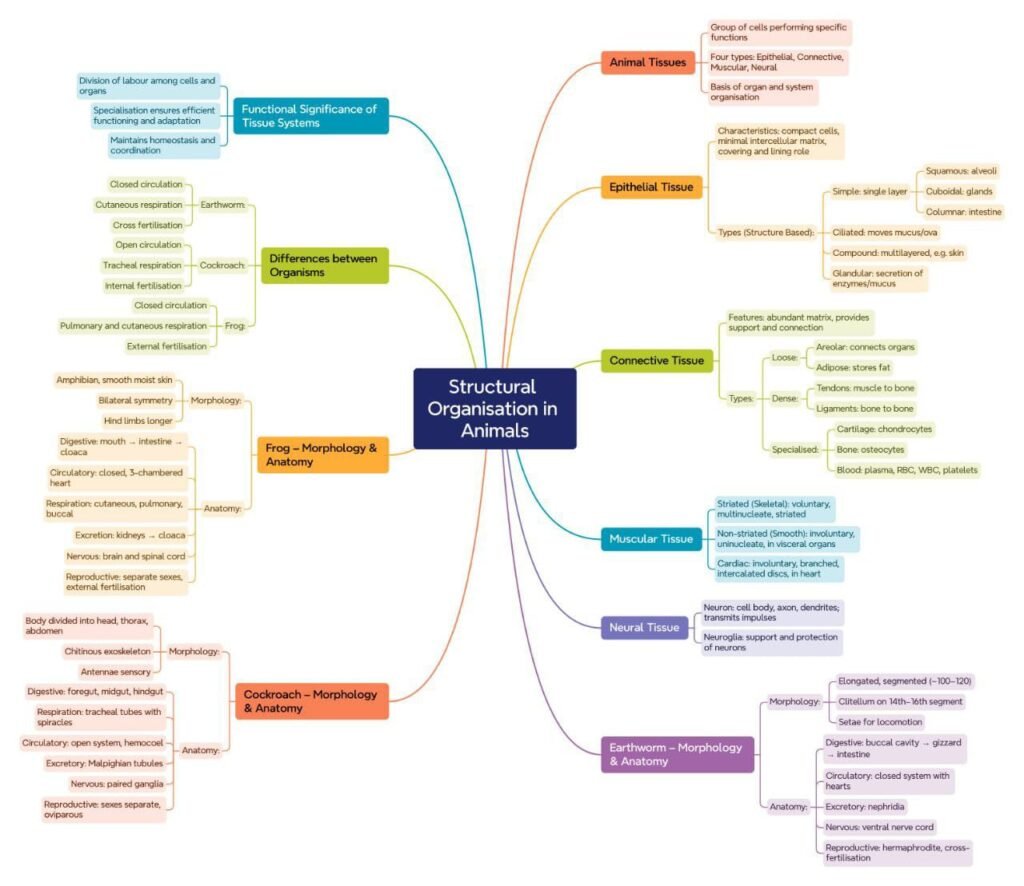
Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 7. Structural Organisation in Animals
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌿✨ Introduction
🧠 The structural organisation of animals refers to how the body is built from the smallest unit (cell) to the most complex (organism).
Each level contributes specific roles, ensuring the animal functions efficiently.
🪴 In multicellular animals, the body is organised into tissues, organs, and organ systems, forming a hierarchy of increasing complexity.
🌿 Studying this chapter helps us understand how animal bodies are built, how tissues perform specialised functions, and how different systems coordinate.
💡 Concept:
Cell → basic unit of life
Tissue → group of similar cells performing a common function
Organ → made of different tissues
Organ system → group of organs performing a collective function
🧫 Levels of Organisation in Animals
1️⃣ Cellular Level – seen in simple animals like sponges; cells are independent and loosely arranged.
2️⃣ Tissue Level – in coelenterates (Hydra); similar cells form tissues for specific functions.
3️⃣ Organ Level – in flatworms (Platyhelminthes); tissues combine to form organs.
4️⃣ Organ System Level – in annelids to chordates; organs form systems with division of labour (digestive, nervous, circulatory).
⚡ Complexity increases from lower to higher animals.
🌸 Animal Tissues
Animals show four main types of tissues, each with unique structure and function:
Epithelial – covering and lining
Connective – binding and support
Muscular – movement
Nervous – coordination
🧬 1️⃣ Epithelial Tissue
💡 Definition: Epithelial tissue forms the outer covering and lining of organs; provides protection, secretion, and absorption.
🧠 Features:
🌿 Cells are tightly packed with minimal intercellular space.
🧪 Supported by basement membrane.
🧴 Lacks blood vessels; nourished by diffusion.
🍃 Types of Epithelial Tissue
🌱 A. Simple Epithelium (single layer)
Designed for absorption, secretion, and exchange.
🪴 Simple squamous – flat cells (lung alveoli, capillaries)
🍀 Cuboidal – cube-shaped cells (kidney tubules, glands)
🌿 Columnar – tall cells (intestine, stomach)
🌸 Ciliated – columnar with cilia (respiratory tract, fallopian tube)
🧪 Glandular – secretes substances (glands)
🌳 B. Compound Epithelium (many layers)
🧠 Function: protection against mechanical/chemical stress
🧴 Found in skin, buccal cavity
✏️ Note: Epithelial tissue forms glands, linings, and coverings, showing specialisations like microvilli, cilia.
🪵 2️⃣ Connective Tissue
💡 Definition: Supports, binds, and connects other tissues.
🧬 Made of cells, fibres (collagen, elastin), and matrix (ground substance).
🌿 Types of Connective Tissue
A. Loose Connective Tissue
🌱 Areolar tissue – binds organs; between skin and muscles
🧈 Adipose tissue – stores fat, cushions organs, insulates
B. Dense Connective Tissue
🪵 Fibres tightly packed → strength
🌾 Ligaments – connect bone to bone (elastic, strength)
⚙️ Tendons – connect muscle to bone (inelastic, strong)
C. Skeletal Connective Tissue
🪨 Cartilage – semi-rigid, flexible (nose, ear, joints)
🪵 Bone – hard matrix (calcium phosphate), forms skeleton, supports, protects
D. Fluid Connective Tissue
💧 Blood – plasma + cells; transports gases, nutrients, wastes
💦 Lymph – returns tissue fluid to blood, defends body
💡 Concept: The matrix composition decides function (solid in bone, fluid in blood).
💪 3️⃣ Muscular Tissue
🧠 Function: Movement through contraction and relaxation.
Contains contractile proteins (actin, myosin).
⚡ Types of Muscles
🏋️ Striated (skeletal) – voluntary, cylindrical, multinucleate, striped, attached to skeleton.
💫 Smooth (non-striated) – involuntary, spindle-shaped, single nucleus, found in internal organs.
❤️ Cardiac – involuntary, branched, striated, with intercalated discs; present in heart wall.
✏️ Note: Muscular tissue converts chemical energy → mechanical energy.
🧠 4️⃣ Nervous Tissue
💡 Function: Coordination and control via electrical impulses.
🧬 Neuron = structural and functional unit.
📡 Parts:
Cell body (cyton) – with nucleus
Dendrites – receive impulses
Axon – transmits impulses
🧪 Neuroglia – supportive cells; protect and nourish neurons.
⚡ Enables reflexes, sensation, thought, and movement.
🧍 Selected Animal Studies
To understand structural organisation, NCERT describes Earthworm, Cockroach, and Frog.
🪴 1️⃣ Earthworm (Pheretima posthuma)
🌿 Habit and Habitat
Terrestrial, burrowing, lives in moist soil; nocturnal.
🍃 Body Organisation
Long, cylindrical, segmented (metameric segmentation)
Each segment similar; clitellum (14–16) for reproduction
Body wall: cuticle → epidermis → muscles → coelomic epithelium
🧪 Digestive System
Straight tube: mouth → buccal cavity → pharynx → oesophagus → gizzard → intestine → anus
🪵 Gizzard grinds food.
🌾 Intestine absorbs nutrients.
💧 Circulatory System
🔴 Closed type with blood vessels and hearts
➡️ Blood flows through dorsal, ventral, and lateral vessels
🧠 Haemoglobin in plasma
⚙️ Excretory System
🧫 Nephridia in all segments
💧 Regulates water and salts
🧠 Nervous System
Paired cerebral ganglia, ventral nerve cord, segmental ganglia
🧬 Reproductive System
Hermaphrodite; male and female organs separate; cross-fertilisation
Eggs in cocoons; development direct.
🌿 Significance: Aerates soil, improves fertility (“farmer’s friend”).
🪳 2️⃣ Cockroach (Periplaneta americana)
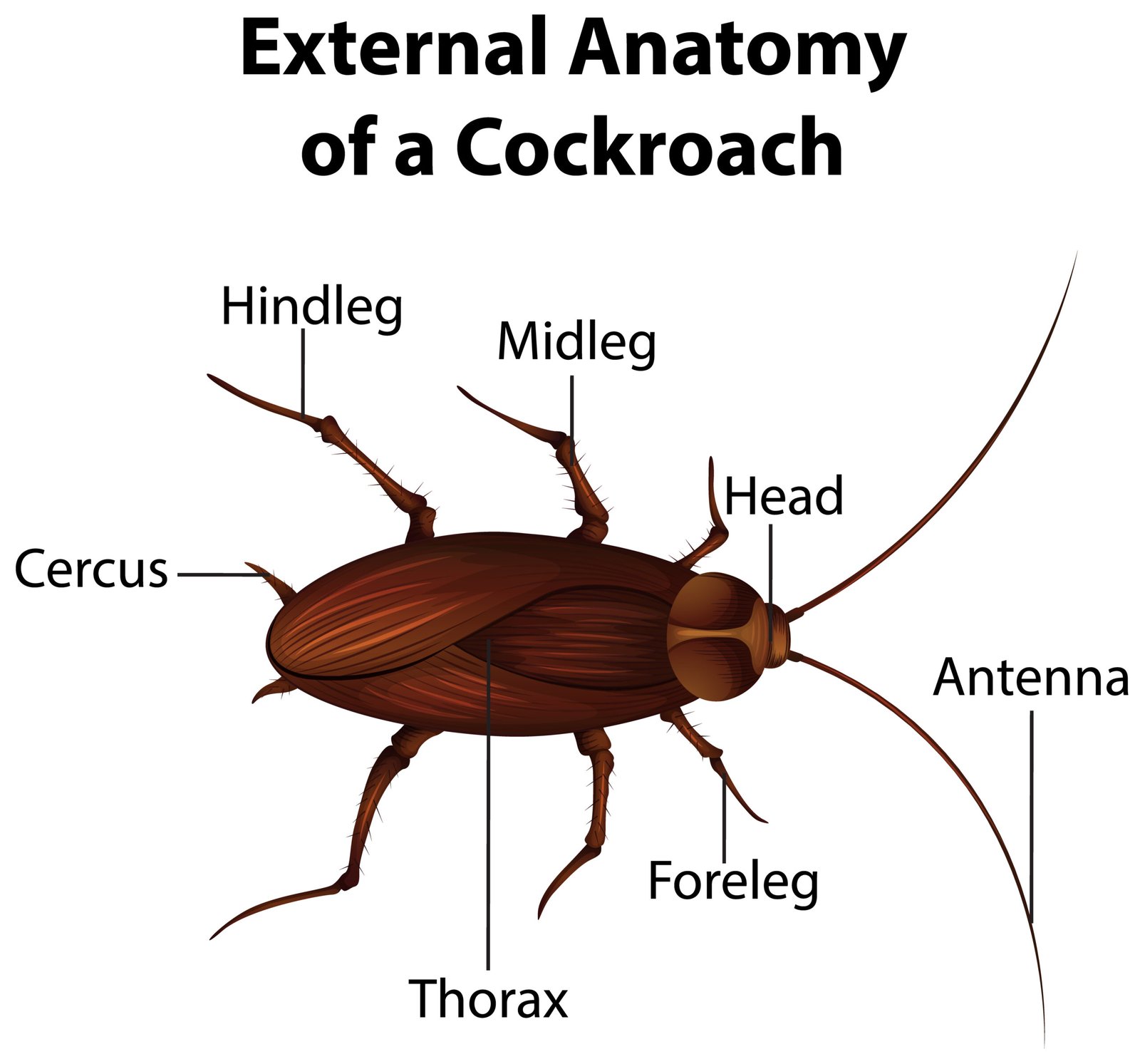
🧠 Habit and Habitat
Nocturnal, omnivorous, found in dark moist places.
🍃 Body Organisation
Exoskeleton of chitin, brown colour
Body regions: head, thorax, abdomen
Appendages: antennae, legs, wings
🧪 Digestive System
Alimentary canal: mouth → pharynx → oesophagus → crop → gizzard → midgut → hindgut
💧 Digestive glands secrete enzymes.
💧 Circulatory System
🩸 Open type; haemolymph circulates in body cavity; no capillaries.
⚡ Respiratory System
Network of tracheae and tracheoles; air enters via spiracles.
Exchange by diffusion.
🧠 Nervous System
Brain + segmental ganglia + ventral nerve cord.
🧬 Excretory System
Malpighian tubules remove nitrogenous waste.
🌿 Reproductive System
Separate sexes.
♀ lays oothecae with eggs.
Development is paurometabolous (gradual).
🐸 3️⃣ Frog (Rana tigrina)
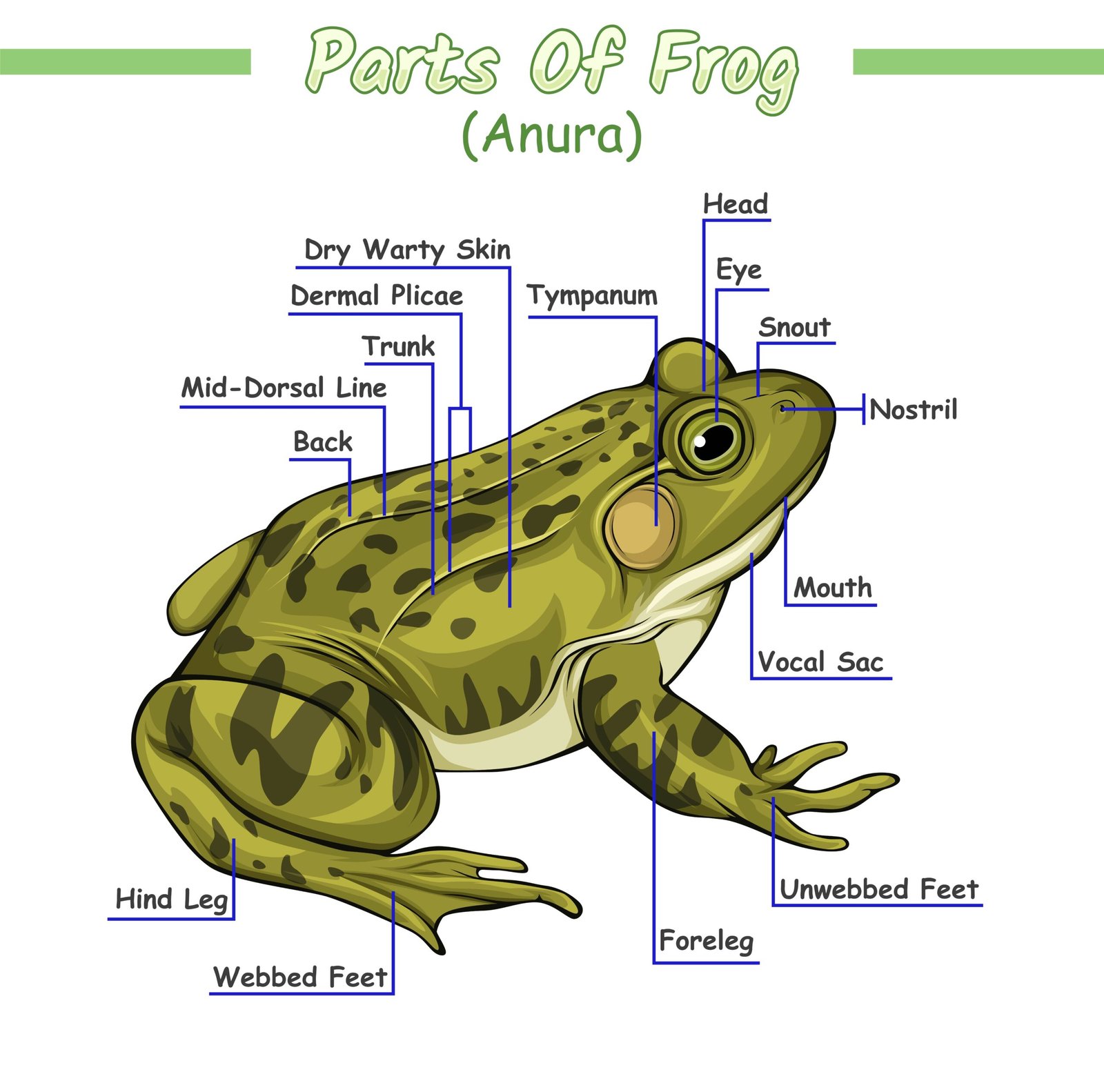
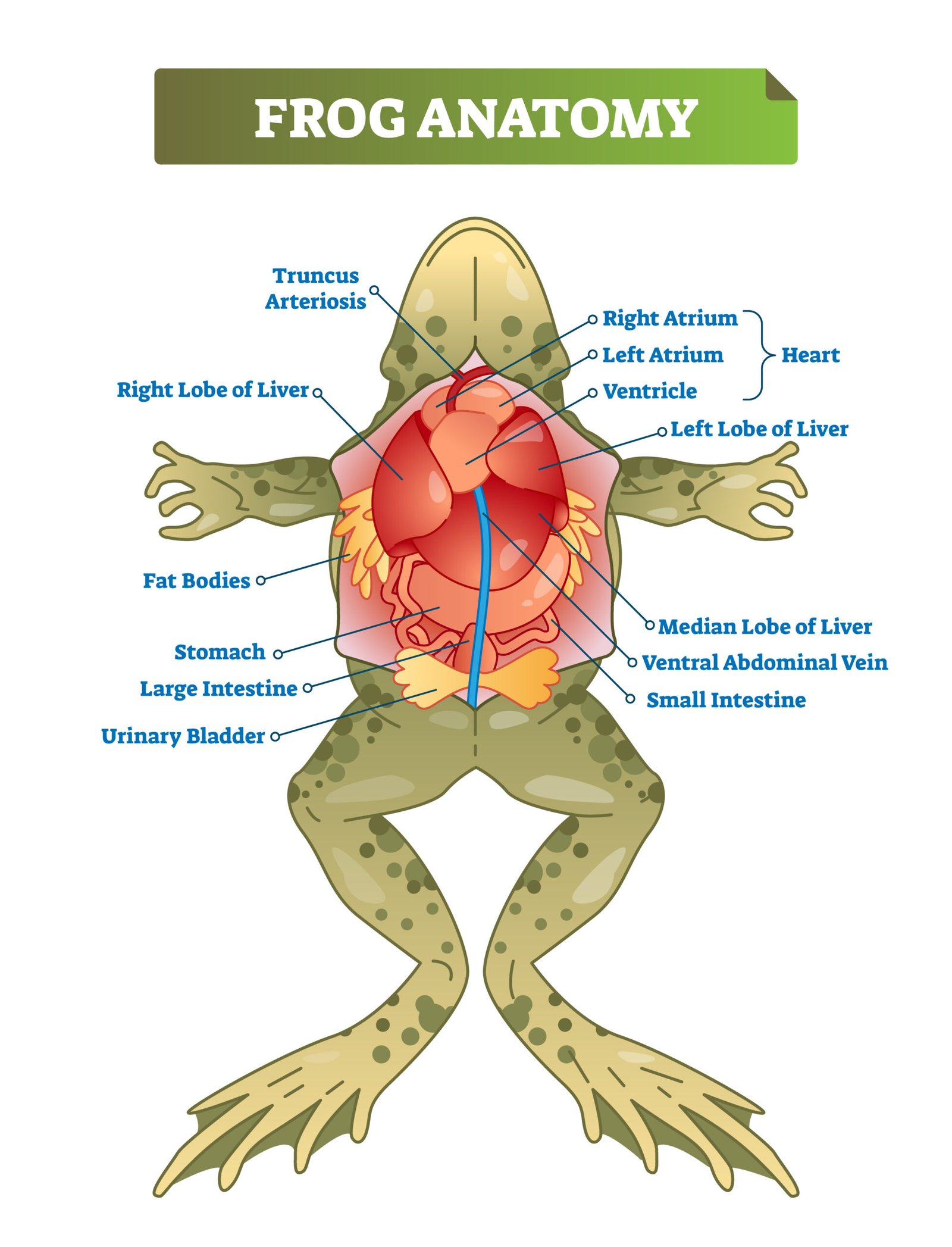
🌿 Habitat
Amphibious – lives on land and in water; carnivorous.
🍃 Body Organisation
Head + trunk; moist, glandular skin; no tail in adult.
🧪 Digestive System
Mouth → buccal cavity → oesophagus → stomach → intestine → cloaca
🧬 Glands: liver, pancreas
💧 Circulatory System
🩸 Closed type, double circulation
❤️ Three-chambered heart (2 atria, 1 ventricle)
⚙️ Respiratory System
By lungs, skin, and buccal cavity (cutaneous, pulmonary, buccopharyngeal)
🧠 Nervous System
Brain + spinal cord; 10 pairs of cranial nerves
Sense organs: eyes, tympanum, olfactory organs
🧬 Reproductive System
Separate sexes; external fertilisation in water
🧫 Eggs → tadpole larva → metamorphosis → adult frog
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🌿 Shows hierarchical organisation of animal body
🧬 Builds base for physiology (circulation, digestion, etc.)
🧠 Enhances understanding of evolution and classification
⚡ Vital for NEET, CBSE boards, and practical zoology
📝 Quick Recap
🧫 Tissues:
Epithelial – covering & lining
Connective – binding & support
Muscular – movement
Nervous – coordination
🪴 Earthworm: segmented, closed circulation, hermaphrodite
🪳 Cockroach: chitinous exoskeleton, open circulation, tracheal respiration
🐸 Frog: amphibian, closed double circulation, metamorphosis
📘 Summary
The animal body shows a clear structural hierarchy.
The cell is the smallest unit; groups form tissues, which organise into organs and systems.
Four tissue types perform distinct roles:
Epithelial protects and secretes,
Connective supports and connects,
Muscular enables movement,
Nervous coordinates responses.
Detailed study of earthworm, cockroach, and frog illustrates diversity and unity of organisation.
Earthworm’s closed circulatory and segmented design show annelid traits; cockroach’s exoskeleton and open system show arthropod features; frog’s amphibious lifestyle and double circulation show vertebrate advancement.
Understanding these internal structures is crucial for zoological classification, physiology, and medical research, linking form and function beautifully in the animal kingdom 🌍.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. Draw a neat diagram of the tissue section of the animal epithelial tissue and label its types.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Epithelial tissues are protective coverings that line body surfaces and cavities. They are classified based on cell shape and layers:
🌿 Types of Epithelial Tissue:
Simple epithelium: Single layer of cells; involved in absorption, secretion.
Simple squamous: Flat cells; e.g. alveoli.
Simple cuboidal: Cube-shaped; e.g. kidney tubules.
Simple columnar: Tall cells; e.g. intestinal lining.
Ciliated epithelium: With cilia; e.g. trachea.
Compound epithelium: Multiple layers; for protection.
Stratified squamous: Skin.
✏️ Diagram description: Shows various types arranged in layers—simple squamous (flat), cuboidal (cube), columnar (tall), and ciliated forms.
✔️ Function: Protection, secretion, absorption, transport.
🔵 Question 2. Differentiate between simple and compound epithelium.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Simple Epithelium Compound Epithelium
Layers Single layer of cells Multiple layers
Function Absorption, secretion Protection from mechanical stress
Location Alveoli, lining of tubules Skin, lining of pharynx
Regeneration Quick Slow
✔️ Conclusion: Simple for exchange, compound for protection.
🔵 Question 3. Write short notes on:
(a) Connective tissues
(b) Muscular tissues
(c) Nervous tissues
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) Connective Tissues:
Bind and support other tissues.
➡️ Types:
Loose: Areolar, adipose.
Dense: Ligaments, tendons.
Skeletal: Bone, cartilage.
Fluid: Blood, lymph.
💡 Functions: Support, transport, storage.
💪 (b) Muscular Tissues:
Responsible for movement; contain contractile proteins (actin, myosin).
➡️ Types:
Skeletal: Striated, voluntary.
Smooth: Non-striated, involuntary.
Cardiac: Striated, involuntary (heart).
🧠 (c) Nervous Tissues:
Made of neurons and neuroglia.
➡️ Function: Conduct impulses, coordinate body activities.
🔵 Question 4. Distinguish between cartilage and bone.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Cartilage Bone
Matrix Flexible, non-calcified Hard, calcified
Cells Chondrocytes in lacunae Osteocytes in lacunae
Blood supply Absent Present
Function Flexibility, support Strength, protection
Example Tip of nose, ear pinna Femur, humerus
✔️ Conclusion: Bone is hard and vascular; cartilage is flexible and avascular.
🔵 Question 5. Describe the structure of a neuron with a labelled diagram.
🟢 Answer:
🧠 Neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
🌿 Parts:
Cell body (cyton): Contains nucleus, Nissl’s granules.
Dendrites: Receive impulses.
Axon: Transmits impulse away from cell body.
Axon terminals: Pass signals to next neuron.
✏️ Diagram description: Shows cell body with dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminal.
✔️ Function: Transmission of electrical impulses for coordination.
🔵 Question 6. Name the types of epithelial tissues present in different parts of the human body.
🟢 Answer:
🌸 Types and Locations:
Simple squamous: Lining of blood vessels (endothelium)
Simple cuboidal: Kidney tubules
Simple columnar: Intestine
Ciliated columnar: Trachea
Stratified squamous: Skin
Transitional: Urinary bladder
✔️ Each type adapted to its function (absorption, protection, secretion).
🔵 Question 7. What are the major components of connective tissue?
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Components:
Cells: Fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, adipocytes.
Fibres: Collagen (strength), elastic (elasticity), reticular (support).
Matrix: Ground substance (intercellular).
✔️ Function: Structural framework and support to organs.
🔵 Question 8. Define tissue. Name the four basic types of tissues in animals.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Tissue: A group of similar cells performing a specific function.
🧠 Four types:
Epithelial (covering/lining)
Connective (supporting)
Muscular (movement)
Nervous (control and coordination)
✔️ Together they form organs and organ systems.
🔵 Question 9. Mention the types of muscle tissues found in the human body and write their characteristics.
🟢 Answer:
Type Striations Control Nucleus Location Function
Skeletal Present Voluntary Multinucleated Attached to bones Movement
Smooth Absent Involuntary Uninucleate Walls of hollow organs Movement of substances
Cardiac Present Involuntary Uninucleate Heart Pumping blood
✔️ Cardiac muscles have intercalated discs for impulse conduction.
🔵 Question 10. Differentiate between tendons and ligaments.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Tendon Ligament
Structure Dense, fibrous Elastic
Connection Muscle to bone Bone to bone
Stretchability Non-elastic Elastic
Function Transmit force Strengthen joints
✔️ Both are dense connective tissues.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
Study of microscopic structure of tissues is called:
🔴1️⃣ Histology
🟢2️⃣ Cytology
🟡3️⃣ Anatomy
🔵4️⃣ Morphology
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Histology
🔴 Question 2:
Which of the following is an example of epithelial tissue?
🔴1️⃣ Bone
🟢2️⃣ Cartilage
🟡3️⃣ Lining of intestine
🔵4️⃣ Ligament
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Lining of intestine
🔴 Question 3:
The cells of simple squamous epithelium are:
🔴1️⃣ Cube-shaped
🟢2️⃣ Columnar
🟡3️⃣ Flat and thin
🔵4️⃣ Irregular
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Flat and thin
🔴 Question 4:
Ciliated epithelium is found in:
🔴1️⃣ Stomach
🟢2️⃣ Intestine
🟡3️⃣ Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
🔵4️⃣ Urinary bladder
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
🔴 Question 5:
Tendons connect:
🔴1️⃣ Bone to bone
🟢2️⃣ Muscle to bone
🟡3️⃣ Muscle to muscle
🔵4️⃣ Organ to organ
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Muscle to bone
🔴 Question 6:
Ligaments connect:
🔴1️⃣ Muscle to muscle
🟢2️⃣ Bone to bone
🟡3️⃣ Muscle to bone
🔵4️⃣ Bone to cartilage
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Bone to bone
🔴 Question 7:
Which connective tissue acts as a fat reservoir?
🔴1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢2️⃣ Bone
🟡3️⃣ Adipose tissue
🔵4️⃣ Areolar tissue
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Adipose tissue
🔴 Question 8:
Which connective tissue connects muscles to skin?
🔴1️⃣ Areolar tissue
🟢2️⃣ Adipose tissue
🟡3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵4️⃣ Ligament
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Areolar tissue
🔴 Question 9:
Which of the following is a fluid connective tissue?
🔴1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢2️⃣ Bone
🟡3️⃣ Blood
🔵4️⃣ Tendon
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Blood
🔴 Question 10:
The contractile protein present in muscle is:
🔴1️⃣ Collagen
🟢2️⃣ Keratin
🟡3️⃣ Actin and Myosin
🔵4️⃣ Elastin
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Actin and Myosin
🔴 Question 11:
Name the basic types of animal tissues.
🟢 Answer:
There are four basic types:
1️⃣ Epithelial tissue — covering & lining.
2️⃣ Connective tissue — support & binding.
3️⃣ Muscular tissue — movement.
4️⃣ Nervous tissue — control & coordination.
🔴 Question 12:
What are compound epithelium and its function?
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Made up of multiple layers of cells.
Function:
✔️ Provides protection against mechanical and chemical stress.
✔️ Found in skin, pharynx, ducts of glands.
🔴 Question 13:
What are the main types of epithelial tissues?
🟢 Answer:
Epithelial tissue covers body surface and lines organs.
Types:
1️⃣ Simple epithelium:
• Single layer, functions in absorption, secretion, diffusion.
• Includes — Squamous, Cuboidal, Columnar, Ciliated, Glandular.
2️⃣ Compound epithelium:
• Multi-layered, provides protection (e.g. skin).
💡 Performs protection, absorption, secretion, and exchange.
🔴 Question 14:
Differentiate between simple squamous and simple columnar epithelium.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Simple Squamous Simple Columnar
Shape Flat and thin Tall and pillar-like
Function Diffusion and filtration Absorption & secretion
Location Alveoli of lungs, lining of blood vessels Intestinal lining, stomach wall
🔴 Question 15:
Describe connective tissues and their types.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Connective tissues support, bind, and protect organs.
Types:
1️⃣ Loose connective tissue:
• Areolar tissue — joins organs, fills spaces.
• Adipose tissue — stores fat, insulates.
2️⃣ Dense connective tissue:
• Ligaments (bone to bone), Tendons (muscle to bone).
3️⃣ Specialised connective tissue:
• Cartilage, Bone, Blood.
🔴 Question 16:
Write a short note on cartilage.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Semi-rigid, non-vascular connective tissue.
• Cells = chondrocytes in lacunae.
Matrix: Chondrin with fibres.
Types:
1️⃣ Hyaline cartilage — tip of nose 👃
2️⃣ Elastic cartilage — pinna of ear 👂
3️⃣ Fibrocartilage — intervertebral discs
Function: Flexibility, support, cushioning.
🔴 Question 17:
Describe the structure and function of bone.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Hard matrix with calcium & collagen.
• Cells = osteocytes in lacunae.
Function:
1️⃣ Provides structural support 🦴.
2️⃣ Protects internal organs.
3️⃣ Stores minerals (Ca, P).
4️⃣ Bone marrow forms blood cells.
🔴 Question 18:
Differentiate between ligaments and tendons.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Ligament Tendon
Connection Bone to bone Muscle to bone
Flexibility Flexible, elastic Tough, less flexible
Fibres Elastic fibres Collagen fibres
Function Provides strength & flexibility Transfers force of contraction
🔴 Question 19:
What are muscular tissues and their types?
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Tissues responsible for movement; contain contractile proteins (actin, myosin).
Types:
1️⃣ Striated (skeletal): Voluntary, multinucleate, cylindrical; e.g. limbs 💪.
2️⃣ Unstriated (smooth): Involuntary, spindle-shaped; e.g. intestine.
3️⃣ Cardiac: Striated, involuntary, branched; e.g. heart ❤️.
🔴 Question 20:
Describe the structure and function of nervous tissue.
🟢 Answer:
Components:
1️⃣ Neuron: Structural and functional unit.
2️⃣ Neuroglia: Support cells.
Neuron structure:
• Cell body with nucleus.
• Dendrites receive impulses.
• Axon transmits impulses.
Function: Transmission of messages and coordination 🧠.
🔴 Question 21:
Describe areolar tissue and its functions.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Loose connective tissue with fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells.
• Matrix with fibres and ground substance.
Functions:
1️⃣ Joins different tissues.
2️⃣ Fills space between organs.
3️⃣ Provides support and elasticity.
4️⃣ Defence through macrophages.
🔴 Question 22:
What are unicellular and multicellular glands? Give examples.
🟢 Answer:
Unicellular glands: Single cell performs secretion — Goblet cell secreting mucus.
Multicellular glands: Group of secretory cells — Salivary glands, Sweat glands.
Function: Secretion of enzymes, mucus, hormones.
🔴 Question 23:
Describe the structure and function of epithelial tissues.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Epithelial tissue forms the covering and lining of body surfaces and internal organs.
Structure:
1️⃣ Cells: Compactly packed with minimal intercellular spaces.
2️⃣ Basement membrane: Non-cellular layer attaching epithelium to connective tissue.
3️⃣ Avascular: Lacks blood vessels; nourished by diffusion.
Functions:
✔️ Protection from injury and microbes.
✔️ Absorption (intestine).
✔️ Secretion (glands).
✔️ Sensory reception (tongue, skin).
Examples:
• Squamous: Diffusion (alveoli).
• Columnar: Absorption (intestine).
• Ciliated: Transport (bronchioles).
🔴 Question 24:
Write a detailed note on connective tissues.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Connective tissue binds, supports, and protects organs.
Main types:
1️⃣ Loose connective tissue:
• Areolar tissue — joins organs, supports epithelium.
• Adipose tissue — stores fat, insulates.
2️⃣ Dense connective tissue:
• Tendons — connect muscles to bones.
• Ligaments — connect bones to bones.
3️⃣ Specialised connective tissue:
• Cartilage: Flexible support (nose 👃, ear 👂).
• Bone 🦴: Hard support, mineral storage.
• Blood 🩸: Fluid tissue, transport.
Functions:
✔️ Support and protection.
✔️ Transport of substances.
✔️ Storage of energy.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain muscular tissues with types and features.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Tissues with contractile proteins (actin, myosin), causing movement.
Types:
1️⃣ Striated (skeletal) muscles:
• Long, cylindrical, multinucleate.
• Voluntary control.
• Found in limbs 💪.
2️⃣ Unstriated (smooth) muscles:
• Spindle-shaped, uninucleate.
• Involuntary control.
• Found in intestine, stomach.
3️⃣ Cardiac muscles ❤️:
• Striated, branched, uninucleate.
• Involuntary; rhythmic contractions in heart.
Function: Locomotion, movement of organs, heartbeat.
🔴 Question 26:
Describe the structure of a neuron 🧠 with its functions.
🟢 Answer:
Neuron: Structural and functional unit of nervous tissue.
Structure:
1️⃣ Cell body (cyton): Contains nucleus, Nissl granules.
2️⃣ Dendrites: Short, branched processes receiving impulses.
3️⃣ Axon: Long process conducting impulses away.
4️⃣ Myelin sheath: Fatty covering; insulates and speeds transmission.
Function:
✔️ Conducts nerve impulses.
✔️ Coordinates body activities.
✔️ Enables reflex actions.
🔴 Question 27:
Write a note on earthworm 🪱 body organisation.
🟢 Answer:
Habitat: Burrowing, moist soil dweller.
Body:
1️⃣ Long, cylindrical, metamerically segmented.
2️⃣ Covered by moist cuticle and epidermis.
3️⃣ Segments 14–16 form clitellum.
Systems:
✔️ Digestive: Straight tube with gizzard and intestine.
✔️ Circulatory: Closed system with blood vessels.
✔️ Respiration: Through moist skin.
✔️ Excretion: Nephridia.
✔️ Reproduction: Hermaphrodite, cross-fertilisation.
🔴 Question 28:
Describe the body organisation of cockroach 🪳.
🟢 Answer:
Body: Dorsoventrally flattened, segmented into:
1️⃣ Head: Compound eyes, antennae, mouthparts.
2️⃣ Thorax: Three segments; each with a pair of legs 🦵; wings on meso & metathorax.
3️⃣ Abdomen: 10 segments, spiracles, genital opening.
Systems:
✔️ Digestive: Alimentary canal with foregut, midgut, hindgut.
✔️ Circulatory: Open system.
✔️ Respiration: Tracheal system with spiracles.
✔️ Excretion: Malpighian tubules.
✔️ Reproduction: Sexual, separate sexes.
🔴 Question 29:
Describe body organisation of frog 🐸.
🟢 Answer:
Habitat: Amphibious — lives on land and in water.
Body:
1️⃣ Divided into head and trunk.
2️⃣ Moist skin with mucous glands.
3️⃣ Two pairs of limbs (hindlimbs for jumping 🦵).
Systems:
✔️ Digestive: Complete; stomach, intestine, cloaca.
✔️ Circulatory: Closed, 3-chambered heart ❤️.
✔️ Respiration: Skin, lungs, buccal cavity.
✔️ Nervous: Brain + spinal cord.
✔️ Reproduction: Sexual, external fertilisation in water 💧.
🔴 Question 30:
Compare the body organisation of earthworm 🪱, cockroach 🪳, and frog 🐸.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Earthworm 🪱 Cockroach 🪳 Frog 🐸
Symmetry Bilateral Bilateral Bilateral
Segmentation Metameric External only Absent
Circulatory Closed Open Closed
Respiration Skin Tracheae Lungs + Skin
Skeleton Hydrostatic Exoskeleton Endoskeleton
💡 Shows increasing complexity from annelids → arthropods → vertebrates.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. Epithelial tissue with thin flat cells forming the lining of blood vessels is called
🟡 A. Cuboidal epithelium
🟡 B. Columnar epithelium
🟡 C. Squamous epithelium
🟡 D. Ciliated epithelium
🟢 Answer: C. Squamous epithelium
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q2. The structural and functional unit of striated muscle is
🟡 A. Sarcomere
🟡 B. Myofibril
🟡 C. Sarcolemma
🟡 D. Z-line
🟢 Answer: A. Sarcomere
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q3. Compound epithelium is found where
🟡 A. Secretion and absorption occur
🟡 B. Exchange of gases takes place
🟡 C. Mechanical protection is required
🟡 D. Filtration of fluids takes place
🟢 Answer: C. Mechanical protection is required
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q4. Dense regular connective tissue forms
🟡 A. Cartilage
🟡 B. Tendons and ligaments
🟡 C. Areolar tissue
🟡 D. Adipose tissue
🟢 Answer: B. Tendons and ligaments
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q5. Non-nucleated blood cells in mammals are
🟡 A. White blood cells
🟡 B. Erythrocytes
🟡 C. Platelets
🟡 D. Neutrophils
🟢 Answer: B. Erythrocytes
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q6. Cardiac muscles are
🟡 A. Unbranched and voluntary
🟡 B. Branched and involuntary
🟡 C. Branched and voluntary
🟡 D. Unbranched and involuntary
🟢 Answer: B. Branched and involuntary
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q7. The exoskeleton of Arthropods is made of
🟡 A. Keratin
🟡 B. Chitin
🟡 C. Cellulose
🟡 D. Collagen
🟢 Answer: B. Chitin
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q8. In cockroach, the respiratory pigment is
🟡 A. Haemocyanin
🟡 B. Haemoglobin
🟡 C. Haemolymph without pigment
🟡 D. Haemoerythrin
🟢 Answer: C. Haemolymph without pigment
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q9. The body cavity of earthworm is
🟡 A. Pseudocoelom
🟡 B. Coelom
🟡 C. Haemocoel
🟡 D. Acoelom
🟢 Answer: B. Coelom
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q10. In cockroach, excretion is carried out by
🟡 A. Nephridia
🟡 B. Green glands
🟡 C. Malpighian tubules
🟡 D. Flame cells
🟢 Answer: C. Malpighian tubules
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q11. Setae in earthworm are
🟡 A. Secretory structures
🟡 B. Locomotory organs
🟡 C. Respiratory structures
🟡 D. Reproductive structures
🟢 Answer: B. Locomotory organs
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q12. The nerve cord in cockroach is
🟡 A. Dorsal and hollow
🟡 B. Dorsal and solid
🟡 C. Ventral and double solid
🟡 D. Ventral and hollow
🟢 Answer: C. Ventral and double solid
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q13. Typhlosole in earthworm increases
🟡 A. Surface area for digestion and absorption
🟡 B. Gaseous exchange
🟡 C. Locomotion efficiency
🟡 D. Reproductive capacity
🟢 Answer: A. Surface area for digestion and absorption
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q14. The circulatory system of cockroach is
🟡 A. Closed with arteries and veins
🟡 B. Open with haemocoel
🟡 C. Closed with capillaries
🟡 D. Absent
🟢 Answer: B. Open with haemocoel
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q15. Nephridia in earthworm help in
🟡 A. Respiration
🟡 B. Digestion
🟡 C. Excretion and osmoregulation
🟡 D. Circulation
🟢 Answer: C. Excretion and osmoregulation
📅 NEET 2021
🔵 Q16. In cockroach, blood is
🟡 A. Colourless and without respiratory pigment
🟡 B. Red with haemoglobin
🟡 C. Blue with haemocyanin
🟡 D. Greenish with chlorocruorin
🟢 Answer: A. Colourless and without respiratory pigment
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q17. The excretory organ of earthworm is
🟡 A. Flame cell
🟡 B. Malpighian tubule
🟡 C. Nephridium
🟡 D. Kidney
🟢 Answer: C. Nephridium
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q18. In cockroach, the mouthparts are
🟡 A. Piercing and sucking type
🟡 B. Chewing type
🟡 C. Sponging type
🟡 D. Siphoning type
🟢 Answer: B. Chewing type
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q19. The nerve cord of earthworm is
🟡 A. Dorsal and hollow
🟡 B. Dorsal and solid
🟡 C. Ventral and double solid
🟡 D. Ventral and hollow
🟢 Answer: C. Ventral and double solid
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q20. The respiratory organ in earthworm is
🟡 A. Skin
🟡 B. Trachea
🟡 C. Gills
🟡 D. Book lungs
🟢 Answer: A. Skin
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q21. Gonapophyses in cockroach are associated with
🟡 A. Locomotion
🟡 B. Reproduction
🟡 C. Feeding
🟡 D. Respiration
🟢 Answer: B. Reproduction
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q22. In earthworm, the dorsal blood vessel functions mainly as
🟡 A. Pumping organ
🟡 B. Distributor
🟡 C. Collector
🟡 D. Respiratory pigment
🟢 Answer: C. Collector
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q23. Spiracles in cockroach are
🟡 A. Paired openings of reproductive system
🟡 B. Paired openings of tracheal system
🟡 C. Openings of Malpighian tubules
🟡 D. Excretory pores
🟢 Answer: B. Paired openings of tracheal system
📅 NEET 2012
🔵 Q24. The nerve cord in cockroach is located
🟡 A. Dorsally below gut
🟡 B. Dorsally above gut
🟡 C. Ventrally below gut
🟡 D. Ventrally above gut
🟢 Answer: C. Ventrally below gut
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q25. The locomotory organs in cockroach are
🟡 A. Antennae
🟡 B. Legs and wings
🟡 C. Spiracles
🟡 D. Cerci
🟢 Answer: B. Legs and wings
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q26. The mouth of earthworm leads into a small chamber called
🟡 A. Crop
🟡 B. Buccal cavity
🟡 C. Gizzard
🟡 D. Pharynx
🟢 Answer: B. Buccal cavity
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q27. Cockroach heart has
🟡 A. 10 chambers
🟡 B. 12 chambers
🟡 C. 13 chambers
🟡 D. 14 chambers
🟢 Answer: C. 13 chambers
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q28. The body of cockroach is divided into
🟡 A. Two regions
🟡 B. Three regions
🟡 C. Four regions
🟡 D. Five regions
🟢 Answer: B. Three regions
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q29. Earthworm belongs to the class
🟡 A. Polychaeta
🟡 B. Hirudinea
🟡 C. Oligochaeta
🟡 D. Archiannelida
🟢 Answer: C. Oligochaeta
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q30. In cockroach, the number of abdominal segments in males is
🟡 A. Eight
🟡 B. Nine
🟡 C. Ten
🟡 D. Eleven
🟢 Answer: B. Ten
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q31. In cockroach, the storage of sperm occurs in
🟡 A. Seminal vesicles
🟡 B. Spermatheca
🟡 C. Ovarioles
🟡 D. Vas deferens
🟢 Answer: B. Spermatheca
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q32. The excretory matter of earthworm is mainly
🟡 A. Uric acid
🟡 B. Urea
🟡 C. Ammonia
🟡 D. Urea and ammonia
🟢 Answer: B. Urea
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q33. Blood vascular system of earthworm is
🟡 A. Closed type
🟡 B. Open type
🟡 C. Lacunar type
🟡 D. Absent
🟢 Answer: A. Closed type
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q34. Salivary glands of cockroach are located in
🟡 A. Thorax
🟡 B. Head
🟡 C. Abdomen
🟡 D. Buccal cavity
🟢 Answer: B. Head
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q35. In cockroach, blood circulation is
🟡 A. Closed type
🟡 B. Open type
🟡 C. Partially closed
🟡 D. Double circulation
🟢 Answer: B. Open type
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q36. Chloragogen cells in earthworm are involved in
🟡 A. Excretion and intermediary metabolism
🟡 B. Reproduction
🟡 C. Respiration
🟡 D. Blood clotting
🟢 Answer: A. Excretion and intermediary metabolism
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q37. The number of salivary gland lobes in cockroach is
🟡 A. Two pairs
🟡 B. Three pairs
🟡 C. Four pairs
🟡 D. Six pairs
🟢 Answer: B. Three pairs
📅 NEET 2021
🔵 Q38. Blood of cockroach is called haemolymph because it is
🟡 A. Without pigment and has plasma and haemocytes
🟡 B. Red with haemoglobin
🟡 C. Blue with haemocyanin
🟡 D. Green with chlorocruorin
🟢 Answer: A. Without pigment and has plasma and haemocytes
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q39. The mouth of cockroach opens into a narrow tubular structure called
🟡 A. Crop
🟡 B. Pharynx
🟡 C. Oesophagus
🟡 D. Gizzard
🟢 Answer: C. Oesophagus
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q40. In earthworm, chloragogen cells are similar in function to
🟡 A. Liver cells of vertebrates
🟡 B. Kidney cells of vertebrates
🟡 C. Lungs of vertebrates
🟡 D. Pancreatic cells of vertebrates
🟢 Answer: A. Liver cells of vertebrates
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q41. Number of ovarioles in cockroach is
🟡 A. Four
🟡 B. Six
🟡 C. Eight
🟡 D. Ten
🟢 Answer: B. Six
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q42. Fertilisation in earthworm is
🟡 A. External
🟡 B. Internal and cross
🟡 C. Internal and self
🟡 D. External and cross
🟢 Answer: B. Internal and cross
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q43. Which one of the following is the common connecting link between annelids and arthropods?
🟡 A. Body segmentation
🟡 B. Closed circulatory system
🟡 C. Malpighian tubules
🟡 D. Jointed appendages
🟢 Answer: A. Body segmentation
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q44. In cockroach, blood vascular system is of
🟡 A. Closed type with arteries and veins
🟡 B. Open type with haemocoel
🟡 C. Closed type with capillaries
🟡 D. Absent
🟢 Answer: B. Open type with haemocoel
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q45. The digestive tract of earthworm is differentiated into
🟡 A. Three regions
🟡 B. Five regions
🟡 C. Four regions
🟡 D. Six regions
🟢 Answer: C. Four regions
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q46. Which one is a paired structure in cockroach reproductive system?
🟡 A. Mushroom gland
🟡 B. Ejaculatory duct
🟡 C. Seminal vesicle
🟡 D. Phallomere
🟢 Answer: A. Mushroom gland
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q47. The chitinous teeth in the gizzard of earthworm help in
🟡 A. Respiration
🟡 B. Grinding food
🟡 C. Secretion of enzymes
🟡 D. Digestion of proteins
🟢 Answer: B. Grinding food
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q48. Gonads in cockroach are located in
🟡 A. Thorax
🟡 B. Abdomen
🟡 C. Head
🟡 D. Legs
🟢 Answer: B. Abdomen
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q49. The salivary glands of cockroach open into
🟡 A. Pharynx
🟡 B. Oesophagus
🟡 C. Hypopharynx
🟡 D. Crop
🟢 Answer: C. Hypopharynx
📅 NEET 2012
🔵 Q50. In cockroach, the haemolymph is
🟡 A. Colourless plasma with haemocytes
🟡 B. Red with haemoglobin
🟡 C. Blue with haemocyanin
🟡 D. Green with chlorocruorin
🟢 Answer: A. Colourless plasma with haemocytes
📅 AIPMT 2014
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Study of tissues is known as:
🔴 1️⃣ Anatomy
🟢 2️⃣ Histology
🟡 3️⃣ Cytology
🔵 4️⃣ Morphology
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Histology
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following is a connective tissue?
🔴 1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢 2️⃣ Epithelium
🟡 3️⃣ Muscle
🔵 4️⃣ Nervous tissue
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 Question 3:
Which tissue covers the body surface and lines internal organs?
🔴 1️⃣ Connective
🟢 2️⃣ Epithelial
🟡 3️⃣ Muscular
🔵 4️⃣ Nervous
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Epithelial
🔵 Question 4:
Striated muscles are:
🔴 1️⃣ Involuntary
🟢 2️⃣ Voluntary
🟡 3️⃣ Uninucleate
🔵 4️⃣ Found in viscera
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Voluntary
🔵 Question 5:
Cardiac muscles are:
🔴 1️⃣ Voluntary and striated
🟢 2️⃣ Involuntary and striated
🟡 3️⃣ Voluntary and unstriated
🔵 4️⃣ Involuntary and unstriated
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Involuntary and striated
🔵 Question 6:
Epithelial tissue lacking blood vessels is called:
🔴 1️⃣ Vascular
🟢 2️⃣ Avascular
🟡 3️⃣ Neural
🔵 4️⃣ Muscular
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Avascular
🔵 Question 7:
Which of the following is an example of simple epithelium?
🔴 1️⃣ Stratified squamous
🟢 2️⃣ Cuboidal
🟡 3️⃣ Columnar
🔵 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
🔵 Question 8:
The main function of cuboidal epithelium is:
🔴 1️⃣ Protection
🟢 2️⃣ Absorption and secretion
🟡 3️⃣ Conduction
🔵 4️⃣ Contraction
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Absorption and secretion
🔵 Question 9:
Goblet cells secrete:
🔴 1️⃣ Enzymes
🟢 2️⃣ Mucus
🟡 3️⃣ Hormones
🔵 4️⃣ Sweat
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mucus
🔵 Question 10:
Ciliated epithelium is present in:
🔴 1️⃣ Stomach
🟢 2️⃣ Trachea
🟡 3️⃣ Kidney
🔵 4️⃣ Tongue
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Trachea
🔵 Question 11:
Bone matrix is rich in:
🔴 1️⃣ Calcium phosphate
🟢 2️⃣ Calcium carbonate
🟡 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 4️⃣ Magnesium carbonate
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 Question 12:
The connective tissue joining muscles to bones is:
🔴 1️⃣ Ligament
🟢 2️⃣ Tendon
🟡 3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Tendon
🔵 Question 13:
Ligament connects:
🔴 1️⃣ Muscle to bone
🟢 2️⃣ Bone to bone
🟡 3️⃣ Bone to cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Muscle to muscle
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bone to bone
🔵 Question 14:
Which connective tissue stores fat?
🔴 1️⃣ Areolar
🟢 2️⃣ Adipose
🟡 3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Bone
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Adipose
🔵 Question 15:
Which one is the fluid connective tissue?
🔴 1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢 2️⃣ Blood
🟡 3️⃣ Bone
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Blood
🔵 Question 16:
The structural and functional unit of nervous tissue is:
🔴 1️⃣ Axon
🟢 2️⃣ Dendrite
🟡 3️⃣ Neuron
🔵 4️⃣ Myelin
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Neuron
🔵 Question 17:
In neuron, impulse travels from:
🔴 1️⃣ Axon to dendrite
🟢 2️⃣ Dendrite to axon
🟡 3️⃣ Cell body to axon
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleus to dendrite
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Dendrite to axon
🔵 Question 18:
The intercalated discs are found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Skeletal muscle
🟢 2️⃣ Smooth muscle
🟡 3️⃣ Cardiac muscle
🔵 4️⃣ All of these
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Cardiac muscle
🔵 Question 19:
Areolar tissue is found:
🔴 1️⃣ Between skin and muscles
🟢 2️⃣ Around blood vessels
🟡 3️⃣ In nerves
🔵 4️⃣ All of these
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ All of these
🔵 Question 20:
The cell responsible for producing bone matrix is:
🔴 1️⃣ Osteoclast
🟢 2️⃣ Osteoblast
🟡 3️⃣ Osteocyte
🔵 4️⃣ Chondrocyte
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Osteoblast
🔵 Question 21:
The non-cellular part of connective tissue is:
🔴 1️⃣ Fibre
🟢 2️⃣ Matrix
🟡 3️⃣ Cell
🔵 4️⃣ Organ
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Matrix
🔵 Question 22:
Myelin sheath is formed by:
🔴 1️⃣ Neuron
🟢 2️⃣ Schwann cells
🟡 3️⃣ Axon
🔵 4️⃣ Dendrite
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Schwann cells
🔵 Question 23:
Haversian canals are characteristic of:
🔴 1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢 2️⃣ Bone
🟡 3️⃣ Ligament
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar tissue
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bone
🔵 Question 24:
The cells of cartilage are called:
🔴 1️⃣ Chondrocytes
🟢 2️⃣ Osteocytes
🟡 3️⃣ Fibroblasts
🔵 4️⃣ Erythrocytes
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Chondrocytes
🔵 Question 25:
The connective tissue with both strength and elasticity is:
🔴 1️⃣ Ligament
🟢 2️⃣ Tendon
🟡 3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Ligament
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following is not a connective tissue?
🔴 1️⃣ Cartilage
🟢 2️⃣ Ligament
🟡 3️⃣ Muscle
🔵 4️⃣ Bone
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Muscle
🔵 Question 27:
Ciliated epithelium is mainly associated with:
🔴 1️⃣ Secretion
🟢 2️⃣ Absorption
🟡 3️⃣ Movement of materials
🔵 4️⃣ Sensation
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Movement of materials
🔵 Question 28:
Which connective tissue connects skin to underlying muscles?
🔴 1️⃣ Ligament
🟢 2️⃣ Areolar tissue
🟡 3️⃣ Adipose tissue
🔵 4️⃣ Cartilage
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Areolar tissue
🔵 Question 29:
In blood, the plasma forms about:
🔴 1️⃣ 45%
🟢 2️⃣ 55%
🟡 3️⃣ 65%
🔵 4️⃣ 75%
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 55%
🔵 Question 30:
Which one of the following does not contain nucleus?
🔴 1️⃣ WBC
🟢 2️⃣ RBC
🟡 3️⃣ Platelets
🔵 4️⃣ Chondrocytes
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ RBC
🔵 Question 31:
The type of epithelium that forms lining of urinary bladder is:
🔴 1️⃣ Cuboidal
🟢 2️⃣ Columnar
🟡 3️⃣ Transitional
🔵 4️⃣ Stratified squamous
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Transitional
🔵 Question 32:
Keratinized epithelium is found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Stomach
🟢 2️⃣ Skin
🟡 3️⃣ Intestine
🔵 4️⃣ Trachea
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Skin
🔵 Question 33:
Nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another through:
🔴 1️⃣ Synapse
🟢 2️⃣ Dendrite
🟡 3️⃣ Axon
🔵 4️⃣ Node of Ranvier
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Synapse
🔵 Question 34:
Which of the following is the hardest connective tissue?
🔴 1️⃣ Bone
🟢 2️⃣ Cartilage
🟡 3️⃣ Ligament
🔵 4️⃣ Tendon
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Bone
🔵 Question 35:
The major protein in white fibres of connective tissue is:
🔴 1️⃣ Elastin
🟢 2️⃣ Collagen
🟡 3️⃣ Myosin
🔵 4️⃣ Actin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Collagen
🔵 Question 36:
Which of the following is not a characteristic of smooth muscle?
🔴 1️⃣ Uninucleate
🟢 2️⃣ Non-striated
🟡 3️⃣ Voluntary
🔵 4️⃣ Spindle-shaped
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Voluntary
🔵 Question 37:
Which connective tissue acts as a shock absorber?
🔴 1️⃣ Bone
🟢 2️⃣ Cartilage
🟡 3️⃣ Ligament
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 Question 38:
Muscle fibres are surrounded by connective tissue layer called:
🔴 1️⃣ Sarcolemma
🟢 2️⃣ Endomysium
🟡 3️⃣ Myofibril
🔵 4️⃣ Myosin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Endomysium
🔵 Question 39:
Which cells are phagocytic in areolar tissue?
🔴 1️⃣ Mast cells
🟢 2️⃣ Macrophages
🟡 3️⃣ Fibroblasts
🔵 4️⃣ Adipocytes
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Macrophages
🔵 Question 40:
The cells secreting heparin and histamine are:
🔴 1️⃣ Fibroblasts
🟢 2️⃣ Mast cells
🟡 3️⃣ Macrophages
🔵 4️⃣ Adipocytes
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mast cells
🔵 Question 41:
Which connective tissue has semi-solid matrix?
🔴 1️⃣ Bone
🟢 2️⃣ Cartilage
🟡 3️⃣ Blood
🔵 4️⃣ Ligament
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 Question 42:
The nerve cell part that receives impulses is:
🔴 1️⃣ Axon
🟢 2️⃣ Dendrite
🟡 3️⃣ Synapse
🔵 4️⃣ Node of Ranvier
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Dendrite
🔵 Question 43:
Which one is not a component of blood?
🔴 1️⃣ RBC
🟢 2️⃣ WBC
🟡 3️⃣ Collagen
🔵 4️⃣ Platelets
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Collagen
🔵 Question 44:
Which connective tissue connects bones and muscles?
🔴 1️⃣ Ligament
🟢 2️⃣ Tendon
🟡 3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Areolar
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Tendon
🔵 Question 45:
Which of the following tissues lacks intercellular spaces?
🔴 1️⃣ Connective
🟢 2️⃣ Muscular
🟡 3️⃣ Epithelial
🔵 4️⃣ Nervous
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Epithelial
🔵 Question 46:
Which connective tissue acts as packing material?
🔴 1️⃣ Areolar
🟢 2️⃣ Ligament
🟡 3️⃣ Cartilage
🔵 4️⃣ Bone
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Areolar
🔵 Question 47:
The type of connective tissue forming framework of liver is:
🔴 1️⃣ Areolar
🟢 2️⃣ Reticular
🟡 3️⃣ Adipose
🔵 4️⃣ Cartilage
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Reticular
🔵 Question 48:
Which of the following muscle types shows branching?
🔴 1️⃣ Smooth
🟢 2️⃣ Cardiac
🟡 3️⃣ Skeletal
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cardiac
🔵 Question 49:
Erythrocytes are formed in:
🔴 1️⃣ Bone marrow
🟢 2️⃣ Liver
🟡 3️⃣ Kidney
🔵 4️⃣ Spleen
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Bone marrow
🔵 Question 50:
Myelin sheath in central nervous system is formed by:
🔴 1️⃣ Schwann cells
🟢 2️⃣ Oligodendrocytes
🟡 3️⃣ Astrocytes
🔵 4️⃣ Microglia
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Oligodendrocytes
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
