Class 12 : Poltical Science (English) – Lesson 4.International Organizations
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

🔹 1. Lesson Explanation (≈ 1700 words)
🌍 Introduction
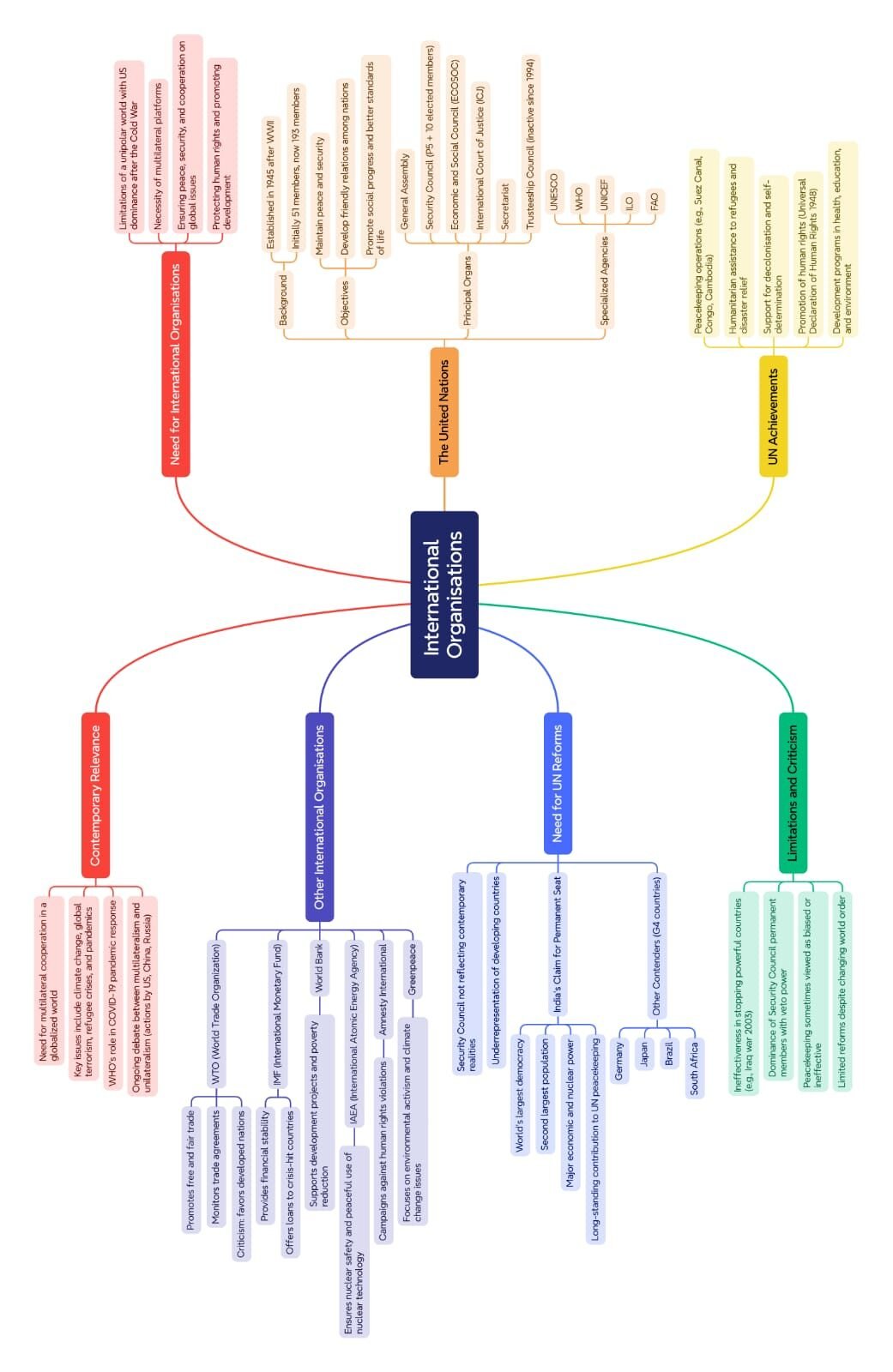
After World War II, the world recognised the need for a global institution to maintain peace, security, and cooperation. Thus, in 1945, the United Nations (UN) was founded, replacing the League of Nations.
Its purpose: prevent wars, uphold human rights, and promote development.
Over time, the UN became a platform for dialogue, peacekeeping, and global problem-solving.
🏛️ Origin and Objectives of the United Nations
📅 Founded: 24 October 1945
👥 Members at inception: 51 nations
🌏 Members today: 193
📜 Charter Objectives: 1️⃣ Maintain international peace and security
2️⃣ Develop friendly relations among nations
3️⃣ Promote human rights and social progress
4️⃣ Foster economic cooperation and development
5️⃣ Serve as a platform for dialogue and diplomacy
⚖️ Structure of the United Nations
🔸 1. General Assembly
All members; one vote each
Discusses global issues, budgets, and elects non-permanent Security Council members
Resolutions are recommendatory, not binding
🔸 2. Security Council (UNSC)
5 permanent members: 🇺🇸 USA, 🇬🇧 UK, 🇫🇷 France, 🇷🇺 Russia, 🇨🇳 China
10 non-permanent (elected for 2 years)
Responsible for peace and security
Can impose sanctions or authorise military action
Veto power of P5 often causes gridlock
🔸 3. Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Coordinates economic, social, and humanitarian activities
Supervises agencies like WHO, UNESCO, UNICEF
🔸 4. International Court of Justice (ICJ)
Located in The Hague, Netherlands
Settles legal disputes among states
🔸 5. Secretariat
Administrative arm; headed by UN Secretary-General
🔸 6. Trusteeship Council
Now inactive (after decolonisation completed)
🕊️ UN Peacekeeping Operations
Aim: maintain peace in post-conflict zones
Tasks: monitoring ceasefires, disarmament, elections, civilian protection
India is a major troop contributor
Successes: Namibia, Cambodia, Mozambique
Failures: Rwanda genocide, Bosnia conflict
🌐 Significance of the UN
1️⃣ Prevented large-scale world wars after 1945
2️⃣ Provides platform for conflict resolution
3️⃣ Promotes human rights, health, education
4️⃣ Coordinates global action on environment and development
5️⃣ Legitimises collective action (e.g. sanctions, peacekeeping)
⚠️ Criticisms and Limitations
Dominance of P5 via veto power
Inaction in many conflicts due to veto deadlocks
Underrepresentation of developing nations
Limited enforcement power
Politicisation of humanitarian decisions
💬 Need for UN Reforms
🌍 Post-1945 realities changed; power distribution shifted
Emerging powers (India, Brazil, Germany, Japan, South Africa) demand greater role
📌 Proposed Reforms: 1️⃣ Expand Security Council to include more permanent members
2️⃣ Limit or reform veto usage
3️⃣ Increase representation of Global South
4️⃣ Strengthen UN’s financial independence
🇮🇳 India’s Case for Permanent Membership
Largest democracy
Second-most populous nation
Major contributor to UN budget and peacekeeping
Rapidly growing economy
Consistent support for multilateralism
🧭 Challenges: Opposition from rivals (Pakistan), reluctance of P5 to dilute power.
🌎 Relevance of UN in Contemporary World
Despite limitations, UN remains indispensable for:
Humanitarian aid (UNICEF, WFP)
Climate initiatives (UNFCCC, COP)
Global health (WHO’s COVID-19 response)
Development goals (SDGs 2030)
🧠 Other International Organisations
🔹 1. WTO (World Trade Organization)
Established 1995
Ensures free trade and resolves trade disputes
Promotes globalisation, but criticised for favouring rich countries
🔹 2. IMF (International Monetary Fund)
Provides financial assistance to countries in crisis
Encourages macroeconomic stability
🔹 3. World Bank
Funds infrastructure and poverty reduction projects
🔹 4. G-20
Forum of major economies addressing global financial issues
🔹 5. Regional Organisations:
EU (European Union): Political and economic union in Europe
ASEAN: Promotes economic cooperation in Southeast Asia
SAARC: Regional cooperation in South Asia
AU (African Union): Pan-African solidarity
🌏 Role of International Organisations
Promote collective decision-making
Provide platform for negotiation
Manage transnational challenges (pandemics, climate, terrorism)
Support global governance
⚖️ UN and Global Conflicts
Role in resolving Korean War, Gulf Wars, Iraq, Afghanistan
Mixed record: success in peacekeeping, criticism for selectivity
Modern threats (cyberwar, climate, refugees) need stronger global coordination
🕊️ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Launched 2015 (Agenda 2030)
17 goals: no poverty, zero hunger, quality education, gender equality, climate action, etc.
UN agencies and national governments collaborate
🧭 India and the UN
Founding member
Advocate of multilateralism and peaceful coexistence
Participated in all major UN missions
Calls for UN reform and inclusive world order
🌍 Conclusion
The UN and international organisations continue to play a vital role in promoting peace, justice, and sustainable development. Though imperfect, reforming them is better than replacing them. Collective global challenges require collective global action—which only these bodies can coordinate.
🔸 2. Summary (≈ 200 words)
The United Nations was formed in 1945 to ensure peace, security, and development.
It comprises major organs like the General Assembly, Security Council, ICJ, ECOSOC, and Secretariat.
The UN has succeeded in avoiding world wars, conducting peacekeeping missions, and advancing human rights.
Yet, its effectiveness is reduced by veto power, P5 dominance, and slow reforms.
There is a strong demand to restructure the Security Council and grant permanent membership to emerging powers like India.
Other international organisations—WTO, IMF, World Bank, G-20, EU, ASEAN—assist in managing trade, finance, and regional issues.
In the 21st century, the UN remains central in tackling global concerns like climate change, terrorism, pandemics, and poverty.
Its future relevance depends on reform, inclusivity, and collective commitment to multilateralism.
🔹 3. Quick Recap (≈ 100 words)
UN Founded: 1945; Members: 193
Main Organs: GA, UNSC, ECOSOC, ICJ, Secretariat
Aims: Peace, cooperation, development
Achievements: Peacekeeping, human rights, SDGs
Limitations: Veto, inequality, slow reform
Need: Expansion of UNSC, inclusion of India
Other Organisations: WTO, IMF, WB, G-20, EU, ASEAN, SAARC
Role: Solve global issues collectively
Essence: Reform, inclusiveness, multilateral cooperation
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Mark correct or wrong against each of the following statements about the veto power.
a. Only the permanent members of the Security Council possess the veto power.
🟢 Answer: Correct
b. It’s a kind of negative power.
🟢 Answer: Correct
c. The Secretary-General uses this power when not satisfied with any decision.
🔴 Answer: Wrong
d. One veto can stall a Security Council resolution.
🟢 Answer: Correct
🔵 Question 2:
Mark correct or wrong against each of the following statements about the way the UN functions.
a. All security and peace-related issues are dealt with in the Security Council.
🟢 Answer: Correct
b. Humanitarian policies are implemented by the main organs and specialised agencies spread across the globe.
🟢 Answer: Correct
c. Having consensus among the five permanent members on security issues is vital for its implementation.
🟢 Answer: Correct
d. The members of the General Assembly are automatically the members of all other principal organs and specialised agencies of the UN.
🔴 Answer: Wrong
🔵 Question 3:
Which among the following would give more weightage to India’s proposal for permanent membership in the Security Council?
Nuclear capability
It has been a member of the UN since its inception
It is located in Asia
India’s growing economic power and stable political system
🟢 Answer: 4. India’s growing economic power and stable political system
🔵 Question 4:
The UN agency concerned with the safety and peaceful use of nuclear technology is:
a. The UN Committee on Disarmament
b. International Atomic Energy Agency
c. UN International Safeguard Committee
d. None of the above
🟢 Answer: b. International Atomic Energy Agency
🔵 Question 5:
WTO is serving as the successor to which of the following organisations?
a. General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs
b. General Arrangement on Trade and Tariffs
c. World Health Organisation
d. UN Development Programme
🟢 Answer: a. General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs
🔵 Question 6:
Fill in the blanks:
a. The prime objective of the UN is to maintain international peace and security.
b. The highest functionary of the UN is called the Secretary-General.
c. The UN Security Council has 5 permanent and 10 non-permanent members.
d. António Guterres is the present UN Secretary-General.
🔵 Question 7:
Match the principal organs and agencies of the UN with their functions:
🔹 Organs/Agencies 🔸 Functions
Economic and Social Council c. Looks into the economic and social welfare of the member countries
International Court of Justice e. Resolves disputes between and among member countries
International Atomic Energy Agency d. Safety and peaceful use of nuclear technology
Security Council b. Preservation of international peace and security
UN High Commission for Refugees f. Provides shelter and medical help during emergencies
World Trade Organisation j. Facilitates free trade among member countries
International Monetary Fund a. Oversees the global financial system
General Assembly g. Debates and discusses global issues
World Health Organisation i. Providing good health for all
Secretariat h. Administration and coordination of UN affairs
🔵 Question 8:
What are the functions of the Security Council?
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Maintains international peace and security.
2️⃣ Investigates disputes and recommends peaceful solutions.
3️⃣ Imposes sanctions or authorises use of force.
4️⃣ Admits new members and appoints the Secretary-General jointly with the General Assembly.
5️⃣ Recommends amendments to the UN Charter.
🔵 Question 9:
As a citizen of India, how would you support India’s candidature for the permanent membership of the Security Council?
🟢 Answer:
India is the world’s largest democracy.
Has been a founding member of the UN and an active participant in peacekeeping.
Second most populous country and fifth largest economy.
Strong commitment to multilateralism and global peace.
Hence, India deserves permanent membership to make the Council more representative and democratic.
🔵 Question 10:
Critically evaluate the difficulties involved in implementing the suggested reforms to reconstruct the UN.
🟢 Answer:
Resistance from P5 to share power.
Lack of consensus among member nations on reform models.
Geopolitical rivalries and regional disputes hinder agreement.
Fear of upsetting balance of power and increasing complexity.
🧭 Reforms require strong political will and global cooperation.
🔵 Question 11:
Though the UN has failed in preventing wars and related miseries, nations prefer its continuation. What makes the UN an indispensable organisation?
🟢 Answer:
Platform for dialogue and diplomacy.
Coordinates peacekeeping, humanitarian aid, and development.
Upholds international law and human rights.
Addresses global issues like climate, health, and poverty.
Thus, despite limitations, the UN remains essential for collective global governance.
🔵 Question 12:
‘Reforming the UN means restructuring of the Security Council’. Do you agree? Give arguments for or against.
🟢 Answer:
✅ For:
Current structure reflects 1945 realities, not today’s power distribution.
Permanent seats limited to 5 nations; excludes major emerging powers.
Reform ensures representation, legitimacy, and fairness.
❌ Against:
Changing structure may cause conflict and delay.
Risk of weakening decision-making.
🧭 Conclusion: Reforming UNSC is essential to make the UN more democratic and effective.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is not a principal organ of the United Nations?
🟢 1. International Monetary Fund
🟡 2. General Assembly
🔴 3. Security Council
🟣 4. International Court of Justice
✅ Answer: 1. International Monetary Fund
🔵 Question 2:
How many permanent members are there in the UN Security Council?
🟢 1. Five
🟡 2. Ten
🔴 3. Fifteen
🟣 4. Six
✅ Answer: 1. Five
🔵 Question 3:
Which of the following countries is not a permanent member of the Security Council?
🟢 1. Russia
🟡 2. France
🔴 3. Germany
🟣 4. China
✅ Answer: 3. Germany
🔵 Question 4:
The veto power is enjoyed by—
🟢 1. Only the permanent members of the Security Council
🟡 2. All members of the UN
🔴 3. Only General Assembly
🟣 4. Non-permanent members
✅ Answer: 1. Only the permanent members of the Security Council
🔵 Question 5:
The main objective of the United Nations is—
🟢 1. To maintain international peace and security
🟡 2. To dominate weaker nations
🔴 3. To expand trade
🟣 4. To control nuclear weapons
✅ Answer: 1. To maintain international peace and security
🔵 Question 6:
WTO replaced which organisation?
🟢 1. GATT
🟡 2. WHO
🔴 3. ILO
🟣 4. IMF
✅ Answer: 1. GATT
🔵 Question 7:
The UN Security Council has how many total members?
🟢 1. 15
🟡 2. 10
🔴 3. 20
🟣 4. 5
✅ Answer: 1. 15
🔵 Question 8:
India has been a member of the UN since—
🟢 1. 1945
🟡 2. 1950
🔴 3. 1960
🟣 4. 1971
✅ Answer: 1. 1945
🔵 Question 9:
The highest functionary of the UN is—
🟢 1. Secretary-General
🟡 2. President of General Assembly
🔴 3. Chairman of Security Council
🟣 4. Director of IMF
✅ Answer: 1. Secretary-General
🔵 Question 10:
Which organisation monitors nuclear energy use for peaceful purposes?
🟢 1. IAEA
🟡 2. WHO
🔴 3. IMF
🟣 4. UNESCO
✅ Answer: 1. IAEA
🔵 Question 11:
Which UN body is known as the ‘World Parliament’?
🟢 1. General Assembly
🟡 2. Security Council
🔴 3. ECOSOC
🟣 4. Secretariat
✅ Answer: 1. General Assembly
🔵 Question 12:
Who is the current UN Secretary-General (2025)?
🟢 1. António Guterres
🟡 2. Ban Ki-moon
🔴 3. Kofi Annan
🟣 4. Boutros Boutros-Ghali
✅ Answer: 1. António Guterres
🧭 Section B – Short Answer Questions (2 marks each)
Answer each question in 50–60 words.
🔵 Question 13:
What is the main objective of the United Nations?
🟢 Answer:
The main objective of the United Nations is to maintain international peace and security. It seeks to prevent wars through collective security, peacekeeping operations, and promoting cooperation among nations to solve economic, social, cultural, and humanitarian problems peacefully.
🔵 Question 14:
What is veto power?
🟢 Answer:
The veto power allows any permanent member of the Security Council to block a resolution by voting against it, even if all other members agree. It is a negative vote used by the five permanent members — China, France, Russia, the UK, and the USA — to prevent adoption of a proposal.
🔵 Question 15:
Mention two functions of the Security Council.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Maintains international peace and security by taking action against threats.
2️⃣ Recommends admission of new members and appoints the Secretary-General jointly with the General Assembly.
🔵 Question 16:
What is the composition of the UN Security Council?
🟢 Answer:
The Security Council has 15 members —
5 permanent (China, France, Russia, UK, USA)
10 non-permanent, elected for 2 years.
Each member has one vote; P5 enjoy veto power.
🔵 Question 17:
What is the role of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
🟢 Answer:
The IMF oversees the global financial system, offers loans to countries facing balance of payment crises, and promotes international monetary cooperation and exchange rate stability.
🔵 Question 18:
Which organ of the UN is known for administration and coordination?
🟢 Answer:
The Secretariat is responsible for the administration and coordination of UN affairs. It carries out day-to-day work, prepares reports, implements decisions, and assists other organs of the UN under the leadership of the Secretary-General.
🧭 Section C – Long Answer Type I (4 marks each)
Answer each question in 100–120 words.
🔵 Question 19:
Explain the functions of the UN General Assembly.
🟢 Answer:
The UN General Assembly (UNGA) is the deliberative organ of the United Nations.
✔️ It discusses global issues like peace, development, and cooperation.
✔️ It approves the UN budget and decides membership admissions.
✔️ It elects non-permanent members of the Security Council and other agencies.
✔️ It makes recommendations to promote international law, human rights, and social progress.
🧭 Although its resolutions are not binding, they carry moral and political weight.
🔵 Question 20:
Discuss the importance of the Security Council in maintaining world peace.
🟢 Answer:
The Security Council is the chief decision-making body for peace and security.
✔️ It investigates disputes and recommends solutions.
✔️ It can impose sanctions or authorize military action to stop aggression.
✔️ It deploys peacekeeping forces in conflict zones.
✔️ Its binding decisions ensure effective global response to crises.
🧭 Thus, the Security Council acts as the guardian of international peace.
🔵 Question 21:
Describe the composition and voting system of the UN Security Council.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ The Security Council consists of 15 members:
5 permanent: China, France, Russia, UK, USA
10 non-permanent, elected for 2 years
✔️ Each member has one vote.
✔️ Decisions require 9 affirmative votes, including all P5.
✔️ Any negative vote by a P5 is a veto, blocking the decision.
🧭 This ensures major powers’ consent but limits reform.
🔵 Question 22:
What are the limitations of the UN?
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Veto power makes the UN biased toward P5 interests.
2️⃣ Failure to stop major wars (e.g., Iraq, Syria) reduces credibility.
3️⃣ Dependence on powerful nations for funding and troops.
4️⃣ Inability to enforce decisions effectively.
🧭 Despite these, the UN remains indispensable for dialogue and cooperation.
🗺️ Section D – Source / Cartoon / Map-based Questions (4 marks each)
Answer each question as directed.
🔵 Question 23:
Interpretation Question: The veto power allows one nation to block majority opinion.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ It is used by P5 to protect national interests.
✔️ Promotes balance of power, but causes deadlocks in crises.
✔️ Example: US vetoes on Israel issues, Russia on Ukraine.
🧭 Reform is needed to make decisions more democratic.
🔵 Question 24:
Source Question: “The UN was created to prevent wars, yet conflicts continue.”
🟢 Answer:
✔️ True — UN has reduced global wars, but local conflicts persist.
✔️ Success in peacekeeping, but failures in Iraq and Syria.
✔️ Lack of enforcement and political will weakens action.
🧭 Still, the UN offers a platform for peaceful negotiation.
🔵 Question 25:
Map-based Question: Identify the headquarters of following organisations:
1️⃣ UN — New York, USA
2️⃣ WTO — Geneva, Switzerland
3️⃣ IMF — Washington D.C., USA
4️⃣ WHO — Geneva, Switzerland
🟢 Answer: Correctly mark these locations on a world map.
🧭 Section E – Long Answer Type II (6 marks each)
Answer each question in 170–180 words.
🔵 Question 26:
Evaluate India’s claim for permanent membership in the Security Council.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ India’s credentials:
Founding member of UN
Largest democracy, 1.4 billion people
Major contributor to UN peacekeeping
5th largest economy, stable polity
✔️ Supports multilateralism and South-South cooperation
✔️ Seeks representation for developing nations
🧭 Conclusion: India’s inclusion would make the UNSC more representative and democratic.
🔵 Question 27:
Explain the need for reform in the UN.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Present structure reflects 1945 realities, not current power distribution.
✔️ P5 dominance causes inequality.
✔️ Developing countries underrepresented.
✔️ Global challenges (terrorism, climate, pandemics) need broader voice.
✔️ Reform in membership, veto, transparency needed.
🧭 Modernisation will make the UN more effective and credible.
🔵 Question 28:
What makes the UN indispensable despite its failures?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Platform for dialogue among 190+ nations.
✔️ Conducts peacekeeping operations.
✔️ Works for human rights, development, climate.
✔️ Agencies (WHO, IMF, UNESCO) tackle global issues.
✔️ Promotes cooperation, law, and stability.
🧭 Despite limits, the UN is the most universal organisation.
🔵 Question 29:
Critically evaluate the difficulties in reforming the UN.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ No consensus among members.
✔️ P5 resistance to change veto powers.
✔️ Regional rivalries over representation.
✔️ Political and economic inequalities.
🧭 Reforms need collective will, compromise, and global unity.
🔵 Question 30:
“Reforming the UN means restructuring the Security Council.” Discuss.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ UNSC reflects post-WWII world.
✔️ New powers (India, Brazil, Japan, Germany) lack seats.
✔️ Veto is undemocratic.
✔️ Restructuring ensures representation, legitimacy, equity.
🧭 Without reform, the UN’s role will decline in global governance.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
