Class : 9 – Science (English) : Lesson 5. The Fundamental Unit of Life
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation

🌟 Introduction to Cell
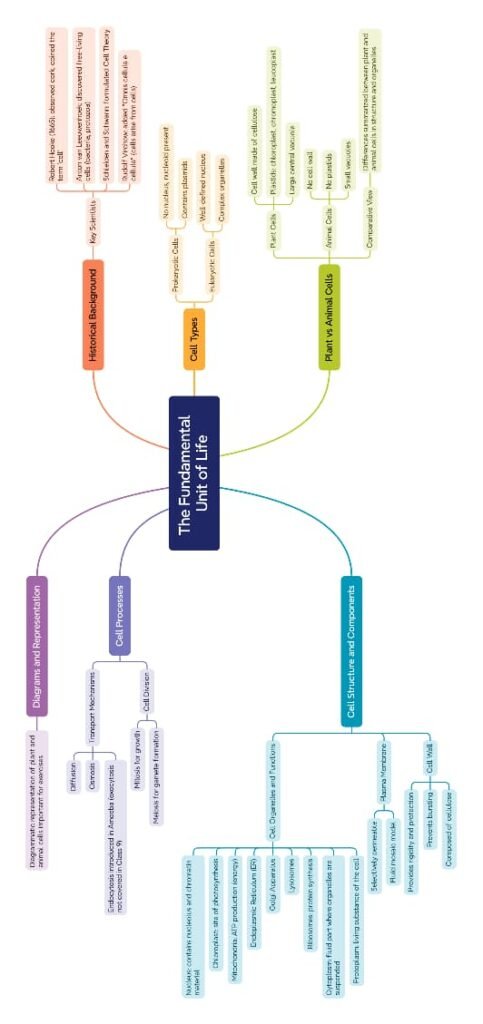
🔵 The cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
🟢 All living organisms are made up of cells.
🟡 The study of cells is called Cytology.
🌍 Discovery:
Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork cells using a simple microscope.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek first saw free-living cells (bacteria).
Schleiden and Schwann → Cell theory: All living beings are made of cells and cell is the basic unit of life.
Virchow → “Cells arise from pre-existing cells.”

🌿 Characteristics of Cells
🔵 Cells are microscopic but vary in shape and size.
🟢 Shapes: spherical (WBC), spindle-shaped (muscle cells), rectangular (plant cells), long thread-like (nerve cells).
🟡 Sizes: smallest (mycoplasma 0.1 µm), largest (ostrich egg).
🌍 All functions of life—nutrition, respiration, excretion—take place inside cells.
🧠 Cell Structure (Overview)
Cells are surrounded by membranes and filled with cytoplasm where organelles perform specific functions.
Main parts:
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Cell Organelles
🔴 Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane)
Thin, flexible boundary around cell.
Functions:
Controls movement of substances (selectively permeable).
Allows exchange of gases, nutrients, waste.
Transport:
🌿 Diffusion → movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
💧 Osmosis → diffusion of water through semi-permeable membrane.
Example: RBCs swell in hypotonic solution, shrink in hypertonic solution.
🟣 Cell Wall (in plants only)
Rigid outer layer made of cellulose.
Provides support, shape, protection.
Allows exchange of materials freely (permeable).
🌞 Nucleus
🟢 Control centre of cell, discovered by Robert Brown (1831).
Components:
Nuclear membrane (double, porous).
Nucleoplasm (fluid).
Chromatin (DNA + proteins, condenses into chromosomes during cell division).
Nucleolus (site of ribosome formation).
Functions: controls heredity, cell growth, division, metabolic activities.
⚡ Cytoplasm
Jelly-like substance between nucleus and membrane.
Contains organelles, enzymes, salts, water.
Site for chemical reactions and transport inside cell.
🟠 Cell Organelles
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of membranes.
Rough ER: with ribosomes → protein synthesis.
Smooth ER: lipid synthesis, detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus
Stack of membrane sacs.
Functions: modify, package, transport proteins and lipids.
Forms lysosomes.
Lysosomes
Spherical sacs with digestive enzymes.
Digest worn-out organelles, foreign materials (“suicidal bags”).
Mitochondria
Double membrane, inner folds = cristae.
Site of respiration, release energy (ATP).
Called “Powerhouse of the cell.”
Plastids (in plants only)
Three types:
Chloroplasts → green pigment (chlorophyll), photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts → coloured pigments (carotenoids).
Leucoplasts → colourless, store starch, oil, proteins.
Vacuoles
Storage sacs for food, water, wastes.
Large in plant cells (maintain turgidity), small in animal cells.
Ribosomes
Tiny, non-membranous, present on RER or free.
Site of protein synthesis.
Centrosome (in animal cells)
With centrioles, helps in cell division (spindle formation).
🌍 Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
🌿 Plant cells: cell wall, chloroplast, large vacuole, fixed shape.
🟠 Animal cells: no cell wall, no chloroplast, small vacuoles, centrosome present.
💡 Cell Division

Mitosis: Produces identical cells (growth, repair).
Meiosis: Produces gametes (half chromosome number).
🟢 Summary
Cell = structural & functional unit of life.
Plasma membrane: selectively permeable, diffusion/osmosis.
Plant cells → extra cell wall.
Nucleus → controls heredity and activities.
Cytoplasm → site of biochemical reactions.
Organelles: ER, Golgi, Lysosome, Mitochondria, Plastids, Vacuole, Ribosome, Centrosome.
Plant vs Animal cells → major differences.
Cell division → mitosis (growth), meiosis (gametes).
📝 Quick Recap
🌟 Robert Hooke → discovered cell.
⚡ Oersted → current-magnetism, Faraday → induction (other chapter).
🔵 Plasma membrane = selective, osmosis important.
🟢 Nucleus = control room.
🔴 Mitochondria = powerhouse.
🌿 Plant cells = chloroplast, wall, vacuole.
🟠 Animal cells = centrosome.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1
Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer
🌿 Plant cells:
Have cell wall of cellulose.
Contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
Have large central vacuole.
Usually have fixed shape.
🐾 Animal cells:
No cell wall.
Lack chloroplasts.
Vacuoles are small or absent.
Shape is usually irregular/flexible.
Question 2
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer
🔵 Prokaryotic:
Primitive nucleus (no nuclear membrane).
No membrane-bound organelles.
Examples: bacteria, blue-green algae.
🟢 Eukaryotic:
True nucleus with nuclear membrane.
Membrane-bound organelles (mitochondria, ER, Golgi, etc.).
Examples: plant and animal cells.
Question 3
What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer
🌍 Plasma membrane controls entry/exit of substances.
🔴 If it breaks → cell contents leak out.
🟡 Cell cannot maintain internal environment → cell dies.
Question 4
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer
🌿 Proteins and lipids could not be modified/packed/transported.
🟠 Lysosomes could not be formed.
⚡ Cell secretions would be disrupted → many functions stop.
Question 5
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer
🔴 Mitochondria.
🟢 They oxidise food and release energy in form of ATP.
⚡ ATP = energy currency of cell → used in all vital functions.
Question 6
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer
🟡 Proteins → by Ribosomes on Rough ER.
🌿 Lipids → by Smooth ER.
Question 7
How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer
🔵 Amoeba uses pseudopodia (false feet) to engulf food → phagocytosis.
🟢 Forms a food vacuole → secretes enzymes → digests food → nutrients absorbed.
Question 8
What is osmosis?
Answer
💧 Osmosis = movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from region of higher water concentration to lower concentration.
🌍 It continues until equilibrium is reached.
Question 9
Carry out the following osmosis experiment… (potato cups).
Answer
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
🟢 In cup B (sugar) and C (salt), solute solution inside → concentration difference.
💧 Water enters from surrounding trough by osmosis.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
🔵 Cup A (empty) acts as control → shows no water collects without solute difference.
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in hollowed portions of A and D.
🟢 A has no solute → no concentration gradient.
🔴 D is from boiled potato → cells dead, membrane destroyed → no osmosis possible.
Question 10
Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Answer
🌿 Mitosis → produces identical cells, needed for growth and repair.
🟡 Meiosis → produces gametes with half chromosome number, needed for sexual reproduction.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
Question 1
The control centre of a cell is:
Ribosome
Nucleus
Lysosome
Golgi apparatus
Answer: 2 🟢
Question 2
Which cell organelle is called the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Endoplasmic reticulum
Nucleus
Answer: 1 🔴
Question 3
Which of these is a single-celled organism?
Amoeba
Human
Mango tree
Fish
Answer: 1 🌿
Question 4
Who discovered the cell in 1665?
Robert Hooke
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Schleiden
Schwann
Answer: 1 🟡
Question 5
Plasma membrane is:
Permeable
Impermeable
Selectively permeable
Non-permeable
Answer: 3 💧
Question 6
Which organelle is absent in animal cells but present in plant cells?
Lysosome
Chloroplast
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Answer: 2 🌱
Question 7
Which organelle helps in packaging and secretion?
Ribosome
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
Plastids
Answer: 2 📦
Question 8
Which of the following is a prokaryotic cell?
Amoeba
Bacterium
Paramecium
Onion cell
Answer: 2 🦠
Question 9
Which organelle is called “suicidal bags”?
Nucleus
Lysosome
Ribosome
Vacuole
Answer: 2 🔴
Question 10
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
Ribosome
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Golgi
Answer: 3 🌿
Question 11 (Assertion–Reason)
A: Plasma membrane allows only selective materials to pass through.
R: It is selectively permeable.
Answer: 1 ✔️
Question 12
A: Plant cells have large vacuoles.
R: Vacuoles help in turgidity and storage.
Answer: 1 🟢
Question 13
A: Lysosomes digest worn-out organelles.
R: They contain digestive enzymes.
Answer: 1 🔴
Question 14
A: Mitochondria release energy in form of ATP.
R: They are called powerhouse of cell.
Answer: 1 ⚡
Question 15
A: Amoeba engulfs food by pseudopodia.
R: This process is called phagocytosis.
Answer: 1 🌊
Question 16
A: Nucleolus is present in cytoplasm.
R: It synthesises ribosomes.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Nucleolus is in nucleus)
Question 17
A: Golgi apparatus forms lysosomes.
R: Golgi packs and modifies proteins.
Answer: 1 📦
Question 18
A: Smooth ER helps in protein synthesis.
R: Rough ER helps in lipid synthesis.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Reverse)
Question 19
A: Plant cells have both cell wall and plasma membrane.
R: Cell wall provides rigidity, membrane controls exchange.
Answer: 1 🌱
Question 20
A: Centrosome is present in plant cells.
R: It helps in cell division.
Answer: 3 ❌ (Centrosome only in animal cells)
Question 21
Define cell theory.
Answer:
All living beings are made of cells.
Cell is the basic unit of life.
New cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Question 22
What is diffusion?
Answer:
Movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration until uniform distribution.
Question 23
Name two cell organelles with double membrane.
Answer:
Mitochondria, Chloroplast.
Question 24
What is protoplasm?
Answer:
Living content of cell including cytoplasm and nucleus.
Question 25
Why are plastids important in plant cells?
Answer:
Chloroplasts → photosynthesis.
Leucoplasts → storage.
Chromoplasts → colour to fruits/flowers.
Question 26
What is nucleoplasm?
Answer:
Jelly-like substance inside nucleus containing chromatin and nucleolus.
Question 27
Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
Prokaryotic: primitive nucleus, no organelles, small size, example bacteria.
Eukaryotic: true nucleus, organelles present, larger size, example onion cell.
Question 28
What is osmosis? Give example.
Answer:
Movement of water through semi-permeable membrane from higher water concentration to lower.
Example: Raisins swell in water.
Question 29
State three functions of nucleus.
Answer:
Controls cell activities.
Carries genetic material.
Directs cell division.
Question 30
Why is plasma membrane called selectively permeable?
Answer:
Allows some substances (oxygen, CO₂, nutrients) to pass, blocks harmful ones.
Question 31
What are ribosomes? State their function.
Answer:
Tiny non-membranous organelles.
Function: protein synthesis.
Question 32
Differentiate between plant and animal cells (two points).
Answer:
Plant: cell wall, chloroplasts, large vacuole.
Animal: no wall, no chloroplasts, small vacuole.
Question 33
What is cytoplasm? Mention its role.
Answer:
Jelly-like fluid between nucleus and membrane.
Site for biochemical reactions, contains organelles.
Question 34
Explain the structure and functions of mitochondria.
Answer:
Double membrane: outer smooth, inner folded (cristae).
Contains its own DNA and ribosomes.
Functions: respiration, release of energy (ATP), powerhouse of cell.
Question 35
Describe endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Differentiate between RER and SER.
Answer:
Network of membranes.
RER: ribosomes present → protein synthesis.
SER: no ribosomes → lipid synthesis, detoxification.
Question 36
Explain the role of Golgi apparatus.
Answer:
Stack of flattened sacs.
Modifies, packages proteins and lipids.
Forms lysosomes, secretory vesicles.
Question 37
Case: A student places raisins in water and observes swelling.
(a) Which process?
(b) What happens if placed in salt solution?
(c) Why does swelling occur?
(d) Name the membrane type.
Answer:
(a) Osmosis.
(b) Shrink (exosmosis).
(c) Water enters from high concentration outside to low inside.
(d) Semi-permeable membrane.
Question 38
Case: Onion peel under microscope with salt water.
(a) What is observed?
(b) Name the process.
(c) Why does it occur?
(d) What if peel placed back in pure water?
Answer:
(a) Cells shrink away from wall.
(b) Plasmolysis.
(c) Water moves out due to higher solute outside.
(d) Cell regains water → deplasmolysis.
Question 39
Case: In an experiment with potato cups and sugar solution, water enters cavity.
(a) Which process shown?
(b) Why water enters?
(c) Why boiled potato does not show effect?
(d) State one daily-life example.
Answer:
(a) Osmosis.
(b) Due to solute concentration difference.
(c) Dead cells, membrane destroyed.
(d) Soaking of pulses in water.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
ACRONYMS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
