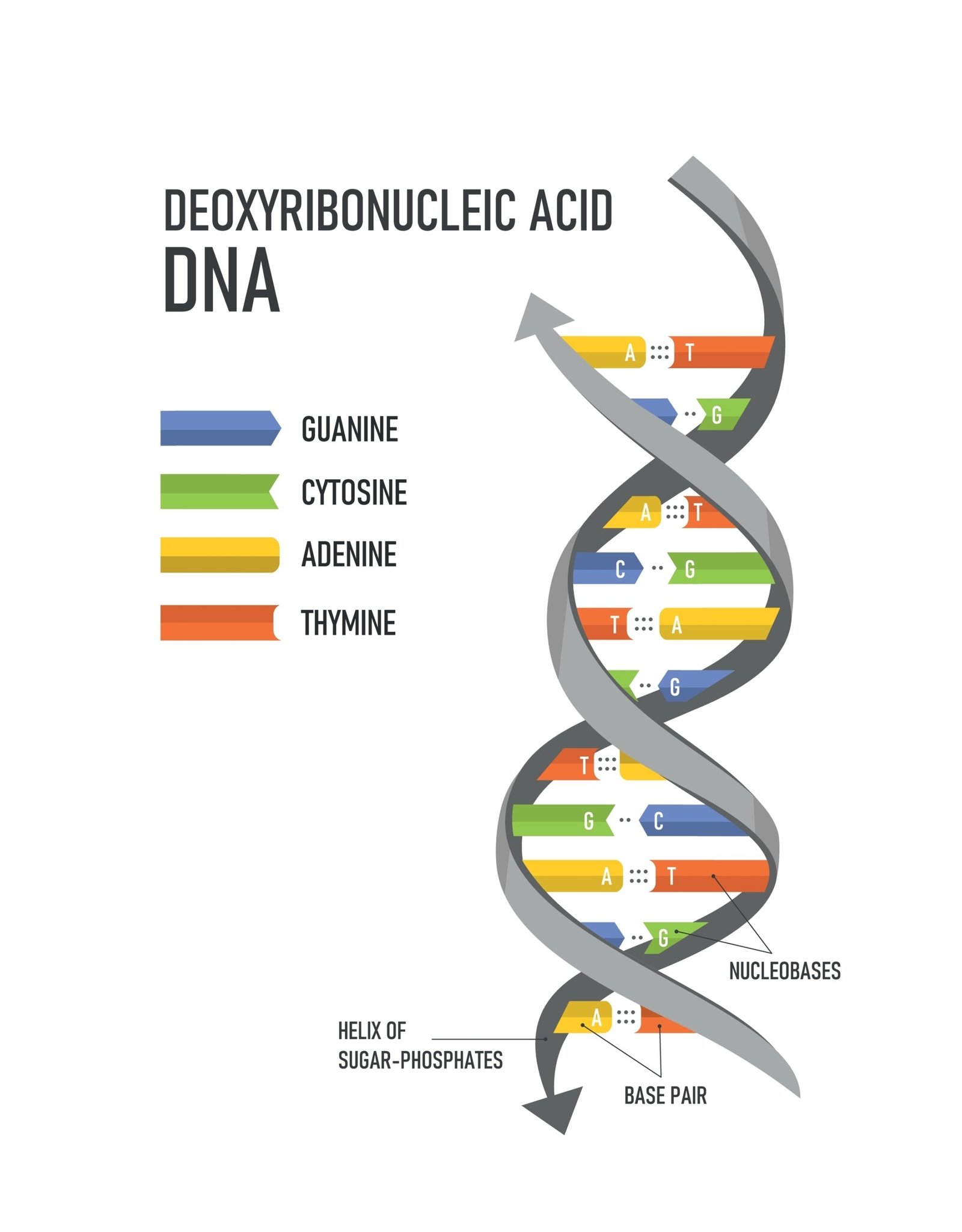
Proposed by Watson and Crick (1953).
🌀 Double helix model: two strands antiparallel, complementary base pairing (A=T, G≡C).
🔗 Chargaff’s Rule: Purine = Pyrimidine.
🔄 Hydrogen bonds: A–T (2 bonds), G–C (3 bonds).
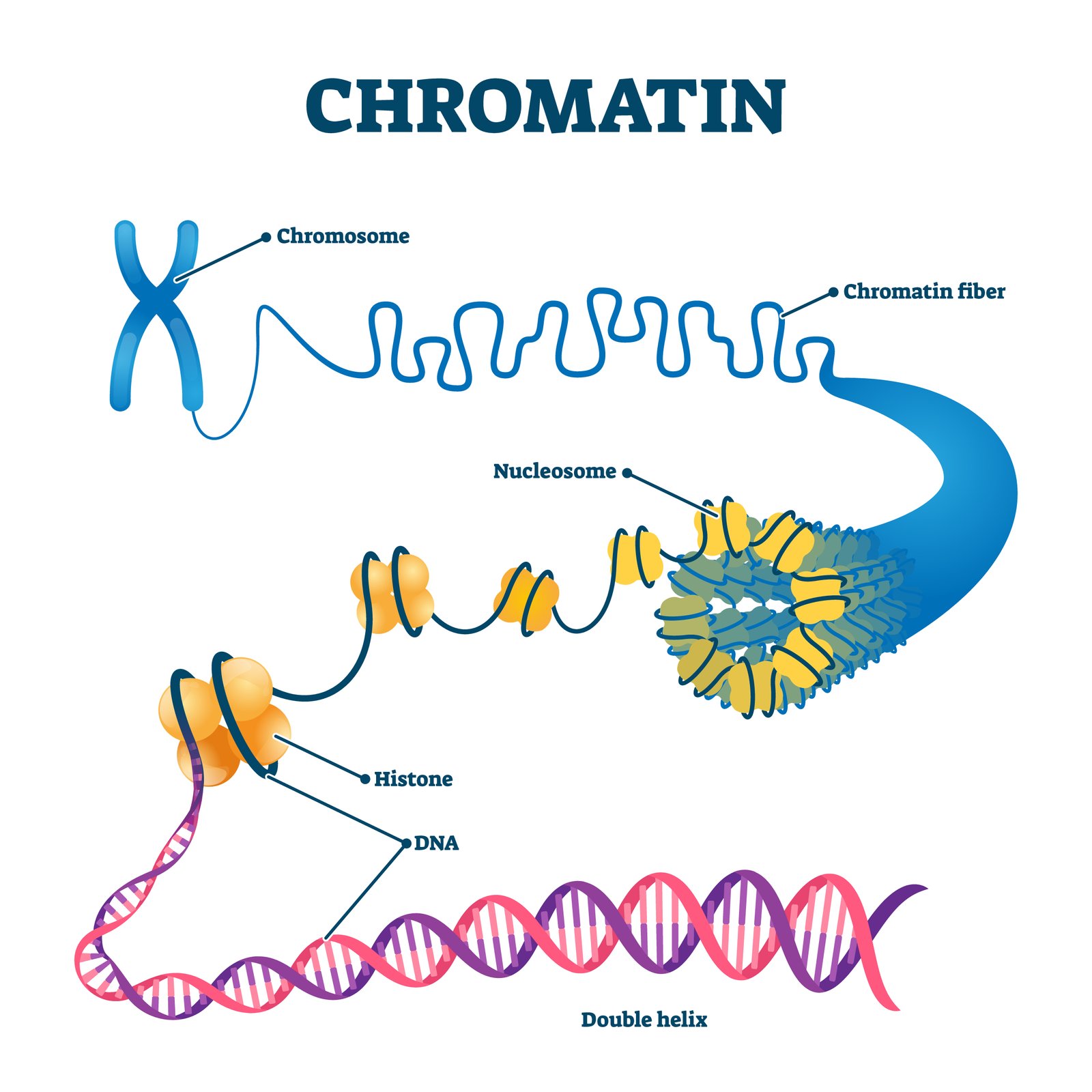
📊 Packaging: In prokaryotes → nucleoid; in eukaryotes → chromatin (DNA + histones → nucleosome “beads on a string”).
🔄 DNA Replication
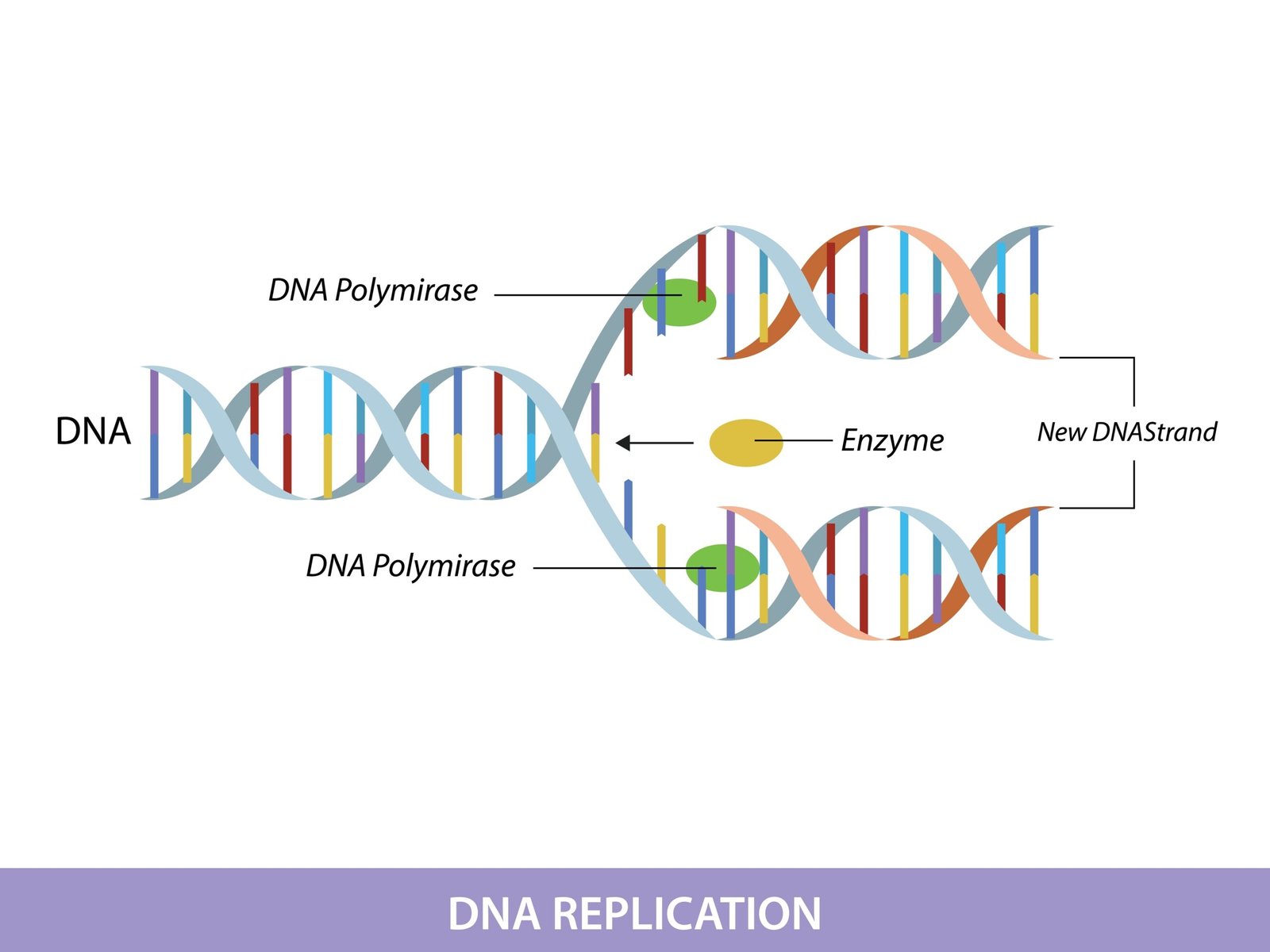
Semi-conservative (Meselson & Stahl experiment, 1958).
Steps:
Unwinding by helicase.
Primase adds RNA primer.
DNA polymerase III elongates new strand (5′→3′).
Leading strand continuous; lagging strand discontinuous → Okazaki fragments.
DNA ligase seals nicks.
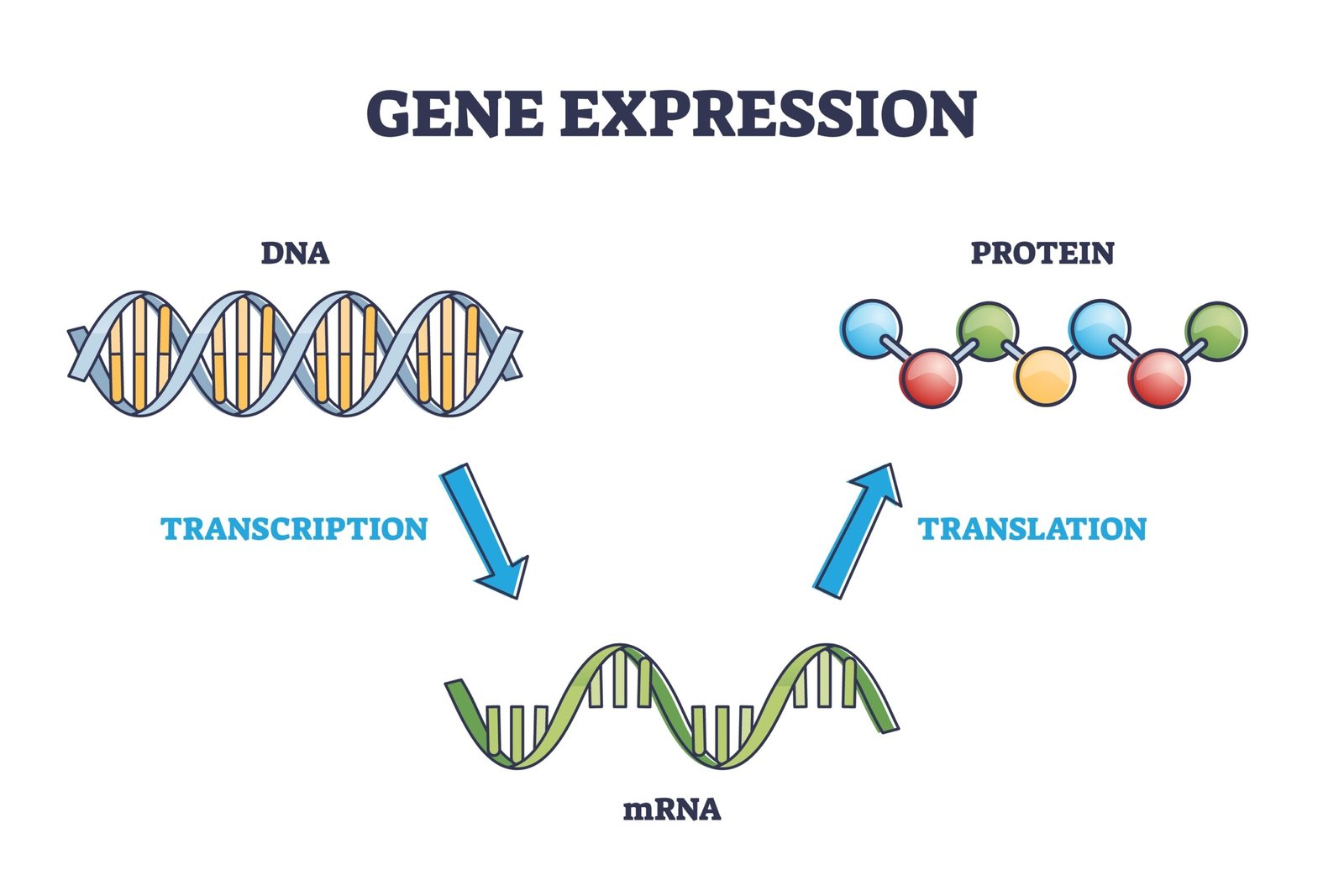
✏️ Transcription (DNA → RNA)

In prokaryotes: Entire process in cytoplasm; single RNA polymerase.
In eukaryotes: Occurs in nucleus; RNA polymerase I (rRNA), II (mRNA), III (tRNA).
Process: Initiation → Elongation → Termination.
Post-transcriptional modifications (eukaryotes):
5′ capping.
3′ poly-A tail.
Splicing (removal of introns, joining of exons).
🧪 Genetic Code
Triplet codons; 64 codons total.
Features: Universal, degenerate, non-overlapping.
AUG = Start codon (methionine).
UAA, UAG, UGA = Stop codons.
🔁 Translation (Protein Synthesis)
Ribosomes = site of translation.
Process:
Initiation → mRNA binds ribosome, tRNA brings amino acid.
Elongation → peptide bond formation.
Termination → stop codon, release factor.
🧩 Regulation of Gene Expression
Prokaryotes: Lac Operon model (Jacob & Monod).
Inducible system: presence of lactose inactivates repressor, transcription occurs.
Eukaryotes: Multiple levels (transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, post-translational).
🌍 Human Genome Project (HGP)
Started 1990, completed 2003.
Aim: Sequence entire human genome.
Findings: 3 billion base pairs, ~20,000–25,000 genes.
Applications: Gene therapy, DNA fingerprinting, medical diagnostics.
🧬 DNA Fingerprinting
Developed by Alec Jeffreys (1985).
Uses VNTRs (Variable Number Tandem Repeats).
Applications: Forensics, paternity testing, genetic diversity studies.
📝 Summary (~300 words)
The molecular basis of inheritance explores DNA as the genetic material. Experiments by Griffith, Avery, and Hershey–Chase established DNA’s role. The Watson–Crick double helix explains structure with base-pair complementarity. DNA replication is semi-conservative, confirmed by Meselson–Stahl. DNA replication requires helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase.
Transcription produces RNA: in prokaryotes via a single polymerase, in eukaryotes via RNA polymerase I, II, III. Eukaryotic transcripts undergo capping, tailing, and splicing. The genetic code is triplet, universal, degenerate, with AUG as start codon and UAA, UAG, UGA as stops. Translation occurs in ribosomes through initiation, elongation, and termination.
Gene expression is regulated by operons in prokaryotes, notably the lac operon. In eukaryotes, regulation is complex at multiple levels. The Human Genome Project sequenced all human genes, revolutionising medicine and diagnostics. DNA fingerprinting, based on VNTRs, has applications in forensics and identity testing.
🎯 Quick Recap
🟢 DNA → Genetic material, double helix.
🔵 Replication → Semi-conservative.
🟠 Transcription → DNA → RNA (with modifications in eukaryotes).
🔴 Translation → Protein synthesis on ribosomes.
🟡 Genetic code → Triplet, universal, degenerate.
🟣 Regulation → Lac operon, eukaryotic control.
🟤 HGP → Sequencing all human genes.
⚫ DNA fingerprinting → Forensics & identity.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔹 Q1. Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine.
✔️ Answer:
Nitrogenous bases: Adenine, Thymine, Uracil, Cytosine.
Nucleosides (base + sugar): Cytidine, Guanosine.
🔹 Q2. If a double stranded DNA has 20% cytosine, calculate the percent of adenine in the DNA.
✔️ Answer (step by step):
In DNA, %C = %G.
If cytosine = 20%, guanine = 20%.
So, C + G = 40%.
Remaining = 60% → A + T.
Since A = T, %A = 30%.
🔹 Q3. If the sequence of one strand of DNA is written as follows:
5′-ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC-3′
Write down the sequence of complementary strand in 5′→3′ direction.
✔️ Answer:
Complementary strand = 5′-GCATGCATGCATGCATGCAT-3′
🔹 Q4. If the sequence of the coding strand in a transcription unit is written as follows:
5′-ATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC-3′
Write down the sequence of mRNA.
✔️ Answer:
Coding strand = mRNA (except T replaced by U).
mRNA = 5′-AUGCAUGCAUGCAUGCAUGC-3′
🔹 Q5. Which property of DNA double helix led Watson and Crick to hypothesise semi-conservative mode of DNA replication? Explain.
✔️ Answer:
The complementary base pairing in double helix (A pairs with T, G pairs with C) suggested that each strand can act as a template for the formation of a new strand.
This led to the semi-conservative model where one parental strand is conserved and one new strand is synthesized.
🔹 Q6. Depending upon the chemical nature of the template (DNA or RNA) and the nature of nucleic acids synthesised from it (DNA or RNA), list the types of nucleic acid polymerases.
✔️ Answer:
DNA-dependent DNA polymerase → DNA synthesis from DNA template.
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase → RNA synthesis from DNA template.
RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase) → DNA synthesis from RNA template.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase → RNA synthesis from RNA template.
🔹 Q7. How did Hershey and Chase differentiate between DNA and protein in their experiment while proving that DNA is the genetic material?
✔️ Answer:
They labeled DNA with ³²P (phosphorus isotope) and protein coat with ³⁵S (sulphur isotope) in bacteriophage.
After infection of bacteria, ³²P was found inside cells while ³⁵S remained outside.
This proved that DNA entered the bacteria and controlled heredity, not protein.
🔹 Q8. Differentiate between the following:
(a) Repetitive DNA and Satellite DNA
✔️ Answer:
Repetitive DNA: Occurs many times, dispersed throughout genome, no specific function.
Satellite DNA: Highly repetitive, present in tandem at specific regions (centromeres, telomeres), used in DNA fingerprinting.
(b) mRNA and tRNA
✔️ Answer:
mRNA: Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosome; template for protein synthesis.
tRNA: Brings amino acids to ribosome; has anticodon complementary to mRNA codon.
(c) Template strand and Coding strand
✔️ Answer:
Template strand: Used by RNA polymerase for transcription; complementary to RNA.
Coding strand: Same sequence as RNA (except T replaced by U); not transcribed.
🔹 Q9. List two essential roles of ribosome during translation.
✔️ Answer:
Provides site for mRNA and tRNA binding.
Catalyses peptide bond formation between amino acids.
🔹 Q10. In the medium where E. coli was growing, lactose was added, which induced the lac operon. Then, why does lac operon shut down some time after addition of lactose in the medium?
✔️ Answer:
Lactose acts as inducer by inactivating repressor → operon switches on.
After lactose is consumed, inducer concentration decreases → repressor binds again → transcription stops.
🔹 Q11. Explain (in one or two lines) the function of the following:
(a) Promoter
✔️ Provides binding site for RNA polymerase, initiates transcription.
(b) tRNA
✔️ Transfers specific amino acids to ribosome during translation, decodes mRNA codons.
(c) Exons
✔️ Coding sequences of eukaryotic genes that remain in mature mRNA after splicing.
🔹 Q12. Why is the Human Genome Project called a mega project?
✔️ Answer:
Enormous scale: sequencing 3 × 10^9 base pairs.
Required high technology, large funds, collaboration of many scientists globally.
🔹 Q13. What is DNA fingerprinting? Mention its application.
✔️ Answer:
DNA fingerprinting: Technique to identify individuals based on unique DNA patterns (VNTRs).
Applications: Forensic analysis, paternity disputes, population genetics, crime detection.
🔹 Q14. Briefly describe the following:
(a) Transcription
✔️ Process of synthesizing RNA from DNA template using RNA polymerase.
(b) Polymorphism
✔️ Genetic variation at a locus within a population, basis of evolution and DNA fingerprinting.
(c) Translation
✔️ Process of protein synthesis from mRNA using ribosomes, tRNA, and amino acids.
(d) Bioinformatics
✔️ Application of computational tools to manage and analyze biological data, especially genome sequences.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🔹 Q1. (MCQ) 🦠 Hershey–Chase used labeled phages to prove DNA is genetic material. The correct isotope pair was:
🔵 (A) ¹⁵N and ¹⁴N
🟢 (B) ³²P and ³⁵S
🟠 (C) ³H and ¹⁴C
🔴 (D) ⁶⁰Co and ³²S
✔️ Answer: (B) ³²P and ³⁵S
🔹 Q2. (MCQ) 🧬 The feature degeneracy of the genetic code means:
🔵 (A) One codon codes for multiple amino acids
🟢 (B) Multiple codons can code for one amino acid
🟠 (C) Codons overlap during reading
🔴 (D) Codons have punctuation marks
✔️ Answer: (B) Multiple codons can code for one amino acid
🔹 Q3. (MCQ) 🧪 The enzyme that seals nicks between Okazaki fragments is:
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase I
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) RNA primase
🔴 (D) Topoisomerase
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
🔹 Q4. (MCQ) 🧫 In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II synthesizes:
🔵 (A) rRNA
🟢 (B) mRNA
🟠 (C) tRNA
🔴 (D) 5S rRNA only
✔️ Answer: (B) mRNA
🔹 Q5. (MCQ) 🌱 The repeating structural unit of chromatin is:
🔵 (A) Solenoid
🟢 (B) Nucleosome
🟠 (C) Looped domain
🔴 (D) Chromatid
✔️ Answer: (B) Nucleosome
🔹 Q6. (MCQ) 🧬 The coding strand of a gene has the same sequence as:
🔵 (A) tRNA (with T instead of U)
🟢 (B) mRNA (with T replaced by U)
🟠 (C) Template strand
🔴 (D) rRNA (with T replaced by U)
✔️ Answer: (B) mRNA (with T replaced by U)
🔹 Q7. (MCQ) 🧪 The start codon in most organisms is:
🔵 (A) UAA
🟢 (B) AUG
🟠 (C) UAG
🔴 (D) UGA
✔️ Answer: (B) AUG
🔹 Q8. (MCQ) 🦋 Lac operon is inducible because the inducer is:
🔵 (A) Lactose/allolactose that inactivates the repressor
🟢 (B) Glucose that activates CAP
🟠 (C) Tryptophan that activates repressor
🔴 (D) IPTG that blocks promoter
✔️ Answer: (A) Lactose/allolactose that inactivates the repressor
🧠 Assertion–Reason format (for Q9–Q10):
1 = A true, R true, R explains A; 2 = A true, R true, R not explanation; 3 = A true, R false; 4 = A false, R true.
🔹 Q9. (A–R MCQ) 🧬 Assertion (A): In eukaryotes, primary transcript (hnRNA) undergoes capping, tailing, and splicing.
Reason (R): Eukaryotic genes are often interrupted by introns that must be removed.
🔵 (1)
🟢 (2)
🟠 (3)
🔴 (4)
✔️ Answer: (1)
🔹 Q10. (A–R MCQ) 🧫 Assertion (A): DNA replication proceeds 5’→3′ on both new strands.
Reason (R): DNA polymerase can extend only from a free 3′-OH end.
🔵 (1)
🟢 (2)
🟠 (3)
🔴 (4)
✔️ Answer: (1)
🟡 Very Short Answer (Q11–Q18, 1 mark each)
🔹 Q11. 🧪 Define Okazaki fragments.
✔️ Answer: Short DNA segments synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during replication.
🔹 Q12. 🧬 State Chargaff’s rule.
✔️ Answer: In dsDNA, [A] = [T] and [G] = [C]; purines equal pyrimidines.
🔹 Q13. 🧫 Name the inducer of lac operon in vivo.
✔️ Answer: Allolactose (isomer of lactose).
🔹 Q14. 🦠 Full form of VNTR used in DNA fingerprinting.
✔️ Answer: Variable Number Tandem Repeats.
🔹 Q15. 🌱 Two stop codons.
✔️ Answer: UAA, UAG (also UGA).
🔹 Q16. 🧬 Name the experiment that proved semi-conservative replication.
✔️ Answer: Meselson–Stahl experiment.
🔹 Q17. 🧪 Enzyme that removes RNA primers in prokaryotes.
✔️ Answer: DNA polymerase I (5’→3′ exonuclease).
🔹 Q18. 🧫 Type of chromatin that is transcriptionally active.
✔️ Answer: Euchromatin.
🟠 Short Answer (Q19–Q27 carry 2–3 marks each) — Part 1 includes Q19–Q20
🔹 Q19. 🧬 Calculate base composition: In a dsDNA, adenine = 36%. Find % of T, G, C.
✔️ Answer (step-by-step):
A = 36% → T = 36%.
A + T = 36 + 36 = 72%.
Therefore G + C = 100 − 72 = 28%.
Hence G = 14% and C = 14%.
🔹 Q20. 🧪 The coding strand of a gene is 5′-ATG GAA TGC TTT GGA-3′. Write the template strand and mRNA sequence.
✔️ Answer (step-by-step):
Coding strand (5’→3′) = 5′-ATG GAA TGC TTT GGA-3′.
Template strand is complementary and antiparallel → 3′-TAC CTT ACG AAA CCT-5′ (or written 5′-TTC CAA A GC AAG GTA? No—keep 3’→5′ form).
mRNA has same sequence as coding strand with U for T → 5′-AUG GAA UGC UUU GGA-3′.
🔹 Q21. 🦠 Write any three features of the genetic code.
✔️ Answer:
Triplet: Three bases code for one amino acid.
Universal: Same in almost all organisms.
Degenerate: More than one codon can code for a single amino acid.
🔹 Q22. 🧬 Differentiate between replication in prokaryotes and eukaryotes (two points).
✔️ Answer:
Prokaryotes: Single origin of replication, faster.
Eukaryotes: Multiple origins of replication, slower.
🔹 Q23. 🧪 Explain splicing, capping, and tailing in eukaryotic mRNA.
✔️ Answer:
Splicing: Removal of introns, joining of exons.
Capping: Addition of methyl guanosine triphosphate at 5′ end.
Tailing: Addition of poly-A tail at 3′ end.
🔹 Q24. 🌱 What is DNA fingerprinting? Mention two applications.
✔️ Answer:
Technique to identify individuals based on unique DNA patterns (VNTRs).
Applications: Forensic identification, paternity disputes.
🔹 Q25. 🧫 What is the role of the repressor protein in lac operon?
✔️ Answer:
Repressor binds to operator region and prevents transcription in absence of lactose.
In presence of lactose, allolactose binds repressor → repressor inactivated → transcription occurs.
🔹 Q26. 🧬 Define polymorphism. How is it important in DNA fingerprinting?
✔️ Answer:
Polymorphism: Genetic variation at a locus present in >1% population.
Provides unique DNA profiles used in DNA fingerprinting.
🔹 Q27. 🧪 What is the role of tRNA during translation?
✔️ Answer:
Carries specific amino acids to ribosome.
Anticodon of tRNA pairs with codon of mRNA to ensure correct amino acid placement.
🟣 Long Answer Questions (5 marks each)
🔹 Q28. 🧬 Explain the Meselson–Stahl experiment proving semi-conservative replication.
✔️ Answer:
E. coli grown in ¹⁵N medium → DNA heavy.
Transferred to ¹⁴N medium → after 1 generation, hybrid DNA.
After 2 generations, 50% hybrid, 50% light DNA.
Proved that each DNA molecule has one parental and one new strand.
🔹 Q29. 🌿 Describe the structure of DNA as proposed by Watson and Crick.
✔️ Answer:
Double helix model.
Two antiparallel strands (5′→3′ and 3′→5′).
Bases paired: A–T (2 H-bonds), G–C (3 H-bonds).
Sugar–phosphate backbone outside, bases inside.
Uniform diameter ~2 nm, 10 base pairs per turn.
🔹 Q30. 🧪 Explain DNA replication in detail with enzymes.
✔️ Answer:
Initiation: Helicase unwinds DNA; primase adds RNA primer.
Elongation: DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands.
Leading strand: continuous.
Lagging strand: discontinuous (Okazaki fragments).
Termination: RNA primers replaced; DNA ligase joins fragments.
🔹 Q31. 🦠 Explain transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
✔️ Answer:
Prokaryotes: Single RNA polymerase binds promoter → elongation → termination by hairpin loop or rho factor.
Eukaryotes: RNA polymerase I (rRNA), II (mRNA), III (tRNA). Post-transcriptional modifications (splicing, capping, tailing).
🔹 Q32. 🧩 Explain the lac operon model of gene regulation.
✔️ Answer:
Operon consists of promoter, operator, regulator, structural genes (Z, Y, A).
Without lactose: Repressor binds operator → no transcription.
With lactose: Allolactose inactivates repressor → transcription proceeds.
Inducible system (genes expressed only when substrate is present).
🔹 Q33. 🧬 Explain the Human Genome Project (HGP) and its applications.
✔️ Answer:
Mega project (1990–2003), sequenced ~3 billion base pairs.
Found ~20,000–25,000 genes, less than expected.
Applications: Gene therapy, medical diagnostics, forensics, evolution studies.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material was first proposed by:
🔵 (A) Frederick Griffith
🟢 (B) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
🟠 (C) Avery, MacLeod and McCarty
🔴 (D) Wilkins and Franklin
✔️ Answer: (B) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
Year: 2023 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q2. Which one acts as an inducer for the lac operon?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Lactose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Galactose
✔️ Answer: (B) Lactose
Year: 2023 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q3. With reference to Hershey–Chase experiments, which is correct?
A: Viruses grown with radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA.
B: Viruses grown with radioactive sulphur contained radioactive protein.
C: Viruses grown with radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive protein.
🔵 (A) A and B only
🟢 (B) B and C only
🟠 (C) A and C only
🔴 (D) A, B and C
✔️ Answer: (A) A and B only
Year: 2023 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q4. Against the codon 5′ UAC 3′, the anticodon on tRNA is:
🔵 (A) 5′ GUA 3′
🟢 (B) 5′ AUG 3′
🟠 (C) 5′ ATG 3′
🔴 (D) 5′ GTA 3′
✔️ Answer: (B) 5′ AUG 3′
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q5. If A and C make 30% and 20% of DNA respectively, the percentages of T and G are:
🔵 (A) T 20%, G 20%
🟢 (B) T 20%, G 30%
🟠 (C) T 30%, G 20%
🔴 (D) T 30%, G 30%
✔️ Answer: (C) T 30%, G 20%
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q6. DNA polymerases catalyse polymerisation only in the 5′→3′ direction. During replication, one strand is continuous and the other discontinuous because:
🔵 (A) Both statements true and R explains A
🟢 (B) Both statements true but R doesn’t explain A
🟠 (C) A true, R false
🔴 (D) A false, R true
✔️ Answer: (A) Both statements true and R explains A
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q7. In lac operon, z gene codes for:
🔵 (A) Repressor
🟢 (B) β-galactosidase
🟠 (C) Permease
🔴 (D) Transacetylase
✔️ Answer: (B) β-galactosidase
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q8. Match the following (lac operon):
I gene — (i) Repressor; z gene — (ii) β-galactosidase; y gene — (iii) Permease; a gene — (iv) Transacetylase. Choose the correct combination:
🔵 (A) I–(iii), z–(iv), a–(i), y–(ii)
🟢 (B) I–(i), z–(iii), y–(ii), a–(iv)
🟠 (C) I–(iii), z–(i), y–(ii), a–(iv)
🔴 (D) I–(iii), z–(i), a–(iv), y–(ii)
✔️ Answer: (D) I–(iii), z–(i), a–(iv), y–(ii)
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q9. Which feature of genetic code allows bacteria to produce human insulin?
🔵 (A) Code is specific
🟢 (B) Code is not ambiguous
🟠 (C) Code is redundant
🔴 (D) Code is nearly universal
✔️ Answer: (D) Code is nearly universal
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q10. Under which condition is there no change in reading frame of 5′-AACAGCGGUGCUAUU-3′?
🔵 (A) Deletion of G at 5th position
🟢 (B) Insertion of G at 5th position
🟠 (C) Deletion of GGU at 7th–9th positions
🔴 (D) Insertion of A and G at 4th and 5th positions
✔️ Answer: (C) Deletion of GGU at 7th–9th positions
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q11. Purines found in both DNA and RNA are:
🔵 (A) Cytosine and thymine
🟢 (B) Adenine and thymine
🟠 (C) Adenine and guanine
🔴 (D) Guanine and cytosine
✔️ Answer: (C) Adenine and guanine
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q12. Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to:
🔵 (A) Novel DNA sequences
🟢 (B) Genes expressed as RNA
🟠 (C) Polypeptide expression
🔴 (D) DNA polymorphism
✔️ Answer: (B) Genes expressed as RNA
Year: 2019 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q13. The start codon is:
🔵 (A) UAA
🟢 (B) UAG
🟠 (C) AUG
🔴 (D) UGA
✔️ Answer: (C) AUG
Year: 2016 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q14. A complex of many ribosomes attached to one mRNA is called:
🔵 (A) Polypeptide
🟢 (B) Okazaki fragment
🟠 (C) Polysome
🔴 (D) Polymer
✔️ Answer: (C) Polysome
Year: 2016 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q15. If the distance between base pairs is 0.34 nm and total base pairs are 6.6×10^9, the DNA length is approximately:
🔵 (A) 2.2 m
🟢 (B) 2.7 m
🟠 (C) 2.0 m
🔴 (D) 2.5 m
✔️ Answer: (A) 2.2 m
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q16. The first phase of translation is:
🔵 (A) Recognition of anticodon
🟢 (B) Aminoacylation (charging) of tRNA
🟠 (C) Binding of mRNA to ribosome
🔴 (D) Recognition of DNA
✔️ Answer: (B) Aminoacylation (charging) of tRNA
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q17. The enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription is:
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
🟠 (C) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Year: 2020 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q18. Which statement about histones is wrong?
🔵 (A) Rich in lysine and arginine
🟢 (B) Positively charged
🟠 (C) Organised as octamer
🔴 (D) Slightly acidic
✔️ Answer: (D) Slightly acidic
Year: 2021 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q19. The codon AUG codes for methionine; AAA and AAG both code for lysine. Choose the correct option:
🔵 (A) I correct, II false
🟢 (B) I false, II correct
🟠 (C) Both true
🔴 (D) Both false
✔️ Answer: (B) I false, II correct
Year: 2021 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q20. Semi-conservative DNA replication was first shown in:
🔵 (A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
🟢 (B) Drosophila melanogaster
🟠 (C) Salmonella typhimurium
🔴 (D) Escherichia coli
✔️ Answer: (D) Escherichia coli
Year: 2018 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q21. Select the correct statement:
🔵 (A) Spliceosomes take part in translation
🟢 (B) Meselson and Stahl showed semi-conservative replication in E. coli
🟠 (C) Franklin Stahl coined “linkage”
🔴 (D) Split genes are typical of prokaryotes
✔️ Answer: (B) Meselson and Stahl showed semi-conservative replication in E. coli
Year: 2018 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q22. DNA polymorphism forms the basis of:
🔵 (A) rDNA technology
🟢 (B) DNA fingerprinting
🟠 (C) Transduction
🔴 (D) Reverse transcription
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA fingerprinting
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q23. In an E. coli strain, i gene product cannot bind inducer. In medium with lactose, the outcome is:
🔵 (A) Operon fully ON
🟢 (B) Only y and z transcribed
🟠 (C) Operon remains OFF (repressor stays bound)
🔴 (D) Only a transcribed
✔️ Answer: (C) Operon remains OFF (repressor stays bound)
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q24. Match genome sizes: ϕX174; λ phage; E. coli; Human (haploid).
🔵 (A) ϕX174–5386 nt; λ–4.6×10^6 bp; E. coli–48502 bp; Human–3.3×10^9 bp
🟢 (B) ϕX174–5386 nt; λ–48502 bp; E. coli–4.6×10^6 bp; Human–3.3×10^9 bp
🟠 (C) ϕX174–48502 bp; λ–5386 nt; E. coli–3.3×10^9 bp; Human–4.6×10^6 bp
🔴 (D) ϕX174–4.6×10^6 bp; λ–5386 nt; E. coli–48502 bp; Human–3.3×10^9 bp
✔️ Answer: (B) ϕX174–5386 nt; λ–48502 bp; E. coli–4.6×10^6 bp; Human–3.3×10^9 bp
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 2)
🔹 Q25. Which pair is NOT correctly matched?
(a) Euchromatin — loosely packed
(b) Heterochromatin — transcriptionally active
(c) Histone octamer — wrapped by negatively charged DNA
(d) Histones — rich in Lys and Arg
🔵 (A) Only (a)
🟢 (B) Only (b)
🟠 (C) Only (c)
🔴 (D) Only (d)
✔️ Answer: (B) Only (b)
Year: 2022 | Exam: NEET (Phase 1)
🔹 Q26. Which statement is true for nucleosomes?
🔵 (A) Negatively charged DNA wrapped around histone octamer
🟢 (B) DNA positively charged, histones negative
🟠 (C) Histones rich in acidic amino acids
🔴 (D) Nucleosomes occur only in prokaryotes
✔️ Answer: (A) Negatively charged DNA wrapped around histone octamer
Year: 2021 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q27. Which of the following is NOT a stop codon?
🔵 (A) UAA
🟢 (B) UAG
🟠 (C) UGA
🔴 (D) AUG
✔️ Answer: (D) AUG
Year: 2018 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q28. Which enzyme catalyses the elongation of a new DNA strand by adding nucleotides?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase III
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✔️ Answer: (A) DNA polymerase III
Year: 2017 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q29. Which is an example of a constitutive gene?
🔵 (A) rRNA gene
🟢 (B) Lac operon genes
🟠 (C) Try operon genes
🔴 (D) Immunoglobulin genes
✔️ Answer: (A) rRNA gene
Year: 2017 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q30. Which best describes Okazaki fragments?
🔵 (A) Short DNA fragments on leading strand
🟢 (B) Short DNA fragments on lagging strand
🟠 (C) RNA fragments on lagging strand
🔴 (D) RNA primers on leading strand
✔️ Answer: (B) Short DNA fragments on lagging strand
Year: 2016 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q31. Which of the following codons is called a nonsense codon?
🔵 (A) AUG
🟢 (B) UAG
🟠 (C) GUG
🔴 (D) UGG
✔️ Answer: (B) UAG
Year: 2016 | Exam: NEET
🔹 Q32. The term “linkage” was coined by:
🔵 (A) Morgan
🟢 (B) Bateson
🟠 (C) Mendel
🔴 (D) Sturtevant
✔️ Answer: (B) Bateson
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q33. What is the length of human DNA?
🔵 (A) 1.5 m
🟢 (B) 2.2 m
🟠 (C) 2.8 m
🔴 (D) 3.3 m
✔️ Answer: (B) 2.2 m
Year: 2015 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q34. Which RNA carries amino acids to ribosomes?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) tRNA
🟠 (C) rRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA
✔️ Answer: (B) tRNA
Year: 2014 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q35. Which of the following is not involved in transcription?
🔵 (A) Promoter
🟢 (B) Terminator
🟠 (C) Enhancer
🔴 (D) DNA ligase
✔️ Answer: (D) DNA ligase
Year: 2014 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q36. The number of base pairs in E. coli genome is approximately:
🔵 (A) 4.6 × 10^6 bp
🟢 (B) 4.6 × 10^7 bp
🟠 (C) 3.3 × 10^9 bp
🔴 (D) 5386 bp
✔️ Answer: (A) 4.6 × 10^6 bp
Year: 2013 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q37. Which one of the following is a stop codon?
🔵 (A) UUU
🟢 (B) UAA
🟠 (C) AUG
🔴 (D) UAC
✔️ Answer: (B) UAA
Year: 2012 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q38. The experimental proof for semiconservative replication of DNA was given by:
🔵 (A) Hershey and Chase
🟢 (B) Meselson and Stahl
🟠 (C) Watson and Crick
🔴 (D) Griffith
✔️ Answer: (B) Meselson and Stahl
Year: 2011 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q39. A triplet of bases coding for an amino acid is called:
🔵 (A) Codon
🟢 (B) Anticodon
🟠 (C) Exon
🔴 (D) Intron
✔️ Answer: (A) Codon
Year: 2011 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q40. Who first demonstrated the central dogma?
🔵 (A) Crick
🟢 (B) Watson
🟠 (C) Beadle and Tatum
🔴 (D) Meselson and Stahl
✔️ Answer: (A) Crick
Year: 2010 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q41. Which of the following is not a pyrimidine base?
🔵 (A) Thymine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Adenine
🔴 (D) Uracil
✔️ Answer: (C) Adenine
Year: 2010 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q42. In which process is DNA ligase used?
🔵 (A) DNA replication
🟢 (B) Protein synthesis
🟠 (C) Transcription
🔴 (D) Translation
✔️ Answer: (A) DNA replication
Year: 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q43. Which type of bond joins nitrogenous base to sugar in nucleotides?
🔵 (A) Hydrogen bond
🟢 (B) Glycosidic bond
🟠 (C) Peptide bond
🔴 (D) Phosphodiester bond
✔️ Answer: (B) Glycosidic bond
Year: 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q44. The process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to RNA is:
🔵 (A) Translation
🟢 (B) Transcription
🟠 (C) Replication
🔴 (D) Transformation
✔️ Answer: (B) Transcription
Year: 2008 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q45. The X-ray diffraction of DNA double helix was given by:
🔵 (A) Rosalind Franklin
🟢 (B) Watson
🟠 (C) Crick
🔴 (D) Chargaff
✔️ Answer: (A) Rosalind Franklin
Year: 2008 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q46. Which RNA is the most abundant in the cell?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) rRNA
🟠 (C) tRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA
✔️ Answer: (B) rRNA
Year: 2007 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q47. In lac operon, when repressor binds operator:
🔵 (A) Transcription starts
🟢 (B) Transcription stops
🟠 (C) RNA polymerase binds
🔴 (D) Lactose is metabolised
✔️ Answer: (B) Transcription stops
Year: 2006 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q48. A nucleosome is composed of:
🔵 (A) DNA + histone octamer
🟢 (B) DNA + RNA
🟠 (C) RNA + protein
🔴 (D) DNA + DNA polymerase
✔️ Answer: (A) DNA + histone octamer
Year: 2005 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q49. Which is NOT a component of nucleotide?
🔵 (A) Phosphate
🟢 (B) Sugar
🟠 (C) Base
🔴 (D) Amino acid
✔️ Answer: (D) Amino acid
Year: 2004 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q50. In DNA, the percentage of adenine always equals:
🔵 (A) Guanine
🟢 (B) Thymine
🟠 (C) Cytosine
🔴 (D) Uracil
✔️ Answer: (B) Thymine
Year: 2002 | Exam: AIPMT
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Who proposed the double helix model of DNA?
🔵 (A) Watson and Crick
🟢 (B) Meselson and Stahl
🟠 (C) Hershey and Chase
🔴 (D) Avery, MacLeod and McCarty
✔️ Answer: (A) Watson and Crick
🔹 Q2. In DNA, adenine pairs with thymine by:
🔵 (A) One hydrogen bond
🟢 (B) Two hydrogen bonds
🟠 (C) Three hydrogen bonds
🔴 (D) Four hydrogen bonds
✔️ Answer: (B) Two hydrogen bonds
🔹 Q3. Which experiment proved DNA replication is semi-conservative?
🔵 (A) Griffith’s experiment
🟢 (B) Meselson and Stahl’s experiment
🟠 (C) Hershey–Chase experiment
🔴 (D) Franklin’s X-ray diffraction
✔️ Answer: (B) Meselson and Stahl’s experiment
🔹 Q4. In eukaryotes, RNA polymerase II transcribes:
🔵 (A) tRNA
🟢 (B) mRNA
🟠 (C) rRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA only
✔️ Answer: (B) mRNA
🔹 Q5. The enzyme that joins Okazaki fragments is:
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase I
🟢 (B) Primase
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✔️ Answer: (C) DNA ligase
🔹 Q6. Which base is not found in RNA?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Uracil
🟠 (C) Thymine
🔴 (D) Cytosine
✔️ Answer: (C) Thymine
🔹 Q7. Which of the following is universal start codon?
🔵 (A) UAA
🟢 (B) AUG
🟠 (C) UAG
🔴 (D) UGA
✔️ Answer: (B) AUG
🔹 Q8. In lac operon, the z gene codes for:
🔵 (A) Permease
🟢 (B) Transacetylase
🟠 (C) β-galactosidase
🔴 (D) Repressor
✔️ Answer: (C) β-galactosidase
🔹 Q9. Which process occurs in both nucleus and cytoplasm in eukaryotes?
🔵 (A) DNA replication
🟢 (B) Transcription
🟠 (C) Translation
🔴 (D) RNA processing
✔️ Answer: (D) RNA processing
🔹 Q10. Which of the following is non-coding region of DNA?
🔵 (A) Exons
🟢 (B) Introns
🟠 (C) Structural genes
🔴 (D) rRNA genes
✔️ Answer: (B) Introns
🔹 Q11. The length of human haploid DNA is approximately:
🔵 (A) 1.1 m
🟢 (B) 2.2 m
🟠 (C) 3.3 m
🔴 (D) 4.6 m
✔️ Answer: (B) 2.2 m
🔹 Q12. Which enzyme unwinds the DNA helix during replication?
🔵 (A) Helicase
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) Topoisomerase
🔴 (D) Primase
✔️ Answer: (A) Helicase
🔹 Q13. Which scientist’s X-ray diffraction photograph helped in discovery of DNA structure?
🔵 (A) Rosalind Franklin
🟢 (B) Alfred Hershey
🟠 (C) Chargaff
🔴 (D) Griffith
✔️ Answer: (A) Rosalind Franklin
🔹 Q14. DNA fingerprinting is based on:
🔵 (A) Introns
🟢 (B) Exons
🟠 (C) VNTRs
🔴 (D) SNPs
✔️ Answer: (C) VNTRs
🔹 Q15. Which property of genetic code ensures codons are read without breaks?
🔵 (A) Universal
🟢 (B) Non-overlapping and commaless
🟠 (C) Degenerate
🔴 (D) Ambiguous
✔️ Answer: (B) Non-overlapping and commaless
🔹 Q16. Which type of RNA has cloverleaf structure?
🔵 (A) rRNA
🟢 (B) mRNA
🟠 (C) tRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA
✔️ Answer: (C) tRNA
🔹 Q17. Which base pairs are stronger in DNA helix?
🔵 (A) A–T
🟢 (B) G–C
🟠 (C) A–U
🔴 (D) None
✔️ Answer: (B) G–C
🔹 Q18. Which enzyme synthesises RNA primer during replication?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) Primase
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase I
🔴 (D) Helicase
✔️ Answer: (B) Primase
🔹 Q19. Which type of bonds link adjacent nucleotides in a DNA strand?
🔵 (A) Hydrogen bonds
🟢 (B) Glycosidic bonds
🟠 (C) Phosphodiester bonds
🔴 (D) Peptide bonds
✔️ Answer: (C) Phosphodiester bonds
🔹 Q20. The coding strand sequence is 5′-ATGCTG-3′. The mRNA sequence will be:
🔵 (A) 3′-UACGAC-5′
🟢 (B) 5′-AUGCUG-3′
🟠 (C) 3′-ATGCTG-5′
🔴 (D) 5′-TACGAC-3′
✔️ Answer: (B) 5′-AUGCUG-3′
🔹 Q21. Which statement best describes “central dogma”?
🔵 (A) RNA → DNA → Protein
🟢 (B) DNA → RNA → Protein
🟠 (C) Protein → RNA → DNA
🔴 (D) RNA → Protein → DNA
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA → RNA → Protein
🔹 Q22. Histone proteins are:
🔵 (A) Acidic and negatively charged
🟢 (B) Basic and positively charged
🟠 (C) Neutral
🔴 (D) Acidic and hydrophobic
✔️ Answer: (B) Basic and positively charged
🔹 Q23. Semi-conservative DNA replication means:
🔵 (A) Both strands are newly synthesised
🟢 (B) Both strands are conserved
🟠 (C) One old and one new strand in each daughter DNA
🔴 (D) Only one strand replicates
✔️ Answer: (C) One old and one new strand in each daughter DNA
🔹 Q24. Which type of mutation does not alter reading frame?
🔵 (A) Point mutation with substitution
🟢 (B) Frameshift mutation
🟠 (C) Insertion mutation
🔴 (D) Deletion mutation
✔️ Answer: (A) Point mutation with substitution
🔹 Q25. Which feature makes the genetic code “degenerate”?
🔵 (A) Some amino acids coded by more than one codon
🟢 (B) One codon coding for many amino acids
🟠 (C) Stop codons coding amino acids
🔴 (D) All codons having same meaning
✔️ Answer: (A) Some amino acids coded by more than one codon
🔹 Q26. Which process involves removal of introns and joining of exons?
🔵 (A) Replication
🟢 (B) Splicing
🟠 (C) Translation
🔴 (D) Transduction
✔️ Answer: (B) Splicing
🔹 Q27. What is the role of the promoter in transcription?
🔵 (A) Codes for protein
🟢 (B) Binding site for RNA polymerase
🟠 (C) Terminates transcription
🔴 (D) Adds cap to mRNA
✔️ Answer: (B) Binding site for RNA polymerase
🔹 Q28. Which type of mutation results when a single base substitution changes one amino acid into another?
🔵 (A) Nonsense mutation
🟢 (B) Missense mutation
🟠 (C) Silent mutation
🔴 (D) Frameshift mutation
✔️ Answer: (B) Missense mutation
🔹 Q29. In eukaryotes, which RNA polymerase transcribes tRNA genes?
🔵 (A) RNA polymerase I
🟢 (B) RNA polymerase II
🟠 (C) RNA polymerase III
🔴 (D) All of these
✔️ Answer: (C) RNA polymerase III
🔹 Q30. Which of the following is an example of a stop codon?
🔵 (A) AUG
🟢 (B) UAA
🟠 (C) GUG
🔴 (D) GAA
✔️ Answer: (B) UAA
🔹 Q31. What does “capping” at the 5′ end of hnRNA involve?
🔵 (A) Addition of adenine residues
🟢 (B) Addition of methyl guanosine triphosphate
🟠 (C) Removal of introns
🔴 (D) Addition of uracil residues
✔️ Answer: (B) Addition of methyl guanosine triphosphate
🔹 Q32. Which enzyme is also known as reverse transcriptase?
🔵 (A) RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase I
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase III
✔️ Answer: (A) RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
🔹 Q33. In Griffith’s experiment, the transformation principle was later identified as:
🔵 (A) Protein
🟢 (B) DNA
🟠 (C) RNA
🔴 (D) Lipid
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA
🔹 Q34. What is the diameter of the DNA double helix?
🔵 (A) 1 nm
🟢 (B) 2 nm
🟠 (C) 10 nm
🔴 (D) 30 nm
✔️ Answer: (B) 2 nm
🔹 Q35. Which property of genetic code is helpful in biotechnology for gene transfer between species?
🔵 (A) Non-overlapping
🟢 (B) Degeneracy
🟠 (C) Universality
🔴 (D) Triplet nature
✔️ Answer: (C) Universality
🔹 Q36. Which region of DNA does a repressor protein bind to in lac operon?
🔵 (A) Structural gene
🟢 (B) Promoter
🟠 (C) Operator
🔴 (D) Terminator
✔️ Answer: (C) Operator
🔹 Q37. Which of the following is a purine base?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Thymine
🟠 (C) Uracil
🔴 (D) Cytosine
✔️ Answer: (A) Adenine
🔹 Q38. Which of these is not a post-transcriptional modification in eukaryotes?
🔵 (A) Capping
🟢 (B) Tailing
🟠 (C) Splicing
🔴 (D) Proofreading
✔️ Answer: (D) Proofreading
🔹 Q39. Who coined the term “nucleosome”?
🔵 (A) Kornberg
🟢 (B) Watson
🟠 (C) Crick
🔴 (D) Franklin
✔️ Answer: (A) Kornberg
🔹 Q40. Which statement is correct about hnRNA?
🔵 (A) It is mature mRNA
🟢 (B) It contains both introns and exons
🟠 (C) It lacks 5′ cap
🔴 (D) It has no poly-A tail
✔️ Answer: (B) It contains both introns and exons
🔹 Q41. The term “split gene” is associated with:
🔵 (A) Prokaryotes
🟢 (B) Eukaryotes
🟠 (C) Viruses
🔴 (D) Bacteria
✔️ Answer: (B) Eukaryotes
🔹 Q42. Which enzyme adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication?
🔵 (A) Ligase
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase III
🟠 (C) Primase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✔️ Answer: (B) DNA polymerase III
🔹 Q43. The nucleosome core consists of:
🔵 (A) Six histones
🟢 (B) Eight histones
🟠 (C) Ten histones
🔴 (D) Twelve histones
✔️ Answer: (B) Eight histones
🔹 Q44. Which is the most abundant RNA in cells?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) rRNA
🟠 (C) tRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA
✔️ Answer: (B) rRNA
🔹 Q45. Which technique is used for DNA fingerprinting?
🔵 (A) PCR and gel electrophoresis
🟢 (B) Southern blotting
🟠 (C) ELISA
🔴 (D) Northern blotting
✔️ Answer: (B) Southern blotting
🔹 Q46. What is the role of RNA primer in DNA replication?
🔵 (A) Proofreading
🟢 (B) Initiation point for DNA synthesis
🟠 (C) Sealing Okazaki fragments
🔴 (D) Unwinding helix
✔️ Answer: (B) Initiation point for DNA synthesis
🔹 Q47. Which one is not a function of DNA polymerase I?
🔵 (A) Removal of RNA primer
🟢 (B) Proofreading
🟠 (C) Ligating Okazaki fragments
🔴 (D) Filling DNA gaps
✔️ Answer: (C) Ligating Okazaki fragments
🔹 Q48. What is the significance of degeneracy of genetic code?
🔵 (A) Allows mutations without affecting proteins
🟢 (B) One codon codes multiple amino acids
🟠 (C) Stop codons code for amino acids
🔴 (D) Codons overlap
✔️ Answer: (A) Allows mutations without affecting proteins
🔹 Q49. Which base pairing is correct according to Chargaff’s rule?
🔵 (A) A=G, T=C
🟢 (B) A=T, G=C
🟠 (C) A=U, G=T
🔴 (D) A=C, G=T
✔️ Answer: (B) A=T, G=C
🔹 Q50. Which is a characteristic of genetic code?
🔵 (A) Ambiguous
🟢 (B) Universal
🟠 (C) Overlapping
🔴 (D) Discontinuous
✔️ Answer: (B) Universal
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
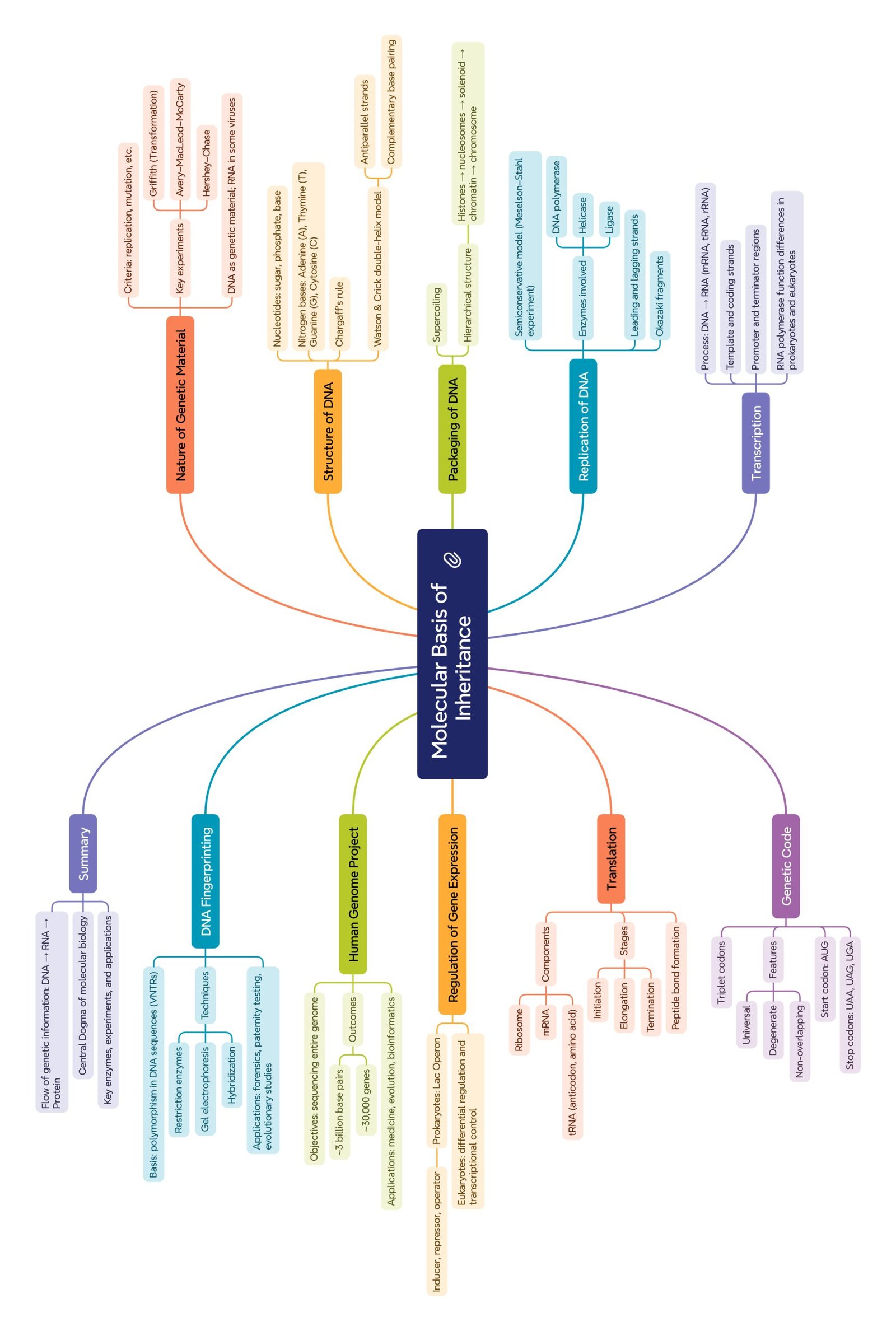
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
