Class 9 : Social Science (In English) – Lesson 6. What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
Introduction:
This chapter introduces the concept of democracy, its key features, and why it is considered the most preferred form of government today. It answers two fundamental questions:
What is democracy? – the meaning and features of a democratic government.
Why democracy? – the need for democracy and why it is better than other forms of government.
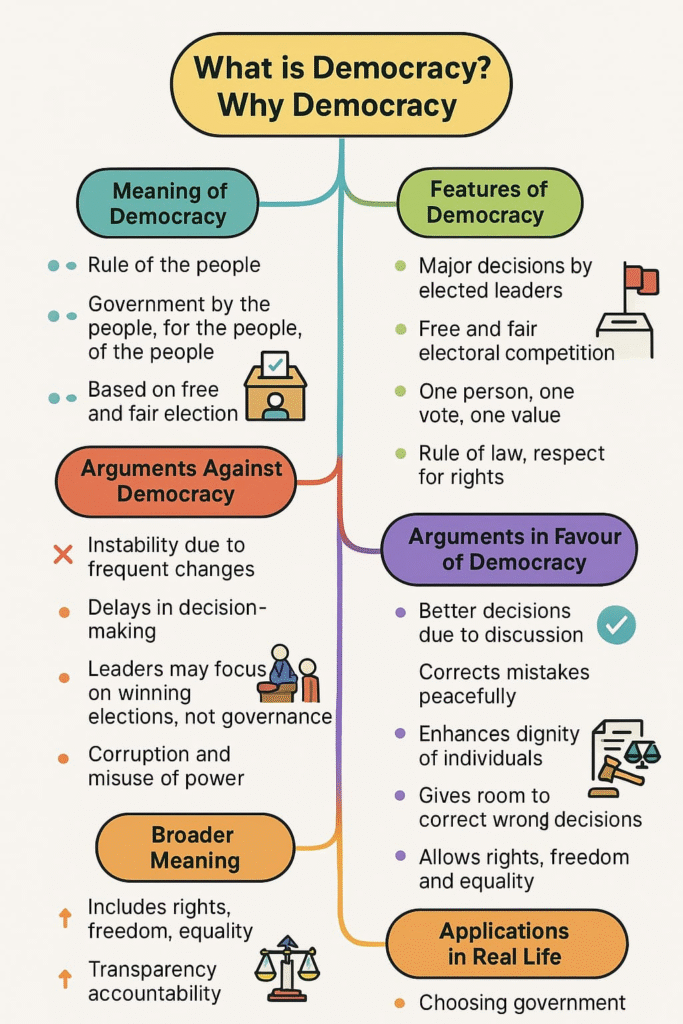
What is Democracy?
Democracy is a form of government where:
The rulers are elected by the people.
The final decision-making power rests with those elected by the people.
Simple Definition:
“Democracy is a government of the people, by the people, and for the people.”
Features of Democracy:
Let’s understand the main features of democracy one by one:
(i) Major decisions by elected leaders:
In a democracy, only elected leaders take all major decisions.
Example: In Pakistan under General Pervez Musharraf (2001), major decisions were taken by the army general, not by elected representatives. Hence, it was not a true democracy.
(ii) Free and fair electoral competition:
In a democracy, elections must offer real choice to the people.
Elections should be free (without force) and fair (equal chance to all candidates).
Example: In China, elections are held, but only the Communist Party can contest. Hence, no real choice.
(iii) One person, one vote, one value:
Every adult citizen has one vote, and each vote has equal value.
This principle is called universal adult franchise.
Exceptions: In some countries, voting rights are denied to certain ethnic groups or women.
(iv) Rule of law and respect for rights:
A democratic government functions within constitutional limits.
Citizens enjoy fundamental rights like freedom of speech, religion, and equality.
Rule of law is followed: No one is above the law.
Why Democracy? (Arguments in favour of Democracy)
Democracy is not perfect, but it is considered better than other forms of government. Here are the main reasons:
(i) Accountable and Responsive Government:
Democratic governments are elected by the people.
They have to answer to the people, especially during elections.
They can be removed if they don’t perform well.
(ii) Transparency:
In a democracy, citizens have the right to information (RTI).
Decisions are taken through proper procedures and public discussion.
(iii) Equality and Dignity:
Democracy promotes equality among all citizens.
It respects every individual’s dignity and freedom.
Discrimination based on caste, religion, or gender is opposed.
(iv) Corrects Its Own Mistakes:
In a democracy, if the government makes a mistake, it can be corrected through debate, elections, and public pressure.
Non-democratic governments may suppress opposition.
(v) Enhances Citizen Participation:
People take part in elections, rallies, debates, etc.
Citizens feel responsible and involved in the decision-making process.
Broader Meaning of Democracy:
Democracy is not just about elections. It also means:
Having a democratic society, where all people are treated equally.
Respect for diversity, tolerance, and non-violence.
Democratic decision-making in schools, families, and other institutions.
Misconceptions about Democracy:
Is democracy only about elections?
No. Democracy is not just holding elections. It also means:
Elections must be free and fair.
People should have real power to change their leaders.
Is any government elected by people democratic?
No. A government is democratic only if it respects basic democratic principles such as:
Political equality
Rule of law
Protection of rights
Freedom of expression
Limitations of Democracy:
Though democracy is the best form of government, it has some limitations:
Decision-making is slow due to discussions and debates.
Sometimes elected leaders may not fulfill promises.
Democracy does not guarantee economic development.
Political competition may lead to division and conflict.
Yet, democracy is the only form of government that allows peaceful correction and improvement.
Conclusion:
Democracy is much more than just a way to elect leaders. It is about ensuring:
Freedom, equality, and participation for all citizens.
A system where the government is answerable to the people.
People enjoy rights and freedoms, and can choose or remove their representatives.
While democracy may have flaws, it is still the most preferred and fair form of government, as it encourages peaceful participation, correction of mistakes, and respect for human dignity.
Key Terms to Remember:
Democracy
Free and fair elections
Universal adult franchise
Rule of law
Dignity and equality
Political rights
Accountable government
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Question 1
Here is some information about four countries. Based on this information, how would you classify each of these countries. Write ‘democratic’, ‘undemocratic’ or ‘not sure’ against each of these.
a) Country A: People who do not accept the country’s official religion do not have a right to vote.
b) Country B: The same party has been winning elections for the last twenty years.
c) Country C: Ruling party has lost in the last three elections.
d) Country D: There is no independent election commission.
Answer:
Country A: Undemocratic (Religious discrimination in voting rights violates democratic principles)
Country B: Not sure (Could be democratic if elections are free and fair)
Country C: Democratic (Peaceful transfer of power indicates healthy democracy)
Country D: Undemocratic (Independent election commission is essential for fair elections)
Question 2
Here is some information about four countries. Based on this information, how would you classify each of these countries. Write ‘democratic’, ‘undemocratic’ or ‘not sure’ against each of these.
a) Country P: The parliament cannot pass a law about the army without the consent of the Chief of Army.
b) Country Q: The parliament cannot pass a law reducing the powers of the judiciary.
c) Country R: The country’s leaders cannot sign any treaty with another country without taking permission from its neighbouring country.
d) Country S: All the major economic decisions about the country are taken by officials of the central bank which the ministers cannot change.
Answer:
Country P: Undemocratic (Military interference in civilian governance)
Country Q: Democratic (Judicial independence is a democratic feature)
Country R: Undemocratic (External control over sovereignty)
Country S: Undemocratic (Unelected officials making major decisions)
Question 3
Which of these is not a good argument in favour of democracy? Why?
a) People feel free and equal in a democracy.
b) Democracies resolve conflict in a better way than others.
c) Democratic government is more accountable to the people.
d) Democracies are more prosperous than others.
Answer:
Option (d) is not a good argument. Democracy does not guarantee economic prosperity. Many democratic countries face poverty and economic challenges, while some non-democratic countries may be economically prosperous. Democracy’s strength lies in political equality, accountability, and peaceful conflict resolution, not necessarily economic outcomes.
Question 4
Each of these statements contains a democratic and an undemocratic element. Write out the two separately for each statement.
a) A minister said that some laws have to be passed by the parliament in order to conform to the regulations decided by the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
b) The Election Commission ordered re-polling in a constituency where large-scale rigging was reported.
c) Women’s representation in the parliament has barely reached 10 per cent. This led women’s organisations to demand one-third seats for women.
Answer:
a) Democratic element: Laws being passed by parliament (elected representatives making decisions)
Undemocratic element: External pressure from WTO limiting parliamentary autonomy
b) Democratic element: Election Commission ensuring free and fair elections
Undemocratic element: Occurrence of large-scale rigging
c) Democratic element: Women’s organisations demanding representation through democratic means
Undemocratic element: Severe under-representation of women in parliament
Question 5
Which of these is not a valid reason for arguing that there is a lesser possibility of famine in a democratic country?
a) Opposition parties can draw attention to hunger and starvation.
b) Free press can report suffering from famine in different parts of the country.
c) Government fears its defeat in the next elections.
d) People are free to believe in and practise any religion.
Answer:
Option (d) is not a valid reason. Religious freedom has no direct connection to preventing famines. The other options relate to democratic mechanisms that help prevent famines through accountability, transparency, and political pressure.
Question 6
There are 40 villages in a district where the government has made no provision for drinking water. These villagers met and considered many methods of forcing the government to respond to their need. Which of these is not a democratic method?
a) Filing a case in the courts claiming that water is part of right to life.
b) Boycotting the next elections to give a message to all parties.
c) Organising public meetings against government’s policies.
d) Paying money to government officials to get water.
Answer:
Option (d) is not a democratic method. Paying bribes to government officials is corruption and goes against democratic principles. The other options represent legitimate democratic ways to seek redress.
Question 7
Write a response to the following arguments against democracy:
a) Army is the most disciplined and corruption-free organisation in the country. Therefore army should rule the country.
b) Rule of the majority means the rule of ignorant people. What we need is the rule of the wise, even if they are in small numbers.
c) If we want religious leaders to guide us in spiritual matters, why not invite them to guide us in politics as well. The country should be ruled by religious leaders.
Answer:
a) Military rule lacks accountability to the people. Democracy ensures that rulers are answerable to citizens through elections. Military training doesn’t necessarily qualify someone for civilian governance, which requires different skills and understanding of diverse social needs.
b) Democracy is not just majority rule but includes protection of minority rights. The “wise” ruling class concept is subjective and can lead to elitism. Democracy ensures that all citizens have equal political rights regardless of their educational background.
c) Religious leadership mixes temporal and spiritual authority, which can lead to discrimination against people of different faiths. Democracy ensures separation of religion and politics, protecting citizens’ freedom of belief and equality before law.
Question 8
Are the following statements in keeping with democracy as a value? Why?
a) Father to daughter: I don’t want to hear your opinion about your marriage. In our family children marry where the parents tell them to.
b) Teacher to student: Don’t disturb my concentration by asking me questions in the classroom.
c) Employee to the officer: Our working hours must be reduced according to the law.
Answer:
a) Not democratic – Denies the daughter’s right to participate in decisions affecting her life. Democratic values emphasize consultation and consent of all affected parties.
b) Not democratic – Discourages questioning and discussion, which are essential for democratic dialogue. Democratic classrooms should encourage student participation.
c) Democratic – Appeals to established laws and procedures, representing legitimate democratic demand for workers’ rights within legal framework.
Question 9
Consider the following facts about a country and decide if you would call it a democracy. Give reasons to support your decision.
All the citizens of the country have right to vote. Elections are held regularly.
The country took loan from international agencies. One of the conditions for giving loan was that the government would reduce its expenses on education and health.
People speak more than seven languages but education is available only in one language, the language spoken by 52 percent people of that country.
Several organisations have given a call for peaceful demonstrations and nation wide strikes in the country to oppose these policies. Government has arrested these leaders.
The government owns the radio and television in the country. All the newspapers have to get permission from the government to publish any news about government’s policies and protests.
Answer:
This country cannot be called a truly democratic despite having elections. While it has democratic elements (universal suffrage, regular elections), it lacks several essential democratic features:
Limited autonomy: External agencies dictating domestic policies
Discrimination: Language policy discriminates against linguistic minorities
Suppression of dissent: Arrest of peaceful protesters violates democratic rights
Lack of press freedom: Government control over media restricts free flow of information
A democracy requires not just elections but also protection of rights, press freedom, and space for political opposition.
Question 10
In 2004 a report published in USA pointed to the increasing inequalities in that country. Inequalities in income reflected in the participation of people in democracy. It also shaped their abilities to influence the decisions taken by the government. The report highlighted that:
If an average Black family earns $100 then the income of average White family is $162. A White family has twelve times more wealth than the average Black family.
In a President’s election ‘nearly 9 out of 10 individuals in families with income over $75,000 have voted. These people are the top 20% of the population in terms of their income. On the other hand only 5 people out of 10 from families with income less than $15,000 have voted. They are the bottom 20% of the population in terms of their income.
About 95% contribution to the political parties comes from the rich. This gives them opportunity to express their opinions and concerns, which is not available to most citizens.
As poor sections participate less in politics, the government does not listen to their concerns – coming out of poverty, getting job, education, health care and housing for them. Politicians hear most regularly about the concerns of business persons and the rich.
11. Write an essay on ‘Democracy and Poverty’ using the information given in this report but using examples from India.
Answer:
Democracy and Poverty: The Indian Context
The relationship between democracy and poverty presents a complex challenge in India, similar to the patterns observed in the United States. Despite being the world’s largest democracy, India faces significant economic inequalities that impact democratic participation and representation.
Income Inequality and Political Participation
In India, economic disparities significantly influence political participation. Wealthy citizens have greater access to political processes through campaign contributions, lobbying, and personal connections with politicians. The poor, despite having voting rights, often lack resources to effectively participate in democratic processes beyond casting votes.
Electoral Participation Patterns
While India has achieved impressive voter turnout rates across economic classes, the quality of participation varies. Affluent citizens can engage in politics through multiple channels – funding campaigns, joining political parties, and influencing policy through various associations. Poor citizens primarily participate through voting, often influenced by immediate benefits or local issues rather than long-term policy considerations.
Access to Political Influence
Similar to the US pattern, wealthy Indians have disproportionate influence on policy-making. Business leaders and affluent citizens can access politicians through formal and informal networks, while the poor depend on intermediaries or mass mobilization to voice their concerns.
Government Response to Different Classes
Government policies often reflect the concerns of economically powerful sections. Issues like industrial development, tax policies, and infrastructure projects receive attention, while problems of rural poverty, unemployment, and basic services lag behind in policy priority.
Challenges and Solutions
To strengthen democracy, India needs to ensure that economic inequality doesn’t translate into political inequality. This requires campaign finance reforms, strengthening of local governance, and creating institutional mechanisms that amplify the voices of the economically disadvantaged.
Conclusion
While democracy provides the poor with formal political equality, substantive equality requires addressing economic disparities that limit effective political participation. India’s democratic success depends on ensuring that poverty doesn’t become a barrier to meaningful political engagement.
Additional Activity
The textbook also includes an activity where students are asked to follow a newspaper’s editorial page for one month and classify articles related to democracy into categories: Constitutional and legal aspects, Citizens’ rights, Electoral and party politics, and Criticism of democracy.
Key Learning Outcomes
These exercise questions help students understand:
Essential features of democracy: Free and fair elections, rule of law, protection of rights, and accountability
Democratic vs. undemocratic practices: How to identify genuine democratic governance
Challenges to democracy: Economic inequality, corruption, and external pressures
Democratic values in daily life: Application of democratic principles beyond government
Critical thinking: Analyzing real-world situations using democratic principles
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER
Part 1: Q1 to Q15
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (Q1–Q10)
Q1. Which one of the following is a feature of democracy?
(a) Rule by one person
(b) Rule by the army
(c) Rule by the people
(d) Rule by the king
Answer: (c) Rule by the people
Q2. In a democracy, who has the final decision-making power?
(a) Army
(b) Elected representatives
(c) Judges
(d) Bureaucrats
Answer: (b) Elected representatives
Q3. Which country had a military ruler named General Pervez Musharraf?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Pakistan
(c) Sri Lanka
(d) Afghanistan
Answer: (b) Pakistan
Q4. The principle of “one person, one vote, one value” is known as:
(a) Equal judiciary
(b) Universal adult franchise
(c) Hereditary rule
(d) Civil rights
Answer: (b) Universal adult franchise
Q5. Which of the following is not a condition for a democracy?
(a) Free and fair elections
(b) Respect for rights
(c) Equal voting rights
(d) Military rule
Answer: (d) Military rule
Q6. Which of the following countries does not allow free and fair elections?
(a) India
(b) Mexico
(c) China
(d) United States
Answer: (c) China
Q7. Which right is most essential for a democracy?
(a) Right to property
(b) Right to vote
(c) Right to travel
(d) Right to religion
Answer: (b) Right to vote
Q8. A democratic government is one where:
(a) The king rules
(b) The military rules
(c) The people elect their representatives
(d) The rich control power
Answer: (c) The people elect their representatives
Q9. Which one of the following statements is true for a democracy?
(a) Rulers are not accountable to the people
(b) Elections are held without any competition
(c) Citizens have the freedom to express their opinions
(d) Minorities are not considered
Answer: (c) Citizens have the freedom to express their opinions
Q10. Which of the following statements about democracy is incorrect?
(a) It is a rule of the people
(b) It promotes equality
(c) It allows a hereditary ruler to govern
(d) It respects individual freedom
Answer: (c) It allows a hereditary ruler to govern
Section B: Short Answer Type Questions (Q11–Q15)
(Answer in 30–50 words)
Q11. Define democracy in simple words.
Answer:
Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people, and the final decision-making power lies with those elected. It promotes equality, freedom, and participation.
Q12. What is meant by ‘universal adult franchise’?
Answer:
Universal adult franchise means that every adult citizen, regardless of caste, gender, or religion, has the right to vote and each vote has equal value.
Q13. Why was the rule of General Pervez Musharraf in Pakistan not democratic?
Answer:
Musharraf took power through a military coup and amended the constitution to give himself power. The people did not have real choice or free and fair elections, so it was not democratic.
Q14. Name any two democratic countries.
Answer:
Two democratic countries are:
India
United States of America
Q15. What is meant by free and fair elections?
Answer:
Free and fair elections mean that citizens can choose their leaders freely, all parties get equal chance, and there is no misuse of power or force to influence voters.
Part 2: Q16 to Q25
Section B: Short Answer Type Questions (continued)
(Answer in 30–50 words)
Q16. What is the role of the Election Commission in a democracy?
Answer:
The Election Commission conducts free and fair elections in a democracy. It ensures that the process is independent, transparent, and all parties get a fair chance to contest, thereby upholding democratic values.
Q17. What is the importance of freedom of expression in a democracy?
Answer:
Freedom of expression allows citizens to express their views, criticize the government, and demand changes. It is essential for informed decision-making and for keeping the government accountable and responsive.
Q18. How does democracy improve the quality of decision-making?
Answer:
Democracy involves discussion and debate before decisions are made. It includes multiple perspectives and reduces the chances of rash or unjust decisions, thus improving the quality of decision-making.
Q19. How does democracy promote equality among citizens?
Answer:
In a democracy, each vote has equal value, and all citizens enjoy equal political rights, regardless of caste, gender, or religion. It ensures equal participation in decision-making.
Q20. How is democracy better than other forms of government?
Answer:
Democracy is better because it allows people to choose their rulers, promotes equality, respects freedom, ensures accountability, and can correct its own mistakes through elections and public pressure.
Section C: Mid-Length Answer Type Questions (Q21–Q25)
(Answer in about 80–100 words)
Q21. Explain any three features of a democratic government.
Answer:
Three key features of democracy are:
Rule by Elected Representatives: People elect their leaders who make laws and policies.
Free and Fair Elections: All citizens have a right to vote and choose from multiple parties and candidates without fear.
Equality and Justice: Democracy ensures equal rights, equal vote value, and justice for all, regardless of background or status.
These features help create a government that is accountable, inclusive, and respectful of people’s rights.
Q22. How does democracy ensure the dignity of citizens?
Answer:
Democracy respects individual rights and freedoms, ensuring that all citizens, including women and minorities, are treated with equality and respect.
It gives people a voice in governance, allows them to challenge injustice, and ensures that the government acts responsibly and ethically.
Democracy supports the belief that every person matters, thereby upholding the dignity of each individual.
Q23. In what ways can a democratic government be accountable to its people?
Answer:
A democratic government is accountable because it is elected by the people and must justify its actions and policies.
If it fails to serve the public interest, people can question, criticize, and even remove it through elections.
Citizens can use media, protests, courts, and Right to Information (RTI) to demand transparency.
Thus, the government is constantly answerable to the public.
Q24. Why is regular election necessary in a democracy?
Answer:
Regular elections ensure that the people have the power to choose or change their leaders.
They make the government accountable and responsible, and leaders are encouraged to work for the public good.
Without regular elections, rulers may become authoritarian.
Elections are the key feature that distinguishes democracy from other forms of government.
Q25. Mention any three arguments against democracy.
Answer:
Some criticisms of democracy are:
Slow Decision-making: Due to consultation and debate, decisions take time.
Uneducated Leadership: Sometimes leaders lack proper education or ability.
Political Instability: Frequent elections and competition can lead to division and conflict.
However, despite these flaws, democracy remains the most desirable form of government.
Part 3: Q26 to Q30
Section D: Long Answer Type Questions (Detailed, Step-by-Step – 120–150 words)
Q26. Define democracy and explain any four essential features of a democratic government.
Answer:
Democracy is a form of government where the rulers are elected by the people, and the final authority lies with these elected representatives.
Key features include:
Elected Rulers:
People choose leaders through elections.
These representatives make decisions and pass laws.
Free and Fair Elections:
Elections must offer real choice.
All parties should be able to contest fairly.
Universal Adult Franchise:
Every adult citizen has the right to vote.
Each vote carries equal value.
Rule of Law and Rights:
The government must follow the Constitution.
Citizens enjoy rights like freedom of expression, equality, and protection of law.
These features ensure that democracy is representative, inclusive, and accountable.
Q27. Why is democracy considered the best form of government? Explain with four points.
Answer:
Democracy is considered the best form of government for the following reasons:
Accountability:
Leaders are answerable to the public.
If they fail, citizens can remove them through elections.
Equality:
All citizens have equal rights and vote value.
No discrimination on the basis of caste, gender, or religion.
Transparency:
Decisions are made openly.
People have the right to information about government work.
Correction of Mistakes:
Unlike dictatorships, democracies can rectify their errors through public debates and elections.
Thus, democracy provides a system where citizens participate, question, and influence governance peacefully.
Q28. How does democracy provide dignity and freedom to its citizens?
Answer:
Democracy recognizes the inherent dignity of every individual by ensuring:
Equal Rights:
Every citizen, rich or poor, man or woman, gets equal value of vote.
Legal and social equality is promoted.
Freedom of Expression:
People can express opinions, protest peacefully, and criticize the government.
Participation in Decision-Making:
Citizens are not passive subjects but active participants through elections and civic activities.
Respect for Diversity:
Minorities, women, and backward communities have voice and protection.
Even in deeply unequal societies, democracy opens up opportunities to challenge oppression, giving people a sense of empowerment and respect.
Q29. Describe the limitations of democracy. Why is it still preferred over other forms?
Answer:
Limitations of democracy include:
Slow Decision-making:
Due to debates, procedures, and consensus-building, decisions take longer.
Risk of Poor Leadership:
Elections may result in unqualified or corrupt leaders being chosen.
Political Conflicts:
Too much competition can lead to instability and division.
Despite these flaws, democracy is still preferred because:
It allows freedom and participation.
Provides peaceful methods for correcting mistakes.
Ensures equal status and accountability.
Thus, its benefits outweigh the drawbacks, making democracy the most desirable system.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————

Manish 7424877081
9784114877