Class 11 : Maths (In English) – Lesson 12. Limits and Derivatives
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔷 Explanation
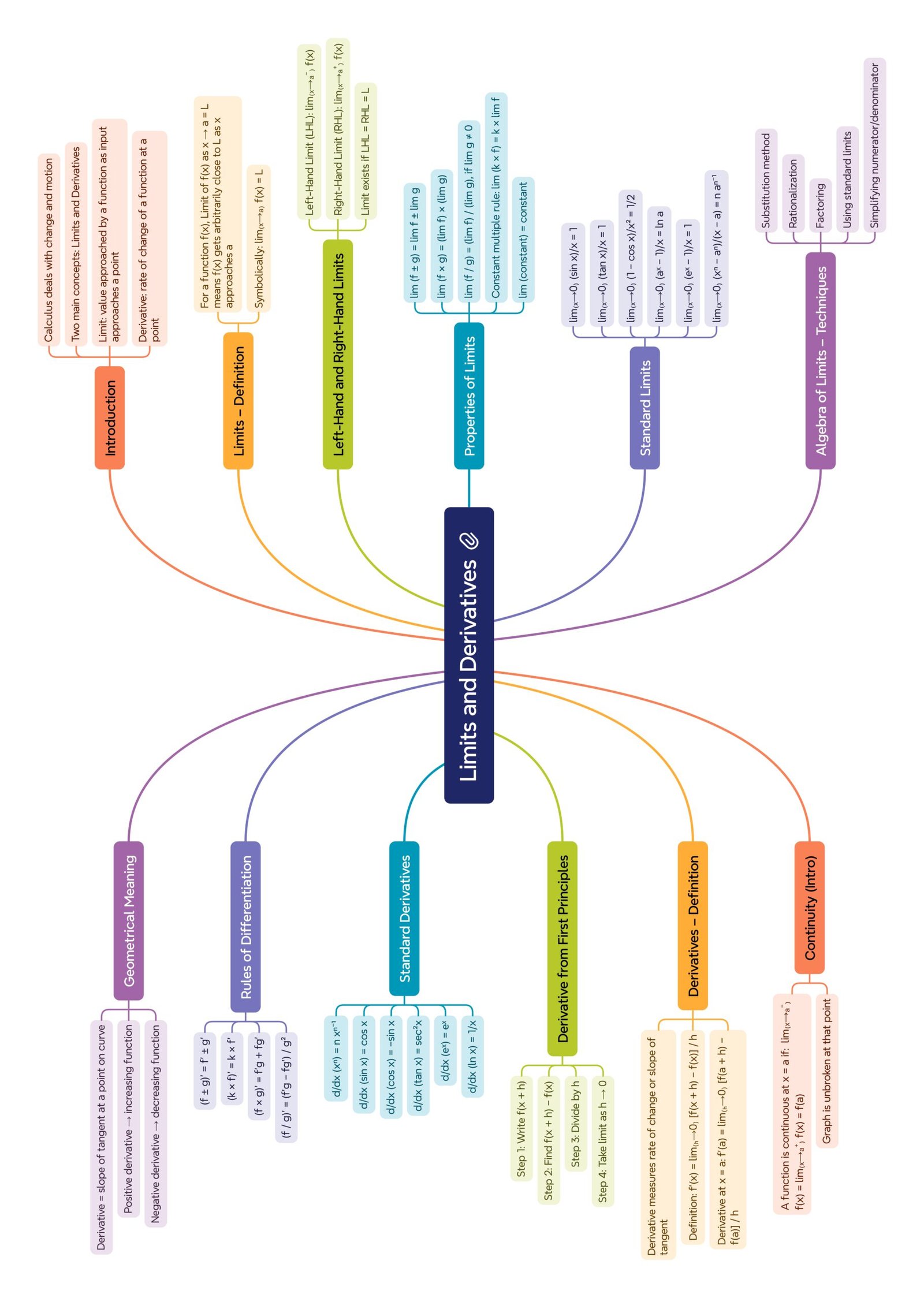
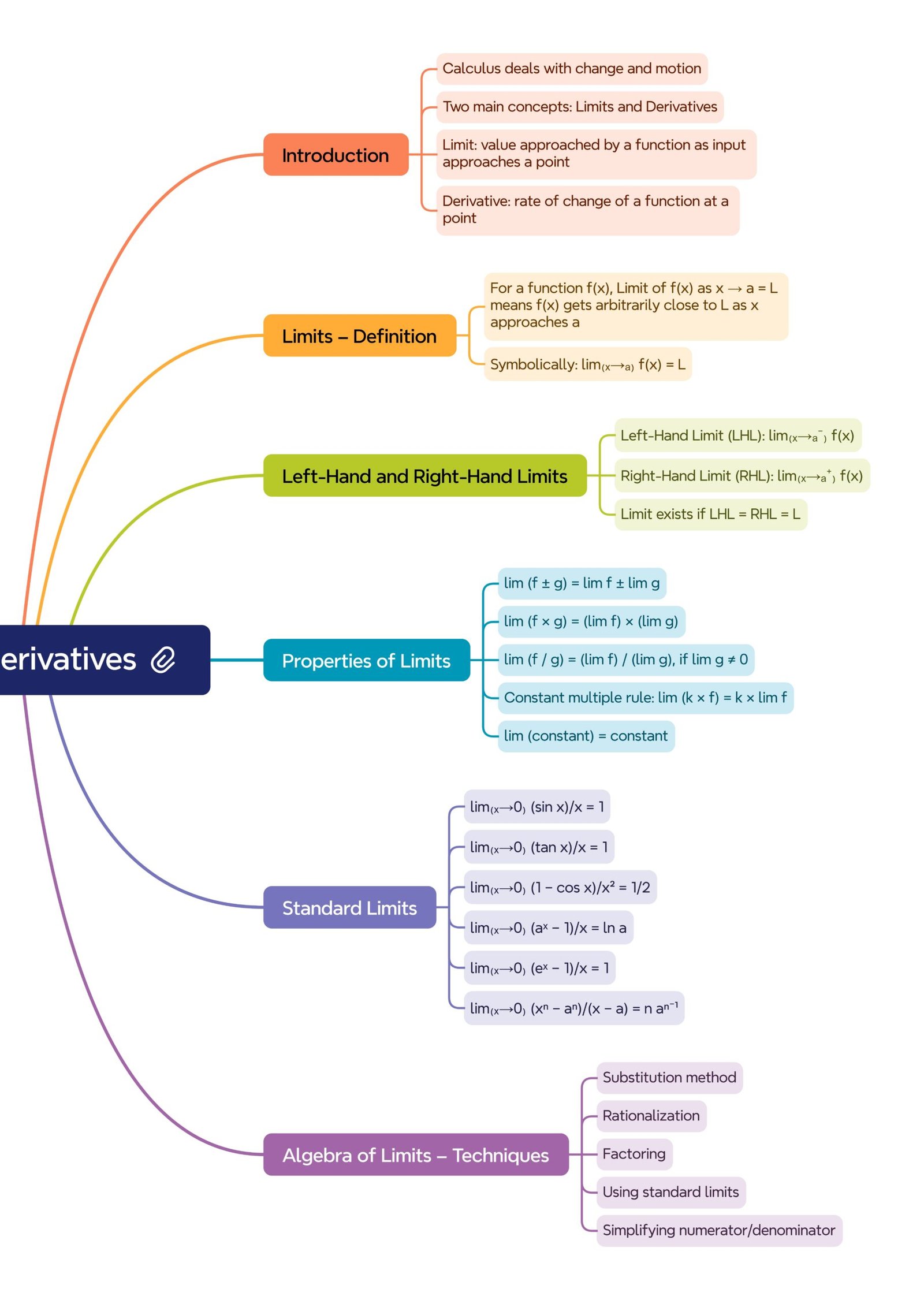
🔹 1. Introduction
🔵 In earlier classes, we studied algebraic manipulation of numbers and variables.
🟢 But in Calculus, we study how quantities change.
🔴 The two main tools of calculus are Limits and Derivatives.
🟡 This chapter introduces these basic ideas using simple functions.
✏️ Note: Calculus deals with continuous change, useful in Physics, Engineering, and Economics.
🔹 2. Concept of Function
🧠 A function is a relation that assigns exactly one value of y for each value of x.
Examples:
f(x) = x²
g(x) = sin x
h(x) = 1/x
We often study how these functions behave near a point.
🔹 3. Concept of a Limit
💡 The limit of a function f(x) as x approaches a value a is the value that f(x) tends to, even if it is not defined at x = a.
✔️ Symbolically:
limₓ→ₐ f(x) = L
means as x gets closer to a (but not equal to a), f(x) gets closer to L.
🔹 4. Left-hand & Right-hand Limits
🔵 Left-hand limit (LHL): value approached by f(x) when x → a⁻ (from left)
🟢 Right-hand limit (RHL): value approached by f(x) when x → a⁺ (from right)
✅ If LHL = RHL = L, then
limₓ→ₐ f(x) = L
🔹 5. Examples
✔️ Example 1:
f(x) = (x² − 1)/(x − 1)
Find limₓ→₁ f(x).
➡️ Step 1: Substitute x = 1 → (1 − 1)/(1 − 1) = 0/0 (indeterminate).
➡️ Step 2: Simplify:
(x² − 1) = (x − 1)(x + 1)
f(x) = (x + 1)
➡️ Step 3: Now, limₓ→₁ f(x) = 1 + 1 = 2
💡 So, limₓ→₁ (x² − 1)/(x − 1) = 2
🔹 6. Indeterminate Forms
🧠 When substitution gives forms like 0/0, ∞/∞, we must simplify before evaluating.
Common forms:
0/0
∞/∞
0×∞
∞ − ∞
We handle them by algebraic manipulation.
🔹 7. Algebra of Limits
For limits where f(x) and g(x) have limits as x→a,
➡️ limₓ→ₐ [f(x) + g(x)] = lim f(x) + lim g(x)
➡️ limₓ→ₐ [f(x) − g(x)] = lim f(x) − lim g(x)
➡️ limₓ→ₐ [f(x)·g(x)] = (lim f(x))·(lim g(x))
➡️ limₓ→ₐ [f(x)/g(x)] = (lim f)/(lim g), if denominator ≠ 0
🔹 8. Standard Limits
Important results:
🔹 limₓ→₀ (sin x)/x = 1
🔹 limₓ→₀ (tan x)/x = 1
🔹 limₓ→₀ (1 − cos x)/x² = 1/2
🔹 limₓ→₀ (aˣ − 1)/x = ln a
🔹 limₓ→₀ (eˣ − 1)/x = 1
🔹 limₓ→₀ (log(1 + x))/x = 1
✏️ Note: For small angles (in radians): sin x ≈ x, tan x ≈ x, cos x ≈ 1 − x²/2
🔹 9. Methods of Evaluation
We use:
1️⃣ Direct Substitution
2️⃣ Simplification (factorization/rationalization)
3️⃣ Standard limit substitution
Example 2:
Find limₓ→₃ (x² − 9)/(x − 3)
➡️ Substitution: 0/0 → indeterminate
➡️ Factorize numerator: (x − 3)(x + 3)
➡️ Cancel (x − 3): Limit = 3 + 3 = 6
Example 3:
Find limₓ→₀ (√(1 + x) − 1)/x
➡️ Multiply numerator & denominator by conjugate:
= [(√(1 + x) − 1)(√(1 + x) + 1)] / [x(√(1 + x) + 1)]
➡️ = [ (1 + x) − 1 ] / [x(√(1 + x) + 1)]
➡️ = 1 / [√(1 + x) + 1]
➡️ Now, x → 0 ⇒ 1 / (1 + 1) = 1/2
🔹 10. Limits of Polynomials and Rational Functions
✔️ For polynomials, direct substitution works.
✔️ For rational functions, divide numerator and denominator by highest power.
Example: limₓ→∞ (2x² + 3x)/(x² + 1)
➡️ Divide by x²: limₓ→∞ (2 + 3/x)/(1 + 1/x²) = 2
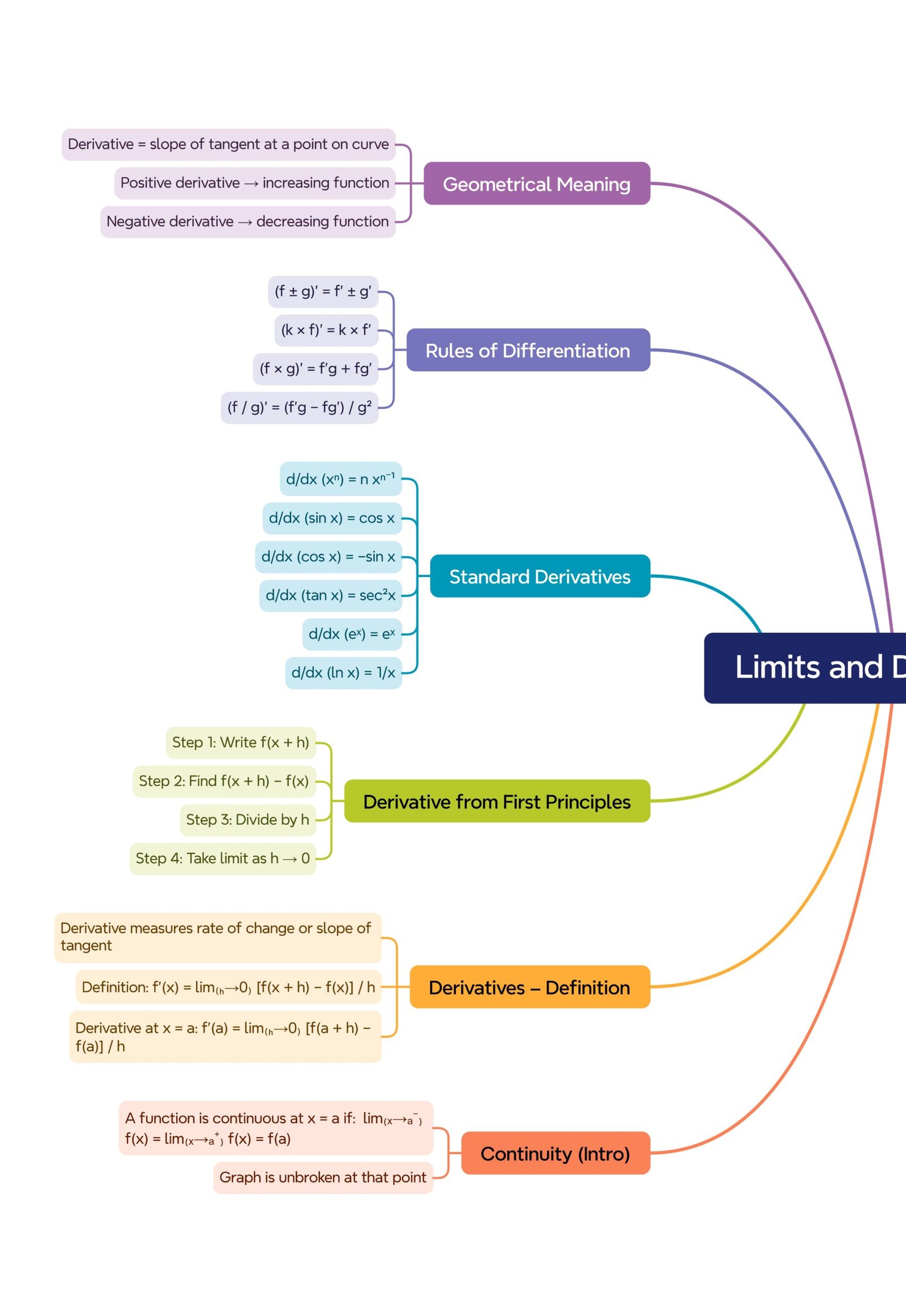
🔹 11. Continuity (Introductory)
A function f(x) is continuous at x = a if:
🔹 limₓ→ₐ⁻ f(x) = limₓ→ₐ⁺ f(x) = f(a)
✏️ If limit exists and equals value, no sudden jump or hole.
🔹 12. Derivative (Concept)
💡 The derivative measures rate of change of function at a point.
✔️ Definition:
f′(a) = limₕ→₀ [f(a + h) − f(a)] / h
(if limit exists)
This is called the first principle or definition of derivative.
🔹 13. Geometrical Meaning
🧭 Derivative at x = a = slope of tangent to curve y = f(x) at point (a, f(a)).
🔹 14. Examples using First Principle
Example 1:
Find derivative of f(x) = x² using definition.
➡️ f(x + h) = (x + h)² = x² + 2xh + h²
➡️ f(x + h) − f(x) = 2xh + h²
➡️ f′(x) = limₕ→₀ (2xh + h²)/h
= limₕ→₀ (2x + h) = 2x
✔️ So derivative of x² is 2x.
Example 2:
f(x) = x³
f(x + h) = (x + h)³ = x³ + 3x²h + 3xh² + h³
Difference = 3x²h + 3xh² + h³
Divide by h: 3x² + 3xh + h²
Limit h→0 ⇒ f′(x) = 3x²
Example 3:
f(x) = 1/x
f(x + h) = 1/(x + h)
Difference = [1/(x + h)] − [1/x] = (x − (x + h)) / [x(x + h)] = −h / [x(x + h)]
Divide by h: −1 / [x(x + h)]
Limit h→0 ⇒ f′(x) = −1/x²
🔹 15. Derivatives of Standard Functions
✔️ d/dx (xⁿ) = n xⁿ⁻¹
✔️ d/dx (sin x) = cos x
✔️ d/dx (cos x) = −sin x
✔️ d/dx (tan x) = sec²x
✔️ d/dx (eˣ) = eˣ
✔️ d/dx (log x) = 1/x
✔️ d/dx (aˣ) = aˣ ln a
🔹 16. Rules of Differentiation
If u = f(x), v = g(x):
➤ Sum Rule: (u + v)′ = u′ + v′
➤ Difference Rule: (u − v)′ = u′ − v′
➤ Product Rule: (uv)′ = u′v + uv′
➤ Quotient Rule: (u/v)′ = (u′v − uv′)/v²
➤ Chain Rule: If y = f(g(x)) ⇒ dy/dx = f′(g(x))·g′(x)
🔹 17. Examples
Example 1:
f(x) = x² + 3x
f′(x) = 2x + 3
Example 2:
y = (x² + 1)(x − 3)
Using product rule:
y′ = (2x)(x − 3) + (x² + 1)(1) = 2x² − 6x + x² + 1 = 3x² − 6x + 1
Example 3:
y = (x² + 1)/(x + 1)
Using quotient rule:
y′ = [(2x)(x + 1) − (x² + 1)(1)] / (x + 1)²
= (2x² + 2x − x² − 1)/(x + 1)² = (x² + 2x − 1)/(x + 1)²
🔹 18. Application
✔️ Instantaneous velocity in physics: derivative of position
✔️ Slope of curve, maximum/minimum points
✔️ Rate of population growth, economics marginal cost
🔹🔹 19. Summary of Derivatives (Direct Formulas)
🧠 Standard Derivatives You Must Remember:
🔵 d/dx (xⁿ) = n·xⁿ⁻¹
🟢 d/dx (sin x) = cos x
🟠 d/dx (cos x) = −sin x
🔴 d/dx (tan x) = sec²x
🟡 d/dx (eˣ) = eˣ
🔵 d/dx (log x) = 1/x
🟢 d/dx (aˣ) = aˣ·ln(a)
✏️ Note:
These formulas are valid when x is measured in radians (for trigonometric functions).
🔷 Summary (~300 words)
Limits:
Describe value function approaches near a point.
Symbol: limₓ→ₐ f(x) = L
Exists if LHL = RHL = L.
Handle 0/0 by simplification.
Standard limits:
limₓ→₀ (sin x)/x = 1,
limₓ→₀ (1 − cos x)/x² = 1/2.
Continuity:
f is continuous at x = a if limit exists and equals f(a).
Derivative:
Measures instantaneous rate of change.
Definition: f′(a) = limₕ→₀ [f(a + h) − f(a)]/h
Geometrically = slope of tangent.
Rules:
Sum: (u + v)′ = u′ + v′
Product: (uv)′ = u′v + uv′
Quotient: (u/v)′ = (u′v − uv′)/v²
Chain: d/dx f(g(x)) = f′(g(x))·g′(x)
Standard Derivatives:
d/dx(xⁿ) = n xⁿ⁻¹
d/dx(sin x) = cos x
d/dx(cos x) = −sin x
d/dx(tan x) = sec²x
d/dx(eˣ) = eˣ
d/dx(log x) = 1/x
d/dx(aˣ) = aˣ ln a
Techniques:
Simplify before substitution
Use standard limits
Apply first principle or rules for derivatives
📝 Quick Recap
✔️ Limit → approaching value
✔️ Continuity → no jump/hole
✔️ Derivative → rate of change / slope
✔️ First principle → basic definition
✔️ Rules simplify long functions
✔️ Derivatives of standard forms must be memorized
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🧾 Exercise 12.1
🔵 Question 1:
lim ₍ₓ → 3₎ (x + 3)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute directly: x = 3
✔️ 3 + 3 = 6
✨ Final Answer = 6
🔵 Question 2:
lim ₍ₓ → π₎ (x − 22/7)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute directly: x = π
✔️ π − 22/7
✨ Final Answer = π − 22/7
🔵 Question 3:
lim ₍ᵣ → 1₎ πr²
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute directly: r = 1
✔️ π × (1)² = π
✨ Final Answer = π
🔵 Question 4:
lim ₍ₓ → 4₎ (4x + 3)/(x − 2)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute x = 4
✔️ Numerator: 4(4) + 3 = 16 + 3 = 19
✔️ Denominator: 4 − 2 = 2
➡️ Therefore, (4x + 3)/(x − 2) = 19/2
✨ Final Answer = 19/2
🔵 Question 5:
lim ₍ₓ → 1₎ (x¹⁰ + x⁵ + 1)/(x − 1)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Form is 0/0, so use L’Hôpital’s Rule
💡 Differentiate numerator & denominator:
Numerator derivative: 10x⁹ + 5x⁴
Denominator derivative: 1
➡️ Substitute x = 1
✔️ (10(1)⁹ + 5(1)⁴) = 10 + 5 = 15
✨ Final Answer = 15
🔵 Question 6:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ ((x + 1)⁵ − 1)/x
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Use formula: lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ ((1 + x)ⁿ − 1)/x = n
✔️ Here n = 5
✨ Final Answer = 5
🔵 Question 7:
lim ₍ₓ → 2₎ (3x² − x − 10)/(x² − 4)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Denominator: x² − 4 = (x − 2)(x + 2)
➡️ Numerator: 3x² − x − 10 = (3x + 5)(x − 2)
➡️ Cancel (x − 2)
✔️ Remaining: (3x + 5)/(x + 2)
➡️ Substitute x = 2
✔️ (3×2 + 5)/(2 + 2) = 11/4
✨ Final Answer = 11/4
🔵 Question 8:
lim ₍ₓ → 3₎ (x⁴ − 81)/(2x² − 5x − 3)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Numerator: x⁴ − 81 = (x² − 9)(x² + 9) = (x − 3)(x + 3)(x² + 9)
➡️ Denominator: 2x² − 5x − 3 = (2x + 1)(x − 3)
➡️ Cancel (x − 3)
✔️ Remaining: ((x + 3)(x² + 9)) / (2x + 1)
➡️ Substitute x = 3
✔️ ((3 + 3)(9 + 9)) / (2×3 + 1) = (6 × 18) / 7 = 108/7
✨ Final Answer = 108/7
🔵 Question 9:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ (ax + b)/(cx + 1)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute x = 0
✔️ Numerator: a(0) + b = b
✔️ Denominator: c(0) + 1 = 1
✨ Final Answer = b
🔵 Question 10:
lim ₍𝓏 → 1₎ ( 𝓏^(1/3) − 1 ) ÷ ( 𝓏^(1/6) − 1 )
🟢 Answer (Plain Text with Visual Style):
✨ Step 1: Let t = 𝓏^(1/6)
➡️ Then 𝓏 = t⁶ and 𝓏^(1/3) = (t⁶)^(1/3) = t²
So the expression becomes:
lim ₍t → 1₎ ( t² − 1 ) ÷ ( t − 1 )
✨ Step 2: Factorize numerator
➡️ t² − 1 = (t − 1)(t + 1)
✂️ Cancel (t − 1)
Remaining: t + 1
✨ Step 3: Substitute t = 1
➡️ 1 + 1 = 2
✔️ Final Answer = 2 ✅
🔵 Question 11:
lim ₍ₓ → 1₎ (a x² + b x + c) / (c x² + b x + a), with a + b + c ≠ 0
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute x = 1
✔️ Numerator: a + b + c
✔️ Denominator: c + b + a = a + b + c
✨ Final Answer = 1
🔵 Question 12:
lim ₍ₓ → −2₎ ( 1/x + 1/2 ) ÷ ( x + 2 )
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Combine the numerator
➡️ 1/x + 1/2 = (2 + x) / (2x)
So,
Expression = [(2 + x) / (2x)] ÷ (x + 2)
✨ Step 2: Simplify
➡️ [(2 + x) / (2x)] × [1 / (x + 2)]
Note that (2 + x) = (x + 2), so
Expression = (x + 2) / (2x × (x + 2))
✂️ Cancel (x + 2)
➡️ Remaining = 1 / (2x)
✨ Step 3: Substitute x = −2
➡️ 1 / [2 × (−2)] = 1 / (−4)
✔️ Final Answer = −1/4 ✅
🔵 Question 13:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ ( sin(ax) ) ÷ ( bx )
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Write as
= (a/b) × [ sin(ax) / (ax) ]
✨ Step 2: Use standard result lim ₍t → 0₎ (sin t / t) = 1
➡️ Therefore, limit = (a/b) × 1 = a/b
✔️ Final Answer = a/b ✅
🔵 Question 14:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ ( sin(ax) ) ÷ ( sin(bx) ), a, b ≠ 0
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Multiply and divide by (ax) and (bx)
= [ sin(ax) / (ax) ] ÷ [ sin(bx) / (bx) ] × (a/b)
✨ Step 2: Use standard result
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ sin(kx)/(kx) = 1
➡️ So, limit = 1 ÷ 1 × (a/b) = a/b
✔️ Final Answer = a/b ✅
🔵 Question 15:
lim ₍ₓ → π₎ [ sin(π − x) ] / [ π − x ]
🟢 Answer:
✨ Let t = π − x ⇒ t → 0.
➡️ Expression → sin t / t.
✔️ Final Answer = 1
🔵 Question 16:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ [ cos x ] / [ π − x ]
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute x = 0 → cos 0 / (π − 0) = 1/π.
✔️ Final Answer = 1/π
🔵 Question 17:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ [ cos 2x − 1 ] / [ cos x − 1 ]
🟢 Answer:
✨ Use identities: cos 2x − 1 = −2 sin²x; cos x − 1 = −2 sin²(x/2).
➡️ Ratio = sin²x / sin²(x/2).
✨ Using sin x = 2 sin(x/2) cos(x/2):
➡️ (2 sin(x/2) cos(x/2))² / sin²(x/2) = 4 cos²(x/2) → 4.
✔️ Final Answer = 4
🔵 Question 18:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ [ a·x + x·cos x ] / [ b·sin x ]
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Numerator = x(a + cos x).
➡️ Expression = (a + cos x)/b × (x/ sin x).
As x → 0: cos x → 1 and x/ sin x → 1.
✔️ Final Answer = (a + 1)/b
🔵 Question 19:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ x·sec x
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Substitute x = 0 → 0 · sec 0 = 0 · 1 = 0.
✔️ Final Answer = 0
🔵 Question 20:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ [ sin(ax) + sin(bx) ] / [ a·x + sin(bx) ], a, b, a+b ≠ 0
🟢 Answer:
✨ For small x: sin(ax) ≈ ax, sin(bx) ≈ bx.
➡️ Numerator ≈ ax + bx, Denominator ≈ ax + bx.
✔️ Final Answer = 1
🔵 Question 21:
lim ₍ₓ → 0₎ ( cosec x − cot x )
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Rewrite: cosec x − cot x = (1 − cos x)/ sin x.
✨ Use 1 − cos x = 2 sin²(x/2) and sin x = 2 sin(x/2) cos(x/2).
➡️ Ratio = tan(x/2) → 0 as x → 0.
✔️ Final Answer = 0
🔵 Question 22:
Evaluate lim₍ₓ → ₓ/2₎ [ tan(2x) / ( x − x/2 ) ]
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Simplify the denominator
➡️ x − x/2 = x/2
So the expression becomes
➡️ lim₍ₓ → ₓ/2₎ [ tan(2x) / (x/2) ]
✨ Step 2: Rewrite as
➡️ 2 × lim₍ₓ → ₓ/2₎ [ tan(2x) / x ]
Now, as x → x/2, the numerator and denominator are both finite,
so substitute directly 👇
✨ Step 3: Substitute
➡️ x = x/2 ⇒ 2x = 2 × (x/2) = x
Hence expression = 2 × [ tan(x) / (x/2) ] = 2 × [ (2 tan x) / x ] = 4 × [ tan x / x ]
✨ Step 4: Use standard result
💡 lim₍θ → 0₎ ( tan θ / θ ) = 1
But here, since x → x/2 ≠ 0, the value is
✔️ 4 × (tan(x/2)/(x/2)) (depends on x)
⚠️ If x → 0, then limit = 4
Otherwise, substitute that specific value of x.
🔵 Question 23
Find lim₍ₓ → 0₎ f(x) and lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x), where
f(x) =
{ 2x + 3, x ≤ 0
{ 3(x + 1), x > 0
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Compute lim₍ₓ → 0⁻₎ f(x)
➡️ As x → 0 from left (x ≤ 0), use f(x) = 2x + 3
⇒ f(x) = 2(0) + 3 = 3
✨ Step 2: Compute lim₍ₓ → 0⁺₎ f(x)
➡️ As x → 0 from right (x > 0), use f(x) = 3(x + 1)
⇒ f(x) = 3(0 + 1) = 3
✔️ Since both sides equal 3,
✅ lim₍ₓ → 0₎ f(x) = 3
✨ Step 3: Compute lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x)
➡️ For x > 0, f(x) = 3(x + 1)
⇒ lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x) = 3(1 + 1) = 6
✅ Final Answers:
✔️ lim₍ₓ → 0₎ f(x) = 3
✔️ lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x) = 6
🔵 Question 24
Find lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x), where
f(x) =
{ x² − 1, x ≤ 1
{ −x² − 1, x > 1
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Left-hand limit (x → 1⁻)
➡️ f(x) = x² − 1
⇒ f(1) = 1² − 1 = 0
✨ Step 2: Right-hand limit (x → 1⁺)
➡️ f(x) = −x² − 1
⇒ f(1) = −1² − 1 = −2
⚠️ Left-hand ≠ Right-hand
❌ So, lim₍ₓ → 1₎ f(x) does not exist
🔵 Question 25
Evaluate lim₍ₓ → 0₎ f(x), where
f(x) =
{ |x| / x, x ≠ 0
{ 0, x = 0
🟢 Answer:
✨ Step 1: Left-hand limit (x → 0⁻)
➡️ When x < 0 ⇒ |x| = −x
⇒ f(x) = (−x)/x = −1
✨ Step 2: Right-hand limit (x → 0⁺)
➡️ When x > 0 ⇒ |x| = x
⇒ f(x) = x/x = 1
⚠️ Left-hand ≠ Right-hand
❌ So, lim₍ₓ → 0₎ f(x) does not exist
🔵 Question 26
Find lim₍ₓ→0₎ f(x), where
f(x) = { x/|x| , x ≠ 0 ; 0 , x = 0 }
🟢 Answer:
✨ Left-hand limit (x → 0⁻): x < 0 ⇒ |x| = −x ⇒ x/|x| = x/(−x) = −1
✨ Right-hand limit (x → 0⁺): x > 0 ⇒ |x| = x ⇒ x/|x| = x/x = 1
⚠️ LHL ≠ RHL ⇒ limit does not exist.
✔️ Final: lim₍ₓ→0₎ f(x) does not exist.
🔵 Question 27
Find lim₍ₓ→5₎ f(x), where f(x) = |x| − 5
🟢 Answer:
✨ |x| is continuous at x = 5 and |5| = 5
➡️ lim₍ₓ→5₎ (|x| − 5) = 5 − 5 = 0
✔️ Final: lim₍ₓ→5₎ f(x) = 0.
🔵 Question 28
Suppose
f(x) = { a + b x , x < 1 ; 4 , x = 1 ; b − a x , x > 1 }
and if lim₍ₓ→1₎ f(x) = f(1) what are possible values of a and b?
🟢 Answer (continuity at x = 1):
✨ Left-hand limit at 1: a + b(1) = a + b
✨ Right-hand limit at 1: b − a(1) = b − a
Given lim₍ₓ→1₎ f(x) = f(1) = 4 ⇒
➡️ a + b = 4 …(1)
➡️ b − a = 4 …(2)
➤ Add (1) and (2): 2b = 8 ⇒ b = 4
➤ From (1): a + 4 = 4 ⇒ a = 0
✔️ Final: a = 0, b = 4.
🔵 Question 29:
Let a₁, a₂, …, aₙ be fixed real numbers and define a function
f(x) = (x − a₁)(x − a₂)…(x − aₙ).
What is lim₍ₓ→aₖ₎ f(x)? For some a ≠ a₁, a₂, …, aₙ, compute lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x).
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Write function
➡️ f(x) = (x − a₁)(x − a₂)…(x − aₙ)
✳️ Step 2: Consider x → aₖ (where aₖ is one of the roots)
➡️ When x = aₖ, the factor (x − aₖ) = 0
✳️ Step 3: Product contains a zero factor
➡️ lim₍ₓ→aₖ₎ f(x) = 0
✳️ Step 4: Now take a ≠ a₁, a₂, …, aₙ
➡️ Function is continuous for x = a
➡️ lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) = f(a) = (a − a₁)(a − a₂)…(a − aₙ)
✔️ Final:
lim₍ₓ→aₖ₎ f(x) = 0
and
lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) = (a − a₁)(a − a₂)…(a − aₙ) (for a ≠ a₁, a₂, …, aₙ)
💡 Concept: Limit at a zero of a continuous product equals zero because one factor vanishes.
🔵 Question 30:
If
f(x) = |x| + 1, x < 0
f(x) = 0, x = 0
f(x) = |x| − 1, x > 0
For what value(s) of a does lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) exist?
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Check limit at any a ≠ 0
➡️ For x > 0 and a > 0: f(x) = x − 1 → lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) = a − 1
➡️ For x < 0 and a < 0: f(x) = −x + 1 → lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) = −a + 1
✅ Both are continuous on respective sides, so limit exists for all a ≠ 0
✳️ Step 2: Check limit at a = 0
➡️ Left limit: lim₍ₓ→0⁻₎ f(x) = |x| + 1 = 0 + 1 = 1
➡️ Right limit: lim₍ₓ→0⁺₎ f(x) = |x| − 1 = 0 − 1 = −1
❌ Left limit ≠ Right limit → limit does not exist at a = 0
✔️ Final:
lim₍ₓ→a₎ f(x) exists for all a ≠ 0
💡 Concept: Piecewise functions must have equal left & right limits at junction points for limit to exist.
🔵 Question 31:
If the function f(x) satisfies
lim₍ₓ→1₎ ( f(x) − 2 ) / ( x² − 1 ) = π, evaluate lim₍ₓ→1₎ f(x).
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Given finite limit L = π ⇒ denominator → 0 as x→1.
✳️ Step 2: For the quotient to stay finite, numerator must also → 0.
➡️ lim₍ₓ→1₎ [f(x) − 2] = 0
✳️ Step 3: Therefore
➡️ lim₍ₓ→1₎ f(x) = 2
✔️ Final: 2
🔵 Question 32:
If
f(x) = { m x² + n, x < 0
n x + m, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
m x³ + m, x > 1 }
For what integers m and n does both lim₍ₓ→0₎ f(x) and lim₍ₓ→1₎ f(x) exist?
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1 (at a = 0):
➡️ Left limit: lim₍ₓ→0⁻₎ f(x) = m·0² + n = n
➡️ Right limit: lim₍ₓ→0⁺₎ f(x) = n·0 + m = m
➡️ Equality for existence ⇒ n = m
✳️ Step 2 (at a = 1):
➡️ Left limit: lim₍ₓ→1⁻₎ f(x) = n·1 + m = n + m
➡️ Right limit: lim₍ₓ→1⁺₎ f(x) = m·1³ + m = 2m
➡️ Equality for existence ⇒ n + m = 2m ⇒ n = m
✳️ Step 3: Combine conditions
➡️ From both points: n = m
📄 EXERCISE 12.2
🔵 Question 1:
Find the derivative of x² − 2 at x = 10.
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Let f(x) = x² − 2
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = 2x
✳️ Step 3: Put x = 10 → f′(10) = 2·10 = 20
✔️ Final: 20
🔵 Question 2:
Find the derivative of x at x = 1.
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Let f(x) = x
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = 1
✳️ Step 3: f′(1) = 1
✔️ Final: 1
🔵 Question 3:
Find the derivative of 99x at x = 100.
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Let f(x) = 99x
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = 99
✳️ Step 3: f′(100) = 99
✔️ Final: 99
🔵 Question 4:
Find the derivative of the following functions from first principle.
🟣 (i) x³ − 27
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: f(x) = x³ − 27
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ [f(x+h) − f(x)]/h
✳️ Step 3: f(x+h) − f(x) = (x+h)³ − x³ = 3x²h + 3xh² + h³
✳️ Step 4: [f(x+h) − f(x)]/h = 3x² + 3xh + h²
✳️ Step 5: lim₍h→0₎ → 3x²
✔️ Final: 3x²
—
🟣 (ii) (x − 1)(x − 2)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: f(x) = (x − 1)(x − 2)
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ [f(x+h) − f(x)]/h
✳️ Step 3: f(x+h) = (x+h−1)(x+h−2)
✳️ Step 4: f(x+h) − f(x) = [(x−1)(x−2) + (2x−3)h + h²] − (x−1)(x−2) = (2x−3)h + h²
✳️ Step 5: [f(x+h) − f(x)]/h = (2x−3) + h
✳️ Step 6: lim₍h→0₎ → 2x − 3
✔️ Final: 2x − 3
—
🟣 (iii) 1/x²
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: f(x) = x⁻²
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ [1/(x+h)² − 1/x²]/h
✳️ Step 3: = lim₍h→0₎ [(x² − (x+h)²) / {x²(x+h)²·h}]
✳️ Step 4: Numerator = x² − (x² + 2xh + h²) = −2xh − h² = −h(2x + h)
✳️ Step 5: ⇒ difference quotient = −(2x + h) / [x²(x+h)²]
✳️ Step 6: lim₍h→0₎ → −2x / (x²·x²) = −2/x³
✔️ Final: −2/x³ (x ≠ 0)
—
🟣 (iv) (x + 1)/(x − 1)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: f(x) = (x + 1)/(x − 1)
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ { [(x+h+1)/(x+h−1)] − [(x+1)/(x−1)] } / h
✳️ Step 3: Combine: = lim₍h→0₎ { [(x+h+1)(x−1) − (x+1)(x+h−1)] / [(x+h−1)(x−1)·h] }
✳️ Step 4: Numerator = [x² + hx − h − 1] − [x² − 1 + hx + h] = −2h
✳️ Step 5: ⇒ difference quotient = −2 / [(x+h−1)(x−1)]
✳️ Step 6: lim₍h→0₎ → −2 / (x−1)²
✔️ Final: −2/(x−1)² (x ≠ 1)
🔵 Question 5:
For the function
f(x) = x¹⁰⁰/100 + x⁹⁹/99 + … + x²/2 + x + 1.
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Differentiate each term using d/dx [xⁿ/n] = xⁿ⁻¹
✳️ Step 2: f′(x) = x⁹⁹ + x⁹⁸ + … + x + 1
✔️ Final: f′(x) = x⁹⁹ + x⁹⁸ + … + x + 1
🔵
Prove that f′(1) = 100 f′(0).
(Here f(x) = x¹⁰⁰/100 + x⁹⁹/99 + … + x²/2 + x + 1.)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Differentiate termwise → f′(x) = x⁹⁹ + x⁹⁸ + … + x + 1
✳️ Step 2: Evaluate at x = 1 → f′(1) = 1 + 1 + … + 1 (100 terms) = 100
✳️ Step 3: Evaluate at x = 0 → f′(0) = 0 + 0 + … + 0 + 1 = 1
✔️ Final: f′(1) = 100 = 100·f′(0)
🔵 Question 6:
Find the derivative of xⁿ + a xⁿ⁻¹ + a² xⁿ⁻² + … + aⁿ⁻¹x + aⁿ (a is fixed).
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Let f(x) = xⁿ + a xⁿ⁻¹ + a² xⁿ⁻² + … + aⁿ⁻¹x + aⁿ
✳️ Step 2: Differentiate termwise
➡️ f′(x) = n xⁿ⁻¹ + a(n−1) xⁿ⁻² + a²(n−2) xⁿ⁻³ + … + aⁿ⁻²·1 + 0
✔️ Final: f′(x) = n xⁿ⁻¹ + a(n−1) xⁿ⁻² + a²(n−2) xⁿ⁻³ + … + aⁿ⁻²
(Last constant aⁿ differentiates to 0; the derivative of aⁿ⁻¹x contributes the final aⁿ⁻² term above.)
🔵 Question 7: For constants a, b, find the derivative of:
🟣 (i) (x − a)(x − b)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Expand → x² − (a + b)x + ab
✳️ Differentiate → 2x − (a + b)
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 2x − (a + b)
🟣 (ii) (a x² + b)²
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Chain rule → 2(a x² + b)·(2a x)
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 4a x (a x² + b)
🟣 (iii) (x − a)/(x − b)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Quotient rule → [(x − b)·1 − (x − a)·1]/(x − b)²
✳️ Simplify numerator → a − b
✔️ Final: f′(x) = (a − b)/(x − b)² (x ≠ b)
🔵 Question 8:
Find the derivative of (xⁿ − aⁿ)/(x − a) (a is constant).
🟢 Answer (clean method):
✳️ Step 1: Use identity (for x ≠ a)
➡️ (xⁿ − aⁿ)/(x − a) = xⁿ⁻¹ + a xⁿ⁻² + a² xⁿ⁻³ + … + aⁿ⁻¹
✳️ Step 2: Differentiate termwise
➡️ f′(x) = (n−1)xⁿ⁻² + (n−2)a xⁿ⁻³ + (n−3)a² xⁿ⁻⁴ + … + aⁿ⁻²
✔️ Final: f′(x) = (n−1)xⁿ⁻² + (n−2)a xⁿ⁻³ + … + aⁿ⁻² (valid for x ≠ a)
✏️ Note: At x = a, use continuity to define derivative of the extended polynomial if needed.
🔵 Question 9: Find the derivative of
🟣 (i) 2x − ³/₄
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Derivative of 2x is 2
✳️ Step 2: Derivative of constant (−³/₄) is 0
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 2
🟣 (ii) (5x³ + 3x − 1)(x − 1)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Use Product Rule: (u·v)′ = u′v + uv′
➡️ u = (5x³ + 3x − 1), v = (x − 1)
✳️ u′ = 15x² + 3, v′ = 1
✳️ f′(x) = (15x² + 3)(x − 1) + (5x³ + 3x − 1)(1)
✳️ Expand: = 15x³ − 15x² + 3x − 3 + 5x³ + 3x − 1
✳️ Simplify: = 20x³ − 15x² + 6x − 4
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 20x³ − 15x² + 6x − 4
🟣 (iii) x⁻³ (5 + 3x)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Use Product Rule
➡️ u = x⁻³, u′ = −3x⁻⁴
➡️ v = (5 + 3x), v′ = 3
✳️ f′(x) = (−3x⁻⁴)(5 + 3x) + x⁻³(3)
✳️ Expand: = −15x⁻⁴ − 9x⁻³ + 3x⁻³
✳️ Combine: = −15x⁻⁴ − 6x⁻³
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −15/x⁴ − 6/x³
🟣 (iv) x⁵ (3 − 6x⁻⁹)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Use Product Rule
➡️ u = x⁵, u′ = 5x⁴
➡️ v = (3 − 6x⁻⁹), v′ = 0 − 6(−9)x⁻¹⁰ = 54x⁻¹⁰
✳️ f′(x) = 5x⁴(3 − 6x⁻⁹) + x⁵(54x⁻¹⁰)
✳️ Expand: = 15x⁴ − 30x⁻⁵ + 54x⁻⁵
✳️ Simplify: = 15x⁴ + 24x⁻⁵
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 15x⁴ + 24/x⁵
🟣 (v) x⁻⁴ (3 − 4x⁻⁵)
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Use Product Rule
➡️ u = x⁻⁴, u′ = −4x⁻⁵
➡️ v = (3 − 4x⁻⁵), v′ = 0 − 4(−5)x⁻⁶ = 20x⁻⁶
✳️ f′(x) = (−4x⁻⁵)(3 − 4x⁻⁵) + x⁻⁴(20x⁻⁶)
✳️ Expand: = −12x⁻⁵ + 16x⁻¹⁰ + 20x⁻¹⁰
✳️ Simplify: = −12x⁻⁵ + 36x⁻¹⁰
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −12/x⁵ + 36/x¹⁰
🟣 (vi) (2/(x+1)) − (x²/(3x−1))
🟢 Answer:
f(x) = 2(x+1)⁻¹ − x²(3x−1)⁻¹
✳️ Differentiate:
➡️ d/dx[2(x+1)⁻¹] = 2(−1)(x+1)⁻² = −2/(x+1)²
➡️ d/dx[x²(3x−1)⁻¹] = (2x)(3x−1)⁻¹ + x²(−1)(3x−1)⁻²(3)
= 2x/(3x−1) − 3x²/(3x−1)²
✳️ Combine:
f′(x) = −2/(x+1)² − [2x/(3x−1) − 3x²/(3x−1)²]
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −2/(x+1)² − 2x/(3x−1) + 3x²/(3x−1)²
🔵 Question 10:
Find the derivative of cos x from first principle.
🟢 Answer:
✳️ f(x) = cos x
✳️ f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ [cos(x+h) − cos x]/h
✳️ Use identity: cos(A+B) − cosA = −2 sin(A + B/2) sin(B/2)
✳️ Simplify → f′(x) = lim₍h→0₎ [−2 sin(x + h/2) sin(h/2)] / h
✳️ = −lim₍h→0₎ [sin(h/2)/(h/2)] · sin(x + h/2)
✳️ As h→0, sin(h/2)/(h/2) → 1, sin(x + h/2) → sin x
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −sin x
🔵 Question 11: Find the derivative of the following functions:
🟣 (i) sin x cos x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Let u = sin x, v = cos x
✳️ Step 2: Use product rule (uv)′ = u′v + uv′
✳️ Step 3: u′ = cos x, v′ = −sin x
✳️ Step 4: f′(x) = (cos x)(cos x) + (sin x)(−sin x)
✳️ Step 5: f′(x) = cos²x − sin²x
✔️ Final: f′(x) = cos²x − sin²x
🟣 (ii) sec x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Recall rule d/dx(sec x) = sec x tan x
✳️ Step 2: Apply directly
✔️ Final: f′(x) = sec x · tan x
🟣 (iii) 5 sec x + 4 cos x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Differentiate termwise
✳️ Step 2: d/dx(5 sec x) = 5 sec x tan x
✳️ Step 3: d/dx(4 cos x) = 4(−sin x) = −4 sin x
✳️ Step 4: Add derivatives
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 5 sec x tan x − 4 sin x
🟣 (iv) cosec x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Recall rule d/dx(cosec x) = −cosec x cot x
✳️ Step 2: Apply directly
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −cosec x · cot x
🟣 (v) 3 cot x + 5 cosec x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: Differentiate termwise
✳️ Step 2: d/dx(3 cot x) = 3(−cosec²x) = −3 cosec²x
✳️ Step 3: d/dx(5 cosec x) = 5(−cosec x cot x) = −5 cosec x cot x
✳️ Step 4: Add derivatives
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −3 cosec²x − 5 cosec x cot x
🟣 (vi) 5 sin x − 6 cos x + 7
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: d/dx(5 sin x) = 5 cos x
✳️ Step 2: d/dx(−6 cos x) = −6(−sin x) = 6 sin x
✳️ Step 3: d/dx(7) = 0
✳️ Step 4: Add derivatives
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 5 cos x + 6 sin x
🟣 (vii) 2 tan x − 7 sec x
🟢 Answer:
✳️ Step 1: d/dx(2 tan x) = 2 sec²x
✳️ Step 2: d/dx(−7 sec x) = −7(sec x tan x)
✳️ Step 3: Combine results
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 2 sec²x − 7 sec x tan x
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
CBSE STYLE MODEL PAPER
ESPECIALLY FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🧭 Section A – Very Short / Objective Type (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1:
The value of limₓ→₂ (x² − 4)/(x − 2) is
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 8
🔴 (D) Does not exist
🟢 Answer: (B) 4
🔵 Question 2:
limₓ→₀ (sin x)/x equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) ∞
🔴 (D) −1
🟢 Answer: (B) 1
🔵 Question 3:
If f(x) = x², then f′(x) using first principle is
🔵 (A) x²
🟢 (B) 2x
🟠 (C) x
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) 2x
🔵 Question 4:
limₓ→₀ (1 − cos x)/x² =
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1/2
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 2
🟢 Answer: (B) 1/2
🔵 Question 5:
If f(x) = 1/x, then derivative f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 1/x²
🟢 (B) −1/x²
🟠 (C) −1/x
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) −1/x²
🔵 Question 6:
If f(x) = x³, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 2x
🟢 (B) 3x²
🟠 (C) x²
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) 3x²
🔵 Question 7:
Derivative of sin x is
🔵 (A) cos x
🟢 (B) −cos x
🟠 (C) −sin x
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (A) cos x
🔵 Question 8:
Derivative of cos x is
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) −sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) −cos x
🟢 Answer: (B) −sin x
🔵 Question 9:
Derivative of tan x is
🔵 (A) sec²x
🟢 (B) cos²x
🟠 (C) 1 + tan²x
🔴 (D) Both A and C
🟢 Answer: (D) Both A and C (since sec²x = 1 + tan²x)
🔵 Question 10:
limₓ→₀ (tan x)/x =
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) ∞
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (A) 1
🔵 Question 11:
limₓ→₀ (eˣ − 1)/x =
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) e
🔴 (D) ∞
🟢 Answer: (B) 1
🔵 Question 12:
Derivative of log x is
🔵 (A) log e
🟢 (B) 1/x
🟠 (C) x
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) 1/x
🔵 Question 13:
If y = eˣ, then dy/dx =
🔵 (A) eˣ
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) x
🟢 Answer: (A) eˣ
🔵 Question 14:
If y = aˣ, then dy/dx =
🔵 (A) aˣ
🟢 (B) aˣ log a
🟠 (C) log a
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) aˣ log a
🔵 Question 15:
limₓ→₀ (log(1 + x))/x =
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) ∞
🔴 (D) −1
🟢 Answer: (B) 1
🔵 Question 16:
Derivative of x² + 3x is
🔵 (A) 2x + 3
🟢 (B) 2x
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) x
🟢 Answer: (A) 2x + 3
🔵 Question 17:
If f(x) = x² + 1/x, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 2x + 1/x²
🟢 (B) 2x − 1/x²
🟠 (C) 2x − 2/x
🔴 (D) None
🟢 Answer: (B) 2x − 1/x²
🔵 Question 18:
If f(x) = sin²x, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 2sin x
🟢 (B) 2sin x·cos x
🟠 (C) 2cos x
🔴 (D) cos²x
🟢 Answer: (B) 2sin x·cos x
🧭 Section B – Short Answer Type (2–3 Marks Each)
🔵 Question 19:
Find limₓ→₀ (sin 3x)/(x).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ We know, limₓ→₀ (sin kx)/(kx) = 1
➡️ Rewrite: (sin 3x)/x = 3 × (sin 3x)/(3x)
➡️ Apply limit: limₓ→₀ 3 × (sin 3x)/(3x) = 3 × 1
✔️ Final Answer: 3
🔵 Question 20:
Evaluate limₓ→₀ (1 − cos 2x)/x².
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: 1 − cos θ = 2sin²(θ/2)
➡️ Substitute: (1 − cos 2x) = 2sin²x
➡️ So expression = limₓ→₀ [2sin²x]/x²
➡️ = 2 × limₓ→₀ (sin x/x)² = 2 × 1²
✔️ Final Answer: 2
🔵 Question 21:
Find limₓ→₀ (tan x − sin x)/x³.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Expand using series:
tan x = x + x³/3 + …
sin x = x − x³/6 + …
➡️ Substitute: (tan x − sin x) = x³(1/3 + 1/6) = x³(1/2)
➡️ Divide by x³: (x³/2)/x³ = 1/2
✔️ Final Answer: 1/2
🔵 Question 22:
Find derivative of f(x) = 1/x using first principle.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: f′(x) = limₕ→₀ [f(x + h) − f(x)] / h
➡️ f(x + h) = 1/(x + h)
➡️ f(x + h) − f(x) = [1/(x + h) − 1/x] = [x − (x + h)] / [x(x + h)] = −h / [x(x + h)]
➡️ Divide by h: (−h) / [h·x(x + h)] = −1 / [x(x + h)]
➡️ Take limit: limₕ→₀ (−1) / [x(x + h)] = −1/x²
✔️ Final Answer: f′(x) = −1/x²
🔵 Question 23:
Differentiate y = √x + 1/x + x².
🟢 Answer:
➡️ y = x^(1/2) + x^(−1) + x²
➡️ dy/dx = (1/2)x^(−1/2) − x^(−2) + 2x
✔️ Final Answer: (1 / (2√x)) − 1/x² + 2x
🧭 Section C – Mid-Length Questions (3 Marks Each)
🔵 Question 24:
Differentiate y = x² sin x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Product rule: d(uv)/dx = u′v + uv′
➡️ u = x², v = sin x
➡️ u′ = 2x, v′ = cos x
➡️ dy/dx = (2x)(sin x) + (x²)(cos x)
✔️ Final Answer: dy/dx = 2x sin x + x² cos x
🔵 Question 25:
Differentiate y = eˣ log x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ u = eˣ, v = log x
➡️ u′ = eˣ, v′ = 1/x
➡️ dy/dx = u′v + uv′ = eˣ log x + eˣ(1/x)
✔️ Final Answer: dy/dx = eˣ(log x + 1/x)
🔵 Question 26:
Differentiate y = x³ eˣ.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ u = x³, v = eˣ
➡️ u′ = 3x², v′ = eˣ
➡️ dy/dx = u′v + uv′ = (3x²)eˣ + x³eˣ
➡️ Factor eˣ: dy/dx = eˣ(3x² + x³)
✔️ Final Answer: eˣ(3x² + x³)
🔵 Question 27:
Find derivative of y = sin x / x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Quotient rule: (v·u′ − u·v′)/v²
➡️ u = sin x, u′ = cos x
➡️ v = x, v′ = 1
➡️ dy/dx = [x(cos x) − sin x(1)] / x²
✔️ Final Answer: (x cos x − sin x)/x²
🔵 Question 28:
Differentiate y = (x² + 1)·(x³ − 2).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Apply Product Rule: d(uv)/dx = u′v + uv′
Let
u = (x² + 1), v = (x³ − 2)
Then
u′ = 2x, v′ = 3x²
➡️ dy/dx = (2x)(x³ − 2) + (x² + 1)(3x²)
➡️ = 2x⁴ − 4x + 3x⁴ + 3x²
➡️ Combine like terms: dy/dx = 5x⁴ + 3x² − 4x
✔️ Final Answer: 5x⁴ + 3x² − 4x
🧭 Section D – Long Answer Type (5 Marks Each)
🔵 Question 29:
Find the derivative of y = (x² + 3x + 2)/(x + 1).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Apply Quotient Rule: (v·u′ − u·v′)/v²
Let
u = x² + 3x + 2, v = x + 1
Then
u′ = 2x + 3, v′ = 1
➡️ dy/dx = [(x + 1)(2x + 3) − (x² + 3x + 2)(1)] / (x + 1)²
➡️ Expand numerator: (2x² + 3x + 2x + 3) − (x² + 3x + 2)
➡️ Simplify: (2x² + 5x + 3 − x² − 3x − 2) = x² + 2x + 1
➡️ Factor: = (x + 1)²
➡️ Therefore, dy/dx = (x + 1)² / (x + 1)² = 1
✔️ Final Answer: 1
🔵 Question 30:
Find the derivative of y = (sin x − cos x) / (sin x + cos x)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: Let
u = sin x − cos x
v = sin x + cos x
➡️ Step 2: Apply Quotient Rule
dy/dx = (v × du/dx − u × dv/dx) / v²
➡️ Step 3: Differentiate
du/dx = cos x + sin x
dv/dx = cos x − sin x
➡️ Step 4: Substitute
dy/dx = [(sin x + cos x)(cos x + sin x) − (sin x − cos x)(cos x − sin x)] / (sin x + cos x)²
➡️ Step 5: Expand numerator
(sin x + cos x)² = sin²x + 2 sin x cos x + cos²x = 1 + 2 sin x cos x
(sin x − cos x)(cos x − sin x) = 2 sin x cos x − 1
➡️ Step 6: Simplify numerator
(1 + 2 sin x cos x) − (2 sin x cos x − 1) = 2
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = 2 / (sin x + cos x)²
🔵 Question 31:
If y = √(1 + sin x), find dy/dx.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ y = (1 + sin x)^(1/2)
➡️ dy/dx = (1/2)(1 + sin x)^(−1/2) × cos x
✔️ Final Answer: dy/dx = [cos x] / [2√(1 + sin x)]
🧭 Section E – Case-Based / Application (5 Marks Each)
🔵 Question 32:
If f(x) = x² − 4x + 3, find slope of tangent at x = 2.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ f′(x) = derivative = 2x − 4
➡️ At x = 2, slope = 2(2) − 4 = 4 − 4 = 0
✔️ Final Answer: Slope = 0 (horizontal tangent)
🔵 Question 33:
If y = x³ − 3x² + 2, find the point(s) where tangent is parallel to x-axis.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Tangent ∥ x-axis ⇒ dy/dx = 0
➡️ y′ = 3x² − 6x
➡️ Set equal to 0: 3x² − 6x = 0
➡️ Divide by 3: x² − 2x = 0
➡️ Factor: x(x − 2) = 0
➡️ So x = 0 or x = 2
➡️ Corresponding y-values:
For x = 0, y = 2
For x = 2, y = 2³ − 3(2²) + 2 = 8 − 12 + 2 = −2
✔️ Final Answer: Tangent ∥ x-axis at (0, 2) and (2, −2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
The value of limₓ→0 (sin 3x / x) is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 3
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 3
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 2:
The value of limₓ→0 (1 − cos x) / x² is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 1/2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 3:
If f(x) = x², then f′(2) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 4
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 4:
If f(x) = sin x, then f′(π/3) =
🟥 1️⃣ cos(π/3)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/2
🟨 3️⃣ √3/2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ cos(π/3) = 1/2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 5:
limₓ→0 (tan x / x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ ∞
🟦 4️⃣ 2
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 1
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 6:
If y = x³, then dy/dx at x = 2 is
🟥 1️⃣ 4
🟩 2️⃣ 6
🟨 3️⃣ 12
🟦 4️⃣ 8
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ 12
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 7:
limₓ→0 (1 + 2x)^(1/x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ e²
🟩 2️⃣ e
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ e²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 8:
If f(x) = √x, then f′(4) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/2
🟩 2️⃣ 1/4
🟨 3️⃣ 1/√x
🟦 4️⃣ 1
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 1/4
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 9:
The derivative of sin⁻¹x is
🟥 1️⃣ 1/√(1 − x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/(1 + x²)
🟨 3️⃣ cos x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1/√(1 − x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 10:
The derivative of logₑ x is
🟥 1️⃣ 1/x
🟩 2️⃣ x
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ eˣ
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1/x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 11:
limₓ→0 (eˣ − 1)/x equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 0
🟨 3️⃣ e
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 12:
If f(x) = 3x² + 2x + 1, then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 6x + 2
🟩 2️⃣ 3x + 2
🟨 3️⃣ 6x
🟦 4️⃣ 2x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 6x + 2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 13:
If y = 1/x, then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ −1/x²
🟩 2️⃣ 1/x²
🟨 3️⃣ −x²
🟦 4️⃣ 1/x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ −1/x²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 14:
limₓ→π/2 (sin x − 1)/(x − π/2) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ cos(π/2)
🟦 4️⃣ −1
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ cos(π/2) = 0
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 15:
If y = eˣ, then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ eˣ
🟩 2️⃣ x eˣ
🟨 3️⃣ eˣ + 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ eˣ
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 16:
If y = ln(1 + x), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/(1 + x)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/x
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ x/(1 + x)
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1/(1 + x)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 17:
The value of limₓ→0 (sin 2x)/(3x) is
🟥 1️⃣ 2/3
🟩 2️⃣ 3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2/3
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 18:
If f(x) = x³, then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 3x²
🟩 2️⃣ x²
🟨 3️⃣ 2x
🟦 4️⃣ x³
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 3x²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 19:
limₓ→0 (aˣ − 1)/x =
🟥 1️⃣ logₑ a
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ a
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ logₑ a
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 20:
The derivative of cos x is
🟥 1️⃣ −sin x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x
🟨 3️⃣ cos x
🟦 4️⃣ −cos x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ −sin x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 21:
The derivative of tan x is
🟥 1️⃣ sec²x
🟩 2️⃣ sin²x
🟨 3️⃣ cos²x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ sec²x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 22:
If y = x⁴, then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 4x³
🟩 2️⃣ 3x²
🟨 3️⃣ 2x
🟦 4️⃣ x³
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 4x³
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 23:
If f(x) = sin 2x, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2 cos 2x
🟩 2️⃣ cos 2x
🟨 3️⃣ sin 2x
🟦 4️⃣ 2 sin 2x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 cos 2x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 24:
The derivative of xⁿ (n ≠ 0) is
🟥 1️⃣ n xⁿ⁻¹
🟩 2️⃣ xⁿ
🟨 3️⃣ n xⁿ
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ n xⁿ⁻¹
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 25:
If f(x) = 2x + 3, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 3
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 26:
If f(x) = cos x, then f′(π/3) equals
🟥 1️⃣ −sin(π/3)
🟩 2️⃣ sin(π/3)
🟨 3️⃣ −1/2
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ −sin(π/3) = −√3/2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 27:
limₓ→0 (sin 5x / sin 3x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 5/3
🟨 3️⃣ 3/5
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 5/3
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 28:
If y = tan⁻¹x, then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/(1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/√(1 − x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1/x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1/(1 + x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 29:
If f(x) = sin x cos x, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ cos²x − sin²x
🟩 2️⃣ 2 sin x cos x
🟨 3️⃣ sin 2x
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ cos²x − sin²x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 30:
If y = x² + 1/x, then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2x − 1/x²
🟩 2️⃣ 2x + 1/x²
🟨 3️⃣ x² − 2/x³
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x − 1/x²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 31:
The derivative of eˣ cos x is
🟥 1️⃣ eˣ (cos x − sin x)
🟩 2️⃣ eˣ (cos x + sin x)
🟨 3️⃣ eˣ sin x
🟦 4️⃣ eˣ cos x
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ eˣ (cos x + sin x)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 32:
If f(x) = ln(x² + 1), then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2x/(x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/(x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ x²/(x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x/(x² + 1)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 33:
If f(x) = x sin x, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x − x cos x
🟨 3️⃣ cos x + x sin x
🟦 4️⃣ x cos x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 34:
If y = logₑ(1 + sin x), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin x)
🟩 2️⃣ sin x / (1 + cos x)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + sin x)
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin x)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 35:
The derivative of tan⁻¹(2x) is
🟥 1️⃣ 2 / (1 + 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (1 + 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2 / (1 + x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 / (1 + 4x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 36:
limₓ→0 (eˣ − cos x) / x equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 0
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 37:
If f(x) = (x² + 1)/(x − 1), then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ (x² − 2x − 1)/(x − 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ (2x(x − 1) − (x² + 1))/(x − 1)²
🟨 3️⃣ (2x − 1)/(x − 1)²
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ (2x(x − 1) − (x² + 1))/(x − 1)²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 38:
If f(x) = sin 2x, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2 cos 2x
🟩 2️⃣ cos 2x
🟨 3️⃣ sin 2x
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 cos 2x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 39:
If y = (x² + 3x + 2)/(x + 1), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ (2x + 3)(x + 1) − (x² + 3x + 2) / (x + 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ (x² + 2x) / (x + 1)²
🟨 3️⃣ (2x + 3)/(x + 1)²
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ (2x + 3)(x + 1) − (x² + 3x + 2) / (x + 1)²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 40:
limₓ→0 (tan x − sin x) / x³ equals
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/3
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 1/2
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 41:
If f(x) = (sin x + cos x), then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ cos x − sin x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x + cos x
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 0
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ cos x − sin x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 42:
The derivative of (x² + 1)³ is
🟥 1️⃣ 6x (x² + 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ 3x²
🟨 3️⃣ 6x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 6x (x² + 1)²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 43:
If y = x² sin x, then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
🟩 2️⃣ 2x cos x + x² sin x
🟨 3️⃣ x² sin x − 2x cos x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 44:
If f(x) = logₑ(sin x), then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ tan x
🟨 3️⃣ 1/sin x
🟦 4️⃣ 1/cos x
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 45:
limₓ→0 (1 + x)^(1/x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ e
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ e
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 46:
The derivative of cos⁻¹x is
🟥 1️⃣ −1/√(1 − x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1/√(1 − x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1/(1 + x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ −1/√(1 − x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 47:
If y = logₑ(tan x), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ sec²x / tan x
🟩 2️⃣ cos x
🟨 3️⃣ sin x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ sec²x / tan x
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 48:
If f(x) = (x³ + 1)/(x² + 1), then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ (3x²(x² + 1) − 2x(x³ + 1))/(x² + 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ (3x² − 2x)/(x² + 1)²
🟨 3️⃣ (x² + 1)/(3x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ (3x²(x² + 1) − 2x(x³ + 1))/(x² + 1)²
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 49:
If y = sin⁻¹(2x√(1 − x²)), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2√(1 − x²) − (2x²/√(1 − x²))
🟩 2️⃣ 2(1 − 2x²)/√(1 − x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1/√(1 − x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 2(1 − 2x²)/√(1 − x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
🔵 Question 50:
If y = e^(tan⁻¹x), then dy/dx equals
🟥 1️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹x)/(1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹x) × (1 + x²)
🟨 3️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹x) × x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹x)/(1 + x²)
📅 Exam: JEE Main 2013
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
If lim (x→0) (sin 3x) / (2x) = k, then k equals
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ 3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/2
🟦 4️⃣ 2/3
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 3/2
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 2:
The value of lim (x→π/4) [(tan x – 1) / (x – π/4)] is
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 3:
If lim (x→0) (1 – cos ax) / (bx²) = 1/2, then b equals
🟥 1️⃣ a²
🟩 2️⃣ a²/2
🟨 3️⃣ a²/4
🟦 4️⃣ 2a²
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ a²/2
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 4:
If f(x) = sin x, then lim (h→0) [f(x+h) – f(x)] / h equals
🟥 1️⃣ cos x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x
🟨 3️⃣ –sin x
🟦 4️⃣ –cos x
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ cos x
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 5:
The value of lim (x→0) [(1 + 3x)^(1/x)] is
🟥 1️⃣ e³
🟩 2️⃣ 3e
🟨 3️⃣ e
🟦 4️⃣ 1
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ e³
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 6:
If lim (x→0) [(1 + ax)^(1/x)] = e³, find a
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 4
✅ Answer: 3️⃣ 3
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 7:
If f(x) = x², the derivative f′(x) using definition is
🟥 1️⃣ 2x
🟩 2️⃣ x²
🟨 3️⃣ x
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2x
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 8:
If lim (x→0) [(1 – cos 2x) / x²] = k, then k =
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 4
🟦 4️⃣ 0
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 9:
If lim (x→0) (tan 2x / 3x) = k, then k =
🟥 1️⃣ 2/3
🟩 2️⃣ 3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 1
🟦 4️⃣ 2
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2/3
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 10:
The derivative of f(x) = sin 2x at x = 0 is
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ –1
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 11:
If f(x) = eˣ, then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ eˣ
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ x
🟦 4️⃣ 0
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ eˣ
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 12:
If f(x) = ln(x), then lim (h→0) [f(x+h) – f(x)] / h equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/x
🟩 2️⃣ x
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ ln(x)
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 1/x
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 13:
If f(x) = |x|, then derivative at x = 0 is
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ –1
🟨 3️⃣ Does not exist
🟦 4️⃣ 0
✅ Answer: 3️⃣ Does not exist
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 14:
If lim (x→0) [(1 + x)^(1/x)] = k, then logₑ k =
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ –1
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2017 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 15:
The value of lim (x→0) [(eˣ – 1) / x] is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ e
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2016 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 16:
If f(x) = x³ – 5x² + 4x – 1, then f′(1) =
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ 3
✅ Answer: 3️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2015 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 17:
If lim (x→0) [(sin x) / x] = k, then k =
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ ∞
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2013 – Paper 1
🔵 Question 18:
If lim (x→0) [(1 + 2x)^(1/x)] = k, then logₑ k equals
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 0
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 19:
If f(x) = sin x + cos x, then f′(x) equals
🟥 1️⃣ cos x – sin x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x + cos x
🟨 3️⃣ –cos x – sin x
🟦 4️⃣ –cos x + sin x
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ cos x – sin x
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 20:
The derivative of f(x) = logₑ (x² + 1) is
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ x / (x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 21:
If f(x) = eˣ cos x, then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ eˣ (cos x – sin x)
🟩 2️⃣ eˣ (cos x + sin x)
🟨 3️⃣ eˣ sin x
🟦 4️⃣ eˣ cos x
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ eˣ (cos x – sin x)
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 22:
If f(x) = x³ – 2x + 1, then f′(–1) =
🟥 1️⃣ –5
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 5
🟦 4️⃣ –1
✅ Answer: 3️⃣ 5
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 23:
If lim (x→0) [(eˣ – e⁻ˣ) / (2x)] = k, then k =
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ e
🟦 4️⃣ ∞
✅ Answer: 2️⃣ 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 24:
The derivative of f(x) = tan⁻¹ x is
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ x / (1 + x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ –1 / (1 + x²)
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 25:
If y = sin⁻¹ (3x – 4x³), then dy/dx at x = 1/2 is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 2
🟦 4️⃣ –1
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 0
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 26:
If f(x) = |x – 3|, then f′(x) at x = 3 is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ –1
🟦 4️⃣ Does not exist
✅ Answer: 4️⃣ Does not exist
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 27:
If f(x) = x² sin x, then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
🟩 2️⃣ 2x cos x + x² sin x
🟨 3️⃣ 2x sin x – x² cos x
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 28:
If f(x) = ln (sin x), then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / sin x
🟨 3️⃣ tan x
🟦 4️⃣ –cot x
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 29:
If f(x) = e^(tan⁻¹ x), then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹ x) / (1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹ x) × (1 + x²)
🟨 3️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹ x) × x
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ e^(tan⁻¹ x) / (1 + x²)
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 30:
If y = (x² + 1)³, then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3(x² + 1)² × 2x
🟩 2️⃣ 2x(x² + 1)³
🟨 3️⃣ 6x(x² + 1)²
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 3️⃣ 6x(x² + 1)²
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 31:
If f(x) = 1 / (1 + eˣ), then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ –eˣ / (1 + eˣ)²
🟩 2️⃣ eˣ / (1 + eˣ)²
🟨 3️⃣ –1 / (1 + eˣ)²
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ –eˣ / (1 + eˣ)²
📘 JEE Advanced 2017 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 32:
If f(x) = √(1 – x²), then f′(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ –x / √(1 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ x / √(1 – x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ –x / √(1 – x²)
📘 JEE Advanced 2016 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 33:
If f(x) = logₑ (sin x), find f′(x)
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ tan x
🟨 3️⃣ –cot x
🟦 4️⃣ sec x
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📘 JEE Advanced 2014 – Paper 2
🔵 Question 34:
If f(x) = tan⁻¹ x, then lim (h→0) [f(1+h) – f(1)] / h equals
🟥 1️⃣ 1/2
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ 1/4
🟦 4️⃣ None
✅ Answer: 1️⃣ 1/2
📘 JEE Advanced 2013 – Paper 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. The value of lim x→2 (x² − 4)/(x − 2) is
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 6
🔴 (D) 8
Answer: (B) 4
Q2. lim x→0 (sin x)/x equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) −1
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (B) 1
Q3. lim x→0 (1 − cos x)/x² equals
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 1/2
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) 1/2
Q4. The right-hand and left-hand limits of f at x = a are equal and finite. Then
🔵 (A) limit does not exist
🟢 (B) lim x→a f(x) exists
🟠 (C) f(a) must equal the limit
🔴 (D) f is discontinuous at a
Answer: (B) lim x→a f(x) exists
Q5. If f(x) = x², then f′(x) by first principle is
🔵 (A) x
🟢 (B) 2x
🟠 (C) x²
🔴 (D) 2
Answer: (B) 2x
Q6. If y = 1/x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 1/x²
🟢 (B) −1/x²
🟠 (C) −1/x
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) −1/x²
Q7. If y = x³, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 3x
🟢 (B) 3x²
🟠 (C) x²
🔴 (D) 2x
Answer: (B) 3x²
Q8. Derivative of sin x is
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) cos x
🟠 (C) −sin x
🔴 (D) −cos x
Answer: (B) cos x
Q9. Derivative of cos x is
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) −sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) −cos x
Answer: (B) −sin x
Q10. lim x→0 (tan x)/x equals
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) ∞
🔴 (D) −1
Answer: (A) 1
Q11. lim x→0 (e^x − 1)/x equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) e
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (B) 1
Q12. d/dx (log x) equals
🔵 (A) x
🟢 (B) 1/x
🟠 (C) e^x
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (B) 1/x
Q13. If y = a^x (a > 0, a ≠ 1), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) a^x
🟢 (B) a^x ln a
🟠 (C) ln a
🔴 (D) 1/(a^x)
Answer: (B) a^x ln a
Q14. lim x→0 (√(1 + x) − 1)/x equals
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 1/2
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) 1/2
Q15. If y = x^n (n is a positive integer), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) n x^(n−1)
🟢 (B) x^n
🟠 (C) n x^n
🔴 (D) x^(n−1)
Answer: (A) n x^(n−1)
Q16. If y = sin²x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2 sin x
🟢 (B) 2 sin x cos x
🟠 (C) cos²x
🔴 (D) −2 sin x cos x
Answer: (B) 2 sin x cos x
Q17. lim x→0 (log(1 + x))/x equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) −1
🔴 (D) ∞
Answer: (B) 1
Q18. If y = √x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 1/(2√x)
🟢 (B) √x
🟠 (C) 2√x
🔴 (D) 1/√x
Answer: (A) 1/(2√x)
Q19. lim x→0 (sin 3x)/x equals
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (C) 3
Q20. lim x→0 (1 − cos 2x)/x² equals
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (C) 2
Q21. If f(x) = (x² − 1)/(x − 1) for x ≠ 1 and f(1) = k, choose k so that f is continuous at x = 1.
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 3
Answer: (C) 2
Q22. If y = (x² + 1)(x − 3), then dy/dx at x = 1 equals
🔵 (A) −4
🟢 (B) −2
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) 2
Answer: (D) 2
Q23. The limit lim x→0 (tan ax)/(ax) equals
🔵 (A) a
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 1/a
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) 1
Q24. If y = (x² + 1)/(x + 1), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) (x² + 2x − 1)/(x + 1)²
🟢 (B) (x² − 1)/(x + 1)²
🟠 (C) (2x + 1)/(x + 1)²
🔴 (D) (2x − 1)/(x + 1)²
Answer: (A) (x² + 2x − 1)/(x + 1)²
Q25. If y = e^x log x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) e^x log x
🟢 (B) e^x( log x + 1/x )
🟠 (C) e^x/x
🔴 (D) log x / x
Answer: (B) e^x( log x + 1/x )
Q26. If y = sin x / x (x ≠ 0), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) (x cos x − sin x)/x²
🟢 (B) (sin x − x cos x)/x²
🟠 (C) cos x / x
🔴 (D) −sin x / x²
Answer: (A) (x cos x − sin x)/x²
Q27. lim x→0 (√(1 + 2x) − 1)/x equals
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (B) 1
Q28. If y = (x − 1)(x + 2), then dy/dx at x = −1 is
🔵 (A) −3
🟢 (B) 0
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) −1
Answer: (C) 3
Q29. If f(x) = x|x|, then f′(0) equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) −1
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (A) 0
Q30. If y = (sin x − cos x)/(sin x + cos x), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 2/(sin x + cos x)²
🟠 (C) 2 sin x cos x/(sin x + cos x)²
🔴 (D) (sin x − cos x)/(sin x + cos x)
Answer: (B) 2/(sin x + cos x)²
Q31. If y = (x² + 1)·e^x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) (2x + 1)e^x
🟢 (B) (x² + 2x + 1)e^x
🟠 (C) (x² + 1)e^x
🔴 (D) (x² − 1)e^x
Answer: (B) (x² + 2x + 1)e^x
Q32. lim x→0 (a^x − 1)/x equals
🔵 (A) a
🟢 (B) ln a
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) ln a
Q33. If y = log(1 + x²), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2x/(1 + x²)
🟢 (B) 1/(1 + x²)
🟠 (C) 2/(1 + x²)
🔴 (D) x/(1 + x²)
Answer: (A) 2x/(1 + x²)
Q34. lim x→0 (sin 5x)/(sin 2x) equals
🔵 (A) 5/2
🟢 (B) 2/5
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) 5/2
Q35. If y = (x² − 4)/(x − 2) for x ≠ 2, then dy/dx at x = 2 equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 6
Answer: (D) 6
Q36. If y = x² sin x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2x sin x + x² cos x
🟢 (B) 2x cos x + x² sin x
🟠 (C) x² cos x − 2x sin x
🔴 (D) 2 sin x + cos x
Answer: (A) 2x sin x + x² cos x
Q37. lim x→0 (tan 3x − sin 3x)/x³ equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 3/2
🟠 (C) 9/2
🔴 (D) 1/2
Answer: (C) 9/2
Q38. If y = (x + 1)/(x − 1), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) −2/(x − 1)²
🟢 (B) 2/(x − 1)²
🟠 (C) 2/(x + 1)²
🔴 (D) −2/(x + 1)²
Answer: (B) 2/(x − 1)²
Q39. If f(x) = |x − 2|, then which is true at x = 2?
🔵 (A) f′(2) exists and equals 1
🟢 (B) f′(2) exists and equals −1
🟠 (C) f′(2) does not exist
🔴 (D) f′(2) equals 0
Answer: (C) f′(2) does not exist
Q40. lim x→0 (√(1 + x) − √(1 − x))/x equals
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 1/2
Answer: (C) 2
Q41. If f(x) = (x³ − 1)/(x − 1) for x ≠ 1 and f(1) = k, then f′(1) equals
🔵 (A) 1
🟢 (B) 2
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (C) 3
Q42. If y = (x² + 1)/(x² − 1), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) −4x/(x² − 1)²
🟢 (B) 4x/(x² − 1)²
🟠 (C) 2x/(x² − 1)
🔴 (D) −2x/(x² − 1)
Answer: (B) 4x/(x² − 1)²
Q43. If y = sin x · e^x, then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) e^x(sin x + cos x)
🟢 (B) e^x(sin x − cos x)
🟠 (C) e^x cos x
🔴 (D) e^x sin x
Answer: (A) e^x(sin x + cos x)
Q44. lim x→0 (1 + ax)^(1/x) equals
🔵 (A) a
🟢 (B) e^a
🟠 (C) 1 + a
🔴 (D) e
Answer: (B) e^a
Q45. If y = (x − 1)²(x + 2), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2(x − 1)(x + 2) + (x − 1)²
🟢 (B) 2(x − 1)(x + 2) + (x − 1)²·1
🟠 (C) 3x² − 2x − 2
🔴 (D) Both A and B
Answer: (D) Both A and B
Q46. If y = log( (1 + x)/(1 − x) ), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2/(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) 1/(1 − x²)
🟠 (C) 2/(1 + x²)
🔴 (D) 1/(1 + x²)
Answer: (A) 2/(1 − x²)
Q47. lim x→0 (a^x − b^x)/x equals
🔵 (A) ln(ab)
🟢 (B) ln a − ln b
🟠 (C) ln a + ln b
🔴 (D) (a − b)
Answer: (B) ln a − ln b
Q48. If y = x^x (x > 0), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) x^x
🟢 (B) x^x(1 + ln x)
🟠 (C) x^(x−1)
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (B) x^x(1 + ln x)
Q49. If y = (sin x + cos x)/(sin x − cos x), then dy/dx equals
🔵 (A) 2/(sin x − cos x)²
🟢 (B) −2/(sin x − cos x)²
🟠 (C) 4 sin x cos x/(sin x − cos x)²
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (B) −2/(sin x − cos x)²
Q50. lim x→0 [ (e^{mx} − 1)/(mx) ] · [ (nx)/(e^{nx} − 1) ] equals
🔵 (A) m/n
🟢 (B) n/m
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (C) 1
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
