Class 11 : History (In English) – Lesson 2. An Empire Across Three Continents
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
AN EMPIRE ACROSS THREE CONTINENTS: THE ROMAN EMPIRE
🔵 INTRODUCTION
This chapter focuses on the history of the Roman Empire, one of the greatest empires in the ancient world, which spanned across three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. It explains how this vast empire was formed, how it was governed, its economic and social structures, and how it eventually declined. The study of this empire is important because it laid down many foundations for modern systems of law, administration, and governance.
🟢 GEOGRAPHICAL SPAN AND EXPANSION
The Roman Empire covered about 5.7 million square kilometers. Its territories included present-day Britain, Spain, North Africa, Egypt, West Asia, and regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea.
➡️ Rome was the center of this massive empire.
🌿 Key Geographical Facts:
The Mediterranean Sea was called the “Heart of the Empire” as it connected many important cities.
Natural features like rivers (Danube, Rhine) and deserts provided defense.
✏️ Note: The Roman Empire was not only about military power; it was also about connecting people through roads, trade, and law.
🔴 POLITICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE STRUCTURE
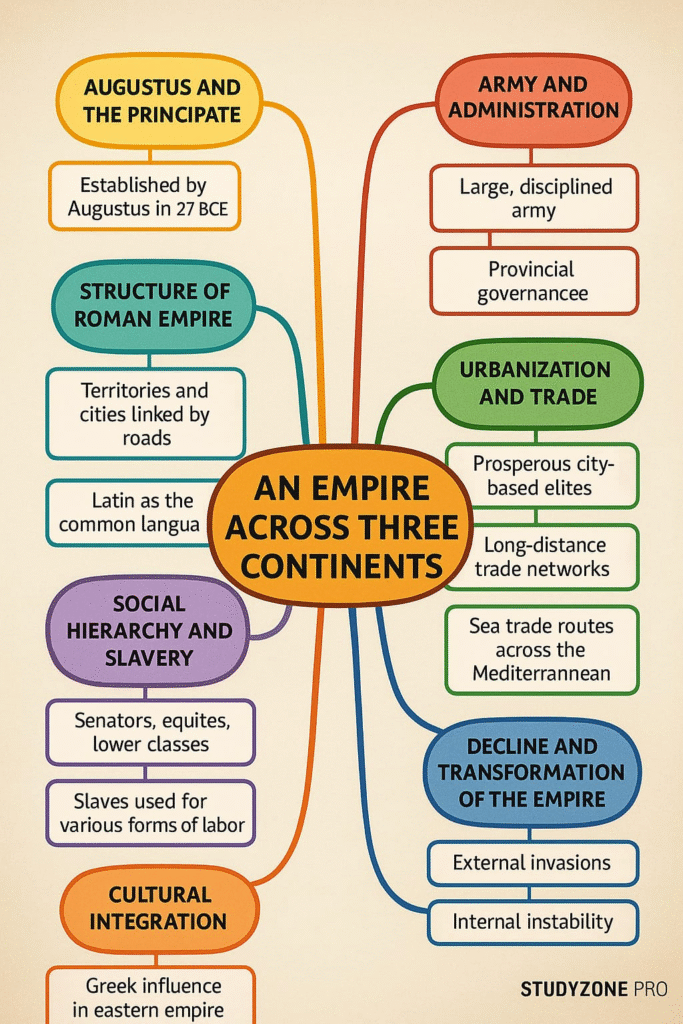
✔️ The Roman Empire was ruled first by Emperors, the most famous being Augustus.
✔️ The emperor had supreme authority, though institutions like the Senate existed but gradually lost real power.
💡 Concept: The Roman political system was highly centralized, and the emperor was considered the source of law and justice.
➡️ Provincial Administration:
The empire was divided into provinces, each headed by governors.
Provinces collected taxes and maintained law and order.
⚡ Army’s Role:
Army ensured control over borders and suppressed rebellions.
Veterans were rewarded with land and wealth.
🟡 ECONOMIC SYSTEM
The economy of the Roman Empire was based on agriculture, trade, and taxation.
🔵 Agriculture:
Agriculture was the main occupation.
Large estates called latifundia were worked by slaves.
Crops: Wheat, olives, grapes.
🔵 Trade and Commerce:
Rome had an extensive road network.
Trade routes connected Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Important imports: Spices, silk, ivory.
🔵 Taxation:
Taxes were collected in cash and kind.
Tax system funded the army, infrastructure, and administration.
✏️ Note: The Roman economy was highly interconnected, relying on both land and sea routes.
🔵 SOCIAL STRUCTURE
Roman society was hierarchical.
🧠 Key Classes:
Senators (Wealthy and powerful)
Equestrians (Rich businessmen)
Plebeians (Common people)
Slaves (No rights, treated as property)
⚡ Slavery:
Slavery was central to agriculture, mining, and households.
Some slaves could earn freedom through manumission.
💡 Concept: Social mobility was limited, but through wealth or imperial favor, lower classes could rise.
🟢 CULTURE AND RELIGION
✔️ Romans admired Greek culture, adopting arts, architecture, and philosophy.
✔️ Latin was the official language, though Greek remained important in the East.
🔴 Religion:
Polytheistic (worshipped multiple gods).
Emperor worship became common.
Christianity began in this period and faced persecution but later became the state religion.
✏️ Note: Roman architecture (arches, aqueducts, amphitheaters) remains influential even today.
🔵 DAILY LIFE IN THE ROMAN EMPIRE
🧠 Cities: Rome, Alexandria, Antioch were urban centers with theatres, baths, temples.
⚡ Urban Life:
Public baths, markets, and amphitheaters were common.
People enjoyed gladiator games, chariot races.
🟡 Rural Life:
Farmers lived in small villages.
Depended on landowners.
🔴 COMMUNICATION AND INFRASTRUCTURE
➡️ Roads: Over 80,000 kilometers of roads linked the empire. ➡️ Sea routes connected ports across the Mediterranean. ✔️ Roads were crucial for military, trade, and governance.
✏️ Note: Roman roads and aqueducts showed advanced engineering skills.
🟢 DECLINE OF THE EMPIRE
The decline began from 3rd century CE onwards.
🧠 Reasons:
Political instability and weak rulers.
Military pressure from barbarian tribes (Goths, Vandals, Huns).
Economic crisis, over-taxation.
Over-reliance on slaves.
Decline of cities and trade.
⚡ Division:
In 395 CE, the empire was divided into Eastern (Byzantine) and Western Roman Empire.
✔️ Western Empire fell in 476 CE; Eastern continued till 1453 CE.
🌿 IMPACT OF THE ROMAN EMPIRE
✔️ Basis of European law and governance. ✔️ Influence on language (Latin roots). ✔️ Spread of Christianity. ✔️ Engineering, architecture inspired future civilizations.
✏️ Note: The Roman legacy shaped the Renaissance, Enlightenment, and modern Europe.
🟢 WHY THIS LESSON MATTERS
💡 Connection to Today:
Modern ideas of law, governance, infrastructure have roots in Rome.
The spread of Christianity and culture shaped Europe and beyond.
Urban planning and architecture still reflect Roman methods.
⚡ In Competitive Exams:
Roman Empire often appears in questions related to world history, governance, and law.
📝 QUICK RECAP:
✔️ Roman Empire: 3 continents, centered on Rome.
✔️ Economy: Agriculture, trade, taxes, slavery.
✔️ Society: Class-based; slaves at bottom.
✔️ Governance: Centralized under emperor, provinces with governors.
✔️ Culture: Latin, Greek influence, arts, religion.
✔️ Decline: Due to internal and external pressures.
✔️ Legacy: Law, infrastructure, religion, language.
✨ 300-WORD SUMMARY
🔵 Summary of ‘An Empire Across Three Continents’
The Roman Empire spread across Europe, Asia, and Africa, covering 5.7 million square kilometers. Rome remained its political and cultural center. The empire was connected through roads, sea routes, and communication systems, allowing efficient governance.
The political system was centralized under the emperor, with provinces managed by governors who collected taxes and maintained law and order. The army played a vital role in defending borders and suppressing revolts.
The economy depended on agriculture, trade, taxation, and slave labor. Large estates (latifundia) were cultivated by slaves, producing wheat, olives, and grapes. An extensive network of trade routes linked Rome to Africa and Asia, ensuring the flow of luxury goods like spices and silk.
Society was divided into clear hierarchies: Senators, Equestrians, Plebeians, and Slaves. Slavery was central to both the economy and daily life, though some slaves could gain freedom.
Culturally, Romans adopted much from Greek civilization. Latin was dominant in the West, Greek in the East. Religion evolved from polytheism to Christianity, which later became the state religion. Roman architecture, engineering, and urban planning were highly advanced.
The empire declined due to political instability, economic problems, military defeats, and reliance on slaves. It split into Eastern and Western parts; the Western Empire fell in 476 CE while the Eastern survived till 1453 CE.
The Roman legacy lives on in law, language, governance, engineering, and religion, profoundly influencing modern Europe and the world.

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
QUESTION 1:
If you had lived in the Roman Empire, where would you rather have lived – in the towns or in the countryside? Explain why.
ANSWER 1:
🔴 I would prefer to live in the towns of the Roman Empire rather than in the countryside.
➡️ The towns in the Roman Empire provided better facilities, opportunities for trade, education, entertainment, and security.
🟢 In towns, there were markets, amphitheatres, public baths, paved roads, and libraries which made life more organized and cultured.
🔵 Urban life offered access to better jobs, social interactions, and political participation as compared to the monotonous rural life of farmers.
🟡 The countryside was largely dependent on agriculture and labor was harsh and backbreaking with very little scope for advancement.
✏️ Note: Town life reflected the prosperity and organization of Roman civilization and would be more preferable for a comfortable life.
QUESTION 2:
Compile a list of some of the towns, cities, rivers, seas and provinces mentioned in this chapter, and then try and find them on the maps. Can you say something about any three of the items in the list you have compiled?
ANSWER 2:
🔴 List of Places Mentioned:
Towns/Cities: Rome, Alexandria, Antioch, Carthage, Constantinople
Rivers: Rhine, Danube
Seas: Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea
Provinces: Egypt, Judea, Hispania, Britannia
🧠 Explanation of Three Important Places: 1️⃣ Rome: Capital of the Roman Empire, center of administration, culture, and political power. Known for architectural marvels like Colosseum and Roman Forum.
2️⃣ Mediterranean Sea: Referred to as ‘the heart of the empire,’ connected various parts of the empire facilitating trade, communication, and military movements.
3️⃣ Rhine River: Natural boundary of the Roman Empire, important for defense against Germanic tribes and controlling northern frontiers.
QUESTION 3:
Imagine that you are a Roman housewife preparing a shopping list for household requirements. What would be on the list?
ANSWER 3:
📝 Shopping List of a Roman Housewife:
🔹 Olive oil
🔹 Wine
🔹 Wheat/grain
🔹 Fresh fruits and vegetables
🔹 Honey
🔹 Cheese
🔹 Meat and fish
🔹 Garments (tunics, wool)
🔹 Pottery and utensils
🔹 Spices (pepper)
✏️ Note: These items were essential for a Roman household, reflecting the dietary habits, lifestyle, and availability of goods in the Roman towns.
QUESTION 4:
Why do you think the Roman government stopped coining in silver? And which metal did it begin to use for the production of coinage?
ANSWER 4:
✔️ The Roman government stopped minting silver coins due to economic crisis, shortage of silver mines, and increasing expenses of maintaining the vast empire.
➡️ To tackle the financial strain, the state reduced the silver content in coins to make them cheaper to produce.
⚡ Later, copper and bronze were increasingly used for minting coins as these metals were more abundant and cheaper.
✏️ Note: This change reflected the declining financial strength and inflationary pressures on the empire.
QUESTION 5:
Suppose the emperor Trajan had actually managed to conquer India and the Romans had held on to the country for several centuries. In what ways do you think India might be different today?
ANSWER 5:
🔵 If India had been conquered and ruled by the Romans, several aspects might have been different today:
1️⃣ Language: Latin might have influenced Indian languages deeply, just like English has today.
2️⃣ Architecture: Indian cities might have displayed Roman architectural styles—amphitheaters, aqueducts, and public baths.
3️⃣ Law and Governance: Roman legal systems could have formed the basis of Indian law, emphasizing codified laws and citizenship rights.
4️⃣ Religion: Christianity might have spread much earlier and wider in India under Roman rule.
5️⃣ Trade and Economy: Indian economy might have been more integrated with Europe through Roman trade networks.
🧠 Conclusion: India’s cultural, administrative, and linguistic landscape would have been vastly different under Roman influence.
QUESTION 6:
Go through the chapter carefully and pick out some basic features of Roman society and economy which you think make it look quite modern.
ANSWER 6:
🌿 Modern Features of Roman Society and Economy:
🔴 Urbanization: Town planning with roads, water supply (aqueducts), sanitation, and public spaces.
🔵 Trade and Commerce: Extensive trade networks connected to Asia and Africa, well-organized markets.
🟡 Infrastructure: Advanced roads, harbors, and architecture which resemble modern urban infrastructure.
🟢 Legal System: Written laws, rights of citizens, courts—basis of modern legal structures.
⚡ Monetary Economy: Use of currency, banking systems, taxation—similar to modern economies.
✔️ Diverse Society: People from different regions lived together, much like modern cosmopolitan societies.
✏️ Note: Despite being ancient, the Roman Empire’s administration, economy, and urban lifestyle appear very advanced and modern in comparison to other ancient societies.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🌸 1️⃣ 10 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs)
Q1. Which sea was considered the ‘heart’ of the Roman Empire?
(A) Red Sea
(B) Arabian Sea
(C) Mediterranean Sea
(D) Black Sea
✔️ Answer: (C) Mediterranean Sea
Q2. Which emperor is considered the founder of the Roman Empire?
(A) Nero
(B) Julius Caesar
(C) Augustus
(D) Constantine
✔️ Answer: (C) Augustus
Q3. What was the main occupation of people in the Roman Empire?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Shipbuilding
(C) Mining
(D) Education
✔️ Answer: (A) Agriculture
Q4. Roman coins were initially made from which metal?
(A) Bronze
(B) Silver
(C) Gold
(D) Copper
✔️ Answer: (B) Silver
Q5. What was the official language of the Roman Empire in the Western provinces?
(A) Greek
(B) Latin
(C) French
(D) Aramaic
✔️ Answer: (B) Latin
Q6. Which river marked the northern boundary of the Roman Empire?
(A) Danube
(B) Nile
(C) Euphrates
(D) Thames
✔️ Answer: (A) Danube
Q7. What was a ‘latifundia’ in the Roman Empire?
(A) A military fort
(B) A large agricultural estate
(C) A public bath
(D) A temple
✔️ Answer: (B) A large agricultural estate
Q8. Which of the following was a famous trade product of the Roman Empire?
(A) Silk
(B) Coal
(C) Oil
(D) Tea
✔️ Answer: (A) Silk
Q9. What was the Roman Senate?
(A) A temple
(B) A legislative body
(C) A market place
(D) A library
✔️ Answer: (B) A legislative body
Q10. Which group was at the bottom of the Roman social hierarchy?
(A) Senators
(B) Equestrians
(C) Plebeians
(D) Slaves
✔️ Answer: (D) Slaves
🌸 2️⃣ 3 FILL IN THE BLANKS QUESTIONS
Q11. The Roman Empire was spread across , , and __.
✔️ Answer: Europe, Asia, Africa
Q12. __ became the official religion of the Roman Empire in later years.
✔️ Answer: Christianity
Q13. The Roman Empire’s cities were connected by well-built __.
✔️ Answer: roads
🌸 3️⃣ 2 TRUE / FALSE QUESTIONS
Q14. Roman trade was limited only within the boundaries of Europe.
✔️ Answer: False
Q15. Roman public baths were common facilities in urban centers.
✔️ Answer: True
🌸 4️⃣ 2 ASSERTION-REASON TYPE MCQs
Q16.
Assertion (A): Roman army played a crucial role in maintaining control over the empire.
Reason (R): Roman army was responsible only for guarding the emperor’s palace.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✔️ Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false.
Q17.
Assertion (A): Rome’s economy depended largely on agriculture and trade.
Reason (R): Urban areas in Rome had no involvement in agricultural production.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✔️ Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false.
🌸 5️⃣ 3 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (30 WORDS LIMIT)
Q18. What were the main reasons for the decline of the Roman Empire?
✔️ Answer: The Roman Empire declined due to political instability, economic problems, invasions by barbarian tribes, over-taxation, and reliance on slave labor.
Q19. What was the importance of the Mediterranean Sea to the Roman Empire?
✔️ Answer: The Mediterranean Sea was central for trade, military control, and communication across the empire, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Q20. What role did slaves play in the Roman economy?
✔️ Answer: Slaves worked in agriculture, mines, households, and construction, making them essential for Rome’s economy and daily life.
🌸 6️⃣ 3 MID-LENGTH ANSWER QUESTIONS (60 WORDS LIMIT)
Q21. Describe the hierarchy of Roman society.
✔️ Answer: Roman society had a clear hierarchy: Senators were the elite rulers, Equestrians were wealthy businessmen, Plebeians were ordinary free citizens, and Slaves were at the lowest level, with no rights. Each class had distinct roles and privileges within society.
Q22. How did Roman cities reflect urban sophistication?
✔️ Answer: Roman cities had structured streets, public baths, amphitheaters, markets, libraries, and temples. These cities were well-planned with proper drainage, aqueducts, and recreational spaces, reflecting a highly urbanized and sophisticated lifestyle.
Q23. What was the role of the Roman Senate?
✔️ Answer: The Roman Senate was an advisory body to the emperor. Although its power reduced later, it was once influential in making laws, handling finances, and supervising administration and foreign policies.
🌸 7️⃣ 2 LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS (120 WORDS LIMIT)
Q24. Explain the economic structure of the Roman Empire.
✔️ Answer: The Roman economy was primarily based on agriculture, with large estates called latifundia worked by slaves. Apart from agriculture, trade was highly developed, with Rome connected to regions like India and Africa for luxury goods like spices and silk. Taxes collected in cash and kind funded the military and infrastructure. Urban centers functioned as trade hubs with markets and public spaces. The monetary economy with coins facilitated internal trade. Infrastructure like roads and ports helped the economy thrive. However, heavy taxation and reliance on slavery became weaknesses, leading to eventual decline.
Q25. Discuss the reasons behind the fall of the Roman Empire.
✔️ Answer: The fall of the Roman Empire was a gradual process influenced by several factors. Political instability due to weak rulers and civil wars weakened governance. Economic crises arose from over-taxation, inflation, and reduced agricultural productivity. Military defeats at the hands of barbarian tribes like Goths and Huns exposed vulnerabilities. The empire grew too vast to manage efficiently, causing administrative fragmentation. Dependence on slave labor stunted technological innovation. Social divisions and declining urban centers further weakened Rome. Finally, the empire split into Eastern and Western parts; the Western Roman Empire fell in 476 CE.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
