Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 12: Ecosystem
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
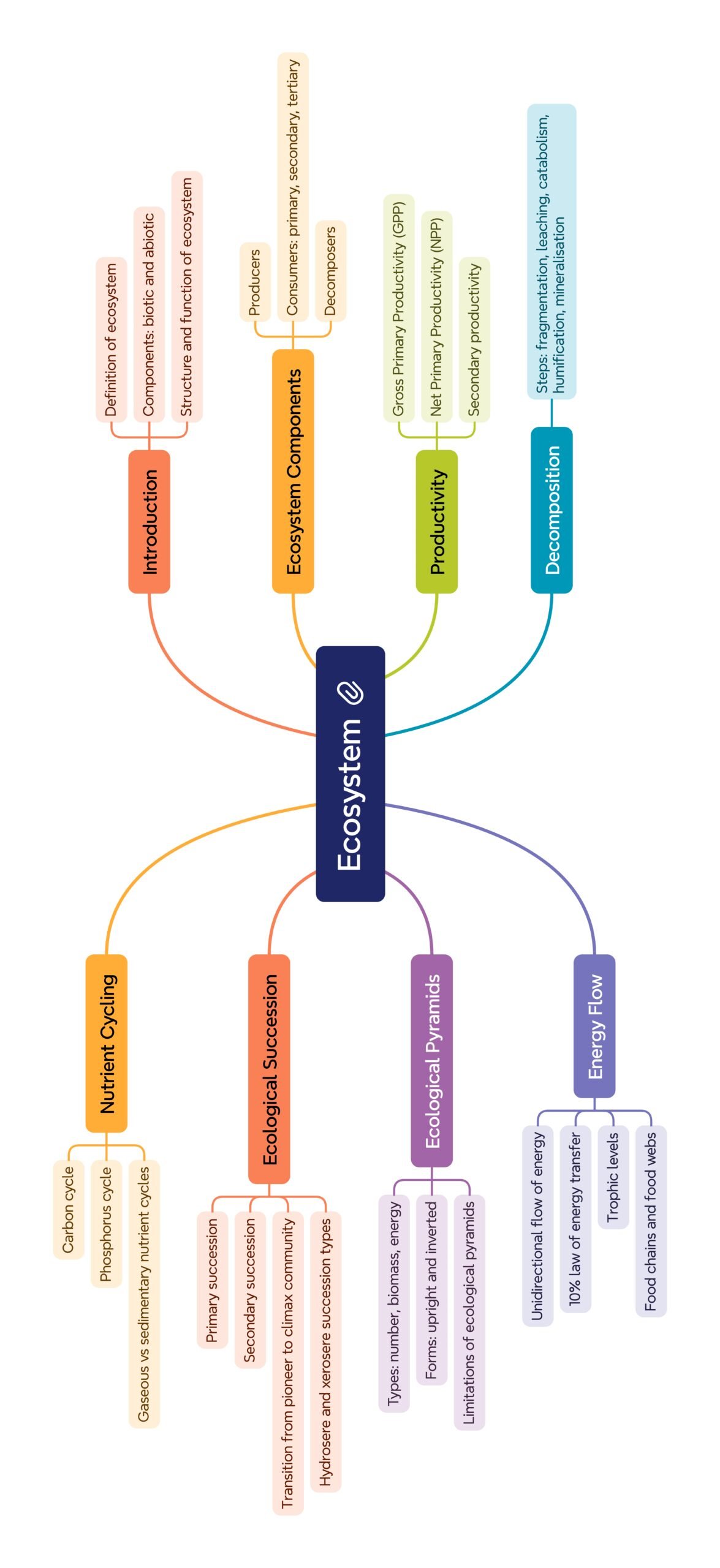
✨ Introduction
🌍 Ecosystem = a functional unit where biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components interact.
🔄 It involves flow of energy and cycling of nutrients to maintain balance.
📊 Examples: Pond, forest, desert, estuary.
🌿 Components of Ecosystem
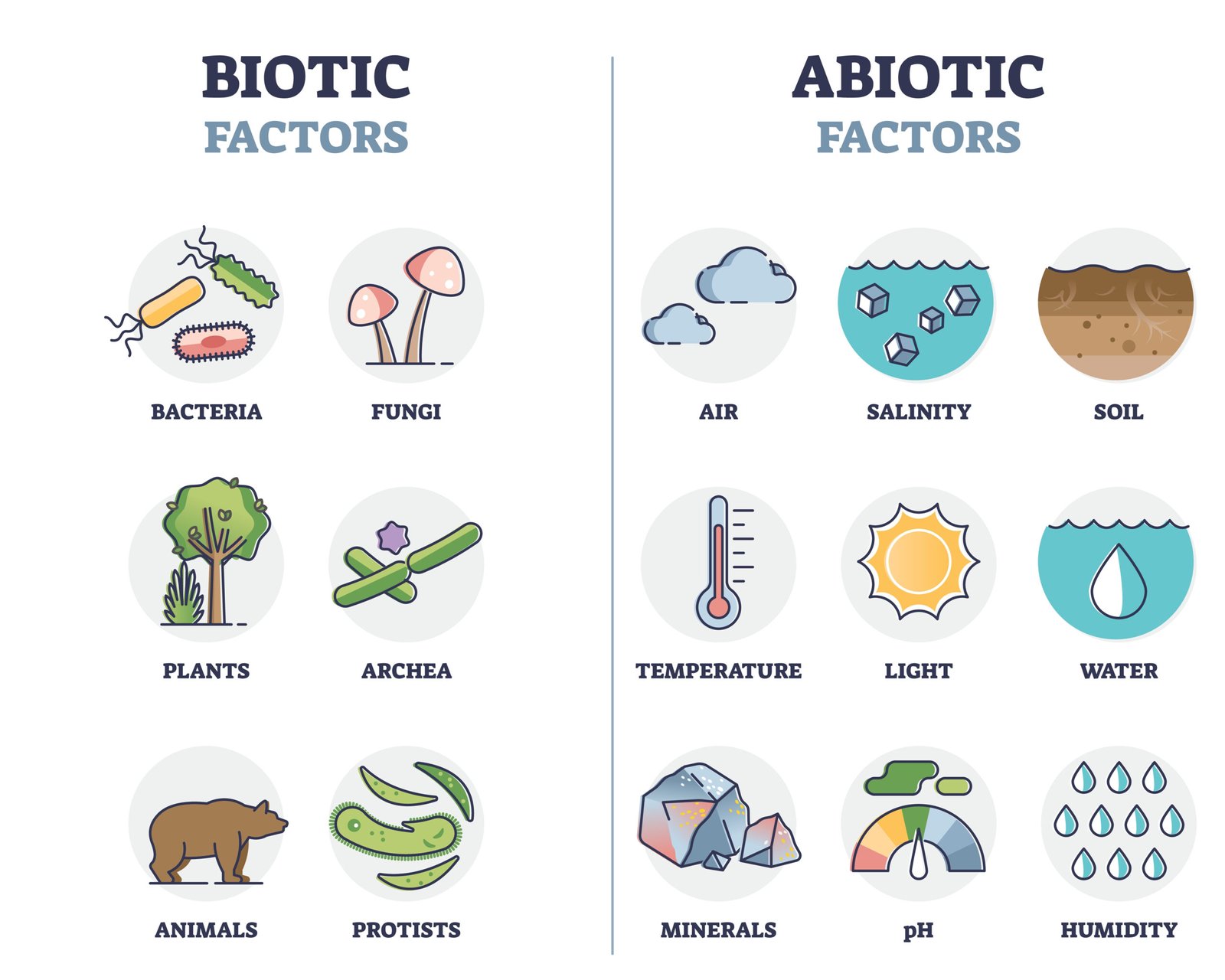
🔵 Abiotic components
☀️ Sunlight, 🌡️ temperature, 💧 water, 🪨 soil, 🌬️ air, inorganic nutrients.
🟢 Biotic components
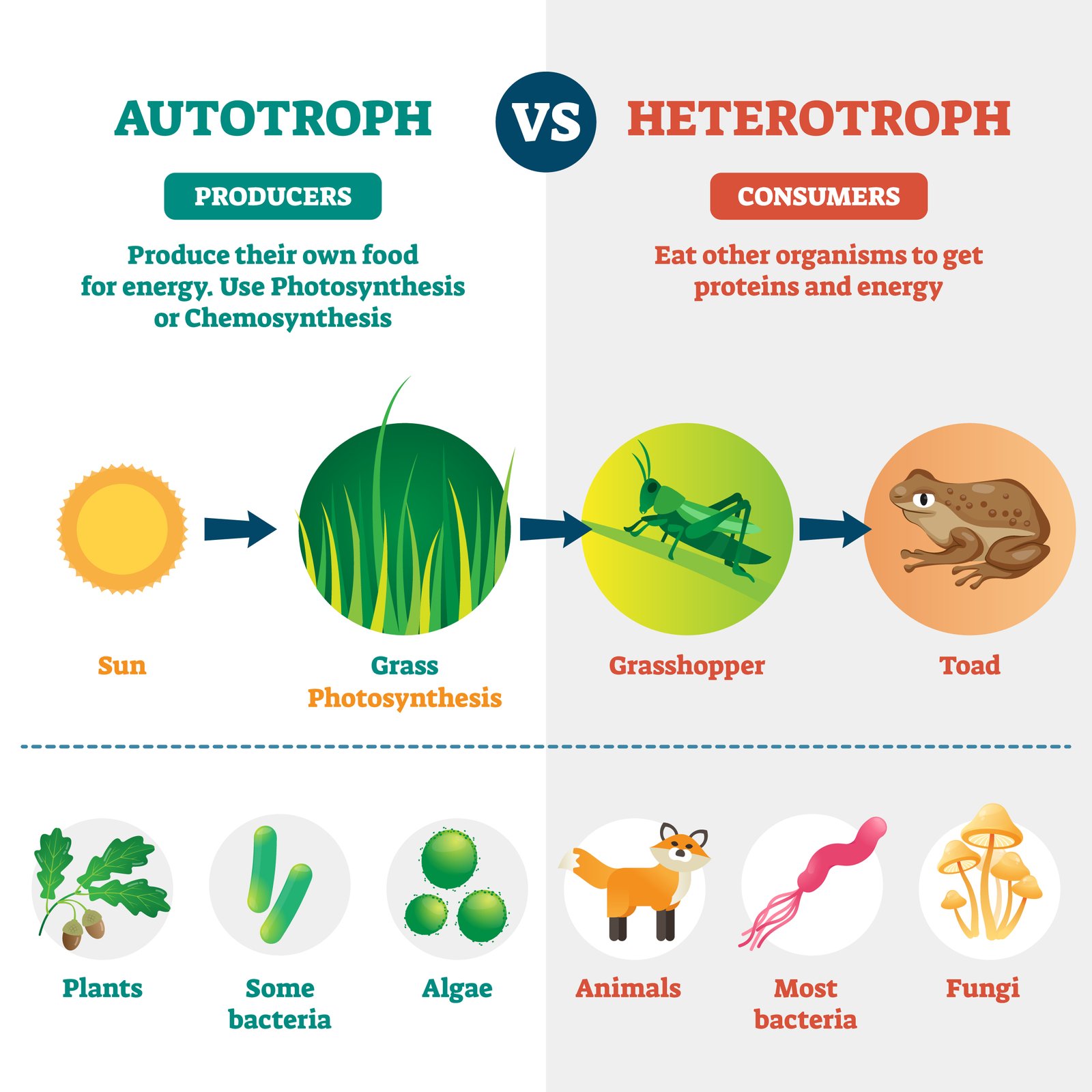
🌱 Producers (autotrophs): green plants, algae, cyanobacteria.
🐟 Consumers (heterotrophs):
Primary (herbivores 🐇, 🐛)
Secondary (carnivores 🦊, 🐍)
Tertiary (top carnivores 🦅, 🦁)
🍂 Decomposers (saprotrophs): bacteria 🦠, fungi 🍄, recycle nutrients.
🌱 Productivity
📌 Productivity = rate of biomass production
🔵 Primary productivity → energy fixed by autotrophs.
Gross primary productivity (GPP): total photosynthetic energy captured.
Net primary productivity (NPP): GPP – energy lost in respiration.
✏️ NPP = GPP – R
🟢 Secondary productivity → energy captured by consumers.
🟠 Community productivity → total productivity of producers & consumers.
🔗 Food Chains
🟢 Grazing food chain (GFC):
🌱 Producers → 🐛 Herbivores → 🐍 Carnivores → 🦅 Top carnivores.
🟠 Detritus food chain (DFC):
🍂 Dead organic matter → 🦠 Decomposers → Small carnivores → Larger carnivores.
⚡ Energy transfer is unidirectional, about 10% efficiency at each step (10% law).

🌐 Food Web
🕸️ Interconnection of food chains → food web.
✅ Provides stability to ecosystem.
📈 Ecological Pyramids
🔺 Pyramid of number → upright in grassland; inverted in parasitic chain.
🔺 Pyramid of biomass → upright in forest; inverted in pond.
🔺 Pyramid of energy → always upright (energy decreases at each level).
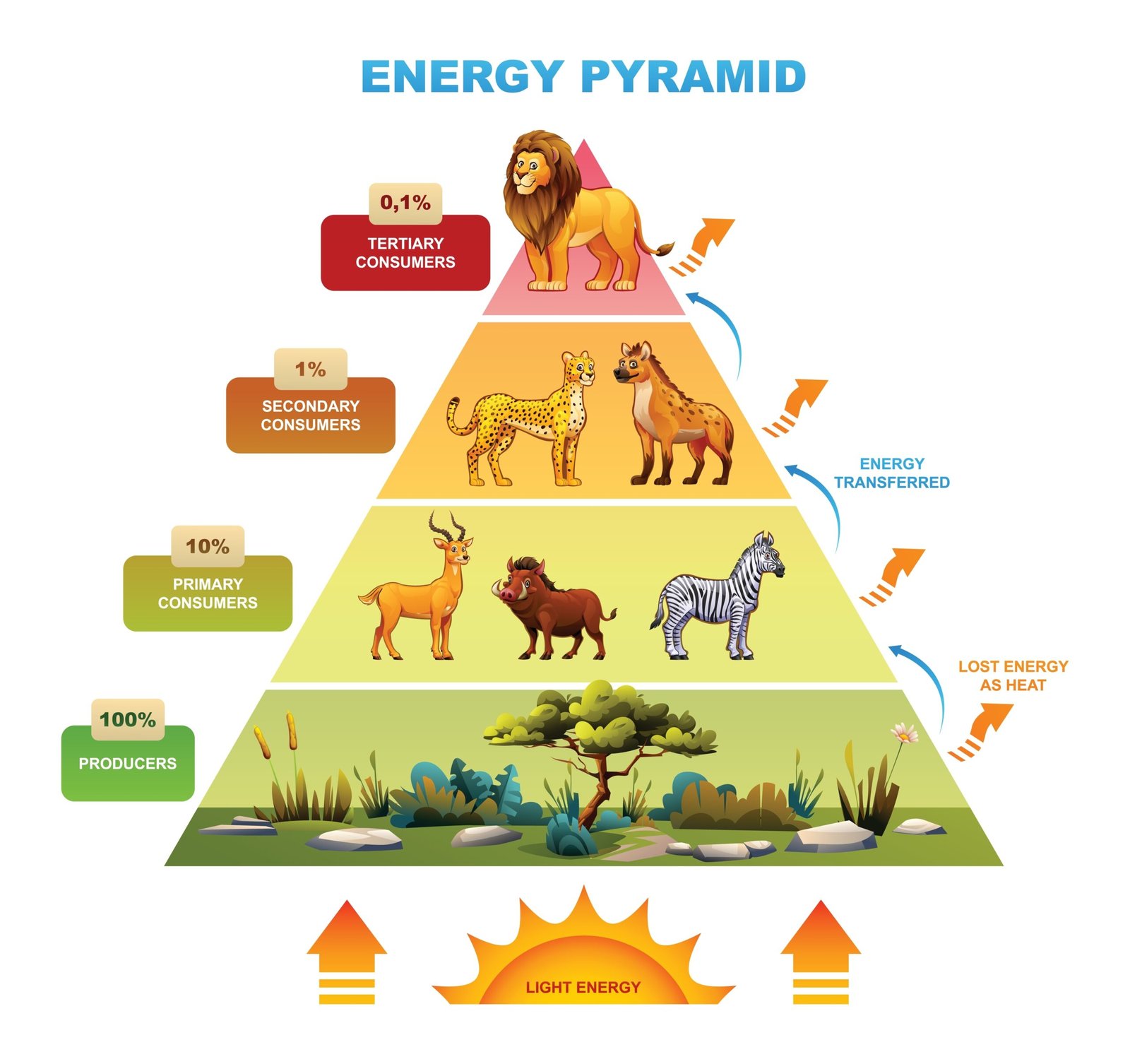
🔄 Ecological Succession
🌱 Natural, gradual change in community composition.
🔵 Primary succession: on bare rocks, sand dunes → pioneer species = lichens/moss.
🟢 Secondary succession: on abandoned fields, cut forests → faster.
🔴 Hydrarch succession: starts in water, ends in forest.
🟠 Xerarch succession: starts in dry habitat, ends in forest.
🌏 Nutrient Cycling
🔄 Circulation of nutrients (C, N, P) in ecosystems.
Carbon cycle: 🌬️ CO₂ fixed by plants → consumed → respired/released → decomposed.
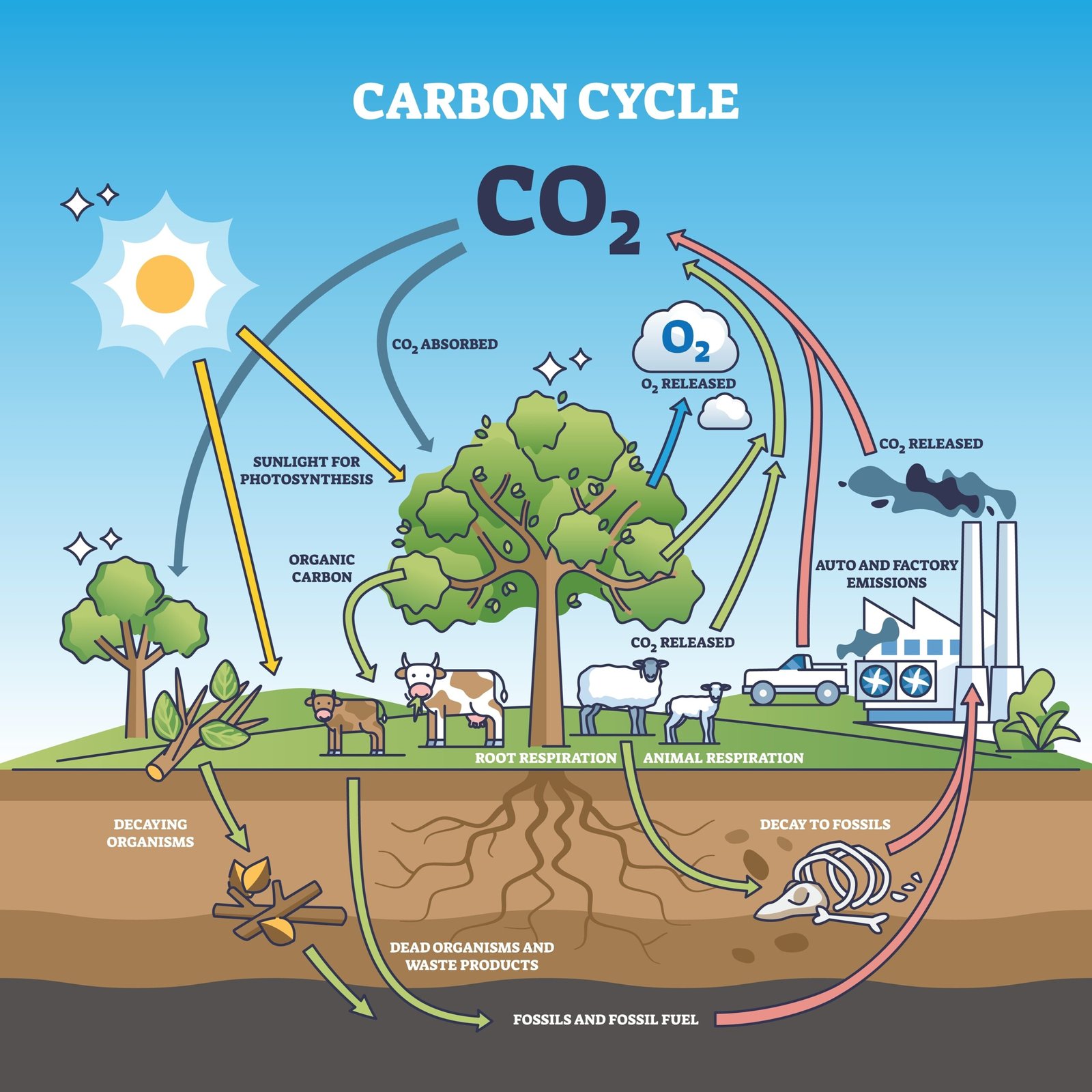
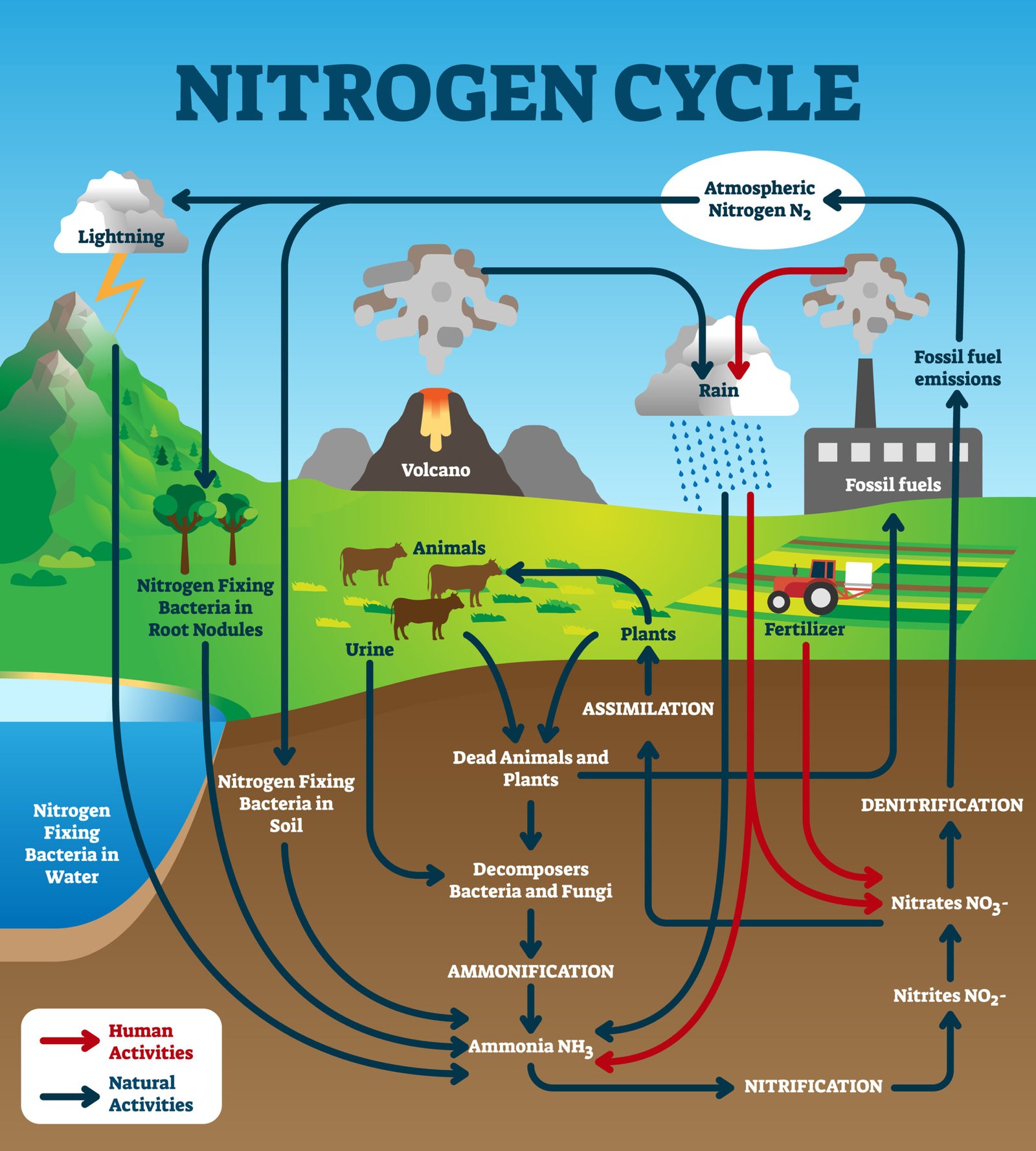
Nitrogen cycle: fixation → nitrification → assimilation → ammonification → denitrification.
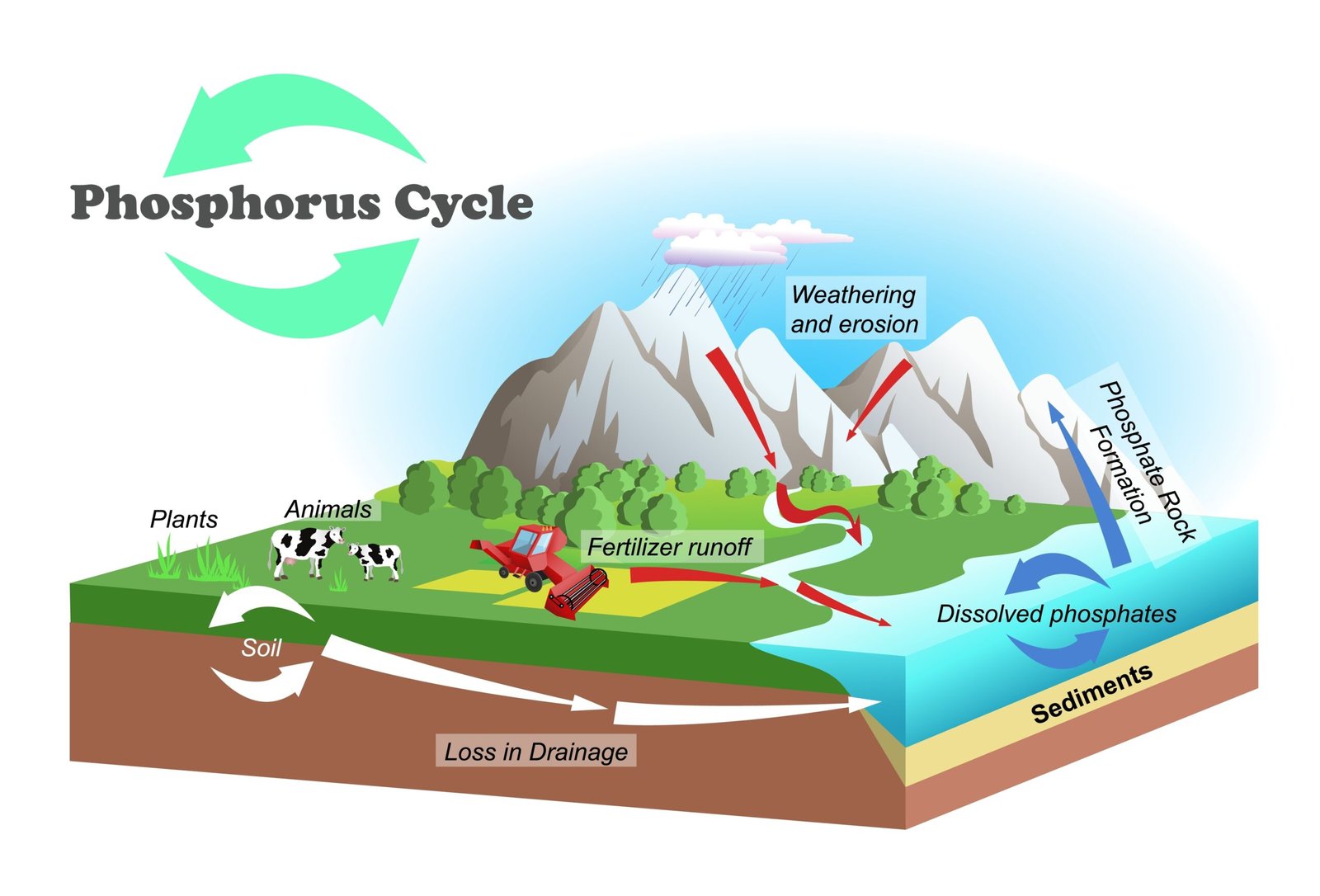
Phosphorus cycle: rocks → soil → plants → animals → detritus → sedimentation.
⚡ Ecosystem Services

Ecosystems provide:
🌬️ Oxygen production
💧 Water purification
🌳 Climate regulation
🌾 Soil fertility
🍎 Food, fuel, fibre, medicine
💡 Value estimated at US $33 trillion/year.
📝 Summary (≈300 words)
An ecosystem is a structural and functional unit where organisms interact with each other and the environment. It has abiotic (climate, soil, water, nutrients) and biotic (producers, consumers, decomposers) components.
Ecosystem functions include energy flow, productivity, food chains, food webs, ecological pyramids, succession, and nutrient cycling.
Productivity is classified as gross primary (GPP), net primary (NPP), and secondary. Food chains may be grazing or detritus; both interlink into food webs ensuring stability.
Ecological pyramids depict structure: energy pyramid is always upright; number and biomass pyramids may be upright or inverted depending on ecosystem.
Succession describes natural replacement of communities: primary succession on bare substrates, secondary succession on pre-existing soil, hydrarch in aquatic habitats, xerarch in dry habitats.
Nutrient cycling ensures reuse of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus. The carbon cycle involves photosynthesis and respiration, nitrogen cycle includes fixation and denitrification, phosphorus cycle links rocks, soil, organisms, sediments.
Ecosystems also provide services: oxygen, water, soil fertility, food, climate regulation, medicines, biodiversity. Their economic valuation highlights their global significance.
Thus, ecosystems maintain life support systems, regulate climate, recycle nutrients, and sustain biodiversity.
🎯 Quick Recap
🟢 Components: Abiotic + Biotic (Producers, Consumers, Decomposers)
🟠 Productivity: GPP, NPP, Secondary
🔵 Food chains: Grazing & Detritus → Food web
🔴 Ecological pyramids: Number, Biomass, Energy
🌱 Succession: Primary, Secondary, Hydrarch, Xerarch
🌍 Nutrient cycles: Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
✨ Ecosystem services: O₂, food, water, soil, climate regulation
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Q1. Fill in the blanks
🟢 (a) Plants are called as producers because they fix carbon dioxide.
🔵 (b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is inverted type.
🟠 (c) In aquatic ecosystems, the limiting factor for the productivity is light.
🔴 (d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are earthworms, termites.
🟡 (e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is ocean.
Q2. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Primary consumers
🟠 (C) Secondary consumers
🔴 (D) Decomposers
✅ Answer: (A) Producers
Q3. The second trophic level in a lake is
🔵 (A) Phytoplankton
🟢 (B) Zooplankton
🟠 (C) Benthos
🔴 (D) Fishes
✅ Answer: (B) Zooplankton
Q4. Secondary producers are
🔵 (A) Herbivores
🟢 (B) Producers
🟠 (C) Carnivores
🔴 (D) None of the above
✅ Answer: (D) None of the above
👉 Explanation: There is no category of “secondary producers” in ecology.
Q5. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation?
🔵 (A) 100%
🟢 (B) 50%
🟠 (C) 1–5%
🔴 (D) 2–10%
✅ Answer: (D) 2–10%
Q6. Distinguish between
🔵 (a) Grazing food chain & Detritus food chain
GFC: Starts with producers → herbivores → carnivores.
DFC: Starts with dead organic matter → decomposers.
🟢 (b) Production & Decomposition
Production: Formation of biomass through photosynthesis.
Decomposition: Breakdown of complex matter into simpler substances.
🟠 (c) Upright & Inverted pyramid
Upright: Energy pyramid, biomass in forest.
Inverted: Pyramid of biomass in pond, pyramid of number in tree ecosystem.
🔴 (d) Food chain & Food web
Food chain: Linear sequence of energy flow.
Food web: Interconnection of food chains.
🟡 (e) Litter & Detritus
Litter: Freshly fallen leaves/twigs.
Detritus: Dead remains undergoing decomposition.
🟣 (f) Primary & Secondary productivity
Primary: Biomass produced by autotrophs.
Secondary: Biomass produced by consumers.
Q7. Describe the components of an ecosystem.
✅ Components:
Abiotic: Light, temperature, water, air, soil, inorganic nutrients.
Biotic:
Producers 🌱 (plants, algae)
Consumers 🐛 (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores)
Decomposers 🍄 (bacteria, fungi).
Q8. Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
✅ Ecological pyramids: Graphical representation of number, biomass, or energy at successive trophic levels.
Pyramid of number: Grassland → Upright, Tree ecosystem → Inverted.
Pyramid of biomass: Forest → Upright, Aquatic pond → Inverted.
Q9. What is primary productivity? Give brief description of factors that affect primary productivity.
✅ Primary productivity: Amount of biomass produced by autotrophs per unit area per unit time.
Factors:
Abiotic (light, temperature, water, nutrients).
Plant factors (species, photosynthetic efficiency).
Community interactions.
Q10. Define decomposition and describe the processes and products of decomposition.
✅ Decomposition: Breakdown of complex organic matter into simple inorganic substances by decomposers.
Steps:
Fragmentation: Detritus broken into small particles.
Leaching: Soluble nutrients washed out.
Catabolism: Enzymatic breakdown.
Humification: Formation of humus.
Mineralisation: Release of inorganic nutrients.
Products: Humus, CO₂, water, nutrients (N, P, K, Ca).
Q11. Give an account of energy flow in an ecosystem.
✅ Energy flow:
Solar energy → captured by producers.
Transfer to herbivores → carnivores → decomposers.
Only 10% energy transferred to next level (10% law).
Unidirectional, always decreases at higher trophic levels.
Represented as ecological pyramid of energy (always upright).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🟢 Section A — MCQs (Q1–Q10)
🔸 Q1. In most ecosystems, the main source of energy is ☀️
🔵 (A) Moonlight
🟢 (B) Sunlight
🟠 (C) Geothermal heat
🔴 (D) Chemical energy
✅ Answer: (B) Sunlight
🔸 Q2. In a forest food chain, the largest population is generally at the level of 🌳
🔵 (A) Tertiary consumers
🟢 (B) Secondary consumers
🟠 (C) Primary consumers
🔴 (D) Producers
✅ Answer: (D) Producers
🔸 Q3. The second trophic level in a lake is 🐟
🔵 (A) Phytoplankton
🟢 (B) Zooplankton
🟠 (C) Benthos
🔴 (D) Fishes
✅ Answer: (B) Zooplankton
🔸 Q4. “Secondary producers” in ecological literature are 📘
🔵 (A) Herbivores
🟢 (B) Carnivores
🟠 (C) Decomposers
🔴 (D) Not used (no such category)
✅ Answer: (D) Not used (no such category)
🔸 Q5. Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) is about ☀️📊
🔵 (A) 100% of insolation
🟢 (B) 50% of insolation
🟠 (C) 1–5%
🔴 (D) 2–10%
✅ Answer: (D) 2–10%
🔸 Q6. In aquatic ecosystems, the principal limiting factor for productivity is 🌊
🔵 (A) Wind
🟢 (B) Light
🟠 (C) Soil pH
🔴 (D) Calcium
✅ Answer: (B) Light
🔸 Q7. In a tree-dominated ecosystem, the pyramid of numbers is 🌲
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Hour-glass
✅ Answer: (B) Inverted
🔸 Q8. Pyramid of energy is ⚡
🔵 (A) Always upright
🟢 (B) Always inverted
🟠 (C) Upright only in forests
🔴 (D) Variable
✅ Answer: (A) Always upright
🔸 Q9. Major reservoir of carbon on Earth is 🌏
🔵 (A) Atmosphere
🟢 (B) Ocean
🟠 (C) Plants
🔴 (D) Soil litter
✅ Answer: (B) Ocean
🔸 Q10. Common detritivores include 🍂
🔵 (A) Earthworms and termites
🟢 (B) Hawks and owls
🟠 (C) Deer and rabbits
🔴 (D) Phytoplankton
✅ Answer: (A) Earthworms and termites
🟡 Section B — Very Short Answer (Q11–Q15)
🔸 Q11. Define Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NPP).
✅ Answer:
GPP: total photosynthetic fixation of energy by producers per unit area per unit time.
NPP: GPP − R (R = respiration loss) per unit area per unit time.
🔸 Q12. State the 10% law of energy transfer.
✅ Answer: About 10% of the energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next higher trophic level; the rest is lost as heat/respiration.
🔸 Q13. Name the two main types of food chains. Give one starter for each.
✅ Answer:
Grazing food chain: starts with producers (grass).
Detritus food chain: starts with detritus (dead leaves) eaten by decomposers/detritivores.
🔸 Q14. Write any two ecosystem services.
✅ Answer: Oxygen production, water purification, climate regulation, soil fertility (any two).
🔸 Q15. List the five steps of decomposition in correct order.
✅ Answer: Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation.
🔴 Section C — Short Answer (Q16–Q17)
🔸 Q16. Distinguish between the following (one line each):
✅ Answer:
(a) Food chain vs Food web: Chain = linear pathway; Web = interlinked chains providing stability.
(b) Litter vs Detritus: Litter = freshly fallen organic matter; Detritus = partly decomposed remains.
(c) Upright vs Inverted biomass pyramid: Forest = upright; Pond = inverted (phytoplankton biomass < zooplankton/fish at an instant).
🔸 Q17. Numericals on productivity: A grassland has GPP = 2000 kJ m^-2 yr^-1 and R = 800 kJ m^-2 yr^-1.
✅ Answer (stepwise):
Step 1: NPP = GPP − R
Step 2: NPP = 2000 − 800
Step 3: NPP = 1200 kJ m^-2 yr^-1
🔸 Q18. Define ecological succession. Differentiate between primary and secondary succession.
✅ Answer:
Ecological succession: gradual, predictable change in species composition in an area.
Primary succession: starts on bare substrates (rock, sand, waterbody) with no soil/organisms; very slow.
Secondary succession: starts on areas with pre-existing soil and life (abandoned fields, cut forests); faster.
🔸 Q19. What is humus? Why is it important for soil fertility?
✅ Answer:
Humus: dark, amorphous, colloidal organic matter formed during decomposition.
Importance: increases soil porosity, nutrient retention, and fertility.
🔸 Q20. Mention two differences between hydrarch succession and xerarch succession.
✅ Answer:
Hydrarch succession: begins in water; pioneer = phytoplankton.
Xerarch succession: begins in dry habitats; pioneer = lichens.
End point (climax): both → forest ecosystem.
🔸 Q21. Explain carbon cycling in nature.
✅ Answer:
CO₂ fixed by plants in photosynthesis → eaten by consumers → released in respiration.
Decomposition and combustion also release CO₂.
Main reservoir = oceans and fossil fuels.
🔸 Q22. Write short notes on nitrogen fixation.
✅ Answer:
Conversion of atmospheric N₂ → usable forms (NH₄⁺, NO₃⁻).
Carried out by free-living bacteria (Azotobacter, Clostridium), symbiotic bacteria (Rhizobium), and by lightning.
🔸 Q23. Explain the structure of a simple pond ecosystem.
✅ Answer:
Abiotic: water, light, temperature, minerals.
Biotic:
Producers: phytoplankton, aquatic plants.
Consumers: zooplankton, fishes.
Decomposers: bacteria, fungi.
Shows grazing and detritus food chains.
🔸 Q24. Name any two ecosystem services and explain their importance.
✅ Answer:
Oxygen production (through photosynthesis): essential for life.
Climate regulation (carbon sequestration): prevents global warming.
🔸 Q25. State the 10% law of Lindeman with an example.
✅ Answer: Only 10% energy at one trophic level is transferred to the next.
Example: Grass (1000 J) → Grasshopper (100 J) → Frog (10 J) → Snake (1 J).
🔴 Section D — Long Answer (Q26–Q30)
🔸 Q26. Describe the process of decomposition.
✅ Answer:
Steps: Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation.
Products: inorganic nutrients, humus, CO₂, water.
🔸 Q27. Explain the energy flow in an ecosystem with a suitable diagram.
✅ Answer:
Unidirectional flow: Sun → Producers → Consumers → Decomposers.
Only 10% energy passed on at each level.
Represented as an upright pyramid of energy.
🔸 Q28. Write an essay on ecosystem services with examples.
✅ Answer: Ecosystem services include:
Provisioning: food, fuel, medicines.
Regulating: climate control, water purification.
Supporting: nutrient cycling, pollination.
Cultural: recreation, aesthetic value.
🔸 Q29. What is ecological pyramid? Explain pyramids of number, biomass, and energy with examples.
✅ Answer:
Pyramid of number: upright (grassland); inverted (tree ecosystem).
Pyramid of biomass: upright (forest); inverted (pond).
Pyramid of energy: always upright.
🔸 Q30. Describe nitrogen cycle with diagrammatic explanation.
✅ Answer:
Steps: Nitrogen fixation → Nitrification → Assimilation → Ammonification → Denitrification.
Reservoir = atmosphere.
Maintains nitrogen balance in biosphere.
🟣 Section E — Case Study & MCQs (Q31–Q33)
📘 Case Study:
In a grassland ecosystem, the GPP = 2500 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹ and respiration loss = 1500 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹. Secondary consumers assimilate 200 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹.
🔸 Q31. Calculate the NPP.
✅ Answer (stepwise):
Formula: NPP = GPP − R
= 2500 − 1500
= 1000 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
🔸 Q32. MCQ: Energy available to secondary consumers is:
🔵 (A) 200 kJ
🟢 (B) 1000 kJ
🟠 (C) 1500 kJ
🔴 (D) 2500 kJ
✅ Answer: (A) 200 kJ
🔸 Q33. MCQ: Which ecological principle is best illustrated in the above case?
🔵 (A) 10% law
🟢 (B) Gause’s competitive exclusion principle
🟠 (C) Principle of succession
🔴 (D) Allen’s rule
✅ Answer: (A) 10% law
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. The pyramid of biomass in sea is usually
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Irregular
✅ Answer: (B) Inverted
Year: NEET 2023 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q2. Which of the following ecological pyramids can never be inverted?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of biomass
🟢 (B) Pyramid of energy
🟠 (C) Pyramid of number
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (B) Pyramid of energy
Year: NEET 2022 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q3. The rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers is called
🔵 (A) Gross primary productivity
🟢 (B) Net primary productivity
🟠 (C) Secondary productivity
🔴 (D) Standing crop
✅ Answer: (C) Secondary productivity
Year: NEET 2021 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q4. Which of the following is not a step in decomposition?
🔵 (A) Fragmentation
🟢 (B) Leaching
🟠 (C) Assimilation
🔴 (D) Humification
✅ Answer: (C) Assimilation
Year: NEET 2020 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q5. Which of the following is the major reservoir of carbon on earth?
🔵 (A) Atmosphere
🟢 (B) Forests
🟠 (C) Oceans
🔴 (D) Fossil fuels
✅ Answer: (C) Oceans
Year: NEET 2019 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q6. Which ecosystem has the maximum productivity?
🔵 (A) Desert
🟢 (B) Grassland
🟠 (C) Coral reef
🔴 (D) Deep sea
✅ Answer: (C) Coral reef
Year: NEET 2019 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q7. Which one of the following processes is not involved in decomposition?
🔵 (A) Leaching
🟢 (B) Catabolism
🟠 (C) Humification
🔴 (D) Photosynthesis
✅ Answer: (D) Photosynthesis
Year: NEET 2018 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q8. The pyramid of numbers in a tree ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Linear
✅ Answer: (B) Inverted
Year: NEET 2017 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q9. Which ecosystem shows inverted biomass pyramid?
🔵 (A) Forest
🟢 (B) Grassland
🟠 (C) Pond
🔴 (D) Desert
✅ Answer: (C) Pond
Year: NEET 2017 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q10. Which of the following is correctly matched?
🔵 (A) Nitrogen fixation – Nitrobacter
🟢 (B) Nitrification – Nitrosomonas
🟠 (C) Denitrification – Nitrosomonas
🔴 (D) Ammonification – Rhizobium
✅ Answer: (B) Nitrification – Nitrosomonas
Year: NEET 2016 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q11. The rate at which the biomass is produced by plants is called
🔵 (A) Gross productivity
🟢 (B) Net productivity
🟠 (C) Secondary productivity
🔴 (D) Decomposition
✅ Answer: (A) Gross productivity
Year: NEET 2016 | Exam: NEET-UG
🔹 Q12. The sequence of communities in ecological succession is termed as
🔵 (A) Sere
🟢 (B) Climax
🟠 (C) Niche
🔴 (D) Ecotone
✅ Answer: (A) Sere
Year: AIPMT 2015 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q13. The decomposers are
🔵 (A) Fungi and bacteria
🟢 (B) Green plants
🟠 (C) Herbivores
🔴 (D) Carnivores
✅ Answer: (A) Fungi and bacteria
Year: AIPMT 2015 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q14. Which of the following ecological pyramids is always upright?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of number
🟢 (B) Pyramid of biomass
🟠 (C) Pyramid of energy
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (C) Pyramid of energy
Year: AIPMT 2014 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q15. Which process is responsible for the release of nutrients in the ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Succession
🟢 (B) Decomposition
🟠 (C) Productivity
🔴 (D) Photosynthesis
✅ Answer: (B) Decomposition
Year: AIPMT 2014 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q16. Which is the pioneer organism in primary succession on rocks?
🔵 (A) Algae
🟢 (B) Bryophytes
🟠 (C) Lichens
🔴 (D) Pteridophytes
✅ Answer: (C) Lichens
Year: AIPMT 2013 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q17. Which of the following biogeochemical cycles does not have a gaseous phase?
🔵 (A) Carbon cycle
🟢 (B) Nitrogen cycle
🟠 (C) Phosphorus cycle
🔴 (D) Oxygen cycle
✅ Answer: (C) Phosphorus cycle
Year: AIPMT 2013 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q18. The pyramid of number in a grassland ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Irregular
🔴 (D) None of these
✅ Answer: (A) Upright
Year: AIPMT 2012 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q19. The role of decomposers is to
🔵 (A) Fix energy
🟢 (B) Release nutrients
🟠 (C) Consume herbivores
🔴 (D) Produce food
✅ Answer: (B) Release nutrients
Year: AIPMT 2012 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q20. Secondary succession takes place in/on
🔵 (A) Newly cooled lava
🟢 (B) Bare rock
🟠 (C) Abandoned farmland
🔴 (D) Newly formed pond
✅ Answer: (C) Abandoned farmland
Year: AIPMT 2011 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q21. Which ecosystem has highest primary productivity?
🔵 (A) Desert
🟢 (B) Grassland
🟠 (C) Tropical rainforest
🔴 (D) Tundra
✅ Answer: (C) Tropical rainforest
Year: AIPMT 2011 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q22. In ecological succession, the final stable community is called
🔵 (A) Seral community
🟢 (B) Pioneer community
🟠 (C) Climax community
🔴 (D) None of these
✅ Answer: (C) Climax community
Year: AIPMT 2010 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q23. Which of the following is a gaseous biogeochemical cycle?
🔵 (A) Sulphur cycle
🟢 (B) Phosphorus cycle
🟠 (C) Carbon cycle
🔴 (D) Sedimentary cycle
✅ Answer: (C) Carbon cycle
Year: AIPMT 2010 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q24. The gradual change in the species composition in an area is called
🔵 (A) Competition
🟢 (B) Succession
🟠 (C) Stratification
🔴 (D) Speciation
✅ Answer: (B) Succession
Year: AIPMT 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q25. Which one of the following is a pioneer species in xerarch succession?
🔵 (A) Lichen
🟢 (B) Bryophyte
🟠 (C) Fern
🔴 (D) Phanerogams
✅ Answer: (A) Lichen
Year: AIPMT 2009 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q26. Which type of pyramid is always upright?
🔵 (A) Biomass pyramid
🟢 (B) Number pyramid
🟠 (C) Energy pyramid
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (C) Energy pyramid
Year: AIPMT 2008 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q27. The chief energy source for ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Moon
🟢 (B) Sun
🟠 (C) Earth’s heat
🔴 (D) Fire
✅ Answer: (B) Sun
Year: AIPMT 2008 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q28. During decomposition, humus is formed in the step called
🔵 (A) Fragmentation
🟢 (B) Humification
🟠 (C) Mineralisation
🔴 (D) Catabolism
✅ Answer: (B) Humification
Year: AIPMT 2007 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q29. Primary succession on bare rock is initiated by
🔵 (A) Algae
🟢 (B) Mosses
🟠 (C) Lichens
🔴 (D) Ferns
✅ Answer: (C) Lichens
Year: AIPMT 2007 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q30. In an aquatic ecosystem, biomass pyramid is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Irregular
✅ Answer: (B) Inverted
Year: AIPMT 2006 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q31. Which of the following is not an ecosystem service?
🔵 (A) Climate regulation
🟢 (B) Pollination
🟠 (C) Nitrogen fixation
🔴 (D) Earthquake
✅ Answer: (D) Earthquake
Year: AIPMT 2006 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q32. Which ecological pyramid can be inverted in a pond ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of biomass
🟢 (B) Pyramid of number
🟠 (C) Pyramid of energy
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (A) Pyramid of biomass
Year: AIPMT 2005 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q33. The functional role played by an organism is called
🔵 (A) Habitat
🟢 (B) Niche
🟠 (C) Community
🔴 (D) Succession
✅ Answer: (B) Niche
Year: AIPMT 2005 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q34. Primary productivity is measured in terms of
🔵 (A) Biomass per unit area per unit time
🟢 (B) Total standing crop
🟠 (C) Standing state of nutrients
🔴 (D) Number of individuals per unit area
✅ Answer: (A) Biomass per unit area per unit time
Year: AIPMT 2004 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q35. Mineralisation releases
🔵 (A) Inorganic nutrients
🟢 (B) Humus
🟠 (C) CO₂ only
🔴 (D) Detritus
✅ Answer: (A) Inorganic nutrients
Year: AIPMT 2004 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q36. Which of the following is not a component of an ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Consumers
🟠 (C) Decomposers
🔴 (D) Stratification
✅ Answer: (D) Stratification
Year: AIPMT 2003 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q37. The step of decomposition which involves enzymatic breakdown of detritus is
🔵 (A) Catabolism
🟢 (B) Fragmentation
🟠 (C) Humification
🔴 (D) Mineralisation
✅ Answer: (A) Catabolism
Year: AIPMT 2003 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q38. Which of the following is a sedimentary cycle?
🔵 (A) Carbon cycle
🟢 (B) Nitrogen cycle
🟠 (C) Phosphorus cycle
🔴 (D) Oxygen cycle
✅ Answer: (C) Phosphorus cycle
Year: AIPMT 2002 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q39. The process by which nitrates are reduced to gaseous nitrogen is
🔵 (A) Nitrification
🟢 (B) Ammonification
🟠 (C) Denitrification
🔴 (D) Nitrogen fixation
✅ Answer: (C) Denitrification
Year: AIPMT 2002 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q40. Standing crop is measured as
🔵 (A) Biomass per unit area
🟢 (B) Number of organisms per unit area
🟠 (C) Energy fixed per unit time
🔴 (D) Productivity per unit time
✅ Answer: (A) Biomass per unit area
Year: AIPMT 2001 | Exam: AIPMT
🔹 Q41. The pioneer community in xerarch succession is
🔵 (A) Lichen
🟢 (B) Moss
🟠 (C) Bryophyte
🔴 (D) Fern
✅ Answer: (A) Lichen
Year: PMT 2000 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q42. Secondary succession occurs in/on
🔵 (A) Bare rock
🟢 (B) Newly formed pond
🟠 (C) Abandoned farmland
🔴 (D) Newly cooled lava
✅ Answer: (C) Abandoned farmland
Year: PMT 2000 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q43. The transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next is
🔵 (A) 1%
🟢 (B) 5%
🟠 (C) 10%
🔴 (D) 20%
✅ Answer: (C) 10%
Year: PMT 1999 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q44. Ecological succession occurring in water is
🔵 (A) Xerarch
🟢 (B) Hydrarch
🟠 (C) Mesarch
🔴 (D) Lithosere
✅ Answer: (B) Hydrarch
Year: PMT 1999 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q45. The total organic matter present in an ecosystem at a given time is
🔵 (A) Productivity
🟢 (B) Standing crop
🟠 (C) Standing state
🔴 (D) Stratification
✅ Answer: (B) Standing crop
Year: PMT 1998 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q46. Which of the following has no decomposer?
🔵 (A) Pond
🟢 (B) Desert
🟠 (C) Deep sea
🔴 (D) Ocean
✅ Answer: (C) Deep sea
Year: PMT 1998 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q47. Which process does not add CO₂ to the atmosphere?
🔵 (A) Photosynthesis
🟢 (B) Respiration
🟠 (C) Combustion
🔴 (D) Decomposition
✅ Answer: (A) Photosynthesis
Year: PMT 1997 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q48. The energy flow in an ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Cyclic
🟢 (B) Linear
🟠 (C) Irregular
🔴 (D) Spiral
✅ Answer: (B) Linear
Year: PMT 1997 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q49. In a grassland ecosystem, the pyramid of number is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Hourglass
✅ Answer: (A) Upright
Year: PMT 1996 | Exam: PMT
🔹 Q50. The community that stabilises in ecological succession is
🔵 (A) Seral stage
🟢 (B) Pioneer stage
🟠 (C) Climax community
🔴 (D) Transitional stage
✅ Answer: (C) Climax community
Year: PMT 1995 | Exam: PMT
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20 (NEET-Level Moderate)
🔹 Q1. In a pond ecosystem, the pyramid of biomass is usually
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Hour-glass shaped
✅ Answer: (B) Inverted
🔹 Q2. The major reservoir of carbon in the biosphere is
🔵 (A) Atmosphere
🟢 (B) Oceans
🟠 (C) Forests
🔴 (D) Fossil fuels
✅ Answer: (B) Oceans
🔹 Q3. Primary productivity of an ecosystem refers to
🔵 (A) Biomass consumed by herbivores
🟢 (B) Biomass produced by autotrophs
🟠 (C) Biomass present at a time
🔴 (D) Energy stored in decomposers
✅ Answer: (B) Biomass produced by autotrophs
🔹 Q4. Which one of the following ecosystems shows highest net primary productivity?
🔵 (A) Tundra
🟢 (B) Desert
🟠 (C) Tropical rainforest
🔴 (D) Grassland
✅ Answer: (C) Tropical rainforest
🔹 Q5. Secondary succession occurs in
🔵 (A) Bare rock
🟢 (B) Newly cooled lava
🟠 (C) Abandoned farmland
🔴 (D) Newly formed pond
✅ Answer: (C) Abandoned farmland
🔹 Q6. Which process does not add CO₂ to the atmosphere?
🔵 (A) Respiration
🟢 (B) Combustion
🟠 (C) Photosynthesis
🔴 (D) Decomposition
✅ Answer: (C) Photosynthesis
🔹 Q7. Which step in decomposition leads to the formation of humus?
🔵 (A) Catabolism
🟢 (B) Humification
🟠 (C) Mineralisation
🔴 (D) Fragmentation
✅ Answer: (B) Humification
🔹 Q8. Which ecological pyramid is always upright?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of number
🟢 (B) Pyramid of biomass
🟠 (C) Pyramid of energy
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (C) Pyramid of energy
🔹 Q9. Lichens are pioneer species in
🔵 (A) Hydrarch succession
🟢 (B) Xerarch succession
🟠 (C) Secondary succession
🔴 (D) All successions
✅ Answer: (B) Xerarch succession
🔹 Q10. Standing crop is measured in terms of
🔵 (A) Energy per unit area
🟢 (B) Biomass per unit area
🟠 (C) Productivity per unit time
🔴 (D) Nutrient content
✅ Answer: (B) Biomass per unit area
🔹 Q11. In ecological succession, the final stable community is called
🔵 (A) Seral stage
🟢 (B) Climax community
🟠 (C) Pioneer community
🔴 (D) Sere
✅ Answer: (B) Climax community
🔹 Q12. Which of the following is not an ecosystem service?
🔵 (A) Soil formation
🟢 (B) Pollination
🟠 (C) Photosynthesis
🔴 (D) Earthquake regulation
✅ Answer: (D) Earthquake regulation
🔹 Q13. The step of decomposition that releases inorganic nutrients into the soil is
🔵 (A) Fragmentation
🟢 (B) Mineralisation
🟠 (C) Leaching
🔴 (D) Humification
✅ Answer: (B) Mineralisation
🔹 Q14. Which factor is most limiting for productivity in aquatic ecosystems?
🔵 (A) Nutrients
🟢 (B) Light
🟠 (C) Temperature
🔴 (D) Oxygen
✅ Answer: (B) Light
🔹 Q15. Which one of the following represents detritus food chain?
🔵 (A) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake
🟢 (B) Dead leaves → Earthworms → Birds
🟠 (C) Algae → Zooplankton → Fish
🔴 (D) Grains → Rats → Snakes
✅ Answer: (B) Dead leaves → Earthworms → Birds
🔹 Q16. Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses equals
🔵 (A) Net productivity
🟢 (B) Standing crop
🟠 (C) Secondary productivity
🔴 (D) Biomass
✅ Answer: (A) Net productivity
🔹 Q17. Which ecological pyramid is inverted in pond ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of number
🟢 (B) Pyramid of biomass
🟠 (C) Pyramid of energy
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (B) Pyramid of biomass
🔹 Q18. Which biogeochemical cycle does not have a gaseous phase?
🔵 (A) Carbon cycle
🟢 (B) Nitrogen cycle
🟠 (C) Phosphorus cycle
🔴 (D) Oxygen cycle
✅ Answer: (C) Phosphorus cycle
🔹 Q19. Which of the following is an example of ecological service provided by microbes?
🔵 (A) Antibiotic production
🟢 (B) Decomposition
🟠 (C) Biofertiliser
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
🔹 Q20. In grassland, the pyramid of number is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Hour-glass shaped
✅ Answer: (A) Upright
🟠 Q21–Q40 (NEET-Level Enhanced)
🔹 Q21. Which one of the following is not a step in decomposition?
🔵 (A) Humification
🟢 (B) Mineralisation
🟠 (C) Nitrification
🔴 (D) Fragmentation
✅ Answer: (C) Nitrification
🔹 Q22. Which of the following represents the correct order in secondary succession?
🔵 (A) Grass → Shrubs → Trees → Forest
🟢 (B) Lichens → Mosses → Shrubs → Forest
🟠 (C) Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small fishes
🔴 (D) Ferns → Lichens → Bryophytes
✅ Answer: (A) Grass → Shrubs → Trees → Forest
🔹 Q23. Which nutrient is the chief limiting factor for productivity in freshwater lakes?
🔵 (A) Nitrogen
🟢 (B) Phosphorus
🟠 (C) Carbon
🔴 (D) Sulphur
✅ Answer: (B) Phosphorus
🔹 Q24. The amount of living matter in a unit area of a habitat at a given time is called
🔵 (A) Standing state
🟢 (B) Standing crop
🟠 (C) Biomagnification
🔴 (D) Productivity
✅ Answer: (B) Standing crop
🔹 Q25. A climax community remains stable due to
🔵 (A) Balanced energy flow and nutrient cycling
🟢 (B) Lack of productivity
🟠 (C) Low biodiversity
🔴 (D) Absence of decomposers
✅ Answer: (A) Balanced energy flow and nutrient cycling
🔹 Q26. Ecological efficiency is lowest in
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Primary consumers
🟠 (C) Secondary consumers
🔴 (D) Top carnivores
✅ Answer: (D) Top carnivores
🔹 Q27. Which of the following pyramids can be both upright and inverted depending on ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of energy
🟢 (B) Pyramid of biomass
🟠 (C) Pyramid of productivity
🔴 (D) Pyramid of decomposition
✅ Answer: (B) Pyramid of biomass
🔹 Q28. The most important ecological function of humus is
🔵 (A) Source of minerals
🟢 (B) Decreasing porosity
🟠 (C) Nutrient immobilisation
🔴 (D) Providing energy to producers
✅ Answer: (A) Source of minerals
🔹 Q29. An inverted pyramid of number is found in
🔵 (A) Grassland
🟢 (B) Forest with trees and insects
🟠 (C) Pond ecosystem
🔴 (D) Desert
✅ Answer: (B) Forest with trees and insects
🔹 Q30. Which of the following is true for ecological pyramids?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of biomass is always upright
🟢 (B) Pyramid of energy is always upright
🟠 (C) Pyramid of number is always upright
🔴 (D) All pyramids are sometimes inverted
✅ Answer: (B) Pyramid of energy is always upright
🔹 Q31. The final stage of succession is
🔵 (A) Pioneer community
🟢 (B) Climax community
🟠 (C) Seral community
🔴 (D) Sere
✅ Answer: (B) Climax community
🔹 Q32. Which ecosystem service directly supports agriculture?
🔵 (A) Pollination
🟢 (B) Oxygen production
🟠 (C) Climate regulation
🔴 (D) Water purification
✅ Answer: (A) Pollination
🔹 Q33. Which is the correct sequence of events in decomposition?
🔵 (A) Leaching → Fragmentation → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation
🟢 (B) Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation
🟠 (C) Humification → Mineralisation → Fragmentation
🔴 (D) Catabolism → Fragmentation → Leaching
✅ Answer: (B) Fragmentation → Leaching → Catabolism → Humification → Mineralisation
🔹 Q34. Which process releases nitrogen back into the atmosphere?
🔵 (A) Nitrification
🟢 (B) Denitrification
🟠 (C) Ammonification
🔴 (D) Assimilation
✅ Answer: (B) Denitrification
🔹 Q35. If GPP = 1800 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹ and respiration = 800 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹, then NPP =
🔵 (A) 800 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
🟢 (B) 1000 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
🟠 (C) 1800 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
🔴 (D) 2600 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
✅ Answer: (B) 1000 kJ m⁻² yr⁻¹
🔹 Q36. A pyramid of number in a grassland ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Upright
🟢 (B) Inverted
🟠 (C) Spindle-shaped
🔴 (D) Hour-glass shaped
✅ Answer: (A) Upright
🔹 Q37. The step of decomposition that produces soluble nutrients is
🔵 (A) Fragmentation
🟢 (B) Leaching
🟠 (C) Humification
🔴 (D) Mineralisation
✅ Answer: (B) Leaching
🔹 Q38. Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by
🔵 (A) Producers
🟢 (B) Consumers
🟠 (C) Decomposers
🔴 (D) All organisms
✅ Answer: (B) Consumers
🔹 Q39. Which of the following best explains ecological niche?
🔵 (A) The physical area occupied by a species
🟢 (B) Functional role of a species in ecosystem
🟠 (C) Association of species in community
🔴 (D) Habitat plus all biotic interactions
✅ Answer: (B) Functional role of a species in ecosystem
🔹 Q40. Which factor determines the shape of energy flow in ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Decomposers
🟢 (B) Unidirectional flow and 10% law
🟠 (C) Climate
🔴 (D) Top carnivores
✅ Answer: (B) Unidirectional flow and 10% law
🔴 Q41–Q50 (NEET-Level Higher Difficulty)
🔹 Q41. Which of the following shows hydrarch succession correctly?
🔵 (A) Planktons → Submerged plants → Floating plants → Reed swamp → Forest
🟢 (B) Moss → Shrubs → Forest
🟠 (C) Lichen → Moss → Fern
🔴 (D) Grass → Shrub → Tree
✅ Answer: (A) Planktons → Submerged plants → Floating plants → Reed swamp → Forest
🔹 Q42. The role of earthworms in ecosystem functioning is mainly as
🔵 (A) Herbivores
🟢 (B) Detritivores
🟠 (C) Producers
🔴 (D) Parasites
✅ Answer: (B) Detritivores
🔹 Q43. Which pyramid will be inverted in a single large tree ecosystem?
🔵 (A) Pyramid of number
🟢 (B) Pyramid of energy
🟠 (C) Pyramid of biomass
🔴 (D) Pyramid of productivity
✅ Answer: (A) Pyramid of number
🔹 Q44. If in an ecosystem, 5000 J of energy is fixed in plants, how much energy approximately will reach tertiary consumers?
🔵 (A) 500 J
🟢 (B) 50 J
🟠 (C) 5 J
🔴 (D) 0.5 J
✅ Answer: (C) 5 J
🔹 Q45. Which ecological principle is violated by excessive use of pesticides leading to biomagnification?
🔵 (A) Energy pyramid
🟢 (B) Nutrient cycling
🟠 (C) Population dynamics
🔴 (D) 10% law
✅ Answer: (B) Nutrient cycling
🔹 Q46. The most stable ecosystem is
🔵 (A) Ocean
🟢 (B) Forest
🟠 (C) Grassland
🔴 (D) Desert
✅ Answer: (A) Ocean
🔹 Q47. Which process contributes maximum CO₂ to the atmosphere?
🔵 (A) Respiration
🟢 (B) Volcanic eruption
🟠 (C) Combustion of fossil fuels
🔴 (D) Decomposition
✅ Answer: (C) Combustion of fossil fuels
🔹 Q48. Which ecological service is most vital for survival of aerobic organisms?
🔵 (A) Pollination
🟢 (B) Oxygen production
🟠 (C) Climate control
🔴 (D) Soil fertility
✅ Answer: (B) Oxygen production
🔹 Q49. Which of the following represents xerarch succession sequence?
🔵 (A) Lichen → Moss → Herb → Shrub → Tree
🟢 (B) Phytoplankton → Submerged plants → Trees
🟠 (C) Grass → Shrub → Forest → Marsh
🔴 (D) Bryophyte → Pteridophyte → Gymnosperm → Angiosperm
✅ Answer: (A) Lichen → Moss → Herb → Shrub → Tree
🔹 Q50. Which of the following best explains why the energy pyramid is always upright?
🔵 (A) Loss of energy as heat at each trophic level
🟢 (B) Increase in biomass at higher levels
🟠 (C) Efficiency of herbivores > carnivores
🔴 (D) All producers are autotrophs
✅ Answer: (A) Loss of energy as heat at each trophic level
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
