Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 19: Chemical Coordination and Integration
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌱✨ Introduction
🧠 The body of a multicellular organism performs numerous activities simultaneously. To maintain coordination, the body uses two systems:
⚡ Nervous system – for rapid, short-term control using electrical impulses
🧪 Endocrine system – for slow, long-term control using chemical messengers known as hormones
💡 Concept: Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals produced in trace amounts that act as intercellular messengers.
🌿 The study of hormones and endocrine glands is known as Endocrinology.
🧬 Human Endocrine System
🧠 The endocrine system is made up of ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
These hormones regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and homeostasis.
📘 Major endocrine glands:
1️⃣ Hypothalamus
2️⃣ Pituitary gland
3️⃣ Pineal gland
4️⃣ Thyroid gland
5️⃣ Parathyroid glands
6️⃣ Thymus
7️⃣ Adrenal glands
8️⃣ Pancreas
9️⃣ Gonads (Testes and Ovaries)
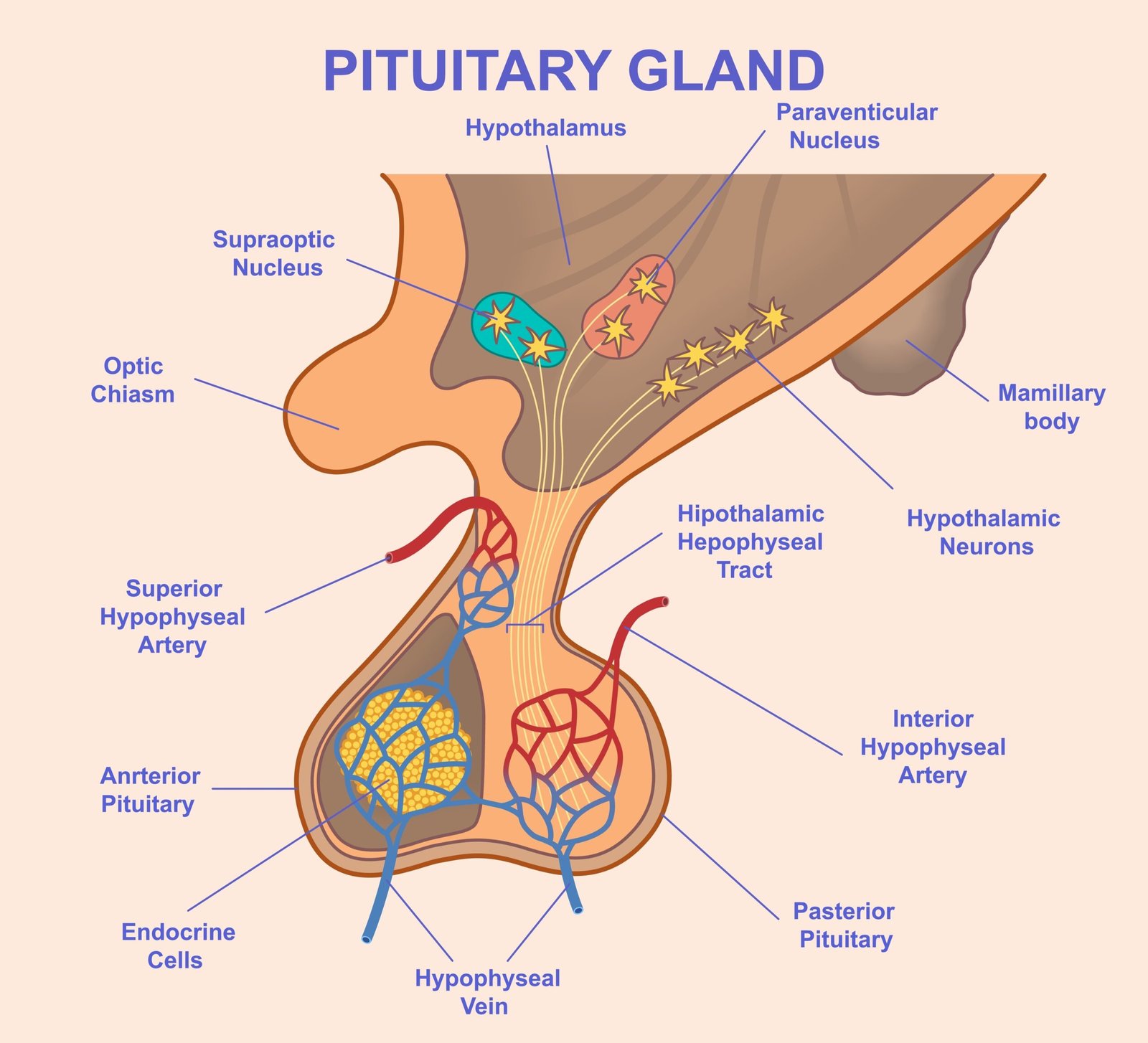
🧠 Hypothalamus
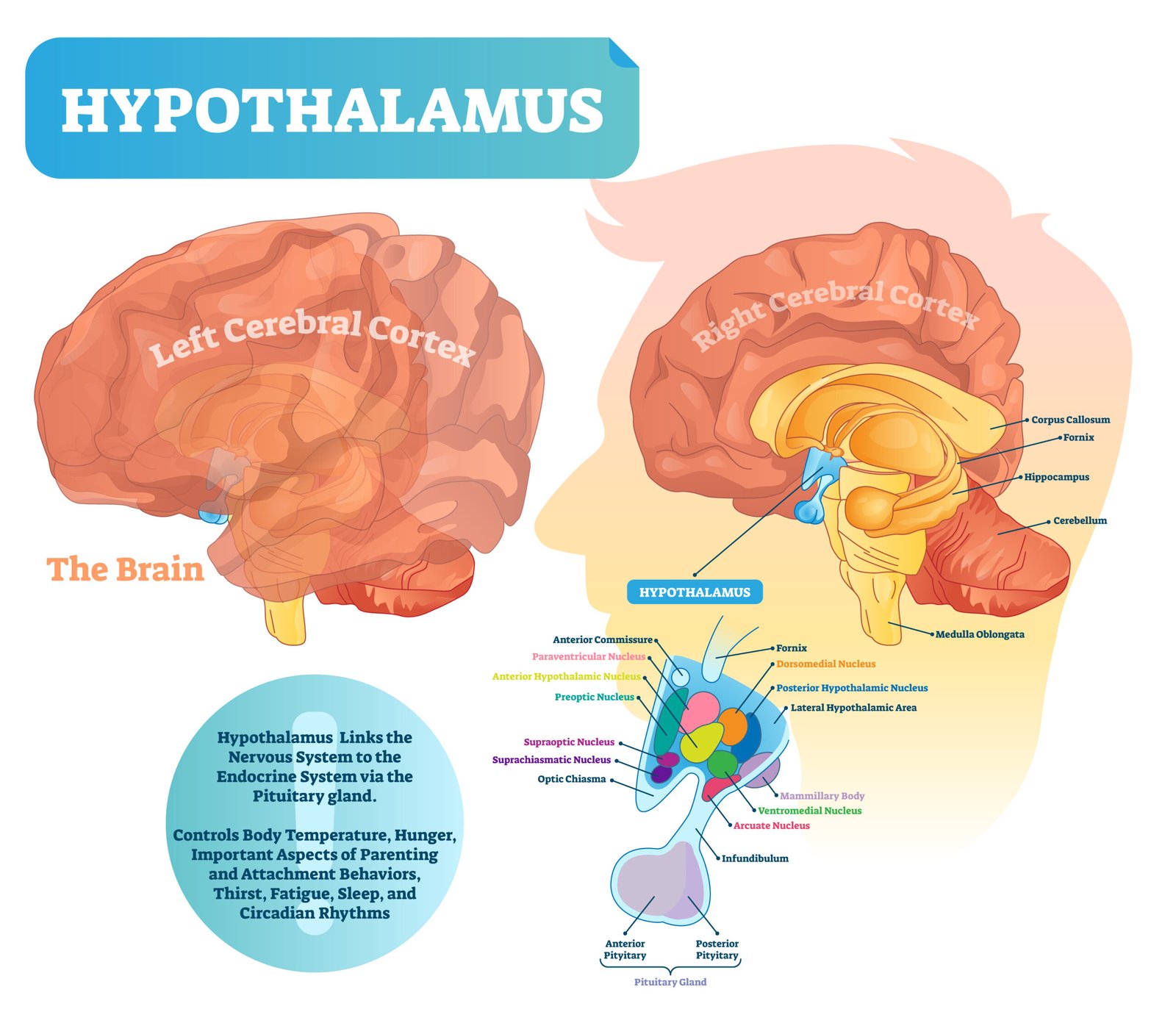
📍 Location: Base of forebrain, below thalamus, above pituitary gland
💡 It acts as the master regulator connecting the nervous and endocrine systems.
🧪 Hormones:
Releasing Hormones (RH): stimulate pituitary
➤ Thyrotropin-RH (TRH)
➤ Gonadotropin-RH (GnRH)
➤ Corticotropin-RH (CRH)
Inhibiting Hormones (IH): suppress pituitary
➤ Growth Hormone-IH (Somatostatin)
⚙️ Function: Controls pituitary gland secretions by releasing or inhibiting hormones.
🧩 Pituitary Gland — “Master Gland”
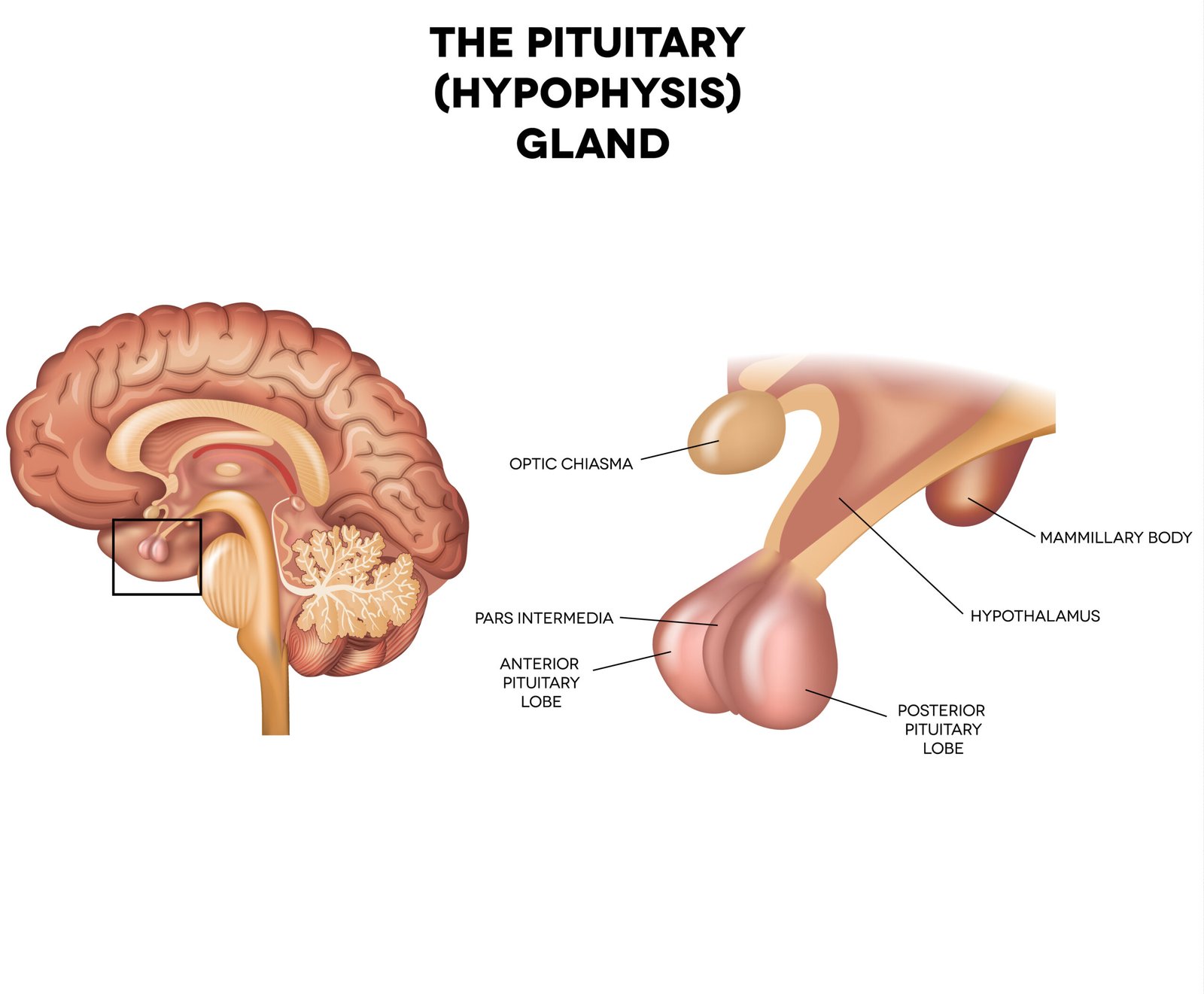
📍 Location: Below hypothalamus in sella turcica of skull
📘 Divisions:
1️⃣ Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis)
2️⃣ Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis)
🧪 Anterior Pituitary Hormones:
🔹 Growth Hormone (GH): stimulates body growth, protein synthesis
🔹 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates thyroid gland
🔹 Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): stimulates adrenal cortex
🔹 Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): gamete formation
🔹 Luteinizing Hormone (LH): ovulation, testosterone secretion
🔹 Prolactin (PRL): milk secretion after childbirth
⚠️ Disorders:
GH excess → Gigantism (in childhood), Acromegaly (in adults)
GH deficiency → Dwarfism
🧪 Posterior Pituitary Hormones:
🔹 Oxytocin: uterine contraction, milk ejection
🔹 Vasopressin (ADH): water reabsorption in kidneys
⚠️ Deficiency of ADH → Diabetes insipidus (excess urination)
🌙 Pineal Gland
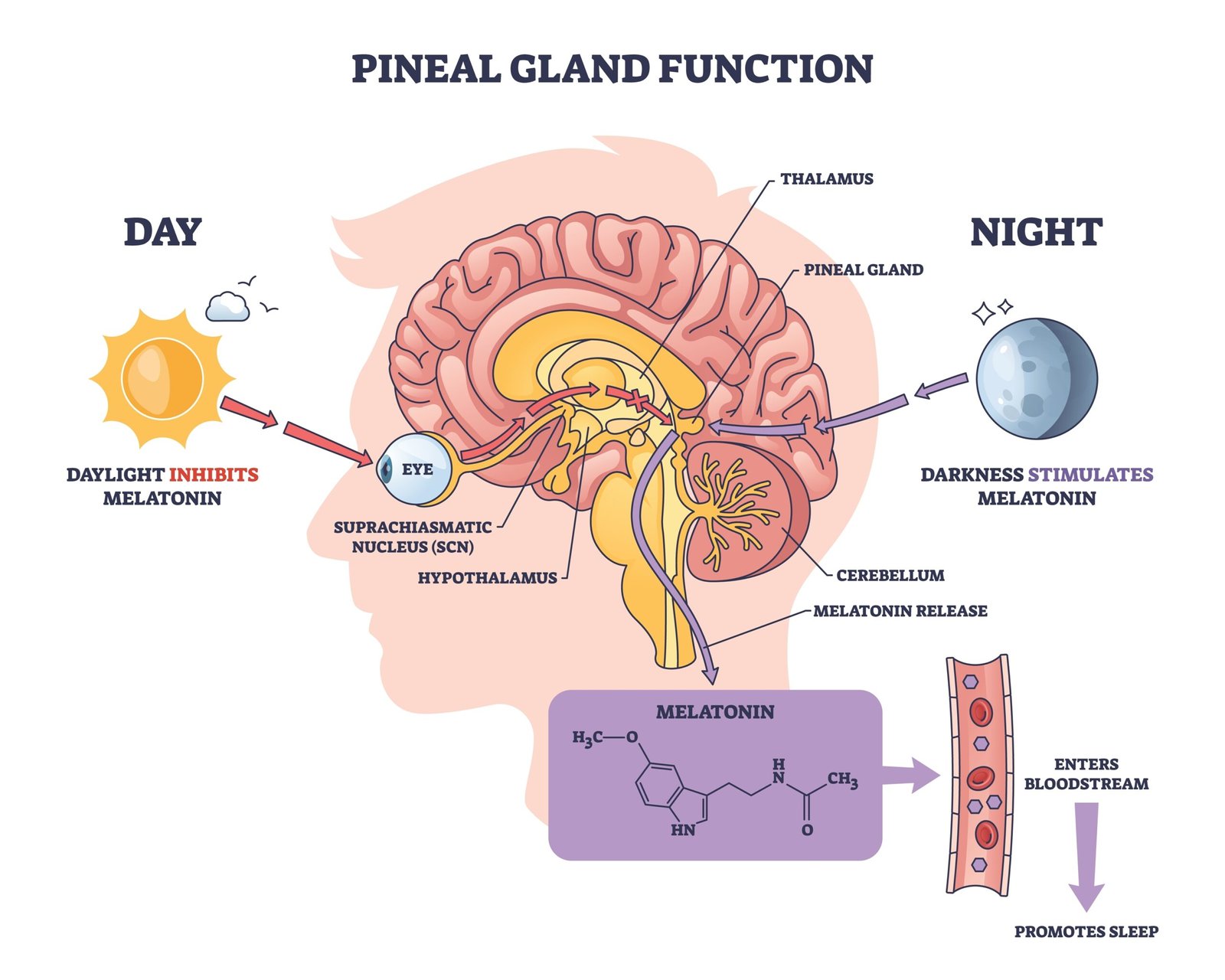
📍 Location: Dorsal part of forebrain
🧪 Hormone: Melatonin
📘 Functions:
Regulates circadian rhythm (sleep–wake cycle)
Influences metabolism and seasonal reproduction
🧠 Thyroid Gland
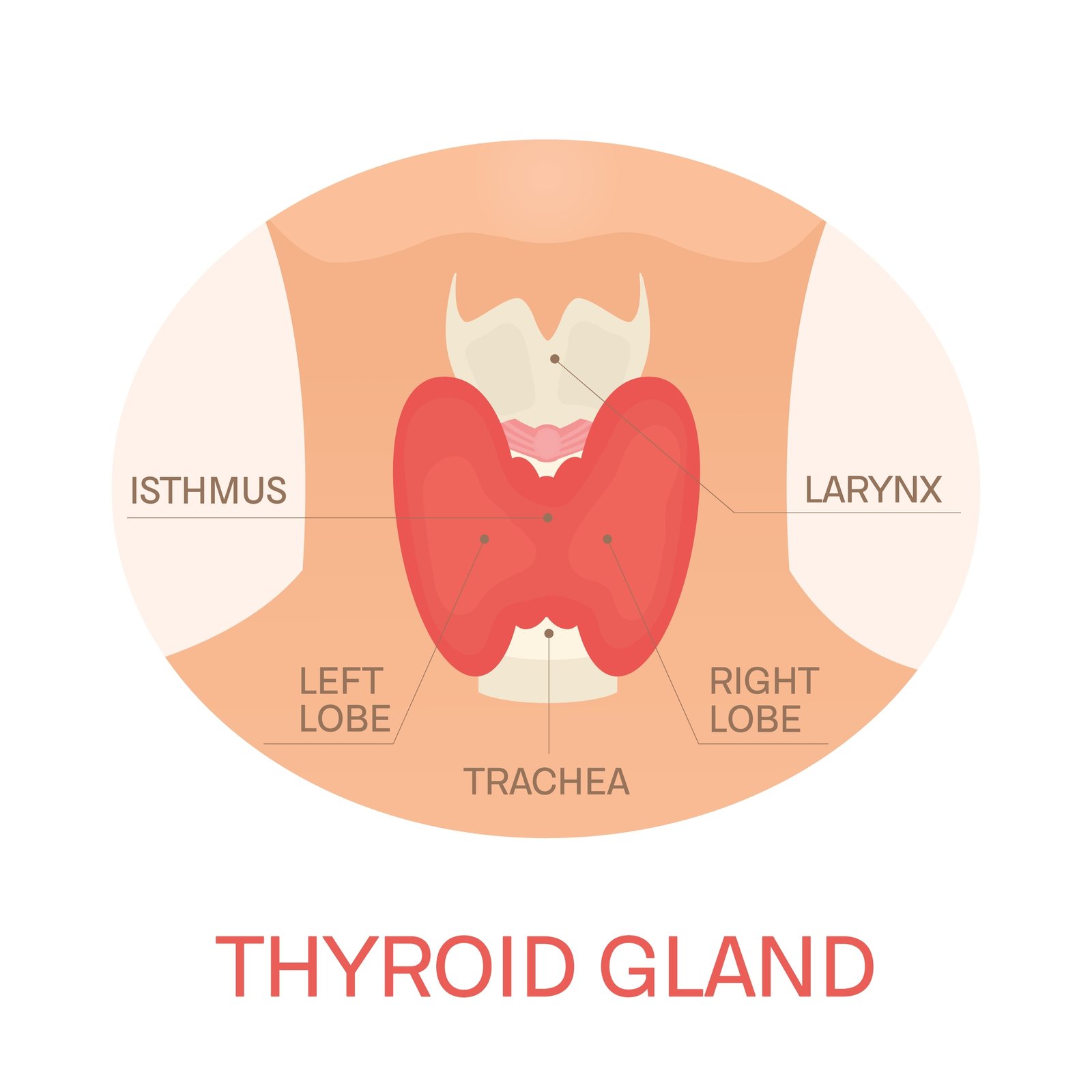
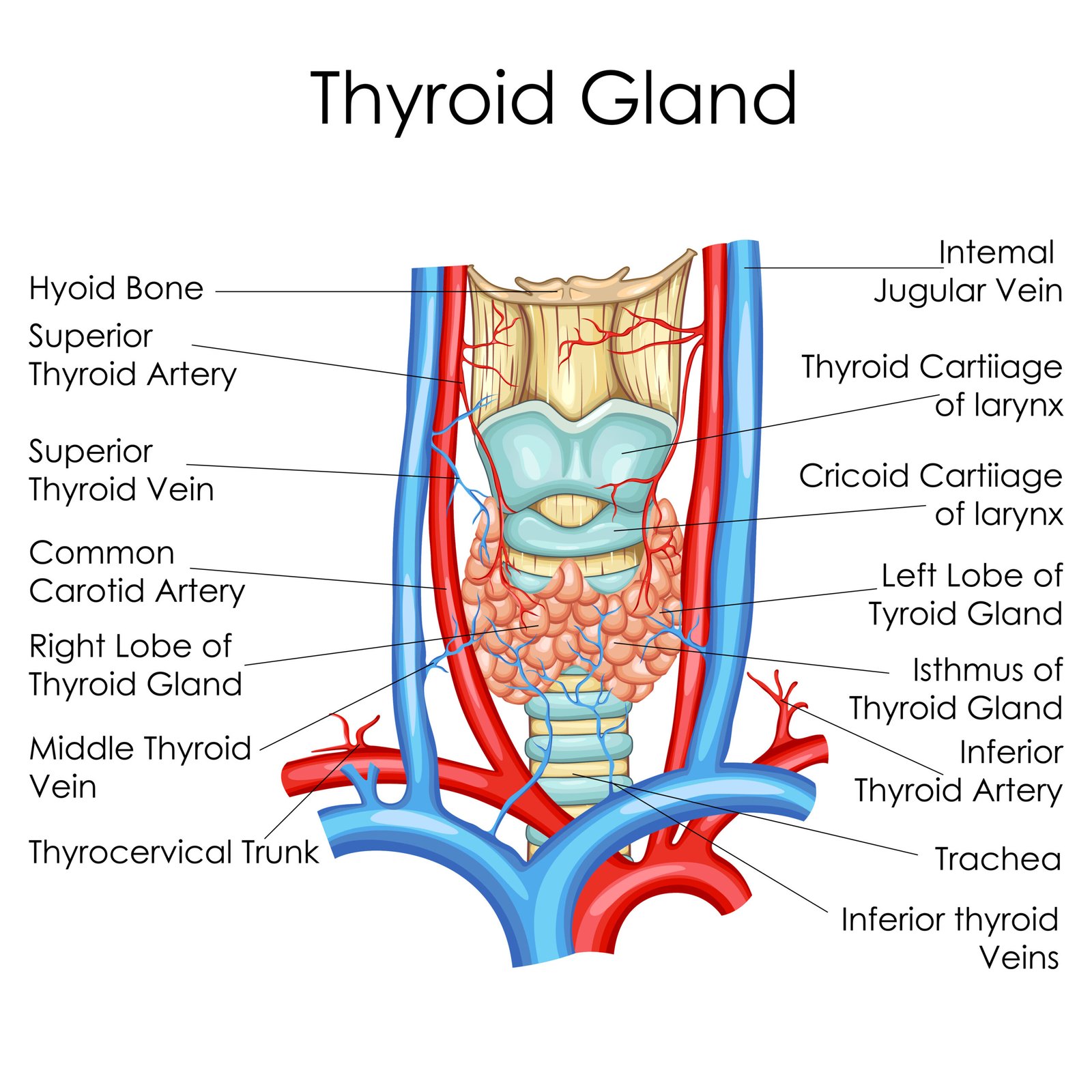
📍 Location: Neck region on either side of trachea
🧪 Hormones:
Thyroxine (T₄)
Triiodothyronine (T₃)
Calcitonin
📘 Functions:
Regulates basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Maintains growth, development, and body temperature
Calcitonin lowers blood calcium
⚠️ Disorders:
Deficiency of iodine → Goitre
Hypothyroidism in children → Cretinism
Hyperthyroidism → Graves’ disease
✏️ Note: Iodine is essential for synthesis of T₃ and T₄.
🧬 Parathyroid Glands
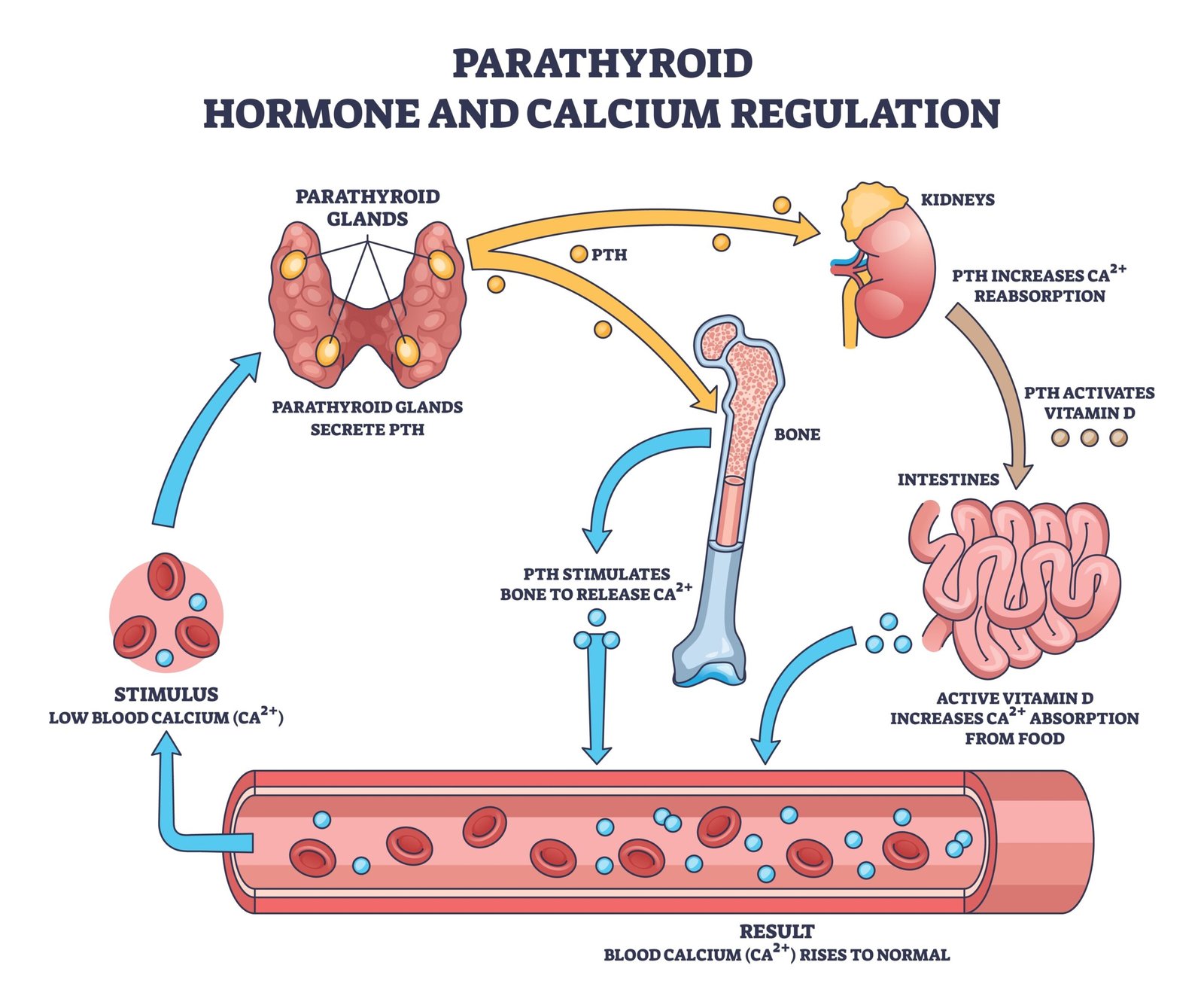
📍 Four small glands behind thyroid
🧪 Hormone: Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
💡 Functions:
Increases blood calcium level
Stimulates bone resorption
Enhances Ca²⁺ reabsorption in kidneys
Activates vitamin D
⚙️ Antagonistic to calcitonin
🧫 Thymus Gland
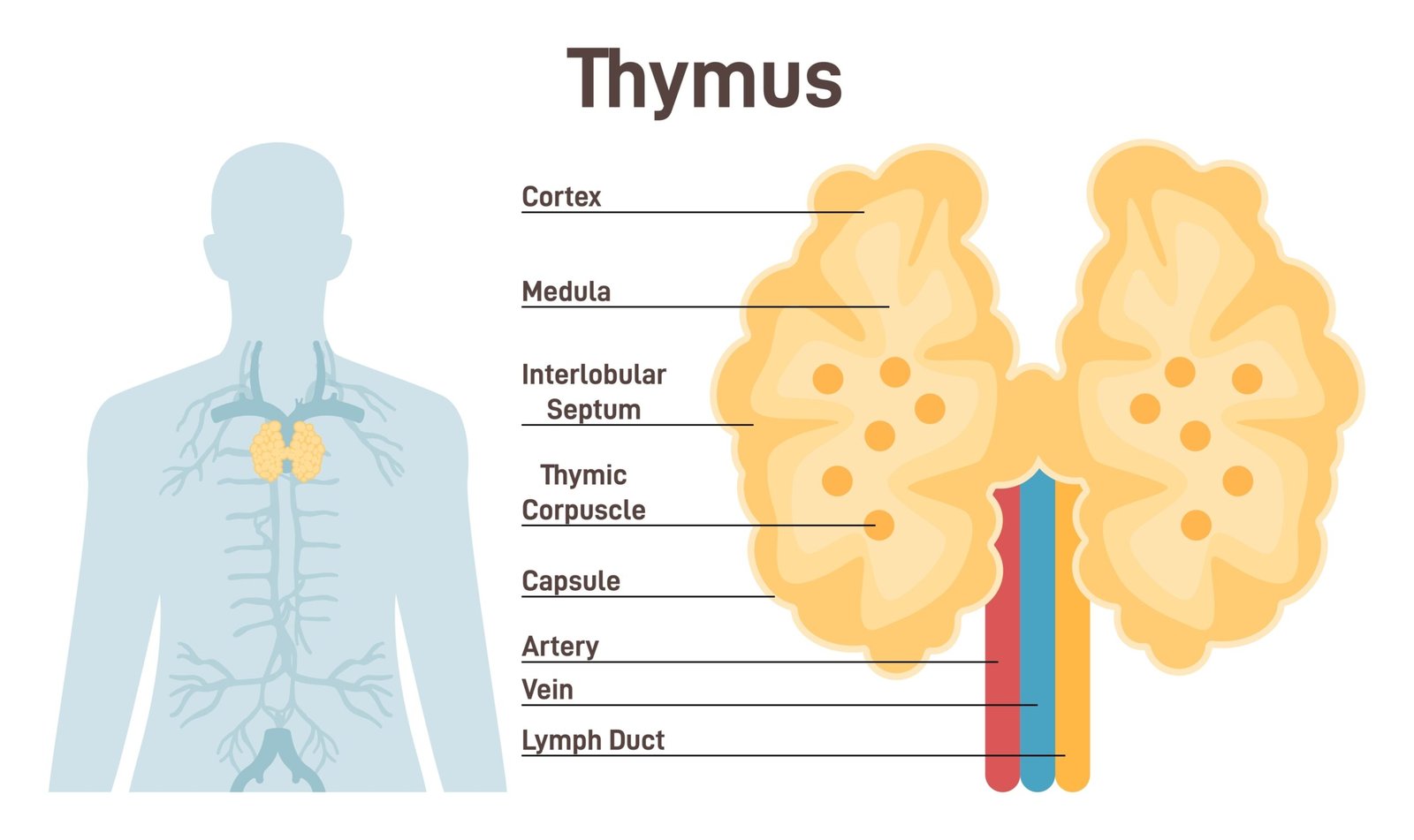
📍 Location: Upper chest, behind sternum
🧪 Hormone: Thymosin
💡 Function: development of T-lymphocytes for immune response
⚠️ Shrinks with age (active in childhood)
⚡ Adrenal Glands
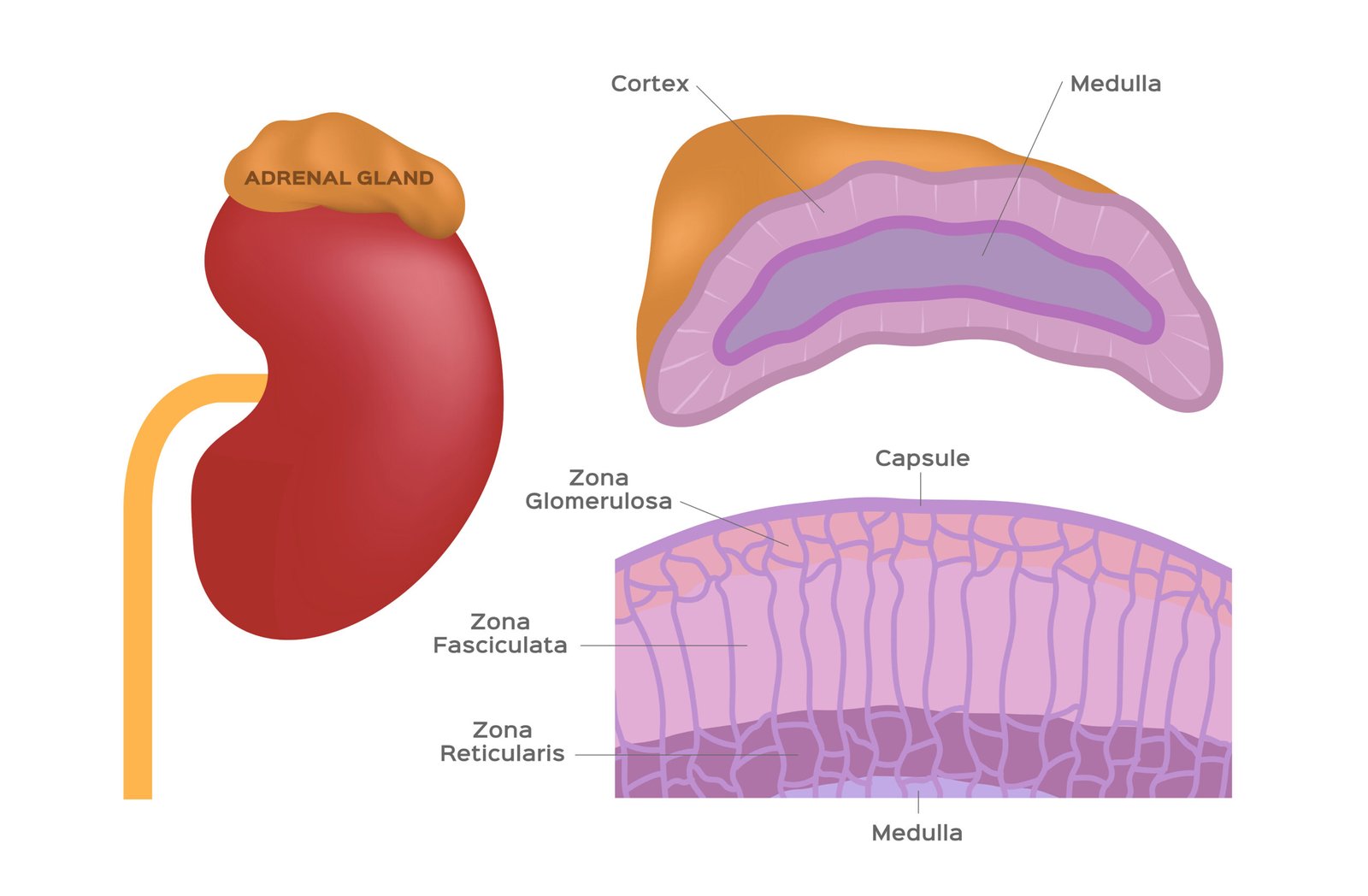
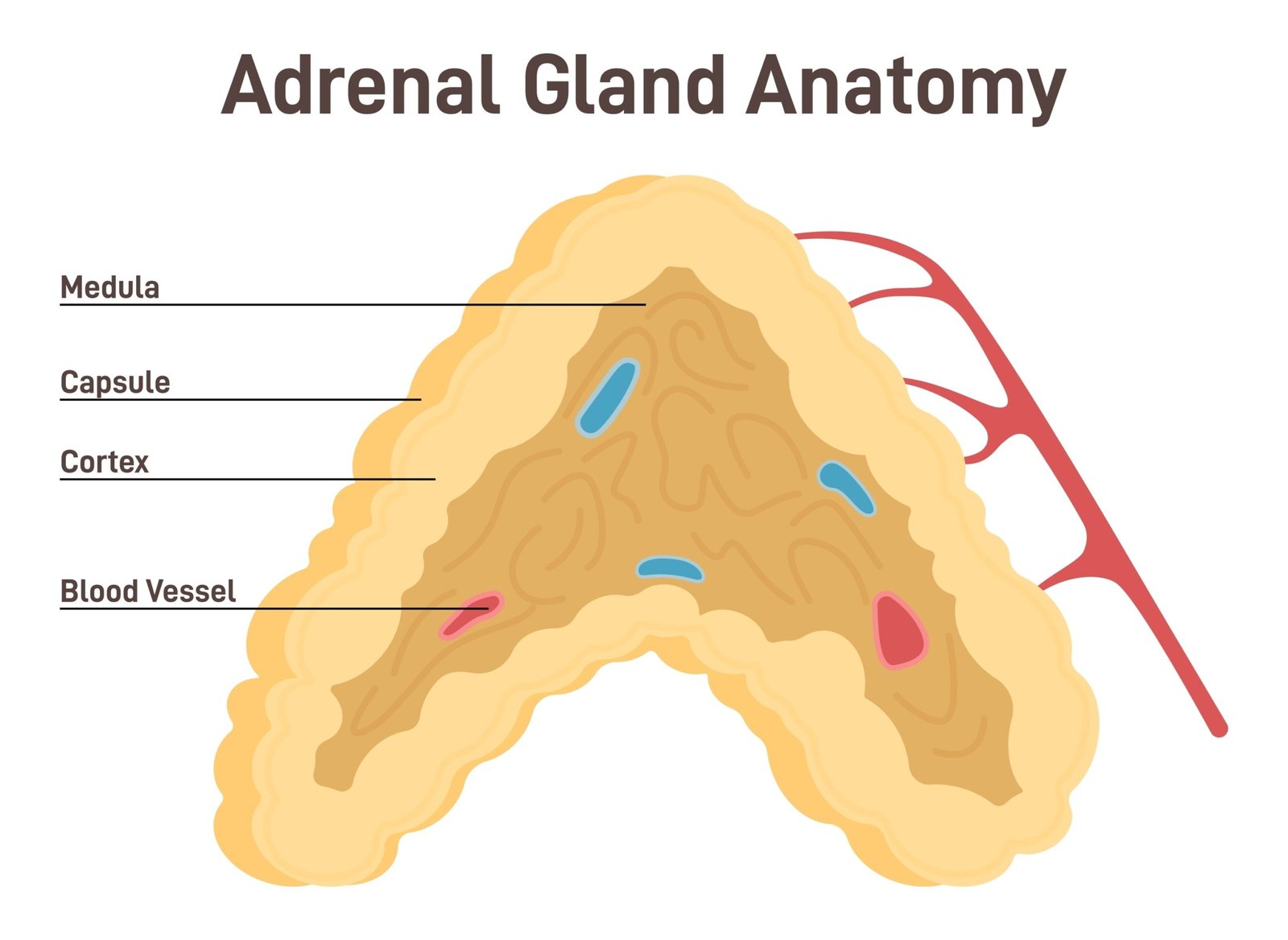
📍 Located above each kidney
🔹 Outer layer: Adrenal cortex
🔹 Inner layer: Adrenal medulla
🧪 Adrenal Cortex Hormones:
1️⃣ Glucocorticoids (Cortisol): regulates metabolism, stress response
2️⃣ Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone): maintains Na⁺/K⁺ balance
3️⃣ Androgens: weak sex hormones
⚙️ Disorders:
Deficiency: Addison’s disease
Excess: Cushing’s syndrome
⚡ Adrenal Medulla Hormones:
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
💡 Fight or flight response: increases heart rate, BP, glucose level
🧪 Pancreas (Mixed Gland)
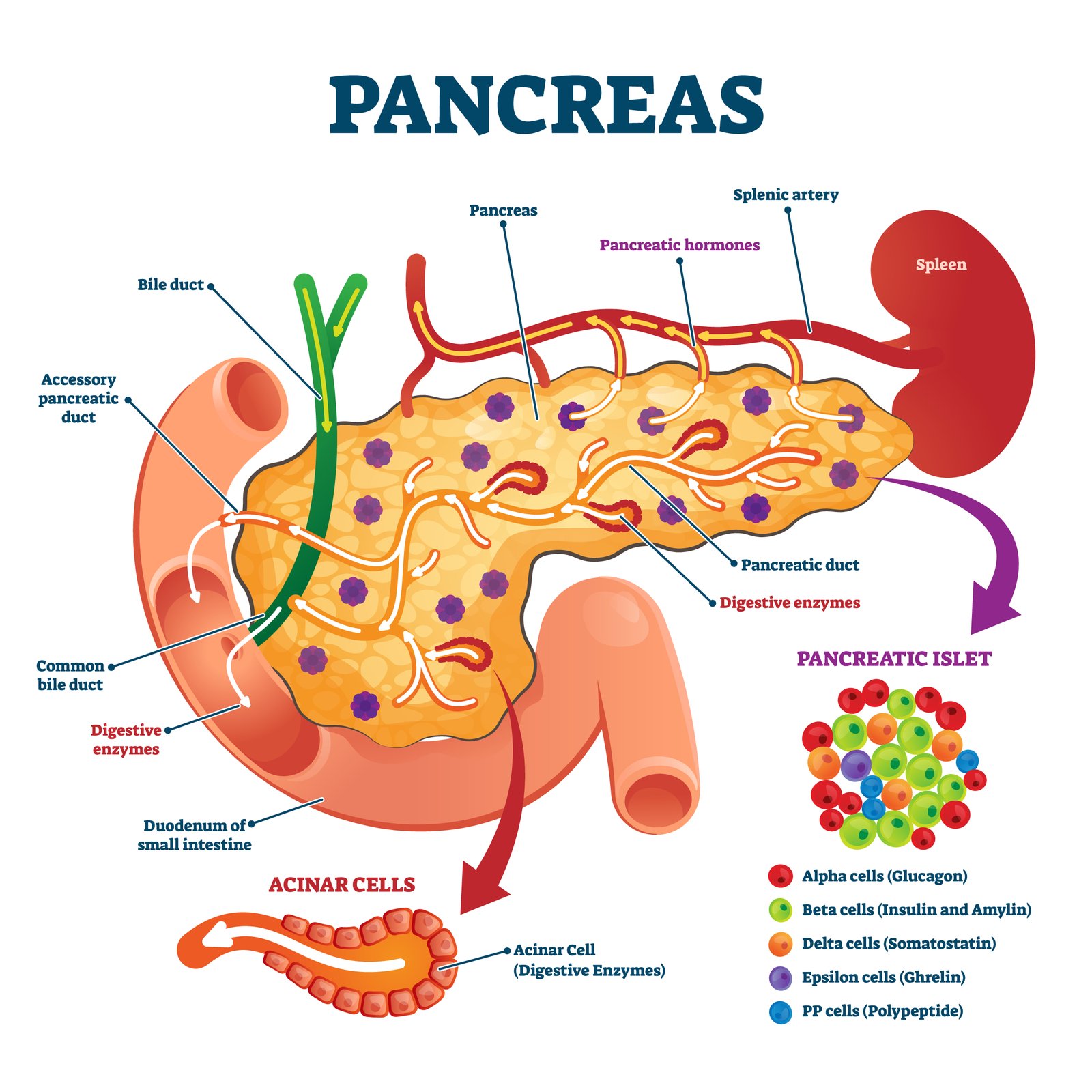
📍 Located behind stomach
Has exocrine part (digestive enzymes) and endocrine part (Islets of Langerhans)
🧠 Islets of Langerhans contain:
Alpha cells: Glucagon
Beta cells: Insulin
💡 Functions:
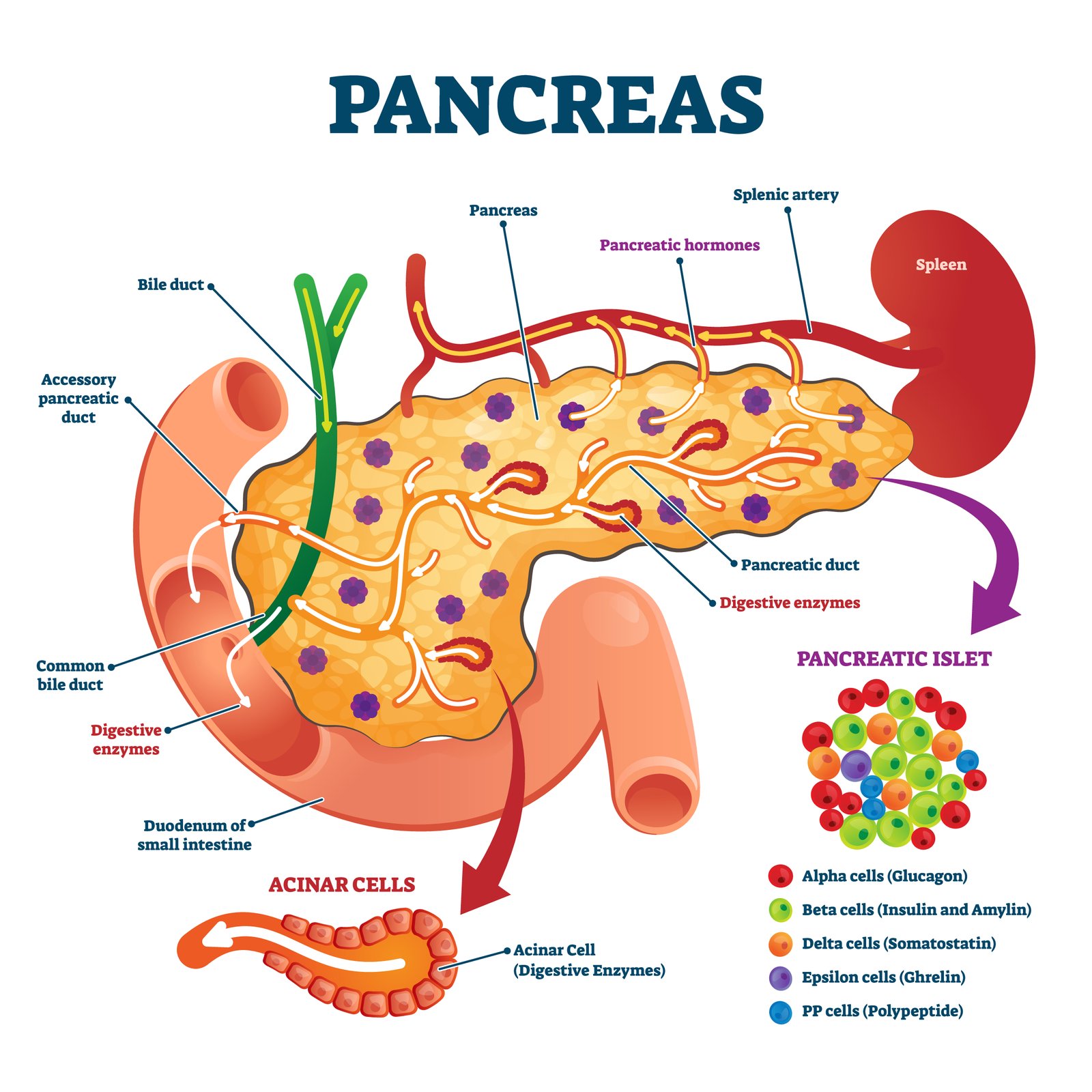
Insulin: lowers blood glucose
Glucagon: raises blood glucose
⚠️ Deficiency of insulin → Diabetes mellitus
✏️ Symptoms: hyperglycemia, glycosuria, polyuria, fatigue
🧬 Gonads
🧠 Testes (in males):
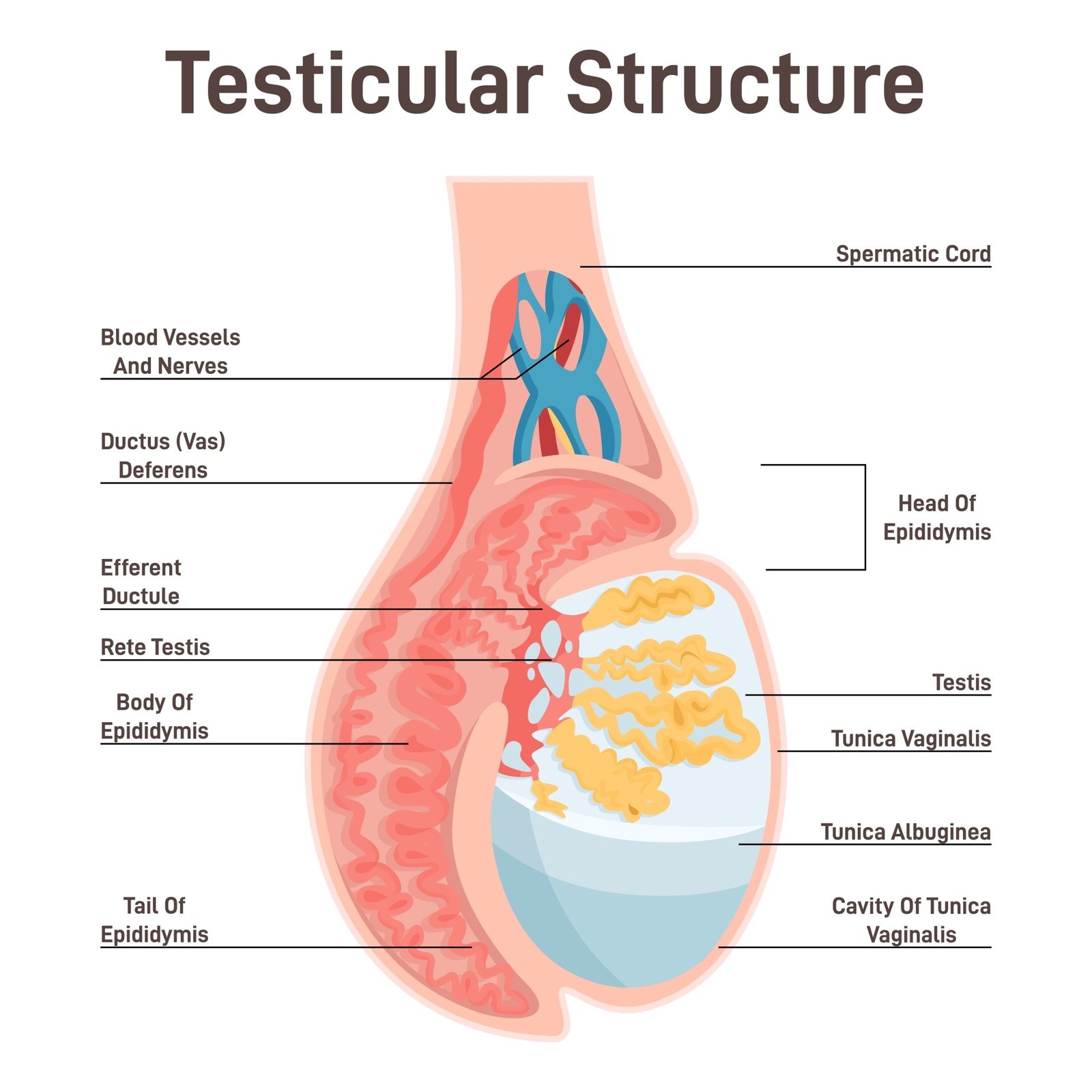
Hormone: Testosterone
Promotes secondary sexual characters, spermatogenesis, muscle growth
🌸 Ovaries (in females):
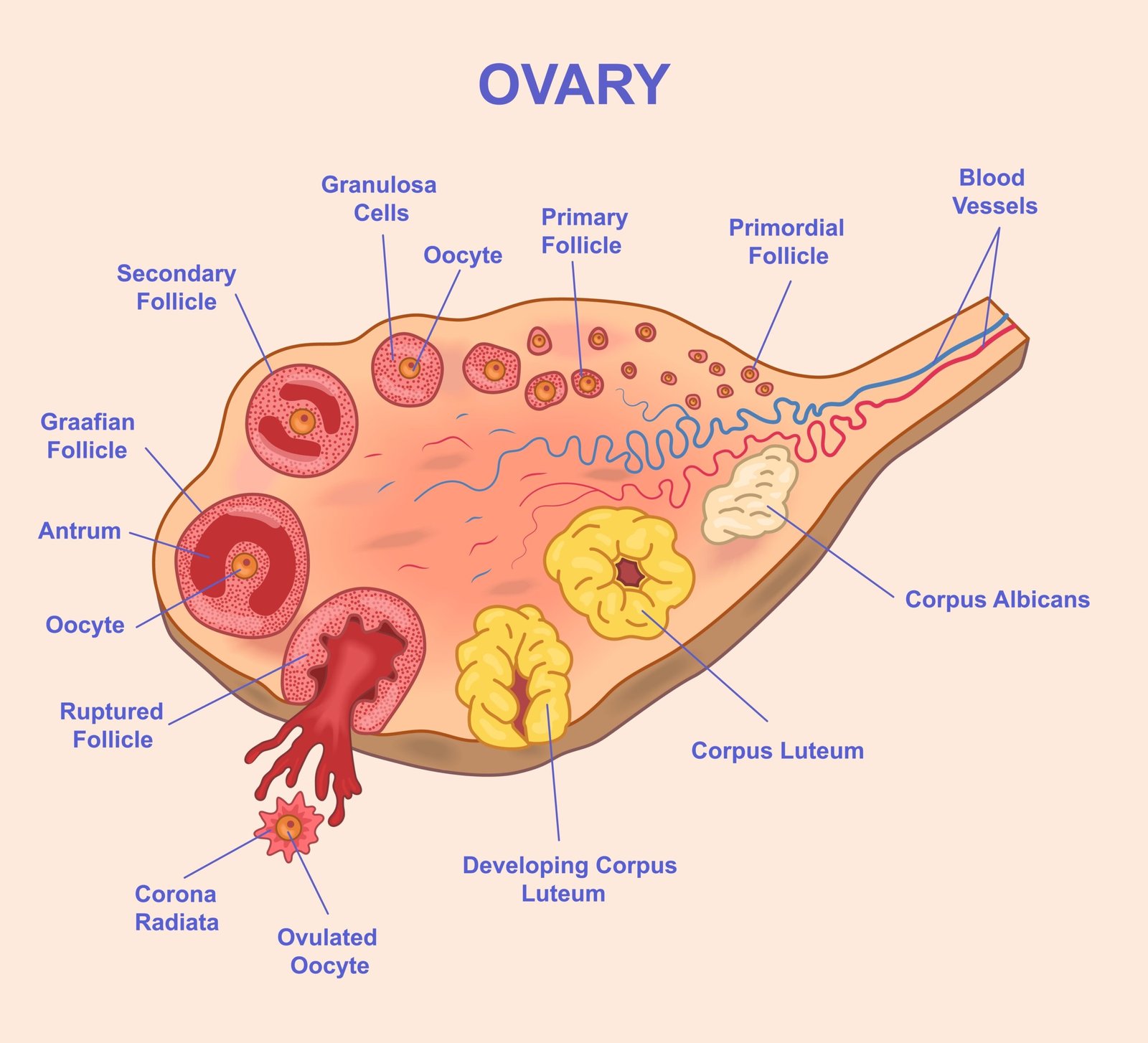
Hormones: Estrogen and Progesterone
Estrogen: development of female characters, ovum maturation
Progesterone: prepares uterus for implantation, maintains pregnancy
🧠 Mechanism of Hormone Action
📘 Hormones act on target cells with specific receptors.
Two types of hormones:
1️⃣ Peptide hormones – water soluble (cannot cross membrane)
2️⃣ Steroid hormones – lipid soluble (cross membrane easily)
💡 Steps in Hormone Action:
Hormone binds receptor
Triggers secondary messenger (e.g., cAMP)
Initiates biochemical changes
Leads to physiological effect
✏️ Example:
Adrenaline → binds receptor → activates cAMP → glycogen breakdown → ↑ glucose
🌿 Feedback Mechanism
🧠 Hormone levels are regulated by feedback loops:
Negative feedback: high hormone → inhibits secretion
Positive feedback: increases secretion
📘 Example:
High T₃/T₄ → inhibits TSH from pituitary (negative feedback)
LH surge during ovulation (positive feedback)
🧠 Coordination Between Nervous and Endocrine System
📘 Hypothalamus is the link
⚙️ Receives neural signals, secretes releasing hormones to control pituitary
💡 Maintains homeostasis through combined neural & hormonal regulation
⚠️ Hormonal Disorders Summary
Disorder Cause Effect
Gigantism GH excess Abnormal height
Dwarfism GH deficiency Short stature
Goitre Iodine deficiency Thyroid enlargement
Cretinism Hypothyroidism in children Mental retardation
Graves’ disease Hyperthyroidism High metabolism
Addison’s Cortisol deficiency Weakness
Cushing’s Cortisol excess Obesity, hypertension
Diabetes mellitus Insulin deficiency Hyperglycemia
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🧠 Understanding hormones explains growth, reproduction, metabolism, and stress management.
🌿 It is essential for treating endocrine disorders and designing therapeutic hormones.
⚙️ Builds foundation for medicine, physiology, and biotechnology.
📝 Quick Recap
🧠 Hormones = chemical messengers
🌿 Hypothalamus → releasing/inhibiting hormones
🧩 Pituitary = master gland (GH, TSH, FSH, LH, PRL)
🌸 Thyroid = T₃, T₄, calcitonin
⚡ Adrenal = cortisol, aldosterone, adrenaline
🧪 Pancreas = insulin, glucagon
🧬 Gonads = estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
🌀 Feedback maintains balance
💡 Disorders: Goitre, Diabetes, Cushing’s, Addison’s
📘 Summary
The endocrine system coordinates body functions through hormones secreted by ductless glands. Each hormone acts on specific target organs to regulate growth, metabolism, reproduction, and homeostasis. The hypothalamus links the nervous and endocrine systems via the pituitary gland. Hormones follow feedback mechanisms to maintain equilibrium. Disorders result from excess or deficiency of hormones. This chapter highlights the integration of chemical signals that sustain life and adaptation.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Define the following:
(a) Exocrine gland
(b) Endocrine gland
(c) Hormone
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) Exocrine gland: These glands possess ducts that transport their secretions to the target site such as surface or cavity.
💡 Examples: Salivary gland, sweat gland, and gastric gland.
🧠 (b) Endocrine gland: These are ductless glands which release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
💡 Examples: Pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
⚡ (c) Hormone: Hormones are non-nutrient chemical messengers secreted in trace amounts by endocrine glands that regulate physiological processes in target tissues.
🔵 Question 2:
Diagrammatically indicate the location of the various endocrine glands in our body.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 The major endocrine glands and their locations are:
✳️ Pituitary gland: Base of the brain below hypothalamus
✳️ Pineal gland: Dorsal part of forebrain
✳️ Thyroid gland: In neck region below larynx
✳️ Parathyroid glands: Four small glands on the posterior surface of the thyroid
✳️ Adrenal glands: On top of each kidney
✳️ Pancreas: Behind the stomach
✳️ Thymus: Behind sternum between lungs
✳️ Gonads: Testes in males, ovaries in females
✳️ Hypothalamus: Lower part of the brain near pituitary
💡 (Draw a labelled diagram showing above glands in the human body)
🔵 Question 3:
List the hormones secreted by the following:
(a) Hypothalamus (b) Pituitary (c) Thyroid (d) Parathyroid (e) Adrenal (f) Pancreas (g) Testis (h) Ovary (i) Thymus (j) Atrium (k) Kidney (l) G-I Tract
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) Hypothalamus: Releasing hormones (RH) and inhibiting hormones (IH) like GnRH, TRH, CRH, GHRH, GHIH.
🌿 (b) Pituitary: Growth hormone (GH), Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH), Prolactin, MSH, Oxytocin, Vasopressin.
🌿 (c) Thyroid: Thyroxine (T₄), Triiodothyronine (T₃), Calcitonin.
🌿 (d) Parathyroid: Parathyroid hormone (PTH).
🌿 (e) Adrenal:
Cortex: Cortisol, Aldosterone, Androgens
Medulla: Adrenaline, Noradrenaline
🌿 (f) Pancreas: Insulin, Glucagon, Somatostatin.
🌿 (g) Testis: Androgens (mainly testosterone).
🌿 (h) Ovary: Estrogens, Progesterone.
🌿 (i) Thymus: Thymosins.
🌿 (j) Atrium: Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF).
🌿 (k) Kidney: Erythropoietin, Renin.
🌿 (l) G-I Tract: Gastrin, Secretin, Cholecystokinin (CCK), GIP.
🔵 Question 4:
Fill in the blanks:
Hormones Target gland
(a) Hypothalamic hormones ➡️ Pituitary gland
(b) Thyrotrophin (TSH) ➡️ Thyroid gland
(c) Corticotrophin (ACTH) ➡️ Adrenal cortex
(d) Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH) ➡️ Gonads (testis/ovary)
(e) Melanotrophin (MSH) ➡️ Skin melanocytes
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Filled as above table.
🔵 Question 5:
Write short notes on the functions of the following hormones:
(a) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) (b) Thyroid hormones (c) Thymosins (d) Androgens (e) Estrogens (f) Insulin and Glucagon
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) PTH: Increases blood calcium level by stimulating bone resorption, reabsorption of Ca²⁺ by kidneys and activating vitamin D.
🌿 (b) Thyroid hormones (T₃, T₄): Regulate basal metabolic rate, growth, development and metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
🌿 (c) Thymosins: Promote differentiation of T-lymphocytes for immune response.
🌿 (d) Androgens: Control development of male secondary sexual characters and spermatogenesis.
🌿 (e) Estrogens: Stimulate growth of female reproductive organs, secondary sexual characters and menstrual cycle.
🌿 (f) Insulin: Lowers blood glucose by promoting glucose uptake.
🌿 Glucagon: Raises blood glucose by promoting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
🔵 Question 6:
Give example(s) of:
(a) Hyperglycemic hormone and hypoglycemic hormone
(b) Hypercalcemic hormone
(c) Gonadotrophic hormones
(d) Progestational hormone
(e) Blood pressure lowering hormone
(f) Androgens and estrogens
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) Glucagon (hyperglycemic), Insulin (hypoglycemic)
🌿 (b) Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
🌿 (c) LH and FSH
🌿 (d) Progesterone
🌿 (e) Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)
🌿 (f) Testosterone (androgen), Estradiol (estrogen)
🔵 Question 7:
Which hormonal deficiency is responsible for the following:
(a) Diabetes mellitus (b) Goitre (c) Cretinism
🟢 Answer:
🌿 (a) Insulin deficiency → Diabetes mellitus
🌿 (b) Iodine or Thyroxine deficiency → Goitre
🌿 (c) Thyroxine deficiency in infancy → Cretinism
🔵 Question 8:
Briefly mention the mechanism of action of FSH.
🟢 Answer:
💡 FSH binds to specific membrane receptors on target gonadal cells.
⚡ It activates adenyl cyclase enzyme → increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) → acts as secondary messenger.
🧬 cAMP activates protein kinases → stimulates gametogenesis and secretion of gonadal hormones.
🔵 Question 9:
Match the following:
Column I Column II
(a) T₄ (ii) Thyroid
(b) PTH (iv
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
Which system coordinates and integrates all activities of the body?
🔴1️⃣ Nervous system
🟢2️⃣ Endocrine system
🟡3️⃣ Circulatory system
🔵4️⃣ Excretory system
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Endocrine system
🔴 Question 2:
Which gland is called the master gland?
🔴1️⃣ Adrenal gland
🟢2️⃣ Pituitary gland
🟡3️⃣ Thyroid gland
🔵4️⃣ Pancreas
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Pituitary gland
🔴 Question 3:
Which hormone regulates the level of calcium in blood?
🔴1️⃣ Thyroxine
🟢2️⃣ Parathormone
🟡3️⃣ Insulin
🔵4️⃣ Adrenaline
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Parathormone
🔴 Question 4:
Insulin is secreted by —
🔴1️⃣ Alpha cells of pancreas
🟢2️⃣ Beta cells of pancreas
🟡3️⃣ Delta cells of pancreas
🔵4️⃣ Gamma cells of pancreas
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Beta cells of pancreas
🔴 Question 5:
Which hormone controls the basal metabolic rate?
🔴1️⃣ Insulin
🟢2️⃣ Thyroxine
🟡3️⃣ Adrenaline
🔵4️⃣ Cortisol
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Thyroxine
🔴 Question 6:
Which gland secretes melatonin?
🔴1️⃣ Pituitary
🟢2️⃣ Pineal
🟡3️⃣ Thyroid
🔵4️⃣ Adrenal
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Pineal
🔴 Question 7:
The adrenal medulla secretes —
🔴1️⃣ Adrenaline and noradrenaline
🟢2️⃣ Cortisol and aldosterone
🟡3️⃣ Glucagon and insulin
🔵4️⃣ Thyroxine and calcitonin
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Adrenaline and noradrenaline
🔴 Question 8:
Which hormone is called fight or flight hormone?
🔴1️⃣ Thyroxine
🟢2️⃣ Adrenaline
🟡3️⃣ Cortisol
🔵4️⃣ Melatonin
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Adrenaline
🔴 Question 9:
Which of the following is both endocrine and exocrine gland?
🔴1️⃣ Adrenal
🟢2️⃣ Pancreas
🟡3️⃣ Thyroid
🔵4️⃣ Pituitary
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Pancreas
🔴 Question 10:
Which hormone is secreted by posterior pituitary?
🔴1️⃣ GH and TSH
🟢2️⃣ ADH and Oxytocin
🟡3️⃣ FSH and LH
🔵4️⃣ ACTH and MSH
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ ADH and Oxytocin
🔴 Question 11:
Define endocrine glands.
🟢 Answer:
Endocrine glands are ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate body functions.
🔴 Question 12:
What is a hormone?
🟢 Answer:
A hormone is a chemical messenger secreted by endocrine glands that regulates physiological processes like growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
🔴 Question 13:
Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
Ducts Ductless Have ducts
Secretion Hormones into blood Enzymes or other substances into specific site
Example Pituitary, thyroid Salivary, sweat glands
💡 Endocrine glands form part of the endocrine system; exocrine glands are part of other organ systems.
🔴 Question 14:
Describe the structure and hormones of the pituitary gland.
🟢 Answer:
Parts:
1️⃣ Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis): Secretes GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, Prolactin.
2️⃣ Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis): Stores and releases ADH and Oxytocin.
Function: Regulates other endocrine glands; controls growth and metabolism.
💡 Called the master gland.
🔴 Question 15:
Mention the functions of thyroid gland hormones.
🟢 Answer:
Hormones:
1️⃣ Thyroxine (T₄) and Triiodothyronine (T₃).
Functions:
✔️ Regulate basal metabolic rate (BMR).
✔️ Control growth and development.
✔️ Maintain calcium balance (via calcitonin).
💡 Deficiency: Goitre, cretinism; Excess: Exophthalmic goitre.
🔴 Question 16:
Write the functions of parathyroid glands.
🟢 Answer:
Secrete Parathormone (PTH).
Functions:
1️⃣ Increases blood calcium by acting on bones, kidney, intestine.
2️⃣ Promotes reabsorption of Ca²⁺ in kidney.
3️⃣ Stimulates osteoclasts to release Ca²⁺ from bones.
💡 Works antagonistically to calcitonin.
🔴 Question 17:
Describe the structure and hormones of adrenal gland.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Adrenal cortex (outer): secretes cortisol, aldosterone, sex corticoids.
2️⃣ Adrenal medulla (inner): secretes adrenaline & noradrenaline.
Functions:
✔️ Cortisol – carbohydrate metabolism.
✔️ Aldosterone – water-salt balance.
✔️ Adrenaline – fight or flight response.
🔴 Question 18:
Explain the endocrine role of pancreas.
🟢 Answer:
Islets of Langerhans contain:
1️⃣ Alpha cells: Glucagon → increases blood sugar.
2️⃣ Beta cells: Insulin → lowers blood sugar.
Together, maintain glucose homeostasis.
💡 Deficiency of insulin causes Diabetes mellitus.
🔴 Question 19:
Write the functions of gonadal hormones.
🟢 Answer:
Testes:
– Secretes Testosterone.
– Functions: spermatogenesis, male secondary sexual characters.
Ovaries:
– Secrete Estrogen and Progesterone.
– Regulate menstrual cycle, pregnancy, female characters.
🔴 Question 20:
Describe the functions of pineal gland.
🟢 Answer:
Secretes Melatonin.
Functions:
1️⃣ Regulates sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm).
2️⃣ Influences reproductive cycle.
3️⃣ Acts as antioxidant.
🔴 Question 21:
Write the functions of thymus gland.
🟢 Answer:
Secretes Thymosin hormone.
Functions:
✔️ Promotes development of T-lymphocytes.
✔️ Strengthens immune system in childhood.
✔️ Degenerates after puberty.
🔴 Question 22:
Explain the hormonal control of blood sugar level.
🟢 Answer:
Insulin (from β-cells): ↓ Blood sugar → converts glucose → glycogen.
Glucagon (from α-cells): ↑ Blood sugar → converts glycogen → glucose.
Together, maintain homeostasis of glucose.
💡 Imbalance causes diabetes or hypoglycemia.
🔴 Question 23:
Explain the role and functions of pituitary gland in human body.
🟢 Answer:
Pituitary gland — small pea-sized gland at base of brain, called master gland.
Divisions:
1️⃣ Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis):
✔️ GH – growth of bones & muscles.
✔️ TSH – stimulates thyroid.
✔️ ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex.
✔️ FSH & LH – control gonads.
✔️ Prolactin – milk secretion.
2️⃣ Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis):
✔️ ADH – reabsorption of water in kidneys.
✔️ Oxytocin – uterine contraction, milk ejection.
💡 Controls all other endocrine glands — hence “master gland.”
🔴 Question 24:
Describe the structure, hormones, and functions of thyroid gland.
🟢 Answer:
Location: Front of neck; two lobes connected by isthmus.
Hormones: Thyroxine (T₄), Triiodothyronine (T₃), Calcitonin.
Functions:
1️⃣ Regulate basal metabolic rate (BMR).
2️⃣ Control growth and development.
3️⃣ Calcitonin reduces blood calcium.
Disorders:
– Hypothyroidism → Cretinism (child), Myxedema (adult).
– Hyperthyroidism → Exophthalmic goitre.
💡 Requires iodine for hormone synthesis.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain the structure and functions of adrenal gland.
🟢 Answer:
Location: On top of each kidney.
Structure:
1️⃣ Adrenal Cortex (outer):
– Mineralocorticoids (Aldosterone): salt–water balance.
– Glucocorticoids (Cortisol): carbohydrate metabolism.
– Sex Corticoids: secondary sexual characters.
2️⃣ Adrenal Medulla (inner):
– Adrenaline, Noradrenaline → fight or flight.
Functions:
✔️ Maintain metabolism and stress response.
✔️ Regulate BP and electrolytes.
🔴 Question 26:
Describe the feedback mechanism of hormone regulation with example.
🟢 Answer:
Feedback mechanism — regulates hormone secretion based on need.
Types:
1️⃣ Negative feedback:
– ↑ Thyroxine → inhibits TSH → maintains balance.
2️⃣ Positive feedback:
– ↑ Oxytocin during childbirth → increases uterine contraction → more oxytocin.
💡 Maintains homeostasis by self-regulation.
🔴 Question 27:
Explain the role of pancreas in glucose homeostasis.
🟢 Answer:
Endocrine part: Islets of Langerhans.
– α-cells: secrete Glucagon → ↑ blood sugar.
– β-cells: secrete Insulin → ↓ blood sugar.
Mechanism:
– High sugar → insulin secretion → glucose → glycogen (liver).
– Low sugar → glucagon secretion → glycogen → glucose.
💡 Maintains normal blood glucose level (≈ 90 mg/dL).
🔴 Question 28:
Differentiate between diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Insipidus
Cause Insulin deficiency ADH deficiency
Effect High blood sugar Excess water loss
Urine Sugary Dilute, large volume
Treatment Insulin therapy ADH administration
💡 Both involve excess urination, but different hormones.
🔴 Question 29:
Explain hormonal regulation of female reproductive cycle.
🟢 Answer:
Hormones: FSH, LH (pituitary); Estrogen, Progesterone (ovary).
Phases:
1️⃣ Follicular: FSH → follicle growth → estrogen ↑ → uterine wall thickens.
2️⃣ Ovulatory: LH surge → ovulation.
3️⃣ Luteal: Corpus luteum → progesterone → maintains endometrium.
4️⃣ If no fertilization: Hormones ↓ → menstruation.
💡 Hormones coordinate ovarian and uterine cycles.
🔴 Question 30:
Write a short note on hypothalamus and its role in endocrine control.
🟢 Answer:
Location: Below thalamus; part of forebrain.
Functions:
1️⃣ Produces releasing and inhibiting hormones (RH/IH) for pituitary.
2️⃣ Controls secretion of GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, etc.
3️⃣ Regulates temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep.
💡 Acts as link between nervous and endocrine systems.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The hormone secreted by β-cells of islets of Langerhans is
🟡 A. Glucagon
🟡 B. Insulin
🟡 C. Somatostatin
🟡 D. Cortisol
🟢 Answer: B. Insulin
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q2. The hormone responsible for lowering blood glucose is
🟡 A. Glucagon
🟡 B. Insulin
🟡 C. Cortisol
🟡 D. Epinephrine
🟢 Answer: B. Insulin
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q3. Which hormone is secreted by the adrenal medulla?
🟡 A. Cortisol
🟡 B. Aldosterone
🟡 C. Epinephrine
🟡 D. Glucocorticoids
🟢 Answer: C. Epinephrine
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q4. The hormone secreted by the pineal gland is
🟡 A. Melatonin
🟡 B. Calcitonin
🟡 C. Oxytocin
🟡 D. Vasopressin
🟢 Answer: A. Melatonin
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q5. Parathyroid hormone increases
🟡 A. Blood calcium level
🟡 B. Blood sodium level
🟡 C. Blood potassium level
🟡 D. Blood phosphate level
🟢 Answer: A. Blood calcium level
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q6. Addison’s disease is caused by deficiency of
🟡 A. Cortisol
🟡 B. Epinephrine
🟡 C. Insulin
🟡 D. Glucagon
🟢 Answer: A. Cortisol
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q7. The hormone that stimulates milk ejection is
🟡 A. Prolactin
🟡 B. Oxytocin
🟡 C. Vasopressin
🟡 D. Estrogen
🟢 Answer: B. Oxytocin
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q8. The gland located on top of kidneys is
🟡 A. Thyroid
🟡 B. Adrenal
🟡 C. Pituitary
🟡 D. Pineal
🟢 Answer: B. Adrenal
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q9. Which hormone is secreted by the corpus luteum?
🟡 A. Estrogen
🟡 B. Progesterone
🟡 C. LH
🟡 D. FSH
🟢 Answer: B. Progesterone
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q10. Diabetes insipidus is caused by deficiency of
🟡 A. Insulin
🟡 B. Vasopressin
🟡 C. Aldosterone
🟡 D. Thyroxine
🟢 Answer: B. Vasopressin
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q11. Which hormone stimulates the thyroid gland to release thyroxine?
🟡 A. TSH
🟡 B. ACTH
🟡 C. LH
🟡 D. FSH
🟢 Answer: A. TSH
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q12. The hormone secreted during emergency is
🟡 A. Aldosterone
🟡 B. Epinephrine
🟡 C. Thyroxine
🟡 D. Prolactin
🟢 Answer: B. Epinephrine
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q13. Graves’ disease is due to hypersecretion of
🟡 A. Thyroxine
🟡 B. Cortisol
🟡 C. Insulin
🟡 D. Aldosterone
🟢 Answer: A. Thyroxine
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q14. Which hormone regulates circadian rhythms?
🟡 A. Oxytocin
🟡 B. Calcitonin
🟡 C. Melatonin
🟡 D. Vasopressin
🟢 Answer: C. Melatonin
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q15. Which gland is called the “master gland”?
🟡 A. Thyroid
🟡 B. Adrenal
🟡 C. Pituitary
🟡 D. Pineal
🟢 Answer: C. Pituitary
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q16. The hormone secreted by α-cells of islets of Langerhans is
🟡 A. Insulin
🟡 B. Glucagon
🟡 C. Somatostatin
🟡 D. Aldosterone
🟢 Answer: B. Glucagon
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q17. Myxedema is caused by
🟡 A. Hyposecretion of thyroxine in adults
🟡 B. Hypersecretion of thyroxine in adults
🟡 C. Hypersecretion of cortisol
🟡 D. Hyposecretion of insulin
🟢 Answer: A. Hyposecretion of thyroxine in adults
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q18. Hormone vasopressin acts on
🟡 A. Liver
🟡 B. Kidney
🟡 C. Heart
🟡 D. Lungs
🟢 Answer: B. Kidney
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q19. Corpus luteum is maintained by
🟡 A. FSH
🟡 B. LH
🟡 C. HCG
🟡 D. Progesterone
🟢 Answer: C. HCG
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q20. The adrenal cortex secretes
🟡 A. Epinephrine and norepinephrine
🟡 B. Cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens
🟡 C. Oxytocin and vasopressin
🟡 D. Thyroxine and calcitonin
🟢 Answer: B. Cortisol, aldosterone, and androgens
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q21. The deficiency of growth hormone in children causes
🟡 A. Gigantism
🟡 B. Dwarfism
🟡 C. Acromegaly
🟡 D. Addison’s disease
🟢 Answer: B. Dwarfism
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q22. The hormone that stimulates milk production is
🟡 A. Oxytocin
🟡 B. Prolactin
🟡 C. LH
🟡 D. FSH
🟢 Answer: B. Prolactin
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q23. Which hormone inhibits the secretion of growth hormone?
🟡 A. Somatostatin
🟡 B. Somatotropin
🟡 C. Prolactin
🟡 D. ACTH
🟢 Answer: A. Somatostatin
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q24. The hormone that increases blood glucose level is
🟡 A. Insulin
🟡 B. Glucagon
🟡 C. Prolactin
🟡 D. Aldosterone
🟢 Answer: B. Glucagon
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q25. Which hormone is secreted by the posterior pituitary?
🟡 A. TSH and ACTH
🟡 B. Vasopressin and oxytocin
🟡 C. Prolactin and GH
🟡 D. FSH and LH
🟢 Answer: B. Vasopressin and oxytocin
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q26. The thyroid gland is located
🟡 A. On top of kidneys
🟡 B. Below the pharynx on either side of trachea
🟡 C. Behind the stomach
🟡 D. Above the pituitary gland
🟢 Answer: B. Below the pharynx on either side of trachea
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q27. Hormone calcitonin is secreted by
🟡 A. Thyroid gland
🟡 B. Parathyroid gland
🟡 C. Adrenal gland
🟡 D. Pancreas
🟢 Answer: A. Thyroid gland
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q28. Cretinism is caused by deficiency of
🟡 A. Insulin in adults
🟡 B. Thyroxine in infants
🟡 C. Growth hormone in adults
🟡 D. Cortisol in infants
🟢 Answer: B. Thyroxine in infants
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q29. The endocrine gland attached to the brain is
🟡 A. Thyroid
🟡 B. Adrenal
🟡 C. Pituitary
🟡 D. Parathyroid
🟢 Answer: C. Pituitary
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q30. The fight-or-flight response is due to secretion of
🟡 A. Glucagon and insulin
🟡 B. Epinephrine and norepinephrine
🟡 C. Cortisol and aldosterone
🟡 D. Thyroxine and calcitonin
🟢 Answer: B. Epinephrine and norepinephrine
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q31. Which hormone stimulates uterine contraction during childbirth?
🟡 A. Prolactin
🟡 B. Vasopressin
🟡 C. Oxytocin
🟡 D. Relaxin
🟢 Answer: C. Oxytocin
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q32. The hormone secreted by the kidneys that stimulates RBC formation is
🟡 A. Renin
🟡 B. Erythropoietin
🟡 C. Aldosterone
🟡 D. Cortisol
🟢 Answer: B. Erythropoietin
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q33. Which hormone is a derivative of cholesterol?
🟡 A. Insulin
🟡 B. Glucagon
🟡 C. Cortisol
🟡 D. Thyroxine
🟢 Answer: C. Cortisol
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q34. The hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary that regulates water balance is
🟡 A. Oxytocin
🟡 B. Vasopressin
🟡 C. ACTH
🟡 D. GH
🟢 Answer: B. Vasopressin
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q35. Hormone that inhibits gastric secretion and motility is
🟡 A. Secretin
🟡 B. Gastrin
🟡 C. Somatostatin
🟡 D. Cholecystokinin
🟢 Answer: C. Somatostatin
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q36. Which hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to release its hormones?
🟡 A. TSH
🟡 B. ACTH
🟡 C. LH
🟡 D. FSH
🟢 Answer: B. ACTH
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q37. Which gland is both endocrine and exocrine?
🟡 A. Thyroid
🟡 B. Pancreas
🟡 C. Adrenal
🟡 D. Pineal
🟢 Answer: B. Pancreas
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q38. Which hormone regulates basal metabolic rate?
🟡 A. Cortisol
🟡 B. Thyroxine
🟡 C. Insulin
🟡 D. Prolactin
🟢 Answer: B. Thyroxine
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q39. Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults leads to
🟡 A. Gigantism
🟡 B. Dwarfism
🟡 C. Acromegaly
🟡 D. Addison’s disease
🟢 Answer: C. Acromegaly
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q40. Hormone that stimulates glycogenolysis is
🟡 A. Glucagon
🟡 B. Insulin
🟡 C. Thyroxine
🟡 D. Aldosterone
🟢 Answer: A. Glucagon
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q41. The adrenal medulla is derived from
🟡 A. Endoderm
🟡 B. Mesoderm
🟡 C. Ectoderm
🟡 D. Neural crest
🟢 Answer: D. Neural crest
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q42. Hormone secretin is produced by
🟡 A. Pancreas
🟡 B. Duodenum
🟡 C. Stomach
🟡 D. Liver
🟢 Answer: B. Duodenum
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q43. Which hormone stimulates the release of milk from mammary glands?
🟡 A. Vasopressin
🟡 B. Oxytocin
🟡 C. Prolactin
🟡 D. Relaxin
🟢 Answer: B. Oxytocin
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q44. Which hormone increases reabsorption of sodium ions in kidney tubules?
🟡 A. Vasopressin
🟡 B. Aldosterone
🟡 C. Cortisol
🟡 D. Epinephrine
🟢 Answer: B. Aldosterone
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q45. Parathyroid hormone deficiency leads to
🟡 A. Hypercalcemia
🟡 B. Hypocalcemia
🟡 C. Goitre
🟡 D. Exophthalmic goitre
🟢 Answer: B. Hypocalcemia
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q46. Which hormone stimulates the thyroid to produce calcitonin?
🟡 A. TSH
🟡 B. PTH
🟡 C. ACTH
🟡 D. GH
🟢 Answer: A. TSH
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q47. Which endocrine gland plays a role in biological rhythms and seasonal reproduction?
🟡 A. Adrenal
🟡 B. Thyroid
🟡 C. Pineal
🟡 D. Pancreas
🟢 Answer: C. Pineal
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q48. Hormones of the posterior pituitary are synthesized in
🟡 A. Posterior pituitary itself
🟡 B. Hypothalamus
🟡 C. Anterior pituitary
🟡 D. Pineal gland
🟢 Answer: B. Hypothalamus
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q49. The hormone responsible for “fight-or-flight” response is
🟡 A. Cortisol
🟡 B. Epinephrine
🟡 C. Aldosterone
🟡 D. Thyroxine
🟢 Answer: B. Epinephrine
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q50. The thyroid hormone contains which element?
🟡 A. Calcium
🟡 B. Iron
🟡 C. Iodine
🟡 D. Magnesium
🟢 Answer: C. Iodine
📅 AIPMT 2010
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Chemical coordination in animals is achieved through:
🔴 1️⃣ Neurons
🟢 2️⃣ Hormones
🟡 3️⃣ Enzymes
🔵 4️⃣ Neurotransmitters
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hormones
🔵 Question 2:
The endocrine glands are:
🔴 1️⃣ Ducted glands
🟢 2️⃣ Ductless glands
🟡 3️⃣ Exocrine glands
🔵 4️⃣ Sebaceous glands
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ductless glands
🔵 Question 3:
The master gland is:
🔴 1️⃣ Thyroid
🟢 2️⃣ Pituitary
🟡 3️⃣ Adrenal
🔵 4️⃣ Pancreas
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pituitary
🔵 Question 4:
The pituitary gland is located at the base of:
🔴 1️⃣ Midbrain
🟢 2️⃣ Hypothalamus
🟡 3️⃣ Cerebrum
🔵 4️⃣ Cerebellum
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hypothalamus
🔵 Question 5:
Which hormone regulates growth?
🔴 1️⃣ TSH
🟢 2️⃣ GH
🟡 3️⃣ FSH
🔵 4️⃣ LH
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ GH
🔵 Question 6:
Excess secretion of GH in adults causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Dwarfism
🟢 2️⃣ Acromegaly
🟡 3️⃣ Gigantism
🔵 4️⃣ Obesity
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Acromegaly
🔵 Question 7:
Excess GH in children causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Dwarfism
🟢 2️⃣ Gigantism
🟡 3️⃣ Obesity
🔵 4️⃣ Myxedema
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Gigantism
🔵 Question 8:
Deficiency of GH causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Gigantism
🟢 2️⃣ Dwarfism
🟡 3️⃣ Acromegaly
🔵 4️⃣ Myxedema
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Dwarfism
🔵 Question 9:
TSH stimulates:
🔴 1️⃣ Adrenal gland
🟢 2️⃣ Thyroid gland
🟡 3️⃣ Pituitary gland
🔵 4️⃣ Gonads
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Thyroid gland
🔵 Question 10:
ACTH stimulates:
🔴 1️⃣ Thyroid
🟢 2️⃣ Adrenal cortex
🟡 3️⃣ Adrenal medulla
🔵 4️⃣ Gonads
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Adrenal cortex
🔵 Question 11:
FSH in females stimulates:
🔴 1️⃣ Ovulation
🟢 2️⃣ Growth of ovarian follicles
🟡 3️⃣ Corpus luteum
🔵 4️⃣ Milk secretion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Growth of ovarian follicles
🔵 Question 12:
LH in females causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Ovulation
🟢 2️⃣ Follicle growth
🟡 3️⃣ Inhibin secretion
🔵 4️⃣ Estrogen secretion
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Ovulation
🔵 Question 13:
In males, LH stimulates:
🔴 1️⃣ Sertoli cells
🟢 2️⃣ Leydig cells
🟡 3️⃣ Spermatogonia
🔵 4️⃣ Epididymis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Leydig cells
🔵 Question 14:
Prolactin is responsible for:
🔴 1️⃣ Ovulation
🟢 2️⃣ Milk production
🟡 3️⃣ Growth
🔵 4️⃣ Stress
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Milk production
🔵 Question 15:
ADH acts on:
🔴 1️⃣ Lungs
🟢 2️⃣ Kidney
🟡 3️⃣ Heart
🔵 4️⃣ Liver
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Kidney
🔵 Question 16:
Oxytocin helps in:
🔴 1️⃣ Ovulation
🟢 2️⃣ Childbirth and milk ejection
🟡 3️⃣ Follicle growth
🔵 4️⃣ Spermatogenesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Childbirth and milk ejection
🔵 Question 17:
Thyroid gland secretes:
🔴 1️⃣ Thyroxine
🟢 2️⃣ Calcitonin
🟡 3️⃣ Both
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Both
🔵 Question 18:
Thyroxine requires which element?
🔴 1️⃣ Sodium
🟢 2️⃣ Iodine
🟡 3️⃣ Calcium
🔵 4️⃣ Phosphorus
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Iodine
🔵 Question 19:
Deficiency of iodine causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Diabetes
🟢 2️⃣ Goitre
🟡 3️⃣ Tetany
🔵 4️⃣ Obesity
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Goitre
🔵 Question 20:
Deficiency of thyroxine in children causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Myxedema
🟢 2️⃣ Cretinism
🟡 3️⃣ Gigantism
🔵 4️⃣ Dwarfism
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cretinism
🔵 Question 21:
Deficiency of thyroxine in adults causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Acromegaly
🟢 2️⃣ Myxedema
🟡 3️⃣ Dwarfism
🔵 4️⃣ Tetany
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Myxedema
🔵 Question 22:
Parathyroid gland secretes:
🔴 1️⃣ Calcitonin
🟢 2️⃣ PTH
🟡 3️⃣ Thyroxine
🔵 4️⃣ Insulin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ PTH
🔵 Question 23:
PTH increases level of:
🔴 1️⃣ Sodium
🟢 2️⃣ Calcium
🟡 3️⃣ Potassium
🔵 4️⃣ Phosphate
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Calcium
🔵 Question 24:
Calcitonin decreases level of:
🔴 1️⃣ Sodium
🟢 2️⃣ Calcium
🟡 3️⃣ Potassium
🔵 4️⃣ Phosphate
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Calcium
🔵 Question 25:
Pancreas is a:
🔴 1️⃣ Exocrine gland only
🟢 2️⃣ Endocrine gland only
🟡 3️⃣ Both endocrine and exocrine
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Both endocrine and exocrine
🔵 Question 26:
The endocrine part of pancreas is called:
🔴 1️⃣ Islets of Langerhans
🟢 2️⃣ Acini
🟡 3️⃣ Duct
🔵 4️⃣ Follicle
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Islets of Langerhans
🔵 Question 27:
Alpha cells of pancreas secrete:
🔴 1️⃣ Insulin
🟢 2️⃣ Glucagon
🟡 3️⃣ Somatostatin
🔵 4️⃣ Trypsin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glucagon
🔵 Question 28:
Beta cells of pancreas secrete:
🔴 1️⃣ Glucagon
🟢 2️⃣ Insulin
🟡 3️⃣ Somatostatin
🔵 4️⃣ Pancreatic juice
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Insulin
🔵 Question 29:
Deficiency of insulin causes:
🔴 1️⃣ Goitre
🟢 2️⃣ Diabetes mellitus
🟡 3️⃣ Cretinism
🔵 4️⃣ Tetany
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Diabetes mellitus
🔵 Question 30:
Insulin converts glucose into:
🔴 1️⃣ Starch
🟢 2️⃣ Glycogen
🟡 3️⃣ Protein
🔵 4️⃣ Lipid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glycogen
🔵 Question 31:
Adrenal glands are located:
🔴 1️⃣ Inside kidney
🟢 2️⃣ Above kidney
🟡 3️⃣ Below kidney
🔵 4️⃣ In pelvis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Above kidney
🔵 Question 32:
The adrenal medulla secretes:
🔴 1️⃣ Aldosterone
🟢 2️⃣ Adrenaline and noradrenaline
🟡 3️⃣ Cortisol
🔵 4️⃣ Insulin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Adrenaline and noradrenaline
🔵 Question 33:
Adrenaline is also known as:
🔴 1️⃣ Stress hormone
🟢 2️⃣ Emergency hormone
🟡 3️⃣ Growth hormone
🔵 4️⃣ Thyroid hormone
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Emergency hormone
🔵 Question 34:
Aldosterone acts on:
🔴 1️⃣ Heart
🟢 2️⃣ Kidney
🟡 3️⃣ Liver
🔵 4️⃣ Brain
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Kidney
🔵 Question 35:
Aldosterone increases:
🔴 1️⃣ Sodium reabsorption
🟢 2️⃣ Potassium reabsorption
🟡 3️⃣ Calcium reabsorption
🔵 4️⃣ Glucose absorption
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Sodium reabsorption
🔵 Question 36:
Cortisol is:
🔴 1️⃣ Mineralocorticoid
🟢 2️⃣ Glucocorticoid
🟡 3️⃣ Sex steroid
🔵 4️⃣ Gonadotropin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Glucocorticoid
🔵 Question 37:
Which hormone regulates sleep-wake cycle?
🔴 1️⃣ Melanin
🟢 2️⃣ Melatonin
🟡 3️⃣ Thyroxine
🔵 4️⃣ Cortisol
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Melatonin
🔵 Question 38:
Melatonin is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Pituitary
🟢 2️⃣ Pineal gland
🟡 3️⃣ Hypothalamus
🔵 4️⃣ Thyroid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pineal gland
🔵 Question 39:
Testosterone is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Leydig cells
🟢 2️⃣ Sertoli cells
🟡 3️⃣ Pituitary
🔵 4️⃣ Adrenal medulla
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Leydig cells
🔵 Question 40:
Estrogen is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Corpus luteum
🟢 2️⃣ Ovarian follicles
🟡 3️⃣ Adrenal cortex
🔵 4️⃣ Pituitary
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ovarian follicles
🔵 Question 41:
Progesterone is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Follicle
🟢 2️⃣ Corpus luteum
🟡 3️⃣ Ovary only
🔵 4️⃣ Pituitary
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Corpus luteum
🔵 Question 42:
Which hormone prepares uterus for implantation?
🔴 1️⃣ Estrogen
🟢 2️⃣ Progesterone
🟡 3️⃣ LH
🔵 4️⃣ FSH
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Progesterone
🔵 Question 43:
Thymus secretes:
🔴 1️⃣ Thymosin
🟢 2️⃣ Thyroxine
🟡 3️⃣ Insulin
🔵 4️⃣ ACTH
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Thymosin
🔵 Question 44:
Thymosin is important for:
🔴 1️⃣ RBC maturation
🟢 2️⃣ T-lymphocyte maturation
🟡 3️⃣ WBC destruction
🔵 4️⃣ B-lymphocyte maturation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ T-lymphocyte maturation
🔵 Question 45:
Gastrin is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Pancreas
🟢 2️⃣ Stomach
🟡 3️⃣ Liver
🔵 4️⃣ Small intestine
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Stomach
🔵 Question 46:
Secretin is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Liver
🟢 2️⃣ Duodenum
🟡 3️⃣ Stomach
🔵 4️⃣ Pancreas
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Duodenum
🔵 Question 47:
ANF (Atrial natriuretic factor) is secreted by:
🔴 1️⃣ Kidney
🟢 2️⃣ Heart
🟡 3️⃣ Liver
🔵 4️⃣ Lungs
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Heart
🔵 Question 48:
ANF decreases:
🔴 1️⃣ Blood pressure
🟢 2️⃣ Blood glucose
🟡 3️⃣ Heartbeat
🔵 4️⃣ Respiration rate
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Blood pressure
🔵 Question 49:
Which hormone is called “anti-stress hormone”?
🔴 1️⃣ Adrenaline
🟢 2️⃣ Cortisol
🟡 3️⃣ Melatonin
🔵 4️⃣ GH
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cortisol
🔵 Question 50:
Which hormone acts as emergency hormone?
🔴 1️⃣ Cortisol
🟢 2️⃣ Adrenaline
🟡 3️⃣ Thyroxine
🔵 4️⃣ GH
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Adrenaline
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
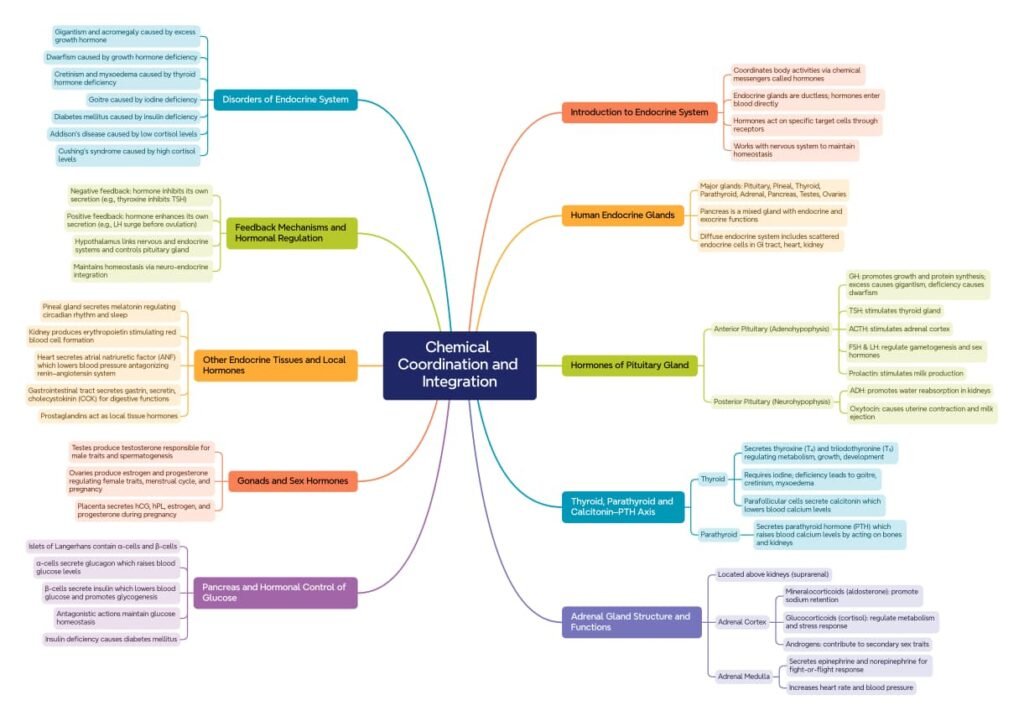
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
