Class 12 : Chemistry (English) – Chapter 10: Biomolecules
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
🔵 Biomolecules are organic molecules that are essential for life.
🟢 They form the structural and functional basis of cells and organisms.
🟠 Classified into carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, along with vitamins and hormones.
🔴 Their study connects chemistry with biology and medicine.


🌿 Carbohydrates
Definition & Types
✔ Carbohydrates = polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or compounds that yield them on hydrolysis.
Monosaccharides: Simple sugars (glucose, fructose).
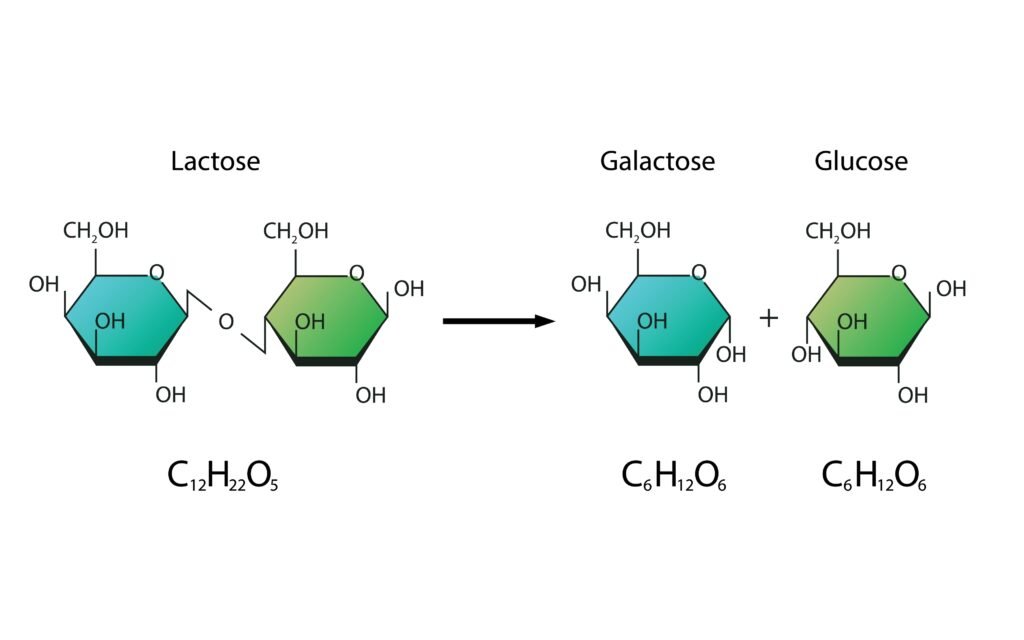
Disaccharides: 2 monosaccharide units (sucrose, maltose, lactose).
Polysaccharides: Large polymers (starch, cellulose, glycogen).
Glucose
Formula: C₆H₁₂O₆.
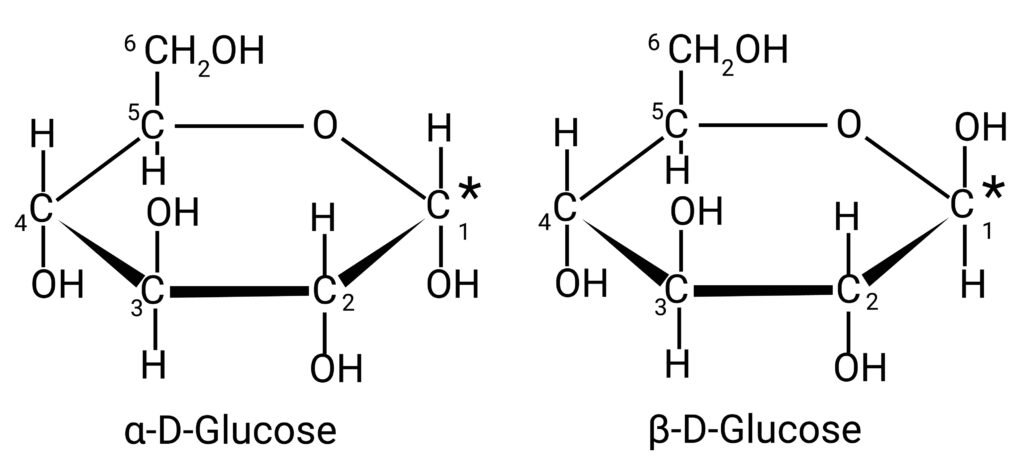
Open-chain and cyclic forms (pyranose/hexose).
Tests: reduction with Tollen’s and Fehling’s reagents.
Fructose
Ketohexose sugar.
Cyclic furanose form predominates.
Polysaccharides
🟩 Starch: Storage in plants, composed of amylose and amylopectin.
🟨 Cellulose: Structural polymer in plant cell walls, β-glycosidic linkages.
🟧 Glycogen: Storage in animals, similar to amylopectin but more branched.
🧬 Proteins
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins.
Contain amino (–NH₂) and carboxyl (–COOH) groups.
Exist as zwitterions at physiological pH.
Structure of Proteins
Primary: Linear sequence of amino acids.
Secondary: α-helix and β-pleated sheet (H-bonding).
Tertiary: 3D folding, stabilised by disulfide bonds, H-bonds, hydrophobic interactions.
Quaternary: Association of multiple polypeptide chains.
Functions
Enzymes (catalysis), hormones, structural proteins (collagen, keratin), transport (haemoglobin).
🌸 Nucleic Acids
Components
Nucleotides = Sugar + Base + Phosphate.
Bases: Purines (adenine, guanine), Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, uracil).
DNA
Double helix model (Watson & Crick).
Complementary base pairing (A–T, G–C).
RNA
Single-stranded.
Types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA.
Involved in protein synthesis.
🌍 Vitamins
Organic compounds needed in small amounts.
Fat-soluble: A, D, E, K.
Water-soluble: B-complex, C.
Deficiency → diseases (scurvy, rickets, night blindness).
🧪 Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands.
Types:
Peptide hormones: insulin, glucagon.
Steroid hormones: testosterone, estrogen.
Amino acid-derived: adrenaline, thyroxine.
🌟 Enzymes
Biological catalysts, mostly proteins.
Specific for substrates.
Lower activation energy.
Activity affected by pH, temperature, inhibitors.







📝 Summary
Biomolecules are molecules essential for life: carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, vitamins, hormones.
Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose), disaccharides (sucrose, maltose, lactose), polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose). Provide energy and storage.
Proteins: Polymers of amino acids, levels of structure from primary to quaternary. Functions include catalysis (enzymes), structure, transport, hormones.
Nucleic acids: DNA (double helix, genetic material) and RNA (protein synthesis). Composed of nucleotides with bases (purines, pyrimidines).
Vitamins: Micronutrients required for metabolism. Fat-soluble (A, D, E, K) and water-soluble (B-complex, C). Deficiency causes disorders like rickets, scurvy.
Hormones: Regulatory biomolecules controlling growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Classified as peptides, steroids, or amine derivatives.
Enzymes: Biological catalysts, highly specific, functioning under mild conditions, essential for biochemical reactions.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 10.1
What are monosaccharides?
Answer:
🔵 Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolysed further into smaller sugar units.
🟢 They are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
🟠 General formula: Cₙ(H₂O)ₙ.
🔴 Examples: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose.
Question 10.2
What are reducing sugars?
Answer:
✔ Reducing sugars are carbohydrates that can reduce Fehling’s solution or Tollen’s reagent.
💡 Reason: They contain a free aldehyde group (–CHO) or a free ketone group (–C=O) in solution.
🌿 Examples: Glucose, Fructose, Maltose, Lactose.
Question 10.3
Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Answer:
🔷 Energy storage: Starch acts as the primary storage carbohydrate.
🔶 Structural role: Cellulose forms the rigid cell wall providing mechanical strength.
Question 10.4
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides: Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose, lactose.
Answer:
🟦 Monosaccharides: Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, Galactose, Fructose.
🟨 Disaccharides: Maltose, Lactose.
Question 10.5
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Answer:
✔ Glycosidic linkage = covalent bond joining two monosaccharides.
🧪 It is formed when the –OH group of one sugar reacts with the anomeric carbon of another sugar with elimination of water.
🌿 Example: In maltose, glucose units are linked by α(1→4) glycosidic bond.
Question 10.6
What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
Answer:
🟢 Glycogen: Storage polysaccharide in animals, highly branched polymer of α-D-glucose.
🟠 Difference from starch:
Starch has two components: amylose (linear) and amylopectin (branched).
Glycogen is structurally similar to amylopectin but more highly branched.
Starch = plant storage; Glycogen = animal storage.
Question 10.7
What are the hydrolysis products of (i) sucrose and (ii) lactose?
Answer:
🟦 Sucrose hydrolysis: → Glucose + Fructose.
🟩 Lactose hydrolysis: → Glucose + Galactose.
Question 10.8
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer:
🔵 Starch: Polymer of α-D-glucose units linked by α(1→4) and α(1→6) bonds.
🟠 Cellulose: Polymer of β-D-glucose units linked by β(1→4) bonds.
🌿 Due to α vs β linkages, starch is digestible by humans but cellulose is not.
Question 10.9
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
(i) HI
(ii) Bromine water
(iii) HNO₃
Answer:
🟦 With HI → n-hexane (reduction to straight-chain hydrocarbon).
🟨 With bromine water → Gluconic acid (oxidation of –CHO to –COOH).
🟩 With HNO₃ → Saccharic acid (oxidation of both –CHO and terminal –CH₂OH).
Question 10.10
Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Answer:
✔ Observed reactions:
Glucose forms pentaacetate with acetic anhydride (5 –OH groups).
Glucose does not give Schiff’s test for free aldehyde.
Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite addition product.
Exists in α- and β- forms (anomers).
🟢 These facts prove glucose has a cyclic hemiacetal structure not explained by simple open chain.
Question 10.11
What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
🟦 Essential amino acids: Cannot be synthesised by the body, must be obtained from diet.
Examples: Valine, Leucine, Lysine, Phenylalanine.
🟩 Non-essential amino acids: Can be synthesised in the body.
Examples: Glycine, Alanine, Glutamic acid, Aspartic acid.
Question 10.12
Define the following as related to proteins:
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation
Answer:
🟦 Peptide linkage: –CO–NH– bond formed between –COOH of one amino acid and –NH₂ of another.
🟨 Primary structure: Linear sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain.
🟩 Denaturation: Loss of biological activity of protein due to disruption of secondary/tertiary structure by heat, pH, etc.
Question 10.13
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
Answer:
✔ Secondary structure refers to regular folding due to hydrogen bonding.
🟦 Two common types:
α-helix (spiral, right-handed).
β-pleated sheet (zigzag, sheet-like).
Question 10.14
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α-helix structure of proteins?
Answer:
🟦 α-helix is stabilised by intra-chain hydrogen bonds.
🟩 These bonds form between –C=O of one amino acid and –NH of another located four residues ahead in the chain.
✔ This coiling gives a right-handed helix.
Question 10.15
Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Answer:
🔷 Globular proteins
Spherical, compact.
Soluble in water.
Biological roles: enzymes, hormones, transport proteins (e.g., insulin, hemoglobin).
🔶 Fibrous proteins
Long, thread-like.
Insoluble in water.
Structural roles (e.g., keratin, collagen).
Question 10.16
How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
Answer:
🟦 Amino acids contain both acidic (–COOH) and basic (–NH₂) groups.
🟨 They exist as zwitterions (–NH₃⁺ and –COO⁻ simultaneously).
✔ Thus, they react with:
Acids → act as base.
Bases → act as acid.
Question 10.17
What are enzymes?
Answer:
🟢 Enzymes are biological catalysts, mostly proteins.
🟦 They speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed.
🌿 Example: Amylase (starch → maltose), Pepsin (protein digestion).
Question 10.18
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Answer:
✔ Denaturation = disruption of secondary and tertiary structures.
🟦 Primary structure remains intact.
🟨 Loss of biological activity occurs (e.g., coagulation of egg white on boiling).
Question 10.19
How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood.
Answer:
🟩 Classification:
Fat-soluble vitamins: A, D, E, K.
Water-soluble vitamins: B-complex, C.
🟦 Vitamin responsible for blood coagulation → Vitamin K.
Question 10.20
Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential to us? Give their important sources.
Answer:
🟢 Vitamin A
Functions: vision, healthy skin, growth.
Sources: carrots, butter, fish liver oil.
🟠 Vitamin C
Functions: healthy gums, wound healing, prevents scurvy.
Sources: citrus fruits, amla, tomatoes.
Question 10.21
What are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions.
Answer:
🟦 Nucleic acids = polymers of nucleotides (DNA, RNA).
🟨 Functions:
Carry genetic information from one generation to next.
Direct protein synthesis in cells.
Question 10.22
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Answer:
✔ Nucleoside = Base + Sugar (no phosphate).
✔ Nucleotide = Base + Sugar + Phosphate group.
Question 10.23
The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain.
Answer:
🟩 Bases pair by hydrogen bonding:
Adenine (A) with Thymine (T).
Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C).
🟦 Hence, the sequence on one strand dictates the complementary sequence on the other.
Question 10.24
Write the important structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
🔷 DNA
Sugar: deoxyribose.
Bases: A, G, C, T.
Structure: double helix.
Function: genetic material in most organisms.
🔶 RNA
Sugar: ribose.
Bases: A, G, C, U.
Structure: single-stranded.
Function: involved in protein synthesis (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA).
Question 10.25
What are the different types of RNA found in the cell?
Answer:
🟦 Three types:
mRNA (messenger RNA): carries genetic code from DNA.
tRNA (transfer RNA): brings amino acids during protein synthesis.
rRNA (ribosomal RNA): structural and catalytic role in ribosomes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Section A (Q1–Q16, MCQs)
(16 × 1 = 16 Marks)
Options for Assertion–Reason Questions:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
A is true, but R is false
A is false, but R is true
Q1. Which of the following is a disaccharide?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Galactose
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: 🟠 (C) Maltose
Q2. The bond linking monosaccharide units in polysaccharides is:
🔵 (A) Glycosidic bond
🟢 (B) Peptide bond
🟠 (C) Hydrogen bond
🔴 (D) Ester bond
Answer: 🔵 (A) Glycosidic bond
Q3. Which one is a reducing sugar?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Lactose
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer: 🔴 (D) Both (B) and (C)
Q4. Which vitamin prevents scurvy?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₁
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: 🟠 (C) Vitamin C
Q5. Which form of glucose is found in polysaccharides like starch?
🔵 (A) D(+) Glucose
🟢 (B) L(−) Glucose
🟠 (C) Both D and L
🔴 (D) Neither D nor L
Answer: 🔵 (A) D(+) Glucose
Q6. The difference between cellulose and starch is due to:
🔵 (A) Type of monosaccharide
🟢 (B) Type of glycosidic linkage
🟠 (C) Molecular formula
🔴 (D) Degree of polymerisation
Answer: 🟢 (B) Type of glycosidic linkage
Q7. Which nucleic acid has thymine as a base?
🔵 (A) DNA
🟢 (B) RNA
🟠 (C) Both
🔴 (D) None
Answer: 🔵 (A) DNA
Q8. Which one is a fibrous protein?
🔵 (A) Haemoglobin
🟢 (B) Keratin
🟠 (C) Myoglobin
🔴 (D) Enzyme
Answer: 🟢 (B) Keratin
Q9. The hydrolysis of sucrose gives:
🔵 (A) Glucose + Glucose
🟢 (B) Glucose + Galactose
🟠 (C) Glucose + Fructose
🔴 (D) Fructose + Galactose
Answer: 🟠 (C) Glucose + Fructose
Q10. Which vitamin is fat soluble?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) None
Answer: 🟠 (C) Vitamin D
Q11. Assertion (A): Glycogen is a storage carbohydrate in animals.
Reason (R): Glycogen has a highly branched structure, making it suitable for quick energy release.
Answer: 1 (Both A and R true, R explains A)
Q12. Assertion (A): Cellulose cannot be digested by humans.
Reason (R): Humans lack the enzyme cellulase.
Answer: 1 (Both A and R true, R explains A)
Q13. Which of the following is NOT an amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Cytosine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: 🟠 (C) Cytosine
Q14. Which type of bond stabilises the α-helix structure of proteins?
🔵 (A) Covalent bond
🟢 (B) Ionic bond
🟠 (C) Hydrogen bond
🔴 (D) Peptide bond
Answer: 🟠 (C) Hydrogen bond
Q15. Which RNA carries amino acids to ribosomes?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) tRNA
🟠 (C) rRNA
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: 🟢 (B) tRNA
Q16. Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Valine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: 🟠 (C) Valine
Section B (Q17–Q21, Very Short Answer, 2 marks each)
(5 × 2 = 10 Marks, ~30 words each)
Q17. Define monosaccharides with examples.
🟦 Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed further.
🟢 Examples — Glucose, Fructose.
Q18. State two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
🌿 Provide energy through respiration.
🌿 Store energy in the form of starch.
Q19. Name two essential amino acids.
✔ Valine
✔ Leucine
Q20. What are nucleosides?
💡 Nucleosides = Nitrogen base + Sugar (ribose/deoxyribose), without phosphate group.
Q21. Name two water-soluble vitamins and their deficiency diseases.
🟢 Vitamin B₁ — Beriberi
🟠 Vitamin C — Scurvy
Section C (Q22–Q28, Short Answer, 3 marks each)
(7 × 3 = 21 Marks, ~50 words each)
Q22. Differentiate between reducing and non-reducing sugars with examples.
🔷 Reducing sugars: Have free aldehyde/ketone group → reduce Tollen’s or Fehling’s reagent. (Examples: Glucose, Maltose, Lactose).
🔶 Non-reducing sugars: No free group, do not reduce reagents. (Example: Sucrose).
Q23. Write two differences between globular and fibrous proteins.
🟩 Globular proteins: Spherical, soluble, functional (e.g., enzymes, haemoglobin).
🟨 Fibrous proteins: Long, insoluble, structural (e.g., keratin, collagen).
Q24. Explain peptide linkage.
🧪 A peptide linkage is formed between –COOH group of one amino acid and –NH₂ group of another with removal of H₂O.
⚗ Example: –CO–NH–
Q25. Differentiate between DNA and RNA.
🔷 DNA: Double stranded, contains deoxyribose, bases = A, G, C, T.
🔶 RNA: Single stranded, contains ribose, bases = A, G, C, U.
Q26. What are enzymes? Write two characteristics.
💡 Enzymes = Biological catalysts, mostly proteins.
✅ Highly specific in action.
✅ Work under mild conditions (pH, temperature).
Q27. What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
🟦 Glycogen = Storage polysaccharide in animals.
🟩 Highly branched structure, stored in liver/muscles.
🟨 Starch = Plant storage polysaccharide with amylose + amylopectin.
Q28. Write the hydrolysis products of sucrose and lactose.
✔ Sucrose → Glucose + Fructose
✔ Lactose → Glucose + Galactose
Section D (Q29–Q30, Case-Based, 4 marks each)
Q29. Read the passage and answer:
Glucose is an important monosaccharide found in fruits and honey. It can exist in open-chain as well as cyclic forms. In aqueous solution, it shows mutarotation due to interconversion of its α- and β- forms.
(i) What is the molecular formula of glucose?
(ii) What is mutarotation?
(iii) Name the cyclic structures of α- and β-glucose.
Answer 29
🟦 (i) Molecular formula = C₆H₁₂O₆.
🟩 (ii) Mutarotation = Change in optical rotation due to interconversion between α- and β- anomers via open-chain form.
🟨 (iii) α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose.
Q30. Read the passage and answer:
Proteins are polymers of amino acids and are essential biomolecules. They exhibit different levels of structural organisation, from primary to quaternary. Their biological activity is sensitive to changes in conditions.
(i) What is the primary structure of protein?
(ii) Which bond is responsible for secondary structure?
(iii) What happens when a protein is denatured?
Answer 30
🟦 (i) Primary structure = Linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
🟩 (ii) Secondary structure = Stabilised by hydrogen bonds (α-helix, β-sheet).
🟨 (iii) Denaturation → Loss of secondary and tertiary structure, loss of biological activity, primary structure remains intact.
Section E (Q31–Q33, Long Answer, 5 marks each, with OR choice)
Q31.
Explain the structural difference between starch and cellulose.
OR
Explain the difference between DNA and RNA.
Answer 31
🟦 Starch vs Cellulose
Both are polysaccharides of glucose.
Starch: α-D-glucose units linked by α(1→4) and α(1→6) linkages (amylose + amylopectin). Digestible by humans.
Cellulose: β-D-glucose units linked by β(1→4) bonds, forms long straight chains with H-bonding. Indigestible to humans.
🟩 OR – DNA vs RNA
DNA: Double stranded, sugar = deoxyribose, bases = A, G, C, T. Genetic material.
RNA: Single stranded, sugar = ribose, bases = A, G, C, U. Role in protein synthesis.
Q32.
Discuss the classification of vitamins with examples.
OR
Explain the functions and deficiency diseases of Vitamin A, D, E, K.
Answer 32
🟦 Classification of Vitamins
Fat soluble: A, D, E, K (stored in liver, can be toxic in excess).
Water soluble: B-complex, C (excess excreted in urine).
🟩 OR – Functions & Deficiencies
Vitamin A: Vision, skin health; deficiency → night blindness.
Vitamin D: Calcium absorption; deficiency → rickets.
Vitamin E: Antioxidant; deficiency → reproductive failure.
Vitamin K: Blood clotting; deficiency → delayed clotting.
Q33.
Describe the role of nucleic acids in transmission of heredity.
OR
Explain the functions of different types of RNA.
Answer 33
🟦 Nucleic Acids & Heredity
DNA carries genetic information in sequence of bases.
Replication ensures transfer to daughter cells.
Base pairing ensures accuracy (A–T, G–C).
Genes on DNA code for proteins which determine traits.
🟩 OR – Types of RNA
mRNA: Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosome.
tRNA: Brings amino acids during translation.
rRNA: Structural and catalytic role in ribosomes.
✔ Together, RNA types ensure accurate protein synthesis.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following monosaccharides is a ketohexose?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Fructose
🟠 (C) Galactose
🔴 (D) Mannose
Answer: (B) Fructose
Year: 2025 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q2. Which biomolecule contains peptide bonds?
🔵 (A) Polysaccharides
🟢 (B) Proteins
🟠 (C) Nucleic acids
🔴 (D) Lipids
Answer: (B) Proteins
Year: 2025 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q3. Which vitamin deficiency causes rickets?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₁₂
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: (D) Vitamin D
Year: 2024 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q4. Which of the following is not a disaccharide?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Lactose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (D) Galactose
Year: 2024 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q5. Which vitamin is essential for blood clotting?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₂
🟠 (C) Vitamin K
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: (C) Vitamin K
Year: 2023 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q6. Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Starch
Answer: (B) Maltose
Year: 2023 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q7. Deficiency of niacin (Vitamin B₃) causes:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Beri-beri
🟠 (C) Scurvy
🔴 (D) Night blindness
Answer: (A) Pellagra
Year: 2022 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q8. Which of the following is a nucleoside?
🔵 (A) Adenosine
🟢 (B) ATP
🟠 (C) NAD⁺
🔴 (D) FAD
Answer: (A) Adenosine
Year: 2022 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q9. In which form is glucose stored in animals?
🔵 (A) Cellulose
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Glycogen
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (C) Glycogen
Year: 2021 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q10. Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
🔵 (A) Lactose
🟢 (B) Sucrose
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Glucose
Answer: (B) Sucrose
Year: 2021 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q11. Which vitamin deficiency causes pernicious anaemia?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₆
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₁₂
🟠 (C) Vitamin A
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: (B) Vitamin B₁₂
Year: 2020 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q12. Which of the following is not a polysaccharide?
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Glycogen
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Maltose
Answer: (D) Maltose
Year: 2020 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q13. The sugar present in RNA is:
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Ribose
🟠 (C) Deoxyribose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (B) Ribose
Year: 2019 | NEET | Shift: 2
Q14. Vitamin C is also known as:
🔵 (A) Retinol
🟢 (B) Ascorbic acid
🟠 (C) Calciferol
🔴 (D) Tocopherol
Answer: (B) Ascorbic acid
Year: 2019 | NEET | Shift: 1
Q15. Which is an essential amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Valine
🟠 (C) Alanine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: (B) Valine
Year: 2018 | NEET
Q16. In nucleic acids, bases are attached to:
🔵 (A) Sugar
🟢 (B) Phosphate
🟠 (C) Both sugar and phosphate
🔴 (D) Nitrogen atom of purine
Answer: (A) Sugar
Year: 2018 | NEET
Q17. Which of the following vitamins is fat soluble?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₁
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin B₂
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Year: 2017 | NEET
Q18. Which polysaccharide forms the exoskeleton of arthropods?
🔵 (A) Cellulose
🟢 (B) Chitin
🟠 (C) Starch
🔴 (D) Glycogen
Answer: (B) Chitin
Year: 2017 | NEET
Q19. Which of the following is a purine base?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Thymine
🔴 (D) Uracil
Answer: (A) Adenine
Year: 2016 | NEET
Q20. Which is the storage polysaccharide in plants?
🔵 (A) Glycogen
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (B) Starch
Year: 2016 | NEET
Q21. Which vitamin deficiency causes night blindness?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (A) Vitamin A
Year: 2015 | AIPMT
Q22. Which nucleic acid contains thymine?
🔵 (A) RNA
🟢 (B) DNA
🟠 (C) Both DNA and RNA
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) DNA
Year: 2015 | AIPMT
Q23. Which sugar is a component of milk?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Lactose
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Sucrose
Answer: (B) Lactose
Year: 2014 | AIPMT
Q24. Deficiency of thiamine (Vitamin B₁) causes:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Beri-beri
🟠 (C) Scurvy
🔴 (D) Rickets
Answer: (B) Beri-beri
Year: 2014 | AIPMT
Q25. The sugar present in DNA is:
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (B) Deoxyribose
Year: 2013 | AIPMT
Q26. Which vitamin is essential for vision?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₁
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin A
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: (C) Vitamin A
Year: 2012 | AIPMT
Q27. Which sugar is an aldohexose?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Fructose
🟠 (C) Ribose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (A) Glucose
Year: 2012 | AIPMT
Q28. Which of the following is a sulphur-containing amino acid?
🔵 (A) Methionine
🟢 (B) Valine
🟠 (C) Alanine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: (A) Methionine
Year: 2011 | AIPMT
Q29. Which vitamin is also known as calciferol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Year: 2011 | AIPMT
Q30. Which of the following is a polysaccharide?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Lactose
Answer: (B) Starch
Year: 2010 | AIPMT
Q31. Which sugar is found in RNA but not in DNA?
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (A) Ribose
Year: 2010 | AIPMT
Q32. Deficiency of Vitamin C causes:
🔵 (A) Rickets
🟢 (B) Night blindness
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Scurvy
Answer: (D) Scurvy
Year: 2009 | AIPMT
Q33. Which one is not a nitrogenous base of nucleic acids?
🔵 (A) Cytosine
🟢 (B) Adenine
🟠 (C) Guanine
🔴 (D) Tyrosine
Answer: (D) Tyrosine
Year: 2009 | AIPMT
Q34. Which is a water-insoluble polysaccharide?
🔵 (A) Glycogen
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Maltose
Answer: (C) Cellulose
Year: 2008 | AIPMT
Q35. Which vitamin is also called tocopherol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin K
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin E
🔴 (D) Vitamin B₂
Answer: (C) Vitamin E
Year: 2008 | AIPMT
Q36. Which of the following is a pentose sugar?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Ribose
🟠 (C) Galactose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (B) Ribose
Year: 2007 | AIPMT
Q37. The main nitrogenous base present in RNA but absent in DNA is:
🔵 (A) Uracil
🟢 (B) Thymine
🟠 (C) Cytosine
🔴 (D) Adenine
Answer: (A) Uracil
Year: 2007 | AIPMT
Q38. Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption?
🔵 (A) Vitamin D
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin A
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (A) Vitamin D
Year: 2006 | AIPMT
Q39. Which sugar is a component of sucrose?
🔵 (A) Glucose and fructose
🟢 (B) Glucose and galactose
🟠 (C) Glucose and ribose
🔴 (D) Glucose only
Answer: (A) Glucose and fructose
Year: 2006 | AIPMT
Q40. Which is a disaccharide?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Galactose
🟠 (C) Sucrose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (C) Sucrose
Year: 2005 | AIPMT
Q41. Which vitamin is called retinol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₆
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin D
Answer: (A) Vitamin A
Year: 2005 | AIPMT
Q42. Which biomolecule forms enzymes?
🔵 (A) Proteins
🟢 (B) Lipids
🟠 (C) Vitamins
🔴 (D) Carbohydrates
Answer: (A) Proteins
Year: 2004 | AIPMT
Q43. Which of the following is a storage carbohydrate in animals?
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Glycogen
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Inulin
Answer: (B) Glycogen
Year: 2004 | AIPMT
Q44. The deficiency of which vitamin causes scurvy?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (B) Vitamin C
Year: 2003 | AIPMT
Q45. Which of the following is a purine base?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Thymine
🔴 (D) Uracil
Answer: (A) Adenine
Year: 2003 | AIPMT
Q46. Which vitamin is essential for coagulation of blood?
🔵 (A) Vitamin C
🟢 (B) Vitamin A
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (D) Vitamin K
Year: 2002 | AIPMT
Q47. Which polysaccharide is the main constituent of plant cell wall?
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Glycogen
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Pectin
Answer: (C) Cellulose
Year: 2002 | AIPMT
Q48. Which vitamin is also known as antirachitic vitamin?
🔵 (A) Vitamin C
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin A
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (B) Vitamin D
Year: 2002 | AIPMT
Q49. The carbohydrate which is a storage form in animals is:
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Cellulose
🟠 (C) Glycogen
🔴 (D) Inulin
Answer: (C) Glycogen
Year: 2001 | AIPMT
Q50. Which vitamin acts as antioxidant?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin E
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Both B and C
Answer: (D) Both B and C
Year: 2000 | PMT
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which monosaccharide is a ketohexose?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Fructose
🟠 (C) Galactose
🔴 (D) Mannose
Answer: (B) Fructose
Year: 2025 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q2. Which vitamin is also called calciferol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Year: 2025 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q3. Which of the following is not a disaccharide?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Lactose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (D) Galactose
Year: 2024 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q4. Vitamin K is essential for:
🔵 (A) Vision
🟢 (B) Blood clotting
🟠 (C) Bone formation
🔴 (D) DNA replication
Answer: (B) Blood clotting
Year: 2024 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q5. Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
🔵 (A) Sucrose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Starch
🔴 (D) Cellulose
Answer: (B) Maltose
Year: 2023 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q6. Deficiency of niacin causes:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Scurvy
🟠 (C) Rickets
🔴 (D) Night blindness
Answer: (A) Pellagra
Year: 2023 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q7. In nucleosides, base is linked to sugar through:
🔵 (A) Glycosidic linkage
🟢 (B) Peptide linkage
🟠 (C) Phosphodiester linkage
🔴 (D) Hydrogen bonding
Answer: (A) Glycosidic linkage
Year: 2022 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q8. Storage form of glucose in animals is:
🔵 (A) Cellulose
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Glycogen
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (C) Glycogen
Year: 2022 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q9. Which sugar is a non-reducing disaccharide?
🔵 (A) Lactose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Sucrose
🔴 (D) Cellulose
Answer: (C) Sucrose
Year: 2021 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q10. Deficiency of vitamin B₁₂ leads to:
🔵 (A) Scurvy
🟢 (B) Pernicious anaemia
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Beri-beri
Answer: (B) Pernicious anaemia
Year: 2021 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q11. The sugar present in RNA is:
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Fructose
Answer: (A) Ribose
Year: 2020 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q12. Vitamin C is chemically:
🔵 (A) Retinol
🟢 (B) Tocopherol
🟠 (C) Ascorbic acid
🔴 (D) Calciferol
Answer: (C) Ascorbic acid
Year: 2020 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q13. Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Valine
🟠 (C) Alanine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: (B) Valine
Year: 2019 | JEE Main | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q14. Bases in nucleic acids are attached to:
🔵 (A) Phosphate group
🟢 (B) Sugar molecule
🟠 (C) Both sugar and phosphate
🔴 (D) Another base
Answer: (B) Sugar molecule
Year: 2019 | JEE Main | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q15. Which vitamin is fat-soluble?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₁
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin B₂
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Year: 2018 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q16. Which polysaccharide forms the exoskeleton of insects?
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Chitin
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Glycogen
Answer: (B) Chitin
Year: 2018 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q17. Which of the following is a purine base?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Thymine
🔴 (D) Uracil
Answer: (A) Adenine
Year: 2017 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q18. Storage carbohydrate in plants is:
🔵 (A) Glycogen
🟢 (B) Starch
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Inulin
Answer: (B) Starch
Year: 2017 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q19. Deficiency of Vitamin A causes:
🔵 (A) Rickets
🟢 (B) Night blindness
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Scurvy
Answer: (B) Night blindness
Year: 2016 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q20. DNA contains:
🔵 (A) Uracil
🟢 (B) Thymine
🟠 (C) Both uracil and thymine
🔴 (D) Neither
Answer: (B) Thymine
Year: 2016 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q21. The sugar present in milk is:
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Lactose
🟠 (C) Maltose
🔴 (D) Sucrose
Answer: (B) Lactose
Year: 2015 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q22. Thiamine deficiency causes:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Beri-beri
🟠 (C) Scurvy
🔴 (D) Rickets
Answer: (B) Beri-beri
Year: 2015 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q23. The sugar in DNA is:
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (B) Deoxyribose
Year: 2014 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q24. Vitamin E is also called:
🔵 (A) Retinol
🟢 (B) Calciferol
🟠 (C) Tocopherol
🔴 (D) Ascorbic acid
Answer: (C) Tocopherol
Year: 2014 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q25. Which base is present in RNA but absent in DNA?
🔵 (A) Thymine
🟢 (B) Uracil
🟠 (C) Cytosine
🔴 (D) Adenine
Answer: (B) Uracil
Year: 2013 | JEE Main | Set: Official
Q26. Vitamin C deficiency causes:
🔵 (A) Rickets
🟢 (B) Scurvy
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Night blindness
Answer: (B) Scurvy
Year: 2012 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q27. Which of the following is a sulphur-containing amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Methionine
🟠 (C) Valine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: (B) Methionine
Year: 2012 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q28. Vitamin D is also called:
🔵 (A) Retinol
🟢 (B) Calciferol
🟠 (C) Tocopherol
🔴 (D) Ascorbic acid
Answer: (B) Calciferol
Year: 2011 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q29. The carbohydrate which is stored in animal body is:
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Glycogen
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Inulin
Answer: (B) Glycogen
Year: 2011 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q30. Which vitamin is also known as tocopherol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin E
Answer: (D) Vitamin E
Year: 2010 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q31. Which of the following is not a nitrogenous base of nucleic acids?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Tyrosine
🔴 (D) Thymine
Answer: (C) Tyrosine
Year: 2010 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q32. Which polysaccharide is a constituent of arthropod exoskeleton?
🔵 (A) Cellulose
🟢 (B) Chitin
🟠 (C) Starch
🔴 (D) Glycogen
Answer: (B) Chitin
Year: 2009 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q33. Which vitamin is essential for coagulation of blood?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₆
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (D) Vitamin K
Year: 2009 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q34. The sugar present in DNA is:
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (B) Deoxyribose
Year: 2008 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q35. Vitamin A is also called:
🔵 (A) Retinol
🟢 (B) Calciferol
🟠 (C) Tocopherol
🔴 (D) Ascorbic acid
Answer: (A) Retinol
Year: 2008 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q36. Which polysaccharide is found in plant cell wall?
🔵 (A) Starch
🟢 (B) Glycogen
🟠 (C) Cellulose
🔴 (D) Inulin
Answer: (C) Cellulose
Year: 2007 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q37. Which vitamin is also known as antirachitic vitamin?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₁
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin E
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Year: 2007 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q38. The sugar present in RNA is:
🔵 (A) Ribose
🟢 (B) Deoxyribose
🟠 (C) Fructose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: (A) Ribose
Year: 2006 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q39. Which vitamin is also known as antisterility vitamin?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin E
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (B) Vitamin E
Year: 2006 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q40. Which nitrogenous base is present in RNA but absent in DNA?
🔵 (A) Thymine
🟢 (B) Uracil
🟠 (C) Adenine
🔴 (D) Guanine
Answer: (B) Uracil
Year: 2005 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q41. Deficiency of thiamine (Vitamin B₁) causes:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Beri-beri
🟠 (C) Scurvy
🔴 (D) Rickets
Answer: (B) Beri-beri
Year: 2005 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q42. Which vitamin is required for normal vision?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (A) Vitamin A
Year: 2004 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q43. Which is a purine base?
🔵 (A) Cytosine
🟢 (B) Adenine
🟠 (C) Uracil
🔴 (D) Thymine
Answer: (B) Adenine
Year: 2004 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q44. Vitamin D deficiency leads to:
🔵 (A) Pellagra
🟢 (B) Rickets
🟠 (C) Scurvy
🔴 (D) Beri-beri
Answer: (B) Rickets
Year: 2003 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q45. Which biomolecule forms enzymes?
🔵 (A) Proteins
🟢 (B) Carbohydrates
🟠 (C) Lipids
🔴 (D) Vitamins
Answer: (A) Proteins
Year: 2003 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q46. The sugar obtained after hydrolysis of sucrose is:
🔵 (A) Glucose + Fructose
🟢 (B) Glucose + Galactose
🟠 (C) Glucose + Ribose
🔴 (D) Glucose + Mannose
Answer: (A) Glucose + Fructose
Year: 2002 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q47. Vitamin C is also called:
🔵 (A) Tocopherol
🟢 (B) Retinol
🟠 (C) Ascorbic acid
🔴 (D) Calciferol
Answer: (C) Ascorbic acid
Year: 2002 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q48. Which vitamin deficiency causes night blindness?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (A) Vitamin A
Year: 2001 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q49. Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin E
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (B) Vitamin D
Year: 2001 | AIEEE | Set: Official
Q50. Which vitamin is also called retinol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin C
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (A) Vitamin A
Year: 2000 | AIEEE | Set: Official
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Questions 1 – 17
Question 1
Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form —
🔴 (A) Oxime
🟢 (B) Aldehyde
🟡 (C) Ketone
🔵 (D) Acid
Answer: (A) Oxime
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2013 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 2
The number of chiral carbons in D-glucose is —
🔴 (A) 2 🟢 (B) 4 🟡 (C) 5 🔵 (D) 6
Answer: (B) 4 (at C2, C3, C4, C5)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2011 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 3
Which of the following gives a positive Fehling’s test?
🔴 (A) Sucrose 🟢 (B) Glucose 🟡 (C) Starch 🔵 (D) Cellulose
Answer: (B) Glucose (reducing sugar)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2012 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 4
Fructose reduces Tollens’ reagent because —
🔴 (A) It is an aldehyde
🟢 (B) It forms an enediol intermediate
🟡 (C) It contains CHO group directly
🔵 (D) It is aromatic
Answer: (B) It is converted to enediol → aldehyde form in basic medium
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2015 | Paper 1 | IIT Bombay
Question 5
Which among the following is a non-reducing sugar?
🔴 (A) Maltose 🟢 (B) Sucrose 🟡 (C) Lactose 🔵 (D) Glucose
Answer: (B) Sucrose (glycosidic link between anomeric carbons)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2014 | Paper 1 | IIT Kharagpur
Question 6
The cyclic form of glucose is a result of —
🔴 (A) Intramolecular hemiacetal formation
🟢 (B) Intramolecular acetal formation
🟡 (C) Hydrogen bonding only
🔵 (D) Aldol condensation
Answer: (A) Intramolecular hemiacetal formation
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2013 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 7
The product of oxidation of glucose with bromine water is —
🔴 (A) Gluconic acid 🟢 (B) Glucaric acid 🟡 (C) Gluconolactone 🔵 (D) Gluconamide
Answer: (A) Gluconic acid
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2017 | Paper 1 | IIT Madras
Question 8
Which one of the following vitamins is fat-soluble?
🔴 (A) Vitamin B1 🟢 (B) Vitamin C 🟡 (C) Vitamin D 🔵 (D) Vitamin B12
Answer: (C) Vitamin D
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2016 | Paper 1 | IIT Guwahati
Question 9
Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
🔴 (A) Glycine 🟢 (B) Alanine 🟡 (C) Valine 🔵 (D) Serine
Answer: (C) Valine
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2015 | Paper 1 | IIT Bombay
Question 10
The number of peptide bonds in tripeptide glycyl-alanyl-glycine is —
🔴 (A) 1 🟢 (B) 2 🟡 (C) 3 🔵 (D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2019 | Paper 1 | IIT Roorkee
Question 11
Which form of glucose rotates plane-polarised light to the right?
🔴 (A) α-Glucose 🟢 (B) β-Glucose 🟡 (C) L-Glucose 🔵 (D) D-Glucose
Answer: (D) D-Glucose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2011 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 12
Which of the following monosaccharides is a ketohexose?
🔴 (A) Glucose 🟢 (B) Fructose 🟡 (C) Ribose 🔵 (D) Arabinose
Answer: (B) Fructose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2018 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 13
The linkage joining monosaccharide units in polysaccharides is —
🔴 (A) Peptide bond
🟢 (B) Glycosidic bond
🟡 (C) Phosphodiester bond
🔵 (D) Disulphide bond
Answer: (B) Glycosidic bond
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2013 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 14
The enzyme that converts glucose into ethanol is —
🔴 (A) Invertase 🟢 (B) Zymase 🟡 (C) Urease 🔵 (D) Maltase
Answer: (B) Zymase
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2014 | Paper 1 | IIT Kharagpur
Question 15
DNA and RNA differ in —
🔴 (A) Type of sugar
🟢 (B) Type of base
🟡 (C) Both (A) and (B)
🔵 (D) Type of phosphate group
Answer: (C) Both (A) and (B) (deoxyribose vs ribose; thymine vs uracil)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2016 | Paper 1 | IIT Guwahati
Question 16
Which base is not present in RNA?
🔴 (A) Adenine 🟢 (B) Thymine 🟡 (C) Guanine 🔵 (D) Uracil
Answer: (B) Thymine
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2017 | Paper 1 | IIT Madras
Question 17
Which among the following is a reducing disaccharide?
🔴 (A) Sucrose 🟢 (B) Maltose 🟡 (C) Cellulose 🔵 (D) Amylose
Answer: (B) Maltose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2020 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 18
Which of the following statements about amino acids is correct?
🔴 (A) They exist only as neutral molecules
🟢 (B) They exist as zwitterions in solution
🟡 (C) They are always acidic
🔵 (D) They are always basic
Answer: (B) They exist as zwitterions in solution
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2013 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 19
The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the pH at which it —
🔴 (A) Exists as a neutral molecule
🟢 (B) Has zero net charge
🟡 (C) Does not migrate in electric field
🔵 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2014 | Paper 1 | IIT Kharagpur
Question 20
Which of the following pairs is correctly matched?
🔴 (A) Vitamin B12 – Ascorbic acid
🟢 (B) Vitamin C – Scurvy
🟡 (C) Vitamin D – Night blindness
🔵 (D) Vitamin A – Rickets
Answer: (B) Vitamin C – Scurvy
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2012 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 21
The alpha-helix structure of proteins is mainly stabilized by —
🔴 (A) Peptide bonds
🟢 (B) Hydrogen bonds
🟡 (C) Disulphide bonds
🔵 (D) Ionic bonds
Answer: (B) Hydrogen bonds
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2015 | Paper 1 | IIT Bombay
Question 22
Which of the following statements is false?
🔴 (A) All proteins are polymers of alpha-amino acids
🟢 (B) Insulin is a protein
🟡 (C) All carbohydrates are reducing agents
🔵 (D) Enzymes are biocatalysts
Answer: (C) All carbohydrates are reducing agents (false, sucrose is not)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2011 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 23
Which of the following compounds gives a purple colour with ninhydrin reagent?
🔴 (A) Amino acids
🟢 (B) Ketones
🟡 (C) Alcohols
🔵 (D) Esters
Answer: (A) Amino acids
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2018 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 24
Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
🔴 (A) Glucose 🟢 (B) Maltose 🟡 (C) Lactose 🔵 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2017 | Paper 1 | IIT Madras
Question 25
Which of the following enzymes hydrolyses starch to maltose?
🔴 (A) Maltase 🟢 (B) Diastase 🟡 (C) Zymase 🔵 (D) Lactase
Answer: (B) Diastase
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2016 | Paper 1 | IIT Guwahati
Question 26
Which of the following is not a polysaccharide?
🔴 (A) Starch 🟢 (B) Cellulose 🟡 (C) Glycogen 🔵 (D) Maltose
Answer: (D) Maltose (disaccharide)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2014 | Paper 1 | IIT Kharagpur
Question 27
Which base pairing is correct in DNA?
🔴 (A) Adenine – Cytosine
🟢 (B) Adenine – Thymine
🟡 (C) Guanine – Thymine
🔵 (D) Cytosine – Thymine
Answer: (B) Adenine – Thymine (via two H-bonds)
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2013 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 28
The bond between phosphate and sugar in nucleic acids is —
🔴 (A) Glycosidic bond
🟢 (B) Phosphodiester bond
🟡 (C) Peptide bond
🔵 (D) Hydrogen bond
Answer: (B) Phosphodiester bond
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2019 | Paper 1 | IIT Roorkee
Question 29
Which of the following is not a nitrogenous base of nucleic acids?
🔴 (A) Adenine 🟢 (B) Thymine 🟡 (C) Cytosine 🔵 (D) Creatine
Answer: (D) Creatine
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2012 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
Question 30
Which one of the following vitamins is water-soluble?
🔴 (A) Vitamin A 🟢 (B) Vitamin D 🟡 (C) Vitamin C 🔵 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: (C) Vitamin C
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2018 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 31
Which of the following compounds contains both peptide and disulphide bonds?
🔴 (A) Glycine 🟢 (B) Insulin 🟡 (C) Collagen 🔵 (D) Albumin
Answer: (B) Insulin
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2014 | Paper 1 | IIT Kharagpur
Question 32
Which of the following monosaccharides is an aldopentose?
🔴 (A) Ribose 🟢 (B) Fructose 🟡 (C) Glucose 🔵 (D) Mannose
Answer: (A) Ribose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2015 | Paper 1 | IIT Bombay
Question 33
Which statement is true for cellulose?
🔴 (A) It is a polymer of glucose
🟢 (B) It is soluble in water
🟡 (C) It gives violet colour with iodine
🔵 (D) It is made of fructose units
Answer: (A) It is a polymer of glucose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2011 | Paper 1 | IIT Kanpur
Question 34
In nucleic acids, the sugar part is —
🔴 (A) Ribose or deoxyribose
🟢 (B) Glucose
🟡 (C) Fructose
🔵 (D) Galactose
Answer: (A) Ribose or deoxyribose
Exam: JEE Advanced | Year 2020 | Paper 1 | IIT Delhi
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 NEET Level (Q1–Q20)
Q1. Which is a monosaccharide?
🔵 (A) Maltose
🟢 (B) Glucose
🟠 (C) Lactose
🔴 (D) Sucrose
Answer: 🟢 (B) Glucose
Q2. The bond linking monosaccharides in disaccharides is:
🔵 (A) Glycosidic bond
🟢 (B) Peptide bond
🟠 (C) Ester bond
🔴 (D) Hydrogen bond
Answer: 🔵 (A) Glycosidic bond
Q3. Which carbohydrate is a non-reducing sugar?
🔵 (A) Lactose
🟢 (B) Maltose
🟠 (C) Glucose
🔴 (D) Sucrose
Answer: 🔴 (D) Sucrose
Q4. Starch is composed of:
🔵 (A) Amylose + Amylopectin
🟢 (B) Cellulose + Glycogen
🟠 (C) Amylopectin + Glucose
🔴 (D) Fructose + Cellulose
Answer: 🔵 (A) Amylose + Amylopectin
Q5. Cellulose is a polymer of:
🔵 (A) α-D-glucose
🟢 (B) β-D-glucose
🟠 (C) Fructose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: 🟢 (B) β-D-glucose
Q6. Hydrolysis of sucrose gives:
🔵 (A) Glucose + Glucose
🟢 (B) Glucose + Galactose
🟠 (C) Glucose + Fructose
🔴 (D) Fructose + Galactose
Answer: 🟠 (C) Glucose + Fructose
Q7. Which vitamin is water-soluble?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin B-complex
🟠 (C) Vitamin D
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: 🟢 (B) Vitamin B-complex
Q8. Vitamin D deficiency causes:
🔵 (A) Night blindness
🟢 (B) Rickets
🟠 (C) Beriberi
🔴 (D) Scurvy
Answer: 🟢 (B) Rickets
Q9. Which protein is fibrous?
🔵 (A) Haemoglobin
🟢 (B) Insulin
🟠 (C) Keratin
🔴 (D) Pepsin
Answer: 🟠 (C) Keratin
Q10. The simplest amino acid is:
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Serine
🔴 (D) Valine
Answer: 🔵 (A) Glycine
Q11. The secondary structure of protein is stabilised by:
🔵 (A) Hydrogen bonds
🟢 (B) Peptide bonds
🟠 (C) Disulfide bonds
🔴 (D) Ionic bonds
Answer: 🔵 (A) Hydrogen bonds
Q12. The nucleic acid having thymine is:
🔵 (A) RNA
🟢 (B) DNA
🟠 (C) Both DNA and RNA
🔴 (D) None
Answer: 🟢 (B) DNA
Q13. Which RNA carries genetic code?
🔵 (A) rRNA
🟢 (B) tRNA
🟠 (C) mRNA
🔴 (D) hnRNA
Answer: 🟠 (C) mRNA
Q14. Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Valine
🟠 (C) Alanine
🔴 (D) Serine
Answer: 🟢 (B) Valine
Q15. Which test detects reducing sugars?
🔵 (A) Fehling’s test
🟢 (B) Biuret test
🟠 (C) Millon’s test
🔴 (D) Xanthoproteic test
Answer: 🔵 (A) Fehling’s test
Q16. Which vitamin is responsible for clotting of blood?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin E
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: 🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Q17. The genetic material in most organisms is:
🔵 (A) RNA
🟢 (B) DNA
🟠 (C) Protein
🔴 (D) Polysaccharide
Answer: 🟢 (B) DNA
Q18. The deficiency of Vitamin C causes:
🔵 (A) Scurvy
🟢 (B) Rickets
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Night blindness
Answer: 🔵 (A) Scurvy
Q19. The nitrogenous bases in DNA are:
🔵 (A) A, G, C, T
🟢 (B) A, G, C, U
🟠 (C) A, T, U, G
🔴 (D) A, C, U, T
Answer: 🔵 (A) A, G, C, T
Q20. Which sugar is a ketohexose?
🔵 (A) Glucose
🟢 (B) Fructose
🟠 (C) Galactose
🔴 (D) Ribose
Answer: 🟢 (B) Fructose
🔹 JEE Main Level (Q21–Q40)
Q21. The cyclic structure of glucose is best represented as:
🔵 (A) Furanose
🟢 (B) Pyranose
🟠 (C) Open chain
🔴 (D) Both pyranose and furanose equally
Answer: 🟢 (B) Pyranose
Q22. The structural difference between α- and β-glucose is:
🔵 (A) Position of OH at C-1
🟢 (B) Number of carbons
🟠 (C) Presence of aldehyde
🔴 (D) Presence of ketone
Answer: 🔵 (A) Position of OH at C-1
Q23. Which of the following is a non-proteinous nitrogen base?
🔵 (A) Adenine
🟢 (B) Cytosine
🟠 (C) Guanine
🔴 (D) Uracil
Answer: 🔴 (D) Uracil
Q24. Mutarotation of glucose occurs due to:
🔵 (A) Interconversion of α- and β-anomers
🟢 (B) Oxidation of glucose
🟠 (C) Reduction of glucose
🔴 (D) Hydrolysis of glucose
Answer: 🔵 (A) Interconversion of α- and β-anomers
Q25. Which of the following amino acids is aromatic?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Phenylalanine
🔴 (D) Valine
Answer: 🟠 (C) Phenylalanine
Q26. The structural difference between starch and cellulose is due to:
🔵 (A) Type of glycosidic linkage
🟢 (B) Type of monosaccharide
🟠 (C) Molecular weight
🔴 (D) Degree of branching
Answer: 🔵 (A) Type of glycosidic linkage
Q27. Which form of nucleic acid contains ribose sugar?
🔵 (A) DNA
🟢 (B) RNA
🟠 (C) Both
🔴 (D) None
Answer: 🟢 (B) RNA
Q28. In proteins, peptide bonds are:
🔵 (A) C–C bonds
🟢 (B) C–N bonds
🟠 (C) C–O bonds
🔴 (D) N–H bonds
Answer: 🟢 (B) C–N bonds
Q29. Which vitamin regulates calcium metabolism?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin E
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: 🟢 (B) Vitamin D
Q30. In nucleic acids, bases are linked to sugars through:
🔵 (A) Phosphodiester bond
🟢 (B) Glycosidic bond
🟠 (C) Peptide bond
🔴 (D) Ester bond
Answer: 🟢 (B) Glycosidic bond
Q31. Which vitamin is also known as calciferol?
🔵 (A) Vitamin A
🟢 (B) Vitamin D
🟠 (C) Vitamin K
🔴 (D) Vitamin E
Answer: 🟢 (B) Vitamin D
Q32. Which one is not a component of nucleotide?
🔵 (A) Base
🟢 (B) Sugar
🟠 (C) Phosphate
🔴 (D) Amino acid
Answer: 🔴 (D) Amino acid
Q33. Enzymes act as catalysts because they:
🔵 (A) Increase activation energy
🟢 (B) Decrease activation energy
🟠 (C) Increase equilibrium constant
🔴 (D) Change ΔG of reaction
Answer: 🟢 (B) Decrease activation energy
Q34. Which vitamin deficiency causes pernicious anaemia?
🔵 (A) Vitamin B₁
🟢 (B) Vitamin B₁₂
🟠 (C) Vitamin C
🔴 (D) Vitamin K
Answer: 🟢 (B) Vitamin B₁₂
Q35. The quaternary structure of proteins is maintained by:
🔵 (A) Hydrogen bonds only
🟢 (B) Peptide bonds only
🟠 (C) Interactions between polypeptide chains
🔴 (D) Ionic bonds only
Answer: 🟠 (C) Interactions between polypeptide chains
Q36. Which sugar is present in RNA but not in DNA?
🔵 (A) Deoxyribose
🟢 (B) Ribose
🟠 (C) Fructose
🔴 (D) Galactose
Answer: 🟢 (B) Ribose
Q37. Which statement about cellulose is correct?
🔵 (A) It is a polymer of α-glucose
🟢 (B) It has β(1→4) linkages
🟠 (C) It is soluble in water
🔴 (D) Humans can digest it
Answer: 🟢 (B) It has β(1→4) linkages
Q38. Vitamin K deficiency leads to:
🔵 (A) Rickets
🟢 (B) Excessive bleeding
🟠 (C) Pellagra
🔴 (D) Night blindness
Answer: 🟢 (B) Excessive bleeding
Q39. Which RNA has a cloverleaf structure?
🔵 (A) mRNA
🟢 (B) tRNA
🟠 (C) rRNA
🔴 (D) snRNA
Answer: 🟢 (B) tRNA
Q40. Which amino acid is neutral but polar?
🔵 (A) Serine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Glycine
🔴 (D) Valine
Answer: 🔵 (A) Serine
🔹 JEE Advanced Level (Q41–Q50)
Q41. Mutarotation proves that glucose exists in:
🔵 (A) Only α form
🟢 (B) Only β form
🟠 (C) Both α and β forms in equilibrium
🔴 (D) Only open chain
Answer: 🟠 (C) Both α and β forms in equilibrium
Q42. Why does sucrose not give Tollen’s test?
🔵 (A) No free aldehyde/ketone group
🟢 (B) Cyclic structure
🟠 (C) Oxidised easily
🔴 (D) Contains fructose
Answer: 🔵 (A) No free aldehyde/ketone group
Q43. Which statement about DNA is correct?
🔵 (A) It contains uracil
🟢 (B) It is single stranded
🟠 (C) It has antiparallel strands
🔴 (D) Sugar is ribose
Answer: 🟠 (C) It has antiparallel strands
Q44. The hydrolysis of RNA yields uracil, but DNA hydrolysis does not. Why?
🔵 (A) DNA lacks uracil
🟢 (B) DNA is single stranded
🟠 (C) RNA is unstable
🔴 (D) RNA has no phosphate
Answer: 🔵 (A) DNA lacks uracil
Q45. The denaturation of protein involves disruption of:
🔵 (A) Primary structure
🟢 (B) Secondary and tertiary structures
🟠 (C) Peptide linkages
🔴 (D) Covalent bonds of amino acids
Answer: 🟢 (B) Secondary and tertiary structures
Q46. The optical activity of glucose is due to:
🔵 (A) Aldehyde group
🟢 (B) Presence of asymmetric carbon atoms
🟠 (C) Cyclic structure
🔴 (D) Mutarotation
Answer: 🟢 (B) Presence of asymmetric carbon atoms
Q47. Which amino acid does not have a chiral carbon?
🔵 (A) Glycine
🟢 (B) Alanine
🟠 (C) Valine
🔴 (D) Leucine
Answer: 🔵 (A) Glycine
Q48. Which sugar is obtained by oxidation of glucose with bromine water?
🔵 (A) Saccharic acid
🟢 (B) Gluconic acid
🟠 (C) Fructose
🔴 (D) Maltose
Answer: 🟢 (B) Gluconic acid
Q49. The backbone of DNA molecule consists of:
🔵 (A) Sugar and phosphate units
🟢 (B) Base pairs only
🟠 (C) Amino acids
🔴 (D) Polypeptides
Answer: 🔵 (A) Sugar and phosphate units
Q50. The base pairing rule in DNA states:
🔵 (A) A pairs with G, T with C
🟢 (B) A pairs with T, G pairs with C
🟠 (C) A pairs with U, G pairs with C
🔴 (D) A pairs with T, G pairs with U
Answer: 🟢 (B) A pairs with T, G pairs with C
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS

