Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 2. Biological Classification
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔷 Introduction
🌿 Biology involves organizing living organisms based on shared characteristics. Initially, organisms were classified into two kingdoms — Plantae and Animalia. However, with advancements in microscopy and molecular biology, scientists realized the need for a more nuanced classification.
➡️ This led to the development of biological classification systems, including the Five Kingdom Classification by R.H. Whittaker in 1969.
🔶 R.H. Whittaker’s Five Kingdom Classification
💡 Concept: R.H. Whittaker proposed dividing life forms into 5 major kingdoms based on: 🔹 Cell structure (Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic)
🔹 Body organization (Unicellular/Multicellular)
🔹 Mode of nutrition (Autotrophs/Heterotrophs)
🔹 Reproduction (Asexual/Sexual)
🔹 Phylogenetic relationships
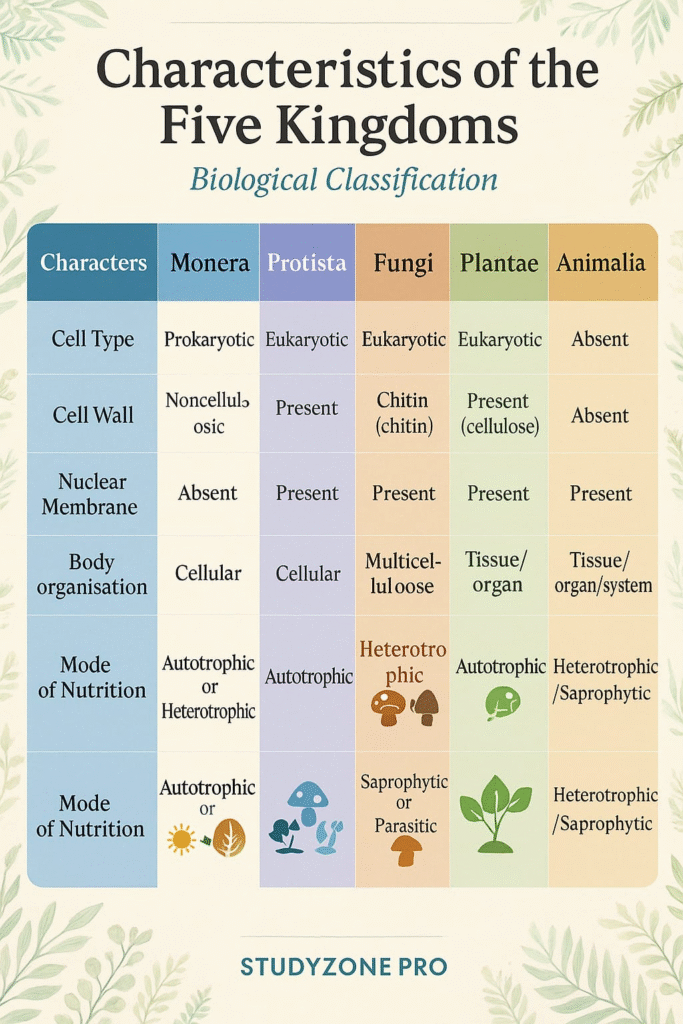
🔵 The Five Kingdoms Are:
Monera
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
🟣 Kingdom Monera
✅ Features:
Unicellular
Prokaryotic
Cell wall present (peptidoglycan)
No membrane-bound organelles
Reproduce asexually (binary fission)

🧫 Types:
Archaebacteria 🌋:
Found in extreme conditions (hot springs, salty lakes)
Unique cell wall structure
Examples: Methanogens, Halophiles, Thermoacidophiles
Eubacteria 🦠:
True bacteria with rigid cell walls
Autotrophic or heterotrophic
Includes Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) that do photosynthesis
✏️ Note: Some monerans show motility using flagella.
🟢 Kingdom Protista
🧠 Eukaryotic, unicellular organisms ⚡ Act as a connecting link between prokaryotes and higher organisms
🔹 Major Groups in Protista:
Chrysophytes 🌊
Includes diatoms and golden algae
Have siliceous cell walls
Important part of marine phytoplankton
Dinoflagellates 💥
Mostly marine
Two flagella (one transverse, one longitudinal)
Cause Red Tides (e.g., Gonyaulax)
Euglenoids 🟢
Found in fresh water
Photosynthetic in light, heterotrophic in dark
No cell wall, have pellicle
Slime Moulds 🌫️
Saprophytic
Form plasmodium during aggregation
Spores dispersed by air currents

Protozoans 👁️
Heterotrophic, animal-like protists
Types:
Amoeboid (Amoeba)
Flagellated (Trypanosoma)
Ciliated (Paramecium)
Sporozoans (Plasmodium)
💡 Concept: Protists show both plant and animal-like characteristics.

🟡 Kingdom Fungi
🍄 Multicellular (except yeasts)
🧬 Eukaryotic, heterotrophic, non-photosynthetic
🌱 Absorb nutrients (saprophytic, parasitic, or symbiotic)
🏗️ Composed of filaments called hyphae, collectively forming mycelium
📌 Reproduction:
Asexual: By spores (conidia, sporangiospores)
Sexual: Fusion of protoplasm (plasmogamy), nuclei (karyogamy), and meiosis
🔸 Groups of Fungi:
Phycomycetes 🍞
Aquatic or moist environment
Asexual: Zoospores, Sexual: Isogamous or anisogamous
Example: Rhizopus, Albugo
Ascomycetes (Sac Fungi) 🥖
Septate hyphae
Asexual: Conidia, Sexual: Ascospores in asci
Example: Aspergillus, Neurospora
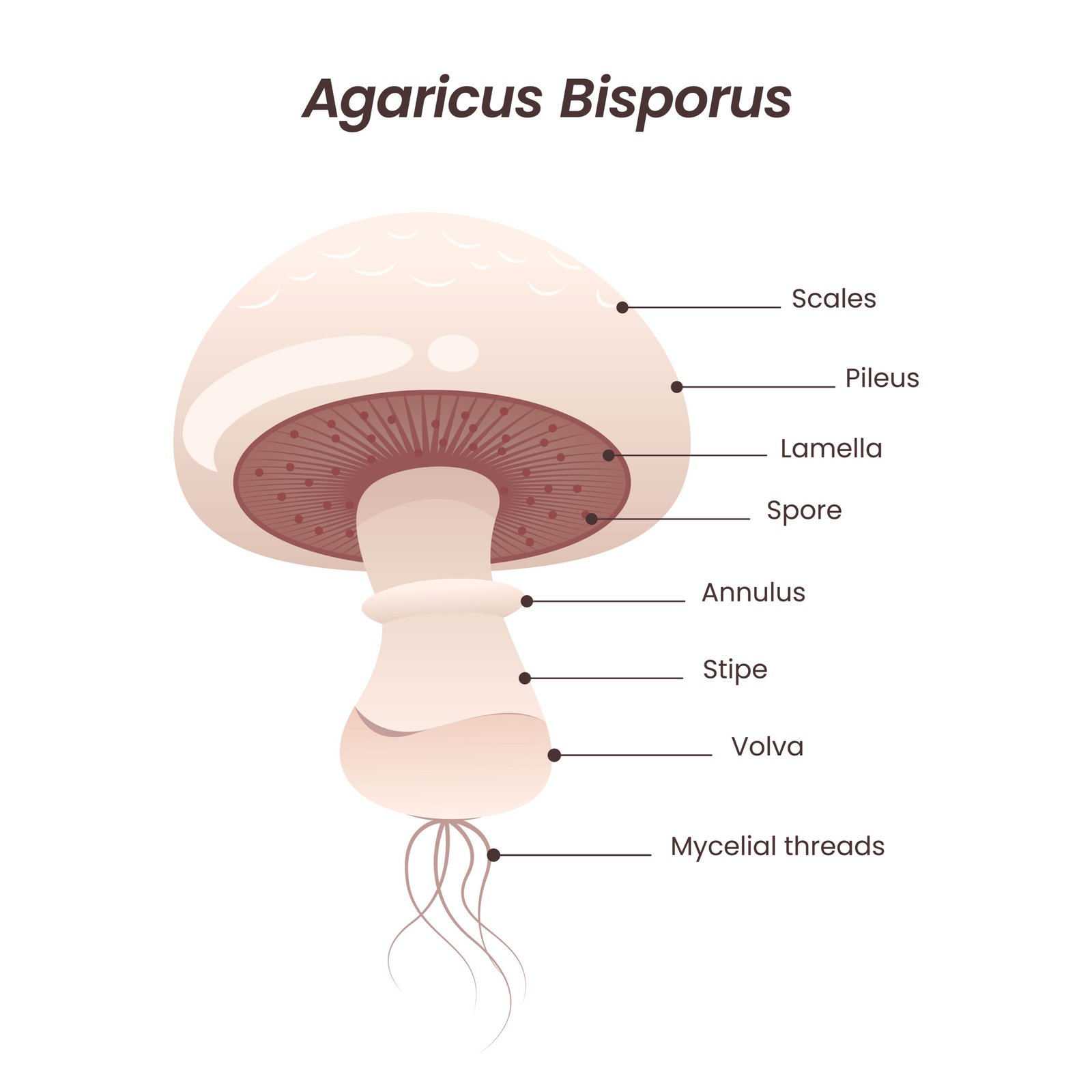
Basidiomycetes (Club Fungi) 🍄
No asexual spores
Produce basidiospores on basidia

Example: Agaricus (mushroom), Puccinia (rust)
Deuteromycetes (Imperfect Fungi) ❓
No known sexual stage
Reproduce via conidia
Example: Alternaria, Colletotrichum
✏️ Note: Some fungi form lichens (symbiotic association with algae or cyanobacteria).
🔴 Kingdom Plantae
🌿 Multicellular eukaryotes with cell wall (cellulose)
☀️ Autotrophic, photosynthetic
🔗 Include algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms
✏️ Note: Reproduction can be vegetative, asexual, or sexual.
🟠 Kingdom Animalia
🐾 Multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic organisms
🎯 No cell walls
🎭 High degree of tissue organization
🚼 Mostly reproduce sexually and show development from zygote stage
💠 Viruses, Viroids, and Lichens
💥 These are not classified in the five-kingdom system as they are non-cellular.
🔹 Viruses:
Between living and non-living
Consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and protein coat
Example: TMV, HIV, Influenza
🔹 Viroids:
Discovered by T.O. Diener
Infectious RNA without protein coat
🔹 Lichens:
Symbiotic association between fungus and algae
Algae provide food; fungi provide shelter and minerals
📦 Why This Lesson Matters
➡️ Biological classification helps us understand the diversity of life, evolutionary relationships, and organize living beings systematically. It is essential in fields like medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔹 Monera – Prokaryotic, unicellular
🔹 Protista – Unicellular eukaryotes
🔹 Fungi – Multicellular heterotrophs with chitinous cell wall
🔹 Plantae – Autotrophic eukaryotes with chlorophyll
🔹 Animalia – Heterotrophic, multicellular, no cell wall
🔹 Viruses – Acellular, parasitic on living organisms
🔹 Viroids – RNA only
🔹 Lichens – Algae + Fungi symbiosis
✅ Summary (~300 Words)
📌 Biological Classification is the scientific method of organizing organisms based on similarities and differences. Initially, only two kingdoms existed. But with scientific advancements, R.H. Whittaker’s Five Kingdom Classification emerged.
🔹 Monera: Prokaryotic unicellular organisms like bacteria, further divided into archaebacteria and eubacteria. Some are autotrophs like cyanobacteria, others heterotrophs. Archaebacteria survive extreme environments.
🔹 Protista: Unicellular eukaryotes such as diatoms, dinoflagellates, slime moulds, euglenoids, and protozoans. They show both plant and animal characteristics.
🔹 Fungi: Mostly multicellular heterotrophs with chitinous cell walls. They absorb nutrients and reproduce via spores. Examples include yeast, Rhizopus, and mushrooms. They may form symbiotic associations (lichens).
🔹 Plantae: Multicellular, autotrophic organisms with chlorophyll. They perform photosynthesis and have a distinct life cycle. Subgroups include algae, mosses, ferns, and flowering plants.
🔹 Animalia: Multicellular, heterotrophic organisms without cell walls. They exhibit growth, locomotion, and reproduction. Animals range from simple sponges to complex mammals.
Additionally, Viruses, Viroids, and Lichens are special cases. Viruses are acellular and parasitic. Viroids are naked RNA particles. Lichens are composite organisms formed by fungi and algae in a mutualistic relationship.
🧠 This classification system provides a framework for understanding the vast biodiversity on Earth and forms the basis for modern taxonomy and systematics.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🟦 Q1. Discuss how classification systems have undergone several changes over a period of time?
✅ Answer:
🔹 2-Kingdom System (Linnaeus): Plants & Animals only
🔸 Problems: Did not account for fungi, bacteria, etc.
🔹 3-Kingdom System (Haeckel): Added Protista
🔸 Still ignored differences in prokaryotes
🔹 4-Kingdom System (Copeland): Included Monera
🔸 Better classification for prokaryotes
🔹 5-Kingdom System (Whittaker): Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
🔸 Based on cell structure, nutrition, reproduction
🔹 Recent Systems:
– 6-Kingdom and 3-Domain System (Carl Woese): Based on molecular data (rRNA studies)
📌 Classification evolves with scientific advances.
🟦 Q2. State two economically important uses of:
(a) Heterotrophic bacteria
✅ Answer:
1️⃣ Production of curd, cheese, vinegar
2️⃣ Sewage treatment and organic waste decomposition
(b) Archaebacteria
✅ Answer:
1️⃣ Enzymes from Thermococcus used in PCR
2️⃣ Biogas production from methanogens
🟦 Q3. What is the nature of cell-walls in diatoms?
✅ Answer:
🟢 Diatom cell walls are:
🔹 Made of silica
🔸 Form two overlapping shells (like a soapbox)
🔹 Indestructible → form diatomaceous earth
🟦 Q4. Find out what do the terms ‘algal bloom’ and ‘red-tides’ signify.
✅ Answer:
🔹 Algal Bloom: Sudden increase in algae in water due to excess nutrients (eutrophication) → oxygen depletion
🔸 Red Tides: Rapid multiplication of red dinoflagellates (e.g., Gonyaulax) → water appears red → can release toxins harmful to aquatic life
🟦 Q5. How are viroids different from viruses?
✅ Answer:
Feature Virus Viroid
Genetic Material DNA or RNA RNA only
Protein Coat Present Absent
Size Larger Smaller
Discovery Earlier Later (by T.O. Diener, 1971)
🟦 Q6. Describe briefly the four major groups of Protozoa.
✅ Answer:
🔹 1. Amoeboid protozoa: Pseudopodia, aquatic – e.g., Amoeba
🔹 2. Flagellated protozoa: Flagella, parasitic – e.g., Trypanosoma
🔹 3. Ciliated protozoa: Cilia, free-living – e.g., Paramecium
🔹 4. Sporozoans: No locomotion, endoparasites – e.g., Plasmodium
🟦 Q7. Plants are autotrophic. Can you think of some plants that are partially heterotrophic?
✅ Answer:
Yes, examples include:
🔸 Cuscuta (dodder) – parasitic on other plants
🔸 Nepenthes (pitcher plant), Drosera – insectivorous
🔸 Monotropa – myco-heterotrophic
🟦 Q8. What do the terms phycobiont and mycobiont signify?
✅ Answer:
They refer to components of lichens:
🔹 Phycobiont – Algal partner (autotrophic, synthesizes food)
🔸 Mycobiont – Fungal partner (heterotrophic, provides shelter & water)
🟦 Q9. Give a comparative account of the classes of Kingdom Fungi under the following:
(i) Mode of Nutrition
Class Nutrition Type
Phycomycetes Saprophytic/parasitic
Ascomycetes Saprophytic/parasitic/symbiotic
Basidiomycetes Saprophytic/parasitic
Deuteromycetes Saprophytic/parasitic
(ii) Mode of Reproduction
Class Reproduction
Phycomycetes Asexual – zoospores; sexual – isogamy, anisogamy
Ascomycetes Asexual – conidia; sexual – ascospores in asci
Basidiomycetes Asexual – rare; sexual – basidiospores on basidia
Deuteromycetes Asexual only – conidia
🟦 Q10. What are the characteristic features of Euglenoids?
✅ Answer:
🔹 Found in freshwater
🔹 No cell wall, have flexible pellicle
🔹 Photosynthetic in light, heterotrophic in dark
🔹 Two flagella (one long, one short)
🔹 Example: Euglena
🟦 Q11. Give a brief account of viruses with respect to their structure and nature of genetic material. Also name four common viral diseases.
✅ Answer:
🦠 Viruses are:
🔸 Acellular, non-living outside host
🔹 Contain DNA or RNA, never both
🔸 Surrounded by protein coat (capsid) made of capsomeres
🔹 Obligate parasites
✅ Viral Diseases:
✔️ Polio
✔️ Influenza
✔️ HIV/AIDS
✔️ Hepatitis B
🟦 Q12. Organise a discussion in your class on the topic – Are viruses living or non-living?
✅ Answer (Suggested Points):
🔸 Living traits: Reproduce, mutate, evolve inside host
🔹 Non-living traits: No cell, no metabolism, inert outside host
📌 Viruses are at the boundary of living and non-living – unique entities
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔹 Q1. Which of the following is a unicellular eukaryote?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Bacteria
(C) Mycoplasma
(D) Nostoc
🔸 Answer: (A) Amoeba
🔹 Q2. In Whittaker’s system of classification, the main basis of classification is:
(A) Type of cell wall
(B) Mode of nutrition
(C) Complexity of body structure
(D) All of these
🔸 Answer: (D) All of these
🔹 Q3. Methanogens are found in:
(A) Salty areas
(B) Hot springs
(C) Marshy areas
(D) Lungs of cattle
🔸 Answer: (C) Marshy areas
🔹 Q4. The cell wall of fungi is composed of:
(A) Cellulose
(B) Pectin
(C) Chitin
(D) Peptidoglycan
🔸 Answer: (C) Chitin
🔹 Q5. Which of the following Kingdoms includes unicellular prokaryotic organisms?
(A) Monera
(B) Protista
(C) Plantae
(D) Fungi
🔸 Answer: (A) Monera
🔹 Q6. Which organism shows both autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition?
(A) Euglena
(B) Paramoecium
(C) Amoeba
(D) Plasmodium
🔸 Answer: (A) Euglena
🔹 Q7. Diatoms belong to the group:
(A) Cyanobacteria
(B) Chrysophytes
(C) Euglenoids
(D) Dinoflagellates
🔸 Answer: (B) Chrysophytes
🔹 Q8. Lichens are good indicators of:
(A) Water pollution
(B) Soil pollution
(C) Noise pollution
(D) Air pollution
🔸 Answer: (D) Air pollution
🔹 Q9. Which of the following are chemoautotrophs?
(A) Cyanobacteria
(B) Mycoplasma
(C) Methanogens
(D) Nitrifying bacteria
🔸 Answer: (D) Nitrifying bacteria
🔹 Q10. The term “Archaebacteria” was given because they:
(A) Live in primitive environment
(B) Cause diseases
(C) Are found in modern habitats
(D) Lack cell membrane
🔸 Answer: (A) Live in primitive environment
🔹 Q11. Which of the following lacks a true nucleus?
(A) Chlamydomonas
(B) Amoeba
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Euglena
🔸 Answer: (C) Cyanobacteria
🔹 Q12. In fungi, the vegetative body is:
(A) Mycelium made of hyphae
(B) Body with true roots and stems
(C) Cellulosic thallus
(D) Septate gametophyte
🔸 Answer: (A) Mycelium made of hyphae
🔹 Q13. Which group includes ‘Red tides’ forming organisms?
(A) Chrysophytes
(B) Euglenoids
(C) Dinoflagellates
(D) Slime moulds
🔸 Answer: (C) Dinoflagellates
🔹 Q14. Which of the following statements is correct for kingdom Protista?
(A) All members are multicellular
(B) All are prokaryotes
(C) They are unicellular eukaryotes
(D) They have no nucleus
🔸 Answer: (C) They are unicellular eukaryotes
🔹 Q15. Slime moulds resemble fungi in:
(A) Mode of nutrition
(B) Motility
(C) Cell wall composition
(D) Lack of nucleus
🔸 Answer: (A) Mode of nutrition
🔹 Q16. Match the columns:
Column I – Column II
P. Methanogens – 1. Salty areas
Q. Halophiles – 2. Hot springs
R. Thermoacidophiles – 3. Marshy areas
(A) P–1, Q–2, R–3
(B) P–3, Q–1, R–2
(C) P–2, Q–3, R–1
(D) P–3, Q–2, R–1
🔸 Answer: (B) P–3, Q–1, R–2
🔍 Assertion and Reasoning (Q17–Q18)
🔹 Q17.
Assertion (A): Viruses are considered as living when they are inside the host.
Reason (R): They can reproduce and show metabolic activity outside the host.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, but R is false
(D) A is false, but R is true
🔸 Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false
🔹 Q18.
Assertion (A): Euglena is considered both plant and animal.
Reason (R): It has chloroplasts and also exhibits movement using flagella.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, but R is false
(D) A is false, but R is true
🔸 Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
✍️ SECTION B: Q19 – Q21
🟠 Very Short Answer Questions (2 Marks Each)
🔸 Q19. What is the significance of the five-kingdom classification by Whittaker?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ The five-kingdom classification is based on:
🔹 Cell type (prokaryotic or eukaryotic)
🔹 Body organization (unicellular or multicellular)
🔹 Mode of nutrition (autotrophic or heterotrophic)
🔹 Reproduction and phylogenetic relationships
➡️ It brought clarity and evolutionary perspective to classification.
🔸 Q20. Why are cyanobacteria called blue-green algae? Name one feature that distinguishes them from true algae.
🟢 Answer:
🔹 Cyanobacteria are called blue-green algae because they have chlorophyll-a and other pigments that give them a bluish-green appearance.
✔️ Unlike true algae, they are prokaryotic and belong to Kingdom Monera.
🔸 Q21. Mention two distinguishing features of Archaebacteria.
🟢 Answer:
🔹 Archaebacteria have:
1️⃣ Unique cell walls lacking peptidoglycan
2️⃣ Ability to survive in extreme environments like high salinity, acidity, or temperature
✍️ SECTION C: Q22 – Q28
🟣 Short Answer Questions (3 Marks Each)
🔹 Q22. State three major characteristics of Kingdom Monera.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Organisms are unicellular and prokaryotic
2️⃣ Cell wall is made of peptidoglycan (except in archaebacteria)
3️⃣ Modes of nutrition vary—autotrophic (chemo/photo) and heterotrophic
🔹 Q23. How are fungi classified on the basis of mode of reproduction? Name any two classes with an example each.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Fungi are classified based on their mode of sexual reproduction:
1️⃣ Zygomycetes (e.g., Rhizopus) – reproduction through zygospores
2️⃣ Ascomycetes (e.g., Aspergillus) – through ascospores in asci
🔹 Q24. Describe the life cycle of slime moulds briefly.
🟢 Answer:
🔸 Slime moulds have a dual-phase life cycle:
✔️ Vegetative Phase – Amoeboid, feeds on organic matter
✔️ Reproductive Phase – Aggregates to form fruiting bodies with spores
✅ Spores are dispersed by air and germinate under favorable conditions
🔹 Q25. Differentiate between Viroids and Viruses.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Viroids Viruses
Structure RNA without protein coat Nucleic acid + protein coat
Discovery Discovered by T.O. Diener Known earlier
Host Infect plants Infect all types of organisms
🔹 Q26. Name any three groups of Protists. Give one example of each.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Chrysophytes – e.g., Diatoms
2️⃣ Dinoflagellates – e.g., Gonyaulax
3️⃣ Protozoans – e.g., Amoeba
🔹 Q27. State three distinguishing features of Kingdom Fungi.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Features:
🔹 Eukaryotic and heterotrophic
🔹 Cell wall made of chitin
🔹 Store food as glycogen (not starch like plants)
🔹 Q28. What is the role of lichens in the environment? How are they formed?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Role: Lichens are indicators of air quality; they are sensitive to pollutants like SO₂.
✔️ Formation: Symbiotic association between algae (providing food) and fungi (providing shelter and moisture).
🧠 SECTION D: Q29 – Q30
🔷 Case-Based Questions (4 Marks Each)
🔹 Q29. Read the case and answer the questions that follow:
A team of microbiologists isolated a microorganism from the hot springs of Manikaran, Himachal Pradesh. The organism showed resistance to high temperature and acidity, and it could survive in the absence of oxygen.
(i) Identify the group this microorganism belongs to.
(ii) Mention one structural feature and one metabolic ability of this group.
(iii) How does this group differ from other bacteria in terms of cell wall composition?
(iv) Name two types of Archaebacteria based on habitat.
🟢 Answer:
(i) Archaebacteria
(ii) Structural: Lack peptidoglycan in cell wall
Metabolic: Can perform methanogenesis or survive in high salinity/acidity
(iii) Their cell wall lacks peptidoglycan and contains pseudopeptidoglycan or polysaccharides
(iv) Methanogens and Halophiles
🔹 Q30. Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
During a biology field trip, students observed yellow, slimy structures on decaying leaves in a moist forest area. Over time, these structures transformed and released spores.
(i) Identify the organism group being described.
(ii) What is the name of its feeding stage and reproductive structure?
(iii) Write one ecological role of this group.
(iv) Mention whether this organism is prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
🟢 Answer:
(i) Slime moulds
(ii) Feeding stage – Plasmodium; Reproductive – Fruiting body with spores
(iii) Help in decomposition and nutrient recycling
(iv) Eukaryotic
🧾 SECTION E: Q31 – Q33
🔶 Long Answer Questions (5 Marks Each)
🔸 Q31. Explain the classification of Kingdom Protista. Describe each subgroup with one example.
🟢 Answer:
Kingdom Protista includes all unicellular eukaryotes. Classification based on mode of nutrition and movement:
✔️ 1. Chrysophytes
– Mostly photosynthetic, e.g., Diatoms
– Siliceous cell walls, float on water
🔹 Ecological role: Major phytoplankton
✔️ 2. Dinoflagellates
– Marine, photosynthetic, e.g., Gonyaulax
– Have cellulose plates and two flagella
🌊 Some cause red tides
✔️ 3. Euglenoids
– Freshwater, mixotrophic, e.g., Euglena
– Have pellicle, flexible body covering
✔️ 4. Slime moulds
– Saprophytic, e.g., Physarum
– Amoeboid feeding phase, fruiting bodies in reproduction
✔️ 5. Protozoans
– Heterotrophic
– Amoeboids (Amoeba), Flagellates (Trypanosoma), Ciliates (Paramecium), Sporozoans (Plasmodium)
🔸 Q32. What are viruses? Describe their structure and nature. How are viroids and prions different from viruses?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Viruses:
➡️ Non-cellular entities with nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) enclosed in protein coat (capsid)
✔️ Obligate parasites, inactive outside host
✔️ Structure:
– Nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
– Protein coat (capsomeres form capsid)
– Some have envelopes (e.g., HIV)
✔️ Viroids:
– Discovered by T.O. Diener
– Small, circular RNA molecules
– No protein coat
– Infect plants (e.g., potato spindle tuber disease)
✔️ Prions:
– Infectious proteins
– No nucleic acid
– Cause diseases like mad cow disease in animals
🔸 Q33. Compare the five kingdoms in Whittaker’s classification based on key features.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Monera Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia
Cell type Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic
Body organisation Unicellular Mostly unicellular Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular
Cell wall Present (peptidoglycan) Present/absent Present (chitin) Present (cellulose) Absent
Mode of nutrition Autotroph/heterotroph Photo/heterotroph Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph
Reproduction Asexual Sexual/asexual Sexual/asexual Mostly sexual Mostly sexual
📌 Importance: Whittaker’s system reflects evolutionary relationships and ecological roles more clearly.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which group of organisms is classified under the kingdom Monera?
(A) Bacteria
(B) Fungi
(C) Algae
(D) Protozoa
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Set: 3
Q2. Which of the following is not a eukaryote?
(A) Euglena
(B) Diatom
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Paramoecium
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 | Set: A
Q3. Which of the following are called ‘chemical factories’ of the world due to their role in nutrient cycling?
(A) Protozoans
(B) Bacteria
(C) Algae
(D) Fungi
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024 | Set: Z
Q4. Which of the following organisms are used as bioindicators of pollution?
(A) Fungi
(B) Mosses
(C) Lichens
(D) Ferns
Answer: (C)
Year: 2023 | Set: 2
Q5. Archaebacteria can survive in:
(A) High light intensity
(B) Acidic marshes
(C) Ice-cold water
(D) Normal tap water
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Set: X
Q6. Which of the following lacks a true nucleus?
(A) Euglena
(B) Diatom
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Amoeba
Answer: (C)
Year: 2022 | Set: A
Q7. Which among the following is not included in the five kingdom classification?
(A) Virus
(B) Monera
(C) Fungi
(D) Protista
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Set: M
Q8. Methanogens are present in:
(A) Aerobic soils
(B) Rice fields
(C) Human intestine
(D) Rumen of cattle
Answer: (D)
Year: 2021 | Set: 1
Q9. Lichens are symbiotic associations of:
(A) Fungi and protozoa
(B) Algae and fungi
(C) Fungi and cyanobacteria
(D) Algae and protozoa
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 | Set: B
Q10. Which kingdom includes unicellular eukaryotes?
(A) Monera
(B) Protista
(C) Fungi
(D) Plantae
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 | Set: R
Q11. Diatoms are chiefly:
(A) Consumers
(B) Parasites
(C) Decomposers
(D) Producers
Answer: (D)
Year: 2019 | Set: W
Q12. Which is known as “golden algae”?
(A) Chrysophytes
(B) Dinoflagellates
(C) Diatoms
(D) Euglenoids
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Set: S
Q13. Which of the following is not a characteristic of viruses?
(A) Can reproduce
(B) Have cell wall
(C) Acellular
(D) Non-cellular
Answer: (B)
Year: 2018 | Set: Q
Q14. Which of the following is a connecting link between bacteria and eukaryotes?
(A) Mycoplasma
(B) Nostoc
(C) Euglena
(D) Cyanobacteria
Answer: (D)
Year: 2018 | Set: T
Q15. Mycoplasma differ from other prokaryotes in having:
(A) Peptidoglycan wall
(B) Steroid-rich membrane
(C) Nuclear membrane
(D) DNA bound by histones
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017 | Set: P
Q16. Which organism is responsible for red tides in oceans?
(A) Euglenoids
(B) Chrysophytes
(C) Red algae
(D) Dinoflagellates
Answer: (D)
Year: 2017 | Set: L
Q17. Which among the following are slime moulds?
(A) Fungi
(B) Protists
(C) Bacteria
(D) Algae
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016 | Set: Z
Q18. Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in:
(A) Mode of nutrition
(B) Cell membrane structure
(C) Ribosome size
(D) DNA replication method
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016 | Set: C
Q19. Diatomaceous earth is formed by the accumulation of:
(A) Dinoflagellates
(B) Euglenoids
(C) Diatom shells
(D) Fungal spores
Answer: (C)
Year: 2015 | Set: A
Q20. Which of the following reproduce only inside living cells?
(A) Fungi
(B) Protozoa
(C) Virus
(D) Bacteria
Answer: (C)
Year: 2015 | Set: B
Q21. Which of the following organisms can fix atmospheric nitrogen?
(A) Euglena
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Dinoflagellates
(D) Fungi
Answer: (B)
Year: 2014 | Set: 2
Q22. The cell wall of fungi is made up of:
(A) Cellulose
(B) Chitin
(C) Pectin
(D) Glycogen
Answer: (B)
Year: 2014 | Set: X
Q23. Viruses were discovered by:
(A) Pasteur
(B) Beijerinck
(C) Linnaeus
(D) Stanley
Answer: (B)
Year: 2013 | Set: Z
Q24. Which of these does not belong to Protista?
(A) Euglena
(B) Paramoecium
(C) Amoeba
(D) Rhizopus
Answer: (D)
Year: 2012 | Set: 3
Q25. Which of the following are saprophytic in nature?
(A) Fungi
(B) Algae
(C) Lichens
(D) Mosses
Answer: (A)
Year: 2012 | Set: A
Q26. Which of the following can live in extreme salty environments?
(A) Methanogens
(B) Halophiles
(C) Thermoacidophiles
(D) Cyanobacteria
Answer: (B)
Year: 2011 | Set: W
Q27. The unique feature of Mycoplasma is:
(A) Cell wall made of chitin
(B) Presence of true nucleus
(C) Absence of DNA
(D) Absence of cell wall
Answer: (D)
Year: 2011 | Set: X
Q28. Which among the following has a siliceous cell wall?
(A) Euglenoids
(B) Dinoflagellates
(C) Diatoms
(D) Slime moulds
Answer: (C)
Year: 2010 | Set: M
Q29. Protists having characteristics of both plants and animals are:
(A) Diatoms
(B) Dinoflagellates
(C) Euglenoids
(D) Slime moulds
Answer: (C)
Year: 2010 | Set: T
Q30. Which organism lacks a cell wall and shows pleomorphism?
(A) Cyanobacteria
(B) Archaebacteria
(C) Euglena
(D) Mycoplasma
Answer: (D)
Year: 2009 | Set: A
Q31. Which of the following is known to have a pellicle instead of a cell wall?
(A) Euglena
(B) Amoeba
(C) Plasmodium
(D) Paramoecium
Answer: (A)
Year: 2009 | Set: B
Q32. In which kingdom are organisms grouped based on the absence of a nuclear membrane?
(A) Protista
(B) Monera
(C) Fungi
(D) Plantae
Answer: (B)
Year: 2008 | Set: Z
Q33. Which of the following is not a characteristic of Monerans?
(A) Prokaryotic cell
(B) Cell wall of peptidoglycan
(C) Presence of histone proteins
(D) No membrane-bound organelles
Answer: (C)
Year: 2008 | Set: 2
Q34. In fungi, stored food is generally:
(A) Cellulose
(B) Glycogen
(C) Starch
(D) Protein
Answer: (B)
Year: 2007 | Set: C
Q35. Which of the following reproduces by zoospores?
(A) Rhizopus
(B) Penicillium
(C) Chlamydomonas
(D) Amoeba
Answer: (C)
Year: 2007 | Set: B
Q36. Dinoflagellates are mostly:
(A) Parasitic
(B) Photosynthetic
(C) Chemosynthetic
(D) Saprophytic
Answer: (B)
Year: 2006 | Set: 1
Q37. Which of these can cause neurotoxins in marine food chains?
(A) Diatoms
(B) Euglenoids
(C) Dinoflagellates
(D) Cyanobacteria
Answer: (C)
Year: 2006 | Set: A
Q38. Which of the following are commonly called blue-green algae?
(A) Archaebacteria
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Protists
(D) Mycoplasma
Answer: (B)
Year: 2005 | Set: T
Q39. Asexual reproduction in fungi usually occurs through:
(A) Zoospores
(B) Gametes
(C) Conidia
(D) Budding
Answer: (C)
Year: 2005 | Set: M
Q40. Which group of Protists is responsible for causing malaria?
(A) Slime moulds
(B) Protozoans
(C) Dinoflagellates
(D) Chrysophytes
Answer: (B)
Year: 2004 | Set: 1
Q41. Slime moulds are unique because they:
(A) Lack cell membrane
(B) Are acellular in one phase
(C) Show alternation of generation
(D) Have multicellular spores
Answer: (B)
Year: 2004 | Set: X
Q42. Which among these are multicellular but without tissue differentiation?
(A) Protozoa
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Mycoplasma
(D) Slime moulds
Answer: (D)
Year: 2003 | Set: C
Q43. The mode of nutrition in fungi is:
(A) Autotrophic
(B) Parasitic only
(C) Saprophytic and parasitic
(D) Chemosynthetic
Answer: (C)
Year: 2003 | Set: 2
Q44. Protistan group includes:
(A) Amoeba, Euglena, Paramoecium
(B) Cyanobacteria, Mycoplasma, Nostoc
(C) Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas, Penicillium
(D) Rhizopus, Mucor, Albugo
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002 | Set: A
Q45. Lichens do not grow in:
(A) Moist areas
(B) Clean air zones
(C) Polluted areas
(D) Cold deserts
Answer: (C)
Year: 2002 | Set: W
Q46. The organism causing Red Tide belongs to:
(A) Euglenoids
(B) Dinoflagellates
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Chrysophytes
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: T
Q47. The fungi imperfecti are those:
(A) Reproducing asexually only
(B) With no known sexual reproduction
(C) With perfect sporulation
(D) With both asexual and sexual stages
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: B
Q48. Monera includes all:
(A) Eukaryotic unicellular organisms
(B) Prokaryotic unicellular organisms
(C) Eukaryotic multicellular organisms
(D) Unicellular fungi
Answer: (B)
Year: 2001 | Set: Q
Q49. Fungal sexual spores include all except:
(A) Zygospores
(B) Ascospores
(C) Basidiospores
(D) Zoospores
Answer: (D)
Year: 2001 | Set: P
Q50. Kingdom Protista includes all of the following except:
(A) Slime moulds
(B) Protozoans
(C) Chrysophytes
(D) Bacteria
Answer: (D)
Year: 2001 | Set: 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. The group of microorganisms that can survive in highly salty environments is called:
(A) Thermoacidophiles
(B) Methanogens
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Halophiles
Answer: (D)
Q2. Which of the following is a feature of Mycoplasma?
(A) Lack of cell wall
(B) Silica-based wall
(C) Binucleated cells
(D) Presence of chlorophyll
Answer: (A)
Q3. Euglena-like organisms are unique because they are:
(A) Both autotrophic and heterotrophic
(B) Only heterotrophic
(C) Only autotrophic
(D) Only saprophytic
Answer: (A)
Q4. Which group is called “primitive bacteria” and found in extreme environments?
(A) Eubacteria
(B) Archaebacteria
(C) Protista
(D) Fungi
Answer: (B)
Q5. Which one of the following belongs to Kingdom Protista?
(A) Paramecium
(B) Escherichia coli
(C) Amoeba proteus
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer: (D)
Q6. Which among the following is known as blue-green algae?
(A) Euglena
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Protozoa
(D) Slime mould
Answer: (B)
Q7. Which of these is a chemosynthetic autotroph?
(A) Nostoc
(B) Nitrosomonas
(C) Rhizobium
(D) Paramecium
Answer: (B)
Q8. Which fungus reproduces through conidia?
(A) Rhizopus
(B) Penicillium
(C) Mucor
(D) Agaricus
Answer: (B)
Q9. Which of these protists move using cilia?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Paramecium
(C) Euglena
(D) Plasmodium
Answer: (B)
Q10. What structure is common in fungi for sexual reproduction?
(A) Fragment
(B) Conidia
(C) Zygospore
(D) Binary fission
Answer: (C)
Q11. Slime moulds belong to:
(A) Fungi
(B) Plantae
(C) Protista
(D) Monera
Answer: (C)
Q12. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
(A) Holozoic
(B) Saprophytic
(C) Autotrophic
(D) Ingestive
Answer: (B)
Q13. Which of the following lacks a true nucleus?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Paramecium
(C) Bacteria
(D) Euglena
Answer: (C)
Q14. Which kingdom includes both unicellular and multicellular organisms?
(A) Monera
(B) Protista
(C) Fungi
(D) Plantae
Answer: (C)
Q15. Which of the following is a nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium?
(A) Nostoc
(B) Volvox
(C) Plasmodium
(D) Ulothrix
Answer: (A)
Q16. The term “Monera” was first used in:
(A) Five Kingdom Classification
(B) Two Kingdom Classification
(C) Three Domain System
(D) Linnaeus Classification
Answer: (A)
Q17. Which of the following has both characteristics of plants and animals?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Euglena
(C) Chlorella
(D) Paramecium
Answer: (B)
Q18. The kingdom Monera includes:
(A) Bacteria and Cyanobacteria
(B) Viruses
(C) Fungi
(D) Algae
Answer: (A)
Q19. Which protist causes malaria?
(A) Plasmodium
(B) Amoeba
(C) Paramecium
(D) Giardia
Answer: (A)
Q20. Which of the following organisms is not photosynthetic?
(A) Nostoc
(B) Euglena
(C) Plasmodium
(D) Volvox
Answer: (C)
Q21. The genetic material in prokaryotes is present in:
(A) Nucleus
(B) Nucleoid
(C) Nucleolus
(D) None of the above
Answer: (B)
Q22. What do diatoms store food as?
(A) Starch
(B) Glycogen
(C) Leucosin and oils
(D) Cellulose
Answer: (C)
Q23. Which kingdom includes archaebacteria?
(A) Protista
(B) Monera
(C) Fungi
(D) Plantae
Answer: (B)
Q24. Which of the following fungi is edible?
(A) Rhizopus
(B) Agaricus
(C) Mucor
(D) Penicillium
Answer: (B)
Q25. Viruses are placed:
(A) In Kingdom Monera
(B) In Kingdom Protista
(C) In their own unique category
(D) In Kingdom Fungi
Answer: (C)
Q26. Which feature distinguishes Archaebacteria from Eubacteria?
(A) Presence of murein in cell wall
(B) Membrane lipids with ether linkages
(C) Presence of double membrane
(D) Presence of true nucleus
Answer: (B)
Q27. Why are cyanobacteria not classified under Kingdom Plantae despite being photosynthetic?
(A) Lack of chlorophyll
(B) Absence of cellulose in cell wall
(C) Prokaryotic cell structure
(D) Presence of starch as reserve food
Answer: (C)
Q28. Match the following:
Methanogens — A. Halophiles
Thermoacidophiles — B. Cattle gut
Halophiles — C. Hot springs
(A) 1-B, 2-C, 3-A
(B) 1-A, 2-B, 3-C
(C) 1-C, 2-B, 3-A
(D) 1-B, 2-A, 3-C
Answer: (A)
Q29. Which of the following is correctly matched?
(A) Plasmodium – Flagella
(B) Amoeba – Pseudopodia
(C) Euglena – Cilia
(D) Paramecium – Contractile vacuole absent
Answer: (B)
Q30. Slime moulds are placed under Kingdom Protista because:
(A) They have cell walls of chitin
(B) They show animal and plant-like features
(C) They are photosynthetic
(D) They have prokaryotic cell structure
Answer: (B)
Q31. The structure responsible for respiration in aerobic bacteria is:
(A) Cell wall
(B) Nucleoid
(C) Mesosome
(D) Ribosome
Answer: (C)
Q32. The correct order of increasing complexity in biological classification (based on NCERT system) is:
(A) Monera < Protista < Fungi < Plantae < Animalia
(B) Monera < Fungi < Protista < Plantae < Animalia
(C) Protista < Monera < Fungi < Plantae < Animalia
(D) Protista < Monera < Plantae < Fungi < Animalia
Answer: (A)
Q33. In fungi, plasmogamy is followed by:
(A) Karyogamy
(B) Cytokinesis
(C) Budding
(D) Fragmentation
Answer: (A)
Q34. Which of the following lacks peptidoglycan in their cell wall?
(A) Eubacteria
(B) Archaebacteria
(C) Cyanobacteria
(D) Mycoplasma
Answer: (B)
Q35. The genetic material in viruses is:
(A) Only DNA
(B) Only RNA
(C) Either DNA or RNA
(D) Both DNA and RNA simultaneously
Answer: (C)
Q36. Which structure is absent in Euglena but present in Paramecium?
(A) Pellicle
(B) Cilia
(C) Eyespot
(D) Chloroplast
Answer: (B)
Q37. Assertion (A): Fungi are saprophytic in nature.
Reason (R): Fungi perform extracellular digestion.
(A) A and R both correct, R explains A
(B) A and R both correct, R doesn’t explain A
(C) A correct, R false
(D) A false, R correct
Answer: (A)
Q38. Which of the following is not a feature of diatoms?
(A) Silica-rich wall
(B) Reserve food is starch
(C) Unicellular nature
(D) Golden-brown chloroplasts
Answer: (B)
Q39. Why is Rhizopus classified under Zygomycetes?
(A) It reproduces by conidia
(B) It produces ascospores
(C) It forms zygospore after sexual reproduction
(D) It forms basidiospores
Answer: (C)
Q40. Which of the following forms symbiotic association with fungi in lichens?
(A) Mycoplasma
(B) Algae or Cyanobacteria
(C) Slime moulds
(D) Protozoa
Answer: (B)
Q41. Assertion (A): Bacteria reproduce by conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
Reason (R): These processes are sexual methods of reproduction.
(A) A correct, R incorrect
(B) A and R both correct
(C) A incorrect, R correct
(D) A correct, R is unrelated
Answer: (A)
Q42. Which group is evolutionarily closest to eukaryotes?
(A) Eubacteria
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Archaebacteria
(D) Protista
Answer: (C)
Q43. The sexual reproduction in Basidiomycetes occurs through:
(A) Oogamy
(B) Isogamy
(C) Plasmogamy and Karyogamy
(D) Budding
Answer: (C)
Q44. Which organism uses a red eye-spot for photoreception?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Euglena
(C) Volvox
(D) Paramecium
Answer: (B)
Q45. Mucor differs from Rhizopus in:
(A) Type of hyphae
(B) Type of spores
(C) Cell wall composition
(D) None of the above
Answer: (D)
Q46. Protistan algae differ from higher plants in:
(A) Having thalloid body
(B) Absence of reproductive organs
(C) Lack of embryo stage
(D) All of the above
Answer: (D)
Q47. Which of the following are known as “living fossils”?
(A) Archaebacteria
(B) Cyanobacteria
(C) Diatoms
(D) Mycoplasma
Answer: (C)
Q48. Which feature in bacteria makes them ideal for genetic experiments?
(A) Plasmids
(B) Flagella
(C) Cell wall
(D) Nucleoid
Answer: (A)
Q49. What makes mycoplasma unique among prokaryotes?
(A) Presence of double membrane
(B) Absence of RNA
(C) Lack of cell wall
(D) Presence of histones
Answer: (C)
Q50. Which characteristic helps differentiate fungi from plants?
(A) Multicellularity
(B) Heterotrophic mode of nutrition
(C) Presence of chlorophyll
(D) Cellulose in cell wall
Answer: (B)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MINDMAPS

