Class 11 : Chemistry (In English) – Chapter 4: Chemical bonding and molecular Structure
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction
All matter in the universe 🌍 is made up of atoms and molecules. But atoms cannot exist in isolation for long; they combine with each other to form stable structures called molecules and compounds. The force that holds atoms together is called a chemical bond.
The study of chemical bonding answers fundamental questions:
Why do atoms combine?
Why are some compounds stable and others reactive?
How do shapes of molecules influence properties?
This chapter builds on atomic structure and shows how bonding leads to the diversity of substances around us 🌟.
🟢 Why Do Atoms Combine?
Atoms combine to achieve stability. Noble gases (He, Ne, Ar) are stable because they have complete octets (8 electrons in outer shell). Other atoms combine to achieve similar stable configurations (octet rule).
🔑 Driving forces for combination:
Lowering of energy (stable state).
Attaining noble gas configuration (duplet for H, He).
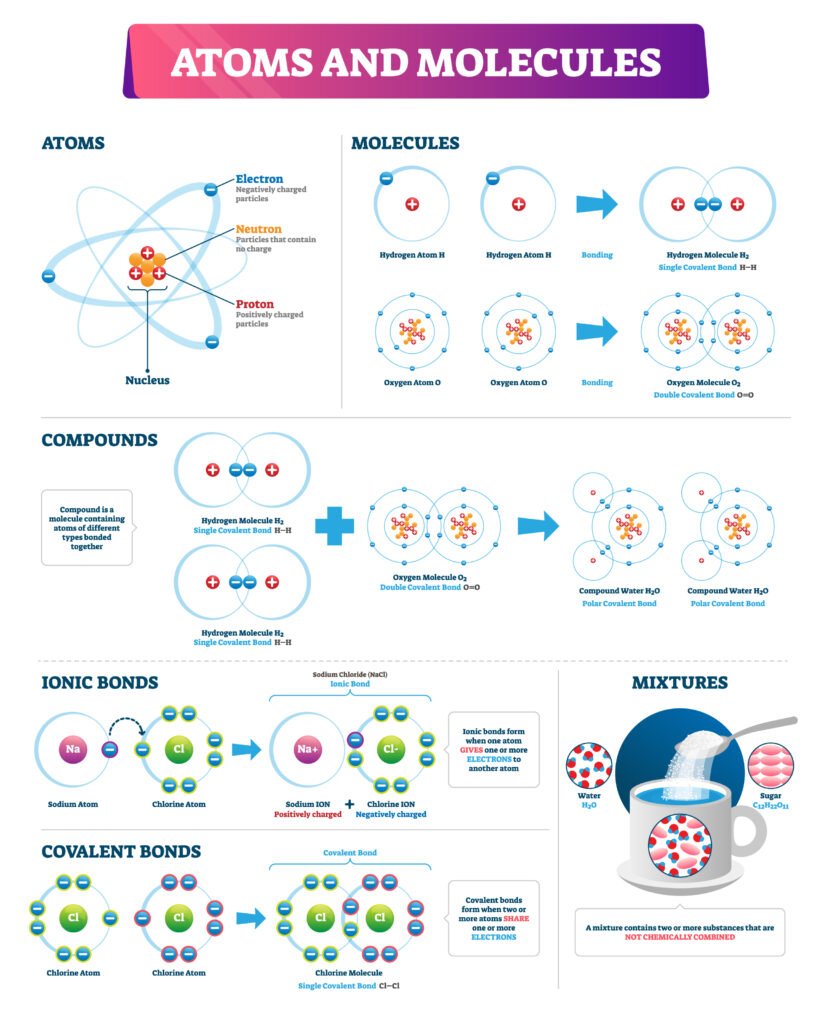
🔵 Types of Chemical Bonds
1️⃣ Ionic Bond (Electrovalent Bond)
Formed by complete transfer of electrons ⚡.
One atom loses electrons (forms cation), other gains (forms anion).
Held by strong electrostatic attraction.
Example: NaCl (Na⁺ + Cl⁻).

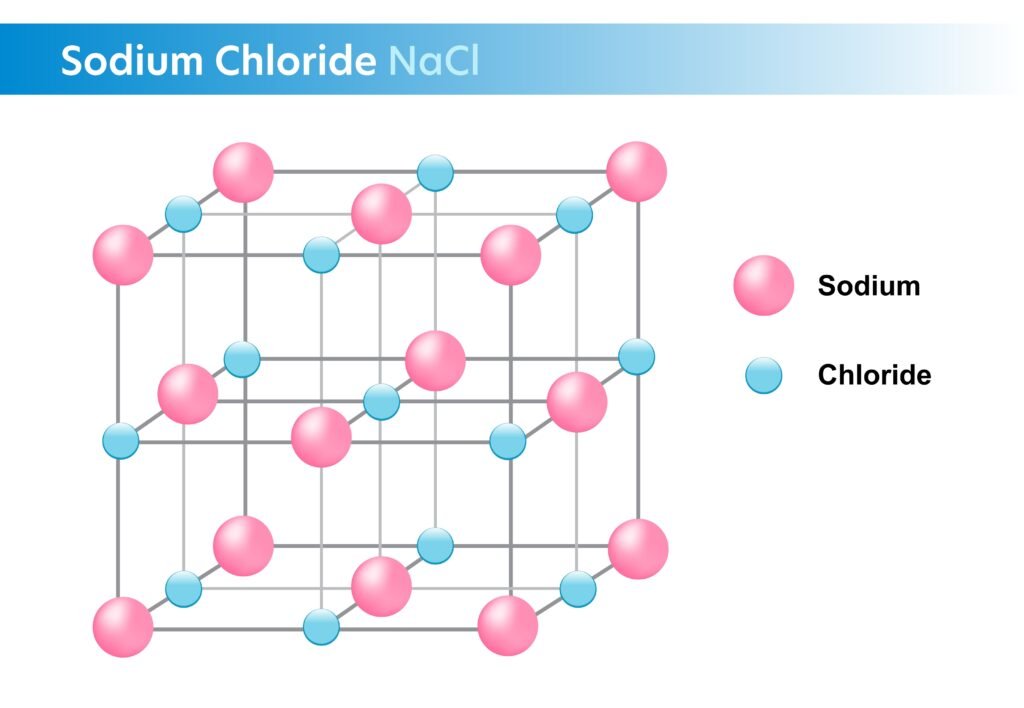
🔹 Properties:
Hard, brittle solids.
High melting and boiling points.
Conduct electricity in molten/aqueous state.
Soluble in polar solvents (e.g., water).
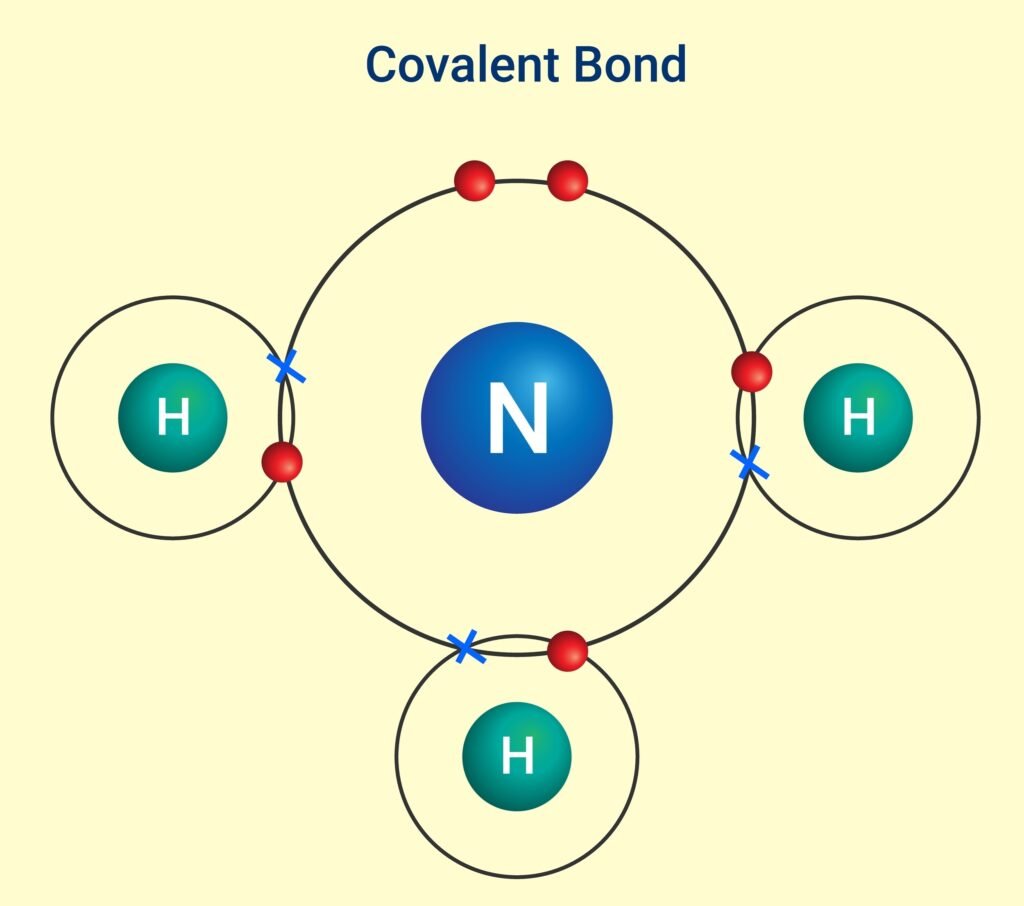
2️⃣ Covalent Bond
Formed by mutual sharing of electrons 🧩.
Shared pair constitutes the bond.
Example: H₂, O₂, CH₄.
🔹 Properties:
Gases, liquids, or soft solids.
Lower melting and boiling points.
Poor conductors of electricity.
Solubility depends on polarity.
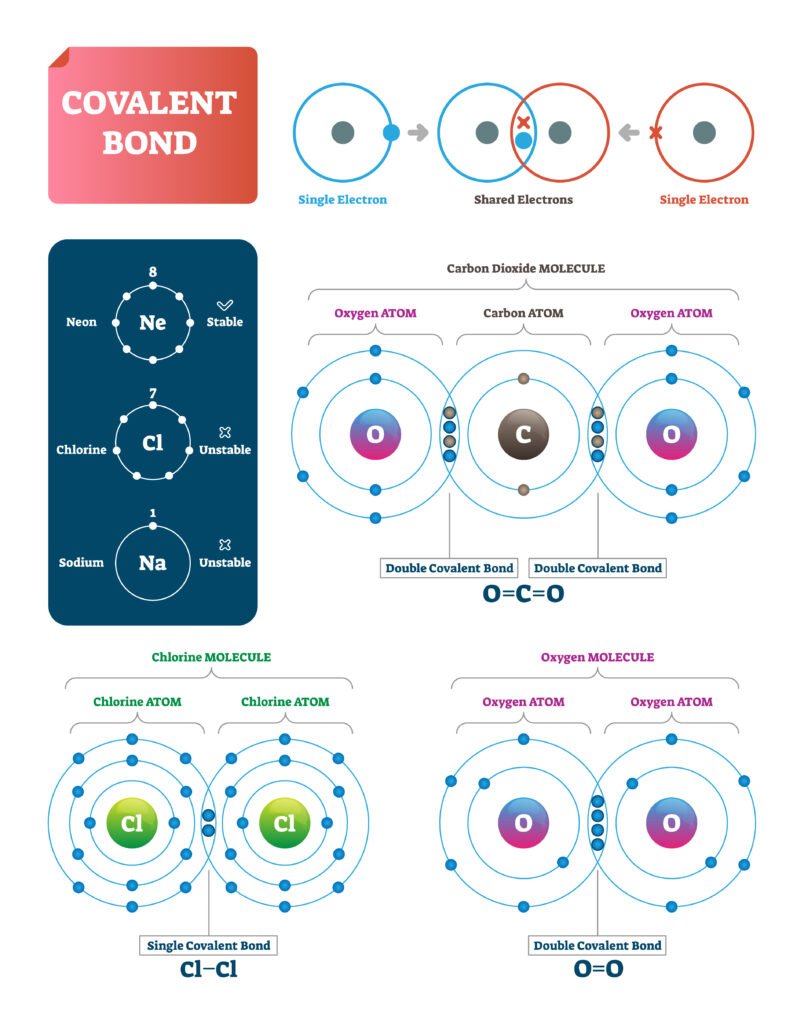

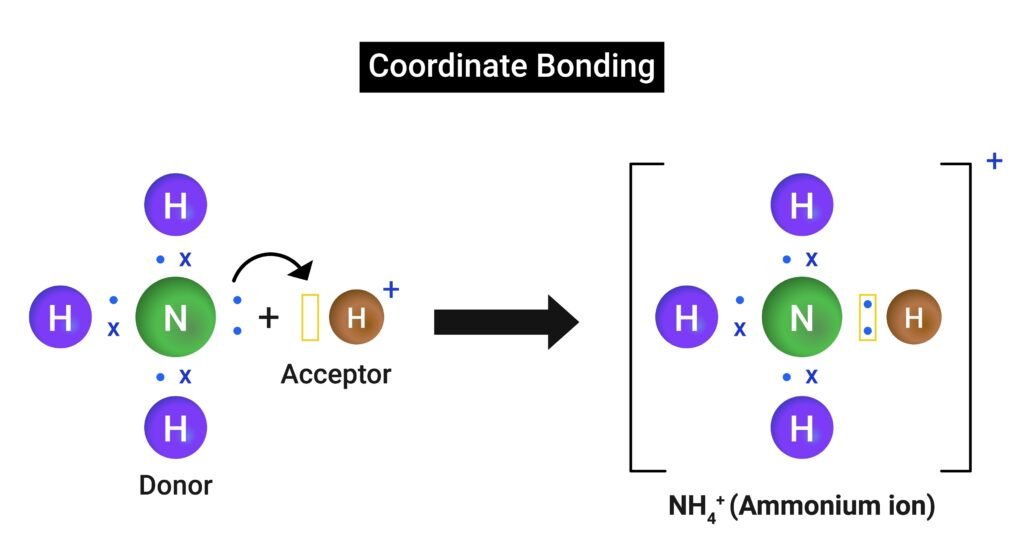
3️⃣ Coordinate (Dative) Bond
Both shared electrons contributed by one atom.
Example: NH₄⁺ ion (from NH₃ + H⁺).

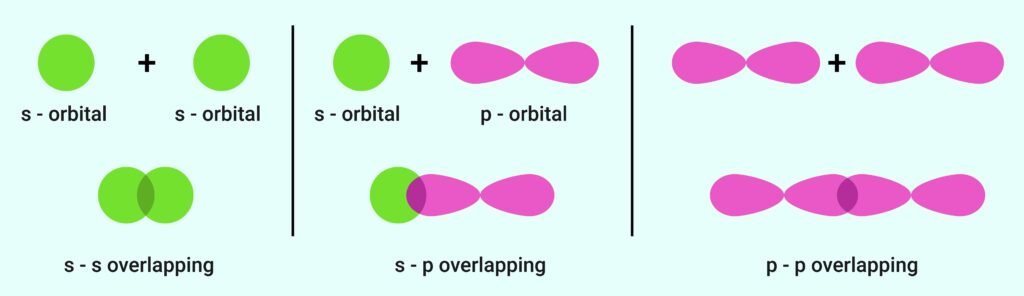
🟡 Valence Bond Theory (VBT)
A chemical bond forms when atomic orbitals of atoms overlap.
Greater overlap → stronger bond.
Overlap types:
s–s overlap (H₂).
s–p overlap (HF).
p–p overlap (O₂).
Bond types:
Sigma (σ) bond → formed by head-on overlap, stronger.
Pi (π) bond → formed by sideways overlap, weaker.
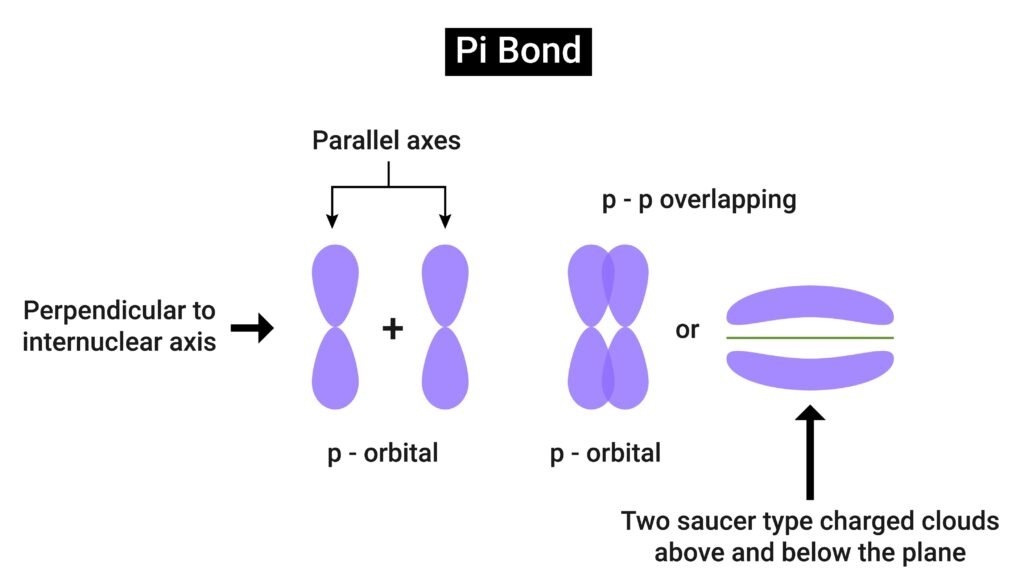
📌 Example: In O₂, one σ bond + one π bond.

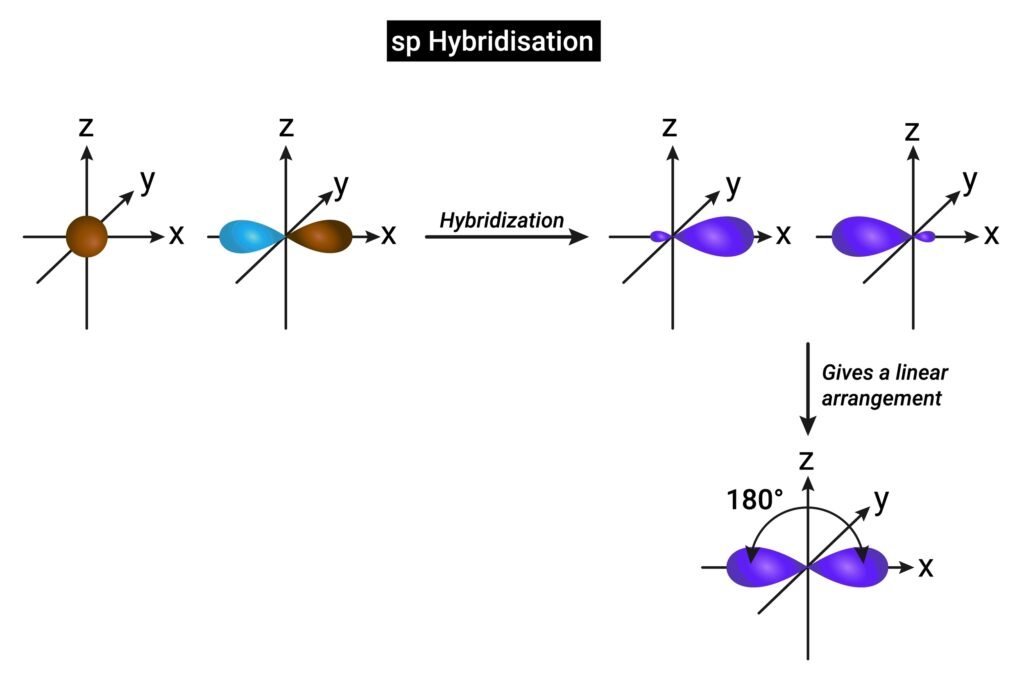
🔴 Hybridization
Hybridization is mixing of atomic orbitals of similar energies to form equivalent hybrid orbitals. It explains shape of molecules.
✔ Types of hybridization:
sp → linear (BeCl₂, 180°).
sp² → trigonal planar (BF₃, 120°).
sp³ → tetrahedral (CH₄, 109.5°).

sp³d → trigonal bipyramidal (PCl₅, 90° & 120°).
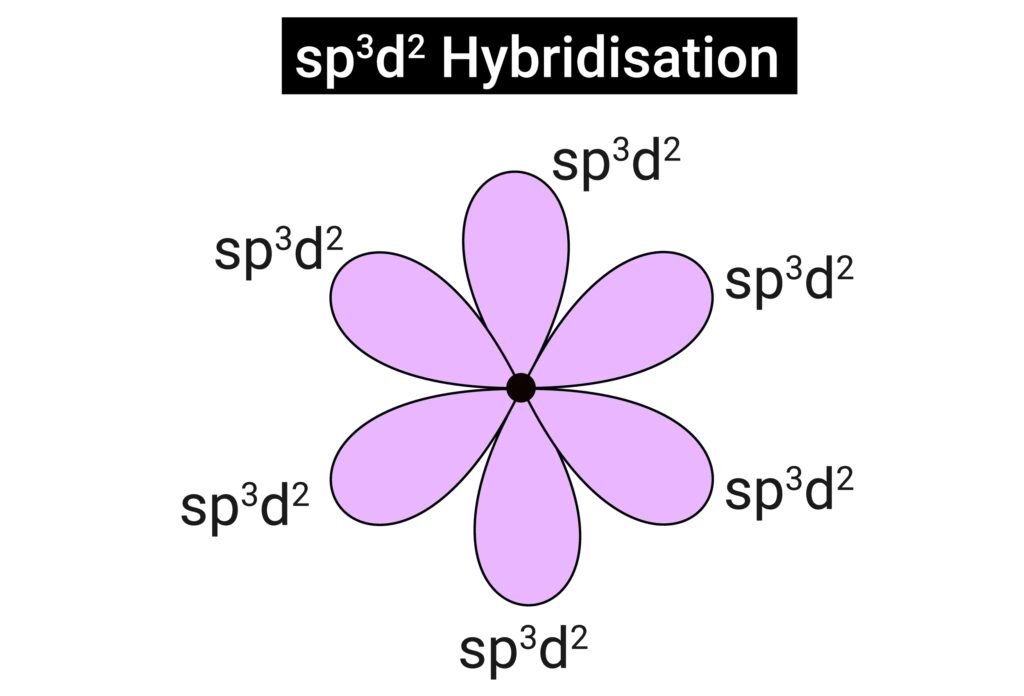
sp³d² → octahedral (SF₆, 90°).
💡 Lone pairs distort shapes:
NH₃ → sp³, pyramidal (107°).
H₂O → sp³, bent (104.5°).
🟢 Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)
VBT had limitations → could not explain magnetism & bond order properly.
MOT by Hund & Mulliken (1932):
Atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals (MOs).
Bonding MOs (lower energy) stabilize; antibonding MOs destabilize.
Bond order = ½ (Nb − Na).
✔ Examples:
H₂ → BO=1 (stable).
He₂ → BO=0 (unstable).
O₂ → BO=2 → paramagnetic (explained magnetism correctly).
🔵 Shapes of Molecules: VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory states that electron pairs (bonding + lone) around central atom repel each other. To minimize repulsion, they adopt maximum separation, giving molecular shape.
✔ Examples:
BeCl₂ → linear (180°).
BF₃ → trigonal planar (120°).
CH₄ → tetrahedral (109.5°).
NH₃ → pyramidal (107°).
H₂O → bent (104.5°).
PCl₅ → trigonal bipyramidal.
SF₆ → octahedral.
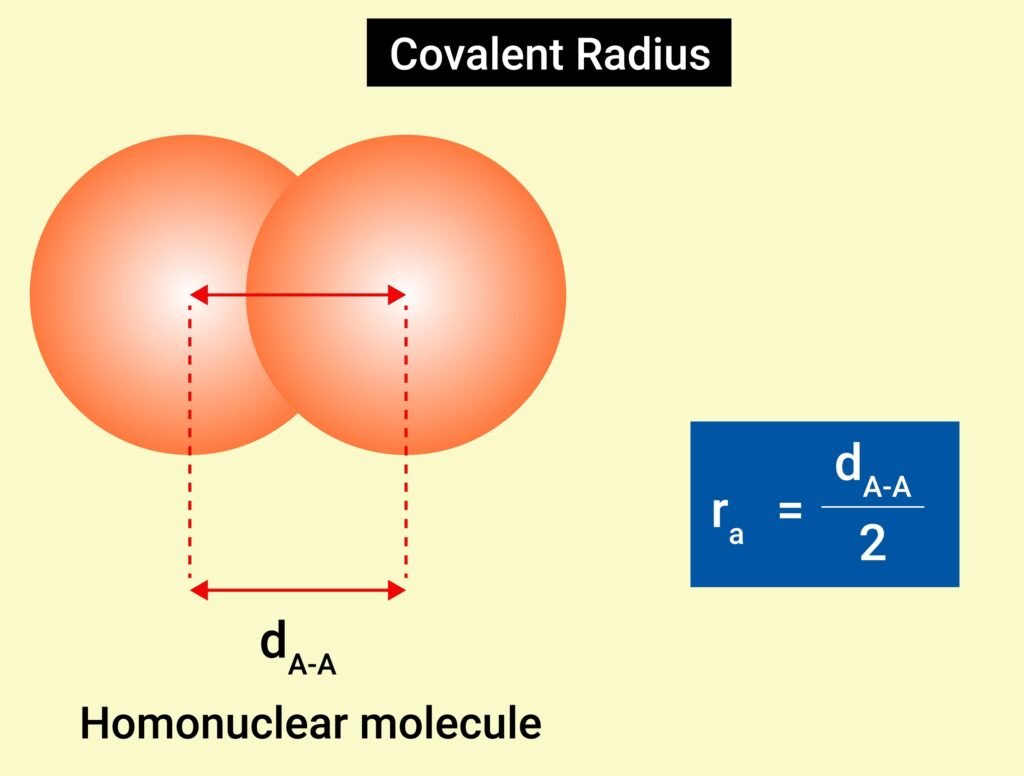
🟡 Bond Parameters
Bond Length
Distance between nuclei of bonded atoms.
Covalent radius trend: decreases with bond multiplicity.
Example: C–C single bond (154 pm), C=C (134 pm), C≡C (120 pm).
Bond Angle
Angle between orbitals of bonded atoms.
Depends on repulsions, hybridization.
Bond Enthalpy
Energy required to break one mole of bonds.
Multiple bonds stronger → higher enthalpy.
Bond Order
Number of bonds between atoms.
Higher BO → shorter, stronger bond.

🔴 Polarity of Bonds
Covalent bond may be polar (unequal sharing) or nonpolar (equal sharing).
Dipole moment (μ) = Q × d measures polarity.
Molecules with symmetrical shape may be nonpolar even if bonds are polar (e.g., CO₂).
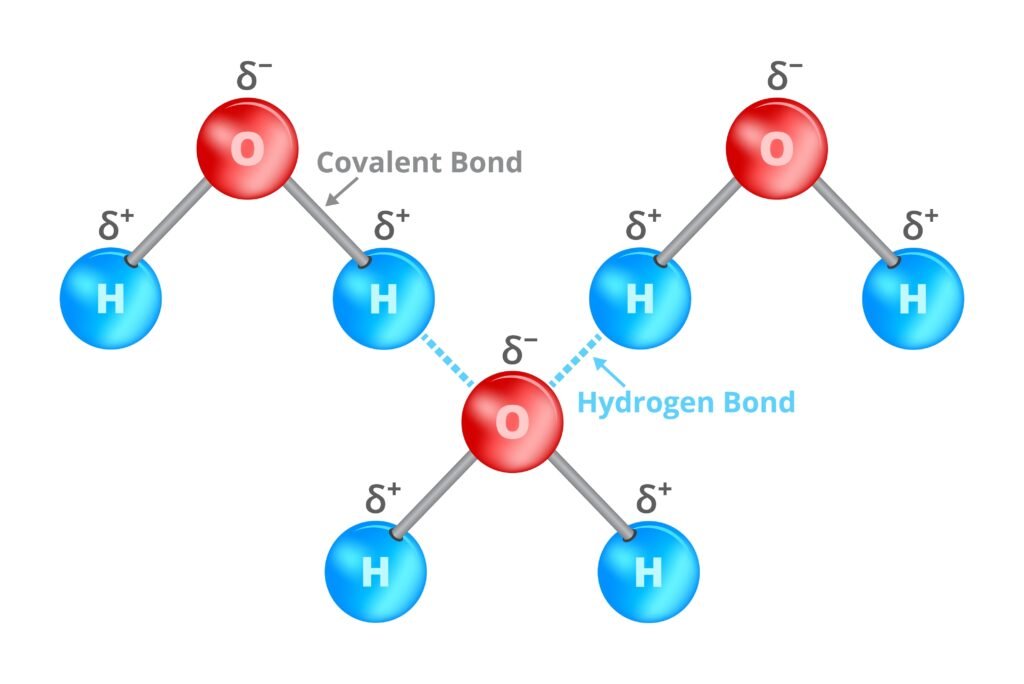
🟢 Hydrogen Bonding
Special bond between hydrogen attached to electronegative atom (N, O, F) and another electronegative atom.
Two types:
Intermolecular (between molecules, e.g., H₂O high boiling).
Intramolecular (within molecule, e.g., o-nitrophenol).
Consequences: higher boiling points, solubility, structure stabilization (DNA double helix 🧬).
🔵 Resonance
When one structure is not enough to explain bonding, a resonance hybrid (average of multiple structures) is considered.
Examples:
Ozone (O₃) ↔ two resonating structures.
Benzene (C₆H₆) ↔ Kekulé structures.
🟡 Applications of Bonding Concepts
✔ Explains stability of molecules.
✔ Determines shape and polarity (important in solubility, boiling point).
✔ Accounts for magnetism (O₂ paramagnetism explained by MOT).
✔ Explains unique properties of water, ammonia, HF (hydrogen bonding).
✔ Foundation for advanced chemistry: organic reactions, complex compounds, biochemistry.
✨ Conclusion
The chapter on Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure is the heart of chemistry. It connects atomic structure to molecular properties, enabling us to predict shapes, polarity, reactivity, and strength of compounds. From simple molecules like H₂ to complex biological macromolecules, bonding explains the architecture of matter 🔬.
🔹 II. Lesson Summary
📌 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure – Key Takeaways
🔵 Why Bonding?
Atoms combine to attain stability (octet rule, duplet for H/He).
🟢 Types of Bonds
Ionic: electron transfer (NaCl).
Covalent: electron sharing (CH₄).
Coordinate: both electrons from one atom (NH₄⁺).
🔴 Theories
VBT: overlap of orbitals → σ and π bonds.
Hybridization: mixing orbitals → sp, sp², sp³, etc.
MOT: bonding/antibonding orbitals, bond order, magnetism.
VSEPR: electron pair repulsion → molecular shapes.
🟡 Bond Parameters
Length: distance between nuclei.
Angle: between bonds.
Enthalpy: energy needed to break.
Order: number of bonds (1, 2, 3).
🌟 Special Topics
Polarity: dipole moment, symmetry.
Hydrogen bonding: inter vs intra, explains high boiling, DNA stability.
Resonance: delocalized bonds (O₃, benzene).
📚 Molecular Shapes Examples
Linear: BeCl₂.
Trigonal planar: BF₃.
Tetrahedral: CH₄.
Pyramidal: NH₃.
Bent: H₂O.
Trigonal bipyramidal: PCl₅.
Octahedral: SF₆.
✨ Importance
Predicts structure, polarity, reactivity.
Explains water anomalies, O₂ magnetism.
Basis of organic, inorganic, and biological chemistry.
🔹 III. Quick Recap
📝 Quick Recap:
✔ Atoms bond to achieve octet stability.
✔ Bonds: ionic (transfer), covalent (sharing), coordinate (donation).
✔ VBT: orbital overlap → σ, π bonds.
✔ Hybridization: sp, sp², sp³ → shapes explained.
✔ MOT: bonding/antibonding orbitals, bond order, magnetism.
✔ VSEPR: molecular shapes depend on electron repulsions.
✔ Bond parameters: length, angle, enthalpy, order.
✔ Polarity, resonance, hydrogen bonding → unique behaviors.
✔ Explains stability, properties, reactivity of compounds.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 4.1
Explain the formation of a chemical bond.
🟢 Answer:
✔ A chemical bond is a force that holds two atoms together to form a stable molecule.
✔ Atoms form bonds to achieve a stable electronic configuration (usually octet).
✔ Driving factors:
Lower potential energy
Attainment of noble gas configuration
✔ Main types:
Ionic bond – transfer of electrons (NaCl)
Covalent bond – sharing of electrons (H₂, O₂)
Coordinate bond – shared pair from one atom (NH₄⁺)
✨ Conclusion: Atoms combine to become more stable.
🔵 Question 4.2
Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements:
Mg, Na, B, O, N, Br
🟢 Answer:
Lewis symbol = dots = number of valence electrons.
Mg (2 valence e⁻): Mg··
Na (1 e⁻): Na·
B (3 e⁻): B···
O (6 e⁻): O······
N (5 e⁻): N·····
Br (7 e⁻): Br·······
🔵 Question 4.3
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions:
S and S²⁻; Al and Al³⁺; H and H⁻
🟢 Answer:
S: 6 valence e⁻ → S······
S²⁻: gains 2 e⁻ → 8 dots → S········
Al: 3 valence e⁻ → Al···
Al³⁺: loses 3 e⁻ → no dots
H: 1 e⁻ → H·
H⁻: 2 e⁻ → H··
🔵 Question 4.4
Draw Lewis structures for:
H₂S, SiCl₄, BeF₂, CO₃²⁻, HCOOH
🟢 Answer:
✔ H₂S:
S has 6 e⁻ → bonds with 2 H → H–S–H, two lone pairs on S
✔ SiCl₄:
Si (4 e⁻) + 4 Cl (7 each) → four single bonds
Structure:
Cl
│
Cl–Si–Cl
│
Cl
✔ BeF₂:
Be (2 e⁻) forms 2 single bonds → F–Be–F, linear
✔ CO₃²⁻:
24 valence e⁻, one C double-bonded to one O, single to two O⁻
Resonance: three equivalent forms
✔ HCOOH (formic acid):
H–C(=O)–OH
🔵 Question 4.5
Define octet rule. Write its significance and limitations.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Octet rule: Atoms tend to gain/lose/share electrons to have 8 in outer shell.
✔ Significance: Explains stability and formation of molecules like NaCl, H₂O.
✔ Limitations:
Fails for odd-electron molecules (NO)
Fails for electron-deficient (BF₃)
Fails for expanded octet (SF₆)
🔵 Question 4.6
Write favourable factors for formation of ionic bond.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Low ionization enthalpy (cation formation easy)
✔ High electron gain enthalpy (anion formation easy)
✔ High lattice enthalpy (stabilizes solid)
Example: NaCl – Na⁺ + Cl⁻ → strong ionic bond
🔵 Question 4.7
Discuss shape of the following molecules using VSEPR model:
BeCl₂, BCl₃, SiCl₄, AsF₅, H₂S, PH₃
🟢 Answer:
BeCl₂: 2 bond pairs, 0 lone → linear
BCl₃: 3 bond pairs → trigonal planar
SiCl₄: 4 bond pairs → tetrahedral
AsF₅: 5 bond pairs → trigonal bipyramidal
H₂S: 2 bond + 2 lone → bent
PH₃: 3 bond + 1 lone → trigonal pyramidal
🔵 Question 4.8
Although NH₃ and H₂O are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water < ammonia. Discuss.
🟢 Answer:
✔ NH₃: 1 lone pair → bond angle 107°
✔ H₂O: 2 lone pairs → more repulsion → bond angle 104.5°
💡 More lone pairs → smaller angle.
🔵 Question 4.9
How do you express bond strength in terms of bond order?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Bond order (B.O.) = ½ (bonding – antibonding electrons)
✔ ↑ Bond order → ↑ bond strength → ↓ bond length
e.g. N₂ (B.O. = 3) > O₂ (B.O. = 2) > F₂ (B.O. = 1)
🔵 Question 4.10
Define bond length.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Bond length = equilibrium distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Measured in pm.
e.g. H–H = 74 pm
Shorter bond → stronger.
🔵 Question 4.11
Explain resonance with reference to CO₃²⁻.
🟢 Answer:
✔ CO₃²⁻ has 3 equivalent structures; true structure is resonance hybrid.
✔ Each C–O bond = same length, B.O. = 4/3.
💡 Resonance increases stability.
🔵 Question 4.12
H₃PO₃ can be represented by two structures. Can these be canonical forms?
🟢 Answer:
❌ No.
Because in (1) and (2), bonding arrangement differs (one has P=O, other has P–O–H), atoms linked differently → not resonance → tautomers, not canonical forms.
🔵 Question 4.13
Write resonance structures of SO₃, NO₂, NO₃⁻.
🟢 Answer:
✔ SO₃: three equivalent structures, S double bonded with each O once.
✔ NO₂: two forms with one double, one single bond.
✔ NO₃⁻: three equivalent forms; each N–O bond = 1⅓ order.
🔵 Question 4.14
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer in:
(a) K and S (b) Ca and O (c) Al and N
🟢 Answer:
(a) K· + :S: → K₂S (K⁺, S²⁻)
(b) Ca·· + :O: → CaO (Ca²⁺, O²⁻)
(c) Al··· + :N: → AlN (Al³⁺, N³⁻)
Each forms stable ionic compounds by complete transfer.
🔵 Question 4.15
Although both CO₂ and H₂O are triatomic molecules, the shape of H₂O molecule is bent while that of CO₂ is linear. Explain on the basis of dipole moment.
🟢 Answer:
✔ CO₂: O=C=O is linear, bond dipoles equal & opposite → cancel out → μ = 0 (non-polar)
✔ H₂O: H–O–H is bent, bond dipoles do not cancel → μ ≠ 0 (polar)
✨ Therefore, CO₂ is non-polar, H₂O is polar.
🔵 Question 4.16
Write the significance/applications of dipole moment.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Measures polarity of a molecule
✔ Helps to predict shape (μ = 0 → symmetrical, linear)
✔ Differentiates polar and non-polar molecules
✔ Explains bond character (μ ∝ % ionic character)
🔵 Question 4.17
Define electronegativity. How does it differ from electron gain enthalpy?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Electronegativity = tendency of an atom to attract shared pair of electrons in a bond.
✔ Electron gain enthalpy = energy change when an isolated atom gains electron.
💡 Difference:
EN → property of bonded atom
ΔegH → property of isolated atom
🔵 Question 4.18
Explain with an example polar covalent bond.
🟢 Answer:
✔ When shared pair is unequally shared → bond has partial charges.
Example: H–Cl
→ Cl more electronegative → δ⁻, H → δ⁺
→ Polar covalent bond
🔵 Question 4.19
Arrange the bonds in order of increasing ionic character:
LiF, K₂O, N₂, SO₂, ClF₃
🟢 Answer:
✔ Greater ΔEN → more ionic.
ΔEN: N₂ (0) < SO₂ < ClF₃ < K₂O < LiF
✅ Order: N₂ < SO₂ < ClF₃ < K₂O < LiF
🔵 Question 4.20
Write correct Lewis structure of acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
🟢 Answer:
✔ Structure:
H
│
H–C–H
│
C=O
│
O–H
💡 Contains 4 single bonds and 1 double bond.
🔵 Question 4.21
Apart from tetrahedral, CH₄ can’t be square planar. Why?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Square planar needs d orbitals, but C lacks d orbitals (only s & p).
✔ sp³ hybridization → tetrahedral only.
🔵 Question 4.22
Explain why BeH₂ has zero dipole moment though Be–H bonds are polar.
🟢 Answer:
✔ BeH₂ is linear.
✔ Bond dipoles equal & opposite → cancel.
→ μ = 0 though each bond is polar.
🔵 Question 4.23
Which has higher dipole moment: NH₃ or NF₃?
🟢 Answer:
✔ NH₃: μ vectors of bonds + lone pair in same direction → μ high (1.46 D)
✔ NF₃: μ vectors oppose → partial cancellation → μ lower (0.24 D)
✅ NH₃ > NF₃
🔵 Question 4.24
What is meant by hybridization? Describe sp, sp², sp³ hybrid orbitals.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Hybridization: Mixing of atomic orbitals of similar energy to form new equivalent orbitals.
sp: 1s + 1p → 2 linear orbitals (180°)
sp²: 1s + 2p → 3 trigonal planar (120°)
sp³: 1s + 3p → 4 tetrahedral (109.5°)
🔵 Question 4.25
Describe change in hybridisation of Al in:
AlCl₃ + Cl⁻ → AlCl₄⁻
🟢 Answer:
✔ AlCl₃ → sp² (3 bonds)
✔ AlCl₄⁻ → accepts lone pair → sp³ (4 bonds)
✨ Hybridisation changes from sp² → sp³
🔵 Question 4.26
Change in hybridisation of B and N in:
BF₃ + NH₃ → F₃B←NH₃
🟢 Answer:
✔ B (in BF₃): sp² → after bonding → sp³
✔ N (in NH₃): sp³ → remains sp³
🔵 Question 4.27
Draw formation of double and triple bonds in C₂H₄ and C₂H₂.
🟢 Answer:
✔ C₂H₄ (Ethene):
Each C: sp² → 1 σ (C–C) + 1 π
→ structure: H₂C=CH₂
✔ C₂H₂ (Ethyne):
Each C: sp → 1 σ + 2 π
→ structure: HC≡CH
🔵 Question 4.28
Total number of σ and π bonds:
(a) C₂H₂ (b) C₂H₄
🟢 Answer:
(a) C₂H₂:
1 C–C σ + 2 π, 2 C–H σ → σ = 3, π = 2
(b) C₂H₄:
1 C–C σ + 1 π, 4 C–H σ → σ = 5, π = 1
🔵 Question 4.2
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis, which out of the following will not form a σ (sigma) bond and why?
(a) 1s and 1s
(b) 1s and 2pₓ
(c) 2pₓ and 2pₓ
(d) 1s and 2s
🟢 Answer:
✔ A σ bond is formed by end-to-end overlap of orbitals along the internuclear axis (x-axis).
(a) 1s–1s → yes, forms σ bond
(b) 1s–2pₓ → yes, forms σ bond
(c) 2pₓ–2pₓ → yes, forms σ bond
(d) 1s–2s → yes, forms σ bond
✅ All can form σ bond, none is excluded.
🔵 Question 4.30
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
(a) CH₃–CH₃
(b) CH₂=CH₂
(c) CH≡CH
(d) CH₃CHO (acetaldehyde)
(e) CH₃COOH (acetic acid)
🟢 Answer:
✔ (a) CH₃–CH₃ → all C atoms sp³
✔ (b) CH₂=CH₂ → each C sp²
✔ (c) CH≡CH → each C sp
✔ (d) CH₃CHO → CH₃ (sp³), CHO carbon (sp²)
✔ (e) CH₃COOH → CH₃ (sp³), COOH carbon (sp²)
🔵 Question 4.31
What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Give one example of each.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Bond pair: electrons shared between two atoms forming a covalent bond.
Example: in H–Cl, one shared pair = bond pair.
✔ Lone pair: non-bonding pair localized on one atom.
Example: in H₂O, oxygen has 2 lone pairs.
🔵 Question 4.32
Distinguish between a σ bond and a π bond.
🟢 Answer:
Feature σ bond π bond
Formation End-to-end overlap Sidewise overlap
Strength Stronger Weaker
Rotation Free Restricted
Example H–H in H₂ C=C in C₂H₄ (one σ, one π)
🔵 Question 4.33
Explain the formation of H₂ molecule on the basis of valence bond theory (VBT).
🟢 Answer:
✔ Each H atom has 1s¹ configuration.
✔ Two 1s orbitals overlap head-on to form one σ bond.
✔ Electron density increases between nuclei → lowers energy → stable H₂.
🔵 Question 4.34
Write the important conditions required for the linear combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Orbitals must have same energy.
✔ Proper symmetry about internuclear axis.
✔ Maximum overlap possible.
✨ These ensure effective bonding/antibonding MO formation.
🔵 Question 4.35
Use molecular orbital theory to explain why Be₂ molecule does not exist.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Be: 1s² 2s²
✔ MO filling: σ1s² σ1s² σ2s² σ2s²
✔ Bond order = (Nb–Na)/2 = (4–4)/2 = 0
✅ Zero bond order → Be₂ unstable, does not exist.
🔵 Question 4.36
Compare relative stability and magnetic property of O₂, O₂⁺, O₂⁻, O₂²⁻.
🟢 Answer:
Species Bond Order Magnetic Stability
O₂ 2 Paramagnetic (2 unpaired) Stable
O₂⁺ 2.5 Paramagnetic More stable
O₂⁻ 1.5 Paramagnetic Less stable
O₂²⁻ 1 Diamagnetic Least stable
✔ Higher bond order → more stability.
🔵 Question 4.37
Write the significance of ‘+’ and ‘–’ sign in representing orbitals.
🟢 Answer:
✔ They show phase of wave function (ψ).
✔ In bonding overlap: same sign → constructive, bonding MO.
✔ Opposite sign → destructive, antibonding MO.
🔵 Question 4.38
Describe hybridisation in PCl₅. Why are axial bonds longer than equatorial?
🟢 Answer:
✔ P: 3s²3p³ + promotion → 3s¹3p³3d¹ → sp³d
✔ Geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
→ 3 equatorial (120°), 2 axial (90°)
✔ Axial bonds face more repulsion → longer & weaker.
🔵 Question 4.39
Define hydrogen bond. Is it weaker or stronger than van der Waals forces?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Attractive force between H (bonded to F, O, N) and lone pair of nearby electronegative atom.
✔ Stronger than van der Waals forces, but weaker than covalent bond.
🔵 Question 4.40
What is meant by bond order? Calculate bond order of N₂, O₂, O₂⁺ and O₂²⁻.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Bond order = ½ (Nb – Na)
N₂: (10–4)/2 = 3
O₂: (10–6)/2 = 2
O₂⁺: (10–5)/2 = 2.5
O₂²⁻: (10–8)/2 = 1
✔ Higher bond order → stronger bond → shorter bond length.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
✳ Section A (Q1–Q16) – MCQs (1 mark each, 16 × 1 = 16 marks)
Options:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
A is true, but R is false
A is false, but R is true
Question 1. Which type of bond is present in NaCl?
Covalent bond
Ionic bond
Metallic bond
Coordinate bond
Answer: 2
Question 2. Which among the following molecules has triple bond?
O₂
N₂
Cl₂
F₂
Answer: 2
Question 3. The molecule with linear shape is:
H₂O
NH₃
CO₂
BF₃
Answer: 3
Question 4. Hybridization of carbon in methane (CH₄) is:
sp
sp²
sp³
dsp²
Answer: 3
Question 5. Which among the following has bent shape?
CO₂
H₂O
BeCl₂
BF₃
Answer: 2
Question 6. Which molecule shows resonance?
CH₄
O₃
H₂O
NH₄⁺
Answer: 2
Question 7. Which bond has highest polarity?
H–H
H–F
H–Cl
H–Br
Answer: 2
Question 8. Which compound shows coordinate bond?
H₂O
NH₄⁺
Cl₂
NaCl
Answer: 2
Question 9. VSEPR theory is used to predict:
Bond length
Bond energy
Molecular shape
Bond order
Answer: 3
Question 10. Bond order of O₂ molecule according to MOT is:
1
2
3
2.5
Answer: 2
Question 11. Paramagnetic molecule is:
O₂
N₂
CO₂
H₂O
Answer: 1
Question 12. Which orbital overlap gives strongest bond?
s–s
s–p
p–p (axial)
p–p (sideways)
Answer: 3
Question 13. Dipole moment of CO₂ is zero because:
It has non-polar bonds
It has polar bonds but linear structure
It has ionic bonds
It has weak bonds
Answer: 2
Question 14. (Assertion–Reason)
Assertion (A): NH₃ has pyramidal shape.
Reason (R): Nitrogen has lone pair of electrons which repels bond pairs.
Answer: 1
Question 15. (Assertion–Reason)
Assertion (A): O₂ is paramagnetic.
Reason (R): According to MOT, O₂ has two unpaired electrons in antibonding orbitals.
Answer: 1
Question 16. Which of the following is isostructural with CO₂?
SO₂
NO₂⁻
BeCl₂
H₂O
Answer: 3
⚡ Section B (Q17–Q21) – Very Short Answer (2 marks each, 5 × 2 = 10 marks)
Q17. Define octet rule with one example.
🟦 Atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons to acquire stable configuration of 8 electrons in valence shell.
🟩 Example: NaCl forms by transfer of 1 electron from Na to Cl.
Q18. Differentiate between sigma and pi bond (two points).
🟦 Sigma bond – formed by head-on overlap; stronger.
🟩 Pi bond – formed by sideways overlap; weaker.
Q19. What is bond order? Write formula.
🟦 Bond order = (Number of bonding electrons – Number of antibonding electrons)/2.
🟩 Greater bond order → stronger bond, shorter bond length.
Q20. Calculate bond order of N₂ using MOT.
➤ Bonding electrons = 10, Antibonding electrons = 4
➤ Bond order = (10 – 4)/2 = 3
✅ Final Answer: Bond order = 3
Q21. Why does H₂O have bent shape according to VSEPR theory?
🟦 Oxygen has 2 lone pairs and 2 bond pairs.
🟩 Lone pair–bond pair repulsion > bond pair–bond pair → bent structure.
🧪 Section C (Q22–Q28) – Short Answer (3 marks each, 7 × 3 = 21 marks)
Q22. State three limitations of octet rule.
🟦 Incomplete octet (H, Be).
🟨 Expanded octet (P, S).
🟩 Odd-electron molecules (NO, NO₂).
Q23. Explain Fajan’s rule with one example.
🟦 Smaller cation and larger anion → more covalent character.
🟨 Example: LiI more covalent than LiF.
🟩 Greater polarization → greater covalency.
Q24. Write the molecular orbital electronic configuration of O₂ and predict its magnetic behaviour.
🟦 O₂ (Z = 8): (σ1s)² (σ1s)² (σ2s)² (σ2s)² (σ2pz)² (π2px = 2, π2py = 2) (π2px = 1, π2py = 1).
🟨 Two unpaired electrons present.
✅ Hence O₂ is paramagnetic.
Q25. State and explain VSEPR theory with example of BF₃.
🟦 Electron pairs around central atom repel each other.
🟨 Shape depends on minimizing repulsion.
🟩 In BF₃: 3 bond pairs → trigonal planar shape.
Q26. What are resonance structures? Give one example.
🟦 Structures with same arrangement of atoms but different arrangement of electrons.
🟨 Actual molecule is hybrid of resonance structures.
🟩 Example: O₃, NO₃⁻.
Q27. Explain formation of NH₄⁺ ion.
🟦 N atom shares 3 electrons with H atoms → NH₃.
🟨 Lone pair on N donated to H⁺ → coordinate bond.
✅ NH₄⁺ formed with tetrahedral structure.
Q28. State three differences between bonding in H₂ and He₂ according to MOT.
🟦 H₂: bond order = 1 → stable molecule.
🟨 He₂: bond order = 0 → unstable, does not exist.
🟩 Reason: antibonding orbitals cancel bonding in He₂.
🧭 Section D (Q29–Q30) – Case-Based Questions (4 marks each, 2 × 4 = 8 marks)
Q29. Read the passage and answer the questions:
The bond in hydrogen chloride (HCl) is polar covalent due to the difference in electronegativity of H and Cl. The molecule has a dipole moment of 1.08 D, showing partial charges.
(a) What type of bond is present in HCl? (1 mark)
(b) Why is the bond polar? (1 mark)
(c) Explain significance of dipole moment in HCl. (2 marks)
🧪 Answer:
(a) Polar covalent bond.
(b) Because Cl is more electronegative than H, electron pair is shifted towards Cl.
(c) Dipole moment shows extent of polarity → partial positive charge on H and negative charge on Cl.
Q30. Read the passage and answer the questions:
According to Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), electronic configurations of molecules can be used to calculate bond order and predict stability. For example, O₂ molecule has bond order 2 and is paramagnetic.
(a) Write the formula for bond order. (1 mark)
(b) Calculate bond order of O₂. (1 mark)
(c) Why is O₂ paramagnetic according to MOT? (2 marks)
🧪 Answer:
(a) Bond order = (Number of bonding electrons – Number of antibonding electrons)/2.
(b) O₂: Bonding e⁻ = 10, Antibonding e⁻ = 6 → BO = (10 – 6)/2 = 2.
(c) O₂ has two unpaired electrons in π2px and π2py orbitals → paramagnetic.
⚡ Section E (Q31–Q33) – Long Answer (5 marks each, 3 × 5 = 15 marks)
Q31. (a) Discuss the main postulates of Valence Bond Theory (VBT) and explain hybridization in CH₄.
OR
(b) Explain the formation of σ and π bonds with neat description.
🧪 Answer (a):
🟦 VBT: A covalent bond forms due to overlap of half-filled orbitals.
🟨 Bond strength ∝ overlap extent.
🟩 Hybridization: Mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals of equal energy.
🧪 In CH₄: C undergoes sp³ hybridization → 4 sp³ orbitals form 4 σ bonds with H.
🎯 Shape: Tetrahedral, bond angle 109.5°.
Answer (b):
🟦 σ-bond: head-on overlap of orbitals (s–s, s–p, p–p axial). Strongest bond.
🟨 π-bond: sideways overlap of p-orbitals after σ bond is formed.
🎯 Example: N₂ has one σ and two π bonds.
Q32. (a) State VSEPR theory. Predict the shapes of (i) BeCl₂, (ii) BF₃, (iii) NH₃, (iv) H₂O.
OR
(b) Discuss Fajan’s rule and factors influencing covalent character in ionic compounds.
🧪 Answer (a):
🟦 VSEPR theory: Shape depends on repulsions between electron pairs in valence shell of central atom.
(i) BeCl₂: 2 bond pairs → Linear (180°).
(ii) BF₃: 3 bond pairs → Trigonal planar (120°).
(iii) NH₃: 3 bond pairs + 1 lone pair → Trigonal pyramidal (107°).
(iv) H₂O: 2 bond pairs + 2 lone pairs → Bent (104.5°).
Answer (b):
🟦 Fajan’s rule: Small, highly charged cation + large, polarizable anion → more covalent character.
🟨 Factors: (i) Size of cation (smaller → more covalent),
(ii) Charge of cation (higher → more covalent),
(iii) Size of anion (larger → more covalent).
🎯 Example: AlCl₃ shows covalent character.
Q33. (a) Explain Molecular Orbital Theory with energy-level diagram up to O₂ molecule. Discuss stability of O₂ and He₂.
OR
(b) Define resonance. Explain resonance in O₃ molecule and its significance.
🧪 Answer (a):
🟦 MOT: Atomic orbitals combine to form bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
🟨 Filling follows Aufbau principle, Pauli’s principle, Hund’s rule.
🟩 O₂ (Z = 8): BO = 2, two unpaired electrons → stable, paramagnetic.
🧪 He₂: BO = 0 → unstable, does not exist.
🎯 MOT explains stability and magnetic behaviour better than VBT.
Answer (b):
🟦 Resonance: When a molecule cannot be represented by a single structure but two or more canonical structures.
🟨 Example: O₃ → O=O–O ↔ O–O=O.
🟩 Actual structure is resonance hybrid, with bond order = 1.5.
🎯 Resonance increases stability and delocalization of electrons.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following molecules has the highest bond order?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁺
🟡 ③ O₂⁻
🔵 ④ O₂²⁻
🟢 Answer: ② O₂⁺
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following has sp hybridization?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ① BeCl₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: A
🔵 Question 3:
Which bond angle is maximum?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ BeCl₂
🟢 Answer: ④ BeCl₂ (180°)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: R2
🔵 Question 4:
Among the following, the molecule with sp² hybridization is:
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ② BF₃
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: C
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following molecules is linear?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② BeCl₂
🟡 ③ SO₂
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ② BeCl₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: S2
🔵 Question 6:
Which of the following molecules contains only sigma bonds?
🔴 ① C₂H₄
🟢 ② C₂H₂
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: ③ CH₄
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 7:
Which has highest ionic character?
🔴 ① HF
🟢 ② HCl
🟡 ③ HBr
🔵 ④ HI
🟢 Answer: ① HF
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: B
🔵 Question 8:
In which of the following molecules the central atom is sp³d hybridized?
🔴 ① PCl₅
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ① PCl₅
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: S
🔵 Question 9:
Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② CO₂
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ② CO₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2008 | Set: C
🔵 Question 10:
The bond order of N₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① 1
🟢 ② 2
🟡 ③ 3
🔵 ④ 4
🟢 Answer: ③ 3
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2020 | Set: Q2
🔵 Question 11:
Which is the correct order of bond length?
🔴 ① N₂ < O₂ < F₂
🟢 ② O₂ < F₂ < N₂
🟡 ③ F₂ < O₂ < N₂
🔵 ④ N₂ < F₂ < O₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂ < O₂ < F₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: P
🔵 Question 12:
Which of the following has pyramidal shape?
🔴 ① BF₃
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ BeCl₂
🟢 Answer: ② NH₃
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: A
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following does not have sp³ hybridization?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ④ BF₃
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: L
🔵 Question 14:
Which of the following compounds shows hydrogen bonding?
🔴 ① H₂S
🟢 ② HF
🟡 ③ HCl
🔵 ④ HI
🟢 Answer: ② HF
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2010 | Set: A
🔵 Question 15:
Which one of the following molecules is non-polar?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: S
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following molecules involves back bonding?
🔴 ① BF₃
🟢 ② CH₄
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ H₂O
🟢 Answer: ① BF₃
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: O2
🔵 Question 17:
Which bond has the highest bond energy?
🔴 ① C–C
🟢 ② C=C
🟡 ③ C≡C
🔵 ④ C–H
🟢 Answer: ③ C≡C
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: B
🔵 Question 18:
Which of the following is the weakest bond?
🔴 ① Ionic
🟢 ② Covalent
🟡 ③ van der Waals
🔵 ④ Hydrogen bond
🟢 Answer: ③ van der Waals
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: R2
🔵 Question 19:
Which of the following species is paramagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② N₂
🟡 ③ CO
🔵 ④ Be₂
🟢 Answer: ① O₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: A
🔵 Question 20:
Hybridization of xenon in XeF₄ is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp³d
🟡 ③ sp³d²
🔵 ④ sp³d³
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³d²
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: S1
🔵 Question 21:
Which one has trigonal planar structure?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ② BF₃
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: C
🔵 Question 22:
Which has highest bond angle?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ① CH₄ (109.5°)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: P1
🔵 Question 23:
Which type of bond exists in KCl?
🔴 ① Covalent
🟢 ② Ionic
🟡 ③ Metallic
🔵 ④ Coordinate
🟢 Answer: ② Ionic
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: 1
🔵 Question 24:
Which molecule has angular shape?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ BF₃
🔵 ④ BeCl₂
🟢 Answer: ② H₂O
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: P
🔵 Question 25:
Which type of overlap leads to formation of π-bond?
🔴 ① End-to-end overlap of orbitals
🟢 ② Sidewise overlap of orbitals
🟡 ③ Overlap of s and p orbitals
🔵 ④ Overlap of hybrid orbitals
🟢 Answer: ② Sidewise overlap of orbitals
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2001 | Set: C
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following species is diamagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁺
🟡 ③ O₂²⁻
🔵 ④ B₂
🟢 Answer: ③ O₂²⁻
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: O2
🔵 Question 27:
In NH₄⁺ ion, the hybridization of nitrogen atom is:
🔴 ① sp
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp³
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2008 | Set: A
🔵 Question 28:
Which of the following molecules has trigonal bipyramidal structure?
🔴 ① SF₆
🟢 ② PCl₅
🟡 ③ XeF₄
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ② PCl₅
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: M
🔵 Question 29:
Bond order of CO molecule is:
🔴 ① 2
🟢 ② 2.5
🟡 ③ 3
🔵 ④ 3.5
🟢 Answer: ③ 3
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: S1
🔵 Question 30:
Which type of bond is present in NH₄Cl?
🔴 ① Covalent and coordinate
🟢 ② Only covalent
🟡 ③ Only ionic
🔵 ④ Metallic
🟢 Answer: ① Covalent and coordinate
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: C
🔵 Question 31:
Which among the following has bond angle less than 109.5°?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ Both NH₃ and H₂O
🟢 Answer: ④ Both NH₃ and H₂O
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: P
🔵 Question 32:
Which molecule has square planar geometry?
🔴 ① XeF₄
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① XeF₄
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2010 | Set: B
🔵 Question 33:
Which one has highest bond dissociation energy?
🔴 ① F₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ Cl₂
🔵 ④ N₂
🟢 Answer: ④ N₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 34:
The molecule having zero dipole moment is:
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: B
🔵 Question 35:
Which one of the following does not exist according to MOT?
🔴 ① He₂
🟢 ② H₂
🟡 ③ Li₂
🔵 ④ B₂
🟢 Answer: ① He₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: P
🔵 Question 36:
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon in C₂H₂?
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ sp³d
🟢 Answer: ③ sp
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: A
🔵 Question 37:
Which is the correct order of bond angle?
🔴 ① H₂O < NH₃ < CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃ < H₂O < CH₄
🟡 ③ CH₄ < H₂O < NH₃
🔵 ④ CH₄ < NH₃ < H₂O
🟢 Answer: ① H₂O < NH₃ < CH₄
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: P2
🔵 Question 38:
Among the following, which has highest bond order?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁺
🟡 ③ O₂⁻
🔵 ④ O₂²⁻
🟢 Answer: ② O₂⁺
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: C
🔵 Question 39:
Which of the following is not a linear molecule?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② BeCl₂
🟡 ③ HCN
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ④ SO₂
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: O
🔵 Question 40:
Which has sp³d² hybridization?
🔴 ① SF₆
🟢 ② PCl₅
🟡 ③ XeF₂
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① SF₆
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 41:
Dipole moment is maximum in:
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② CO₂
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ① NH₃
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: A
🔵 Question 42:
Which of the following molecules has square planar structure?
🔴 ① XeF₄
🟢 ② SF₄
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ ClF₃
🟢 Answer: ① XeF₄
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 43:
Which of the following is not paramagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁻
🟡 ③ N₂
🔵 ④ B₂
🟢 Answer: ③ N₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2001 | Set: B
🔵 Question 44:
Which one is not correctly matched?
🔴 ① sp³ – CH₄
🟢 ② sp² – BF₃
🟡 ③ sp³d – SF₆
🔵 ④ sp³d² – XeF₄
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³d – SF₆
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: Q2
🔵 Question 45:
Which one of the following molecules is angular?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ② H₂O
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: C
🔵 Question 46:
Bond angle of SO₂ is approximately:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 104.5°
🟡 ③ 119°
🔵 ④ 180°
🟢 Answer: ③ 119°
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: S
🔵 Question 47:
In CO₂ molecule, hybridization of C atom is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: B
🔵 Question 48:
Which of the following molecules is not correctly matched with geometry?
🔴 ① CH₄ – Tetrahedral
🟢 ② BF₃ – Trigonal planar
🟡 ③ XeF₂ – Square planar
🔵 ④ NH₃ – Pyramidal
🟢 Answer: ③ XeF₂ – Square planar
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2020 | Set: O1
🔵 Question 49:
The molecule with seesaw shape is:
🔴 ① XeF₂
🟢 ② SF₄
🟡 ③ XeF₄
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ② SF₄
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: R
🔵 Question 50:
Bond angle of CH₄ is:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 107°
🟡 ③ 109.5°
🔵 ④ 120°
🟢 Answer: ③ 109.5°
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: C
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
Among the following, which has highest bond order according to Molecular Orbital Theory?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁺
🟡 ③ O₂²⁻
🔵 ④ O₂⁻
🟢 Answer: ② O₂⁺
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 2
The shape of XeF₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① Linear
🟢 ② T-shaped
🟡 ③ Trigonal planar
🔵 ④ Bent
🟢 Answer: ① Linear
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 3
Which of the following molecules has zero dipole moment?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ BF₃
🔵 ④ HCl
🟢 Answer: ③ BF₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 4
The bond angle in NH₃ is:
🔴 ① 120°
🟢 ② 109.5°
🟡 ③ 107°
🔵 ④ 104.5°
🟢 Answer: ③ 107°
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 5
Which of the following species has bond order 3?
🔴 ① N₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ F₂
🔵 ④ O₂⁻
🟢 Answer: ① N₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 6
Which molecule has sp² hybridisation of central atom?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ H₂O
🟢 Answer: ② BF₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 7
Which one of the following bonds is most polar?
🔴 ① H–H
🟢 ② H–F
🟡 ③ H–Cl
🔵 ④ H–Br
🟢 Answer: ② H–F
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 8
Which of the following molecules is linear?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② CO₂
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ② CO₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 9
Which of the following molecules shows hydrogen bonding?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CCl₄
🔵 ④ SiH₄
🟢 Answer: ② NH₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 10
Which molecule is paramagnetic according to MOT?
🔴 ① N₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ CO
🔵 ④ Be₂
🟢 Answer: ② O₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 11
In H₂O, the bond angle is less than that in NH₃ because:
🔴 ① O is more electronegative than N
🟢 ② Lone pair–bond pair repulsion is greater in H₂O
🟡 ③ H is less electronegative in H₂O
🔵 ④ Bond pair–bond pair repulsion dominates
🟢 Answer: ② Lone pair–bond pair repulsion is greater in H₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 12
Which of the following species is diamagnetic?
🔴 ① B₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ C₂
🔵 ④ O₂⁻
🟢 Answer: ③ C₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 13
The number of σ and π bonds in benzene are:
🔴 ① 9 σ, 3 π
🟢 ② 12 σ, 3 π
🟡 ③ 6 σ, 6 π
🔵 ④ 9 σ, 6 π
🟢 Answer: ② 12 σ, 3 π
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 14
Which of the following compounds shows resonance?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₃²⁻
🔵 ④ NH₄⁺
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₃²⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 15
Which orbital overlap gives rise to sigma bond?
🔴 ① s–s
🟢 ② s–p
🟡 ③ p–p axial
🔵 ④ All of these
🟢 Answer: ④ All of these
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 16
Bond order of CO molecule is:
🔴 ① 2
🟢 ② 2.5
🟡 ③ 3
🔵 ④ 3.5
🟢 Answer: ③ 3
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 17
Which of the following molecules has trigonal bipyramidal geometry?
🔴 ① PCl₅
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ IF₇
🔵 ④ XeF₄
🟢 Answer: ① PCl₅
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 18
The hybridisation of carbon in diamond is:
🔴 ① sp
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp³
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 19
Which molecule has bond angle 180°?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① BeCl₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 20
Which species has the shortest bond length?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁻
🟡 ③ O₂²⁻
🔵 ④ O₂⁺
🟢 Answer: ④ O₂⁺
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 21
The correct order of bond angle is:
🔴 ① NH₃ > H₂O > CH₄
🟢 ② CH₄ > NH₃ > H₂O
🟡 ③ H₂O > CH₄ > NH₃
🔵 ④ CH₄ > H₂O > NH₃
🟢 Answer: ② CH₄ > NH₃ > H₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 22
Which molecule has sp hybridisation?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② CH₄
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ① CO₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 23
Which is true about ionic bonds?
🔴 ① They are directional
🟢 ② They are non-directional
🟡 ③ They are covalent
🔵 ④ They have high covalency
🟢 Answer: ② They are non-directional
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 24
The species with bond order 2.5 is:
🔴 ① O₂⁻
🟢 ② O₂²⁻
🟡 ③ O₂
🔵 ④ N₂⁺
🟢 Answer: ① O₂⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 25
Which of the following molecules has pyramidal shape?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ① NH₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 26
Which of the following molecules has square planar geometry?
🔴 ① SF₆
🟢 ② XeF₄
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ② XeF₄
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 27
Which of the following has bond order 2?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② N₂
🟡 ③ C₂
🔵 ④ CO
🟢 Answer: ① O₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 28
Which species is paramagnetic?
🔴 ① CO
🟢 ② N₂
🟡 ③ O₂⁻
🔵 ④ Be₂
🟢 Answer: ③ O₂⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 29
Which bond has the least bond dissociation energy?
🔴 ① F₂
🟢 ② Cl₂
🟡 ③ Br₂
🔵 ④ I₂
🟢 Answer: ① F₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 30
Which molecule has bond angle 180°?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ① BeCl₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 31
In SF₆, the hybridisation of S is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp³d²
🟡 ③ sp²
🔵 ④ sp³d
🟢 Answer: ② sp³d²
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 32
Which has maximum bond angle?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ BeCl₂
🟢 Answer: ④ BeCl₂ (180°)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 33
Which of the following is not isostructural?
🔴 ① BF₃ and BCl₃
🟢 ② NH₄⁺ and CH₄
🟡 ③ XeF₂ and CO₂
🔵 ④ SF₆ and PF₅
🟢 Answer: ④ SF₆ and PF₅
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 34
The bond angle in CO₂ is:
🔴 ① 109.5°
🟢 ② 180°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 90°
🟢 Answer: ② 180°
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 35
Which molecule has maximum number of lone pairs on the central atom?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ XeF₂
🔵 ④ SF₆
🟢 Answer: ③ XeF₂ (3 lone pairs)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 36
Which bond is purely covalent?
🔴 ① NaCl
🟢 ② HCl
🟡 ③ Cl₂
🔵 ④ KBr
🟢 Answer: ③ Cl₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 37
The correct order of bond order is:
🔴 ① N₂ > O₂ > F₂
🟢 ② F₂ > O₂ > N₂
🟡 ③ O₂ > N₂ > F₂
🔵 ④ N₂ > F₂ > O₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂ > O₂ > F₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 38
Which of the following has sp³ hybridisation?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ① CH₄
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 39
Which of the following species is isoelectronic with CO₂?
🔴 ① NO₂
🟢 ② N₂O
🟡 ③ CN⁻
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ② N₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 40
Bond angle in ClF₃ is:
🔴 ① 180°
🟢 ② 109.5°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 87.5°
🟢 Answer: ④ 87.5°
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 41
Which of the following has highest bond dissociation energy?
🔴 ① N₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ F₂
🔵 ④ Cl₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 42
Which species is diamagnetic?
🔴 ① B₂
🟢 ② C₂
🟡 ③ O₂
🔵 ④ O₂⁻
🟢 Answer: ② C₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 43
Which one has sp³d³ hybridisation?
🔴 ① IF₇
🟢 ② XeF₆
🟡 ③ SF₆
🔵 ④ PCl₅
🟢 Answer: ① IF₇
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 44
Which of the following molecules has linear geometry?
🔴 ① XeF₂
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① XeF₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 45
Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ CCl₄
🟢 Answer: ① H₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 46
Which molecule has the smallest bond angle?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ② H₂O (104.5°)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 47
Which of the following species has bond order 0?
🔴 ① He₂
🟢 ② H₂
🟡 ③ Li₂
🔵 ④ Be₂
🟢 Answer: ① He₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 48
Which is the correct order of increasing bond length?
🔴 ① N₂ < O₂ < F₂
🟢 ② F₂ < O₂ < N₂
🟡 ③ O₂ < N₂ < F₂
🔵 ④ N₂ < F₂ < O₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂ < O₂ < F₂
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 49
In NO₃⁻ ion, the formal charge on each oxygen atom is:
🔴 ① –1/3
🟢 ② –2/3
🟡 ③ –1
🔵 ④ 0
🟢 Answer: ① –1/3
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 50
Which of the following has the maximum number of lone pairs on central atom?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ XeF₆
🔵 ④ SF₆
🟢 Answer: ③ XeF₆ (1 lone pair on Xe)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following molecules has zero dipole moment?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ BF₃
🔵 ④ CHCl₃
🟢 Answer: ③ BF₃
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following species is isoelectronic with CO₂?
🔴 ① NO₂
🟢 ② N₂O
🟡 ③ SO₂
🔵 ④ O₃
🟢 Answer: ② N₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 3:
Among the following, which has the highest bond order?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁺
🟡 ③ O₂⁻
🔵 ④ O₂²⁻
🟢 Answer: ② O₂⁺
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 4:
Which one of the following has sp³d hybridization?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② PCl₅
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ② PCl₅
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following has a bond angle less than 109.5°?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ Both ② and ③
🟢 Answer: ④ Both ② and ③
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 6:
Which of the following molecules is not linear?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② CO₂
🟡 ③ SO₂
🔵 ④ HCN
🟢 Answer: ③ SO₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 7:
The bond order of N₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① 2
🟢 ② 3
🟡 ③ 1
🔵 ④ 2.5
🟢 Answer: ② 3
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 8:
Which of the following molecules has the smallest bond angle?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ① H₂O
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 9:
The correct order of bond dissociation energy is:
🔴 ① N₂ > O₂ > F₂
🟢 ② O₂ > N₂ > F₂
🟡 ③ F₂ > O₂ > N₂
🔵 ④ O₂ > F₂ > N₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂ > O₂ > F₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 10:
In SO₂ molecule, the shape is:
🔴 ① Linear
🟢 ② Angular (bent)
🟡 ③ Tetrahedral
🔵 ④ Trigonal planar
🟢 Answer: ② Angular (bent)
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 11:
Which one of the following has π and σ bonds?
🔴 ① H₂
🟢 ② N₂
🟡 ③ O₂
🔵 ④ Both ② and ③
🟢 Answer: ④ Both N₂ and O₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 12:
Which of the following statements is correct regarding resonance?
🔴 ① Resonance increases the energy of the molecule
🟢 ② Resonance decreases the stability of molecule
🟡 ③ Resonance hybrid has lower energy than canonical forms
🔵 ④ Resonance involves actual shifting of atoms
🟢 Answer: ③ Resonance hybrid has lower energy than canonical forms
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 13:
The bond angle in NH₃ is:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 107°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 109.5°
🟢 Answer: ② 107°
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 14:
The molecule with square planar geometry is:
🔴 ① XeF₄
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① XeF₄
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 15:
Which of the following species has the maximum bond order?
🔴 ① C₂
🟢 ② C₂⁺
🟡 ③ C₂⁻
🔵 ④ CO
🟢 Answer: ④ CO
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 16:
The bond angle of CO₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① 120°
🟢 ② 180°
🟡 ③ 109.5°
🔵 ④ 90°
🟢 Answer: ② 180°
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2008 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 17:
The hybridization of central atom in NH₃ molecule is:
🔴 ① sp
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp³
🔵 ④ sp³d
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 18:
Which of the following molecules is expected to show resonance?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② O₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ② O₃
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 19:
Which of the following has bond order equal to 2.5?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁻
🟡 ③ O₂²⁻
🔵 ④ O₂⁺
🟢 Answer: ② O₂⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 20:
Which molecule is linear according to VSEPR theory?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② SO₂
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ① BeCl₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 21:
Which among the following molecules contains both ionic and covalent bonds?
🔴 ① NaCl
🟢 ② NH₄Cl
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ② NH₄Cl
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 22:
In PCl₅ molecule, the axial bonds are longer than the equatorial bonds because:
🔴 ① Axial bonds involve d-orbitals
🟢 ② Axial bonds experience more repulsion
🟡 ③ Axial bonds are formed later
🔵 ④ Equatorial bonds are weaker
🟢 Answer: ② Axial bonds experience more repulsion
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 23:
Which molecule has a bond angle of exactly 120°?
🔴 ① BF₃
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ① BF₃
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 24:
Which of the following species is paramagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁻
🟡 ③ CO
🔵 ④ N₂
🟢 Answer: ① O₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 25:
Which of the following has sp² hybridization?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② C₂H₄
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ C₂H₂
🟢 Answer: ② C₂H₄
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following molecules is non-polar?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 27:
The bond angle in CH₄ molecule is:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 109.5°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 180°
🟢 Answer: ② 109.5°
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 28:
Which among the following molecules has dsp² hybridization?
🔴 ① XeF₂
🟢 ② [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ SF₆
🟢 Answer: ② [Ni(CN)₄]²⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 29:
The correct order of bond length is:
🔴 ① N≡N < N=N < N–N
🟢 ② N–N < N=N < N≡N
🟡 ③ N=N < N–N < N≡N
🔵 ④ N≡N < N–N < N=N
🟢 Answer: ① N≡N < N=N < N–N
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 30:
Which of the following species is diamagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂²⁻
🟡 ③ B₂
🔵 ④ C₂
🟢 Answer: ② O₂²⁻
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 31:
Which one of the following molecules is linear?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② BeCl₂
🟡 ③ SO₂
🔵 ④ NH₃
🟢 Answer: ② BeCl₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 32:
The number of π-bonds in benzene is:
🔴 ① 3
🟢 ② 6
🟡 ③ 9
🔵 ④ 12
🟢 Answer: ① 3
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 33:
Which of the following molecules contains coordinate bond?
🔴 ① NH₄⁺
🟢 ② CH₄
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CO₂
🟢 Answer: ① NH₄⁺
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 34:
The bond angle in sp hybridized molecules is:
🔴 ① 120°
🟢 ② 180°
🟡 ③ 109.5°
🔵 ④ 90°
🟢 Answer: ② 180°
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
The concept of octet rule was first introduced by:
🔴 ① Kossel and Lewis
🟢 ② Mendeleev
🟡 ③ Moseley
🔵 ④ Dalton
🟢 Answer: ① Kossel and Lewis
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 2:
Which type of bond is formed by complete transfer of electrons?
🔴 ① Covalent bond
🟢 ② Ionic bond
🟡 ③ Metallic bond
🔵 ④ Hydrogen bond
🟢 Answer: ② Ionic bond
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 3:
Which of the following is a polar covalent molecule?
🔴 ① H₂
🟢 ② HCl
🟡 ③ O₂
🔵 ④ Cl₂
🟢 Answer: ② HCl
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 4:
Which bond is directional in nature?
🔴 ① Ionic bond
🟢 ② Covalent bond
🟡 ③ Metallic bond
🔵 ④ Vander Waals bond
🟢 Answer: ② Covalent bond
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 5:
The bond present in NH₄⁺ ion is:
🔴 ① Covalent and coordinate
🟢 ② Only covalent
🟡 ③ Only ionic
🔵 ④ Metallic
🟢 Answer: ① Covalent and coordinate
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 6:
VSEPR theory is used to predict:
🔴 ① Bond energy
🟢 ② Molecular shape
🟡 ③ Hybridization
🔵 ④ Bond polarity
🟢 Answer: ② Molecular shape
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 7:
Which of the following molecules has linear shape?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② BeCl₂
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ SO₂
🟢 Answer: ② BeCl₂
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 8:
The bond angle in methane (CH₄) is:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 109.5°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 180°
🟢 Answer: ② 109.5°
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 9:
Which of the following contains sp² hybridisation?
🔴 ① Ethyne
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Methane
🔵 ④ Ammonia
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 10:
Number of lone pairs in NH₃ is:
🔴 ① 0
🟢 ② 1
🟡 ③ 2
🔵 ④ 3
🟢 Answer: ② 1
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 11:
Which type of bond exists in metallic crystals?
🔴 ① Ionic
🟢 ② Covalent
🟡 ③ Metallic
🔵 ④ Vander Waals
🟢 Answer: ③ Metallic
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 12:
Which molecule has a pyramidal structure?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② NH₃
🟡 ③ BF₃
🔵 ④ BeCl₂
🟢 Answer: ② NH₃
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following bonds is the strongest?
🔴 ① σ bond
🟢 ② π bond
🟡 ③ Hydrogen bond
🔵 ④ Vander Waals bond
🟢 Answer: ① σ bond
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 14:
Which of the following molecules does not obey the octet rule?
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ H₂O
🟢 Answer: ② BF₃
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 15:
The geometry of CO₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① Linear
🟢 ② Bent
🟡 ③ Trigonal planar
🔵 ④ Tetrahedral
🟢 Answer: ① Linear
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 16:
Hybridisation in NH₄⁺ ion is:
🔴 ① sp²
🟢 ② sp³
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ② sp³
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 17:
The shape of SF₆ molecule is:
🔴 ① Square planar
🟢 ② Octahedral
🟡 ③ Tetrahedral
🔵 ④ Trigonal bipyramidal
🟢 Answer: ② Octahedral
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 18:
Bond order of N₂ molecule is:
🔴 ① 2
🟢 ② 3
🟡 ③ 1
🔵 ④ 4
🟢 Answer: ② 3
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 19:
Which molecule is non-polar despite having polar bonds?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ HF
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₂
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 20:
In VSEPR theory, a double bond is counted as:
🔴 ① One region of electron density
🟢 ② Two regions of electron density
🟡 ③ Three regions of electron density
🔵 ④ Four regions of electron density
🟢 Answer: ① One region of electron density
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 21:
The bond angle in water molecule is approximately:
🔴 ① 90°
🟢 ② 104.5°
🟡 ③ 120°
🔵 ④ 109.5°
🟢 Answer: ② 104.5°
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 22:
Which rule is violated in the ground state of oxygen molecule?
🔴 ① Pauli exclusion principle
🟢 ② Hund’s rule
🟡 ③ Aufbau principle
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ④ None
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 23:
In which of the following molecules does back-bonding occur?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② BF₃
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ② BF₃
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 24:
Which of the following has the shortest bond length?
🔴 ① N₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ F₂
🔵 ④ Cl₂
🟢 Answer: ① N₂
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 25:
Which of the following molecules has sp³d hybridisation?
🔴 ① PCl₅
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ CH₄
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ① PCl₅
🔵 Question 26:
Which molecule has bond angle greater than 109.5°?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② CH₄
🟡 ③ H₂O
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ④ BF₃
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 27:
The correct order of bond strength is:
🔴 ① σ < π
🟢 ② π < σ
🟡 ③ σ = π
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ② π < σ
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 28:
Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ NF₃
🟢 Answer: ③ CO₂
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 29:
Bond order of O₂⁻ ion is:
🔴 ① 1.5
🟢 ② 2.0
🟡 ③ 2.5
🔵 ④ 3.0
🟢 Answer: ③ 2.5
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 30:
Which molecule does not exist according to MOT?
🔴 ① He₂
🟢 ② H₂
🟡 ③ Li₂
🔵 ④ O₂
🟢 Answer: ① He₂
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 31:
Which has the maximum bond angle?
🔴 ① NH₃
🟢 ② H₂O
🟡 ③ BeCl₂
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ③ BeCl₂
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 32:
Hybridisation of central atom in XeF₄ is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp³d
🟡 ③ sp³d²
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³d²
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 33:
Which of the following is paramagnetic?
🔴 ① N₂
🟢 ② O₂
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ H₂O
🟢 Answer: ② O₂
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 34:
Which bond has the highest percentage ionic character?
🔴 ① H–F
🟢 ② H–Cl
🟡 ③ H–Br
🔵 ④ H–I
🟢 Answer: ① H–F
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 35:
Which of the following molecules shows sp hybridisation?
🔴 ① BeCl₂
🟢 ② C₂H₂
🟡 ③ CO₂
🔵 ④ All of these
🟢 Answer: ④ All of these
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 36:
Which statement about resonance is correct?
🔴 ① Resonance structures are real
🟢 ② Resonance hybrid is more stable than any single structure
🟡 ③ Resonance is imaginary and has no real effect
🔵 ④ Resonance decreases stability
🟢 Answer: ② Resonance hybrid is more stable than any single structure
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 37:
Among SO₂, CO₂, and H₂O, which molecule(s) are bent?
🔴 ① Only SO₂
🟢 ② SO₂ and H₂O
🟡 ③ CO₂ and H₂O
🔵 ④ All three
🟢 Answer: ② SO₂ and H₂O
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 38:
Which of the following has maximum bond order?
🔴 ① O₂⁻
🟢 ② O₂²⁻
🟡 ③ O₂
🔵 ④ O₂⁺
🟢 Answer: ④ O₂⁺
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 39:
The bond angle in NH₃ is less than CH₄ because:
🔴 ① Lone pair–bond pair repulsion in NH₃
🟢 ② Bond pair–bond pair repulsion in CH₄
🟡 ③ Bond length differences
🔵 ④ Hydrogen bonding in NH₃
🟢 Answer: ① Lone pair–bond pair repulsion in NH₃
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 40:
Which of the following statements is true?
🔴 ① Bond order increases with increase in bond length
🟢 ② Bond order increases with increase in bond strength
🟡 ③ Bond order decreases with bond strength
🔵 ④ Bond order and bond strength are unrelated
🟢 Answer: ② Bond order increases with increase in bond strength
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🚀 Advanced-level (Q41–Q50):
🔵 Question 41:
Which species has the shortest bond length?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂⁻
🟡 ③ O₂²⁻
🔵 ④ O₂⁺
🟢 Answer: ④ O₂⁺
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 42:
What is the hybridisation of central atom in IF₇?
🔴 ① sp³d
🟢 ② sp³d²
🟡 ③ sp³d³
🔵 ④ dsp³
🟢 Answer: ③ sp³d³
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 43:
Among CO, CN⁻, and NO⁺, the species with highest bond order is:
🔴 ① CO
🟢 ② CN⁻
🟡 ③ NO⁺
🔵 ④ All equal
🟢 Answer: ③ NO⁺
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 44:
Which molecule cannot be explained by Lewis theory but is explained by MOT?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② HCl
🟡 ③ NH₃
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① O₂
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 45:
What is the structure of ClF₃ molecule?
🔴 ① Linear
🟢 ② T-shaped
🟡 ③ Square planar
🔵 ④ Trigonal bipyramidal
🟢 Answer: ② T-shaped
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 46:
In NO₃⁻ ion, all N–O bond lengths are equal due to:
🔴 ① Hydrogen bonding
🟢 ② Resonance
🟡 ③ Ionic nature
🔵 ④ Hybridisation
🟢 Answer: ② Resonance
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 47:
Which of the following molecules is diamagnetic?
🔴 ① O₂
🟢 ② O₂²⁻
🟡 ③ O₂⁺
🔵 ④ B₂
🟢 Answer: ② O₂²⁻
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 48:
Which molecule shows dsp² hybridisation?
🔴 ① Ni(CN)₄²⁻
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ CH₄
🟢 Answer: ① Ni(CN)₄²⁻
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 49:
In PF₅, the axial bonds are longer than equatorial bonds due to:
🔴 ① Back bonding
🟢 ② Bond pair–bond pair repulsion
🟡 ③ Lone pair–bond pair repulsion
🔵 ④ Different electronegativity
🟢 Answer: ② Bond pair–bond pair repulsion
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 50:
Which of the following molecules has square planar geometry?
🔴 ① XeF₄
🟢 ② SF₆
🟡 ③ PCl₅
🔵 ④ BF₃
🟢 Answer: ① XeF₄
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
