Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 1. The Living World
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Introduction: What is Living?
Life is an intricate phenomenon, manifesting itself in countless forms — from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and human beings. But what truly distinguishes the living from the non-living?
🌿 Defining Life:
Scientists define living organisms based on a combination of characteristics:
Growth
Reproduction
Metabolism
Consciousness
Cellular organization
Let’s understand each in detail.
🟢 Growth – A Fundamental Feature
➡️ Growth refers to an increase in mass and number of individuals.
✔️ In unicellular organisms (like Amoeba), growth means cell division.
✔️ In multicellular organisms (like plants and animals), it involves cell multiplication and size increase.
💡 Note: Non-living things (like crystals) also grow, but by external addition. In contrast, biological growth is internal and regulated.
🔴 Reproduction – Continuity of Life
Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring.
✔️ Unicellular organisms: Reproduction = growth (binary fission)
✔️ Multicellular organisms: Involves sexual/asexual reproduction.
✏️ Exceptions:
Mules, sterile worker bees, and infertile humans do not reproduce — yet they are living.
So reproduction is not a defining feature in all contexts.
🟡 Metabolism – Chemical Symphony of Life
🧬 All living organisms undergo metabolic reactions – the sum total of all chemical reactions happening in the body.
✔️ Anabolism: Constructive processes (e.g., photosynthesis)
✔️ Catabolism: Destructive processes (e.g., respiration)
💡 Tip: Isolated metabolic reactions in vitro are also considered living reactions — a unique property of life.
🔵 Consciousness – Awareness of Surroundings
🧠 The ability to sense and respond to environmental stimuli (light, chemicals, touch, etc.) is called consciousness.
✔️ Plants bend towards light (phototropism)
✔️ Animals respond to hunger, temperature, fear
✔️ Humans exhibit self-consciousness — a higher level of awareness
🧠 Highlight: Consciousness is the most definitive and unique property of living organisms.
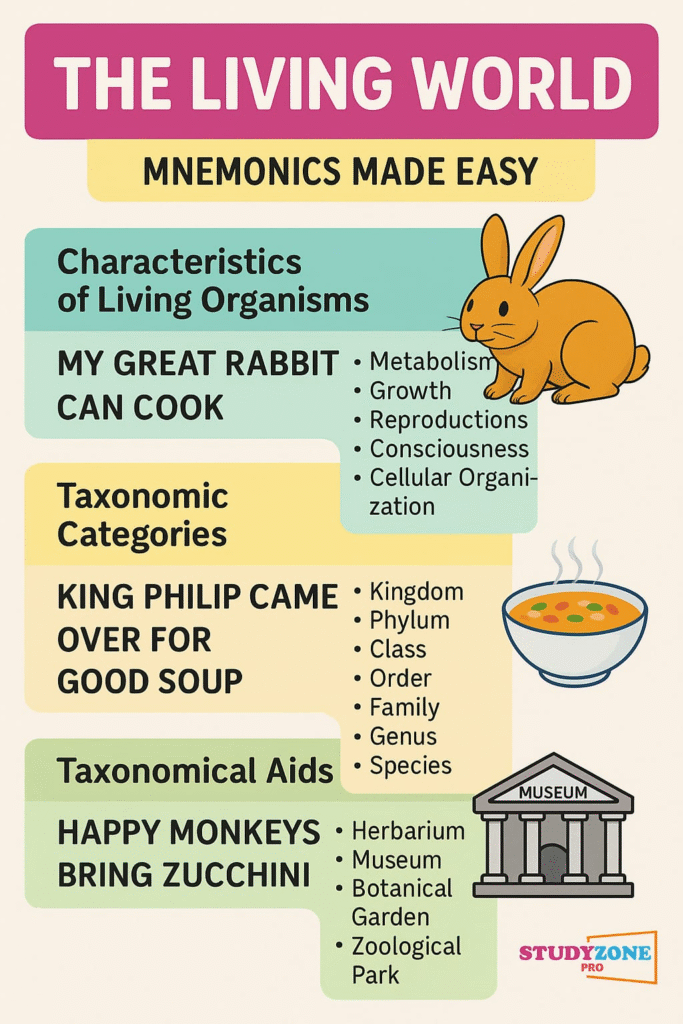
🟢 Summary of Defining Features of Living Beings
Let’s summarize living characteristics:
🔹 Cellular structure
🔹 Growth
🔹 Reproduction
🔹 Metabolism
🔹 Consciousness
🧬 Metabolism and Consciousness are universal and defining features.
🧾 Diversity in the Living World
The earth harbors millions of species, from viruses to whales, from fungi to flowering plants.
📚 Biology classifies and organizes them through taxonomy and systematics.
🔴 Need for Classification
⚡Why classify?
✔️ To study organisms in a structured manner
✔️ To identify evolutionary relationships
✔️ To predict characteristics of newly discovered organisms
🟡 Taxonomy – The Science of Naming & Classifying
🔬 Taxonomy involves:
Identification – Recognizing an organism
Nomenclature – Giving it a scientific name
Classification – Placing it into a taxonomic group
📌 Developed and standardized by taxonomists through rules like ICBN (plants) and ICZN (animals)
🔵 Binomial Nomenclature – Carl Linnaeus’ Contribution
🧠 Linnaeus gave the 2-word naming system:
Genus + species
Example: Homo sapiens
✔️ Written in italics
✔️ Genus starts with capital letter
✔️ Species is lowercase
✔️ Handwritten names are underlined
💡 Tip: Binomial names are universally accepted and avoid confusion caused by local/common names.
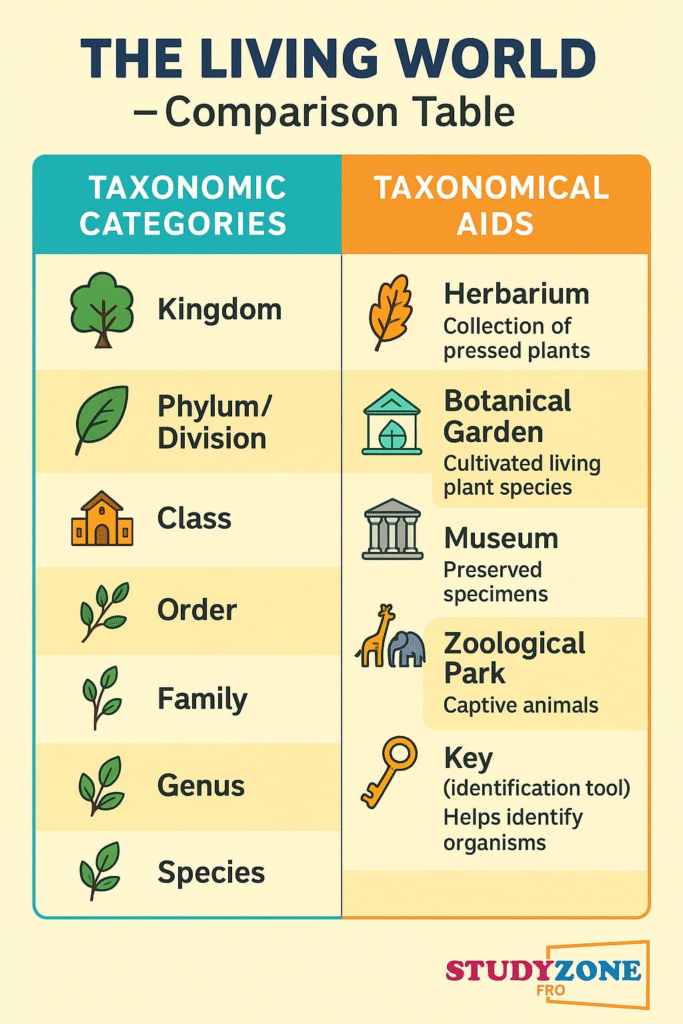
🟢 Taxonomic Categories – Hierarchical Levels
Classification follows a hierarchy:
🧬 Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
🌿 Mnemonic: King Philip Came Over For Good Soup
✔️ Each level is called a taxon
✔️ As we go up, organisms become more diverse and similar only in basic traits
📌 Example: Mango (Mangifera indica)
Kingdom: Plantae
Family: Anacardiaceae
Genus: Mangifera
Species: indica
🔴 Taxonomical Aids – Tools for Identification
Scientists need help identifying and classifying the enormous biodiversity. Some tools include:
🌿 1. Herbarium
📦 A collection of pressed, dried plant specimens mounted on sheets.
✔️ Labelled with scientific name, family, place of collection, date, etc.
💡 Found in botanical gardens, research institutes, universities
🌳 2. Botanical Gardens
Public or research gardens growing and maintaining live plant species for reference.
✔️ Useful for field study and research
✔️ Plants are labelled and categorized
🧪 3. Museum
🏛️ Preserves both plant and animal specimens.
✔️ Dried animals, stuffed birds, skeletons, and preserved insects
✔️ Used for study and comparison
📕 4. Zoological Parks
Places where animals are kept in protected environments resembling natural habitat.
✔️ Useful for observing behavior, diet, and lifestyle
✔️ Helps in conservation
📗 5. Keys
🗝️ A pair of contrasting characters used to identify organisms.
✔️ Example: Presence vs absence of vertebral column
✔️ Based on similarities/differences
✔️ Dichotomous – two options at each step
🔵 Flora, Manuals, Monographs & Catalogues
✔️ Flora – All plant species of a region
✔️ Manual – Identification of species
✔️ Monograph – Detailed study of one taxon
✔️ Catalogue – Alphabetical list of species
These are important reference tools in systematics.
🌟 Real-Life Applications of Classification
🔹 Useful in medical research: Understanding similar species helps study drug effects.
🔹 Helps in conservation efforts: Identifying endangered species.
🔹 Assists in agriculture: Cross-breeding species for better yields.
💬 Why This Lesson Matters
📦 The Living World introduces students to the building blocks of biology — what life is, how it is structured, and how it is organized into systems. Without classification, the biological world would be chaotic.
🌍 It is foundational for:
Biodiversity studies
Evolutionary biology
Genetics
Ecology and environmental conservation
Understanding this chapter equips students to view life with a structured lens — from a cell to the biosphere.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔹 Growth ≠ Life (non-living can grow)
🔹 Reproduction not universal (e.g., mules)
🔹 Metabolism & consciousness are defining
🔹 Taxonomy: Identification, naming, classification
🔹 Binomial nomenclature: Genus + species
🔹 Hierarchy: Kingdom to Species
🔹 Taxonomic Aids: Herbarium, keys, gardens, museums
🔹 Classification = order, predictability, research

📘 Summary (~300 Words)
🔹 Life is characterized by growth, reproduction, metabolism, and consciousness.
🔹 Growth involves increase in mass or number of cells. In unicellular organisms, growth and reproduction are the same.
🔹 Reproduction can be sexual or asexual. However, it is not universal to all living organisms.
🔹 Metabolism is a unique and defining feature — all chemical reactions in a living body.
🔹 Consciousness is the most defining trait, especially in humans who possess self-awareness.
🔹 Taxonomy is the branch of biology that deals with the classification, identification, and nomenclature of organisms.
🔹 Binomial nomenclature, given by Carl Linnaeus, uses a two-part name system (Genus + species).
🔹 The hierarchy of classification includes Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species.
🔹 Taxonomic aids such as herbariums, botanical gardens, museums, and zoological parks are used to identify and study species.
🔹 Keys help in distinguishing organisms based on contrasting characters.
🔹 Flora, Manuals, and Monographs are important literature for identification and reference.
🔹 Classification helps in understanding biodiversity, conserving species, and applying knowledge in medicine, agriculture, and ecology.
This lesson builds the essential framework for all biological understanding. It helps students perceive life as a system of organized, interconnected forms governed by evolutionary principles and scientific rules.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🟦 Q1. Why are living organisms classified?
✅ Answer:
🔹 To study and understand the vast diversity of life in an organized manner
🔹 To identify similarities and differences among organisms
🔹 To trace evolutionary relationships
🔹 To ease scientific naming and universal understanding
🟦 Q2. Why are the classification systems changing every now and then?
✅ Answer:
🔸 Discovery of new organisms
🔸 Advancements in molecular biology and genetics (e.g., DNA sequencing)
🔸 Improved understanding of evolutionary relationships
🔸 Need for better accuracy in reflecting phylogeny
🟦 Q3. What different criteria would you choose to classify people that you meet often?
✅ Answer:
✔ Physical features (e.g., height, skin tone)
✔ Language or region
✔ Profession or occupation
✔ Hobbies and interests
✔ Behavioural traits
🟦 Q4. What do we learn from identification of individuals and populations?
✅ Answer:
🔹 Proper naming and classification of species
🔹 Understanding of biodiversity in a region
🔹 Evolutionary and ecological studies
🔹 Conservation of endangered species
🔹 Detection of diseases and medical research
🟦 Q5. Given below is the scientific name of Mango. Identify the correctly written name.
Mangifera Indica
Mangifera indica
✅ Answer: ✔ Mangifera indica
📌 Genus name begins with a capital letter, species name with a small letter. The full name is italicised (or underlined when handwritten).
🟦 Q6. Define a taxon. Give some examples of taxa at different hierarchical levels.
✅ Answer:
🟢 Taxon: A unit of classification representing a group of organisms.
📌 Example Taxa:
🔸 Kingdom – Animalia
🔹 Phylum – Chordata
🔸 Class – Mammalia
🔹 Order – Primates
🔸 Family – Hominidae
🔹 Genus – Homo
🔸 Species – sapiens
🟦 Q7. Can you identify the correct sequence of taxonomical categories?
(a) Species → Order → Phylum → Kingdom
(b) Genus → Species → Order → Kingdom
(c) Species → Genus → Order → Phylum
✅ Answer: ✔ (c) Species → Genus → Order → Phylum
🧠 Correct taxonomic hierarchy:
Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum → Kingdom
🟦 Q8. Try to collect all the currently accepted meanings for the word ‘species’. Discuss with your teacher the meaning of species in case of higher plants and animals on one hand, and bacteria on the other hand.
✅ Answer (Crisp Summary):
🔸 Species (Traditional Definition):
A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
🔹 In Plants and Animals:
Members of a species have structural similarity and reproductive compatibility.
🔹 In Bacteria (Asexual):
Species defined based on biochemical, genetic similarity, and ecological roles.
🟦 Q9. Define and understand the following terms:
✅ (i) Phylum:
Group of related classes.
E.g., Chordata includes mammals, birds, reptiles, etc.
✅ (ii) Class:
Group of related orders.
E.g., Mammalia – includes primates, carnivores.
✅ (iii) Family:
Group of related genera.
E.g., Felidae – includes lion (Panthera) and cat (Felis).
✅ (iv) Order:
Group of related families.
E.g., Carnivora – includes Felidae, Canidae.
✅ (v) Genus:
Group of closely related species.
E.g., Panthera – lion, tiger, leopard.
🟦 Q10. Illustrate the taxonomical hierarchy with suitable examples of a plant and an animal.
✅ Answer:
🪴 Plant Example – Mango (Mangifera indica)
🔹 Kingdom – Plantae
🔸 Division – Angiospermae
🔹 Class – Dicotyledonae
🔸 Order – Sapindales
🔹 Family – Anacardiaceae
🔸 Genus – Mangifera
🔹 Species – indica
🦁 Animal Example – Human (Homo sapiens)
🔹 Kingdom – Animalia
🔸 Phylum – Chordata
🔹 Class – Mammalia
🔸 Order – Primates
🔹 Family – Hominidae
🔸 Genus – Homo
🔹 Species – sapiens
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🟡 SECTION A – MCQs & Assertion-Reason (Q1 to Q16)
(Each question carries 1 mark)
🔹 Q1. Which of the following is not a defining property of living organisms?
(A) Growth
(B) Metabolism
(C) Reproduction
(D) Consciousness
✅ Answer: (A) Growth
🔹 Q2. Which of these organisms reproduces by binary fission?
(A) Yeast
(B) Amoeba
(C) Hydra
(D) Paramoecium
✅ Answer: (B) Amoeba
🔹 Q3. Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched?
(A) Herbarium – Pressed plant specimens
(B) Zoological park – Ex-situ conservation
(C) Botanical garden – Animal preservation
(D) Museum – Skeleton and stuffed specimens
✅ Answer: (C) Botanical garden – Animal preservation
🔹 Q4. What is the correct order of taxonomic hierarchy?
(A) Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Genus → Family → Species
(B) Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
(C) Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum → Kingdom
(D) Species → Family → Genus → Class → Order → Phylum → Kingdom
✅ Answer: (B) Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
🔹 Q5. Binomial nomenclature was first introduced by:
(A) Aristotle
(B) John Ray
(C) Carl Linnaeus
(D) Huxley
✅ Answer: (C) Carl Linnaeus
🔹 Q6. Which one is a correct binomial name?
(A) Mangifera Indica
(B) Homo Sapiens
(C) Mangifera indica
(D) homo sapiens
✅ Answer: (C) Mangifera indica
🔹 Q7. Which of the following aids is not used for classification of plants?
(A) Herbarium
(B) Museum
(C) Botanical garden
(D) Flora
✅ Answer: (B) Museum
🔹 Q8. In taxonomy, the smallest taxon is:
(A) Family
(B) Genus
(C) Species
(D) Order
✅ Answer: (C) Species
🔹 Q9. Which characteristic is most universal and defining of life?
(A) Growth
(B) Reproduction
(C) Metabolism
(D) Movement
✅ Answer: (C) Metabolism
🔹 Q10. Which is not a part of taxonomic aids?
(A) Flora
(B) Manuals
(C) Monographs
(D) Hybridisation
✅ Answer: (D) Hybridisation
🔹 Q11. Scientific name of man is:
(A) Homo Sapiens
(B) Homo sapiens
(C) homo Sapiens
(D) homo sapiens
✅ Answer: (B) Homo sapiens
🔹 Q12. Identify the odd one out based on taxonomic hierarchy:
(A) Order
(B) Genus
(C) Species
(D) Variety
✅ Answer: (D) Variety
🔹 Q13. Which taxonomic aid helps in identification using contrasting characters?
(A) Manual
(B) Flora
(C) Key
(D) Catalogue
✅ Answer: (C) Key
🔹 Q14. Which taxon includes organisms with maximum similarity?
(A) Family
(B) Genus
(C) Species
(D) Class
✅ Answer: (C) Species
🔹 Q15. The branch of biology that deals with classification is:
(A) Morphology
(B) Anatomy
(C) Ecology
(D) Taxonomy
✅ Answer: (D) Taxonomy
🔹 Q16. Which is the correct representation of a scientific name?
(A) Solanum tuberosum
(B) Solanum Tuberosum
(C) solanum tuberosum
(D) solanum Tuberosum
✅ Answer: (A) Solanum tuberosum
🔴 Assertion-Reason Questions (Q17–Q18)
Select the correct option:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
🔹 Q17.
🧠 Assertion (A): Consciousness is considered the most defining property of living organisms.
🧠 Reason (R): Only plants and microorganisms show consciousness.
✅ Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false.
🔹 Q18.
🧠 Assertion (A): Binomial nomenclature helps in universal identification of species.
🧠 Reason (R): Common names are sufficient for scientific communication.
✅ Answer: (C) A is true, but R is false.
🟢 SECTION B – Very Short Answer Questions (Q19 to Q21)
(Each question carries 2 marks)
🔹 Q19.
✍️ Define metabolism. Why is it considered a defining property of life?
✅ Answer:
🧬 Metabolism is the sum total of all chemical reactions occurring inside a living organism, including both anabolic (constructive) and catabolic (destructive) processes.
🧠 It is considered a defining property because no non-living object exhibits metabolism. Even isolated reactions in test tubes are considered living reactions.
🔹 Q20.
✍️ What is a key? How is it useful in taxonomy?
✅ Answer:
🗝️ A key is a taxonomical tool used for identification of organisms based on contrasting characters.
🔍 It typically presents a pair of statements (dichotomous) that help narrow down species by choice.
📚 It is used in field guides and manuals to identify unknown organisms efficiently.
🔹 Q21.
✍️ Why is reproduction not considered a defining feature of living organisms? Give one example.
✅ Answer:
❗ Although most living organisms reproduce, some living beings like mules, infertile human couples, and worker bees do not reproduce.
🔬 Hence, reproduction is not a universal feature and cannot alone define life.
🔴 SECTION C – Short Answer Questions (Q22 to Q28)
(Each question carries 3 marks)
🔹 Q22.
✍️ Describe the steps involved in the process of taxonomy.
✅ Answer:
📌 1. Identification – Recognizing and recording distinguishing features of an organism.
📌 2. Nomenclature – Assigning a scientific name using binomial system.
📌 3. Classification – Grouping organisms into categories based on similarities and evolutionary traits.
🔍 These steps help organize biodiversity and aid in scientific communication.
🔹 Q23.
✍️ List any three limitations of using common names of organisms.
✅ Answer:
❌ 1. Regional variation – Same species may have different names in different areas.
❌ 2. Language barrier – A common name in one language may not be understood in another.
❌ 3. Ambiguity – One common name may refer to different species in different places.
✔️ Hence, scientific naming is essential for accuracy.
🔹 Q24.
✍️ Differentiate between flora, manual, and monograph.
✅ Answer:
📗 Flora – A comprehensive list of plant species in a specific area, with details.
📘 Manual – A guide to identify species with brief descriptions and keys.
📒 Monograph – A detailed account of a single taxon (like a genus or family).
🌿 All are essential tools for botanists and taxonomists.
🔹 Q25.
✍️ Explain binomial nomenclature and write its key features.
✅ Answer:
🧬 Binomial Nomenclature was introduced by Carl Linnaeus. It assigns a two-part Latin name to each organism:
➤ Genus name (capitalized)
➤ Species name (lowercase)
✨ Rules:
✔️ Italicized when printed; underlined when handwritten
✔️ Universally accepted system
Example: Homo sapiens
🔹 Q26.
✍️ State three differences between living and non-living things with examples.
✅ Answer:
Feature Living Non-living
Metabolism Present (e.g., humans) Absent (e.g., rock)
Reproduction Most can reproduce Cannot reproduce
Consciousness Respond to stimuli No awareness or response
🔹 Q27.
✍️ What are taxonomic categories? List any three with examples.
✅ Answer:
🧬 Taxonomic categories are ranks used in classification to group organisms.
Examples:
🔸 Kingdom – Animalia (e.g., dog)
🔹 Genus – Panthera (e.g., Panthera leo)
🟢 Species – Homo sapiens (humans)
They help in organizing biological diversity.
🔹 Q28.
✍️ Explain how botanical gardens and museums help in taxonomic studies.
✅ Answer:
🌳 Botanical Gardens:
✔️ Grow live plant species
✔️ Help observe plant traits
✔️ Aid in field-based identification
🏛️ Museums:
✔️ Preserve animal and plant specimens
✔️ Include skeletons, insects, birds
✔️ Provide reference material for students and taxonomists
🔴 SECTION D – Case-Based Questions (Q29 to Q30)
(Each question carries 4 marks)
🔹 Q29.
📚 Read the passage and answer the questions:
In biological classification, species is the basic unit and includes individuals with similar features. The next higher category is genus, which includes related species. Family includes related genera. These categories continue upward till Kingdom. An example of classification is: Panthera leo (lion) and Panthera tigris (tiger) belong to the same genus Panthera, while Felis domesticus (domestic cat) is of a different genus but same family Felidae.
✍️ Answer the following:
(i) Identify the genus and family of domestic cat.
✅ Answer:
Genus: Felis
Family: Felidae
(ii) How many categories are there from species to kingdom? List them.
✅ Answer:
There are seven categories:
🔸 Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class → Phylum → Kingdom
(iii) Give an example of two organisms of the same genus.
✅ Answer:
Panthera leo and Panthera tigris are two organisms of the same genus.
(iv) Why is classification important in biology?
✅ Answer:
Classification helps:
✔️ Organize knowledge about biodiversity
✔️ Understand evolutionary relationships
✔️ Enable accurate identification and communication
🔹 Q30.
📚 Read the data and answer the questions:
A taxonomist visited a botanical garden and observed three plant species:
Mangifera indica
Solanum tuberosum
Solanum melongena
He noted that two of them belonged to the same genus.
✍️ Answer the following:
(i) Identify the two species with the same genus.
✅ Answer:
Solanum tuberosum and Solanum melongena
(ii) What does the term “Solanum” represent in these names?
✅ Answer:
“Solanum” is the genus of these species.
(iii) How is binomial nomenclature written correctly?
✅ Answer:
✔️ Italicized when typed
✔️ Genus capitalized, species lowercase
Example: Mangifera indica
(iv) State any one advantage of binomial nomenclature.
✅ Answer:
It provides a universal name for each organism, avoiding confusion caused by local names.
🟢 SECTION E – Long Answer Questions (Q31 to Q33)
(Each question carries 5 marks)
🔹 Q31.
✍️ Explain the characteristics of living organisms in detail. Which of them is truly defining?
✅ Answer:
The major characteristics of living organisms include:
🟢 1. Growth – Increase in mass and number of cells (e.g., cell division in Amoeba).
🟢 2. Reproduction – Ability to produce offspring (sexual/asexual).
🟢 3. Metabolism – Sum of all biochemical reactions. ✔️ Defining
🟢 4. Consciousness – Awareness of surroundings. ✔️ Truly defining
🟢 5. Cellular organization – Made of one or more cells.
📌 Of these, metabolism and consciousness are truly universal and defining features.
🔹 Q32.
✍️ Describe the hierarchical system of classification with an example.
✅ Answer:
🧬 Taxonomic hierarchy is a system of arranging organisms into successive levels based on similarities.
💡 Levels (from highest to lowest):
🔸 Kingdom
🔸 Phylum
🔸 Class
🔸 Order
🔸 Family
🔸 Genus
🔸 Species
📌 Example: Human (Homo sapiens)
Kingdom – Animalia
Phylum – Chordata
Class – Mammalia
Order – Primates
Family – Hominidae
Genus – Homo
Species – sapiens
✔️ Each level represents a rank with increasing specificity from kingdom to species.
🔹 Q33.
✍️ What are taxonomic aids? Describe four types with functions.
✅ Answer:
📦 Taxonomic aids are tools that help in identification and classification of organisms.
✔️ 1. Herbarium
Collection of dried, pressed plant specimens
Mounted on sheets with labels
Used as reference for plant identification
✔️ 2. Botanical Gardens
Grow live plants for study
Each plant labelled with scientific name
Useful for conservation and research
✔️ 3. Museum
Houses preserved plant and animal specimens
Insects in boxes, stuffed birds, skeletons
Helpful in comparative study
✔️ 4. Zoological Parks
Animals kept in natural habitats
Observed for behaviour, diet, adaptations
Promotes education and biodiversity protection
These aids are essential for students, researchers, and taxonomists.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🧪 Questions 1 to 25:
Q1. Which one of the following is not a correct statement?
(A) Botanical gardens have a collection of living plants for reference.
(B) A museum has a collection of preserved plant and animal specimens.
(C) Key is a taxonomic aid for identification of specimens.
(D) Herbarium houses dry, living plant specimens.
Answer: (D) Herbarium houses dry, living plant specimens.
Year: 2025 | Set: 1
Q2. Which of the following taxonomic categories contains organisms least similar to one another?
(A) Genus
(B) Class
(C) Species
(D) Order
Answer: (B) Class
Year: 2024 | Set: 3
Q3. The term “systematics” refers to:
(A) Identification and classification of plants and animals
(B) Nomenclature and identification of plants
(C) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relationship
(D) Study of fossils
Answer: (C) Diversity of kinds of organisms and their relationship
Year: 2024 | Set: 2
Q4. The correct sequence of taxonomic categories is:
(A) Species → Order → Genus → Family → Class
(B) Genus → Species → Family → Order → Class
(C) Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class
(D) Order → Family → Genus → Species → Class
Answer: (C) Species → Genus → Family → Order → Class
Year: 2023 | Set: Q
Q5. Scientific name of Mango is:
(A) Mangifera indica
(B) Mangifera Indica
(C) Mangifera Indica Linn
(D) Mangifera Indica L.
Answer: (A) Mangifera indica
Year: 2023 | Set: Z
Q6. Binomial nomenclature was given by:
(A) Aristotle
(B) Linnaeus
(C) Theophrastus
(D) Darwin
Answer: (B) Linnaeus
Year: 2022 | Set: 2
Q7. Which one is the odd one?
(A) Flora
(B) Fauna
(C) Manuals
(D) Monograph
Answer: (B) Fauna
Year: 2022 | Set: Q
Q8. Which among the following is not a taxonomic aid?
(A) Botanical garden
(B) Zoological park
(C) Museum
(D) Library
Answer: (D) Library
Year: 2021 | Set: 3
Q9. The term ‘taxon’ refers to:
(A) Rank or level in classification
(B) A taxonomic group of any rank
(C) Only genus or species
(D) Only species
Answer: (B) A taxonomic group of any rank
Year: 2021 | Set: Z
Q10. Herbarium is a:
(A) Garden where medicinal plants are grown
(B) Dry, preserved plant specimen mounted on sheets
(C) Collection of rare herb plants
(D) Greenhouse for growing herbs
Answer: (B) Dry, preserved plant specimen mounted on sheets
Year: 2020 | Set: 2
Q11. Which one is a defining characteristic of living organisms?
(A) Reproduction
(B) Metabolism
(C) Movement
(D) Consciousness
Answer: (B) Metabolism
Year: 2020 | Set: 5
Q12. Nomenclature is governed by certain universal rules. Which one is not a rule?
(A) Biological names are generally in Latin
(B) Names are written in italics
(C) Generic name starts with capital letter
(D) Species name starts with capital letter
Answer: (D) Species name starts with capital letter
Year: 2019 | Set: 1
Q13. ICZN stands for:
(A) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
(B) Indian Council of Zoological Nomenclature
(C) Indian Code of Zoological Names
(D) International Congress on Zoological Names
Answer: (A) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
Year: 2019 | Set: R
Q14. The scientific name of the frog is written as Rana tigrina. Which of the following is correct?
(A) It is correctly written.
(B) Genus and species names both capitalized
(C) It should be italicized
(D) Only genus should be italicized
Answer: (C) It should be italicized
Year: 2018 | Set: P
Q15. Match the following:
Key
Flora
Manual
Catalogue
(A) Systematic arrangement of species
(B) Gives information about habitat
(C) Helps in identification
(D) Contains instructions for identification
Answer:
1 → C
2 → B
3 → D
4 → A
Year: 2017 | Set: S
Q16. The branch of biology dealing with identification, nomenclature, and classification is:
(A) Ecology
(B) Cytology
(C) Taxonomy
(D) Morphology
Answer: (C) Taxonomy
Year: 2016 | Set: A
Q17. Which one of the following shows maximum diversity?
(A) Insects
(B) Mammals
(C) Birds
(D) Fungi
Answer: (A) Insects
Year: 2015 | Set: M
Q18. Which of the following is the correct sequence of classification?
(A) Kingdom → Division → Class → Family → Genus → Species
(B) Phylum → Class → Order → Genus → Family → Species
(C) Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
(D) Phylum → Division → Class → Family → Species → Genus
Answer: (C) Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
Year: 2014 | Set: Q
Q19. The term “new systematics” was coined by:
(A) Linnaeus
(B) Bentham
(C) Huxley
(D) John Ray
Answer: (C) Huxley
Year: 2013 | Set: S
Q20. The species is the basic unit of:
(A) Taxonomy
(B) Ecology
(C) Genetics
(D) Evolution
Answer: (A) Taxonomy
Year: 2013 | Set: Z
Q21. A group of interbreeding organisms forms a:
(A) Genus
(B) Class
(C) Family
(D) Species
Answer: (D) Species
Year: 2012 | Set: X
Q22. Who is known as Father of Taxonomy?
(A) Darwin
(B) Linnaeus
(C) Aristotle
(D) Hooker
Answer: (B) Linnaeus
Year: 2012 | Set: Z
Q23. Manuals are useful in providing information for:
(A) Classification of plants
(B) Evolutionary trends
(C) Identification of names
(D) Locations of species
Answer: (C) Identification of names
Year: 2011 | Set: Y
Q24. Which one of the following organisms is correctly matched with its taxonomic category?
(A) Tiger – tigris, species
(B) Housefly – Musca, family
(C) Man – primata, family
(D) Wheat – Triticum aestivum, genus
Answer: (A) Tiger – tigris, species
Year: 2010 | Set: 1
Q25. Which of the following features is a distinguishing characteristic of all living organisms?
(A) Growth
(B) Reproduction
(C) Consciousness
(D) Metabolism
Answer: (D) Metabolism
Year: 2010 | Set: Z
Q26. The taxonomic key helps in:
(A) Identification of unknown organisms
(B) Describing biological specimens
(C) Conducting genetic tests
(D) Creating new species
Answer: (A) Identification of unknown organisms
Year: 2009 | Set: 2
Q27. Scientific name should be:
(A) Written in capital letters
(B) Written in local language
(C) Italicized or underlined
(D) Enclosed in brackets
Answer: (C) Italicized or underlined
Year: 2009 | Set: W
Q28. In taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characters will decrease from:
(A) Species to Kingdom
(B) Kingdom to Species
(C) Genus to Species
(D) Order to Class
Answer: (A) Species to Kingdom
Year: 2008 | Set: A
Q29. Which of the following is not true for a species?
(A) Members can interbreed
(B) Have similar morphological features
(C) Do not breed with other species
(D) Live in different geographical locations
Answer: (D) Live in different geographical locations
Year: 2008 | Set: M
Q30. Binomial nomenclature means naming with:
(A) Two names – family and genus
(B) Two names – genus and species
(C) Three names – kingdom, phylum, genus
(D) One name only
Answer: (B) Two names – genus and species
Year: 2007 | Set: P
Q31. Which of the following is not true for manuals?
(A) Contain information for identification
(B) Provide details of a particular area
(C) Describe all organisms of the world
(D) Used as a taxonomic aid
Answer: (C) Describe all organisms of the world
Year: 2007 | Set: Q
Q32. Which of the following is not included in the systematics?
(A) Classification
(B) Nomenclature
(C) Evolutionary relationship
(D) Pathology
Answer: (D) Pathology
Year: 2006 | Set: A
Q33. A group of plants or animals with similar traits of any rank is called:
(A) Order
(B) Taxon
(C) Genus
(D) Species
Answer: (B) Taxon
Year: 2006 | Set: R
Q34. Which one of the following has the smallest number of organisms with maximum similar characters?
(A) Genus
(B) Class
(C) Order
(D) Species
Answer: (D) Species
Year: 2005 | Set: Z
Q35. Who coined the term ‘taxonomy’?
(A) John Ray
(B) Linnaeus
(C) A.P. de Candolle
(D) Aristotle
Answer: (C) A.P. de Candolle
Year: 2005 | Set: W
Q36. A taxon is:
(A) A class
(B) A species
(C) A taxonomic group of any rank
(D) A genus
Answer: (C) A taxonomic group of any rank
Year: 2004 | Set: M
Q37. Which of the following is a correct match?
(A) Family – Muscidae
(B) Order – Primata
(C) Class – Mammalia
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Year: 2004 | Set: P
Q38. The scientific name of an organism is composed of:
(A) Kingdom + Phylum
(B) Genus + Family
(C) Genus + Species
(D) Class + Order
Answer: (C) Genus + Species
Year: 2003 | Set: R
Q39. Taxonomy does not include:
(A) Identification
(B) Classification
(C) Nomenclature
(D) Habitat description
Answer: (D) Habitat description
Year: 2003 | Set: Y
Q40. A collection of dried, pressed plant specimens is known as:
(A) Herbarium
(B) Museum
(C) Botanical garden
(D) Flora
Answer: (A) Herbarium
Year: 2002 | Set: A
Q41. The largest taxonomic category among the following is:
(A) Kingdom
(B) Phylum
(C) Genus
(D) Class
Answer: (A) Kingdom
Year: 2002 | Set: Q
Q42. The basic unit of classification is:
(A) Order
(B) Genus
(C) Species
(D) Class
Answer: (C) Species
Year: 2001 | Set: S
Q43. Manuals are particularly useful for:
(A) Evolutionary relationships
(B) Identification of species
(C) Describing extinct species
(D) Genetic engineering
Answer: (B) Identification of species
Year: 2001 | Set: X
Q44. Which one of the following is not a category in taxonomy?
(A) Class
(B) Order
(C) Phylum
(D) Species name
Answer: (D) Species name
Year: 2001 | Set: P
Q45. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(A) Organisms are classified to make study easy
(B) Classification is based on similarities
(C) All members of a class have identical features
(D) Taxonomic hierarchy is from general to specific
Answer: (C) All members of a class have identical features
Year: 2001 | Set: Z
Q46. The number of common characteristics will increase from:
(A) Species to Kingdom
(B) Genus to Species
(C) Class to Phylum
(D) Kingdom to Species
Answer: (D) Kingdom to Species
Year: 2000 | Set: M
Q47. Growth and reproduction are characteristics of:
(A) Only plants
(B) Only animals
(C) Living organisms
(D) Non-living things
Answer: (C) Living organisms
Year: 2000 | Set: R
Q48. Systematics includes:
(A) Identification only
(B) Classification and nomenclature
(C) Description of plants only
(D) Evolutionary relationships
Answer: (D) Evolutionary relationships
Year: 2000 | Set: A
Q49. The term ‘New Systematics’ includes:
(A) Morphology
(B) Physiology
(C) Genetics
(D) All of the above
Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: 1999 | Set: P
Q50. Which taxonomic aid provides preserved animal specimens?
(A) Herbarium
(B) Botanical garden
(C) Museum
(D) Zoological park
Answer: (C) Museum
Year: 1998 | Set: 2
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. Which of the following is a defining property of living organisms?
(A) Growth
(B) Metabolism
(C) Movement
(D) Reproduction
Answer: (B)
Year: Expert-Created (NCERT-aligned)
Q2. Taxonomic hierarchy was introduced by:
(A) Linnaeus
(B) Aristotle
(C) Darwin
(D) Haeckel
Answer: (A)
Q3. Which of the following organisms can reproduce but is not considered truly living?
(A) Amoeba
(B) Virus
(C) Bacteria
(D) Plasmodium
Answer: (B)
Q4. The term “Systema Naturae” is associated with:
(A) Theophrastus
(B) Linnaeus
(C) Aristotle
(D) Mayr
Answer: (B)
Q5. Binomial nomenclature uses:
(A) Genus and family
(B) Species and genus
(C) Order and genus
(D) Family and species
Answer: (B)
Q6. The universal rules of nomenclature are governed by:
(A) WHO
(B) IUCN
(C) ICZN and ICBN
(D) FAO
Answer: (C)
Q7. Which of the following is not a taxonomic category?
(A) Class
(B) Order
(C) Family
(D) Flora
Answer: (D)
Q8. Metabolism includes:
(A) Only catabolism
(B) Only anabolism
(C) Both anabolism and catabolism
(D) Only digestion
Answer: (C)
Q9. The biological concept of species was proposed by:
(A) Linnaeus
(B) Mayr
(C) Aristotle
(D) Darwin
Answer: (B)
Q10. Growth in multicellular organisms occurs by:
(A) Increase in mass only
(B) Increase in cell number only
(C) Increase in cell size
(D) Increase in cell number and mass
Answer: (D)
Q11. Which of the following can be described as ‘interbreeding natural population’?
(A) Genus
(B) Species
(C) Class
(D) Order
Answer: (B)
Q12. The label on a herbarium sheet does NOT include:
(A) Local name
(B) Family
(C) Barcode
(D) Date of collection
Answer: (C)
Q13. Which one is the correct sequence of taxonomic hierarchy?
(A) Kingdom > Class > Phylum > Order > Family > Genus > Species
(B) Kingdom > Phylum > Class > Order > Family > Genus > Species
(C) Phylum > Kingdom > Class > Order > Family > Species > Genus
(D) Kingdom > Phylum > Order > Class > Family > Genus > Species
Answer: (B)
Q14. Scientific name of mango is:
(A) Mangifera indica
(B) Mangifera Indica
(C) Mangifera indica L.
(D) Mangifera indica Linn.
Answer: (C)
Q15. The first step in taxonomy is:
(A) Naming
(B) Classification
(C) Identification
(D) Taxonomic hierarchy
Answer: (C)
Q16. Which of the following features is not considered a criterion for being ‘living’?
(A) Cellular organization
(B) Consciousness
(C) Reproduction
(D) Ability to float
Answer: (D)
Q17. Which is an example of a monotypic genus?
(A) Panthera
(B) Homo
(C) Mangifera
(D) Felis
Answer: (B)
Q18. The living world can be described as:
(A) Static
(B) Evolving
(C) Uniform
(D) Discontinuous
Answer: (B)
Q19. ICZN stands for:
(A) International Code of Zoological Naming
(B) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
(C) International Council for Zoological Naming
(D) International Confederation of Zoological Naming
Answer: (B)
Q20. Reproduction is not a defining feature because:
(A) All organisms reproduce
(B) Some organisms never reproduce
(C) Reproduction is not related to living
(D) It occurs in all non-living things
Answer: (B)
Q21. Consciousness is best observed in:
(A) Animals
(B) Plants
(C) Viruses
(D) Bacteria
Answer: (A)
Q22. Flora refers to:
(A) Animal species of an area
(B) Bacterial species
(C) Plant species
(D) Aquatic organisms
Answer: (C)
Q23. All living organisms are linked to one another because:
(A) They are composed of similar elements
(B) They perform similar activities
(C) They have common genetic material
(D) All of these
Answer: (D)
Q24. Which of the following is not true for a species?
(A) Interbreeding group
(B) Similar morphological traits
(C) Common reproductive behaviour
(D) Belong to different genera
Answer: (D)
Q25. A taxon is:
(A) A group of related species
(B) A category in classification
(C) A taxonomic unit
(D) All of these
Answer: (D)
🔶 Q26. In a plant species, taxonomic hierarchy is observed as:
Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species.
Which of the following options shows the correct decrease in number of organisms but increase in similarity?
(A) Kingdom → Genus
(B) Class → Order
(C) Family → Genus
(D) Genus → Species
Answer: (D)
🔶 Q27. If two organisms belong to the same family but different genera, then:
(A) They will have similar species names
(B) They share the same genus
(C) They belong to different phyla
(D) They belong to the same order
Answer: (D)
🔶 Q28. In binomial nomenclature, the second word represents:
(A) Family
(B) Species
(C) Genus
(D) Specific epithet
Answer: (D)
🔶 Q29. Choose the correct pair for taxonomic aid and its use:
(A) Flora – Animals of a particular area
(B) Monograph – Brief description of one species
(C) Key – Used for identification
(D) Manual – For laboratory dissection
Answer: (C)
🔶 Q30. Which of the following exhibits both anabolic and catabolic processes?
(A) Dead organisms
(B) Non-living objects
(C) Living organisms
(D) Fossils
Answer: (C)
🔶 Q31. The order of classification for Homo sapiens from kingdom to species is:
(A) Animalia → Mammalia → Chordata → Primates → Hominidae → Homo → sapiens
(B) Animalia → Chordata → Mammalia → Primates → Hominidae → Homo → sapiens
(C) Animalia → Vertebrata → Mammalia → Hominidae → Primates → Homo → sapiens
(D) Animalia → Hominidae → Chordata → Mammalia → Primates → Homo → sapiens
Answer: (B)
🔶 Q32. Choose the incorrect statement:
(A) All living organisms require energy
(B) Reproduction is a must for survival of individual
(C) Viruses are considered living only when inside host
(D) Growth is an irreversible increase
Answer: (B)
🔶 Q33. Metabolic reactions can also be studied in:
(A) Non-living systems
(B) In vitro systems
(C) Living tissues only
(D) Only during growth
Answer: (B)
🔶 Q34. Which of the following terms is NOT associated with systematics?
(A) Evolutionary relationships
(B) Identification
(C) Nomenclature
(D) Pathology
Answer: (D)
🔶 Q35. Select the correct increasing order of taxonomic categories:
(A) Genus < Family < Order < Class
(B) Family < Genus < Order < Class
(C) Species < Genus < Family < Class
(D) Class < Order < Family < Genus
Answer: (C)
🔶 Q36. The function of a key in taxonomy is:
(A) To provide genetic information
(B) To identify organisms
(C) To describe habitats
(D) To list species alphabetically
Answer: (B)
🔶 Q37. Taxonomic aids do not include:
(A) Flora
(B) Monographs
(C) Encyclopedias
(D) Herbaria
Answer: (C)
🔶 Q38. Match the following and choose the correct combination:
Herbarium – a. List of names
Flora – b. Book on a single taxon
Monograph – c. Dry pressed plant specimens
Catalogue – d. Area-wise plant description
(A) 1–c, 2–d, 3–b, 4–a
(B) 1–b, 2–c, 3–a, 4–d
(C) 1–d, 2–b, 3–c, 4–a
(D) 1–c, 2–a, 3–d, 4–b
Answer: (A)
🔶 Q39. Which is NOT a correct characteristic of living beings?
(A) Cellular structure
(B) Consciousness
(C) Locomotion
(D) Metabolism
Answer: (C)
🔶 Q40. Which of the following cannot reproduce?
(A) Mules
(B) Amoeba
(C) Fungi
(D) Algae
Answer: (A)
🟥 Q41. An organism grows in mass but does not reproduce or show consciousness. It undergoes chemical reactions. Which category does it belong to?
(A) Living
(B) Non-living
(C) Dead
(D) Borderline
Answer: (D)
🟥 Q42. Consciousness is the most evolved feature observed in:
(A) Unicellular organisms
(B) Plants
(C) Humans
(D) Bacteria
Answer: (C)
🟥 Q43. Assertion (A): Metabolism is a defining feature of all living organisms.
Reason (R): All metabolic reactions can only occur inside living cells.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, R is false
(D) A is false, R is true
Answer: (B)
🟥 Q44. Assertion (A): Viruses are non-living outside a host body.
Reason (R): They can carry out metabolic functions only in host cells.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, R is false
(D) A is false, R is true
Answer: (A)
🟥 Q45. Which is a correct feature of ‘species’?
(A) Group of different organisms living together
(B) Interbreeding population
(C) Plants growing in the same area
(D) Set of individuals with different genetic traits
Answer: (B)
🟥 Q46. Choose the odd one out:
(A) Key
(B) Flora
(C) Virus
(D) Manual
Answer: (C)
🟥 Q47. Which of the following processes is not always associated with life?
(A) Growth
(B) Reproduction
(C) Metabolism
(D) Consciousness
Answer: (B)
🟥 Q48. A group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring is called:
(A) Genus
(B) Species
(C) Family
(D) Order
Answer: (B)
🟥 Q49. Which taxonomic category includes organisms more similar than those in a class?
(A) Kingdom
(B) Phylum
(C) Family
(D) Order
Answer: (D)
🟥 Q50. A preserved plant specimen with its taxonomic label is stored in a:
(A) Zoological park
(B) Herbarium
(C) Museum
(D) Aquarium
Answer: (B)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
