Class 12 : Geography (English) – Lesson 10.Human Settlements
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN SETTLEMENTS
Human settlements are places where people build their homes and live together. These settlements reflect human relationships with nature and the environment. Settlements are not just about houses; they include the social, cultural, and economic activities of people. Settlements can be permanent or temporary, rural or urban, depending on factors like location, occupation, and infrastructure.
🌿 Definition: A human settlement is defined as a cluster of dwellings of any type or size where human beings live.
✔️ Settlements evolve based on environmental conditions, availability of resources, and socio-economic activities.
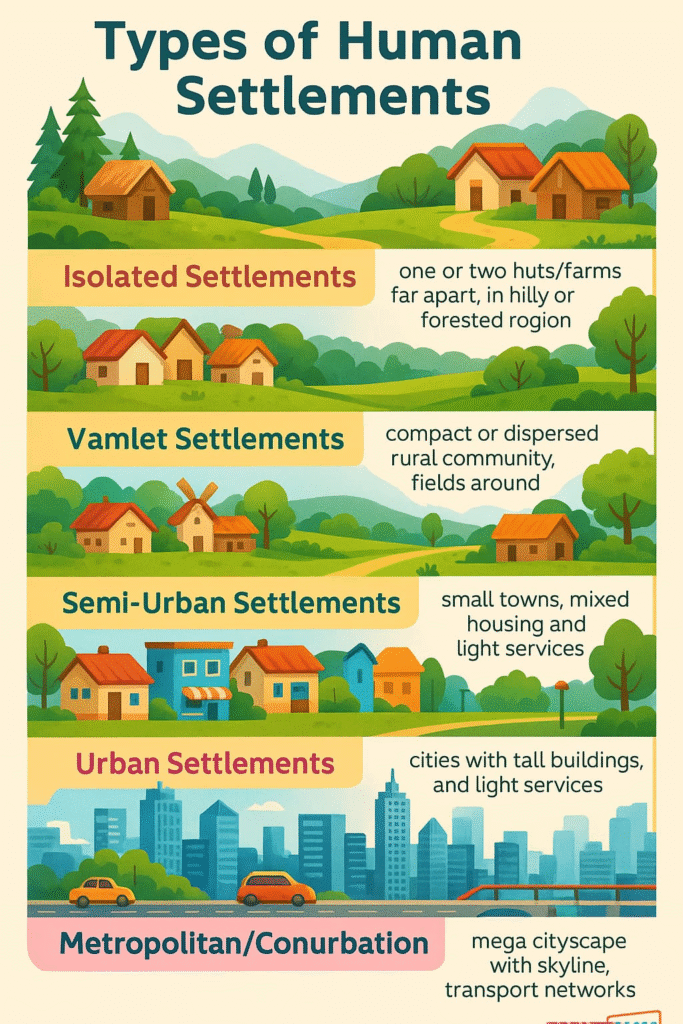
🟢 TYPES OF HUMAN SETTLEMENTS
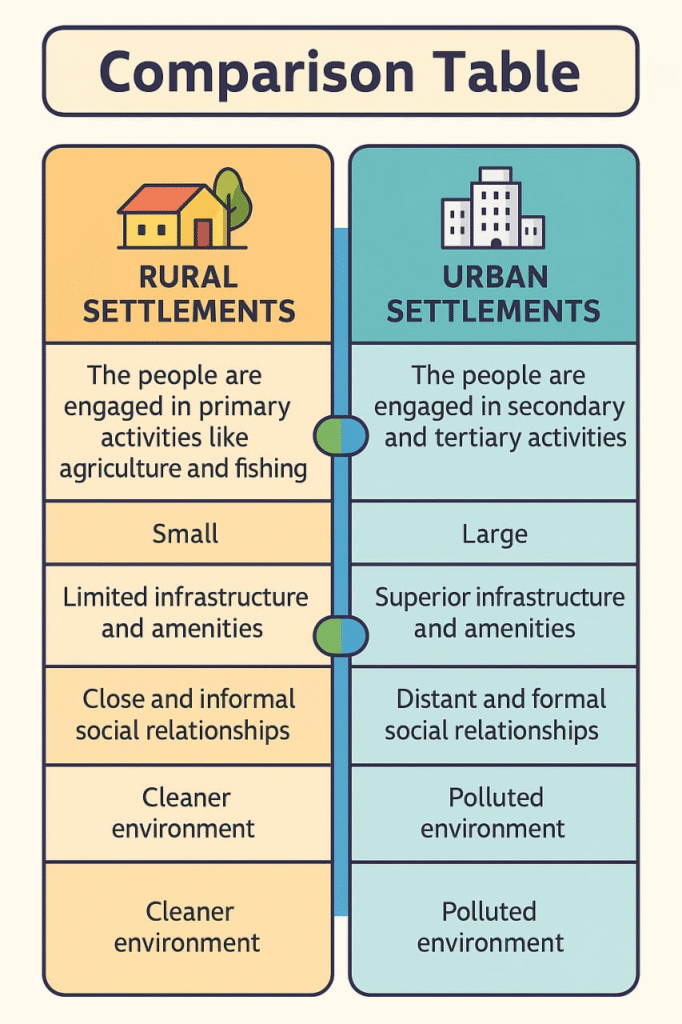
1️⃣ Rural Settlements
➡️ Primarily associated with agriculture, fishing, forestry, and crafts.
➡️ People are directly dependent on natural resources.
➡️ They are usually small and closely related to nature.
Types of Rural Settlements:
🔵 Clustered/Nucleated: Houses are closely built together. Found in fertile plains.
🟢 Semi-Clustered: Groups of houses separated by fields.
🔴 Hamleted: Small clusters spread within a village boundary.
🟡 Dispersed: Isolated houses; found in forests, hills.
Characteristics of Rural Settlements:
✔️ Poor infrastructure
✔️ Primary occupations dominate
✔️ Close-knit communities
2️⃣ Urban Settlements
➡️ People are engaged in secondary and tertiary activities like industries, trade, and services.
➡️ Better infrastructure compared to rural settlements.
Characteristics of Urban Settlements:
✔️ High population density
✔️ Developed infrastructure (roads, electricity, water supply)
✔️ Variety of occupations
✔️ Better healthcare and education facilities
🔴 EVOLUTION OF SETTLEMENTS IN INDIA
Historical Evolution:
➡️ Early settlements developed near rivers, forests, and fertile lands.
➡️ Civilisations like the Indus Valley grew due to agricultural surplus.
Factors Influencing Evolution:
✔️ Physical factors (water, soil, climate)
✔️ Economic factors (trade, agriculture)
✔️ Cultural and political influences
✏️ Note: Settlements changed with the advent of transport and industrial revolutions.
🟡 RURAL SETTLEMENTS IN INDIA
Regional Patterns:
🔵 Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana: Clustered settlements due to fertile lands.
🟢 Himalayas, Central India: Dispersed settlements due to rugged terrain.
🔴 Coastal and Delta Regions: Semi-clustered due to frequent flooding.
Problems in Rural Settlements:
✔️ Lack of clean drinking water
✔️ Poor sanitation and healthcare
✔️ Poor housing quality
✔️ Lack of roads and transport
💡 Concept: Development in rural settlements depends on improving infrastructure and living standards.
🔵 URBAN SETTLEMENTS IN INDIA
Types of Urban Settlements (Based on Functions):
1️⃣ Administrative Towns: Capitals and headquarters (Delhi, Chandigarh)
2️⃣ Industrial Towns: Centres of manufacturing (Jamshedpur, Bhilai)
3️⃣ Transport Towns: Ports, airports, railway hubs (Mumbai, Kolkata)
4️⃣ Commercial Towns: Business and trade centres (Ahmedabad, Kanpur)
5️⃣ Cultural Towns: Centres of art, education, religion (Varanasi, Madurai)
6️⃣ Recreational Towns: Tourism-based (Shimla, Mussoorie)
Urbanisation in India:
Meaning: Increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas.
➡️ Driven by migration from rural areas, industrialisation, and economic opportunities.
Trends:
✔️ Fastest in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Delhi
✔️ Large cities attract population due to better facilities
Problems of Urban Settlements:
🔴 Housing: Shortage leading to slums
🟡 Water Supply: Inadequate in fast-growing cities
🟢 Sanitation: Poor waste management
🔵 Traffic Congestion: Overburdened transport
⚡ Pollution: Air, water, noise hazards
🌿 Urban planning is essential to address these challenges.
🟢 HIERARCHY OF URBAN SETTLEMENTS IN INDIA
Classification (Based on Population):
✔️ Town
✔️ City
✔️ Metropolitan City
✔️ Megacity
Examples:
➡️ Towns: Less than 1 lakh population
➡️ Cities: 1 lakh or more
➡️ Metros: Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai
➡️ Mega Cities: More than 10 million (Delhi, Mumbai)
🔴 FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATION OF TOWNS
Single Function Towns:
✔️ Defence (Cantonments)
✔️ Religious (Varanasi)
Multi-Functional Towns:
✔️ Administration + Industry + Trade (Delhi, Mumbai)
💡 Concept: Towns evolve from single to multi-functional with growth.
🟡 FACTORS AFFECTING THE GROWTH OF SETTLEMENTS
Physical Factors:
✔️ Climate
✔️ Water availability
✔️ Topography
Economic Factors:
✔️ Agriculture, trade, industries
✔️ Employment opportunities
Social and Political Factors:
✔️ Peace, safety
✔️ Cultural and religious importance
🔵 GROWTH PATTERNS IN URBAN SETTLEMENTS
Horizontal Expansion: Cities spreading outwards into surrounding areas.
Vertical Growth: High-rise buildings in limited land space.
⚡ Mega cities expand in both patterns due to space constraints and increasing population.
🟢 REAL-LIFE CONNECTION
✔️ Planning of towns and cities impacts employment, housing, and quality of life.
✔️ Smart Cities and AMRUT schemes are focused on improving urban living.
✔️ Rural development schemes aim to improve infrastructure and reduce migration pressure.
🔴 WHY THIS LESSON MATTERS
➡️ Settlements influence the economy, environment, and social life.
➡️ Urban-rural balance is crucial for sustainable development.
➡️ Proper planning helps avoid problems like overcrowding, pollution, and resource scarcity.
🌿 Understanding settlements is key to building a sustainable future.
📝 QUICK RECAP:
🔵 Rural – Agriculture-based, poor infrastructure
🟢 Urban – Industry, services, better facilities
🔴 Types – Clustered, dispersed; towns, cities, metros
🟡 Issues – Housing, water, sanitation, transport
⚡ Growth – Horizontal, vertical expansion
➡️ Urbanisation – Rapid but challenging
SUMMARY (300 WORDS)
🔵 Human Settlements Overview:
Settlements are places where people live and carry out social and economic activities. They are broadly classified as rural or urban.
🟢 Rural Settlements:
Rural settlements are connected to primary activities like agriculture, fishing, and forestry. They vary in patterns: clustered, semi-clustered, hamleted, or dispersed. Rural areas face issues like lack of infrastructure, clean water, healthcare, and sanitation.
🔴 Urban Settlements:
Urban areas focus on secondary and tertiary occupations like manufacturing, trade, and services. Urbanisation is driven by industrialisation, better opportunities, and facilities. Cities are classified based on population into towns, cities, metros, and mega-cities.
🟡 Types of Towns (Functional Basis):
Administrative, industrial, commercial, transport, cultural, and recreational towns serve varied functions. Many towns have evolved from single to multi-functional.
⚡ Growth of Urban Areas:
Urban growth occurs horizontally (expansion into nearby areas) and vertically (high-rise buildings). Urban settlements face challenges like slums, traffic congestion, pollution, and infrastructure shortages.
🌿 Importance of Studying Settlements:
Knowledge of settlements is essential for planning infrastructure, managing population, ensuring sustainability, and reducing disparities between urban and rural areas.
Conclusion:
Balanced development of rural and urban settlements is vital for economic progress, environmental sustainability, and improved quality of life.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
QUESTION 1
Choose the right answers of the following from the given options.
(i) Which one of the following towns is NOT located on a river bank?
(A) Agra
(B) Bhopal
(C) Patna
(D) Kolkata
ANSWER 1 (i)
➡️ Correct Answer: (B) Bhopal
🔵 Bhopal is not located on the bank of a major river. It is known for its lakes, not river banks.
QUESTION 1 (ii)
Which one of the following is NOT a part of the definition of a town as per the census of India?
(A) Population density of 400 persons per sq km.
(B) Presence of municipality, corporation, etc.
(C) More than 75% of the population engaged in primary sector.
(D) Population size of more than 5,000 persons.
ANSWER 1 (ii)
➡️ Correct Answer: (C) More than 75% of the population engaged in primary sector.
🟢 Towns are characterised by non-primary occupations like trade, industry, services.
QUESTION 1 (iii)
In which one of the following environments does one expect the presence of dispersed rural settlements?
(A) Alluvial plains of Ganga
(B) Arid and semi-arid regions of Rajasthan
(C) Lower valleys of Himalayas
(D) Forests and hills in north-east
ANSWER 1 (iii)
➡️ Correct Answer: (D) Forests and hills in north-east
🟡 Dispersed settlements are common in difficult terrains like forests and hills due to isolation and land use patterns.
QUESTION 2
Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) What are garrison towns? What is their function?
ANSWER 2 (i)
🔴 Garrison towns are towns where military establishments are located.
🟢 Their primary function is to serve the needs of the defence sector and accommodate military personnel and their families.
QUESTION 2 (ii)
What are the main factors for the location of villages in desert regions?
ANSWER 2 (ii)
🔵 Villages in desert areas are mostly located near water sources such as oases or wells.
🟢 Availability of water for domestic use and agriculture is the main determining factor in such harsh climates.
QUESTION 3
Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Discuss the features of different types of rural settlements. What are the factors responsible for the settlement patterns in different physical environments?
ANSWER 3 (i)
🔵 Types of Rural Settlements:
1️⃣ Clustered Settlements: Houses built close together in fertile plains, especially in North India.
2️⃣ Semi-Clustered Settlements: Smaller groups of houses separated by fields; found in transitional areas.
3️⃣ Hamleted Settlements: Small clusters forming part of a single village; common in plateau areas.
4️⃣ Dispersed Settlements: Isolated houses scattered over large areas; common in forests, hills.
🟢 Factors Influencing Settlement Patterns:
✔️ Topography: Plains support clustered settlements; hills support dispersed ones.
✔️ Climate: Extreme climates discourage dense settlements.
✔️ Water Availability: Areas with reliable water sources attract settlements.
✔️ Soil Fertility: Fertile land encourages dense, clustered patterns.
QUESTION 3 (ii)
Can one imagine the presence of only one-function town? Why do the cities become multi-functional?
ANSWER 3 (ii)
🔴 Single-function towns may exist initially (like defence towns or religious centres), but over time they grow beyond their original purpose.
🟢 Reasons for Multi-Functional Nature:
✔️ Increase in population demands varied services.
✔️ Growth in trade, industry, education, healthcare, and administration.
✔️ Improved transport and communication links attract more people and businesses.
✔️ Economic development leads to diversification of occupations and functions.
💡 Conclusion: Urban settlements evolve from single-purpose to multi-functional to support the growing and varied needs of their population.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
SECTION A (Q1–Q18)
(1 mark each)
Q1. Which of the following towns is NOT located on a river bank?
(A) Agra
(B) Bhopal
(C) Patna
(D) Kolkata
Answer: (B) Bhopal
Q2. Which factor is least important for selecting the site of a settlement?
(A) Water availability
(B) Defence
(C) Pleasant climate
(D) Political ideology
Answer: (D) Political ideology
Q3. In which region are dispersed rural settlements commonly found?
(A) Ganga Plains
(B) Rajasthan Desert
(C) North-east Hills
(D) Coastal Andhra Pradesh
Answer: (C) North-east Hills
Q4. Which is a feature of urban settlements?
(A) Agriculture based
(B) Industry and services based
(C) Dependent on rainfall
(D) Located in forests
Answer: (B) Industry and services based
Q5. Which of the following is a Garrison town?
(A) Agra
(B) Ambala
(C) Ahmedabad
(D) Allahabad
Answer: (B) Ambala
Q6. Clustered settlements are found in:
(A) Flood-prone areas
(B) Fertile plains
(C) Desert regions
(D) Mountain regions
Answer: (B) Fertile plains
Q7. Which is NOT a feature of rural settlements?
(A) Small in size
(B) Agricultural economy
(C) High density of population
(D) Close relation with nature
Answer: (C) High density of population
Q8. Which is NOT a function of urban settlements?
(A) Industry
(B) Services
(C) Fishing
(D) Trade
Answer: (C) Fishing
Q9. Which one is a planned city in India?
(A) Mumbai
(B) Delhi
(C) Chandigarh
(D) Kolkata
Answer: (C) Chandigarh
Q10. Which city developed as an industrial town?
(A) Jamshedpur
(B) Jaipur
(C) Varanasi
(D) Shimla
Answer: (A) Jamshedpur
Q11. Which of the following is NOT a problem of urban areas?
(A) Overcrowding
(B) Pollution
(C) Lack of services
(D) Fertile land
Answer: (D) Fertile land
Q12. Assertion (A): Clustered settlements are found in fertile plains.
Reason (R): Fertile land and availability of water encourage people to live close together.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R explains A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R does not explain A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) Both A and R are false.
Answer: (A)
Q13. Which of the following is NOT a reason for dispersed settlements?
(A) Steep slopes
(B) Dense forests
(C) Fertile plains
(D) Poor soils
Answer: (C) Fertile plains
Q14. What is urbanisation?
(A) Growth of rural population
(B) Decline of rural areas
(C) Growth of towns and cities
(D) Agricultural expansion
Answer: (C) Growth of towns and cities
Q15. Which of these is NOT an administrative town?
(A) Delhi
(B) Chandigarh
(C) Jaipur
(D) Jamshedpur
Answer: (D) Jamshedpur
Q16. Which is NOT a factor of settlement growth?
(A) Availability of water
(B) Political stability
(C) Climate
(D) Internet speed
Answer: (D) Internet speed
Q17. Which town is famous for religious activities?
(A) Varanasi
(B) Surat
(C) Bhopal
(D) Indore
Answer: (A) Varanasi
Q18. Which sector dominates urban economy?
(A) Primary
(B) Secondary
(C) Tertiary
(D) Both B and C
Answer: (D) Both B and C
SECTION B (Q19–Q23)
(2 Marks Each)
Q19. Define urban settlement. How is it different from a rural settlement?
Answer:
🔵 Urban settlements are areas where people are mainly engaged in secondary and tertiary activities such as industries, trade, transport, and services.
🟢 Unlike rural settlements which depend primarily on agriculture and natural resources, urban settlements have better infrastructure and higher population density.
Q20. What are garrison towns? Mention one example.
Answer:
🔴 Garrison towns are towns where military establishments are located, serving as defence bases.
🟡 Example: Ambala is a well-known garrison town in India.
Q21. State two problems faced by people living in urban settlements.
Answer:
🔵 Overcrowding and shortage of housing facilities lead to the growth of slums.
🟢 Pollution from industries and vehicles affects air and water quality in urban areas.
Q22. Mention any two characteristics of rural settlements.
Answer:
🔴 Rural settlements are small in size and population.
🟡 They primarily depend on agriculture and natural resources for livelihood.
Q23. What is the main function of a commercial town? Give an example.
Answer:
🔵 Commercial towns mainly serve as centres for trade, business, and commerce.
🟢 Example: Mumbai is a prominent commercial town in India.
SECTION C (Q24–Q28)
(3 Marks Each)
Q24. Explain three factors that influence the growth of settlements.
Answer:
🔵 Water Availability: Settlements grow near rivers and lakes which provide water for drinking, agriculture, and transport.
🟢 Climate: Moderate climates attract settlements, while extreme climates discourage them.
🟡 Economic Activities: Industrial, trade, and service centres attract more population due to job opportunities.
Q25. Differentiate between clustered and dispersed settlements.
Answer:
🔵 Clustered Settlements:
✔️ Houses are closely built together.
✔️ Found in fertile plains with good agricultural land.
🟢 Dispersed Settlements:
✔️ Houses are spread over large areas.
✔️ Found in hilly, forested, or desert regions where land is scattered.
Q26. Describe any three problems associated with unplanned urban growth.
Answer:
🔵 Housing Shortage: Leads to slums and poor living conditions.
🟢 Traffic Congestion: Overcrowded roads increase travel time and pollution.
🟡 Pollution: Unregulated industrialisation and vehicles cause air and water pollution.
Q27. Explain three functions of urban settlements.
Answer:
🔵 Administrative Functions: Capitals and headquarters for governance (e.g., Delhi).
🟢 Industrial Functions: Manufacturing hubs (e.g., Jamshedpur).
🟡 Commercial Functions: Centres for trade and business (e.g., Mumbai).
Q28. What are the main reasons for migration from rural to urban areas in India?
Answer:
🔵 Employment Opportunities: Urban areas offer more jobs in industries and services.
🟢 Better Facilities: Healthcare, education, and infrastructure are better in cities.
🟡 Modern Lifestyle: Urban areas offer higher standards of living and modern amenities.
SECTION D (Q29–Q31)
(4 Marks Each – Case-Based Questions with Internal Parts)
Q29. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
“Clustered settlements are generally found in fertile plains and regions with good agricultural facilities. These settlements reflect social bonding among the people.”
(i) Name one state where clustered settlements are common. (1)
(ii) Why do people prefer clustered settlements in fertile regions? (1)
(iii) Mention two advantages of clustered settlements. (2)
ANSWER 29:
(i) Uttar Pradesh.
(ii) Due to availability of fertile land and water resources which support agriculture.
(iii)
🔵 Easy access to social and economic facilities.
🟢 Strong social bonds and community support.
Q30. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
“Urban settlements develop due to various functions such as administration, trade, industry, and education. Over time, cities expand beyond their original purpose.”
(i) Name a city that started as an administrative town. (1)
(ii) Name a city famous for trade and commerce. (1)
(iii) Give two reasons why cities become multifunctional. (2)
ANSWER 30:
(i) New Delhi.
(ii) Mumbai.
(iii)
🔵 Increase in population creates demand for diverse services.
🟢 Growth of infrastructure attracts varied economic activities.
Q31. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below:
“Urban settlements face challenges due to unplanned growth such as housing shortage, traffic congestion, and pollution.”
(i) Name one Indian megacity facing these challenges. (1)
(ii) Mention one cause of housing shortage. (1)
(iii) Explain two impacts of unplanned urban growth. (2)
ANSWER 31:
(i) Delhi.
(ii) Rapid migration from rural to urban areas.
(iii)
🔵 Development of slums and unhygienic living conditions.
🟢 Increased environmental pollution and health hazards.
SECTION E (Q32–Q35)
(5 Marks Each – Long Answer Questions)
Q32. Explain the types and characteristics of rural settlements in India.
ANSWER 32:
🔵 Types of Rural Settlements:
1️⃣ Clustered Settlements: Closely built houses in fertile plains.
2️⃣ Semi-Clustered Settlements: Smaller groups of houses separated by fields.
3️⃣ Hamleted Settlements: Small clusters forming part of one village.
4️⃣ Dispersed Settlements: Isolated houses scattered across forests, hills.
🟢 Characteristics:
✔️ Small population size.
✔️ Primary activities like agriculture, fishing.
✔️ Close relation with nature.
✔️ Poor infrastructure facilities.
Q33. Explain the problems faced by people in urban settlements.
ANSWER 33:
🔵 Housing Shortage: Leads to growth of slums and overcrowding.
🟢 Water and Sanitation: Inadequate clean water and waste disposal.
🟡 Traffic Congestion: Overloaded transport systems cause delays.
🔴 Pollution: Industrial and vehicular pollution affect health.
⚡ Employment Issues: Limited jobs lead to unemployment and poverty.
🌿 Conclusion: Planned urban development is necessary for sustainable living.
Q34. Discuss the factors affecting the growth of settlements in India.
ANSWER 34:
🔵 Physical Factors:
✔️ Water availability.
✔️ Fertile land.
✔️ Moderate climate.
🟢 Economic Factors:
✔️ Industrial growth.
✔️ Trade and commerce hubs.
🟡 Social and Political Factors:
✔️ Peace and safety attract people.
✔️ Government policies and infrastructure development.
➡️ These factors together shape the size and nature of settlements.
Q35. Explain why cities develop from single-function to multifunctional settlements.
ANSWER 35:
🔵 Cities often start with one function – administration, trade, or industry.
🟢 Growth in population demands multiple services like education, healthcare, entertainment.
🟡 Economic opportunities lead to diversification of activities.
🔴 Improved transport and communication attract varied businesses.
⚡ Migration boosts the workforce, requiring varied facilities.
🌿 Conclusion: Urban settlements evolve naturally into multifunctional centres due to the interdependence of economic, social, and cultural needs.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Which of the following is NOT considered an essential characteristic of an urban settlement in India?
(A) Presence of a municipality
(B) More than 75% of population engaged in non-agricultural activities
(C) Population exceeding 5000
(D) Availability of internet services
✅ Answer: (D) Availability of internet services
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2016
📝 Explanation: Urban areas defined by population size, function, not technology.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q2. Which of the following is NOT a function of a rural settlement?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Fishing
(C) Mining
(D) IT hub
✅ Answer: (D) IT hub
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2017
📝 Explanation: IT hubs are urban features.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q3. Which city in India has been classified as a megacity due to population exceeding 10 million?
(A) Kolkata
(B) Mumbai
(C) Hyderabad
(D) Pune
✅ Answer: (B) Mumbai
📅 Exam: SSC JE 2017
📝 Explanation: Mumbai is recognized as a megacity.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q4. Urban sprawl is best associated with:
(A) Rapid increase in agricultural output
(B) Expansion of cities into surrounding areas
(C) Rise of traditional crafts
(D) Increasing literacy
✅ Answer: (B) Expansion of cities into surrounding areas
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2016
📝 Explanation: Urban sprawl refers to city expansion.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. Slum areas in cities typically lack:
(A) Good sanitation
(B) Political rights
(C) Labour force
(D) Youth population
✅ Answer: (A) Good sanitation
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2016
📝 Explanation: Poor sanitation is a major issue in slums.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q6. The primary reason for the growth of urban settlements is:
(A) Availability of agricultural land
(B) Industrialization and economic activities
(C) Migration for religious purposes
(D) Military expansion
✅ Answer: (B) Industrialization and economic activities
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2015
📝 Explanation: Economic factors drive urban growth.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. Which of the following is a function of urban settlements?
(A) Defence
(B) Mining
(C) Administration
(D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
📅 Exam: SSC GD 2017
📝 Explanation: Urban areas serve multiple functions.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q8. Which census year first introduced the term ‘Census Town’ in India?
(A) 1961
(B) 1971
(C) 1981
(D) 1991
✅ Answer: (B) 1971
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2013
📝 Explanation: 1971 Census defined census towns.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q9. Smart cities mission focuses on:
(A) Rural development
(B) Urban infrastructure and services
(C) Defence installations
(D) Agriculture
✅ Answer: (B) Urban infrastructure and services
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
📝 Explanation: Aims at modern urban development.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
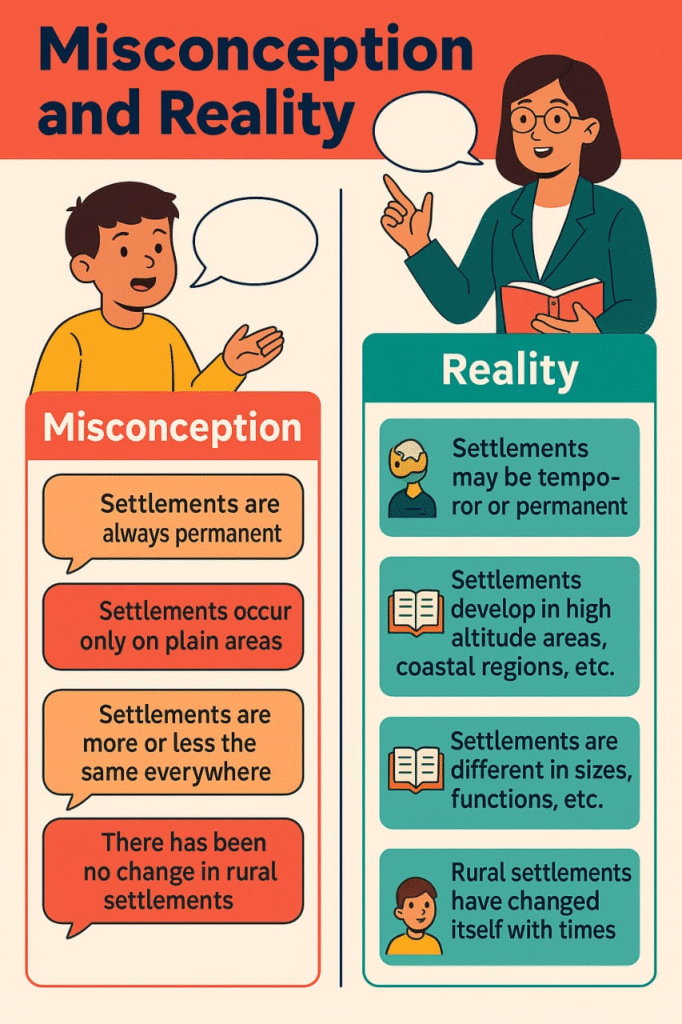
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
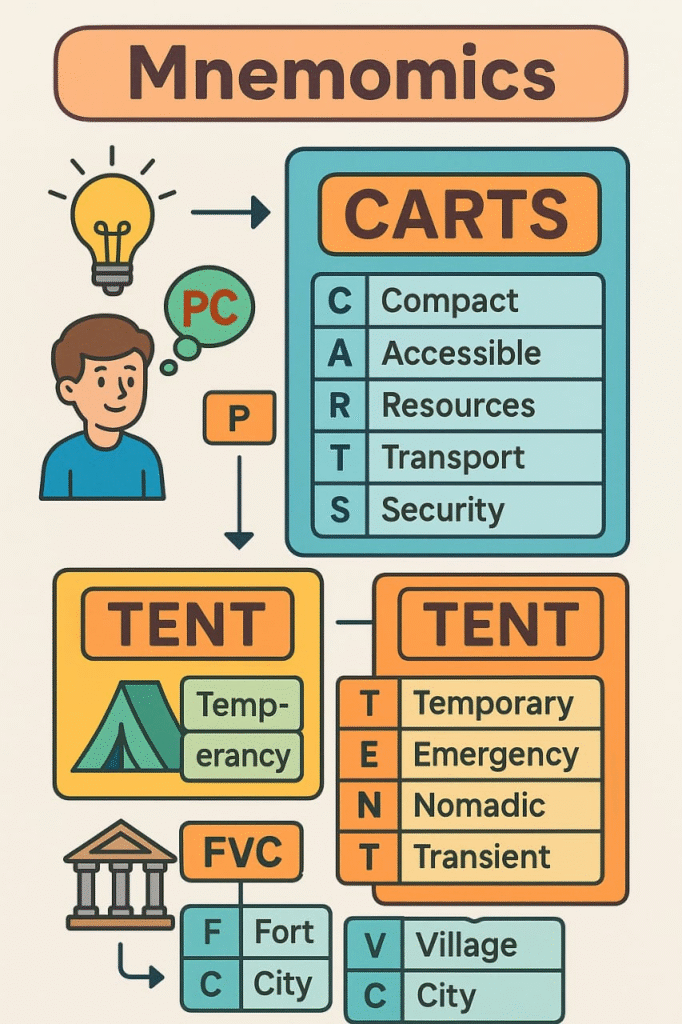
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
