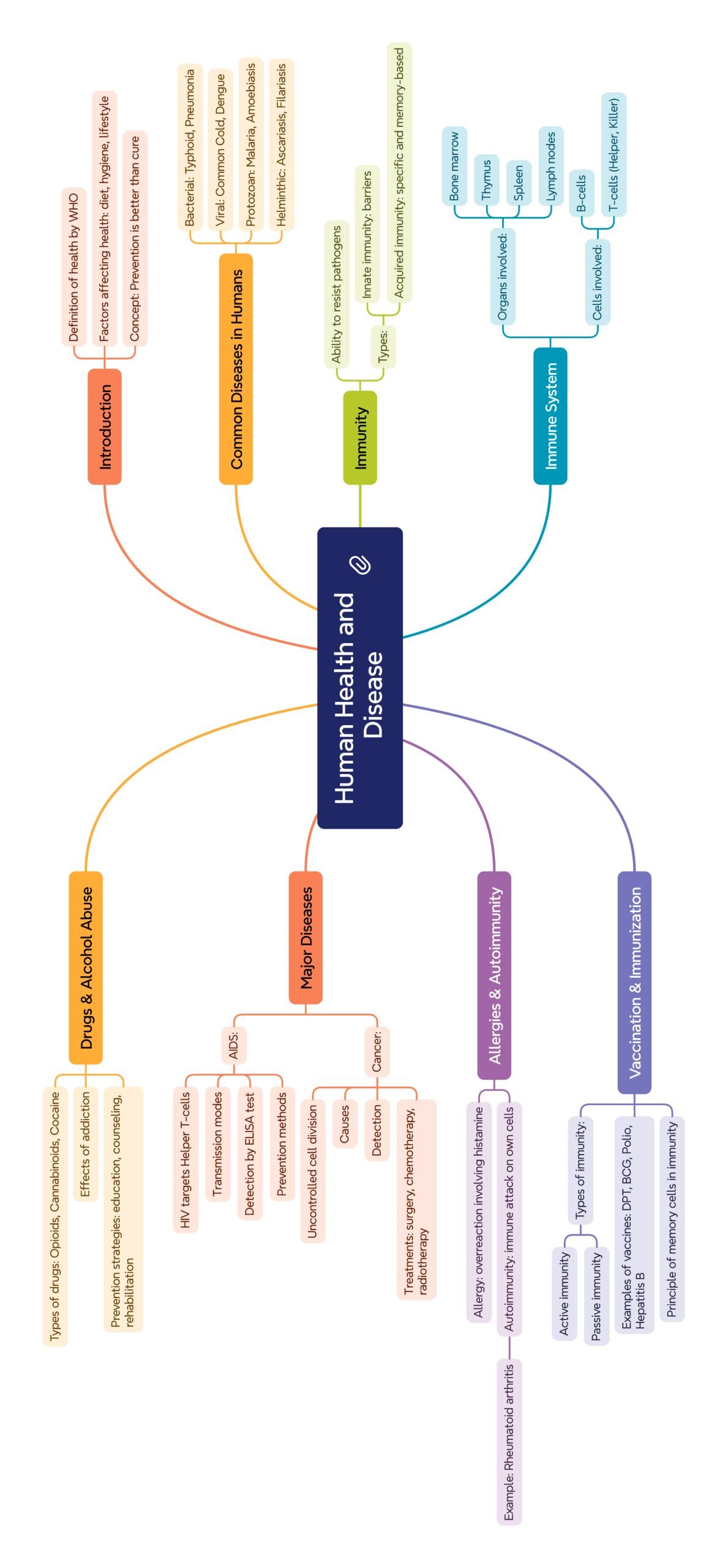
Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 7: Human Health and Disease
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
🧬 Human health = complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
🦠 Diseases disturb normal functioning, caused by bacteria 🧫, viruses 🦠, protozoa 🦟, helminths 🪱, or lifestyle/genetic factors.
💉 The chapter highlights infectious diseases, immunity, vaccination, cancer, and drug/alcohol abuse.
🧫 Bacterial Diseases
🧫 Typhoid: caused by Salmonella typhi
➡️ Transmission: contaminated food/water
➡️ Symptoms: fever, stomach pain, intestinal ulcers
➡️ Diagnosis: Widal test
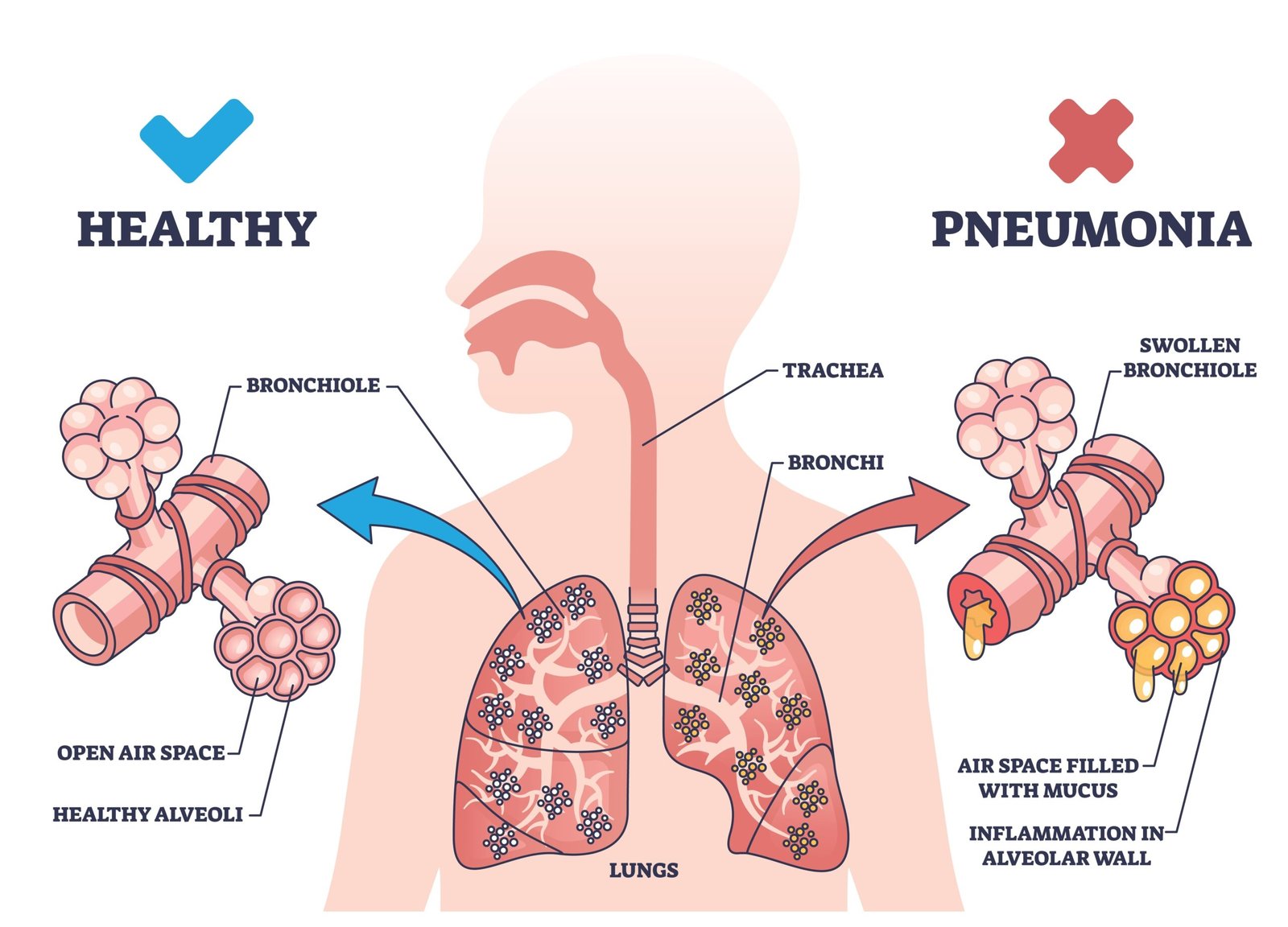
🧫 Pneumonia: caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae / Haemophilus influenzae
➡️ Infection of alveoli, fluid accumulation
➡️ Symptoms: cough, fever, breathing difficulty
🦠 Viral Diseases
🦠 Common Cold: Rhinoviruses
➡️ Symptoms: nasal congestion, sore throat, cough
🦠 HIV/AIDS: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
➡️ Transmission: sexual contact, blood transfusion, needles, mother-to-child
➡️ Attacks helper T-lymphocytes, weakens immunity
➡️ Test: ELISA
🦟 Protozoan Diseases
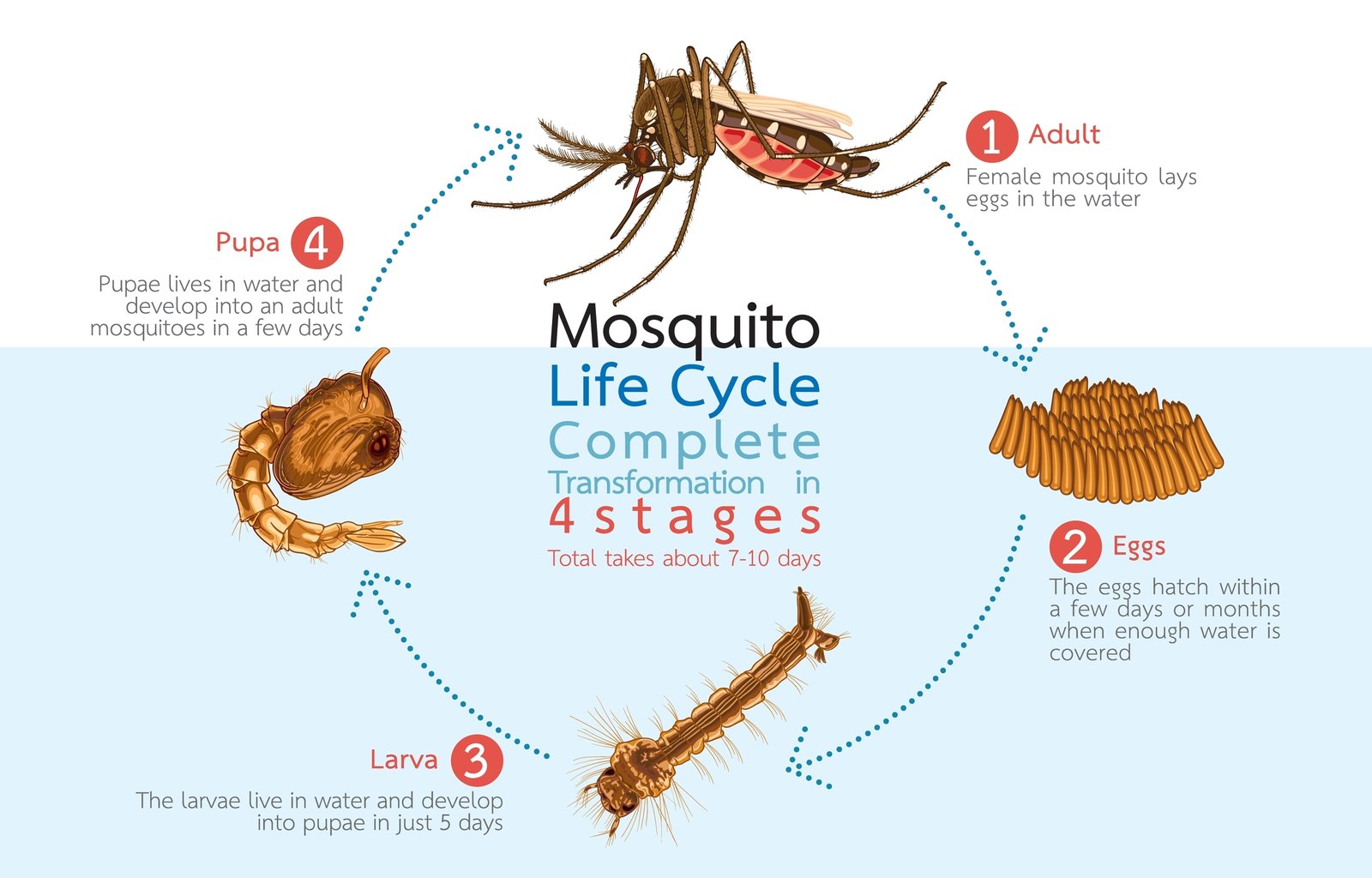
🦟 Malaria: Plasmodium vivax, falciparum, malariae

➡️ Vector: female Anopheles mosquito
➡️ Cycle: sporozoites → liver → RBCs
➡️ Symptoms: chills, fever, anemia
🪱 Helminthic Diseases
🪱 Ascariasis: caused by Ascaris lumbricoides
➡️ Spread: contaminated food/water
➡️ Symptoms: abdominal pain, anaemia
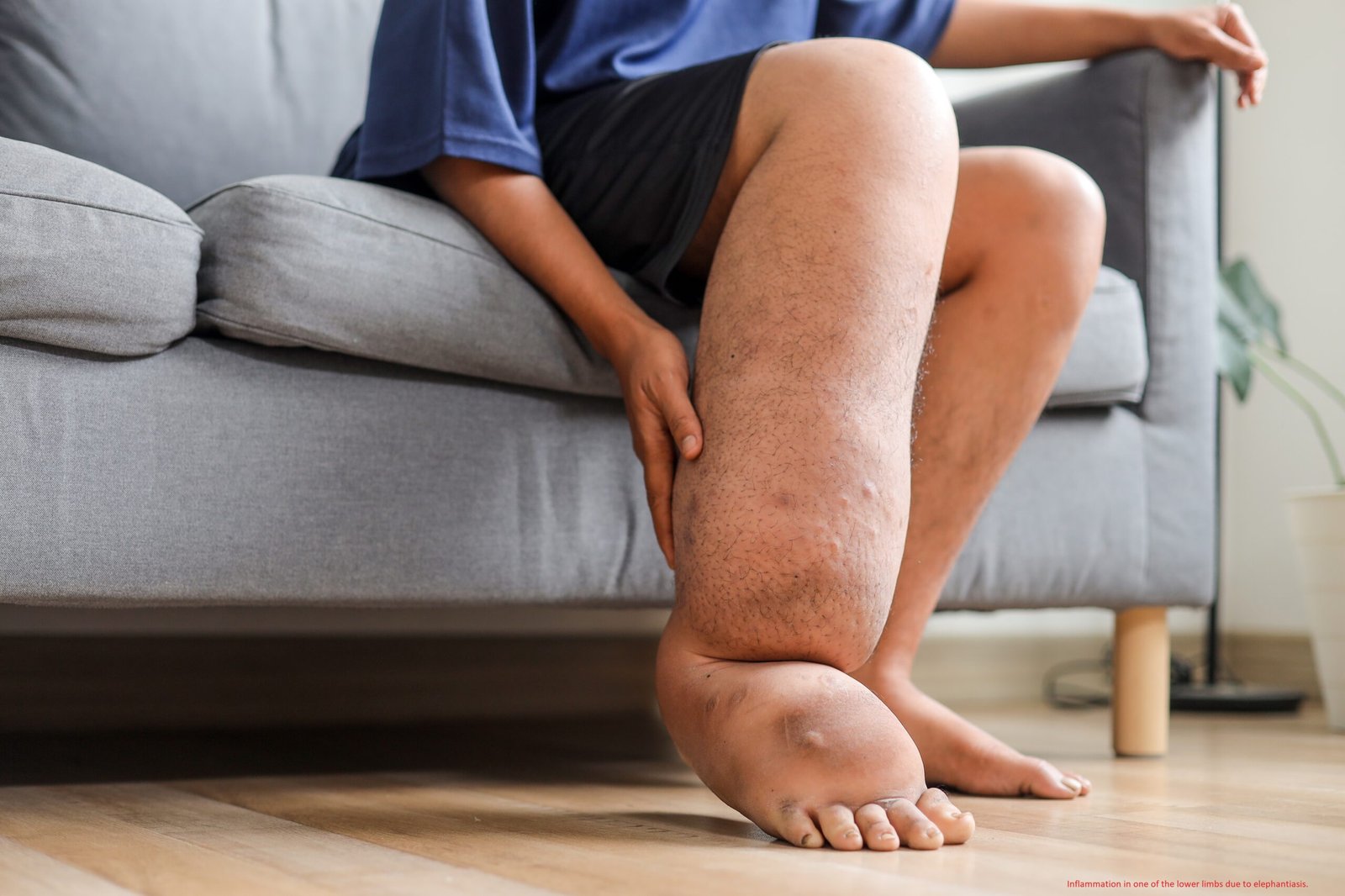
🪱 Filariasis (Elephantiasis): caused by Wuchereria bancrofti
➡️ Vector: Culex mosquito
➡️ Symptoms: chronic swelling of limbs, genital organs

This Diagram showing ringworm affected area of the skin.
🛡️ Immunity
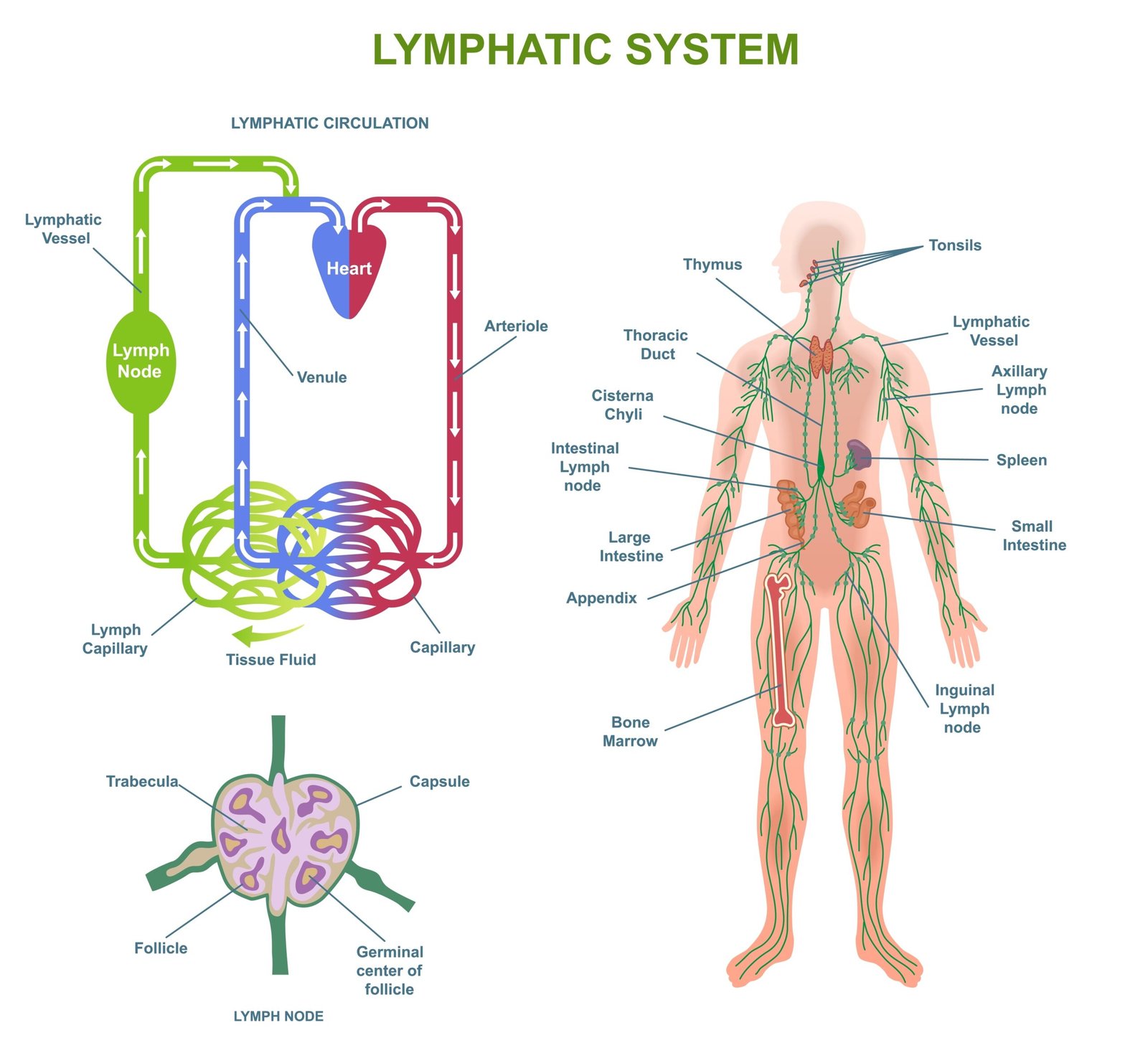
🌟 Innate Immunity (present at birth)
🧱 Physical barriers: skin, mucous membranes
💧 Physiological barriers: HCl, saliva, tears
🧑⚕️ Cellular barriers: phagocytes, NK cells
📡 Cytokine barriers: interferons
🧬 Acquired Immunity (specific, memory-based)
Humoral immunity: antibodies by B-cells
Cell-mediated immunity: T-lymphocytes
💡 Features: specificity, memory, diversity, self vs non-self recognition
💉 Vaccination and Immunisation
🧪 Vaccines = inactivated/weakened pathogens
Examples:
🟢 BCG (tuberculosis)
🔵 OPV (polio)
🟠 Hepatitis-B vaccine
👶 National Immunisation Programs: measles, tetanus, polio
🧠 Lifestyle Diseases
🎗️ Cancer: uncontrolled cell division, metastasis
➡️ Causes: carcinogens, oncogenic viruses, mutations
➡️ Treatment: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy
🍷 Drug & Alcohol Abuse:



➡️ Damage to brain and liver
➡️ Dependence and withdrawal symptoms
➡️ Social & health impacts
🌟 Summary (~300 words)
Human health is protected by strong immunity and preventive strategies. Pathogens such as 🧫 Salmonella (typhoid), 🦠 HIV (AIDS), 🦟 Plasmodium (malaria), and 🪱 Ascaris/Wuchereria cause significant human diseases.
Immunity is of two types: 🌟 innate (non-specific) and 🧬 acquired (specific). Vaccines provide long-term active immunity by stimulating memory cells.
Cancer results from uncontrolled cell division, while lifestyle risks like drug and alcohol abuse damage organs and impair social well-being.
Public health measures — sanitation, awareness, immunisation, and vector control — are essential for prevention.
🎯 Quick Recap
🧫 Bacterial diseases: Typhoid, Pneumonia
🦠 Viral diseases: Common cold, AIDS
🦟 Protozoan disease: Malaria
🪱 Helminthic diseases: Ascariasis, Filariasis
🛡️ Immunity: Innate + Acquired
💉 Vaccines: BCG, OPV, Hepatitis-B
🎗️ Lifestyle diseases: Cancer, Drug/alcohol abuse
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔹 Q1. What are the various public health measures which you would suggest as safeguard against infectious diseases?
✔️ Answer:
🧼 Personal hygiene: regular hand-washing, clean clothes, bathing.
🚰 Safe drinking water: chlorination, filtration, boiling.
🦟 Vector control: use of nets, insecticides, eliminating stagnant water.
💉 Vaccination programs: BCG, OPV, MMR, Hepatitis-B.
🏥 Community measures: sanitation, waste disposal, awareness campaigns.
🔹 Q2. In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
✔️ Answer:
🔬 Discovery of pathogens (bacteria 🧫, viruses 🦠, protozoa 🦟).
💊 Development of antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin).
💉 Production of vaccines (BCG, polio, Hepatitis-B).
🧪 Diagnostic tools like ELISA, Widal, PCR.
🚫 Public health measures like sanitation, immunisation drives.
🔹 Q3. How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place?
(a) Amoebiasis 🦠 — by contaminated food/water with cysts of Entamoeba histolytica.
(b) Malaria 🦟 — bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito, carrying Plasmodium.
(c) Ascariasis 🪱 — ingestion of eggs of Ascaris lumbricoides via contaminated food/water.
(d) Pneumonia 🧫 — inhalation of droplets containing Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae.
🔹 Q4. What measure would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
✔️ Answer:
🚰 Drinking safe, boiled or chlorinated water.
🧼 Washing hands before meals.
🍲 Eating properly cooked food.
🛑 Avoiding open defecation and ensuring proper sewage disposal.
🔹 Q5. Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ mean in the context of DNA vaccines.
✔️ Answer:
🧬 A “suitable gene” is one that codes for an antigenic protein of the pathogen.
💉 When introduced into host cells, this gene expresses the antigen → stimulates immune response → provides protection.
Example: Hepatitis-B surface antigen gene used in vaccines.
🔹 Q6. Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
✔️ Answer:
🟢 Primary lymphoid organs: Bone marrow, Thymus.
🔵 Secondary lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes, Spleen, MALT (Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue).
🔹 Q7. The following are some well-known abbreviations. Expand each:
(a) MALT — Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue
(b) CMI — Cell-Mediated Immunity
(c) AIDS — Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome
(d) NACO — National AIDS Control Organisation
(e) HIV — Human Immunodeficiency Virus
🔹 Q8. Differentiate the following and give examples:
(a) Innate vs Acquired Immunity 🛡️
Innate: Present at birth, non-specific (skin, mucosa, phagocytes).
Acquired: Develops after infection, specific & has memory (B-cells, T-cells).
(b) Active vs Passive Immunity 💉
Active: Produced by body’s own immune response after infection/vaccination (e.g., polio vaccine).
Passive: Ready-made antibodies transferred (e.g., tetanus antitoxin, mother’s milk).
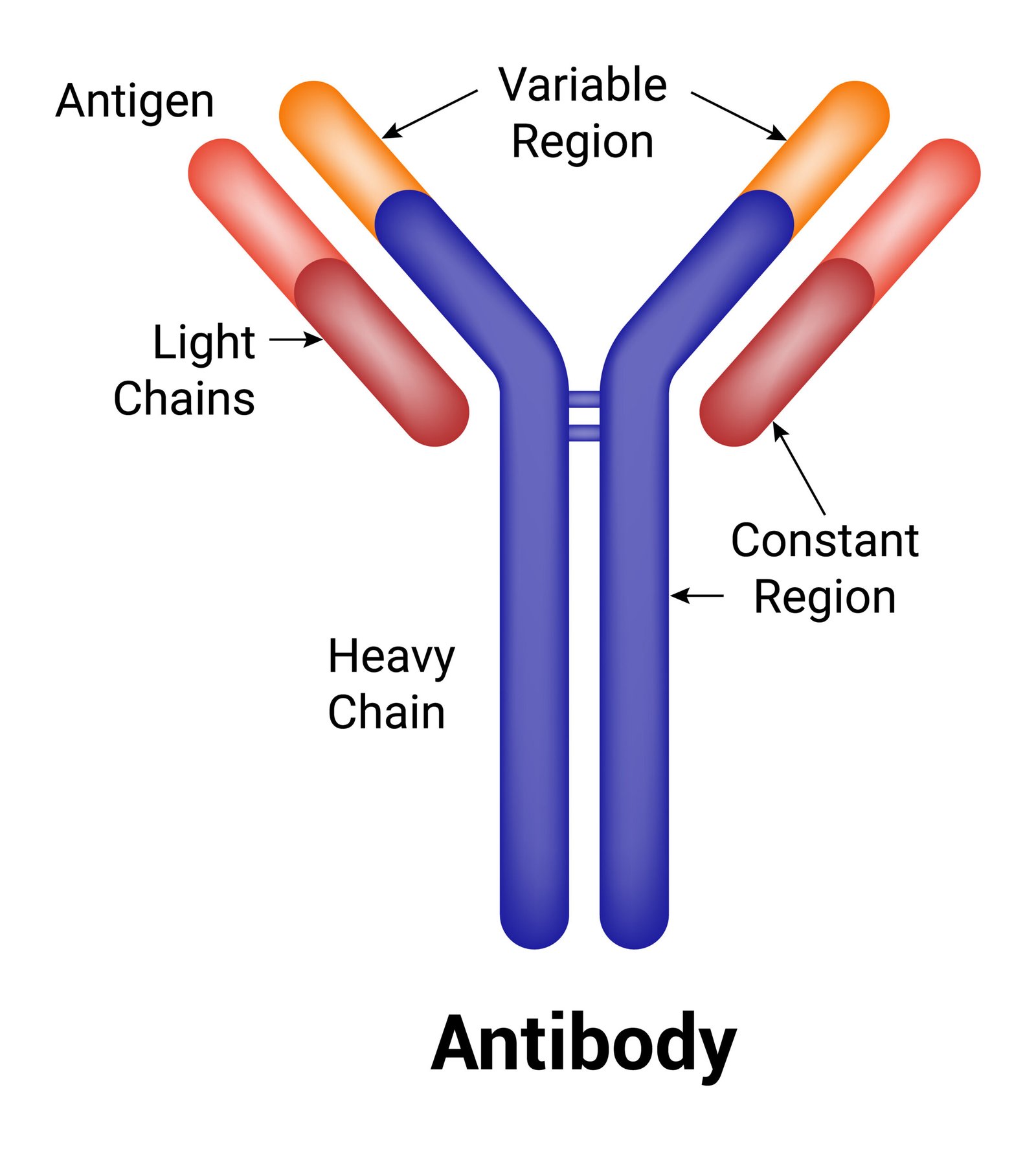
🔹 Q9. Draw a well-labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
✔️ Answer (Explanation):
Y-shaped structure with:
✨ Two light chains (outer arms).
✨ Two heavy chains (inner arms).
✨ Antigen-binding sites at tips of Y.
✨ Fc region at stem.
(Drawing to be made by student as per NCERT Fig. 8.2)
🔹 Q10. What are the various routes by which transmission of human immuno-deficiency virus (HIV) takes place?
✔️ Answer:
🩸 Blood transfusion with infected blood.
💉 Sharing contaminated needles/syringes.
❤️ Unprotected sexual contact with infected partner.
🤱 From infected mother to child (placenta, delivery, breastfeeding).
🔹 Q11. What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes deficiency of immune system of the infected person?
✔️ Answer:
🦠 HIV targets CD4⁺ T-lymphocytes (helper T-cells).
🧬 Viral RNA → DNA by reverse transcriptase → integrates into host genome.
⛔ Continuous destruction of T-cells → weakened immune system.
🩺 The patient becomes vulnerable to opportunistic infections (tuberculosis, pneumonia, fungal infections).
🔹 Q12. How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cell?
✔️ Answer:
🟢 Normal cell: growth regulated, contact inhibition present.
🔴 Cancer cell: uncontrolled growth, loss of contact inhibition, forms tumours, metastasis possible.
🔹 Q13. Explain what is meant by metastasis.
✔️ Answer:
🎗️ Spread of cancer cells from the site of origin → other body parts.
🧠 Carried via blood or lymph.
🦴 Forms secondary tumours in distant organs.
🔹 Q14. List the harmful effects caused by alcohol/drug abuse.
✔️ Answer:
🧠 Damage to brain: impaired judgement, depression.
🍷 Damage to liver: cirrhosis, hepatitis.
❤️ Damage to heart: high blood pressure, cardiac risk.
🚨 Accidents, violence, criminal behaviour.
👶 Harm to foetus if consumed during pregnancy.
💔 Social consequences: family breakdown, academic/financial decline.
🔹 Q15. Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
✔️ Answer:
✅ Yes, peer pressure strongly influences adolescents.
🔒 Protection measures:
Building self-confidence.
Choosing positive peer groups.
Strong family/teacher support.
Awareness of harmful effects.
🔹 Q16. Why is that once a person starts taking alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit? Discuss it with your teacher.
✔️ Answer:
🧠 Drugs/alcohol cause addiction & dependence.
💉 Withdrawal symptoms: anxiety, nausea, tremors, depression.
⚡ Affects brain’s reward system → craving → compulsive use.
🛠️ Requires counselling, medical treatment, rehabilitation.
🔹 Q17. In your view what motivates youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs and how can this be avoided?
✔️ Answer:
⚠️ Motivating factors: peer pressure, stress, curiosity, easy availability, family issues.
🛡️ Avoidance measures:
Education & awareness campaigns.
Stress management through sports, yoga, hobbies.
Counselling and emotional support.
Strict law enforcement against sale to minors.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🟢 Section A — Very Short Answer (1 mark each)
🔹 Q1. Name the bacterium that causes typhoid.
🔵 (A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
🟢 (B) Salmonella typhi
🟠 (C) Vibrio cholerae
🔴 (D) Streptococcus pneumoniae
✔️ Answer: (B) Salmonella typhi
🔹 Q2. Which virus causes AIDS?
🔵 (A) Hepatitis-B virus
🟢 (B) Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
🟠 (C) Rhinovirus
🔴 (D) Influenza virus
✔️ Answer: (B) Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
🔹 Q3. Which protozoan causes malaria?
🔵 (A) Plasmodium vivax
🟢 (B) Plasmodium falciparum
🟠 (C) Plasmodium malariae
🔴 (D) All of these
✔️ Answer: (D) All of these
🔹 Q4. Name the worm that causes filariasis.
🔵 (A) Taenia solium
🟢 (B) Ascaris lumbricoides
🟠 (C) Wuchereria bancrofti
🔴 (D) Enterobius vermicularis
✔️ Answer: (C) Wuchereria bancrofti
🔹 Q5. Which test is used to diagnose typhoid fever?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Widal test
🟠 (C) Mantoux test
🔴 (D) PCR
✔️ Answer: (B) Widal test
🔹 Q6. Which cells are attacked by HIV?
🔵 (A) B-lymphocytes
🟢 (B) CD4⁺ T-helper cells
🟠 (C) RBCs
🔴 (D) Platelets
✔️ Answer: (B) CD4⁺ T-helper cells
🟡 Section B — Short Answer I (2 marks each)
🔹 Q7. Differentiate between active and passive immunity.
✔️ Answer:
Active: Produced by body’s immune response (long-lasting).
Passive: Ready-made antibodies transferred (short-lived).
🔹 Q8. Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity.
✔️ Answer:
Innate: Present at birth, non-specific (skin, mucosa).
Acquired: Develops after infection/vaccination, specific & has memory.
🔹 Q9. Explain the role of interferons in viral infection.
✔️ Answer: Interferons are proteins secreted by virus-infected cells that protect neighbouring cells by preventing viral multiplication.
🔹 Q10. State two symptoms of pneumonia.
✔️ Answer: Cough with sputum, fever, difficulty in breathing.
🔹 Q11. Mention two withdrawal symptoms of drug abuse.
✔️ Answer: Anxiety, nausea, sweating, depression.
🔴 Section C — Short Answer II (3 marks each)
🔹 Q12. Explain the life cycle of Plasmodium in human host.
✔️ Answer:
Enters as sporozoites via mosquito bite.
First infects liver cells (schizogony).
Enters RBCs, multiplies → RBCs burst → fever/chills.
Gametocytes taken by mosquito → continue cycle.
🔹 Q13. Write three differences between normal and cancerous cells.
✔️ Answer:
Normal: Contact inhibition; Cancer: No contact inhibition.
Normal: Controlled division; Cancer: Uncontrolled.
Normal: No metastasis; Cancer: Metastasis present.
🔹 Q14. Mention three public health measures to control infectious diseases.
✔️ Answer:
Vaccination & immunisation programs.
Safe drinking water and sanitation.
Vector control (nets, insecticides).
🔹 Q15. What is drug dependence?
✔️ Answer: A condition where repeated use of a drug leads to tolerance, craving, and inability to function normally without it.
🔹 Q16. Write the full forms of: MALT, CMI, AIDS, HIV.
✔️ Answer:
MALT: Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue
CMI: Cell Mediated Immunity
AIDS: Acquired Immuno-Deficiency Syndrome
HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus
🧪 Numerical / Reasoning
🔹 Q17. A population has 64% individuals with homozygous dominant trait (p² = 0.64). Calculate frequency of recessive allele (q).
✔️ Answer:
Step 1: p² = 0.64 → p = 0.8
Step 2: p + q = 1 → q = 1 – 0.8 = 0.2
✔️ Frequency of recessive allele = 0.2
🟠 Section D — Long Answer (5 marks each)
🔹 Q18. Explain the life cycle of Plasmodium in both human host and mosquito vector.
✔️ Answer:
🦟 In mosquito (vector): Ingests gametocytes → gametes fuse → zygote → ookinete → oocyst → sporozoites (migrate to salivary glands).
🧬 In human: Sporozoites enter → liver (schizogony) → merozoites → infect RBCs → rupture → fever/chills. Gametocytes form and cycle continues.
🔹 Q19. Write the differences between active and passive immunity with examples.
✔️ Answer:
Active: Body produces antibodies after infection/vaccination (e.g., polio vaccine).
Passive: Ready-made antibodies introduced (e.g., tetanus antitoxin, mother’s milk).
🔹 Q20. Explain the causes and symptoms of malaria.
✔️ Answer:
Cause: Plasmodium species (vivax, falciparum, malariae).
Vector: Female Anopheles mosquito.
Symptoms: Recurring fever, chills, sweating, anaemia, spleen enlargement.
🔹 Q21. Define metastasis. How does cancer spread?
✔️ Answer:
🎗️ Metastasis = Spread of malignant cells from primary tumour to distant organs.
Cancerous cells travel via blood/lymph, invade new tissues, form secondary tumours.
🔹 Q22. Explain the role of vaccines in disease prevention.
✔️ Answer:
💉 Vaccines contain killed/weakened pathogens or antigenic proteins.
Stimulate immune response → memory cells → long-lasting protection.
Examples: BCG, OPV, Hepatitis-B vaccine.
🔹 Q23. What are withdrawal symptoms of drug abuse?
✔️ Answer:
Physical/mental reactions after stopping drug use: nausea, sweating, tremors, anxiety, irritability, depression, restlessness.
🔹 Q24. Describe innate immunity with its different types of barriers.
✔️ Answer:
🧱 Physical: skin, mucous membranes.
💧 Physiological: HCl in stomach, saliva, tears.
🧑⚕️ Cellular: phagocytes, NK cells.
📡 Cytokine: interferons.
🔹 Q25. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
✔️ Answer:
Benign: Localised, slow growth, non-invasive.
Malignant: Fast growth, invasive, metastasis.
🔹 Q26. Explain antibody structure with a labelled diagram.
✔️ Answer:
Y-shaped, 2 heavy chains + 2 light chains.
Antigen-binding sites at tips of Y.
Stem = Fc region.
(Diagram as per NCERT Fig. 8.2 to be drawn in exam.)
🔹 Q27. Mention five public health measures to control infectious diseases.
✔️ Answer:
Sanitation and hygiene.
Vector control.
Vaccination programs.
Safe drinking water.
Awareness campaigns.
🔵 MCQs (1 mark each, with options)
🔹 Q28. Which pathogen causes pneumonia?
🔵 (A) Salmonella typhi
🟢 (B) Streptococcus pneumoniae
🟠 (C) Haemophilus influenzae
🔴 (D) Both B and C
✔️ Answer: (D) Both B and C
🔹 Q29. Which test is used to detect AIDS?
🔵 (A) Widal test
🟢 (B) ELISA test
🟠 (C) Mantoux test
🔴 (D) PCR
✔️ Answer: (B) ELISA test
🔹 Q30. Which organ is primarily affected in filariasis?
🔵 (A) Lungs
🟢 (B) Intestine
🟠 (C) Limbs/genital organs
🔴 (D) Brain
✔️ Answer: (C) Limbs/genital organs
🔹 Q31. Which lymphoid organ filters blood?
🔵 (A) Bone marrow
🟢 (B) Thymus
🟠 (C) Spleen
🔴 (D) Lymph nodes
✔️ Answer: (C) Spleen
🔹 Q32. Which pathogen causes common cold?
🔵 (A) Rhinovirus
🟢 (B) Influenza virus
🟠 (C) HIV
🔴 (D) Hepatitis virus
✔️ Answer: (A) Rhinovirus
🔹 Q33. Which statement about cancer is incorrect?
🔵 (A) Cancer cells lose contact inhibition
🟢 (B) Benign tumours spread by metastasis
🟠 (C) Cancer cells divide uncontrollably
🔴 (D) Carcinogens may cause cancer
✔️ Answer: (B) Benign tumours spread by metastasis
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Typhoid fever in humans is caused by:
🔵 (A) Mycobacterium tuberculosis
🟢 (B) Salmonella typhi
🟠 (C) Streptococcus pneumoniae
🔴 (D) Haemophilus influenzae
✔️ Answer: (B) Salmonella typhi
📅 Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q2. Which test is used to confirm HIV infection?
🔵 (A) Widal test
🟢 (B) ELISA test
🟠 (C) Mantoux test
🔴 (D) Western blot
✔️ Answer: (B) ELISA test
📅 Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q3. Which disease is transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito?
🔵 (A) Filariasis
🟢 (B) Malaria
🟠 (C) Dengue
🔴 (D) Yellow fever
✔️ Answer: (B) Malaria
📅 Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q4. Which pathogen causes pneumonia?
🔵 (A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
🟢 (B) Salmonella typhi
🟠 (C) Entamoeba histolytica
🔴 (D) Ascaris lumbricoides
✔️ Answer: (A) Streptococcus pneumoniae
📅 Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q5. Which disease is caused by a protozoan?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
📅 Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q6. Which organ is primarily affected in filariasis?
🔵 (A) Brain
🟢 (B) Limbs and genital organs
🟠 (C) Lungs
🔴 (D) Liver
✔️ Answer: (B) Limbs and genital organs
📅 Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q7. The virus responsible for common cold infects:
🔵 (A) Alveoli
🟢 (B) Nose and respiratory passage
🟠 (C) Liver cells
🔴 (D) Blood plasma
✔️ Answer: (B) Nose and respiratory passage
📅 Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q8. Which lymphoid organ filters blood?
🔵 (A) Spleen
🟢 (B) Lymph nodes
🟠 (C) Bone marrow
🔴 (D) Thymus
✔️ Answer: (A) Spleen
📅 Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q9. Which of the following is not a sexually transmitted disease?
🔵 (A) AIDS
🟢 (B) Syphilis
🟠 (C) Gonorrhoea
🔴 (D) Malaria
✔️ Answer: (D) Malaria
📅 Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q10. The test commonly used to diagnose typhoid fever is:
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Widal test
🟠 (C) PCR
🔴 (D) Western blot
✔️ Answer: (B) Widal test
📅 Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q11. Which type of immunity is provided by vaccination?
🔵 (A) Active acquired
🟢 (B) Passive acquired
🟠 (C) Innate
🔴 (D) Cellular innate
✔️ Answer: (A) Active acquired
📅 Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q12. Which disease is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Filariasis
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Filariasis
📅 Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q13. Which lymphoid organ matures T-lymphocytes?
🔵 (A) Thymus
🟢 (B) Spleen
🟠 (C) Lymph node
🔴 (D) Bone marrow
✔️ Answer: (A) Thymus
📅 Year: NEET 2015
🔹 Q14. Which is not an autoimmune disease?
🔵 (A) Rheumatoid arthritis
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Myasthenia gravis
🔴 (D) Multiple sclerosis
✔️ Answer: (B) AIDS
📅 Year: NEET 2014
🔹 Q15. Which is not a bacterial disease?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) Ascariasis
🔴 (D) Plague
✔️ Answer: (C) Ascariasis
📅 Year: NEET 2014
🔹 Q16. Which part of immune system provides memory?
🔵 (A) B- and T-lymphocytes
🟢 (B) Macrophages
🟠 (C) Neutrophils
🔴 (D) Eosinophils
✔️ Answer: (A) B- and T-lymphocytes
📅 Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q17. Which disease is caused by a virus?
🔵 (A) Malaria
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Filariasis
🔴 (D) Typhoid
✔️ Answer: (B) AIDS
📅 Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q18. Antibodies are produced by:
🔵 (A) B-lymphocytes
🟢 (B) T-lymphocytes
🟠 (C) Monocytes
🔴 (D) Neutrophils
✔️ Answer: (A) B-lymphocytes
📅 Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q19. Which organ is primarily affected in ascariasis?
🔵 (A) Lungs
🟢 (B) Intestine
🟠 (C) Kidney
🔴 (D) Heart
✔️ Answer: (B) Intestine
📅 Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q20. Which is a cancer-causing virus?
🔵 (A) Retrovirus
🟢 (B) Oncogenic virus
🟠 (C) Rhinovirus
🔴 (D) Arbovirus
✔️ Answer: (B) Oncogenic virus
📅 Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q21. Which barrier is part of innate immunity?
🔵 (A) Interferons
🟢 (B) Skin
🟠 (C) Antibodies
🔴 (D) T-lymphocytes
✔️ Answer: (B) Skin
📅 Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q22. Which organ is affected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
🔵 (A) Lungs
🟢 (B) Brain
🟠 (C) Liver
🔴 (D) Kidney
✔️ Answer: (A) Lungs
📅 Year: PMT 2010
🔹 Q23. Which cells are also called natural killers?
🔵 (A) B-cells
🟢 (B) T-cells
🟠 (C) NK cells
🔴 (D) Neutrophils
✔️ Answer: (C) NK cells
📅 Year: PMT 2010
🔹 Q24. The disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica is:
🔵 (A) Amoebiasis
🟢 (B) Malaria
🟠 (C) Typhoid
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (A) Amoebiasis
📅 Year: PMT 2009
🔹 Q25. Which type of cancer affects blood-forming cells?
🔵 (A) Carcinoma
🟢 (B) Sarcoma
🟠 (C) Leukemia
🔴 (D) Lymphoma
✔️ Answer: (C) Leukemia
📅 Year: PMT 2009
🔹 Q26. Which immune cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity?
🔵 (A) B-lymphocytes
🟢 (B) T-lymphocytes
🟠 (C) NK cells
🔴 (D) Neutrophils
✔️ Answer: (B) T-lymphocytes
📅 Year: PMT 2008
🔹 Q27. Which type of tumour spreads rapidly and invades other tissues?
🔵 (A) Benign
🟢 (B) Malignant
🟠 (C) Localised
🔴 (D) Dormant
✔️ Answer: (B) Malignant
📅 Year: PMT 2008
🔹 Q28. Which disease is caused by Entamoeba histolytica?
🔵 (A) Malaria
🟢 (B) Amoebiasis
🟠 (C) Pneumonia
🔴 (D) Filariasis
✔️ Answer: (B) Amoebiasis
📅 Year: PMT 2007
🔹 Q29. Which test is used to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Mantoux test
🟠 (C) Widal test
🔴 (D) PCR
✔️ Answer: (B) Mantoux test
📅 Year: PMT 2007
🔹 Q30. Which mosquito transmits filariasis?
🔵 (A) Aedes
🟢 (B) Culex
🟠 (C) Anopheles
🔴 (D) Mansonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Culex
📅 Year: PMT 2006
🔹 Q31. Which disease is prevented by BCG vaccine?
🔵 (A) Tuberculosis
🟢 (B) Typhoid
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (A) Tuberculosis
📅 Year: PMT 2006
🔹 Q32. Which cells secrete antibodies?
🔵 (A) Plasma cells
🟢 (B) T-helper cells
🟠 (C) NK cells
🔴 (D) Monocytes
✔️ Answer: (A) Plasma cells
📅 Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q33. Which organ matures B-lymphocytes?
🔵 (A) Bone marrow
🟢 (B) Thymus
🟠 (C) Spleen
🔴 (D) Lymph nodes
✔️ Answer: (A) Bone marrow
📅 Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q34. Which is a symptom of ascariasis?
🔵 (A) Cough with blood
🟢 (B) Abdominal pain and anaemia
🟠 (C) Swelling of limbs
🔴 (D) Breathlessness
✔️ Answer: (B) Abdominal pain and anaemia
📅 Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q35. Which disease is caused by a retrovirus?
🔵 (A) AIDS
🟢 (B) Typhoid
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (A) AIDS
📅 Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q36. Which is an example of passive immunity?
🔵 (A) Vaccination
🟢 (B) Mother’s milk
🟠 (C) Antigen exposure
🔴 (D) Booster dose
✔️ Answer: (B) Mother’s milk
📅 Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q37. Which type of cancer affects lymphatic system?
🔵 (A) Sarcoma
🟢 (B) Lymphoma
🟠 (C) Leukemia
🔴 (D) Carcinoma
✔️ Answer: (B) Lymphoma
📅 Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q38. Which of the following is a bacterial disease?
🔵 (A) Malaria
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Pneumonia
🔴 (D) Filariasis
✔️ Answer: (C) Pneumonia
📅 Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q39. Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?
🔵 (A) Gonorrhoea
🟢 (B) Syphilis
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
📅 Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q40. Which disease is caused by helminths?
🔵 (A) Pneumonia
🟢 (B) Filariasis
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Common cold
✔️ Answer: (B) Filariasis
📅 Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q41. Which type of immunity is produced by vaccination?
🔵 (A) Passive acquired
🟢 (B) Active acquired
🟠 (C) Innate
🔴 (D) Artificial passive
✔️ Answer: (B) Active acquired
📅 Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q42. Which vector transmits malaria?
🔵 (A) Culex
🟢 (B) Aedes
🟠 (C) Anopheles
🔴 (D) Mansonia
✔️ Answer: (C) Anopheles
📅 Year: PMT 2000
🔹 Q43. Which cells mediate antibody production?
🔵 (A) B-cells
🟢 (B) T-cells
🟠 (C) NK cells
🔴 (D) Neutrophils
✔️ Answer: (A) B-cells
📅 Year: PMT 2000
🔹 Q44. Which test is used to detect cancer?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Biopsy
🟠 (C) Widal
🔴 (D) Mantoux
✔️ Answer: (B) Biopsy
📅 Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q45. Which organ is affected by ascariasis?
🔵 (A) Lungs
🟢 (B) Intestine
🟠 (C) Heart
🔴 (D) Brain
✔️ Answer: (B) Intestine
📅 Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q46. Which cancer originates from epithelial cells?
🔵 (A) Carcinoma
🟢 (B) Sarcoma
🟠 (C) Leukemia
🔴 (D) Lymphoma
✔️ Answer: (A) Carcinoma
📅 Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q47. Which barrier is part of innate immunity?
🔵 (A) Antibodies
🟢 (B) Skin
🟠 (C) T-cells
🔴 (D) Interleukins
✔️ Answer: (B) Skin
📅 Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q48. Which disease is not caused by bacteria?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) AIDS
🔴 (D) Plague
✔️ Answer: (C) AIDS
📅 Year: PMT 1997
🔹 Q49. Which mosquito spreads dengue?
🔵 (A) Aedes aegypti
🟢 (B) Anopheles
🟠 (C) Culex
🔴 (D) Mansonia
✔️ Answer: (A) Aedes aegypti
📅 Year: PMT 1997
🔹 Q50. Which immune cells destroy tumour cells?
🔵 (A) NK cells
🟢 (B) B-cells
🟠 (C) T-helper cells
🔴 (D) Eosinophils
✔️ Answer: (A) NK cells
📅 Year: PMT 1996
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. Typhoid is primarily transmitted through:
🔵 (A) Mosquito bites
🟢 (B) Contaminated food and water
🟠 (C) Air droplets
🔴 (D) Blood transfusion
✔️ Answer: (B) Contaminated food and water
🔹 Q2. Pneumonia-causing bacteria infect which part of the body?
🔵 (A) Liver
🟢 (B) Kidneys
🟠 (C) Alveoli of lungs
🔴 (D) Stomach
✔️ Answer: (C) Alveoli of lungs
🔹 Q3. Which mosquito transmits filariasis?
🔵 (A) Aedes aegypti
🟢 (B) Culex
🟠 (C) Anopheles
🔴 (D) Mansonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Culex
🔹 Q4. ELISA test is used to detect:
🔵 (A) Malaria
🟢 (B) Tuberculosis
🟠 (C) AIDS
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (C) AIDS
🔹 Q5. Which of the following diseases is caused by a helminth?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Filariasis
🟠 (C) Pneumonia
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (B) Filariasis
🔹 Q6. The protozoan disease among the following is:
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
🔹 Q7. Which one is not a sexually transmitted disease?
🔵 (A) Syphilis
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Gonorrhoea
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
🔹 Q8. Which lymphoid organ is the site of T-cell maturation?
🔵 (A) Bone marrow
🟢 (B) Thymus
🟠 (C) Spleen
🔴 (D) Lymph nodes
✔️ Answer: (B) Thymus
🔹 Q9. Which barrier of innate immunity is provided by tears and saliva?
🔵 (A) Physical
🟢 (B) Physiological
🟠 (C) Cellular
🔴 (D) Cytokine
✔️ Answer: (B) Physiological
🔹 Q10. Which is a feature of acquired immunity?
🔵 (A) Present at birth
🟢 (B) Memory and specificity
🟠 (C) Non-specific defense
🔴 (D) No discrimination between self and non-self
✔️ Answer: (B) Memory and specificity
🔹 Q11. Which organ acts as a filter of blood and site for immune response?
🔵 (A) Thymus
🟢 (B) Spleen
🟠 (C) Bone marrow
🔴 (D) Lymph nodes
✔️ Answer: (B) Spleen
🔹 Q12. Which of the following is an example of passive immunity?
🔵 (A) Vaccination
🟢 (B) Mother’s milk to infant
🟠 (C) Natural infection
🔴 (D) Booster dose
✔️ Answer: (B) Mother’s milk to infant
🔹 Q13. Cancer is caused by uncontrolled:
🔵 (A) Cell growth and division
🟢 (B) Cell death
🟠 (C) Differentiation
🔴 (D) Cell migration
✔️ Answer: (A) Cell growth and division
🔹 Q14. Which of the following is not an autoimmune disorder?
🔵 (A) Rheumatoid arthritis
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Myasthenia gravis
🔴 (D) Multiple sclerosis
✔️ Answer: (B) AIDS
🔹 Q15. Which vaccine is used against tuberculosis?
🔵 (A) OPV
🟢 (B) BCG
🟠 (C) MMR
🔴 (D) Hepatitis-B
✔️ Answer: (B) BCG
🔹 Q16. Which of the following is an example of a carcinogen?
🔵 (A) Radiation
🟢 (B) Oncogenic virus
🟠 (C) Chemicals like tobacco
🔴 (D) All of these
✔️ Answer: (D) All of these
🔹 Q17. Which of the following is an opportunistic infection in AIDS patients?
🔵 (A) Tuberculosis
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) Fungal infections
🔴 (D) All of these
✔️ Answer: (D) All of these
🔹 Q18. Which type of immunity is responsible for graft rejection?
🔵 (A) Humoral
🟢 (B) Innate
🟠 (C) Cell-mediated
🔴 (D) Passive
✔️ Answer: (C) Cell-mediated
🔹 Q19. Which disease is characterized by the enlargement of limbs?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Filariasis
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Filariasis
🔹 Q20. Which lymphoid tissue is associated with mucosa of respiratory and digestive tracts?
🔵 (A) MALT
🟢 (B) GALT
🟠 (C) SALT
🔴 (D) All of these
✔️ Answer: (A) MALT
🔹 Q21. Which of the following is not a viral disease?
🔵 (A) AIDS
🟢 (B) Common cold
🟠 (C) Typhoid
🔴 (D) Hepatitis-B
✔️ Answer: (C) Typhoid
🔹 Q22. Helper T-lymphocytes are also called:
🔵 (A) CD8⁺ cells
🟢 (B) CD4⁺ cells
🟠 (C) Plasma cells
🔴 (D) Natural killers
✔️ Answer: (B) CD4⁺ cells
🔹 Q23. Which of the following is a symptom of malaria?
🔵 (A) Swelling of limbs
🟢 (B) Anaemia and fever with chills
🟠 (C) Chronic cough
🔴 (D) Skin rash
✔️ Answer: (B) Anaemia and fever with chills
🔹 Q24. Which of the following is not a lifestyle-related disease?
🔵 (A) Cancer
🟢 (B) Drug addiction
🟠 (C) Pneumonia
🔴 (D) Alcoholism
✔️ Answer: (C) Pneumonia
🔹 Q25. The Widal test is performed for diagnosis of:
🔵 (A) Malaria
🟢 (B) Typhoid
🟠 (C) Pneumonia
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (B) Typhoid
🔹 Q26. Which immune response is antibody-mediated?
🔵 (A) Innate immunity
🟢 (B) Humoral immunity
🟠 (C) Cell-mediated immunity
🔴 (D) Passive immunity
✔️ Answer: (B) Humoral immunity
🔹 Q27. Which cell type is primarily destroyed by HIV?
🔵 (A) CD4⁺ T-lymphocytes
🟢 (B) B-lymphocytes
🟠 (C) RBCs
🔴 (D) Platelets
✔️ Answer: (A) CD4⁺ T-lymphocytes
🔹 Q28. Which disease is not caused by bacteria?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) Pneumonia
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Plague
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
🔹 Q29. Which is not a symptom of malaria?
🔵 (A) Anaemia
🟢 (B) Recurring fever with chills
🟠 (C) Swelling of limbs
🔴 (D) Enlargement of spleen
✔️ Answer: (C) Swelling of limbs
🔹 Q30. Which of the following is an autoimmune disease?
🔵 (A) AIDS
🟢 (B) Rheumatoid arthritis
🟠 (C) Typhoid
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Rheumatoid arthritis
🔹 Q31. Which lymphoid organ produces B-cells?
🔵 (A) Thymus
🟢 (B) Spleen
🟠 (C) Bone marrow
🔴 (D) Lymph nodes
✔️ Answer: (C) Bone marrow
🔹 Q32. Which method is used to confirm cancer?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Biopsy
🟠 (C) Widal test
🔴 (D) Mantoux test
✔️ Answer: (B) Biopsy
🔹 Q33. Which vaccine is used against polio?
🔵 (A) BCG
🟢 (B) OPV
🟠 (C) Hepatitis-B
🔴 (D) MMR
✔️ Answer: (B) OPV
🔹 Q34. Which is a vector-borne disease?
🔵 (A) Typhoid
🟢 (B) AIDS
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) Cancer
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
🔹 Q35. Which immune cells are phagocytic?
🔵 (A) Neutrophils and monocytes
🟢 (B) B-lymphocytes
🟠 (C) Plasma cells
🔴 (D) NK cells
✔️ Answer: (A) Neutrophils and monocytes
🔹 Q36. Which is not a component of innate immunity?
🔵 (A) Skin
🟢 (B) Interferons
🟠 (C) Antibodies
🔴 (D) Phagocytes
✔️ Answer: (C) Antibodies
🔹 Q37. Which lymphoid tissue guards the respiratory and digestive tracts?
🔵 (A) SALT
🟢 (B) MALT
🟠 (C) GALT
🔴 (D) Spleen
✔️ Answer: (B) MALT
🔹 Q38. Which one is not a lifestyle disease?
🔵 (A) Cancer
🟢 (B) Malaria
🟠 (C) Drug abuse
🔴 (D) Alcoholism
✔️ Answer: (B) Malaria
🔹 Q39. Which pathogen causes amoebiasis?
🔵 (A) Plasmodium vivax
🟢 (B) Entamoeba histolytica
🟠 (C) Ascaris lumbricoides
🔴 (D) Wuchereria bancrofti
✔️ Answer: (B) Entamoeba histolytica
🔹 Q40. Which one is not an STD?
🔵 (A) Gonorrhoea
🟢 (B) Syphilis
🟠 (C) Malaria
🔴 (D) AIDS
✔️ Answer: (C) Malaria
🔹 Q41. Which cancer originates in connective tissue?
🔵 (A) Carcinoma
🟢 (B) Sarcoma
🟠 (C) Leukemia
🔴 (D) Lymphoma
✔️ Answer: (B) Sarcoma
🔹 Q42. Which immunity is transferred from mother to foetus through placenta?
🔵 (A) Active
🟢 (B) Passive
🟠 (C) Innate
🔴 (D) Acquired
✔️ Answer: (B) Passive
🔹 Q43. Which is a symptom of ascariasis?
🔵 (A) Abdominal pain and anaemia
🟢 (B) Swelling of limbs
🟠 (C) Cough with blood
🔴 (D) Enlargement of spleen
✔️ Answer: (A) Abdominal pain and anaemia
🔹 Q44. Which organ is affected in tuberculosis?
🔵 (A) Intestine
🟢 (B) Lungs
🟠 (C) Liver
🔴 (D) Brain
✔️ Answer: (B) Lungs
🔹 Q45. Which test is commonly used to detect typhoid?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) Widal test
🟠 (C) PCR
🔴 (D) Mantoux
✔️ Answer: (B) Widal test
🔹 Q46. Which disease is caused by Mycobacterium leprae?
🔵 (A) Tuberculosis
🟢 (B) Leprosy
🟠 (C) Typhoid
🔴 (D) Pneumonia
✔️ Answer: (B) Leprosy
🔹 Q47. Which cells are destroyed during graft rejection?
🔵 (A) CD4⁺ T-cells
🟢 (B) CD8⁺ T-cells
🟠 (C) B-cells
🔴 (D) NK cells
✔️ Answer: (B) CD8⁺ T-cells
🔹 Q48. Which one is not a feature of cancer cells?
🔵 (A) Metastasis
🟢 (B) Loss of contact inhibition
🟠 (C) Controlled cell division
🔴 (D) Formation of tumours
✔️ Answer: (C) Controlled cell division
🔹 Q49. Which immune response involves memory cells?
🔵 (A) Innate
🟢 (B) Acquired
🟠 (C) Passive
🔴 (D) Physiological
✔️ Answer: (B) Acquired
🔹 Q50. Which organism causes kala-azar?
🔵 (A) Leishmania donovani
🟢 (B) Entamoeba histolytica
🟠 (C) Ascaris lumbricoides
🔴 (D) Plasmodium vivax
✔️ Answer: (A) Leishmania donovani
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
