Class 11 : Chemistry (In English) – Chapter 9: Hydrocarbons
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction
Hydrocarbons are compounds of only carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) 🧪. They form the skeleton of organic chemistry and are the basis of petroleum, natural gas, coal, and many industrial products. Hydrocarbons act as fuels, solvents, lubricants, and raw materials for polymers and drugs.
Hydrocarbons are broadly classified into Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic hydrocarbons. Each class has unique structures, properties, and reactions.
🟢 Alkanes (Saturated Hydrocarbons)
✔ General formula: CₙH₂ₙ₊₂
✔ All C–C bonds are single, sp³ hybridized, tetrahedral geometry (bond angle ~109.5°).
✔ Examples: Methane (CH₄), Ethane (C₂H₆), Propane (C₃H₈).
Nomenclature: Suffix –ane.
Isomerism in Alkanes:
Structural: chain isomers appear from butane (C₄H₁₀).
Conformational: different spatial arrangements due to rotation about C–C bond.
Eclipsed and staggered conformations (Newman projection).
Staggered is more stable due to less repulsion.
Preparation of Alkanes
Hydrogenation of alkenes/alkynes (Ni/Pt catalyst).
Wurtz reaction: 2R–X + 2Na → R–R + 2NaX.
Kolbe’s electrolysis (sodium acetate → ethane).
Reactions of Alkanes
Substitution reactions via free radical mechanism:
Halogenation (CH₄ + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + HCl, under UV light).
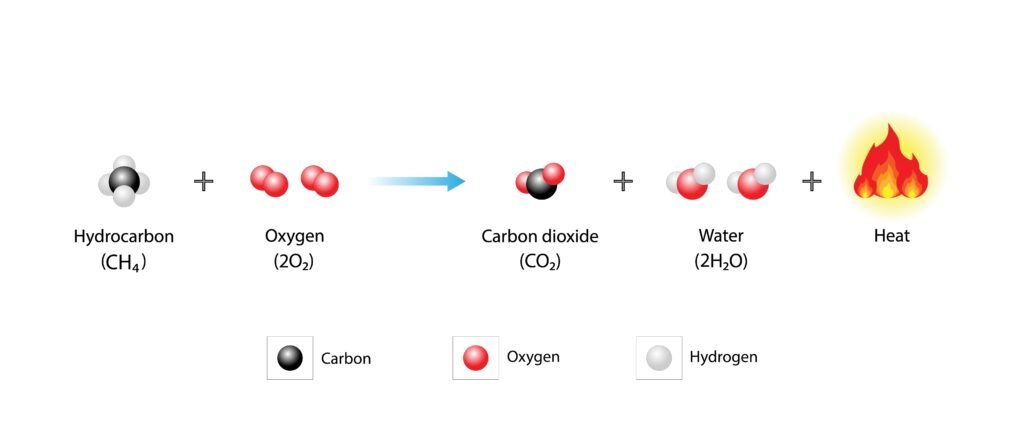
Combustion: produces CO₂ + H₂O + energy.
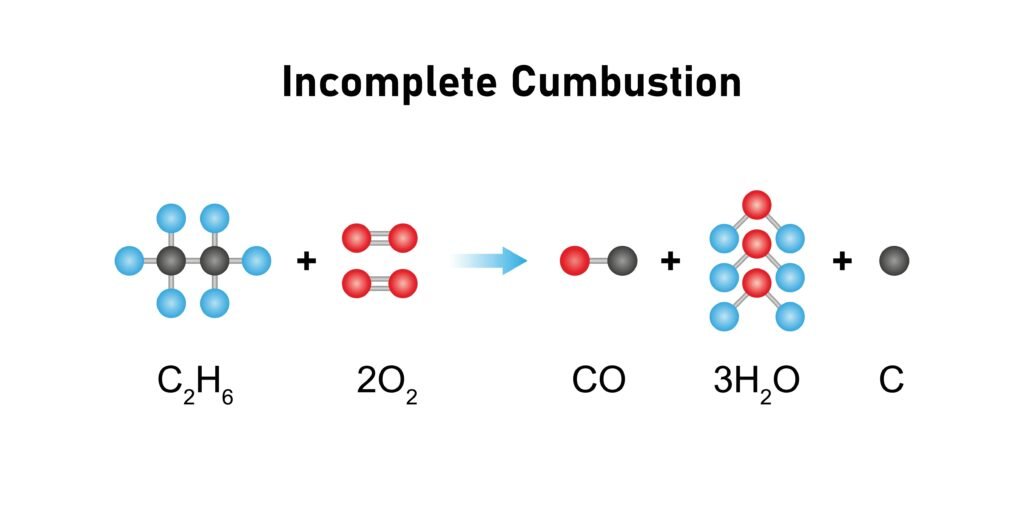
Pyrolysis (cracking): high T breaks alkanes into smaller fragments.
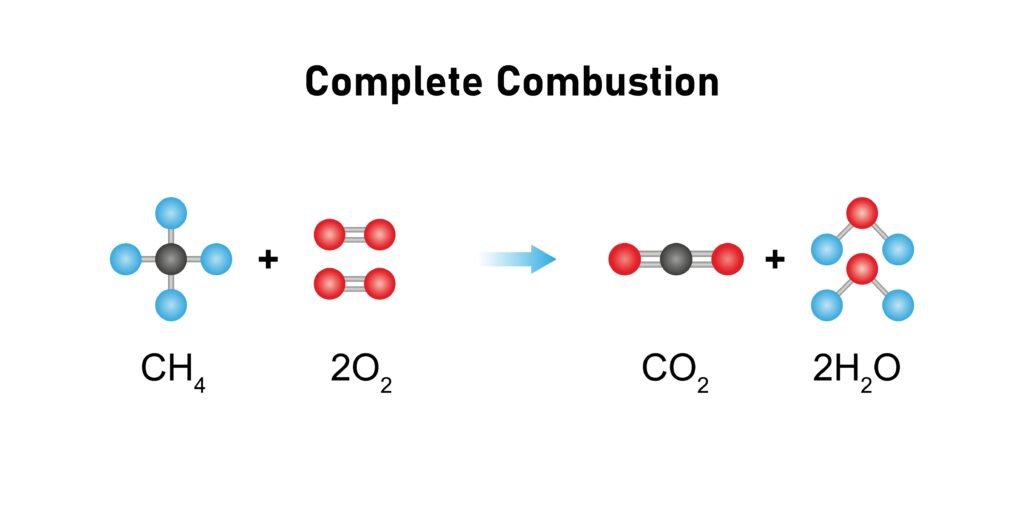
🔵 Alkenes (Unsaturated Hydrocarbons)
✔ General formula: CₙH₂ₙ
✔ Contain at least one C=C double bond (sp² hybridized, trigonal planar geometry, 120°).
✔ Example: Ethene (CH₂=CH₂).
Nomenclature: Suffix –ene.
Isomerism:
Structural (position of double bond).
Geometrical isomerism (cis–trans, due to restricted rotation around C=C).
Preparation of Alkenes
Dehydration of alcohols: CH₃CH₂OH → CH₂=CH₂ + H₂O (conc. H₂SO₄, 443 K).
Dehydrohalogenation: CH₃–CH₂–Cl + alc. KOH → CH₂=CH₂.
Kolbe’s method (from alkynes, partial hydrogenation).
Reactions of Alkenes
Addition reactions:
H₂ (hydrogenation).
Halogens (Br₂ → test for unsaturation: bromine water decolorizes).
HX (Markovnikov’s rule: H adds to C with more H).
Anti-Markovnikov addition (peroxides present).
Oxidation:
KMnO₄ (Baeyer’s test → pink color disappears).
Ozonolysis: cleavage of double bond with ozone → carbonyl compounds.
Polymerization: Ethene → Polyethylene.
🟡 Alkynes (Unsaturated, Triple Bond)
✔ General formula: CₙH₂ₙ₋₂
✔ At least one C≡C triple bond (sp hybridized, linear geometry, 180°).
✔ Example: Ethyne (C₂H₂, acetylene).
Nomenclature: Suffix –yne.
Preparation of Alkynes
Dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides (CH₂Br–CH₂Br → HC≡CH).
From calcium carbide (CaC₂ + H₂O → C₂H₂).
Reactions of Alkynes
Addition: H₂, halogens, HX (similar to alkenes).
Oxidation: KMnO₄ cleavage → acids/ketones.
Ozonolysis: forms carboxylic acids.
Acidity of terminal alkynes (pKa ~25): forms sodium acetylide with NaNH₂.
🔴 Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Arenes)
Benzene (C₆H₆) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon.
Characteristics of Aromaticity (Hückel’s Rule):
Cyclic, planar, conjugated system.
Contains (4n+2) π electrons (n = 0,1,2…).
Benzene has 6 π electrons → aromatic.
Structure of Benzene
Resonance hybrid of Kekulé structures.
All C–C bonds equal in length (140 pm).
Reactions of Benzene
Electrophilic Substitution:
Nitration: C₆H₆ + HNO₃ → C₆H₅NO₂.
Sulphonation: C₆H₆ + SO₃ → C₆H₅SO₃H.
Halogenation: C₆H₆ + Cl₂ → C₆H₅Cl.
Friedel–Crafts alkylation/acylation (R–Cl or RCOCl with AlCl₃).
Combustion: produces CO₂, H₂O, soot.
Side-chain reactions: alkylbenzenes undergo oxidation → benzoic acid.
🟢 Important Concepts Related to Hydrocarbons
1️⃣ Isomerism
Chain, position, functional, geometrical, optical.
2️⃣ Resonance in Benzene
Delocalized π electrons → stability (aromatic stabilization).
3️⃣ Tests for Unsaturation
Bromine water test (decolorization).
Baeyer’s test (alkaline KMnO₄ → decolorization).
4️⃣ Applications of Hydrocarbons
Fuels: methane, LPG, CNG, petrol, diesel.
Industrial feedstock: ethylene, propylene (plastics, polymers).
Acetylene: oxyacetylene welding.
Aromatics: benzene, toluene → solvents, drugs, dyes.
✨ Conclusion
Hydrocarbons are the simplest but most important organic compounds 🌍. They provide the framework of organic chemistry, fuels for energy, and raw materials for the chemical industry. The study of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatics sets the stage for advanced organic reactions and mechanisms.
📌 Hydrocarbons – Key Takeaways
🔵 Alkanes
Saturated (CₙH₂ₙ₊₂), single bonds, tetrahedral (109.5°).
Reactions: substitution (halogenation), combustion, cracking.
Example: Methane, propane.
🟢 Alkenes
Unsaturated (CₙH₂ₙ), double bond, planar (120°).
Show cis–trans isomerism.
Reactions: addition (H₂, HX, halogens), oxidation (ozonolysis, Baeyer’s test), polymerization.
Example: Ethene.
🔴 Alkynes
Unsaturated (CₙH₂ₙ₋₂), triple bond, linear (180°).
Reactions: addition, oxidation, acidity of terminal alkyne.
Example: Ethyne.
🟡 Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Benzene and derivatives.
Aromaticity → Hückel’s rule (4n+2 π electrons).
Electrophilic substitution: nitration, sulphonation, halogenation, Friedel–Crafts.
Side-chain oxidation → benzoic acid.
🌟 Special Notes
Resonance in benzene explains stability.
Tests for unsaturation: bromine water, KMnO₄.
📚 Applications
Fuels (CNG, LPG, petrol, diesel).
Polymers (polyethylene, polypropylene).
Acetylene in welding.
Benzene in dyes, drugs, plastics.
📝 Quick Recap:
✔ Hydrocarbons are compounds of only C and H.
✔ Alkanes: saturated, substitution + combustion reactions.
✔ Alkenes: double bond, addition reactions, polymerization, cis–trans isomerism.
✔ Alkynes: triple bond, acidic hydrogen, addition/oxidation reactions.
✔ Aromatic hydrocarbons: benzene, aromaticity, electrophilic substitution.
✔ Unsaturation detected by bromine water & Baeyer’s test.
✔ Hydrocarbons = fuels, industrial feedstock, raw materials for plastics, dyes, medicines.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 9.1:
How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
🟢 Answer:
✳ Chlorination of methane is a free radical substitution reaction.
When chlorine reacts with methane in the presence of sunlight (hv), free radicals are formed:
➡ Step 1: Chain initiation
Cl₂ → 2Cl• (by sunlight)
➡ Step 2: Chain propagation
Cl• + CH₄ → CH₃• + HCl
CH₃• + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + Cl•
🔁 The CH₃• radical can also react with another CH₃•:
✔ CH₃• + CH₃• → C₂H₆ (ethane)
💡 Thus, ethane forms as a minor product due to radical combination.
🔵 Question 9.2:
Write IUPAC names of the following compounds:
🟢 Answer:
(a) CH₃CH=C(CH₃)₂
➡ Longest chain: 4 carbons
➡ Double bond at position 2
➡ Methyl at position 3
✔ Name: 3-Methylbut-2-ene
(b) CH₂=CH–C≡C–CH₃
➡ Chain: 5 carbons
➡ Double bond at 1, triple at 3
✔ Name: Pent-1-en-3-yne
(c) ![structure with hexagon double bond CH2CH3]
Structure: Ethylbenzene
✔ Name: Ethylbenzene
(d) ![cyclohexane with propyl group]
Structure: Propylcyclohexane
✔ Name: Propylcyclohexane
(e) CH₃–CH(OH)–CH₂–CH₃
➡ 4-carbon chain with OH at position 2
✔ Name: Butan-2-ol
(f) (CH₃)₂CH–CH₂–CH(CH₃)₂
➡ Longest chain: 5 carbons
➡ Two methyls at positions 2 and 4
✔ Name: 2,4-Dimethylpentane
(g) CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH≡C–CH=CH₂
➡ 8-carbon chain
➡ Double bonds at 2,7; triple bond at 5
✔ Name: Octa-2,7-dien-5-yne
🔵 Question 9.3:
For the following compounds, write structural formulas and IUPAC names for all possible isomers having the number of double or triple bonds as indicated:
(a) C₄H₈ (one double bond)
(b) C₅H₈ (one triple bond)
🟢 Answer:
(a) C₄H₈ (one double bond)
Formula: CₙH₂ₙ → Alkenes
✔ Isomers:
1️⃣ But-1-ene → CH₂=CH–CH₂–CH₃
2️⃣ But-2-ene → CH₃–CH=CH–CH₃
3️⃣ 2-Methylprop-1-ene → CH₂=C(CH₃)₂
💡 Total = 3 isomers
(b) C₅H₈ (one triple bond)
Formula: CₙH₂ₙ₋₂ → Alkynes
✔ Isomers:
1️⃣ Pent-1-yne → HC≡C–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
2️⃣ Pent-2-yne → CH₃–C≡C–CH₂–CH₃
3️⃣ 3-Methylbut-1-yne → HC≡C–CH(CH₃)₂
💡 Total = 3 isomers
🔵 Question 9.4:
Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by ozonolysis of the following compounds:
(i) Pent-2-ene
(ii) 3,4-Dimethylhept-3-ene
(iii) 2-Ethylbut-1-ene
(iv) 1-Phenylbut-1-ene
🟢 Answer:
💥 Ozonolysis cleaves the C=C bond forming carbonyl compounds (aldehydes/ketones).
(i) Pent-2-ene:
CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₃ → on ozonolysis →
➡ CH₃–CH=O (ethanal) + CH₃–CH₂–CHO (propanal)
(ii) 3,4-Dimethylhept-3-ene:
→ CH₃–CH₂–C(CH₃)=C(CH₃)–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
➡ Products: 2 moles of 3-methylbutan-2-one
(iii) 2-Ethylbut-1-ene:
→ CH₂=CH–CH(CH₃)–CH₃
➡ Products: Methanal (HCHO) + 3-Pentanone
(iv) 1-Phenylbut-1-ene:
→ C₆H₅–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₃
➡ Products: Benzaldehyde (C₆H₅CHO) + Propanal (CH₃CH₂CHO)
🔵 Question 9.5:
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one.
Write structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
🟢 Answer:
💡 Ozonolysis breaks C=C bond into two carbonyl compounds.
Let ‘A’ = CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
On ozonolysis:
CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃ → CH₃CHO (ethanal) + CH₃COCH₂CH₃ (pentan-3-one)
✔ Structure: CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
✔ Name: Hex-2-ene
🔵 Question 9.6:
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C–C, eight C–H σ bonds and one C–C π bond.
‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u.
Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
🟢 Answer:
Aldehyde of molar mass 44 = Ethanal (CH₃CHO)
💡 Hence ‘A’ gives 2 moles of ethanal ⇒ structure must be CH₂=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₂=CH₂? No.
We need CH₂=CH–CH=CH₂ gives? No.
➡ The alkene which on cleavage gives 2 CH₃CHO = But-2-ene (CH₃–CH=CH–CH₃)
✔ Name: But-2-ene
🔵 Question 9.7:
Propanal and pentan-3-one are ozonolysis products of an alkene.
What is the structural formula of the alkene?
🟢 Answer:
💡 Combine both fragments across double bond:
Propanal: CH₃–CH₂–CHO
Pentan-3-one: CH₃–CH₂–CO–CH₂–CH₃
Reversing cleavage:
Structure of alkene = CH₃–CH₂–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃
✔ Name: Hept-3-ene
🔵 Question 9.8:
Write chemical equations for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbons:
(i) Butane (ii) Pentene (iii) Hexyne (iv) Toluene
🟢 Answer:
(i) Butane (C₄H₁₀):
C₄H₁₀ + (13/2)O₂ → 4CO₂ + 5H₂O
(ii) Pentene (C₅H₁₀):
C₅H₁₀ + (15/2)O₂ → 5CO₂ + 5H₂O
(iii) Hexyne (C₆H₁₀):
C₆H₁₀ + (17/2)O₂ → 6CO₂ + 5H₂O
(iv) Toluene (C₇H₈):
C₇H₈ + 9O₂ → 7CO₂ + 4H₂O
🔵 Question 9.9:
Draw the cis and trans structures of hex-2-ene. Which isomer has higher boiling point and why?
🟢 Answer:
✔ cis-Hex-2-ene:
CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃ (methyl groups on same side)
✔ trans-Hex-2-ene:
CH₃–CH=CH–CH₂–CH₂–CH₃ (methyl groups opposite)
💡 cis-isomer has higher boiling point due to greater polarity and stronger dipole–dipole interactions.
🔵 Question 9.10:
Why is benzene extraordinarily stable though it contains three double bonds?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Benzene has delocalised π electrons over all 6 carbons forming a resonance hybrid.
✔ Equal bond length (1.39 Å) and aromatic stability.
✔ Delocalisation energy ≈ 150 kJ/mol stabilises benzene.
✔ Hence, benzene is more stable than expected from three isolated C=C bonds.
🔵 Question 9.11:
What are the necessary conditions for any system to be aromatic?
🟢 Answer:
To be aromatic, a compound must satisfy Hückel’s rule.
✔ The conditions are:
🔹 Planarity – The molecule must be planar so that π-electrons are delocalized.
🔹 Cyclic conjugation – It must be cyclic and each atom in the ring must have a p-orbital for conjugation.
🔹 Complete delocalization – The π-electrons must be delocalized over the entire ring.
🔹 Hückel’s Rule – The number of π-electrons should satisfy 4n + 2 (n = 0,1,2,3…).
🧠 Example: Benzene has 6 π-electrons → 4n + 2 = 6 ⇒ n = 1 → ✔ Aromatic.
🔵 Question 9.12:
Explain why the following systems are not aromatic:
(i)
CH₂
╱ ╲
╲ ╱
(ii) Cyclobutadiene
(iii) Cyclooctatetraene
🟢 Answer:
(i) Cyclopropenylidene (CH₂) → lacks full conjugation; not aromatic.
(ii) Cyclobutadiene → planar and conjugated, but has 4 π-electrons (4n), ❌ fails Hückel’s rule.
(iii) Cyclooctatetraene → has 8 π-electrons (4n), adopts non-planar tub shape → ❌ not aromatic.
🔵 Question 9.13:
How will you convert benzene into:
(i) p-nitrobromobenzene
(ii) m-nitrochlorobenzene
(iii) p-nitrotoluene
(iv) acetophenone
🟢 Answer:
(i) Benzene → Bromobenzene → p-Nitrobromobenzene
Step 1: Bromination with Br₂/FeBr₃ → Bromobenzene
Step 2: Nitration with HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ → p-Nitrobromobenzene (major).
(ii) Benzene → Chlorobenzene → m-Nitrochlorobenzene
Step 1: Chlorination → Chlorobenzene
Step 2: Nitration → m-Nitrochlorobenzene (Cl is deactivating, meta-directing).
(iii) Benzene → Toluene → p-Nitrotoluene
Step 1: Friedel–Crafts alkylation with CH₃Cl/AlCl₃ → Toluene
Step 2: Nitration → p-Nitrotoluene (major).
(iv) Benzene → Acetophenone
Friedel–Crafts acylation using CH₃COCl/AlCl₃ → Acetophenone.
🔵 Question 9.14:
In the alkane H₃C–CH₂–C(CH₃)₂–CH₂–CH₃, identify 1°, 2°, 3° carbon atoms and give number of H atoms bonded to each one.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
CH₃–CH₂–C(CH₃)₂–CH₂–CH₃
➡ 1° carbon: terminal CH₃ and CH₃ groups (attached to one C) → 4 such → 4×3H = 12H
➡ 2° carbon: CH₂ (attached to 2 C) → 2 such → 2×2H = 4H
➡ 3° carbon: central C (attached to 3 C, no H) → 1 such → 0H
✅ Total = 16 H atoms ✔
🔵 Question 9.15:
What effect does branching of an alkane chain have on its boiling point?
🟢 Answer:
🔹 Branching decreases boiling point because:
It reduces surface area.
Weaker van der Waals (London dispersion) forces.
💡 Thus, n-pentane > isopentane > neopentane in b.p.
🔵 Question 9.16:
Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Without peroxide (ionic mechanism):
Markovnikov’s Rule → H adds to C with more H, Br to other.
→ Product: 2-bromopropane.
Mechanism: electrophilic addition.
✔ With peroxide (radical mechanism):
Anti-Markovnikov addition due to peroxide effect.
Free radical adds Br to less substituted carbon → 1-bromopropane.
🔵 Question 9.17:
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1,2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Ozonolysis of o-xylene yields:
Glyoxal and biacetyl → indicates presence of three double bonds in benzene ring.
✅ Supports Kekulé structure with alternating double bonds.
🔵 Question 9.18:
Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason.
🟢 Answer:
Order: C₂H₂ (ethyne) > C₆H₆ (benzene) > C₆H₁₄ (n-hexane)
✔ Reason:
Acidic strength ∝ s-character of C–H bond.
Ethyne (sp, 50%) > Benzene (sp², 33%) > Alkane (sp³, 25%).
➡ Thus, ethyne most acidic.
uestions and detailed, lucid, step-by-step answers given)
🔵 Question 9.19:
Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty?
🟢 Answer:
✔ Reason for electrophilic substitution:
Benzene is rich in π-electrons due to conjugated double bonds.
The electron cloud attracts electrophiles (electron-seeking species).
Substitution preserves the aromaticity of the ring.
✔ Reason for difficulty in nucleophilic substitution:
Benzene ring is electron-rich, so it repels nucleophiles (electron donors).
Nucleophilic substitution would require breaking aromaticity, which is energetically unfavorable.
✅ Hence, benzene prefers electrophilic substitution reactions.
🔵 Question 9.20:
How would you convert the following compounds into benzene?
(i) Ethyne
(ii) Ethene
(iii) Hexane
🟢 Answer:
(i) Ethyne → Benzene
Trimerization in presence of red-hot iron tube (873 K):
3 C₂H₂ → C₆H₆ (Benzene)
(ii) Ethene → Benzene
Convert ethene to acetylene:
C₂H₄ → C₂H₂ (by dehydrogenation)
Then trimerize acetylene:
3 C₂H₂ → C₆H₆
(iii) Hexane → Benzene
Aromatization at 773 K over Cr₂O₃ / Al₂O₃:
C₆H₁₄ → C₆H₆ + 4 H₂
🔵 Question 9.21:
Write structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2-methylbutane.
🟢 Answer:
Target product: 2-Methylbutane (C₅H₁₂)
🔹 Possible alkenes (C₅H₁₀):
1️⃣ 2-Methyl-1-butene
CH₂=C(CH₃)CH₂CH₃
2️⃣ 2-Methyl-2-butene
CH₃C(CH₃)=CHCH₃
3️⃣ 3-Methyl-1-butene (same as 2-methyl-1-butene upon rotation)
➡ All these on hydrogenation (H₂/Ni) → 2-Methylbutane
🔵 Question 9.22:
Arrange the following set of compounds in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E⁺:
(a) Chlorobenzene, 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene, p-Nitrochlorobenzene
(b) Toluene, p-H₃C–C₆H₄–NO₂, p-O₂N–C₆H₄–NO₂
🟢 Answer:
(a) Order of reactivity:
Chlorobenzene > p-Nitrochlorobenzene > 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
💡 Nitro groups are electron-withdrawing, deactivate ring for electrophilic substitution.
(b) Order of reactivity:
Toluene > p-Nitrotoluene > p-Dinitrobenzene
✔ CH₃ = electron donating → activates ring
✔ NO₂ = electron withdrawing → deactivates ring
🔵 Question 9.23:
Out of benzene, m-dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why?
🟢 Answer:
Order: Toluene > Benzene > m-Dinitrobenzene
✔ Toluene: –CH₃ group donates electrons (+I effect), activates ring.
✔ m-Dinitrobenzene: two –NO₂ groups strongly withdraw electrons, deactivate ring, nitration becomes very difficult.
🔵 Question 9.24:
Suggest the name of a Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
🟢 Answer:
Alternative Lewis acids:
✔ FeCl₃
✔ BF₃
✔ AlBr₃
These can act as catalysts in Friedel–Crafts alkylation (ethylation).
🔵 Question 9.25:
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example.
🟢 Answer:
✔ Wurtz reaction:
2 R–X + 2 Na → R–R + 2 NaX
When two different alkyl halides used → mixture of three products.
🧠 Example:
CH₃Br + C₂H₅Br + 2Na →
(i) C₂H₆
(ii) C₃H₈
(iii) C₄H₁₀
➡ Mixture formed → difficult to separate.
Hence, not preferred for odd-carbon alkanes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Section A (Q1–Q16): MCQs (1 mark each)
Q1. Which of the following is the general formula of alkanes?
CₙH₂ₙ₋₂
CₙH₂ₙ₊₂
CₙH₂ₙ
CₙH₂ₙ₊₁
Answer: 2
Q2. The hybridisation of carbon in ethene (C₂H₄) is:
sp³
sp²
sp
dsp²
Answer: 2
Q3. Which of the following reactions is used for the preparation of alkanes?
Wurtz reaction
Friedel–Crafts reaction
Kolbe reaction
Sandmeyer reaction
Answer: 1
Q4. Benzene undergoes:
Electrophilic addition
Nucleophilic addition
Electrophilic substitution
Elimination
Answer: 3
Q5. The major product in the reaction of propane with Cl₂ in presence of sunlight is:
1-chloropropane
2-chloropropane
Propan-2-ol
Dichloropropane
Answer: 2
Q6. Which of the following is not aromatic?
Benzene
Cyclooctatetraene
Naphthalene
Toluene
Answer: 2
Q7. Which of the following reactions gives acetylene (C₂H₂)?
Hydrolysis of calcium carbide
Wurtz reaction
Decarboxylation of acetic acid
Kolbe’s reaction
Answer: 1
Q8. The product obtained when benzene reacts with Cl₂ in presence of FeCl₃ is:
Chlorobenzene
Benzyl chloride
Dichlorobenzene
Benzene hexachloride
Answer: 1
Q9. The oxidising agent used in Baeyer’s test is:
HNO₃
Br₂
KMnO₄
HCl
Answer: 3
Q10. Which alkane is used as LPG?
Methane + Ethane
Propane + Butane
Pentane + Hexane
Ethane + Propane
Answer: 2
Assertion–Reason (key before first A/R)
Options:
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
A is true, but R is false
A is false, but R is true
Q11. Assertion (A): Benzene shows high stability.
Reason (R): This is due to resonance and delocalisation of π electrons.
Answer: 1
Q12. Assertion (A): Alkanes are called paraffins.
Reason (R): They are chemically less reactive due to strong C–C and C–H bonds.
Answer: 1
Q13. Assertion (A): Ethyne undergoes polymerisation to give benzene.
Reason (R): This occurs due to cyclic trimerisation of ethyne.
Answer: 1
Q14. Which of the following is an anti-knocking agent?
Tetraethyl lead
Methane
Ethanol
Benzene
Answer: 1
Q15. Ozonolysis of ethene gives:
Ethanol
Ethanal
Ethanoic acid
Formaldehyde
Answer: 2
Q16. Which of the following is aromatic according to Huckel’s rule?
Cyclobutadiene
Cyclooctatetraene
Cyclopentadienyl anion
Cycloheptatrienyl cation
Answer: 3
Section B (Q17–Q21): Very Short Answer (2 marks each)
Q17. Define aromatic hydrocarbons with one example.
🟦 Aromatic hydrocarbons are cyclic, planar compounds with conjugated π electrons satisfying Huckel’s rule (4n+2 π).
🟩 Example: Benzene (C₆H₆).
Q18. Write two differences between alkanes and alkenes.
🔷 Alkanes — saturated hydrocarbons, single bonds only.
🔶 Alkenes — unsaturated hydrocarbons, contain C=C double bond.
Q19. Name the products formed when propane undergoes complete combustion.
🟦 Propane + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + energy
✅ Products: Carbon dioxide and water.
Q20. Which catalyst is used in hydrogenation of alkenes? Write the reaction for hydrogenation of ethene.
🟨 Catalyst: Ni/Pd/Pt.
⚗ Reaction: CH₂=CH₂ + H₂ → CH₃–CH₃ (in presence of Ni).
Q21. Write two differences between electrophilic addition in alkenes and electrophilic substitution in arenes.
🟦 In alkenes: π bond breaks, electrophile adds to carbon.
🟩 In arenes: aromatic ring preserved, H replaced by electrophile.
Section C (Q22–Q28: Short Answer, 3 marks each)
Q22. State Huckel’s rule for aromaticity. Apply it to benzene.
🔷 Huckel’s rule: A cyclic, planar molecule is aromatic if it has (4n+2) π electrons.
🔶 Benzene has 6 π electrons (n=1).
🎯 Therefore, benzene is aromatic and highly stable.
Q23. Explain Wurtz reaction with equation.
🧪 Reaction: 2R–X + 2Na → R–R + 2NaX (dry ether).
🔷 Used for preparation of higher alkanes from alkyl halides.
⚗ Example: 2CH₃Cl + 2Na → C₂H₆ + 2NaCl.
Q24. Write the steps involved in ozonolysis of ethene.
🟦 Step 1: Ethene reacts with O₃ → Ozonide.
🟨 Step 2: Ozonide decomposed with Zn/H₂O → 2 molecules of ethanal.
✅ Overall: CH₂=CH₂ + O₃ → 2CH₃CHO.
Q25. Write the mechanism of halogenation of alkanes.
🧪 Step 1 (Initiation): Cl₂ → 2Cl· (UV light).
🧪 Step 2 (Propagation): CH₄ + Cl· → CH₃· + HCl; CH₃· + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + Cl·.
🧪 Step 3 (Termination): Radicals combine → stable molecules.
Q26. Differentiate between 1°, 2°, and 3° carbocations with example.
🔷 1° carbocation: –CH₂⁺ (e.g., CH₃CH₂⁺).
🔶 2° carbocation: –CH⁺– (e.g., CH₃–CH⁺–CH₃).
🟩 3° carbocation: –C⁺– (e.g., (CH₃)₃C⁺).
🎯 Stability order: 1° < 2° < 3°.
Q27. Write a short note on coal gasification.
🟦 Coal reacts with O₂ and steam → mixture of CO and H₂ (synthesis gas).
⚗ Reaction: C + H₂O → CO + H₂.
✅ Used as industrial fuel and in synthesis of methanol.
Q28. Explain with reaction: Friedel–Crafts alkylation of benzene.
🧪 Reaction: C₆H₆ + R–Cl → C₆H₅R (in presence of AlCl₃).
🔷 Mechanism: Generation of carbocation → electrophilic attack → substitution.
✅ Example: C₆H₆ + CH₃Cl → C₆H₅CH₃.
Section D (Q29–Q30: Case-Based, 4 marks each)
Q29. Read the passage and answer the questions below:
Alkenes undergo characteristic reactions due to the presence of a double bond. One of the important reactions is ozonolysis, which is useful in locating the position of a double bond.
a) Write the product of ozonolysis of propene. (1 mark)
b) State the role of zinc in ozonolysis. (1 mark)
c) Write the balanced reaction for ozonolysis of propene. (2 marks)
🟦 a) Products: Ethanal (CH₃CHO) and formaldehyde (HCHO).
🟨 b) Zinc prevents oxidation of aldehydes to acids.
🧪 c) Reaction:
CH₃–CH=CH₂ + O₃ → CH₃CHO + HCHO
Q30. Read the passage and answer the questions below:
Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions. One such reaction is nitration, carried out using a nitrating mixture.
a) Write the electrophile formed during nitration of benzene. (1 mark)
b) Write the reaction of benzene with the electrophile. (1 mark)
c) Why does benzene prefer substitution instead of addition? (2 marks)
🟦 a) Electrophile: Nitronium ion (NO₂⁺).
🟨 b) C₆H₆ + NO₂⁺ → C₆H₅NO₂ + H⁺.
🟩 c) Substitution retains aromaticity; addition would destroy resonance stabilisation.
Section E (Q31–Q33: Long Answer, 5 marks each with OR)
Q31. Explain the preparation of alkanes by (a) Wurtz reaction, (b) Kolbe’s electrolysis, and (c) Decarboxylation.
🟦 (a) Wurtz reaction: 2R–X + 2Na → R–R + 2NaX (dry ether). Example: 2CH₃Cl + 2Na → C₂H₆ + 2NaCl.
🟨 (b) Kolbe’s electrolysis: Electrolysis of sodium acetate → ethane at anode. Reaction: 2CH₃COONa → C₂H₆ + 2CO₂ + 2Na.
🟩 (c) Decarboxylation: Sodium salt of acid + soda lime → alkane. Example: CH₃COONa + NaOH → CH₄ + Na₂CO₃.
✅ Thus, different methods are used depending on the starting compound.
OR
Discuss the combustion and halogenation reactions of alkanes with equations.
🔷 Combustion: CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + Δ (energy). Complete combustion gives CO₂ + H₂O. Incomplete combustion gives CO.
🔶 Halogenation: CH₄ + Cl₂ (UV light) → CH₃Cl + HCl; further substitution yields CH₂Cl₂, CHCl₃, CCl₄.
🎯 These reactions show both industrial (fuel) and synthetic (halogenated products) importance.
Q32. Explain Markovnikov’s rule and its peroxide effect (anti-Markovnikov). Give equations.
🟦 Markovnikov’s rule: In the addition of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene, the negative part (X⁻) attaches to the more substituted carbon.
🟨 Example: CH₃–CH=CH₂ + HBr → CH₃–CHBr–CH₃.
🟩 Peroxide effect: In presence of ROOR, addition follows anti-Markovnikov’s rule due to free-radical mechanism.
🧪 Example: CH₃–CH=CH₂ + HBr (ROOR) → CH₃–CH₂–CH₂Br.
OR
Describe the mechanism of halogenation of alkanes.
🧪 Step 1 (Initiation): Cl₂ → 2Cl· (UV light).
🧪 Step 2 (Propagation): CH₄ + Cl· → CH₃· + HCl; CH₃· + Cl₂ → CH₃Cl + Cl·.
🧪 Step 3 (Termination): Radicals combine to form stable molecules.
✅ Outcome: Mixture of mono- and poly-halogenated products.
Q33. Describe the mechanism of electrophilic substitution in benzene with nitration as an example.
🟦 Step 1: Generation of electrophile (NO₂⁺): HNO₃ + H₂SO₄ → NO₂⁺ + HSO₄⁻ + H₂O.
🟨 Step 2: Attack of NO₂⁺ on benzene → σ-complex.
🟩 Step 3: Deprotonation regenerates aromaticity → nitrobenzene formed.
✅ This is called electrophilic substitution as H is replaced by electrophile.
OR
Explain the ozonolysis of alkenes. Why is it important?
🧪 Reaction: CH₂=CH₂ + O₃ → [Ozonide] → (Zn/H₂O) → 2HCHO.
🟨 Ozonolysis cleaves double bonds and gives carbonyl compounds.
🎯 Importance: Used to detect position of double bonds in unknown alkenes.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is an aromatic hydrocarbon?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: P
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following alkanes has only one isomer?
🔴 ① Methane
🟢 ② Ethane
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ① Methane
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: A
🔵 Question 3:
Which of the following alkanes does not show chain isomerism?
🔴 ① Butane
🟢 ② Pentane
🟡 ③ Hexane
🔵 ④ Propane
🟢 Answer: ④ Propane
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: O2
🔵 Question 4:
The number of possible isomers of C₄H₁₀ is:
🔴 ① 1
🟢 ② 2
🟡 ③ 3
🔵 ④ 4
🟢 Answer: ② 2
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: C
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following does not show geometrical isomerism?
🔴 ① 2-butene
🟢 ② 1-butene
🟡 ③ 2-pentene
🔵 ④ 2-hexene
🟢 Answer: ② 1-butene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: R1
🔵 Question 6:
Which hydrocarbon undergoes addition reactions most readily?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexane
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: M
🔵 Question 7:
Which hydrocarbon gives a sooty flame on burning?
🔴 ① Alkanes
🟢 ② Alkenes
🟡 ③ Alkynes
🔵 ④ Aromatic compounds
🟢 Answer: ④ Aromatic compounds
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: B
🔵 Question 8:
Which reagent is used for distinguishing between alkane and alkene?
🔴 ① Br₂ in CCl₄
🟢 ② KMnO₄ solution
🟡 ③ Ozone
🔵 ④ Both (1) and (2)
🟢 Answer: ④ Both (1) and (2)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: P
🔵 Question 9:
Which is the correct order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution?
🔴 ① Benzene < Toluene < Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② Nitrobenzene < Benzene < Toluene
🟡 ③ Toluene < Nitrobenzene < Benzene
🔵 ④ Benzene < Nitrobenzene < Toluene
🟢 Answer: ② Nitrobenzene < Benzene < Toluene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 10:
The hybridisation of carbon in acetylene is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: C
🔵 Question 11:
Which among the following is most acidic?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Ethyne
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ③ Ethyne
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: P2
🔵 Question 12:
The addition of HBr to propene in the presence of peroxide gives:
🔴 ① n-Propyl bromide
🟢 ② Isopropyl bromide
🟡 ③ Allyl bromide
🔵 ④ Vinyl bromide
🟢 Answer: ① n-Propyl bromide (Anti-Markovnikov)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: O
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following does not undergo Friedel–Crafts reaction?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: A
🔵 Question 14:
Which is the product when acetylene reacts with ammoniacal Cu₂Cl₂?
🔴 ① CuC≡CH (copper acetylide)
🟢 ② CH₃–CH₃
🟡 ③ CH₂=CH₂
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ① CuC≡CH (copper acetylide)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: M
🔵 Question 15:
Which of the following is an isomeric pair?
🔴 ① Ethane and Propane
🟢 ② Butane and Isobutane
🟡 ③ Ethane and Ethene
🔵 ④ Benzene and Toluene
🟢 Answer: ② Butane and Isobutane
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2011 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following shows resonance?
🔴 ① Cyclohexane
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Ethane
🔵 ④ Propane
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2008 | Set: C
🔵 Question 17:
Which hydrocarbon gives a positive Baeyer’s test?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexane
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: S
🔵 Question 18:
The reaction of benzene with Cl₂/FeCl₃ gives:
🔴 ① Chlorobenzene
🟢 ② Benzyl chloride
🟡 ③ Dichlorobenzene
🔵 ④ Benzyl alcohol
🟢 Answer: ① Chlorobenzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2001 | Set: A
🔵 Question 19:
Which of the following does not give addition reaction?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: R
🔵 Question 20:
Which is the correct order of reactivity towards hydrogenation?
🔴 ① Alkynes > Alkenes > Alkanes
🟢 ② Alkenes > Alkynes > Alkanes
🟡 ③ Alkanes > Alkenes > Alkynes
🔵 ④ Benzene > Alkenes > Alkynes
🟢 Answer: ② Alkenes > Alkynes > Alkanes
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: B
🔵 Question 21:
Which is the major product of nitration of benzene?
🔴 ① m-Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② o-Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ p-Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Nitrobenzene
🟢 Answer: ④ Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: P
🔵 Question 22:
Which hydrocarbon is most reactive in electrophilic substitution?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: S1
🔵 Question 23:
Which of the following is formed when acetylene reacts with hydrogen in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene (cis)
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Vinyl chloride
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene (cis)
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: A
🔵 Question 24:
Which of the following does not decolourise bromine water?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Propene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: R1
🔵 Question 25:
Which of the following is an alkyne?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② C₂H₆
🟡 ③ C₂H₂
🔵 ④ C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: ③ C₂H₂
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: B
🔵 Question 26:
The reaction of ethene with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO₄ solution gives:
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethanol
🟡 ③ Ethane-1,2-diol
🔵 ④ Acetaldehyde
🟢 Answer: ③ Ethane-1,2-diol
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: P
🔵 Question 27:
Which of the following is aromatic according to Huckel’s rule?
🔴 ① Cyclobutadiene
🟢 ② Cyclooctatetraene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclopentadiene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2003 | Set: C
🔵 Question 28:
Which of the following has maximum heat of hydrogenation?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Cyclohexene
🟡 ③ 1,3-Butadiene
🔵 ④ Ethene
🟢 Answer: ④ Ethene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 29:
The product of ozonolysis of ethene is:
🔴 ① Acetaldehyde
🟢 ② Formaldehyde
🟡 ③ Acetone
🔵 ④ Ethanol
🟢 Answer: ① Acetaldehyde
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2001 | Set: A
🔵 Question 30:
Which of the following reactions follows Markovnikov’s rule?
🔴 ① Addition of HBr to propene in absence of peroxide
🟢 ② Addition of HBr to propene in presence of peroxide
🟡 ③ Addition of HCl to acetylene with peroxide
🔵 ④ Addition of Br₂ to ethene
🟢 Answer: ① Addition of HBr to propene in absence of peroxide
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2012 | Set: O
🔵 Question 31:
Which compound does not give test with ammoniacal AgNO₃?
🔴 ① Ethyne
🟢 ② Propyne
🟡 ③ 2-Butyne
🔵 ④ Acetylene
🟢 Answer: ③ 2-Butyne
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2007 | Set: C
🔵 Question 32:
Which of the following is not an alkyne?
🔴 ① C₂H₂
🟢 ② C₃H₄
🟡 ③ C₄H₆
🔵 ④ C₃H₈
🟢 Answer: ④ C₃H₈
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: S
🔵 Question 33:
Which is the major product when benzene reacts with conc. HNO₃ in presence of conc. H₂SO₄?
🔴 ① o-Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② p-Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ m-Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Nitrobenzene
🟢 Answer: ④ Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: O
🔵 Question 34:
Which of the following undergoes substitution reaction most easily?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Ethene
🔵 ④ Ethyne
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2004 | Set: B
🔵 Question 35:
Which of the following is anti-aromatic?
🔴 ① Cyclooctatetraene
🟢 ② Cyclopropenyl cation
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Toluene
🟢 Answer: ② Cyclopropenyl cation
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: L
🔵 Question 36:
Which compound will not decolourise Baeyer’s reagent?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Propyne
🔵 ④ But-1-ene
🟢 Answer: ① Benzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: C
🔵 Question 37:
Which hydrocarbon gives a white precipitate with ammoniacal AgNO₃ solution?
🔴 ① Acetylene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Ethane
🟢 Answer: ① Acetylene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 38:
In electrophilic substitution reactions, nitro group in nitrobenzene is:
🔴 ① o- and p-directing
🟢 ② m-directing
🟡 ③ Activating
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ② m-directing
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: M
🔵 Question 39:
Which of the following is least reactive towards electrophilic substitution?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Anisole
🟢 Answer: ② Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2008 | Set: A
🔵 Question 40:
The correct order of decreasing stability is:
🔴 ① Benzene > Anthracene > Naphthalene
🟢 ② Anthracene > Benzene > Naphthalene
🟡 ③ Benzene > Naphthalene > Anthracene
🔵 ④ Naphthalene > Benzene > Anthracene
🟢 Answer: ① Benzene > Anthracene > Naphthalene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2019 | Set: P
🔵 Question 41:
Which hydrocarbon gives substitution reaction with Cl₂ in sunlight?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Ethyne
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ① Ethane
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2002 | Set: C
🔵 Question 42:
Which of the following alkanes does not show isomerism?
🔴 ① Butane
🟢 ② Propane
🟡 ③ Pentane
🔵 ④ Hexane
🟢 Answer: ② Propane
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2016 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 43:
Which compound will undergo polymerisation?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethane
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Methane
🟢 Answer: ① Ethene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2014 | Set: M
🔵 Question 44:
The reaction of acetylene with water in presence of Hg²⁺/H₂SO₄ gives:
🔴 ① Acetaldehyde
🟢 ② Acetone
🟡 ③ Ethanol
🔵 ④ Ethane
🟢 Answer: ① Acetaldehyde
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2005 | Set: A
🔵 Question 45:
Which of the following is an alkane?
🔴 ① C₂H₂
🟢 ② C₂H₄
🟡 ③ C₂H₆
🔵 ④ C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: ③ C₂H₆
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2018 | Set: R
🔵 Question 46:
Which is the major product when ethene reacts with HBr (no peroxide)?
🔴 ① Ethyl bromide
🟢 ② Vinyl bromide
🟡 ③ Allyl bromide
🔵 ④ Isopropyl bromide
🟢 Answer: ① Ethyl bromide (Markovnikov product)
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2015 | Set: O
🔵 Question 47:
The hydrogenation of benzene gives:
🔴 ① Cyclohexane
🟢 ② Cyclohexene
🟡 ③ Hexane
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ① Cyclohexane
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2009 | Set: B
🔵 Question 48:
Which of the following is not aromatic?
🔴 ① Pyrrole
🟢 ② Furan
🟡 ③ Cyclobutadiene
🔵 ④ Thiophene
🟢 Answer: ③ Cyclobutadiene
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2017 | Set: Q
🔵 Question 49:
Which hydrocarbon undergoes substitution rather than addition?
🔴 ① Alkanes
🟢 ② Alkenes
🟡 ③ Alkynes
🔵 ④ Aromatic hydrocarbons
🟢 Answer: ④ Aromatic hydrocarbons
📘 Exam: NEET
📅 Year: 2013 | Set: S
🔵 Question 50:
Which of the following is not a hydrocarbon?
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② C₂H₂
🟡 ③ C₂H₅OH
🔵 ④ C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: ③ C₂H₅OH
📘 Exam: AIPMT
📅 Year: 2006 | Set: A
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1
Which hydrocarbon is most reactive towards electrophilic substitution?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene (+I effect of –CH₃)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 2
In the Wurtz reaction, the product obtained from 2 moles of CH₃Br with sodium is:
🔴 ① CH₄
🟢 ② C₂H₆
🟡 ③ C₃H₈
🔵 ④ C₄H₁₀
🟢 Answer: ② C₂H₆
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 3
Which of the following alkanes has highest boiling point?
🔴 ① Pentane
🟢 ② Isopentane
🟡 ③ Neopentane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ① Pentane (straight chain > branched)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 4
Which one is aromatic according to Huckel’s rule?
🔴 ① Cyclooctatetraene
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Cyclobutadiene
🔵 ④ Cyclopentadienyl anion
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene (4n+2 rule, n=1)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 5
Alkyne on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia gives:
🔴 ① Trans-alkene
🟢 ② Cis-alkene
🟡 ③ Alkane
🔵 ④ Alcohol
🟢 Answer: ① Trans-alkene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 6
What is the major product of chlorination of benzene?
🔴 ① m-chlorobenzene
🟢 ② o-chlorobenzene
🟡 ③ p-chlorobenzene
🔵 ④ A mixture of o- and p-chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ④ A mixture of o- and p-chlorobenzene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 7
Which compound will decolorise bromine water?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Ethane
🔵 ④ Toluene
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene (unsaturation test)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 8
The ozonolysis of ethene produces:
🔴 ① Formaldehyde
🟢 ② Acetaldehyde
🟡 ③ Acetic acid
🔵 ④ Ethanol
🟢 Answer: ① Formaldehyde (HCHO)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 9
Which catalyst is used in hydrogenation of alkenes?
🔴 ① Fe
🟢 ② Ni
🟡 ③ Cu
🔵 ④ Sn
🟢 Answer: ② Ni (also Pt, Pd)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 10
Benzene on nitration gives:
🔴 ① Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② o-nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ p-nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ m-nitrobenzene
🟢 Answer: ① Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 11
Which of the following alkenes gives only one product on ozonolysis?
🔴 ① Propene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ But-1-ene
🔵 ④ But-2-ene
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 12
Which reaction is used for the preparation of higher alkanes from alkyl halides?
🔴 ① Wurtz reaction
🟢 ② Finkelstein reaction
🟡 ③ Cannizzaro reaction
🔵 ④ Kolbe’s reaction
🟢 Answer: ① Wurtz reaction
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 13
Toluene on sulphonation with conc. H₂SO₄ gives mainly:
🔴 ① o-toluenesulphonic acid
🟢 ② p-toluenesulphonic acid
🟡 ③ m-toluenesulphonic acid
🔵 ④ o- and p-mixture
🟢 Answer: ④ o- and p-mixture (major p-)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 14
Which of the following alkanes is most reactive towards halogenation?
🔴 ① Methane
🟢 ② Ethane
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Tertiary butane
🟢 Answer: ④ Tertiary butane (3° H is most reactive)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 15
What is the product of dehydrohalogenation of 2-bromopropane with alcoholic KOH?
🔴 ① Propane
🟢 ② Prop-1-ene
🟡 ③ Prop-2-ene
🔵 ④ Propyne
🟢 Answer: ② Prop-1-ene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 16
Benzene reacts with Cl₂ in presence of sunlight to give:
🔴 ① Chlorobenzene
🟢 ② Benzyl chloride
🟡 ③ Hexachlorocyclohexane
🔵 ④ Benzotrichloride
🟢 Answer: ③ Hexachlorocyclohexane (addition)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 17
The reaction of ethyl bromide with alc. KOH is:
🔴 ① Elimination
🟢 ② Substitution
🟡 ③ Addition
🔵 ④ Rearrangement
🟢 Answer: ① Elimination (β-elimination → ethene)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 18
How many π bonds are present in benzene?
🔴 ① 2
🟢 ② 3
🟡 ③ 6
🔵 ④ 1
🟢 Answer: ② 3
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 19
What is formed when acetylene reacts with ammoniacal Cu₂Cl₂?
🔴 ① Acetaldehyde
🟢 ② Acetylide salt
🟡 ③ Acetic acid
🔵 ④ Ethanol
🟢 Answer: ② Acetylide salt
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 20
Which is the correct order of acidity?
🔴 ① Alkyne > Alkene > Alkane
🟢 ② Alkane > Alkene > Alkyne
🟡 ③ Alkene > Alkyne > Alkane
🔵 ④ Alkane > Alkyne > Alkene
🟢 Answer: ① Alkyne > Alkene > Alkane
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 21
Which of the following is used in Friedel–Crafts alkylation?
🔴 ① AlCl₃
🟢 ② FeCl₃
🟡 ③ CuCl₂
🔵 ④ ZnCl₂
🟢 Answer: ① AlCl₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 22
The ozonolysis of 1-butene gives:
🔴 ① Acetaldehyde only
🟢 ② Formaldehyde and propanal
🟡 ③ 2 molecules of acetaldehyde
🔵 ④ Acetic acid
🟢 Answer: ③ 2 molecules of acetaldehyde
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 23
Which of the following gives white ppt. with ammoniacal AgNO₃?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Propane
🟢 Answer: ② Ethyne
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 24
What is the hybridisation of carbon in benzene?
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ② sp²
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 25
Which alkene does not show geometrical isomerism?
🔴 ① But-2-ene
🟢 ② Prop-1-ene
🟡 ③ Hex-2-ene
🔵 ④ Pent-2-ene
🟢 Answer: ② Prop-1-ene (one end H₂C=)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 26
Which of the following undergoes electrophilic substitution most readily?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ③ Toluene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 27
Which alkane is obtained in Kolbe’s electrolysis of sodium acetate?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Methane
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ④ Butane
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 28
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with H₃PO₂ to give:
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Chlorobenzene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Phenol
🟢 Answer: ① Benzene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 29
The IUPAC name of neopentane is:
🔴 ① 2-methylbutane
🟢 ② 2,2-dimethylpropane
🟡 ③ 3-methylbutane
🔵 ④ Pentane
🟢 Answer: ② 2,2-dimethylpropane
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 30
The product of hydration of ethyne in presence of HgSO₄ and H₂SO₄ is:
🔴 ① Ethanol
🟢 ② Ethanal
🟡 ③ Acetone
🔵 ④ Acetic acid
🟢 Answer: ② Ethanal (via enol → tautomerism)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 31
Which of the following shows resonance?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Cyclohexane
🔵 ④ Ethane
🟢 Answer: ① Benzene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 32
The product formed when toluene is oxidised with KMnO₄ is:
🔴 ① Benzyl alcohol
🟢 ② Benzoic acid
🟡 ③ Benzaldehyde
🔵 ④ Benzophenone
🟢 Answer: ② Benzoic acid
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 33
Which compound does not give addition reaction with Br₂?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene (prefers substitution)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 34
Which alkene on ozonolysis gives acetaldehyde only?
🔴 ① Propene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ But-1-ene
🔵 ④ But-2-ene
🟢 Answer: ① Propene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 35
What is the product of bromination of ethene in presence of CCl₄?
🔴 ① 1,1-dibromoethane
🟢 ② 1,2-dibromoethane
🟡 ③ Bromoethane
🔵 ④ Ethyl bromide
🟢 Answer: ② 1,2-dibromoethane
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 36
The compound with highest stability is:
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclobutadiene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene (aromatic stability)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 37
Which gas is evolved in dehydrogenation of ethane with Ni catalyst?
🔴 ① Hydrogen
🟢 ② Oxygen
🟡 ③ Carbon dioxide
🔵 ④ Methane
🟢 Answer: ① Hydrogen
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 38
Which is not aromatic?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Tropylium ion
🟡 ③ Cyclobutadiene
🔵 ④ Cyclopropenyl cation
🟢 Answer: ③ Cyclobutadiene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 39
Which reagent is used in Friedel–Crafts acylation?
🔴 ① AlCl₃
🟢 ② H₂SO₄
🟡 ③ NaOH
🔵 ④ ZnCl₂
🟢 Answer: ① AlCl₃
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 40
Which of the following shows geometrical isomerism?
🔴 ① But-2-ene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Propene
🔵 ④ 2-methylpropene
🟢 Answer: ① But-2-ene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 41
The main product of hydration of propene in presence of H₂SO₄ is:
🔴 ① Propan-1-ol
🟢 ② Propan-2-ol
🟡 ③ Ethanol
🔵 ④ Methanol
🟢 Answer: ② Propan-2-ol (Markovnikov addition)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 42
What is formed when benzene reacts with Cl₂ in presence of FeCl₃?
🔴 ① Benzyl chloride
🟢 ② Chlorobenzene
🟡 ③ Hexachlorocyclohexane
🔵 ④ Benzotrichloride
🟢 Answer: ② Chlorobenzene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 43
Which hydrocarbon forms explosive mixture with air?
🔴 ① Acetylene
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Methane
🔵 ④ Ethane
🟢 Answer: ① Acetylene
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2015 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 44
The resonance energy of benzene is approximately:
🔴 ① 36 kcal/mol
🟢 ② 150 kcal/mol
🟡 ③ 15 kcal/mol
🔵 ④ 50 kcal/mol
🟢 Answer: ① 36 kcal/mol
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 45
Which of the following is an anti-knock compound?
🔴 ① Tetraethyl lead
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Methane
🔵 ④ Propane
🟢 Answer: ① Tetraethyl lead
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2016 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 46
When acetylene is burnt with limited oxygen, it gives:
🔴 ① Carbon dioxide
🟢 ② Carbon monoxide
🟡 ③ Water
🔵 ④ Methane
🟢 Answer: ② Carbon monoxide
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2019 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 47
The reduction of benzene by H₂ in presence of Ni gives:
🔴 ① Cyclohexene
🟢 ② Cyclohexane
🟡 ③ Hexane
🔵 ④ Hexadiene
🟢 Answer: ② Cyclohexane
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2017 | Shift: Morning
🔵 Question 48
The addition of HBr to propene in presence of peroxide follows:
🔴 ① Markovnikov’s rule
🟢 ② Anti-Markovnikov’s rule
🟡 ③ Racemisation
🔵 ④ None
🟢 Answer: ② Anti-Markovnikov’s rule (peroxide effect)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2014 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 49
How many σ and π bonds are present in naphthalene?
🔴 ① 19 σ, 5 π
🟢 ② 21 σ, 5 π
🟡 ③ 24 σ, 5 π
🔵 ④ 25 σ, 5 π
🟢 Answer: ② 21 σ, 5 π
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2018 | Shift: Evening
🔵 Question 50
Which compound undergoes substitution instead of addition?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Propene
🔵 ④ But-1-ene
🟢 Answer: ① Benzene (aromatic stability)
📘 Exam: JEE Main
📅 Year: 2013 | Shift: Evening
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
The major product obtained when propene is treated with HBr in presence of peroxide is:
🔴 ① 1-bromopropane
🟢 ② 2-bromopropane
🟡 ③ 3-bromopropane
🔵 ④ Allyl bromide
🟢 Answer: ① 1-bromopropane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 2:
The product obtained when benzene reacts with CH₃Cl in presence of AlCl₃ is:
🔴 ① Toluene
🟢 ② Chlorobenzene
🟡 ③ Benzyl chloride
🔵 ④ Cumene
🟢 Answer: ① Toluene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 3:
The hybridisation of carbon atoms in ethyne (C₂H₂) molecule is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 4:
Which of the following alkanes will give only one monochlorination product?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Propane
🟡 ③ Butane
🔵 ④ Neopentane
🟢 Answer: ④ Neopentane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following alkenes will show geometrical isomerism?
🔴 ① CH₂=CH₂
🟢 ② CH₃–CH=CH–CH₃
🟡 ③ CH₃–CH=CH₂
🔵 ④ C₆H₆
🟢 Answer: ② CH₃–CH=CH–CH₃
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 6:
Benzene reacts with Cl₂ in presence of sunlight to give:
🔴 ① Chlorobenzene
🟢 ② Benzyl chloride
🟡 ③ Hexachlorocyclohexane
🔵 ④ Dichlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ③ Hexachlorocyclohexane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 7:
The order of reactivity of alkanes towards halogenation is:
🔴 ① 3° > 2° > 1°
🟢 ② 1° > 2° > 3°
🟡 ③ 2° > 3° > 1°
🔵 ④ 3° > 1° > 2°
🟢 Answer: ① 3° > 2° > 1°
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 8:
Which of the following does not give addition reactions?
🔴 ① Alkanes
🟢 ② Alkenes
🟡 ③ Alkynes
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ① Alkanes
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 9:
The major product obtained when ethyne reacts with cold dilute KMnO₄ solution is:
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② CH₃COOH
🟡 ③ Ethylene glycol
🔵 ④ Oxalic acid
🟢 Answer: ③ Ethylene glycol
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2008 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 10:
Which among the following is aromatic?
🔴 ① Cyclooctatetraene
🟢 ② Cyclobutadiene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclopropene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 11:
The product formed when propyne reacts with 1 mole of HCl is:
🔴 ① CH₃–CCl=CH₂
🟢 ② CH₃–CHCl–CH₃
🟡 ③ CH₂Cl–CH=CH₂
🔵 ④ CH₃–CCl₂–CH₃
🟢 Answer: ① CH₃–CCl=CH₂
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 12:
The correct order of stability of carbocations is:
🔴 ① CH₃⁺ < 1° < 2° < 3° < Benzyl
🟢 ② CH₃⁺ < 1° < 2° < Benzyl < 3°
🟡 ③ Benzyl < 3° < 2° < 1° < CH₃⁺
🔵 ④ 1° < CH₃⁺ < 3° < 2° < Benzyl
🟢 Answer: ① CH₃⁺ < 1° < 2° < 3° < Benzyl
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following alkanes has the lowest boiling point?
🔴 ① n-Butane
🟢 ② Isobutane
🟡 ③ Neopentane
🔵 ④ Propane
🟢 Answer: ③ Neopentane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 14:
When benzene is treated with CH₃Cl and AlCl₃, the product formed is:
🔴 ① Benzyl chloride
🟢 ② Chlorobenzene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Cumene
🟢 Answer: ③ Toluene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 15:
The hydrogenation of alkynes in presence of Pd/BaSO₄ gives:
🔴 ① Cis-alkenes
🟢 ② Trans-alkenes
🟡 ③ Alkanes
🔵 ④ Aromatic hydrocarbons
🟢 Answer: ① Cis-alkenes
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following is most stable carbocation?
🔴 ① Allyl
🟢 ② Benzyl
🟡 ③ Tertiary butyl
🔵 ④ Vinyl
🟢 Answer: ② Benzyl
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 17:
Which hydrocarbon decolourises bromine water?
🔴 ① Propane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexane
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 18:
The major product formed in the reaction of ethene with cold, dilute alkaline KMnO₄ is:
🔴 ① CO₂
🟢 ② Ethane
🟡 ③ Ethylene glycol
🔵 ④ Oxalic acid
🟢 Answer: ③ Ethylene glycol
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2009 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 19:
Which of the following alkenes will give only one product on ozonolysis?
🔴 ① Propene
🟢 ② 2-butene
🟡 ③ 1-butene
🔵 ④ 2-methylpropene
🟢 Answer: ② 2-butene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 20:
The compound formed when acetylene reacts with ammoniacal Cu₂Cl₂ is:
🔴 ① CuC≡C–Cu (copper acetylide)
🟢 ② CH₃–CH₃
🟡 ③ C₆H₆
🔵 ④ CH₃CHO
🟢 Answer: ① CuC≡C–Cu (copper acetylide)
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 21:
Which of the following statements is correct about benzene?
🔴 ① Benzene undergoes addition reactions easily
🟢 ② Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions
🟡 ③ Benzene is unstable
🔵 ④ Benzene has localized π bonds
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 22:
Which of the following alkanes has the highest boiling point?
🔴 ① n-Pentane
🟢 ② Isopentane
🟡 ③ Neopentane
🔵 ④ Cyclopentane
🟢 Answer: ① n-Pentane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 23:
The major product obtained when propyne reacts with excess HCl is:
🔴 ① CH₃–CCl=CH₂
🟢 ② CH₃–CCl₂–CH₃
🟡 ③ CH₂Cl–CH=CH₂
🔵 ④ CH₃–CHCl–CH₃
🟢 Answer: ② CH₃–CCl₂–CH₃
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 24:
Which among the following is non-aromatic?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Cyclobutadiene
🟡 ③ Cyclopropenyl cation
🔵 ④ Cyclopentadienyl anion
🟢 Answer: ② Cyclobutadiene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 25:
The number of σ and π bonds in benzene is:
🔴 ① 6 σ, 6 π
🟢 ② 12 σ, 3 π
🟡 ③ 9 σ, 6 π
🔵 ④ 6 σ, 3 π
🟢 Answer: ② 12 σ, 3 π
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2008 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Roorkee
🔵 Question 26:
The hybridisation of carbon in benzene is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ② sp²
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2007 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 27:
Which one of the following will not decolourise bromine water?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexene
🟢 Answer: ③ Benzene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2014 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 28:
Catalytic hydrogenation of benzene gives:
🔴 ① Cyclohexene
🟢 ② Cyclohexane
🟡 ③ n-Hexane
🔵 ④ Benzyl alcohol
🟢 Answer: ② Cyclohexane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Kanpur
🔵 Question 29:
Which compound gives a positive test with ammoniacal Cu₂Cl₂?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethyne
🟡 ③ Ethene
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ② Ethyne
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2011 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 30:
Which alkane has only primary hydrogen atoms?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Neopentane
🟡 ③ Isobutane
🔵 ④ n-Butane
🟢 Answer: ② Neopentane
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2012 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Delhi
🔵 Question 31:
The reaction of benzene with CH₃COCl in presence of AlCl₃ gives:
🔴 ① Acetophenone
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Benzaldehyde
🔵 ④ Benzyl chloride
🟢 Answer: ① Acetophenone
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2013 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
🔵 Question 32:
How many monochlorination products are possible for isobutane?
🔴 ① 1
🟢 ② 2
🟡 ③ 3
🔵 ④ 4
🟢 Answer: ② 2
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Madras
🔵 Question 33:
The major product formed in the nitration of benzene is:
🔴 ① o-Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② m-Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ p-Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Nitrobenzene
🟢 Answer: ④ Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2010 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Guwahati
🔵 Question 34:
The correct order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution is:
🔴 ① Benzene > Toluene > Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② Toluene > Benzene > Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene > Benzene > Toluene
🔵 ④ Benzene > Nitrobenzene > Toluene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene > Benzene > Nitrobenzene
📘 Exam: JEE Advanced
📅 Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Conducted by: IIT Bombay
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is the general formula of alkanes?
🔴 ① CnH₂n
🟢 ② CnH₂n+2
🟡 ③ CnH₂n–2
🔵 ④ CnH₂n+1
🟢 Answer: ② CnH₂n+2
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 2:
The first member of the alkene series is:
🔴 ① Methene
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Propene
🔵 ④ Butene
🟢 Answer: ② Ethene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 3:
The simplest alkyne is:
🔴 ① Ethyne
🟢 ② Methyne
🟡 ③ Propine
🔵 ④ Propyne
🟢 Answer: ① Ethyne
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 4:
Which of the following hydrocarbons is aromatic?
🔴 ① C₂H₂
🟢 ② C₆H₆
🟡 ③ C₂H₄
🔵 ④ C₃H₆
🟢 Answer: ② C₆H₆
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 5:
The hybridisation of carbon in ethyne is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ③ sp
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 6:
Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
🔴 ① Methane
🟢 ② Ethane
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ④ Butane
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 7:
The common name of ethyne is:
🔴 ① Marsh gas
🟢 ② Acetylene
🟡 ③ Olefiant gas
🔵 ④ Natural gas
🟢 Answer: ② Acetylene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 8:
Alkanes are also called:
🔴 ① Olefins
🟢 ② Paraffins
🟡 ③ Acetylenes
🔵 ④ Arenes
🟢 Answer: ② Paraffins
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 9:
Which reagent is used to distinguish between alkane and alkene?
🔴 ① H₂O
🟢 ② Bromine water
🟡 ③ NaOH
🔵 ④ HCl
🟢 Answer: ② Bromine water
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 10:
Which reaction is used to convert alkenes into alkanes?
🔴 ① Dehydrogenation
🟢 ② Hydrogenation
🟡 ③ Halogenation
🔵 ④ Substitution
🟢 Answer: ② Hydrogenation
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 11:
The catalyst used in hydrogenation of alkenes is:
🔴 ① Fe
🟢 ② Ni
🟡 ③ Al
🔵 ④ Cu
🟢 Answer: ② Ni
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 12:
Benzene reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight to give:
🔴 ① C₆H₅Cl
🟢 ② Hexachlorocyclohexane
🟡 ③ Chlorobenzene
🔵 ④ Benzyl chloride
🟢 Answer: ② Hexachlorocyclohexane
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following shows addition reaction?
🔴 ① Alkane
🟢 ② Alkene
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Cyclohexane
🟢 Answer: ② Alkene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 14:
Which of the following is used as an anaesthetic?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Chloroform
🟡 ③ Ethane
🔵 ④ Methane
🟢 Answer: ② Chloroform
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 15:
The first member of aromatic hydrocarbon series is:
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Naphthalene
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following is not an alkyne?
🔴 ① Propyne
🟢 ② Butyne
🟡 ③ Propene
🔵 ④ Ethyne
🟢 Answer: ③ Propene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 17:
The hybridisation of carbon in benzene is:
🔴 ① sp³
🟢 ② sp²
🟡 ③ sp
🔵 ④ dsp²
🟢 Answer: ② sp²
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 18:
Which of the following is not aromatic?
🔴 ① Toluene
🟢 ② Cyclohexane
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Naphthalene
🟢 Answer: ② Cyclohexane
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 19:
The reaction of benzene with concentrated HNO₃ in presence of conc. H₂SO₄ gives:
🔴 ① Benzyl alcohol
🟢 ② Nitrobenzene
🟡 ③ Benzaldehyde
🔵 ④ Aniline
🟢 Answer: ② Nitrobenzene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 20:
Which test is used to detect unsaturation in hydrocarbons?
🔴 ① Baeyer’s test
🟢 ② Brown ring test
🟡 ③ FeCl₃ test
🔵 ④ Lassaigne’s test
🟢 Answer: ① Baeyer’s test
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 21:
Which gas is called marsh gas?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Methane
🟡 ③ Propane
🔵 ④ Butane
🟢 Answer: ② Methane
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 22:
In alkanes, the type of bond present is:
🔴 ① π bonds only
🟢 ② σ bonds only
🟡 ③ σ and π bonds
🔵 ④ Coordinate bonds
🟢 Answer: ② σ bonds only
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 23:
Which of the following has the highest reactivity towards addition reaction?
🔴 ① Alkane
🟢 ② Alkene
🟡 ③ Alkyne
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ② Alkene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 24:
Alkenes are also known as:
🔴 ① Paraffins
🟢 ② Olefins
🟡 ③ Acetylenes
🔵 ④ Arenes
🟢 Answer: ② Olefins
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 25:
Which of the following compounds is used in the preparation of TNT (Trinitrotoluene)?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Xylene
🔵 ④ Phenol
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene
🎯 Difficulty: NEET
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following alkanes gives only one monochlorinated product?
🔴 ① Propane
🟢 ② Neopentane
🟡 ③ Butane
🔵 ④ Isobutane
🟢 Answer: ② Neopentane
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 27:
Which alkene gives only one product on ozonolysis?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Propene
🟡 ③ 2-butene
🔵 ④ 1-butene
🟢 Answer: ③ 2-butene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 28:
Which hydrocarbon does not decolorize bromine water?
🔴 ① Ethane
🟢 ② Ethene
🟡 ③ Ethyne
🔵 ④ Butadiene
🟢 Answer: ① Ethane
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 29:
Which reaction converts alkyl halides into alkanes?
🔴 ① Wurtz reaction
🟢 ② Kolbe’s reaction
🟡 ③ Friedel–Crafts reaction
🔵 ④ Cannizzaro reaction
🟢 Answer: ① Wurtz reaction
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 30:
The product of hydrogenation of benzene is:
🔴 ① Cyclohexane
🟢 ② Cyclohexene
🟡 ③ Hexane
🔵 ④ Hexene
🟢 Answer: ① Cyclohexane
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 31:
Markovnikov’s rule is applicable in the addition of HBr to:
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Propene
🟡 ③ Acetylene
🔵 ④ Benzene
🟢 Answer: ② Propene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 32:
Anti-Markovnikov’s addition of HBr occurs in the presence of:
🔴 ① Light
🟢 ② Organic peroxide
🟡 ③ Concentrated H₂SO₄
🔵 ④ FeCl₃
🟢 Answer: ② Organic peroxide
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 33:
Which of the following reactions gives alkynes from vicinal dihalides?
🔴 ① Dehydrohalogenation
🟢 ② Wurtz reaction
🟡 ③ Kolbe’s reaction
🔵 ④ Friedel–Crafts reaction
🟢 Answer: ① Dehydrohalogenation
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 34:
Aromaticity in benzene is explained by:
🔴 ① Valence bond theory
🟢 ② Huckel’s rule
🟡 ③ Hybridisation concept
🔵 ④ VSEPR theory
🟢 Answer: ② Huckel’s rule
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 35:
Which of the following will show geometrical isomerism?
🔴 ① Propene
🟢 ② 2-butene
🟡 ③ Ethane
🔵 ④ Methane
🟢 Answer: ② 2-butene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 36:
Which of the following is the most reactive towards electrophilic substitution?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 37:
What is the hybridisation of carbon in allene (C₃H₄)?
🔴 ① sp³ and sp²
🟢 ② sp and sp²
🟡 ③ sp² and sp³
🔵 ④ sp³ only
🟢 Answer: ② sp and sp²
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 38:
Which of the following is used in the preparation of polystyrene?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Styrene
🟡 ③ Toluene
🔵 ④ Ethylbenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Styrene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 39:
Which one undergoes polymerisation to form PVC?
🔴 ① Ethene
🟢 ② Vinyl chloride
🟡 ③ Styrene
🔵 ④ Propene
🟢 Answer: ② Vinyl chloride
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🔵 Question 40:
The reaction of benzene with CH₃Cl in presence of anhydrous AlCl₃ gives:
🔴 ① Chlorobenzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Benzyl chloride
🔵 ④ Cumene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Main
🚀 Advanced-level (Q41–Q50):
🔵 Question 41:
Which hydrocarbon follows Huckel’s (4n + 2) π electron rule?
🔴 ① Cyclobutadiene
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Cyclooctatetraene
🔵 ④ Cyclopentadienyl cation
🟢 Answer: ② Benzene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 42:
The major product of but-1-ene with HBr in presence of peroxide is:
🔴 ① 1-bromobutane
🟢 ② 2-bromobutane
🟡 ③ 2,2-dibromobutane
🔵 ④ 3-bromobutane
🟢 Answer: ① 1-bromobutane
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 43:
Which compound will give the highest heat of hydrogenation?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Cyclohexene
🟡 ③ 1,3-butadiene
🔵 ④ Ethene
🟢 Answer: ④ Ethene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 44:
In electrophilic substitution of benzene, the role of Lewis acid catalyst (like AlCl₃) is to:
🔴 ① Provide H⁺ ions
🟢 ② Generate electrophile
🟡 ③ Act as a nucleophile
🔵 ④ Remove π electrons
🟢 Answer: ② Generate electrophile
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 45:
Which of the following compounds will be most reactive towards bromination?
🔴 ① Nitrobenzene
🟢 ② Benzene
🟡 ③ Phenol
🔵 ④ Toluene
🟢 Answer: ③ Phenol
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 46:
Which product is obtained when ethyne reacts with water in presence of HgSO₄/H₂SO₄?
🔴 ① Acetaldehyde
🟢 ② Acetone
🟡 ③ Formaldehyde
🔵 ④ Methanol
🟢 Answer: ① Acetaldehyde
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 47:
Which among the following is anti-aromatic?
🔴 ① Cyclobutadiene
🟢 ② Cyclopentadienyl anion
🟡 ③ Benzene
🔵 ④ Naphthalene
🟢 Answer: ① Cyclobutadiene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 48:
Which of the following is the correct order of acidity?
🔴 ① CH≡CH > CH₂=CH₂ > CH₃–CH₃
🟢 ② CH₃–CH₃ > CH₂=CH₂ > CH≡CH
🟡 ③ CH₂=CH₂ > CH≡CH > CH₃–CH₃
🔵 ④ All equal
🟢 Answer: ① CH≡CH > CH₂=CH₂ > CH₃–CH₃
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 49:
Which of the following will undergo electrophilic substitution most readily?
🔴 ① Benzene
🟢 ② Toluene
🟡 ③ Nitrobenzene
🔵 ④ Chlorobenzene
🟢 Answer: ② Toluene
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
🔵 Question 50:
In the ozonolysis of benzene, the product obtained is:
🔴 ① Acetone
🟢 ② Glyoxal
🟡 ③ Maleic anhydride
🔵 ④ Glyoxal + other dicarbonyl compounds
🟢 Answer: ④ Glyoxal + other dicarbonyl compounds
🎯 Difficulty: JEE Advanced
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
