Class 11 : Maths (In English) – Lesson 4. Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
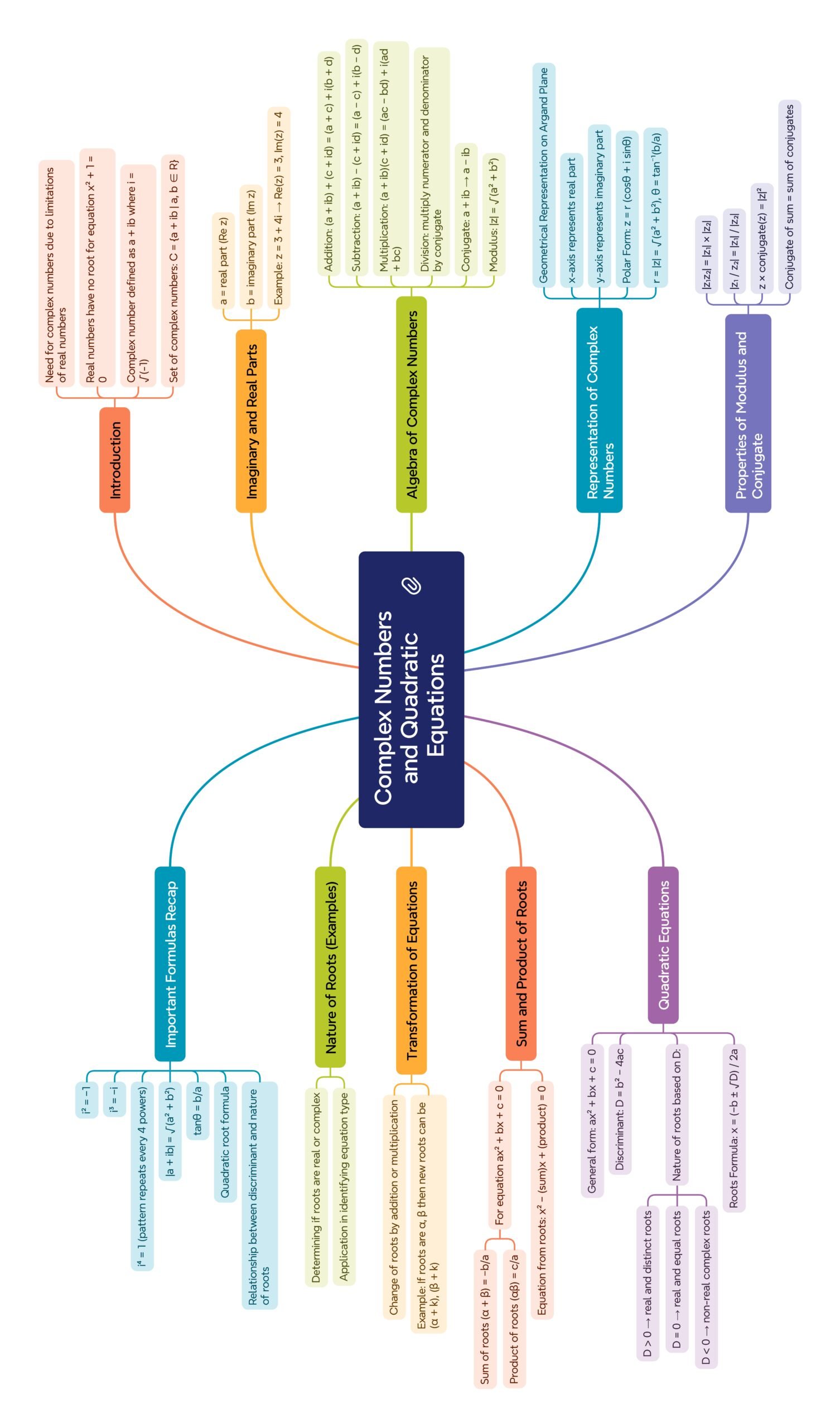
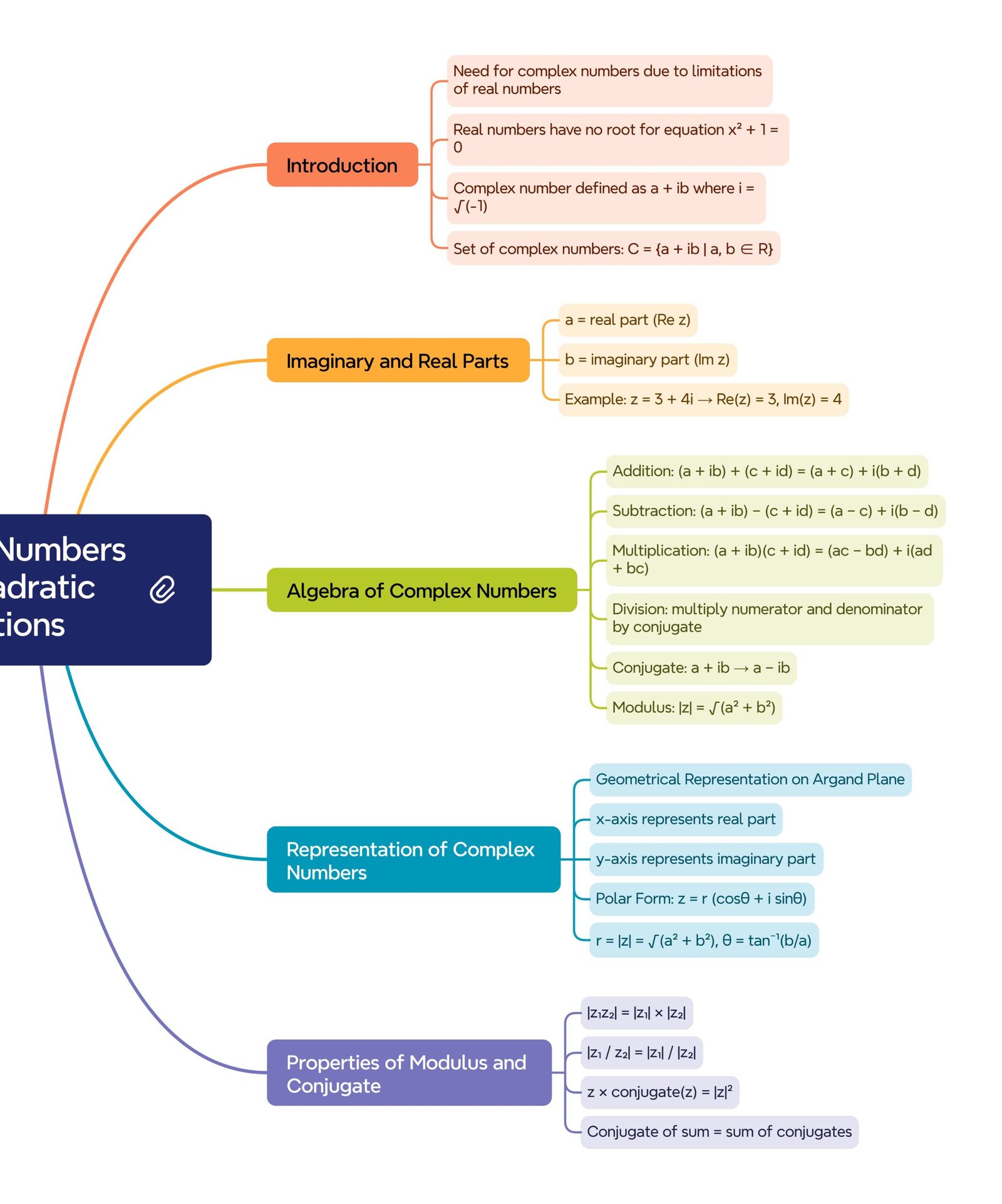
1️⃣ Introduction
🔵 A quadratic equation a·x² + b·x + c = 0 has real roots only when the discriminant D = b² − 4ac ≥ 0.
🟢 When D < 0, roots are not real. To handle such cases, mathematicians introduced a new number i such that i² = −1.
💡 Using i, we form complex numbers which extend the real number system.
✨ Complex numbers help solve equations that cannot be solved in real numbers.
2️⃣ Imaginary Unit
📘 Definition: i = √(−1)
✔ i² = −1, i³ = −i, i⁴ = 1 (then repeats)
🧠 Examples:
🔹 √(−4) = 2i
🔹 √(−9) = 3i
🔹 √(−25) = 5i
3️⃣ Definition of Complex Number
🔵 A complex number is of the form z = a + i·b
➡ a = real part, Re(z)
➡ b = imaginary part, Im(z)
📌 Set of all complex numbers is denoted by C.
🧾 Examples:
1️⃣ 3 + 2i → Re = 3, Im = 2
2️⃣ −5i → Re = 0, Im = −5
3️⃣ 7 → purely real (Im = 0)
4️⃣ 4i → purely imaginary (Re = 0)
4️⃣ Equality of Complex Numbers
Two complex numbers a + i·b and c + i·d are equal if
✅ a = c
✅ b = d
Example: 2 + 3i = 2 + 3i ✔ but ≠ 3 + 2i ❌
5️⃣ Representation on Argand Plane
🧭 Complex number z = a + i·b is represented as point (a, b).
📈 x-axis → real part
📉 y-axis → imaginary part
💡 This plane is called the Argand Plane.
📍 Example: z = 3 + 4i → point (3, 4)
6️⃣ Modulus of a Complex Number
🔹 The modulus is the distance from origin (0, 0) to (a, b).
Formula: |z| = √(a² + b²)
Example: z = 3 + 4i → |z| = √(9 + 16) = 5
📏 Represents length of vector.
7️⃣ Argument (Amplitude)
🔸 Argument θ is the angle made by line joining origin to (a, b) with positive x-axis.
Formula: tan θ = b / a
🧭 Quadrant check:
• I: a > 0, b > 0
• II: a < 0, b > 0
• III: a < 0, b < 0
• IV: a > 0, b < 0
✏️ Example: z = 1 + √3·i → tan θ = √3 ⇒ θ = π/3
8️⃣ Conjugate of a Complex Number
🔹 Conjugate of z = a + i·b is z̄ = a − i·b
🧾 Properties:
1️⃣ z·z̄ = a² + b² = |z|²
2️⃣ (z₁ + z₂)̄ = z̄₁ + z̄₂
3️⃣ (z₁·z₂)̄ = z̄₁ · z̄₂
📘 Example: z = 3 + 4i → z̄ = 3 − 4i
✔ z·z̄ = 25
9️⃣ Operations on Complex Numbers
Let z₁ = a + i·b, z₂ = c + i·d
➕ Addition: z₁ + z₂ = (a + c) + i·(b + d)
➖ Subtraction: z₁ − z₂ = (a − c) + i·(b − d)
✖ Multiplication: z₁·z₂ = (a·c − b·d) + i·(a·d + b·c)
➗ Division: z₁ ÷ z₂ = [(a + i·b)(c − i·d)] / (c² + d²)
🧠 Example: (3 + 2i) ÷ (1 − i)
= [(3 + 2i)(1 + i)] / 2
= (1/2) + (5/2)i
🔟 Polar (Trigonometric) Form
🧭 Any complex number z = a + i·b can be written as
z = r (cos θ + i·sin θ)
where r = √(a² + b²), θ = argument
✏️ Example: z = 1 + i
r = √2, θ = π/4
So z = √2 (cos π/4 + i·sin π/4)
1️⃣1️⃣ Euler Form
Using e^(iθ) = cos θ + i·sin θ
✔ z = r·e^(iθ)
1️⃣2️⃣ Algebraic Properties
🟢 Commutative: z₁ + z₂ = z₂ + z₁, z₁·z₂ = z₂·z₁
🟡 Associative: (z₁ + z₂) + z₃ = z₁ + (z₂ + z₃)
🔵 Distributive: z₁·(z₂ + z₃) = z₁·z₂ + z₁·z₃
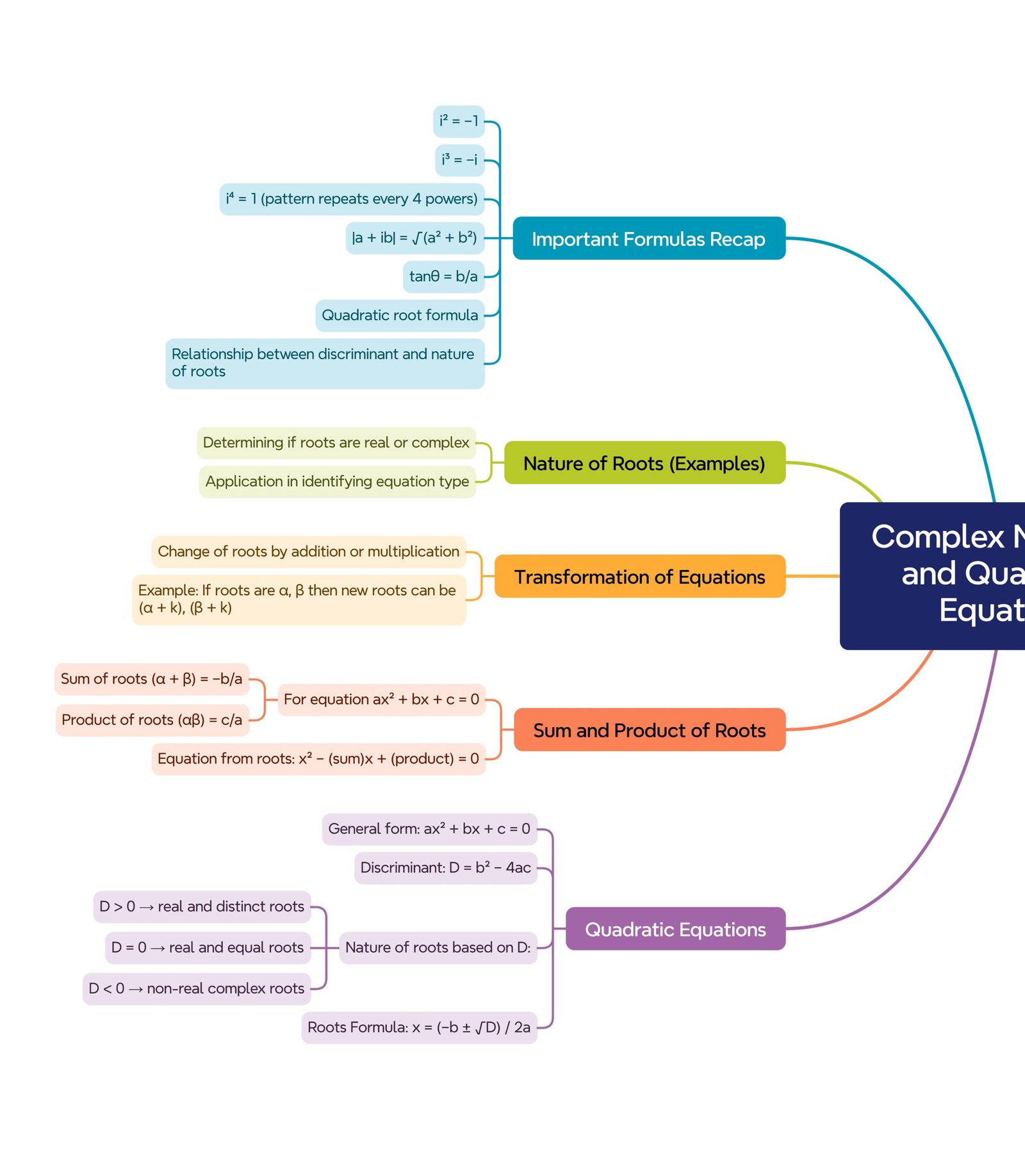
1️⃣3️⃣ Quadratic Equation
General: a·x² + b·x + c = 0 (a ≠ 0)
Discriminant D = b² − 4ac
📊 Nature of Roots:
• D > 0 → real, distinct
• D = 0 → real, equal
• D < 0 → complex conjugate
Roots: x = [−b ± √D] / (2a)
If D < 0 → √D = i√|D|
✏️ Example: x² + 4x + 8 = 0
D = 16 − 32 = −16
Roots: x = (−4 ± 4i) / 2 = −2 ± 2i
1️⃣4️⃣ Relations between Roots and Coefficients
If α, β are roots:
α + β = −b/a
α·β = c/a
1️⃣5️⃣ Formation of Quadratic Equation from Roots
If roots are α, β → x² − (α + β)x + αβ = 0
1️⃣6️⃣ Cube Roots of Unity
Numbers satisfying x³ = 1 → 1, ω, ω²
ω = (−1 + i√3)/2, ω² = (−1 − i√3)/2
Properties:
• ω³ = 1
• 1 + ω + ω² = 0
• ω ≠ 1
1️⃣7️⃣ Geometrical Interpretation
🧭 Each complex number = vector from origin to (a, b).
• Length = |z|
• Angle = θ
✔ Multiplying by i rotates 90° anticlockwise.
Example: 1 × i = i
1️⃣8️⃣ Key Identities
📘 i² = −1, i³ = −i, i⁴ = 1
✔ z·z̄ = |z|²
✔ |z₁·z₂| = |z₁||z₂|
✔ arg(z₁·z₂) = arg(z₁) + arg(z₂)
✔ (z₁·z₂)̄ = z̄₁·z̄₂
1️⃣9️⃣ Applications
🧠 Used to solve equations with negative discriminant
⚡ Electrical circuits (AC)
📈 Vector rotations
🧪 Quantum mechanics
🔶 Summary (≈300 words)
• z = a + i·b
• i² = −1, i³ = −i, i⁴ = 1
• Re(z) = a, Im(z) = b
• |z| = √(a² + b²)
• z̄ = a − i·b
• Polar: r(cos θ + i·sin θ)
• Euler: r·e^(iθ)
• Argand plane → point (a, b)
Quadratic eq: a·x² + b·x + c = 0
D > 0 → real, distinct
D = 0 → real, equal
D < 0 → complex conjugates
Roots: (−b ± i√|D|)/2a
α + β = −b/a, αβ = c/a
Cube roots of unity: 1, ω, ω²
ω = (−1 + i√3)/2
ω³ = 1, 1 + ω + ω² = 0
📝 Quick Recap
✔ z = a + i·b
✔ i² = −1
✔ |z| = √(a² + b²)
✔ Conjugate = a − i·b
✔ Polar = r(cos θ + i·sin θ)
✔ D < 0 → complex roots
✔ Cube roots unity: 1, ω, ω²
✔ 1 + ω + ω² = 0
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
📗 Exercise 4.1
🔵 Question 1
(5i) (−3i/5). Express in the form a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ (5i)(−3i/5) = (5·−3/5)·i²
➡️ = (−3)·(−1)
➡️ = 3
✔️ Result: 3 + 0i
🔵 Question 2
i⁹ + i¹⁹. Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ i⁴ = 1 ⇒ powers repeat every 4
➡️ i⁹ = i¹ (since 9 ≡ 1 mod 4) = i
➡️ i¹⁹ = i³ (since 19 ≡ 3 mod 4) = −i
➡️ i⁹ + i¹⁹ = i + (−i) = 0
✔️ Result: 0 + 0i
🔵 Question 3
i⁻³⁹. Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ i⁻³⁹ = 1 / i³⁹
➡️ i³⁹ = i³ (since 39 ≡ 3 mod 4) = −i
➡️ 1/(−i) = i
✔️ Result: 0 + 1i
🔵 Question 4
3(7 + 7i) + i(7 + 7i). Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ 3(7 + 7i) = 21 + 21i
➡️ i(7 + 7i) = 7i + 7i² = 7i − 7
➡️ Sum = (21 − 7) + (21i + 7i)
➡️ = 14 + 28i
✔️ Result: 14 + 28i
🔵 Question 5
(1 − i) − (−1 + 6i). Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ = 1 − i + 1 − 6i
➡️ = 2 − 7i
✔️ Result: 2 − 7i
🔵 Question 6
(1/5 + (2/5)i) − (4 + (5/2)i). Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ Real: 1/5 − 4 = −19/5
➡️ Imag: 2/5 − 5/2 = (4/10 − 25/10) = −21/10
✔️ Result: −19/5 − (21/10)i
🔵 Question 7
[(1/3 + (7/3)i) + (4 + (1/3)i)] − (−4/3 + i). Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ Inside sum: real = 1/3 + 4 = 13/3; imag = 7/3 + 1/3 = 8/3
➡️ Subtract: (13/3 − (−4/3)) + (8/3 − 1)i
➡️ = 17/3 + (5/3)i
✔️ Result: 17/3 + (5/3)i
🔵 Question 8
(1 − i)⁴. Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ (1 − i)² = 1 − 2i + i² = −2i
➡️ (−2i)² = 4i² = −4
✔️ Result: −4 + 0i
🔵 Question 9
(1/3 + 3i)³. Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ Let a = 1/3, b = 3i
➡️ (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³
➡️ a³ = 1/27
➡️ 3a²b = 3·(1/9)·3i = i
➡️ 3ab² = 3·(1/3)·(3i)² = 1·9i² = −9
➡️ b³ = (3i)³ = 27i³ = −27i
➡️ Sum = (1/27 − 9) + (i − 27i)
➡️ = (−242/27) − 26i
✔️ Result: −242/27 − 26i
🔵 Question 10
(−2 − (1/3)i)³. Express in a + ib.
🟢 Answer
➡️ Let a = −2, b = −(1/3)i
➡️ (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³
➡️ a³ = −8
➡️ 3a²b = 3·4·(−1/3)i = −4i
➡️ b² = (−1/3 i)² = −1/9
➡️ 3ab² = 3·(−2)·(−1/9) = 2/3
➡️ b³ = (−1/3 i)³ = (1/27)i
➡️ Sum = (−8 + 2/3) + (−4 + 1/27)i
➡️ Real = −22/3; Imag = (−108/27 + 1/27)i = (−107/27)i
✔️ Result: −22/3 − (107/27)i
🔵 Question 11
Find the multiplicative inverse of 4 − 3i.
🟢 Answer
➡️ 1/(4 − 3i) = (4 + 3i)/(4² + 3²)
➡️ = (4 + 3i)/25
✔️ Inverse: 4/25 + (3/25)i
🔵 Question 12
Find the multiplicative inverse of √5 + 3i.
🟢 Answer
➡️ 1/(√5 + 3i) = (√5 − 3i)/( (√5)² + 3² )
➡️ = (√5 − 3i)/(5 + 9)
➡️ = (√5 − 3i)/14
✔️ Inverse: (√5)/14 − (3/14)i
🔵 Question 13
Find the multiplicative inverse of −i.
🟢 Answer
➡️ 1/(−i) = i
✔️ Inverse: 0 + 1i
🔵 Question 14
Express in the form a + ib:
[(3 + i√5)(3 − i√5)] / [(√3 + √2 i) − (√3 − i√2)]
🟢 Answer
➡️ Numerator: (a + ib)(a − ib) = a² + b²
➡️ = 3² + (√5)² = 9 + 5 = 14
➡️ Denominator: (√3 + √2 i) − (√3 − √2 i)
➡️ = √3 − √3 + √2 i − (−√2 i) = 2√2 i
➡️ Fraction = 14 / (2√2 i) = 7/(√2 i)
➡️ 1/i = −i ⇒ 7/(√2 i) = −(7/√2) i
➡️ = −(7√2/2) i
✔️ Result: 0 − (7√2/2)i
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🟦 Section A – MCQs (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1:
The value of i² + i⁴ + i⁶ + i⁸ is
1️⃣ 4
2️⃣ 0
3️⃣ 2
4️⃣ –4
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 0
🔵 Question 2:
If z = 3 + 4i, then |z| equals
1️⃣ 5
2️⃣ 7
3️⃣ 1
4️⃣ 25
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 5
🔵 Question 3:
Conjugate of (2 – 5i) is
1️⃣ 2 + 5i
2️⃣ –2 – 5i
3️⃣ 2 – 5i
4️⃣ –2 + 5i
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 + 5i
🔵 Question 4:
The real part of (3i + 5) is
1️⃣ 3
2️⃣ 5
3️⃣ 8
4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 5
🔵 Question 5:
If z = 2 + i√3, then argument of z is
1️⃣ π/6
2️⃣ π/3
3️⃣ π/2
4️⃣ π
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ π/3
🔵 Question 6:
For any complex number z, z·z̄ equals
1️⃣ |z|²
2️⃣ z²
3️⃣ z
4️⃣ |z|
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ |z|²
🔵 Question 7:
If i = √(–1), then i⁵ equals
1️⃣ i
2️⃣ –1
3️⃣ –i
4️⃣ 1
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ i
🔵 Question 8:
The modulus of 1 – i is
1️⃣ √2
2️⃣ 1
3️⃣ 2
4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ √2
🔵 Question 9:
The value of i³ + i⁵ is
1️⃣ –i
2️⃣ 0
3️⃣ i
4️⃣ –2i
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 0
🔵 Question 10:
If z = 4i, then Re(z) is
1️⃣ 4
2️⃣ 0
3️⃣ i
4️⃣ –4
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 0
🔵 Question 11:
Cube roots of unity satisfy
1️⃣ x² + x + 1 = 0
2️⃣ x³ – 1 = 0
3️⃣ x³ + 1 = 0
4️⃣ x² – x + 1 = 0
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ x³ – 1 = 0
🔵 Question 12:
If ω is cube root of unity, then ω² + ω + 1 =
1️⃣ 1
2️⃣ 0
3️⃣ –1
4️⃣ 2
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 0
🔵 Question 13:
If α, β are roots of x² + 3x + 2 = 0, then α + β =
1️⃣ 2
2️⃣ –2
3️⃣ –3
4️⃣ 3
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ –3
🔵 Question 14:
If α, β are roots of x² + bx + c = 0, then αβ =
1️⃣ b
2️⃣ c
3️⃣ c/b
4️⃣ c/a
🟢 Answer: 4️⃣ c/a
🔵 Question 15:
If z = a + ib, then Im(z) is
1️⃣ a
2️⃣ b
3️⃣ i·b
4️⃣ a + b
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ b
🔵 Question 16:
The polar form of 1 + i is
1️⃣ √2 (cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
2️⃣ 2 (cos π/2 + i sin π/2)
3️⃣ √2 (cos π/3 + i sin π/3)
4️⃣ 1 (cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ √2 (cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
🔵 Question 17:
If z₁ = 2 + 3i, z₂ = 1 – 2i, then Re(z₁ + z₂) =
1️⃣ 2
2️⃣ 3
3️⃣ 1
4️⃣ 4
🟢 Answer: 4️⃣ 4
🔵 Question 18:
The cube roots of unity are
1️⃣ 1, ω, ω²
2️⃣ 1, –1, i
3️⃣ 1, i, –i
4️⃣ 1, –1, ω
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1, ω, ω²
🟨 Section B – Very Short Answer (2 marks each)
🔵 Question 19: Find the modulus and argument of z = 1 – i.
🟢 Answer: |z| = √(1² + (–1)²) = √2, θ = tan⁻¹(–1) = –π/4
🔵 Question 20: Express (1 + i)/(1 – i) in the form a + ib.
🟢 Answer: Multiply by conjugate:
(1 + i)/(1 – i) × (1 + i)/(1 + i) = (1 + 2i + i²)/2 = i
🔵 Question 21: If z₁ = 3 + 4i and z₂ = 1 – 2i, find z₁·z₂.
🟢 Answer: (3 + 4i)(1 – 2i) = 3 – 6i + 4i – 8i² = 11 – 2i
🔵 Question 22: Write the conjugate of (2 – 3i)/(4 + i).
🟢 Answer: First simplify:
Multiply by conjugate (4 – i): (2 – 3i)(4 – i)/(16 + 1) = (8 – 2i – 12i + 3i²)/17 = (8 – 14i – 3)/17 = (5 – 14i)/17
Conjugate = (5 + 14i)/17
🔵 Question 23: Solve x² + x + 1 = 0.
🟢 Answer: D = 1 – 4 = –3
x = [–1 ± i√3]/2 = –½ ± (√3/2)i
🟧 Section C – Short Answer (3 marks each)
🔵 Question 24: Find modulus and argument of z = –1 + √3 i.
🟢 Answer:
|z| = √[ (–1)² + (√3)² ] = √4 = 2
θ = tan⁻¹(√3 / –1) → QII → π – π/3 = 2π/3
z = 2 (cos 2π/3 + i sin 2π/3)
🔵 Question 25: If z₁ = 3 + 4i, z₂ = 1 + 2i, find |z₁·z₂| and |z₁|·|z₂|.
🟢 Answer:
z₁·z₂ = (3 + 4i)(1 + 2i) = 3 + 6i + 4i + 8i² = –5 + 10i
|z₁·z₂| = √( (–5)² + 10² ) = √125 = 5√5
|z₁| = 5, |z₂| = √5 → |z₁|·|z₂| = 5√5
✔ Verified |z₁z₂| = |z₁||z₂|
🔵 Question 26: Express z = 1 – √3 i in polar form.
🟢 Answer:
r = √(1² + (–√3)²) = 2
θ = tan⁻¹(–√3/1) = –π/3
z = 2 (cos(–π/3) + i sin(–π/3))
🔵 Question 27: Show that (1 + i)⁴ = –4.
🟢 Answer:
(1 + i)² = 1 + 2i + i² = 2i
(1 + i)⁴ = (2i)² = 4i² = –4
🔵 Question 28: If roots of x² + 2x + 5 = 0 are α, β, verify α·β = c/a.
🟢 Answer:
D = 4 – 20 = –16
α = –1 + 2i, β = –1 – 2i
α·β = (–1)² – (2i)² = 1 – (–4) = 5 = c/a ✔
🟥 Section D – Long Answer (5 marks each)
🔵 Question 29: Solve x² + 4x + 13 = 0 and represent the roots on Argand plane.
🟢 Answer:
D = 16 – 52 = –36
Roots: x = [–4 ± i√36]/2 = –2 ± 3i
🧭 Points: (–2, 3) and (–2, –3)
🔵 Question 30: Find all cube roots of 8( cos 300° + i sin 300° ).
🟢 Answer:
r = 8, θ = 300°
Cube roots: √[3]{8} [cos((300° + 360°k)/3) + i sin((300° + 360°k)/3)]
= 2[cos(100°), cos(220°), cos(340°)] with corresponding sines.
🔵 Question 31: Show that ω and ω² are complex cube roots of unity and find 1 + ω + ω².
🟢 Answer:
ω = (–1 + i√3)/2, ω² = (–1 – i√3)/2
ω³ = 1
1 + ω + ω² = 0 ✔
🟫 Section E – Case/Application (5 marks each)
🔵 Question 32:
A quadratic equation represents motion with complex roots.
Given: x² + 6x + 13 = 0
(a) Find the roots.
(b) Interpret geometrically.
🟢 Answer:
D = 36 – 52 = –16
Roots = –3 ± 2i
Representation: points (–3, 2), (–3, –2) on Argand plane.
🔵 Question 33:
An alternating current is given by I = 10(cos ωt + i sin ωt).
Find |I| and interpret.
🟢 Answer:
|I| = 10 √(cos² ωt + sin² ωt) = 10
Interpretation: amplitude of current = 10 units.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
If z = 3 + 4i, then modulus of z is
🟥 1️⃣ 5
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 7
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 5
📘 (JEE Main 2024)
🔵 Question 2
If z1 = 2 + 3i and z2 = 3 − 4i, then z1 × z2 =
🟥 1️⃣ 18 − i
🟩 2️⃣ 6 + i
🟨 3️⃣ 18 + i
🟦 4️⃣ 6 − i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 18 − i
📘 (JEE Main 2023)
🔵 Question 3
If z = a + ib satisfies |z| = 5 and a = 3, then b equals
🟥 1️⃣ 4 or −4
🟩 2️⃣ 2 or −2
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 1
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 4 or −4
📘 (JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 4
If z = x + iy satisfies |z − 3| = 5, then locus of z is
🟥 1️⃣ Circle with centre (3, 0) and radius 5
🟩 2️⃣ Circle with centre (0, 3) and radius 5
🟨 3️⃣ Line parallel to x-axis
🟦 4️⃣ Line parallel to y-axis
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Circle with centre (3, 0) and radius 5
📘 (JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 5
Conjugate of 2 − 3i is
🟥 1️⃣ 2 + 3i
🟩 2️⃣ −2 + 3i
🟨 3️⃣ −2 − 3i
🟦 4️⃣ 2 − 3i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 2 + 3i
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 6
If z = 1 + i, then z⁴ =
🟥 1️⃣ −4
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 4i
🟦 4️⃣ 2i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −4
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 7
If z = 2(cos 60° + i sin 60°), then z³ equals
🟥 1️⃣ 8(cos 180° + i sin 180°)
🟩 2️⃣ 8(cos 120° + i sin 120°)
🟨 3️⃣ 6(cos 60° + i sin 60°)
🟦 4️⃣ 8(cos 90° + i sin 90°)
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 8(cos 180° + i sin 180°)
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 8
If one root of x² + 5x + 6 = 0 is −2, the other root is
🟥 1️⃣ −3
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ −6
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −3
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 9
For x² + 4x + 5 = 0, roots are
🟥 1️⃣ Real and equal
🟩 2️⃣ Real and distinct
🟨 3️⃣ Imaginary and conjugate
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer: 🟨 3️⃣ Imaginary and conjugate
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 10
If discriminant of ax² + bx + c = 0 is zero, then roots are
🟥 1️⃣ Equal and real
🟩 2️⃣ Unequal and real
🟨 3️⃣ Imaginary
🟦 4️⃣ Distinct and rational
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Equal and real
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 11
If roots of x² + 6x + 9 = 0 are
🟥 1️⃣ Equal and real
🟩 2️⃣ Imaginary
🟨 3️⃣ Distinct real
🟦 4️⃣ Complex conjugate
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Equal and real
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 12
If one root of x² − 5x + k = 0 is 2, find k
🟥 1️⃣ 6
🟩 2️⃣ 8
🟨 3️⃣ 10
🟦 4️⃣ 12
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 6
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 13
For quadratic equation x² + px + q = 0 with roots α, β, value of α² + β² is
🟥 1️⃣ p² − 2q
🟩 2️⃣ q² − 2p
🟨 3️⃣ p² + 2q
🟦 4️⃣ q² + 2p
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ p² − 2q
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 14
If equation x² − 4x + 8 = 0 has roots α, β, then α + β =
🟥 1️⃣ 4
🟩 2️⃣ −4
🟨 3️⃣ 8
🟦 4️⃣ −8
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 4
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 15
If sum of roots is 5 and product is 6, equation is
🟥 1️⃣ x² − 5x + 6 = 0
🟩 2️⃣ x² + 5x + 6 = 0
🟨 3️⃣ x² − 6x + 5 = 0
🟦 4️⃣ x² + 6x + 5 = 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ x² − 5x + 6 = 0
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 16
If roots of x² − 2x + 1 = 0 are α, β, then α = β =
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ −1
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 17
If z = 1 − i, then |z|² equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 4
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 2
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 18
If α and β are roots of x² − 5x + 6 = 0, then 1/α + 1/β =
🟥 1️⃣ 5/6
🟩 2️⃣ 6/5
🟨 3️⃣ 11/6
🟦 4️⃣ 1
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 5/6
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 19
For x² + 2x + 5 = 0, real roots exist?
🟥 1️⃣ No
🟩 2️⃣ Yes
🟨 3️⃣ Equal
🟦 4️⃣ Multiple
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ No
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 20
If α, β are conjugate roots of x² − 4x + 5 = 0, then α × β =
🟥 1️⃣ 5
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 5
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 21
If one root is double the other in x² − 6x + 8 = 0, find roots
🟥 1️⃣ 2, 4
🟩 2️⃣ 1, 2
🟨 3️⃣ 4, 2
🟦 4️⃣ 3, 6
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 2, 4
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 22
For equation x² + 2x + 2 = 0, roots are
🟥 1️⃣ Complex conjugates
🟩 2️⃣ Real and equal
🟨 3️⃣ Real and distinct
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Complex conjugates
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 23
If z = 3 − 4i, then Re(z) =
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ −3
🟨 3️⃣ 4
🟦 4️⃣ −4
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 3
📘 (JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 24
If roots of x² + px + 4 = 0 are equal, then p =
🟥 1️⃣ ±4
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ −4
🟦 4️⃣ 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ ±4
📘 (JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 25
If x² + x + 1 = 0, roots are
🟥 1️⃣ ω, ω²
🟩 2️⃣ 1, ω
🟨 3️⃣ 1, ω²
🟦 4️⃣ −1, 1
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ ω, ω²
📘 (JEE Main 2011)
🔵 Question 26
If z₁ = 2 + 2i and z₂ = 1 − 3i, then z₁ / z₂ equals
🟥 1️⃣ −0.2 + 0.8i
🟩 2️⃣ 0.2 + 0.8i
🟨 3️⃣ 0.5 + i
🟦 4️⃣ −0.5 + i
Answer: 🟩 2️⃣ 0.2 + 0.8i
📘 (JEE Main 2024)
🔵 Question 27
If z = a + ib satisfies z + z̄ = 6, then Re(z) =
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ 6
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 3
📘 (JEE Main 2023)
🔵 Question 28
If |z| = 5 and z lies on real axis, then z equals
🟥 1️⃣ 5
🟩 2️⃣ −5
🟨 3️⃣ ±5
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer: 🟨 3️⃣ ±5
📘 (JEE Main 2023)
🔵 Question 29
If equation x² − 3x + k = 0 has equal roots, then k equals
🟥 1️⃣ 9/4
🟩 2️⃣ 3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 4
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 9/4
📘 (JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 30
If roots of x² − 2x + 5 = 0 are α and β, then α² + β² equals
🟥 1️⃣ 6
🟩 2️⃣ 8
🟨 3️⃣ 10
🟦 4️⃣ 12
Answer: 🟩 2️⃣ 8
📘 (JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 31
If z = cos(π/3) + i sin(π/3), then z⁶ equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ −1
🟨 3️⃣ i
🟦 4️⃣ −i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 32
If roots of quadratic equation are purely imaginary, then discriminant is
🟥 1️⃣ Negative
🟩 2️⃣ Positive
🟨 3️⃣ Zero
🟦 4️⃣ One
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Negative
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 33
If α and β are roots of x² + 4x + 13 = 0, then α³ + β³ equals
🟥 1️⃣ −52
🟩 2️⃣ −64
🟨 3️⃣ 52
🟦 4️⃣ 64
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −52
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 34
If z = 2 − 3i, then 1/z equals
🟥 1️⃣ (2 + 3i)/13
🟩 2️⃣ (2 − 3i)/13
🟨 3️⃣ (3 + 2i)/13
🟦 4️⃣ (3 − 2i)/13
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ (2 + 3i)/13
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 35
If equation ax² + bx + c = 0 has purely imaginary roots, then
🟥 1️⃣ b = 0 and ac > 0
🟩 2️⃣ b = 0 and ac < 0 🟨 3️⃣ b ≠ 0 and ac < 0 🟦 4️⃣ None Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ b = 0 and ac > 0
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 36
If one root of x² + 7x + 12 = 0 is −3, then other root is
🟥 1️⃣ −4
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −4
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 37
If sum of roots = 1 and product = −6, then equation is
🟥 1️⃣ x² − x − 6 = 0
🟩 2️⃣ x² + x + 6 = 0
🟨 3️⃣ x² + x − 6 = 0
🟦 4️⃣ x² − x + 6 = 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ x² − x − 6 = 0
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 38
If z = 3 + 4i, then 1/|z| equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/5
🟩 2️⃣ 1/3
🟨 3️⃣ 1/4
🟦 4️⃣ 5
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 1/5
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 39
If z = x + iy satisfies |z − 2| = 3, then locus is
🟥 1️⃣ Circle centre (2, 0), radius 3
🟩 2️⃣ Circle centre (0, 2), radius 3
🟨 3️⃣ Line parallel x-axis
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ Circle centre (2, 0), radius 3
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 40
If equation x² + 6x + k = 0 has equal roots, k equals
🟥 1️⃣ 9
🟩 2️⃣ 36
🟨 3️⃣ 6
🟦 4️⃣ 3
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 9
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 41
If α and β are roots of x² − 2x + 3 = 0, then αβ equals
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ −3
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ −2
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 3
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 42
If x² + 4x + 8 = 0, then roots are
🟥 1️⃣ −2 ± 2i
🟩 2️⃣ −2 ± 4i
🟨 3️⃣ 2 ± 2i
🟦 4️⃣ 2 ± 4i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −2 ± 2i
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 43
If z = 1 + i, argument of z is
🟥 1️⃣ π/4
🟩 2️⃣ π/2
🟨 3️⃣ π/3
🟦 4️⃣ π/6
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ π/4
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 44
If z = 2(cos 60° + i sin 60°), then |z³| =
🟥 1️⃣ 8
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 6
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 8
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 45
If z = 3 + 4i, then conjugate is
🟥 1️⃣ 3 − 4i
🟩 2️⃣ −3 + 4i
🟨 3️⃣ −3 − 4i
🟦 4️⃣ 3 + 4i
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 3 − 4i
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 46
If α and β are roots of x² + px + 1 = 0, then α² + β² equals
🟥 1️⃣ p² − 2
🟩 2️⃣ p² + 2
🟨 3️⃣ 2p² − 2
🟦 4️⃣ p²
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ p² − 2
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 47
If equation x² + bx + 1 = 0 has equal roots, then b equals
🟥 1️⃣ ±2
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ −2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ ±2
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 48
If z = cosθ + i sinθ, then zⁿ =
🟥 1️⃣ cos(nθ) + i sin(nθ)
🟩 2️⃣ cosθ + i sin(nθ)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(nθ) + i sinθ
🟦 4️⃣ cosθ + i sinθ
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ cos(nθ) + i sin(nθ)
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 49
If roots of equation x² − 10x + k = 0 differ by 4, then k equals
🟥 1️⃣ 21
🟩 2️⃣ 24
🟨 3️⃣ 25
🟦 4️⃣ 26
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ 21
📘 (JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 50
If equation x² − 2x + 5 = 0 has roots α, β, then α³ + β³ equals
🟥 1️⃣ −14
🟩 2️⃣ 14
🟨 3️⃣ 28
🟦 4️⃣ −28
Answer: 🟥 1️⃣ −14
📘 (JEE Main 2011)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. If z = 3 + 4i, then the modulus |z| is
🔵 (A) 5
🟢 (B) 7
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 3
Answer: (A) 5 | JEE Adv 2019, Paper 1
Q2. If z₁ = 1 + i and z₂ = 1 − i, then z₁·z₂ =
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) −2
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 2 | JEE Adv 2018, Paper 1
Q3. The conjugate of z = 2 − 5i is
🔵 (A) 2 + 5i
🟢 (B) −2 + 5i
🟠 (C) −2 − 5i
🔴 (D) 2 − 5i
Answer: (A) 2 + 5i | JEE Adv 2017, Paper 1
Q4. The value of |1 + i|⁴ is
🔵 (A) 4
🟢 (B) 8
🟠 (C) 16
🔴 (D) 2
Answer: (C) 16 | JEE Adv 2016, Paper 1
Q5. The argument of z = 1 + i√3 is
🔵 (A) π/6
🟢 (B) π/3
🟠 (C) π/2
🔴 (D) π/4
Answer: (B) π/3 | JEE Adv 2015, Paper 1
Q6. If z = cosθ + i sinθ, then zⁿ =
🔵 (A) cos nθ + i sin nθ
🟢 (B) cosθ + i sin nθ
🟠 (C) cos nθ − i sinθ
🔴 (D) cosθ − i sinθ
Answer: (A) cos nθ + i sin nθ | JEE Adv 2015, Paper 1
Q7. If the roots of x² + 2x + 2 = 0 are α, β, then α² + β² =
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) −2
🟠 (C) −4
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 2 | JEE Adv 2014, Paper 1
Q8. If z = a + ib satisfies z·z̄ = 25, then |z| =
🔵 (A) 5
🟢 (B) 25
🟠 (C) 10
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 5 | JEE Adv 2013, Paper 1
Q9. If z = (1 + i)/(1 − i), then Arg(z) is
🔵 (A) π/4
🟢 (B) π/2
🟠 (C) π
🔴 (D) 3π/4
Answer: (B) π/2 | JEE Adv 2013, Paper 1
Q10. The equation z² = −9 has roots
🔵 (A) ±3
🟢 (B) ±3i
🟠 (C) ±√3i
🔴 (D) ±i
Answer: (B) ±3i | JEE Adv 2012, Paper 1
Q11. The quadratic equation with roots 2 + 3i, 2 − 3i is
🔵 (A) x² − 4x + 13 = 0
🟢 (B) x² − 4x + 10 = 0
🟠 (C) x² − 4x + 9 = 0
🔴 (D) x² − 2x + 13 = 0
Answer: (A) x² − 4x + 13 = 0 | JEE Adv 2011, Paper 1
Q12. The value of i⁴³ is
🔵 (A) i
🟢 (B) −i
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) −1
Answer: (B) −i | JEE Adv 2010, Paper 1
Q13. The equation x² + px + q = 0 has real roots if
🔵 (A) p² < 4q
🟢 (B) p² = 4q
🟠 (C) p² > 4q
🔴 (D) None of these
Answer: (C) p² > 4q | JEE Adv 2010, Paper 1
Q14. If z = e^(iθ), then z̄ =
🔵 (A) e^(iθ)
🟢 (B) e^(−iθ)
🟠 (C) −e^(iθ)
🔴 (D) e^(2iθ)
Answer: (B) e^(−iθ) | JEE Adv 2009, Paper 1
Q15. The sum of the roots of x² + 5x + 6 = 0 is
🔵 (A) −5
🟢 (B) 5
🟠 (C) 6
🔴 (D) −6
Answer: (A) −5 | JEE Adv 2008, Paper 1
Q16. If |z − 2| = 3, then z lies on a circle whose center and radius are
🔵 (A) Center 2, Radius 3
🟢 (B) Center −2, Radius 3
🟠 (C) Center 2, Radius 6
🔴 (D) Center 0, Radius 3
Answer: (A) Center 2, Radius 3 | JEE Adv 2007, Paper 1
Q17. If z = 3(cos60° + i sin60°), then the conjugate of z is
🔵 (A) 3(cos60° + i sin60°)
🟢 (B) 3(cos60° − i sin60°)
🟠 (C) 3(cos30° + i sin30°)
🔴 (D) 3(cos30° − i sin30°)
Answer: (B) 3(cos60° − i sin60°) | JEE Adv 2007, Paper 1
Q18. If z₁ = 2 + 3i and z₂ = 1 − 2i, then z₁ / z₂ equals
🔵 (A) 0.2 + 1i
🟢 (B) 0.8 + 1.6i
🟠 (C) 0.2 − 1i
🔴 (D) 0.8 − 1.6i
Answer: (B) 0.8 + 1.6i | JEE Adv 2019, Paper 2
Q19. The conjugate of (1 + i)⁵ is
🔵 (A) (1 − i)⁵
🟢 (B) −(1 + i)⁵
🟠 (C) (1 + i)⁻⁵
🔴 (D) −(1 − i)⁵
Answer: (A) (1 − i)⁵ | JEE Adv 2018, Paper 2
Q20. The modulus of z = 2(cos120° + i sin120°) is
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) √3
Answer: (A) 2 | JEE Adv 2017, Paper 2
Q21. If (1 + i)⁴⁰ + (1 − i)⁴⁰ = k, then k equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 2⁴⁰
🟠 (C) −2⁴⁰
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) 2⁴⁰ | JEE Adv 2016, Paper 2
Q22. The quadratic equation whose roots are conjugates of each other is
🔵 (A) x² + 2x + 2 = 0
🟢 (B) x² − 2x + 2 = 0
🟠 (C) x² − 4x + 4 = 0
🔴 (D) x² + 4x + 4 = 0
Answer: (A) x² + 2x + 2 = 0 | JEE Adv 2015, Paper 2
Q23. If z = x + iy satisfies |z − 3| = |z + 1|, then the locus of z is
🔵 (A) x = −1
🟢 (B) x = 1
🟠 (C) y = 2
🔴 (D) y = 0
Answer: (B) x = 1 | JEE Adv 2014, Paper 2
Q24. The minimum value of |z − 2| + |z + 2| for all complex z is
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 8
Answer: (C) 4 | JEE Adv 2013, Paper 2
Q25. The sum of the arguments of z₁ = 1 + i and z₂ = 1 − i is
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) π
🟠 (C) π/4
🔴 (D) π/2
Answer: (A) 0 | JEE Adv 2013, Paper 2
Q26. The product of the roots of x² − 4x + 13 = 0 is
🔵 (A) 13
🟢 (B) −13
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) −4
Answer: (A) 13 | JEE Adv 2012, Paper 2
Q27. The value of (1 + i)⁶ is
🔵 (A) 8i
🟢 (B) −8i
🟠 (C) 8
🔴 (D) −8
Answer: (B) −8i | JEE Adv 2012, Paper 2
Q28. The point representing z = 3 + 4i lies in
🔵 (A) First quadrant
🟢 (B) Second quadrant
🟠 (C) Third quadrant
🔴 (D) Fourth quadrant
Answer: (A) First quadrant | JEE Adv 2011, Paper 2
Q29. The value of i²⁵⁶ is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) −1
🟠 (C) i
🔴 (D) −i
Answer: (A) 1 | JEE Adv 2010, Paper 2
Q30. The quadratic equation whose roots are −2 ± 3i is
🔵 (A) x² + 4x + 13 = 0
🟢 (B) x² + 4x + 9 = 0
🟠 (C) x² + 2x + 13 = 0
🔴 (D) x² − 4x + 13 = 0
Answer: (A) x² + 4x + 13 = 0 | JEE Adv 2009, Paper 2
Q31. If z₁ = 2(cos30° + i sin30°) and z₂ = 2(cos60° + i sin60°), then z₁·z₂ =
🔵 (A) 4(cos90° + i sin90°)
🟢 (B) 4(cos30° + i sin30°)
🟠 (C) 2(cos90° + i sin90°)
🔴 (D) 8(cos30° + i sin30°)
Answer: (A) 4(cos90° + i sin90°) | JEE Adv 2008, Paper 2
Q32. The sum of the roots of x² − 6x + 25 = 0 is
🔵 (A) 6
🟢 (B) −6
🟠 (C) 25
🔴 (D) −25
Answer: (A) 6 | JEE Adv 2007, Paper 2
Q33. If z = cosθ + i sinθ, then |z| equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) √2
Answer: (B) 1 | JEE Adv 2007, Paper 2
Q34. The equation x² + 4x + 8 = 0 has
🔵 (A) Real and distinct roots
🟢 (B) Real and equal roots
🟠 (C) Complex conjugate roots
🔴 (D) Imaginary unequal roots
Answer: (C) Complex conjugate roots | JEE Adv 2007, Paper 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Level (Q1–Q20)
Q1. The value of i² is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) –1
🟠 (C) i
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) –1
Q2. The number 3 + 2i is
🔵 (A) purely real
🟢 (B) purely imaginary
🟠 (C) complex
🔴 (D) not defined
Answer: (C) complex
Q3. The real part of z = 5 – 3i is
🔵 (A) 5
🟢 (B) –3
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 5
Q4. The imaginary part of z = 7 + 4i is
🔵 (A) 4
🟢 (B) 7
🟠 (C) –4
🔴 (D) 11
Answer: (A) 4
Q5. If z = 3 + 4i, then |z| =
🔵 (A) 3
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 5
🔴 (D) 7
Answer: (C) 5
Q6. Conjugate of 2 – 5i is
🔵 (A) 2 + 5i
🟢 (B) –2 + 5i
🟠 (C) –2 – 5i
🔴 (D) 2 – 5i
Answer: (A) 2 + 5i
Q7. |3 – 4i| equals
🔵 (A) 5
🟢 (B) 7
🟠 (C) 25
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 5
Q8. The modulus of 1 + i is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) √2
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) √3
Answer: (B) √2
Q9. The argument of 1 + i is
🔵 (A) π/2
🟢 (B) π/4
🟠 (C) 3π/4
🔴 (D) π
Answer: (B) π/4
Q10. If z = 2(cos π/3 + i sin π/3), then Re(z) =
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) √3
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 1
Q11. The conjugate of 1 + i√3 is
🔵 (A) 1 – i√3
🟢 (B) –1 + i√3
🟠 (C) –1 – i√3
🔴 (D) 1 + i√3
Answer: (A) 1 – i√3
Q12. The square of i is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) i
🟠 (C) –1
🔴 (D) –i
Answer: (C) –1
Q13. The product of z and its conjugate z̄ equals
🔵 (A) z
🟢 (B) |z|²
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) |z|²
Q14. The value of (1 + i)² is
🔵 (A) 2i
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) 2i – 1
Answer: (D) 2i – 1
Q15. The value of (1 – i)(1 + i) is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) –1
Answer: (C) 2
Q16. If z = 3 – 2i, then z̄ =
🔵 (A) 3 + 2i
🟢 (B) –3 + 2i
🟠 (C) –3 – 2i
🔴 (D) 3 – 2i
Answer: (A) 3 + 2i
Q17. The argument of –1 + i is
🔵 (A) 3π/4
🟢 (B) π/4
🟠 (C) π/2
🔴 (D) π
Answer: (A) 3π/4
Q18. The polar form of 1 + i is
🔵 (A) √2(cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
🟢 (B) √2(cos π/2 + i sin π/2)
🟠 (C) 2(cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
🔴 (D) 1(cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
Answer: (A) √2(cos π/4 + i sin π/4)
Q19. If z = 2 + 2i, then arg(z) =
🔵 (A) π/4
🟢 (B) π/2
🟠 (C) 3π/4
🔴 (D) π
Answer: (A) π/4
Q20. If |z| = 1, then z̄ = 1/z is
🔵 (A) True
🟢 (B) False
🟠 (C) Sometimes true
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) True
🔶 JEE MAIN LEVEL (Q21–Q40)
Q21. If z₁ = 3 + 4i and z₂ = 4 + 3i, then z₁ + z₂ equals
🔵 (A) 7 + 7i
🟢 (B) 12 + 12i
🟠 (C) 1 + i
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 7 + 7i
Q22. If z₁ = 2 + i and z₂ = 1 – 3i, then z₁ – z₂ equals
🔵 (A) 1 + 4i
🟢 (B) 1 – 4i
🟠 (C) 3 + 2i
🔴 (D) –1 + 2i
Answer: (A) 1 + 4i
Q23. If z = 1 + i, then z² equals
🔵 (A) 2i
🟢 (B) 1 + 2i
🟠 (C) 2i – 1
🔴 (D) –1 + 2i
Answer: (C) 2i – 1
Q24. If z₁ = 3 + 4i and z₂ = 3 – 4i, then z₁ × z₂ =
🔵 (A) 25
🟢 (B) –25
🟠 (C) 7
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 25
Q25. If z = 1 + i, then 1/z =
🔵 (A) (1 – i)/2
🟢 (B) (1 + i)/2
🟠 (C) 1 – i
🔴 (D) 1 + i
Answer: (A) (1 – i)/2
Q26. The conjugate of 3(cos θ + i sin θ) is
🔵 (A) 3(cos θ + i sin θ)
🟢 (B) 3(cos θ – i sin θ)
🟠 (C) –3(cos θ + i sin θ)
🔴 (D) –3(cos θ – i sin θ)
Answer: (B) 3(cos θ – i sin θ)
Q27. If z₁ = r₁(cos θ₁ + i sin θ₁) and z₂ = r₂(cos θ₂ + i sin θ₂), then z₁z₂ equals
🔵 (A) r₁r₂[cos(θ₁ – θ₂) + i sin(θ₁ – θ₂)]
🟢 (B) r₁r₂[cos(θ₁ + θ₂) + i sin(θ₁ + θ₂)]
🟠 (C) r₁r₂[cos(θ₁) + i sin(θ₂)]
🔴 (D) r₁r₂[cos θ₁ + cos θ₂ + i(sin θ₁ + sin θ₂)]
Answer: (B) r₁r₂[cos(θ₁ + θ₂) + i sin(θ₁ + θ₂)]
Q28. If z = 2(cos 60° + i sin 60°), then z² equals
🔵 (A) 4(cos 120° + i sin 120°)
🟢 (B) 4(cos 30° + i sin 30°)
🟠 (C) 2(cos 120° + i sin 120°)
🔴 (D) 4(cos 60° + i sin 60°)
Answer: (A) 4(cos 120° + i sin 120°)
Q29. The value of i⁷ is
🔵 (A) i
🟢 (B) –i
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) –1
Answer: (B) –i
Q30. The value of i⁸ is
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) –1
🟠 (C) i
🔴 (D) –i
Answer: (A) 1
Q31. The equation x² + 4x + 5 = 0 has roots
🔵 (A) –2 ± i
🟢 (B) –2 ± 2i
🟠 (C) 2 ± i
🔴 (D) –1 ± i
Answer: (A) –2 ± i
Q32. If α and β are roots of x² + 6x + 13 = 0, then α + β =
🔵 (A) –6
🟢 (B) 6
🟠 (C) 13
🔴 (D) –13
Answer: (A) –6
Q33. In the same equation, αβ =
🔵 (A) 6
🟢 (B) 13
🟠 (C) –6
🔴 (D) –13
Answer: (B) 13
🔵 Q34
The discriminant of x² + 2x + 5 = 0 is
🔵 (A) 16
🟢 (B) –16
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) –4
Answer: (B) –16
✏️ Check:
D = b² – 4ac = 2² – 4(1)(5) = 4 – 20 = –16 ✅
Q35. The roots of x² + 2x + 5 = 0 are
🔵 (A) –1 ± 2i
🟢 (B) 1 ± 2i
🟠 (C) –2 ± i
🔴 (D) –1 ± i
Answer: (A) –1 ± 2i
Q36. If z₁ = 2 + 3i and z₂ = 1 – 4i, then z₁/z₂ equals
🔵 (A) (10 + 11i)/17
🟢 (B) (10 – 11i)/17
🟠 (C) (11 + 10i)/17
🔴 (D) (11 – 10i)/17
Answer: (A) (10 + 11i)/17
Q37. |3 + 4i| + |4 + 3i| equals
🔵 (A) 5
🟢 (B) 10
🟠 (C) 7
🔴 (D) 6
Answer: (B) 10
Q38. The cube roots of unity are
🔵 (A) 1, i, –i
🟢 (B) 1, ω, ω²
🟠 (C) 1, –1, i
🔴 (D) 1, –ω, –ω²
Answer: (B) 1, ω, ω²
Q39. If ω is a cube root of unity, then ω² + ω + 1 =
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) –1
🔴 (D) 2
Answer: (B) 0
Q40. The value of ω³ is
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) ω
🔴 (D) ω²
Answer: (B) 1
🔷 JEE ADVANCED LEVEL (Q41–Q50)
Q41. If z = a + i·b, and |z| = 1, then z̄ = 1/z
🔵 (A) Always true
🟢 (B) Always false
🟠 (C) True only if a = b
🔴 (D) True only if a ≠ b
Answer: (A) Always true
Q42. If z = r(cos θ + i sin θ), then zⁿ =
🔵 (A) rⁿ(cos nθ + i sin nθ)
🟢 (B) rⁿ(cos θ + i sin θⁿ)
🟠 (C) r(cos nθ + i sin θ)
🔴 (D) rⁿ(cos θ + sin θ)
Answer: (A) rⁿ(cos nθ + i sin nθ)
Q43. If z₁ = 2(cos 30° + i sin 30°) and z₂ = 3(cos 45° + i sin 45°), then z₁ × z₂ equals
🔵 (A) 6(cos 75° + i sin 75°)
🟢 (B) 5(cos 75° + i sin 75°)
🟠 (C) 6(cos 15° + i sin 15°)
🔴 (D) 5(cos 15° + i sin 15°)
Answer: (A) 6(cos 75° + i sin 75°)
Q44. The sum of the cube roots of unity is
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) –1
Answer: (A) 0
Q45. If z = cos θ + i sin θ, then 1/z =
🔵 (A) cos θ – i sin θ
🟢 (B) cos θ + i sin θ
🟠 (C) –cos θ + i sin θ
🔴 (D) cos(–θ) + i sin(–θ)
Answer: (A) cos θ – i sin θ
Q46. If α, β are roots of x² – 2x + 2 = 0, then α² + β² =
🔵 (A) 4
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) 6
Answer: (A) 4
Q47. If z = cos θ + i sin θ, then zⁿ + z⁻ⁿ =
🔵 (A) 2 cos nθ
🟢 (B) 2 sin nθ
🟠 (C) cos nθ
🔴 (D) sin nθ
Answer: (A) 2 cos nθ
Q48. If |z₁| = 3, |z₂| = 4, then |z₁z₂| =
🔵 (A) 7
🟢 (B) 12
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) 12
🔵 Q49
If z = 1 + i√3, then z³ equals
🔵 (A) –8
🟢 (B) 8
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) –8
✏️ Check:
z = 1 + i√3 = 2(cos 60° + i sin 60°)
⇒ z³ = 2³ [cos(180°) + i sin(180°)] = 8(–1 + 0i) = –8 ✅
Q50. If z₁ = cos 40° + i sin 40°, z₂ = cos 20° + i sin 20°, then z₁ × z₂ =
🔵 (A) cos 60° + i sin 60°
🟢 (B) cos 20° + i sin 20°
🟠 (C) cos 40° + i sin 40°
🔴 (D) cos 80° + i sin 80°
Answer: (A) cos 60° + i sin 60°
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
