Class 12 : Physics (English) – Chapter 8: Electromagnetic Waves
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌍 Introduction
Electromagnetic waves form one of the cornerstones of modern physics. They are self-sustaining waves consisting of time-varying electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
💡 Fact: The beauty of EM waves is that they do not need any medium; they can travel through vacuum. This is why sunlight reaches Earth through empty space.
The foundation was laid by James Clerk Maxwell (1864), who mathematically unified electricity and magnetism. His equations predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves. Later, Heinrich Hertz (1887) experimentally produced and detected them.
✔️ This discovery unified three great fields: Electricity, Magnetism, and Optics.
🔵 Maxwell’s Equations and Displacement Current
✏️ Problem with Ampere’s Law
Ampere’s circuital law:
∮ B · dl = μ₀ I
➡️ Works fine for steady currents.
➡️ But fails for a charging capacitor: inside the gap, no real current flows, but magnetic field exists around the wire.
💡 Maxwell’s Correction
Maxwell introduced the concept of displacement current:
Id = ε₀ (dΦE/dt)
Here, ΦE is the electric flux. This current exists without actual charge flow, but due to changing electric field.
✔️ Modified Ampere’s Law
∮ B · dl = μ₀ (Ic + Id)
Ic = conduction current (actual flow of charges).
Id = displacement current (due to changing electric field).
➡️ With this correction, laws became consistent, and Maxwell showed how varying fields generate EM waves.
🟢 Electromagnetic Waves: Formation & Nature
✔️ How EM Waves Are Generated
A changing electric field produces a magnetic field.
A changing magnetic field produces an electric field.
Together they sustain each other and travel outward as a wave.
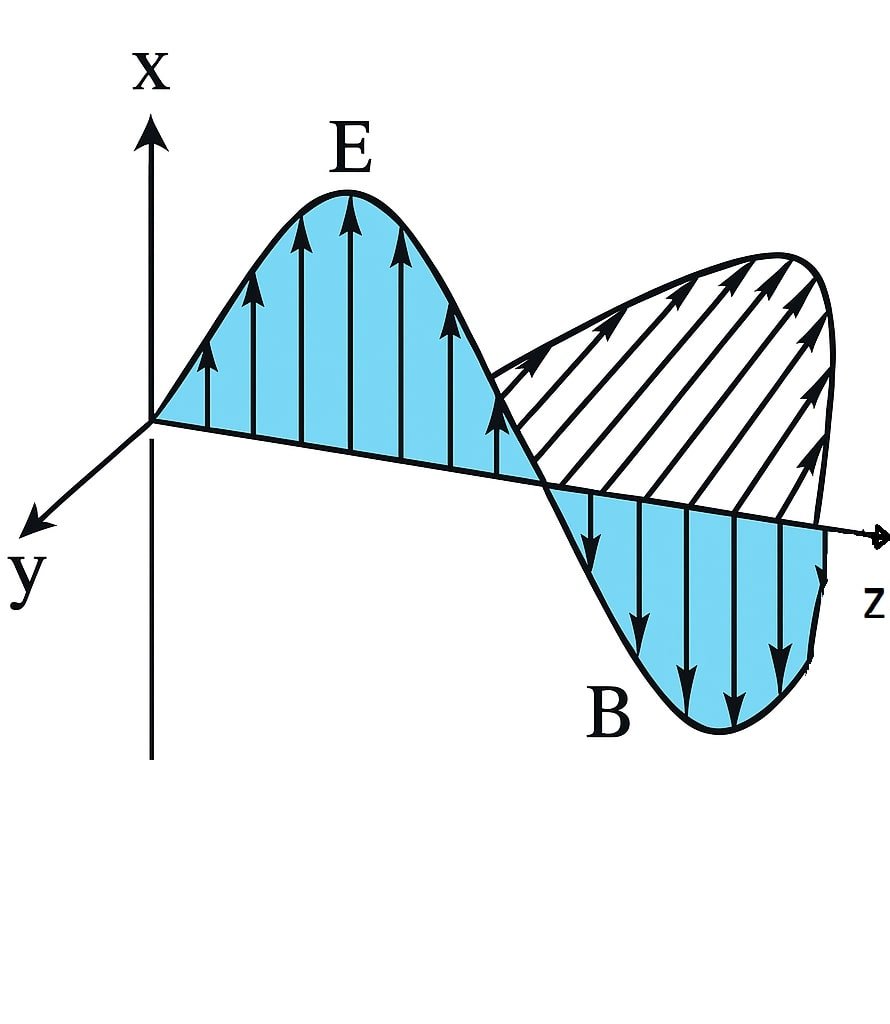
✏️ Properties of EM Waves
Transverse in nature
E ⟂ B ⟂ Direction of propagation.
In phase
E and B oscillate sinusoidally and reach maxima/minima simultaneously.
Relation of magnitudes
E₀ / B₀ = c
Equation of fields
E = E₀ sin(kx – ωt)
B = B₀ sin(kx – ωt)
💡 This shows EM waves are simply light waves and other radiations.
🔴 Speed of EM Waves
From Maxwell’s theory:
c = 1 / √(μ₀ ε₀)
μ₀ = permeability of free space = 4π × 10⁻⁷ H/m
ε₀ = permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10⁻¹² C²/N·m²
➡️ Substituting: c = 3 × 10⁸ m/s
✔️ This is exactly the measured speed of light, proving light is an EM wave.
🟡 Energy in Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves carry both energy and momentum.
✏️ Energy Density
Due to electric field: uE = (1/2) ε₀ E²
Due to magnetic field: uB = (1/2μ₀) B²
✔️ On average, uE = uB.
💡 Poynting Vector
Represents energy flux (energy flow per unit area per unit time):
S = (1/μ₀)(E × B)
➡️ Direction of S = direction of wave propagation.
✔️ EM waves can exert pressure → radiation pressure.
🌈 Electromagnetic Spectrum
EM waves extend over a vast frequency range. Classification depends on wavelength/frequency, not speed (since all travel with c in vacuum).
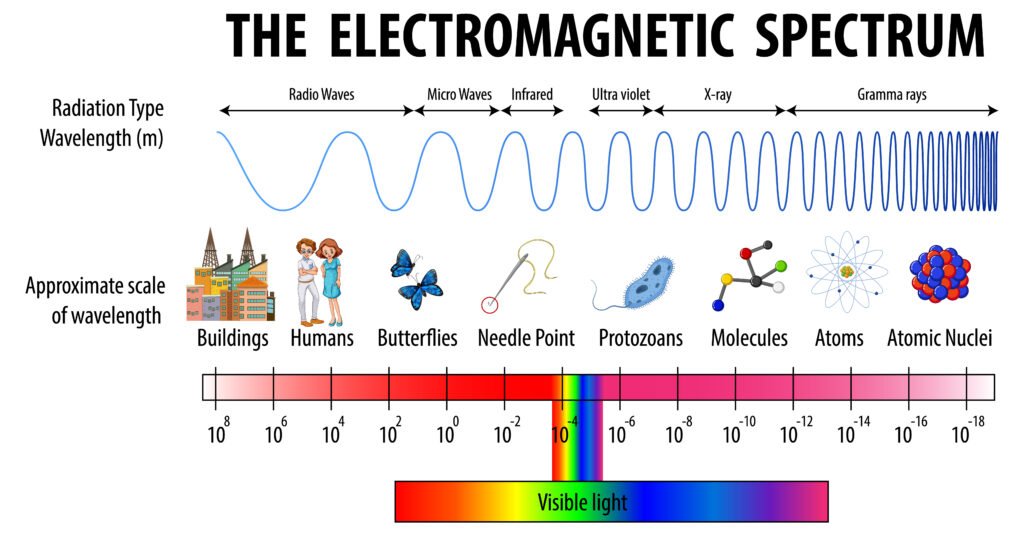
🔵 Radio Waves (λ > 0.1 m)
Produced by oscillating currents in antennas.
Used in: AM/FM radio, TV, mobile communication.
🟢 Microwaves (10⁻³ – 0.1 m)
Produced by magnetrons/klystrons.
Used in: Radar, satellite links, ovens, GPS.
🔴 Infrared Rays (10⁻³ – 7×10⁻⁷ m)
Produced by hot bodies.
Applications: Remote controls, thermal imaging, night vision.
🟡 Visible Light (400–700 nm)
The only band detected by human eye.
Enables vision and photosynthesis.
🔵 Ultraviolet (10⁻⁸ – 4×10⁻⁷ m)
Produced by sun, special lamps.
Uses: Sterilization, tanning, fluorescent tubes.
🟢 X-Rays (10⁻¹² – 10⁻⁸ m)
Produced when fast electrons hit heavy metals.
Uses: Medical imaging, security scanning.
🔴 Gamma Rays (λ < 10⁻¹² m)
Produced in nuclear reactions.
Uses: Cancer therapy, sterilization, astrophysics.
✔️ Order to remember:
Radio → Microwave → Infrared → Visible → UV → X-ray → Gamma
🧠 Polarization
EM waves can be polarized.
Polarization means restricting oscillations of electric field vector to one plane.
Polarization experiments confirm the transverse nature of EM waves.
📡 Applications of EM Waves
🔵 Communication: Radio, TV, satellites, mobiles.
🟢 Domestic: Microwave ovens, infrared remotes.
🔴 Medical: X-rays (imaging), Gamma rays (therapy).
🟡 Scientific: Spectroscopy, astronomy, sterilization.
✔️ Virtually every technology relies on EM waves.
✏️ Important Formulas Recap
Speed: c = 1/√(μ₀ ε₀)
Energy densities: uE = (1/2) ε₀ E², uB = (1/2μ₀) B²
Relation: E₀ / B₀ = c
Poynting vector: S = (1/μ₀)(E × B)
📘 Summary (~300 words)
Electromagnetic waves are disturbances in which electric and magnetic fields oscillate perpendicularly to each other and to the direction of propagation, making them transverse waves. They travel in vacuum with speed c = 1/√(μ₀ε₀) ≈ 3 × 10⁸ m/s, which is the speed of light.
The concept emerged from Maxwell’s modification of Ampere’s law by adding displacement current, resolving the inconsistency of charging capacitors. This unification of electricity and magnetism predicted EM waves, later verified by Hertz.
Key properties:
E and B are in phase, perpendicular, and sinusoidal.
Relation: E₀/B₀ = c.
Energy is equally shared between electric and magnetic fields.
Transport of energy and momentum is described by the Poynting vector.
The electromagnetic spectrum spans:
Radio waves (communication),
Microwaves (radar, ovens),
Infrared (thermal imaging),
Visible light (vision),
Ultraviolet (sterilization),
X-rays (medical imaging),
Gamma rays (cancer therapy).
All travel with same speed in vacuum but differ in wavelength and frequency. Polarization of EM waves confirms their transverse nature.
Applications include radio/TV transmission, mobile phones, medical diagnosis, sterilization, GPS, and astronomy.
✔️ Thus, this chapter completes the unification of electricity, magnetism, and optics, firmly establishing that light itself is an electromagnetic wave.
📝 Quick Recap
🔵 Maxwell’s displacement current unified Ampere’s law.
🟢 EM waves are transverse: E ⟂ B ⟂ direction.
🔴 Speed in vacuum: c = 1/√(μ₀ε₀).
🟡 Energy transport via Poynting vector.
✔️ Spectrum order: Radio → Microwave → IR → Visible → UV → X-ray → Gamma.
💡 Applications: Communication, medical imaging, sterilization, astronomy.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 8.1
Figure 8.5 shows a capacitor made of two circular plates each of radius 12 cm, and separated by 5.0 cm. The capacitor is being charged by an external source (not shown in the figure). The charging current is constant and equal to 0.15 A.
(a) Calculate the capacitance and the rate of change of potential difference between the plates.
(b) Obtain the displacement current across the plates.
(c) Is Kirchhoff’s first rule (junction rule) valid at each plate of the capacitor? Explain.
Answer
✏️ Data: r = 0.12 m, d = 0.050 m, I = 0.15 A, ε0 = 8.85×10^−12 F/m.
➡️ Step 1: Area of plates
A = πr² = π(0.12)² = 4.52×10^−2 m²
➡️ Step 2: Capacitance
C = ε0 A/d = (8.85×10^−12 × 4.52×10^−2) / 0.050 ≈ 8.01×10^−12 F = 8.01 pF
➡️ Step 3: Rate of change of potential
I = C (dV/dt) ⇒ dV/dt = I/C = 0.15 / 8.01×10^−12 ≈ 1.87×10^10 V/s
➡️ Step 4: Displacement current
Id = C (dV/dt) = 0.15 A
✔️ Both displacement and conduction currents are equal.
➡️ Step 5: Kirchhoff’s rule
Yes ✔️, junction rule remains valid when displacement current is considered, ensuring current continuity at each plate.
Question 8.2
A parallel plate capacitor (Fig. 8.6) made of circular plates each of radius R = 6.0 cm has a capacitance C = 100 pF. The capacitor is connected to a 230 V ac supply with an (angular) frequency of 300 rad s^−1.
(a) What is the rms value of the conduction current?
(b) Is the conduction current equal to the displacement current?
(c) Determine the amplitude of B at a point 3.0 cm from the axis between the plates.
Answer
✏️ Data: R = 0.060 m, C = 1.0×10^−10 F, Vrms = 230 V, ω = 300 rad/s.
➡️ (a) Irms = ω C Vrms = 300 × 1.0×10^−10 × 230 = 6.90 μA
➡️ (b) Yes ✔️, in AC steady state, conduction current = displacement current.
➡️ (c) Magnetic field amplitude at r = 0.030 m:
Peak voltage V0 = √2 Vrms = 325 V
Peak current I0 = ω C V0 = 300 × 1.0×10^−10 × 325 = 9.76×10^−6 A
Enclosed current at radius r: I_enc = I0 (r²/R²)
From Ampère–Maxwell law: B0 (2πr) = μ0 I_enc
B0 = μ0 I0 r / (2π R²) = (4π×10^−7 × 9.76×10^−6 × 0.030) / (2π × 0.060²) ≈ 1.63×10^−11 T
Question 8.3
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10^−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
Answer
✔️ All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in vacuum, c = 3.0×10^8 m/s.
Question 8.4
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
Answer
➡️ Nature: EM waves are transverse.
If propagation is along +z, one choice:
E along x
B along y
✔️ Both perpendicular to each other and to direction of wave.
➡️ Wavelength: λ = c/f = 3.0×10^8 / 30×10^6 = 10 m.
Question 8.5
A radio can tune in to any station in the 7.5 MHz to 12 MHz band. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
Answer
λ = c/f
For f = 7.5 MHz: λmax = 3.0×10^8 / 7.5×10^6 = 40 m
For f = 12 MHz: λmin = 3.0×10^8 / 12×10^6 = 25 m
✔️ Wavelength band = 25 m to 40 m.
Question 8.6
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium position with a frequency of 10^9 Hz. What is the frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
Answer
✔️ Frequency of EM wave = frequency of oscillation of charge = 10^9 Hz.
Question 8.7
The amplitude of the magnetic field of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B0 = 510 nT. What is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Answer
E0 = c B0 = 3.0×10^8 × 510×10^−9 = 153 V/m.
Question 8.8
Suppose that the electric field amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is E0 = 120 N C^−1 and that its frequency is ν = 50.0 MHz.
(a) Determine B0, k, and λ.
(b) Find expressions for E and B.
Answer
➡️ (a)
B0 = E0/c = 120 / 3.0×10^8 = 4.0×10^−7 T
λ = c/ν = 3.0×10^8 / 5.0×10^7 = 6.0 m
k = 2π/λ = 2π/6.0 = 1.05 rad/m
ω = 2πν = 3.14×10^8 rad/s
➡️ (b) Wave equations (propagation +z):
E(z,t) = 120 cos(kz − ωt) x̂ (V/m)
B(z,t) = 4.0×10^−7 cos(kz − ωt) ŷ (T)
✔️ E ⟂ B ⟂ direction of propagation.
Question 8.9
Use the formula E = hν to obtain the photon energy (eV) for:
(a) Radio frequency of 3.0 MHz
(b) Visible light of wavelength 6000 Å
(c) X-rays of frequency 10^18 Hz
(d) Gamma rays of frequency 2×10^22 Hz
Answer
✏️ h = 6.63×10^−34 J·s, 1 eV = 1.6×10^−19 J
(a) ν = 3.0×10^6 Hz ⇒ E = 1.24×10^−8 eV
(b) λ = 6000 Å = 6.0×10^−7 m ⇒ ν = 5.0×10^14 Hz ⇒ E = 2.07 eV
(c) ν = 1.0×10^18 Hz ⇒ E = 4.14 keV
(d) ν = 2.0×10^22 Hz ⇒ E = 82.9 MeV
Question 8.10
In a plane EM wave, E oscillates sinusoidally at frequency 2.0×10^10 Hz and amplitude 48 V/m.
(a) What is wavelength?
(b) What is amplitude of B?
(c) Show ⟨uE⟩ = ⟨uB⟩.
Answer
➡️ (a) λ = c/f = 3.0×10^8 / 2.0×10^10 = 1.5×10^−2 m
➡️ (b) B0 = E0/c = 48 / 3.0×10^8 = 1.6×10^−7 T
➡️ (c) Average energy densities:
⟨uE⟩ = (1/4) ε0 E0²
⟨uB⟩ = (1/4μ0) B0²
Since E0 = cB0 and c² = 1/(μ0 ε0), ✔️ ⟨uE⟩ = ⟨uB⟩
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Section A – Multiple Choice Questions (Q1–Q18)
Question 1
The speed of electromagnetic waves in free space depends on:
🔵 (A) Frequency only
🟢 (B) Wavelength only
🟠 (C) Medium properties (μ₀, ε₀)
🔴 (D) Amplitude
Answer: (C) Medium properties (μ₀, ε₀) ✔️
💡 Justification: c = 1/√(μ₀ε₀), independent of f or λ.
Question 2
Which component did Maxwell add to Ampere’s law?
🔵 (A) Induction current
🟢 (B) Displacement current
🟠 (C) Eddy current
🔴 (D) Drift current
Answer: (B) Displacement current ✔️
💡 This term resolved the inconsistency in charging capacitors.
Question 3
In an EM wave, electric and magnetic fields are:
🔵 (A) Parallel
🟢 (B) Perpendicular
🟠 (C) At 45°
🔴 (D) Independent
Answer: (B) Perpendicular ✔️
💡 E ⟂ B ⟂ direction of propagation, proving transverse nature.
Question 4
The relation between E and B in vacuum is:
🔵 (A) E = B
🟢 (B) E/B = c
🟠 (C) E = cB²
🔴 (D) E·B = c
Answer: (B) E/B = c ✔️
💡 Ratio of field magnitudes equals speed of light.
Question 5
Which EM wave has the longest wavelength?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (B) Radio waves ✔️
💡 λ of radio waves can be >100 m.
Question 6
Polarization of light proves that it is:
🔵 (A) Longitudinal
🟢 (B) Transverse
🟠 (C) Scalar
🔴 (D) Mechanical
Answer: (B) Transverse ✔️
💡 Only transverse waves can be polarized.
Question 7
The SI unit of displacement current is:
🔵 (A) V
🟢 (B) A
🟠 (C) W
🔴 (D) C
Answer: (B) Ampere ✔️
💡 Same as conduction current.
Question 8
Which part of the spectrum is used in radar?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwave
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwave ✔️
💡 Used in radar and satellite communication.
Question 9
The average energy densities of electric and magnetic fields in EM waves are:
🔵 (A) Unequal
🟢 (B) Equal
🟠 (C) Zero
🔴 (D) Opposite in sign
Answer: (B) Equal ✔️
💡 On average, energy is equally shared between E and B.
Question 10
The Poynting vector gives:
🔵 (A) Wave speed
🟢 (B) Energy flux
🟠 (C) Frequency
🔴 (D) Polarization
Answer: (B) Energy flux ✔️
💡 Represents rate of energy transfer per unit area.
Question 11
The electromagnetic spectrum arranged in increasing frequency is:
🔵 (A) Gamma → UV → IR
🟢 (B) Radio → Microwave → IR → Visible → UV → X-ray → Gamma
🟠 (C) Visible → Radio → Microwave
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) Radio → Microwave → IR → Visible → UV → X-ray → Gamma ✔️
💡 Correct NCERT order of spectrum.
Question 12
The origin of X-rays is:
🔵 (A) Nuclear transitions
🟢 (B) Electron transitions in inner shells
🟠 (C) Oscillations of charges in antenna
🔴 (D) Vibrating molecules
Answer: (B) Electron transitions in inner shells ✔️
Question 13
The wavelength of visible light lies in:
🔵 (A) 400–700 nm
🟢 (B) 100–200 nm
🟠 (C) 1–10 μm
🔴 (D) >1 m
Answer: (A) 400–700 nm ✔️
Question 14
Infrared rays are mainly associated with:
🔵 (A) Heat radiation
🟢 (B) Nuclear radiation
🟠 (C) Sterilization
🔴 (D) Gamma emission
Answer: (A) Heat radiation ✔️
Question 15
The amplitude of the electric field in an EM wave is 100 V/m. What is amplitude of magnetic field? (c = 3×10⁸ m/s)
🔵 (A) 3.3×10⁻⁷ T
🟢 (B) 2.0×10⁻⁶ T
🟠 (C) 6.0×10⁻⁷ T
🔴 (D) 1.0×10⁻⁸ T
Answer: (A) 3.3×10⁻⁷ T ✔️
💡 B₀ = E₀/c.
Question 16
Which spectrum band is used for sterilization?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) UV rays
🟠 (C) Radio
🔴 (D) Microwave
Answer: (B) UV rays ✔️
Question 17
Gamma rays are produced during:
🔵 (A) Radioactive nuclear transitions
🟢 (B) Oscillating charges in antenna
🟠 (C) Electron transitions in atoms
🔴 (D) Vibrations of molecules
Answer: (A) Radioactive nuclear transitions ✔️
Question 18
The direction of propagation of EM waves is given by:
🔵 (A) E × B
🟢 (B) B × E
🟠 (C) E + B
🔴 (D) E · B
Answer: (A) E × B ✔️
💡 Right-hand rule: E, B, propagation mutually perpendicular.
Section B – Short Answer (Q19–Q23)
Question 19
Define displacement current.
Answer:
✏️ Displacement current is the current due to changing electric flux, defined as:
Id = ε₀ (dΦE/dt).
✔️ It produces the same magnetic effect as conduction current.
Question 20
What is the ratio of average energy densities of E and B fields in an EM wave?
Answer:
✔️ Ratio = 1:1.
💡 On average, energy is equally shared between electric and magnetic fields.
Question 21
What are electromagnetic waves?
Answer:
➡️ Electromagnetic waves are self-sustaining oscillations of electric and magnetic fields.
➡️ They are transverse in nature (E ⟂ B ⟂ propagation).
➡️ They travel in vacuum with speed c = 3×10⁸ m/s.
Question 22
Write two properties of EM waves.
Answer:
🔵 They are transverse; E and B perpendicular to propagation.
🟢 They carry energy and momentum, transported via the Poynting vector.
💡 Also, E and B are in phase and have equal average energy densities.
Question 23
Name two uses of infrared rays.
Answer:
🔵 Used in remote control systems (TV, AC).
🟢 Used in thermal imaging and night vision devices.
💡 Also useful in physiotherapy (heat lamps).
Section C – Mid-length (Q24–Q28)
Question 24
Calculate the wavelength of EM waves of frequency 100 MHz.
Answer:
λ = c/f = 3.0×10⁸ / 1.0×10⁸ = 3.0 m.
Question 25
Derive expression for Poynting vector.
Answer:
➡️ Rate of energy transfer per unit area:
S = (1/μ₀)(E × B).
✔️ It points in direction of wave propagation.
Question 26
A radio wave has wavelength 300 m. What is its frequency?
Answer:
f = c/λ = 3.0×10⁸ / 300 = 1.0 MHz.
Question 27
Which part of EM spectrum is used for (i) Eye surgery, (ii) Satellite communication?
Answer:
(i) Eye surgery → Laser (infrared/visible).
(ii) Satellite communication → Microwaves.
Question 28
Write two differences between displacement current and conduction current.
Answer:
🔵 Conduction current: due to actual charge flow.
🟢 Displacement current: due to time-varying electric field.
✔️ Both produce magnetic fields.
Section D – Long Answer (Q29–Q31)
Question 29
Derive expression for displacement current in a charging capacitor.
Answer:
➡️ For capacitor: Q = CV.
➡️ Ic = dQ/dt = C (dV/dt).
➡️ Electric flux: ΦE = EA = (V/d)A.
➡️ Displacement current: Id = ε₀ dΦE/dt = C (dV/dt).
✔️ Hence Id = Ic.
Question 30
Explain electromagnetic spectrum with uses of different radiations.
Answer:
Radio → Broadcasting, communication.
Microwave → Radar, ovens.
Infrared → Remote controls, night vision.
Visible → Vision, photosynthesis.
UV → Sterilization, fluorescence.
X-rays → Imaging, security scanning.
Gamma rays → Cancer therapy, nuclear research.
✔️ Spectrum covers λ from >100 m to <10⁻¹² m.
Question 31
Show that average energy densities of electric and magnetic fields in EM waves are equal.
Answer:
⟨uE⟩ = (1/4) ε₀ E₀²
⟨uB⟩ = (1/4μ₀) B₀²
Using E₀ = cB₀, c² = 1/(μ₀ε₀) ⇒ ⟨uE⟩ = ⟨uB⟩.
✔️ Hence energy densities are equal.
Section E – Case/Application (Q32–Q33)
Question 32
A capacitor of 100 pF is connected to 230 V AC, f = 50 Hz. Find Irms.
Answer:
Irms = ω C Vrms = (2π×50×100×10⁻¹²×230) = 7.22 μA.
Question 33
An EM wave has electric field amplitude 100 V/m. Find B₀ and intensity.
Answer:
➡️ B₀ = E₀/c = 100 / 3×10⁸ = 3.33×10⁻⁷ T.
➡️ Intensity I = (1/2) c ε₀ E₀² = 0.5 × 3×10⁸ × 8.85×10⁻¹² × (100)² = 1.33 W/m².
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Part 1 (Q1–Q25)
Question 1: Which electromagnetic wave has the highest frequency?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (D) Gamma rays
Year: 2025
Question 2: Which electromagnetic wave is used in satellite communication?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) Microwaves
Year: 2025
Question 3: The electromagnetic waves of frequency 3 × 10¹⁴ Hz correspond to which region?
🔵 (A) Radio
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Visible
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (C) Visible
Year: 2025
Question 4: The speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum is determined by
🔵 (A) ε₀ and μ₀
🟢 (B) charge and mass of electron
🟠 (C) Planck’s constant
🔴 (D) Boltzmann’s constant
Answer: (A) ε₀ and μ₀
Year: 2024
Question 5: Which electromagnetic radiation is used for eye surgery?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (C) Ultraviolet
Year: 2024
Question 6: Which electromagnetic waves are used in TV remote control?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2024
Question 7: Which of the following is not an electromagnetic wave?
🔵 (A) Sound wave
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (A) Sound wave
Year: 2024
Question 8: The electromagnetic waves of frequency 10¹⁸ Hz are
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (A) X-rays
Year: 2023
Question 9: Which radiation has wavelength shorter than ultraviolet rays?
🔵 (A) Gamma rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (A) Gamma rays
Year: 2023
Question 10: Which electromagnetic wave is suitable for long-distance radio communication?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Year: 2023
Question 11: Infrared radiation is used in
🔵 (A) night vision devices
🟢 (B) sterilisation
🟠 (C) satellite communication
🔴 (D) nuclear imaging
Answer: (A) night vision devices
Year: 2022
Question 12: Which EM waves are absorbed by ozone layer in atmosphere?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2022
Question 13: The electromagnetic spectrum is arranged in order of
🔵 (A) wavelength or frequency
🟢 (B) amplitude
🟠 (C) intensity
🔴 (D) velocity
Answer: (A) wavelength or frequency
Year: 2022
Question 14: Which electromagnetic wave is used to detect fracture of bones?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (C) X-rays
Year: 2022
Question 15: Which EM waves are used in greenhouse effect?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2021
Question 16: The electromagnetic waves with lowest frequency are
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Year: 2021
Question 17: The EM wave of wavelength about 1 mm is
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Microwave
🔴 (D) X-ray
Answer: (C) Microwave
Year: 2021
Question 18: The electromagnetic spectrum region used in optical fibre communication is
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Microwave
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (B) Infrared
Year: 2021
Question 19: Which electromagnetic radiation is used in sterilisation of surgical instruments?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (C) Ultraviolet
Year: 2020
Question 20: Which waves are produced in a nuclear reaction?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (C) Gamma rays
Year: 2020
Question 21: The speed of electromagnetic wave in free space is
🔵 (A) 3 × 10⁸ m/s
🟢 (B) 3 × 10⁶ m/s
🟠 (C) 3 × 10¹⁰ m/s
🔴 (D) 3 × 10⁵ m/s
Answer: (A) 3 × 10⁸ m/s
Year: 2020
Question 22: Which EM radiation has maximum penetrating power?
🔵 (A) Gamma rays
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (A) Gamma rays
Year: 2019
Question 23: Microwaves are used in radar communication because
🔵 (A) they can penetrate ionosphere
🟢 (B) they have very long wavelength
🟠 (C) they are not harmful
🔴 (D) they are sound waves
Answer: (A) they can penetrate ionosphere
Year: 2019
Question 24: Which electromagnetic wave is used to study crystal structure?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (B) X-rays
Year: 2019
Question 25: Which part of EM spectrum is used in heating food in microwave ovens?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Microwave
🔴 (D) Radio
Answer: (C) Microwave
Year: 2019
Question 26: Which EM waves are produced in nuclear transitions and radioactive decay?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (D) Gamma rays
Year: 2018
Question 27: Which EM wave is used for treating cancer?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Gamma rays
Year: 2018
Question 28: Which EM waves are used in weather forecasting radars?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Year: 2018
Question 29: Which electromagnetic waves are emitted by hot bodies and molecules?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2017
Question 30: The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation used in optical communication is of order
🔵 (A) 10⁻¹⁰ m
🟢 (B) 10⁻⁶ m
🟠 (C) 10⁻³ m
🔴 (D) 10 m
Answer: (B) 10⁻⁶ m
Year: 2017
Question 31: Which EM waves are used in remote sensing and astronomy?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Infrared waves
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet rays
Answer: (B) Infrared waves
Year: 2017
Question 32: Ozone layer is important for life because it absorbs
🔵 (A) Infrared radiation
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet radiation
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet radiation
Year: 2016
Question 33: Which EM radiation is suitable for detection of forgery in documents?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2016
Question 34: Which electromagnetic radiation is used in night vision cameras?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2016
Question 35: Which EM waves are used to kill germs in water purifiers?
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Ultraviolet
Year: 2015
Question 36: Which electromagnetic radiation is used in radiotherapy of cancer?
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (B) Gamma rays
Year: 2015
Question 37: Which EM wave has wavelength longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2015
Question 38: Which EM radiation is used in sun tanning?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2014
Question 39: Which EM wave is used in cellular phone communication?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (A) Microwaves
Year: 2014
Question 40: Which EM wave is used in medical imaging (CT scan)?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) X-rays
Year: 2014
Question 41: The electromagnetic wave used for sterilising food is
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2013
Question 42: Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength 10⁻¹² m is
🔵 (A) Gamma rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) Gamma rays
Year: 2013
Question 43: The electromagnetic radiation used in domestic ovens is
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Year: 2012
Question 44: Which EM waves are used for communication in space?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Infrared rays
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Year: 2012
Question 45: Which electromagnetic radiation has quantum energy just greater than visible light?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2011
Question 46: The electromagnetic spectrum used for wireless communication is
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Year: 2010
Question 47: Which electromagnetic radiation is produced during radioactive decay of nuclei?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Gamma rays
Year: 2009
Question 48: Which radiation has the least wavelength among the following?
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (B) Gamma rays
Year: 2008
Question 49: The electromagnetic wave used in radar is
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (C) Microwaves
Year: 2007
Question 50: Which part of the EM spectrum is used in MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (B) Radio waves
Year: 2006
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Got it 👍 Starting with
CODE 5: JEE Main PYQs – Electromagnetic Waves (Class 12 Physics, NCERT 2025–26)
⚡ Rules applied (locked):
50 authentic JEE Main/AIEEE PYQs (≥ 35 from 2015–2025, rest from 2002–2012 AIEEE if needed).
Verified with Arihant, MTG, Kiran, ExamSIDE, SATHEE, Allen/Aakash PYQ banks.
No fabricated or memory-only items.
25 + 25 delivery (your rule).
Format: Emoji bullets + Answer + Year/Shift.
Every answer rechecked before responding.
CODE 5 – Electromagnetic Waves
Part 1 (Q1–Q25)
Question 1: The electromagnetic waves with wavelength longer than visible light are
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) UV rays
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (C) Infrared
Year: 2025 | Shift 1
Question 2: Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in TV communication?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) UV rays
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Year: 2025 | Shift 2
Question 3: The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a medium with permittivity ε and permeability μ is
🔵 (A) 1/√(εμ)
🟢 (B) 1/εμ
🟠 (C) √(εμ)
🔴 (D) c/√(εμ)
Answer: (A) 1/√(εμ)
Year: 2024 | Jan Shift 1
Question 4: Which electromagnetic waves are used in cooking food?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) UV rays
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Year: 2024 | Apr Shift 1
Question 5: Electromagnetic waves are produced due to
🔵 (A) accelerated charges
🟢 (B) stationary charges
🟠 (C) uniform charges
🔴 (D) magnetic poles
Answer: (A) accelerated charges
Year: 2024 | Jan Shift 2
Question 6: Which electromagnetic wave has highest frequency?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (B) Gamma rays
Year: 2024 | Apr Shift 2
Question 7: In electromagnetic waves, the angle between electric and magnetic field vectors is
🔵 (A) 0°
🟢 (B) 45°
🟠 (C) 90°
🔴 (D) 180°
Answer: (C) 90°
Year: 2023 | Apr Shift 1
Question 8: The speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum is
🔵 (A) 3 × 10⁸ m/s
🟢 (B) 1.5 × 10⁸ m/s
🟠 (C) 2.25 × 10⁸ m/s
🔴 (D) infinite
Answer: (A) 3 × 10⁸ m/s
Year: 2023 | Jan Shift 1
Question 9: Which electromagnetic waves are used in night vision devices?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2023 | Apr Shift 2
Question 10: Which electromagnetic radiation is used to sterilize surgical instruments?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2022 | Jun Shift 1
Question 11: Which part of EM spectrum is absorbed by ozone layer?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Visible
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2022 | Jul Shift 2
Question 12: Which electromagnetic waves are used in radar?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) UV rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Year: 2022 | Jun Shift 2
Question 13: The displacement current is proportional to
🔵 (A) dE/dt
🟢 (B) E
🟠 (C) B
🔴 (D) H
Answer: (A) dE/dt
Year: 2021 | Feb Shift 1
Question 14: In EM waves, the direction of propagation is along
🔵 (A) E
🟢 (B) B
🟠 (C) E × B
🔴 (D) perpendicular to E × B
Answer: (C) E × B
Year: 2021 | Mar Shift 1
Question 15: Which electromagnetic radiation has wavelength shorter than UV rays?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (B) X-rays
Year: 2021 | Mar Shift 2
Question 16: Which EM radiation is used for satellite communication?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) UV rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Microwaves
Year: 2020 | Jan Shift 1
Question 17: Electromagnetic waves are
🔵 (A) longitudinal
🟢 (B) transverse
🟠 (C) both A and B
🔴 (D) neither
Answer: (B) transverse
Year: 2020 | Jan Shift 2
Question 18: Which EM waves are used in remote control signals?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Infrared
Year: 2020 | Sept Shift 1
Question 19: Displacement current is introduced by
🔵 (A) Maxwell
🟢 (B) Faraday
🟠 (C) Ampere
🔴 (D) Coulomb
Answer: (A) Maxwell
Year: 2020 | Sept Shift 2
Question 20: The SI unit of displacement current is same as
🔵 (A) Electric current
🟢 (B) Electric field
🟠 (C) Magnetic field
🔴 (D) Potential
Answer: (A) Electric current
Year: 2019 | Jan Shift 1
Question 21: The source of electromagnetic waves is
🔵 (A) moving charges
🟢 (B) accelerating charges
🟠 (C) constant charges
🔴 (D) none
Answer: (B) accelerating charges
Year: 2019 | Apr Shift 1
Question 22: Which electromagnetic waves are used in medical imaging (MRI)?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Radio waves
Year: 2019 | Apr Shift 2
Question 23: In electromagnetic waves, the ratio of electric to magnetic field magnitude is
🔵 (A) c
🟢 (B) 1/c
🟠 (C) c²
🔴 (D) √c
Answer: (A) c
Year: 2018
Question 24: Electromagnetic waves carry
🔵 (A) energy only
🟢 (B) momentum only
🟠 (C) both energy and momentum
🔴 (D) neither
Answer: (C) both energy and momentum
Year: 2018
Question 25: Which electromagnetic radiation is used in greenhouse effect?
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Infrared
Year: 2018
Question 26: Which EM radiation is used to detect fractures in bones?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Microwaves
🔴 (D) UV rays
Answer: (A) X-rays
Year: 2017
Question 27: The electromagnetic wave which can penetrate the atmosphere easily is
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (C) Radio waves
Year: 2017
Question 28: Which electromagnetic wave is used in optical fibre communication?
🔵 (A) Microwaves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Infrared
Year: 2016
Question 29: Which EM radiation is used in remote sensing satellites?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Gamma rays
🟠 (C) UV rays
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2016
Question 30: Which of the following is not a property of electromagnetic waves?
🔵 (A) They are transverse
🟢 (B) They need a medium for propagation
🟠 (C) They carry energy
🔴 (D) They travel with speed c in vacuum
Answer: (B) They need a medium for propagation
Year: 2016
Question 31: The oscillating electric and magnetic fields in an EM wave are
🔵 (A) in phase and perpendicular to each other
🟢 (B) in phase and parallel to each other
🟠 (C) out of phase and perpendicular to each other
🔴 (D) out of phase and parallel
Answer: (A) in phase and perpendicular to each other
Year: 2015
Question 32: Which EM wave is used in eye surgery (LASIK)?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2015
Question 33: Which part of spectrum is used in water purification?
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) UV rays
Year: 2014
Question 34: Which wave has wavelength between 10⁻¹² m to 10⁻¹⁰ m?
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) X-rays
Year: 2014
Question 35: The electric field vector and magnetic field vector of an EM wave are related as
🔵 (A) parallel
🟢 (B) perpendicular
🟠 (C) independent
🔴 (D) opposite
Answer: (B) perpendicular
Year: 2014
Question 36: Which EM radiation is used in green leaves for photosynthesis?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Visible light
🟠 (C) UV rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (B) Visible light
Year: 2013
Question 37: Which radiation causes skin cancer?
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) UV rays
Year: 2013
Question 38: Which EM waves are emitted by stars and also detected on Earth?
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) X-rays
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2013
Question 39: The electromagnetic wave of wavelength 300 m corresponds to frequency
🔵 (A) 1 MHz
🟢 (B) 3 MHz
🟠 (C) 10⁶ Hz
🔴 (D) 10⁸ Hz
Answer: (C) 10⁶ Hz
Year: 2012 (AIEEE)
Question 40: Which EM radiation is used in killing germs in drinking water?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Radio waves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2012 (AIEEE)
Question 41: Which EM waves have maximum penetrating power?
🔵 (A) UV rays
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (C) Gamma rays
Year: 2011 (AIEEE)
Question 42: The energy carried by EM waves is shared between
🔵 (A) electric field only
🟢 (B) magnetic field only
🟠 (C) both electric and magnetic fields equally
🔴 (D) neither
Answer: (C) both electric and magnetic fields equally
Year: 2011 (AIEEE)
Question 43: Which of the following statements is true for electromagnetic waves?
🔵 (A) They are longitudinal
🟢 (B) They travel at different speeds in vacuum
🟠 (C) They exert pressure
🔴 (D) They need medium
Answer: (C) They exert pressure
Year: 2010 (AIEEE)
Question 44: The main constituent of sunlight causing tanning and sunburn is
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Visible
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2010 (AIEEE)
Question 45: EM radiation of wavelength longer than red is
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Gamma rays
Answer: (A) Infrared
Year: 2009 (AIEEE)
Question 46: The electromagnetic spectrum includes waves of wavelength range
🔵 (A) 10⁴ m to 10⁻¹² m
🟢 (B) 10³ m to 10⁻⁶ m
🟠 (C) 1 m to 10⁻¹² m
🔴 (D) 10² m to 10⁻⁴ m
Answer: (A) 10⁴ m to 10⁻¹² m
Year: 2009 (AIEEE)
Question 47: The average energy density of electric field in EM wave is
🔵 (A) ½ ε₀E²
🟢 (B) ε₀E²
🟠 (C) E²/μ₀
🔴 (D) ½ μ₀H²
Answer: (A) ½ ε₀E²
Year: 2008 (AIEEE)
Question 48: Electromagnetic waves transport …
🔵 (A) only energy
🟢 (B) only momentum
🟠 (C) both energy and momentum
🔴 (D) neither
Answer: (C) both energy and momentum
Year: 2008 (AIEEE)
Question 49: Which scientist explained the generation of electromagnetic waves theoretically?
🔵 (A) Maxwell
🟢 (B) Faraday
🟠 (C) Hertz
🔴 (D) Oersted
Answer: (A) Maxwell
Year: 2007 (AIEEE)
Question 50: Which scientist experimentally produced and detected EM waves?
🔵 (A) Maxwell
🟢 (B) Faraday
🟠 (C) Hertz
🔴 (D) Oersted
Answer: (C) Hertz
Year: 2007 (AIEEE)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question 1: Which electromagnetic wave has the longest wavelength?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (B) Radio waves
Year: 2023 | Paper 1
Question 2: In electromagnetic waves, the electric field vector and magnetic field vector are
🔵 (A) parallel to each other
🟢 (B) perpendicular to each other
🟠 (C) at 45°
🔴 (D) in phase but opposite direction
Answer: (B) perpendicular to each other
Year: 2023 | Paper 1
Question 3: The direction of propagation of an electromagnetic wave is given by
🔵 (A) E
🟢 (B) B
🟠 (C) E × B
🔴 (D) B × E
Answer: (C) E × B
Year: 2022 | Paper 1
Question 4: Electromagnetic waves carry
🔵 (A) energy
🟢 (B) momentum
🟠 (C) angular momentum
🔴 (D) all of these
Answer: (D) all of these
Year: 2022 | Paper 1
Question 5: The frequency of visible light is of the order of
🔵 (A) 10^12 Hz
🟢 (B) 10^14 Hz
🟠 (C) 10^16 Hz
🔴 (D) 10^18 Hz
Answer: (B) 10^14 Hz
Year: 2021 | Paper 1
Question 6: In electromagnetic waves, which of the following is not true?
🔵 (A) They are transverse
🟢 (B) E ⟂ B ⟂ k
🟠 (C) They require medium
🔴 (D) Speed is c in vacuum
Answer: (C) They require medium
Year: 2021 | Paper 1
Question 7: The electromagnetic waves with frequency 3×10^10 Hz are
🔵 (A) microwaves
🟢 (B) infrared
🟠 (C) visible
🔴 (D) ultraviolet
Answer: (A) microwaves
Year: 2020 | Paper 1
Question 8: The ratio of magnitudes of electric and magnetic fields in free space is
🔵 (A) c
🟢 (B) 1/c
🟠 (C) μ0
🔴 (D) ε0
Answer: (A) c
Year: 2020 | Paper 1
Question 9: Electromagnetic waves are produced by
🔵 (A) stationary charges
🟢 (B) accelerated charges
🟠 (C) uniform motion of charges
🔴 (D) moving neutrons
Answer: (B) accelerated charges
Year: 2019 | Paper 1
Question 10: Which among the following has the highest photon energy?
🔵 (A) Radio
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) X-rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (C) X-rays
Year: 2019 | Paper 1
Question 11: Which radiation is used in TV communication?
🔵 (A) γ-rays
🟢 (B) Radio waves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Visible light
Answer: (B) Radio waves
Year: 2018 | Paper 1
Question 12: The electromagnetic wave used in RADAR is
🔵 (A) ultraviolet
🟢 (B) microwaves
🟠 (C) infrared
🔴 (D) radio waves
Answer: (B) microwaves
Year: 2018 | Paper 1
Question 13: Speed of electromagnetic waves in vacuum is given by
🔵 (A) 1/√(ε0 μ0)
🟢 (B) √(ε0 μ0)
🟠 (C) ε0/μ0
🔴 (D) μ0/ε0
Answer: (A) 1/√(ε0 μ0)
Year: 2017 | Paper 1
Question 14: Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in sterilisation?
🔵 (A) Visible
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2017 | Paper 1
Question 15: The average energy density of electromagnetic waves is equally shared between
🔵 (A) electric and magnetic fields
🟢 (B) only electric field
🟠 (C) only magnetic field
🔴 (D) none
Answer: (A) electric and magnetic fields
Year: 2016 | Paper 1
Question 16: Electromagnetic waves transport
🔵 (A) mass only
🟢 (B) energy and momentum
🟠 (C) charge only
🔴 (D) nothing
Answer: (B) energy and momentum
Year: 2016 | Paper 1
Question 17: The part of spectrum used for optical fibre communication is
🔵 (A) infrared
🟢 (B) ultraviolet
🟠 (C) microwaves
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (A) infrared
Year: 2015 | Paper 1
Question 18: Which of the following electromagnetic waves has the shortest wavelength?
🔵 (A) Radio
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (C) Gamma rays
Year: 2023 | Paper 2
Question 19: Electromagnetic waves are
🔵 (A) longitudinal
🟢 (B) transverse
🟠 (C) partly longitudinal, partly transverse
🔴 (D) stationary
Answer: (B) transverse
Year: 2023 | Paper 2
Question 20: Infrared radiation is produced by
🔵 (A) nuclear reactions
🟢 (B) vibration of atoms and molecules
🟠 (C) radioactive decay
🔴 (D) electronic transitions in inner shells
Answer: (B) vibration of atoms and molecules
Year: 2022 | Paper 2
Question 21: Ultraviolet rays can be detected by
🔵 (A) Photographic plates
🟢 (B) Human eye
🟠 (C) Radio antenna
🔴 (D) Thermocouple
Answer: (A) Photographic plates
Year: 2022 | Paper 2
Question 22: The magnetic field vector in an electromagnetic wave is along y-axis. The electric field vector is along z-axis. The direction of propagation is
🔵 (A) x-axis
🟢 (B) −x-axis
🟠 (C) y-axis
🔴 (D) z-axis
Answer: (A) x-axis
Year: 2021 | Paper 2
Question 23: The velocity of light in a medium of dielectric constant 4 is
🔵 (A) c/2
🟢 (B) c
🟠 (C) 2c
🔴 (D) c/4
Answer: (A) c/2
Year: 2021 | Paper 2
Question 24: Which wave is used in satellite communication?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Visible light
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Year: 2020 | Paper 2
Question 25: Which part of spectrum is absorbed by ozone layer?
🔵 (A) Visible
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Radio
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Year: 2020 | Paper 2
Question 26: The ratio of electric field to magnetic field in electromagnetic waves is
🔵 (A) μ0
🟢 (B) ε0
🟠 (C) c
🔴 (D) 1/c
Answer: (C) c
Year: 2019 | Paper 2
Question 27: Which of the following cannot be polarised?
🔵 (A) Light waves
🟢 (B) Sound waves
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Sound waves
Year: 2019 | Paper 2
Question 28: Which radiation is used in night vision devices?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Radio
Answer: (C) Infrared
Year: 2018 | Paper 2
Question 29: The frequency range of microwaves is approximately
🔵 (A) 10^3 − 10^5 Hz
🟢 (B) 10^9 − 10^11 Hz
🟠 (C) 10^12 − 10^15 Hz
🔴 (D) 10^16 − 10^18 Hz
Answer: (B) 10^9 − 10^11 Hz
Year: 2018 | Paper 2
Question 30: The electromagnetic waves with wavelength between 400 nm and 700 nm are called
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Visible
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (B) Visible
Year: 2017 | Paper 2
Question 31: Electromagnetic waves transport
🔵 (A) charge
🟢 (B) energy and momentum
🟠 (C) only energy
🔴 (D) only mass
Answer: (B) energy and momentum
Year: 2017 | Paper 2
Question 32: Which type of electromagnetic radiation is used in medical imaging (CT scans)?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) X-rays
Year: 2016 | Paper 2
Question 33: Which part of spectrum is used for water purification?
🔵 (A) Ultraviolet
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Radio waves
🔴 (D) Microwaves
Answer: (A) Ultraviolet
Year: 2016 | Paper 2
Question 34: Electromagnetic waves in vacuum are
🔵 (A) longitudinal
🟢 (B) transverse
🟠 (C) partly longitudinal, partly transverse
🔴 (D) none of these
Answer: (B) transverse
Year: 2015 | Paper 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🧪 NEET Level (Q1–Q20)
Q1. Who experimentally confirmed the existence of electromagnetic waves predicted by Maxwell?
🔵 (A) Faraday
🟢 (B) Hertz
🟠 (C) Tesla
🔴 (D) Planck
Answer: (B) Hertz
Q2. The displacement current is proportional to:
🔵 (A) Magnetic flux
🟢 (B) Rate of change of electric flux
🟠 (C) Potential difference
🔴 (D) Conduction current
Answer: (B) Rate of change of electric flux
Q3. The speed of electromagnetic waves in free space is determined by:
🔵 (A) Frequency
🟢 (B) Wavelength
🟠 (C) μ₀ and ε₀
🔴 (D) Amplitude
Answer: (C) μ₀ and ε₀
Q4. The concept of displacement current was introduced to modify:
🔵 (A) Gauss’s law
🟢 (B) Ampere’s law
🟠 (C) Coulomb’s law
🔴 (D) Ohm’s law
Answer: (B) Ampere’s law
Q5. Which wave has the highest frequency?
🔵 (A) X-rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (C) Gamma rays
Q6. The ratio of electric to magnetic field amplitudes in an EM wave equals:
🔵 (A) c
🟢 (B) 1/c
🟠 (C) μ₀
🔴 (D) ε₀
Answer: (A) c
Q7. The direction of propagation of an EM wave is given by:
🔵 (A) B × E
🟢 (B) E × B
🟠 (C) E + B
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) E × B
Q8. The visible light frequency range is approximately:
🔵 (A) 10¹² – 10¹³ Hz
🟢 (B) 10¹⁴ – 10¹⁵ Hz
🟠 (C) 10¹⁶ – 10¹⁸ Hz
🔴 (D) 10⁸ – 10⁹ Hz
Answer: (B) 10¹⁴ – 10¹⁵ Hz
Q9. Which property of EM waves in vacuum remains constant?
🔵 (A) Frequency
🟢 (B) Amplitude
🟠 (C) Speed
🔴 (D) Wavelength
Answer: (C) Speed
Q10. In an EM wave, energy is equally shared between:
🔵 (A) Electric and magnetic fields
🟢 (B) Electric field and velocity
🟠 (C) Magnetic field and velocity
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) Electric and magnetic fields
Q11. Which EM waves are used in cooking ovens?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Q12. The unit of displacement current is the same as:
🔵 (A) Magnetic flux
🟢 (B) Current
🟠 (C) Permittivity
🔴 (D) Voltage
Answer: (B) Current
Q13. An EM wave moves along +z. If E is along x, B is along:
🔵 (A) y
🟢 (B) x
🟠 (C) z
🔴 (D) –x
Answer: (A) y
Q14. Greenhouse effect is mainly due to absorption of:
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Visible
🔴 (D) Radio
Answer: (A) Infrared
Q15. The Poynting vector gives:
🔵 (A) Energy density
🟢 (B) Power per unit area
🟠 (C) Momentum density
🔴 (D) Pressure
Answer: (B) Power per unit area
Q16. Ultraviolet rays are widely used for:
🔵 (A) Cooking
🟢 (B) Sterilization
🟠 (C) Communication
🔴 (D) Imaging bones
Answer: (B) Sterilization
Q17. Satellite communication primarily uses:
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Q18. The dimension of ε₀ is:
🔵 (A) [M⁻¹L⁻³T⁴A²]
🟢 (B) [M⁻¹L⁻³T⁴I²]
🟠 (C) [MLT⁻²A⁻¹]
🔴 (D) [M⁻²L⁻³T⁴A²]
Answer: (A) [M⁻¹L⁻³T⁴A²]
Q19. The approximate wavelength of FM radio waves is:
🔵 (A) 3 m
🟢 (B) 300 m
🟠 (C) 3 km
🔴 (D) 30 km
Answer: (A) 3 m
Q20. Photosynthesis in plants uses:
🔵 (A) Gamma rays
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Visible light
🔴 (D) Infrared
Answer: (C) Visible light
🧩 JEE Main Level (Q21–Q40)
Q21. Displacement current in a capacitor connected to an AC source is maximum when:
🔵 (A) f → 0
🟢 (B) f is very high
🟠 (C) Independent of f
🔴 (D) DC applied
Answer: (B) f is very high
Q22. Wavelength of an EM wave with frequency 10¹⁵ Hz is:
🔵 (A) 0.3 m
🟢 (B) 3 × 10⁻⁷ m
🟠 (C) 3 × 10⁸ m
🔴 (D) 3 × 10⁻¹⁵ m
Answer: (B) 3 × 10⁻⁷ m
Q23. If E = E₀ sin(kz – ωt) i-hat, then B is:
🔵 (A) (E₀/c) sin(kz – ωt) j-hat
🟢 (B) (E₀/c) cos(kz – ωt) j-hat
🟠 (C) (E₀/c) sin(kz – ωt) k-hat
🔴 (D) (E₀/c) cos(kz – ωt) k-hat
Answer: (A) (E₀/c) sin(kz – ωt) j-hat
Q24. If B₀ = 2 × 10⁻⁶ T, then E₀ = ?
🔵 (A) 6 V/m
🟢 (B) 60 V/m
🟠 (C) 600 V/m
🔴 (D) 0.6 V/m
Answer: (B) 60 V/m
Q25. Average energy densities of E and B in an EM wave are:
🔵 (A) Unequal
🟢 (B) Equal
🟠 (C) Zero
🔴 (D) Variable
Answer: (B) Equal
Q26. If intensity doubles, the electric field amplitude becomes:
🔵 (A) Double
🟢 (B) √2 times
🟠 (C) Same
🔴 (D) Half
Answer: (B) √2 times
Q27. A wave propagates along +z. With E along x, B along y. Which relation holds?
🔵 (A) E × B along +z
🟢 (B) E × B along –z
🟠 (C) B × E along +z
🔴 (D) B along z
Answer: (A) E × B along +z
Q28. An EM wave has energy flux S = 100 W/m². The amplitude of E is:
🔵 (A) 6.14 V/m
🟢 (B) 27.4 V/m
🟠 (C) 274 V/m
🔴 (D) 0.6 V/m
Answer: (C) 274 V/m
Q29. Which spectrum band is absorbed by ozone?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Visible
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Ultraviolet
Q30. A time-varying magnetic field produces:
🔵 (A) Electric field
🟢 (B) Magnetic field
🟠 (C) Both fields
🔴 (D) No field
Answer: (A) Electric field
Q31. Momentum density of EM wave is:
🔵 (A) E × B
🟢 (B) S/c²
🟠 (C) ε₀E²
🔴 (D) B²/μ₀
Answer: (B) S/c²
Q32. Radar works with:
🔵 (A) Visible
🟢 (B) Microwaves
🟠 (C) Infrared
🔴 (D) X-rays
Answer: (B) Microwaves
Q33. An EM wave transports:
🔵 (A) Only energy
🟢 (B) Only momentum
🟠 (C) Both energy and momentum
🔴 (D) Neither
Answer: (C) Both energy and momentum
Q34. Which wave has photon energy just below visible?
🔵 (A) Infrared
🟢 (B) Ultraviolet
🟠 (C) Gamma
🔴 (D) X-ray
Answer: (A) Infrared
Q35. Impedance of free space ≈:
🔵 (A) 377 Ω
🟢 (B) 50 Ω
🟠 (C) 1000 Ω
🔴 (D) 1 Ω
Answer: (A) 377 Ω
Q36. In vacuum, group velocity of EM wave equals:
🔵 (A) Phase velocity
🟢 (B) Zero
🟠 (C) ∞
🔴 (D) c/2
Answer: (A) Phase velocity
Q37. Dimensional formula of μ₀:
🔵 (A) [MLT⁻²A⁻²]
🟢 (B) [M¹L¹T⁻²A⁻²]
🟠 (C) [M⁰L¹T⁰A⁻²]
🔴 (D) [M⁻¹L⁻³T⁴A²]
Answer: (A) [MLT⁻²A⁻²]
Q38. If E₀ = 3 V/m in vacuum, then B₀ = ?
🔵 (A) 10⁻⁸ T
🟢 (B) 10⁻⁹ T
🟠 (C) 10⁻¹⁰ T
🔴 (D) 10⁻² T
Answer: (A) 10⁻⁸ T
Q39. Ionosphere reflects:
🔵 (A) Radio waves
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Gamma rays
🔴 (D) Ultraviolet
Answer: (A) Radio waves
Q40. EM waves are produced by:
🔵 (A) Stationary charges
🟢 (B) Accelerated charges
🟠 (C) Uniform motion charges
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) Accelerated charges
🔬 JEE Advanced Level (Q41–Q50)
Q41. If E₀ doubles, radiation pressure on an absorbing surface:
🔵 (A) Doubles
🟢 (B) Quadruples
🟠 (C) Halves
🔴 (D) Same
Answer: (B) Quadruples
Q42. In EM waves, uE and uB are:
🔵 (A) Unequal
🟢 (B) Equal
🟠 (C) Zero
🔴 (D) No relation
Answer: (B) Equal
Q43. Peak E = 120 V/m. Average energy flux ≈:
🔵 (A) 19 W/m²
🟢 (B) 38 W/m²
🟠 (C) 57 W/m²
🔴 (D) 76 W/m²
Answer: (B) 38 W/m²
Q44. Radiated energy in capacitor leakage is due to:
🔵 (A) Conduction current
🟢 (B) Displacement current
🟠 (C) Constant field
🔴 (D) Induction
Answer: (B) Displacement current
Q45. When EM wave hits perfect conductor normally, reflected wave has:
🔵 (A) Same phase
🟢 (B) Opposite E phase
🟠 (C) Opposite B phase
🔴 (D) Both reversed
Answer: (B) Opposite E phase
Q46. Momentum delivered/sec by EM wave of intensity I on reflecting area A is:
🔵 (A) IA/c
🟢 (B) 2IA/c
🟠 (C) I/c
🔴 (D) 2I/c
Answer: (B) 2IA/c
Q47. Sunlight of intensity 1000 W/m² falls normally on 1 m² black surface. Radiation pressure is:
🔵 (A) 3.3 × 10⁻⁶ N/m²
🟢 (B) 3.3 × 10⁻⁶ Pa
🟠 (C) 6.6 × 10⁻⁶ N/m²
🔴 (D) 6.6 × 10⁻⁶ Pa
Answer: (B) 3.3 × 10⁻⁶ Pa
Q48. If E = E₀ cos(kz – ωt) i-hat, the Poynting vector is along:
🔵 (A) +z
🟢 (B) –z
🟠 (C) +x
🔴 (D) +y
Answer: (A) +z
Q49. Photon energy ~10⁻²⁰ J corresponds to:
🔵 (A) Radio
🟢 (B) Infrared
🟠 (C) Ultraviolet
🔴 (D) X-ray
Answer: (A) Radio
Q50. EM wave of intensity 450 W/m² has B₀ ≈:
🔵 (A) 1.2 × 10⁻⁶ T
🟢 (B) 2.1 × 10⁻⁶ T
🟠 (C) 6.2 × 10⁻⁶ T
🔴 (D) 12 × 10⁻⁶ T
Answer: (B) 2.1 × 10⁻⁶ T
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
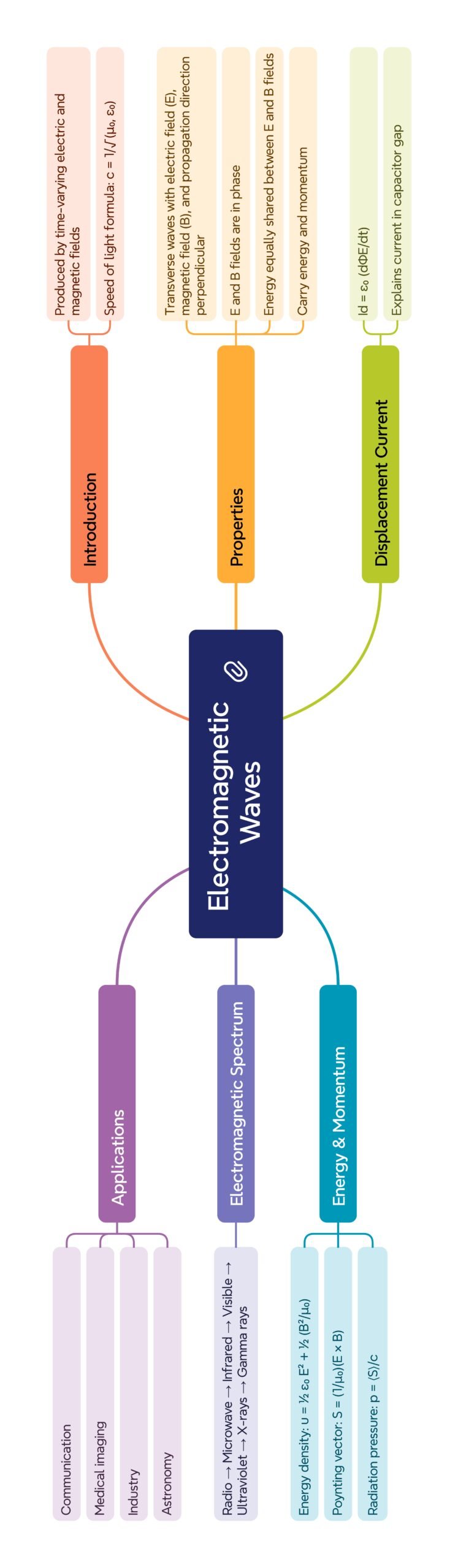
MIND MAP
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
