Class : 9 – Science (English) : Lesson 6. Tissues
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
🌿 Introduction
🔵 A tissue is a group of similar cells performing a specific function.
🟢 In unicellular organisms → all life functions are in one cell.
🟡 In multicellular organisms → cells are organised into tissues for division of labour.
🌍 Broad categories: Plant tissues and Animal tissues.


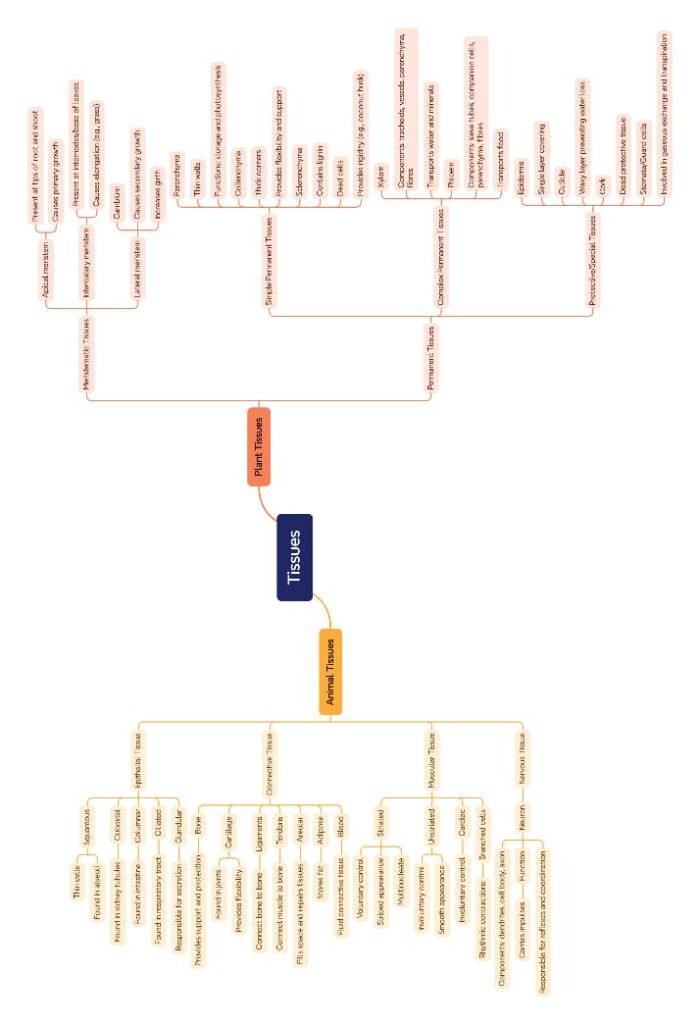
🌱 Plant Tissues
Meristematic Tissue
🔵 Made of actively dividing cells.
🟢 Features: thin walls, dense cytoplasm, large nucleus, no vacuoles.
🟡 Types:
Apical meristem: at tips of roots and shoots; increases length.
Intercalary meristem: at internodes/base of leaves; increases length.
Lateral meristem (cambium): increases girth/thickness.
Permanent Tissue
Formed when meristematic tissue loses capacity to divide and becomes specialised.
(a) Simple Permanent Tissue
🔵 Parenchyma:
Living, thin-walled, stores food.
Special type → chlorenchyma (photosynthesis), aerenchyma (air cavities in aquatic plants).
🟢 Collenchyma:
Living, elongated, unevenly thickened at corners.
Provides mechanical support and flexibility.
🟡 Sclerenchyma:
Dead, thick walls with lignin.
Provides strength, rigidity.
Example: husk of coconut, fibres.
(b) Complex Permanent Tissue
Involved in conduction of food and water.

🔴 Xylem: transports water and minerals (tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres, xylem parenchyma).
🟠 Phloem: transports food (sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, phloem parenchyma).
Protective Tissues
🟢 Epidermis: outermost layer, protects against water loss, mechanical injury.
💧 Cuticle (waxy layer) prevents water loss.
🌿 Stomata regulate gaseous exchange and transpiration.
🟡 Cork (phellem): outer layer in woody plants; protective.
🐾 Animal Tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surface and internal organs.
Functions: protection, absorption, secretion.
Types:
Squamous epithelium: flat cells (alveoli, capillaries).
Cuboidal epithelium: cube-shaped (glands, kidney tubules).
Columnar epithelium: tall cells (intestine, stomach lining).
Ciliated epithelium: columnar with cilia (respiratory tract).
Connective Tissue
Joins different body parts; supports and protects.
Types:
Bone: hard matrix of calcium salts, supports body.
Cartilage: flexible, smooth surface at joints, nose, ear.
Ligaments: connect bone to bone (elastic, strength).
Tendons: connect muscle to bone (inelastic, strong).
Areolar tissue: fills space, supports organs.
Adipose tissue: stores fat, insulates.
Blood: fluid connective tissue, transports substances.
Muscular Tissue
Responsible for movement.
Types:
Striated (voluntary, skeletal): long, cylindrical, multinucleated, shows stripes.
Unstriated (smooth, involuntary): spindle-shaped, uninucleate, walls of internal organs.
Cardiac muscle: involuntary, branched, striated, in heart.
Nervous Tissue
🧠 Made of neurons.
Components:
Cell body (cyton).
Dendrites receive signals.
Axon carries impulses away.
Function: transmits messages quickly, coordinates responses.
🟢 Summary
Tissue = group of cells specialised for a function.
Plants → Meristematic (growth), Permanent (support, conduction, protection).
Animals → Epithelial (covering), Connective (support), Muscular (movement), Nervous (coordination).
📝 Quick Recap
🌱 Meristematic → division, growth.
🌿 Permanent → parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma.
💧 Complex tissues → xylem, phloem.
🟢 Protective → epidermis, cork.
🐾 Animal tissues:
Epithelial → lining.
Connective → bone, cartilage, blood.
Muscular → striated, smooth, cardiac.
Nervous → neuron.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1
Define the term “tissue”.
Answer
🔵 Tissue is a group of similar cells that are structurally similar and perform a specific function in an organism.
Question 2
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer
🟢 Xylem consists of four types of elements:
Tracheids
Vessels
Xylem fibres
Xylem parenchyma
Question 3
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer
🔵 Simple tissues: made up of only one type of cells performing the same function (parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma).
🟢 Complex tissues: made up of more than one type of cells working together for conduction of food and water (xylem, phloem).
Question 4
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer
🌿 Parenchyma: thin-walled, living cells.
🟡 Collenchyma: cell walls thickened at corners with cellulose/pectin.
🔴 Sclerenchyma: very thick lignified walls, dead cells.
Question 5
What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer
💧 Exchange of gases (O₂, CO₂) during respiration and photosynthesis.
🌍 Loss of excess water in form of vapour (transpiration).
Question 6
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer (description)
🔵 Striated muscle: long, cylindrical, multinucleate, voluntary, alternating light and dark bands.
🟢 Unstriated muscle: spindle-shaped, uninucleate, involuntary, no bands.
🟡 Cardiac muscle: branched, striated, involuntary, found in heart.
Question 7
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer
❤️ Cardiac muscles contract and relax throughout life rhythmically, pumping blood to all body parts without fatigue.
Question 8
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer
🔵 Striated muscle: long, cylindrical, striped, multinucleate, voluntary; found in limbs.
🟢 Unstriated muscle: spindle-shaped, no stripes, uninucleate, involuntary; found in stomach, intestine, iris.
❤️ Cardiac muscle: branched, striated, involuntary, uninucleate; found in heart walls.
Question 9
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer (description)
🧠 Neuron structure:
Cell body (cyton)
Dendrites (receive impulses)
Axon (transmits impulse)
Axon terminal
Question 10
Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth → 🔵 Squamous epithelium
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans → 🟢 Tendons
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants → 🌿 Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body → 🟡 Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix → 🔴 Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain → 🧠 Nervous tissue
Question 11
Identify the type of tissue in the following:
Skin → 🔵 Epithelial tissue
Bark of tree → 🌿 Cork/protective tissue
Bone → 🟠 Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule → 🟡 Cuboidal epithelium
Vascular bundle → 🌍 Complex permanent tissue (xylem + phloem)
Question 12
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer
🌿 Parenchyma present in soft parts of plants: cortex, pith, mesophyll cells of leaves, fruits.
Question 13
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer
🟢 Protects against water loss, mechanical injury, pathogens.
💧 Has cuticle, prevents excessive transpiration.
🌿 Contains stomata for gaseous exchange.
Question 14
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer
🔴 Cork cells are dead with thick walls impregnated with suberin.
🌍 Prevents water loss, resists infection, protects from mechanical injury.
Question 15
Complete the following chart:
Permanent Tissue
Simple → Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
Complex → Xylem, Phloem
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Section A (Q1–20: MCQs, 1 mark each; Q11–20 Assertion–Reason)
Question 1
Which tissue makes up the husk of a coconut?
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Phloem
Answer: 3 🔴
Question 2
Which of the following is not a simple permanent tissue?
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Xylem
Sclerenchyma
Answer: 3 🌿
Question 3
Which connective tissue stores fat in our body?
Areolar tissue
Adipose tissue
Bone
Cartilage
Answer: 2 🟡
Question 4
Which tissue transports food in plants?
Xylem
Phloem
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Answer: 2 🌿
Question 5
Which epithelium forms the inner lining of kidney tubules?
Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Ciliated
Answer: 2 🔵
Question 6
Which tissue connects bone to bone?
Tendons
Ligaments
Cartilage
Areolar tissue
Answer: 2 🟢
Question 7
Cardiac muscles are:
Voluntary and striated
Involuntary and striated
Voluntary and unstriated
Involuntary and unstriated
Answer: 2 ❤️
Question 8
Which tissue is responsible for photosynthesis in leaves?
Aerenchyma
Chlorenchyma
Collenchyma
Xylem
Answer: 2 🌱
Question 9
Which connective tissue has a fluid matrix?
Bone
Cartilage
Blood
Ligament
Answer: 3 💧
Question 10
Which tissue is called “suicidal bags”?
Lysosomes (not tissue but organelle)
Sclerenchyma
Phloem
Xylem
Answer: 2 🔴 (because cells are dead at maturity and provide rigidity)
Question 11 (Assertion–Reason)
A: Xylem conducts water and minerals.
R: Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, xylem fibres.
Answer: 1 ✔️
Question 12
A: Phloem conducts food.
R: Phloem contains sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, phloem parenchyma.
Answer: 1 🟢
Question 13
A: Collenchyma provides flexibility.
R: Its cell walls are unevenly thickened at corners.
Answer: 1 🟡
Question 14
A: Parenchyma is always dead tissue.
R: It stores food and water.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Parenchyma is living)
Question 15
A: Ligaments connect bone to bone.
R: Tendons connect muscle to bone.
Answer: 1 🟢
Question 16
A: Striated muscles are involuntary.
R: They are found in limbs.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Striated = voluntary)
Question 17
A: Cartilage is soft connective tissue.
R: Found in nose, ear, trachea.
Answer: 1 🟡
Question 18
A: Nervous tissue transmits messages.
R: Neurons consist of axon, dendrites, cell body.
Answer: 1 🧠
Question 19
A: Cork is protective tissue in plants.
R: Cork cells are living and have suberin.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Cork cells are dead)
Question 20
A: Areolar tissue fills spaces between organs.
R: It also supports internal organs.
Answer: 1 🌍
🟢 Section B (Q21–26: Very Short Answers, 2 marks)
Question 21
Define tissue.
Answer:
A group of similar cells organised to perform a specific function.
Question 22
Name two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
Xylem, Phloem.
Question 23
Which tissue provides mechanical support in plants and allows bending?
Answer:
Collenchyma.
Question 24
What is the role of adipose tissue?
Answer:
Stores fat, provides insulation, cushions organs.
Question 25
Name two voluntary and two involuntary muscles.
Answer:
Voluntary: muscles of limbs, face.
Involuntary: muscles of stomach, cardiac muscles.
Question 26
What is the structural and functional unit of nervous tissue?
Answer:
Neuron.
🟡 Section C (Q27–33: Short Answers, 3 marks)
Question 27
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma (any three points).
Answer:
Parenchyma: living, thin-walled, stores food.
Collenchyma: living, thickened corners, flexibility.
Sclerenchyma: dead, thick lignified walls, rigidity.
Question 28
Explain functions of xylem and phloem.
Answer:
Xylem: conducts water/minerals from roots to aerial parts.
Phloem: transports food from leaves to rest of plant.
Question 29
Give two functions of epithelial tissue.
Answer:
Protection of underlying tissues.
Absorption and secretion.
Question 30
Differentiate between ligaments and tendons.
Answer:
Ligaments: connect bone to bone, elastic.
Tendons: connect muscle to bone, strong, inelastic.
Question 31
Explain role of stomata in plants.
Answer:
Exchange of gases.
Control of transpiration.
Question 32
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles.
Answer:
Striated: voluntary, striped, multinucleate.
Unstriated: involuntary, spindle-shaped, no stripes.
Cardiac: branched, involuntary, striated.
Question 33
State two functions of blood.
Answer:
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones.
Removes carbon dioxide, waste.
🔴 Section D (Q34–36: Long Answers, 5 marks)
Question 34
Describe structure and function of neuron.
Answer:
Cell body (cyton) with nucleus.
Dendrites receive impulses.
Axon carries impulses away.
Nerve endings transmit signals to next cell.
Function: communication and coordination.
Question 35
Explain protective tissues in plants.
Answer:
Epidermis: outer layer, prevents water loss, mechanical injury.
Stomata: exchange of gases, transpiration.
Cork: dead cells with suberin, waterproof and protective.
Question 36
Describe connective tissues in animals with examples.
Answer:
Bone: rigid support.
Cartilage: flexible support.
Ligaments: bone to bone.
Tendons: muscle to bone.
Adipose: stores fat.
Blood: transports materials.
🟣 Section E (Q37–39: Case-Based, 4 marks)
Question 37
Case: A student observed onion peel cells with lignified thick walls.
(a) Which tissue was observed?
(b) Living or dead?
(c) Function of tissue?
(d) Give another example.
Answer:
(a) Sclerenchyma.
(b) Dead.
(c) Provides strength and rigidity.
(d) Husk of coconut.
Question 38
Case: A patient suffers a fracture and swelling in joints.
(a) Which connective tissues are involved?
(b) Function of bone?
(c) Function of cartilage?
(d) Why is healing slow in cartilage?
Answer:
(a) Bone and cartilage.
(b) Provides support and shape.
(c) Smoothens joint surface, flexibility.
(d) Limited blood supply.
Question 39
Case: In an experiment, water moves from soil into root xylem.
(a) Which tissue conducts water?
(b) Name its two conducting elements.
(c) What if xylem vessels are blocked?
(d) Name tissue transporting food.
Answer:
(a) Xylem.
(b) Tracheids, vessels.
(c) Plant wilts due to no water supply.
(d) Phloem.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
