Class 12 : Chemistry (English) – Chapter 2: Electrochemistry
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔷 Introduction
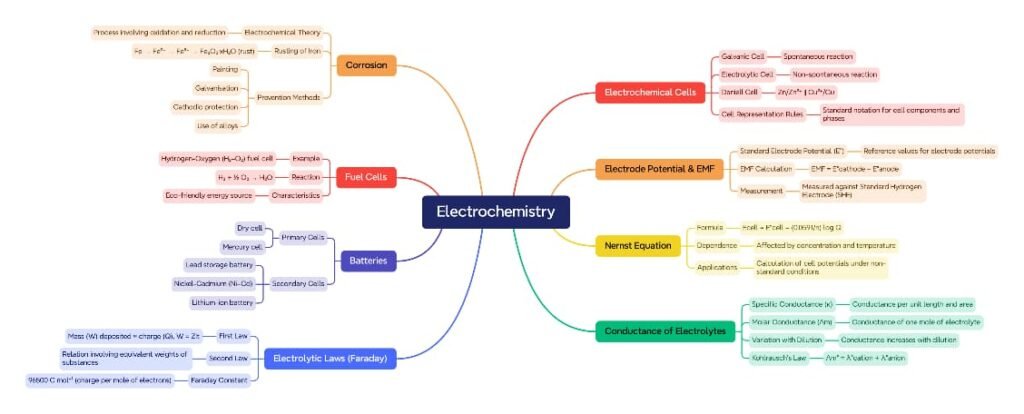
Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes. It plays a vital role in modern science and technology, including batteries, corrosion control, electroplating, and industrial processes.
There are two primary types of electrochemical processes:
Electrochemical (Galvanic) Cells – Convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
Electrolytic Cells – Use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous chemical reactions.
🔷 Redox Reactions and Electrode Processes
Electrochemical reactions are based on redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
In electrochemistry, oxidation always occurs at the anode, and reduction always occurs at the cathode.
To study these reactions systematically, we use electrochemical cells, which consist of two half-cells connected via an external wire and a salt bridge.
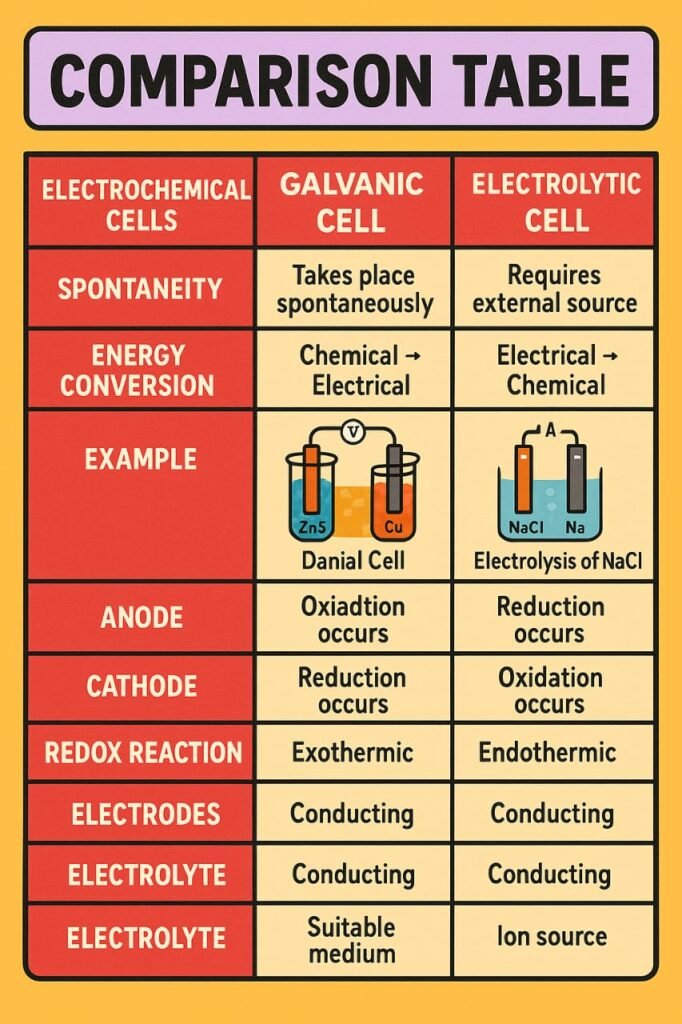
🔷 Electrochemical Cells (Galvanic Cells)
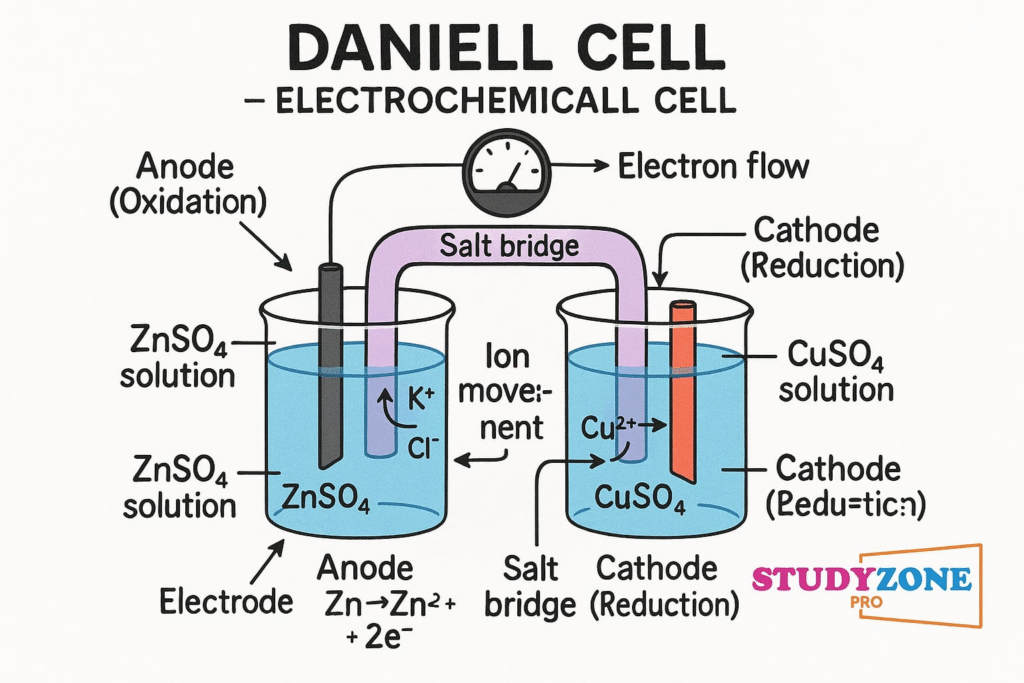
A galvanic cell generates electricity through a spontaneous redox reaction.
Example: Daniel Cell
This cell consists of a zinc electrode dipped in zinc sulfate (ZnSO₄) and a copper electrode dipped in copper sulfate (CuSO₄). The two half-cells are connected through a salt bridge (typically KCl in agar gel), which maintains electrical neutrality.
Anode (oxidation): Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
Cathode (reduction): Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
The flow of electrons is from zinc to copper through the external circuit.
🔷 Representation of an Electrochemical Cell
An electrochemical cell is represented as:
Zn | Zn²⁺ (1M) || Cu²⁺ (1M) | Cu
Here:
Single vertical line (|) represents a phase boundary.
Double vertical line (||) represents the salt bridge.
Left side: Anode; Right side: Cathode.
🔷 Standard Electrode Potential (E°)
The potential difference between the electrode and its solution is called electrode potential. Standard electrode potential (E°) is measured under standard conditions:
1 M concentration
1 atm pressure
25°C (298 K)
By convention, standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is assigned a potential of 0 V and is used as a reference to measure the potentials of other electrodes.
SHE Setup:
Platinum electrode
H₂ gas at 1 atm
H⁺ (aq) of 1 M concentration
🔷 Electromotive Force (EMF) of a Cell
EMF is the voltage generated by the electrochemical cell. It is calculated as:
EMF (E°cell) = E°cathode – E°anode
If EMF is positive, the reaction is spontaneous. If negative, the reaction is non-spontaneous.
🔷 Electrochemical Series
An electrochemical series lists standard electrode potentials of elements. It helps predict:
The feasibility of redox reactions
The strength of oxidizing and reducing agents
Metals higher in the series are better reducing agents and get oxidized easily (more negative E°).
🔷 Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation helps calculate electrode potential under non-standard conditions.
For a half-cell:
E = E° – (0.0591/n) × log([Red]/[Ox])
For the full cell reaction:
Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/n) × log(Q)
Where:
E°cell = Standard EMF
n = Number of electrons transferred
Q = Reaction quotient
🔷 Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions
Electrolytes conduct electricity by the movement of ions. Their ability to conduct depends on:
Nature of electrolyte
Concentration
Temperature
🔷 Types of Conductance
Conductivity (κ): Conductance of a solution between electrodes of 1 cm² area placed 1 cm apart.
Unit: S cm⁻¹
Molar Conductivity (Λm): Conductivity of a solution containing 1 mole of electrolyte.
Λm = κ × 1000 / M
Unit: S cm² mol⁻¹
Equivalent Conductivity (Λeq): Conductivity of solution containing 1 equivalent of electrolyte.
Λeq = κ × 1000 / N
🔷 Variation of Conductivity with Concentration
Conductivity (κ) decreases with dilution due to fewer ions per unit volume.
Molar Conductivity (Λm) increases with dilution due to complete ionization at infinite dilution.
🔷 Kohlrausch’s Law
At infinite dilution, the molar conductivity of an electrolyte is the sum of the molar conductivities of its ions:
Λ°m = λ⁰⁺ + λ⁰⁻
Applications:
Determining degree of dissociation
Calculating molar conductivity of weak electrolytes
Estimating solubility of sparingly soluble salts
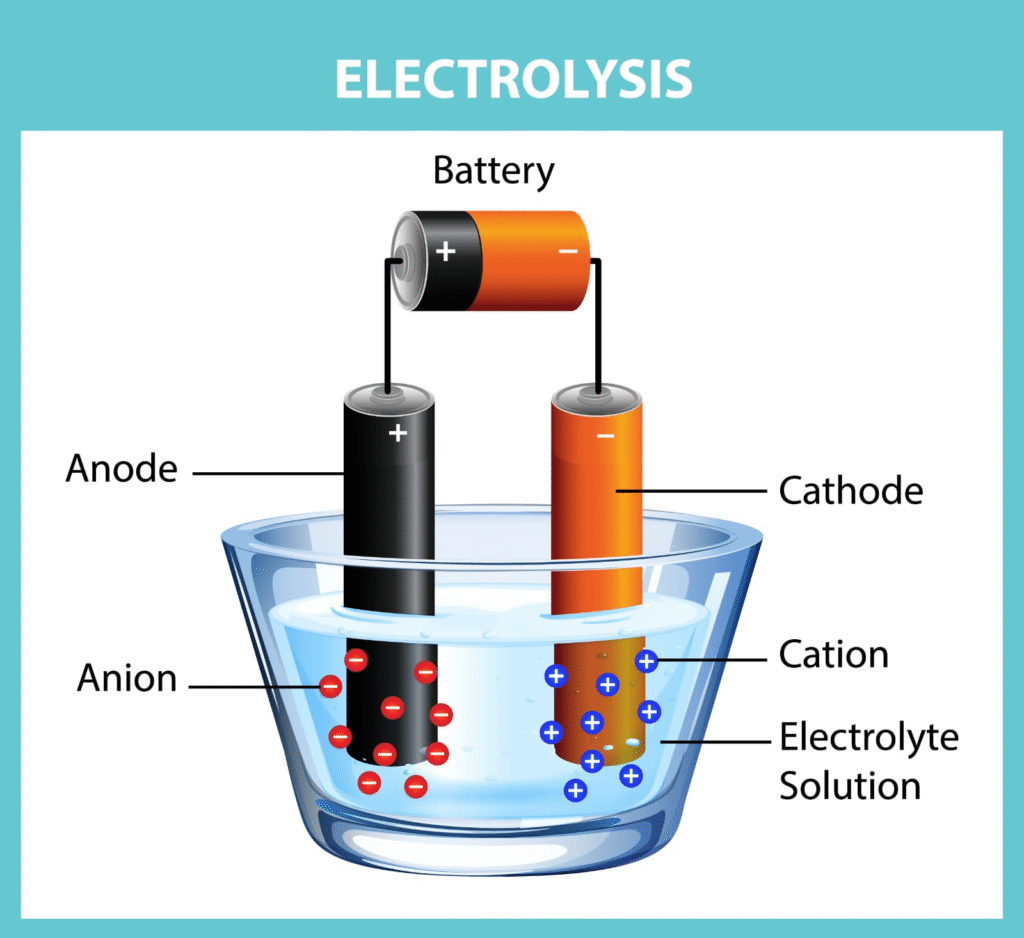
🔷 Electrolytic Cells and Electrolysis
Electrolytic cells use electrical energy to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
Electrolysis: Process of breaking down a compound using electric current.
Example: Electrolysis of molten NaCl
At cathode: Na⁺ + e⁻ → Na
At anode: Cl⁻ → ½Cl₂ + e⁻
🔷 Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis
1st Law: Mass of substance deposited or liberated is directly proportional to quantity of electricity passed.
m = Z × Q = Z × I × t
Where:
m = mass
Z = electrochemical equivalent
I = current
t = time
2nd Law: When same quantity of electricity is passed through different electrolytes, masses of substances are proportional to their equivalent weights.
🔷 Products of Electrolysis
The products depend on:
Electrode material
Nature of electrolyte
Ion discharge potential
Concentration of solution
Example: Electrolysis of aqueous NaCl gives H₂ (at cathode) and Cl₂ (at anode), not Na metal.
🔷 Batteries
Batteries are electrochemical cells designed to produce electricity.
Types:
Primary Batteries – Cannot be recharged (e.g., Dry cell)
Secondary Batteries – Can be recharged (e.g., Lead-acid battery, Lithium-ion battery)
Dry Cell:
Anode: Zinc container
Cathode: Carbon rod
Electrolyte: NH₄Cl + ZnCl₂ + MnO₂ paste
Not rechargeable
Lead Storage Battery:
Anode: Pb plates
Cathode: PbO₂ plates
Electrolyte: Dil. H₂SO₄
Rechargeable
Lithium-ion Battery:
Anode: Graphite
Cathode: Li metal oxide (e.g., LiCoO₂)
Electrolyte: Li⁺ salt in organic solvent
High efficiency, rechargeable
🔷 Fuel Cells
Fuel cells convert chemical energy from fuel (like H₂) into electricity.
Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell:
Anode: H₂ gas → H⁺ + e⁻
Cathode: O₂ gas + H⁺ + e⁻ → H₂O
Advantages:
High efficiency
No pollution
Used in spacecrafts
🔷 Corrosion
Corrosion is the degradation of metals due to chemical reactions with the environment (mainly oxidation).
Rusting of Iron:
Fe is oxidized in presence of water and oxygen.
Forms hydrated iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O)
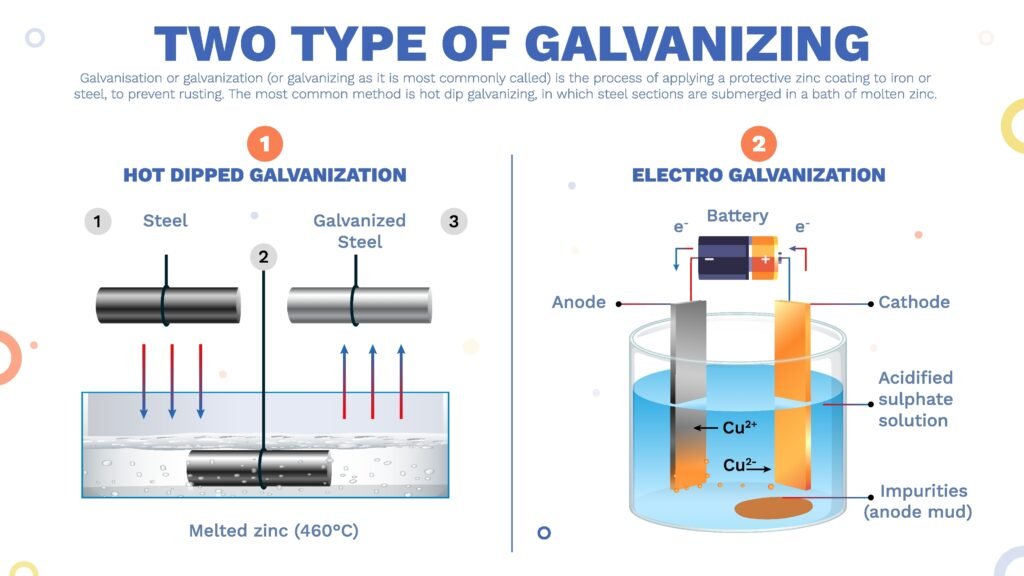
Prevention:
Galvanization (zinc coating)
Painting
Alloying
Cathodic protection
📌 Chapter Summary
Electrochemistry explores the link between electrical energy and chemical change, primarily through redox reactions.
In electrochemical cells, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode. Galvanic cells generate electricity via spontaneous reactions; electrolytic cells require electricity to initiate reactions.
The Daniel cell is a classic galvanic cell, where zinc oxidizes and copper ions reduce to form solid copper. The salt bridge completes the circuit.
Standard electrode potentials (E°) help in comparing tendencies of species to gain electrons. The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is the universal reference with 0 V potential.
The EMF of a cell (E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode) determines whether a redox reaction is spontaneous.
The Nernst equation allows calculation of electrode potential under non-standard conditions.
Conductivity (κ), molar conductivity (Λm), and equivalent conductivity (Λeq) are measures of a solution’s electrical conduction capability.
Kohlrausch’s Law helps determine conductivity at infinite dilution and is useful for weak electrolytes and sparingly soluble salts.
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis quantify the relationship between electric charge and the amount of substance produced at electrodes.
Batteries include dry cells, lead-acid, and lithium-ion cells; the last two are rechargeable.
Fuel cells use continuous fuel supply (like H₂) to produce electricity efficiently and cleanly.
Corrosion, especially rusting of iron, is an electrochemical process that can be minimized through protective measures like galvanization and cathodic protection.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 2.1
Arrange the following metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts:
Al, Cu, Fe, Mg and Zn.
Answer:
The ability of a metal to displace another metal from its salt solution depends on its reactivity (reducing power). The order of reactivity, based on standard electrode potentials, is:
Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu.
Question 2.2
Given the standard electrode potentials,
K⁺/K = –2.93 V, Ag⁺/Ag = 0.80 V, Hg²⁺/Hg = 0.79 V, Mg²⁺/Mg = –2.37 V, Cr³⁺/Cr = –0.74 V
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
Answer:
A more negative standard electrode potential indicates stronger reducing power. Therefore, the increasing order of reducing power is:
Ag < Hg < Cr < Mg < K.
Question 2.3
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction
Zn(s) + 2Ag⁺(aq) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2Ag(s) takes place. Further show:
(i) Which of the electrode is negatively charged?
(ii) The carriers of the current in the cell.
(iii) Individual reaction at each electrode.
Answer:
The cell representation is:
Zn(s) | Zn²⁺(aq) || Ag⁺(aq) | Ag(s).
(i) The zinc electrode (anode) is negatively charged.
(ii) Electrons are the current carriers in the external circuit, while ions are carriers in the internal circuit through the salt bridge (cations towards cathode, anions towards anode).
(iii) Reactions at electrodes:
Anode (oxidation): Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
Cathode (reduction): 2Ag⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → 2Ag(s).
Question 2.4
Calculate the standard cell potentials of galvanic cell in which the following reactions take place:
(i) 2Cr(s) + 3Cd²⁺(aq) → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 3Cd(s)
(ii) Fe²⁺(aq) + Ag⁺(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Ag(s)
Calculate the ΔG° and equilibrium constant of the reactions.
Answer:
(i) For the reaction:
2Cr(s) + 3Cd²⁺(aq) → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 3Cd(s)
E°cell = E°(Cd²⁺/Cd) – E°(Cr³⁺/Cr).
Using standard reduction potentials, calculate E°cell, then use
ΔG° = –nFE°cell (n = 6)
and
K = antilog (nE°cell × F / 2.303RT).
(ii) For the reaction:
Fe²⁺(aq) + Ag⁺(aq) → Fe³⁺(aq) + Ag(s)
The cell potential is:
E°cell = E°(Ag⁺/Ag) – E°(Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺).
Then, calculate ΔG° = –nFE°cell (n = 1) and equilibrium constant K using the above relation.
(Note: Exact numerical answers depend on standard electrode potential values provided in tables.)
Question 2.5
Write the Nernst equation and emf of the following cells at 298 K:
(i) Mg(s) | Mg²⁺(0.0001 M) || Cu²⁺(0.0001 M) | Cu(s)
(ii) Fe(s) | Fe²⁺(0.001 M) || H⁺(1 M) | H₂(g)(1 bar) | Pt(s)
(iii) Sn(s) | Sn²⁺(0.050 M) || H⁺(0.020 M) | H₂(g)(1 bar) | Pt(s)
(iv) Pt(s) | Br₂(l) | Br⁻(1 M) || H⁺(0.030 M) | H₂(g)(1 bar) | Pt(s).
Answer:
The Nernst equation is:
Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/n) log Q,
where n = number of electrons, and Q = reaction quotient.
For each cell:
(i) Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/2) log ([Mg²⁺]/[Cu²⁺])
(ii) Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/2) log (1/[H⁺]²)
(iii) Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/2) log ([Sn²⁺]/[H⁺]²)
(iv) Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/2) log (1/[Br⁻]²[H⁺]²).
Question 2.6
In the button cells widely used in watches and other devices the following reaction takes place:
Zn(s) + Ag₂O(s) + H₂O(l) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2Ag(s) + 2OH⁻(aq)
Determine ΔᵣG° and E° for the reaction.
✅ Answer:
Given reaction:
Zn(s) + Ag₂O(s) + H₂O(l) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2Ag(s) + 2OH⁻(aq)
To find ΔᵣG° and E°, we use:
🔹 Step 1: Find E°cell using standard reduction potentials:
E°(Ag₂O/Ag) and E°(Zn²⁺/Zn) (from standard tables).
Let’s assume:
E°(Ag₂O + H₂O + 2e⁻ → 2Ag + 2OH⁻) = +0.34 V
E°(Zn²⁺/Zn) = –0.76 V
Then,
E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode = 0.34 – (–0.76) = 1.10 V
🔹 Step 2: Calculate ΔᵣG°
ΔᵣG° = –nFE°cell
Here, n = 2
F = 96500 C/mol
ΔᵣG° = –2 × 96500 × 1.10 = –2.123 × 10⁵ J/mol = –212.3 kJ/mol
Question 2.7
Define conductivity and molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. Discuss their variation with concentration.
✅ Answer:
🔹 Conductivity (κ):
It is the conductance of a solution per unit length and unit cross-sectional area.
Unit: S m⁻¹ (siemens per metre)
Symbol: κ (kappa)
🔹 Molar Conductivity (Λₘ):
It is the conductivity of an electrolyte solution divided by its molar concentration (C), and is given by:
Λₘ = κ / C
Unit: S m² mol⁻¹
🔹 Variation with Concentration:
– Conductivity (κ): Decreases with dilution, because the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
– Molar Conductivity (Λₘ): Increases with dilution. It approaches a maximum value at infinite dilution, called Λₘ⁰.
Question 2.8
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.0248 S cm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity.
✅ Answer:
Given:
C = 0.20 mol L⁻¹
κ = 0.0248 S cm⁻¹ = 0.0248 × 100 S m⁻¹ = 2.48 S m⁻¹
But since molar conductivity uses S cm² mol⁻¹:
Λₘ = κ × 1000 / C
= (0.0248 × 1000) / 0.20
= 124 S cm² mol⁻¹
Question 2.9
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω.
What is the cell constant if conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹?
✅ Answer:
Given:
R = 1500 Ω
κ = 0.146 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
Cell constant (G*) = κ × R
G = 0.146 × 10⁻³ × 1500*
= 0.219 cm⁻¹
Question 2.10
The conductivity of sodium chloride at 298 K has been determined at different concentrations and the results are given below:
Concentration (M) κ (×10² S m⁻¹)
0.001 1.237
0.010 11.85
0.020 23.15
0.050 55.53
0.100 106.74
Calculate Λₘ for all concentrations and draw a plot between Λₘ and √C.
Find the value of Λₘ⁰.
✅ Answer:
Formula:
Λₘ = κ × 1000 / C
Now compute Λₘ values:
🔹 For 0.001 M:
Λₘ = (1.237 × 10⁻² × 1000) / 0.001 = 12370 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 For 0.010 M:
Λₘ = (11.85 × 10⁻² × 1000) / 0.010 = 11850 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 For 0.020 M:
Λₘ = (23.15 × 10⁻² × 1000) / 0.020 = 11575 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 For 0.050 M:
Λₘ = (55.53 × 10⁻² × 1000) / 0.050 = 11106 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 For 0.100 M:
Λₘ = (106.74 × 10⁻² × 1000) / 0.100 = 10674 S cm² mol⁻¹
Now plot Λₘ vs √C and extrapolate to C → 0 to get Λₘ⁰
→ From the plot, the intercept gives Λₘ⁰ ≈ 126.4 S cm² mol⁻¹ (typical value for NaCl).
Question 2.11
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10⁻⁵ S cm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity. If Λₘ⁰ for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm² mol⁻¹, what is its dissociation constant?
✅ Answer:
Given:
C = 0.00241 mol L⁻¹
κ = 7.896 × 10⁻⁵ S cm⁻¹
Λₘ⁰ = 390.5 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 Step 1: Calculate Λₘ
Λₘ = κ × 1000 / C
= (7.896 × 10⁻⁵ × 1000) / 0.00241
= 32.76 S cm² mol⁻¹
🔹 Step 2: Degree of dissociation (α)
α = Λₘ / Λₘ⁰ = 32.76 / 390.5 = 0.0839
🔹 Step 3: Dissociation constant (Ka)
Ka = C × α² / (1 – α)
Ka = 0.00241 × (0.0839)² / (1 – 0.0839)
Ka ≈ 1.85 × 10⁻⁵
Question 2.12
How much charge is required for the following reductions:
(i) 1 mol of Al³⁺ to Al
(ii) 1 mol of Cu²⁺ to Cu
(iii) 1 mol of MnO₄⁻ to Mn²⁺
✅ Answer:
Formula: Q = n × F (n = number of electrons, F = 96500 C/mol)
(i) Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al
Q = 3 × 96500 = 289500 C
(ii) Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
Q = 2 × 96500 = 193000 C
(iii) MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂O
Q = 5 × 96500 = 482500 C
Question 2.13
How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce:
(i) 20.0 g of Ca from molten CaCl₂?
(ii) 40.0 g of Al from molten Al₂O₃?
✅ Answer:
(i) For Ca:
Molar mass = 40 g/mol, n = 2 (Ca²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ca)
20 g = 0.5 mol → Faradays = 0.5 × 2 = 1.0 F
(ii) For Al:
Molar mass = 27 g/mol, n = 3 (Al³⁺ + 3e⁻ → Al)
40 g = 40/27 ≈ 1.481 mol
Faradays = 1.481 × 3 ≈ 4.44 F
Question 2.14
How much electricity is required in coulombs for the oxidation of:
(i) 1 mol of H₂O to O₂
(ii) 1 mol of FeO to Fe₂O₃
✅ Answer:
(i) 2H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ (4 electrons per mol O₂)
Q = 4 × 96500 = 386000 C
(ii) 4FeO → 2Fe₂O₃ + 4e⁻ (Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺, 1 e⁻ per Fe)
For 1 mol FeO, Q = 1 × 96500 = 96500 C
Question 2.15
A solution of Ni(NO₃)₂ is electrolysed between platinum electrodes using a current of 5 amperes for 20 minutes. What mass of Ni is deposited at the cathode?
✅ Answer:
Given:
Current (I) = 5 A, Time (t) = 20 × 60 = 1200 s
Q = I × t = 5 × 1200 = 6000 C
Reaction: Ni²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ni (n = 2)
Molar mass of Ni = 58.7 g/mol
Mass deposited = (M × Q) / (n × F)
= (58.7 × 6000) / (2 × 96500) ≈ 1.83 g
Question 2.16
Three electrolytic cells A, B, C containing solutions of ZnSO₄, AgNO₃, and CuSO₄ respectively are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5 amperes was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and zinc were deposited?
✅ Answer:
Step 1: For Ag deposition
M = 107.9 g/mol, n = 1
m = 1.45 g
t = (m × n × F) / (M × I)
= (1.45 × 96500) / (107.9 × 1.5) ≈ 864 s
Step 2: Mass of Cu (n = 2, M = 63.5):
m = (M × I × t) / (n × F)
= (63.5 × 1.5 × 864) / (2 × 96500) ≈ 0.426 g
Step 3: Mass of Zn (n = 2, M = 65.4):
m = (65.4 × 1.5 × 864) / (2 × 96500) ≈ 0.438 g
Question 2.17
Using the standard electrode potentials given in Table 3.1, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible:
(i) Fe³⁺(aq) and I⁻(aq)
(ii) Ag⁺(aq) and Cu(s)
(iii) Fe³⁺(aq) and Br⁻(aq)
(iv) Ag(s) and Fe³⁺(aq)
(v) Br₂(aq) and Fe²⁺(aq)
✅ Answer:
To check feasibility, calculate E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode. If E°cell > 0 → feasible.
(i) Fe³⁺ + e⁻ → Fe²⁺ (E° = +0.77 V)
2I⁻ → I₂ + 2e⁻ (E° = +0.54 V)
E°cell = 0.77 – 0.54 = +0.23 V → Feasible
(ii) Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag (0.80 V), Cu → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ (–0.34 V)
E°cell = 0.80 – (–0.34) = +1.14 V → Feasible
(iii) Br⁻ oxidation: 2Br⁻ → Br₂ + 2e⁻ (E° = +1.09 V)
E°cell = 0.77 – 1.09 = –0.32 V → Not feasible
(iv) Ag oxidation: Ag → Ag⁺ + e⁻ (–0.80 V), Fe³⁺ reduction: +0.77 V
E°cell = 0.77 – 0.80 = –0.03 V → Not feasible
(v) Br₂ + 2e⁻ → 2Br⁻ (E° = +1.09 V), Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺ + e⁻ (–0.77 V)
E°cell = 1.09 – 0.77 = +0.32 V → Feasible
Question 2.18
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following:
(i) An aqueous solution of AgNO₃ with silver electrodes.
(ii) An aqueous solution of AgNO₃ with platinum electrodes.
(iii) A dilute solution of H₂SO₄ with platinum electrodes.
(iv) An aqueous solution of CuCl₂ with platinum electrodes.
✅ Answer:
(i) AgNO₃ + Ag electrodes:
Cathode: Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag (deposition)
Anode: Ag → Ag⁺ + e⁻ (dissolution)
→ No net change in Ag⁺ concentration
(ii) AgNO₃ + Pt electrodes:
Cathode: Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag (deposition)
Anode: H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
→ Silver deposited and oxygen gas evolved
(iii) Dilute H₂SO₄ + Pt electrodes:
Cathode: 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂ (hydrogen gas)
Anode: H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
→ Hydrogen and oxygen gases are evolved
(iv) CuCl₂ + Pt electrodes:
Cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
Anode: 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
→ Copper deposited and chlorine gas released
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Q1. In an electrochemical cell, the flow of electrons is:
(A) From cathode to anode through the salt bridge
(B) From anode to cathode through the external circuit
(C) From anode to cathode through the salt bridge
(D) From cathode to anode through the external circuit
Answer: (B) From anode to cathode through the external circuit
Q2. In the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE), the electrode used is:
(A) Copper
(B) Platinum
(C) Zinc
(D) Carbon
Answer: (B) Platinum
Q3. The cell notation for Daniel cell is:
(A) Cu | Cu²⁺ (1M) || Zn²⁺ (1M) | Zn
(B) Zn | Zn²⁺ (1M) || Cu²⁺ (1M) | Cu
(C) Zn²⁺ (1M) | Zn || Cu | Cu²⁺ (1M)
(D) Cu²⁺ (1M) | Cu || Zn | Zn²⁺ (1M)
Answer: (B) Zn | Zn²⁺ (1M) || Cu²⁺ (1M) | Cu
Q4. The standard electrode potential of Zn²⁺/Zn is –0.76 V and that of Cu²⁺/Cu is +0.34 V. The EMF of the cell Zn | Zn²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu is:
(A) –1.10 V
(B) +1.10 V
(C) +0.42 V
(D) –0.42 V
Answer: (B) +1.10 V
Q5. Assertion (A): In a galvanic cell, reduction takes place at the cathode.
Reason (R): Electrons flow from cathode to anode in the external circuit.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, R is false
(D) A is false, R is true
Answer: (C) A is true, R is false
Q6. The Nernst equation for a half-cell reaction Mn⁺ + ne⁻ ⇌ M is:
(A) E = E° + (0.0591/n) log [Mn⁺]
(B) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log [Mn⁺]
(C) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log [M]
(D) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log [M/Mn⁺]
Answer: (B) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log [Mn⁺]
Q7. Which of the following electrolytes shows maximum molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) CH₃COOH
(B) NaOH
(C) KCl
(D) HCl
Answer: (D) HCl
Q8. The electrochemical equivalent of a substance is defined as:
(A) Mass deposited per mole
(B) Mass deposited per coulomb
(C) Volume deposited per mole
(D) Volume deposited per coulomb
Answer: (B) Mass deposited per coulomb
Q9. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the function of the salt bridge?
(A) It supplies electrons to the electrolyte
(B) It provides a path for the flow of electrons
(C) It completes the circuit and maintains charge balance
(D) It supplies ions to the electrode
Answer: (C) It completes the circuit and maintains charge balance
Q10. Which among the following cells is not rechargeable?
(A) Lead-acid battery
(B) Lithium-ion battery
(C) Nickel-cadmium battery
(D) Dry cell
Answer: (D) Dry cell
Q11. The unit of conductivity (κ) in SI is:
(A) ohm⁻¹ cm
(B) ohm⁻¹ cm² mol⁻¹
(C) S m⁻¹
(D) S mol⁻¹
Answer: (C) S m⁻¹
Q12. The species that migrates toward the cathode during electrolysis is:
(A) Anion
(B) Cation
(C) Electron
(D) Proton
Answer: (B) Cation
Q13. In the electrolysis of molten NaCl, the product at the cathode is:
(A) Na
(B) H₂
(C) Cl₂
(D) O₂
Answer: (A) Na
Q14. Which of the following is not used as a primary reference electrode?
(A) Standard hydrogen electrode
(B) Calomel electrode
(C) Silver-silver chloride electrode
(D) Copper electrode
Answer: (D) Copper electrode
Q15. Assertion (A): Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte increases sharply on dilution.
Reason (R): Ionisation of weak electrolyte increases on dilution.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, R is false
(D) A is false, R is true
Answer: (A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Q16. Which of the following is a correct expression for molar conductivity?
(A) Λm = κ × M
(B) Λm = κ / M
(C) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
(D) Λm = κ × M / 1000
Answer: (C) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
Q17. In a lead storage battery, the electrolyte used is:
(A) Concentrated HCl
(B) Dilute NaOH
(C) Concentrated H₂SO₄
(D) Dilute H₂SO₄
Answer: (D) Dilute H₂SO₄
Q18. Which of the following is a correct expression of Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis?
(A) m = E × I
(B) m = Z × I × t
(C) m = Z / I
(D) m = I / Z
Answer: (B) m = Z × I × t
🔹 Section B: Q19–Q23 (2 Marks Each)
Q19. Define conductivity and molar conductivity. How does molar conductivity vary with dilution for a weak electrolyte?
Answer:
Conductivity (κ) is the conductance of a solution between two electrodes 1 cm apart and having 1 cm² area of cross-section. Unit: S cm⁻¹.
Molar conductivity (Λm) is the conductivity of a solution containing 1 mole of electrolyte, placed between electrodes 1 cm apart.
Λm = κ × (1000 / M), where M is molarity.
For a weak electrolyte, molar conductivity increases sharply with dilution because ionization increases significantly.
Q20. What is meant by limiting molar conductivity? Write its units. How is it useful for weak electrolytes?
Answer:
Limiting molar conductivity (Λm⁰) is the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution, where ion-ion interactions are negligible and complete ionization occurs.
Unit: S cm² mol⁻¹
It is useful for weak electrolytes because their Λm⁰ can be calculated using Kohlrausch’s law, even though they are not completely ionized at ordinary concentrations.
Q21. Calculate the EMF of the following cell at 298 K:
Zn | Zn²⁺ (0.1 M) || Cu²⁺ (1 M) | Cu
Given: E°(Zn²⁺/Zn) = –0.76 V, E°(Cu²⁺/Cu) = +0.34 V
Answer:
Step 1: E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
= 0.34 – (–0.76) = 1.10 V
Step 2: Nernst equation for the cell:
Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/n) × log([Zn²⁺]/[Cu²⁺])
= 1.10 – (0.0591/2) × log(0.1 / 1)
= 1.10 – 0.02955 × (–1)
= 1.10 + 0.02955
= 1.13 V
Q22. State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions. Give one application.
Answer:
Statement:
Kohlrausch’s law states that at infinite dilution, the molar conductivity of an electrolyte is equal to the sum of the individual contributions of the cation and anion.
Λm⁰ = λ⁰⁺ + λ⁰⁻
Application:
To calculate the Λm⁰ of weak electrolytes (like CH₃COOH) using values of strong electrolytes.
Q23. What is corrosion? Explain the electrochemical theory of rusting of iron.
Answer:
Corrosion is the gradual deterioration of metals due to chemical/electrochemical reactions with the environment.
Electrochemical theory:
Iron surface has small electrochemical cells.
At anode: Fe → Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻
Electrons flow to cathodic region where: O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
Fe²⁺ reacts with OH⁻ to form Fe(OH)₂, which oxidizes to brown Fe₂O₃·xH₂O (rust).
🔹 Section C: Q24–Q28 (3 Marks Each)
Q24. The conductivity of 0.001 M acetic acid is 4.95 × 10⁻⁵ S cm⁻¹. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given: Λm⁰(CH₃COOH) = 390.5 S cm² mol⁻¹
Answer:
Step 1: Molar conductivity
Λm = κ × 1000 / M
= (4.95 × 10⁻⁵) × 1000 / 0.001
= 49.5 S cm² mol⁻¹
Step 2: Degree of dissociation (α)
α = Λm / Λm⁰
= 49.5 / 390.5
≈ 0.127 or 12.7%
Q25. A current of 1.5 A was passed through an electrolyte for 15 minutes. Calculate the mass of copper deposited if the electrolyte is CuSO₄. (Atomic mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol⁻¹)
Answer:
Step 1: Charge (Q) = I × t
Q = 1.5 A × 15 × 60 s = 1350 C
Step 2: m = (E × Q) / F
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
Equivalent weight of Cu = 63.5 / 2 = 31.75
F = 96500 C/mol
m = (31.75 × 1350) / 96500
= 0.444 g
Answer: 0.444 g of Cu
Q26. Write the reactions taking place during discharge and recharge of a lead-acid battery.
Answer:
During discharge:
Anode: Pb → Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻ → PbSO₄
Cathode: PbO₂ + 4H⁺ + SO₄²⁻ + 2e⁻ → PbSO₄ + 2H₂O
During recharge (reverse of discharge):
Anode: PbSO₄ → Pb + SO₄²⁻
Cathode: PbSO₄ + 2H₂O → PbO₂ + SO₄²⁻ + 4H⁺ + 2e⁻
Q27. What is the difference between a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell? Give one example of each.
Answer:
Galvanic Cell Electrolytic Cell
Converts chemical energy into electrical energy Converts electrical energy into chemical energy
Spontaneous redox reaction Non-spontaneous redox reaction
Example: Daniel cell Example: Electrolysis of molten NaCl
Q28. Calculate the amount of charge required to deposit 5.4 g of aluminum (Al) from Al³⁺ ions. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g/mol)
Answer:
Step 1: Number of moles of Al = 5.4 / 27 = 0.2 mol
Step 2: Each mole of Al³⁺ requires 3 moles of electrons
So, total moles of e⁻ = 0.2 × 3 = 0.6 mol
Charge = 0.6 × 96500 C = 57900 C
🔹 Section D: Case-Based Questions (4 Marks Each)
Q29. Read the following passage and answer the questions below:
In an electrochemical cell, a zinc electrode is immersed in 1 M ZnSO₄ solution and a copper electrode in 1 M CuSO₄ solution. The two half-cells are connected using a salt bridge and a voltmeter. The standard electrode potentials are:
E°(Zn²⁺/Zn) = –0.76 V; E°(Cu²⁺/Cu) = +0.34 V.
(i) Write the cell reaction.
(ii) Calculate the standard EMF of the cell.
(iii) Identify the anode and cathode.
(iv) What is the direction of electron flow?
Answer:
(i) Cell reaction: Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
(ii) E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode = 0.34 – (–0.76) = 1.10 V
(iii) Anode: Zn; Cathode: Cu
(iv) Electrons flow from Zn to Cu (anode to cathode)
Q30. Read the following extract and answer the questions:
Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte. Its degree of dissociation (α) increases with dilution. At 25°C, the molar conductivity of 0.001 M acetic acid is found to be 49.5 S cm² mol⁻¹. The molar conductivity at infinite dilution is 390.5 S cm² mol⁻¹.
(i) Define molar conductivity.
(ii) Calculate the degree of dissociation (α).
(iii) Why does α increase with dilution?
(iv) What will happen to conductivity (κ) if the solution is diluted further?
Answer:
(i) Molar conductivity (Λm) is the conductance of all ions produced by 1 mole of electrolyte in solution.
(ii) α = Λm / Λm⁰ = 49.5 / 390.5 ≈ 0.127 (or 12.7%)
(iii) Dilution reduces interionic attraction, increasing ionization.
(iv) κ will decrease due to lower ion concentration per unit volume.
Q31. Study the following scenario:
In a galvanic cell involving the reaction Fe²⁺ + Cu → Fe + Cu²⁺, the standard electrode potentials are:
E°(Fe²⁺/Fe) = –0.44 V; E°(Cu²⁺/Cu) = +0.34 V.
(i) Write the half-cell reactions.
(ii) Calculate E°cell.
(iii) Which metal is more reactive?
(iv) Is the reaction spontaneous?
Answer:
(i)
Anode: Fe → Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻
Cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
(ii) E°cell = 0.34 – (–0.44) = 0.78 V
(iii) Fe is more reactive (more negative E°)
(iv) Yes, since E°cell is positive, the reaction is spontaneous.
🔹 Section E: Long Answer Questions (5 Marks Each)
Q32. Derive the Nernst equation for a general redox reaction:
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD and apply it to a galvanic cell.
Answer:
For a redox reaction:
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
Reaction quotient Q = ([C]^c × [D]^d)/([A]^a × [B]^b)
Nernst equation:
E = E° – (0.0591/n) × log Q
Where:
E = electrode potential under non-standard conditions
E° = standard electrode potential
n = number of electrons transferred
Q = reaction quotient
For a galvanic cell:
Zn | Zn²⁺ (a M) || Cu²⁺ (b M) | Cu
Ecell = E°cell – (0.0591/n) × log([Zn²⁺]/[Cu²⁺])
This equation helps calculate cell potential under any concentration.
Q33. A solution of copper sulfate is electrolyzed using inert platinum electrodes. A current of 2 amperes is passed for 10 minutes. Calculate:
(i) the charge passed
(ii) moles of electrons
(iii) mass of copper deposited (Atomic mass = 63.5 g/mol)
Answer:
(i) Q = I × t = 2 A × 10 × 60 s = 1200 C
(ii) 1 mol e⁻ = 96500 C → mol of e⁻ = 1200 / 96500 = 0.01244 mol
(iii)
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu
So, 2 mol e⁻ → 1 mol Cu
→ 0.01244 mol e⁻ → 0.01244 / 2 = 0.00622 mol Cu
Mass = 0.00622 × 63.5 ≈ 0.395 g
Q34. Write a detailed note on fuel cells. Explain the working of H₂-O₂ fuel cell with reactions. Mention any two advantages.
Answer:
Fuel cells convert chemical energy of fuels into electrical energy continuously.
H₂–O₂ fuel cell:
Anode: H₂ gas → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
Cathode: O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
Overall: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O + energy
Electrolyte: KOH or acidic H₂SO₄
Electrodes: Porous graphite with catalysts
Advantages:
High efficiency
Eco-friendly (only water is produced)
Used in spacecrafts, submarines, and clean energy tech.
Q35. Explain Faraday’s laws of electrolysis with mathematical expressions. Calculate the mass of Ag deposited by passing 4 amperes of current through AgNO₃ solution for 40 minutes.
(Atomic mass of Ag = 108 g/mol, n = 1)
Answer:
First Law:
m ∝ Q → m = Z × I × t
Second Law:
m₁/m₂ = E₁/E₂ for same Q
Given:
I = 4 A, t = 40 × 60 = 2400 s
n = 1, F = 96500 C/mol
Z = E / nF = 108 / 96500 g/C
m = Z × I × t
= (108 / 96500) × 4 × 2400
≈ 10.75 g of Ag
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following statements about galvanic cells is incorrect?
(A) Electrons flow from anode to cathode through external circuit
(B) Oxidation occurs at anode
(C) Reduction occurs at cathode
(D) Cations move toward cathode through salt bridge
Answer: (D) Cations move toward cathode through salt bridge
Year: 2025 | Set: Z
Q2. In electrolysis of aqueous CuSO₄ using platinum electrodes, the products at cathode and anode are:
(A) Cu and O₂
(B) H₂ and O₂
(C) Cu and Cl₂
(D) H₂ and Cl₂
Answer: (B) H₂ and O₂
Year: 2025 | Set: 3
Q3. Molar conductivity of a solution increases with:
(A) increase in concentration
(B) decrease in temperature
(C) dilution
(D) pressure
Answer: (C) dilution
Year: 2024 | Set: Z
Q4. For the reaction Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu, the correct EMF at standard conditions is:
(A) +1.10 V
(B) –1.10 V
(C) 0.00 V
(D) +0.42 V
Answer: (A) +1.10 V
Year: 2024 | Set: 1
Q5. Which of the following cells is a secondary cell?
(A) Mercury cell
(B) Dry cell
(C) Lead storage battery
(D) Fuel cell
Answer: (C) Lead storage battery
Year: 2023 | Set: M2
Q6. In the standard hydrogen electrode, hydrogen gas is bubbled at:
(A) 273 K and 2 atm
(B) 298 K and 1 atm
(C) 273 K and 1 atm
(D) 298 K and 2 atm
Answer: (B) 298 K and 1 atm
Year: 2023 | Set: R
Q7. The salt bridge is used in electrochemical cells:
(A) to provide electrons
(B) to stop the reaction
(C) to maintain electrical neutrality
(D) to change electrode potentials
Answer: (C) to maintain electrical neutrality
Year: 2022 | Set: Q
Q8. Which of the following shows maximum molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) CH₃COOH
(B) NH₄OH
(C) NaOH
(D) HCl
Answer: (D) HCl
Year: 2022 | Set: 2
Q9. Which of the following expressions is correct for the Nernst equation of Zn²⁺/Zn?
(A) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log [Zn²⁺]
(B) E = E° + 0.0591 log [Zn²⁺]
(C) E = E° + (0.0591/2) log [Zn²⁺]
(D) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log [Zn]
Answer: (A) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log [Zn²⁺]
Year: 2021 | Set: S1
Q10. During electrolysis of aqueous NaCl using inert electrodes, what is liberated at the cathode?
(A) Na
(B) Cl₂
(C) H₂
(D) O₂
Answer: (C) H₂
Year: 2021 | Set: T1
Q11. In a galvanic cell, electrons flow:
(A) from salt bridge to electrolyte
(B) from cathode to anode
(C) from anode to cathode
(D) from electrolyte to salt bridge
Answer: (C) from anode to cathode
Year: 2020 | Set: Q
Q12. Unit of molar conductivity is:
(A) S m² mol⁻¹
(B) ohm cm² mol⁻¹
(C) S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) ohm⁻¹ cm mol⁻¹
Answer: (C) S cm² mol⁻¹
Year: 2020 | Set: S
Q13. Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis is given by:
(A) m ∝ Q
(B) m ∝ I²
(C) m ∝ V
(D) m ∝ P
Answer: (A) m ∝ Q
Year: 2019 | Set: 3
Q14. The number of electrons required to deposit 1 mole of Al from Al³⁺ is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 6
Answer: (C) 3
Year: 2019 | Set: 1
Q15. Which battery is used in mobile phones and laptops?
(A) Lead storage battery
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Dry cell
(D) Lithium-ion battery
Answer: (D) Lithium-ion battery
Year: 2018 | Set: R2
Q16. Which of the following is not a feature of fuel cells?
(A) Continuous supply of reactants
(B) High efficiency
(C) Pollution-free
(D) Rechargeable
Answer: (D) Rechargeable
Year: 2018 | Set: Q2
Q17. Which of the following will not act as a primary cell?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Lead storage battery
(C) Mercury cell
(D) Daniell cell
Answer: (B) Lead storage battery
Year: 2017 | Set: Code X
Q18. The electrode potential of a half-cell depends on:
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Concentration
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2017 | Set: Code Z
Q19. Electrochemical equivalent (Z) is:
(A) mass per coulomb
(B) coulomb per mass
(C) mass per ampere
(D) mass per mole
Answer: (A) mass per coulomb
Year: 2016 | Set: Code 1
Q20. A current of 1 ampere flows for 965 seconds. How many moles of electrons are transferred?
(A) 1
(B) 0.5
(C) 2
(D) 1.5
Answer: (A) 1
Year: 2016 | Set: Code 3
Q21. The conductivity of a solution depends on:
(A) Nature of electrolyte
(B) Concentration of ions
(C) Temperature
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2015 | Set: Q
Q22. Which of the following expressions is correct for Λm?
(A) Λm = κ × M
(B) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
(C) Λm = κ / M
(D) Λm = κ × N
Answer: (B) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
Year: 2015 | Set: R
Q23. Fuel cell used in spacecraft uses:
(A) H₂ and O₂
(B) CH₄ and O₂
(C) CO and O₂
(D) C₂H₂ and O₂
Answer: (A) H₂ and O₂
Year: 2014 | Set: 2
Q24. Conductivity decreases with:
(A) Increase in concentration
(B) Increase in temperature
(C) Dilution
(D) Decrease in concentration
Answer: (D) Decrease in concentration
Year: 2014 | Set: 1
Q25. Which of the following is correct for oxidation?
(A) Loss of electrons
(B) Gain of electrons
(C) Increase in mass
(D) Loss of protons
Answer: (A) Loss of electrons
Year: 2013 | Set: 3
Q26. The number of faradays required to deposit 1 mol of Mg from Mg²⁺ is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Year: 2013 | Set: 1
Q27. What is the main function of electrolyte in electrolysis?
(A) Provide electrons
(B) Allow flow of ions
(C) Act as oxidizing agent
(D) Dissolve electrodes
Answer: (B) Allow flow of ions
Year: 2012 | Set: Q
Q28. In a dry cell, the depolarizer is:
(A) Zn
(B) MnO₂
(C) NH₄Cl
(D) Carbon
Answer: (B) MnO₂
Year: 2012 | Set: R
Q29. Which among the following is a primary cell?
(A) Lead-acid cell
(B) Fuel cell
(C) Dry cell
(D) Nickel-cadmium cell
Answer: (C) Dry cell
Year: 2011 | Set: P
Q30. What is the effect of increasing temperature on conductivity?
(A) Increases
(B) Decreases
(C) Remains constant
(D) First increases, then decreases
Answer: (A) Increases
Year: 2011 | Set: Z
Q31. The reaction at cathode in H₂-O₂ fuel cell is:
(A) O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
(B) H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
(C) O₂ + H₂ → H₂O
(D) H⁺ + OH⁻ → H₂O
Answer: (A) O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
Year: 2010 | Set: S
Q32. Which of the following metals will displace Cu from CuSO₄ solution?
(A) Ag
(B) Hg
(C) Zn
(D) Pt
Answer: (C) Zn
Year: 2009 | Set: M
Q33. How many grams of Ag are deposited by 9650 C if E(Ag⁺/Ag) = +0.80 V?
(A) 1.08 g
(B) 10.8 g
(C) 5.4 g
(D) 21.6 g
Answer: (B) 10.8 g
Year: 2009 | Set: A
Q34. Which is used as electrolyte in lead-acid battery?
(A) NaOH
(B) H₂SO₄
(C) HCl
(D) KOH
Answer: (B) H₂SO₄
Year: 2008 | Set: Q
Q35. In electrolysis, the quantity of electricity required to deposit one mole of aluminum from Al³⁺ is:
(A) 1 Faraday
(B) 2 Faradays
(C) 3 Faradays
(D) 6 Faradays
Answer: (C) 3 Faradays
Year: 2008 | Set: M
Q36. Which is true for a spontaneous redox reaction in a galvanic cell?
(A) E°cell is negative
(B) ΔG° is positive
(C) E°cell is positive
(D) No current flows
Answer: (C) E°cell is positive
Year: 2007 | Set: Z
Q37. Which of the following metals has the highest tendency to lose electrons?
(A) Cu
(B) Zn
(C) Ag
(D) Au
Answer: (B) Zn
Year: 2007 | Set: P
Q38. Which gas is evolved at the cathode in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl?
(A) O₂
(B) Cl₂
(C) H₂
(D) Na
Answer: (C) H₂
Year: 2006 | Set: A
Q39. In a Daniel cell, electrons flow from:
(A) Copper to zinc
(B) Cathode to anode
(C) Anode to cathode
(D) Salt bridge to electrode
Answer: (C) Anode to cathode
Year: 2006 | Set: M
Q40. In a lead-acid battery, the active material of the cathode during discharge is:
(A) Pb
(B) PbSO₄
(C) PbO₂
(D) Pb(NO₃)₂
Answer: (C) PbO₂
Year: 2005 | Set: X
Q41. Molar conductivity of strong electrolytes at infinite dilution:
(A) decreases with dilution
(B) becomes zero
(C) increases and becomes constant
(D) decreases sharply
Answer: (C) increases and becomes constant
Year: 2005 | Set: S
Q42. During electrolysis of water, volume of H₂ and O₂ liberated is in the ratio:
(A) 1:1
(B) 2:1
(C) 1:2
(D) 3:1
Answer: (B) 2:1
Year: 2004 | Set: Y
Q43. The conductivity of a 0.1 M solution of a weak electrolyte is found to be 5 × 10⁻⁵ S cm⁻¹. Its molar conductivity is:
(A) 0.5 S cm² mol⁻¹
(B) 1 S cm² mol⁻¹
(C) 5 S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) 50 S cm² mol⁻¹
Answer: (D) 50 S cm² mol⁻¹
Year: 2004 | Set: Z
Q44. The product obtained at the cathode in electrolysis of molten NaCl is:
(A) Na
(B) Cl₂
(C) H₂
(D) O₂
Answer: (A) Na
Year: 2003 | Set: Q
Q45. The standard electrode potential of a cell is 1.10 V. The cell is:
(A) Non-spontaneous
(B) Reversible only
(C) Spontaneous
(D) Cannot say
Answer: (C) Spontaneous
Year: 2003 | Set: R
Q46. The mass of copper deposited by 1 Faraday of electricity is:
(A) 31.75 g
(B) 63.5 g
(C) 27 g
(D) 108 g
Answer: (A) 31.75 g
Year: 2002 | Set: M
Q47. Which of the following batteries is used in cars?
(A) Mercury cell
(B) Dry cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Lithium battery
Answer: (C) Lead-acid battery
Year: 2002 | Set: 2
Q48. What is the role of Zn in a dry cell?
(A) Depolarizer
(B) Electrolyte
(C) Cathode
(D) Anode
Answer: (D) Anode
Year: 2001 | Set: A
Q49. During electrolysis of water, the cathode reaction is:
(A) O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
(B) 2H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
(C) 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
(D) H₂O → H₂ + ½O₂
Answer: (C) 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
Year: 2001 | Set: Z
Q50. A current of 2 A is passed through AgNO₃ solution for 1 hour. What is the mass of silver deposited?
(Atomic mass = 108 g/mol)
(A) 8.0 g
(B) 2.16 g
(C) 4.32 g
(D) 6.48 g
Answer: (D) 6.48 g
Year: 2001 | Set: M
Q51. In an electrochemical cell, the function of the salt bridge is:
(A) Allow movement of electrons
(B) Provide ion pathway to maintain charge balance
(C) Connect cathode and anode
(D) Source of electrolyte
Answer: (B) Provide ion pathway to maintain charge balance
Year: 2025 | Set: 1
Q52. The electrolysis of molten NaCl gives:
(A) Na at cathode, Cl₂ at anode
(B) Cl₂ at cathode, Na at anode
(C) NaOH at cathode, H₂ at anode
(D) Cl₂ and H₂
Answer: (A) Na at cathode, Cl₂ at anode
Year: 2024 | Set: 2
Q53. The EMF of a galvanic cell is 1.5 V. The cell reaction involves 2 electrons. What is the value of ΔG°?
(A) –289.5 kJ
(B) +289.5 kJ
(C) –150.0 kJ
(D) –96.5 kJ
Answer: (A) –289.5 kJ
Year: 2024 | Set: X
(ΔG° = –nFE = –2 × 96500 × 1.5 = –289500 J = –289.5 kJ)
Q54. The correct order of conductivity is:
(A) Solid NaCl > Molten NaCl > Aqueous NaCl
(B) Aqueous NaCl > Molten NaCl > Solid NaCl
(C) Molten NaCl > Aqueous NaCl > Solid NaCl
(D) Aqueous NaCl > Solid NaCl > Molten NaCl
Answer: (B) Aqueous NaCl > Molten NaCl > Solid NaCl
Year: 2023 | Set: 2
Q55. The EMF of a cell is affected by:
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Concentration
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2022 | Set: Y
Q56. A fuel cell converts:
(A) Electrical to chemical energy
(B) Mechanical to thermal energy
(C) Chemical to electrical energy
(D) Kinetic to potential energy
Answer: (C) Chemical to electrical energy
Year: 2022 | Set: 1
Q57. The cell reaction in H₂–O₂ fuel cell produces:
(A) CO₂
(B) NH₃
(C) H₂O
(D) NO₂
Answer: (C) H₂O
Year: 2021 | Set: Z
Q58. Which is the correct expression for Nernst equation?
(A) E = E° + (0.0591/n) log Q
(B) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log Q
(C) E = E° + log Q
(D) E = E° – Q
Answer: (B) E = E° – (0.0591/n) log Q
Year: 2021 | Set: 2
Q59. In an electrochemical cell, the reduction takes place at:
(A) Anode
(B) Cathode
(C) Salt bridge
(D) Electrolyte
Answer: (B) Cathode
Year: 2020 | Set: P
Q60. Which condition is required to define standard electrode potential?
(A) 1 atm pressure
(B) 1 M solution
(C) 25°C
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2020 | Set: S
Q61. When a solution of AgNO₃ is electrolyzed using Ag electrodes, the anode reaction is:
(A) Ag → Ag⁺ + e⁻
(B) Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag
(C) NO₃⁻ + H₂O → HNO₃ + OH⁻
(D) H₂O → O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻
Answer: (A) Ag → Ag⁺ + e⁻
Year: 2019 | Set: Q2
Q62. Which is the correct relation for conductance (G)?
(A) G = 1/R
(B) G = R
(C) G = R × κ
(D) G = 1/κ
Answer: (A) G = 1/R
Year: 2019 | Set: 3
Q63. How many grams of Mg are deposited by 193000 C? (Mg = 24 g/mol)
(A) 12 g
(B) 24 g
(C) 48 g
(D) 36 g
Answer: (B) 24 g
Year: 2018 | Set: P
Q64. Which cell does not involve electrolyte solution?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Daniel cell
(C) Mercury cell
(D) Fuel cell
Answer: (C) Mercury cell
Year: 2018 | Set: M
Q65. What is the function of MnO₂ in a dry cell?
(A) Oxidizer
(B) Reducing agent
(C) Electrolyte
(D) Solvent
Answer: (A) Oxidizer
Year: 2017 | Set: Z
Q66. In a galvanic cell, the anode is:
(A) Positively charged
(B) Negatively charged
(C) Neutral
(D) None
Answer: (B) Negatively charged
Year: 2016 | Set: S1
Q67. The product at anode during electrolysis of dilute H₂SO₄ is:
(A) O₂
(B) H₂
(C) SO₂
(D) H₂O
Answer: (A) O₂
Year: 2016 | Set: T2
Q68. The number of electrons required to deposit 1 mole of Cu from Cu²⁺ is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Year: 2015 | Set: R2
Q69. The cathode in a lithium-ion battery is made of:
(A) Graphite
(B) Zinc
(C) Li metal oxide
(D) Copper
Answer: (C) Li metal oxide
Year: 2014 | Set: Q1
Q70. Which of the following is NOT true about electrolytic cells?
(A) Anode is positive
(B) Cathode is negative
(C) Electrons enter through anode
(D) Oxidation occurs at anode
Answer: (C) Electrons enter through anode
Year: 2013 | Set: Z
Q71. In a Daniel cell, which statement is true?
(A) Copper is oxidized
(B) Zinc is reduced
(C) Electrons flow from Cu to Zn
(D) Electrons flow from Zn to Cu
Answer: (D) Electrons flow from Zn to Cu
Year: 2013 | Set: P
Q72. Electrolysis of aqueous CuSO₄ using copper electrodes results in:
(A) Deposition of Cu at anode
(B) Increase in SO₄²⁻ ions
(C) No change in electrolyte concentration
(D) Decrease in Cu²⁺ ion concentration
Answer: (C) No change in electrolyte concentration
Year: 2012 | Set: S
Q73. The metal that will not displace hydrogen from acids is:
(A) Zn
(B) Cu
(C) Mg
(D) Fe
Answer: (B) Cu
Year: 2012 | Set: M
Q74. In which of the following, EMF is generated by chemical reaction?
(A) Galvanic cell
(B) Electrolytic cell
(C) Fuel cell
(D) Photovoltaic cell
Answer: (A) Galvanic cell
Year: 2011 | Set: T
Q75. EMF of the cell increases with:
(A) Increase in concentration of products
(B) Decrease in temperature
(C) Decrease in reactant concentration
(D) Increase in concentration of reactants
Answer: (D) Increase in concentration of reactants
Year: 2011 | Set: P
Q76. Electrolysis is used in:
(A) Electroplating
(B) Battery charging
(C) Purification of metals
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2010 | Set: Q2
Q77. The electrode reaction of Cl₂ at anode is:
(A) Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
(B) Cl₂ + 2e⁻ → 2Cl⁻
(C) Cl₂ → 2Cl⁻ + 2e⁻
(D) 2Cl⁻ + 2e⁻ → Cl₂
Answer: (A) Cl⁻ → Cl₂ + 2e⁻
Year: 2010 | Set: Z
Q78. One Faraday of electricity will deposit how many grams of Al (atomic mass 27)?
(A) 27 g
(B) 13.5 g
(C) 9 g
(D) 81 g
Answer: (C) 9 g
Year: 2009 | Set: X
(Al³⁺ needs 3e⁻, so 1 F deposits 1/3 mole = 9 g)
Q79. Electrochemical cell that cannot be recharged is:
(A) Secondary cell
(B) Dry cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Li-ion battery
Answer: (B) Dry cell
Year: 2009 | Set: M
Q80. The equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte:
(A) Increases with dilution
(B) Decreases with dilution
(C) Remains constant
(D) Becomes zero
Answer: (A) Increases with dilution
Year: 2008 | Set: Z
Q81. Which of the following is not an application of electrochemistry?
(A) Electroplating
(B) Metal refining
(C) Battery operation
(D) Fermentation
Answer: (D) Fermentation
Year: 2008 | Set: A
Q82. The EMF of a galvanic cell can be increased by:
(A) Increasing temperature
(B) Using concentrated solutions
(C) Adding inert electrolyte
(D) None of these
Answer: (B) Using concentrated solutions
Year: 2007 | Set: Q
Q83. Which cell produces electric current by redox reaction?
(A) Electrolytic cell
(B) Galvanic cell
(C) Both A and B
(D) None of these
Answer: (B) Galvanic cell
Year: 2007 | Set: R
Q84. Electrolyte used in dry cell is:
(A) NaOH
(B) NH₄Cl paste
(C) H₂SO₄
(D) ZnSO₄
Answer: (B) NH₄Cl paste
Year: 2006 | Set: Y
Q85. What is the molar conductivity of 0.01 M NaCl with conductivity 1.26 × 10⁻² S cm⁻¹?
(A) 12.6
(B) 126
(C) 1.26
(D) 0.126
Answer: (B) 126 S cm² mol⁻¹
Year: 2006 | Set: M
(Λm = κ × 1000 / M = 1.26×10⁻² × 1000 / 0.01 = 126)
Q86. Galvanic cell differs from electrolytic cell because:
(A) Current flows externally
(B) EMF is negative
(C) Electrodes are reversed
(D) It uses non-spontaneous reactions
Answer: (A) Current flows externally
Year: 2005 | Set: X
Q87. Which of the following decreases with dilution?
(A) Conductivity
(B) Molar conductivity
(C) Ionization
(D) Electrode potential
Answer: (A) Conductivity
Year: 2005 | Set: S
Q88. Which law states that different substances deposit in equivalent proportions?
(A) Faraday’s 1st
(B) Faraday’s 2nd
(C) Ohm’s Law
(D) Raoult’s Law
Answer: (B) Faraday’s 2nd
Year: 2004 | Set: Q
Q89. What is the oxidation number of Zn in Zn → Zn²⁺?
(A) 0 to +2
(B) +2 to 0
(C) 0 to –2
(D) +1 to +2
Answer: (A) 0 to +2
Year: 2004 | Set: R
Q90. Which electrode potential is most negative?
(A) Zn²⁺/Zn = –0.76 V
(B) Cu²⁺/Cu = +0.34 V
(C) Fe²⁺/Fe = –0.44 V
(D) H⁺/H₂ = 0.00 V
Answer: (A) Zn²⁺/Zn
Year: 2003 | Set: Z
Q91. Which of the following is a spontaneous process?
(A) EMF < 0 (B) ΔG > 0
(C) EMF > 0
(D) E = 0
Answer: (C) EMF > 0
Year: 2002 | Set: Q
Q92. In a cell, if E°cell is negative, then:
(A) Reaction is spontaneous
(B) Reaction is non-spontaneous
(C) Cell is working
(D) Electrons flow from cathode to anode
Answer: (B) Reaction is non-spontaneous
Year: 2002 | Set: R
Q93. The anode of a galvanic cell is:
(A) Where reduction occurs
(B) Negatively charged
(C) Positively charged
(D) Not connected
Answer: (B) Negatively charged
Year: 2001 | Set: X
Q94. The unit of conductivity in SI is:
(A) S cm⁻¹
(B) S m⁻¹
(C) S mol⁻¹
(D) S m² mol⁻¹
Answer: (B) S m⁻¹
Year: 2001 | Set: Y
Q95. What is the amount of charge on 1 mol of electrons?
(A) 9650 C
(B) 96500 C
(C) 1 C
(D) 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
Answer: (B) 96500 C
Year: 2001 | Set: M
Q96. In electroplating, the metal to be plated is always:
(A) Anode
(B) Cathode
(C) Electrolyte
(D) Inert
Answer: (B) Cathode
Year: 2001 | Set: A
Q97. In lead storage battery, discharge products are:
(A) Pb and PbO₂
(B) PbSO₄ and H₂O
(C) Pb and H₂O
(D) PbSO₄ and H₂
Answer: (B) PbSO₄ and H₂O
Year: 2000 | Set: Z
Q98. The efficiency of fuel cell is higher than conventional cells because:
(A) Heat loss is more
(B) Energy conversion is direct
(C) Uses fossil fuel
(D) Electrolyte is better
Answer: (B) Energy conversion is direct
Year: 2000 | Set: Q
Q99. A Daniell cell has an EMF of 1.10 V. If concentration of Zn²⁺ increases, EMF:
(A) Increases
(B) Decreases
(C) Remains constant
(D) Becomes zero
Answer: (B) Decreases
Year: 2000 | Set: M
Q100. In a galvanic cell:
(A) Oxidation takes place at cathode
(B) Reduction takes place at anode
(C) Oxidation takes place at anode
(D) Electrons flow from cathode to anode
Answer: (C) Oxidation takes place at anode
Year: 2000 | Set: X
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. In a galvanic cell, the salt bridge is used to:
(A) Stop the cell reaction
(B) Provide electrons to the reaction
(C) Maintain electrical neutrality
(D) Transfer electrons from anode to cathode
Answer: (C) Maintain electrical neutrality
Year: 2024 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q2. The standard reduction potential values are:
Zn²⁺/Zn = –0.76 V, Cu²⁺/Cu = +0.34 V
The EMF of the cell Zn | Zn²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu is:
(A) –1.10 V
(B) +0.42 V
(C) +1.10 V
(D) –0.42 V
Answer: (C) +1.10 V
Year: 2024 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q3. Molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte increases sharply with dilution due to:
(A) Increase in temperature
(B) Increase in number of ions
(C) Complete ionization at infinite dilution
(D) Decrease in viscosity
Answer: (C) Complete ionization at infinite dilution
Year: 2023 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q4. Which one of the following is a primary cell?
(A) Lead storage battery
(B) Dry cell
(C) Fuel cell
(D) Nickel-cadmium cell
Answer: (B) Dry cell
Year: 2023 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q5. Faraday’s second law of electrolysis is applicable in:
(A) Concentration cells
(B) Redox titrations
(C) Electroplating of metals
(D) Galvanization
Answer: (C) Electroplating of metals
Year: 2022 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q6. In a standard hydrogen electrode, the pressure of hydrogen gas is:
(A) 2 atm
(B) 1 atm
(C) 0.5 atm
(D) 10 atm
Answer: (B) 1 atm
Year: 2022 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q7. Which of the following increases with dilution for a weak electrolyte?
(A) Degree of ionization
(B) Conductivity
(C) Number of ions per unit volume
(D) Ionic strength
Answer: (A) Degree of ionization
Year: 2021 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q8. Which of the following is NOT a component of dry cell?
(A) Zinc container
(B) Manganese dioxide
(C) Ammonium chloride
(D) Sodium hydroxide
Answer: (D) Sodium hydroxide
Year: 2021 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q9. The function of MnO₂ in dry cell is to:
(A) Oxidize zinc
(B) Act as depolarizer
(C) Provide electrolyte
(D) Reduce ammonium ion
Answer: (B) Act as depolarizer
Year: 2020 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q10. Which of the following is correct?
(A) Λm = κ × M
(B) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
(C) Λm = M / κ
(D) Λm = κ / 1000
Answer: (B) Λm = κ × 1000 / M
Year: 2020 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q11. Which of the following electrolytes has the highest conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) NaCl
(B) CH₃COOH
(C) NH₄Cl
(D) HCl
Answer: (D) HCl
Year: 2019 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q12. Which of the following does not involve redox reaction?
(A) Electrolysis of water
(B) Rusting of iron
(C) Neutralization of HCl and NaOH
(D) Galvanic cell operation
Answer: (C) Neutralization of HCl and NaOH
Year: 2019 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q13. Which is correct for the half-cell reaction: Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ ⇌ Zn?
(A) E = E° + (0.0591/2) log[Zn²⁺]
(B) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log[Zn²⁺]
(C) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log[Zn]
(D) E = E° + log[Zn²⁺]
Answer: (B) E = E° – (0.0591/2) log[Zn²⁺]
Year: 2018 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q14. A galvanic cell has the reaction:
Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
Which statement is correct?
(A) Zn is reduced
(B) Cu is oxidized
(C) Zn is the cathode
(D) Zn is the anode
Answer: (D) Zn is the anode
Year: 2018 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q15. The main product at cathode in electrolysis of dilute H₂SO₄ using Pt electrodes is:
(A) H₂
(B) O₂
(C) SO₂
(D) H₂O
Answer: (A) H₂
Year: 2017 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q16. The number of coulombs required to deposit 1 mole of Al (Z = 3) is:
(A) 96500
(B) 193000
(C) 289500
(D) 482500
Answer: (C) 289500
Year: 2017 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q17. Which of the following is a rechargeable battery?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Fuel cell
Answer: (C) Lead-acid battery
Year: 2016 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q18. In an electrolytic cell, oxidation occurs at:
(A) Cathode
(B) Electrolyte
(C) Anode
(D) Salt bridge
Answer: (C) Anode
Year: 2016 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q19. Which of the following affects cell potential?
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Concentration
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2015 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q20. The standard cell potential for a reaction is 1.10 V. What is ΔG°?
(n = 2)
(A) –212.3 kJ
(B) +212.3 kJ
(C) –105.6 kJ
(D) +105.6 kJ
Answer: (A) –212.3 kJ
Year: 2015 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
(ΔG° = –nFE° = –2 × 96500 × 1.10)
Q21. The oxidation number of Fe changes from +2 to +3. It means:
(A) Fe gains electron
(B) Fe loses electron
(C) Fe is reduced
(D) No redox occurs
Answer: (B) Fe loses electron
Year: 2014 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q22. Which gas is evolved at anode during electrolysis of brine?
(A) Cl₂
(B) O₂
(C) H₂
(D) N₂
Answer: (A) Cl₂
Year: 2014 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q23. In a fuel cell, the overall reaction is:
(A) H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
(B) CH₄ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
(C) H₂ + Cl₂ → HCl
(D) Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
Answer: (A) H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
Year: 2013 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q24. The role of electrolyte in electrochemical cell is to:
(A) Block current
(B) Allow ionic conduction
(C) Oxidize the electrode
(D) Prevent ion flow
Answer: (B) Allow ionic conduction
Year: 2013 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q25. Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis states that:
(A) m ∝ Q
(B) m ∝ Q²
(C) m ∝ 1/Q
(D) m ∝ V
Answer: (A) m ∝ Q
Year: 2012 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q26. Which of the following is correct for a spontaneous cell reaction?
(A) E°cell = 0
(B) ΔG° > 0
(C) E°cell > 0
(D) E°cell < 0 Answer: (C) E°cell > 0
Year: 2012 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q27. The EMF of a cell is given by:
(A) Ecell = E°cathode – E°anode
(B) Ecell = E°anode – E°cathode
(C) Ecell = –(E°anode + E°cathode)
(D) Ecell = E°cathode + E°anode
Answer: (A) Ecell = E°cathode – E°anode
Year: 2011 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q28. The equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte:
(A) Increases with concentration
(B) Decreases with dilution
(C) Remains constant
(D) Increases slightly with dilution and becomes constant
Answer: (D) Increases slightly with dilution and becomes constant
Year: 2011 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q29. Unit of cell constant is:
(A) cm⁻¹
(B) cm
(C) S
(D) S cm²
Answer: (A) cm⁻¹
Year: 2010 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q30. In lead-acid battery during discharge:
(A) Pb is converted to PbO₂
(B) PbSO₄ is converted to Pb
(C) PbO₂ and Pb are converted to PbSO₄
(D) H₂SO₄ is formed
Answer: (C) PbO₂ and Pb are converted to PbSO₄
Year: 2010 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q31. What is the amount of charge on one mole of electrons?
(A) 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
(B) 6.022 × 10²³ C
(C) 96500 C
(D) 1 C
Answer: (C) 96500 C
Year: 2009 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q32. The standard hydrogen electrode has an electrode potential of:
(A) 1.00 V
(B) –1.00 V
(C) 0.00 V
(D) +0.44 V
Answer: (C) 0.00 V
Year: 2009 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q33. The number of electrons required to deposit 1 mole of Mg (Mg²⁺) is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Year: 2008 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q34. In a galvanic cell, oxidation takes place at:
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Salt bridge
(D) Electrolyte
Answer: (B) Anode
Year: 2008 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q35. Which of the following represents a spontaneous redox reaction?
(A) Cu + Zn²⁺ → Cu²⁺ + Zn
(B) Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
(C) Zn²⁺ + Cu → Zn + Cu²⁺
(D) Cu²⁺ + Zn²⁺ → Cu + Zn
Answer: (B) Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
Year: 2007 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q36. A battery is a device which converts:
(A) Mechanical energy into chemical energy
(B) Electrical energy into chemical energy
(C) Chemical energy into electrical energy
(D) Potential energy into kinetic energy
Answer: (C) Chemical energy into electrical energy
Year: 2007 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q37. In electrolysis of CuSO₄ solution using copper electrodes:
(A) Cu dissolves from cathode
(B) Cu is deposited on anode
(C) Cu is deposited on cathode
(D) Electrolyte concentration decreases
Answer: (C) Cu is deposited on cathode
Year: 2006 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q38. In a cell, the electrons flow:
(A) From cathode to anode
(B) From anode to cathode
(C) Through salt bridge
(D) Do not flow
Answer: (B) From anode to cathode
Year: 2006 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q39. Electrochemical series is arranged on the basis of:
(A) Oxidation potential
(B) Reduction potential
(C) Ionization energy
(D) Atomic mass
Answer: (B) Reduction potential
Year: 2005 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q40. In an electrolytic cell, which is correct?
(A) Anode is negative, cathode is positive
(B) Anode is positive, cathode is negative
(C) Both electrodes are positive
(D) Both electrodes are negative
Answer: (B) Anode is positive, cathode is negative
Year: 2005 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q41. The EMF of a cell is 1.10 V. If 2 moles of electrons are involved, ΔG° is:
(A) –212.3 kJ
(B) –105.6 kJ
(C) +105.6 kJ
(D) +212.3 kJ
Answer: (A) –212.3 kJ
Year: 2004 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q42. Unit of conductivity in SI system is:
(A) S cm⁻¹
(B) S m⁻¹
(C) ohm⁻¹ cm
(D) ohm cm
Answer: (B) S m⁻¹
Year: 2004 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q43. The quantity of electricity (in Faradays) required to deposit 1 mol of Ag from Ag⁺ is:
(A) 1
(B) 0.5
(C) 2
(D) 3
Answer: (A) 1
Year: 2003 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q44. The role of salt bridge is to:
(A) Allow electron flow
(B) Maintain charge neutrality
(C) Generate potential
(D) Convert chemical to electrical energy
Answer: (B) Maintain charge neutrality
Year: 2003 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q45. Conductivity of an electrolyte solution depends on:
(A) Nature of electrolyte
(B) Temperature
(C) Concentration
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2002 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q46. Which among the following has the lowest Λm° value?
(A) HCl
(B) CH₃COOH
(C) NaCl
(D) KCl
Answer: (B) CH₃COOH
Year: 2002 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q47. In the reaction Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu, which species is oxidized?
(A) Cu²⁺
(B) Cu
(C) Zn
(D) Zn²⁺
Answer: (C) Zn
Year: 2001 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q48. Which device uses redox reactions to produce electricity?
(A) Electrolytic cell
(B) Galvanic cell
(C) Solar cell
(D) Thermocouple
Answer: (B) Galvanic cell
Year: 2001 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q49. Fuel cell efficiency is high due to:
(A) Heat dissipation
(B) Internal resistance
(C) Direct energy conversion
(D) Non-volatile electrolyte
Answer: (C) Direct energy conversion
Year: 2001 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q50. The expression for ΔG° in electrochemical cells is:
(A) ΔG° = –nFE°
(B) ΔG° = nFE°
(C) ΔG° = E°/nF
(D) ΔG° = –FE°
Answer: (A) ΔG° = –nFE°
Year: 2001 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following correctly represents the standard electrode potential?
(A) E°cell = E°anode + E°cathode
(B) E°cell = E°anode – E°cathode
(C) E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
(D) E°cell = –(E°cathode – E°anode)
Answer: (C) E°cell = E°cathode – E°anode
Year: 2025 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q2. In the electrolysis of aqueous CuSO₄ using platinum electrodes, the product formed at anode is:
(A) Cu
(B) H₂
(C) O₂
(D) SO₂
Answer: (C) O₂
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q3. The molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte:
(A) Decreases with dilution
(B) Remains constant with dilution
(C) First increases, then decreases
(D) Increases slightly and becomes constant at infinite dilution
Answer: (D) Increases slightly and becomes constant at infinite dilution
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q4. The quantity of electricity required to deposit 108 g of silver from AgNO₃ solution is:
(A) 96500 C
(B) 193000 C
(C) 289500 C
(D) 482500 C
Answer: (A) 96500 C
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q5. In a galvanic cell, which one of the following statements is true?
(A) Oxidation occurs at the cathode
(B) Reduction occurs at the anode
(C) Electrons flow from anode to cathode
(D) Electrons flow through salt bridge
Answer: (C) Electrons flow from anode to cathode
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q6. Which of the following is used as a reference electrode?
(A) Glass electrode
(B) Hydrogen electrode
(C) Calomel electrode
(D) Platinum electrode
Answer: (B) Hydrogen electrode
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q7. The unit of molar conductivity in SI system is:
(A) S cm mol⁻¹
(B) S m² mol⁻¹
(C) S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) S mol⁻¹
Answer: (B) S m² mol⁻¹
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 3
Q8. What is the oxidation number of Zn in Zn → Zn²⁺?
(A) +2
(B) 0
(C) –2
(D) –1
Answer: (A) +2
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q9. Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis states that:
(A) Mass deposited ∝ current
(B) Mass deposited ∝ time
(C) Mass deposited ∝ charge
(D) Mass deposited ∝ voltage
Answer: (C) Mass deposited ∝ charge
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q10. During electrolysis of water using inert electrodes, the cathode reaction is:
(A) 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
(B) H₂O → ½O₂ + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
(C) O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
(D) H⁺ + e⁻ → ½H₂
Answer: (A) 2H₂O + 2e⁻ → H₂ + 2OH⁻
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q11. In a cell, Zn | Zn²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu, what is the correct direction of electron flow?
(A) From Cu to Zn
(B) From Zn to Cu
(C) From salt bridge to electrodes
(D) No electron flow
Answer: (B) From Zn to Cu
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q12. The function of the salt bridge is to:
(A) Provide electrons
(B) Balance ionic charge
(C) Generate current
(D) Absorb heat
Answer: (B) Balance ionic charge
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 3
Q13. Which of the following electrolytes has highest molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) NaCl
(B) KCl
(C) HCl
(D) NH₄Cl
Answer: (C) HCl
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q14. The value of ΔG° for a cell reaction is related to EMF by the equation:
(A) ΔG° = –nFE°
(B) ΔG° = nFE°
(C) ΔG° = –FE°
(D) ΔG° = –nF/E°
Answer: (A) ΔG° = –nFE°
Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q15. In a lithium-ion battery, the cathode is made of:
(A) Graphite
(B) Li-metal oxide
(C) Zinc
(D) Lead
Answer: (B) Li-metal oxide
Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q16. Which of the following is used as a depolarizer in dry cell?
(A) MnO₂
(B) KOH
(C) Zn
(D) Graphite
Answer: (A) MnO₂
Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q17. Electrochemical equivalent is defined as:
(A) Mass deposited per mole
(B) Mass deposited per coulomb
(C) Volume of gas liberated
(D) Energy per mole
Answer: (B) Mass deposited per coulomb
Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q18. Fuel cell used in spacecrafts uses:
(A) CH₄ and O₂
(B) CO and O₂
(C) H₂ and O₂
(D) H₂ and Cl₂
Answer: (C) H₂ and O₂
Year: 2025 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q19. The EMF of a Daniell cell is 1.10 V. The reaction is spontaneous because:
(A) ΔG° > 0
(B) ΔG° < 0
(C) ΔG° = 0
(D) EMF < 0
Answer: (B) ΔG° < 0
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q20. Which statement is false for a galvanic cell?
(A) Oxidation occurs at anode
(B) Electrons move from anode to cathode
(C) EMF is negative
(D) Salt bridge maintains neutrality
Answer: (C) EMF is negative
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q21. In electrolysis of molten NaCl, product at cathode is:
(A) Na
(B) Cl₂
(C) H₂
(D) O₂
Answer: (A) Na
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q22. Molar conductivity (Λm) increases with dilution because:
(A) Interionic attraction increases
(B) Viscosity increases
(C) Ionization increases
(D) Pressure decreases
Answer: (C) Ionization increases
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q23. Conductivity (κ) of a solution decreases with:
(A) Increase in temperature
(B) Dilution
(C) Concentration
(D) Ionic mobility
Answer: (B) Dilution
Year: 2022 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q24. In a fuel cell, the electrode reactions are:
(A) Redox
(B) Precipitation
(C) Complexation
(D) Substitution
Answer: (A) Redox
Year: 2022 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q25. The unit of conductivity in SI is:
(A) S cm⁻¹
(B) S m⁻¹
(C) Ω⁻¹ cm
(D) Ω cm
Answer: (B) S m⁻¹
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q26. Which of the following is not a primary cell?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Fuel cell
(D) Lead-acid battery
Answer: (D) Lead-acid battery
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 3
Q27. The potential of a hydrogen electrode dipped in 0.01 M HCl at 25°C is:
(A) 0.0591 V
(B) –0.0591 V
(C) 0.00 V
(D) –1.00 V
Answer: (B) –0.0591 V
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q28. Which of the following is reduced in the Daniell cell?
(A) Zn
(B) Cu²⁺
(C) Zn²⁺
(D) SO₄²⁻
Answer: (B) Cu²⁺
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q29. Fuel cells are efficient because:
(A) Heat loss is high
(B) They convert chemical energy directly to electrical energy
(C) They use hydrocarbons
(D) Electrolytes are volatile
Answer: (B) They convert chemical energy directly to electrical energy
Year: 2019 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q30. Which of the following correctly describes the function of a salt bridge?
(A) Transfers electrons
(B) Prevents mixing of electrolytes
(C) Maintains charge balance
(D) Acts as a conductor
Answer: (C) Maintains charge balance
Year: 2019 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q31. The product at anode during electrolysis of molten NaCl is:
(A) Na
(B) Cl₂
(C) H₂
(D) O₂
Answer: (B) Cl₂
Year: 2018 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q32. Conductivity of a solution depends on:
(A) Nature of solvent
(B) Nature of solute
(C) Concentration of ions
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2018 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q33. Which electrode reaction occurs in a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
(A) H₂ + 2OH⁻ → 2H₂O + 2e⁻
(B) H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
(C) O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O
(D) Both B and C
Answer: (D) Both B and C
Year: 2017 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q34. The equivalent conductivity at infinite dilution is calculated using:
(A) Faraday’s Law
(B) Kohlrausch’s Law
(C) Raoult’s Law
(D) Nernst equation
Answer: (B) Kohlrausch’s Law
Year: 2017 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MODEL PRATICE SET FOR COMPETITION EXAMS
Q1. Which of the following is true for a salt bridge in a galvanic cell?
(A) Allows flow of electrons between half-cells
(B) Maintains electrical neutrality by ion migration
(C) Transfers ions through the external circuit
(D) Prevents redox reactions in the cell
Answer: (B)
Q2. The standard EMF of a cell is positive. This means the reaction is:
(A) Endothermic
(B) Non-spontaneous
(C) Spontaneous
(D) At equilibrium
Answer: (C)
Q3. Which among the following has the highest molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) NaCl
(B) NH₄OH
(C) CH₃COOH
(D) HCl
Answer: (D)
Q4. In an electrolytic cell, the anode is:
(A) Negatively charged
(B) Positively charged
(C) Neutral
(D) Non-conducting
Answer: (B)
Q5. Faraday’s first law of electrolysis states that:
(A) Mass ∝ atomic number
(B) Mass ∝ charge passed
(C) Mass ∝ resistance
(D) Mass ∝ volume of electrolyte
Answer: (B)
Q6. The electrode at which oxidation takes place is called:
(A) Cathode
(B) Salt bridge
(C) Anode
(D) Electrolyte
Answer: (C)
Q7. Which of the following conditions is used to define standard electrode potential?
(A) 1 atm pressure and 1 M solution
(B) 0°C and 1 M solution
(C) 1 atm pressure and 2 M solution
(D) 25°C and 0.5 M solution
Answer: (A)
Q8. For a cell reaction to be spontaneous, the EMF should be:
(A) Negative
(B) Zero
(C) Positive
(D) Equal to temperature
Answer: (C)
Q9. The SI unit of conductivity is:
(A) S cm⁻¹
(B) S m⁻¹
(C) ohm⁻¹
(D) S mol⁻¹
Answer: (B)
Q10. If 1 Faraday of electricity is passed, how many moles of Ag will be deposited from AgNO₃ solution?
(A) 0.5 mol
(B) 1 mol
(C) 2 mol
(D) 3 mol
Answer: (B)
Q11. Which of the following does not affect conductivity of an electrolyte?
(A) Temperature
(B) Concentration
(C) Pressure
(D) Nature of ions
Answer: (C)
Q12. Which cell is a primary cell?
(A) Fuel cell
(B) Dry cell
(C) Lead storage battery
(D) Nickel-cadmium cell
Answer: (B)
Q13. In the Nernst equation, E = E° – (0.059/n) log [products]/[reactants], the value 0.059 is valid at:
(A) 298 K
(B) 273 K
(C) 310 K
(D) 100 K
Answer: (A)
Q14. Standard hydrogen electrode is assigned a potential of:
(A) 0.059 V
(B) 1.0 V
(C) 0.00 V
(D) –0.76 V
Answer: (C)
Q15. In a galvanic cell, electrons flow from:
(A) Cathode to anode
(B) Salt bridge to cathode
(C) Anode to cathode
(D) Electrolyte to salt bridge
Answer: (C)
Q16. Which of the following shows maximum molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) NaCl
(B) KCl
(C) CH₃COOH
(D) HNO₃
Answer: (D)
Q17. Which of the following reactions is used in fuel cells?
(A) CH₄ + O₂
(B) Zn + HCl
(C) H₂ + O₂
(D) Na + Cl₂
Answer: (C)
Q18. The term “electrochemical equivalent” refers to:
(A) Mass deposited per mole
(B) Mass per ampere
(C) Mass per volt
(D) Mass per coulomb
Answer: (D)
Q19. Which of the following is a reversible cell?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Daniel cell
Answer: (D)
Q20. A decrease in temperature generally:
(A) Increases conductivity
(B) Decreases conductivity
(C) Has no effect
(D) Converts electrolytic to galvanic cell
Answer: (B)
Q21. Electrolysis of molten NaCl gives:
(A) H₂ at cathode
(B) Cl₂ at anode
(C) O₂ at anode
(D) NaOH at cathode
Answer: (B)
Q22. Fuel cells are better than conventional cells because:
(A) They use fossil fuels
(B) They violate thermodynamic laws
(C) They do not involve Carnot cycle
(D) They waste more energy
Answer: (C)
Q23. Which one acts as a depolarizer in a dry cell?
(A) NaOH
(B) MnO₂
(C) Zn
(D) NH₄Cl
Answer: (B)
Q24. The correct order of E° values is:
(A) Zn < Fe < Cu
(B) Cu < Zn < Fe
(C) Fe < Cu < Zn
(D) Zn < Cu < Fe
Answer: (A)
Q25. The overall cell reaction in a Daniel cell is:
(A) Cu + Zn²⁺ → Zn + Cu²⁺
(B) Zn + Cu²⁺ → Zn²⁺ + Cu
(C) Zn²⁺ + Cu → Zn + Cu²⁺
(D) Zn²⁺ + Cu²⁺ → Zn + Cu
Answer: (B)
Q26. Which of the following affects Λm more with dilution?
(A) Strong electrolyte
(B) Weak electrolyte
(C) Non-electrolyte
(D) None of the above
Answer: (B)
Q27. Limiting molar conductivity is denoted by:
(A) κ
(B) Λ
(C) Λ₀m
(D) Λm
Answer: (C)
Q28. The role of salt bridge is to:
(A) Prevent the circuit from breaking
(B) Provide salt for redox
(C) Allow electron transfer
(D) Maintain charge balance
Answer: (D)
Q29. Which battery is rechargeable?
(A) Mercury cell
(B) Dry cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Silver oxide cell
Answer: (C)
Q30. Which of the following pairs are used in Daniel cell?
(A) Zn, Cu
(B) Ag, Cl
(C) Fe, Al
(D) Zn, Pb
Answer: (A)
Q31. At which electrode does reduction take place in a galvanic cell?
(A) Salt bridge
(B) Electrolyte
(C) Anode
(D) Cathode
Answer: (D)
Q32. The Nernst equation can be used to calculate:
(A) Enthalpy
(B) Entropy
(C) EMF at non-standard conditions
(D) Heat of neutralization
Answer: (C)
Q33. Which of the following increases with dilution?
(A) Conductivity
(B) Resistance
(C) Molar conductivity
(D) Current
Answer: (C)
Q34. The electrochemical cell stops working when:
(A) Electrodes dissolve
(B) EMF becomes negative
(C) Concentration becomes equal
(D) Temperature increases
Answer: (C)
Q35. The EMF of a cell is found to be 1.10 V. If the standard electrode potentials are E°(Cu²⁺/Cu) = +0.34 V and E°(Zn²⁺/Zn) = –0.76 V, what is the correct cell representation?
(A) Zn | Zn²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Cu
(B) Cu | Cu²⁺ || Zn²⁺ | Zn
(C) Zn | Cu²⁺ || Zn²⁺ | Cu
(D) Cu | Zn²⁺ || Cu²⁺ | Zn
Answer: (A)
Q36. If 0.5 mol of electrons are passed through molten AlCl₃, the amount of aluminium deposited is:
(A) 4.5 g
(B) 9 g
(C) 13.5 g
(D) 27 g
Answer: (C)
Q37. Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.02 M KCl is 500 Ω. The specific conductance of solution is 2.5 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹. What is the cell constant?
(A) 1.25 cm⁻¹
(B) 0.125 cm⁻¹
(C) 0.025 cm⁻¹
(D) 0.0025 cm⁻¹
Answer: (A)
Q38. The limiting molar conductivity of CH₃COOH is 390.5 S cm² mol⁻¹, and its molar conductivity at 0.01 M is 49.5 S cm² mol⁻¹. Degree of dissociation is:
(A) 0.127
(B) 0.215
(C) 0.327
(D) 0.585
Answer: (C)
Q39. The cell reaction for the galvanic cell: Zn(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Zn²⁺(aq) + Cu(s), is spontaneous because:
(A) Zn has lower reduction potential
(B) Cu²⁺ gets oxidised
(C) Zn acts as cathode
(D) EMF is negative
Answer: (A)
Q40. The quantity of electricity required to deposit 1 mol of Al³⁺ is:
(A) 96500 C
(B) 193000 C
(C) 289500 C
(D) 482500 C
Answer: (C)
Q41. The equivalent conductance of a weak electrolyte increases sharply with dilution because:
(A) Interionic attractions decrease
(B) Ion mobility increases
(C) Degree of dissociation increases
(D) Ionization constant increases
Answer: (C)
Q42. The conductivity of 0.01 M solution of a weak electrolyte is 1.6 × 10⁻⁴ S cm⁻¹ and cell constant is 1.0 cm⁻¹. What is Λm?
(A) 1.6 S cm² mol⁻¹
(B) 16 S cm² mol⁻¹
(C) 160 S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) 1600 S cm² mol⁻¹
Answer: (C)
Q43. EMF of a cell is zero when:
(A) Concentration is very high
(B) Reaction is spontaneous
(C) System reaches equilibrium
(D) Reaction is endothermic
Answer: (C)
Q44. What is the oxidation number of oxygen in KO₂?
(A) –1
(B) –½
(C) –2
(D) –1½
Answer: (B)
Q45. For a given cell at 298 K, EMF is 0.059 V when [Zn²⁺] = 1 M and [Cu²⁺] = x M. E°cell = 1.10 V. Find x.
(A) 10
(B) 1
(C) 0.1
(D) 0.01
Answer: (D)
Q46. The equivalent conductance at infinite dilution for a salt is 150 S cm² mol⁻¹. If the degree of dissociation at a given dilution is 0.40, then Λm at that dilution is:
(A) 60 S cm² mol⁻¹
(B) 90 S cm² mol⁻¹
(C) 45 S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) 75 S cm² mol⁻¹
Answer: (A)
Q47. The correct relation between ΔG° and E°cell is:
(A) ΔG° = –nFE°cell
(B) ΔG° = +nFE°cell
(C) ΔG° = –FE°cell
(D) ΔG° = –E°cell/F
Answer: (A)
Q48. The cell constant of a conductivity cell is 1.25 cm⁻¹. If the measured conductance is 0.0025 S, specific conductivity is:
(A) 3.125 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
(B) 2.0 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
(C) 1.25 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
(D) 0.0032 S cm⁻¹
Answer: (A)
Q49. If 10⁻⁴ mol of Cu²⁺ is reduced, how many coulombs are needed?
(A) 9.65 C
(B) 19.3 C
(C) 0.965 C
(D) 0.4825 C
Answer: (B)
Q50. Nernst equation predicts:
(A) ΔH of the cell
(B) ΔS of the system
(C) EMF under non-standard conditions
(D) Ionic strength
Answer: (C)
Q51. Conductivity of an electrolytic solution increases with:
(A) Decreasing temperature
(B) Increasing pressure
(C) Increasing ion mobility
(D) Decreasing ion concentration
Answer: (C)
Q52. Galvanic cells convert:
(A) Chemical energy into electrical energy
(B) Heat into work
(C) Mechanical into electrical energy
(D) Thermal into light energy
Answer: (A)
Q53. A current of 5 A was passed through molten CaCl₂ for 1930 s. The amount of Ca deposited is:
(A) 0.25 mol
(B) 0.5 mol
(C) 0.75 mol
(D) 1 mol
Answer: (A)
Q54. For which of the following electrolytes does Kohlrausch’s law not apply?
(A) Weak electrolytes
(B) Strong electrolytes
(C) Insoluble salts
(D) All types
Answer: (C)
Q55. Which of the following is not a primary cell?
(A) Dry cell
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Lead-acid battery
(D) Daniell cell
Answer: (C)
Q56. Conductance is inversely proportional to:
(A) Resistance
(B) Voltage
(C) Current
(D) Capacitance
Answer: (A)
Q57. Which of the following is correct for a concentration cell?
(A) EMF = 0
(B) EMF arises due to concentration gradient
(C) Electrodes are different
(D) Electrolytes are of different nature
Answer: (B)
Q58. In conductometric titration of HCl vs NH₄OH, the conductivity:
(A) Increases continuously
(B) Decreases then increases
(C) Remains constant
(D) Increases then decreases
Answer: (B)
Q59. Which of the following affects EMF of a cell?
(A) Pressure
(B) Temperature
(C) Concentration
(D) All of these
Answer: (D)
Q60. The number of Faradays required to reduce 1 mol of MnO₄⁻ to Mn²⁺ is:
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer: (C)
Q61. The resistance of 0.01 M NaCl solution is 100 ohms. Cell constant is 1.0 cm⁻¹. Calculate conductivity.
(A) 0.01 S cm⁻¹
(B) 0.001 S cm⁻¹
(C) 0.1 S cm⁻¹
(D) 1.0 S cm⁻¹
Answer: (B)
Q62. What happens to Λm of CH₃COOH with dilution?
(A) Increases gradually
(B) Decreases rapidly
(C) Remains constant
(D) First increases, then decreases
Answer: (A)
Q63. The electrolyte used in the lead-acid battery is:
(A) NaOH
(B) HCl
(C) H₂SO₄
(D) KOH
Answer: (C)
Q64. The factor n in Nernst equation refers to:
(A) Number of molecules
(B) Number of electrons
(C) Number of moles
(D) Avogadro’s number
Answer: (B)
Q65. In a cell, zinc is oxidised and copper is reduced. Which is correct?
(A) Copper is anode
(B) Zinc is cathode
(C) Zinc is anode
(D) Electrons flow from Cu to Zn
Answer: (C)
Q66. EMF of a cell is measured using:
(A) Ammeter
(B) Voltmeter
(C) Potentiometer
(D) Conductivity meter
Answer: (C)
Q67. The slope of the plot of Λm vs √c for strong electrolytes gives:
(A) Limiting conductivity
(B) Conductance
(C) Interionic attraction
(D) Debye-Hückel constant
Answer: (C)
Q68. Which of the following parameters do not influence the standard electrode potential of a half-cell?
(A) Temperature
(B) Nature of the electrode
(C) Surface area of the electrode
(D) Concentration of the solution
Answer: (C)
Q69. The standard EMF of a cell is 1.10 V. If the cell reaction involves 2 moles of electrons, calculate the standard Gibbs free energy change.
(A) –212.2 kJ
(B) –110.0 kJ
(C) –220.0 kJ
(D) –200.2 kJ
Answer: (A)
Q70. A certain electrolytic cell contains molten CaCl₂. How many grams of calcium will be deposited by passing a current of 5 A for 9650 seconds?
(A) 5 g
(B) 10 g
(C) 20 g
(D) 40 g
Answer: (B)
Q71. In an electrolytic cell, current was passed for 30 minutes, depositing 0.324 g of copper. What is the current passed? (Atomic mass of Cu = 63.5 g mol⁻¹)
(A) 0.25 A
(B) 0.5 A
(C) 1 A
(D) 2 A
Answer: (A)
Q72. Which of the following is true about the Debye-Hückel-Onsager equation?
(A) It applies to strong electrolytes at high concentration
(B) It supports Kohlrausch’s law
(C) It applies only to non-electrolytes
(D) It is used to calculate ionization energy
Answer: (B)
Q73. A cell has E° = 1.100 V at 298 K. The cell involves a two-electron process. Calculate equilibrium constant K.
(A) 1.0 × 10⁻⁷
(B) 1.0 × 10⁷
(C) 1.0 × 10³⁷
(D) 1.0 × 10⁻³⁷
Answer: (C)
Q74. Which condition is necessary for a Daniel cell to work continuously?
(A) High pressure
(B) Constant temperature
(C) Constant electrolyte concentration
(D) Separation of two half cells
Answer: (D)
Q75. A galvanic cell is set up as: Pt | H₂ (1 atm) | HCl (1 M) || Ag⁺ (1 M) | Ag. The EMF of the cell is:
(A) +0.799 V
(B) –0.799 V
(C) +0.0 V
(D) –1.10 V
Answer: (A)
Q76. The resistance of a conductivity cell was found to be 250 Ω with 0.02 M KCl. The cell constant is 1.25 cm⁻¹. Calculate the conductivity.
(A) 0.005 S cm⁻¹
(B) 0.005 M⁻¹
(C) 0.005 cm⁻¹
(D) 0.005 ohm⁻¹ cm⁻¹
Answer: (D)
Q77. Which statement is incorrect regarding limiting molar conductivity (Λₘ°)?
(A) It is the sum of individual ionic conductances
(B) It decreases with increase in dilution
(C) It is used in Kohlrausch’s law
(D) It is constant for a given electrolyte at a given temperature
Answer: (B)
Q78. What is the unit of molar conductivity in SI units?
(A) S m² mol⁻¹
(B) S cm mol⁻¹
(C) Ω⁻¹ cm mol⁻¹
(D) S m mol⁻¹
Answer: (A)
Q79. In a conductivity cell, the conductance of a solution was measured to be 2.0 × 10⁻³ S. The cell constant is 0.5 cm⁻¹. The specific conductivity is:
(A) 1.0 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
(B) 2.5 × 10⁻³ S cm⁻¹
(C) 1.0 × 10⁻² S cm⁻¹
(D) 2.0 × 10⁻² S cm⁻¹
Answer: (A)
Q80. An increase in temperature generally:
(A) Increases ionic conductance
(B) Decreases specific conductance
(C) Does not affect conductivity
(D) Reduces molar conductance
Answer: (A)
Q81. The value of standard electrode potential of a half-cell does not depend upon:
(A) Temperature
(B) Pressure
(C) Nature of electrode
(D) Mass of electrode
Answer: (D)
Q82. Which of the following is used to determine EMF more accurately than a voltmeter?
(A) Ammeter
(B) Multimeter
(C) Potentiometer
(D) Galvanometer
Answer: (C)
Q83. How much charge (in coulombs) is required to reduce 0.5 mol of Fe³⁺ to Fe²⁺?
(A) 48,250 C
(B) 96,500 C
(C) 24,125 C
(D) 48,250 × 2 C
Answer: (A)
Q84. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(A) Dry cell is a primary cell
(B) Fuel cell converts chemical energy to electrical energy
(C) Standard EMF is independent of temperature
(D) Mercury cell is used in watches
Answer: (C)
Q85. The conductance of a solution decreases on dilution because:
(A) Number of ions increases
(B) Mobility of ions decreases
(C) Number of ions per unit volume decreases
(D) Viscosity decreases
Answer: (C)
Q86. Which one of the following has the highest molar conductivity at infinite dilution?
(A) NaCl
(B) CH₃COOH
(C) NH₄Cl
(D) HCl
Answer: (D)
Q87. Which is the correct statement regarding fuel cells?
(A) They require recharging
(B) They are primary cells
(C) They are equilibrium cells
(D) They have continuous supply of reactants
Answer: (D)
Q88. The overall redox reaction in a galvanic cell is spontaneous because:
(A) Electrons flow from cathode to anode
(B) EMF is negative
(C) ΔG is positive
(D) ΔG is negative
Answer: (D)
Q89. In a cell, 1.5 g of Ag is deposited. Find the number of electrons involved. (Atomic mass Ag = 108 g/mol)
(A) 8.37 × 10²¹
(B) 1.24 × 10²²
(C) 2.75 × 10²¹
(D) 3.41 × 10²⁰
Answer: (A)
Q90. Which factor has no effect on EMF of a galvanic cell?
(A) Concentration
(B) Pressure
(C) Type of salt bridge
(D) Temperature
Answer: (C)
Q91. The electrolysis of molten NaCl produces:
(A) H₂ and Cl₂
(B) Na and Cl₂
(C) NaOH and Cl₂
(D) NaCl and H₂
Answer: (B)
Q92. Which of the following obeys Faraday’s second law?
(A) Cu and Zn depositing in different cells
(B) NaCl electrolysis and HCl electrolysis
(C) Two reactions involving same electrolyte
(D) Electrolysis of water and urea
Answer: (A)
Q93. What is the role of inert electrode (like Pt) in electrochemical cells?
(A) Acts as a salt bridge
(B) Participates in redox
(C) Allows electron transfer
(D) Provides surface for reaction
Answer: (D)
Q94. The best electrolyte for conducting titration between HCl and NH₄OH is:
(A) NaCl
(B) KCl
(C) H₂SO₄
(D) CH₃COONa
Answer: (B)
Q95. Which of the following is true for a concentration cell?
(A) Same electrode, different concentration
(B) Different electrode, same solution
(C) No salt bridge
(D) Electrodes are reactive
Answer: (A)
Q96. Electrochemical cells are not feasible if:
(A) Both electrodes are cathodes
(B) Both half cells are identical
(C) EMF = 0
(D) Any of the above
Answer: (D)
Q97. If conductivity is 0.001 S cm⁻¹ and concentration is 0.001 M, the molar conductivity is:
(A) 1 S cm² mol⁻¹
(B) 10 S cm² mol⁻¹
(C) 100 S cm² mol⁻¹
(D) 0.1 S cm² mol⁻¹
Answer: (C)
Q98. Which of the following cells is irreversible?
(A) Daniell cell
(B) Mercury cell
(C) Nickel-cadmium cell
(D) Fuel cell
Answer: (A)
Q99. When 1 Faraday charge is passed through Al³⁺ solution, the amount of aluminium deposited is:
(A) 9 g
(B) 18 g
(C) 27 g
(D) 13.5 g
Answer: (D)
Q100. The best method to measure EMF without drawing current is:
(A) Galvanometer
(B) Ammeter
(C) Potentiometer
(D) Voltmeter
Answer: (C)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
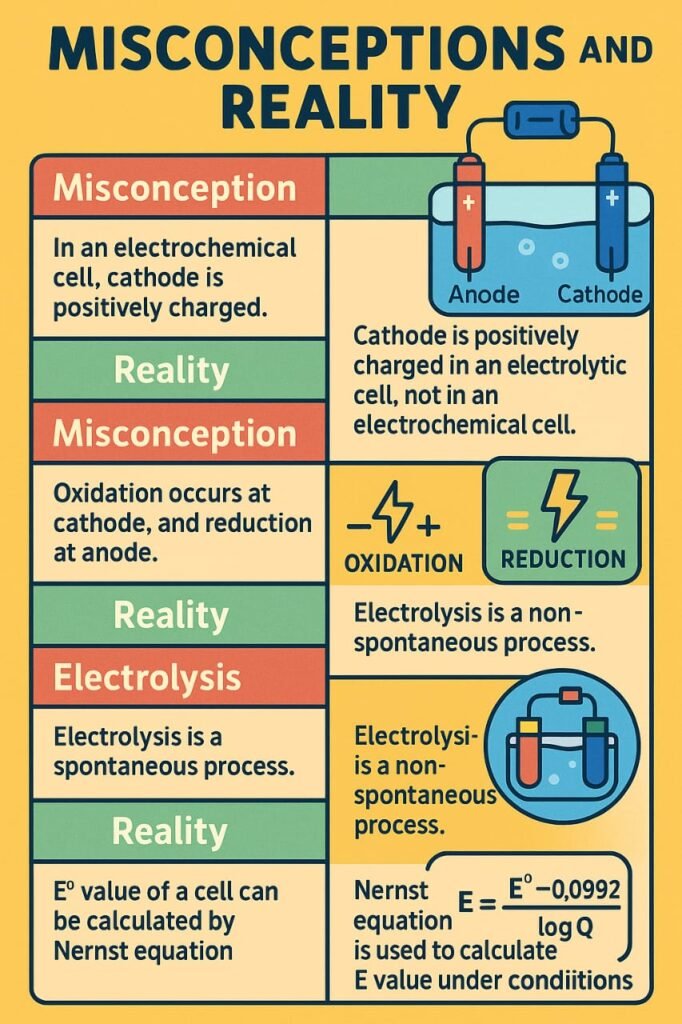
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
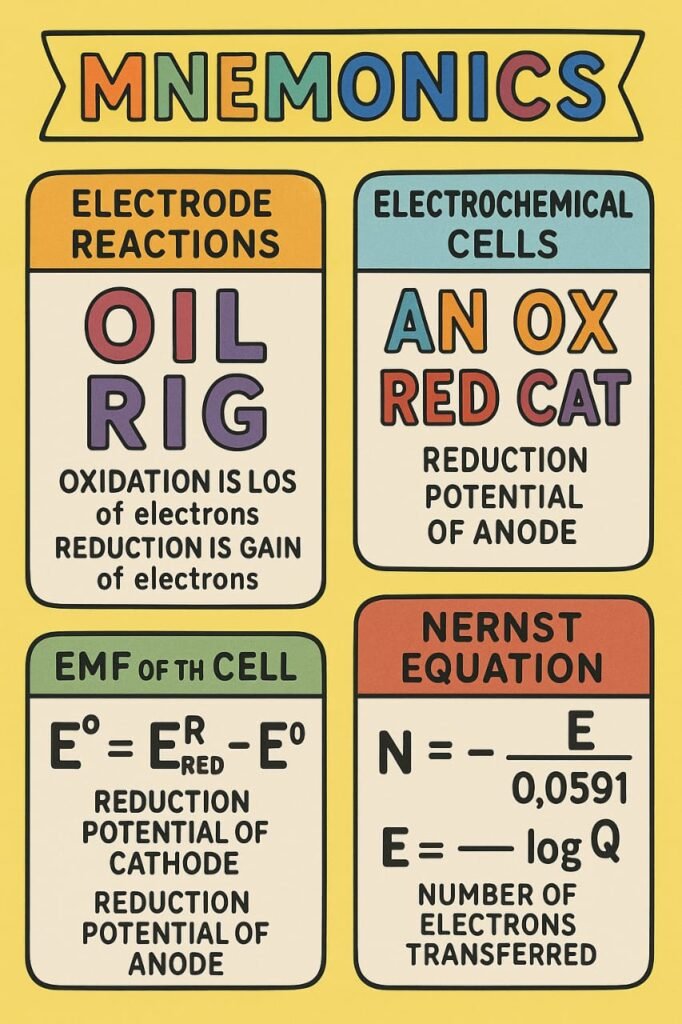
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MINDMAPS