Class 12 : Poltical Science (English) – Lesson 2.Contemporary Centres of Power
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

Asean Countries
🔵 Introduction
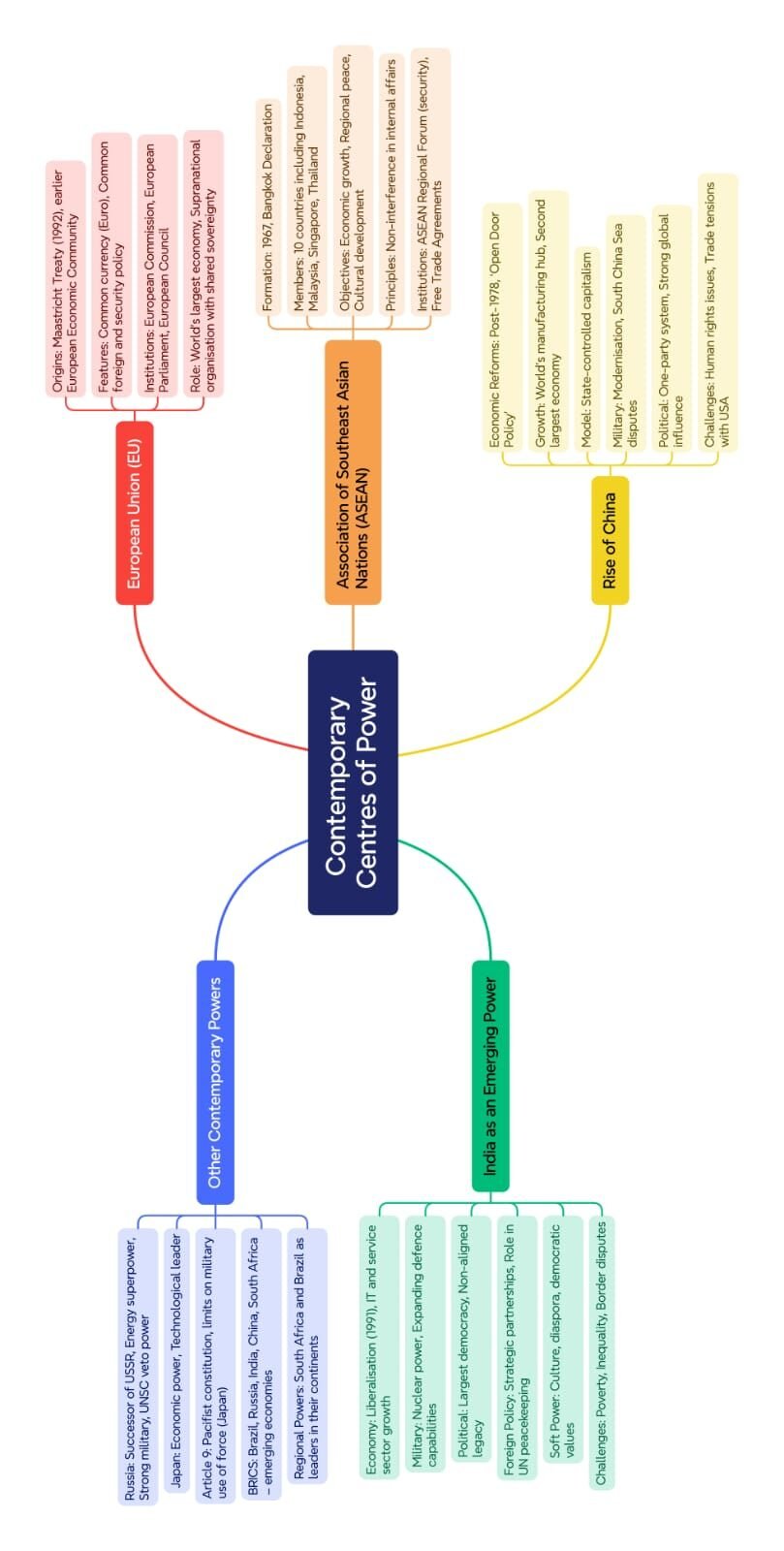
The chapter ‘Contemporary Centres of Power’ from Class 12 Political Science discusses the changing nature of global politics after the end of bipolarity in 1991. The Cold War era was dominated by two superpowers – the USA and the USSR. After the disintegration of the USSR, many scholars believed that the USA would now dominate the world alone. However, the world moved towards multi-polarity, where multiple centres of power emerged across continents.
These centres are not only military or political but also economic. The chapter introduces the rise of the European Union (EU), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), China, and India as new centres of power that significantly influence international politics today.
🟢 European Union (EU): A Supranational Organisation
The European Union is one of the most powerful economic and political unions in the world today. It was established after World War II to ensure peace and prosperity among European nations through economic cooperation.
🔶 Formation and Features:
➡️ Initially, organisations like the European Economic Community (EEC) were formed.
➡️ The European Union (EU) was formally established in 1992 through the Maastricht Treaty.
🔶 Economic Power of the EU:
✔️ The EU’s combined GDP is higher than that of the USA.
✔️ It is a significant trading bloc and a powerful player in the World Trade Organisation (WTO).
✔️ The Euro is one of the most traded currencies globally.
🔶 Political and Military Influence:
✔️ The EU has its own parliament, central bank, and common foreign policies.
✔️ It has influence over the policies of its member states.
✔️ Some members are also part of NATO.
💡 Concept: The EU balances between national sovereignty and regional integration, making it unique.
🔴 Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN): Growth through Cooperation
🔶 Formation:
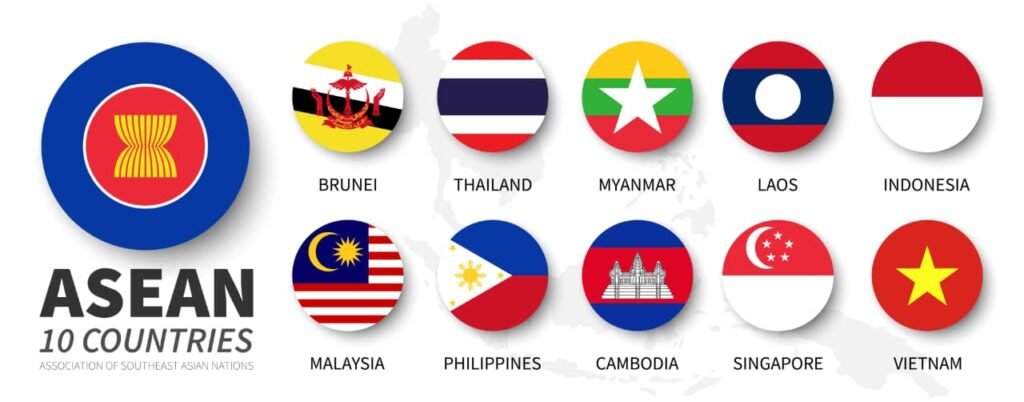
➡️ Established in 1967 with 5 founding members (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand).
➡️ Now has 10 members.
🔶 Objectives:
✔️ Promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development.
✔️ Ensure peace and stability through mutual cooperation.
🔶 Achievements:
🌿 Created the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA).
🌿 Became an economic powerhouse in the region.
🌿 Maintains a policy of non-interference and consensus-building.
🔶 Political and Strategic Importance:
➡️ ASEAN has avoided military conflicts within its region.
➡️ Plays a significant role in East Asia Summits and dialogues with the USA, China, and India.
✏️ Note: ASEAN showcases how regional cooperation can ensure prosperity without military alliances.
🟡 China: Rise of an Economic Superpower
🔶 Historical Background:
➡️ Adopted Communism in 1949 under Mao Zedong.
➡️ Shifted towards economic liberalisation in 1978 under Deng Xiaoping.
🔶 Features of Chinese Power:
1️⃣ Economic:
✔️ World’s second-largest economy.
✔️ Significant contributor to global manufacturing and trade.
2️⃣ Military:
✔️ Large, modern army with nuclear capabilities.
✔️ Increasing influence in the South China Sea and through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
3️⃣ Diplomatic:
✔️ Permanent member of the UN Security Council.
✔️ Active in regional organisations like SCO and BRICS.
💡 Concept: China’s rise is based on a mix of socialism, capitalism, and nationalism.
🔵 India: An Emerging Global Power
🔶 Post-1991 Reforms:
➡️ Adopted liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation (LPG) policies.
➡️ Experienced rapid growth in IT, manufacturing, and services.
🔶 Strengths of India:
1️⃣ Democracy: World’s largest democratic country.
2️⃣ Economy: Growing rapidly with focus on technology and infrastructure.
3️⃣ Military: Nuclear power with significant defence capabilities.
4️⃣ Diaspora: Strong global presence of Indian-origin communities.
🔶 India’s Role in International Relations:
✔️ Active in United Nations, WTO, BRICS, G-20.
✔️ Strong partnerships with USA, Russia, EU, ASEAN, and Africa.
✏️ Note: India balances its relations with both Western and Eastern blocs, making it a flexible player.
🔴 United Nations: Continuing Relevance
🔶 Role of the UN:
✔️ Maintains global peace and security through the Security Council.
✔️ Promotes human rights, development, and cooperation.
🔶 Structure:
1️⃣ Security Council: Maintains peace (5 permanent members with veto).
2️⃣ General Assembly: Discusses global issues with all member states.
3️⃣ ECOSOC, ICJ, Secretariat play important roles.
🔶 Challenges:
➡️ Calls for reform in the Security Council.
➡️ Demands for including emerging powers like India, Germany, Brazil, and Japan as permanent members.
🟢 Real-Life Connection: Global Interdependence
➡️ In today’s world, no country can progress in isolation.
➡️ Trade, technology, security, environment – all require global cooperation.
➡️ These centres of power shape international decisions that affect everyone’s life.
⚡ Why This Lesson Matters
✔️ Helps understand how global power is distributed today.
✔️ Highlights the importance of regional cooperation and diplomacy.
✔️ Shows how India fits into the changing world order.
✔️ Encourages awareness of international organisations and foreign policy.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔵 European Union – Economic + Political Power
🟢 ASEAN – Regional cooperation, peaceful growth
🔴 China – Economic + Military expansion
🟡 India – Rising democracy, growing influence
🔵 United Nations – Global peacekeeper but needs reforms
Summary (~300 words):
🔵 Contemporary Centres of Power – Overview
The chapter explains how the world moved from bipolarity to multipolarity after the Cold War. New centres of power emerged in the form of regional organisations and rising nations.
🟢 European Union (EU):
A supranational body balancing economic and political power.
Strongest in trade and economy with the Euro as a key currency.
Influence over foreign and security policies of its members.
🔴 ASEAN:
Focus on economic progress and peace through cooperation.
Promotes non-interference and consensus.
Important in East Asian politics and economy.
🟡 China:
From communist state to economic giant.
Huge military strength, expanding global influence via BRI.
Plays active roles in UN, SCO, BRICS.
🔵 India:
Rapid economic growth post-1991.
Balances relations with multiple global players.
Strong role in technology, military, diplomacy.
🟢 United Nations:
Still relevant in maintaining global peace.
Structure needs reform to include new powers like India.
⚡ Importance of the Chapter:
Explains the new global order.
Highlights the role of regional powers and organisations.
Shows how India is positioning itself as a key player.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Question 1:
Arrange the following in chronological order.
a. China’s accession to WTO
b. Establishment of the EEC
c. Establishment of the EU
d. Birth of ARF
Answer 1:
➡️ Correct Chronological Order:
1️⃣ Establishment of the EEC (1957)
2️⃣ Birth of ARF (1994)
3️⃣ Establishment of the EU (1992 – Treaty signed, formally in 1993)
4️⃣ China’s accession to WTO (2001)
Question 2:
The ‘ASEAN Way’
a. Reflects the life style of ASEAN members
b. A form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative
c. The defence policy followed by the ASEAN members
d. The road that connects all the ASEAN members
Answer 2:
✅ Correct Answer: (b) A form of interaction among ASEAN members that is informal and cooperative.
💡 Concept: The ‘ASEAN Way’ is based on informality, consensus-building, and non-interference.
Question 3:
Which of the following nations adopted an ‘open door’ policy?
a. China
b. South Korea
c. Japan
d. USA
Answer 3:
✅ Correct Answer: (a) China
🔵 Explanation: China adopted the ‘Open Door Policy’ in 1978 under Deng Xiaoping to encourage foreign trade and investments.
Question 4:
Fill in the blanks:
a. The border conflict between China and India in 1962 was principally over _ and _ region.
Answer:
✅ Aksai Chin and Arunachal Pradesh
b. ARF was established in the year __.
Answer:
✅ 1994
c. China entered into bilateral relations with __ (a major country) in 1972.
Answer:
✅ The United States of America (USA)
d. __ Plan influenced the establishment of the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation in 1948.
Answer:
✅ The Marshall Plan
e. __ is the organisation of ASEAN that deals with security.
Answer:
✅ ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF)
Question 5:
What are the objectives of establishing regional organisations?
Answer 5:
🟢 Objectives of Regional Organisations:
✔️ Promote peace, stability, and security in the region.
✔️ Enhance economic cooperation and integration among member states.
✔️ Strengthen cultural and social ties.
✔️ Protect and promote mutual interests collectively on the global stage.
Question 6:
How does geographical proximity influence the formation of regional organisations?
Answer 6:
🔵 Influence of Geographical Proximity:
✔️ Countries located close to each other share common security and economic concerns.
✔️ Easier to facilitate trade, transport, and communication links.
✔️ Common historical, cultural, and political experiences often bind neighbours together.
✔️ Regional organisations emerge to ensure peace and prosperity through cooperation.
Question 7:
What are the components of the ASEAN Vision 2020?
Answer 7:
🔴 Components of ASEAN Vision 2020:
1️⃣ A stable, prosperous, and highly competitive ASEAN.
2️⃣ A region with reduced poverty and socio-economic disparities.
3️⃣ A community that fosters people-centered development.
4️⃣ Promotion of shared cultural heritage.
5️⃣ Strengthening peace, security, and stability.
Question 8:
Name the pillars and the objectives of the ASEAN Community.
Answer 8:
🟡 Three Pillars of ASEAN Community:
1️⃣ ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC)
2️⃣ ASEAN Economic Community (AEC)
3️⃣ ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC)
✔️ Objectives:
Promote peace, security, and stability.
Achieve economic integration and growth.
Encourage social progress and cultural cooperation.
Question 9:
In what ways does the present Chinese economy differ from its command economy?
Answer 9:
🌿 Differences Between Current and Command Economy in China:
🔵 Earlier Command Economy (Pre-1978):
✔️ Government controlled all industries and production.
✔️ No private ownership; state owned resources.
✔️ Focus on heavy industries and military sectors.
🟢 Present Economy (Post-1978 Reforms):
✔️ Market-oriented reforms, foreign investments allowed.
✔️ Growth in private enterprises and international trade.
✔️ Greater integration with the global economy through WTO.
Question 10:
How did the European countries resolve their post-Second World War problem? Briefly outline the attempts that led to the formation of the European Union.
Answer 10:
🔴 Efforts Towards European Unity:
✔️ Marshall Plan (1948) helped rebuild European economies.
✔️ Formation of Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC).
✔️ Establishment of European Economic Community (EEC) in 1957 for common markets.
✔️ Signing of the Maastricht Treaty in 1992 created the European Union (EU).
✔️ Adoption of Euro currency and common policies unified Europe economically and politically.
Question 11:
What makes the European Union a highly influential regional organisation?
Answer 11:
🟢 Reasons for EU’s Influence:
✔️ Largest economy collectively surpassing even the USA in GDP.
✔️ A significant player in global trade and WTO.
✔️ Strong political and diplomatic influence.
✔️ Own parliament, central bank, currency (Euro), and foreign policy mechanisms.
✔️ Important member-states contribute to UN and global security.
Question 12:
The emerging economies of China and India have great potential to challenge the unipolar world. Do you agree with the statement? Substantiate your arguments.
Answer 12:
🟡 Yes, I agree.
✔️ China’s Rise:
Second-largest economy globally.
Increasing influence through Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Strong military power and technology advancements.
✔️ India’s Emergence:
Largest democracy with growing global partnerships.
Rapid progress in technology, space, and economy.
Active participation in WTO, UN, BRICS, and G20.
➡️ Both nations challenge the dominance of Western powers and contribute towards multipolarity.
Question 13:
The peace and prosperity of countries lay in the establishment and strengthening of regional economic organisations. Justify this statement.
Answer 13:
🔵 Justification:
✔️ Promotes Trade and Economic Growth: Shared markets boost development.
✔️ Ensures Peace and Stability: Cooperation reduces chances of conflicts.
✔️ Collective Security: Strong regional ties deter external threats.
✔️ Addresses Common Issues: Together tackle poverty, climate change, and health.
✔️ Increases Bargaining Power: Regional blocks gain more influence globally.
Question 14:
Identify the contentious issues between China and India. How could these be resolved for greater cooperation? Give your suggestions.
Answer 14:
🔴 Contentious Issues:
1️⃣ Border disputes in Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin.
2️⃣ China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) passing through PoK.
3️⃣ Trade imbalances in favour of China.
4️⃣ India’s entry into international groups like NSG blocked by China.
🟢 Suggestions for Resolution:
✔️ Regular bilateral dialogues.
✔️ Confidence-building measures at borders.
✔️ Promote economic cooperation and fair trade practices.
✔️ Engage through regional forums like BRICS and SCO.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Question 1.
Which year was ASEAN established?
(A) 1965
(B) 1967
(C) 1970
(D) 1975
Answer: (B) 1967
Question 2.
Which of the following nations adopted the ‘Open Door Policy’?
(A) India
(B) China
(C) Japan
(D) USA
Answer: (B) China
Question 3.
The European Union was formally established through which treaty?
(A) Maastricht Treaty
(B) Versailles Treaty
(C) Lisbon Treaty
(D) Warsaw Pact
Answer: (A) Maastricht Treaty
Question 4.
The ASEAN Way refers to:
(A) Defence pact
(B) Informal and cooperative interaction
(C) Cultural lifestyle
(D) ASEAN Highway
Answer: (B) Informal and cooperative interaction
Question 5.
China became a member of WTO in which year?
(A) 1998
(B) 1999
(C) 2000
(D) 2001
Answer: (D) 2001
Question 6.
Which organisation deals with security in ASEAN?
(A) AFTA
(B) ARF
(C) NATO
(D) SAARC
Answer: (B) ARF
Question 7.
Which of the following is a feature of the European Union?
(A) It has its own currency
(B) It has no political influence
(C) It excludes economic integration
(D) It avoids all military alliances
Answer: (A) It has its own currency
Question 8.
Which country is not a part of ASEAN?
(A) Thailand
(B) Vietnam
(C) Indonesia
(D) China
Answer: (D) China
Question 9.
Which among the following is an objective of ASEAN?
(A) Establish nuclear weapons
(B) Ensure peace and stability
(C) Establish military dictatorship
(D) Establish economic isolation
Answer: (B) Ensure peace and stability
Question 10.
The European Union’s combined GDP is:
(A) Lesser than India
(B) Equal to China
(C) Greater than the USA
(D) Negligible
Answer: (C) Greater than the USA
Question 11.
Assertion (A): ASEAN focuses on consensus and non-interference.
Reason (R): ASEAN was formed for military purposes.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) Both A and R are false.
Answer: (C) A is true but R is false.
Question 12.
Which organisation promotes free trade among ASEAN nations?
(A) NATO
(B) AFTA
(C) WTO
(D) SAARC
Answer: (B) AFTA
Question 13.
What was the initial name of the European Union before 1993?
(A) European Economic Community
(B) European Peace Union
(C) Euro Alliance
(D) European Commerce Body
Answer: (A) European Economic Community
Question 14.
Which region is a focus of China’s territorial expansion?
(A) South China Sea
(B) Arabian Sea
(C) Mediterranean Sea
(D) Baltic Sea
Answer: (A) South China Sea
Question 15.
Which country is known for Belt and Road Initiative?
(A) India
(B) USA
(C) China
(D) France
Answer: (C) China
Question 16.
Which country is the largest democracy involved in the emerging global centres of power?
(A) Japan
(B) China
(C) USA
(D) India
Answer: (D) India
Question 17.
What is the full form of ARF in the context of ASEAN?
(A) ASEAN Rights Forum
(B) ASEAN Regional Forum
(C) Asian Resource Federation
(D) ASEAN Rules Federation
Answer: (B) ASEAN Regional Forum
Question 18.
India’s participation in organisations like BRICS reflects:
(A) Isolationism
(B) Economic partnership
(C) Military alliance
(D) Environmental negligence
Answer: (B) Economic partnership
Question 19.
State two major objectives of ASEAN.
Answer 19:
🟢 Objectives of ASEAN:
1️⃣ Promote economic growth, social progress, and cultural development among member nations.
2️⃣ Ensure regional peace and stability through mutual cooperation and respect for sovereignty.
Question 20.
Name any two key features of the European Union’s power.
Answer 20:
🔵 Features of EU Power:
1️⃣ Economic Power: The EU collectively has a GDP higher than the USA and significant influence in global trade.
2️⃣ Political Influence: The EU plays an important role in world politics through its unified foreign and security policies.
Question 21.
How did the ASEAN countries ensure peace within the region? Mention any two ways.
Answer 21:
🟡 Peace Measures by ASEAN:
1️⃣ Followed the ASEAN Way, focusing on consensus-building and non-interference in internal matters.
2️⃣ Promoted regional cooperation in economic and security matters to avoid conflicts.
Question 22.
List any two reasons for China’s growing global influence.
Answer 22:
🔴 Reasons for China’s Influence:
1️⃣ Economic Growth: China is the world’s second-largest economy with a major role in global manufacturing and trade.
2️⃣ Military Strength: China possesses strong military capabilities and is expanding its influence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Question 23.
State any two reasons why India is considered a rising power in the contemporary world.
Answer 23:
🟢 Reasons for India’s Rise:
1️⃣ Strong Democratic Foundations: World’s largest democracy, contributing to global governance platforms like the UN, WTO, BRICS, and G20.
2️⃣ Rapid Economic Development: Significant growth in technology, services, and defence sectors.
Question 24.
Explain how ASEAN has transformed into an economic powerhouse.
Answer 24:
🔵 ASEAN as Economic Powerhouse:
✔️ Established the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) to promote trade among members.
✔️ Opened markets to foreign investments and technology.
✔️ Achieved rapid economic growth through cooperation, becoming one of the most dynamic regions globally.
Question 25.
How did China shift from a command economy to a market economy?
Answer 25:
🟡 China’s Economic Shift:
✔️ Introduced Open Door Policy in 1978 under Deng Xiaoping.
✔️ Encouraged foreign investments, privatization, and trade reforms.
✔️ Gradually integrated into the global market economy and joined WTO in 2001.
Question 26.
Mention any three key features of the European Union as a supranational organisation.
Answer 26:
🔴 Features of the European Union:
1️⃣ Common Currency (Euro) among many member countries.
2️⃣ Unified Political and Foreign Policies.
3️⃣ Strong representation in global platforms like WTO, UN.
Question 27.
Explain the role of the United Nations in maintaining global peace.
Answer 27:
🟢 UN’s Role in Global Peace:
✔️ The Security Council handles issues of war and peace with five permanent members.
✔️ Deploys peacekeeping forces in conflict zones.
✔️ Promotes dialogue and negotiations to resolve international conflicts.
Question 28.
State any three differences between the earlier Soviet economy and the present Chinese economy.
Answer 28:
🔵 Differences Between Soviet and Present Chinese Economy:
Soviet Economy Present Chinese Economy
Complete state control Market-oriented reforms
No foreign investment allowed Encourages foreign trade
Focus on heavy industries Focus on consumer goods & tech
Question 29.
Case-Based Question:
Read the following carefully and answer the questions given below:
The European Union today stands as a powerful economic and political organisation. It began with a focus on economic cooperation post-Second World War and evolved into a supranational entity with its own Parliament, common currency, and foreign policy.
(i) What is the common currency of the European Union?
(ii) What is the EU’s main purpose?
(iii) Name two areas where the EU has significant influence.
(iv) How did the EU evolve from economic cooperation to political power?
Answer 29:
(i) Euro
(ii) To promote economic integration, peace, and political stability among European nations.
(iii) Trade and diplomacy
(iv) Through the Maastricht Treaty, the EU moved from being purely economic to also adopting common foreign and security policies.
Question 30.
Case-Based Question:
Study the following and answer the questions:
China’s rise is marked by rapid economic growth, increased trade relations, and strong military advancements. The Open Door Policy initiated in 1978 transformed China from a closed economy to one of the biggest players in the global market.
(i) In which year did China introduce the Open Door Policy?
(ii) What was the purpose of this policy?
(iii) Mention one global initiative led by China to expand its influence.
(iv) How has China balanced communism with capitalism?
Answer 30:
(i) 1978
(ii) To modernize its economy through foreign trade and investment.
(iii) Belt and Road Initiative (BRI)
(iv) By combining state control in key sectors with a free-market approach for growth and trade.
Question 31.
Case-Based Question:
Read the following passage and answer:
ASEAN was formed to promote regional cooperation in Southeast Asia. Known for the ‘ASEAN Way,’ it focuses on consensus and non-interference. Through economic agreements like AFTA, ASEAN has become a powerful regional bloc.
(i) What is the ASEAN Way?
(ii) How does ASEAN ensure peace?
(iii) Name the economic agreement for trade among ASEAN nations.
(iv) Why is ASEAN considered successful?
Answer 31:
(i) Informal and cooperative interaction through consensus.
(ii) Through dialogue, consensus-building, and non-interference.
(iii) ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
(iv) Due to its economic growth, political stability, and regional unity.
SECTION E (5 Marks Each)
Question 32.
Explain the significance of ASEAN as a contemporary centre of power in detail.
Answer 32:
🟢 Significance of ASEAN:
✔️ Economic Strength: ASEAN is one of the fastest-growing economies with agreements like AFTA boosting intra-regional trade.
✔️ Political Stability: Follows the ASEAN Way focusing on consensus and cooperation.
✔️ Peace and Security: Establishes forums like ARF to ensure regional security.
✔️ Global Influence: Engages in dialogues with major powers like USA, China, India.
✔️ Model of Cooperation: Proves that regional unity without military alliances can achieve stability and growth.
Question 33.
Explain India’s rise as a contemporary centre of power with examples.
Answer 33:
🔵 India’s Rise:
✔️ Economic Growth: Rapid growth post-1991 in sectors like IT, services, manufacturing.
✔️ Strategic Diplomacy: Active in BRICS, G20, WTO, SCO, and UN.
✔️ Military Strength: Nuclear power, significant defence capabilities.
✔️ Technological Advancements: Leadership in space, pharmaceuticals, and innovation.
✔️ Global Recognition: Strong ties with USA, Russia, EU, ASEAN highlighting India’s balanced and influential diplomacy.
Question 34.
Describe the role and limitations of the United Nations as a global centre of power.
Answer 34:
🟡 Role of United Nations:
✔️ Maintains Peace: Through Security Council resolutions and peacekeeping forces.
✔️ Promotes Rights: Upholds human rights, sustainable development, and humanitarian aid.
✔️ Global Dialogue: Acts as a forum for resolving international conflicts.
🔴 Limitations:
❌ Veto Power Misuse: Permanent members often block resolutions.
❌ Lack of Reforms: Does not reflect the rise of new powers like India, Brazil.
❌ Ineffectiveness in Certain Conflicts: Failed to prevent many modern conflicts.
Question 35.
Examine the changing nature of power in world politics after the end of bipolarity.
Answer 35:
🔴 Changing Nature of Power:
✔️ Shift from bipolarity (USA-USSR) to multipolarity.
✔️ Emergence of new centres of power: EU, ASEAN, China, India.
✔️ Greater focus on economic strength over military might.
✔️ Rise of regional organisations influencing global policies.
✔️ Increased interdependence through globalisation, trade, technology, and diplomacy.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. The Maastricht Treaty is related to the formation of:
(A) NATO
(B) EU
(C) ASEAN
(D) SAARC
✅ Answer: (B) EU
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2013
📝 Explanation: Maastricht Treaty (1992) led to the formation of the European Union.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q2. ASEAN was established in:
(A) 1961
(B) 1967
(C) 1975
(D) 1985
✅ Answer: (B) 1967
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2014
📝 Explanation: ASEAN was founded by the Bangkok Declaration in 1967.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q3. Which of the following is not a founding member of ASEAN?
(A) Malaysia
(B) Thailand
(C) Indonesia
(D) China
✅ Answer: (D) China
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2016
📝 Explanation: China is not a member of ASEAN.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q4. WTO was established in:
(A) 1991
(B) 1993
(C) 1995
(D) 1999
✅ Answer: (C) 1995
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2018
📝 Explanation: WTO replaced GATT in 1995.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. Headquarters of WTO is located at:
(A) New York
(B) Paris
(C) Geneva
(D) Washington DC
✅ Answer: (C) Geneva
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2015
📝 Explanation: WTO headquarters is in Geneva, Switzerland.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q6. The main purpose of IMF is:
(A) To eradicate poverty
(B) To promote international monetary cooperation
(C) To help poor countries directly
(D) To fund wars
✅ Answer: (B) To promote international monetary cooperation
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
📝 Explanation: IMF promotes monetary stability globally.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. Which country is not a member of G-7?
(A) USA
(B) Germany
(C) Russia
(D) Japan
✅ Answer: (C) Russia
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2015
📝 Explanation: Russia is not part of G-7; it was briefly in G-8.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q8. Headquarters of International Court of Justice is in:
(A) Geneva
(B) The Hague
(C) Paris
(D) New York
✅ Answer: (B) The Hague
📅 Exam: SSC MTS 2015
📝 Explanation: ICJ is headquartered at The Hague, Netherlands.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q9. Which of the following organizations controls oil prices globally?
(A) WTO
(B) IMF
(C) OPEC
(D) ASEAN
✅ Answer: (C) OPEC
📅 Exam: SSC CPO 2017
📝 Explanation: OPEC influences global oil prices.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q10. BRICS does not include which country?
(A) Brazil
(B) Russia
(C) Indonesia
(D) South Africa
✅ Answer: (C) Indonesia
📅 Exam: NDA 2018
📝 Explanation: BRICS includes Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q11. Headquarters of European Union is located at:
(A) Brussels
(B) Paris
(C) Berlin
(D) London
✅ Answer: (A) Brussels
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
📝 Explanation: Brussels is the de facto EU capital.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q12. ASEAN Secretariat is located at:
(A) Bangkok
(B) Jakarta
(C) Singapore
(D) Manila
✅ Answer: (B) Jakarta
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2017
📝 Explanation: ASEAN Secretariat is in Jakarta, Indonesia.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q13. G-20 was founded in:
(A) 1997
(B) 1999
(C) 2000
(D) 2005
✅ Answer: (B) 1999
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2016
📝 Explanation: G-20 was founded to stabilize the global economy.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q14. Which of the following is the largest economy in the EU?
(A) France
(B) Germany
(C) Italy
(D) Spain
✅ Answer: (B) Germany
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2017
📝 Explanation: Germany is the largest economy in the EU.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q15. Which country was the last to join the EU among these?
(A) Romania
(B) Bulgaria
(C) Croatia
(D) Poland
✅ Answer: (C) Croatia
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
📝 Explanation: Croatia joined the EU in 2013.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q16. Which of these is not a function of the World Bank?
(A) Promoting foreign trade
(B) Financing development projects
(C) Providing loans to governments
(D) Regulating exchange rates
✅ Answer: (D) Regulating exchange rates
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2018
📝 Explanation: IMF regulates exchange rates, not World Bank.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q17. The largest contributor to IMF quotas is:
(A) USA
(B) Germany
(C) UK
(D) Japan
✅ Answer: (A) USA
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2016
📝 Explanation: USA is the largest IMF quota contributor.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
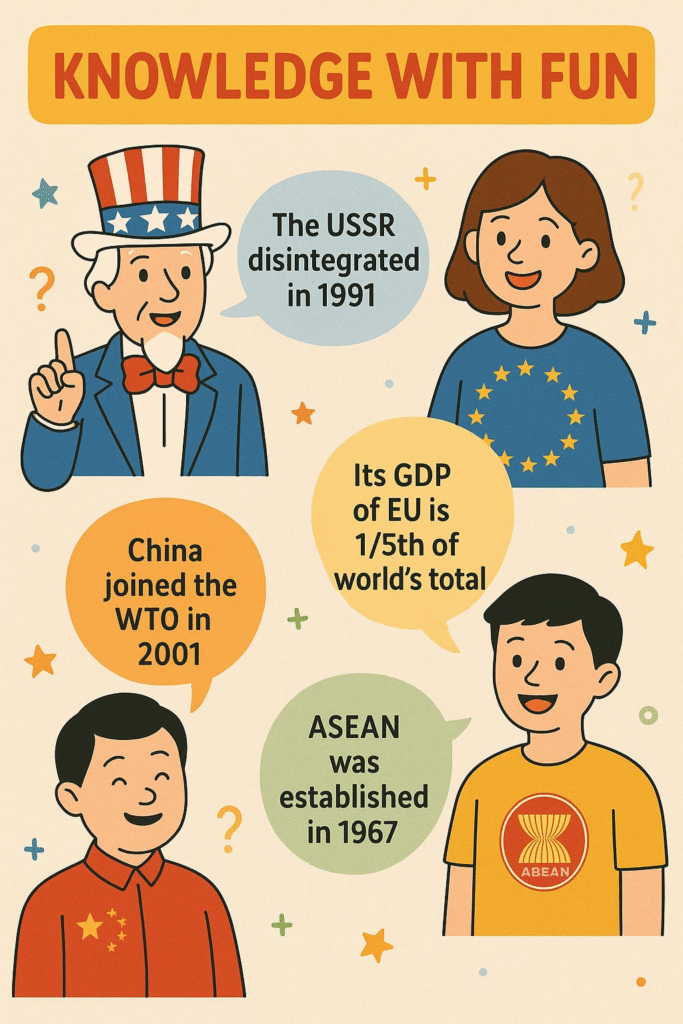
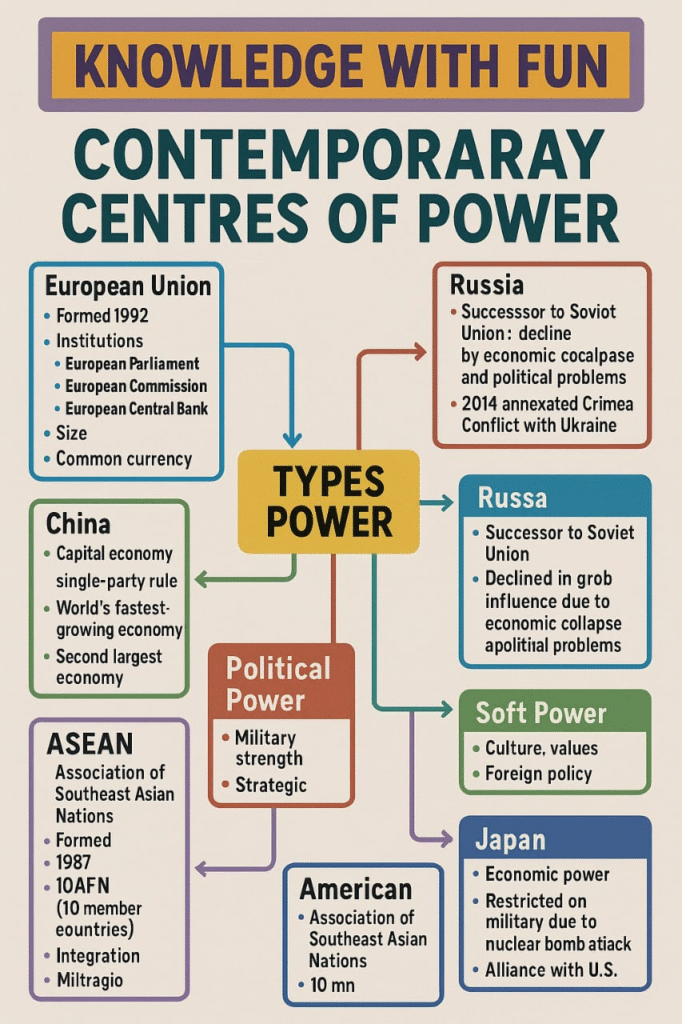
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————