Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 9. Biomolecules
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌿✨ Introduction
🧠 Biomolecules are organic compounds produced by living organisms that form the building blocks of life.
They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and metabolites essential for growth, structure, and metabolism.
🌿 Every living cell is a chemical factory performing numerous reactions simultaneously using these biomolecules.
Without them, life processes like energy production, genetic transmission, and structural formation are impossible.
💡 Concept:
Life is chemical; cell = chemical system.
Understanding biomolecules explains how life functions at molecular level.
🧬 Types of Biomolecules
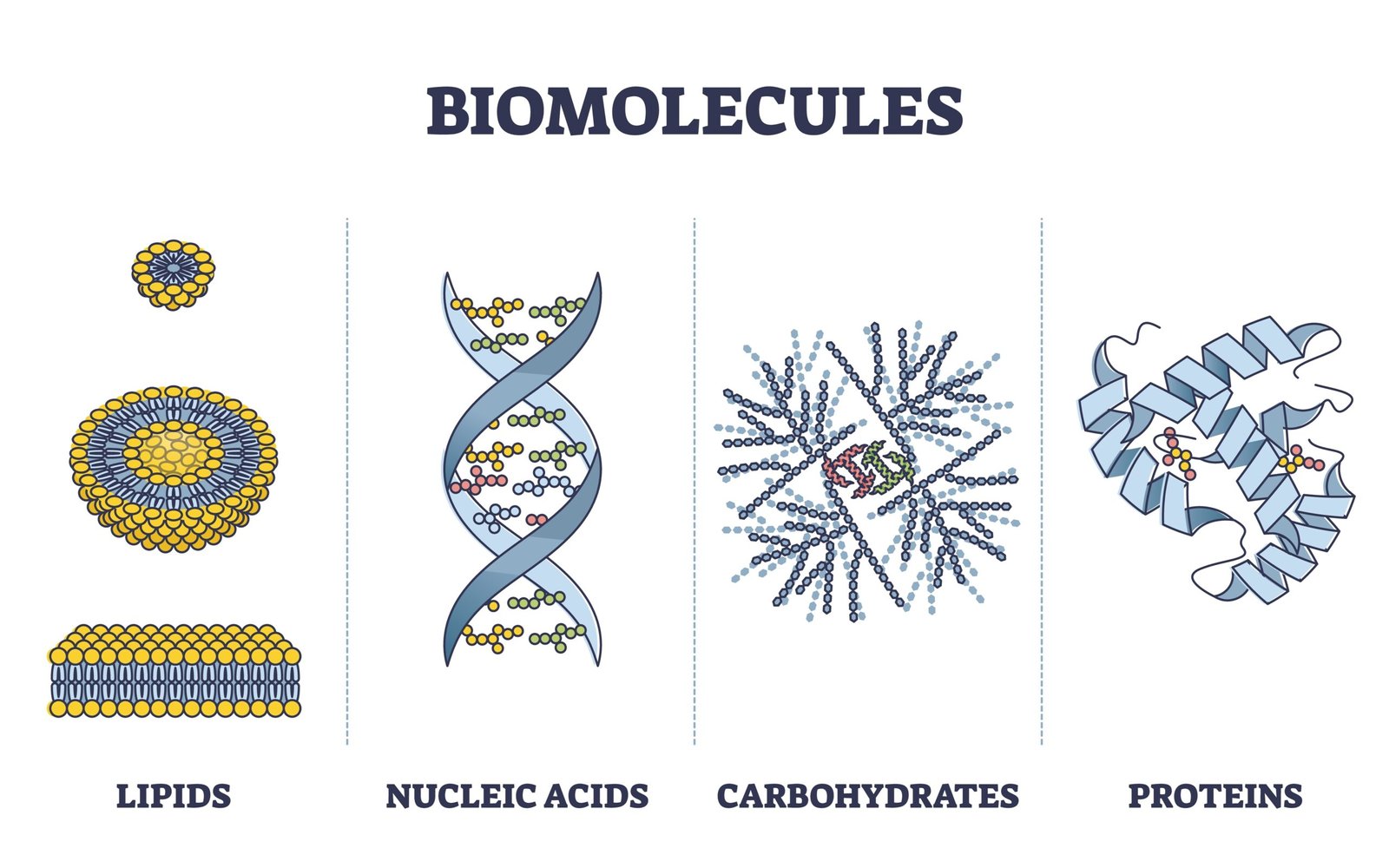
Living organisms contain inorganic (water, salts, minerals) and organic (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) compounds.
1️⃣ Inorganic Biomolecules
💧 Water – universal solvent; ~70% of cell weight
🧂 Minerals – Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, phosphate, essential for enzymes, structure, and osmoregulation
2️⃣ Organic Biomolecules
🧠 Contain carbon; form complex macromolecules performing structural and functional roles.
🌾 Carbohydrates
🧠 Definition: Organic compounds with C, H, O, generally Cₙ(H₂O)ₙ
💡 Called saccharides; primary energy source.
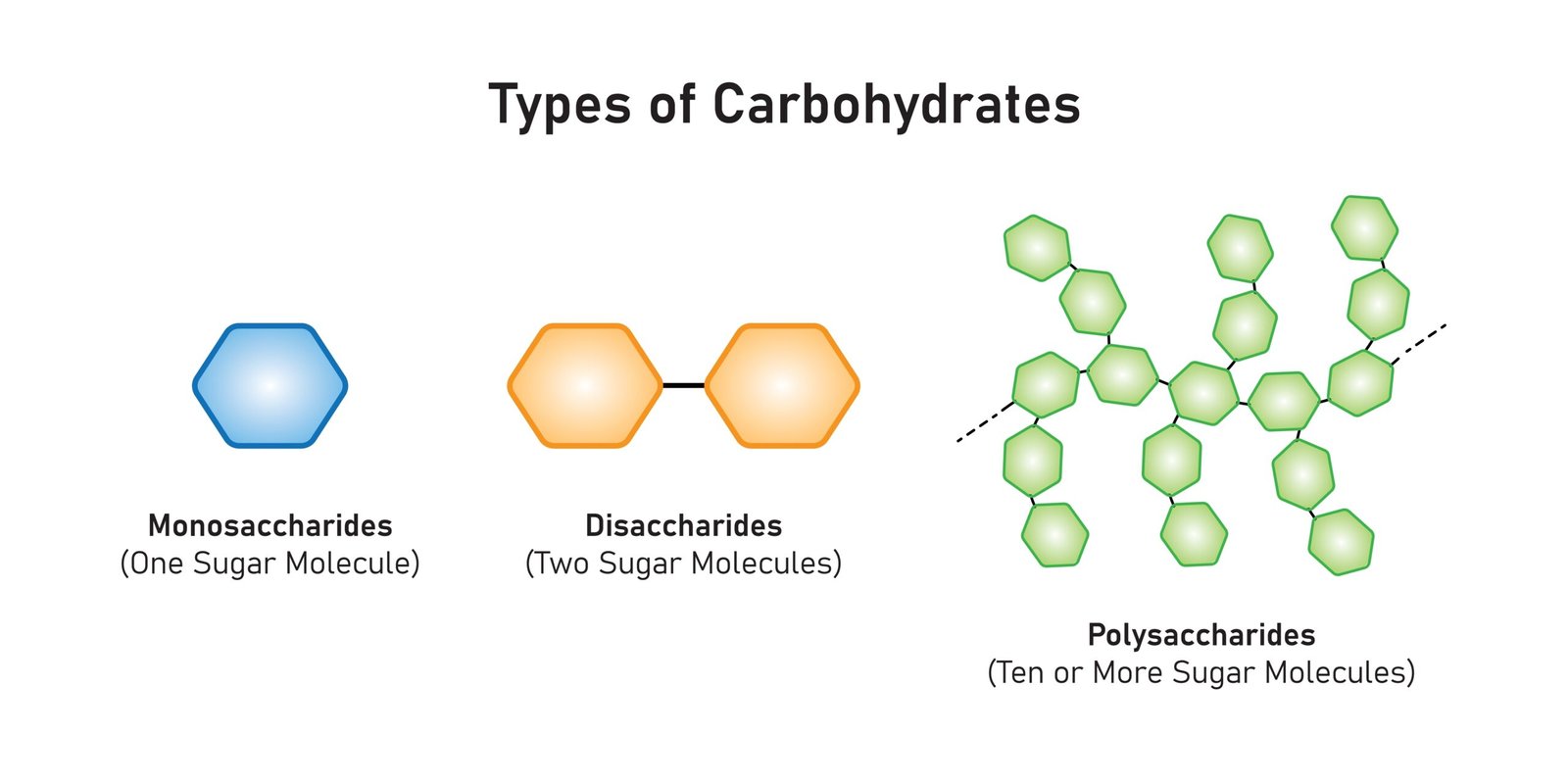
🧩 Classification
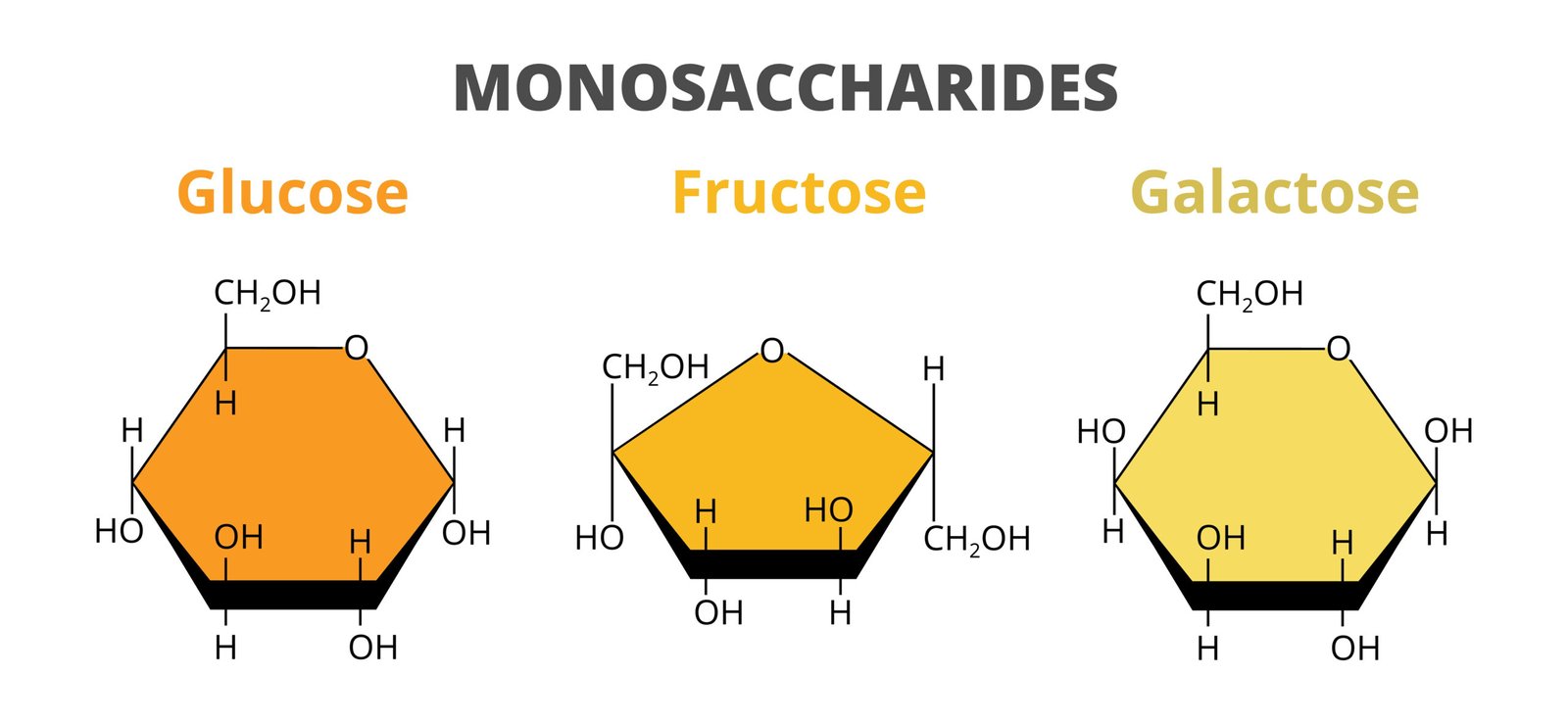
🍬 1. Monosaccharides
Simple sugars, 1 unit
Examples: Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
Soluble, sweet, energy-rich
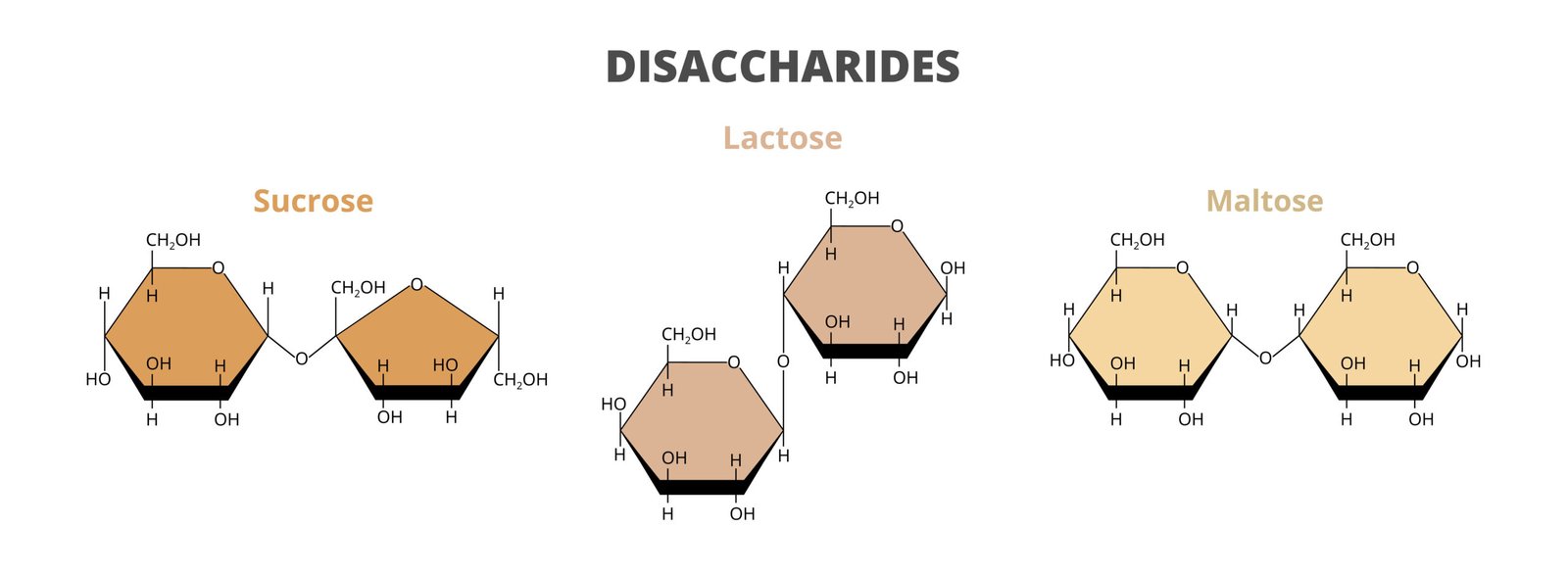
🍭 2. Disaccharides
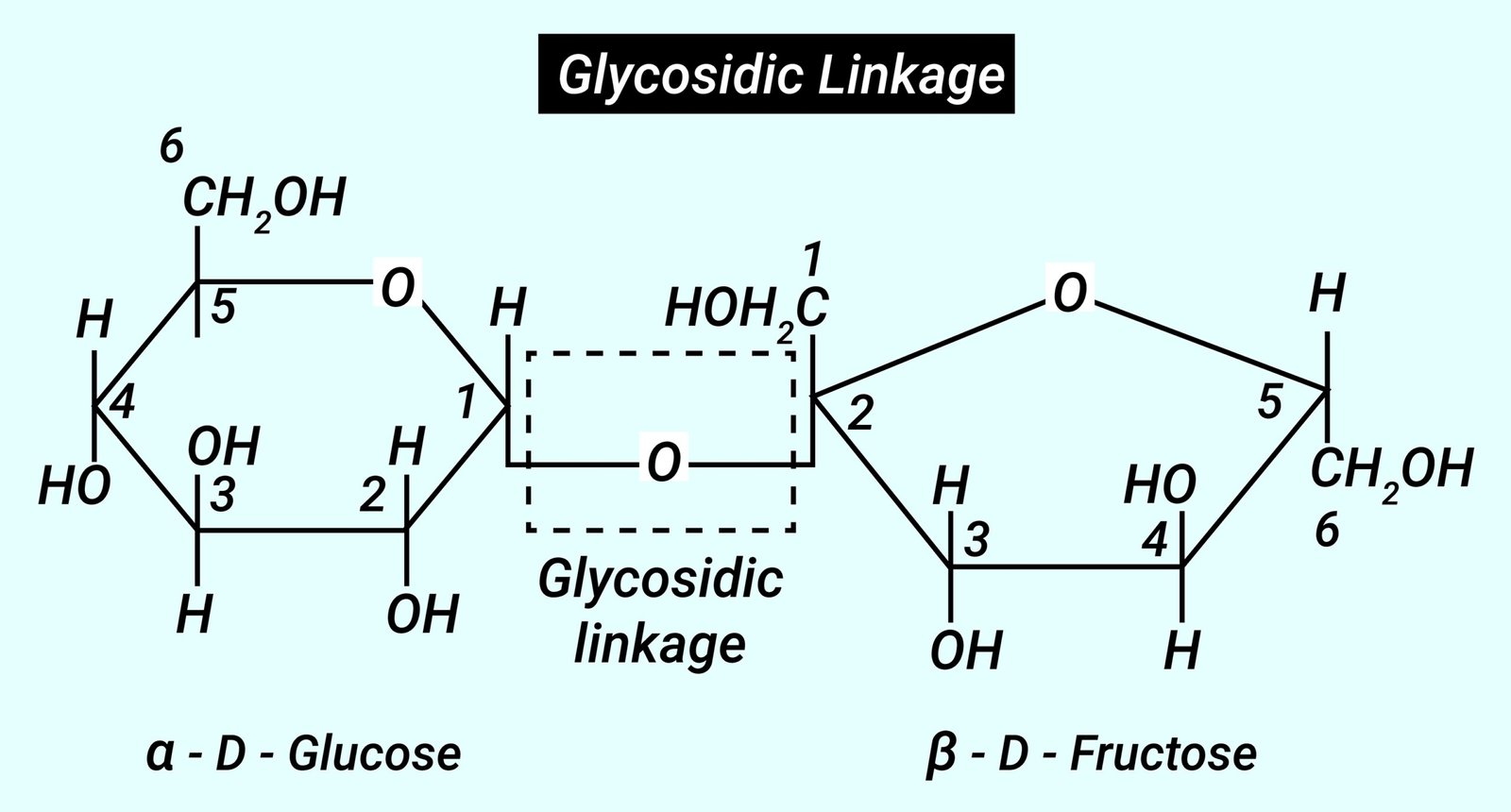
2 monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bond
Examples: Sucrose (glucose + fructose), Maltose (glucose + glucose), Lactose (glucose + galactose)
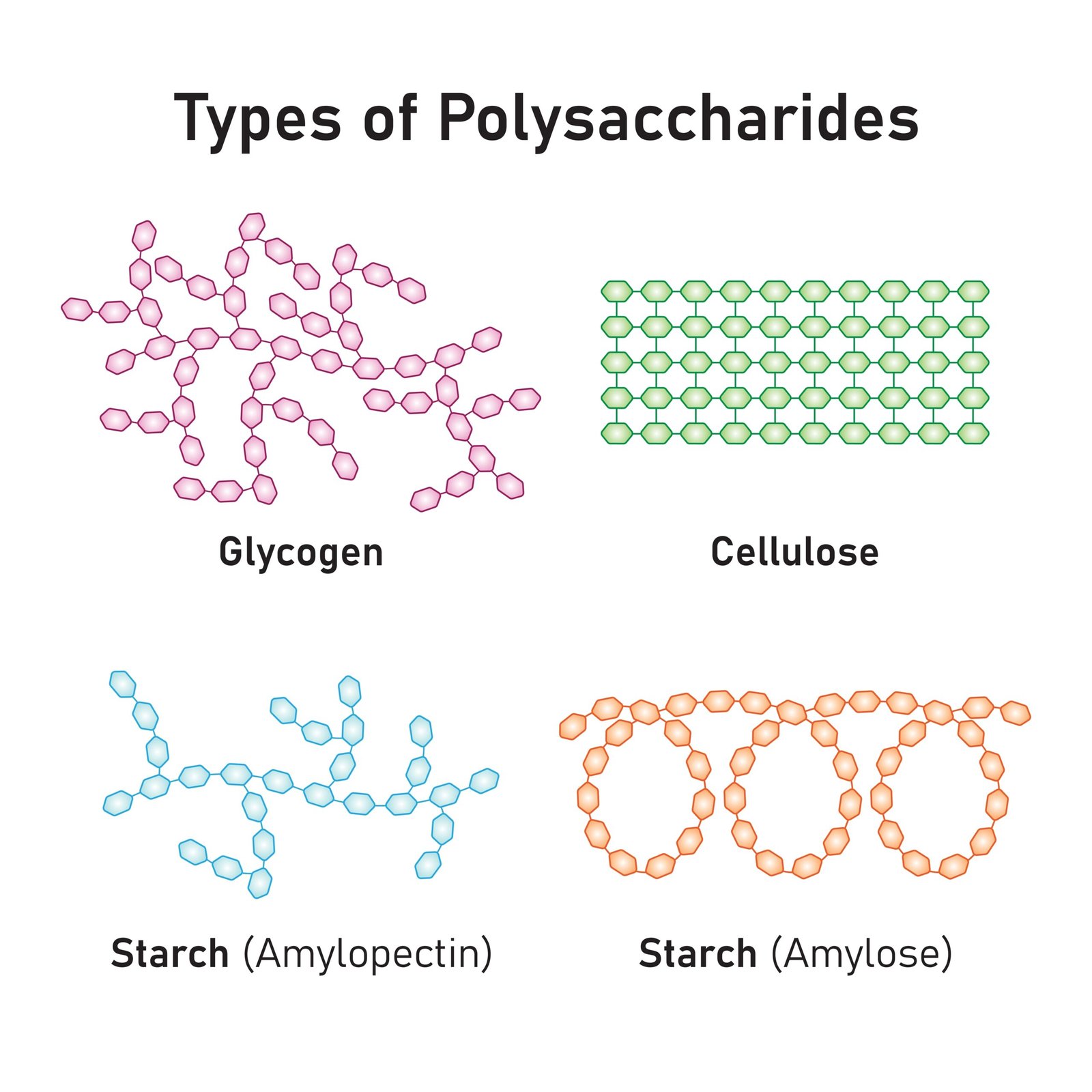
🍞 3. Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides
Storage: Starch (plants), Glycogen (animals)
Structural: Cellulose (plants), Chitin (arthropods)
✏️ Note: Hydrolysis of polysaccharides yields simple sugars.
💡 Concept:
Carbohydrates = instant energy source (4 kcal/g).
🧈 Lipids
🧠 Definition: Heterogeneous group of compounds like fats, oils, waxes, insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
⚙️ Functions:
Energy storage (9 kcal/g)
Structural (cell membranes = phospholipids)
Protective (cuticle, insulation)
Hormonal precursors (steroids)
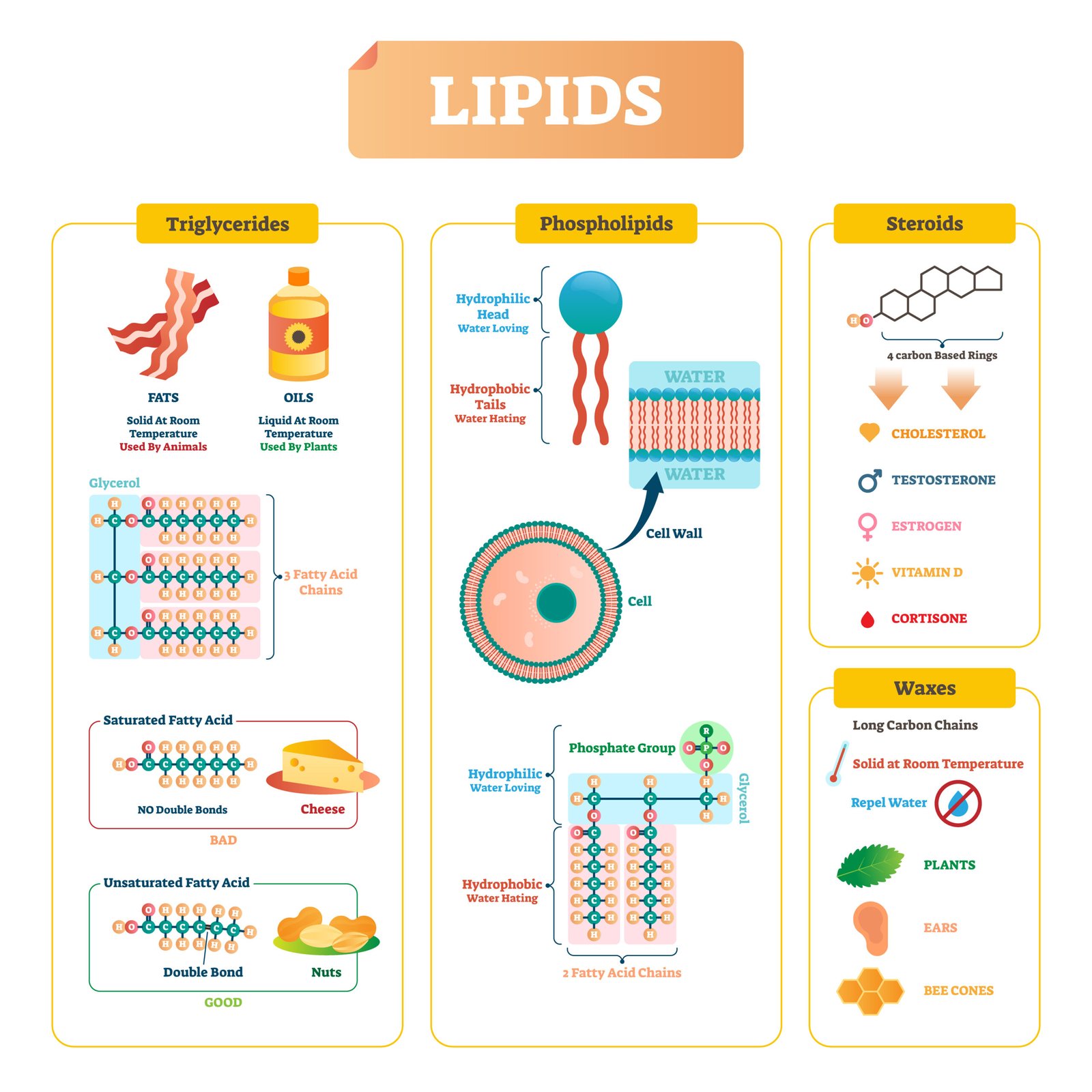
🧪 Types
1️⃣ Simple lipids – esters of fatty acids + glycerol (triglycerides)
2️⃣ Compound lipids – with other groups (phospholipids, glycolipids)
3️⃣ Derived lipids – steroids (cholesterol), fat-soluble vitamins
🌿 Fatty acids:
Saturated – single bonds (butter)
Unsaturated – double bonds (oils)
💡 Concept: Lipids store 2.5× more energy than carbohydrates.
🧬 Proteins
🧠 Definition: Complex macromolecules of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
🧪 Elements: C, H, O, N (sometimes S, P)
🧱 Structure
1️⃣ Primary: linear chain of amino acids
2️⃣ Secondary: α-helix or β-sheet (H-bonds)
3️⃣ Tertiary: 3D folding (functional shape)
4️⃣ Quaternary: multiple polypeptides (e.g., haemoglobin)
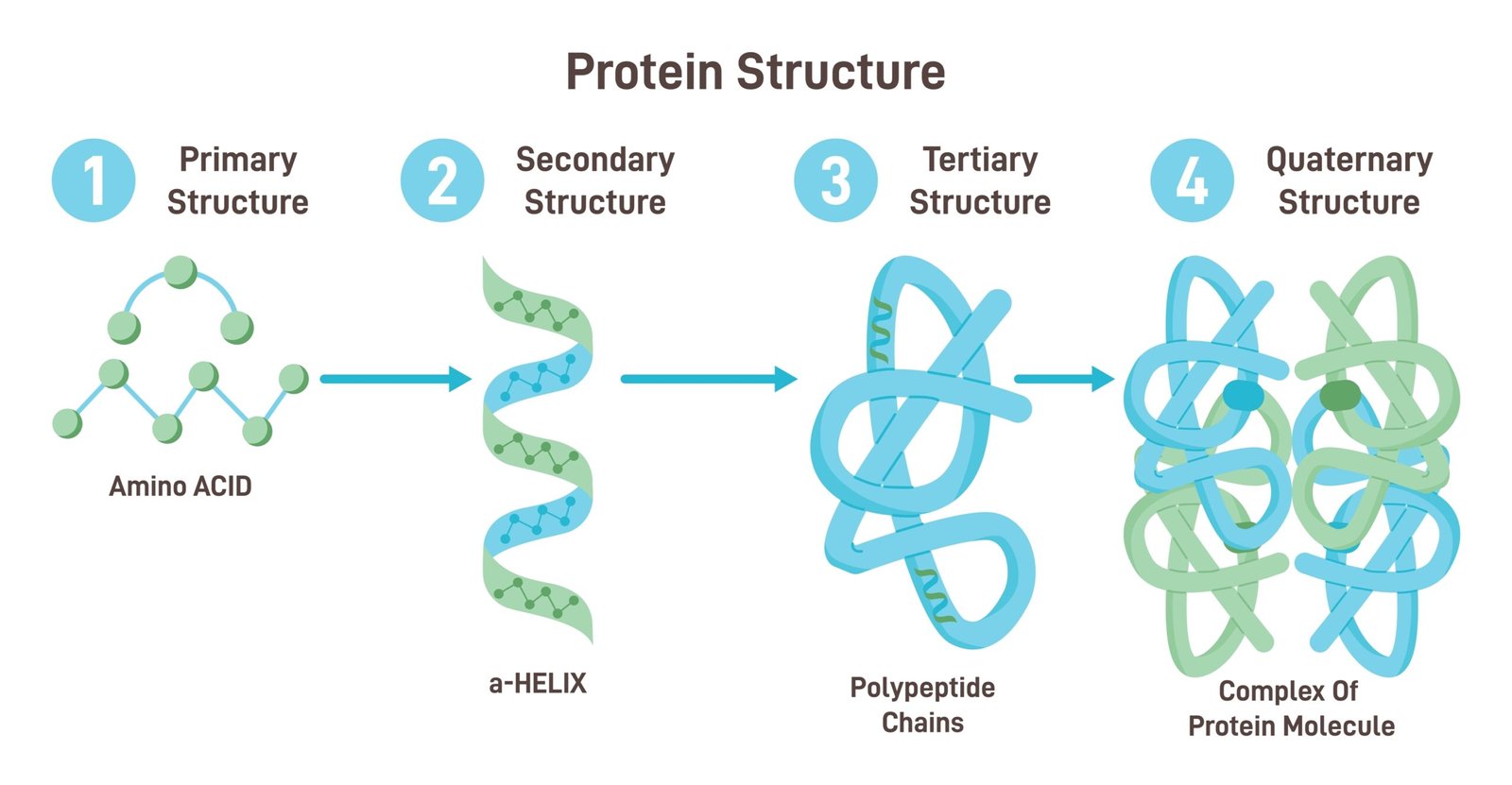
🧠 Functions
🧬 Enzymatic – catalyse reactions (amylase)
💪 Structural – keratin, collagen
⚙️ Transport – haemoglobin
🧫 Defense – antibodies
💡 Regulatory – hormones (insulin)
🔋 Energy source during starvation
✏️ Note: ~20 amino acids form all proteins.
💡 Concept: Proteins = “workhorses” of the cell.
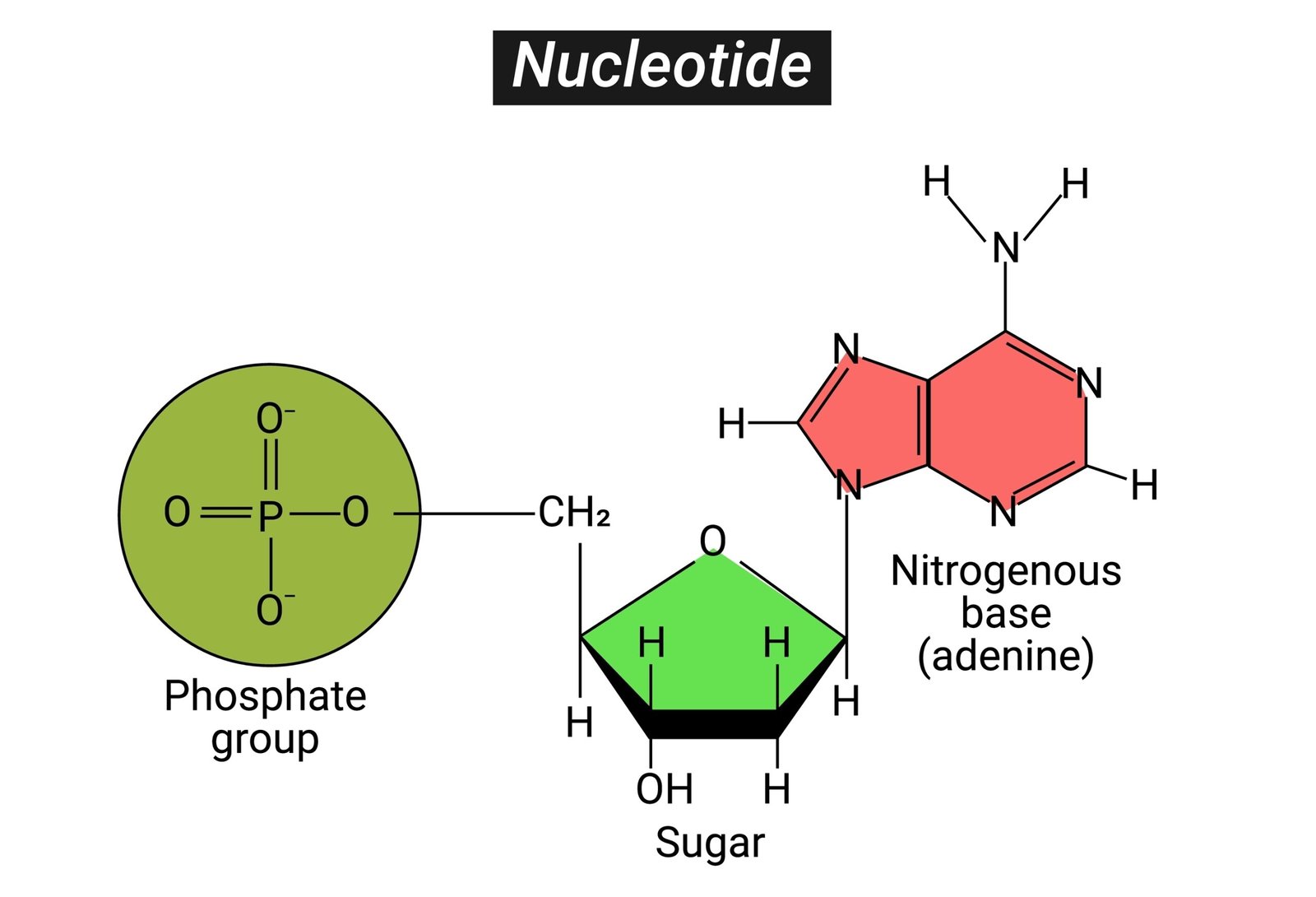
🧫 Nucleic Acids
🧠 Definition: Polymers of nucleotides; store and transmit genetic information.
🧩 Nucleotide = nitrogen base + sugar + phosphate
🌿 Types
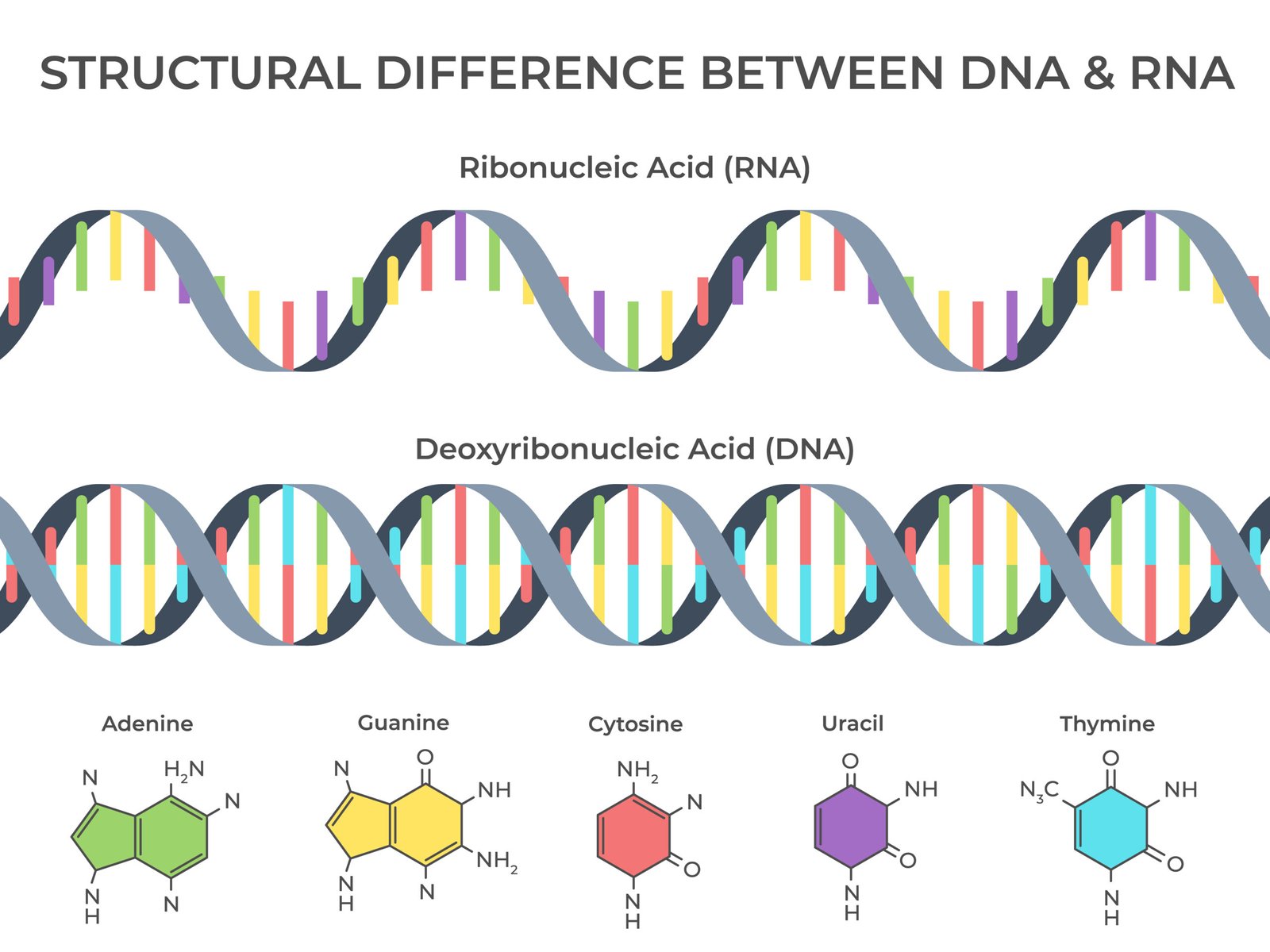
🧬 DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Double helix (Watson & Crick model)
Sugar: deoxyribose
Bases: A, T, G, C
Base pairing: A–T (2 H-bonds), G–C (3 H-bonds)
Function: genetic code, heredity
💡 RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
Single-stranded
Sugar: ribose
Bases: A, U, G, C
Types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Function: protein synthesis
💡 Concept:
DNA = blueprint; RNA = messenger & worker.
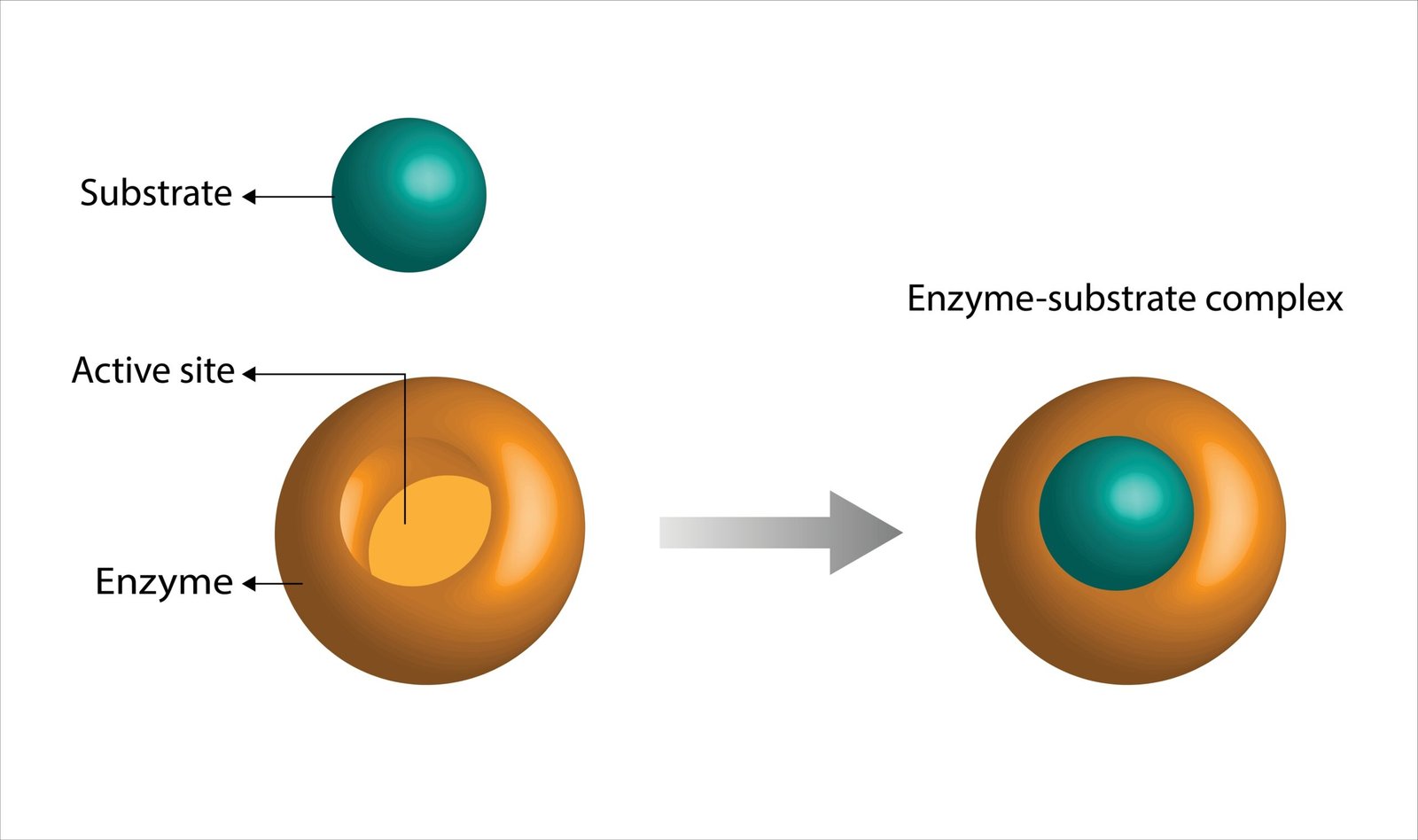
🧪 Enzymes
🧠 Definition: Biological catalysts made of proteins, speed up reactions without being consumed.
⚙️ Properties:
Specific to substrate
Function under optimum pH and temperature
Reusable
Inhibited by poisons
🧩 Mechanism
🧬 Lock and Key Model – substrate fits enzyme
🧪 Induced Fit Model – enzyme adjusts to substrate
💡 Example: Amylase converts starch → maltose.
🧪 Metabolites
🌿 1. Primary Metabolites
🧠 Found in all cells; essential for life
💧 Examples: amino acids, sugars, nucleotides
🌸 2. Secondary Metabolites
🌿 Specific to species; not essential but useful
⚙️ Examples: alkaloids (morphine), pigments, essential oils
✏️ Note: Secondary metabolites have medicinal, ecological value.
🧠 Analysis of Chemical Composition
🧪 Living tissue analysis reveals 98% weight from:
C, H, O, N, P, S, Ca, Mg, K, Na, Cl
⚙️ About 5000+ compounds found in cells.
🌿 Bonds in Biomolecules
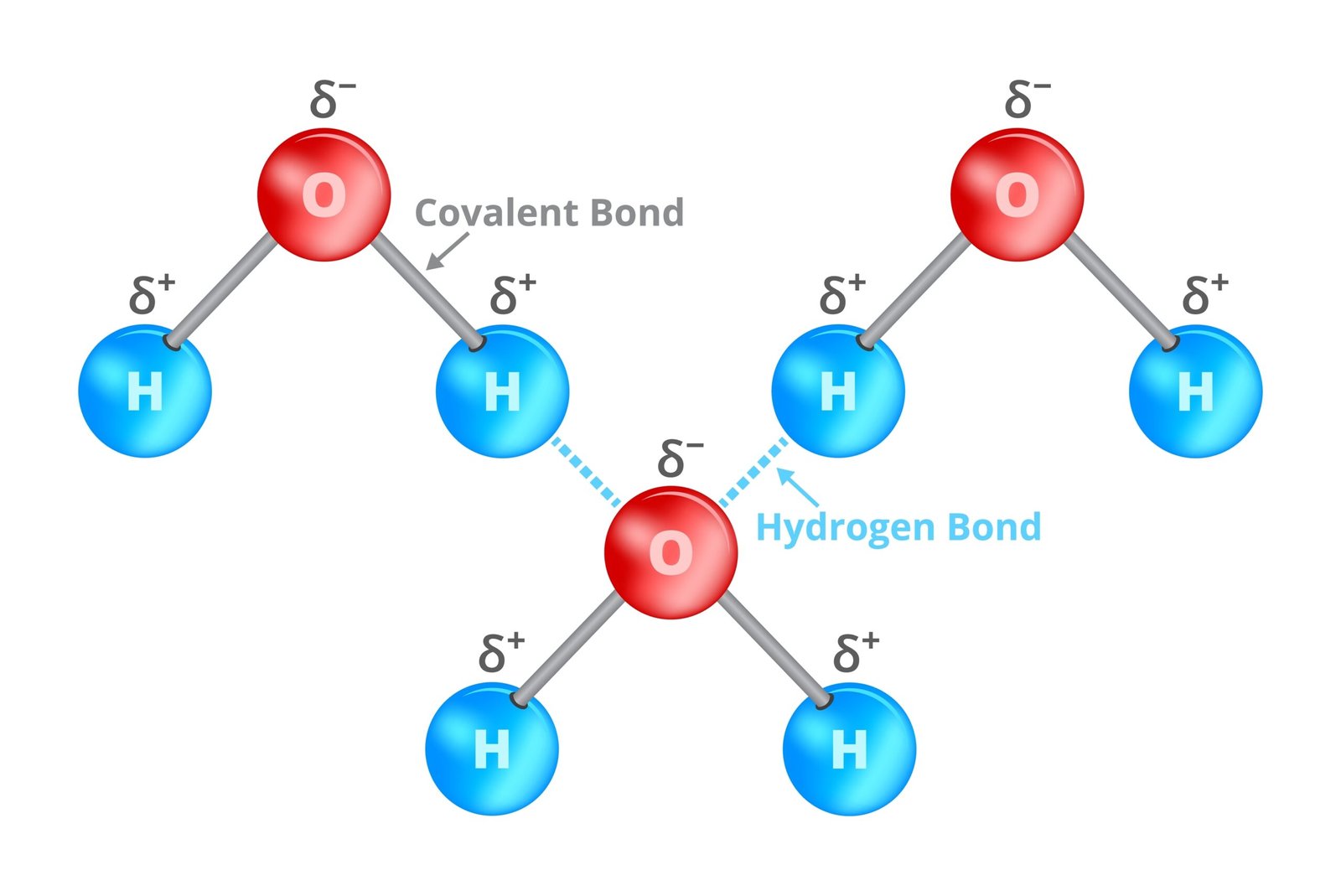
Covalent bonds – strong, stable (C–C, peptide)
Hydrogen bonds – weak, stabilise DNA, proteins
Ionic bonds – between charged groups
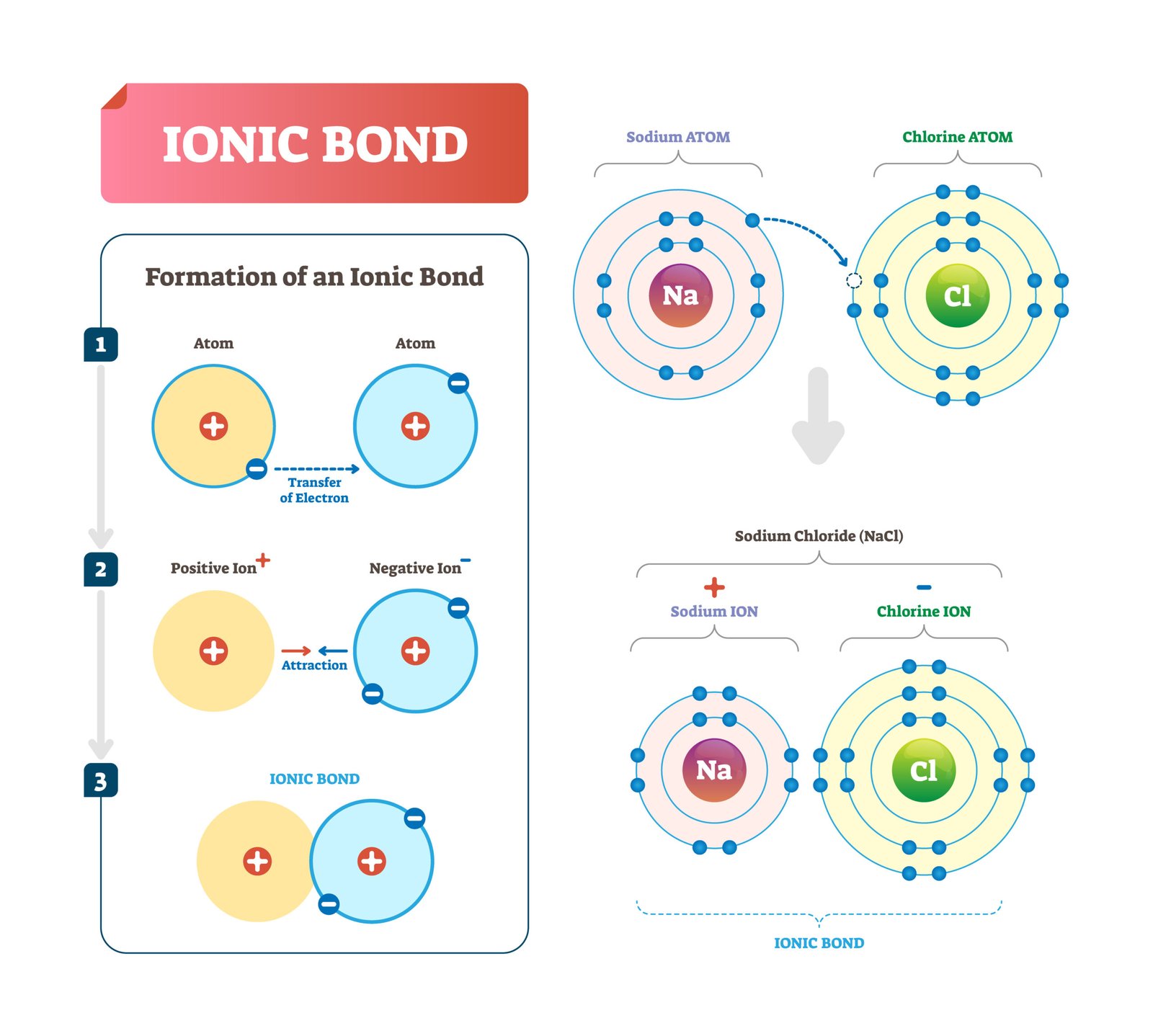
Glycosidic – carbohydrate link
Ester bond – lipid formation
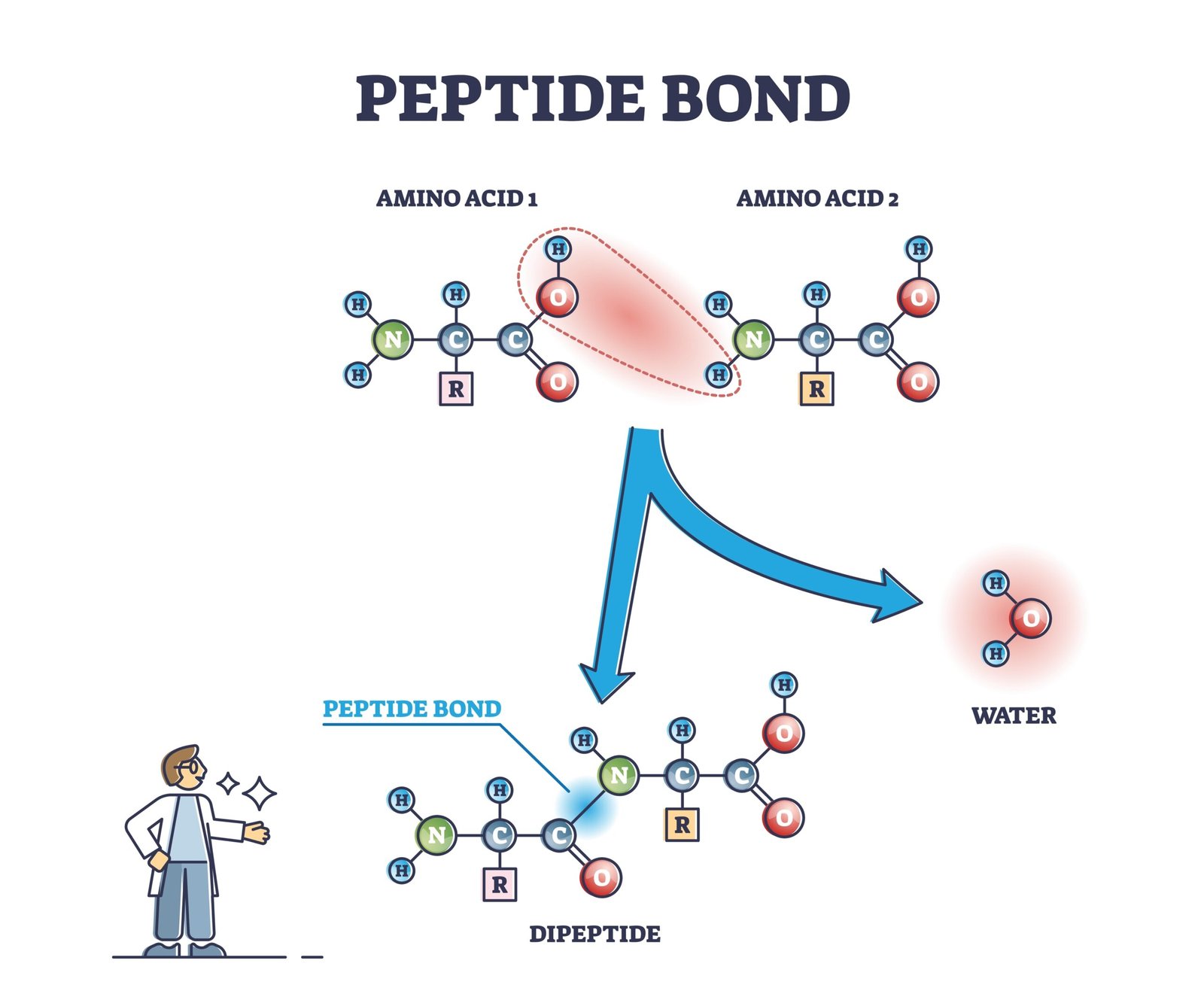
Peptide bond – amino acids linkage
💡 Concept: Bonds determine structure and function.
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🌿 Connects chemistry and biology
🧬 Explains molecular basis of life processes
🧠 Builds foundation for biochemistry and genetics
⚡ Vital for NEET, CBSE, and research fields
📝 Quick Recap
🧪 Biomolecules: organic + inorganic compounds
🍞 Carbohydrates: energy source (mono, di, poly)
🧈 Lipids: energy storage, structure, insulation
💪 Proteins: amino acid polymers; functional molecules
🧬 Nucleic acids: DNA (genetic), RNA (protein synthesis)
⚙️ Enzymes: biological catalysts
🌸 Metabolites: primary (essential), secondary (specialised)
📘 Summary
All living cells contain a variety of biomolecules that form the chemical basis of life.
Carbohydrates provide energy, lipids store energy and form membranes, proteins perform structural and functional roles, and nucleic acids carry genetic information.
Enzymes catalyse biochemical reactions, ensuring life runs efficiently.
These molecules interact to sustain metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Studying biomolecules bridges chemistry and biology, revealing how simple molecules create the complexity of living systems.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. What are macromolecules? Give examples.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Macromolecules are large, complex molecules formed by the polymerization of smaller units called monomers. They have high molecular weight and are essential for the structure and function of cells.
🌿 Examples:
➡️ Polysaccharides (e.g., starch, glycogen)
➡️ Proteins (e.g., enzymes, collagen)
➡️ Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA)
➡️ Lipids (though not always polymeric, some are macromolecular in size)
✔️ Function: Structural, catalytic, genetic, and energy storage roles.
🔵 Question 2. What is meant by tertiary structure of proteins?
🟢 Answer:
🧫 The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional folding of a protein chain resulting from interactions among amino acid side chains.
🌿 Types of bonds responsible:
➡️ Hydrogen bonds
➡️ Ionic bonds
➡️ Disulfide bridges
➡️ Hydrophobic interactions
💡 This structure determines the functional shape of a protein (globular or fibrous).
✔️ Example: Enzymes like pepsin and hemoglobin.
🔵 Question 3. Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry which manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers.
🟢 Answer:
🌸 Examples of small molecular weight biomolecules:
Glucose
Fructose
Ribose
Glycerol
Amino acids (glycine, alanine)
Fatty acids
Nucleotides
Urea
Cholesterol
Lactic acid
🏭 Industries: Pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries isolate these molecules.
🛒 Buyers: Research laboratories, hospitals, food industries, cosmetic companies.
✔️ Purpose: Used in medicines, nutrition, and biochemical research.
🔵 Question 4. Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., Cosmetics etc.)
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Proteins as therapeutic agents:
➡️ Insulin: Diabetes treatment
➡️ Interferons: Antiviral, anticancer
➡️ Monoclonal antibodies: Cancer therapy
➡️ Albumin: Maintains osmotic pressure in patients
➡️ Thrombin/Fibrinogen: Blood clotting
💄 Other applications:
Collagen: Cosmetics, anti-aging creams
Keratin: Hair products
Casein: Nutritional supplements
✔️ Significance: Proteins play key roles in medicine and industry.
🔵 Question 5. Explain the composition of triglyceride.
🟢 Answer:
⚗️ Triglyceride = 1 molecule of glycerol + 3 molecules of fatty acids.
Each fatty acid is linked to glycerol by ester bonds.
🧠 Formula:
Glycerol (C₃H₅(OH)₃) + 3 Fatty acids → Triglyceride + 3H₂O
✔️ Function: Major form of energy storage in animals and plants.
🔵 Question 6. Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models)?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Yes, Ball and Stick models help visualize the 3D arrangement of atoms and bonds in biomolecules.
💡 Students can model glucose, amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids to understand spatial orientation.
✔️ Useful in studying molecular geometry and bond angles.
🔵 Question 7. Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Structure of Alanine (C₃H₇NO₂):
Central α-carbon bonded to:
➡️ Amino group (-NH₂)
➡️ Carboxyl group (-COOH)
➡️ Hydrogen atom
➡️ Methyl group (-CH₃)
✏️ Diagram description:
H
|
H2N–C–COOH
|
CH3
✔️ Alanine is a non-polar, aliphatic amino acid.
🔵 Question 8. What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Gums are polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates) secreted by plants for protection.
➡️ Examples: Gum arabic, guar gum, tragacanth.
🧪 Fevicol is synthetic, made of polyvinyl acetate (PVA), not a natural polysaccharide.
✔️ Hence, Fevicol is different from natural gums.
🔵 Question 9. Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Tests:
Proteins: Biuret test (violet color)
Fats and oils: Sudan III test (red color)
Amino acids: Ninhydrin test (blue-violet color)
💡 Application: Test biological samples like saliva, fruit juice, urine for presence of biomolecules.
🔵 Question 10. Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man annually. What a loss of vegetation!
🟢 Answer:
🌱 Plants produce ~ 10¹¹–10¹² tonnes of cellulose annually (largest organic compound on Earth).
🏭 Paper industry consumes millions of tonnes annually, leading to deforestation.
💡 Impact: Loss of vegetation, biodiversity, ecological imbalance.
✔️ Promotes need for sustainable practices and recycling.
🔵 Question 11. Describe the important properties of enzymes.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins (or RNA).
🌿 Properties:
Catalytic efficiency — increase reaction rate.
Specificity — act on specific substrates.
Optimum conditions — best at specific pH and temperature.
Reversibility — can catalyse both forward and backward reactions.
Saturation — rate increases with substrate concentration up to a limit.
Denaturation — lose activity at high temperature or extreme pH.
✔️ Conclusion: Enzymes regulate all metabolic reactions in living cells.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
Biomolecules are primarily composed of:
🔴1️⃣ C, H, O, N
🟢2️⃣ Na, K, Mg, Ca
🟡3️⃣ Fe, Cu, Zn, Co
🔵4️⃣ P, S, Cl, F
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ C, H, O, N
🔴 Question 2:
Which of the following is a monosaccharide?
🔴1️⃣ Sucrose
🟢2️⃣ Glucose
🟡3️⃣ Maltose
🔵4️⃣ Lactose
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Glucose
🔴 Question 3:
The simplest carbohydrate is:
🔴1️⃣ Sucrose
🟢2️⃣ Fructose
🟡3️⃣ Glucose
🔵4️⃣ Monosaccharide
🟢 Answer: 4️⃣ Monosaccharide
🔴 Question 4:
Which of the following is a disaccharide?
🔴1️⃣ Glucose
🟢2️⃣ Sucrose
🟡3️⃣ Starch
🔵4️⃣ Cellulose
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Sucrose
🔴 Question 5:
The storage polysaccharide in plants 🌿 is:
🔴1️⃣ Glycogen
🟢2️⃣ Starch
🟡3️⃣ Cellulose
🔵4️⃣ Chitin
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Starch
🔴 Question 6:
The storage polysaccharide in animals 🐾 is:
🔴1️⃣ Starch
🟢2️⃣ Cellulose
🟡3️⃣ Glycogen
🔵4️⃣ Fructose
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Glycogen
🔴 Question 7:
Proteins are polymers of:
🔴1️⃣ Sugars
🟢2️⃣ Fatty acids
🟡3️⃣ Amino acids
🔵4️⃣ Nucleotides
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Amino acids
🔴 Question 8:
The basic structural unit of nucleic acids is:
🔴1️⃣ Nucleotide
🟢2️⃣ Ribose
🟡3️⃣ Nitrogen base
🔵4️⃣ Deoxyribose
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Nucleotide
🔴 Question 9:
Which one is a purine base?
🔴1️⃣ Adenine
🟢2️⃣ Thymine
🟡3️⃣ Cytosine
🔵4️⃣ Uracil
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Adenine
🔴 Question 10:
Which vitamin is fat soluble?
🔴1️⃣ Vitamin C
🟢2️⃣ Vitamin B
🟡3️⃣ Vitamin D
🔵4️⃣ Vitamin H
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Vitamin D
🔴 Question 11:
Name the two types of nucleic acids found in living organisms.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid): Genetic material in most organisms.
2️⃣ RNA (Ribonucleic acid): Involved in protein synthesis.
🔴 Question 12:
Define metabolites and name their types.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Molecules present in cells involved in metabolism.
Types:
1️⃣ Primary metabolites: Essential for life (e.g. amino acids, sugars).
2️⃣ Secondary metabolites: Non-essential, specialised roles (e.g. alkaloids, pigments).
🔴 Question 13:
What are carbohydrates? Write their classification with examples.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Organic compounds made of C, H, O in ratio 1:2:1; main energy source.
Classification:
1️⃣ Monosaccharides: Single sugar unit; e.g. Glucose, Fructose.
2️⃣ Disaccharides: Two monosaccharides; e.g. Sucrose (Glucose + Fructose).
3️⃣ Polysaccharides: Many sugar units; e.g. Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose.
💡 Function: Provide energy, structural support.
🔴 Question 14:
What are lipids? Mention their functions.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Organic compounds made of C, H, O; insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
Examples: Fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids, waxes.
Functions:
1️⃣ Energy storage (twice that of carbohydrates).
2️⃣ Component of cell membrane (phospholipids).
3️⃣ Insulation and protection.
4️⃣ Hormone formation (steroids).
🔴 Question 15:
What are proteins? Describe their structure and functions.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Structure:
1️⃣ Primary: Sequence of amino acids.
2️⃣ Secondary: Coiling (α-helix) or folding (β-sheet).
3️⃣ Tertiary: 3D structure.
4️⃣ Quaternary: Two or more polypeptides.
Functions:
✔️ Structural (collagen),
✔️ Enzymatic (amylase),
✔️ Transport (haemoglobin),
✔️ Defence (antibodies).
🔴 Question 16:
What are nucleic acids? Write their components and types.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Macromolecules carrying genetic information.
Components:
1️⃣ Nitrogen base: Purines (A, G), Pyrimidines (T, C, U).
2️⃣ Pentose sugar: Ribose / Deoxyribose.
3️⃣ Phosphate group.
Types:
1️⃣ DNA: Genetic material in most organisms.
2️⃣ RNA: Helps in protein synthesis.
🔴 Question 17:
Write differences between DNA and RNA.
🟢 Answer:
Feature DNA RNA
Sugar Deoxyribose Ribose
Bases A, T, G, C A, U, G, C
Strand Double-stranded Single-stranded
Function Genetic material Protein synthesis
🔴 Question 18:
What are enzymes? Mention their properties.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Biocatalysts made of protein, speed up reactions.
Properties:
1️⃣ Specific in action.
2️⃣ Required in small amounts.
3️⃣ Highly efficient.
4️⃣ Affected by temperature, pH.
5️⃣ Not consumed in reaction.
Example: Amylase, Lipase.
🔴 Question 19:
What are co-factors? Mention their types.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Non-protein components required by enzymes for activity.
Types:
1️⃣ Prosthetic group: Tightly bound (e.g. FAD).
2️⃣ Coenzyme: Loosely bound organic molecules (e.g. NAD⁺, CoA).
3️⃣ Metal ions: Inorganic activators (e.g. Mg²⁺, Zn²⁺).
💡 Enzyme + Co-factor = Holoenzyme.
🔴 Question 20:
Write a note on primary and secondary metabolites.
🟢 Answer:
Primary metabolites:
✔️ Essential for normal metabolism.
✔️ Examples: Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids.
Secondary metabolites:
✔️ Non-essential; specialised functions (defence, pigments).
✔️ Examples: Alkaloids, flavonoids, rubber, essential oils.
🔴 Question 21:
What is a peptide bond? How is it formed?
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Covalent bond joining two amino acids.
Formation:
• Between carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid and amino group (-NH₂) of another.
• Involves removal of water (condensation reaction).
Example: Formation of dipeptide from two amino acids.
🔴 Question 22:
What is denaturation of proteins?
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Loss of native structure of protein without breaking peptide bonds.
Causes: Heat, pH change, chemicals.
Result: Loss of biological activity.
Example: White of egg (albumin) becomes solid on boiling.
🔴 Question 23:
Describe the structure of an amino acid and explain the different types of amino acids.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
Each amino acid consists of —
1️⃣ Amino group (-NH₂)
2️⃣ Carboxyl group (-COOH)
3️⃣ Hydrogen atom (H)
4️⃣ Side chain (R group) attached to α-carbon.
🧪 General formula: NH₂–CH(R)–COOH
Classification (based on R group):
1️⃣ Non-polar: Glycine, Alanine.
2️⃣ Polar uncharged: Serine, Threonine.
3️⃣ Acidic: Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid.
4️⃣ Basic: Lysine, Arginine.
5️⃣ Aromatic: Phenylalanine, Tyrosine.
💡 Function: Building blocks of proteins; structural and enzymatic roles.
🔴 Question 24:
Explain the structure and functions of enzymes.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Globular proteins with active sites.
2️⃣ Apoenzyme (protein part) + Cofactor = Holoenzyme (active form).
3️⃣ Active site: Region binding substrate forming enzyme-substrate complex.
Functions:
✔️ Lower activation energy.
✔️ Catalyse metabolic reactions (digestion, respiration).
✔️ Highly specific to substrate.
✔️ Can be reused; work at optimum temperature & pH.
💡 Examples:
• Amylase → converts starch → maltose.
• Lipase → converts lipids → fatty acids & glycerol.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain enzyme action mechanism (Lock and Key model).
🟢 Answer:
Proposed by: Emil Fischer (1894).
Concept:
1️⃣ Enzyme’s active site fits substrate specifically like a key fits a lock.
2️⃣ Forms enzyme-substrate complex.
3️⃣ Reaction occurs → product formed.
4️⃣ Enzyme released unchanged.
🧠 Equation:
E + S → ES → E + P
Feature: Explains specificity; enzyme reusable.
🔴 Question 26:
Describe the structure of DNA.
🟢 Answer:
Proposed by: Watson and Crick (1953).
Structure:
1️⃣ Double helix of two polynucleotide chains.
2️⃣ Backbone: Sugar (deoxyribose) + phosphate.
3️⃣ Bases: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C).
4️⃣ Base pairing: A = T (2 H-bonds), G ≡ C (3 H-bonds).
5️⃣ Antiparallel strands: 5’→3′ and 3’→5′.
6️⃣ One turn = 10 base pairs (distance 3.4 nm).
💡 Function: Genetic material; stores hereditary information.
🔴 Question 27:
Explain the structure of RNA and its types.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Single-stranded polynucleotide chain.
2️⃣ Sugar: Ribose.
3️⃣ Bases: A, G, C, U (uracil replaces thymine).
Types:
1️⃣ mRNA: Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosome.
2️⃣ tRNA: Brings amino acids for protein synthesis.
3️⃣ rRNA: Structural component of ribosomes.
💡 Function: Involved in protein synthesis.
🔴 Question 28:
Discuss the factors affecting enzyme activity.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Temperature:
• Activity increases with temperature till optimum (~37°C).
• High temperature → denaturation.
2️⃣ pH:
• Each enzyme has optimum pH (e.g. Pepsin – pH 2).
3️⃣ Substrate concentration:
• Increases activity till saturation.
4️⃣ Enzyme concentration:
• Directly proportional to rate (if substrate excess).
5️⃣ Cofactors presence:
• Required for maximum activity.
🔴 Question 29:
What are cofactors? Describe their types with examples.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Non-protein components helping enzyme action.
Types:
1️⃣ Prosthetic group: Tightly bound, e.g. FAD in succinate dehydrogenase.
2️⃣ Coenzyme: Loosely attached organic molecules, e.g. NAD⁺, CoA.
3️⃣ Metal ions: Inorganic activators, e.g. Mg²⁺, Zn²⁺.
💡 Holoenzyme = Apoenzyme + Cofactor
🔴 Question 30:
Explain metabolic pathways with an example.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Series of enzyme-mediated reactions in a cell.
Example: Glycolysis
1️⃣ Glucose → Glucose-6-phosphate
2️⃣ → Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
3️⃣ → Pyruvic acid
Each step catalysed by a specific enzyme.
Significance: Converts substrates into useful products, releases energy.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The monomeric unit of proteins is
🟡 A. Fatty acid
🟡 B. Amino acid
🟡 C. Nucleotide
🟡 D. Monosaccharide
🟢 Answer: B. Amino acid
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q2. Cellulose is a polymer of
🟡 A. Glucose
🟡 B. Fructose
🟡 C. Galactose
🟡 D. Ribose
🟢 Answer: A. Glucose
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q3. Which of the following biomolecules is amphipathic?
🟡 A. Starch
🟡 B. Lipid
🟡 C. Protein
🟡 D. Cellulose
🟢 Answer: B. Lipid
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q4. Glycosidic bonds are present in
🟡 A. Nucleic acids
🟡 B. Lipids
🟡 C. Carbohydrates
🟡 D. Proteins
🟢 Answer: C. Carbohydrates
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q5. The bond linking two amino acids is called
🟡 A. Phosphodiester bond
🟡 B. Peptide bond
🟡 C. Glycosidic bond
🟡 D. Hydrogen bond
🟢 Answer: B. Peptide bond
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q6. The prosthetic group of haemoglobin is
🟡 A. Chlorophyll
🟡 B. Haem
🟡 C. NADP⁺
🟡 D. FAD
🟢 Answer: B. Haem
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q7. A nucleotide is composed of
🟡 A. Sugar + Base + Phosphate
🟡 B. Sugar + Base
🟡 C. Base + Phosphate
🟡 D. Sugar + Phosphate
🟢 Answer: A. Sugar + Base + Phosphate
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q8. DNA and RNA are polymers of
🟡 A. Amino acids
🟡 B. Nucleotides
🟡 C. Monosaccharides
🟡 D. Fatty acids
🟢 Answer: B. Nucleotides
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q9. The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by
🟡 A. Hydrogen bonds
🟡 B. Ionic bonds
🟡 C. Disulfide bonds
🟡 D. Peptide bonds
🟢 Answer: A. Hydrogen bonds
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q10. The storage polysaccharide in animals is
🟡 A. Starch
🟡 B. Glycogen
🟡 C. Cellulose
🟡 D. Chitin
🟢 Answer: B. Glycogen
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q11. Which of the following is a saturated fatty acid?
🟡 A. Oleic acid
🟡 B. Palmitic acid
🟡 C. Linoleic acid
🟡 D. Arachidonic acid
🟢 Answer: B. Palmitic acid
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q12. The sugar present in RNA is
🟡 A. Deoxyribose
🟡 B. Ribose
🟡 C. Glucose
🟡 D. Fructose
🟢 Answer: B. Ribose
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q13. Which biomolecule carries genetic information?
🟡 A. Lipid
🟡 B. DNA
🟡 C. Protein
🟡 D. Carbohydrate
🟢 Answer: B. DNA
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q14. The primary structure of proteins refers to
🟡 A. Sequence of amino acids
🟡 B. Alpha helices and beta sheets
🟡 C. Tertiary folding
🟡 D. Quaternary association
🟢 Answer: A. Sequence of amino acids
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q15. Which of these is not a polysaccharide?
🟡 A. Glycogen
🟡 B. Cellulose
🟡 C. Starch
🟡 D. Maltose
🟢 Answer: D. Maltose
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q16. In DNA, the complementary base pairing is between
🟡 A. Adenine–Cytosine & Guanine–Thymine
🟡 B. Adenine–Thymine & Guanine–Cytosine
🟡 C. Adenine–Uracil & Guanine–Cytosine
🟡 D. Adenine–Guanine & Cytosine–Thymine
🟢 Answer: B. Adenine–Thymine & Guanine–Cytosine
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q17. The number of amino acids used in protein synthesis is
🟡 A. 18
🟡 B. 20
🟡 C. 22
🟡 D. 24
🟢 Answer: B. 20
📅 NEET 2021
🔵 Q18. Phospholipids are major components of
🟡 A. Enzymes
🟡 B. Plasma membranes
🟡 C. DNA
🟡 D. Ribosomes
🟢 Answer: B. Plasma membranes
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q19. Chitin is a
🟡 A. Protein in vertebrates
🟡 B. Polysaccharide in fungal cell walls
🟡 C. Lipid in insects
🟡 D. Nucleic acid in bacteria
🟢 Answer: B. Polysaccharide in fungal cell walls
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q20. Nucleosomes are units of
🟡 A. RNA packaging
🟡 B. Protein synthesis
🟡 C. DNA packaging
🟡 D. Lipid synthesis
🟢 Answer: C. DNA packaging
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q21. Enzymes are mainly composed of
🟡 A. Carbohydrates
🟡 B. Proteins
🟡 C. Nucleotides
🟡 D. Lipids
🟢 Answer: B. Proteins
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q22. Which vitamin is a component of coenzyme NAD⁺?
🟡 A. Vitamin A
🟡 B. Vitamin B₃ (Niacin)
🟡 C. Vitamin C
🟡 D. Vitamin K
🟢 Answer: B. Vitamin B₃ (Niacin)
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q23. DNA differs from RNA in
🟡 A. Sugar and base composition
🟡 B. Phosphate content
🟡 C. Presence of ribose in DNA
🟡 D. Presence of uracil in DNA
🟢 Answer: A. Sugar and base composition
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q24. The most abundant protein in animals is
🟡 A. Actin
🟡 B. Myosin
🟡 C. Collagen
🟡 D. Keratin
🟢 Answer: C. Collagen
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q25. The vitamin involved in blood clotting is
🟡 A. Vitamin D
🟡 B. Vitamin B₁₂
🟡 C. Vitamin A
🟡 D. Vitamin K
🟢 Answer: D. Vitamin K
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q26. The vitamin that acts as an antioxidant is
🟡 A. Vitamin D
🟡 B. Vitamin E
🟡 C. Vitamin B₆
🟡 D. Vitamin K
🟢 Answer: B. Vitamin E
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q27. The sugar present in DNA is
🟡 A. Ribose
🟡 B. Deoxyribose
🟡 C. Glucose
🟡 D. Fructose
🟢 Answer: B. Deoxyribose
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q28. The polysaccharide found in exoskeleton of arthropods is
🟡 A. Cellulose
🟡 B. Chitin
🟡 C. Glycogen
🟡 D. Starch
🟢 Answer: B. Chitin
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q29. The base not present in RNA is
🟡 A. Adenine
🟡 B. Guanine
🟡 C. Uracil
🟡 D. Thymine
🟢 Answer: D. Thymine
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q30. The number of peptide bonds in a tripeptide is
🟡 A. One
🟡 B. Two
🟡 C. Three
🟡 D. Four
🟢 Answer: B. Two
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q31. The primary source of energy in living organisms is
🟡 A. Lipids
🟡 B. Carbohydrates
🟡 C. Proteins
🟡 D. Vitamins
🟢 Answer: B. Carbohydrates
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q32. The quaternary structure of a protein refers to
🟡 A. Sequence of amino acids
🟡 B. Alpha helices and beta sheets
🟡 C. Overall folding of a single polypeptide
🟡 D. Arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains
🟢 Answer: D. Arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q33. Nitrogenous base present only in RNA is
🟡 A. Uracil
🟡 B. Thymine
🟡 C. Cytosine
🟡 D. Adenine
🟢 Answer: A. Uracil
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q34. The enzyme that unwinds DNA during replication is
🟡 A. DNA polymerase
🟡 B. DNA ligase
🟡 C. DNA helicase
🟡 D. Primase
🟢 Answer: C. DNA helicase
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q35. Lipids that form the main structural component of plasma membranes are
🟡 A. Glycolipids
🟡 B. Phospholipids
🟡 C. Steroids
🟡 D. Waxes
🟢 Answer: B. Phospholipids
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q36. Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
🟡 A. Sucrose
🟡 B. Cellulose
🟡 C. Maltose
🟡 D. Starch
🟢 Answer: C. Maltose
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q37. The nucleotide having three phosphate groups is
🟡 A. AMP
🟡 B. ADP
🟡 C. ATP
🟡 D. GMP
🟢 Answer: C. ATP
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q38. Which one of the following is a fibrous protein?
🟡 A. Collagen
🟡 B. Hemoglobin
🟡 C. Insulin
🟡 D. Myoglobin
🟢 Answer: A. Collagen
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q39. The enzyme that joins Okazaki fragments during DNA replication is
🟡 A. DNA helicase
🟡 B. DNA polymerase I
🟡 C. DNA ligase
🟡 D. Primase
🟢 Answer: C. DNA ligase
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q40. Vitamin B₁₂ contains which metal ion?
🟡 A. Iron
🟡 B. Magnesium
🟡 C. Cobalt
🟡 D. Zinc
🟢 Answer: C. Cobalt
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q41. The sugar present in ATP is
🟡 A. Ribose
🟡 B. Deoxyribose
🟡 C. Glucose
🟡 D. Fructose
🟢 Answer: A. Ribose
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q42. Which of the following is a storage polysaccharide in plants?
🟡 A. Cellulose
🟡 B. Glycogen
🟡 C. Starch
🟡 D. Chitin
🟢 Answer: C. Starch
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q43. The sugar-phosphate backbone is a feature of
🟡 A. Proteins
🟡 B. Nucleic acids
🟡 C. Polysaccharides
🟡 D. Lipids
🟢 Answer: B. Nucleic acids
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q44. The peptide bond is a type of
🟡 A. Hydrogen bond
🟡 B. Covalent bond
🟡 C. Ionic bond
🟡 D. Disulfide bond
🟢 Answer: B. Covalent bond
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q45. The protein hormone insulin is made of
🟡 A. One polypeptide chain
🟡 B. Two polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bridges
🟡 C. Two carbohydrate chains
🟡 D. Three polypeptide chains
🟢 Answer: B. Two polypeptide chains linked by disulfide bridges
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q46. The primary alcohol present in nucleotides is
🟡 A. Glycerol
🟡 B. Ribose
🟡 C. Deoxyribose
🟡 D. Ethanol
🟢 Answer: B. Ribose
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q47. Which vitamin deficiency causes scurvy?
🟡 A. Vitamin A
🟡 B. Vitamin C
🟡 C. Vitamin D
🟡 D. Vitamin E
🟢 Answer: B. Vitamin C
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q48. The bond that holds the two strands of DNA together is
🟡 A. Covalent bond
🟡 B. Hydrogen bond
🟡 C. Ionic bond
🟡 D. Peptide bond
🟢 Answer: B. Hydrogen bond
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q49. Which element is present in all amino acids but not in carbohydrates?
🟡 A. Hydrogen
🟡 B. Oxygen
🟡 C. Nitrogen
🟡 D. Carbon
🟢 Answer: C. Nitrogen
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q50. Vitamin D is also known as
🟡 A. Calciferol
🟡 B. Riboflavin
🟡 C. Thiamine
🟡 D. Tocopherol
🟢 Answer: A. Calciferol
📅 NEET 2016
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Biomolecules are organic compounds found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Non-living matter
🟢 2️⃣ Living organisms
🟡 3️⃣ Atmosphere
🔵 4️⃣ Soil
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Living organisms
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following is a macromolecule?
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Protein
🟡 3️⃣ Amino acid
🔵 4️⃣ Fructose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Protein
🔵 Question 3:
The building blocks of proteins are:
🔴 1️⃣ Sugars
🟢 2️⃣ Amino acids
🟡 3️⃣ Fatty acids
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleotides
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Amino acids
🔵 Question 4:
Which bond links amino acids in proteins?
🔴 1️⃣ Hydrogen bond
🟢 2️⃣ Peptide bond
🟡 3️⃣ Glycosidic bond
🔵 4️⃣ Phosphodiester bond
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Peptide bond
🔵 Question 5:
Monosaccharides are:
🔴 1️⃣ Simple sugars
🟢 2️⃣ Complex sugars
🟡 3️⃣ Polysaccharides
🔵 4️⃣ Proteins
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Simple sugars
🔵 Question 6:
Which of the following is a polysaccharide?
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Sucrose
🟡 3️⃣ Starch
🔵 4️⃣ Maltose
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Starch
🔵 Question 7:
Which sugar is present in RNA?
🔴 1️⃣ Deoxyribose
🟢 2️⃣ Ribose
🟡 3️⃣ Glucose
🔵 4️⃣ Fructose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ribose
🔵 Question 8:
Which element is present in proteins but not in carbohydrates?
🔴 1️⃣ Carbon
🟢 2️⃣ Hydrogen
🟡 3️⃣ Nitrogen
🔵 4️⃣ Oxygen
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Nitrogen
🔵 Question 9:
The energy currency of the cell is:
🔴 1️⃣ ADP
🟢 2️⃣ ATP
🟡 3️⃣ AMP
🔵 4️⃣ GTP
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ ATP
🔵 Question 10:
Which bond is found in polysaccharides?
🔴 1️⃣ Peptide
🟢 2️⃣ Glycosidic
🟡 3️⃣ Hydrogen
🔵 4️⃣ Disulfide
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycosidic
🔵 Question 11:
Which of the following is a derived lipid?
🔴 1️⃣ Steroid
🟢 2️⃣ Fatty acid
🟡 3️⃣ Triglyceride
🔵 4️⃣ Wax
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Steroid
🔵 Question 12:
The number of amino acids present in proteins is:
🔴 1️⃣ 10
🟢 2️⃣ 20
🟡 3️⃣ 30
🔵 4️⃣ 50
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 20
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following is not a lipid?
🔴 1️⃣ Cholesterol
🟢 2️⃣ Phospholipid
🟡 3️⃣ Glucose
🔵 4️⃣ Wax
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Glucose
🔵 Question 14:
The base pairing in DNA follows:
🔴 1️⃣ A–C, G–T
🟢 2️⃣ A–T, G–C
🟡 3️⃣ A–G, T–C
🔵 4️⃣ A–A, T–T
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ A–T, G–C
🔵 Question 15:
Which of the following is a reducing sugar?
🔴 1️⃣ Sucrose
🟢 2️⃣ Glucose
🟡 3️⃣ Starch
🔵 4️⃣ Cellulose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glucose
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
🔴 1️⃣ Maltose
🟢 2️⃣ Sucrose
🟡 3️⃣ Lactose
🔵 4️⃣ Glucose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Sucrose
🔵 Question 17:
The nitrogenous bases are derivatives of:
🔴 1️⃣ Pyrrole
🟢 2️⃣ Purine and pyrimidine
🟡 3️⃣ Indole
🔵 4️⃣ Benzene
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Purine and pyrimidine
🔵 Question 18:
The enzyme that converts starch into maltose is:
🔴 1️⃣ Maltase
🟢 2️⃣ Amylase
🟡 3️⃣ Invertase
🔵 4️⃣ Sucrase
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Amylase
🔵 Question 19:
DNA and RNA differ in:
🔴 1️⃣ Sugar
🟢 2️⃣ Base composition
🟡 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 Question 20:
Which of the following is amphipathic in nature?
🔴 1️⃣ Triglyceride
🟢 2️⃣ Phospholipid
🟡 3️⃣ Cholesterol
🔵 4️⃣ Fatty acid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Phospholipid
🔵 Question 21:
The monomers of nucleic acids are:
🔴 1️⃣ Amino acids
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleotides
🟡 3️⃣ Fatty acids
🔵 4️⃣ Monosaccharides
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nucleotides
🔵 Question 22:
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water?
🔴 1️⃣ Proteins
🟢 2️⃣ Lipids
🟡 3️⃣ Carbohydrates
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleic acids
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lipids
🔵 Question 23:
DNA differs from RNA in having:
🔴 1️⃣ Ribose sugar
🟢 2️⃣ Thymine base
🟡 3️⃣ Uracil base
🔵 4️⃣ Double helix
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Thymine base
🔵 Question 24:
The base not found in RNA is:
🔴 1️⃣ Adenine
🟢 2️⃣ Cytosine
🟡 3️⃣ Thymine
🔵 4️⃣ Uracil
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Thymine
🔵 Question 25:
Which of the following is an example of a conjugated protein?
🔴 1️⃣ Albumin
🟢 2️⃣ Hemoglobin
🟡 3️⃣ Keratin
🔵 4️⃣ Collagen
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hemoglobin
🔵 Question 26:
Which among the following is a disaccharide?
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Maltose
🟡 3️⃣ Fructose
🔵 4️⃣ Galactose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Maltose
🔵 Question 27:
In nucleic acids, the sugar is linked to the base through:
🔴 1️⃣ Hydrogen bond
🟢 2️⃣ Glycosidic bond
🟡 3️⃣ Peptide bond
🔵 4️⃣ Phosphodiester bond
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycosidic bond
🔵 Question 28:
Which is the most abundant protein in animal body?
🔴 1️⃣ Hemoglobin
🟢 2️⃣ Collagen
🟡 3️⃣ Albumin
🔵 4️⃣ Globulin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Collagen
🔵 Question 29:
The secondary structure of protein is maintained by:
🔴 1️⃣ Peptide bonds
🟢 2️⃣ Hydrogen bonds
🟡 3️⃣ Ionic bonds
🔵 4️⃣ Disulfide bonds
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hydrogen bonds
🔵 Question 30:
Which is the storage polysaccharide in animals?
🔴 1️⃣ Cellulose
🟢 2️⃣ Glycogen
🟡 3️⃣ Starch
🔵 4️⃣ Inulin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycogen
🔵 Question 31:
Denaturation of proteins leads to loss of:
🔴 1️⃣ Primary structure
🟢 2️⃣ Secondary and tertiary structure
🟡 3️⃣ Only quaternary structure
🔵 4️⃣ Peptide bonds
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Secondary and tertiary structure
🔵 Question 32:
Which one is a nucleoside?
🔴 1️⃣ Adenine + ribose
🟢 2️⃣ Adenine + ribose + phosphate
🟡 3️⃣ Ribose + phosphate
🔵 4️⃣ Base + phosphate
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Adenine + ribose
🔵 Question 33:
Which is the energy-rich bond in ATP?
🔴 1️⃣ Between base and sugar
🟢 2️⃣ Between sugar and first phosphate
🟡 3️⃣ Between terminal phosphates
🔵 4️⃣ Between base and phosphate
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Between terminal phosphates
🔵 Question 34:
Which element is found in nucleic acids but not in carbohydrates?
🔴 1️⃣ Carbon
🟢 2️⃣ Nitrogen
🟡 3️⃣ Oxygen
🔵 4️⃣ Hydrogen
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nitrogen
🔵 Question 35:
Name the test used to detect proteins:
🔴 1️⃣ Benedict’s test
🟢 2️⃣ Biuret test
🟡 3️⃣ Iodine test
🔵 4️⃣ Molisch test
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Biuret test
🔵 Question 36:
Phosphodiester bond is found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Proteins
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleic acids
🟡 3️⃣ Polysaccharides
🔵 4️⃣ Lipids
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nucleic acids
🔵 Question 37:
Which of the following is not a polysaccharide?
🔴 1️⃣ Inulin
🟢 2️⃣ Cellulose
🟡 3️⃣ Glycogen
🔵 4️⃣ Maltose
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Maltose
🔵 Question 38:
The double helical structure of DNA was proposed by:
🔴 1️⃣ Watson and Crick
🟢 2️⃣ Franklin and Wilkins
🟡 3️⃣ Chargaff
🔵 4️⃣ Hershey and Chase
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Watson and Crick
🔵 Question 39:
Which of the following is a storage polysaccharide in plants?
🔴 1️⃣ Starch
🟢 2️⃣ Glycogen
🟡 3️⃣ Cellulose
🔵 4️⃣ Inulin
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Starch
🔵 Question 40:
In DNA, the ratio of purines to pyrimidines is always:
🔴 1️⃣ 1:2
🟢 2️⃣ 2:1
🟡 3️⃣ 1:1
🔵 4️⃣ Variable
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 1:1
🔵 Question 41:
Which base is not found in RNA?
🔴 1️⃣ Uracil
🟢 2️⃣ Thymine
🟡 3️⃣ Cytosine
🔵 4️⃣ Adenine
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Thymine
🔵 Question 42:
The number of hydrogen bonds between A and T in DNA is:
🔴 1️⃣ One
🟢 2️⃣ Two
🟡 3️⃣ Three
🔵 4️⃣ Four
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Two
🔵 Question 43:
Which is an essential amino acid?
🔴 1️⃣ Alanine
🟢 2️⃣ Lysine
🟡 3️⃣ Glycine
🔵 4️⃣ Serine
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lysine
🔵 Question 44:
DNA is acidic due to presence of:
🔴 1️⃣ Nitrogen bases
🟢 2️⃣ Phosphate group
🟡 3️⃣ Ribose
🔵 4️⃣ Deoxyribose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Phosphate group
🔵 Question 45:
Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in:
🔴 1️⃣ Alcohol
🟢 2️⃣ Ether
🟡 3️⃣ Chloroform
🔵 4️⃣ All of these
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ All of these
🔵 Question 46:
The structural polysaccharide in plant cell wall is:
🔴 1️⃣ Starch
🟢 2️⃣ Cellulose
🟡 3️⃣ Glycogen
🔵 4️⃣ Pectin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cellulose
🔵 Question 47:
Nitrogenous base present only in RNA is:
🔴 1️⃣ Thymine
🟢 2️⃣ Uracil
🟡 3️⃣ Cytosine
🔵 4️⃣ Adenine
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Uracil
🔵 Question 48:
Which one is a fibrous protein?
🔴 1️⃣ Insulin
🟢 2️⃣ Collagen
🟡 3️⃣ Hemoglobin
🔵 4️⃣ Enzyme
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Collagen
🔵 Question 49:
Number of different types of nitrogen bases in DNA are:
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 3
🟡 3️⃣ 4
🔵 4️⃣ 5
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 4
🔵 Question 50:
Chargaff’s rule states that:
🔴 1️⃣ A = G
🟢 2️⃣ A = T, G = C
🟡 3️⃣ A + T = G + C
🔵 4️⃣ A + G = T + C
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ A = T, G = C
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
