Class 12 : Poltical Science (English) – Lesson 1.The End of Bipolarity
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction
The chapter ‘The End of Bipolarity’ deals with one of the most significant events in modern history — the disintegration of the Soviet Union in 1991, which brought an end to the bipolar world order that had dominated international relations since the end of the Second World War. This lesson helps students understand not just the reasons behind the collapse of the USSR, but also the emergence of new political, economic, and social realities in the world thereafter.
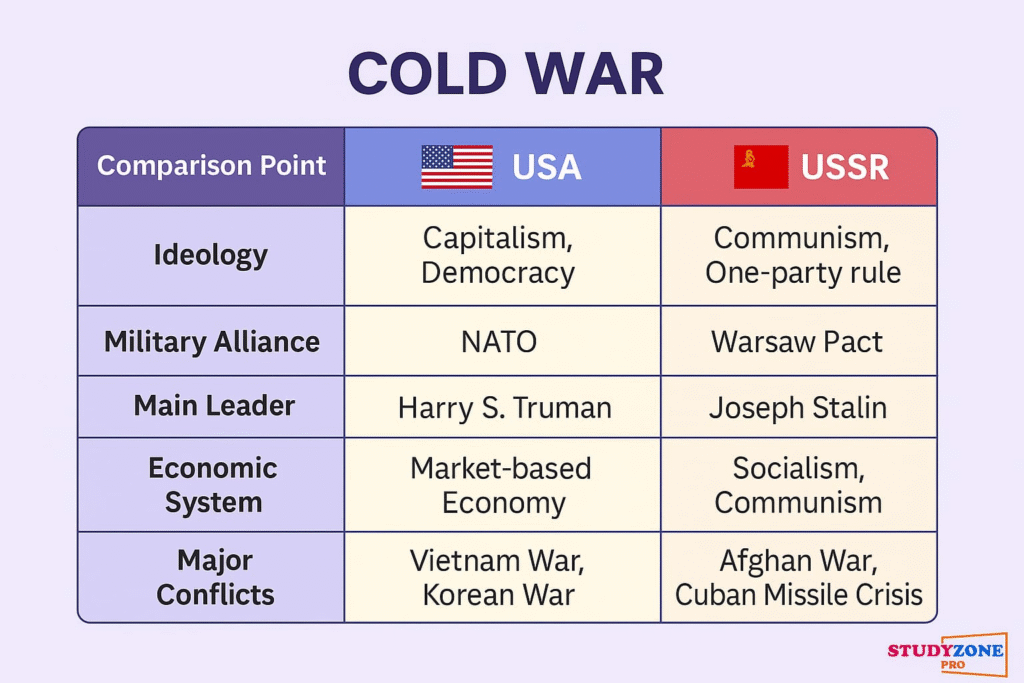
➡️ The Cold War had divided the world into two major power blocs:
✔️ The Capitalist Bloc led by the USA
✔️ The Communist Bloc led by the USSR
The collapse of the Soviet Union ended this bipolarity and led to a unipolar world order dominated by the United States.
🟢 The Soviet System: Features and Nature
🌿 The USSR was established after the Russian Revolution of 1917 and became a union of 15 republics. It was governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU).
Key Features of the Soviet System:
🔹 One-party system without political competition.
🔹 State ownership of resources and centrally planned economy.
🔹 Priority to the military sector over consumer goods.
🔹 Suppression of dissent and lack of basic freedoms.
🧠 Economic Achievements of USSR:
✔️ Advanced in space technology and nuclear power.
✔️ Produced goods for both civilian and military use.
✔️ Ensured basic welfare: health, education, and employment.
⚡ Social Achievements:
✔️ Low unemployment and poverty.
✔️ Women enjoyed better rights compared to many Western countries.
✔️ State provided housing and education.
🔴 Reasons for the Disintegration of the Soviet Union
The disintegration of the USSR did not happen suddenly but was the result of multiple deep-rooted factors over decades.
1️⃣ Economic Stagnation:
➡️ The Soviet economy failed to keep pace with the USA and Western Europe.
➡️ Poor quality of goods, lack of competition, inefficiency.
➡️ Overemphasis on heavy industries neglected consumer goods.
2️⃣ Political and Administrative Weaknesses:
➡️ Centralization of power in Moscow alienated the republics.
➡️ Lack of democracy created frustration among people.
3️⃣ Failure of Reforms:
💡 Gorbachev’s Reforms aimed to revive the system but accelerated its collapse:
✔️ Perestroika (Restructuring): Intended to reform the economy but confused officials.
✔️ Glasnost (Openness): Led to more criticism of the government.
✔️ Democratization: Weakened the hold of the Communist Party.
4️⃣ Nationalist Movements:
➡️ Rising ethnic and nationalist aspirations in the republics.
➡️ Demands for independence grew louder.
5️⃣ External Factors:
✔️ Arms race with the USA drained resources.
✔️ Western media exposed the flaws of the Soviet system.
✔️ Influence of liberal ideas.
✏️ Note: The Coup attempt of 1991 by hardliners further weakened Gorbachev’s authority, hastening the collapse.
🟡 Consequences of the Disintegration of the USSR
🔵 End of Bipolarity
➡️ The world became unipolar with the USA as the sole superpower.
🟢 Emergence of New Countries
✔️ 15 independent countries emerged from the USSR.
✔️ Russia recognized as the successor state.
✔️ New countries faced political instability and economic hardships.
🔴 End of the Cold War
✔️ Ended ideological confrontations between capitalism and communism.
✔️ Opened scope for cooperation between former enemies.
🟡 Transformation of World Politics
✔️ Shift towards liberal democracy and free-market economies.
✔️ Formation of regional organizations (EU, ASEAN strengthened).
✔️ Rise of China, European Union, and others balancing US dominance.
🔵 Shock Therapy in Post-Communist Countries
Shock Therapy: Sudden shift from state-controlled to capitalist economies in the 1990s, especially in Russia and Eastern Europe.
Key Features:
➡️ End of subsidies
➡️ Removal of price controls
➡️ Rapid privatization of state assets
➡️ Integration into global capitalist economy
💡 Impact on People:
✔️ Unemployment increased
✔️ Social security collapsed
✔️ Rise in poverty and inequality
✔️ Mafia and oligarchs controlled resources
✔️ Life expectancy fell in some areas
⚡ Political Consequences:
✔️ Rise of authoritarian tendencies in some countries.
✔️ Economic hardships led to political instability.
🟢 India’s Relations with Post-Soviet States
India maintained close relations with Russia and other former Soviet republics.
✔️ Continuity of Relations with Russia:
➡️ Russia recognized India as a trusted partner.
➡️ Defence cooperation remained strong.
➡️ Russia supported India in forums like UNSC.
✔️ Areas of Cooperation:
🌿 Military: Supply of defence equipment, joint exercises.
🌿 Energy: Cooperation in oil, gas, and nuclear power.
🌿 Space Technology: Continued collaboration.
🌿 Trade: India imports defence goods, exports pharmaceuticals.
💡 Concept: India’s ties with Russia remain important for strategic balance, energy needs, and defence self-sufficiency.
🔴 India’s Relations with Other Republics
India also built diplomatic and economic ties with Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Belarus, etc., focusing on:
➡️ Trade in energy resources
➡️ Cooperation in education and technology
➡️ Cultural exchanges
✏️ Note: India’s diplomatic strategy focused on mutual benefit and non-interference in internal politics of these nations.
🟡 Real-Life Connection
The world we live in today, dominated by economic globalization, regional cooperation, and the rise of new powers like China and India, is a direct outcome of the end of bipolarity.
Nations now work through alliances and diplomacy rather than ideologies of the Cold War era.
⚡ Why This Lesson Matters
✔️ Helps understand current global politics and India’s foreign policy choices.
✔️ Explains why the world shifted from ideological blocks to economic partnerships.
✔️ Shows how internal weaknesses can dismantle even superpowers.
✔️ Highlights the importance of democracy, economic reforms, and adaptability.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔵 Collapse of USSR ➡️ End of bipolarity
🟢 Reasons: Economic stagnation, political weakness, reforms failed, nationalism, foreign pressure
🔴 Consequences: Unipolar world, rise of USA, new countries, end of Cold War
🟡 Shock Therapy: Economic hardships, privatization, poverty
🔵 India’s relations: Continued strong ties with Russia, expanded to other republics
Summary (~300 words)
🔵 The End of Bipolarity – Key Points
USSR’s disintegration (1991) ended the Cold War and the world’s bipolar structure.
The Soviet system was based on one-party rule, central planning, and suppression of dissent.
Despite strengths like nuclear power and space achievements, it suffered from economic stagnation, lack of freedoms, and inefficiency.
🟢 Causes of Collapse
Economic weaknesses (inefficient industries, poor quality goods)
Political centralization and lack of democracy
Gorbachev’s reforms (Perestroika, Glasnost) backfired
Rising nationalism among Soviet republics
External pressures (arms race, exposure to liberal ideas)
Coup of 1991 hastened the end
🔴 Consequences
15 new countries emerged, Russia being the successor.
The world became unipolar with US dominance.
Former republics suffered due to shock therapy — sudden shift to capitalism led to poverty, unemployment, and rise of mafias.
End of ideological conflict between capitalism and communism.
🟡 India’s Response
Maintained strong ties with Russia: defence, energy, space.
Developed new relations with other post-Soviet states like Ukraine, Kazakhstan.
⚡ Importance
Explains how internal weaknesses can collapse empires.
Shows how world politics shifted towards economy over ideology.
Helps understand India’s strategic partnerships in a changed world.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Question 1:
Which among the following statements that describe the nature of Soviet economy is wrong?
a. Socialism was the dominant ideology
b. State ownership/control existed over the factors of production
c. People enjoyed economic freedom
d. Every aspect of the economy was planned and controlled by the State
Answer 1:
✅ The wrong statement is (c) — People enjoyed economic freedom.
🔵 Explanation:
In the Soviet system, there was no concept of individual economic freedom.
All resources and industries were owned and controlled by the state.
Economic activities were dictated by centralized planning.
Therefore, people had very limited say in how resources were used or what occupations they could pursue.
Question 2:
Arrange the following in chronological order:
a. Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
b. Fall of the Berlin Wall
c. Disintegration of the Soviet Union
d. Russian Revolution
Answer 2:
➡️ Correct Chronological Order:
1️⃣ Russian Revolution (1917)
2️⃣ Soviet invasion of Afghanistan (1979)
3️⃣ Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)
4️⃣ Disintegration of the Soviet Union (1991)
Question 3:
Which among the following is NOT an outcome of the disintegration of the USSR?
a. End of the ideological war between the US and USSR
b. Birth of CIS
c. Change in the balance of power in the world order
d. Crises in the Middle East
Answer 3:
✅ The correct answer is (d) — Crises in the Middle East.
🔵 Explanation:
Crises in the Middle East were not directly caused by the disintegration of the USSR.
Other outcomes such as the end of the Cold War, the formation of CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States), and changes in the global power structure were direct consequences.
Question 4:
Match the following:
| i. Mikhail Gorbachev | a. Successor of USSR |
| ii. Shock Therapy | b. Military pact |
| iii. Russia | c. Introduced reforms |
| iv. Boris Yeltsin | d. Economic model |
| v. Warsaw | e. President of Russia |
Answer 4:
| i. Mikhail Gorbachev | c. Introduced reforms |
| ii. Shock Therapy | d. Economic model |
| iii. Russia | a. Successor of USSR |
| iv. Boris Yeltsin | e. President of Russia|
| v. Warsaw | b. Military pact |
Question 5:
Fill in the blanks.
a. The Soviet political system was based on ideology.
b. _ was the military alliance started by the USSR.
c. _ party dominated the Soviet Union’s political system.
d. _ initiated the reforms in the USSR in 1985.
e. The fall of the __ symbolised the end of the Cold War.
Answer 5:
a. Communist
b. Warsaw Pact
c. Communist
d. Mikhail Gorbachev
e. Berlin Wall
Question 6:
Mention any three features that distinguish the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US.
Answer 6:
🔵 Key Features of the Soviet Economy:
1️⃣ State Ownership:
➡️ All resources were owned and controlled by the State, unlike capitalist economies where private ownership is dominant.
2️⃣ Centralised Planning:
➡️ The economy functioned according to a Five-Year Plan formulated by the state, determining production, distribution, and pricing.
3️⃣ Absence of Economic Freedom:
➡️ People had no freedom to choose their business or investments; the government decided all economic activities.
Question 7: What were the factors that forced Gorbachev to initiate the reforms in the USSR?
Answer 7: 🟢 Factors Leading to Reforms:
✅ Economic Stagnation:
➡️ The Soviet economy was unable to compete with the West in technology and production.
✅ Failure of the Existing System:
➡️ Centralised planning led to inefficiencies and poor quality of goods.
✅ Desire for Openness:
➡️ The younger generation desired freedom of speech and political participation.
✅ Arms Race Burden:
➡️ Military expenditure drained resources needed for public welfare.
✅ International Isolation:
➡️ The USSR lagged behind the West in modernization and global engagement.
Question 8:
What were the major consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union for countries like India?
Answer 8:
🔴 Consequences for India:
1️⃣ Loss of Strategic Support:
➡️ India lost its trusted ally and counterbalance to the US in the world order.
2️⃣ Economic Challenges:
➡️ Trade agreements collapsed, affecting India’s defence supplies and energy imports.
3️⃣ New Opportunities:
➡️ India developed new relations with Russia and other republics for energy, trade, and defence.
Question 9:
What was Shock Therapy? Was this the best way to make a transition from communism to capitalism?
Answer 9:
🟡 Shock Therapy:
➡️ It was a sudden shift from a state-controlled economy to a capitalist one adopted by post-Soviet countries like Russia in the 1990s.
🔵 Key Features:
✔️ End of subsidies
✔️ Privatization of industries
✔️ Free market reforms
⚡ Impact:
➡️ Led to unemployment, poverty, and rise of mafias.
➡️ Economy became dependent on foreign aid and loans.
🔴 Was it the Best Way?
❌ No. It caused immense hardships to ordinary people, though it was seen as necessary by Western economists for quick reform.
Question 10:
Write an essay for or against the following proposition:
“With the disintegration of the second world, India should change its foreign policy and focus more on friendship with the US rather than with traditional friends like Russia.”
Answer 10:
📝 Answer (Balanced View):
✔️ Arguments For Changing Policy:
The USA emerged as the sole superpower after 1991.
India could benefit from economic cooperation, technology, and investments.
Improved ties could help India’s global standing.
✔️ Arguments Against Changing Policy:
Russia remains an important defence and strategic partner.
Historical ties and trust between India and Russia cannot be ignored.
Over-dependence on one superpower can lead to imbalance in foreign policy.
🌿 Conclusion:
India should maintain friendly relations with both — the USA for economic and technological growth and Russia for defence and strategic needs. A balanced foreign policy is best suited to India’s interests.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Question 1.
Which year did the Soviet Union officially disintegrate?
a) 1989
b) 1991
c) 1993
d) 1995
Answer 1:
✅ b) 1991
Question 2.
Which political ideology was dominant in the Soviet Union?
a) Capitalism
b) Liberalism
c) Communism
d) Social democracy
Answer 2:
✅ c) Communism
Question 3.
The military alliance formed by the Soviet Union was called:
a) NATO
b) SEATO
c) Warsaw Pact
d) CENTO
Answer 3:
✅ c) Warsaw Pact
Question 4.
Name the leader who introduced Perestroika and Glasnost reforms.
a) Boris Yeltsin
b) Nikita Khrushchev
c) Vladimir Putin
d) Mikhail Gorbachev
Answer 4:
✅ d) Mikhail Gorbachev
Question 5.
Identify the correct full form of CIS.
a) Commonwealth of Independent States
b) Confederation of Independent Sovereigns
c) Common International System
d) Council of Independent Societies
Answer 5:
✅ a) Commonwealth of Independent States
Question 6.
Which of the following was NOT a reason for the disintegration of the USSR?
a) Political centralisation
b) Economic stagnation
c) Democratic institutions
d) Nationalist movements
Answer 6:
✅ c) Democratic institutions
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Shock Therapy benefited the common people.
Reason (R): It was a sudden shift from socialism to capitalism.
a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is false, but R is true.
d) Both A and R are false.
Answer 7:
✅ c) A is false, but R is true.
Question 8.
Name the military alliance established by the USA during the Cold War.
a) NATO
b) Warsaw Pact
c) SEATO
d) CENTO
Answer 8:
✅ a) NATO
Question 9.
What symbolized the end of the Cold War?
a) Fall of the Berlin Wall
b) Korean War
c) Cuban Missile Crisis
d) Vietnam War
Answer 9:
✅ a) Fall of the Berlin Wall
Question 10.
The Communist Party controlled the politics of:
a) USA
b) USSR
c) France
d) UK
Answer 10:
✅ b) USSR
Question 11.
Who became the first President of Russia after the USSR disintegrated?
a) Mikhail Gorbachev
b) Boris Yeltsin
c) Vladimir Putin
d) Leonid Brezhnev
Answer 11:
✅ b) Boris Yeltsin
Question 12.
Which sector was prioritised in the Soviet economy?
a) Agriculture
b) Heavy Industries
c) Tourism
d) Information Technology
Answer 12:
✅ b) Heavy Industries
Question 13.
Which of the following is NOT true of the Soviet political system?
a) One-party rule
b) State ownership of industries
c) Freedom of expression
d) Central planning
Answer 13:
✅ c) Freedom of expression
Question 14.
The world after the Cold War was described as:
a) Bipolar
b) Multipolar
c) Unipolar
d) Tri-polar
Answer 14:
✅ c) Unipolar
Question 15.
Which of the following statements is true about Gorbachev’s reforms?
a) They were instantly successful.
b) They failed and accelerated disintegration.
c) They established capitalism successfully.
d) They strengthened communism.
Answer 15:
✅ b) They failed and accelerated disintegration.
Question 16.
Which of the following countries was NOT a part of the former Soviet Union?
a) Kazakhstan
b) Ukraine
c) Poland
d) Belarus
Answer 16:
✅ c) Poland
Question 17.
What is the primary reason India maintained strong ties with Russia post-1991?
a) Military and defence cooperation
b) Cultural exchanges only
c) Competition with China
d) To stop NATO expansion
Answer 17:
✅ a) Military and defence cooperation
Question 18.
Assertion (A): The disintegration of the USSR strengthened India’s strategic ties with the USA.
Reason (R): The USA became the only superpower post-Cold War.
a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c) A is false, but R is true.
d) Both A and R are false.
Answer 18:
✅ b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 19.
State any two features of the Soviet political system.
Answer 19:
🔵 Features of Soviet Political System:
✔️ It was a one-party system, controlled by the Communist Party.
✔️ The state controlled all political, economic, and social activities through centralized planning.
Question 20.
Mention any two economic impacts of the disintegration of the Soviet Union on Russia.
Answer 20:
🟢 Economic Impacts on Russia:
✔️ The sudden shift to capitalism led to unemployment and poverty.
✔️ The economy became controlled by oligarchs and suffered from inflation.
Question 21.
How did Gorbachev’s reforms lead to the disintegration of the USSR? Mention two points.
Answer 21:
🔴 Impact of Gorbachev’s Reforms:
✔️ Perestroika (restructuring) and Glasnost (openness) exposed the system’s flaws.
✔️ These reforms led to increased criticism of the government and demands for independence.
Question 22.
What is meant by Shock Therapy in the context of post-communist countries?
Answer 22:
🟡 Meaning of Shock Therapy:
It was a policy of rapid transition from a socialist economy to a capitalist market economy, involving privatization, removal of subsidies, and integration with global markets.
Question 23.
Give two reasons why India maintained strong relations with Russia even after the end of the Cold War.
Answer 23:
🌿 Reasons for India-Russia Relations:
✔️ Defence cooperation: Russia remained India’s largest arms supplier.
✔️ Energy needs: India depended on Russia for nuclear energy cooperation.
Question 24.
Explain the role of nationalism in the disintegration of the USSR.
Answer 24:
🔴 Role of Nationalism:
✔️ Various ethnic groups and republics within the USSR demanded independence.
✔️ The centralized Soviet structure failed to accommodate regional aspirations.
✔️ Nationalist movements in Baltic states, Ukraine, Georgia, and others weakened the unity of the USSR.
Question 25.
What were the key features of the Soviet economy?
Answer 25:
🔵 Features of Soviet Economy:
1️⃣ State Ownership: All industries and agriculture were owned by the state.
2️⃣ Centralized Planning: Economy run through Five-Year Plans.
3️⃣ Focus on Heavy Industry: Military and heavy industries were prioritized over consumer goods.
Question 26.
Explain how the end of bipolarity affected world politics.
Answer 26:
🟡 Effects on World Politics:
✔️ The USA emerged as the sole superpower.
✔️ The world moved towards unipolarity and economic globalization.
✔️ Regional organizations like EU and ASEAN gained prominence, while international cooperation became more flexible.
Question 27.
What impact did the disintegration of the USSR have on the security of the world?
Answer 27:
🔴 Impact on Global Security:
✔️ Reduction in nuclear confrontation as arms race ended.
✔️ Rise of US military dominance in absence of USSR counterbalance.
✔️ Emergence of new conflicts within former USSR territories, like Chechnya.
Question 28.
How did India benefit from its relations with post-Soviet Russia? Explain.
Answer 28:
🟢 Benefits for India:
✔️ Russia supplied advanced defence technology and nuclear cooperation.
✔️ Enhanced trade relations in oil, gas, and diamonds.
✔️ Continued strategic support in international platforms like the UN.
Question 29.
Case-Based Question:
Read the following carefully and answer the questions given below:
“After the disintegration of the USSR in 1991, Russia emerged as its successor state. India maintained its close ties with Russia despite the collapse of the Soviet Union. Russia continued to support India on issues related to Kashmir, defence cooperation, and nuclear energy.”
(i) Name one area of cooperation between India and Russia post-1991.
(ii) Why did India continue its relations with Russia?
(iii) How did Russia support India at the global level?
(iv) State one impact of this relationship on India’s security.
Answer 29:
🟢 (i) Defence cooperation
🟢 (ii) India maintained relations to ensure strategic balance, military supplies, and energy needs.
🟢 (iii) Russia supported India’s stance on Kashmir and vetoed against anti-India moves at the UN.
🟢 (iv) India’s military security improved through defence deals and technology from Russia.
Question 30.
Case-Based Question:
Study the following case carefully and answer the questions:
“Shock Therapy refers to the sudden transition from a controlled socialist economy to a capitalist one. This led to privatization, removal of subsidies, and integration with the global market. However, it caused widespread unemployment and poverty in post-Soviet states.”
(i) What was Shock Therapy?
(ii) Mention one major impact of Shock Therapy on the people.
(iii) Name any two countries where this policy was implemented.
(iv) Why is Shock Therapy criticized?
Answer 30:
🔴 (i) Shock Therapy was the policy of shifting from socialism to capitalism rapidly.
🔴 (ii) It caused unemployment and poverty among common people.
🔴 (iii) Russia and Ukraine.
🔴 (iv) It is criticized for causing social and economic hardships to ordinary people.
Question 31.
Case-Based Question:
Analyze the following:
“The Soviet system was based on centralized planning, one-party rule, and suppression of freedoms. Despite its achievements in space and defence, it lagged in consumer goods and innovation. Gorbachev’s reforms of openness and restructuring accelerated its collapse.”
(i) What type of economic system existed in the Soviet Union?
(ii) Name the two key reforms introduced by Gorbachev.
(iii) Mention one achievement of the USSR.
(iv) State one reason why these reforms failed.
Answer 31:
🔵 (i) Centralized and state-controlled socialist economy.
🔵 (ii) Perestroika and Glasnost.
🔵 (iii) Success in space technology and defence.
🔵 (iv) Reforms failed because they weakened party control and encouraged criticism.
Question 32.
Explain in detail the causes of the disintegration of the USSR.
Answer 32:
🔴 Causes of Disintegration of USSR:
1️⃣ Economic Weakness:
➡️ Industries became inefficient, poor quality goods were produced.
2️⃣ Political Centralization:
➡️ Moscow controlled everything, creating dissatisfaction among republics.
3️⃣ Failure of Reforms:
➡️ Gorbachev’s Perestroika and Glasnost reforms weakened the party’s authority.
4️⃣ Nationalism:
➡️ Ethnic groups wanted independence, especially in Baltic states.
5️⃣ External Pressures:
➡️ Arms race with USA drained resources.
6️⃣ Coup of 1991:
➡️ The failed coup weakened Gorbachev further and quickened collapse.
Question 33.
Describe the impact of the end of bipolarity on global politics.
Answer 33:
🟢 Impact of End of Bipolarity:
1️⃣ Unipolar World Order:
➡️ USA emerged as the sole superpower.
2️⃣ Globalisation:
➡️ Free trade and capitalism spread.
3️⃣ Regional Powers Rose:
➡️ EU, ASEAN gained importance.
4️⃣ No Ideological Confrontation:
➡️ Cold War ideological divisions ended.
5️⃣ New Conflicts:
➡️ Local wars and ethnic conflicts increased in former USSR regions.
Question 34.
What were the objectives and consequences of Shock Therapy in post-communist countries?
Answer 34:
🔵 Objectives of Shock Therapy:
✔️ Transition from state-controlled to capitalist economy.
✔️ Encourage private ownership.
✔️ Integrate with global markets.
🔴 Consequences:
1️⃣ Unemployment increased.
2️⃣ Poverty and inequality widened.
3️⃣ Rise of mafias and oligarchs.
4️⃣ Economic instability and inflation.
5️⃣ Decline in public health and education facilities.
Question 35.
Explain India’s relationship with Russia and other post-Soviet republics after 1991.
Answer 35:
🟡 India-Russia Relations:
✔️ Defence Cooperation: Arms supply, joint military exercises.
✔️ Energy Cooperation: Oil, gas, nuclear technology.
✔️ Space Research: Continued collaboration.
✔️ Political Support: Russia supports India on Kashmir and UN matters.
🟢 Relations with Other Republics:
✔️ Kazakhstan, Ukraine — energy trade.
✔️ Uzbekistan, Belarus — cultural and educational exchanges.
🌿 India pursued balanced diplomacy for mutual benefits, focusing on trade, defence, and strategic partnerships.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. In which year did the USSR officially collapse?
(A) 1989
(B) 1990
(C) 1991
(D) 1992
✅ Answer: (C) 1991
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2017
📝 Explanation: USSR dissolved on 26th December 1991.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q2. The policy of Glasnost was associated with which leader?
(A) Stalin
(B) Khrushchev
(C) Brezhnev
(D) Gorbachev
✅ Answer: (D) Gorbachev
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2011
📝 Explanation: Glasnost was Gorbachev’s policy of transparency.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q3. The policy of Perestroika aimed at:
(A) Arms race
(B) Economic restructuring
(C) Military occupation
(D) Nuclear escalation
✅ Answer: (B) Economic restructuring
📅 Exam: UPPSC 2015
📝 Explanation: Perestroika focused on reforming USSR’s economy.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q4. Which one of the following is not a member of CIS?
(A) Russia
(B) Ukraine (initially)
(C) Belarus
(D) China
✅ Answer: (D) China
📅 Exam: BPSC 2016
📝 Explanation: China never joined CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States).
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. NAM was founded in the context of:
(A) Cold War
(B) Decolonization
(C) Globalization
(D) Environmental Movement
✅ Answer: (A) Cold War
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2014
📝 Explanation: NAM was a response to the bipolar world order.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q6. Gorbachev was awarded Nobel Peace Prize for ending:
(A) World War II
(B) The Cold War
(C) Nuclear energy disputes
(D) Korean War
✅ Answer: (B) The Cold War
📅 Exam: CAPF 2017
📝 Explanation: His reforms ended USSR’s confrontation with the West.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. The fall of the Berlin Wall symbolized:
(A) Rise of USSR
(B) End of Second World War
(C) Collapse of Communism in Europe
(D) Start of Cold War
✅ Answer: (C) Collapse of Communism in Europe
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2016
📝 Explanation: 1989 marked the end of Communist control in Eastern Europe.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q8. Which summit formally ended the Cold War?
(A) Yalta
(B) Malta
(C) Tehran
(D) Potsdam
✅ Answer: (B) Malta
📅 Exam: NDA 2018
📝 Explanation: Malta Summit 1989, Bush-Gorbachev, declared end of Cold War.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q9. Which organization emerged after USSR’s collapse?
(A) SAARC
(B) CIS
(C) ASEAN
(D) NATO
✅ Answer: (B) CIS
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2016
📝 Explanation: CIS replaced USSR structure for former Soviet states.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q10. The Cold War term was coined by:
(A) George Orwell
(B) Churchill
(C) Truman
(D) Stalin
✅ Answer: (A) George Orwell
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
📝 Explanation: Orwell first used this in 1945 writings.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q11. Who was the last President of the USSR?
(A) Khrushchev
(B) Brezhnev
(C) Gorbachev
(D) Yeltsin
✅ Answer: (C) Gorbachev
📅 Exam: SSC GD 2016
📝 Explanation: Gorbachev resigned in 1991 ending USSR.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q12. The economic crisis in USSR in 1980s was primarily due to:
(A) Excessive defense spending
(B) Agricultural failure
(C) Foreign occupation
(D) High birth rate
✅ Answer: (A) Excessive defense spending
📅 Exam: CAPF 2014
📝 Explanation: Arms race drained USSR’s economy.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q13. Which European body expanded post-Cold War?
(A) NATO
(B) Warsaw Pact
(C) OPEC
(D) SEATO
✅ Answer: (A) NATO
📅 Exam: SSC CPO 2018
📝 Explanation: NATO grew by adding Eastern Europe after USSR collapse.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q14. German Unification happened in:
(A) 1987
(B) 1989
(C) 1990
(D) 1991
✅ Answer: (C) 1990
📅 Exam: SSC MTS 2015
📝 Explanation: East and West Germany united in 1990.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q15. Yugoslavia broke into:
(A) 3 countries
(B) 5 countries
(C) 6+ countries
(D) Remained united
✅ Answer: (C) 6+ countries
📅 Exam: NDA 2017
📝 Explanation: Yugoslavia disintegrated into many nations post-1991.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q16. Which of the following does NOT relate to the Cold War?
(A) Cuban Missile Crisis
(B) Vietnam War
(C) Gulf War
(D) Berlin Blockade
✅ Answer: (C) Gulf War
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2015
📝 Explanation: Gulf War was post-Cold War (1991).
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q17. The Warsaw Pact dissolved in:
(A) 1989
(B) 1990
(C) 1991
(D) 1992
✅ Answer: (C) 1991
📅 Exam: SSC JE 2019
📝 Explanation: Dissolved after USSR’s breakup.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q18. Which country did not join EU post-1991?
(A) Poland
(B) Hungary
(C) Norway
(D) Bulgaria
✅ Answer: (C) Norway
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2016
📝 Explanation: Norway rejected EU via referendum.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q19. Non-Alignment Movement was established in:
(A) 1947
(B) 1955
(C) 1961
(D) 1971
✅ Answer: (C) 1961
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2018
📝 Explanation: NAM started at Belgrade 1961, to avoid bipolarity.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
