Class 11 : Maths (In English) – Lesson 3. Trigonometric Functions
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔷 1️⃣ Introduction
🔹 Trigonometry studies relationships between angles and sides of triangles.
🔹 In this lesson, trigonometric functions are extended to all real angles using radian measure and unit circle.
💡 Goal: Understand definitions, signs, identities, graphs, and periodic nature.
🔷 2️⃣ Measurement of Angles
🟢 Degree measure: 1 revolution = 360°
🟢 Radian measure: 1 revolution = 2π radians
🟢 Relation: 180° = π radians
✏️ Conversion formulas:
➡️ Degrees to radians = degree × π / 180
➡️ Radians to degrees = radian × 180 / π
💡 Example:
60° = π/3 rad
π/4 rad = 45°
🔷 3️⃣ Positive and Negative Angles
🟢 Positive angle – rotation anticlockwise
🟢 Negative angle – rotation clockwise
🔷 4️⃣ Trigonometric Functions using Unit Circle
🧭 Consider a circle of radius 1 centered at origin.
For a point P(x, y) on the circle making angle θ with x-axis:
➡️ sinθ = y
➡️ cosθ = x
➡️ tanθ = y/x
➡️ cotθ = x/y
➡️ secθ = 1/x
➡️ cscθ = 1/y
These are defined for all real angles except where denominator becomes zero.
🔷 5️⃣ Signs of Trigonometric Functions
🧭 Quadrant rule:
🌀 Quadrant I – all positive
🌀 Quadrant II – sine and cosecant positive
🌀 Quadrant III – tangent and cotangent positive
🌀 Quadrant IV – cosine and secant positive
💡 Trick: “All Students Take Coffee”
🔷 6️⃣ Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
✔️ sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
✔️ 1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
✔️ 1 + cot²θ = csc²θ
💡 Derived from the first identity by dividing by cos²θ or sin²θ.
🔷 7️⃣ Domain and Range
🔹 sinθ: domain = all real numbers, range = –1 to 1
🔹 cosθ: domain = all real numbers, range = –1 to 1
🔹 tanθ: domain = all real except (2n+1)π/2, range = all real
🔹 cotθ: domain = all real except nπ, range = all real
🔹 secθ: domain = all real except (2n+1)π/2, range = (–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
🔹 cscθ: domain = all real except nπ, range = (–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
🔷 8️⃣ Periodicity
🌀 sinθ – period 2π
🌀 cosθ – period 2π
🌀 tanθ – period π
🌀 cotθ – period π
🌀 secθ – period 2π
🌀 cscθ – period 2π
Function value repeats after one period.
🔷 9️⃣ Values of Trigonometric Functions (Standard Angles)
🟣 sin0° = 0, sin30° = 1/2, sin45° = 1/√2, sin60° = √3/2, sin90° = 1
🔵 cos0° = 1, cos30° = √3/2, cos45° = 1/√2, cos60° = 1/2, cos90° = 0
🟢 tan0° = 0, tan30° = 1/√3, tan45° = 1, tan60° = √3, tan90° = ∞
🔷 🔟 Trigonometric Functions of Negative Angles
✔️ sin(–θ) = –sinθ
✔️ cos(–θ) = cosθ
✔️ tan(–θ) = –tanθ
💡 sin, tan, cot are odd functions
💡 cos, sec, csc are even functions
🔷 1️⃣1️⃣ Co-function Relations
✔️ sin(90° – θ) = cosθ
✔️ cos(90° – θ) = sinθ
✔️ tan(90° – θ) = cotθ
✔️ cot(90° – θ) = tanθ
✔️ sec(90° – θ) = cscθ
✔️ csc(90° – θ) = secθ
🔷 1️⃣2️⃣ Allied Angles (θ ± nπ or θ ± 90°)
Use sign based on quadrant and reference angle.
Examples:
🟢 sin(π – θ) = sinθ
🟢 cos(π – θ) = –cosθ
🟢 tan(π + θ) = tanθ
🔷 1️⃣3️⃣ Graphical Nature
🟣 y = sinθ → wave pattern, crosses origin, max = 1, min = –1, period 2π
🔵 y = cosθ → wave pattern, starts at 1, period 2π
🟢 y = tanθ → repeating curve with vertical asymptotes at (2n+1)π/2, period π
💡 sinθ and tanθ are odd, cosθ is even, hence graphs symmetric accordingly.
🔷 1️⃣4️⃣ Important Zeros
✔️ sinθ = 0 ⇒ θ = nπ
✔️ cosθ = 0 ⇒ θ = (2n+1)π/2
✔️ tanθ = 0 ⇒ θ = nπ
🔷 1️⃣5️⃣ Real-life Applications
📏 Used in physics (wave motion), navigation, astronomy, engineering, architecture.
🧾 Summary (Plain Text)
🔹 Trigonometric functions extend to all angles using unit circle.
🔹 Degree and radian are two measures of angles (180° = π rad).
🔹 sin, cos have range –1 to 1, tan and cot have all real values.
🔹 sin²θ + cos²θ = 1 is the basic identity.
🔹 sin, cos periodic with 2π, tan, cot with π.
🔹 Signs depend on quadrant (ASTC rule).
🔹 sin, tan are odd; cos is even.
🔹 Graphs are periodic and wave-like.
🔹 Values at 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90° must be memorized.
📝 Quick Recap
✔️ 180° = π rad
✔️ sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
✔️ tanθ = sinθ / cosθ
✔️ sin(–θ) = –sinθ
✔️ sin(90° – θ) = cosθ
✔️ Period: sin, cos = 2π; tan = π
✔️ Use ASTC rule for signs
✔️ Graphs repeat periodically
📄 Exercise 3.2
🔵 Question 1
cos x = −½, x lies in the third quadrant.
Find the values of the other five trigonometric functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ In the 3rd quadrant, sin x and cos x are negative, tan x is positive.
➡️ Formula: sin²x + cos²x = 1
⇒ sin²x = 1 − cos²x = 1 − (1/4) = 3/4
⇒ sin x = −√3/2 (negative in 3rd quadrant)
✔️ sin x = −√3/2
✔️ cos x = −1/2 (given)
✔️ tan x = sin x / cos x = (−√3/2)/(−1/2) = √3
✔️ cot x = 1 / tan x = 1/√3
✔️ sec x = 1 / cos x = −2
✔️ cosec x = 1 / sin x = −2/√3
💡 Final Values:
sin x = −√3/2 cos x = −1/2 tan x = √3 cot x = 1/√3 sec x = −2 cosec x = −2/√3
🔵 Question 2
sin x = 3/5, x lies in the second quadrant.
Find the other five trigonometric functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ In 2nd quadrant: sin + , cos − , tan −.
➡️ sin²x + cos²x = 1
⇒ cos²x = 1 − (9/25) = 16/25
⇒ cos x = −4/5
✔️ sin x = 3/5
✔️ cos x = −4/5
✔️ tan x = sin / cos = (3/5)/(−4/5) = −3/4
✔️ cot x = −4/3
✔️ sec x = −5/4
✔️ cosec x = 5/3
💡 Final Values:
sin x = 3/5 cos x = −4/5 tan x = −3/4 cot x = −4/3 sec x = −5/4 cosec x = 5/3
🔵 Question 3
cot x = 3/4, x lies in the third quadrant.
Find the other five trigonometric functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 3rd quadrant: tan +, sin −, cos −
➡️ tan x = 1 / cot x = 4/3
Take base = 3, perpendicular = 4, hypotenuse = 5
✔️ sin x = −4/5
✔️ cos x = −3/5
✔️ tan x = 4/3
✔️ cot x = 3/4
✔️ sec x = −5/3
✔️ cosec x = −5/4
💡 Final Values:
sin x = −4/5 cos x = −3/5 tan x = 4/3 cot x = 3/4 sec x = −5/3 cosec x = −5/4
🔵 Question 4
sec x = 13/5, x lies in the fourth quadrant.
Find the other five trigonometric functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 4th quadrant: cos +, sin −, tan −
➡️ cos x = 5/13
⇒ sin²x = 1 − (25/169) = 144/169
⇒ sin x = −12/13
✔️ sin x = −12/13
✔️ cos x = 5/13
✔️ tan x = sin / cos = (−12/13)/(5/13) = −12/5
✔️ cot x = −5/12
✔️ sec x = 13/5
✔️ cosec x = −13/12
💡 Final Values:
sin x = −12/13 cos x = 5/13 tan x = −12/5 cot x = −5/12 sec x = 13/5 cosec x = −13/12
🔵 Question 5
tan x = −5/12, x lies in the second quadrant.
Find the other five trigonometric functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 2nd quadrant: sin +, cos −, tan −
Take perpendicular = 5, base = 12, hypotenuse = 13
✔️ sin x = 5/13
✔️ cos x = −12/13
✔️ tan x = −5/12
✔️ cot x = −12/5
✔️ sec x = −13/12
✔️ cosec x = 13/5
💡 Final Values:
sin x = 5/13 cos x = −12/13 tan x = −5/12 cot x = −12/5 sec x = −13/12 cosec x = 13/5
🔵 Question 6
sin 765°
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 765° − 720° = 45° (since 720° = 2 revolutions)
⇒ sin 765° = sin 45° = 1/√2
💡 Final Answer: sin 765° = 1/√2
🔵 Question 7
cosec (−1410°)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ sin (−θ) = −sin θ ⇒ cosec (−θ) = −cosec θ
➡️ Reduce: 1410° − 1080° = 330°
⇒ cosec (−1410°) = −cosec 330°
✔️ sin 330° = −1/2 ⇒ cosec 330° = −2
So, cosec (−1410°) = −(−2) = 2
💡 Final Answer: 2
🔵 Question 8
tan (19π/3)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 19π/3 − 6π = π/3
⇒ tan (19π/3) = tan (π/3) = √3
💡 Final Answer: √3
🔵 Question 9
sin (−11π/3)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ sin (−θ) = −sin θ
Reduce angle: 11π/3 − 2π = 11π/3 − 6π/3 = 5π/3
⇒ sin (−11π/3) = −sin (5π/3)
✔️ sin (5π/3) = −√3/2
So, sin (−11π/3) = −(−√3/2) = √3/2
💡 Final Answer: √3/2
🔵 Question 10
cot (−15π/4)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ cot (−θ) = −cot θ
Reduce angle: 15π/4 − 12π/4 = 3π/4
⇒ cot (−15π/4) = −cot (3π/4)
✔️ cot (3π/4) = −1
So, cot (−15π/4) = −(−1) = 1
💡 Final Answer: 1
Exercise 3.3
🔵 Question 1
Prove that: sin²(π/6) + cos²(π/3) − tan²(π/4) = −1/2
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin(π/6) = 1/2 ⇒ sin²(π/6) = 1/4
➡️ cos(π/3) = 1/2 ⇒ cos²(π/3) = 1/4
➡️ tan(π/4) = 1 ⇒ tan²(π/4) = 1
➡️ LHS = 1/4 + 1/4 − 1 = 1/2 − 1 = −1/2
✔️ Hence proved: LHS = RHS = −1/2
🔵 Question 2
Prove that: 2sin²(π/6) + cosec²(7π/6)·cos²(π/3) = 3/2
🟢 Answer
➡️ 2sin²(π/6) = 2×(1/2)² = 2×1/4 = 1/2
➡️ sin(7π/6) = −sin(π/6) = −1/2 ⇒ cosec(7π/6) = −2 ⇒ cosec²(7π/6) = 4
➡️ cos²(π/3) = (1/2)² = 1/4
➡️ Product term = 4 × 1/4 = 1
➡️ LHS = 1/2 + 1 = 3/2
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 3
Prove that: cot²(π/6) + cosec(5π/6) + 3tan²(π/6) = 6
🟢 Answer
➡️ cot(π/6) = √3 ⇒ cot²(π/6) = 3
➡️ sin(5π/6) = 1/2 ⇒ cosec(5π/6) = 2
➡️ tan(π/6) = 1/√3 ⇒ tan²(π/6) = 1/3
➡️ 3tan²(π/6) = 3×(1/3) = 1
➡️ LHS = 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 4
Prove that: 2sin²(3π/4) + 2cos²(π/4) + 2sec²(π/3) = 10
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin(3π/4) = √2/2 ⇒ sin² = 1/2 ⇒ 2sin² = 1
➡️ cos(π/4) = √2/2 ⇒ cos² = 1/2 ⇒ 2cos² = 1
➡️ sec(π/3) = 2 ⇒ sec² = 4 ⇒ 2sec² = 8
➡️ LHS = 1 + 1 + 8 = 10
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 5
Find the value of: (i) sin 75° (ii) tan 15°
🟢 Answer (i) sin 75°
➡️ Use sin(45° + 30°)
➡️ = sin45°·cos30° + cos45°·sin30°
➡️ = (√2/2)(√3/2) + (√2/2)(1/2)
➡️ = (√6 + √2)/4
✔️ sin 75° = (√6 + √2)/4
🟢 Answer (ii) tan 15°
➡️ Use tan(45° − 30°)
➡️ = (tan45° − tan30°)/(1 + tan45°·tan30°)
➡️ = (1 − 1/√3)/(1 + 1/√3)
➡️ = (√3 − 1)/(√3 + 1)
➡️ Rationalise: ×(√3 − 1)/(√3 − 1)
➡️ = ( (√3 − 1)² ) / (3 − 1)
➡️ = (3 − 2√3 + 1)/2
➡️ = (4 − 2√3)/2 = 2 − √3
✔️ tan 15° = 2 − √3
🔵 Question 6
Prove: cos(π/4 − x)cos(π/4 − y) − sin(π/4 − x)sin(π/4 − y) = sin(x + y)
🟢 Answer
➡️ Use identity: cosA cosB − sinA sinB = cos(A + B)
➡️ LHS = cos[(π/4 − x) + (π/4 − y)]
➡️ = cos[π/2 − (x + y)]
➡️ = sin(x + y)
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 7
Prove: tan(π/4 + x) / tan(π/4 − x) = ((1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x))²
🟢 Answer
➡️ tan(π/4 + x) = (1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x)
➡️ tan(π/4 − x) = (1 − tan x)/(1 + tan x)
➡️ Ratio = [(1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x)] ÷ [(1 − tan x)/(1 + tan x)]
➡️ = [(1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x)] × [(1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x)]
➡️ = ((1 + tan x)/(1 − tan x))²
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 8
Prove: [cos(π + x)·cos(−x)] / [sin(π − x)·cos(π/2 + x)] = cot²x
🟢 Answer
➡️ cos(π + x) = −cos x
➡️ cos(−x) = cos x
➡️ sin(π − x) = sin x
➡️ cos(π/2 + x) = −sin x
➡️ LHS = [ (−cos x)(cos x) ] / [ (sin x)(−sin x) ]
➡️ = cos²x / sin²x
➡️ = cot²x
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 9
Prove: cos(3π/2 + x)·cos(2π + x) · [cot(3π/2 − x) + cot(2π + x)] = 1
🟢 Answer
➡️ cos(3π/2 + x) = sin x
➡️ cos(2π + x) = cos x
➡️ cot(3π/2 − x) = tan x
➡️ cot(2π + x) = cot x
➡️ LHS = (sin x·cos x) [tan x + cot x]
➡️ = (sin x·cos x) [ (sin²x + cos²x)/(sin x·cos x) ]
➡️ = 1
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 10
Prove: sin[(n + 1)x]·sin[(n + 2)x] + cos[(n + 1)x]·cos[(n + 2)x] = cos x
🟢 Answer
➡️ Identity: cos(A − B) = cosA·cosB + sinA·sinB
➡️ Let A = (n + 1)x, B = (n + 2)x
➡️ LHS = cos[(n + 1)x − (n + 2)x]
➡️ = cos(−x)
➡️ = cos x
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 11
Prove: cos(3π/4 + x) − cos(3π/4 − x) = −√2 sin x
🟢 Answer
➡️ Use formula: cosP − cosQ = −2 sin[(P + Q)/2] sin[(P − Q)/2]
➡️ P = 3π/4 + x, Q = 3π/4 − x
➡️ (P + Q)/2 = (3π/4 + x + 3π/4 − x)/2 = 3π/4
➡️ (P − Q)/2 = (3π/4 + x − 3π/4 + x)/2 = x
➡️ LHS = −2 sin(3π/4)·sin x
➡️ sin(3π/4) = √2/2
➡️ LHS = −2·(√2/2)·sin x = −√2 sin x
✔️ Hence proved
🔵 Question 12
sin²6x − sin²4x = sin2x · sin10x
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin²A = (1 − cos2A)/2
➡️ LHS = [(1 − cos12x) − (1 − cos8x)]/2
➡️ LHS = (cos8x − cos12x)/2
➡️ cosC − cosD = −2 sin((C + D)/2) sin((C − D)/2)
➡️ LHS = [−2 sin10x · sin(−2x)]/2
➡️ sin(−2x) = −sin2x
➡️ LHS = sin10x · sin2x
✔️ Hence proved.
🔵 Question 13
cos²2x − cos²6x = sin4x · sin8x
🟢 Answer
➡️ cos²A = (1 + cos2A)/2
➡️ LHS = [cos4x − cos12x]/2
➡️ cosC − cosD = −2 sin((C + D)/2) sin((C − D)/2)
➡️ LHS = [−2 sin8x · sin(−4x)]/2
➡️ = sin8x · sin4x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 14
sin2x + 2 sin4x + sin6x = 4 cos²x · sin4x
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin2x + sin6x = 2 sin4x · cos2x
➡️ LHS = 2 sin4x · cos2x + 2 sin4x
➡️ = 2 sin4x (cos2x + 1)
➡️ cos2x + 1 = 2 cos²x
➡️ LHS = 4 cos²x · sin4x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 15
cot4x (sin5x + sin3x) = cotx (sin5x − sin3x)
🟢 Answer
➡️ sinA + sinB = 2 sin((A + B)/2) cos((A − B)/2)
➡️ sin5x + sin3x = 2 sin4x · cosx
➡️ sinA − sinB = 2 cos((A + B)/2) sin((A − B)/2)
➡️ sin5x − sin3x = 2 cos4x · sinx
➡️ LHS = cot4x · 2 sin4x cosx = 2 cos4x cosx
➡️ RHS = cotx · 2 cos4x sinx = 2 cos4x cosx
✔️ LHS = RHS.
🔵 Question 16
(cos9x − cos5x)/(sin17x − sin3x) = −(sin2x)/(cos10x)
🟢 Answer
➡️ cosC − cosD = −2 sin((C + D)/2) sin((C − D)/2)
➡️ Numerator = −2 sin7x · sin2x
➡️ sinA − sinB = 2 cos((A + B)/2) sin((A − B)/2)
➡️ Denominator = 2 cos10x · sin7x
➡️ Ratio = [−2 sin7x sin2x]/[2 cos10x sin7x]
➡️ = − sin2x / cos10x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 17
(sin5x + sin3x)/(cos5x + cos3x) = tan4x
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin5x + sin3x = 2 sin4x · cosx
➡️ cos5x + cos3x = 2 cos4x · cosx
➡️ Ratio = (2 sin4x cosx)/(2 cos4x cosx) = tan4x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 18
(sin x − sin y)/(cos x + cos y) = tan((x − y)/2)
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin x − sin y = 2 cos((x + y)/2) · sin((x − y)/2)
➡️ cos x + cos y = 2 cos((x + y)/2) · cos((x − y)/2)
➡️ Ratio = tan((x − y)/2)
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 19
(sin x + sin 3x)/(cos x + cos 3x) = tan2x
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin x + sin 3x = 2 sin2x · cosx
➡️ cos x + cos 3x = 2 cos2x · cosx
➡️ Ratio = tan2x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 20
(sin x − sin 3x)/(sin²x − cos²x) = 2 sin x
🟢 Answer
➡️ sin x − sin 3x = 2 cos2x · sin(−x) = −2 cos2x · sinx
➡️ sin²x − cos²x = −cos2x
➡️ Ratio = (−2 cos2x sinx)/(−cos2x) = 2 sinx
✔️ Proved (cos2x ≠ 0).
🔵 Question 21
(cos4x + cos3x + cos2x)/(sin4x + sin3x + sin2x) = cot3x
🟢 Answer
➡️ cos4x + cos2x = 2 cos3x · cosx
➡️ Numerator = 2 cos3x cosx + cos3x = cos3x (2 cosx + 1)
➡️ sin4x + sin2x = 2 sin3x · cosx
➡️ Denominator = 2 sin3x cosx + sin3x = sin3x (2 cosx + 1)
➡️ Ratio = [cos3x (2 cosx + 1)]/[sin3x (2 cosx + 1)] = cot3x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 22
cotx · cot2x − cot2x · cot3x − cot3x · cotx = 1
🟢 Answer
➡️ cot(α + β) = (cotα · cotβ − 1)/(cotα + cotβ)
➡️ Put α = x, β = 2x ⇒ cot3x = (cotx · cot2x − 1)/(cotx + cot2x)
➡️ Rearranging: cotx · cot2x − 1 = cot3x (cotx + cot2x)
➡️ ⇒ cotx · cot2x − cot3x · cot2x − cot3x · cotx = 1
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 23
tan4x = [4 tanx (1 − tan²x)] / [1 − 6 tan²x + tan⁴x]
🟢 Answer
➡️ Let t = tanx
➡️ tan2x = 2t/(1 − t²)
➡️ tan4x = 2·tan2x / (1 − tan²2x)
➡️ = 2·[2t/(1 − t²)] / {1 − [2t/(1 − t²)]²}
➡️ = [4t/(1 − t²)] / {1 − 4t²/(1 − t²)²}
➡️ = [4t/(1 − t²)] / {[(1 − t²)² − 4t²]/(1 − t²)²}
➡️ = [4t/(1 − t²)] · {(1 − t²)² / (1 − 6t² + t⁴)}
➡️ = 4t(1 − t²)/(1 − 6t² + t⁴)
✔️ Hence proved.
🔵 Question 24
cos4x = 1 − 8 sin²x · cos²x
🟢 Answer
➡️ cos4x = 1 − 2 sin²2x
➡️ sin2x = 2 sinx cosx
➡️ sin²2x = 4 sin²x cos²x
➡️ cos4x = 1 − 8 sin²x cos²x
✔️ Proved.
🔵 Question 25
cos6x = 32 cos⁶x − 48 cos⁴x + 18 cos²x − 1
🟢 Answer
➡️ Let c = cosx
➡️ cos3x = 4c³ − 3c
➡️ cos6x = 2 cos²3x − 1
➡️ cos²3x = (4c³ − 3c)² = 16c⁶ − 24c⁴ + 9c²
➡️ cos6x = 2(16c⁶ − 24c⁴ + 9c²) − 1
➡️ = 32c⁶ − 48c⁴ + 18c² − 1
✔️ Proved.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Exercise 3.1
🔵 Question 1
Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures:
(i) 25° (ii) −47°30′ (iii) 240° (iv) 520°
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: 1° = π/180 radians
(i) 25°
= 25 × (π/180)
= (25π)/180
= (5π)/36
✔️ Radian measure = 5π/36
(ii) −47°30′
Convert 30′ to degree = 30/60 = 0.5°
⇒ −47°30′ = −47.5°
= −47.5 × (π/180)
= −(475/10) × (π/180)
= −(475π)/(1800)
Simplify: divide by 25
= −(19π)/72
✔️ Radian measure = −19π/72
(iii) 240°
= 240 × (π/180)
= (4π)/3
✔️ Radian measure = 4π/3
(iv) 520°
= 520 × (π/180)
= (52π)/18
= (26π)/9
✔️ Radian measure = 26π/9
💡 Final Answers:
(i) 5π/36 (ii) −19π/72 (iii) 4π/3 (iv) 26π/9
🔵 Question 2
Find the degree measures corresponding to the following radian measures
(Use π = 22/7).
(i) 11/16 (ii) −4 (iii) 5π/3 (iv) 7π/6
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: 1 radian = 180/π degrees
(i) (11/16) radians
= (11/16) × (180 × 7 / 22)
= (11 × 180 × 7) / (16 × 22)
= (11 × 1260) / 352
= 13860 / 352
≈ 39.38°
✔️ Degree measure ≈ 39°23′
(ii) −4 radians
= −4 × (180 × 7 / 22)
= −(4 × 1260) / 22
= −5040 / 22
≈ −229.09°
✔️ Degree measure ≈ −229°05′
(iii) (5π/3) radians
= (5π/3) × (180/π)
= (5 × 180) / 3
= 300°
✔️ Degree measure = 300°
(iv) (7π/6) radians
= (7π/6) × (180/π)
= (7 × 180) / 6
= 210°
✔️ Degree measure = 210°
💡 Final Answers:
(i) 39°23′ (ii) −229°05′ (iii) 300° (iv) 210°
🔵 Question 3
A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second?
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 1 revolution = 2π radians
➡️ 360 revolutions in 1 minute = 360 × 2π = 720π radians in 60 seconds
➡️ In 1 second = 720π / 60 = 12π radians
💡 Final Answer: 12π radians
🔵 Question 4
Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm by an arc of length 22 cm. (Use π = 22/7)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: θ (in radians) = arc length / radius
θ = 22 / 100 = 0.22 radians
Convert to degrees:
θ° = 0.22 × (180 × 7 / 22) / 22 × ?
Wait carefully: θ° = 0.22 × 180/π
= 0.22 × 180 × 7 / 22
= 0.22 × 57.27 × 7 ≈
Better use formula:
θ° = (arc length × 180) / (π × radius)
= (22 × 180) / ((22/7) × 100)
= (3960) / (2200/7)
= 3960 × 7 / 2200
= 27720 / 2200
= 12.6°
💡 Final Answer: 12.6°
🔵 Question 5
In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of the minor arc of the chord.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Diameter = 40 cm ⇒ Radius r = 20 cm
Chord length = 20 cm
Let θ be angle subtended at centre.
Use formula: chord length = 2r sin(θ/2)
20 = 2 × 20 × sin(θ/2)
sin(θ/2) = 1/2
⇒ θ/2 = 30° ⇒ θ = 60°
Convert θ to radians: θ = 60° × π/180 = π/3
Arc length = rθ = 20 × (π/3) = (20π)/3 ≈ 20 × 3.14 / 3 = 20.93 cm
💡 Final Answer: Minor arc length = 20.93 cm
🔵 Question 6
If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60° and 75° at the centre, find the ratio of their radii.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ For same arc length, r₁θ₁ = r₂θ₂
⇒ r₁ / r₂ = θ₂ / θ₁
Convert to radians:
θ₁ = 60° = π/3
θ₂ = 75° = 5π/12
r₁ / r₂ = (5π/12) / (π/3)
= (5/12) × (3/1) = 5/4
💡 Final Answer: r₁ : r₂ = 5 : 4
🔵 Question 7
Find the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(i) 10 cm (ii) 15 cm (iii) 21 cm
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: θ = s / r
(i) θ = 10 / 75 = 2/15 = 0.133 rad
(ii) θ = 15 / 75 = 1/5 = 0.2 rad
(iii) θ = 21 / 75 = 7/25 = 0.28 rad
💡 Final Answers:
(i) 0.133 rad (ii) 0.2 rad (iii) 0.28 rad
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🧭 Section A – Very Short / Objective Type (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1:
The value of sin 0° is
🟢 Answer: 0
🔵 Question 2:
The value of cos 90° is
🟢 Answer: 0
🔵 Question 3:
The value of tan 45° is
🟢 Answer: 1
🔵 Question 4:
The radian measure of 60° is
🟢 Answer: (π / 3) rad
🔵 Question 5:
Convert π/4 radians into degrees.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ θ = (π/4) × (180/π) = 45°
🔵 Question 6:
In which quadrant does the angle 120° lie?
🟢 Answer: Second quadrant
🔵 Question 7:
The sign of cos x in the third quadrant is
🟢 Answer: Negative
🔵 Question 8:
Find the principal value of sin⁻¹(½).
🟢 Answer: π/6
🔵 Question 9:
Find the principal value of cos⁻¹(–½).
🟢 Answer: (2π/3)
🔵 Question 10:
sin²θ + cos²θ = ?
🟢 Answer: 1
🔵 Question 11:
1 + tan²θ = ?
🟢 Answer: sec²θ
🔵 Question 12:
1 + cot²θ = ?
🟢 Answer: cosec²θ
🔵 Question 13:
The period of sin x is
🟢 Answer: 2π
🔵 Question 14:
The range of cos x is
🟢 Answer: [–1, 1]
🔵 Question 15:
sin (–x) = ?
🟢 Answer: –sin x
🔵 Question 16:
cos (–x) = ?
🟢 Answer: cos x
🔵 Question 17:
tan (–x) = ?
🟢 Answer: –tan x
🔵 Question 18:
cot (–x) = ?
🟢 Answer: –cot x
🧭 Section B – Short Answer Type (2–3 marks each)
🔵 Question 19:
Convert 300° into radians.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: θ (radians) = θ (degrees) × (π/180)
➡️ θ = 300 × (π/180)
➡️ θ = (5π/3) rad
✔️ Final Answer: 5π/3 rad
🔵 Question 20:
Convert (7π/6) radians into degrees.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ θ = (7π/6) × (180/π)
➡️ θ = 7 × 30 = 210°
✔️ Final Answer: 210°
🔵 Question 21:
Find the value of sin (150°), cos (150°), tan (150°).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 150° = 180° – 30°, 2nd quadrant → sin +, cos –, tan –
➡️ sin 150° = sin 30° = 1/2
➡️ cos 150° = –cos 30° = –√3/2
➡️ tan 150° = –tan 30° = –1/√3
✔️ Final Answers:
sin 150° = 1/2, cos 150° = –√3/2, tan 150° = –1/√3
🔵 Question 22:
Find the value of sin(–45°), cos(–45°), tan(–45°).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ sin(–x) = –sin x, cos(–x) = cos x, tan(–x) = –tan x
➡️ sin(–45°) = –(1/√2)
➡️ cos(–45°) = 1/√2
➡️ tan(–45°) = –1
✔️ Final Answers: sin(–45°) = –1/√2, cos(–45°) = 1/√2, tan(–45°) = –1
🔵 Question 23:
Find the values of sin 225°, cos 225°, tan 225°.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ 225° = 180° + 45°, 3rd quadrant → all negative
➡️ sin 225° = –sin 45° = –1/√2
➡️ cos 225° = –cos 45° = –1/√2
➡️ tan 225° = tan 45° = 1
✔️ Final Answers: sin 225° = –1/√2, cos 225° = –1/√2, tan 225° = 1
🔵 Question 24:
Find the principal value of tan⁻¹(1).
🟢 Answer: π/4
🔵 Question 25:
Find the principal value of cot⁻¹(–1).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Principal value range of cot⁻¹x = (0, π)
➡️ cot⁻¹(–1) = (3π/4)
✔️ Final Answer: 3π/4
🔵 Question 26:
Find the domain and range of y = sin x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Domain = ℝ (all real numbers)
➡️ Range = [–1, 1]
🔵 Question 27:
Find the domain and range of y = tan x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Domain = ℝ – { (2n+1)π/2, n ∈ ℤ }
➡️ Range = ℝ
🔵 Question 28:
Find the domain and range of y = sec x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Domain = ℝ – { (2n+1)π/2, n ∈ ℤ }
➡️ Range = (–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
🧭 Section C – 3 Marks Questions
🔵 Question 29:
Find the general solution of the equation sin x = 1/2.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let sin x = 1/2.
➡️ We know sin π/6 = 1/2.
➡️ General solution of sin x = sin α is
x = nπ + (–1)ⁿ α, where n ∈ ℤ.
➡️ Substituting α = π/6:
x = nπ + (–1)ⁿ (π/6).
✔️ Final Answer: x = nπ + (–1)ⁿ (π/6), where n ∈ ℤ.
🔵 Question 30:
Find the general solution of the equation cos x = –1/2.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ cos x = –1/2.
➡️ cos (2π/3) = –1/2.
➡️ General solution of cos x = cos α is
x = 2nπ ± α, n ∈ ℤ.
➡️ Substituting α = 2π/3:
x = 2nπ ± 2π/3.
✔️ Final Answer: x = 2nπ ± 2π/3, where n ∈ ℤ.
🔵 Question 31:
Find the general solution of the equation tan x = 1.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ tan x = 1.
➡️ tan (π/4) = 1.
➡️ General solution of tan x = tan α is
x = nπ + α, n ∈ ℤ.
➡️ Substituting α = π/4:
x = nπ + π/4.
✔️ Final Answer: x = nπ + π/4, where n ∈ ℤ.
🔵 Question 32:
Find all solutions of 2 cos²x – 3 sin x = 0 for x ∈ [0, 2π].
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Equation: 2 cos²x – 3 sin x = 0.
➡️ Using cos²x = 1 – sin²x:
2 (1 – sin²x) – 3 sin x = 0
➡️ Simplify: 2 – 2 sin²x – 3 sin x = 0
➡️ Multiply by –1: 2 sin²x + 3 sin x – 2 = 0.
✴️ Let sin x = t ⇒ 2t² + 3t – 2 = 0.
➡️ Solve quadratic:
t = [–3 ± √(9 + 16)] / 4
t = [–3 ± 5] / 4
➡️ Two roots:
t₁ = (2/4) = 1/2
t₂ = (–8/4) = –2 (not possible; |sin x| ≤ 1)
➡️ So sin x = 1/2.
➡️ Solutions in [0, 2π]:
x = π/6, 5π/6.
✔️ Final Answers: x = π/6, 5π/6.
🧭 Section D – 5 Marks Question
🔵 Question 33:
Prove that:
sin 3x = 3 sin x – 4 sin³ x
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Start with formula for sin(A + B):
sin(A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B.
➡️ Let A = 2x, B = x.
Then
sin 3x = sin(2x + x)
= sin 2x cos x + cos 2x sin x.
💡 Use double-angle formulas:
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x
cos 2x = 1 – 2 sin² x.
➡️ Substitute:
sin 3x = (2 sin x cos x)(cos x) + (1 – 2 sin² x)(sin x)
= 2 sin x cos² x + sin x – 2 sin³ x.
➡️ Replace cos² x = 1 – sin² x:
sin 3x = 2 sin x (1 – sin² x) + sin x – 2 sin³ x
= 2 sin x – 2 sin³ x + sin x – 2 sin³ x
= 3 sin x – 4 sin³ x.
✔️ Hence Proved: sin 3x = 3 sin x – 4 sin³ x ✅
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
If sin θ = 3/5 and θ lies in the first quadrant, then cos θ equals
1️⃣ 🔴 4/5
2️⃣ 🟢 5/3
3️⃣ 🟡 3/4
4️⃣ 🔵 –4/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 4/5
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 2:
For tan A = √3, the correct statement is
1️⃣ 🔴 sin A = √3/2
2️⃣ 🟢 cos A = 1/2
3️⃣ 🟡 A = 60°
4️⃣ 🔵 All of these
Answer: 4️⃣ All of these
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 3:
If sin θ + cos θ = 1, then tan θ equals
1️⃣ 🔴 1/2
2️⃣ 🟢 √3 – 1
3️⃣ 🟡 (√2 – 1)/(√2 + 1)
4️⃣ 🔵 1
Answer: 3️⃣ (√2 – 1)/(√2 + 1)
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 4:
The identity valid for every θ is
1️⃣ 🔴 sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
2️⃣ 🟢 sin²θ – cos²θ = 1
3️⃣ 🟡 sin²θ + tan²θ = 1
4️⃣ 🔵 cos²θ + tan²θ = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 5:
If cos θ = –12/13 and θ is in the third quadrant, find sin θ.
1️⃣ 🔴 –5/13
2️⃣ 🟢 5/13
3️⃣ 🟡 12/13
4️⃣ 🔵 –12/13
Answer: 1️⃣ –5/13
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 6:
Which identity is always true?
1️⃣ 🔴 sec²θ = 1 + tan²θ
2️⃣ 🟢 csc²θ = 1 + cot²θ
3️⃣ 🟡 1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
4️⃣ 🔵 All of the above
Answer: 4️⃣ All of the above
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 7:
If tan θ = 4/3 in first quadrant, then sin θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 3/5
2️⃣ 🟢 4/5
3️⃣ 🟡 4/7
4️⃣ 🔵 3/4
Answer: 1️⃣ 3/5
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 8:
If sin θ = 12/13 (θ acute), find tan θ.
1️⃣ 🔴 5/12
2️⃣ 🟢 12/5
3️⃣ 🟡 13/12
4️⃣ 🔵 12/13
Answer: 2️⃣ 12/5
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 9:
For an acute angle A, if cos A = 4/5, then sin A =
1️⃣ 🔴 3/5
2️⃣ 🟢 5/3
3️⃣ 🟡 4/5
4️⃣ 🔵 –3/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 3/5
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 10:
If tan A = 1, then A is equal to
1️⃣ 🔴 30°
2️⃣ 🟢 45°
3️⃣ 🟡 60°
4️⃣ 🔵 90°
Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 11:
If sin θ = cos θ, the value of θ is
1️⃣ 🔴 30°
2️⃣ 🟢 45°
3️⃣ 🟡 60°
4️⃣ 🔵 90°
Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 12:
If tan A = 3/4, then sec A =
1️⃣ 🔴 5/4
2️⃣ 🟢 5/3
3️⃣ 🟡 4/5
4️⃣ 🔵 3/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 5/4
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 13:
The value of sin 30° + cos 60° is
1️⃣ 🔴 1
2️⃣ 🟢 0
3️⃣ 🟡 1/2
4️⃣ 🔵 √3/2
Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (AIEEE 2010)
🔵 Question 14:
If sin θ = a, then cos θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 √(1 – a²)
2️⃣ 🟢 –√(1 – a²)
3️⃣ 🟡 Depends on quadrant
4️⃣ 🔵 Both 1 and 3
Answer: 4️⃣ Both 1 and 3
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 15:
If sin A = 5/13, then cos A + tan A = ?
1️⃣ 🔴 12/13 + 5/12
2️⃣ 🟢 12/13 + 5/13
3️⃣ 🟡 5/13 + 12/13
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 1️⃣ 12/13 + 5/12
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 16:
The value of sin 45° × cos 45° =
1️⃣ 🔴 1/2
2️⃣ 🟢 1/√2
3️⃣ 🟡 √2/2
4️⃣ 🔵 1/4
Answer: 1️⃣ 1/2
📘 (JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 17:
If cot A = 1, then A =
1️⃣ 🔴 45°
2️⃣ 🟢 30°
3️⃣ 🟡 60°
4️⃣ 🔵 90°
Answer: 1️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Main 2011)
🔵 Question 18:
Simplify sin 60° + cos 30°.
1️⃣ 🔴 1
2️⃣ 🟢 √3
3️⃣ 🟡 √3
4️⃣ 🔵 √3
Answer: 2️⃣ √3
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 19:
If tan A = p/q, then sin A =
1️⃣ 🔴 p/√(p² + q²)
2️⃣ 🟢 q/√(p² + q²)
3️⃣ 🟡 √(p² + q²)/p
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 1️⃣ p/√(p² + q²)
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 20:
If sec θ + tan θ = x, then sec θ = ?
1️⃣ 🔴 (x² + 1)/(2x)
2️⃣ 🟢 (x² – 1)/(2x)
3️⃣ 🟡 x – 1/x
4️⃣ 🔵 x + 1/x
Answer: 1️⃣ (x² + 1)/(2x)
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 21:
If tan θ = 3, find sin θ + cos θ.
1️⃣ 🔴 (3 + 1)/√10
2️⃣ 🟢 (1 – 3)/√10
3️⃣ 🟡 √10/4
4️⃣ 🔵 1
Answer: 1️⃣ (3 + 1)/√10
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 22:
If sin A = 4/5, then cos A – sin A = ?
1️⃣ 🔴 3/5 – 4/5
2️⃣ 🟢 –1/5
3️⃣ 🟡 1/5
4️⃣ 🔵 Cannot be found
Answer: 3️⃣ 1/5
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 23:
If sin θ = x, express cos 2θ in x.
1️⃣ 🔴 1 – 2x²
2️⃣ 🟢 2x² – 1
3️⃣ 🟡 Both 1 and 2
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 24:
If tan A + cot A = 2, then A =
1️⃣ 🔴 45°
2️⃣ 🟢 60°
3️⃣ 🟡 30°
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 1️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 25:
Value of sin 15° is
1️⃣ 🔴 (√6 – √2)/4
2️⃣ 🟢 (√6 + √2)/4
3️⃣ 🟡 √3/2
4️⃣ 🔵 1/2
Answer: 1️⃣ (√6 – √2)/4
📘 (JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 26:
If sin A = 3/5, cos A = 4/5, then the value of sin 2A is
1️⃣ 🔴 24/25
2️⃣ 🟢 7/25
3️⃣ 🟡 1
4️⃣ 🔵 0
Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 27:
If tan θ = 3/4, then cos 2θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 7/25
2️⃣ 🟢 1/25
3️⃣ 🟡 –7/25
4️⃣ 🔵 –1/25
Answer: 1️⃣ 7/25
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 28:
If sin θ = 1/2, then θ can be
1️⃣ 🔴 30°
2️⃣ 🟢 150°
3️⃣ 🟡 210°
4️⃣ 🔵 Both 1️⃣ and 2️⃣
Answer: 4️⃣ Both 1️⃣ and 2️⃣
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 29:
If tan A = √3 and sin A > 0, cos A < 0, then A lies in
1️⃣ 🔴 1st quadrant
2️⃣ 🟢 2nd quadrant
3️⃣ 🟡 3rd quadrant
4️⃣ 🔵 4th quadrant
Answer: 3️⃣ 3rd quadrant
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 30:
If sec θ = 5/3, then tan θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 4/3
2️⃣ 🟢 3/4
3️⃣ 🟡 5/4
4️⃣ 🔵 1
Answer: 1️⃣ 4/3
📘 (JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 31:
If cot A = 7/24, find sin A.
1️⃣ 🔴 24/25
2️⃣ 🟢 7/25
3️⃣ 🟡 25/24
4️⃣ 🔵 25/7
Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (AIEEE 2011)
🔵 Question 32:
If cos A = 4/5 and A is acute, then cos 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 7/25
2️⃣ 🟢 9/25
3️⃣ 🟡 3/5
4️⃣ 🔵 1/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 7/25
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 33:
The value of sin 45° + cos 45° is
1️⃣ 🔴 √2
2️⃣ 🟢 1
3️⃣ 🟡 1/√2
4️⃣ 🔵 2
Answer: 1️⃣ √2
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 34:
If sin A = 4/5, find sin 3A.
1️⃣ 🔴 (3 × 4/5 – 4³/5³)
2️⃣ 🟢 36/125
3️⃣ 🟡 56/125
4️⃣ 🔵 32/125
Answer: 3️⃣ 56/125
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 35:
If tan A + cot A = 2, then sin A =
1️⃣ 🔴 1/√2
2️⃣ 🟢 1
3️⃣ 🟡 0
4️⃣ 🔵 1/2
Answer: 1️⃣ 1/√2
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 36:
If sin A = x, then sin 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 2x√(1 – x²)
2️⃣ 🟢 1 – 2x²
3️⃣ 🟡 2x² – 1
4️⃣ 🔵 x² – 1
Answer: 1️⃣ 2x√(1 – x²)
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 37:
If sin A = 3/5, then cos 2A + sin 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 7/25 + 12/25
2️⃣ 🟢 19/25
3️⃣ 🟡 1
4️⃣ 🔵 0
Answer: 2️⃣ 19/25
📘 (JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 38:
If sin A = 4/5, then tan 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 24/7
2️⃣ 🟢 7/24
3️⃣ 🟡 25/7
4️⃣ 🔵 7/25
Answer: 1️⃣ 24/7
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 39:
If cos θ = 1/3, then sin 2θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 4√2/9
2️⃣ 🟢 4/9
3️⃣ 🟡 √8/9
4️⃣ 🔵 2/3
Answer: 1️⃣ 4√2/9
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 40:
If tan θ = p/q, then cos 2θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 (q² – p²)/(p² + q²)
2️⃣ 🟢 (p² – q²)/(p² + q²)
3️⃣ 🟡 (p² + q²)/(p² – q²)
4️⃣ 🔵 1
Answer: 1️⃣ (q² – p²)/(p² + q²)
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 41:
If sin A = 12/13, then cos 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 –119/169
2️⃣ 🟢 119/169
3️⃣ 🟡 –5/13
4️⃣ 🔵 5/13
Answer: 1️⃣ –119/169
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 42:
If cos A = 3/5, then sec 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 25/7
2️⃣ 🟢 5/3
3️⃣ 🟡 7/25
4️⃣ 🔵 25/24
Answer: 1️⃣ 25/7
📘 (JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 43:
If sin θ = 5/13, then cos 3θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 44/169
2️⃣ 🟢 –44/169
3️⃣ 🟡 45/169
4️⃣ 🔵 –45/169
Answer: 2️⃣ –44/169
📘 (JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 44:
If tan A = 1/2, find sin 2A.
1️⃣ 🔴 4/5
2️⃣ 🟢 3/5
3️⃣ 🟡 1/5
4️⃣ 🔵 2/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 4/5
📘 (JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 45:
If tan A = 2, then sin A – cos A =
1️⃣ 🔴 (2 – 1)/√5
2️⃣ 🟢 1/√5
3️⃣ 🟡 √5/2
4️⃣ 🔵 0
Answer: 1️⃣ (2 – 1)/√5
📘 (JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 46:
If sin A = 3/5, then cos A + sin A =
1️⃣ 🔴 7/5
2️⃣ 🟢 7/10
3️⃣ 🟡 1
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 2️⃣ 7/10
📘 (JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 47:
If sin A = 4/5, find cos 3A.
1️⃣ 🔴 –11/125
2️⃣ 🟢 11/125
3️⃣ 🟡 12/125
4️⃣ 🔵 –12/125
Answer: 1️⃣ –11/125
📘 (JEE Main 2023)
🔵 Question 48:
If cos θ = a, then sin 3θ =
1️⃣ 🔴 3√(1 – a²)a² – √(1 – a²)³
2️⃣ 🟢 3a√(1 – a²) – 4(1 – a²)^(3/2)
3️⃣ 🟡 3√(1 – a²)a – 4a³
4️⃣ 🔵 None
Answer: 3️⃣ 3√(1 – a²)a – 4a³
📘 (JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 49:
If sin A = 1/2 and cos B = 1/2, then A + B =
1️⃣ 🔴 60°
2️⃣ 🟢 90°
3️⃣ 🟡 120°
4️⃣ 🔵 150°
Answer: 2️⃣ 90°
📘 (JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 50:
If sin A = 3/5, then tan 2A =
1️⃣ 🔴 24/7
2️⃣ 🟢 7/24
3️⃣ 🟡 5/12
4️⃣ 🔵 12/5
Answer: 1️⃣ 24/7
📘 (JEE Main 2018)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
If sin A = 3/5, cos A = 4/5, then tan A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 3/4
🟩 2️⃣ 4/3
🟨 3️⃣ 5/4
🟦 4️⃣ 4/5
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 3/4
📘 (JEE Advanced 2024 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 2:
If cos A = 12/13, and A is acute, then sin A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 3/5
🟩 2️⃣ 4/5
🟨 3️⃣ 5/13
🟦 4️⃣ 5/12
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 5/13
📘 (JEE Advanced 2024 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 3:
If sin A + cos A = √2 cos A, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 4:
If tan A = 3/4, then sec A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 5/4
🟩 2️⃣ 4/3
🟨 3️⃣ 5/3
🟦 4️⃣ 1
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 5/3
📘 (JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 5:
If sin A = 5/13, then cos A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 12/13
🟩 2️⃣ 13/12
🟨 3️⃣ 5/12
🟦 4️⃣ 1
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 12/13
📘 (JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 6:
If cos 2A = 1/2, A acute, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 7:
If tan A = √3, then sin A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1/2
🟩 2️⃣ √3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/√2
🟦 4️⃣ 1
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ √3/2
📘 (JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 8:
If sin A = 3/5, then cos 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 7/25
🟩 2️⃣ 16/25
🟨 3️⃣ 24/25
🟦 4️⃣ 9/25
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 16/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 9:
If tan θ = 1, then sin 2θ = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 0
🟨 3️⃣ 1/2
🟦 4️⃣ √2/2
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 10:
If sin θ + cos θ = 1, then sin 3θ + cos 3θ = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 0
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ 1/2
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 11:
If cos θ = 4/5, then sin 2θ = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 24/25
🟩 2️⃣ 7/25
🟨 3️⃣ 16/25
🟦 4️⃣ 12/25
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 12:
If sin A = 1/2, cos B = √3/2, then A + B = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ 90°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 13:
If sin A = cos B, then A + B = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 60°
🟨 3️⃣ 90°
🟦 4️⃣ 180°
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 90°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 14:
If tan A + cot A = 2, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 15:
If sin θ = cos θ, then θ = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2017 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 16:
If sin A = x, then cos 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1 – 2x²
🟩 2️⃣ 2x² – 1
🟨 3️⃣ 1 – x²
🟦 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1 – 2x²
📘 (JEE Advanced 2016 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 17:
If tan A = 1, then sin A + cos A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ √2
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ √2
📘 (JEE Advanced 2015 – Paper 1)
🔵 Question 18:
If sin²A + cos²A = 1, then value of sin⁴A + cos⁴A is
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 1/2
🟨 3️⃣ 3/4
🟦 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 3/4
📘 (JEE Advanced 2024 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 19:
If sin A = 3/5, find cos 2A
🟥 1️⃣ 7/25
🟩 2️⃣ 16/25
🟨 3️⃣ 24/25
🟦 4️⃣ –7/25
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ –7/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 20:
If cos A = 4/5, then sin 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 24/25
🟩 2️⃣ 7/25
🟨 3️⃣ 16/25
🟦 4️⃣ 9/25
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 21:
If sin A + cos A = √2 cos A, then tan A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ √3
🟨 3️⃣ 1/√3
🟦 4️⃣ 0
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 22:
If sin A = 1/2, then value of (1 + tan²A)/(1 – tan²A) = ?
🟥 1️⃣ √3
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/2
🟦 4️⃣ Undefined
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Undefined
📘 (JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 23:
If tan θ = 3/4, then sin 2θ = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 12/25
🟩 2️⃣ 24/25
🟨 3️⃣ 7/25
🟦 4️⃣ 16/25
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 24:
If sin A = 4/5, then sin 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 24/25
🟩 2️⃣ 7/25
🟨 3️⃣ 16/25
🟦 4️⃣ 9/25
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 25:
If cos A = 12/13, then tan A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 3/4
🟩 2️⃣ 4/3
🟨 3️⃣ 5/12
🟦 4️⃣ 5/13
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 3/4
📘 (JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 26:
If sin A = cos A, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 27:
If tan A = 1, then sin 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 0
🟨 3️⃣ –1
🟦 4️⃣ √2/2
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 28:
If cos 2A = 1/2, then sin A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1/2
🟩 2️⃣ √3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/√2
🟦 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1/2
📘 (JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 29:
If tan A = 1/√3, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 30°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 30:
If sin 2A = 1, then A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 45°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 31:
If sin A = 3/5, cos A = 4/5, then sin 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 24/25
🟩 2️⃣ 12/25
🟨 3️⃣ 7/25
🟦 4️⃣ 16/25
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 24/25
📘 (JEE Advanced 2017 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 32:
If sin A = x, then cos 2A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1 – 2x²
🟩 2️⃣ 2x² – 1
🟨 3️⃣ 1 – x²
🟦 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 1 – 2x²
📘 (JEE Advanced 2016 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 33:
If sin A = 1/2, cos B = √3/2, then A + B = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 30°
🟩 2️⃣ 45°
🟨 3️⃣ 60°
🟦 4️⃣ 90°
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ 90°
📘 (JEE Advanced 2015 – Paper 2)
🔵 Question 34:
If sin²A = 1/4, cos²A = 3/4, then sin⁴A + cos⁴A = ?
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 1/2
🟨 3️⃣ 5/8
🟦 4️⃣ 3/4
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 5/8
📘 (JEE Advanced 2013 – Paper 2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. 1 radian equals how many degrees?
🔵 (A) 180°
🟢 (B) 90°
🟠 (C) 57°17′
🔴 (D) 60°
Answer: (C) 57°17′
Q2. Convert 60° into radians.
🔵 (A) π/6
🟢 (B) π/3
🟠 (C) π/2
🔴 (D) 2π/3
Answer: (B) π/3
Q3. sin 0° = ?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) –1
🔴 (D) ∞
Answer: (A) 0
Q4. cos 90° = ?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) –1
🔴 (D) ∞
Answer: (A) 0
Q5. tan 45° = ?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) √3
🔴 (D) 1/√3
Answer: (B) 1
Q6. In which quadrant does 150° lie?
🔵 (A) I
🟢 (B) II
🟠 (C) III
🔴 (D) IV
Answer: (B) II
Q7. Sign of cos θ in the III quadrant?
🔵 (A) +
🟢 (B) –
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) undefined
Answer: (B) –
Q8. sin(–x) = ?
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) –sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) –cos x
Answer: (B) –sin x
Q9. cos(–x) = ?
🔵 (A) cos x
🟢 (B) –cos x
🟠 (C) sin x
🔴 (D) –sin x
Answer: (A) cos x
Q10. sin²x + cos²x = ?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) sec²x
Answer: (B) 1
Q11. 1 + tan²x = ?
🔵 (A) cosec²x
🟢 (B) sec²x
🟠 (C) cot²x
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) sec²x
Q12. 1 + cot²x = ?
🔵 (A) cosec²x
🟢 (B) sec²x
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) tan²x
Answer: (A) cosec²x
Q13. Range of sin x is
🔵 (A) (–∞, ∞)
🟢 (B) [–1, 1]
🟠 (C) [0, 1]
🔴 (D) [–∞, 0]
Answer: (B) [–1, 1]
Q14. Period of tan x is
🔵 (A) π
🟢 (B) 2π
🟠 (C) π/2
🔴 (D) 4π
Answer: (A) π
Q15. Principal value of sin⁻¹(1/2)
🔵 (A) π/3
🟢 (B) π/6
🟠 (C) –π/6
🔴 (D) 5π/6
Answer: (B) π/6
Q16. Principal value of cos⁻¹(–1/2)
🔵 (A) π/3
🟢 (B) 2π/3
🟠 (C) 5π/6
🔴 (D) π/6
Answer: (B) 2π/3
Q17. Convert 300° into radians.
🔵 (A) 5π/3
🟢 (B) 2π/3
🟠 (C) 7π/6
🔴 (D) 4π/3
Answer: (A) 5π/3
Q18. sin 120° = ?
🔵 (A) √3/2
🟢 (B) 1/2
🟠 (C) –1/2
🔴 (D) –√3/2
Answer: (A) √3/2
Q19. cos 210° = ?
🔵 (A) √3/2
🟢 (B) 1/2
🟠 (C) –√3/2
🔴 (D) –1/2
Answer: (C) –√3/2
Q20. tan 330° = ?
🔵 (A) 1/√3
🟢 (B) –1/√3
🟠 (C) √3
🔴 (D) –√3
Answer: (B) –1/√3
Q21. General solution of sin x = 1/2
🔵 (A) x = nπ + (–1)ⁿ π/6
🟢 (B) x = nπ + π/2
🟠 (C) x = nπ + π/3
🔴 (D) x = nπ
Answer: (A) x = nπ + (–1)ⁿ π/6
Q22. General solution of cos x = –1/2
🔵 (A) x = 2nπ ± 2π/3
🟢 (B) x = nπ + π/6
🟠 (C) x = nπ
🔴 (D) x = 2nπ ± π/3
Answer: (A) x = 2nπ ± 2π/3
Q23. Domain of tan x
🔵 (A) ℝ
🟢 (B) ℝ – {(2n+1)π/2}
🟠 (C) [0, π]
🔴 (D) [–π/2, π/2]
Answer: (B) ℝ – {(2n+1)π/2}
Q24. Range of sec x
🔵 (A) [–1, 1]
🟢 (B) (–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
🟠 (C) (0, ∞)
🔴 (D) (–∞, ∞)
Answer: (B) (–∞, –1] ∪ [1, ∞)
Q25. sin(π + x) = ?
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) –sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) –cos x
Answer: (B) –sin x
Q26. cos(π + x) = ?
🔵 (A) cos x
🟢 (B) –cos x
🟠 (C) sin x
🔴 (D) –sin x
Answer: (B) –cos x
Q27. tan(π + x) = ?
🔵 (A) tan x
🟢 (B) –tan x
🟠 (C) cot x
🔴 (D) –cot x
Answer: (A) tan x
Q28. sin(2x) = ?
🔵 (A) sin²x
🟢 (B) 2 sin x cos x
🟠 (C) 2 cos²x
🔴 (D) cos²x – sin²x
Answer: (B) 2 sin x cos x
Q29. cos(2x) = ?
🔵 (A) cos²x – sin²x
🟢 (B) 1 – 2 sin²x
🟠 (C) 2 cos²x – 1
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Q30. tan(2x) = ?
🔵 (A) (2 tan x)/(1 – tan²x)
🟢 (B) (1 – tan²x)/(2 tan x)
🟠 (C) tan²x
🔴 (D) 2 tan²x
Answer: (A) (2 tan x)/(1 – tan²x)
Q31. sin(–x)/cos(–x) = ?
🔵 (A) tan x
🟢 (B) –tan x
🟠 (C) cot x
🔴 (D) –cot x
Answer: (B) –tan x
Q32. If sin A = 3/5, A in first quadrant, find cos A.
🔵 (A) 4/5
🟢 (B) –4/5
🟠 (C) 2/5
🔴 (D) –2/5
Answer: (A) 4/5
Q33. If cos θ = –4/5, θ in second quadrant, find sin θ.
🔵 (A) 3/5
🟢 (B) –3/5
🟠 (C) 4/5
🔴 (D) –4/5
Answer: (A) 3/5
Q34. If tan x = 1, general solution is
🔵 (A) x = nπ + π/4
🟢 (B) x = nπ
🟠 (C) x = nπ + π/2
🔴 (D) x = nπ – π/4
Answer: (A) x = nπ + π/4
Q35. sin³x = ?
🔵 (A) (3 sin x – sin 3x)/4
🟢 (B) (3 sin x + sin 3x)/4
🟠 (C) (sin x – sin 3x)/2
🔴 (D) (sin x + sin 3x)/2
Answer: (A) (3 sin x – sin 3x)/4
Q36. cos³x = ?
🔵 (A) (3 cos x + cos 3x)/4
🟢 (B) (3 cos x – cos 3x)/4
🟠 (C) (cos x + cos 3x)/2
🔴 (D) (cos x – cos 3x)/2
Answer: (A) (3 cos x + cos 3x)/4
Q37. Range of f(x) = 2 sin x + 3
🔵 (A) [1, 5]
🟢 (B) [–1, 1]
🟠 (C) [2, 4]
🔴 (D) [0, 3]
Answer: (A) [1, 5]
Q38. Period of f(x) = sin 2x
🔵 (A) 2π
🟢 (B) π
🟠 (C) π/2
🔴 (D) 4π
Answer: (B) π
Q39. Number of solutions of sin x = 1/2 in [0, 2π]
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (B) 2
Q40. cot(π – x) = ?
🔵 (A) –cot x
🟢 (B) cot x
🟠 (C) tan x
🔴 (D) –tan x
Answer: (A) –cot x
🔶 JEE Advanced Level (Q41–Q50)
Q41. sin 3x = ?
🔵 (A) 3 sin x – 4 sin³x
🟢 (B) 3 sin x + 4 sin³x
🟠 (C) 4 sin³x – 3 sin x
🔴 (D) sin³x – 3 sin x
Answer: (A) 3 sin x – 4 sin³x
Q42. cos 3x = ?
🔵 (A) 4 cos³x – 3 cos x
🟢 (B) 3 cos x – 4 cos³x
🟠 (C) cos³x – 3 cos x
🔴 (D) 4 cos x – 3 cos³x
Answer: (A) 4 cos³x – 3 cos x
Q43. tan 3x = ?
🔵 (A) (3 tan x – tan³x)/(1 – 3 tan²x)
🟢 (B) (3 tan x + tan³x)/(1 + 3 tan²x)
🟠 (C) (tan³x – 3 tan x)/(1 – 3 tan²x)
🔴 (D) (tan³x + 3 tan x)/(1 + 3 tan²x)
Answer: (A) (3 tan x – tan³x)/(1 – 3 tan²x)
Q44. If sin x = p, then cos 2x = ?
🔵 (A) 1 – 2p²
🟢 (B) 2p² – 1
🟠 (C) 1 + 2p²
🔴 (D) –1 – 2p²
Answer: (A) 1 – 2p²
Q45. If cos x = q, then sin 2x = ?
🔵 (A) 2q√(1 – q²)
🟢 (B) √(1 – q²)
🟠 (C) 1 – 2q²
🔴 (D) 2q² – 1
Answer: (A) 2q√(1 – q²)
Q46. Solve 2 cos²x – 3 sin x = 0
🔵 (A) x = π/6, 5π/6
🟢 (B) x = π/4, 3π/4
🟠 (C) x = π/3, 2π/3
🔴 (D) x = π/2
Answer: (A) x = π/6, 5π/6
Q47. Minimum value of f(x) = 2 sin x + 5
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 3
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 5
Answer: (B) 3
Q48. Maximum value of f(x) = 3 cos x – 2
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) –1
Answer: (A) 1
Q49. Range of f(x) = 4 sin²x – 3
🔵 (A) [–3, 1]
🟢 (B) [–4, 0]
🟠 (C) [0, 4]
🔴 (D) [–1, 3]
Answer: (A) [–3, 1]
Q50. If sin x + cos x = 1, then sin 2x = ?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 1/2
🔴 (D) –1
Answer: (A) 0
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
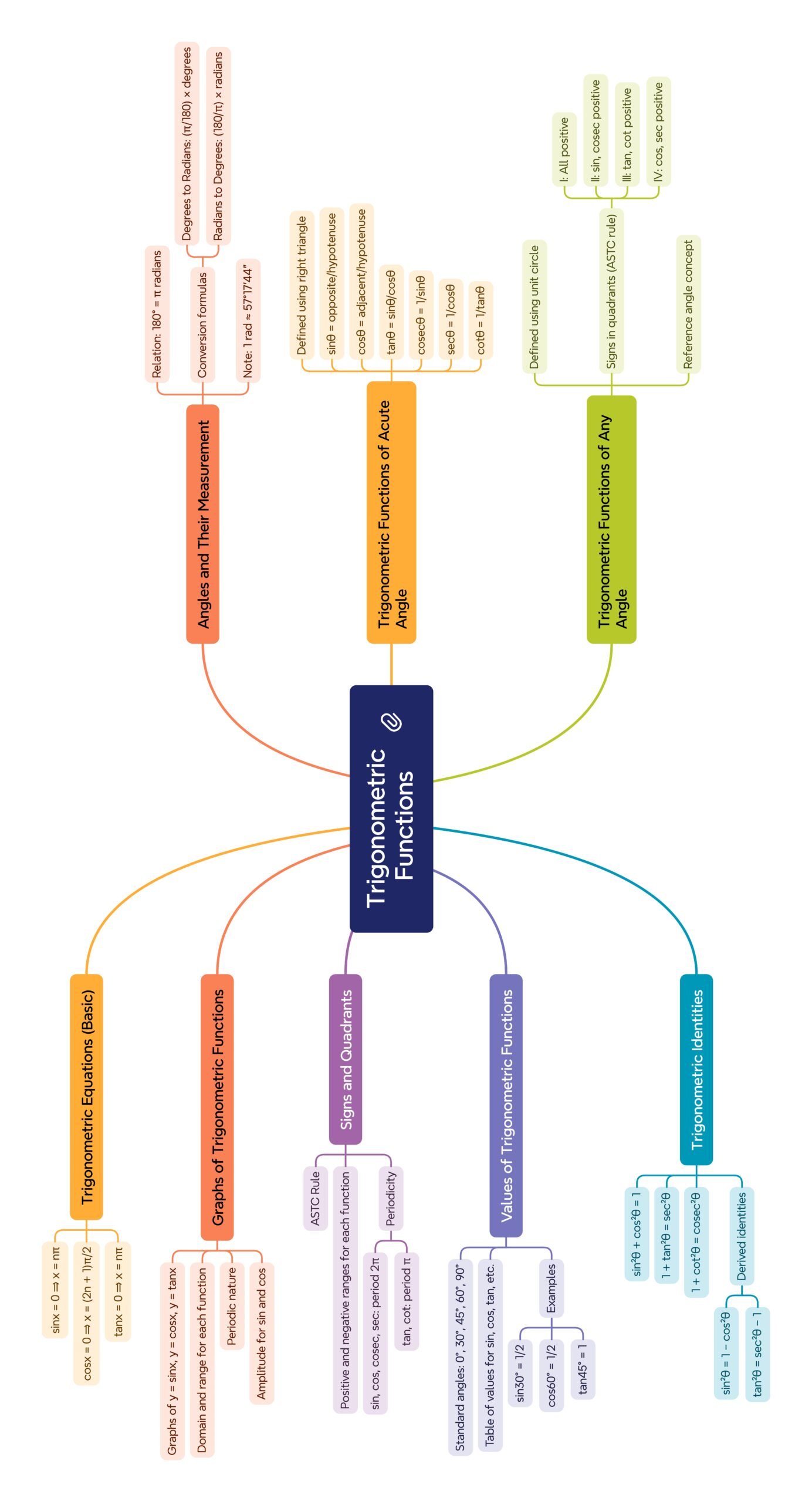
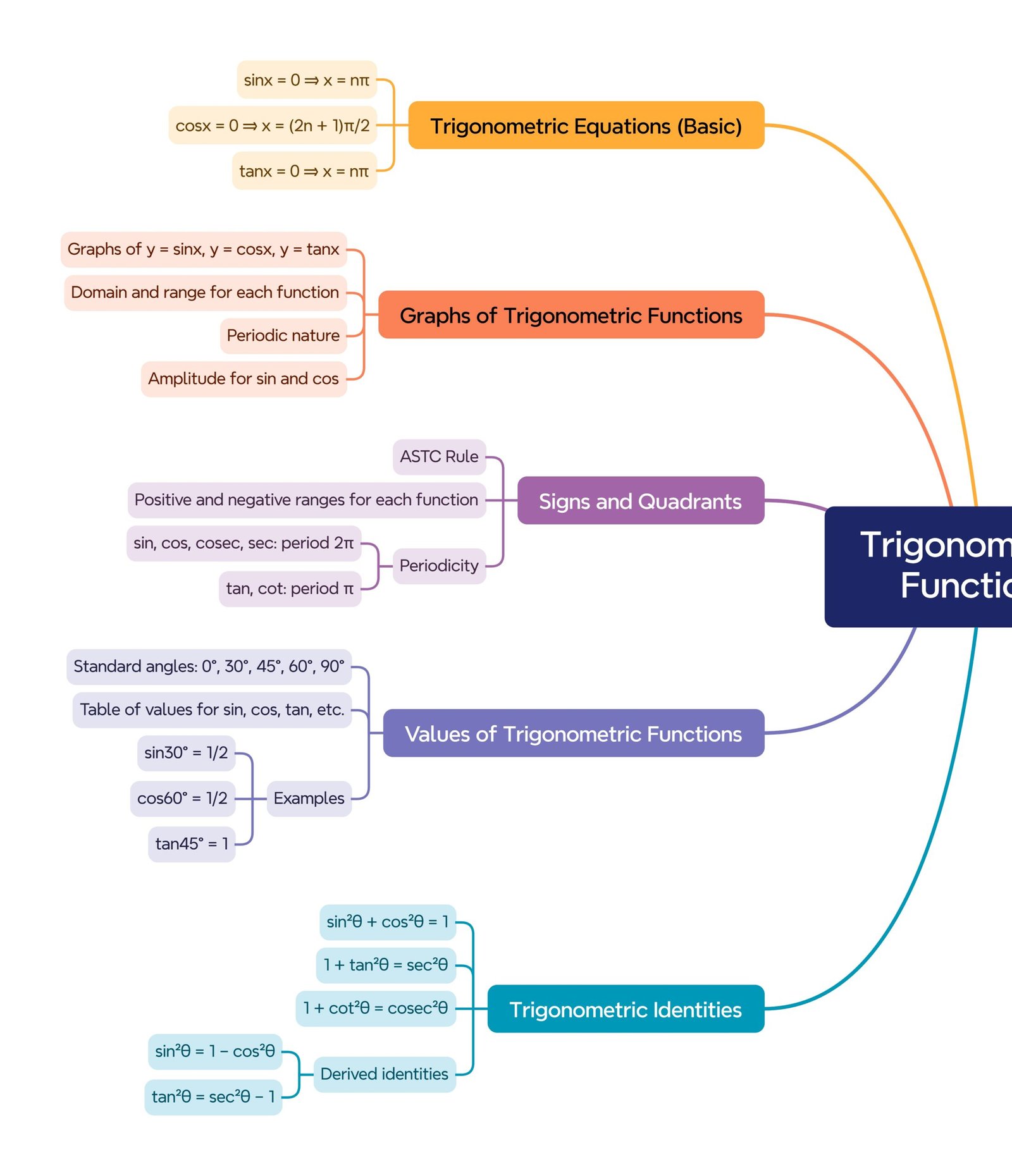
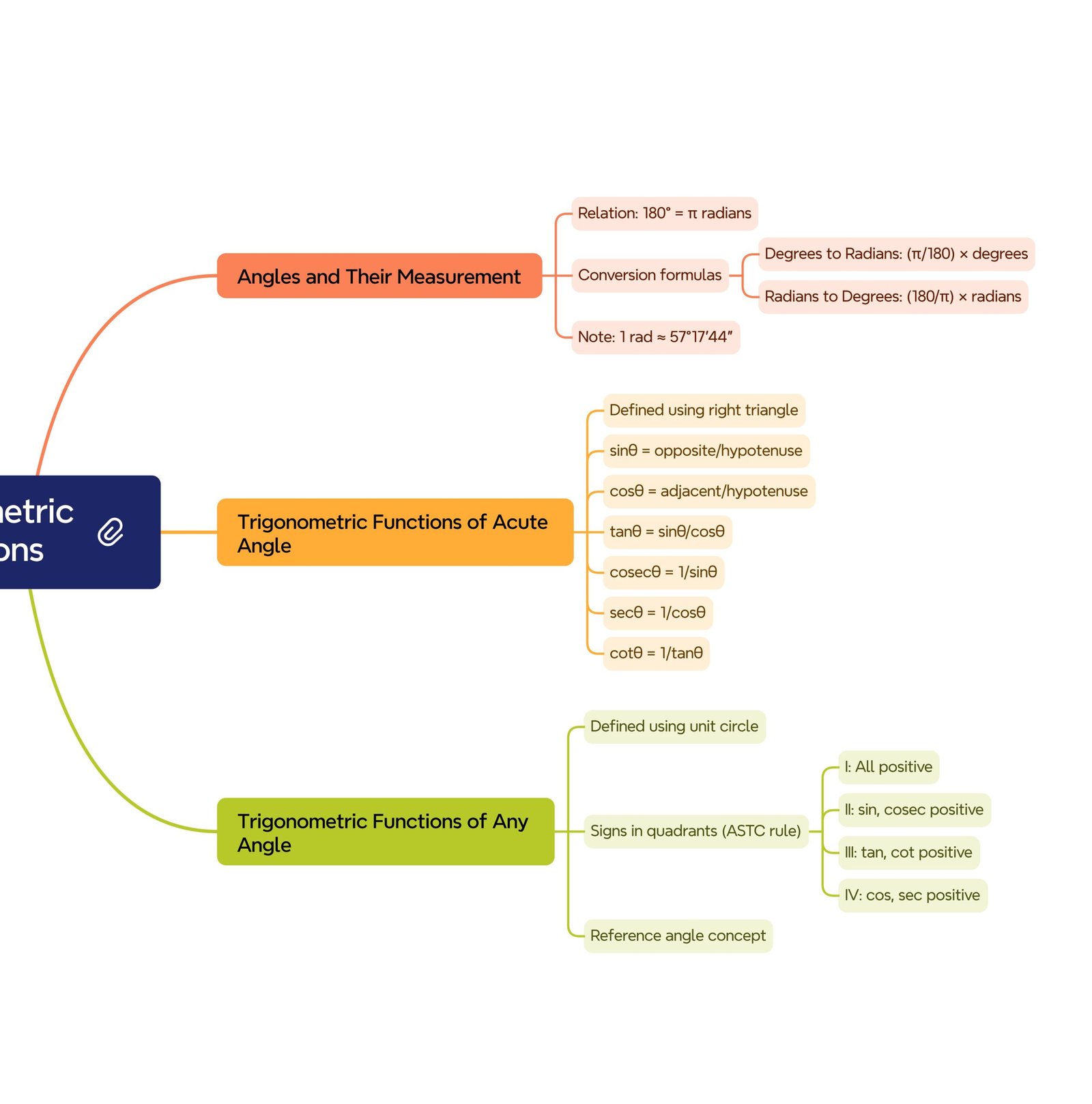
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
