Class 12 : Chemistry (English) – Chapter 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

INTRODUCTION
This chapter deals with haloalkanes and haloarenes—organic compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane or arene have been replaced by halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I). These compounds play crucial roles in both synthetic chemistry and industry, as they are intermediates in the preparation of numerous pharmaceuticals, pesticides, polymers, and solvents.
CLASSIFICATION OF HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES

1.1 Based on Number of Halogen Atoms
Monohalo compounds: One halogen atom
Example: CH₃Cl (chloromethane)
Dihalo compounds: Two halogen atoms
Example: CH₂Cl₂ (dichloromethane)
Trihalo compounds: Three halogen atoms
Example: CHCl₃ (chloroform)
Polyhalo compounds: More than three halogen atoms
Example: CCl₄ (carbon tetrachloride)
1.2 Based on Type of Carbon Chain
(a) Alkyl halides (haloalkanes)
Contain a halogen attached to an sp³-hybridised carbon of an alkyl group.
Example: CH₃CH₂Cl (ethyl chloride)
Primary (1°): Halogen attached to a carbon bonded to one other carbon
Secondary (2°): Halogen attached to carbon bonded to two other carbons
Tertiary (3°): Halogen attached to carbon bonded to three other carbons
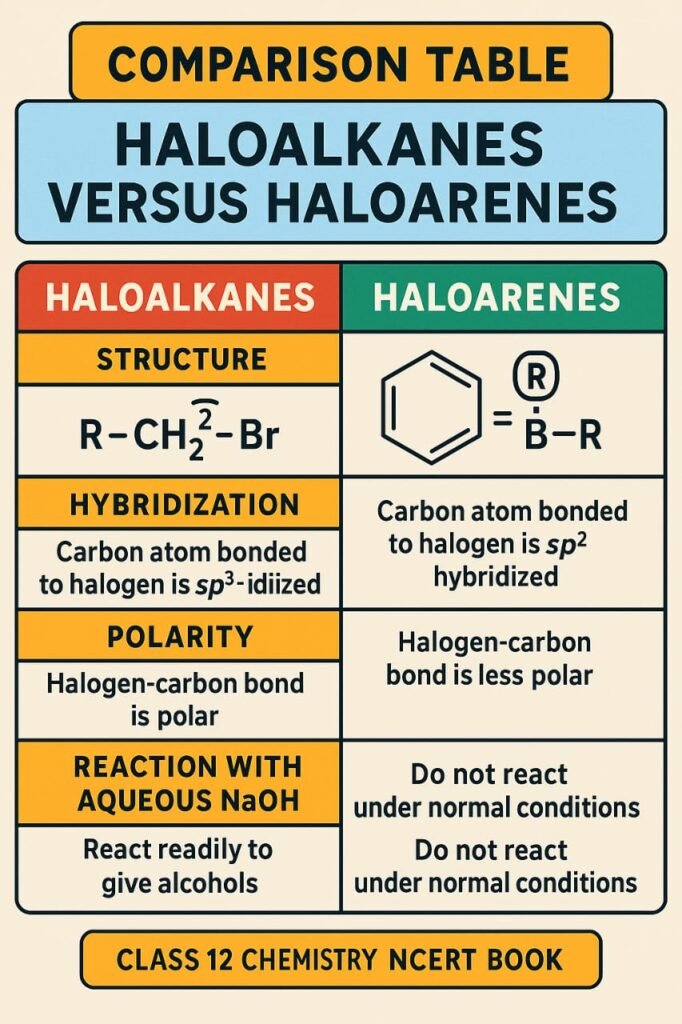
(b) Aryl halides (haloarenes)
Halogen attached to an aromatic ring, usually benzene
Example: C₆H₅Cl (chlorobenzene)
NOMENCLATURE
2.1 IUPAC System
Select the longest carbon chain containing the halogen
Number the chain such that the carbon bearing the halogen gets the lowest possible number
Name the halogen as a prefix (fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo)
Example:
CH₃CHClCH₂CH₃ → 2-chlorobutane
2.2 Common Names
Halogen is treated as a substituent on an alkyl group
Example: CH₃CH₂Cl → ethyl chloride
For aryl halides: name is derived from parent arene
Example: C₆H₅Br → bromobenzene
METHODS OF PREPARATION
3.1 From Alcohols
R–OH + HX → R–X + H₂O
Alcohol reacts with hydrogen halides (HX) in the presence of ZnCl₂ (Lucas reagent for HCl).
Example:
C₂H₅OH + HCl → C₂H₅Cl + H₂O
3.2 From Hydrocarbons
(a) Free Radical Halogenation (Alkanes)
CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl (in presence of sunlight)
(b) Electrophilic Substitution (Arenes)
C₆H₆ + Cl₂ → C₆H₅Cl + HCl (in presence of FeCl₃ catalyst)
3.3 From Alkenes
Addition of HX:
CH₂=CH₂ + HBr → CH₃CH₂Br
Anti-Markovnikov Addition: In presence of peroxides, Br adds to less substituted carbon
3.4 From Halogen Exchange Reactions
Finkelstein Reaction:
R–Cl + NaI → R–I + NaCl (in acetone)
Swarts Reaction:
R–Cl + SbF₃ → R–F (used to prepare alkyl fluorides)
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Boiling Points: Increase with molecular weight and decrease with branching
Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents
Density: Generally higher than hydrocarbons; heavier halogens → higher density
Key trend:
RI > RBr > RCl > RF (boiling point and density)
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF HALOALKANES
5.1 Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
General Reaction:
R–X + Nu⁻ → R–Nu + X⁻
(Nu⁻ = nucleophile; X⁻ = leaving group)
Two main mechanisms:
(a) SN1 Mechanism (Unimolecular)
Two-step reaction:
Formation of carbocation (slow)
Nucleophilic attack (fast)
Follows first-order kinetics
Favoured by:
Polar protic solvents
3° > 2° > 1° (stability of carbocation)
Example:
(CH₃)₃CBr + H₂O → (CH₃)₃COH + HBr
(b) SN2 Mechanism (Bimolecular)
One-step reaction: nucleophile attacks from backside
Follows second-order kinetics
Favoured by:
Polar aprotic solvents
1° > 2° > 3° (due to steric hindrance)
Example:
CH₃Br + OH⁻ → CH₃OH + Br⁻
5.2 Elimination Reactions
When haloalkanes react with strong bases → alkenes form
Dehydrohalogenation
R–CH₂–CH₂–X + alcoholic KOH → R–CH=CH₂ + KX + H₂O
Follows Zaitsev’s Rule: More substituted alkene is major product
5.3 Reaction with Metals
Wurtz Reaction:
2R–X + 2Na → R–R + 2NaX
(Synthesis of higher alkanes)
POLYHALOGEN COMPOUNDS
6.1 DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane)
Insecticide
Non-biodegradable, harmful to environment
6.2 Chloroform (CHCl₃)
Anaesthetic (now obsolete due to toxicity)
Reacts with oxygen and light to form phosgene (COCl₂), a toxic gas
Storage: In dark bottles, with ethanol as stabilizer
6.3 Iodoform (CHI₃)
Yellow crystalline solid with antiseptic smell
Used as a test for methyl ketones
HALOARENES
7.1 Preparation
From Arenes:
C₆H₆ + Cl₂ → C₆H₅Cl + HCl (FeCl₃ catalyst)
From Diazonium Salts (Sandmeyer Reaction):
C₆H₅N₂⁺Cl⁻ + CuCl → C₆H₅Cl + N₂
7.2 Properties
Less reactive than haloalkanes toward nucleophilic substitution
Reason: Partial double bond character in C–X bond due to resonance
7.3 Reactions
(a) Electrophilic Substitution
Reactivity is slower than benzene due to –I effect of halogen
However, halogen is ortho-para directing due to resonance
Examples:
Nitration: C₆H₅Cl + HNO₃ → o- and p-chloronitrobenzene
Sulphonation, Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation also occur
(b) Nucleophilic Substitution
Much more difficult due to resonance stabilization
Can occur under extreme conditions or when electron-withdrawing groups are present (e.g. –NO₂ at ortho or para)
Example:
C₆H₅Cl + NaOH → C₆H₅OH (at 623 K, 300 atm)
ENVIRONMENTAL EFFECTS AND SAFETY
8.1 CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons)
Stable, non-toxic compounds used in refrigerants and aerosols
Major cause of ozone layer depletion
Example: Freon-12 (CCl₂F₂)
8.2 Ozone Layer Depletion
CFCs release Cl⁻ radicals under UV light which degrade ozone (O₃)
Cl• + O₃ → ClO• + O₂
ClO• + O → Cl• + O₂
(Net: O₃ + O → 2O₂)
CONCLUSION
Haloalkanes and haloarenes are key classes of organic compounds with wide industrial and pharmaceutical applications. Their chemical reactivity is primarily influenced by the nature of the carbon–halogen bond, type of carbon skeleton, and solvent effects. Understanding the mechanisms (SN1, SN2, E2), physical trends, and environmental implications (like ozone depletion) forms the foundation for studying synthetic organic chemistry further.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Exercise 6.1
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
(i) (CH₃)₂CHCH(Cl)CH₃
Answer: 2-Chloro-3-methylbutane (Secondary alkyl halide)
(ii) CH₃CH₂CH(CH₃)CH(C₂H₅)Cl
Answer: 3-Chloro-4-methylhexane (Secondary alkyl halide)
(iii) CH₃CH₂C(CH₃)₂CH₂I
Answer: 1-Iodo-2,2-dimethylbutane (Primary alkyl halide)
(iv) (CH₃)₃CCH₂CH(Br)C₆H₅
Answer: 1-Bromo-3,3-dimethyl-1-phenylbutane (Secondary benzylic halide)
(v) CH₃CH(CH₃)CH(Br)CH₃
Answer: 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane (Secondary alkyl halide)
(vi) CH₃C(C₂H₅)₂CH₂Br
Answer: 1-Bromo-2-ethyl-2-methylbutane (Primary alkyl halide)
(vii) CH₃C(Cl)(C₂H₅)CH₂CH₃
Answer: 3-Chloro-3-methylpentane (Tertiary alkyl halide)
(viii) CH₃CH=C(Cl)CH₂CH(CH₃)₂
Answer: 3-Chloro-5-methylhex-2-ene (Vinylic halide)
(ix) CH₃CH=CHC(Br)(CH₃)₂
Answer: 4-Bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene (Allylic halide)
Exercise 6.2
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) CH₃CH(Cl)CH(Br)CH₃
Answer: 2-Bromo-3-chlorobutane
(ii) CHF₂CBrClF
Answer: 1-Bromo-1-chloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
(iii) ClCH₂C≡CCH₂Br
Answer: 1-Bromo-4-chlorobut-2-yne
Exercise 6.3
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
Answer: CH₃–CH(Cl)–CH(CH₃)–CH₂–CH₃
(ii) p-Bromochlorobenzene
Answer: Benzene ring with Br and Cl in para positions
(iii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Answer: Cyclohexane ring with Cl at position 1 and ethyl group at position 4
Exercise 6.4
Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment? CH₂Cl₂, CHCl₃ or CCl₄
Answer: CH₂Cl₂ has the highest dipole moment.
Exercise 6.5
A hydrocarbon C₅H₁₀ does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Answer: Cyclopentane
Exercise 6.6
Write the isomers of the compound having formula C₄H₉Br.
Answer:
(i) 1-Bromobutane
(ii) 2-Bromobutane
(iii) 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane
(iv) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
Exercise 6.7
Write the equation for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from:
(i) 1-Butanol
Answer: CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂OH + KI + H₃PO₄ → CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂I + H₂O + KH₂PO₄
(ii) 1-Chlorobutane
Answer: CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Cl + KI (acetone) → CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂I + KCl
(iii) But-1-ene
Answer: CH₃CH₂CH=CH₂ + HBr (peroxide) → CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br
CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Br + NaI (acetone) → CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂I + NaBr
Exercise 6.8
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Answer: Ambident nucleophiles can attack at two sites. Example: CN⁻ attacks via carbon (cyanide) or nitrogen (isocyanide).
Exercise 6.9
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH⁻?
(i) CH₃Br or CH₃I
Answer: CH₃I (I⁻ is a better leaving group)
(ii) (CH₃)₃CCl or CH₃Cl
Answer: CH₃Cl (less steric hindrance)
Exercise 6.10
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
(i) 1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Answer: 1-Methylcyclohexene (Major)
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
Answer: 2-Methylbut-2-ene (Major according to Saytzeff’s rule)
Exercise 6.11
How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Ethanol to but-1-yne
Answer: CH₃CH₂OH → CH₃CH₂Cl → CH₃CH₂C≡CH
(ii) Propene to 1-nitropropane
Answer: CH₃CH=CH₂ → CH₃CH₂CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂CH₂NO₂
Exercise 6.12
Explain why:
(i) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride
Answer: Due to resonance and sp² carbon in chlorobenzene, which reduces polarity
(ii) Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water
Answer: Because they cannot form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
(iii) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions
Answer: They react with water to form alkanes and lose reactivity
Exercise 6.13
Give the uses of Freon-12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Answer:
Freon-12: Refrigerant and aerosol propellant
DDT: Insecticide
Carbon tetrachloride: Solvent, fire extinguisher
Iodoform: Antiseptic (historical)
Exercise 6.14
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
(i) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl + NaI (acetone, heat)
Answer: CH₃CH₂CH₂I
(ii) (CH₃)₃CBr + KOH (ethanol)
Answer: (CH₃)₂C=CH₂ (2-Methylpropene)
Exercise 6.15
Write the mechanism of the following reaction: n-BuBr + KCN → n-BuCN
Answer: CN⁻ attacks via carbon atom (SN2 pathway) → n-Butyl cyanide
Exercise 6.16
Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
Answer: 1-Bromopentane > 2-Bromopentane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
Exercise 6.17
Out of C₆H₅CH₂Cl and C₆H₅CHClC₆H₅, which is more easily hydrolyzed by aqueous KOH?
Answer: C₆H₅CHClC₆H₅ (forms more stable carbocation)
Exercise 6.18
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Answer: Due to greater symmetry and stronger crystal packing
Exercise 6.19
How can the following conversions be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
Answer: CH₃CH=CH₂ → CH₃CH₂CH₂Br → CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
(ii) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
Answer: C₆H₆ → C₆H₅Br → p-Bromonitrobenzene
Exercise 6.20
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
Answer: Aqueous KOH gives substitution; alcoholic KOH gives elimination
Exercise 6.21
Primary alkyl halide C₄H₉Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Compound (b) is reacted with HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C₈H₁₈ which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
Answer:
(a) Isobutyl bromide → (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Br
(b) 2-Methylpropene → (CH₃)₂C=CH₂
(c) tert-Butyl bromide → (CH₃)₃CBr
(d) 2,5-Dimethylhexane
Exercise 6.22
What happens when:
(i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH
Answer: But-1-ene is formed
(ii) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether
Answer: Phenylmagnesium bromide is formed
(iii) Chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis
Answer: No reaction under normal conditions
(iv) Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH
Answer: Ethanol is formed
(v) Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether
Answer: Ethane is formed (Wurtz reaction)
(vi) Methyl chloride is treated with KCN
Answer: Methyl cyanide (CH₃CN) is formed
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔹 SECTION 1: DEFINITIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 1. Define haloalkanes.
Answer: Haloalkanes are alkanes in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogen atoms such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine.
Question 2. What are primary alkyl halides?
Answer: In primary alkyl halides, the carbon atom attached to the halogen is bonded to only one other carbon atom.
Question 3. Define the term chirality.
Answer: Chirality is the property of a molecule that makes it non-superimposable on its mirror image. Such molecules are called chiral.
Question 4. What is a nucleophile?
Answer: A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron pair to form a new covalent bond. It is electron-rich.
Question 5. Define the term racemisation.
Answer: Racemisation is the process of conversion of an optically active compound into an optically inactive racemic mixture.
🔹 SECTION 2: VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 6. Which carbon in haloalkane is sp³ hybridised?
Answer: The carbon atom bonded to the halogen in a haloalkane is sp³ hybridised.
Question 7. What is the major product when tert-butyl bromide reacts with aqueous KOH?
Answer: The major product is tert-butyl alcohol, via SN1 mechanism.
Question 8. What is the IUPAC name of CH₃CHBrCH₃?
Answer: 2-Bromopropane.
Question 9. Which halogen is most reactive in nucleophilic substitution?
Answer: Iodine, due to weakest C–I bond.
Question 10. Write the general formula of alkyl halides.
Answer: CₙH₂ₙ₊₁X, where X = F, Cl, Br, or I.
🔹 SECTION 3: SHORT NUMERICAL QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 11. Calculate the number of molecules in 0.5 mole of CH₃Cl.
Answer: 0.5 mol = 0.5 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.011 × 10²³ molecules.
Question 12. Determine the number of carbon atoms in 1 mole of C₂H₅Cl.
Answer: 1 mol C₂H₅Cl = 2 mol C atoms → 2 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 1.2044 × 10²⁴ atoms.
Question 13. Find the mass of 2 moles of CH₃CH₂Br. (M = 109 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Mass = 2 × 109 = 218 g.
Question 14. How many moles are present in 218 g of CH₃CH₂Br?
Answer: Moles = 218 / 109 = 2 mol.
Question 15. What is the molecular weight of CH₂Cl₂?
Answer: C = 12, H = 2 × 1, Cl = 2 × 35.5 → 12 + 2 + 71 = 85 g mol⁻¹.
🔹 SECTION 4: MID-LENGTH NUMERICAL QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 16. Calculate the mass of chlorine required to prepare 1 mole of CH₃Cl from methane and chlorine.
Answer: Balanced reaction: CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl
1 mole CH₃Cl requires 1 mole Cl₂ = 71 g
Mass of chlorine = 71 g
Question 17. How many molecules are present in 10 g of C₂H₅Cl? (M = 64.5 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Moles = 10 / 64.5 = 0.155 mol
Molecules = 0.155 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 9.334 × 10²² molecules
Question 18. Calculate the number of Cl atoms in 1 mole of CCl₄.
Answer: 1 molecule CCl₄ has 4 Cl atoms
1 mole CCl₄ = 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
Cl atoms = 4 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 2.409 × 10²⁴ atoms
Question 19. What is the mass of 0.2 mole of CHBr₃? (M = 252.8 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Mass = 0.2 × 252.8 = 50.56 g
Question 20. How many grams of bromine are needed to prepare 2 moles of CH₂Br₂?
Answer: Reaction: CH₄ + 2Br₂ → CH₂Br₂ + 2HBr
2 moles CH₂Br₂ need 4 mol Br₂
Mass = 4 × 160 = 640 g
🔹 SECTION 5: LONG NUMERICAL QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 21. Calculate the number of Br atoms in 5 g of CH₂Br₂. (M = 173.8 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Moles = 5 / 173.8 ≈ 0.0288 mol
Each molecule has 2 Br atoms
Br atoms = 2 × 0.0288 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.47 × 10²² atoms
Question 22. Determine the number of moles in 27.4 g of CH₃CH₂Cl. (M = 64.5 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Moles = 27.4 / 64.5 = 0.4256 mol
Question 23. How many molecules are present in 0.1 mol of CHCl₃?
Answer: Molecules = 0.1 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 6.022 × 10²² molecules
Question 24. Calculate the total number of atoms in 1 mole of CH₃Cl.
Answer: CH₃Cl has 5 atoms (1C, 3H, 1Cl)
Total atoms = 5 × 6.022 × 10²³ = 3.011 × 10²⁴ atoms
Question 25. Find the mass of 1.5 moles of C₆H₅Cl (chlorobenzene). (M = 112.5 g mol⁻¹)
Answer: Mass = 1.5 × 112.5 = 168.75
🔹 SECTION 6: MID-LENGTH THEORY QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 26. What is the difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions?
Answer: SN1 is a two-step reaction involving a carbocation intermediate and gives racemisation.
SN2 is a one-step reaction with backside attack and leads to inversion of configuration.
SN1 favored by tertiary haloalkanes; SN2 by primary haloalkanes.
Question 27. Why is the C–X bond in haloalkanes polar?
Answer: Halogen atoms are more electronegative than carbon. Thus, the shared electrons in the C–X bond are pulled towards halogen, making it polar.
Question 28. What is optical activity? How is it affected by SN1 reaction?
Answer: Optical activity is the ability of chiral compounds to rotate plane-polarised light. In SN1, the planar carbocation intermediate allows attack from both sides, leading to racemisation.
Question 29. Explain the reactivity order of halides in SN2 mechanism.
Answer: Reactivity: RI > RBr > RCl > RF
It depends on the bond strength; weaker C–X bonds (like in RI) undergo SN2 more easily due to easier bond cleavage.
Question 30. What happens when chlorobenzene is treated with NaOH at high temperature and pressure?
Answer: Chlorobenzene reacts with aqueous NaOH at 623 K and 300 atm to form phenol.
🔹 SECTION 7: LONG ANSWER THEORY QUESTIONS (5 QUESTIONS)
Question 31. Describe the preparation of haloalkanes from alcohols.
Answer: Haloalkanes are prepared by treating alcohols with halogen acids (HX), phosphorus halides (PX₅ or PX₃), or thionyl chloride (SOCl₂).
Example:
CH₃CH₂OH + HCl → CH₃CH₂Cl + H₂O (in presence of ZnCl₂)
This method is most common and is based on substitution reaction.
Question 32. Discuss the physical properties of haloalkanes.
Answer: Boiling points increase with molecular mass and branching.
They are less soluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Density increases with number and atomic mass of halogen atoms.
These properties are due to dipole-dipole and van der Waals forces.
Question 33. Explain the reaction of haloalkanes with aqueous KOH and alcoholic KOH.
Answer: Aqueous KOH gives nucleophilic substitution forming alcohol:
R–X + KOH (aq) → R–OH + KX
Alcoholic KOH gives elimination reaction forming alkene:
R–X + KOH (alc) → Alkene + KX + H₂O
Question 34. What is the mechanism of SN2 reaction in haloalkanes?
Answer: SN2 proceeds via a single-step mechanism involving simultaneous bond formation and bond breaking.
A nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon from the opposite side of the leaving group, leading to inversion of configuration.
Question 35. Discuss the environmental effects of polyhalogen compounds.
Answer: Polyhalogen compounds like CFCs contribute to ozone depletion. Carbon tetrachloride is toxic and affects the nervous system. DDT is a non-biodegradable pesticide harmful to wildlife.
These compounds persist in the environment and bioaccumulate in food chains.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question.1 Which of the following compounds will undergo SN1 reaction most readily?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Ethyl chloride
(C) Isopropyl chloride
(D) Methyl chloride
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025
Question.2 Which of the following is used in the preparation of DDT?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) Phenol
(C) Toluene
(D) Benzyl chloride
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024
Question.3 What is the major product when 2-bromobutane is treated with alcoholic KOH?
(A) Butanol
(B) Butene
(C) Butane
(D) Butanal
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024
Question.4 In the SN2 reaction of CH₃Cl with OH⁻, the rate of reaction depends on:
(A) Concentration of CH₃Cl
(B) Concentration of OH⁻
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither
Answer: (C)
Year: 2023
Question.5 Which of the following can be used as an anesthetic?
(A) Chloroform
(B) Ethanol
(C) Diethyl ether
(D) Phenol
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023
Question.6 Which reagent converts alcohol to alkyl chloride?
(A) HCl + ZnCl₂
(B) HNO₃
(C) NaOH
(D) H₂SO₄
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022
Question.7 A compound reacts with Na metal to form alkane. It must be:
(A) R–Cl
(B) R–OH
(C) R–COOH
(D) C₆H₆
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022
Question.8 Which of the following undergoes hydrolysis most easily?
(A) CH₃CH₂Br
(B) (CH₃)₃CBr
(C) CH₃Br
(D) C₂H₅I
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021
Question.9 Which is the correct increasing order of reactivity for SN2 reaction?
(A) 3° > 2° > 1°
(B) 1° > 2° > 3°
(C) 2° > 1° > 3°
(D) 3° > 1° > 2°
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021
Question.10 Which halide is most reactive towards SN1?
(A) Methyl chloride
(B) Isopropyl chloride
(C) Benzyl chloride
(D) Vinyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020
Question.11 Which of the following is the best leaving group?
(A) OH⁻
(B) Cl⁻
(C) I⁻
(D) Br⁻
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020
Question.12 The major product formed in the reaction of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane with aqueous NaOH is:
(A) Alcohol
(B) Alkene
(C) Ether
(D) Ester
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019
Question.13 The reaction of ethyl bromide with alcoholic KOH gives:
(A) Ethene
(B) Ethanol
(C) Ethyne
(D) Diethyl ether
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019
Question.14 Which of the following will not give SN1 reaction easily?
(A) Allyl chloride
(B) Benzyl chloride
(C) Vinyl chloride
(D) Tert-butyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2018
Question.15 Which of the following is most reactive towards hydrolysis by aqueous NaOH?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Vinyl chloride
(C) Chlorobenzene
(D) Methyl chloride
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018
Question.16 Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on hydrolysis with aqueous KOH?
(A) 1-Chloropropane
(B) 2-Chlorobutane
(C) 1-Chloro-2-methylpropane
(D) Chlorobenzene
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017
Question.17 Which is the major product in the dehydrohalogenation of 2-bromobutane with alcoholic KOH?
(A) But-2-ene
(B) But-1-ene
(C) Butanol
(D) Butane
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017
Question.18 Which of the following halides undergoes nucleophilic substitution most easily?
(A) Vinyl chloride
(B) Isopropyl chloride
(C) Benzyl chloride
(D) Chlorobenzene
Answer: (C)
Year: 2016
Question.19 Which one gives fastest SN1 reaction?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Year: 2016
Question.20 The hybridisation of carbon in CCl₄ is:
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (C)
Year: 2015
Question.21 Which of the following is not used as refrigerant?
(A) CCl₃F
(B) CHCl₃
(C) CCl₂F₂
(D) CBrF₃
Answer: (B)
Year: 2015
Question.22 Which of the following is most reactive in SN2 reaction?
(A) CH₃CH₂Br
(B) CH₃CHBrCH₃
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Br
(D) (CH₃)₃CBr
Answer: (A)
Year: 2014
Question.23 SN1 reactions are best carried out in:
(A) Non-polar solvents
(B) Polar protic solvents
(C) Polar aprotic solvents
(D) Inert atmosphere
Answer: (B)
Year: 2014
Question.24 Which alkyl halide undergoes elimination most readily?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) C₂H₅Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Year: 2013
Question.25 Which of the following is used in the Wurtz reaction?
(A) CH₃CH₂Br
(B) CH₃COOH
(C) CH₃OH
(D) CH₃CHO
Answer: (A)
Year: 2013
Question.26 The reaction of an alkyl halide with Mg in dry ether is known as:
(A) Wurtz reaction
(B) Sandmeyer reaction
(C) Grignard reaction
(D) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer: (C)
Year: 2012
Question.27 Which of the following is a freon?
(A) CCl₄
(B) C₂H₆
(C) CCl₂F₂
(D) CH₃OH
Answer: (C)
Year: 2012
Question.28 What is formed when CH₃Br reacts with AgCN?
(A) CH₃CN
(B) CH₃NC
(C) CH₃OH
(D) CH₄
Answer: (B)
Year: 2011
Question.29 In the SN2 reaction, which of the following factors increases the rate?
(A) Steric hindrance
(B) Polar protic solvent
(C) Polar aprotic solvent
(D) Tertiary carbon
Answer: (C)
Year: 2011
Question.30 Best reagent to convert alcohol into bromoalkane is:
(A) HBr
(B) Br₂
(C) PBr₃
(D) KBr
Answer: (C)
Year: 2010
Question.31 The major product formed in the reaction of C₂H₅Cl with aqueous KOH is:
(A) C₂H₆
(B) C₂H₅OH
(C) C₂H₄
(D) CH₃CH₂ONa
Answer: (B)
Year: 2010
Question.32 Which halide undergoes hydrolysis most easily?
(A) Vinyl chloride
(B) Chlorobenzene
(C) Benzyl chloride
(D) Ethyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2009
Question.33 Which compound on reaction with AgNO₂ gives nitroalkane?
(A) R–Cl
(B) R–OH
(C) R–Br
(D) R–I
Answer: (A)
Year: 2009
Question.34 The product formed when ethyl bromide is treated with alcoholic AgNO₂ is:
(A) Ethyl nitrite
(B) Ethyl nitrate
(C) Nitroethane
(D) Ethanol
Answer: (C)
Year: 2008
Question.35 Which of the following has maximum dipole moment?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CHCl₃
(C) CH₂Cl₂
(D) CH₃Cl
Answer: (C)
Year: 2008
Question.36 Which is the best leaving group?
(A) OH⁻
(B) Cl⁻
(C) Br⁻
(D) I⁻
Answer: (D)
Year: 2007
Question.37 Which of the following shows +R and –I effect?
(A) –NO₂
(B) –Cl
(C) –CH₃
(D) –OH
Answer: (B)
Year: 2007
Question.38 Which reaction gives alkane?
(A) RCl + Zn/HCl
(B) RBr + Na
(C) RBr + Mg
(D) RCl + KCN
Answer: (B)
Year: 2006
Question.39 SN2 reactions are accompanied by:
(A) Retention
(B) Racemization
(C) Inversion
(D) Elimination
Answer: (C)
Year: 2006
Question.40 The hydrolysis of tert-butyl chloride proceeds via:
(A) SN1
(B) SN2
(C) E1
(D) E2
Answer: (A)
Year: 2005
Question.41 The product formed in the reaction CH₃CH₂Br + KOH (aq) is:
(A) CH₃CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH₃
(C) CH₂=CH₂
(D) CH₃CHO
Answer: (A)
Year: 2005
Question.42 Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution most readily?
(A) C₆H₅Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(D) CH₂=CHCl
Answer: (C)
Year: 2005
Question.43 The decreasing order of SN1 reactivity is:
(A) Benzyl > 3° > 2° > 1°
(B) 3° > Benzyl > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 2° > Benzyl > 1°
(D) Benzyl > 2° > 3° > 1°
Answer: (A)
Year: 2004
Question.44 Which of the following undergoes elimination reaction most readily?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Year: 2004
Question.45 Which of the following compounds reacts fastest with NaI in acetone?
(A) CH₃CH₂CH₂Br
(B) CH₃CHBrCH₃
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Br
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2004
Question.46 Which of the following is not a correct pair?
(A) CH₃Br – methyl bromide
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl – ethyl chloride
(C) CH₃CHClCH₃ – isopropyl chloride
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl – aryl chloride
Answer: (D)
Year: 2004
Question.47 Which of the following shows the highest dipole moment?
(A) CHCl₃
(B) CCl₄
(C) CH₃Cl
(D) CH₂Cl₂
Answer: (D)
Year: 2004
Question.48 The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is:
(A) Use of PCl₅
(B) Use of SOCl₂
(C) Use of HCl
(D) Use of ZnCl₂
Answer: (B)
Year: 2004
Question.49 Which of the following has a partial double bond character in the C–Cl bond?
(A) Methyl chloride
(B) Benzyl chloride
(C) Vinyl chloride
(D) Ethyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2003
Question.50 The boiling point of CH₃Cl is lower than CH₃CH₂Cl because:
(A) CH₃Cl is more polar
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl has more molar mass
(C) CH₃Cl is a gas
(D) None of these
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003
Question.51 The order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN2 reaction is:
(A) 3° > 2° > 1°
(B) 1° > 2° > 3°
(C) 2° > 1° > 3°
(D) 3° > 1° > 2°
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003
Question.52 Which reagent is used to convert alcohol into iodoalkane?
(A) HI
(B) I₂
(C) NaI
(D) PI₃
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.53 The major product of chlorination of methane is:
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₂Cl₂
(C) CHCl₃
(D) CCl₄
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.54 Which of the following is not involved in the SN1 mechanism?
(A) Carbocation
(B) Leaving group
(C) Nucleophile
(D) Transition state
Answer: (D)
Year: 2003
Question.55 Which compound gives only one monohalogenated product on reaction with Cl₂ (sunlight)?
(A) Isobutane
(B) n-Butane
(C) Cyclopentane
(D) 2-Methylpropane
Answer: (C)
Year: 2003
Question.56 Which compound reacts fastest in SN2?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CHClCH₃
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCH₂Cl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.57 Reaction of CH₃CH₂Br with KCN gives:
(A) CH₃CH₂CN
(B) CH₃CH₂NC
(C) CH₃CH₂OH
(D) CH₃CH₃
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.58 Alkyl halides react with sodium metal in dry ether to give:
(A) Alcohol
(B) Alkane
(C) Alkene
(D) Ether
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003
Question.59 Which reagent is best for converting alcohol to chloride?
(A) SOCl₂
(B) NaCl
(C) HCl
(D) Cl₂
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.60 In SN1 reaction, the slowest step is:
(A) Carbocation formation
(B) Nucleophilic attack
(C) Leaving group departure
(D) Product formation
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.61 The hydrolysis of CH₃CH₂Cl with aqueous KOH gives:
(A) CH₃CH₃
(B) CH₃CH₂OH
(C) CH₂=CH₂
(D) CH₃CHO
Answer: (B)
Year: 2002
Question.62 Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution most readily?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) C₆H₅Cl
(C) CH₂=CHCl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (D)
Year: 2002
Question.63 The number of monochloro derivatives formed in the free radical chlorination of methane is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002
Question.64 Which of the following solvents favors SN1 reaction?
(A) Benzene
(B) Diethyl ether
(C) Water
(D) Hexane
Answer: (C)
Year: 2002
Question.65 Which is not a characteristic of SN2 reaction?
(A) Bimolecular
(B) Inversion of configuration
(C) Carbocation intermediate
(D) Transition state
Answer: (C)
Year: 2002
Question.66 Which of the following alkyl halides is least reactive in SN1?
(A) Methyl chloride
(B) Ethyl chloride
(C) Isopropyl chloride
(D) Benzyl chloride
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002
Question.67 The hybridization of carbon in vinyl chloride is:
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (B)
Year: 2002
Question.68 In the reaction of alkyl halide with aqueous KOH, the mechanism is:
(A) Electrophilic substitution
(B) Nucleophilic substitution
(C) Electrophilic addition
(D) Free radical mechanism
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.69 Reaction of C₂H₅Cl with NaI in acetone is known as:
(A) SN1
(B) SN2
(C) Free radical
(D) Elimination
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.70 Which of the following undergoes substitution reaction with NaOH?
(A) Benzene
(B) Benzyl chloride
(C) Toluene
(D) Vinyl chloride
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.71 The halogen atom in aryl halides is:
(A) Electron-donating
(B) Electron-withdrawing
(C) Neutral
(D) Amphoteric
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.72 Which of the following shows both +R and –I effect?
(A) –NO₂
(B) –CH₃
(C) –Cl
(D) –OH
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.73 CCl₄ is not hydrolysed because:
(A) It is non-polar
(B) It is soluble in water
(C) It cannot form carbocation
(D) Carbon is fully bonded
Answer: (D)
Year: 2001
Question.74 The best method for preparation of alkyl iodide from alkyl bromide is:
(A) Finkelstein reaction
(B) Sandmeyer reaction
(C) Wurtz reaction
(D) Free radical reaction
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.75 Which of the following is least reactive in nucleophilic substitution?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Allyl chloride
(C) Vinyl chloride
(D) Ethyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.76 Which compound is used in fire extinguishers?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CHCl₃
(C) CH₄
(D) CH₃Cl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.77 CFCs cause ozone depletion by:
(A) Forming O₂
(B) Releasing Cl atoms
(C) Absorbing UV rays
(D) Emitting IR radiation
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.78 Which compound on hydrolysis gives phenol?
(A) Benzene
(B) Toluene
(C) Chlorobenzene
(D) Benzyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.79 The best method for preparing iodoalkanes is:
(A) From alcohol using HI
(B) From alkene and I₂
(C) From alkyl chloride and NaI
(D) From alkyl bromide and KI
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.80 The hybridisation of carbon in CH₃Cl is:
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.81 Final set (Questions 81 to 100) will follow next.
Which of the following is used in dry cleaning?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CHCl₃
(C) CH₃OH
(D) C₂H₅Cl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.82 Which compound is formed when methyl chloride reacts with KCN?
(A) CH₃CN
(B) CH₃NC
(C) CH₄
(D) CH₃OH
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.83 What happens when methyl chloride is treated with sodium metal in dry ether?
(A) C₂H₆ is formed
(B) CH₄ is formed
(C) CH₃ONa is formed
(D) CH₃CH₂OH is formed
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.84 Which reagent gives methyl cyanide from methyl bromide?
(A) AgCN
(B) KCN
(C) HCN
(D) NaCN
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.85 The best reagent for converting CH₃CH₂OH to CH₃CH₂Cl is:
(A) SOCl₂
(B) PCl₅
(C) HCl/ZnCl₂
(D) Cl₂
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.86 Which of the following undergoes inversion of configuration during nucleophilic substitution?
(A) SN1 reaction
(B) SN2 reaction
(C) E1 reaction
(D) E2 reaction
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.87 The correct increasing order of SN1 reactivity is:
(A) CH₃Cl < CH₃CH₂Cl < (CH₃)₃CCl
(B) (CH₃)₃CCl < CH₃CH₂Cl < CH₃Cl
(C) CH₃CH₂Cl < CH₃Cl < (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) CH₃Cl < (CH₃)₃CCl < CH₃CH₂Cl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.88 Which halogen compound shows resonance in its structure?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) C₂H₅Br
(C) C₆H₅Cl
(D) CH₃I
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.89 Which of the following is least reactive towards nucleophilic substitution?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Methyl chloride
(C) Allyl chloride
(D) Vinyl chloride
Answer: (D)
Year: 2001
Question.90 What is the effect of Cl on benzene ring?
(A) –I and +R
(B) +I and –R
(C) +I and +R
(D) –I and –R
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.91 Which of the following is most likely to undergo nucleophilic substitution?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) Benzyl chloride
(C) Vinyl chloride
(D) Toluene
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.92 Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution due to:
(A) Resonance stabilization
(B) Electronegativity
(C) Size of halogen
(D) Stability of transition state
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.93 What is formed on boiling chlorobenzene with aqueous NaOH at high pressure?
(A) Benzene
(B) Phenol
(C) Benzyl alcohol
(D) Benzaldehyde
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001
Question.94 Which halide gives the fastest SN2 reaction?
(A) CH₃I
(B) CH₃Br
(C) CH₃Cl
(D) CH₃F
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.95 Which alkyl halide gives only one monochloro product on halogenation?
(A) Methane
(B) Ethane
(C) Cyclopentane
(D) 2-Methylpropane
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001
Question.96 Which of the following reagents is used in the conversion of alcohol to bromoalkane?
(A) PBr₃
(B) NaBr
(C) HBr
(D) KBr
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003
Question.97 What is the product when chlorobenzene is heated with NaOH under high pressure?
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Phenol
(C) Benzene
(D) Chlorophenol
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003
Question.98 In haloarenes, the halogen is:
(A) Electron donating by +R, withdrawing by –I
(B) Electron donating by –I
(C) Electron withdrawing by both
(D) Electron donating by both
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002
Question.99 What is the hybridisation of the carbon atom in CH₃Cl?
(A) sp³
(B) sp²
(C) sp
(D) dsp²
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
Question.100 A compound used as a refrigerant but causes ozone depletion is:
(A) CCl₃F
(B) CCl₄
(C) CHCl₃
(D) C₂H₅Cl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question.1 Which of the following compounds undergoes nucleophilic substitution most easily?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) Vinyl chloride
(C) Ethyl chloride
(D) Benzyl chloride
Answer: (D)
Year: 2025
Question.2 What is the major product formed when tert-butyl bromide is treated with aqueous KOH?
(A) tert-Butyl alcohol
(B) Isobutene
(C) sec-Butyl alcohol
(D) 1-Butanol
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025
Question.3 The rate of SN1 reaction depends on:
(A) Concentration of nucleophile
(B) Nature of solvent
(C) Carbocation stability
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer: (D)
Year: 2024
Question.4 The reaction of ethyl chloride with alcoholic KOH gives:
(A) Ethane
(B) Ethene
(C) Ethanol
(D) Acetaldehyde
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024
Question.5 Which of the following will give racemic mixture on hydrolysis?
(A) Methyl bromide
(B) Ethyl chloride
(C) 2-bromobutane
(D) Vinyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Year: 2023
Question.6 Which one is most reactive towards SN2?
(A) 1° alkyl halide
(B) 2° alkyl halide
(C) 3° alkyl halide
(D) Aryl halide
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023
Question.7 Which product is obtained when chlorobenzene reacts with Cl₂ in presence of FeCl₃?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(C) 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
(D) 1,4-Dichlorobenzene
Answer: (B) and (D)
Year: 2022
Question.8 Which statement is correct about C–Cl bond in chlorobenzene?
(A) Easily broken
(B) Weak and reactive
(C) Shows partial double bond character
(D) Similar to alkyl halides
Answer: (C)
Year: 2022
Question.9 What is the function of ZnCl₂ in Lucas reagent?
(A) Oxidising agent
(B) Reducing agent
(C) Catalyst to form carbocation
(D) Dehydrating agent
Answer: (C)
Year: 2021
Question.10 Which will react fastest with HBr?
(A) CH₃CH₂OH
(B) (CH₃)₃COH
(C) CH₃OH
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021
Question.11 Which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(C) CH₃Cl
(D) CH₂=CHCl
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020
Question.12 What is formed when CH₃CH₂Br reacts with aqueous KOH?
(A) CH₃CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH=CH₂
(C) CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
(D) CH₄
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020
Question.13 In SN2 reaction of CH₃Cl and OH⁻, configuration of product is:
(A) Retained
(B) Inverted
(C) Racemised
(D) No change
Answer: (B)
Year: 2019
Question.14 IUPAC name of CH₃CHClCH₂CH₃ is:
(A) 1-chlorobutane
(B) 2-chlorobutane
(C) 3-chlorobutane
(D) Butyl chloride
Answer: (B)
Year: 2019
Question.15 Which will show racemization in aqueous KOH?
(A) n-butyl chloride
(B) sec-butyl chloride
(C) isobutyl chloride
(D) tert-butyl chloride
Answer: (B)
Year: 2018
Question.16 Reaction of chlorobenzene with NaOH at 623 K and 300 atm gives:
(A) Benzene
(B) Phenol
(C) Benzyl alcohol
(D) Toluene
Answer: (B)
Year: 2018
Question.17 Order of reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution:
(A) CH₃Cl > CH₃Br > CH₃I
(B) CH₃I > CH₃Br > CH₃Cl
(C) CH₃Br > CH₃I > CH₃Cl
(D) CH₃Cl = CH₃Br = CH₃I
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017
Question.18 Reactivity order in SN2:
(A) 3° > 2° > 1°
(B) 1° > 2° > 3°
(C) 2° > 1° > 3°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017
Question.19 Which compound will give white precipitate with AgNO₃ fastest?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) CH₃CH₂F
Answer: (C)
Year: 2016
Question.20 Sandmeyer reaction is used for preparation of:
(A) Alcohols
(B) Haloarenes
(C) Aldehydes
(D) Ketones
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016
Question.21 When bromobenzene reacts with Mg in dry ether, the product is:
(A) Phenyl magnesium bromide
(B) Benzene
(C) Toluene
(D) Diphenyl
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015
Question.22 Which of the following cannot be prepared by Wurtz reaction?
(A) Butane
(B) Isobutane
(C) 2-Methylbutane
(D) Methane
Answer: (D)
Year: 2015
Question.23 The product of hydrolysis of C₂H₅Br with aqueous KOH is:
(A) C₂H₆
(B) C₂H₄
(C) C₂H₅OH
(D) CH₃CHO
Answer: (C)
Year: 2014
Question.24 Iodoform test is given by:
(A) CH₃CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
(C) CH₃CHO
(D) CH₃CH(OH)CH₃
Answer: (D)
Year: 2014
Question.25 Which of the following has partial double bond character?
(A) C–Cl in CH₃Cl
(B) C–Cl in chlorobenzene
(C) C–Br in C₂H₅Br
(D) C–I in iodomethane
Answer: (B)
Year: 2013
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Question.1 Which of the following undergoes SN1 reaction most rapidly?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CHClCH₃
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) CH₃Cl
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 (Paper 1)
Question.2 Which one of the following compounds will react most readily with AgNO₃?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) CH₃CH₂F
Answer: (C)
Year: 2023 (Paper 2)
Question.3 Which halide undergoes racemisation during hydrolysis with aqueous KOH?
(A) CH₃CH₂Br
(B) (CH₃)₂CHBr
(C) CH₃CHBrCH₃
(D) (CH₃)₃CBr
Answer: (D)
Year: 2023 (Paper 1)
Question.4 In the SN2 mechanism, the attacking nucleophile approaches:
(A) From front side of leaving group
(B) From backside of leaving group
(C) Randomly
(D) From both sides
Answer: (B)
Year: 2022 (Paper 2)
Question.5 Which of the following has the strongest C–X bond?
(A) C–F
(B) C–Cl
(C) C–Br
(D) C–I
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 (Paper 1)
Question.6 Which of the following is a correct statement regarding SN1 reaction?
(A) Inversion of configuration
(B) First-order reaction
(C) Involves transition state
(D) Requires strong nucleophile
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021 (Paper 2)
Question.7 On treatment with NaOH at high temperature and pressure, chlorobenzene gives:
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Benzene
(C) Phenol
(D) Toluene
Answer: (C)
Year: 2021 (Paper 1)
Question.8 The intermediate in Sandmeyer reaction is:
(A) Carbocation
(B) Free radical
(C) Diazonium ion
(D) Carbene
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020 (Paper 1)
Question.9 Which compound will give a positive iodoform test?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH(OH)CH₃
(C) CH₃CH₂OH
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₃
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 (Paper 2)
Question.10 Which statement is true about SN2 reactions?
(A) Proceeds via carbocation
(B) Rate = k[substrate][nucleophile]
(C) Occurs in polar protic solvents
(D) Favoured by bulky groups
Answer: (B)
Year: 2019 (Paper 1)
Question.11 Lucas test gives turbidity fastest with:
(A) Primary alcohol
(B) Secondary alcohol
(C) Tertiary alcohol
(D) Benzyl alcohol
Answer: (C)
Year: 2019 (Paper 2)
Question.12 Which is correct order of bond strength:
(A) C–I > C–Cl > C–Br > C–F
(B) C–F > C–Cl > C–Br > C–I
(C) C–Cl > C–Br > C–F > C–I
(D) C–Br > C–Cl > C–I > C–F
Answer: (B)
Year: 2018 (Paper 1)
Question.13 Aryl halides are less reactive in nucleophilic substitution due to:
(A) Inductive effect
(B) Resonance effect
(C) Steric hindrance
(D) Electron donation
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017 (Paper 2)
Question.14 What is the product formed when 1-bromopropane is treated with alc. KOH?
(A) Propan-1-ol
(B) Propene
(C) Isopropanol
(D) Acetone
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016 (Paper 1)
Question.15 In Wurtz reaction, the major product formed is:
(A) R–R
(B) R–OH
(C) R–Cl
(D) R–CH₂–OH
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015 (Paper 2)
Question.16 Order of reactivity for SN1 is:
(A) 1° > 2° > 3°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 2° > 3° > 1°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
Answer: (B)
Year: 2013 (Paper 1)
Question.17 Which of the following is not an isomer of C₄H₉Br?
(A) 1-bromobutane
(B) 2-bromobutane
(C) tert-butyl bromide
(D) 1-bromopropane
Answer: (D)
Year: 2010 (Paper 2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MODEL PRATICE SET FOR COMPETITION EXAMS
Question.1 What is the IUPAC name of CH₃CHClCH₃?
(A) 1-Chloropropane
(B) 2-Chloropropane
(C) Isopropyl chloride
(D) Methyl chloride
Answer: (B)
Question.2 Which compound is most reactive towards SN1?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) C₂H₅Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.3 Chlorobenzene reacts with Cl₂ in the presence of FeCl₃ to give:
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) 1,2-Dichlorobenzene
(C) 1,3-Dichlorobenzene
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer: (D)
Question.4 Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides in nucleophilic substitution because:
(A) Aromaticity
(B) –I effect
(C) Resonance stabilization
(D) Steric hindrance
Answer: (C)
Question.5 The boiling point increases with:
(A) Increase in halogen size
(B) Decrease in molecular mass
(C) Branching
(D) None
Answer: (A)
Question.6 Which compound forms white precipitate with AgNO₃ fastest?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) CH₃CH₂F
Answer: (C)
Question.7 The order of reactivity towards SN2 is:
(A) 3° > 2° > 1°
(B) 1° > 2° > 3°
(C) 2° > 1° > 3°
(D) 3° > 1° > 2°
Answer: (B)
Question.8 The Lucas test is used to distinguish:
(A) Haloalkanes
(B) Alcohols
(C) Acids
(D) Esters
Answer: (B)
Question.9 Which of the following is a Freon used in refrigeration?
(A) CHCl₃
(B) CCl₄
(C) CCl₂F₂
(D) C₂H₅Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.10 Which of the following will give racemic mixture on hydrolysis?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CHClCH₃
(C) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.11 Which of the following is used in the preparation of iodoalkane from alcohol?
(A) HI
(B) NaI
(C) PCl₅
(D) Zn
Answer: (A)
Question.12 What is the hybridization of carbon in CH₃Cl?
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (C)
Question.13 Which halogen shows the strongest C–X bond?
(A) I
(B) Br
(C) Cl
(D) F
Answer: (D)
Question.14 Which of the following undergoes SN2 reaction fastest?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) (CH₃)₃CCl
(C) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (A)
Question.15 Which of the following is a greenhouse gas and depletes ozone?
(A) CH₄
(B) CO₂
(C) CFCs
(D) SO₂
Answer: (C)
Question.16 SN1 mechanism proceeds through:
(A) Carbocation
(B) Free radical
(C) Transition metal
(D) Carbene
Answer: (A)
Question.17 Which of the following does NOT undergo nucleophilic substitution easily?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Vinyl chloride
(C) Ethyl chloride
(D) Isopropyl chloride
Answer: (B)
Question.18 Which of the following halides has the lowest boiling point?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃Br
(C) CH₃I
(D) CH₃F
Answer: (A)
Question.19 Which of the following can form Grignard reagent?
(A) CH₃OH
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) C₂H₅OH
(D) CH₃COOH
Answer: (B)
Question.20 Which of the following is most reactive towards AgNO₃ in ethanol?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.21 Which product is formed when CH₃CH₂Br reacts with KCN?
(A) CH₃CH₂NC
(B) CH₃CH₂CN
(C) CH₃CH₂OH
(D) CH₃CH₃
Answer: (B)
Question.22 What is formed when chlorobenzene is heated with NaOH at high pressure?
(A) Phenol
(B) Benzene
(C) Aniline
(D) Benzyl chloride
Answer: (A)
Question.23 What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
(A) Ethanol
(B) Ethene
(C) Ethyne
(D) Diethyl ether
Answer: (A)
Question.24 The reaction of CH₃CH₂Br with Mg in dry ether forms:
(A) Ethyl alcohol
(B) Ethane
(C) Ethyl magnesium bromide
(D) Acetic acid
Answer: (C)
Question.25 C–X bond in alkyl halide is:
(A) Non-polar
(B) Pure covalent
(C) Polar covalent
(D) Ionic
Answer: (C)
Question.26 Which of the following will give only one mono-halogenated product?
(A) Ethane
(B) Propane
(C) Cyclopentane
(D) Butane
Answer: (C)
Question.27 Which of the following undergoes hydrolysis most easily?
(A) C₂H₅Br
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CBr
(D) CH₃CH₂F
Answer: (C)
Question.28 Which is best for preparing alkyl iodide?
(A) Finkelstein reaction
(B) Sandmeyer reaction
(C) Wurtz reaction
(D) Reimer–Tiemann reaction
Answer: (A)
Question.29 CCl₄ does not undergo hydrolysis because:
(A) C–Cl is too strong
(B) It is non-polar
(C) Carbon lacks vacant d-orbitals
(D) It is gaseous
Answer: (C)
Question.30 What is the product of CH₃CH₂Cl + AgNO₂?
(A) Ethyl nitrate
(B) Ethyl nitrite
(C) Nitroethane
(D) Ethanol
Answer: (C)
Question.31 Which halide is least reactive in SN2?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) CH₃CH₂Br
Answer: (C)
Question.32 Racemization in SN1 is due to:
(A) Carbocation being planar
(B) Attack of nucleophile from one side
(C) Presence of solvent
(D) Loss of optical activity
Answer: (A)
Question.33 Which is best for converting ROH to RCl?
(A) SOCl₂
(B) HCl
(C) Cl₂
(D) NaCl
Answer: (A)
Question.34 Grignard reagents are prepared in:
(A) Water
(B) Ethanol
(C) Dry ether
(D) Dil. HCl
Answer: (C)
Question.35 Which has the weakest C–X bond?
(A) C–F
(B) C–Cl
(C) C–Br
(D) C–I
Answer: (D)
Question.36 Which is most reactive towards SN2?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (A)
Question.37 Which is least reactive in nucleophilic substitution?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) CH₃CH₂F
Answer: (D)
Question.38 CH₃CH₂CH₂Br + KOH (alc) →
(A) CH₃CH₂CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH=CH₂
(C) CH₃CH₂CH₃
(D) CH₃CH₂OCH₂CH₃
Answer: (B)
Question.39 Which is used in the preparation of DDT?
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Phenol
(C) Chlorobenzene
(D) Toluene
Answer: (C)
Question.40 Which of the following shows +R effect?
(A) –NO₂
(B) –CH₃
(C) –OH
(D) –Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.41 Which of the following undergoes fastest SN1 reaction?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.42 The presence of electron-withdrawing groups on aryl halides:
(A) Increases nucleophilic substitution
(B) Decreases reactivity
(C) Does not affect reactivity
(D) Inhibits electrophilic substitution
Answer: (A)
Question.43 Which undergoes inversion of configuration during nucleophilic substitution?
(A) SN1
(B) SN2
(C) E1
(D) E2
Answer: (B)
Question.44 The hybridization of carbon in CH₂=CHCl is:
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (B)
Question.45 What is the product when methyl chloride reacts with AgCN?
(A) CH₃CN
(B) CH₃NC
(C) CH₃OH
(D) CH₄
Answer: (B)
Question.46 Which one undergoes hydrolysis most easily?
(A) C₆H₅Cl
(B) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(C) CH₂=CHCl
(D) CH₃CH₂Cl
Answer: (B)
Question.47 The mechanism of hydrolysis of (CH₃)₃CCl involves:
(A) Free radical
(B) Carbocation
(C) Carbanion
(D) None
Answer: (B)
Question.48 Which shows the maximum dipole moment?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₂Cl₂
(C) CHCl₃
(D) CCl₄
Answer: (B)
Question.49 Resonance in aryl halides involves:
(A) pπ–pπ overlap
(B) s–s overlap
(C) p–s overlap
(D) dπ–pπ overlap
Answer: (A)
Question.50 The leaving group ability increases in the order:
(A) F⁻ < Cl⁻ < Br⁻ < I⁻
(B) I⁻ < Br⁻ < Cl⁻ < F⁻
(C) Cl⁻ < Br⁻ < I⁻ < F⁻
(D) Br⁻ < I⁻ < F⁻ < Cl⁻
Answer: (A)
Question.51 Which halide undergoes SN2 fastest?
(A) (CH₃)₃CBr
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) C₆H₅CH₂Br
(D) C₆H₅Br
Answer: (B)
Question.52 Which of the following shows both +R and –I effect?
(A) –NO₂
(B) –Cl
(C) –OH
(D) –CH₃
Answer: (B)
Question.53 Which reaction gives racemised product?
(A) SN1 of chiral alkyl halide
(B) SN2 of chiral alkyl halide
(C) E1 of symmetrical alkane
(D) E2 of alkene
Answer: (A)
Question.54 Which is most stable carbocation?
(A) CH₃CH₂⁺
(B) C₆H₅CH₂⁺
(C) (CH₃)₃C⁺
(D) CH₂=CHCH₂⁺
Answer: (C)
Question.55 Which reagent converts ROH to RBr?
(A) HBr
(B) PBr₃
(C) NaBr
(D) Br₂
Answer: (B)
Question.56 Which one is not a nucleophile?
(A) CN⁻
(B) NH₃
(C) BF₃
(D) OH⁻
Answer: (C)
Question.57 The best solvent for SN1 reaction is:
(A) Diethyl ether
(B) Acetone
(C) Water
(D) Hexane
Answer: (C)
Question.58 Which alkyl halide undergoes elimination most readily?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.59 Vinyl chloride is less reactive due to:
(A) Steric hindrance
(B) Strong C–Cl bond
(C) Resonance stabilization
(D) Hyperconjugation
Answer: (C)
Question.60 Which of the following will react with NaOH (aq) under ordinary conditions?
(A) Benzyl chloride
(B) Chlorobenzene
(C) Vinyl chloride
(D) Nitrobenzene
Answer: (A)
Question.61 The configuration of product in SN2 is:
(A) Racemic
(B) Retained
(C) Inverted
(D) No change
Answer: (C)
Question.62 Which statement about C–X bond strength is correct?
(A) C–I > C–Br
(B) C–F < C–Cl (C) C–F > C–Cl > C–Br > C–I
(D) All equal
Answer: (C)
Question.63 Which of the following gives only one monohalogenated product?
(A) Cyclopentane
(B) Propane
(C) Butane
(D) Pentane
Answer: (A)
Question.64 Which of the following undergoes fastest SN1 reaction in water?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.65 The order of reactivity towards nucleophilic substitution is:
(A) CH₃Cl > CH₃Br > CH₃I
(B) CH₃I > CH₃Br > CH₃Cl
(C) CH₃Br > CH₃Cl > CH₃I
(D) CH₃Cl > CH₃I > CH₃Br
Answer: (B)
Question.66 Which undergoes nucleophilic substitution most easily?
(A) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
(B) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(C) CH₂=CHCH₂Cl
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Br
Answer: (B)
Question.67 Which of the following is least reactive towards SN2?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.68 Reaction of CH₃CH₂Br with AgNO₂ gives:
(A) Ethyl nitrite
(B) Ethyl nitrate
(C) Nitroethane
(D) Ethanol
Answer: (C)
Question.69 Racemisation occurs in:
(A) SN1
(B) SN2
(C) E2
(D) Free radical
Answer: (A)
Question.70 Which halide gives the highest rate of SN2 reaction?
(A) Methyl iodide
(B) Methyl bromide
(C) Methyl chloride
(D) Methyl fluoride
Answer: (A)
Question.71 Which product is formed when CH₃CHClCH₃ is treated with alc. KOH?
(A) Propanol
(B) Propene
(C) Propane
(D) Propyne
Answer: (B)
Question.72 Which of the following forms SN1 intermediate most stable?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CHClCH₃
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.73 CH₃CH₂Cl + KOH (aq) →
(A) CH₃CH₂OH
(B) CH₃CH₂CH₃
(C) CH₃CH=CH₂
(D) CH₃CH₂OCH₃
Answer: (A)
Question.74 What is the major product in Wurtz reaction of 1-chloropropane?
(A) Propane
(B) Butane
(C) Hexane
(D) Pentane
Answer: (C)
Question.75 Which is used in dry cleaning?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CH₃OH
(C) CH₄
(D) C₂H₅Cl
Answer: (A)
Question.76 The hybridisation of carbon in CH₃CH₂Cl is:
(A) sp
(B) sp²
(C) sp³
(D) dsp²
Answer: (C)
Question.77 Which halide forms Grignard reagent most easily?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃Br
(C) CH₃I
(D) CH₃F
Answer: (C)
Question.78 Which gives turbidity fastest in Lucas test?
(A) Primary alcohol
(B) Secondary alcohol
(C) Tertiary alcohol
(D) Phenol
Answer: (C)
Question.79 Which undergoes SN2 with inversion?
(A) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
(B) (CH₃)₃CCl
(C) C₆H₅Cl
(D) CH₂=CHCl
Answer: (A)
Question.80 Which of the following will NOT form Grignard reagent?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) CH₃CH₂OH
(D) CH₃I
Answer: (C)
🔹 Q81–90: JEE Main Level
Question.81 Which reagent is most suitable for converting alcohol to chloroalkane?
(A) PCl₅
(B) SOCl₂
(C) Cl₂
(D) HCl
Answer: (B)
Question.82 Which alkyl halide will not form Grignard reagent in presence of moisture?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Br
(C) CH₃CH₂I
(D) CH₃CH₂OH
Answer: (D)
Question.83 The product formed in the reaction CH₃CH₂Br + Mg (dry ether) is:
(A) Ethyl magnesium bromide
(B) Ethanol
(C) Ethene
(D) Acetic acid
Answer: (A)
Question.84 Which of the following undergoes E2 reaction most readily?
(A) CH₃CH₂Br
(B) CH₃CH₂CH₂Br
(C) (CH₃)₃CBr
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.85 Which halogen compound has least bond dissociation enthalpy?
(A) CH₃F
(B) CH₃Cl
(C) CH₃Br
(D) CH₃I
Answer: (D)
Question.86 Which alkyl halide gives maximum inversion in SN2?
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(C) (CH₃)₃CCl
(D) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
Answer: (A)
Question.87 Which of the following reactions does not proceed via carbocation?
(A) SN1
(B) E1
(C) E2
(D) Dehydration
Answer: (C)
Question.88 Which pair will give the same major alkene on dehydrohalogenation?
(A) 1-Bromopentane and 2-Bromopentane
(B) 2-Bromobutane and 2-Chlorobutane
(C) 1-Bromobutane and 2-Chlorobutane
(D) 2-Bromopentane and 3-Bromopentane
Answer: (D)
Question.89 Which of the following is most reactive in SN1?
(A) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) CH₃CHClCH₃
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.90 Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CHCl₃
(C) CH₃Cl
(D) CH₂Cl₂
Answer: (D)
🔹 Q91–100: JEE Advanced-Style (Multi-Concept)
Question.91 In the reaction:
C₆H₅–N₂⁺Cl⁻ + CuCl → ?
The product is:
(A) C₆H₅Cl
(B) C₆H₅OH
(C) C₆H₅CN
(D) C₆H₅NO₂
Answer: (A)
Question.92 Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution most easily?
(A) Chlorobenzene
(B) Vinyl chloride
(C) Benzyl chloride
(D) Ethyl chloride
Answer: (C)
Question.93 Which halide does not undergo SN2 due to resonance?
(A) CH₃Cl
(B) CH₃CH₂Cl
(C) C₆H₅Cl
(D) CH₃CH₂CH₂Cl
Answer: (C)
Question.94 Racemisation is seen in hydrolysis of:
(A) CH₃CH₂Cl
(B) (CH₃)₂CHCl
(C) C₆H₅CH₂Cl
(D) (CH₃)₃CCl
Answer: (D)
Question.95 Which is correct about Lucas test?
(A) Distinguishes alcohols based on SN2
(B) Based on elimination
(C) Tertiary alcohol gives turbidity fastest
(D) No turbidity observed in SN1
Answer: (C)
Question.96 Which is NOT applicable to haloarenes?
(A) Undergo electrophilic substitution
(B) Undergo nucleophilic substitution easily
(C) Have resonance stabilization
(D) Undergo halogenation
Answer: (B)
Question.97 In SN2, the configuration of the product is:
(A) Retained
(B) Inverted
(C) Racemised
(D) Random
Answer: (B)
Question.98 The major product in Wurtz reaction of 1-bromopropane:
(A) Propene
(B) Butane
(C) Hexane
(D) Pentane
Answer: (C)
Question.99 Which has the strongest C–X bond?
(A) C–F
(B) C–Cl
(C) C–Br
(D) C–I
Answer: (A)
Question.100 Which of the following is a greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance?
(A) CCl₄
(B) CH₃Cl
(C) CHCl₃
(D) CFCs
Answer: (D)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
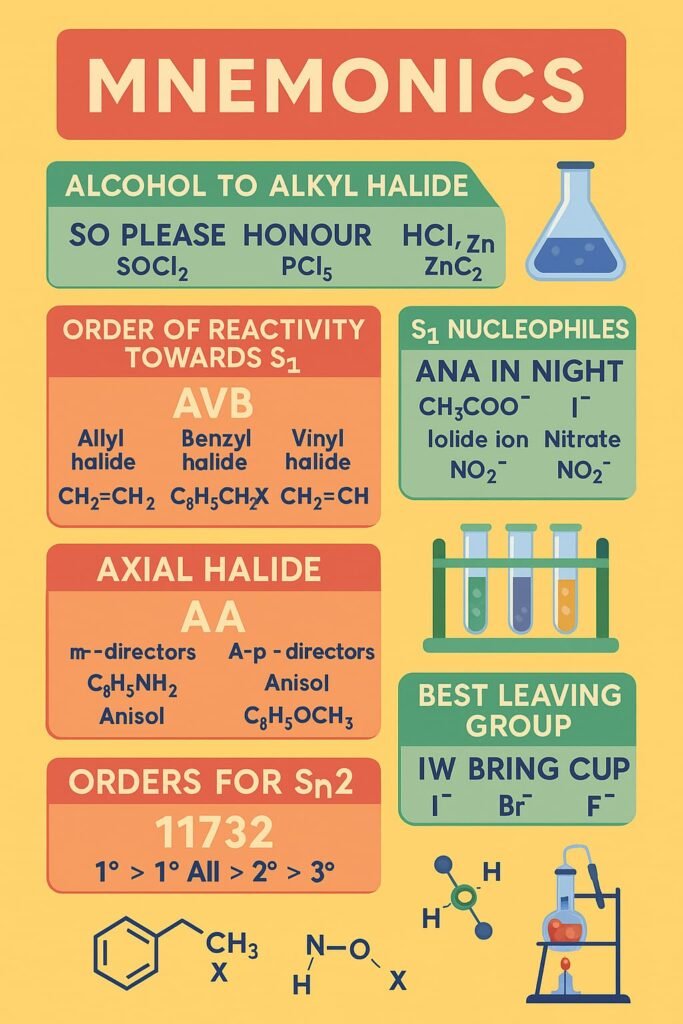
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
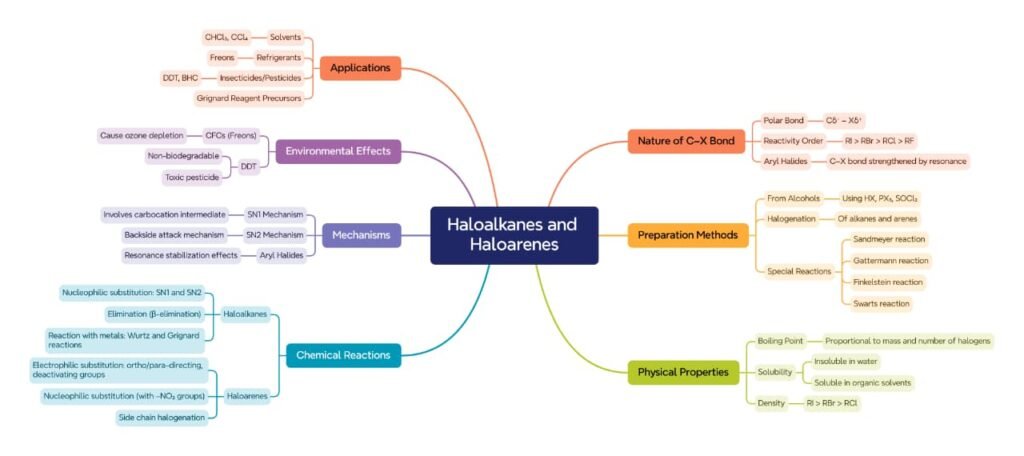
MINDMAPS