Class 11 : Geography (In English) – Lesson 15. India: Location
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
This chapter focuses on understanding the location of (India) from the geographical perspective. It deals with India’s position on the globe, its longitudinal and latitudinal extent, standard time, and its importance at the national and international levels.
🔵 Location of (India) on the Globe
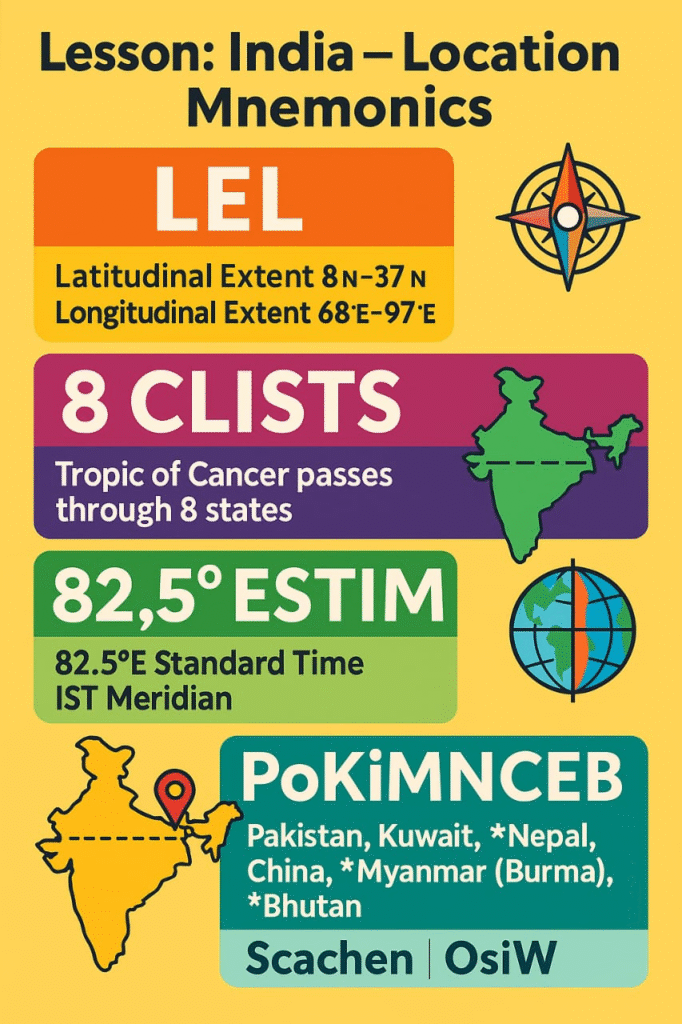
(India) is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere. It lies between latitudes 8°4’ North and 37°6’ North and longitudes 68°7’ East and 97°25’ East.
➡️ Tropic of Cancer (23°30’ North) passes approximately through the middle of the country, dividing it into almost two equal halves – the Northern Temperate Zone and the Torrid Zone.
🌿 Extension from East to West: About 2,933 km
🌿 Extension from North to South: About 3,214 km
🟢 Size of (India)
➡️ (India) has an area of about 32.87 lakh square kilometres.
➡️ It accounts for 2.4% of the total geographical area of the world.
➡️ (India) is the seventh largest country in the world by area.
🧠 Land Boundary: Approximately 15,200 km
🧠 Coastline including (Andaman) and (Nicobar): 7,516.6 km
🔴 India’s Neighbours
(India) shares its boundaries with 7 countries –
1️⃣ Pakistan
2️⃣ Afghanistan
3️⃣ China
4️⃣ Nepal
5️⃣ Bhutan
6️⃣ Bangladesh
7️⃣ Myanmar
🌿 Water Boundaries:
Arabian Sea)
Bay of Bengal)
Indian Ocean)
🟡 Significance of India’s Location
🔵 Location at the Head of Indian Ocean
➡️ India) commands the important sea routes of the Indian Ocean connecting Western Asia,Africa and South-East Asia.
🧠 Impact: Strengthens India’s strategic importance in trade, politics, and defence.
🔵 India as a Link Between East and West
➡️ From ancient times, India acted as a bridge between East) and West through trade routes – both land and sea.
💡 Concept: The Silk Route and Spice Route enhanced India’s global cultural and economic connections.
🔵 Proximity to Tropic of Cancer
➡️ Due to its central location between the East and West, and stretching between the Torrid and Temperate Zones, Indiaexperiences diverse climates, vegetation, and agriculture.
🟢 Time and Standard Meridian
➡️ The longitudinal extent of India results in a time difference of nearly 2 hours between its eastern and western extremes.
➡️ To standardize time, 82°30’ E longitude passing through Mirzapur) in (Uttar Pradesh) is adopted as the Indian Standard Time (IST).
🧠 IST is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
✏️ Note: This prevents confusion in daily life, government functions, and communication across the country.
🔴 India’s Strategic and Geographical Importance
🌿 India’s position in the Indian Ocean: Provides access to Middle East, Africa, Europe on the West and South-East Asia, Australia on the East.
➡️ Controls sea routes – vital for international trade and naval dominance.
🌿 Geographical Diversity: Mountains in the north, plains, plateaus, deserts, rivers, forests, and coastal regions.
💡 Concept: Its location shapes its climate, agriculture, biodiversity, and economic activities.
🟡 Real-life Application and Connection
➡️ Trade Routes: Major sea ports like Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, connect India globally.
➡️ Cultural Exchange: India’s location helped in exchanges with Greece, Iran, Arab nations and China since ancient times.
➡️ Geopolitical Importance: India’s location makes it a key player in Indian Ocean geopolitics, shaping relations with global powers.
🔴 Why This Lesson Matters
✔️ Helps understand India’s geographical advantages.
✔️ Explains India’s strategic role in world trade and politics.
✔️ Provides clarity on India’s diverse natural and cultural landscape.
✔️ Builds foundational knowledge for future geography and geopolitics studies.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔵 Latitudinal extent: 8°4’ N to 37°6’ N
🟢 Longitudinal extent: 68°7’ E to 97°25’ E
🔴 IST: 82°30’ E through Mirzapur.
🟡 7 neighbouring countries
🌿 Strategic location in Indian Ocean
✔️ Acts as a bridge between East and West
✨ Summary (300 Words)
🔵 India’s Location chapter explains the geographical position of India on the world map and its global importance.
🟢 India lies between latitudes 8°4’ N and 37°6’ N and longitudes 68°7’ E and 97°25’ E. The Tropic of Cancer (23°30’ N) divides it into two halves. It covers an area of 32.87 lakh sq km, ranks seventh largest globally, with 15,200 km land boundary and 7,516.6 km coastline.
🔴 India shares borders with Pakistan, Afghanistan,China,Nepal, Bhutan ,Bangladesh, and Myanmar. Water bodies surround it on three sides – Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean.
🟡 India’s location provides it with a strategic advantage in the Indian Ocean, linking trade between the West and South-East Asia. It is centrally positioned for maritime trade and cultural exchange, historically and presently.
🌿 The Indian Standard Time (IST) is fixed at 82°30’ E longitude through Mirzapur, 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT, to manage the east-west time difference.
✔️ India’s geography influences its climate, biodiversity, agriculture, trade, and global relations. This lesson builds foundational understanding of how geography shapes a country’s role globally.
➡️ Understanding India’s location strengthens knowledge of its geography and strategic significance in world affairs.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Q 1. Multiple Choice Questions
(i) Which one of the following latitudinal extent is relevant for the extent of India’s area?
(A) 8°41’N – 35°7’N
(B) 8°4’N – 37°6’N
(C) 8°4’N – 35°6’N
(D) 6°45’N – 37°6’N
✅ Answer: (B) 8°4’N – 37°6’N
(ii) Which one of the following countries shares the longest land frontier with India?
(A) Bangladesh
(B) China
(C) Pakistan
(D) Myanmar
✅ Answer: (A) Bangladesh
(iii) Which one of the following countries is larger in area than India?
(A) China
(B) Egypt
(C) France
(D) Iran
✅ Answer: (A) China
(iv) Which one of the following longitudes is the standard meridian for India?
(A) 69°30’E
(B) 82°30’E
(C) 75°30’E
(D) 90°30’E
✅ Answer: (B) 82°30’E
🔴 Q 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Does India need to have more than one standard time? If yes, why do you think so?
✅ Answer: India is a vast country with a longitudinal extent of about 30°, causing a time difference of nearly two hours from east to west. Having more than one standard time may help improve efficiency in administration, business, and daily life in the eastern states like Arunachal Pradesh) and Nagaland).
(ii) What are the implications of India having a long coastline?
✅ Answer: India’s long coastline of 7,516.6 km is significant for trade, maritime activities, fisheries, and national security. It facilitates connections with South-East Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. It also influences the monsoon winds, supports coastal tourism, and provides access to rich marine resources.
(iii) How is the latitudinal spread of India advantageous to her?
✅ Answer: The latitudinal spread from 8°4’N to 37°6’N provides India with a variety of climates, ranging from tropical in the south to temperate in the north. This diversity supports multiple crops, biodiversity, tourism, and cultural variation. It allows year-round agricultural activities and rich natural resources.
(iv) While the sun rises earlier in the east, say Nagaland and also sets earlier, how do the watches at Kohima and New Delhi show the same time?
✅ Answer: Despite the sun rising and setting earlier in the east, India follows a single time zone based on 82°30’E longitude through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh. Therefore, the clocks in both Kohima and New Delhi show the same Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔵 1️⃣ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) (Q1–Q10)
🌷 Q1. Through which Indian city does the Standard Meridian of India pass?
(A) Delhi
(B) Mirzapur
(C) Kolkata
(D) Mumbai
✅ Answer: (B) Mirzapur
🌷 Q2. India’s total geographical area is approximately:
(A) 2.4 million sq km
(B) 3.28 million sq km
(C) 32.8 lakh sq km
(D) 7 million sq km
✅ Answer: (C) 32.8 lakh sq km
🌷 Q3. India shares its longest land boundary with which country?
(A) Pakistan
(B) Nepal
(C) Bangladesh
(D) China
✅ Answer: (C) Bangladesh
🌷 Q4. Which of the following is located in the Eastern Hemisphere?
(A) India
(B) Brazil
(C) USA
(D) Argentina
✅ Answer: (A) India
🌷 Q5. Which sea lies to the west of India?
(A) Bay of Bengal
(B) Arabian Sea
(C) Pacific Ocean
(D) Red Sea
✅ Answer: (B) Arabian Sea
🌷 Q6. The southernmost point of India is called:
(A) Indira Point
(B) Kanyakumari
(C) Port Blair
(D) Rameswaram
✅ Answer: (A) Indira Point
🌷 Q7. The Tropic of Cancer divides India into:
(A) Two unequal halves
(B) Two equal halves
(C) Three parts
(D) Northern and Eastern zones
✅ Answer: (B) Two equal halves
🌷 Q8. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) India lies entirely in the Southern Hemisphere
(B) India lies entirely in the Eastern Hemisphere
(C) India lies entirely in the Western Hemisphere
(D) India lies in both Hemispheres
✅ Answer: (B) India lies entirely in the Eastern Hemisphere
🌷 Q9. India’s coastline is approximately:
(A) 5,000 km
(B) 7,516.6 km
(C) 10,000 km
(D) 12,000 km
✅ Answer: (B) 7,516.6 km
🌷 Q10. Which neighbouring country lies to the northwest of India?
(A) Myanmar
(B) Bangladesh
(C) Afghanistan
(D) Sri Lanka
✅ Answer: (C) Afghanistan
🟢 2️⃣ FILL IN THE BLANKS (Q11–Q13)
🌿 Q11. India’s Standard Time is fixed at __ longitude.
✅ Answer: 82°30’ E
🌿 Q12. The Tropic of Cancer passes through the __ part of India.
✅ Answer: middle
🌿 Q13. India’s northernmost latitude is approximately __.
✅ Answer: 37°6’ N
🔴 3️⃣ TRUE / FALSE (Q14–Q15)
🍀 Q14. India lies entirely in the Northern Hemisphere.
✅ Answer: True
🍀 Q15. India shares maritime boundaries with Maldives and Sri Lanka.
✅ Answer: True
🟡 4️⃣ ASSERTION AND REASON (Q16–Q17)
🌼 Q16.
Assertion (A): India’s location is advantageous for trade.
Reason (R): India has a long coastline along major sea routes.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🌼 Q17.
Assertion (A): India experiences time difference across its east and west.
Reason (R): India uses two different time zones to manage this.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false.
🔵 5️⃣ SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (30 words limit) (Q18–Q20)
💠 Q18. Why is India called a subcontinent?
✅ Answer: India is called a subcontinent due to its vast size, distinct geographical identity, and cultural diversity within the larger continent of Asia.
💠 Q19. What is the significance of India’s central location?
✅ Answer: India’s central location connects Western Asia, Africa, and South-East Asia, making it important for trade, defence, and cultural exchanges.
💠 Q20. Name two neighbouring countries sharing water boundaries with India.
✅ Answer: Sri Lanka and Maldives share maritime boundaries with India.
🟢 6️⃣ MID-LENGTH ANSWER QUESTIONS (60 words limit) (Q21–Q23)
🌟 Q21. Explain the significance of 82°30’ E longitude for India.
✅ Answer: The 82°30’ E longitude passing through Mirzapur is India’s Standard Meridian. It is used to calculate Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5 hours 30 minutes ahead of GMT. This helps unify time across the country despite its wide longitudinal extent.
🌟 Q22. How does India’s location influence its climate?
✅ Answer: India’s location between the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator results in diverse climatic conditions. It experiences tropical climate in the south and temperate in the north. The long coastline affects monsoon winds, bringing rainfall.
🌟 Q23. State the strategic importance of India’s maritime position.
✅ Answer: India’s maritime position in the Indian Ocean allows it control over vital sea routes linking the West and East. It aids in defence, trade, and maritime diplomacy, strengthening India’s strategic influence.
🔴 7️⃣ LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS (120 words limit) (Q24–Q25)
🌻 Q24. Explain how India’s geographical extent influences its time, climate, and agriculture.
✅ Answer: India’s wide longitudinal spread causes a time difference of nearly 2 hours from east to west, but IST standardizes time. Latitudinally, it spans tropical to temperate zones, resulting in varied climates – hot and humid in the south, cooler in the north. This diversity supports agriculture of multiple crops – rice, wheat, tea, spices. Coastal areas benefit from fishing and maritime trade. Climate variation shapes population distribution, settlements, and livelihoods.
🌻 Q25. Describe the geographical features that make India’s location globally significant.
✅ Answer: India’s location at the head of the Indian Ocean connects it to Western Asia, Africa, and South-East Asia, facilitating ancient and modern trade routes. Its long coastline with major ports aids global commerce. The Himalayas protect the northern frontiers, while fertile plains support agriculture. Proximity to global sea routes enhances its defence and maritime dominance.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Through which place does the standard meridian of India (82°30′ E) pass?
(A) Bhopal
(B) Mirzapur
(C) Bengaluru
(D) Nagpur
✅ Answer: (B) Mirzapur
📅 Exam: DSSSB PRT, 11 Nov 2019, Shift 2
📝 Explanation: The Indian Standard Time is based on the 82°30′ E longitude, passing through Mirzapur, making it the reference meridian for IST.
🔵 Q2. The standard meridian of India is:
(A) 82° 30′ E
(B) 82° 50′ E
(C) 82° 00′ E
(D) 83° 30′ E
✅ Answer: (A) 82° 30′ E
📅 Exam: CTET Nov 2012 Paper II
📝 Explanation: Officially, IST is based on 82°30′ E, chosen as the central longitude.
🔵 Q3. India’s mainland lies between which latitudinal bands?
(A) 8°41′ N – 35°07′ N
(B) 8°04′ N – 37°06′ N
(C) 6°45′ N – 37°06′ N
(D) 8°04′ N – 35°06′ N
✅ Answer: (B) 8°04′ N – 37°06′ N
📅 Exam: SSC Geography Chapter 1 (based on NCERT)
📝 Explanation: The official latitude range of India is exactly between 8°04′ N and 37°06′ N.
🔵 Q4. Which of the following cities lies closest to India’s Standard Meridian?
(A) Bengaluru
(B) Hyderabad
(C) Kolkata
(D) Delhi
✅ Answer: (A) Bengaluru
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2018
📝 Explanation: Among given cities, Bengaluru (approximately 77°E) is nearest in longitude to IST’s reference.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
