Class 11 : Maths (In English) – Lesson 10. Conic Sections
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔷 Explanation
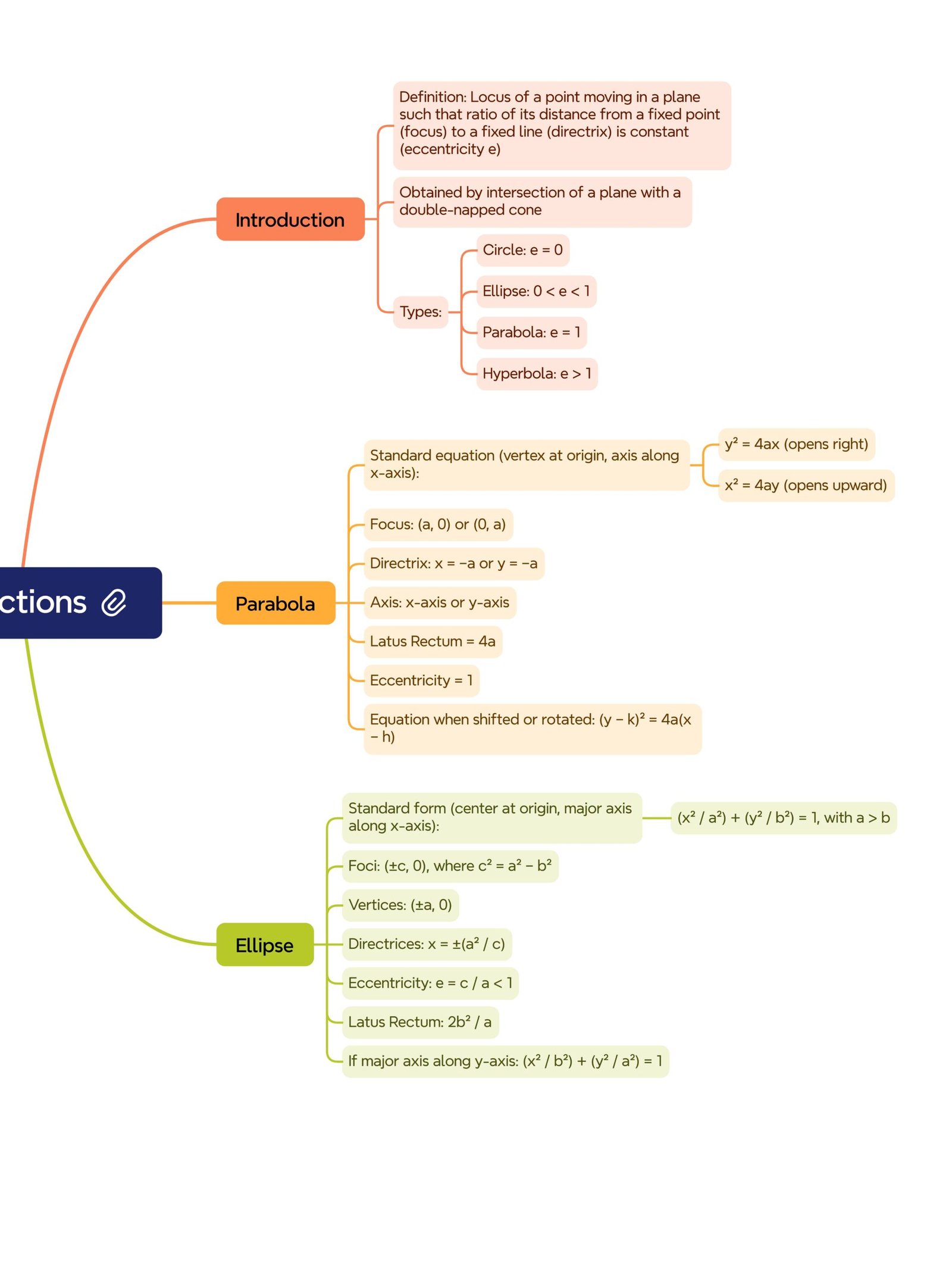
🔹 1. Introduction
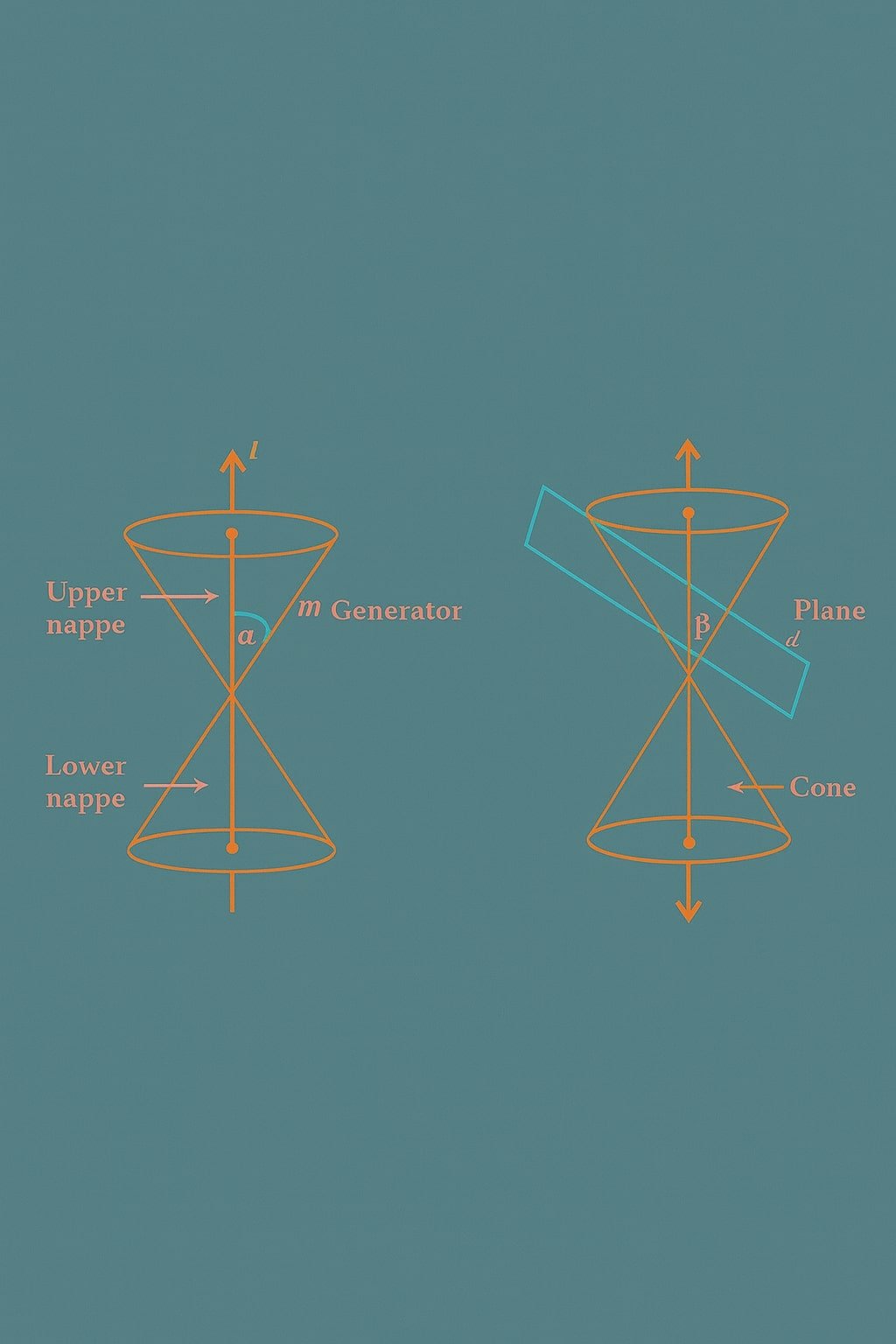
🔵 Conic sections are the curves obtained by intersecting a double right circular cone with a plane.
🟢 Depending on the angle of inclination of the plane with the cone’s axis, we obtain:
➡️ Circle
➡️ Ellipse
➡️ Parabola
➡️ Hyperbola
💡 Concept: The general equation of all conic sections is of second degree:
🧠 Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
🔹 2. Circle
🔵 Definition: The set of all points which are at a constant distance (radius) from a fixed point (centre).
🧠 Let centre = (h, k), radius = r.
✔️ Equation: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
➡️ If centre = origin (0, 0): x² + y² = r²
✏️ Note: The general equation x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents a circle if
✔️ g² + f² − c > 0
➡️ Centre = (−g, −f), radius = √(g² + f² − c)
🔹 3. Parabola
🔵 Definition: The set of all points (x, y) in a plane such that distance from a fixed point (focus) = distance from a fixed line (directrix).
🧠 Standard Form:
✔️ y² = 4ax → Axis along x-axis, vertex at origin, focus (a, 0), directrix x = −a
✔️ x² = 4ay → Axis along y-axis, vertex at origin, focus (0, a), directrix y = −a
💡 Eccentricity (e) = 1
✏️ Key Properties:
• Vertex = (0, 0)
• Axis = x-axis or y-axis
• Latus Rectum = line through focus perpendicular to axis
• Length = 4a
🔹 4. Ellipse
🔵 Definition: The set of all points such that the sum of distances from two fixed points (foci) is constant.
🧠 Standard Forms:
1️⃣ Major axis along x-axis:
(x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1, a > b
Focus: (±c, 0), where c² = a² − b²
Eccentricity e = c/a, 0 < e < 1
2️⃣ Major axis along y-axis:
(x²/b²) + (y²/a²) = 1, a > b
Focus: (0, ±c), c² = a² − b²
💡 Special Case: If a = b ⇒ circle.
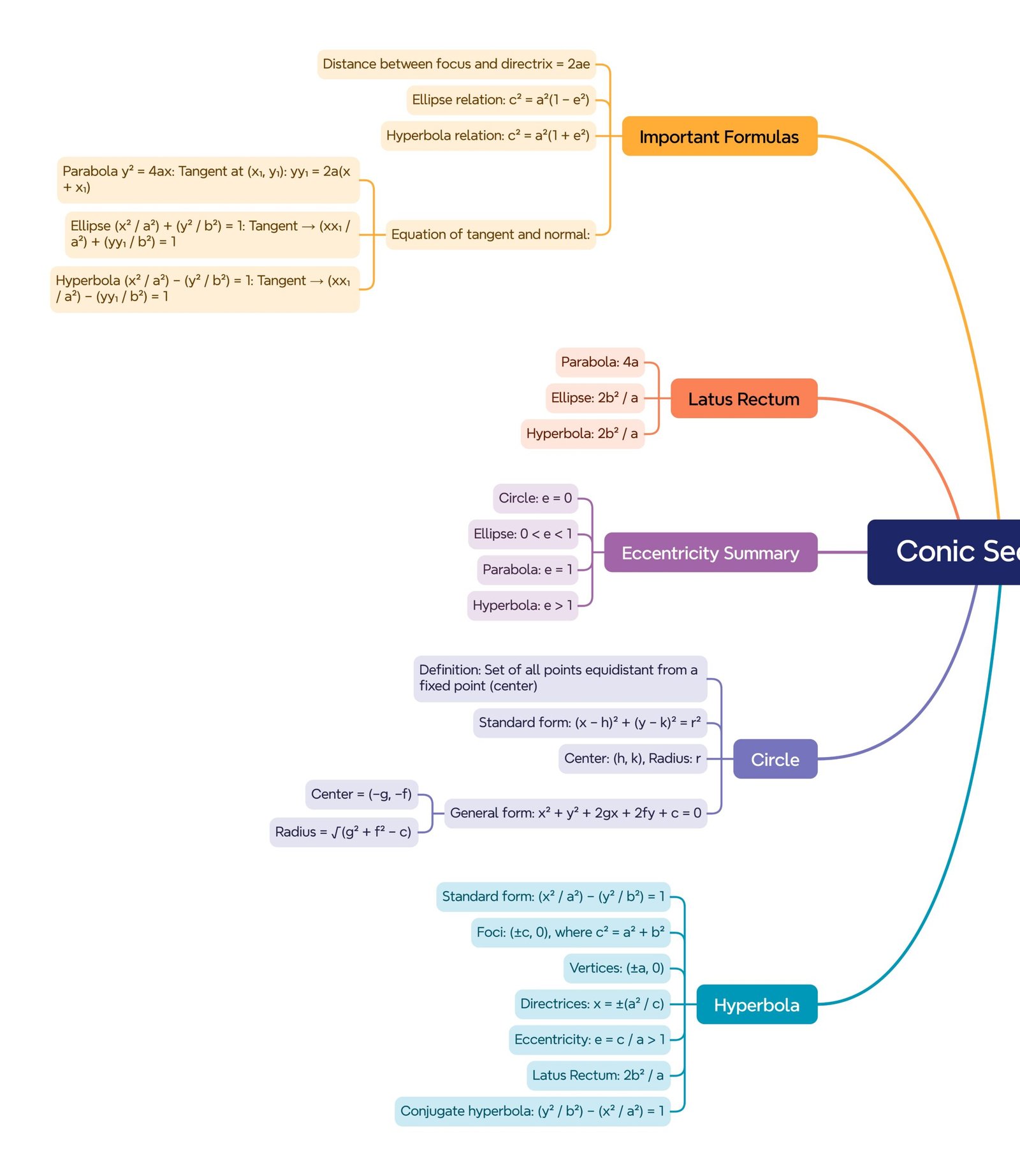
🔹 5. Hyperbola
🔵 Definition: The set of all points such that the difference of distances from two fixed points (foci) is constant.
🧠 Standard Forms:
1️⃣ Transverse axis along x-axis:
(x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1
Foci: (±c, 0), where c² = a² + b²
Eccentricity e = c/a, e > 1
2️⃣ Transverse axis along y-axis:
(y²/a²) − (x²/b²) = 1
✏️ Note: Asymptotes → lines passing through centre:
y = ±(b/a)x
🔹 6. Focus–Directrix Property
🧠 A conic is defined by:
Distance from focus = e × distance from directrix,
where e = eccentricity.
✔️ e < 1 → Ellipse
✔️ e = 1 → Parabola
✔️ e > 1 → Hyperbola
💡 This property gives a unified definition of all conics.
🔹 7. General Equation of Conic
🧠 General second-degree equation:
Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
✳️ Discriminant Δ = H² − AB
✔️ Δ = 0 → Parabola
✔️ Δ < 0 → Ellipse (if A = B, circle)
✔️ Δ > 0 → Hyperbola
🔹 8. Translation of Axes
🧠 To remove linear terms (2Gx, 2Fy), shift origin to (h, k):
Let
x = X + h, y = Y + k
Substitute into equation → new coordinates (X, Y) may simplify the form.
🔹 9. Important Relations
✔️ Ellipse: c² = a² − b²
✔️ Hyperbola: c² = a² + b²
✔️ Latus Rectum:
• Parabola → 4a
• Ellipse → 2b²/a
• Hyperbola → 2b²/a
🔹 10. Tangents and Normals
💡 Tangent at (x₁, y₁):
➡️ Circle: x·x₁ + y·y₁ = r²
➡️ Parabola (y² = 4ax): yy₁ = 2a(x + x₁)
➡️ Ellipse: (x·x₁)/a² + (y·y₁)/b² = 1
➡️ Hyperbola: (x·x₁)/a² − (y·y₁)/b² = 1
💡 Normal: Perpendicular line to tangent at (x₁, y₁)
🔹 11. Auxiliary Circle (Ellipse & Hyperbola)
🔵 Circle with centre same as conic, radius = semi-major axis a.
Used to find eccentric angles and geometrical properties.
🔹 12. Focal Chord and Parametric Form
🧠 Parabola y² = 4ax:
Point = (a t², 2a t)
Tangent: t y = x + a t²
Normal: y + t x = 2a t + a t³
🧠 Ellipse (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1:
Parametric form: (a cos θ, b sin θ)
🧠 Hyperbola (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1:
Parametric form: (a sec θ, b tan θ)
🔹 13. Real-life Applications
✔️ Circle: Wheels, circular tracks
✔️ Parabola: Reflectors, satellite dishes
✔️ Ellipse: Planetary orbits
✔️ Hyperbola: Radio navigation, cooling towers
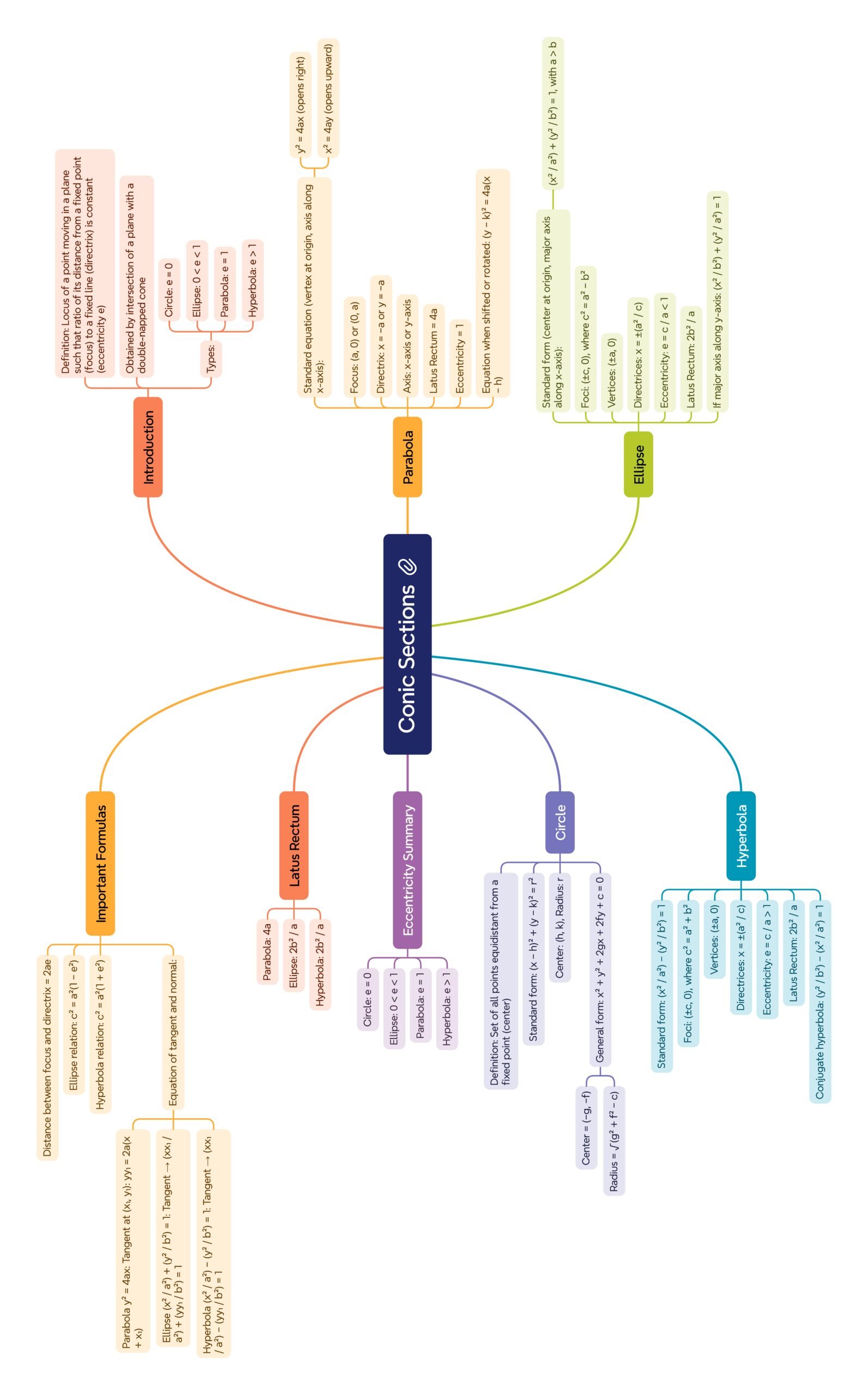
🟣 Summary (~300 words)
🔸 Conic Sections Overview
• Curves formed by intersection of a cone and a plane.
• Types: Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola.
🔸 Equations
🔹 Circle: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
🔹 Parabola: y² = 4ax or x² = 4ay
🔹 Ellipse: (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1
🔹 Hyperbola: (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1
🔸 Eccentricity (e)
• e < 1 → Ellipse
• e = 1 → Parabola
• e > 1 → Hyperbola
🔸 Key Relations
✔️ Ellipse: c² = a² − b²
✔️ Hyperbola: c² = a² + b²
🔸 Latus Rectum
• Parabola: 4a
• Ellipse: 2b²/a
• Hyperbola: 2b²/a
🔸 Discriminant (H² − AB)
• = 0 → Parabola
• < 0 → Ellipse (circle if A = B, H = 0)
• > 0 → Hyperbola
🔸 Tangents
General:
➡️ Ellipse: (x·x₁)/a² + (y·y₁)/b² = 1
➡️ Hyperbola: (x·x₁)/a² − (y·y₁)/b² = 1
🔸 Parametric Forms
• Parabola: (a t², 2a t)
• Ellipse: (a cos θ, b sin θ)
• Hyperbola: (a sec θ, b tan θ)
🔸 Applications
Used in engineering, astronomy, and physics.
📝 Quick Recap
✔️ Conics = Circle, Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola
✔️ Defined via focus–directrix property
✔️ Circle: e = 0, Ellipse: e < 1, Parabola: e = 1, Hyperbola: e > 1
✔️ Key forms:
• Circle: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
• Parabola: y² = 4ax
• Ellipse: (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1
• Hyperbola: (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1
✔️ Tangent & normal equations derived from standard form
✔️ Conics appear in optics, architecture, astronomy
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🧠 Exercise 10.1
🔵 Question 1:
Find the equation of the circle with centre (0, 2) and radius 2.
🟢 Answer:
💡 Formula: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
Substitute: h = 0, k = 2, r = 2
➡️ (x − 0)² + (y − 2)² = 2²
➡️ x² + (y − 2)² = 4 ✅
🔵 Question 2:
Centre (−2, 3) and radius 4
🟢 Answer:
➡️ (x + 2)² + (y − 3)² = 4²
➡️ (x + 2)² + (y − 3)² = 16 ✅
🔵 Question 3:
Centre (1/2, −1/4), radius 1/12
🟢 Answer:
➡️ (x − 1/2)² + (y + 1/4)² = (1/12)²
➡️ (x − 1/2)² + (y + 1/4)² = 1/144 ✅
🔵 Question 4:
Centre (1, 1), radius √2
🟢 Answer:
➡️ (x − 1)² + (y − 1)² = (√2)²
➡️ (x − 1)² + (y − 1)² = 2 ✅
🔵 Question 5:
Centre (−a, −b), radius √(a² − b²)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ (x + a)² + (y + b)² = (√(a² − b²))²
➡️ (x + a)² + (y + b)² = a² − b² ✅
🔵 Question 6:
(x + 5)² + (y − 3)² = 36
🟢 Answer:
💡 Standard form ⇒ Centre (−5, 3), Radius = √36 = 6
✔️ Centre (−5, 3), Radius 6
🔵 Question 7:
x² + y² − 4x − 8y − 45 = 0
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Complete squares:
x² − 4x + y² − 8y = 45
(x² − 4x + 4) + (y² − 8y + 16) = 45 + 4 + 16
➡️ (x − 2)² + (y − 4)² = 65
✔️ Centre (2, 4), Radius √65
🔵 Question 8:
x² + y² − 8x + 10y − 12 = 0
🟢 Answer:
➡️ x² − 8x + y² + 10y = 12
(x² − 8x + 16) + (y² + 10y + 25) = 12 + 16 + 25
➡️ (x − 4)² + (y + 5)² = 53
✔️ Centre (4, −5), Radius √53
🔵 Question 9:
2x² + 2y² − x = 0
🟢 Answer:
Divide by 2:
x² + y² − (1/2)x = 0
➡️ Complete square: x² − (1/2)x + y² = 0
(x² − (1/2)x + 1/16) + y² = 1/16
➡️ (x − 1/4)² + y² = (1/4)²
✔️ Centre (1/4, 0), Radius 1/4
🔵 Question 10:
Find equation of circle through (4, 1), (6, 5), centre on 4x + y = 16
🟢 Answer:
Let centre = (h, k), r = radius
Points satisfy:
(4 − h)² + (1 − k)² = r² …(i)
(6 − h)² + (5 − k)² = r² …(ii)
Subtract (ii − i):
(6² − 4²) + (5² − 1²) − 2h(6 − 4) − 2k(5 − 1) = 0
(36 − 16) + (25 − 1) − 4h − 8k = 0
44 − 4h − 8k = 0 ⇒ h + 2k = 11 …(iii)
Also centre on 4x + y = 16 ⇒ 4h + k = 16 …(iv)
Solve (iii), (iv):
Multiply (iii) by 4: 4h + 8k = 44
Subtract (iv): 7k = 28 ⇒ k = 4
Substitute: h + 8 = 11 ⇒ h = 3
Centre (3, 4)
Radius from (4, 1): r² = (4 − 3)² + (1 − 4)² = 1 + 9 = 10
✔️ Equation: (x − 3)² + (y − 4)² = 10
🔵 Question 11:
Circle through (2, 3), (−1, 1), centre on x − 3y − 11 = 0
🟢 Answer:
Let centre = (h, k), radius = r
(2 − h)² + (3 − k)² = r² …(i)
(−1 − h)² + (1 − k)² = r² …(ii)
Subtract (i − ii):
(4 − (−1)²) + (9 − 1) − 2h(2 + 1) − 2k(3 − 1) = 0
(4 − 1) + 8 − 6h − 4k = 0
11 − 6h − 4k = 0 ⇒ 3h + 2k = 11 …(iii)
Also x − 3y − 11 = 0 ⇒ h − 3k = 11 …(iv)
Solve: multiply (iv) by 2: 2h − 6k = 22
Subtract from (iii×?): We find
(3h + 2k) − (2h − 6k) = 11 − 22 ⇒ h + 8k = −11
Solve with (iv): h = 11 + 3k ⇒ substitute: (11 + 3k) + 8k = −11 ⇒ 11k = −22 ⇒ k = −2
h = 11 + 3(−2) = 5
Centre (5, −2)
Radius from (2, 3): r² = (2 − 5)² + (3 + 2)² = 9 + 25 = 34
✔️ (x − 5)² + (y + 2)² = 34
🔵 Question 12:
Circle with radius 5, centre on x-axis, passes through (2, 3)
🟢 Answer:
Let centre = (h, 0)
Distance = radius ⇒ (2 − h)² + (3 − 0)² = 5²
➡️ (2 − h)² + 9 = 25 ⇒ (2 − h)² = 16
→ 2 − h = ±4
Case 1: h = −2, Case 2: h = 6
✔️ Equations:
(1) (x + 2)² + y² = 25
(2) (x − 6)² + y² = 25 ✅
🔵 Question 13:
Circle through origin, intercepts a, b on axes
🟢 Answer:
Equation: x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy = 0 (since passes through origin ⇒ c = 0)
Intercepts:
x-intercept ⇒ y = 0 ⇒ x(x + 2g) = 0 ⇒ other point (−2g, 0) = (a, 0) ⇒ g = −a/2
y-intercept ⇒ x = 0 ⇒ y(y + 2f) = 0 ⇒ other (0, −2f) = (0, b) ⇒ f = −b/2
Equation:
✔️ x² + y² − ax − by = 0
🔵 Question 14:
Centre (2, 2), passes through (4, 5)
🟢 Answer:
r² = (4 − 2)² + (5 − 2)² = 4 + 9 = 13
✔️ (x − 2)² + (y − 2)² = 13
🔵 Question 15:
Check if (−2.5, 3.5) lies inside, on, or outside circle x² + y² = 25
🟢 Answer:
Compute: x² + y² = (−2.5)² + (3.5)² = 6.25 + 12.25 = 18.5
Compare with 25: 18.5 < 25 ⇒ point lies inside
✔️ Inside the circle ✅
📄 Exercise 10.2
🔵 Question 1:
y² = 12x
Find: focus, axis, directrix, and length of latus rectum.
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Compare with standard form: y² = 4a·x
➡️ 4a = 12 ⇒ a = 3
✨ Focus = (a, 0) = (3, 0)
✨ Axis: x-axis ⇒ y = 0
✨ Directrix: x = −a = −3
✨ Latus rectum length = 4a = 12
✨ Endpoints of latus rectum: (3, ±6)
🔵 Question 2:
x² = 6y
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Compare with: x² = 4a·y
➡️ 4a = 6 ⇒ a = 3/2
✨ Focus = (0, a) = (0, 3/2)
✨ Axis: y-axis ⇒ x = 0
✨ Directrix: y = −a = −3/2
✨ Latus rectum = 4a = 6
✨ Endpoints: (±3, 3/2)
🔵 Question 3:
y² = −8x
🟢 Answer:
⭐ 4a = −8 ⇒ a = −2 (opens left)
✨ Focus = (a, 0) = (−2, 0)
✨ Axis: y = 0
✨ Directrix: x = −a = 2
✨ Latus rectum length = 4|a| = 8
✨ Endpoints: (−2, ±4)
🔵 Question 4:
x² = −16y
🟢 Answer:
⭐ 4a = −16 ⇒ a = −4 (opens downward)
✨ Focus = (0, −4)
✨ Axis: x = 0
✨ Directrix: y = 4
✨ Latus rectum = 4|a| = 16
✨ Endpoints: (±8, −4)
🔵 Question 5:
y² = 10x
🟢 Answer:
⭐ 4a = 10 ⇒ a = 5/2
✨ Focus = (5/2, 0)
✨ Axis: y = 0
✨ Directrix: x = −5/2
✨ Latus rectum = 10
✨ Endpoints: (5/2, ±5)
🔵 Question 6:
x² = −9y
🟢 Answer:
⭐ 4a = −9 ⇒ a = −9/4
✨ Focus = (0, −9/4)
✨ Axis: x = 0
✨ Directrix: y = 9/4
✨ Latus rectum = 9
✨ Endpoints: (±9/2, −9/4)
🔵 Question 7:
Focus (6, 0); directrix x = −6
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Vertex = origin
➡️ a = 6
✨ Equation: y² = 4a·x ⇒ y² = 24x
🔵 Question 8:
Focus (0, −3); directrix y = 3
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Vertex = origin
➡️ a = −3 (opens downward)
✨ Equation: x² = 4a·y ⇒ x² = −12y
🔵 Question 9:
Vertex (0, 0); focus (3, 0)
🟢 Answer:
⭐ a = 3
✨ Equation: y² = 4a·x ⇒ y² = 12x
🔵 Question 10:
Vertex (0, 0); focus (−2, 0)
🟢 Answer:
⭐ a = −2
✨ Equation: y² = 4a·x ⇒ y² = −8x
🔵 Question 11:
Vertex (0, 0), passes through (2, 3), axis along x-axis
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Form: y² = 4a·x
➡️ Substitute (2, 3): 3² = 4a·2 ⇒ 9 = 8a ⇒ a = 9/8
✨ Equation: y² = 4a·x ⇒ y² = (9/2)x
🔵 Question 12:
Vertex (0, 0), passes through (5, 2), symmetric about y-axis
🟢 Answer:
⭐ Form: x² = 4a·y
➡️ Substitute (5, 2): 5² = 4a·2 ⇒ 25 = 8a ⇒ a = 25/8
✨ Equation: x² = 4a·y ⇒ x² = (25/2)y
Exercise 10.3
🔵 Question 1
x²/36 + y²/16 = 1. Find foci, vertices, lengths of major/minor axes, eccentricity, latus rectum.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 36, b² = 16 ⇒ a = 6, b = 4, c² = a² − b² = 20 ⇒ c = 2√5.
➡️ Centre (0,0); major axis along x.
➡️ Vertices (±6,0); foci (±2√5,0).
➡️ Major = 2a = 12; Minor = 2b = 8.
➡️ e = c/a = √5/3.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 2·16/6 = 16/3. ✔️
🔵 Question 2
x²/4 + y²/25 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 25 (y-axis major), b² = 4 ⇒ a = 5, b = 2, c² = 21 ⇒ c = √21.
➡️ Vertices (0,±5); foci (0,±√21).
➡️ Major = 10; Minor = 4; e = √21/5; L.R. = 2b²/a = 8/5. ✔️
🔵 Question 3
x²/16 + y²/9 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 16, b² = 9 ⇒ a = 4, b = 3, c² = 7 ⇒ c = √7.
➡️ Vertices (±4,0); foci (±√7,0); Major = 8; Minor = 6; e = √7/4; L.R. = 2b²/a = 18/4 = 9/2. ✔️
🔵 Question 4
x²/25 + y²/100 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 100 (vertical), b² = 25 ⇒ a = 10, b = 5, c² = 75 ⇒ c = 5√3.
➡️ Vertices (0,±10); foci (0,±5√3); Major = 20; Minor = 10; e = √3/2; L.R. = 2b²/a = 5. ✔️
🔵 Question 5
x²/49 + y²/36 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 49, b² = 36 ⇒ a = 7, b = 6, c² = 13 ⇒ c = √13.
➡️ Vertices (±7,0); foci (±√13,0); Major = 14; Minor = 12; e = √13/7; L.R. = 2b²/a = 72/7. ✔️
🔵 Question 6
x²/100 + y²/400 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 400 (vertical), b² = 100 ⇒ a = 20, b = 10, c² = 300 ⇒ c = 10√3.
➡️ Vertices (0,±20); foci (0,±10√3); Major = 40; Minor = 20; e = √3/2; L.R. = 2b²/a = 10. ✔️
🔵 Question 7
36x² + 4y² = 144.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 144 ⇒ x²/4 + y²/36 = 1; a² = 36 (vertical), b² = 4.
➡️ a = 6, b = 2, c² = 32 ⇒ c = 4√2.
➡️ Vertices (0,±6); foci (0,±4√2); e = c/a = 2√2/3; L.R. = 2b²/a = 8/6 = 4/3. ✔️
🔵 Question 8
16x² + y² = 16.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 16 ⇒ x²/1 + y²/16 = 1; a² = 16 (vertical), b² = 1.
➡️ a = 4, b = 1, c² = 15 ⇒ c = √15.
➡️ Vertices (0,±4); foci (0,±√15); e = √15/4; L.R. = 2b²/a = 1/2. ✔️
🔵 Question 9
4x² + 9y² = 36.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 36 ⇒ x²/9 + y²/4 = 1; a² = 9, b² = 4, c² = 5.
➡️ a = 3, b = 2, c = √5.
➡️ Vertices (±3,0); foci (±√5,0); e = √5/3; L.R. = 2b²/a = 8/3. ✔️
🔵 Question 10
Vertices (±5,0), foci (±4,0). Find equation.
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 5, c = 4 ⇒ b² = a² − c² = 25 − 16 = 9.
➡️ Equation: x²/25 + y²/9 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 11
Vertices (0,±13), foci (0,±5).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 13 (vertical), c = 5 ⇒ b² = a² − c² = 169 − 25 = 144.
➡️ Equation: x²/144 + y²/169 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 12
Vertices (±6,0), foci (±4,0).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 6, c = 4 ⇒ b² = 36 − 16 = 20.
➡️ Equation: x²/36 + y²/20 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 13
Ends of major (±3,0); ends of minor (0,±2).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 3, b = 2 (horizontal).
➡️ Equation: x²/9 + y²/4 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 14
Ends of major (0,±√5); ends of minor (±1,0).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = √5 (vertical), b = 1.
➡️ Equation: x²/1 + y²/5 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 15
Length of major axis 26, foci (±5,0).
🟢 Answer
💡 2a = 26 ⇒ a = 13; c = 5 ⇒ b² = 169 − 25 = 144.
➡️ Equation: x²/169 + y²/144 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 16
Length of minor axis 16, foci (0,±6).
🟢 Answer
💡 2b = 16 ⇒ b = 8; vertical with c = 6.
➡️ a² = b² + c² = 64 + 36 = 100 ⇒ a = 10.
➡️ Equation: x²/64 + y²/100 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 17
Foci (±3,0), a = 4.
🟢 Answer
💡 c = 3; b² = a² − c² = 16 − 9 = 7.
➡️ Equation: x²/16 + y²/7 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 18
b = 3, c = 4, centre at origin; foci on x-axis.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = b² + c² = 9 + 16 = 25 ⇒ a = 5 (horizontal).
➡️ Equation: x²/25 + y²/9 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 19
Centre (0,0); major axis on y-axis; passes through (3,2) and (1,6).
🟢 Answer
💡 Form: x²/b² + y²/a² = 1 with a > b.
➡️ From (3,2): 9/b² + 4/a² = 1.
➡️ From (1,6): 1/b² + 36/a² = 1.
💡 Let X = 1/b², Y = 1/a².
➡️ 9X + 4Y = 1; X + 36Y = 1.
➡️ Solve: Y = 1/40, X = 1/10 ⇒ a² = 40, b² = 10.
➡️ Equation: x²/10 + y²/40 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 20
Major axis on x-axis; passes through (4,3) and (6,2).
🟢 Answer
💡 Form: x²/a² + y²/b² = 1 (a > b).
➡️ With U = 1/a², V = 1/b²:
16U + 9V = 1; 36U + 4V = 1.
➡️ Solve: U = 1/52, V = 1/13 ⇒ a² = 52, b² = 13.
➡️ Equation: x²/52 + y²/13 = 1. ✔️
📄 Exercise 10.4
🔵 Question 1
x²/16 − y²/9 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 16, b² = 9 ⇒ a = 4, b = 3.
➡️ c² = a² + b² = 25 ⇒ c = 5.
➡️ Vertices: (±4, 0); Foci: (±5, 0).
➡️ Eccentricity e = c/a = 5/4.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 18/4 = 9/2. ✔️
🔵 Question 2
y²/9 − x²/27 = 1.
🟢 Answer
💡 a² = 9, b² = 27 ⇒ a = 3, b = 3√3.
➡️ c² = a² + b² = 36 ⇒ c = 6.
➡️ Vertices: (0, ±3); Foci: (0, ±6).
➡️ e = c/a = 2.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 54/3 = 18. ✔️
🔵 Question 3
9y² − 4x² = 36.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 36 ⇒ y²/4 − x²/9 = 1.
➡️ a² = 4, b² = 9 ⇒ a = 2, b = 3.
➡️ c² = 13 ⇒ c = √13.
➡️ Vertices: (0, ±2); Foci: (0, ±√13).
➡️ e = √13/2.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 18/2 = 9. ✔️
🔵 Question 4
16x² − 9y² = 576.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 576 ⇒ x²/36 − y²/64 = 1.
➡️ a² = 36, b² = 64 ⇒ a = 6, b = 8.
➡️ c² = 100 ⇒ c = 10.
➡️ Vertices: (±6, 0); Foci: (±10, 0).
➡️ e = 10/6 = 5/3.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 128/6 = 64/3. ✔️
🔵 Question 5
5y² − 9x² = 36.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 36 ⇒ y²/(36/5) − x²/4 = 1.
➡️ a² = 36/5, b² = 4.
➡️ c² = a² + b² = 56/5 ⇒ c = √(56/5).
➡️ Vertices: (0, ±6/√5); Foci: (0, ±√(56/5)).
➡️ e = c/a = √(56/5) ÷ (6/√5) = √14/3.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 8/(6/√5) = 4√5/3. ✔️
🔵 Question 6
49y² − 16x² = 784.
🟢 Answer
💡 Divide 784 ⇒ y²/16 − x²/49 = 1.
➡️ a² = 16, b² = 49 ⇒ a = 4, b = 7.
➡️ c² = 65 ⇒ c = √65.
➡️ Vertices: (0, ±4); Foci: (0, ±√65).
➡️ e = √65/4.
➡️ Latus rectum = 2b²/a = 98/4 = 49/2. ✔️
🔵 Question 7
Vertices (±2, 0), foci (±3, 0).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 2, c = 3 ⇒ b² = c² − a² = 9 − 4 = 5.
➡️ Equation: x²/4 − y²/5 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 8
Vertices (0, ±5), foci (0, ±8).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 5, c = 8 ⇒ b² = c² − a² = 64 − 25 = 39.
➡️ Equation: y²/25 − x²/39 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 9
Vertices (0, ±3), foci (0, ±5).
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 3, c = 5 ⇒ b² = c² − a² = 25 − 9 = 16.
➡️ Equation: y²/9 − x²/16 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 10
Foci (±5, 0), transverse axis length = 8.
🟢 Answer
💡 2a = 8 ⇒ a = 4, c = 5 ⇒ b² = c² − a² = 25 − 16 = 9.
➡️ Equation: x²/16 − y²/9 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 11
Foci (0, ±13), conjugate axis length = 24.
🟢 Answer
💡 2b = 24 ⇒ b = 12, c = 13 ⇒ a² = c² − b² = 169 − 144 = 25 ⇒ a = 5.
➡️ Equation: y²/25 − x²/144 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 12
Foci (±3√5, 0), latus rectum = 8.
🟢 Answer
💡 c = 3√5 ⇒ c² = 45.
➡️ L.R. = 2b²/a = 8.
➡️ c² = a² + b² ⇒ b² = c² − a².
➡️ 2b²/a = 8 ⇒ b² = 4a.
➡️ 45 = a² + 4a ⇒ a² + 4a − 45 = 0.
➡️ Solve: a = 5 (valid), b² = 20.
➡️ Equation: x²/25 − y²/20 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 13
Foci (±4, 0), latus rectum = 12.
🟢 Answer
💡 c = 4 ⇒ c² = 16.
➡️ L.R. = 2b²/a = 12 ⇒ b² = 6a.
➡️ c² = a² + b² = a² + 6a.
➡️ Equation: a² + 6a = 16 ⇒ a² + 6a − 16 = 0.
➡️ Roots: a = 2 (valid) ⇒ b² = 12.
➡️ Equation: x²/4 − y²/12 = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 14
Vertices (±7, 0), e = 4/3.
🟢 Answer
💡 a = 7, e = c/a = 4/3 ⇒ c = 28/3.
➡️ b² = c² − a² = (784/9) − 49 = 343/9.
➡️ Equation: x²/49 − y²/(343/9) = 1. ✔️
🔵 Question 15
Foci (0, ±√10), passing through (2,3).
🟢 Answer
💡 c = √10 ⇒ c² = 10.
➡️ c² = a² + b².
➡️ Equation: y²/a² − x²/b² = 1.
➡️ Substitute (2,3): 9/a² − 4/b² = 1.
➡️ Also 10 = a² + b².
➡️ Solving: a² = 5, b² = 5.
➡️ Equation: y²/5 − x²/5 = 1. ✔️
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
CBSE STYLE BOARD PAPER
ESPECIALLY FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🧭 Section A – Very Short / Objective Type (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is the general equation of a conic?
🔵 (A) Ax² + By² + C = 0
🟢 (B) Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
🟠 (C) ax + by + c = 0
🔴 (D) ax² + by² = 1
🟢 Answer: (B) Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
🔵 Question 2:
If eccentricity (e) = 1, the conic is a:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
🟢 Answer: (C) Parabola
🔵 Question 3:
Equation of a circle with centre at origin and radius r is:
🔵 (A) x² + y² = r
🟢 (B) x² + y² = r²
🟠 (C) (x − r)² + (y − r)² = 0
🔴 (D) x² + y² − 2r = 0
🟢 Answer: (B) x² + y² = r²
🔵 Question 4:
If e < 1, the conic represents:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
🟢 Answer: (B) Ellipse
🔵 Question 5:
For parabola y² = 4ax, focus is at:
🔵 (A) (a, 0)
🟢 (B) (0, a)
🟠 (C) (−a, 0)
🔴 (D) (0, −a)
🟢 Answer: (A) (a, 0)
🔵 Question 6:
Equation (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1 represents:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
🟢 Answer: (B) Ellipse
🔵 Question 7:
For hyperbola (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1, eccentricity is:
🔵 (A) e = c/a < 1
🟢 (B) e = c/a = 1
🟠 (C) e = c/a > 1
🔴 (D) e = 0
🟢 Answer: (C) e = c/a > 1
🔵 Question 8:
In ellipse (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1, relation is:
🔵 (A) c² = a² + b²
🟢 (B) c² = a² − b²
🟠 (C) a² = b² + c²
🔴 (D) b² = c² + a²
🟢 Answer: (B) c² = a² − b²
🔵 Question 9:
Latus rectum of y² = 4ax is:
🔵 (A) 2a
🟢 (B) 3a
🟠 (C) 4a
🔴 (D) a
🟢 Answer: (C) 4a
🔵 Question 10:
Equation of tangent to circle x² + y² = r² at (x₁, y₁):
🔵 (A) x + y = r
🟢 (B) x·x₁ + y·y₁ = r²
🟠 (C) x + y₁ = 0
🔴 (D) x + y = 0
🟢 Answer: (B) x·x₁ + y·y₁ = r²
🔵 Question 11:
Focus of ellipse (x²/9) + (y²/4) = 1 is:
🔵 (A) (±3, 0)
🟢 (B) (±√5, 0)
🟠 (C) (0, ±3)
🔴 (D) (0, ±√5)
🟢 Answer: (B) (±√5, 0)
🔵 Question 12:
Equation of directrix for y² = 4ax:
🔵 (A) x = a
🟢 (B) x = −a
🟠 (C) y = a
🔴 (D) y = −a
🟢 Answer: (B) x = −a
🔵 Question 13:
In hyperbola (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1, asymptotes are:
🔵 (A) y = ±(a/b)x
🟢 (B) y = ±(b/a)x
🟠 (C) x = ±(a/b)y
🔴 (D) x = ±(b/a)y
🟢 Answer: (B) y = ±(b/a)x
🔵 Question 14:
Centre of circle x² + y² + 4x − 6y + 9 = 0 is:
🧠 Complete square: (x + 2)² + (y − 3)² = 4
🔵 (A) (−2, 3)
🟢 (B) (2, 3)
🟠 (C) (−2, −3)
🔴 (D) (2, −3)
🟢 Answer: (A) (−2, 3)
🔵 Question 15:
Parabola x² = 4ay opens:
🔵 (A) Upward
🟢 (B) Downward
🟠 (C) Right
🔴 (D) Left
🟢 Answer: (A) Upward
🔵 Question 16:
Eccentricity of circle is:
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) >1
🔴 (D) Undefined
🟢 Answer: (A) 0
🔵 Question 17:
General equation x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents a circle if:
🔵 (A) g² + f² + c = 0
🟢 (B) g² + f² − c > 0
🟠 (C) g² + f² + c > 0
🔴 (D) g² + f² − c < 0
🟢 Answer: (B) g² + f² − c > 0
🔵 Question 18:
Discriminant H² − AB equals zero ⇒ conic is:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
🟢 Answer: (C) Parabola
🧭 Section B – Short Answer Type (2–3 marks each)
🔵 Question 19:
Find equation of circle with centre (2, −1) and radius 3.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Formula: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
➡️ Substitute: (x − 2)² + (y + 1)² = 9
✔️ Equation: x² + y² − 4x + 2y − 4 = 0
🔵 Question 20:
Find coordinates of focus, axis, directrix, and latus rectum of parabola y² = 8x.
🟢 Answer:
Compare with y² = 4ax → 4a = 8 ⇒ a = 2
✔️ Focus: (2, 0)
✔️ Axis: x-axis
✔️ Directrix: x = −2
✔️ Latus Rectum: length = 4a = 8, equation y = ±4
🔵 Question 21:
Find centre, vertices, foci, and eccentricity of ellipse (x²/16) + (y²/9) = 1.
🟢 Answer:
a² = 16, b² = 9 ⇒ a = 4, b = 3
➡️ c² = a² − b² = 7 ⇒ c = √7
✔️ Centre: (0, 0)
✔️ Vertices: (±4, 0)
✔️ Foci: (±√7, 0)
✔️ Eccentricity: e = c/a = √7 / 4
🔵 Question 22:
Find equation of hyperbola with transverse axis along x-axis, vertices (±3, 0), and eccentricity e = 5/3.
🟢 Answer:
a = 3, e = 5/3 ⇒ c = a·e = 5 ⇒ c² = 25
For hyperbola, c² = a² + b² ⇒ 25 = 9 + b² ⇒ b² = 16
✔️ Equation: (x²/9) − (y²/16) = 1
🔵 Question 23:
Find equation of tangent to circle x² + y² = 25 at point (3, 4).
🟢 Answer:
Tangent: x·x₁ + y·y₁ = r²
➡️ Substitute: 3x + 4y = 25
✔️ Equation: 3x + 4y − 25 = 0
🔵 Question 24:
Find the equation of the ellipse whose foci are (±4, 0) and the length of the major axis is 10.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Centre = (0, 0) since foci are symmetric about origin.
➤ Step 2: Major axis length = 2a = 10 ⇒ a = 5.
➤ Step 3: Distance of focus = c = 4.
➤ Step 4: For ellipse, relation: c² = a² − b²
➡️ 4² = 5² − b²
➡️ 16 = 25 − b²
➡️ b² = 9.
✔️ Equation of ellipse:
(x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1
🔵 Question 25:
Find the coordinates of foci and vertices, length of latus rectum of the hyperbola:
(x²/9) − (y²/4) = 1
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: a² = 9, b² = 4 ⇒ a = 3, b = 2.
➤ Step 2: For hyperbola: c² = a² + b² = 9 + 4 = 13 ⇒ c = √13.
✔️ Vertices: (±a, 0) = (±3, 0)
✔️ Foci: (±c, 0) = (±√13, 0)
✔️ Length of latus rectum = 2b²/a = 2×4 / 3 = 8/3
🔵 Question 26:
Find equation of tangent to the parabola y² = 12x at point (3, 6).
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Compare with y² = 4ax, we get 4a = 12 ⇒ a = 3.
➤ Step 2: Equation of tangent at (x₁, y₁):
y·y₁ = 2a(x + x₁)
➤ Step 3: Substitute values:
6y = 6(x + 3)
⇒ 6y = 6x + 18
⇒ 6x − 6y + 18 = 0 or x − y + 3 = 0
✔️ Tangent: x − y + 3 = 0
🔵 Question 27:
Find equation of circle passing through (0, 0) and (1, 1), and whose centre lies on x-axis.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Let centre = (h, 0), radius = r.
Equation: (x − h)² + y² = r²
➤ Step 2: Passes through (0, 0):
(0 − h)² + 0² = r² ⇒ r² = h²
➤ Step 3: Passes through (1, 1):
(1 − h)² + 1² = r² = h²
Expand: 1 − 2h + h² + 1 = h²
Simplify: 2 − 2h = 0 ⇒ h = 1
➤ Step 4: r² = h² = 1 ⇒ r = 1
✔️ Equation: (x − 1)² + y² = 1
🔵 Question 28:
Find equation of ellipse whose centre is at origin, major axis is along x-axis, length of major axis = 20, and eccentricity e = 3/5.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: a = ½ × 20 = 10
➤ Step 2: e = 3/5 ⇒ c = a·e = 10 × (3/5) = 6
➤ Step 3: For ellipse, c² = a² − b²
36 = 100 − b²
⇒ b² = 64
✔️ Equation: (x²/100) + (y²/64) = 1
🔵 Question 29:
Find equation of hyperbola with centre (0, 0), transverse axis along y-axis, vertices at (0, ±4), and eccentricity e = 5/4.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: a = 4
➤ Step 2: e = 5/4 ⇒ c = a·e = 5
➤ Step 3: For hyperbola, c² = a² + b²
25 = 16 + b² ⇒ b² = 9
✔️ Equation: (y²/16) − (x²/9) = 1
🔵 Question 30:
Find equation of tangent and normal to parabola y² = 4x at point (1, 2).
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: For parabola y² = 4ax, compare: 4a = 4 ⇒ a = 1
➤ Step 2: Tangent at (x₁, y₁): y·y₁ = 2a(x + x₁)
⇒ 2y = 2(x + 1) ⇒ x − y + 1 = 0
✔️ Tangent: x − y + 1 = 0
➤ Step 3: Slope of tangent = 1 ⇒ Slope of normal = −1
Normal through (1, 2):
Equation: y − 2 = −1(x − 1)
⇒ y − 2 = −x + 1
⇒ x + y − 3 = 0
✔️ Normal: x + y − 3 = 0
🔵 Question 31:
Find equation of circle passing through (2, 3), (3, 2), and having centre on line x + y = 4.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Let centre = (h, k) satisfying h + k = 4.
Equation: (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
➤ Step 2: Substitute (2, 3): (2 − h)² + (3 − k)² = r²
Substitute (3, 2): (3 − h)² + (2 − k)² = r²
Subtract:
[(2 − h)² + (3 − k)²] − [(3 − h)² + (2 − k)²] = 0
⇒ (4 − 4h + h² + 9 − 6k + k²) − (9 − 6h + h² + 4 − 4k + k²) = 0
Simplify: (13 − 4h − 6k) − (13 − 6h − 4k) = 0
⇒ 2h − 2k = 0 ⇒ h = k
➤ Step 3: From h + k = 4 ⇒ 2h = 4 ⇒ h = k = 2
Centre = (2, 2)
➤ Step 4: Substitute (2, 3): (2 − 2)² + (3 − 2)² = r² ⇒ r² = 1
✔️ Equation: (x − 2)² + (y − 2)² = 1
🔵 Question 32 (Case-Based):
A parabola has vertex at origin, focus at (2, 0).
Find:
(a) Equation of parabola
(b) Equation of directrix
(c) Equation of tangent at point (1, 2)
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Distance of focus = a = 2
(a) Equation: y² = 4ax = 8x
(b) Directrix: x = −2
(c) Tangent at (1, 2): y·y₁ = 2a(x + x₁)
2y = 4(x + 1) ⇒ 2y − 4x − 4 = 0
✔️ Tangent: 2y − 4x − 4 = 0
🔵 Question 33 (Application):
A communication dish is shaped like a parabola. The receiver is placed at focus, 2 m from vertex. Find the width of the dish 6 m from vertex.
🟢 Answer:
➤ Step 1: Equation of parabola: y² = 4ax, a = 2
At x = 6, y² = 4×2×6 = 48 ⇒ y = ±√48 = ±6.928
Width = 2|y| = 2×6.928 = 13.856 m
✔️ Width ≈ 13.86 m
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
The eccentricity of a parabola is
🟥 1️⃣ 0
🟩 2️⃣ 1
🟨 3️⃣ Greater than 1
🟦 4️⃣ Less than 1
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 1
📘 JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 2
For the parabola y² = 8x, the focus is
🟥 1️⃣ (2, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (4, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, 2)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, 4)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (4, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 3
For the parabola y² = 12x, the directrix is
🟥 1️⃣ x = 3
🟩 2️⃣ x = −3
🟨 3️⃣ x = 6
🟦 4️⃣ x = −6
Answer : 🟦 4️⃣ x = −6
📘 JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 4
Ellipse x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1 has foci at
🟥 1️⃣ (±5, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±4, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (±3, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±5)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (±4, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 5
Eccentricity of ellipse x² / 25 + y² / 16 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 5
🟩 2️⃣ 4 / 5
🟨 3️⃣ 5 / 3
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / 2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 4 / 5
📘 JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 6
For hyperbola x² / 9 − y² / 4 = 1, the directrices are
🟥 1️⃣ x = ±3 / 2
🟩 2️⃣ x = ±9 / 2
🟨 3️⃣ y = ±3 / 2
🟦 4️⃣ y = ±9 / 2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ x = ±9 / 2
📘 JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 7
Length of latus rectum of parabola y² = 4ax is
🟥 1️⃣ a
🟩 2️⃣ 2a
🟨 3️⃣ 3a
🟦 4️⃣ 4a
Answer : 🟦 4️⃣ 4a
📘 JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 8
Vertices of ellipse x² / 25 + y² / 16 = 1 are
🟥 1️⃣ (±5, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, ±4)
🟨 3️⃣ Both (±5, 0) and (0, ±4)
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟨 3️⃣ Both (±5, 0) and (0, ±4)
📘 JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 9
Eccentricity of hyperbola x² / 16 − y² / 9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 2
🟩 2️⃣ 5 / 4
🟨 3️⃣ √(25 / 16)
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 2
📘 JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 10
Equation y² = 16x represents a parabola whose vertex is
🟥 1️⃣ (4, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (−4, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, 4)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (0, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 11
Ellipse 9x² + 16y² = 144 has major axis along
🟥 1️⃣ x-axis
🟩 2️⃣ y-axis
🟨 3️⃣ Line x = y
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ y-axis
📘 JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 12
Focus of parabola x² = 12y is
🟥 1️⃣ (0, 3)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, 6)
🟨 3️⃣ (3, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (6, 0)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (0, 3)
📘 JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 13
Eccentricity of ellipse x² / 9 + y² / 4 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ √5 / 3
🟩 2️⃣ 2 / 3
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / 2
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / 3
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 2 / 3
📘 JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 14
Directrix of parabola y² = 8x is
🟥 1️⃣ x = −2
🟩 2️⃣ x = −4
🟨 3️⃣ x = 4
🟦 4️⃣ x = 2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ x = −4
📘 JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 15
Latus rectum length of ellipse x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 18 / 5
🟩 2️⃣ 9 / 5
🟨 3️⃣ 6 / 5
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 9 / 5
📘 JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 16
For hyperbola x² / 9 − y² / 16 = 1, transverse axis lies along
🟥 1️⃣ x-axis
🟩 2️⃣ y-axis
🟨 3️⃣ x = y
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x-axis
📘 JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 17
Equation of ellipse with centre (0, 0), major axis along x-axis, a = 5, b = 3 is
🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x² / 9 + y² / 25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x² + y² = 25
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
📘 JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 18
For parabola x² = 8y, length of latus rectum is
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 6
🟦 4️⃣ 8
Answer : 🟦 4️⃣ 8
📘 JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 19
Focus of ellipse x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1 are
🟥 1️⃣ (±5, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±√7, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, ±5)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±√7)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (±√7, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 20
Eccentricity of ellipse x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 4
🟩 2️⃣ √7 / 4
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / 2
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 4
📘 JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 21
Focus of parabola y² = 4x is
🟥 1️⃣ (1, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, 1)
🟨 3️⃣ (4, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, 4)
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ (1, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 22
Eccentricity of hyperbola x² / a² − y² / b² = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ √(1 + b² / a²)
🟩 2️⃣ √(1 − b² / a²)
🟨 3️⃣ b / a
🟦 4️⃣ a / b
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ √(1 + b² / a²)
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 23
Length of latus rectum of hyperbola x² / a² − y² / b² = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 2b² / a
🟩 2️⃣ 2a² / b
🟨 3️⃣ 2ab
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 2b² / a
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 24
For ellipse x² / 9 + y² / 4 = 1, minor axis length is
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 3
🟨 3️⃣ 4
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟨 3️⃣ 4
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 25
The vertex of parabola y² = 12x is
🟥 1️⃣ (0, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (3, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, 3)
🟦 4️⃣ (−3, 0)
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ (0, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 26
The equation of directrix of the parabola y² = 12x is
🟥 1️⃣ x = −3
🟩 2️⃣ x = −6
🟨 3️⃣ x = 3
🟦 4️⃣ x = 6
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ x = −3
📘 JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 27
The length of latus rectum of the parabola x² = 8y is
🟥 1️⃣ 2
🟩 2️⃣ 4
🟨 3️⃣ 6
🟦 4️⃣ 8
Answer : 🟦 4️⃣ 8
📘 JEE Main 2024
🔵 Question 28
The eccentricity of the ellipse x² / 9 + y² / 4 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 2 / 3
🟩 2️⃣ √5 / 3
🟨 3️⃣ 3 / 4
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / 2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ √5 / 3
📘 JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 29
The coordinates of the focus of the parabola y² = 16x are
🟥 1️⃣ (0, 4)
🟩 2️⃣ (4, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (2, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (8, 0)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (4, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2023
🔵 Question 30
Equation of ellipse with centre at origin, major axis along x-axis, and foci (±4, 0), vertices (±5, 0) is
🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x² / 9 + y² / 25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
📘 JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 31
The length of latus rectum of hyperbola x² / 16 − y² / 9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 9 / 4
🟩 2️⃣ 18 / 4
🟨 3️⃣ 2b² / a = 2(9)/4
🟦 4️⃣ 9 / 2
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 2b² / a = 2(9)/4 = 9 / 2
📘 JEE Main 2022
🔵 Question 32
For ellipse x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1, the coordinates of foci are
🟥 1️⃣ (±4, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±3, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (±√16, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±4)
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ (±4, 0)
📘 JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 33
Eccentricity of hyperbola x² / 9 − y² / 4 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5 / 3
🟩 2️⃣ 3 / 2
🟨 3️⃣ √(13 / 9)
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 3 / 2
📘 JEE Main 2021
🔵 Question 34
Equation of parabola with focus (2, 0) and directrix x = −2 is
🟥 1️⃣ y² = 8x
🟩 2️⃣ x² = 8y
🟨 3️⃣ x² = 8x
🟦 4️⃣ y² = 8y
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ y² = 8x
📘 JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 35
For ellipse x² / a² + y² / b² = 1, eccentricity is
🟥 1️⃣ √(1 − b² / a²)
🟩 2️⃣ √(1 + b² / a²)
🟨 3️⃣ b / a
🟦 4️⃣ a / b
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ √(1 − b² / a²)
📘 JEE Main 2020
🔵 Question 36
Equation of directrix of hyperbola x² / 9 − y² / 16 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ x = ±9 / 4
🟩 2️⃣ x = ±4 / 3
🟨 3️⃣ y = ±9 / 4
🟦 4️⃣ y = ±4 / 3
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x = ±9 / 4
📘 JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 37
For ellipse x² / 4 + y² / 3 = 1, length of latus rectum is
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 2
🟩 2️⃣ 3 / 4
🟨 3️⃣ 3 / 1
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 3 / 2
📘 JEE Main 2019
🔵 Question 38
Parabola y² = 4x passes through which of the following points?
🟥 1️⃣ (1, 2)
🟩 2️⃣ (2, 1)
🟨 3️⃣ (3, 4)
🟦 4️⃣ (4, 2)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (2, 1)
📘 JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 39
Latus rectum length of hyperbola x² / a² − y² / b² = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 2b² / a
🟩 2️⃣ 2a² / b
🟨 3️⃣ a² / b
🟦 4️⃣ 2ab
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 2b² / a
📘 JEE Main 2018
🔵 Question 40
Eccentricity of ellipse 9x² + 16y² = 144 is
🟥 1️⃣ √(1 − 9/16)
🟩 2️⃣ 3 / 4
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / 2
🟦 4️⃣ √(1 − 16/9)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 3 / 4
📘 JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 41
Focus of parabola x² = 8y is
🟥 1️⃣ (0, 2)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, 4)
🟨 3️⃣ (4, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (2, 0)
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ (0, 2)
📘 JEE Main 2017
🔵 Question 42
Equation of ellipse whose foci are (±4, 0) and major axis length 10 is
🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x² / 9 + y² / 25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
📘 JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 43
Eccentricity of hyperbola 9x² − 16y² = 144 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5 / 3
🟩 2️⃣ 4 / 3
🟨 3️⃣ √(25 / 9)
🟦 4️⃣ 3 / 2
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 5 / 3
📘 JEE Main 2016
🔵 Question 44
The directrix of parabola x² = 4y is
🟥 1️⃣ y = 1
🟩 2️⃣ y = −1
🟨 3️⃣ y = 2
🟦 4️⃣ y = −2
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ y = −1
📘 JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 45
For ellipse x² / 16 + y² / 9 = 1, minor axis length is
🟥 1️⃣ 4
🟩 2️⃣ 6
🟨 3️⃣ 8
🟦 4️⃣ 10
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ 6
📘 JEE Main 2015
🔵 Question 46
For ellipse x² / a² + y² / b² = 1, foci are
🟥 1️⃣ (±√(a² − b²), 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±√(b² − a²), 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, ±√(a² − b²))
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±√(b² − a²))
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ (±√(a² − b²), 0)
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 47
The eccentricity of hyperbola x² / 9 − y² / 16 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5 / 3
🟩 2️⃣ 4 / 3
🟨 3️⃣ 3 / 2
🟦 4️⃣ √(25 / 9)
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ 5 / 3
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 48
The equation of parabola whose vertex is at origin and focus (0, −2) is
🟥 1️⃣ x² = 8y
🟩 2️⃣ x² = −8y
🟨 3️⃣ y² = 8x
🟦 4️⃣ y² = −8x
Answer : 🟩 2️⃣ x² = −8y
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 49
Length of latus rectum of parabola y² = 12x is
🟥 1️⃣ 6
🟩 2️⃣ 8
🟨 3️⃣ 12
🟦 4️⃣ 4
Answer : 🟨 3️⃣ 12
📘 JEE Main 2014
🔵 Question 50
Equation of ellipse with eccentricity 3 / 5, centre (0, 0), major axis along x-axis, a = 5 is
🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 16 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x² / 16 + y² / 25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x² / 9 + y² / 25 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 9 = 1
Answer : 🟥 1️⃣ x² / 25 + y² / 16 = 1
📘 JEE Main 2014
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
The focus of the parabola y² = 8x is
🟥 1️⃣ (2, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (4, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, 2)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, 4)
Answer: 2️⃣ (4, 0)
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 2
The length of the latus rectum of parabola y² = 12x is
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ 6
🟨 3️⃣ 12
🟦 4️⃣ 24
Answer: 3️⃣ 12
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 3
The equation of ellipse with centre at origin, foci (±5, 0), and major axis 12 units is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/36 + y²/11 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/9 + y²/25 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/11 + y²/36 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/36 + y²/11 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 4
Eccentricity of hyperbola x²/9 − y²/16 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5/3
🟩 2️⃣ 3/2
🟨 3️⃣ 4/3
🟦 4️⃣ √(25/9)
Answer: 1️⃣ 5/3
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 5
The equation of directrix of parabola x² = 8y is
🟥 1️⃣ y = 2
🟩 2️⃣ y = −2
🟨 3️⃣ y = 4
🟦 4️⃣ y = −4
Answer: 2️⃣ y = −2
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 6
Equation of tangent to parabola y² = 4ax at (at², 2at) is
🟥 1️⃣ ty = x + at²
🟩 2️⃣ ty = x − at²
🟨 3️⃣ y = tx + a/t
🟦 4️⃣ y = tx + a/t²
Answer: 1️⃣ ty = x + at²
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 7
Equation of ellipse with vertices (±5, 0) and eccentricity 3/5 is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/9 + y²/25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/16 + y²/9 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 8
Length of latus rectum of hyperbola x²/16 − y²/9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 9/2
🟩 2️⃣ 18/4
🟨 3️⃣ 9/4
🟦 4️⃣ 4
Answer: 1️⃣ 9/2
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 9
The coordinates of foci of ellipse x²/25 + y²/9 = 1 are
🟥 1️⃣ (±4, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±3, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (0, ±4)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±3)
Answer: 1️⃣ (±4, 0)
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 10
The eccentricity of ellipse x²/9 + y²/5 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ √(4/9)
🟩 2️⃣ 2/3
🟨 3️⃣ 3/4
🟦 4️⃣ √5 / 3
Answer: 4️⃣ √5 / 3
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 11
For parabola y² = 4ax, slope of tangent at (at², 2at) is
🟥 1️⃣ 1/t
🟩 2️⃣ 2t
🟨 3️⃣ t
🟦 4️⃣ t²
Answer: 3️⃣ t
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 12
Equation of ellipse with foci (±5, 0) and minor axis 6 is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/16 + y²/9 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/9 + y²/25 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ None
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 13
Equation of directrix of parabola y² = 4x is
🟥 1️⃣ x = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x = −1
🟨 3️⃣ y = 1
🟦 4️⃣ y = −1
Answer: 2️⃣ x = −1
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 14
Eccentricity of hyperbola 9x² − 16y² = 144 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5/3
🟩 2️⃣ 4/3
🟨 3️⃣ 3/2
🟦 4️⃣ √(25/9)
Answer: 1️⃣ 5/3
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 15
Equation of tangent to parabola y² = 4ax with slope m is
🟥 1️⃣ y = mx + a/m
🟩 2️⃣ y = mx − a/m
🟨 3️⃣ y = mx + m/a
🟦 4️⃣ y = mx − m/a
Answer: 1️⃣ y = mx + a/m
📘 JEE Advanced 2017 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 16
Latus rectum of parabola x² = 16y is
🟥 1️⃣ 4
🟩 2️⃣ 8
🟨 3️⃣ 16
🟦 4️⃣ 12
Answer: 3️⃣ 16
📘 JEE Advanced 2016 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 17
Equation of ellipse with eccentricity 3/5 and major axis 10 is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/16 + y²/25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/9 + y²/25 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2015 (Paper 1)
🔵 Question 18
For the parabola y² = 8x, the equation of its directrix is
🟥 1️⃣ x = 2
🟩 2️⃣ x = −2
🟨 3️⃣ y = 2
🟦 4️⃣ y = −2
Answer: 2️⃣ x = −2
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 19
The eccentricity of the ellipse x²/25 + y²/9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ √(1 − 9/25)
🟩 2️⃣ 4/5
🟨 3️⃣ 3/5
🟦 4️⃣ 5/3
Answer: 2️⃣ 4/5
📘 JEE Advanced 2024 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 20
The equation of the tangent to the parabola y² = 4x at (1, 2) is
🟥 1️⃣ y = x + 1
🟩 2️⃣ y = 2x
🟨 3️⃣ y = 2x − 1
🟦 4️⃣ y = 2x + 1
Answer: 3️⃣ y = 2x − 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 21
The focus of the parabola x² = 8y is
🟥 1️⃣ (0, 2)
🟩 2️⃣ (0, 4)
🟨 3️⃣ (4, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (2, 0)
Answer: 2️⃣ (0, 2)
📘 JEE Advanced 2023 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 22
For the ellipse x²/16 + y²/9 = 1, the coordinates of the foci are
🟥 1️⃣ (±√7, 0)
🟩 2️⃣ (±√13, 0)
🟨 3️⃣ (±√5, 0)
🟦 4️⃣ (0, ±√7)
Answer: 2️⃣ (±√7, 0)
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 23
Equation of hyperbola with transverse axis on x-axis, foci (±5, 0), and asymptotes y = ±(3/4)x is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 − y²/9 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/9 − y²/25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/16 − y²/9 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/25 − y²/16 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 − y²/9 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2022 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 24
The length of latus rectum of hyperbola x²/9 − y²/4 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 8/3
🟩 2️⃣ 2b²/a = 8/3
🟨 3️⃣ 3
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 2️⃣ 8/3
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 25
Equation of ellipse with eccentricity 3/5 and major axis length 10 is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/16 + y²/25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/9 + y²/25 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/25 + y²/9 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2021 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 26
The slope of tangent to the parabola y² = 4x at (1, 2) is
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ 2
🟨 3️⃣ 1/2
🟦 4️⃣ −2
Answer: 2️⃣ 2
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 27
The equation of directrix of the parabola y² = 8x is
🟥 1️⃣ x = 2
🟩 2️⃣ x = −2
🟨 3️⃣ y = 2
🟦 4️⃣ y = −2
Answer: 2️⃣ x = −2
📘 JEE Advanced 2020 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 28
The eccentricity of hyperbola x²/16 − y²/9 = 1 is
🟥 1️⃣ 5/4
🟩 2️⃣ 4/3
🟨 3️⃣ 3/2
🟦 4️⃣ 2
Answer: 2️⃣ 4/3
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 29
Equation of tangent to ellipse x²/25 + y²/9 = 1 having slope 4/3 is
🟥 1️⃣ 4x + 3y = 25
🟩 2️⃣ 4x + 3y = 20
🟨 3️⃣ 4x + 3y = 15
🟦 4️⃣ 4x + 3y = 30
Answer: 3️⃣ 4x + 3y = 15
📘 JEE Advanced 2019 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 30
For parabola y² = 4ax, the equation of chord passing through focus is
🟥 1️⃣ t₁t₂ = −1
🟩 2️⃣ t₁t₂ = 1
🟨 3️⃣ t₁ + t₂ = 0
🟦 4️⃣ t₁t₂ = 0
Answer: 3️⃣ t₁ + t₂ = 0
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 31
Equation of ellipse with focus at (3, 0), eccentricity 3/5 and centre at origin is
🟥 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
🟩 2️⃣ x²/16 + y²/25 = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x²/9 + y²/16 = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x²/16 + y²/9 = 1
Answer: 1️⃣ x²/25 + y²/16 = 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2018 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 32
Latus rectum of parabola x² = 12y is
🟥 1️⃣ 3
🟩 2️⃣ 6
🟨 3️⃣ 12
🟦 4️⃣ 24
Answer: 3️⃣ 12
📘 JEE Advanced 2017 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 33
The eccentricity of ellipse 9x² + 16y² = 144 is
🟥 1️⃣ 3/4
🟩 2️⃣ 4/5
🟨 3️⃣ 1/2
🟦 4️⃣ √(1 − 9/16)
Answer: 1️⃣ 3/4
📘 JEE Advanced 2017 (Paper 2)
🔵 Question 34
Equation of tangent to parabola y² = 4x at (1, 2) is
🟥 1️⃣ y = 2x
🟩 2️⃣ y = 2x − 1
🟨 3️⃣ y = x + 1
🟦 4️⃣ y = x − 1
Answer: 2️⃣ y = 2x − 1
📘 JEE Advanced 2016 (Paper 2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🧭 Q1–Q20: NEET Level (Basic to Moderate)
Q1. The general equation of a conic is:
🔵 (A) Ax² + By² + C = 0
🟢 (B) Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
🟠 (C) ax + by + c = 0
🔴 (D) x² + y² = r²
Answer: (B) Ax² + 2Hxy + By² + 2Gx + 2Fy + C = 0
Q2. For e = 0, the conic is a:
🔵 (A) Parabola
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Circle
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
Answer: (C) Circle
Q3. For e = 1, the conic is a:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
Answer: (C) Parabola
Q4. For e > 1, the curve is a:
🔵 (A) Circle
🟢 (B) Ellipse
🟠 (C) Parabola
🔴 (D) Hyperbola
Answer: (D) Hyperbola
Q5. Equation of a circle with centre (h, k) and radius r is:
🔵 (A) (x + h)² + (y + k)² = r²
🟢 (B) (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
🟠 (C) (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r
🔴 (D) (x + h)² + (y + k)² = r
Answer: (B) (x − h)² + (y − k)² = r²
Q6. The standard equation of a parabola with vertex at origin and axis along x-axis is:
🔵 (A) x² = 4ay
🟢 (B) y² = 4ax
🟠 (C) y² = 2ax
🔴 (D) x² = 2ay
Answer: (B) y² = 4ax
Q7. In ellipse (x²/a²) + (y²/b²) = 1, if a > b, then eccentricity is:
🔵 (A) e = c/a
🟢 (B) e = c/b
🟠 (C) e = b/a
🔴 (D) e = 0
Answer: (A) e = c/a
Q8. For ellipse, the relation between a, b, c is:
🔵 (A) c² = a² + b²
🟢 (B) c² = a² − b²
🟠 (C) a² = b² − c²
🔴 (D) b² = a² + c²
Answer: (B) c² = a² − b²
Q9. For hyperbola, the relation is:
🔵 (A) c² = a² − b²
🟢 (B) c² = a² + b²
🟠 (C) a² = b² + c²
🔴 (D) b² = a² + c²
Answer: (B) c² = a² + b²
Q10. Focus of parabola y² = 8x is:
🔵 (A) (2, 0)
🟢 (B) (4, 0)
🟠 (C) (−2, 0)
🔴 (D) (0, 2)
Answer: (A) (2, 0)
Q11. Directrix of y² = 4ax is:
🔵 (A) x = a
🟢 (B) x = −a
🟠 (C) y = a
🔴 (D) y = −a
Answer: (B) x = −a
Q12. Eccentricity of ellipse with a = 5, b = 3 is:
🔵 (A) 4/5
🟢 (B) 3/5
🟠 (C) 5/3
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 4/5
Q13. Latus rectum length of parabola y² = 12x:
🔵 (A) 12
🟢 (B) 6
🟠 (C) 3
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (A) 12
Q14. Centre of circle x² + y² − 4x + 6y = 0:
🔵 (A) (−2, 3)
🟢 (B) (2, −3)
🟠 (C) (2, 3)
🔴 (D) (−2, −3)
Answer: (A) (2, −3)
Q15. Equation of tangent to circle x² + y² = r² at (x₁, y₁):
🔵 (A) xx₁ + yy₁ = r²
🟢 (B) x + y = r²
🟠 (C) x + y = 0
🔴 (D) xx₁ + yy₁ = 0
Answer: (A) xx₁ + yy₁ = r²
Q16. The curve y² = 16x has vertex at:
🔵 (A) (4, 0)
🟢 (B) (0, 0)
🟠 (C) (8, 0)
🔴 (D) (−4, 0)
Answer: (B) (0, 0)
Q17. Latus rectum of ellipse (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1:
🔵 (A) 18/5
🟢 (B) 9/5
🟠 (C) 2b²/a = 18/5
🔴 (D) 2a²/b
Answer: (C) 18/5
Q18. Foci of hyperbola (x²/9) − (y²/4) = 1 are:
🔵 (A) (±3, 0)
🟢 (B) (±√13, 0)
🟠 (C) (0, ±3)
🔴 (D) (0, ±√13)
Answer: (B) (±√13, 0)
Q19. Asymptotes of (x²/a²) − (y²/b²) = 1 are:
🔵 (A) y = ±(a/b)x
🟢 (B) y = ±(b/a)x
🟠 (C) x = ±(b/a)y
🔴 (D) x = ±(a/b)y
Answer: (B) y = ±(b/a)x
Q20. Discriminant H² − AB < 0 implies:
🔵 (A) Ellipse
🟢 (B) Parabola
🟠 (C) Hyperbola
🔴 (D) Line
Answer: (A) Ellipse
🧭 Q21–Q40: JEE Main Level (Multi-Step Reasoning)
Q21. Equation of circle passing through (0, 0) and (2, 0) with centre on y-axis:
🔵 (A) x² + y² = 4
🟢 (B) x² + y² − 2x = 0
🟠 (C) x² + y² + 2x = 0
🔴 (D) x² + y² − 2x + 1 = 0
Answer: (B) x² + y² − 2x = 0
Q22. Focus of parabola y² = 16x is:
🔵 (A) (4, 0)
🟢 (B) (0, 4)
🟠 (C) (2, 0)
🔴 (D) (8, 0)
Answer: (A) (4, 0)
Q23. Eccentricity of ellipse 9x² + 16y² = 144 is:
Divide by 144 → (x²/16) + (y²/9) = 1 ⇒ a = 4, b = 3
e = √(1 − 9/16) = √(7/16) = √7 / 4
🔵 (A) 1/2
🟢 (B) √7 / 4
🟠 (C) 3/4
🔴 (D) √5 / 4
Answer: (B) √7 / 4
Q24. Equation of parabola whose focus is (3, 0) and directrix is x = −3:
Distance = 2a = 6 ⇒ a = 3 ⇒ equation: y² = 12x
🔵 (A) y² = 6x
🟢 (B) y² = 12x
🟠 (C) x² = 12y
🔴 (D) y² = 4x
Answer: (B) y² = 12x
Q25. Latus rectum length of ellipse (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1 is:
= 2b²/a = 2×9 / 5 = 18/5
🔵 (A) 18/5
🟢 (B) 9/5
🟠 (C) 5/9
🔴 (D) 2a
Answer: (A) 18/5
Q26. For circle x² + y² + 4x − 6y + 9 = 0, radius = ?
r² = g² + f² − c = (2² + (−3)² − 9) = 4 + 9 − 9 = 4 ⇒ r = 2
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 3
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 2
Q27. For ellipse (x²/49) + (y²/25) = 1, distance between foci:
c² = a² − b² = 49 − 25 = 24 ⇒ c = 2√6 ⇒ distance = 2c = 4√6
🔵 (A) 2√6
🟢 (B) 4√6
🟠 (C) 6
🔴 (D) 8
Answer: (B) 4√6
Q28. Equation of directrix of parabola y² = 20x:
4a = 20 ⇒ a = 5 ⇒ directrix x = −5
🔵 (A) x = 5
🟢 (B) x = −5
🟠 (C) y = 5
🔴 (D) y = −5
Answer: (B) x = −5
Q29. Coordinates of vertices of ellipse (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1:
(±a, 0) = (±5, 0)
🔵 (A) (±3, 0)
🟢 (B) (±5, 0)
🟠 (C) (0, ±3)
🔴 (D) (0, ±5)
Answer: (B) (±5, 0)
Q30. Tangent to y² = 8x at (2, 4):
yy₁ = 2a(x + x₁) → 4y = 4(x + 2) → x − y + 2 = 0
🔵 (A) x + y − 2 = 0
🟢 (B) x − y + 2 = 0
🟠 (C) y − x + 2 = 0
🔴 (D) y + x = 0
Answer: (B) x − y + 2 = 0
Q31. Centre of ellipse 9x² + 16y² − 18x + 32y − 11 = 0:
Complete squares → (x − 1)²/16 + (y + 1)²/9 = 1
Centre = (1, −1)
🔵 (A) (1, 1)
🟢 (B) (1, −1)
🟠 (C) (−1, 1)
🔴 (D) (−1, −1)
Answer: (B) (1, −1)
Q32. Circle passing through (0, 0), (2, 0), (0, 2):
Let eqn: x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy = 0
Substitute → g = f = −1 ⇒ (x − 1)² + (y − 1)² = 2
🔵 (A) x² + y² − 2x − 2y = 0
🟢 (B) (x − 1)² + (y − 1)² = 2
🟠 (C) (x + 1)² + (y + 1)² = 2
🔴 (D) x² + y² + 2x + 2y = 0
Answer: (B) (x − 1)² + (y − 1)² = 2
Q33. Parabola y² = 4x has directrix at:
🔵 (A) x = 1
🟢 (B) x = −1
🟠 (C) y = 1
🔴 (D) y = −1
Answer: (B) x = −1
Q34. Eccentricity of hyperbola (x²/9) − (y²/4) = 1:
c² = 9 + 4 = 13 ⇒ e = √13 / 3
🔵 (A) √13 / 3
🟢 (B) √5 / 3
🟠 (C) 5/3
🔴 (D) √13 / 4
Answer: (A) √13 / 3
Q35. Equation of circle with diameter joining (2, 3) and (4, 5):
Midpoint (3, 4), radius = distance/2 = √8 / 2 = √2
(x − 3)² + (y − 4)² = 2
🔵 (A) (x − 3)² + (y − 4)² = 2
🟢 (B) (x + 3)² + (y + 4)² = 2
🟠 (C) x² + y² = 2
🔴 (D) x² + y² − 6x − 8y = 0
Answer: (A) (x − 3)² + (y − 4)² = 2
Q36. Length of transverse axis of hyperbola (x²/9) − (y²/16) = 1:
= 2a = 6
🔵 (A) 6
🟢 (B) 8
🟠 (C) 10
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (A) 6
Q37. Length of conjugate axis = ?
For above, 2b = 8
🔵 (A) 8
🟢 (B) 6
🟠 (C) 4
🔴 (D) 10
Answer: (A) 8
Q38. Vertex of parabola x² = 4y is at:
🔵 (A) (0, 0)
🟢 (B) (0, 1)
🟠 (C) (1, 0)
🔴 (D) (1, 1)
Answer: (A) (0, 0)
Q39. Foci of ellipse (x²/25) + (y²/16) = 1:
c² = 25 − 16 = 9 ⇒ c = 3 ⇒ (±3, 0)
🔵 (A) (±3, 0)
🟢 (B) (±4, 0)
🟠 (C) (0, ±3)
🔴 (D) (0, ±4)
Answer: (A) (±3, 0)
Q40. Equation of tangent to ellipse (x²/9) + (y²/4) = 1 at (√5, 4/3):
(x·x₁)/a² + (y·y₁)/b² = 1 ⇒ (x·√5)/9 + (y·4/3)/4 = 1 ⇒ simplified: (√5/9)x + (y/3) = 1
🔵 (A) (√5/9)x + (y/3) = 1
🟢 (B) (√5/3)x + (y/9) = 1
🟠 (C) (√5/9)x − (y/3) = 1
🔴 (D) (√5/3)x − (y/9) = 1
Answer: (A) (√5/9)x + (y/3) = 1
🧭 Q41–Q50: JEE Advanced Level (High Conceptual)
Q41. If eccentricity of ellipse is 4/5 and latus rectum is 5, find a.
LR = 2b²/a, c = ae = 4a/5, b² = a²(1 − e²) = a²(1 − 16/25) = (9/25)a²
→ 2(9/25)a² / a = 5 ⇒ a = 25/6
🔵 (A) 25/6
🟢 (B) 6
🟠 (C) 5
🔴 (D) 4
Answer: (A) 25/6
Q42. If distance between foci of ellipse is 6 and major axis = 10, find eccentricity.
2c = 6 ⇒ c = 3, 2a = 10 ⇒ a = 5 ⇒ e = c/a = 3/5
🔵 (A) 3/5
🟢 (B) 4/5
🟠 (C) 1/2
🔴 (D) 5/3
Answer: (A) 3/5
Q43. Equation of ellipse with foci (±4, 0) and minor axis 6:
b = 3, c = 4 ⇒ a² = b² + c² = 25 ⇒ (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1
🔵 (A) (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1
🟢 (B) (x²/9) + (y²/25) = 1
🟠 (C) (x²/16) + (y²/9) = 1
🔴 (D) (x²/9) + (y²/16) = 1
Answer: (A) (x²/25) + (y²/9) = 1
Q44. Find equation of parabola with vertex at origin, focus (0, 3).
Focus ⇒ along y-axis, a = 3 ⇒ equation: x² = 12y
🔵 (A) x² = 12y
🟢 (B) y² = 12x
🟠 (C) x² = 6y
🔴 (D) y² = 6x
Answer: (A) x² = 12y
Q45. Equation of circle touching x-axis at (3, 0) and passing through (0, 4):
Centre = (3, r), since tangent at (3,0) ⇒ radius = r
Substitute (0,4): 9 + (4 − r)² = r² ⇒ 9 + 16 − 8r + r² = r² ⇒ r = 25/8 = 3.125
Equation: (x − 3)² + (y − 3.125)² = (3.125)²
🔵 (A) (x − 3)² + (y − 3.125)² = 9.77
🟢 (B) (x − 3)² + (y − 3)² = 9
🟠 (C) (x + 3)² + (y − 3)² = 9
🔴 (D) (x − 3)² + y² = 9
Answer: (A) (x − 3)² + (y − 3.125)² = 9.77
Q46. If circle x² + y² + 4x + 6y + 9 = 0 is transformed by x = X − 2, y = Y − 3, find new equation.
Substitute → (X−2)² + (Y−3)² + 4(X−2) + 6(Y−3) + 9 = 0 ⇒ X² + Y² − 4 − 9 + 9 = 0 ⇒ X² + Y² = 4
🔵 (A) X² + Y² = 4
🟢 (B) X² + Y² = 9
🟠 (C) X² + Y² = 1
🔴 (D) X² + Y² = 16
Answer: (A) X² + Y² = 4
Q47. If asymptotes of hyperbola intersect at 45°, find relation between a and b.
tanθ = b/a = 1 ⇒ a = b
🔵 (A) a = b
🟢 (B) a = 2b
🟠 (C) a = b/2
🔴 (D) a ≠ b
Answer: (A) a = b
Q48. If circle passes through origin and has centre (h, k), then equation is:
🔵 (A) x² + y² + 2hx + 2ky = 0
🟢 (B) (x − h)² + (y − k)² = h² + k²
🟠 (C) (x + h)² + (y + k)² = 0
🔴 (D) x² + y² + 2gx + 2fy = 0
Answer: (B) (x − h)² + (y − k)² = h² + k²
Q49. Find length of latus rectum of parabola x² = 16y.
4a = 16 ⇒ a = 4 ⇒ LR = 4a = 16
🔵 (A) 4
🟢 (B) 8
🟠 (C) 12
🔴 (D) 16
Answer: (D) 16
Q50. Distance between vertex and focus in parabola y² = 8x is:
4a = 8 ⇒ a = 2 ⇒ distance = 2
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 8
Answer: (A) 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MI
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
