Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 2: Human Reproduction
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌱 Introduction
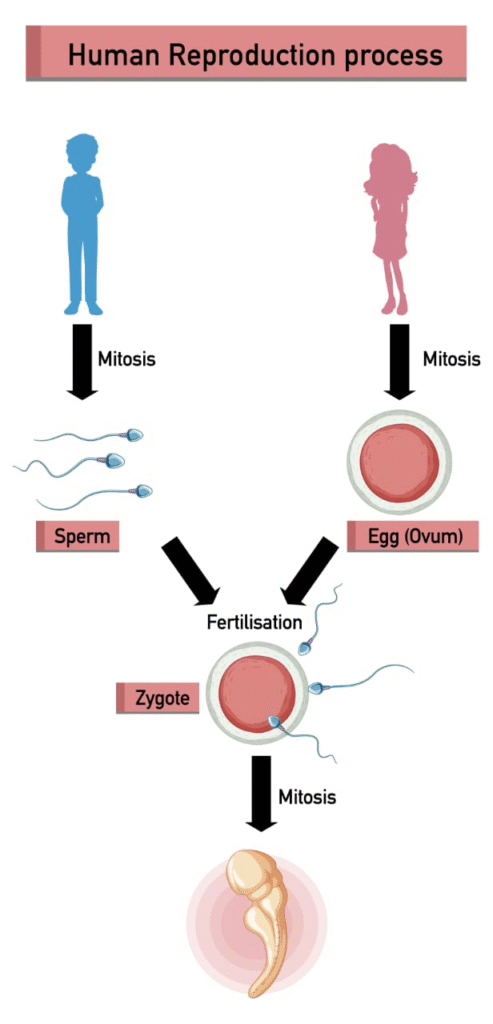
Reproduction is one of the fundamental characteristics of living organisms, ensuring the continuity of species. In humans, it is sexual, involving two parents, and it results in the formation of offspring through the process of gamete fusion (fertilisation), development of the embryo, and birth.
The process of human reproduction can be divided into the following stages: ➤ Gametogenesis
➤ Insemination
➤ Fertilisation
➤ Implantation
➤ Gestation
➤ Parturition
👨 Male Reproductive System
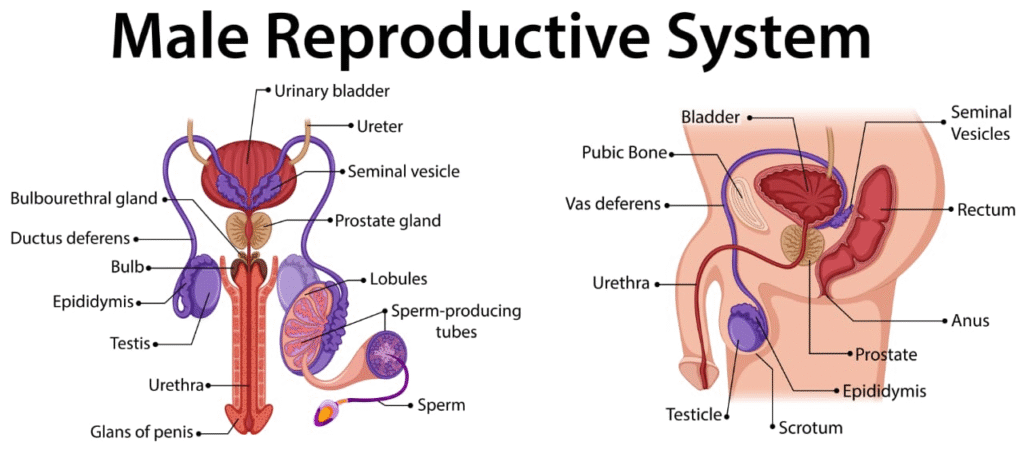
The male reproductive system consists of:
Pair of testes
Reproductive ducts
Accessory glands
External genitalia
Testes:
Each testis is oval-shaped, enclosed in a scrotum which keeps the testes 2–2.5°C below body temperature (necessary for spermatogenesis). Each testis has about 250 compartments called testicular lobules, and each lobule contains 1–3 seminiferous tubules, the site of sperm formation.
Seminiferous Tubules:
These have two types of cells:
Spermatogenic cells – develop into sperm
Sertoli cells – nourish the developing sperms
In between the tubules lie Leydig cells, which secrete androgens (mainly testosterone).
Duct System:
Sperm from seminiferous tubules are transported through: • Rete testis → Vasa efferentia → Epididymis → Vas deferens
Vas deferens unites with the duct of the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct, which opens into the urethra that runs through the penis.
Accessory Glands:
Seminal vesicles (secrete fructose-rich alkaline fluid)
Prostate gland (adds enzymes and calcium)
Bulbourethral glands (secrete mucus for lubrication)
👩 Female Reproductive System
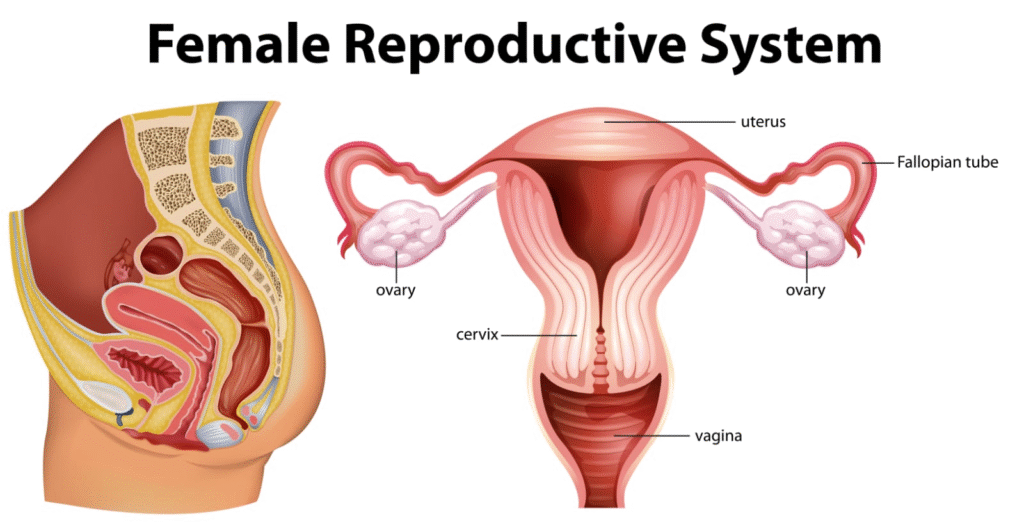
The female reproductive system consists of:
A pair of ovaries
A pair of oviducts (fallopian tubes)
A uterus
A vagina
External genitalia
Ovaries:
Primary female sex organs producing ova and hormones (estrogen, progesterone). Covered by germinal epithelium and divided into cortex and medulla.
Oviducts (Fallopian Tubes):
Each tube is 10–12 cm long and divided into:
Infundibulum with fimbriae to collect ova
Ampulla – site of fertilisation
Isthmus – narrow segment connecting to uterus
Uterus (Womb):
Pear-shaped, thick-walled organ lined with endometrium, muscular myometrium, and outer perimetrium.
Vagina:
Elastic muscular canal that receives the penis during intercourse and serves as the birth canal.
External Genitalia (Vulva):
Includes mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and vaginal orifice.
Mammary Glands:
Modified sweat glands involved in lactation. Composed of lobes, lobules, alveoli (milk-secreting), ducts, and nipple.
🧬 Gametogenesis
🧪 Spermatogenesis:
Occurs in seminiferous tubules
Begins at puberty under hormonal control
Steps:
➤ Spermatogonia (2n) → primary spermatocytes
➤ Primary spermatocyte (2n) → meiosis I → 2 secondary spermatocytes (n)
➤ Meiosis II → 4 spermatids
➤ Spermiogenesis: Spermatids → Sperm
➤ Spermiation: Sperm released into tubule lumen
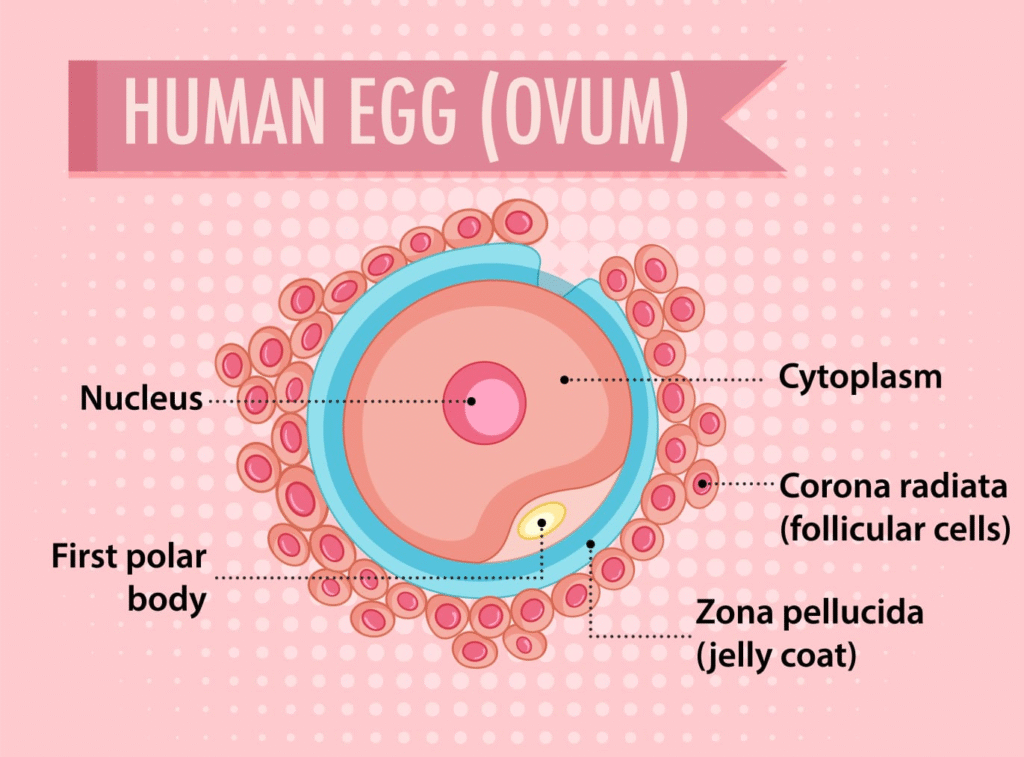
🧪 Oogenesis:
Begins during fetal life
Oogonia (2n) → primary oocytes (arrested in prophase I)
At puberty, one primary oocyte completes meiosis I each cycle
➤ Primary oocyte → secondary oocyte (n) + first polar body
➤ Secondary oocyte is ovulated and arrested in metaphase II
➤ Meiosis II completes only upon fertilisation → ovum + second polar body
💉 Hormonal Control of Gametogenesis
GnRH from hypothalamus → stimulates pituitary
Pituitary secretes:
➤ FSH – acts on Sertoli cells and ovarian follicles
➤ LH – triggers testosterone (in males) and ovulation (in females)
Inhibin (from Sertoli cells) → inhibits FSH
Estrogen & Progesterone → regulate female cycle and pregnancy
🧪 Menstrual Cycle
Cycle of ~28 days in human females.
Phases:
Menstrual Phase (Days 1–5):
Shedding of endometrium if fertilisation does not occur
Follicular Phase (Days 6–13):
FSH stimulates follicle growth; estrogen rebuilds endometrium
Ovulation (Day 14):
LH surge causes ovulation (release of secondary oocyte)
Luteal Phase (Days 15–28):
Corpus luteum secretes progesterone → maintains endometrium
If no fertilisation → corpus luteum degenerates → menstruation begins again
🧬 Fertilisation
Occurs in the ampullary-isthmic junction of fallopian tube.
Process:
Sperm travels through uterus and fallopian tube
Acrosome enzymes help sperm penetrate zona pellucida
Fusion of male and female gametes → zygote (2n)
Meiosis II completes in oocyte only after sperm entry
🌱 Implantation and Pregnancy
Zygote → undergoes cleavage → forms morula → blastocyst
Blastocyst has:
Trophoblast (outer layer) → forms placenta
Inner cell mass → develops into embryo
Implantation:
Blastocyst attaches to endometrium on 7th day post-fertilisation
🌾 Placenta and Embryonic Development
Placenta:
Temporary organ that connects embryo to uterine wall
Exchanges nutrients, gases, waste
Secretes hormones: hCG, hPL, estrogen, progesterone, relaxin
Embryonic Development: • Weeks 1–8: Embryo
After week 8: Fetus
All organs developed by 12 weeks
Movement by ~5 months
Lungs mature by 7th month
Fetus is fully developed by 9th month
🤱 Parturition (Childbirth)
Triggered by: ➤ Fetal hormones (like cortisol)
➤ Oxytocin – stimulates strong uterine contractions
➤ Relaxin – softens cervix
Process involves positive feedback loop: Uterine contraction → oxytocin → stronger contractions → delivery
🍼 Lactation
After parturition, prolactin stimulates milk production
Oxytocin aids in milk ejection or let-down reflex
Milk provides passive immunity to the infant via colostrum (rich in antibodies)
✍️ SUMMARY (~300 Words)
Humans reproduce sexually, involving the fusion of haploid gametes to form a diploid zygote.
The male reproductive system includes testes, ducts, glands, and penis. Spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules. Sertoli cells provide nutrition; Leydig cells secrete testosterone.
The female reproductive system includes ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and mammary glands. Oogenesis begins in fetal life and completes upon fertilisation.
The menstrual cycle (28 days) is regulated by FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone. Ovulation is induced by an LH surge.
Fertilisation occurs in the ampullary-isthmic junction. Sperm penetrates the ovum via acrosomal enzymes, forming a zygote.
The zygote undergoes cleavage to form a blastocyst, which implants into the uterus. This marks the beginning of pregnancy.
The placenta forms from trophoblast cells and enables nutrient/gas exchange. It secretes hormones like hCG, hPL, and progesterone.
The embryo develops into a fetus by the 9th week. Organs develop by 12 weeks, and full fetal development is complete by 9 months.
Parturition is initiated by hormonal signals including oxytocin and relaxin. It involves strong uterine contractions and results in childbirth.
Lactation is controlled by prolactin and oxytocin. Initial milk called colostrum provides immunity to the newborn.
This chapter lays the foundation for understanding reproductive physiology, hormonal control, and human developmental biology.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Humans reproduce sexually
(b) Humans are viviparous
(c) Fertilisation is internal in humans
(d) Male and female gametes are haploid
(e) Zygote is diploid
(f) The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ovulation
(g) Ovulation is induced by a hormone called LH (Luteinising Hormone)
(h) The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilisation
(i) Fertilisation takes place in fallopian tube (oviduct)
(j) Zygote divides to form blastocyst which is implanted in uterus
(k) The structure which provides vascular connection between foetus and uterus is called placenta
Question 2. Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
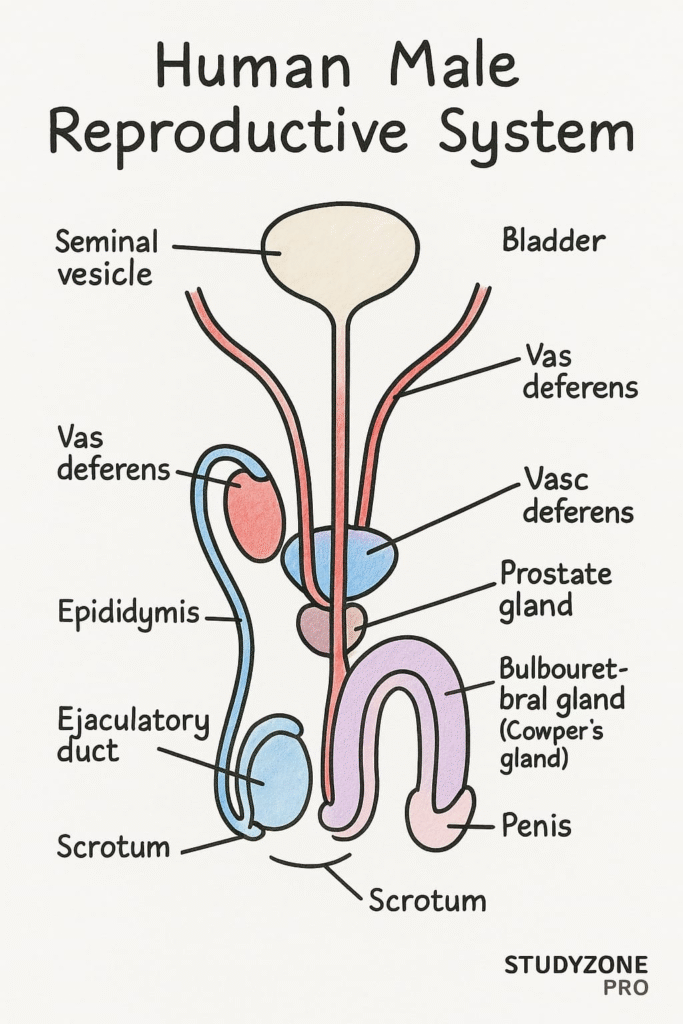
Answer: Please refer to NCERT textbook diagram (Figure 2.1). A proper labelled diagram includes:
Testis
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicle
Prostate gland
Urethra
Penis
Scrotum
Question 3. Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
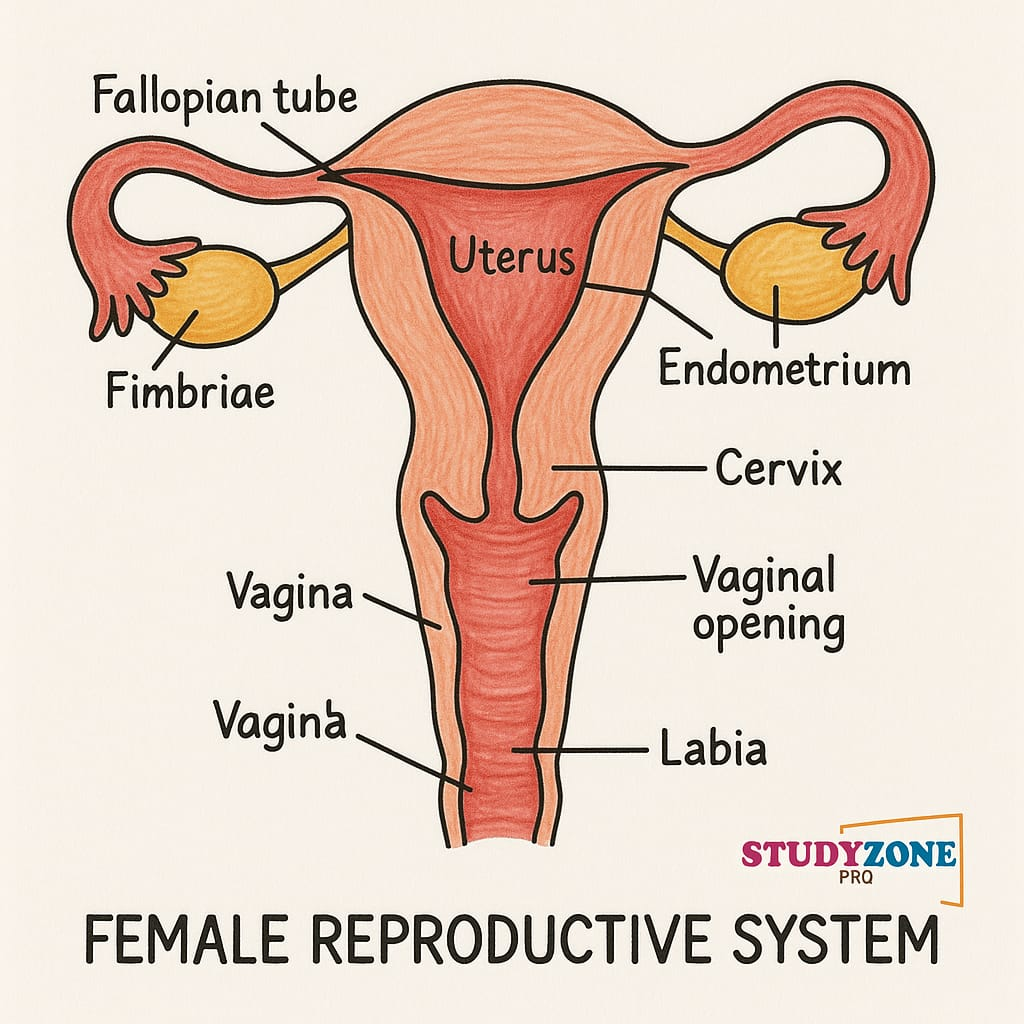
Answer: Please refer to NCERT textbook diagram (Figure 2.2). It should include:
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
Fimbriae
Endometrium
Question 4. Write two major functions each of testis and ovary.
Testis:
Produces male gametes (sperms) through spermatogenesis.
Secretes androgens (mainly testosterone) which regulate male secondary sexual characters and reproductive functions.
Ovary:
Produces female gametes (ova) through oogenesis.
Secretes female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone), which regulate menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Question 5. Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubule.
Answer:
Seminiferous tubules are coiled structures located in the testes, where sperm production occurs.
Structure:
Lined with a germinal epithelium that consists of two types of cells:
Spermatogenic cells – which form sperms in different stages of development.
Sertoli cells – which provide nourishment to developing sperms.
The space between tubules contains Leydig cells (interstitial cells) that produce androgens (testosterone).
Question 6. What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of male gametes (sperms) in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. It occurs in the following stages:
Multiplication phase:
Spermatogonia (diploid, 2n) undergo mitosis to form more spermatogonia. Some grow into primary spermatocytes.
Growth phase:
Primary spermatocytes (2n) grow in size.
Maturation phase:
Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis I to form two secondary spermatocytes (haploid, n).
Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II to form two spermatids (haploid, n).
So, one primary spermatocyte gives rise to four spermatids.
Spermiogenesis:
Spermatids transform into mature spermatozoa (sperms).
Question 7. Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
The hormones regulating spermatogenesis are:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH): Secreted by the hypothalamus; it stimulates the anterior pituitary.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Stimulates Sertoli cells to support spermatogenesis.
Luteinising Hormone (LH): Stimulates Leydig cells to produce androgens (mainly testosterone).
Testosterone: Promotes sperm maturation and development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Inhibin: Secreted by Sertoli cells, it regulates FSH secretion via negative feedback.
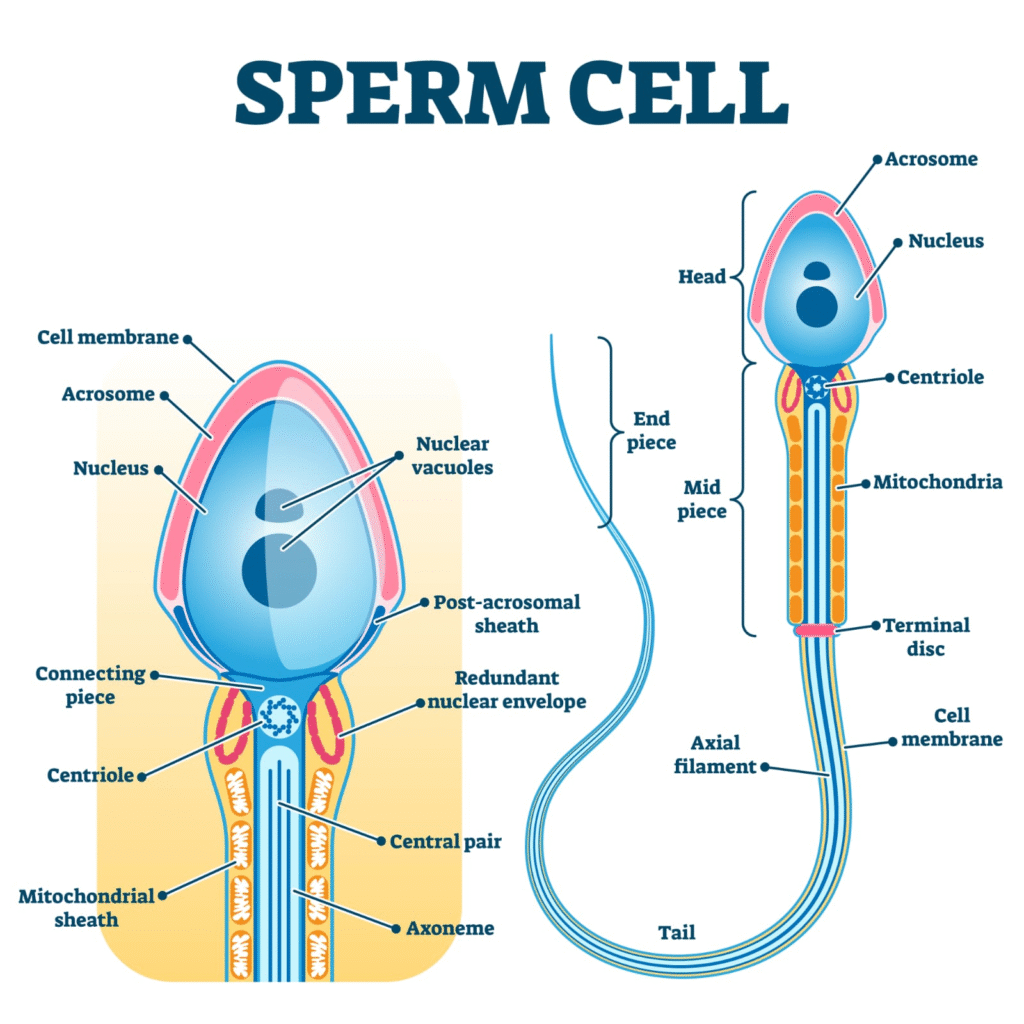
Question 8. Define spermiogenesis and spermiation.Answer:
Spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of non-motile, round spermatids into mature, motile spermatozoa (sperms). This includes development of tail, condensation of nucleus, formation of acrosome, and removal of excess cytoplasm.
Spermiation is the process by which mature spermatozoa are released from the Sertoli cells into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule.
Question 9. Draw a labelled diagram of sperm.
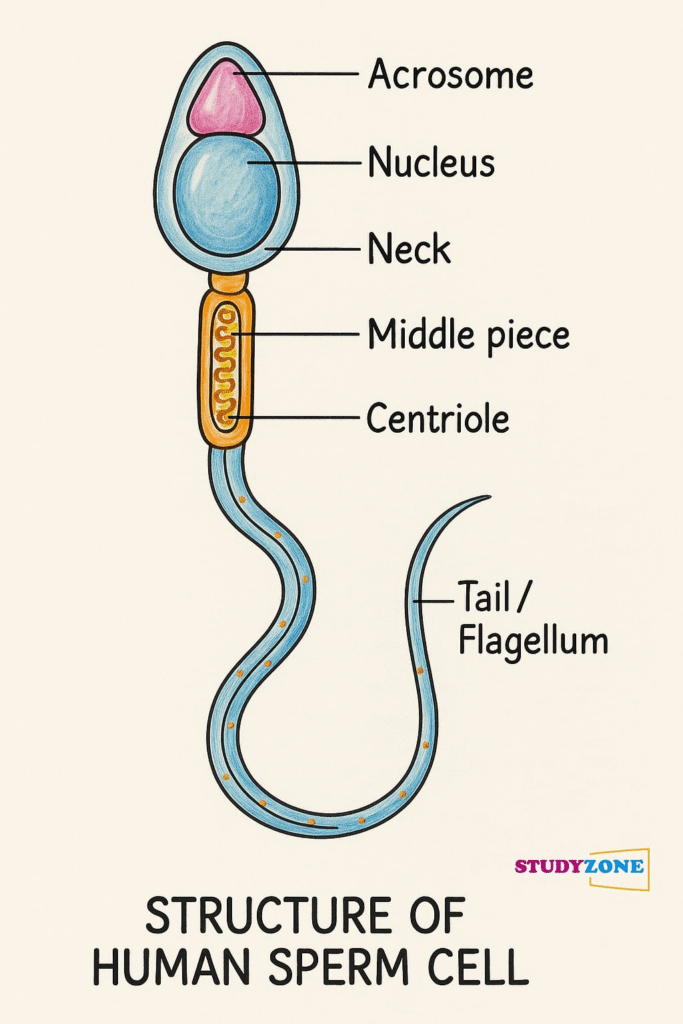
Answer: Refer to NCERT Figure 2.3. Labelled parts include:
Head (nucleus + acrosome)
Neck
Middle piece (with mitochondria)
Tail
Question 10. What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Answer:
Seminal plasma is the fluid part of semen and is rich in:
Fructose – provides energy to sperms.
Calcium and enzymes – help in sperm motility and viability.
Prostaglandins – aid in sperm transport in female reproductive tract.
Buffers – maintain pH for sperm survival.
It is secreted mainly by:
Seminal vesicles (60%)
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Question 11. What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Answer:
Accessory Ducts:
Epididymis: Storage and maturation of sperms.
Vas deferens: Transports sperms from epididymis to urethra.
Ejaculatory duct: Conveys sperms and secretions of glands into urethra.
Accessory Glands:
Seminal vesicles: Secrete fructose-rich alkaline fluid, the main part of semen.
Prostate gland: Adds enzymes and calcium, enhances sperm motility.
Bulbourethral glands: Secrete mucus that lubricates and neutralizes acidic urine traces in urethra.
Question 12. What is oogenesis? Give a brief account of oogenesis.
Answer:
Oogenesis is the process of formation of female gametes (ova) in the ovaries.
Stages:
Foetal Stage:
Oogonia (2n) divide mitotically to form millions of primary oocytes (2n), which begin meiosis I but get arrested in prophase I.
Puberty Onward:
Each menstrual cycle, a few primary oocytes resume meiosis. Only one completes meiosis I to form:
Secondary oocyte (n)
First polar body (n)
Secondary oocyte begins meiosis II but is arrested in metaphase II.
Fertilization:
Meiosis II completes only if sperm fertilizes the ovum, forming:
Ovum (n)
Second polar body (n)
Question 13. Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
Answer: Refer to NCERT Figure 2.4. Diagram should include:
Germinal epithelium
Cortex and medulla
Primary follicle
Secondary follicle
Tertiary follicle
Graafian follicle
Corpus luteum
(Use textbook or biology practical book for accurate drawing.)
Question 14. Draw a labelled diagram of a Graafian follicle.
Answer: Refer to NCERT Figure 2.5. Labels should include:
Secondary oocyte
Zona pellucida
Corona radiata
Antrum
Theca interna and externa
Cumulus oophorus
Follicular cells
(Kindly draw it neatly in your notebook as diagrams are not included here.)
Question 15. Name the functions of the following:(a) Corpus luteum:
Secretes progesterone which maintains the endometrium and supports implantation and early pregnancy.
(b) Endometrium:
Inner lining of the uterus; undergoes cyclic changes and is essential for implantation of the blastocyst.
(c) Acrosome:
Cap-like structure in the sperm head that contains hydrolytic enzymes (like hyaluronidase) to digest the egg coverings during fertilisation.
(d) Sperm tail:
Provides motility to the sperm, enabling it to swim toward the ovum.
(e) Fimbriae:
Finger-like projections at the end of fallopian tubes that help in capturing the ovum released from the ovary.
Question 16. Identify True/False statements. Correct each false statement to make it true.
(a) Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells. – False
Correction: Androgens are produced by Leydig cells, not Sertoli cells.
(b) Spermatozoa get nutrition from Sertoli cells. – True
(c) Leydig cells are found in ovary. – False
Correction: Leydig cells are found in testes, not ovary.
(d) Leydig cells synthesise androgens. – True
(e) Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. – False
Correction: Oogenesis takes place in the ovary, not corpus luteum.
(f) Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. – True
(g) Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. – True
Question 17. What is menstrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Answer:
The menstrual cycle is a series of cyclic changes in the female reproductive system (mainly uterus and ovary) that prepares the body for pregnancy. It usually lasts for 28 days and includes:
Menstrual phase (Days 1–5): Shedding of endometrial lining.
Follicular phase (Days 6–13): Follicle growth and endometrium repair.
Ovulation (Day 14): Release of mature ovum from ovary.
Luteal phase (Days 15–28): Corpus luteum forms and secretes progesterone to maintain endometrium.
Hormones involved:
GnRH from hypothalamus
FSH and LH from anterior pituitary
Estrogen and progesterone from ovary
Question 18. What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Answer:
Parturition is the process of childbirth or delivery of the baby from the uterus at the end of pregnancy.
Hormones involved:
Oxytocin: Secreted by maternal posterior pituitary; induces uterine contractions.
Relaxin: Helps in softening the cervix and relaxation of pelvic ligaments.
Cortisol (from fetus): Matures fetal organs and helps initiate labour.
Estrogens: Promote uterine sensitivity to oxytocin.
(Positive feedback mechanism between uterine contractions and oxytocin secretion.)
Question 19. In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Answer:
This belief is scientifically incorrect and socially unjust. Sex of the child is determined by the type of sperm that fertilizes the ovum:
All ova carry an X chromosome.
Sperms can carry either X or Y chromosome.
If an X-bearing sperm fertilizes the ovum → female (XX)
If a Y-bearing sperm fertilizes the ovum → male (XY)
Thus, it is the male gamete (sperm) that determines the sex of the baby, not the female.
Question 20. How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Answer:
Normally, one egg is released per month.
Identical twins arise from one fertilised egg (zygote) that splits into two embryos. So, only one ovum is released.
Fraternal twins are formed when two separate eggs are fertilised by two different sperms. So, in that case, two ova would have been released.
Question 21. How many eggs do you think were released by the ovary of a female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Answer:
Dogs are polytocous animals (give birth to multiple offspring at once).
To give birth to 6 puppies, the female dog must have released 6 ova, each fertilised by a separate sperm.
Therefore, approximately 6 eggs were released.
.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Q1. In human males, the urethra carries
(A) urine only
(B) semen only
(C) both urine and semen
(D) neither urine nor semen
Answer: (C) both urine and semen
Q2. Which of the following hormones triggers ovulation in human females?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Estrogen
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (B) LH
Q3. In which part of the female reproductive system does fertilisation normally occur?
(A) Vagina
(B) Uterus
(C) Fallopian Tube
(D) Ovary
Answer: (C) Fallopian Tube
Q4. The acrosome of a sperm is derived from which cell organelle?
(A) Nucleus
(B) Mitochondria
(C) Golgi body
(D) Ribosome
Answer: (C) Golgi body
Q5. Identify the correct pair:
(A) Sertoli cells – nutrition to sperm
(B) Leydig cells – produce FSH
(C) Graafian follicle – secretes testosterone
(D) Corpus luteum – produces FSH
Answer: (A) Sertoli cells – nutrition to sperm
Q6. Which layer of the uterus is shed during menstruation?
(A) Perimetrium
(B) Myometrium
(C) Endometrium
(D) Epimetrium
Answer: (C) Endometrium
Q7. Sperm maturation occurs in:
(A) Vas deferens
(B) Epididymis
(C) Ureter
(D) Urethra
Answer: (B) Epididymis
Q8. Menstrual flow occurs due to sudden reduction of which hormones?
(A) LH and FSH
(B) Estrogen and Progesterone
(C) Testosterone and LH
(D) LH and Progesterone
Answer: (B) Estrogen and Progesterone
Q9. Identify the function of the prostate gland:
(A) Produces sperm
(B) Provides nourishment to sperm
(C) Adds fluid for sperm motility
(D) Secretes testosterone
Answer: (C) Adds fluid for sperm motility
Q10. Ovulation typically occurs on which day of a 28-day menstrual cycle?
(A) Day 7
(B) Day 14
(C) Day 21
(D) Day 28
Answer: (B) Day 14
Q11. Number of chromosomes in a secondary oocyte:
(A) 46
(B) 23
(C) 92
(D) 44
Answer: (B) 23
Q12. Which is not a part of the human male reproductive system?
(A) Seminal vesicle
(B) Fallopian tube
(C) Vas deferens
(D) Epididymis
Answer: (B) Fallopian tube
Q13. The entry of sperm induces completion of:
(A) Mitosis
(B) First meiotic division
(C) Second meiotic division
(D) Cleavage
Answer: (C) Second meiotic division
Q14. Assertion (A): Corpus luteum secretes progesterone.
Reason (R): Progesterone helps in maintaining pregnancy.
(A) Both A and R are true; R explains A.
(B) Both A and R are true; R does not explain A.
(C) A is true, R is false.
(D) Both A and R are false.
Answer: (A) Both A and R are true; R explains A.
Q15. Assertion (A): Epididymis helps in the storage and maturation of sperm.
Reason (R): Epididymis secretes testosterone.
(A) Both A and R are true; R explains A.
(B) Both A and R are true; R does not explain A.
(C) A is true, R is false.
(D) Both A and R are false.
Answer: (C) A is true, R is false.
Q16. Identify the odd one out:
(A) Seminiferous tubules
(B) Vas deferens
(C) Prostate gland
(D) Fallopian tube
Answer: (D) Fallopian tube
Q17. Case-Based MCQ:
Read the following and answer:
During the menstrual cycle, the levels of LH peak sharply around mid-cycle, leading to the release of the ovum. The endometrial lining prepares for implantation.
What happens if fertilisation does not occur?
(A) Endometrium remains thick
(B) Progesterone levels rise further
(C) Endometrial lining breaks down
(D) LH remains high
Answer: (C) Endometrial lining breaks down
Q18. Case-Based MCQ:
During spermatogenesis, primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis to form haploid cells.
Which cells result directly from the first meiotic division?
(A) Spermatids
(B) Secondary spermatocytes
(C) Spermatozoa
(D) Spermatogonia
Answer: (B) Secondary spermatocytes
Q19. Write the role of oxytocin during parturition.
Answer:
Oxytocin stimulates strong uterine contractions during parturition (childbirth). These contractions help in the expulsion of the fetus from the uterus through the birth canal.
Q20. How does zona pellucida help in preventing polyspermy?
Answer:
After the first sperm successfully penetrates the zona pellucida, it undergoes chemical changes (zona reaction) which hardens the zona pellucida. This prevents the entry of additional sperms, thus avoiding polyspermy.
Q21. What is colostrum? Mention its significance.
Answer:
Colostrum is the first yellowish milk produced by the mother after childbirth. It is rich in antibodies (mainly IgA) and provides immunity to the newborn against infections.
Q22. How is the sex of a child determined in humans?
Answer:
The sex of a child is determined by the type of sperm that fertilizes the ovum.
Sperm carrying X chromosome → Female child (XX)
Sperm carrying Y chromosome → Male child (XY)
Since females produce only X-bearing eggs, the male determines the sex of the offspring.
Q23. List two major functions of placenta during pregnancy.
Answer:
It facilitates the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between mother and fetus.
It acts as an endocrine organ by secreting hormones like hCG, estrogen, and progesterone to maintain pregnancy.
Q24. Describe the structure of a human sperm with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Structure of Human Sperm:
Head: Contains the nucleus with haploid chromosomes and is covered by the acrosome which contains enzymes for penetrating the egg.
Middle Piece: Contains mitochondria arranged spirally around the axial filament, providing energy for movement.
Tail: Long and slender, helps in the motility of the sperm.
(Labelled diagram should be drawn by student: Head → Middle Piece → Tail with clear parts marked)
Q25. Explain menstrual cycle phases briefly with key hormonal changes.
Answer:
Menstrual Phase (Days 1–5): Endometrium sheds; low levels of estrogen and progesterone.
Follicular Phase (Days 6–13): FSH stimulates follicle growth; estrogen levels rise, endometrium thickens.
Ovulation (Day 14): LH surge causes release of ovum from Graafian follicle.
Luteal Phase (Days 15–28): Corpus luteum forms, secretes progesterone to maintain endometrium.
Q26. Differentiate between spermatogenesis and oogenesis in three points.
Answer:
Feature Spermatogenesis Oogenesis
Site Seminiferous tubules (testes) Ovaries
Time of Initiation Puberty Fetal stage
Final Products 4 functional sperms 1 ovum and 2–3 polar bodies
Q27. Write the names and functions of any three hormones involved in the female reproductive cycle.
Answer:
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone): Stimulates growth of ovarian follicles.
LH (Luteinizing Hormone): Triggers ovulation and formation of corpus luteum.
Progesterone: Prepares and maintains the endometrium for implantation.
Q28. Explain the process of fertilisation in humans.
Answer:
Sperm reaches the ampullary-isthmic junction of the fallopian tube where fertilisation occurs.
Acrosomal enzymes help sperm penetrate corona radiata and zona pellucida.
The sperm and ovum membranes fuse; sperm nucleus enters the ovum.
Meiosis II of ovum completes; male and female pronuclei fuse to form the diploid zygote.
Q29. Case-Based Question:
Read the following carefully and answer the questions below:
In humans, gamete formation is a complex process involving meiosis. Male gametes are produced in large numbers continuously after puberty, whereas female gametes are formed much earlier but complete their development later.
(i) Name the process of gamete formation in males and females.
(ii) Where does each of these processes occur?
(iii) Mention the ploidy of the gametes produced.
(iv) Give one difference between the timing of these processes in males and females.
Answer:
(i) Male: Spermatogenesis; Female: Oogenesis
(ii) Spermatogenesis occurs in seminiferous tubules of testes; Oogenesis occurs in ovaries.
(iii) Gametes produced are haploid (n).
(iv) Spermatogenesis starts at puberty and continues lifelong; Oogenesis starts during fetal development and pauses till puberty, completing only after fertilisation.
Q30. Case-Based Question:
Read the following carefully and answer the questions below:
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones from the pituitary and ovary. Disruptions in hormone levels can disturb the cycle.
(i) Which hormones from the pituitary are involved?
(ii) What are the roles of estrogen and progesterone?
(iii) What happens to the uterine lining if fertilisation does not occur?
(iv) Name the structure that secretes progesterone after ovulation.
Answer:
(i) FSH and LH from the pituitary.
(ii) Estrogen: Thickens endometrium; Progesterone: Maintains it for implantation.
(iii) Uterine lining breaks down, resulting in menstruation.
(iv) Corpus luteum.
Q31. Case-Based Question:
Read the passage and answer the following:
A newly fertilised egg travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus where it implants and starts forming an embryo. Several events occur during this period which ensure proper development.
(i) Name the process of attachment of the embryo to the uterine wall.
(ii) What forms the placenta?
(iii) State any two functions of the placenta.
(iv) Which hormone confirms pregnancy in a woman’s urine?
Answer:
(i) Implantation
(ii) Chorionic villi of the embryo and uterine tissue
(iii) Exchange of nutrients and gases; Secretes hormones like hCG
(iv) hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin)
Q32. Explain the process of spermatogenesis in human males with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Process of Spermatogenesis:
Spermatogonia (2n): Divide by mitosis, some differentiate into primary spermatocytes.
Primary Spermatocytes (2n): Undergo meiosis I to form two secondary spermatocytes (n).
Secondary Spermatocytes (n): Undergo meiosis II to form four spermatids (n).
Spermatids: Differentiate into spermatozoa through spermiogenesis.
Labelled Diagram:
(Seminiferous tubule cross-section showing stages: spermatogonia → primary spermatocyte → secondary spermatocyte → spermatid → spermatozoa.)
Final Products: 4 functional haploid sperm from each primary spermatocyte.
Q33. Describe the role of hormones during pregnancy and parturition.
Answer:
During Pregnancy:
hCG: Maintains corpus luteum, supports progesterone production.
Progesterone: Maintains endometrium, inhibits uterine contractions.
Estrogen: Supports uterine growth, breast development.
hPL (Human Placental Lactogen): Prepares mammary glands, regulates metabolism.
Relaxin: Softens cervix, loosens pelvic ligaments.
During Parturition:
Oxytocin: Stimulates strong uterine contractions for delivery.
Positive feedback loop: Contractions → more oxytocin → stronger contractions.
Progesterone declines; estrogen promotes uterine sensitivity to oxytocin.
Q34. Explain the structure and functions of the human female reproductive system with a neat, labelled diagram.
Answer:
Structure:
Ovaries: Produce ova and hormones (estrogen, progesterone).
Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts): Site of fertilisation; transport ovum.
Uterus: Thick muscular organ for implantation and fetal development.
Cervix: Connects uterus to vagina; controls passage.
Vagina: Birth canal, copulatory organ.
Functions:
Oogenesis, fertilisation, implantation, pregnancy support, parturition.
Diagram: Clearly labelled uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix, vagina.
Q35. Describe the process of oogenesis with neat, labelled stages.
Answer:
Stages of Oogenesis:
Multiplication Phase (Fetal stage): Oogonia (2n) divide mitotically to form primary oocytes (2n).
Growth Phase: Primary oocytes grow in size.
Maturation Phase:
Primary oocyte completes meiosis I → secondary oocyte (n) + first polar body.
Secondary oocyte starts meiosis II, arrested at metaphase II until fertilisation.
On fertilisation, meiosis II completes → ovum (n) + second polar body.
Diagram: Clearly show oogonium → primary oocyte → secondary oocyte → ovum stages.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Human placenta is
(A) Chorioallantoic, non-deciduate
(B) Yolk sac, deciduate
(C) Chorioallantoic, deciduate
(D) Allantochorionic, non-deciduate
Answer: (C) Chorioallantoic, deciduate
Year: 2025 | Set: Z
Q2. In the human female, menstruation is a result of
(A) Breakdown of endometrial lining due to progesterone withdrawal
(B) Increase in FSH and LH
(C) Ovulation
(D) Fertilisation
Answer: (A) Breakdown of endometrial lining due to progesterone withdrawal
Year: 2025 | Set: Q
Q3. Acrosome of sperm is formed by
(A) Centriole
(B) Nucleus
(C) Golgi body
(D) Mitochondria
Answer: (C) Golgi body
Year: 2024 | Set: M
Q4. The function of relaxin hormone is
(A) Stimulates uterine contraction
(B) Softens the cervix and pelvic ligaments during parturition
(C) Maintains corpus luteum
(D) Initiates menstruation
Answer: (B) Softens the cervix and pelvic ligaments during parturition
Year: 2024 | Set: Y
Q5. Implantation of embryo occurs in
(A) Uterus
(B) Fallopian tube
(C) Ovary
(D) Cervix
Answer: (A) Uterus
Year: 2023 | Set: R
Q6. Capacitation of sperms occurs in
(A) Testes
(B) Epididymis
(C) Vagina
(D) Female reproductive tract
Answer: (D) Female reproductive tract
Year: 2023 | Set: S2
Q7. Which layer of the blastocyst facilitates implantation?
(A) Inner cell mass
(B) Trophoblast
(C) Blastocoel
(D) Zona pellucida
Answer: (B) Trophoblast
Year: 2022 | Set: W
Q8. The stage at which the embryo gets implanted in the uterus is
(A) Zygote
(B) Blastocyst
(C) Morula
(D) Gastrula
Answer: (B) Blastocyst
Year: 2022 | Set: Z
Q9. Which hormone is secreted by placenta during pregnancy?
(A) LH
(B) FSH
(C) hCG
(D) Prolactin
Answer: (C) hCG
Year: 2021 | Set: Y
Q10. In humans, fertilisation occurs in
(A) Cervix
(B) Uterus
(C) Vagina
(D) Ampulla of fallopian tube
Answer: (D) Ampulla of fallopian tube
Year: 2021 | Set: Q
Q11. The Leydig cells are found in the
(A) Ovary and secrete estrogen
(B) Testis and secrete testosterone
(C) Pancreas and secrete glucagon
(D) Liver and secrete bile
Answer: (B) Testis and secrete testosterone
Year: 2020 | Set: M
Q12. Function of acrosomal enzymes in sperm is to
(A) Stimulate ovum
(B) Digest corona radiata and zona pellucida
(C) Provide energy
(D) Attract the egg
Answer: (B) Digest corona radiata and zona pellucida
Year: 2020 | Set: S1
Q13. Ovulation in human female occurs around
(A) 14th day of menstrual cycle
(B) 1st day of cycle
(C) 28th day
(D) 7th day
Answer: (A) 14th day of menstrual cycle
Year: 2019 | Set: Z
Q14. Which of the following is responsible for the initiation of parturition?
(A) Placental estrogen
(B) Cortisol from fetal adrenal
(C) Relaxin from mother
(D) Oxytocin from pituitary
Answer: (B) Cortisol from fetal adrenal
Year: 2019 | Set: Q
Q15. In a mature Graafian follicle, the ovum is released from
(A) Primary oocyte
(B) Secondary oocyte
(C) Oogonium
(D) Tertiary oocyte
Answer: (B) Secondary oocyte
Year: 2018 | Set: 2
Q16. Which one of the following is not a function of placenta?
(A) Nutrient supply
(B) Excretion of nitrogenous waste
(C) Secretion of FSH
(D) Hormone production
Answer: (C) Secretion of FSH
Year: 2018 | Set: X
Q17. Acrosome of human sperm contains
(A) Mitochondria
(B) DNA
(C) Ribosomes
(D) Hydrolytic enzymes
Answer: (D) Hydrolytic enzymes
Year: 2017 | Set: Z
Q18. Which hormone ensures implantation of embryo?
(A) Estrogen
(B) Progesterone
(C) Relaxin
(D) Prolactin
Answer: (B) Progesterone
Year: 2017 | Set: P
Q19. The outer layer of blastocyst that attaches to the endometrium is
(A) Inner cell mass
(B) Zona pellucida
(C) Trophoblast
(D) Blastocoel
Answer: (C) Trophoblast
Year: 2016 | Set: Z
Q20. LH surge causes
(A) Growth of follicle
(B) Ovulation
(C) Implantation
(D) Corpus luteum degeneration
Answer: (B) Ovulation
Year: 2016 | Set: Q
Q21. Prolactin hormone is secreted by
(A) Anterior pituitary
(B) Posterior pituitary
(C) Thyroid
(D) Corpus luteum
Answer: (A) Anterior pituitary
Year: 2015 | Set: 1
Q22. Morula is a developmental stage formed
(A) Prior to blastocyst
(B) After implantation
(C) From trophoblast
(D) Before zygote
Answer: (A) Prior to blastocyst
Year: 2015 | Set: M
Q23. Which hormone inhibits FSH and LH during pregnancy?
(A) hCG
(B) Progesterone
(C) Oxytocin
(D) Relaxin
Answer: (B) Progesterone
Year: 2014 | Set: W
Q24. Menstrual flow occurs due to
(A) Increased estrogen
(B) Increased LH
(C) Degeneration of endometrium
(D) Increased progesterone
Answer: (C) Degeneration of endometrium
Year: 2014 | Set: Y
Q25. Capacitation is
(A) Final step of fertilisation
(B) Morphological change in sperm after acrosomal reaction
(C) Functional maturation of sperm in female tract
(D) Increase in sperm motility in epididymis
Answer: (C) Functional maturation of sperm in female tract
Year: 2013 | Set: P
Q26. Which structure in sperm contains mitochondria?
(A) Head
(B) Middle piece
(C) Acrosome
(D) Tail
Answer: (B) Middle piece
Year: 2013 | Set: R
Q27. Which structure in ovary releases ovum?
(A) Primary follicle
(B) Corpus luteum
(C) Graafian follicle
(D) Germinal epithelium
Answer: (C) Graafian follicle
Year: 2012 | Set: Z
Q28. Placenta is formed by
(A) Embryonic and maternal tissues
(B) Only maternal tissue
(C) Only embryonic tissue
(D) Corpus luteum
Answer: (A) Embryonic and maternal tissues
Year: 2012 | Set: S2
Q29. Ovulation occurs due to sudden increase in
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Progesterone
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (B) LH
Year: 2011 | Set: 2
Q30. Which hormone is essential for milk ejection reflex?
(A) Prolactin
(B) Oxytocin
(C) Estrogen
(D) Cortisol
Answer: (B) Oxytocin
Year: 2011 | Set: A
Q31. Inner cell mass of blastocyst gives rise to
(A) Placenta
(B) Embryo
(C) Trophoblast
(D) Umbilical cord
Answer: (B) Embryo
Year: 2010 | Set: M
Q32. Which hormone is absent in non-pregnant females?
(A) hCG
(B) Estrogen
(C) Progesterone
(D) FSH
Answer: (A) hCG
Year: 2010 | Set: Q
Q33. Number of chromosomes in secondary oocyte of human female is
(A) 46
(B) 44
(C) 23
(D) 92
Answer: (C) 23
Year: 2009 | Set: Y
Q34. The first menstruation is known as
(A) Ovulation
(B) Menopause
(C) Menarche
(D) Parturition
Answer: (C) Menarche
Year: 2009 | Set: Z
Q35. The role of inhibin is to
(A) Stimulate ovulation
(B) Inhibit FSH secretion
(C) Increase LH secretion
(D) Promote estrogen secretion
Answer: (B) Inhibit FSH secretion
Year: 2008 | Set: P
Q36. How many spermatozoa are formed from one primary spermatocyte?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Four
(D) Eight
Answer: (C) Four
Year: 2008 | Set: S
Q37. Which among the following is not an event of fertilisation?
(A) Acrosome reaction
(B) Completion of meiosis-II in ovum
(C) Cleavage
(D) Cortical reaction
Answer: (C) Cleavage
Year: 2007 | Set: R
Q38. The entry of sperm induces the completion of
(A) Meiosis-I
(B) Meiosis-II
(C) Mitosis
(D) Fertilisation
Answer: (B) Meiosis-II
Year: 2007 | Set: Q
Q39. Prolactin is responsible for
(A) Milk ejection
(B) Milk production
(C) Ovulation
(D) Uterine contraction
Answer: (B) Milk production
Year: 2006 | Set: Z
Q40. Which of the following provides nourishment to sperms?
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Sertoli cells
(C) Epididymis
(D) Vas deferens
Answer: (B) Sertoli cells
Year: 2006 | Set: X
Q41. Which of the following initiates milk ejection reflex?
(A) Prolactin
(B) Estrogen
(C) Oxytocin
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (C) Oxytocin
Year: 2005 | Set: 2
Q42. The function of Sertoli cells is to
(A) Secrete androgens
(B) Provide nutrition to sperms
(C) Secrete testosterone
(D) Store sperms
Answer: (B) Provide nutrition to sperms
Year: 2005 | Set: W
Q43. Which structure forms the placenta?
(A) Inner cell mass
(B) Embryonic and maternal tissue
(C) Trophoblast only
(D) Endometrium only
Answer: (B) Embryonic and maternal tissue
Year: 2004 | Set: Z
Q44. Which hormone is responsible for growth of endometrium?
(A) LH
(B) Progesterone
(C) Estrogen
(D) hCG
Answer: (C) Estrogen
Year: 2004 | Set: Q
Q45. Ovum is surrounded by
(A) Zona pellucida
(B) Corona radiata
(C) Both A and B
(D) None
Answer: (C) Both A and B
Year: 2003 | Set: M
Q46. Acrosome of sperm contains
(A) DNA
(B) Mitochondria
(C) Enzymes
(D) Centriole
Answer: (C) Enzymes
Year: 2003 | Set: R
Q47. When does crossing over occur in oogenesis?
(A) Zygotene
(B) Pachytene of prophase I
(C) Anaphase
(D) Telophase
Answer: (B) Pachytene of prophase I
Year: 2002 | Set: X
Q48. Which of the following structures in a sperm contains mitochondria?
(A) Head
(B) Neck
(C) Tail
(D) Middle piece
Answer: (D) Middle piece
Year: 2002 | Set: Y
Q49. Which hormone regulates spermatogenesis?
(A) Testosterone only
(B) FSH only
(C) LH only
(D) FSH and LH
Answer: (D) FSH and LH
Year: 2001 | Set: P
Q50. Inner cell mass of blastocyst develops into
(A) Placenta
(B) Fetus
(C) Umbilical cord
(D) Trophoblast
Answer: (B) Fetus
Year: 2001 | Set: Z
Q51. What does morula represent?
(A) Solid ball of cells
(B) Hollow ball
(C) Single-cell zygote
(D) Gastrula
Answer: (A) Solid ball of cells
Year: 2001 | Set: Y
Q52. Function of zona pellucida is
(A) Help sperm entry
(B) Prevent polyspermy
(C) Initiate meiosis
(D) Protect embryo
Answer: (B) Prevent polyspermy
Year: 2025 | Set: X
Q53. What triggers the acrosome reaction in sperm?
(A) Hormonal secretion
(B) Binding to zona pellucida
(C) Change in temperature
(D) Enzyme activation in epididymis
Answer: (B) Binding to zona pellucida
Year: 2024 | Set: R
Q54. Inhibin is secreted by
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Sertoli cells
(C) Hypothalamus
(D) Seminal vesicle
Answer: (B) Sertoli cells
Year: 2023 | Set: S1
Q55. Ovulation occurs when
(A) LH and FSH levels are low
(B) Progesterone is high
(C) Estrogen and LH surge
(D) hCG is released
Answer: (C) Estrogen and LH surge
Year: 2023 | Set: T
Q56. Role of oxytocin in reproduction is
(A) Stimulates follicular growth
(B) Induces labor contractions
(C) Initiates menstruation
(D) Matures oocytes
Answer: (B) Induces labor contractions
Year: 2022 | Set: Z
Q57. Which hormone is directly involved in sperm motility?
(A) FSH
(B) Testosterone
(C) LH
(D) Oxytocin
Answer: (B) Testosterone
Year: 2022 | Set: W
Q58. Sperm capacitation occurs due to
(A) Uterine environment
(B) Changes in epididymis
(C) Enzyme activation in testes
(D) Binding to egg
Answer: (A) Uterine environment
Year: 2021 | Set: X
Q59. Ovulation is induced by
(A) FSH
(B) LH surge
(C) Progesterone
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (B) LH surge
Year: 2021 | Set: S1
Q60. Trophoblast gives rise to
(A) Embryo
(B) Amnion
(C) Placenta
(D) Blastocoel
Answer: (C) Placenta
Year: 2020 | Set: Y
Q61. FSH acts on
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Spermatogonia
(C) Sertoli cells
(D) Epididymis
Answer: (C) Sertoli cells
Year: 2020 | Set: Q
Q62. During pregnancy, which hormone prevents menstruation?
(A) Estrogen
(B) Progesterone
(C) Oxytocin
(D) FSH
Answer: (B) Progesterone
Year: 2019 | Set: W
Q63. Which fetal hormone initiates parturition?
(A) Cortisol
(B) Oxytocin
(C) Prolactin
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (A) Cortisol
Year: 2019 | Set: R
Q64. Function of human placenta:
(A) Hormone secretion
(B) Waste elimination
(C) Nutrition supply
(D) All of the above
Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: 2018 | Set: Z
Q65. Cortical reaction prevents
(A) Fertilisation
(B) Entry of sperm
(C) Polyspermy
(D) Acrosome reaction
Answer: (C) Polyspermy
Year: 2018 | Set: Q
Q66. Prolactin is involved in
(A) Milk secretion
(B) Milk ejection
(C) Ovulation
(D) Fertilisation
Answer: (A) Milk secretion
Year: 2017 | Set: R
Q67. Menstrual cycle ceases during
(A) Menopause
(B) Ovulation
(C) Fertilisation
(D) Pregnancy
Answer: (D) Pregnancy
Year: 2017 | Set: Z
Q68. In females, oogenesis is initiated
(A) After birth
(B) At puberty
(C) During embryonic development
(D) Before ovulation
Answer: (C) During embryonic development
Year: 2016 | Set: Y
Q69. First polar body is formed during
(A) Fertilisation
(B) Meiosis I
(C) Meiosis II
(D) Ovulation
Answer: (B) Meiosis I
Year: 2016 | Set: P
Q70. Number of sperms formed from 100 primary spermatocytes is
(A) 100
(B) 200
(C) 300
(D) 400
Answer: (D) 400
Year: 2015 | Set: Q
Q71. Role of follicle stimulating hormone in males is to
(A) Stimulate testosterone production
(B) Regulate spermatogenesis via Sertoli cells
(C) Stimulate Leydig cells
(D) Promote sperm motility
Answer: (B) Regulate spermatogenesis via Sertoli cells
Year: 2015 | Set: R
Q72. Primary spermatocytes are
(A) Haploid
(B) Diploid
(C) Triploid
(D) Polyploid
Answer: (B) Diploid
Year: 2014 | Set: Z
Q73. The human oocyte is released at what stage of meiosis?
(A) Metaphase I
(B) Prophase II
(C) Metaphase II
(D) Anaphase I
Answer: (C) Metaphase II
Year: 2014 | Set: Y
Q74. Corpus luteum is formed from
(A) Tertiary follicle
(B) Graafian follicle after ovulation
(C) Ovulated ovum
(D) Zona pellucida
Answer: (B) Graafian follicle after ovulation
Year: 2013 | Set: Q
Q75. Hormone responsible for milk ejection is
(A) Estrogen
(B) Prolactin
(C) Oxytocin
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (C) Oxytocin
Year: 2013 | Set: S
Q76. Which of the following is not secreted by the placenta?
(A) hCG
(B) Estrogen
(C) Progesterone
(D) Oxytocin
Answer: (D) Oxytocin
Year: 2012 | Set: M
Q77. The mitochondria in sperm are located in the
(A) Head
(B) Tail
(C) Acrosome
(D) Middle piece
Answer: (D) Middle piece
Year: 2012 | Set: N
Q78. Which part of sperm is responsible for egg penetration?
(A) Tail
(B) Head
(C) Acrosome
(D) Middle piece
Answer: (C) Acrosome
Year: 2011 | Set: A
Q79. The hormone which facilitates implantation is
(A) Estrogen
(B) Oxytocin
(C) Progesterone
(D) FSH
Answer: (C) Progesterone
Year: 2011 | Set: Z
Q80. Which hormone maintains pregnancy?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Estrogen
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (D) Progesterone
Year: 2010 | Set: M
Q81. Graafian follicle ruptures during
(A) Ovulation
(B) Fertilisation
(C) Implantation
(D) Cleavage
Answer: (A) Ovulation
Year: 2010 | Set: Y
Q82. Which hormone is absent in non-pregnant females but present during pregnancy?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) hCG
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (C) hCG
Year: 2009 | Set: R
Q83. Which hormone suppresses FSH and LH during pregnancy?
(A) Progesterone
(B) Estrogen
(C) hCG
(D) Relaxin
Answer: (A) Progesterone
Year: 2009 | Set: T
Q84. Function of cortical granules after fertilisation is
(A) Trigger meiosis
(B) Prevent polyspermy
(C) Stimulate cleavage
(D) Form trophoblast
Answer: (B) Prevent polyspermy
Year: 2008 | Set: Q
Q85. Parturition is initiated by
(A) hCG
(B) Oxytocin from fetus
(C) Cortisol from fetal adrenal
(D) Progesterone drop
Answer: (C) Cortisol from fetal adrenal
Year: 2008 | Set: M
Q86. Which hormone is not secreted by anterior pituitary?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Prolactin
(D) hCG
Answer: (D) hCG
Year: 2007 | Set: P
Q87. Completion of meiosis-II in human ovum occurs
(A) After ovulation
(B) After fertilisation
(C) Before ovulation
(D) Before menstruation
Answer: (B) After fertilisation
Year: 2007 | Set: R
Q88. Umbilical cord connects
(A) Embryo and placenta
(B) Ovary and uterus
(C) Fetus and mother directly
(D) Endometrium and amnion
Answer: (A) Embryo and placenta
Year: 2006 | Set: S
Q89. Graafian follicle is present in
(A) Uterus
(B) Cervix
(C) Ovary
(D) Fallopian tube
Answer: (C) Ovary
Year: 2006 | Set: Q
Q90. Meiosis II is completed in human ovum at
(A) Ovulation
(B) Fertilisation
(C) Menstruation
(D) Follicle rupture
Answer: (B) Fertilisation
Year: 2005 | Set: M
Q91. Which of the following induces formation of corpus luteum?
(A) Estrogen
(B) LH
(C) FSH
(D) hCG
Answer: (B) LH
Year: 2005 | Set: Y
Q92. Colostrum is rich in
(A) Vitamin D
(B) Iron
(C) Antibodies
(D) Protein only
Answer: (C) Antibodies
Year: 2004 | Set: W
Q93. The zona pellucida is
(A) Innermost egg membrane
(B) Thick glycoprotein layer
(C) Seminal covering
(D) Layer in endometrium
Answer: (B) Thick glycoprotein layer
Year: 2004 | Set: Q
Q94. Function of estrogen in menstrual cycle is
(A) Thickening of endometrium
(B) Ovulation
(C) Shedding of endometrium
(D) Degeneration of corpus luteum
Answer: (A) Thickening of endometrium
Year: 2003 | Set: Z
Q95. Human sperm contains
(A) 46 chromosomes
(B) 23 chromosomes
(C) 22 chromosomes
(D) 24 chromosomes
Answer: (B) 23 chromosomes
Year: 2003 | Set: X
Q96. Ovulation is directly triggered by
(A) Progesterone
(B) LH surge
(C) FSH
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (B) LH surge
Year: 2002 | Set: M
Q97. Progesterone is secreted by
(A) Follicle
(B) Graafian follicle
(C) Corpus luteum
(D) Endometrium
Answer: (C) Corpus luteum
Year: 2002 | Set: Y
Q98. The process of sperm release is
(A) Spermatogenesis
(B) Spermiogenesis
(C) Spermiation
(D) Capacitation
Answer: (C) Spermiation
Year: 2001 | Set: R
Q99. Which of the following regulates menstrual cycle?
(A) GnRH
(B) FSH
(C) LH
(D) All of the above
Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: 2001 | Set: Q
Q100. Fertilisation in humans normally occurs in
(A) Ovary
(B) Uterus
(C) Ampulla of fallopian tube
(D) Cervix
Answer: (C) Ampulla of fallopian tube
Year: 2001 | Set: P
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which structure in the sperm is responsible for penetration through the zona pellucida of the ovum?
(A) Head
(B) Acrosome
(C) Middle piece
(D) Tail
Answer: (B) Acrosome
Q2. Which hormone is secreted by the Sertoli cells that helps regulate spermatogenesis?
(A) Testosterone
(B) Inhibin
(C) LH
(D) Estrogen
Answer: (B) Inhibin
Q3. In the human female, meiosis II in the ovum is completed
(A) At the time of fertilisation
(B) During ovulation
(C) Just before menstruation
(D) During implantation
Answer: (A) At the time of fertilisation
Q4. The process by which spermatids transform into mature spermatozoa is called
(A) Spermatogenesis
(B) Spermiogenesis
(C) Spermiation
(D) Capacitation
Answer: (B) Spermiogenesis
Q5. Which part of the blastocyst is responsible for forming the embryo?
(A) Trophoblast
(B) Blastocoel
(C) Inner cell mass
(D) Zona pellucida
Answer: (C) Inner cell mass
Q6. Ovulation is triggered by a sudden surge in the level of
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Estrogen
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (B) LH
Q7. Which of the following provides nutrition to the developing sperm cells in the seminiferous tubules?
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Sertoli cells
(C) Spermatogonia
(D) Rete testis
Answer: (B) Sertoli cells
Q8. Which stage of the embryo gets implanted into the uterus?
(A) Zygote
(B) Morula
(C) Blastocyst
(D) Gastrula
Answer: (C) Blastocyst
Q9. Which hormone is secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) hCG
(D) Oxytocin
Answer: (C) hCG
Q10. Which of the following structures releases the ovum during ovulation?
(A) Corpus luteum
(B) Primary follicle
(C) Graafian follicle
(D) Oogonium
Answer: (C) Graafian follicle
Q11. The main function of the middle piece of a sperm is to
(A) Carry genetic material
(B) Secrete enzymes
(C) Generate energy for motility
(D) Penetrate the egg membrane
Answer: (C) Generate energy for motility
Q12. Which cells secrete androgens in the male reproductive system?
(A) Spermatogonia
(B) Sertoli cells
(C) Leydig cells
(D) Epididymal cells
Answer: (C) Leydig cells
Q13. Fertilisation in humans occurs in
(A) Uterus
(B) Cervix
(C) Fallopian tube
(D) Ovary
Answer: (C) Fallopian tube
Q14. What prevents polyspermy in humans after the sperm enters the ovum?
(A) Zona pellucida thickening
(B) Cortical reaction
(C) Release of hCG
(D) Activation of mitochondria
Answer: (B) Cortical reaction
Q15. The layer that lines the uterus and undergoes cyclic changes during the menstrual cycle is
(A) Myometrium
(B) Perimetrium
(C) Endometrium
(D) Epimetrium
Answer: (C) Endometrium
Q16. Menarche refers to
(A) First ovulation
(B) First menstruation
(C) Last ovulation
(D) Menstrual pain
Answer: (B) First menstruation
Q17. Capacitation of sperm takes place in the
(A) Epididymis
(B) Vas deferens
(C) Female reproductive tract
(D) Seminal vesicle
Answer: (C) Female reproductive tract
Q18. The hormone primarily responsible for maintenance of the endometrium during the luteal phase is
(A) Estrogen
(B) FSH
(C) LH
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (D) Progesterone
Q19. The function of fimbriae in the fallopian tube is to
(A) Transport sperm
(B) Attach embryo to uterus
(C) Capture the ovum after ovulation
(D) Stimulate hormone production
Answer: (C) Capture the ovum after ovulation
Q20. The corpus luteum secretes
(A) Estrogen
(B) Progesterone
(C) FSH
(D) hCG
Answer: (B) Progesterone
Q21. Which of the following marks the beginning of pregnancy?
(A) Ovulation
(B) Fertilisation
(C) Implantation
(D) Meiosis
Answer: (C) Implantation
Q22. Which part of the sperm carries the genetic material?
(A) Tail
(B) Acrosome
(C) Head
(D) Middle piece
Answer: (C) Head
Q23. What prevents menstruation during pregnancy?
(A) Low LH
(B) Increased FSH
(C) High estrogen and progesterone
(D) hPL secretion
Answer: (C) High estrogen and progesterone
Q24. The hormone oxytocin is released from the
(A) Anterior pituitary
(B) Posterior pituitary
(C) Ovary
(D) Placenta
Answer: (B) Posterior pituitary
Q25. Which of the following is not part of the female external genitalia?
(A) Clitoris
(B) Labia majora
(C) Cervix
(D) Mons pubis
Answer: (C) Cervix
Q26. Human sperms are
(A) Diploid
(B) Triploid
(C) Tetraploid
(D) Haploid
Answer: (D) Haploid
Q27. The structure that helps in the formation of the placenta is
(A) Inner cell mass
(B) Zona pellucida
(C) Trophoblast
(D) Morula
Answer: (C) Trophoblast
Q28. Which of the following events occurs in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
(A) Ovulation
(B) Endometrial shedding
(C) Corpus luteum formation
(D) LH surge
Answer: (C) Corpus luteum formation
Q29. The first step in the process of fertilisation is
(A) Cortical reaction
(B) Sperm capacitation
(C) Zygote formation
(D) Implantation
Answer: (B) Sperm capacitation
Q30. What is the function of hCG during early pregnancy?
(A) Stimulate mammary glands
(B) Induce parturition
(C) Maintain corpus luteum
(D) Induce ovulation
Answer: (C) Maintain corpus luteum
Q31. In which part of the testis does spermatogenesis occur?
(A) Vas deferens
(B) Epididymis
(C) Rete testis
(D) Seminiferous tubules
Answer: (D) Seminiferous tubules
Q32. Colostrum is rich in
(A) Carbohydrates
(B) Fats
(C) Antibodies
(D) Enzymes
Answer: (C) Antibodies
Q33. Menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones secreted from
(A) Ovary only
(B) Hypothalamus, pituitary, and ovary
(C) Pituitary only
(D) Uterus only
Answer: (B) Hypothalamus, pituitary, and ovary
Q34. Which hormone promotes the development of secondary sexual characters in males?
(A) Progesterone
(B) Estrogen
(C) Testosterone
(D) FSH
Answer: (C) Testosterone
Q35. If fertilisation does not occur, the levels of which hormone(s) fall, leading to menstruation?
(A) FSH and LH
(B) Estrogen and Progesterone
(C) hCG and Progesterone
(D) Oxytocin and FSH
Answer: (B) Estrogen and Progesterone
Q36. Select the correct hormonal pathway initiating spermatogenesis in a young male:
(A) LH → Leydig cells → Testosterone → Sertoli cells
(B) FSH → Leydig cells → Progesterone
(C) hCG → Sertoli cells → Testosterone
(D) Estrogen → FSH → Leydig cells
Answer: (A) LH → Leydig cells → Testosterone → Sertoli cells
Q37. Which of the following sequences is correct in embryonic development?
(A) Zygote → Blastula → Morula → Gastrula
(B) Zygote → Morula → Blastocyst → Gastrula
(C) Morula → Zygote → Gastrula → Blastula
(D) Zygote → Blastocyst → Morula → Embryo
Answer: (B) Zygote → Morula → Blastocyst → Gastrula
Q38. Which combination of cells controls oogenesis and ovulation in the ovary?
(A) Theca interna and theca externa
(B) Graafian follicle and corpus luteum
(C) Primary follicle and secondary oocyte
(D) Leydig cells and Sertoli cells
Answer: (B) Graafian follicle and corpus luteum
Q39. In humans, implantation occurs approximately how many days after fertilisation?
(A) 1–2 days
(B) 3–4 days
(C) 5–6 days
(D) 9–10 days
Answer: (C) 5–6 days
Q40. Inhibin and testosterone together regulate spermatogenesis through feedback to
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
(C) Seminiferous tubules
(D) Epididymis
Answer: (B) Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
Q41. Ovum is released from ovary in which meiotic stage?
(A) Prophase I
(B) Metaphase II
(C) Anaphase I
(D) Telophase II
Answer: (B) Metaphase II
Q42. After how many meiotic divisions do spermatogonia form mature sperm?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four
Answer: (B) Two
Q43. Match the following:
Acrosome → a. Energy
Mitochondria → b. Fertilisation
Nucleus → c. Hydrolytic enzymes
Tail → d. Genetic material
(A) 1–c, 2–a, 3–d, 4–b
(B) 1–a, 2–b, 3–c, 4–d
(C) 1–c, 2–b, 3–a, 4–d
(D) 1–d, 2–c, 3–b, 4–a
Answer: (A) 1–c, 2–a, 3–d, 4–b
Q44. The hormone responsible for the proliferation of endometrium is
(A) Progesterone
(B) FSH
(C) Estrogen
(D) LH
Answer: (C) Estrogen
Q45. Which part of the blastocyst comes in direct contact with the endometrium?
(A) Inner cell mass
(B) Zona pellucida
(C) Trophoblast
(D) Blastocoel
Answer: (C) Trophoblast
Q46. Absence of menstruation during pregnancy is due to
(A) Constant high levels of FSH
(B) Drop in LH
(C) High levels of hCG, estrogen, and progesterone
(D) Continuous ovulation
Answer: (C) High levels of hCG, estrogen, and progesterone
Q47. During fertilisation, fusion of gametes leads to
(A) Increase in chromosome number to 92
(B) Diploid zygote with 46 chromosomes
(C) Haploid zygote
(D) Four polar bodies
Answer: (B) Diploid zygote with 46 chromosomes
Q48. Which statement about corpus luteum is correct?
(A) Degenerates before ovulation
(B) Secretes estrogen and FSH
(C) Secretes progesterone
(D) Active throughout pregnancy
Answer: (C) Secretes progesterone
Q49. Select the correct statement regarding hormones and pregnancy:
(A) FSH is essential for embryo development
(B) Progesterone is not required after fertilisation
(C) hCG maintains corpus luteum in early pregnancy
(D) LH remains high throughout gestation
Answer: (C) hCG maintains corpus luteum in early pregnancy
Q50. If the secondary oocyte is not fertilised, it
(A) Becomes a zygote
(B) Undergoes mitosis
(C) Degenerates within 24 hours
(D) Forms a corpus luteum
Answer: (C) Degenerates within 24 hours
Q51. Which hormone peaks just before ovulation and triggers its occurrence?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Estrogen
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (B) LH
Q52. Spermiation refers to
(A) Fusion of sperm and ovum
(B) Release of sperm from Sertoli cells
(C) Formation of sperm from spermatids
(D) Capacitation of sperm
Answer: (B) Release of sperm from Sertoli cells
Q53. The female reproductive system develops from
(A) Mesodermal Müllerian ducts
(B) Ectodermal grooves
(C) Yolk sac derivatives
(D) Endodermal invaginations
Answer: (A) Mesodermal Müllerian ducts
Q54. hPL secreted by the placenta
(A) Stimulates milk ejection
(B) Prepares mammary glands for lactation
(C) Induces ovulation
(D) Causes uterine contraction
Answer: (B) Prepares mammary glands for lactation
Q55. The duration of a typical menstrual cycle is approximately
(A) 20 days
(B) 24 days
(C) 28 days
(D) 35 days
Answer: (C) 28 days
Q56. The first mitotic division in the zygote is called
(A) Meiosis
(B) Cleavage
(C) Ovulation
(D) Implantation
Answer: (B) Cleavage
Q57. The hormone that directly supports implantation is
(A) FSH
(B) hCG
(C) Progesterone
(D) Oxytocin
Answer: (C) Progesterone
Q58. Which hormone causes contraction of the smooth muscles during parturition?
(A) Prolactin
(B) Estrogen
(C) Oxytocin
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (C) Oxytocin
Q59. Which of the following cells is arrested in prophase I until puberty?
(A) Primary spermatocyte
(B) Primary oocyte
(C) Secondary oocyte
(D) Oogonium
Answer: (B) Primary oocyte
Q60. The correct path of sperm in male reproductive tract is
(A) Testis → Epididymis → Urethra → Vas deferens
(B) Epididymis → Testis → Vas deferens → Urethra
(C) Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Urethra
(D) Vas deferens → Epididymis → Urethra → Testis
Answer: (C) Seminiferous tubules → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Urethra
Q61. Estrogen level is highest during
(A) Menstrual phase
(B) Follicular phase
(C) Luteal phase
(D) Ovulation
Answer: (D) Ovulation
Q62. Which gland contributes the most volume to semen?
(A) Prostate gland
(B) Bulbourethral gland
(C) Seminal vesicle
(D) Cowper’s gland
Answer: (C) Seminal vesicle
Q63. Which of the following correctly describes colostrum?
(A) Fluid from follicle
(B) Thick yellow milk rich in antibodies
(C) Placental discharge
(D) Menstrual fluid
Answer: (B) Thick yellow milk rich in antibodies
Q64. Which of the following is not true about trophoblast?
(A) Forms inner cell mass
(B) Attaches to uterine wall
(C) Helps in placenta formation
(D) Secretes hCG
Answer: (A) Forms inner cell mass
Q65. Duration of pregnancy in humans is approximately
(A) 210 days
(B) 270 days
(C) 280 days
(D) 300 days
Answer: (C) 280 days
Q66. The presence of which hormone in urine confirms pregnancy?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) hCG
(D) Progesterone
Answer: (C) hCG
Q67. The blood-placenta barrier is responsible for
(A) Mixing of maternal and fetal blood
(B) Nutrient exchange without blood mixing
(C) Preventing fertilisation
(D) Formation of amniotic fluid
Answer: (B) Nutrient exchange without blood mixing
Q68. A female undergoing IVF treatment produces multiple secondary oocytes. Each is artificially fertilised and transferred to different surrogate mothers. Two surrogates deliver genetically identical babies. Which conclusion is correct?
(A) Only one oocyte was used and split post-fertilisation
(B) Both oocytes had same genotype
(C) All zygotes were from different oocytes
(D) None underwent cleavage
Answer: (A) Only one oocyte was used and split post-fertilisation
Q69. In a female with inactive corpus luteum post-ovulation, which event is most likely?
(A) Implantation
(B) Progesterone surge
(C) Menstruation
(D) Prolactin release
Answer: (C) Menstruation
Q70. During spermatogenesis, a diploid cell undergoes two successive meiotic divisions. If 100 such cells initiate meiosis I, how many total spermatids will be produced?
(A) 100
(B) 200
(C) 300
(D) 400
Answer: (D) 400
Q71. In a female with defective LH surge, what will most likely fail?
(A) Menstruation
(B) Estrogen production
(C) Ovulation
(D) Graafian follicle formation
Answer: (C) Ovulation
Q72. Which combination of events will prevent pregnancy even if fertilisation occurs?
(A) No ovulation and low FSH
(B) No hCG and early degeneration of corpus luteum
(C) High estrogen and sustained FSH
(D) High oxytocin and low progesterone
Answer: (B) No hCG and early degeneration of corpus luteum
Q73. Zona pellucida is removed experimentally from a human ovum. Which process will fail?
(A) Sperm binding
(B) Ovulation
(C) Meiosis II
(D) Cortical reaction
Answer: (A) Sperm binding
Q74. In a patient, Sertoli cells are non-functional but Leydig cells are intact. Which will most likely occur?
(A) Normal testosterone, impaired spermatogenesis
(B) No testosterone and no sperm
(C) Excess LH secretion
(D) Enhanced FSH activity
Answer: (A) Normal testosterone, impaired spermatogenesis
Q75. After fertilisation, the diploid zygote undergoes successive mitotic divisions. At 16-cell stage, the embryo is termed
(A) Zygote
(B) Morula
(C) Blastocyst
(D) Gastrula
Answer: (B) Morula
Q76. A defect in the trophoblast layer during implantation can affect:
(A) Inner cell mass differentiation
(B) Corpus luteum activity
(C) Placenta formation
(D) Zona pellucida dissolution
Answer: (C) Placenta formation
Q77. The Graafian follicle transforms into the corpus luteum only if
(A) Meiosis II is completed
(B) Estrogen remains low
(C) LH surge occurs
(D) Endometrium detaches
Answer: (C) LH surge occurs
Q78. Which hormone provides negative feedback to inhibit FSH secretion during late follicular phase?
(A) Estrogen
(B) Progesterone
(C) LH
(D) hCG
Answer: (A) Estrogen
Q79. Which cell type will increase in number due to continuous stimulation by FSH?
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Spermatogonia
(C) Sertoli cells
(D) Spermatozoa
Answer: (D) Spermatozoa
Q80. A mutation prevents formation of acrosomal enzymes. What will fail during reproduction?
(A) Entry of sperm into oviduct
(B) Ovum release
(C) Penetration through zona pellucida
(D) Sperm motility
Answer: (C) Penetration through zona pellucida
Q81. If primary oocytes fail to arrest in prophase I during fetal development, the female will:
(A) Have premature menopause
(B) Not form any ova
(C) Continue menstruation without fertility
(D) Have multiple ovulations
Answer: (B) Not form any ova
Q82. Which hormonal condition is essential to maintain pregnancy in the first trimester?
(A) High FSH and LH
(B) High hCG, progesterone and estrogen
(C) Low progesterone and low estrogen
(D) High oxytocin and low hCG
Answer: (B) High hCG, progesterone and estrogen
Q83. If oxytocin is inhibited in a full-term pregnant female, the likely result is:
(A) Immediate labor
(B) Premature birth
(C) Delay or failure in parturition
(D) Defective placenta
Answer: (C) Delay or failure in parturition
Q84. Which event initiates a positive feedback mechanism during childbirth?
(A) Uterine relaxation
(B) Cervical dilation
(C) Placental separation
(D) Progesterone withdrawal
Answer: (B) Cervical dilation
Q85. Secondary oocyte formation is directly triggered by:
(A) hCG
(B) Estrogen
(C) LH
(D) FSH
Answer: (C) LH
Q86. A human embryo implants into the uterus. Which layer of the uterus is responsible for its nourishment initially?
(A) Myometrium
(B) Endometrium
(C) Perimetrium
(D) Chorion
Answer: (B) Endometrium
Q87. Which of the following is not secreted by the placenta?
(A) Progesterone
(B) Oxytocin
(C) hCG
(D) hPL
Answer: (B) Oxytocin
Q88. A sudden drop in hCG levels during early pregnancy indicates
(A) Healthy pregnancy
(B) Start of implantation
(C) Corpus luteum activation
(D) Possible miscarriage
Answer: (D) Possible miscarriage
Q89. In vitro fertilisation leads to formation of a blastocyst in the lab. The embryo is ready for transfer into the uterus after
(A) Ovulation
(B) Fertilisation
(C) Cleavage
(D) Implantation
Answer: (C) Cleavage
Q90. Fertilisation restores the diploid number because
(A) Ovum is diploid
(B) Sperm contributes one haploid set
(C) Both gametes are tetraploid
(D) Ovum and sperm are already diploid
Answer: (B) Sperm contributes one haploid set
Q91. If zona pellucida is prematurely lost, what may happen?
(A) Delayed cleavage
(B) Polyspermy
(C) Implantation in oviduct
(D) No sperm binding
Answer: (B) Polyspermy
Q92. Which is most critical for successful embryo implantation?
(A) Functional fimbriae
(B) Capacitated sperm
(C) Receptive endometrium
(D) Active oxytocin
Answer: (C) Receptive endometrium
Q93. Which gene is expressed for testis formation in male embryo?
(A) TDF
(B) FSH
(C) SRY
(D) HOX
Answer: (C) SRY
Q94. The chromosomal makeup of a secondary oocyte in a human is:
(A) 46 chromosomes, diploid
(B) 23 chromosomes, haploid
(C) 23 chromosomes, diploid
(D) 22 chromosomes, haploid
Answer: (B) 23 chromosomes, haploid
Q95. Which of the following stages is arrested in oocytes of newborn girls?
(A) Metaphase II
(B) Telophase I
(C) Prophase I
(D) Anaphase II
Answer: (C) Prophase I
Q96. Which part of sperm provides motility using ATP?
(A) Tail
(B) Acrosome
(C) Head
(D) Middle piece
Answer: (D) Middle piece
Q97. Which hormone ensures maintenance of endometrium after implantation?
(A) FSH
(B) LH
(C) Progesterone
(D) Oxytocin
Answer: (C) Progesterone
Q98. The correct descending order of stages after fertilisation is:
(A) Zygote → Blastocyst → Morula → Embryo
(B) Morula → Zygote → Blastocyst → Embryo
(C) Zygote → Morula → Blastocyst → Embryo
(D) Zygote → Embryo → Blastula → Morula
Answer: (C) Zygote → Morula → Blastocyst → Embryo
Q99. Which organ shows positive feedback regulation during parturition?
(A) Pituitary gland
(B) Uterus
(C) Placenta
(D) Ovary
Answer: (B) Uterus
Q100. Which maternal hormone level sharply rises to initiate parturition?
(A) Estrogen
(B) Progesterone
(C) Oxytocin
(D) hCG
Answer: (C) Oxytocin
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
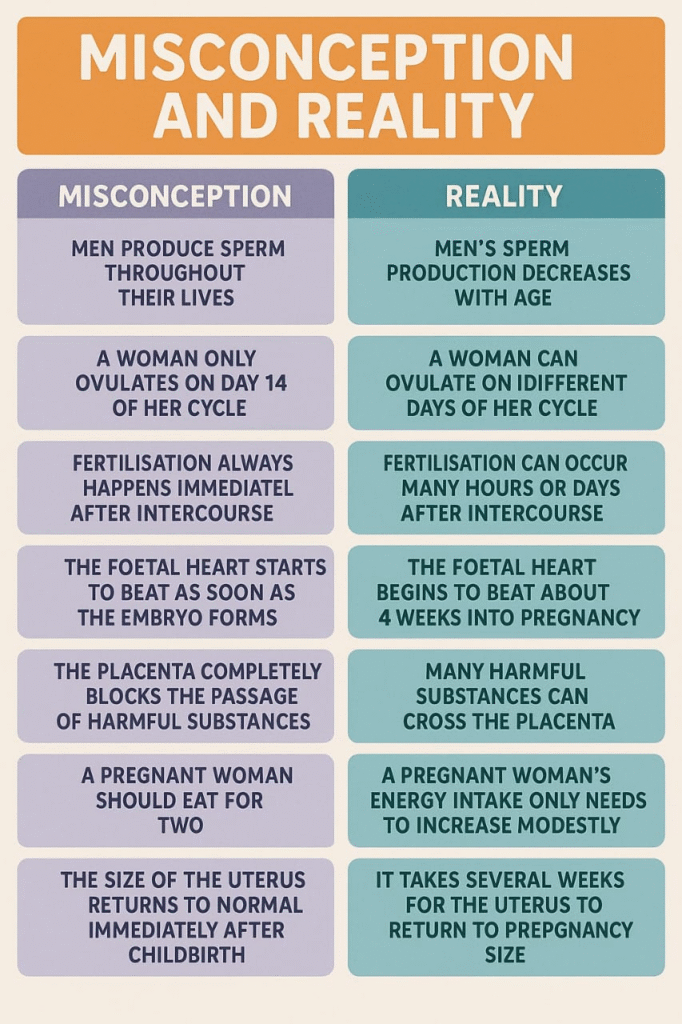
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
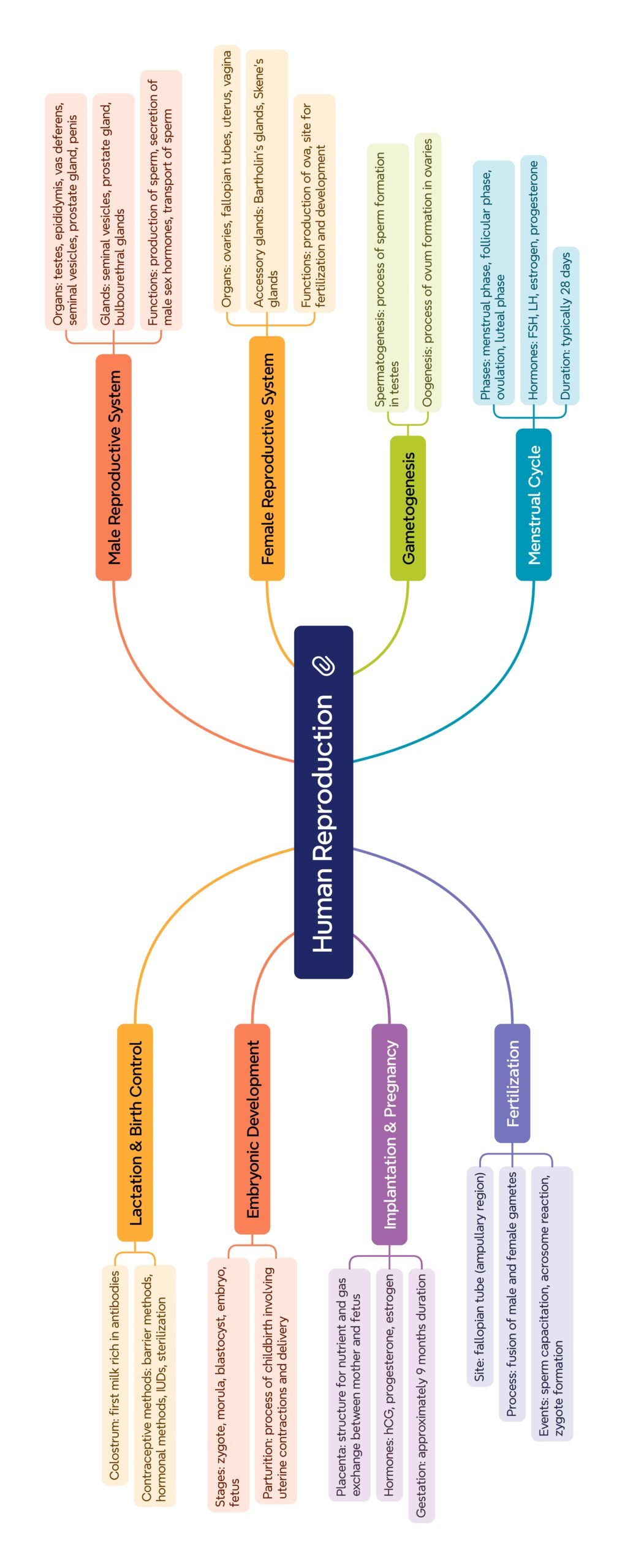
MIND MAP
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
