Class 11 : Poltical Science (In English) – Lesson 12. Freedom
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔴 Introduction
This chapter explains the importance, nature, limits, and various dimensions of freedom in human life. Freedom is not just freedom from the government but is connected to the overall development and self-respect of an individual. Freedom relates to thought, expression, action, and all aspects of life.
🟢 Meaning of Freedom
➡️ Freedom means liberation from unnecessary or unjust restrictions.
🌿 It implies that an individual is free to follow their desires, thoughts, and actions as long as they do not infringe upon others’ rights.
🧠 Core elements of Freedom —
✔️ Life without unnecessary barriers
✔️ Self-dependence and dignity
✔️ Freedom of choice
✏️ Note: Freedom is not only about ‘freedom from doing something’ but also about ‘having opportunities to do something’.
🔵 Why is Freedom Necessary?
✔️ For the development of personality.
✔️ For creativity and innovation.
✔️ For a dignified life in society.
✔️ For the functioning of democratic systems.
🌿 Without freedom, human beings become victims of slavery and injustice.
🟡 Various Dimensions of Freedom
1️⃣ Freedom of Thought – Freedom to think, question, and express ideas.
2️⃣ Freedom of Expression – Freedom to express through speech, writing, art, or other media.
3️⃣ Freedom of Association – Freedom to assemble and form organizations.
4️⃣ Economic Freedom – Freedom to work, earn, and produce.
✔️ The purpose of all these is to ensure a life free from fear and full of dignity.
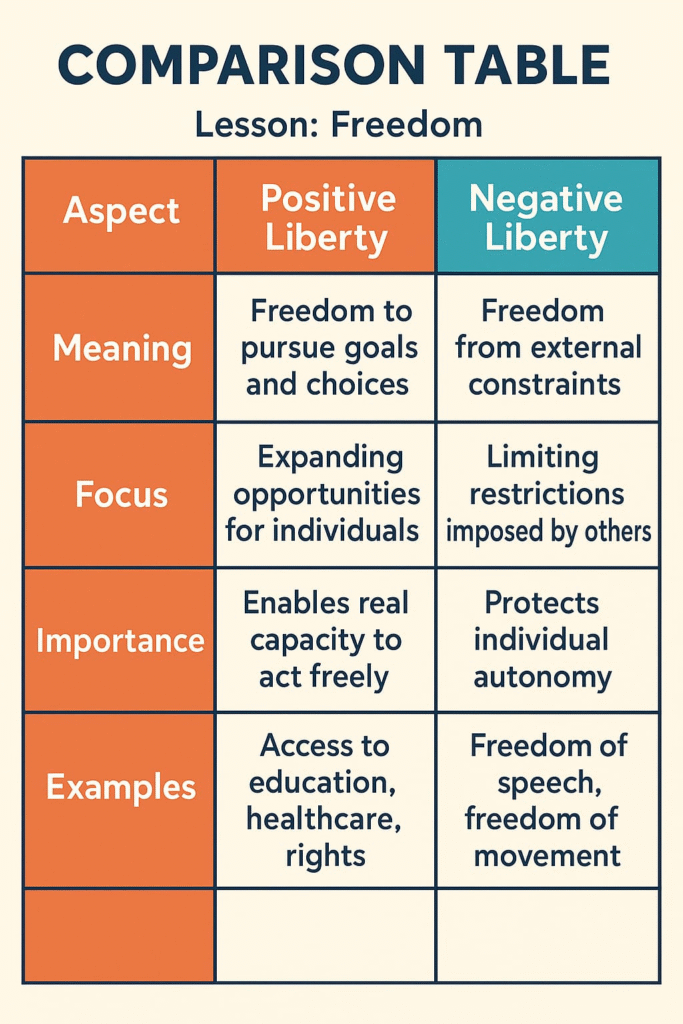
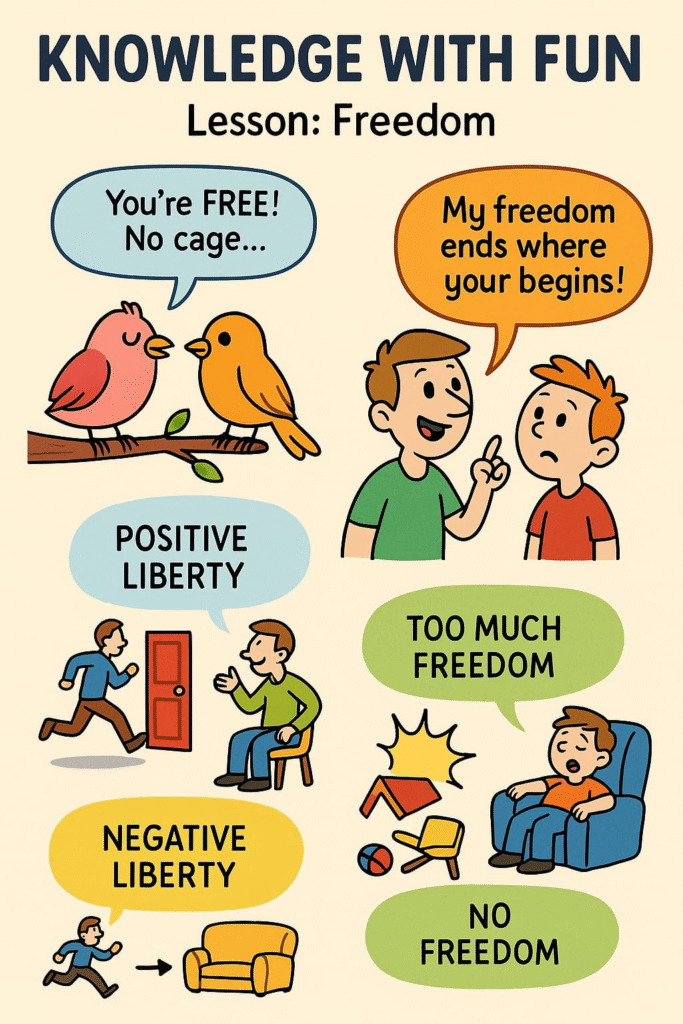
🔴 Negative and Positive Freedom
🟢 Negative Freedom:
➡️ Freedom from external restrictions.
✔️ Focuses on ‘what should not be’.
Example: The government should not act arbitrarily or oppress people.
🟡 Positive Freedom:
➡️ Opportunities and resources necessary for self-development.
✔️ Focuses on ‘what should be’.
Example: Facilities for education, health, livelihood.
✏️ Note: Both types of freedom complement each other.
🔵 Relationship between Freedom and Law
➡️ Freedom is not possible without law.
✔️ Law ensures rules and equality in society.
✔️ Without freedom, law becomes oppression.
✔️ Without law, freedom turns into anarchy.
💡 Example: Traffic rules do not limit freedom but ensure safety.
🟡 Relationship of Freedom with Other Values
✔️ Freedom is connected with equality, justice, and dignity.
✔️ Freedom for only the powerful is not true freedom.
✔️ Equal opportunities are essential for all citizens.
🔴 Freedom and Democracy
➡️ Democracy is fundamentally based on freedom.
✔️ Without freedom of expression, democracy is mere pretense.
✔️ Voting, protest, questioning – all are parts of freedom.
✏️ Note: Democracy and freedom are complementary to each other.
🟢 Why are Limits on Freedom Necessary?
✔️ If everyone had absolute freedom, others’ rights would be violated.
✔️ For the interest and order of society, some limits are necessary.
✔️ Limits must be rational, necessary, and minimal.
🌿 When are limits wrong?
➡️ When they suppress expression, promote injustice, or violate rights.
🔴 Nature of Freedom in India
➡️ Protection of freedom as a fundamental right through the Constitution.
✔️ Freedom of expression, association, movement, residence, trade, and thought.
✔️ Can be restricted during emergencies but never fully abolished.
🧠 Example: Right to Information – an extension of citizen freedom.
🟡 How to Utilize Freedom Properly?
✔️ Freedom comes with responsibility.
✔️ Respecting others’ rights is necessary.
✔️ One must act with awareness of the impact and scope of their actions.
✏️ Note: Freedom is linked with discipline.
🔵 Freedom and Modern Challenges
⚡ Censorship, invasion of privacy, surveillance, and oppressive laws are challenges to freedom.
✔️ Citizens must remain alert in modern democracies.
✔️ Protection of freedom requires continuous struggle and vigilance.
🟢 Why is This Chapter Important?
💡 This chapter teaches:
✔️ Freedom is not just a right but a responsibility.
✔️ The role of freedom in law, equality, and democracy.
✔️ Threats to freedom in modern society and their solutions.
🌿 Practical Life Application:
➡️ Thought, writing, protest, voting, employment – all are aspects of freedom.
📝 Quick Revision:
🔵 Freedom = Freedom from unjust restrictions
🟢 Types = Negative, Positive
🔴 Essential = Law, Equality, Democracy
🟡 Threats = Censorship, Oppression, Intolerance
🔵 Responsibility = Respecting others’ rights
🔵 Summary (Approx. 300 words)
This chapter clarifies the meaning, necessity, and various aspects of freedom. Freedom is not just liberation from the government but is tied to an individual’s life, thought, expression, and actions. Its aim is to provide individuals with a life free from fear and filled with dignity.
There are two forms of freedom – negative, which means freedom from external restrictions, and positive, which means opportunities for development. Freedom is directly connected to law, equality, justice, and democracy. Without law, freedom turns into chaos; without freedom, law becomes oppression.
In a democracy, citizens enjoy freedoms such as expression, association, thought, and voting. Without freedom, democracy is hollow. Freedom also comes with responsibility to respect others’ rights.
Freedom can be limited if it harms others’ rights or the public interest. However, limits should be reasonable and justified. In India, the Constitution guarantees freedom as a fundamental right.
From this chapter, it is clear that freedom is not just a right but is tied to responsibility and awareness. In modern times, citizens must remain vigilant to protect their freedoms.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
What is meant by freedom? Is there a relationship between freedom for the individual and freedom for the nation?
🟢 Answer 1:
Freedom means the absence of unnecessary restrictions and the presence of opportunities for individuals to develop their abilities and realize their potential. It is the condition where individuals can think, express, and act according to their own choice without fear, as long as it does not harm others.
There is a close relationship between individual freedom and the freedom of a nation. A nation that is free ensures that its citizens enjoy civil and political rights, freedom of expression, and opportunities for self-development. Similarly, individuals who are free contribute to the growth, strength, and democratic functioning of the nation. Thus, freedom for individuals and freedom for the nation are interdependent and complementary.
🔴 Question 2:
What is the difference between the negative and positive conception of liberty?
🟢 Answer 2:
Negative liberty means freedom from external interference, especially from the government or authority. It stresses on the absence of obstacles or restrictions imposed by others on one’s actions. It is about ‘freedom from’ constraints.
Positive liberty, on the other hand, is about having the capacity and opportunities to act in ways that one desires. It ensures access to necessary conditions like education, health, and resources to achieve personal goals. It is about ‘freedom to’ realize one’s potential.
In summary, negative liberty focuses on non-interference, while positive liberty emphasizes enabling conditions and actual opportunities.
🔵 Question 3:
What is meant by social constraints? Are constraints of any kind necessary for enjoying freedom?
🟢 Answer 3:
Social constraints are the limitations imposed by society in the form of laws, rules, traditions, and moral codes to regulate human behavior. They ensure that an individual’s freedom does not infringe upon the rights and freedoms of others.
Constraints are necessary for enjoying freedom because unchecked freedom can lead to chaos and harm to others. Reasonable restrictions help maintain social harmony, protect individual rights, and prevent actions that could threaten peace and security. Therefore, some constraints are essential to ensure that everyone enjoys their freedom in a balanced manner.
🔴 Question 4:
What is the role of the state in upholding freedom of its citizens?
🟢 Answer 4:
The state plays a crucial role in upholding the freedom of its citizens by creating a legal framework that protects rights and ensures justice. It prevents the misuse of power by individuals or groups and safeguards against exploitation, discrimination, and injustice.
The state provides security, enforces laws, and guarantees fundamental rights like freedom of speech, association, and movement. It also ensures positive freedom by offering opportunities for education, healthcare, and economic well-being. By doing so, the state creates an environment where individuals can realize their full potential while maintaining peace and order.
🔵 Question 5:
What is meant by freedom of expression? What in your view would be a reasonable restriction on this freedom? Give examples.
🟢 Answer 5:
Freedom of expression means the right to express one’s ideas, thoughts, beliefs, and opinions freely through speech, writing, art, or any other means. It is a cornerstone of democratic societies and essential for personal development and social progress.
However, this freedom is not absolute. Reasonable restrictions are necessary to maintain public order, protect the rights of others, and prevent hate speech, violence, or defamation. For example, spreading rumors that incite violence or publishing false information that harms an individual’s reputation should be restricted. These limitations ensure that freedom of expression is exercised responsibly without harming society or individuals.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🌸 1️⃣ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (10 Questions)
🔵 Q1. What is the core idea of freedom?
(A) Complete absence of all rules
(B) Absence of unnecessary restrictions
(C) Total disobedience of laws
(D) Dominance over others
✅ Answer: (B) Absence of unnecessary restrictions
🟢 Q2. Freedom is necessary because:
(A) It allows exploitation
(B) It helps in personal and social development
(C) It leads to anarchy
(D) It promotes violence
✅ Answer: (B) It helps in personal and social development
🔴 Q3. Which one of the following is NOT a type of freedom?
(A) Freedom of Thought
(B) Freedom of Speech
(C) Freedom to Harm Others
(D) Freedom of Movement
✅ Answer: (C) Freedom to Harm Others
🟡 Q4. Negative liberty refers to:
(A) Absence of external restrictions
(B) Providing all resources
(C) Obeying every rule
(D) Accepting slavery
✅ Answer: (A) Absence of external restrictions
🔵 Q5. Positive liberty is about:
(A) External barriers
(B) Providing opportunities for growth
(C) Unjust restrictions
(D) Arbitrary laws
✅ Answer: (B) Providing opportunities for growth
🟢 Q6. Freedom cannot be absolute because:
(A) It may harm others
(B) It should be enjoyed without boundaries
(C) All restrictions are bad
(D) Laws are not necessary
✅ Answer: (A) It may harm others
🔴 Q7. Which of the following helps in protecting freedom?
(A) Arbitrary Rule
(B) Rule of Law
(C) Dictatorship
(D) Exploitation
✅ Answer: (B) Rule of Law
🟡 Q8. Which of these rights ensures freedom of expression?
(A) Right to Equality
(B) Right to Freedom
(C) Right against Exploitation
(D) Right to Constitutional Remedies
✅ Answer: (B) Right to Freedom
🔵 Q9. Freedom is closely linked with:
(A) Discipline and Responsibility
(B) Ignorance
(C) Suppression
(D) Fear
✅ Answer: (A) Discipline and Responsibility
🟢 Q10. Freedom without reasonable restrictions leads to:
(A) Order and Harmony
(B) Chaos and Harm
(C) Respect for Others
(D) Better Society
✅ Answer: (B) Chaos and Harm
🌸 2️⃣ FILL IN THE BLANKS (3 Questions)
🔴 Q11. Freedom is essential for the development of _ potential.
✅ Answer: human
🟢 Q12. Positive liberty ensures the availability of _ and opportunities.
✅ Answer: resources
🔵 Q13. Freedom must be used with _ towards others’ rights.
✅ Answer: responsibility
🌸 3️⃣ TRUE / FALSE (2 Questions)
🟡 Q14. Freedom means living without any laws or rules.
✅ Answer: False
🔴 Q15. Freedom helps in expressing one’s ideas and thoughts.
✅ Answer: True
🌸 4️⃣ ASSERTION-REASON TYPE (2 Questions)
🔵 Q16.
Assertion (A): Freedom and law go hand in hand.
Reason (R): Laws protect individuals’ rights and ensure fair use of freedom.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A)
🟢 Q17.
Assertion (A): Absolute freedom is necessary for human progress.
Reason (R): Unrestricted freedom leads to discipline and order.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (D)
🌸 5️⃣ SHORT ANSWER (30 words limit) (3 Questions)
🔵 Q18. What is the importance of freedom?
✅ Answer: Freedom is essential for personal growth, expressing thoughts, making choices, and living with dignity. It enables individuals to realize their potential and contribute to society.
🟢 Q19. Mention one reason why restrictions are necessary on freedom.
✅ Answer: Restrictions are necessary to protect others’ rights, maintain public order, and prevent harm or chaos resulting from unchecked actions.
🔴 Q20. How does freedom contribute to democracy?
✅ Answer: Freedom allows citizens to speak, protest, and participate actively in democratic processes, ensuring accountability and transparency in governance.
🌸 6️⃣ MID-LENGTH ANSWER (60 words limit) (3 Questions)
🟡 Q21. Explain the difference between positive and negative liberty.
✅ Answer: Negative liberty means freedom from interference or restrictions. Positive liberty refers to having opportunities, resources, and the capacity to achieve goals. While negative liberty stresses absence of restrictions, positive liberty focuses on creating conditions that enable people to develop and grow.
🔵 Q22. Why is social responsibility important in enjoying freedom?
✅ Answer: Freedom cannot be enjoyed in isolation. It requires understanding others’ rights and acting responsibly. Social responsibility ensures that one’s freedom does not harm others, maintaining harmony and mutual respect in society.
🟢 Q23. How does the state protect freedom?
✅ Answer: The state protects freedom through laws, courts, and rights. It ensures equal opportunities, prevents discrimination, and safeguards against injustice. The state guarantees rights like speech, movement, and association, creating a just environment.
🌸 7️⃣ LONG ANSWER (120 words limit) (2 Questions)
🔴 Q24. Discuss the relationship between freedom and law.
✅ Answer: Freedom and law are closely related. Laws define the boundaries within which individuals can exercise their freedom without infringing upon others’ rights. Without laws, freedom may lead to chaos, while laws without freedom lead to oppression. A balance is necessary to ensure that citizens enjoy liberty while respecting public order. Reasonable restrictions on freedom are placed to protect individuals and the society. For example, laws against hate speech or violence prevent misuse of freedom. Thus, laws safeguard rights, promote justice, and help individuals exercise freedom responsibly.
🟡 Q25. Why is freedom essential in modern society?
✅ Answer: Freedom is the foundation of human dignity and democracy. In modern societies, it allows individuals to think, express, work, and live without fear. It supports creativity, innovation, and participation in governance. Freedom enables people to question, protest, and seek justice, strengthening democratic institutions. It ensures respect for diversity and protects minorities. Without freedom, oppression and injustice thrive. Therefore, freedom is essential for progress, equality, and harmony in society.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
