Class 11 : Geography (In English) – Lesson 2. The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
The chapter ‘The Origin and Evolution of Earth’ explains the scientific understanding of how the Earth originated and how its present form has evolved through billions of years. This lesson connects cosmology, astronomy, and earth sciences to explain Earth’s place in the universe.
🔵 Early Theories on Origin of the Earth
In ancient times, human curiosity about Earth led to various ideas about its origin. However, these ideas lacked scientific proof. Early myths and legends explained Earth’s origin through divine or supernatural acts.
🟢 Modern scientific approaches replaced myths with evidence-based explanations through observation, experiments, and logic.
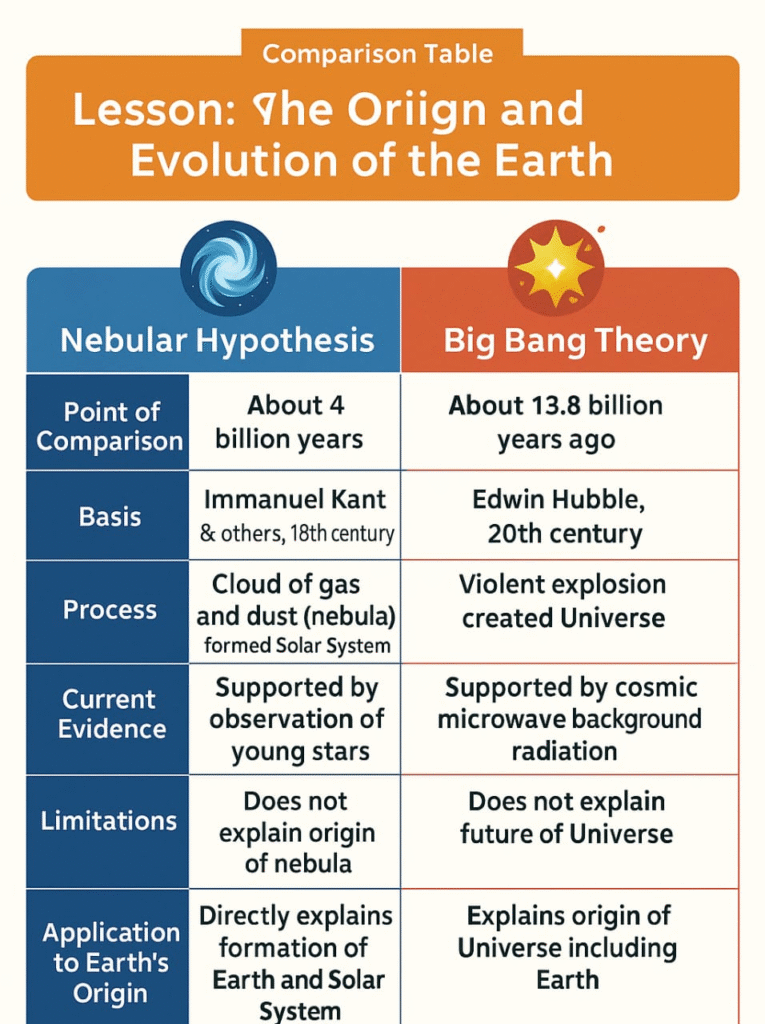
🔴 Big Bang Theory (Formation of Universe)
➡️ The most accepted theory about the origin of the universe is the Big Bang Theory.
➡️ Proposed in 1931 by Belgian scientist George Lemaitre.
🌿 Main Points of Big Bang Theory:
✔️ Universe originated from a single tiny, dense, and hot point called a singularity about 13.7 billion years ago.
✔️ A huge explosion (Big Bang) scattered this energy in all directions.
✔️ Matter began forming as particles cooled.
✔️ Gradually, galaxies, stars, and planets formed.
💡 Concept: Universe is still expanding.
✏️ Note: The lightest elements, hydrogen and helium, were formed first.
🟢 Formation of Stars and Galaxies
🌿 Formation of Galaxies:
✔️ After the Big Bang, clouds of gases condensed under gravity forming galaxies.
✔️ Our galaxy is called the Milky Way .
🌿 Formation of Stars:
✔️ Stars were formed from huge clouds of gases and dust called nebulae .
✔️ Gravitational force compressed gases, raising temperature and igniting nuclear fusion.
✔️ Sun is a star formed in this way.
🔴 Solar System Formation
➡️ The Solar System formed about 4.6 billion years ago from a rotating cloud of gas and dust known as the solar nebula.
🌿 Stages of Formation:
1️⃣ Gravitational forces pulled particles together.
2️⃣ Sun formed at the center due to maximum mass concentration.
3️⃣ Remaining matter formed planets, moons, asteroids.
🧠 Concept: This theory is called the Nebular Hypothesis .
✔️ Earth is the third planet from the Sun.
🟡 Evolution of Earth
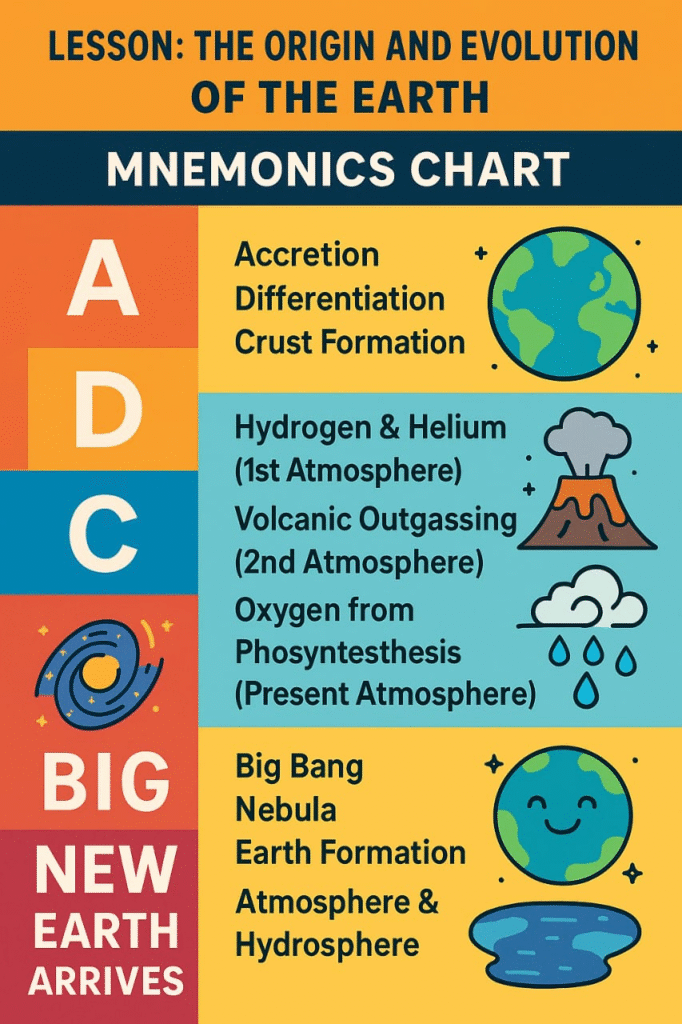
🔵 Stage 1: Accretion of Particles
➡️ Small particles collided and merged due to gravity, forming larger bodies.
➡️ These gradually formed the Earth.
🔵 Stage 2: Differentiation
➡️ Heavier materials (iron, nickel) moved to the center forming the core .
➡️ Lighter materials formed the crust and mantle .
🌿 Earth’s Structure Today:
✔️ Core — Inner most, metallic
✔️ Mantle — Semi-solid
✔️ Crust — Outer solid surface
✏️ Note: This internal layering is called chemical differentiation.
🔴 Origin of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
🌿 Formation of Atmosphere
✔️ Initially, Earth had no atmosphere.
✔️ Volcanic eruptions released gases: Water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide.
✔️ Cooling allowed water vapor to condense as rain.
🧠 Concept: First atmosphere lacked free oxygen.
🌿 Formation of Hydrosphere
✔️ Continuous rainfall filled depressions forming oceans.
✔️ Oceans absorbed carbon dioxide, reducing its amount in the air.
🟢 Origin of Life on Earth
🌿 Conditions for Life:
✔️ Suitable temperature
✔️ Presence of water
✔️ Protective atmosphere
➡️ Life is believed to have started about 3.8 billion years ago in oceans.
⚡ Chemical Evolution Theory: Life started from simple molecules forming complex organic compounds.
🌿 Stages:
1️⃣ Formation of amino acids
2️⃣ Formation of proteins
3️⃣ Creation of primitive cells (protocells)
✏️ Note: This theory is supported by Miller-Urey experiment (1953).
🔴 Evolution of Present Atmosphere
➡️ Over time, photosynthetic organisms released oxygen (O₂).
➡️ Oxygen formed ozone (O₃) layer, protecting Earth from harmful radiation.
🌿 Present Atmosphere Composition:
✔️ Nitrogen – 78%
✔️ Oxygen – 21%
✔️ Other gases – 1%
💡 Impact: This atmosphere supports complex life.
🟡 Evolution of Continents and Oceans
➡️ Initially Earth’s crust was unstable.
➡️ Continents formed from rising lighter materials.
➡️ Oceans formed in low-lying areas filled with water.
🌿 Theory of Plate Tectonics:
✔️ Earth’s crust divided into plates.
✔️ Movement of plates shaped continents and oceans.
🔵 Geological Time Scale
➡️ Earth’s history is divided into Eras, Periods, and Epochs.
🧠 Major Eras:
1️⃣ Precambrian Era – Origin of Earth, first life
2️⃣ Paleozoic Era – First plants, fishes
3️⃣ Mesozoic Era – Dinosaurs, reptiles
4️⃣ Cenozoic Era – Mammals, humans
✏️ Note: Human evolution is very recent in Earth’s timeline.
🔴 Role of Earth’s Magnetic Field
➡️ Earth’s molten outer core generates magnetic field.
➡️ Protects Earth from harmful solar winds.
💡 Importance: Keeps atmosphere intact, aids navigation.
🟢 Why This Lesson Matters:
✔️ Helps understand Earth’s place in the universe.
✔️ Explains origin of life, continents, atmosphere.
✔️ Makes us aware of environmental fragility.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔵 Big Bang – 13.7 billion years ago
🟢 Solar System – 4.6 billion years ago
🔴 Earth formation – Accretion, Differentiation
🟡 Atmosphere, Oceans – Volcanic activity, Rain
🌿 Life – 3.8 billion years ago
✔️ Continents – Plate tectonics
✨ Summary (300 Words)
🔵 The Origin and Evolution of Earth describes the scientific processes behind Earth’s formation and development.
🟢 The Big Bang Theory explains the universe’s origin about 13.7 billion years ago. Matter cooled, forming galaxies and stars like our Sun.
🔴 The Solar System emerged about 4.6 billion years ago through the Nebular Hypothesis, where dust and gases formed planets including Earth.
🟡 Earth’s formation involved Accretion of particles and Differentiation into Core, Mantle, and Crust.
🌿 Atmosphere originated through volcanic emissions of gases like water vapor and CO₂. Cooling condensed vapor into water, forming Hydrosphere (oceans).
🧠 Life began about 3.8 billion years ago in oceans through chemical evolution, supported by experiments like Miller-Urey. Photosynthesis gradually released oxygen, creating the ozone layer.
⚡ Continents formed through plate tectonics, shaping the Earth’s land and oceans. Geological time is divided into Eras—Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic—marking milestones like the appearance of plants, animals, and humans.
🌍 Earth’s magnetic field from its core protects life from solar radiation and maintains atmospheric stability.
✔️ This lesson helps us understand Earth’s uniqueness, environmental significance, and humanity’s place in this vast timeline. It connects natural sciences to environmental awareness and sustainable living.
➡️ Understanding Earth’s origin enhances our appreciation for its fragility and the need for conservation.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Q 1. Multiple Choice Questions
(i) Which one of the following figures represents the age of the Earth?
(A) 4.6 million years
(B) 4.6 billion years
(C) 13.7 billion years
(D) 13.7 trillion years
✅ Answer: (B) 4.6 billion years
(ii) Which one of the following is not related to the formation or modification of the present atmosphere?
(A) Solar winds
(B) Differentiation
(C) Degassing
(D) Photosynthesis
✅ Answer: (B) Differentiation
(iii) Life on the Earth appeared around how many years before the present?
(A) 13.7 billion
(B) 4.6 billion
(C) 3.8 million
(D) 3.8 billion
✅ Answer: (D) 3.8 billion
🔴 Q 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) What is meant by the process of differentiation?
✅ Answer: Differentiation is the process through which Earth separated into different layers based on the density of materials. Heavier elements like iron moved towards the core, while lighter materials rose to form the crust.
(ii) What was the nature of the Earth’s surface initially?
✅ Answer: Initially, the Earth’s surface was extremely hot, with frequent volcanic eruptions. It was unstable, lacked a solid crust, and had constant bombardment from cosmic debris.
(iii) What were the gases which initially formed the Earth’s atmosphere?
✅ Answer: The gases that initially formed the Earth’s atmosphere were hydrogen, helium, water vapor, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and ammonia released through volcanic activities. Oxygen was absent initially.
🟢 Q 3. Answer the following questions in about 150 words.
(i) Write an explanatory note on the ‘Big Bang Theory’.
✅ Answer: The Big Bang Theory explains the origin of the Universe. It states that around 13.7 billion years ago, the entire Universe existed as a singular, dense, and hot mass. A massive explosion, termed the Big Bang, caused this dense mass to expand rapidly. As it expanded, the temperature decreased, allowing particles to combine and form simple elements like hydrogen and helium. Gradually, clouds of these gases condensed under gravity to form galaxies, stars, and other celestial bodies. The Milky Way and the Solar System, including Earth, formed later. The Universe is still expanding today. This theory is supported by scientific evidence like the cosmic microwave background radiation and the observation of galaxies moving away from each other.
(ii) List the stages in the evolution of the Earth and explain each stage in brief.
✅ Answer: The evolution of the Earth occurred in several stages:
1️⃣ Formation of Earth: Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago through accretion of dust and gas.
2️⃣ Differentiation: Heavier elements sank to form the core; lighter ones formed the crust and mantle.
3️⃣ Formation of Atmosphere and Oceans: Volcanic eruptions released gases; water vapor condensed to form oceans.
4️⃣ Origin of Life: Life appeared about 3.8 billion years ago in oceans through chemical evolution.
5️⃣ Formation of Present Atmosphere: Oxygen produced by photosynthesis led to the ozone layer and supported life.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔵 1️⃣ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) (Q1–Q10)
🌷 Q1. Which scientist first proposed the Big Bang Theory?
(A) George Lemaitre
(B) Isaac Newton
(C) Galileo
(D) Alfred Wegener
✅ Answer: (A) George Lemaitre
🌷 Q2. Which of the following is the correct sequence of the formation of the universe?
(A) Planets → Stars → Universe
(B) Stars → Planets → Universe
(C) Big Bang → Galaxies → Stars → Planets
(D) Galaxies → Big Bang → Planets
✅ Answer: (C) Big Bang → Galaxies → Stars → Planets
🌷 Q3. Which of these is NOT part of the early atmosphere of Earth?
(A) Water vapour
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Oxygen
(D) Carbon dioxide
✅ Answer: (C) Oxygen
🌷 Q4. Which term describes the division of Earth into core, mantle, and crust?
(A) Accretion
(B) Differentiation
(C) Degassing
(D) Fusion
✅ Answer: (B) Differentiation
🌷 Q5. Which layer of the Earth is composed mainly of iron and nickel?
(A) Crust
(B) Mantle
(C) Inner Core
(D) Lithosphere
✅ Answer: (C) Inner Core
🌷 Q6. How did oceans primarily form on Earth?
(A) Due to asteroid impacts
(B) Due to condensation of water vapour
(C) Due to rivers
(D) Due to melting glaciers
✅ Answer: (B) Due to condensation of water vapour
🌷 Q7. What caused the release of gases to form Earth’s early atmosphere?
(A) Meteor showers
(B) Volcanic eruptions
(C) Rainfall
(D) Earthquakes
✅ Answer: (B) Volcanic eruptions
🌷 Q8. Which element was absent in the Earth’s first atmosphere?
(A) Nitrogen
(B) Hydrogen
(C) Oxygen
(D) Helium
✅ Answer: (C) Oxygen
🌷 Q9. What process formed the Earth about 4.6 billion years ago?
(A) Accretion of cosmic particles
(B) Cooling of water
(C) Folding of mountains
(D) Creation of life
✅ Answer: (A) Accretion of cosmic particles
🌷 Q10. What protects Earth from harmful solar winds?
(A) Hydrosphere
(B) Lithosphere
(C) Magnetic field
(D) Atmosphere
✅ Answer: (C) Magnetic field
🟢 2️⃣ FILL IN THE BLANKS (Q11–Q13)
🌿 Q11. Earth’s atmosphere initially lacked __ gas.
✅ Answer: Oxygen
🌿 Q12. The process through which Earth’s interior separated into layers is called __.
✅ Answer: Differentiation
🌿 Q13. Oceans were formed as water vapour condensed and filled __ on Earth’s surface.
✅ Answer: Depressions
🔴 3️⃣ TRUE / FALSE (Q14–Q15)
🍀 Q14. The process of photosynthesis contributed to the release of oxygen in the atmosphere.
✅ Answer: True
🍀 Q15. Earth’s magnetic field is generated by its crust.
✅ Answer: False
🟡 4️⃣ ASSERTION AND REASON (Q16–Q17)
🌼 Q16.
Assertion (A): Earth’s early atmosphere had no oxygen.
Reason (R): Oxygen was produced later through photosynthesis by early organisms.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🌼 Q17.
Assertion (A): Oceans are essential for regulating Earth’s climate.
Reason (R): Oceans absorb carbon dioxide and store heat.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🔵 5️⃣ SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (30 words limit) (Q18–Q20)
💠 Q18. What is meant by accretion in Earth’s formation?
✅ Answer: Accretion is the gradual growth of Earth by accumulation and collision of cosmic particles under gravitational forces about 4.6 billion years ago.
💠 Q19. What was the role of volcanoes in forming the atmosphere?
✅ Answer: Volcanoes released gases like water vapour, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide which helped form the early atmosphere.
💠 Q20. Why is the magnetic field important for Earth?
✅ Answer: Earth’s magnetic field protects from harmful solar winds and helps maintain the atmosphere.
🟢 6️⃣ MID-LENGTH ANSWER QUESTIONS (60 words limit) (Q21–Q23)
🌟 Q21. Describe the formation of the present-day atmosphere.
✅ Answer: The present atmosphere evolved through volcanic outgassing. Initial gases were replaced as photosynthesis increased oxygen. Carbon dioxide reduced due to ocean absorption, forming an atmosphere rich in nitrogen and oxygen.
🌟 Q22. How did life originate on Earth?
✅ Answer: Life originated about 3.8 billion years ago through chemical evolution in oceans. Simple molecules formed complex compounds, creating primitive cells through processes like Miller-Urey experiment demonstrated.
🌟 Q23. Write the main characteristics of the Earth’s early surface.
✅ Answer: The early Earth’s surface was hot, unstable, and lacked a solid crust. It had frequent volcanic activity and bombardment by cosmic bodies, creating harsh living conditions.
🔴 7️⃣ LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS (120 words limit) (Q24–Q25)
🌻 Q24. Explain the stages of the Earth’s formation in brief.
✅ Answer: Earth formed 4.6 billion years ago through accretion. Initially, small particles combined under gravity forming a large mass. Through differentiation, heavier materials moved towards the core forming iron-nickel core; lighter materials formed the crust. Volcanic eruptions released gases forming the early atmosphere. Water vapour condensed into oceans. Life appeared in oceans and gradually, oxygen accumulated creating a life-supporting atmosphere. Continents and oceans evolved with time through tectonic processes.
🌻 Q25. Describe the importance of Big Bang Theory in understanding Earth’s origin.
✅ Answer: The Big Bang Theory explains the universe’s origin about 13.7 billion years ago. It describes how matter expanded from a singularity forming galaxies, stars, and planets. Understanding this helps trace Earth’s formation as part of the Solar System. It links cosmic events to Earth’s evolution, making it foundational to geographical and astronomical studies.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
