Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 15: Body Fluids and Circulation
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌱✨ Introduction
🧠 Circulation is the process of transporting materials (nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes) throughout the body.
🌿 In multicellular organisms like humans, body fluids (🩸 blood and 💧 lymph) serve as transport media.
⚙️ A pumping organ (heart) and a network of vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries) ensure efficient distribution.
💡 Concept:
➡️ Blood = main fluid for transport
➡️ Lymph = secondary fluid for drainage and immunity
📘 This chapter explains composition of body fluids, structure of heart, mechanism of circulation, and regulation.
🩸 Body Fluids
🧬 1️⃣ Blood

A connective tissue composed of plasma and formed elements.
🧪 (a) Plasma
Straw-colored fluid (~55% of blood)
90–92% water + 6–8% proteins (albumin, globulin, fibrinogen) + ions, glucose, hormones
Functions:
Transport of nutrients, gases, wastes
Maintain osmotic pressure
Blood clotting and immunity
✏️ Note: Fibrinogen → clotting; Albumin → osmotic balance; Globulins → defense.
🧫 (b) Formed Elements
🩸 45% of blood; consist of:
1️⃣ Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Biconcave, enucleated cells (in mammals)
Contain hemoglobin (Hb) — oxygen carrier
Life span: ~120 days; destroyed in spleen (graveyard of RBCs)
Formed in bone marrow
Function: O₂ transport
2️⃣ Leukocytes (WBCs)
Nucleated, colorless, defense cells
Types:
Granulocytes: Neutrophils (phagocytosis), Eosinophils (allergy), Basophils (histamine release)
Agranulocytes: Lymphocytes (immunity), Monocytes (phagocytosis)
Function: Immunity
3️⃣ Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Small fragments, no nucleus
Lifespan: 7–10 days
Help in blood clotting
Count: 1.5–3 lakh/mm³
💡 Concept: Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets = Whole blood
💧 2️⃣ Lymph (Tissue Fluid)
Formed from plasma leaking out of capillaries
Lacks RBC, has WBC (lymphocytes)
Flows in lymph vessels
Functions:
Transport of fat (from intestine)
Returns excess fluid to blood
Role in defense
✏️ Note: Lymphatic system maintains fluid balance and immunity.
🫀 Human Circulatory System
🧠 Closed circulatory system with heart, blood vessels, valves.
🩸 Blood flows in fixed pathways, ensuring controlled pressure.

❤️ Structure of Human Heart

📘 Location: Thoracic cavity, between lungs
🧩 Size: Fist-sized, ~300 g
💡 Covering: Pericardium with pericardial fluid
🫀 Four chambers:
Right atrium (RA)
Right ventricle (RV)
Left atrium (LA)
Left ventricle (LV)
💡 Valves:
Tricuspid – between RA & RV
Bicuspid (Mitral) – between LA & LV
Semilunar valves – at exits of ventricles
🧬 Function: Prevent backflow; ensure unidirectional flow.
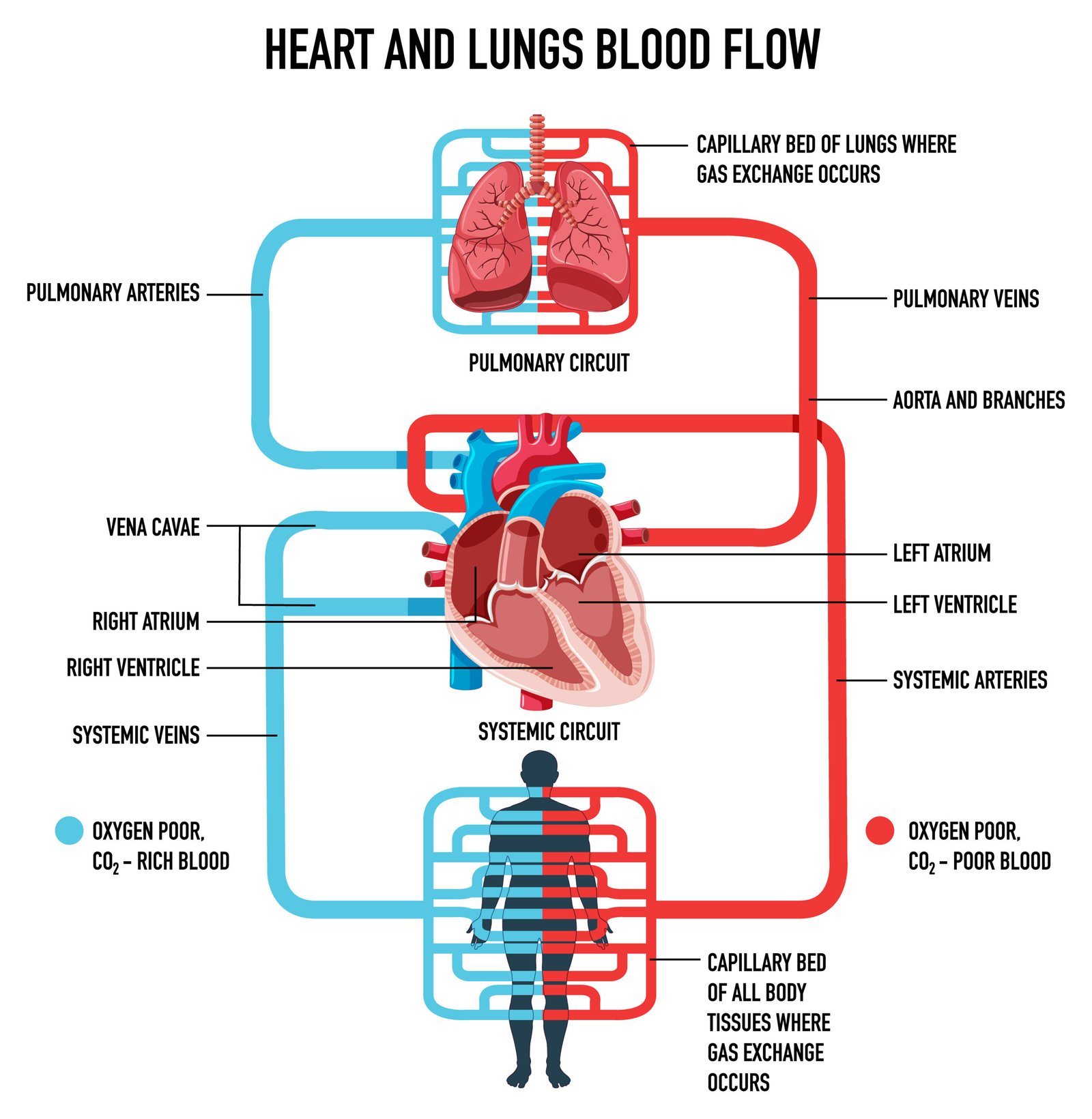
💨 Blood Flow Pathway
1️⃣ Deoxygenated blood:
Body → vena cava → RA → tricuspid → RV → pulmonary artery → lungs
2️⃣ Oxygenated blood:
Lungs → pulmonary veins → LA → bicuspid → LV → aorta → body
💡 Concept: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood; pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood.
🔁 Circulation Types
🌀 1️⃣ Pulmonary Circulation
Blood between heart ↔ lungs
Enables gas exchange
🌍 2️⃣ Systemic Circulation
Blood between heart ↔ body tissues
Delivers O₂, removes CO₂
💡 Double circulation = Pulmonary + Systemic
➡️ Maintains complete separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood (in mammals).
⚙️ Cardiac Cycle
🧠 Sequence of events in one heartbeat (~0.8 sec):
1️⃣ Atrial systole – atria contract, blood → ventricles
2️⃣ Ventricular systole – ventricles contract, blood → arteries
3️⃣ Joint diastole – relaxation, chambers fill
🫀 Heart rate: ~72 beats/min
💓 Stroke volume: ~70 mL
🩸 Cardiac output: HR × SV = 72 × 70 ≈ 5040 mL/min (~5 L/min)
✏️ Note: Cardiac output = total blood pumped per minute.
🧬 Heart Sounds
🎧 LUB – closure of AV valves (systole start)
🎧 DUB – closure of semilunar valves (systole end)
💡 Abnormal sounds → murmurs (valve defects)
⚡ Heartbeat Regulation
🧠 Myogenic heart – initiated by SA node (natural pacemaker)
SA node → generates impulse → atria contract
Impulse → AV node → Bundle of His → Purkinje fibers → ventricles contract
💡 Nervous control:
Sympathetic → increases rate
Parasympathetic → decreases rate
Adrenaline → increases rate
📈 Electrocardiogram (ECG)

🧪 Graph of electrical activity
P wave → atrial depolarization
QRS complex → ventricular depolarization
T wave → ventricular repolarization
💡 Used to diagnose cardiac abnormalities.
💉 Blood Vessels
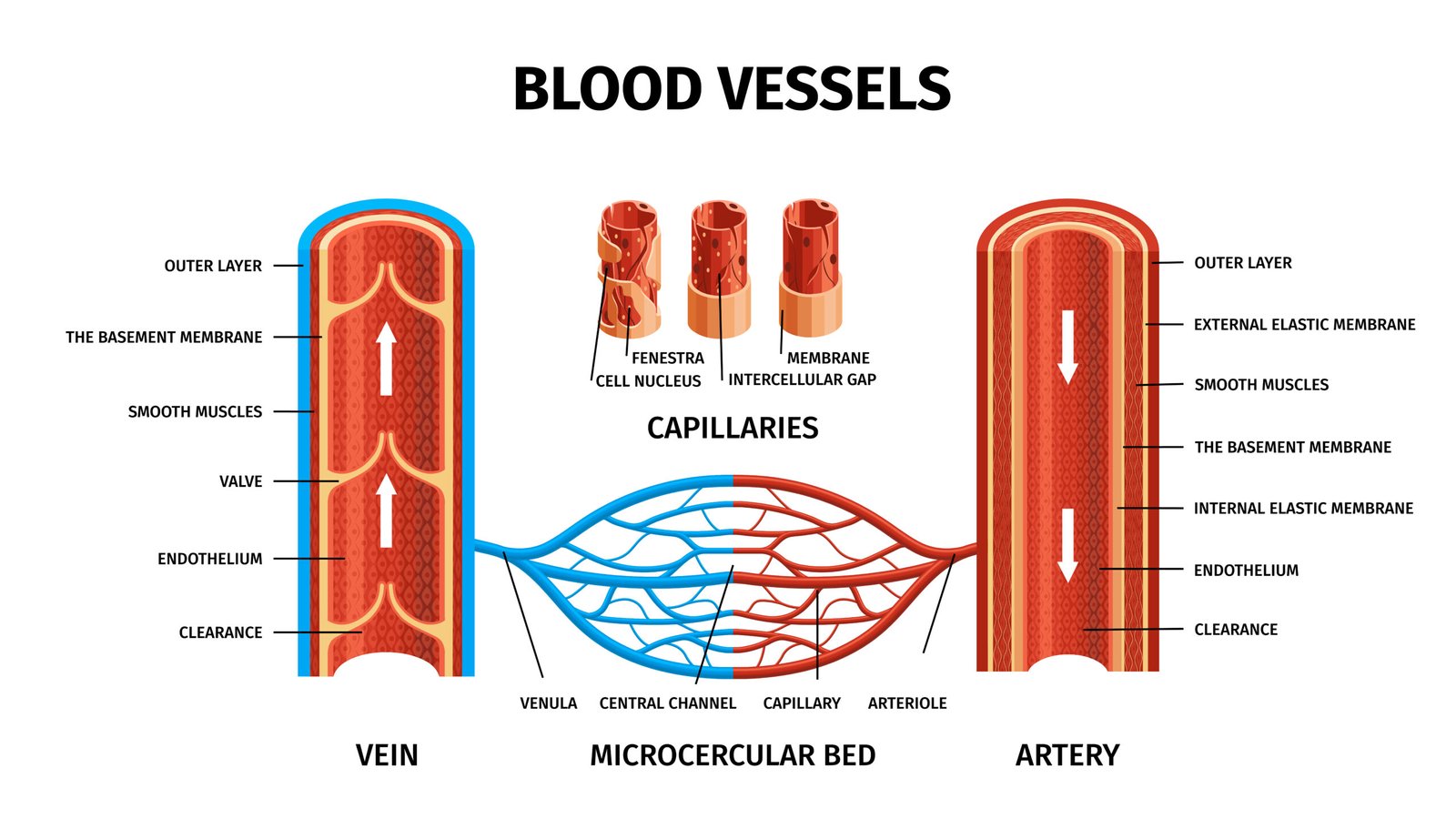
Vessel Direction Feature
Arteries Heart → body Thick wall, high pressure
Veins Body → heart Thin wall, valves, low pressure
Capillaries Between arteries & veins Thin, exchange site
✏️ Note: Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood; pulmonary vein carries oxygenated.
💧 Portal System
🧠 Blood flows through two capillary beds before returning to heart.
📘 Example: Hepatic portal system – gut → liver → vena cava
💡 Helps in nutrient regulation and detoxification.
🧪 Blood Pressure
🧠 Force exerted by blood on arterial walls
Systolic: during ventricular contraction (~120 mmHg)
Diastolic: during relaxation (~80 mmHg)
📈 Measured by sphygmomanometer
⚠️ Hypertension: >140/90 mmHg
⚠️ Hypotension: <90/60 mmHg
🧠 Regulation of Cardiac Activity
📘 Controlled by nervous and hormonal systems
Medulla oblongata – cardiac center
Hormones – adrenaline, noradrenaline
Baroreceptors – detect pressure changes
Chemoreceptors – sense pO₂, pCO₂
💡 Maintains stable cardiac output and blood supply.
🧬 Disorders
1️⃣ Hypertension: High BP → heart strain
2️⃣ Coronary artery disease (CAD): plaque buildup
3️⃣ Angina pectoris: temporary chest pain
4️⃣ Myocardial infarction: heart attack due to blockage
5️⃣ Heart failure: inefficient pumping
💡 Lifestyle, diet, and stress affect heart health.
🌍 Importance of Circulation
🩸 Delivers O₂, nutrients
💨 Removes CO₂, wastes
⚡ Distributes hormones
🧠 Maintains homeostasis
🌿 Defends via immune cells
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
❤️ Core understanding of human physiology
🧠 Foundation for medicine, nursing, diagnostics
📊 Explains blood tests, ECG, BP readings
⚙️ Key for understanding diseases and lifestyle management
📝 Quick Recap
🩸 Blood = plasma + cells
💧 Lymph = tissue fluid + WBC
🫀 Heart = 4 chambers, valves
🔁 Double circulation = pulmonary + systemic
⚙️ Cardiac cycle = systole + diastole
🎧 Heart sounds: LUB, DUB
📈 ECG = electrical activity
💉 BP = 120/80 mmHg
🧠 SA node = pacemaker
🩺 Disorders: Hypertension, CAD, MI
📘 Summary
The human circulatory system transports essential materials via blood and lymph. Blood consists of plasma and formed elements. The heart, a four-chambered pump, ensures double circulation—oxygenated and deoxygenated blood remain separate. The cardiac cycle coordinates contraction and relaxation, producing heart sounds and measurable blood pressure. SA node initiates impulses, regulated by neural and hormonal signals. ECG traces electrical activity. Disorders like hypertension, angina, and heart attack emphasize the need for cardiovascular health. Circulation sustains life by maintaining homeostasis, transport, and defense.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Formed elements:
🌿 Erythrocytes (RBCs): Transport of oxygen using haemoglobin.
🌸 Leucocytes (WBCs): Defence and immunity.
• Granulocytes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
• Agranulocytes: lymphocytes, monocytes.
⚗️ Platelets (Thrombocytes): Help in blood clotting.
✔️ Together, they form about 45% of blood volume.
🔵 Question 2. What is the importance of plasma proteins?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Plasma proteins perform vital roles:
Albumins – Maintain osmotic balance and blood volume.
Globulins – Provide immunity (antibodies).
Fibrinogen – Essential for blood clotting.
✔️ Also transport hormones and lipids.
🔵 Question 3. Match Column I with Column II:
Column I Column II
(a) Eosinophils (iii) Resist infections
(b) RBC (v) Gas transport
(c) AB Group (ii) Universal recipient
(d) Platelets (i) Coagulation
(e) Systole (iv) Contraction of heart
🧠 Correct match:
(a)-(iii), (b)-(v), (c)-(ii), (d)-(i), (e)-(iv)
🔵 Question 4. Why do we consider blood as a connective tissue?
🟢 Answer:
🩸 Blood is a connective tissue because:
It originates from mesoderm (like other connective tissues).
Has cells (RBC, WBC, platelets) suspended in matrix (plasma).
Connects different organs by transporting materials (O₂, CO₂, nutrients, hormones).
✔️ Provides integration and regulation.
🔵 Question 5. What is the difference between lymph and blood?
🟢 Answer:
Feature Blood Lymph
Colour Red (haemoglobin) Colourless
RBC Present Absent
Platelets Present Few
Function Transport gases, nutrients Return interstitial fluid, immunity
Circulation Closed Open-ended vessels
✔️ Lymph carries lymphocytes and returns tissue fluid to blood.
🔵 Question 6. What is meant by double circulation? What is its significance?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Double circulation: Blood passes twice through heart in one complete cycle —
Pulmonary circulation (heart → lungs → heart)
Systemic circulation (heart → body → heart)
💡 Significance:
Prevents mixing of O₂ and CO₂ blood.
Maintains high oxygen supply.
Efficient for warm-blooded animals.
🔵 Question 7. Write the differences between:
🧪 (a) Blood and Lymph — (see Q5)
(b) 🌸 Open and Closed system of circulation
Feature Open Closed
Flow Blood flows into spaces Blood confined in vessels
Pressure Low High
Example Arthropods Vertebrates
(c) 🌿 Systole and Diastole
Feature Systole Diastole
Action Contraction of heart Relaxation of heart
Pressure High Low
Purpose Pumps blood out Allows filling
(d) 💡 P-wave and T-wave
Wave Description
P-wave Atrial depolarization (contraction)
T-wave Ventricular repolarization (relaxation)
🔵 Question 8. Describe the evolutionary change in the pattern of heart among the vertebrates.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Evolution shows increasing separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood:
🐟 Fish – 2-chambered (1 auricle, 1 ventricle)
🐸 Amphibians – 3-chambered (2 auricles, 1 ventricle)
🐍 Reptiles – Incomplete 4-chambered
🐦🐘 Birds and mammals – Complete 4-chambered heart
✔️ Improves efficiency of oxygen transport and temperature regulation.
🔵 Question 9. Why do we call our heart myogenic?
🟢 Answer:
🫀 Human heart’s contractions originate within cardiac muscles themselves, not from nerves.
💡 The SA node generates impulses → automatic rhythmicity.
✔️ Hence, heart is myogenic.
🔵 Question 10. Sino-atrial node is called the pacemaker of our heart. Why?
🟢 Answer:
🧠 SA node (in right atrium) generates electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat.
➡️ Sets rhythm and rate of contraction.
✔️ Therefore called natural pacemaker.
🔵 Question 11. What is the significance of atrio-ventricular node and atrio-ventricular bundle in the functioning of heart?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 AV node receives impulse from SA node and delays it slightly for atrial contraction.
⚡ AV bundle (Bundle of His) conducts impulse to ventricles via Purkinje fibres → coordinated contraction.
✔️ Ensures sequential atrial → ventricular contraction.
🔵 Question 12. Define a cardiac cycle and the cardiac output.
🟢 Answer:
🫀 Cardiac cycle: Sequence of one complete heartbeat (atrial + ventricular systole and diastole).
⏱ Duration ≈ 0.8 sec.
💡 Cardiac output: Volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute.
📏 CO = Stroke volume × Heart rate
= 70 mL × 72/min ≈ 5 L/min
🔵 Question 13. Explain heart sounds.
🟢 Answer:
🧠 Two main sounds:
‘Lub’ – closure of AV valves (beginning of systole)
‘Dub’ – closure of semilunar valves (end of systole)
✔️ Abnormal sounds = heart murmurs.
🔵 Question 14. Draw a standard ECG and explain the different segments in it.
🟢 Answer:
🩺 Electrocardiogram (ECG): Graphical record of electrical activity of heart.
Waves:
P-wave: Atrial depolarization
QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization
T-wave: Ventricular repolarization
💡 PR interval: Atrial contraction and conduction delay
ST segment: Plateau phase of ventricular contraction
✔️ Used clinically to detect heart abnormalities.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
Which is the chief circulating fluid in human body?
🔴1️⃣ Lymph
🟢2️⃣ Blood
🟡3️⃣ Plasma
🔵4️⃣ Serum
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Blood
🔴 Question 2:
The fluid matrix of blood is called —
🔴1️⃣ Lymph
🟢2️⃣ Plasma
🟡3️⃣ Serum
🔵4️⃣ Tissue fluid
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Plasma
🔴 Question 3:
Which blood cells are responsible for immunity?
🔴1️⃣ RBC
🟢2️⃣ WBC
🟡3️⃣ Platelets
🔵4️⃣ All of these
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ WBC
🔴 Question 4:
Which component helps in blood clotting?
🔴1️⃣ RBC
🟢2️⃣ Platelets
🟡3️⃣ WBC
🔵4️⃣ Plasma
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Platelets
🔴 Question 5:
Universal donor blood group is —
🔴1️⃣ AB
🟢2️⃣ O
🟡3️⃣ A
🔵4️⃣ B
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ O
🔴 Question 6:
Universal recipient blood group is —
🔴1️⃣ A
🟢2️⃣ AB
🟡3️⃣ O
🔵4️⃣ B
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ AB
🔴 Question 7:
The pacemaker of human heart is —
🔴1️⃣ AV node
🟢2️⃣ SA node
🟡3️⃣ Purkinje fibres
🔵4️⃣ Bundle of His
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ SA node
🔴 Question 8:
Normal blood pressure in humans is —
🔴1️⃣ 80/120 mmHg
🟢2️⃣ 120/80 mmHg
🟡3️⃣ 100/60 mmHg
🔵4️⃣ 140/90 mmHg
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 120/80 mmHg
🔴 Question 9:
Pulmonary vein carries —
🔴1️⃣ Deoxygenated blood from lungs
🟢2️⃣ Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🟡3️⃣ Deoxygenated blood from heart
🔵4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🔴 Question 10:
Which valve prevents backflow of blood from ventricles to atria?
🔴1️⃣ Semilunar valve
🟢2️⃣ Atrioventricular valve
🟡3️⃣ Pulmonary valve
🔵4️⃣ Aortic valve
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Atrioventricular valve
🔴 Question 11:
Define plasma.
🟢 Answer:
The liquid matrix of blood containing water, proteins, salts, hormones, and nutrients (~55% of blood volume).
🔴 Question 12:
Name the types of blood corpuscles.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ RBC (Erythrocytes) – transport O₂
2️⃣ WBC (Leucocytes) – immunity
3️⃣ Platelets (Thrombocytes) – clotting
🔴 Question 13:
List the main components of blood and their functions.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Plasma (55%) — Liquid part carrying nutrients, hormones, wastes.
2️⃣ RBCs (Erythrocytes) — Transport oxygen using haemoglobin ❤️.
3️⃣ WBCs (Leucocytes) — Provide immunity 🧠.
4️⃣ Platelets (Thrombocytes) — Help in blood clotting 🩸.
💡 Together, they maintain homeostasis and transport essential substances.
🔴 Question 14:
Differentiate between open and closed circulatory systems.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Open Closed
Blood flow In body cavities In vessels
Pressure Low High
Exchange Direct with tissues Through capillaries
Example Arthropods Vertebrates
💡 Humans have a closed circulatory system.
🔴 Question 15:
Write short notes on plasma and lymph.
🟢 Answer:
Plasma:
– Fluid part of blood (90–92% water).
– Contains proteins (albumin, fibrinogen), nutrients, hormones.
– Function: Transport of substances.
Lymph:
– Tissue fluid formed from blood plasma.
– Contains WBCs (mainly lymphocytes).
– Function: Immunity, fat absorption (via lacteals).
🔴 Question 16:
Describe the structure of human heart.
🟢 Answer:
Four-chambered organ (2 atria + 2 ventricles).
Right side: Deoxygenated blood; Left side: Oxygenated blood.
Valves:
– Tricuspid: Right atrium–ventricle
– Bicuspid (mitral): Left atrium–ventricle
– Semilunar valves: At pulmonary artery and aorta.
💡 Functions as a double pump maintaining circulation.
🔴 Question 17:
What is double circulation? Explain its significance.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Blood passes through the heart twice in one complete cycle.
Types:
1️⃣ Pulmonary circulation: Heart → lungs → heart.
2️⃣ Systemic circulation: Heart → body → heart.
Significance:
✔️ Separates oxygenated & deoxygenated blood.
✔️ Maintains high efficiency in mammals.
🔴 Question 18:
Explain the cardiac cycle briefly.
🟢 Answer:
Steps:
1️⃣ Atrial systole: Atria contract → blood to ventricles.
2️⃣ Ventricular systole: Ventricles contract → blood to aorta & pulmonary artery.
3️⃣ Joint diastole: All chambers relax → blood fills again.
Duration: ~0.8 sec.
💡 Ensures continuous and rhythmic blood flow.
🔴 Question 19:
What are heart sounds? How are they produced?
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ ‘Lub’ – Closure of AV valves (tricuspid & bicuspid) during ventricular systole.
2️⃣ ‘Dub’ – Closure of semilunar valves during diastole.
💡 Heard by stethoscope; indicate proper functioning of valves.
🔴 Question 20:
Explain the composition and function of lymph.
🟢 Answer:
Composition: Clear fluid with WBCs, no RBCs or platelets, low protein.
Functions:
1️⃣ Transport of fat from intestine (via lacteals).
2️⃣ Return of interstitial fluid to blood.
3️⃣ Role in immunity (lymphocytes).
🔴 Question 21:
Describe the conduction system of the heart.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ SA node (pacemaker): Initiates impulse → atrial contraction.
2️⃣ AV node: Receives impulse → passes to ventricles.
3️⃣ Bundle of His & Purkinje fibres: Distribute impulse → ventricular contraction.
💡 Ensures rhythmic coordinated heartbeat. ❤️
🔴 Question 22:
What is ECG? State its components.
🟢 Answer:
ECG (Electrocardiogram): Graphical record of electrical activity of heart.
Components:
1️⃣ P wave: Atrial depolarization.
2️⃣ QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization.
3️⃣ T wave: Ventricular repolarization.
💡 Used for diagnosis of cardiac disorders.
🔴 Question 23:
Explain the mechanism of blood clotting.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Protective mechanism to prevent blood loss from injured vessels.
Steps:
1️⃣ Injury to blood vessel → Platelets release thromboplastin.
2️⃣ Thromboplastin + Ca²⁺ + clotting factors → Converts prothrombin → thrombin.
3️⃣ Thrombin converts fibrinogen → fibrin (insoluble threads).
4️⃣ Fibrin mesh traps RBCs and forms clot 🩸.
Result: Bleeding stops; wound heals.
💡 Vitamin K essential for synthesis of prothrombin.
🔴 Question 24:
Describe the cardiac cycle in detail.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Atrial systole (0.1 s): Atria contract → blood flows into ventricles.
2️⃣ Ventricular systole (0.3 s): Ventricles contract → AV valves close (lub), semilunar valves open → blood enters aorta & pulmonary artery.
3️⃣ Joint diastole (0.4 s): All chambers relax → semilunar valves close (dub); blood flows from veins to atria.
Total duration: ~0.8 sec per cycle.
Heart rate: ~72/min = 72 × 0.8 = 57.6 sec ≈ 1 min.
💡 Ensures unidirectional blood flow ❤️.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain the structure of human heart with labelled flow of blood.
🟢 Answer:
Four chambers:
– Right atrium & ventricle: Receive and pump deoxygenated blood.
– Left atrium & ventricle: Receive and pump oxygenated blood.
Blood flow:
1️⃣ Vena cava → Right atrium → Tricuspid valve → Right ventricle
2️⃣ Pulmonary artery → Lungs → Oxygenation
3️⃣ Pulmonary vein → Left atrium → Bicuspid valve → Left ventricle
4️⃣ Aorta → Body tissues
Valves prevent backflow.
💡 Heart works as double pump maintaining circulation.
🔴 Question 26:
Differentiate between pulmonary and systemic circulation.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Pulmonary Circulation Systemic Circulation
Path Heart → Lungs → Heart Heart → Body → Heart
Function Oxygenation of blood Supply of O₂ & nutrients
Blood type Deoxygenated → Oxygenated Oxygenated → Deoxygenated
Vessels Pulmonary artery & vein Aorta & venae cavae
💡 Together form double circulation ensuring complete separation of blood.
🔴 Question 27:
Explain the regulation of cardiac activity.
🟢 Answer:
Myogenic heart: Initiates its own impulse via SA node.
Autonomic control:
– Sympathetic nerves: Increase heart rate (tachycardia).
– Parasympathetic (vagus) nerves: Decrease heart rate (bradycardia).
Hormonal control: Adrenaline & noradrenaline ↑ heart rate.
Medullary centre: Integrates responses to CO₂, BP.
✅ Ensures heart adjusts to body’s metabolic demands.
🔴 Question 28:
Discuss ECG and its clinical significance.
🟢 Answer:
ECG (Electrocardiogram): Graphical record of electrical activity of heart.
Waves:
1️⃣ P wave: Atrial depolarization.
2️⃣ QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization.
3️⃣ T wave: Ventricular repolarization.
Significance:
✔️ Detects irregular heartbeat, blockages.
✔️ Diagnoses myocardial infarction, arrhythmia.
💡 Non-invasive tool for cardiac diagnosis.
🔴 Question 29:
Describe the ABO blood group system.
🟢 Answer:
Based on antigens (A, B) on RBCs & antibodies in plasma.
Group Antigen Antibody Donates to Receives from
A A Anti-B A, AB A, O
B B Anti-A B, AB B, O
AB A & B None AB All (universal recipient)
O None Anti-A & Anti-B All (universal donor) O
💡 Compatibility essential for safe transfusion.
🔴 Question 30:
Write short notes on common cardiovascular disorders.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Hypertension: High BP (>140/90 mmHg); damages arteries.
2️⃣ Coronary artery disease (CAD): Fat deposition narrows arteries.
3️⃣ Angina pectoris: Chest pain due to low O₂ supply.
4️⃣ Heart failure: Inability to pump adequate blood.
5️⃣ Atherosclerosis: Cholesterol buildup; reduces elasticity.
💡 Lifestyle management & medication prevent risks.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The universal donor blood group is
🟡 A. AB⁺
🟡 B. AB⁻
🟡 C. O⁺
🟡 D. O⁻
🟢 Answer: D. O⁻
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q2. The universal recipient blood group is
🟡 A. O⁺
🟡 B. AB⁺
🟡 C. A⁺
🟡 D. B⁺
🟢 Answer: B. AB⁺
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q3. The respiratory pigment of vertebrate blood is
🟡 A. Hemocyanin
🟡 B. Hemerythrin
🟡 C. Hemoglobin
🟡 D. Myoglobin
🟢 Answer: C. Hemoglobin
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q4. Which blood component helps in clotting?
🟡 A. RBC
🟡 B. WBC
🟡 C. Platelets
🟡 D. Plasma proteins only
🟢 Answer: C. Platelets
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q5. The normal human heart beat rate is about
🟡 A. 60/min
🟡 B. 72/min
🟡 C. 90/min
🟡 D. 100/min
🟢 Answer: B. 72/min
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q6. Which valve prevents backflow of blood from right ventricle to right atrium?
🟡 A. Bicuspid valve
🟡 B. Tricuspid valve
🟡 C. Semilunar valve
🟡 D. Mitral valve
🟢 Answer: B. Tricuspid valve
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q7. The pulmonary artery carries
🟡 A. Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🟡 B. Deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
🟡 C. Deoxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🟡 D. Oxygenated blood from heart to lungs
🟢 Answer: B. Deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q8. The heart sound “lub” is produced by
🟡 A. Closing of semilunar valves
🟡 B. Opening of semilunar valves
🟡 C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
🟡 D. Opening of atrioventricular valves
🟢 Answer: C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q9. The bundle of His is a part of
🟡 A. Nervous system
🟡 B. Circulatory conduction system
🟡 C. Lymphatic system
🟡 D. Endocrine system
🟢 Answer: B. Circulatory conduction system
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q10. SA node acts as the pacemaker because it
🟡 A. Delays impulse conduction
🟡 B. Generates the maximum number of action potentials
🟡 C. Conducts impulses rapidly
🟡 D. Has thick musculature
🟢 Answer: B. Generates the maximum number of action potentials
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q11. The blood vessel carrying oxygenated blood from lungs to heart is
🟡 A. Pulmonary vein
🟡 B. Pulmonary artery
🟡 C. Coronary artery
🟡 D. Aorta
🟢 Answer: A. Pulmonary vein
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q12. Double circulation means
🟡 A. Two atria and two ventricles
🟡 B. Blood passes twice through the heart in one cycle
🟡 C. Blood flows twice through lungs
🟡 D. Two systemic circuits
🟢 Answer: B. Blood passes twice through the heart in one cycle
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q13. The ECG wave corresponding to ventricular depolarisation is
🟡 A. P wave
🟡 B. QRS complex
🟡 C. T wave
🟡 D. U wave
🟢 Answer: B. QRS complex
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q14. The “dub” heart sound is caused by
🟡 A. Opening of semilunar valves
🟡 B. Closing of semilunar valves
🟡 C. Closing of AV valves
🟡 D. Opening of AV valves
🟢 Answer: B. Closing of semilunar valves
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q15. Lymph lacks
🟡 A. Plasma
🟡 B. Proteins
🟡 C. RBCs
🟡 D. WBCs
🟢 Answer: C. RBCs
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q16. The normal systolic pressure in a healthy adult is about
🟡 A. 80 mmHg
🟡 B. 100 mmHg
🟡 C. 120 mmHg
🟡 D. 140 mmHg
🟢 Answer: C. 120 mmHg
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q17. The hepatic portal vein carries blood from
🟡 A. Liver to heart
🟡 B. Kidney to heart
🟡 C. Digestive tract to liver
🟡 D. Lungs to liver
🟢 Answer: C. Digestive tract to liver
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q18. The longest vein in the human body is
🟡 A. Jugular vein
🟡 B. Pulmonary vein
🟡 C. Hepatic vein
🟡 D. Great saphenous vein
🟢 Answer: D. Great saphenous vein
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q19. Blood pressure is measured by
🟡 A. Sphygmomanometer
🟡 B. Barometer
🟡 C. Hygrometer
🟡 D. Manometer
🟢 Answer: A. Sphygmomanometer
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q20. The vascular connection between digestive tract and liver is
🟡 A. Renal portal system
🟡 B. Hepatic portal system
🟡 C. Pulmonary circuit
🟡 D. Coronary circulation
🟢 Answer: B. Hepatic portal system
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q21. Stroke volume refers to
🟡 A. Volume of blood pumped in one minute
🟡 B. Volume of blood pumped per beat by each ventricle
🟡 C. Volume of blood returning to atrium per beat
🟡 D. Residual volume in ventricles
🟢 Answer: B. Volume of blood pumped per beat by each ventricle
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q22. The volume of blood pumped out by each ventricle per minute is
🟡 A. End-systolic volume
🟡 B. Cardiac output
🟡 C. Stroke volume
🟡 D. Residual volume
🟢 Answer: B. Cardiac output
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q23. The condition of low blood pressure is called
🟡 A. Hypertension
🟡 B. Hypotension
🟡 C. Atherosclerosis
🟡 D. Arrhythmia
🟢 Answer: B. Hypotension
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q24. Which blood cells are phagocytic in nature?
🟡 A. Eosinophils
🟡 B. Basophils
🟡 C. Neutrophils and monocytes
🟡 D. Lymphocytes
🟢 Answer: C. Neutrophils and monocytes
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q25. The function of lymph nodes is to
🟡 A. Transport oxygen
🟡 B. Filter lymph and activate immune responses
🟡 C. Store RBCs
🟡 D. Produce platelets
🟢 Answer: B. Filter lymph and activate immune responses
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q26. The opening between right atrium and right ventricle is guarded by
🟡 A. Bicuspid valve
🟡 B. Tricuspid valve
🟡 C. Semilunar valve
🟡 D. Aortic valve
🟢 Answer: B. Tricuspid valve
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q27. The closing of semilunar valves produces the
🟡 A. First heart sound (lub)
🟡 B. Second heart sound (dub)
🟡 C. Murmur sound
🟡 D. Pacemaker impulse
🟢 Answer: B. Second heart sound (dub)
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q28. The lymphatic system returns excess tissue fluid to
🟡 A. Right atrium
🟡 B. Left ventricle
🟡 C. Venous blood circulation
🟡 D. Arterial blood circulation
🟢 Answer: C. Venous blood circulation
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q29. Coronary arteries supply blood to the
🟡 A. Lungs
🟡 B. Liver
🟡 C. Heart muscle
🟡 D. Kidney
🟢 Answer: C. Heart muscle
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q30. Erythropoietin hormone stimulates production of
🟡 A. Platelets
🟡 B. Lymphocytes
🟡 C. Erythrocytes
🟡 D. Neutrophils
🟢 Answer: C. Erythrocytes
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q31. The blood vessel carrying blood from the heart to the lungs is
🟡 A. Pulmonary artery
🟡 B. Pulmonary vein
🟡 C. Aorta
🟡 D. Coronary vein
🟢 Answer: A. Pulmonary artery
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q32. Which blood cells are involved in immune responses?
🟡 A. RBCs
🟡 B. WBCs
🟡 C. Platelets
🟡 D. Erythrocytes
🟢 Answer: B. WBCs
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q33. The nodal tissue in the lower right atrium that relays impulses is
🟡 A. SA node
🟡 B. AV node
🟡 C. Bundle of His
🟡 D. Purkinje fibres
🟢 Answer: B. AV node
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q34. Which layer of the heart wall is responsible for contraction?
🟡 A. Endocardium
🟡 B. Myocardium
🟡 C. Epicardium
🟡 D. Pericardium
🟢 Answer: B. Myocardium
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q35. The blood group having no antigens on RBCs is
🟡 A. AB
🟡 B. A
🟡 C. O
🟡 D. B
🟢 Answer: C. O
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q36. Pulmonary veins carry
🟡 A. Deoxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🟡 B. Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
🟡 C. Deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
🟡 D. Oxygenated blood from heart to lungs
🟢 Answer: B. Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q37. Which component of blood helps in maintaining osmotic balance and pH?
🟡 A. Platelets
🟡 B. Plasma proteins
🟡 C. WBCs
🟡 D. RBCs
🟢 Answer: B. Plasma proteins
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q38. Cardiac output is calculated by
🟡 A. Stroke volume × Heart rate
🟡 B. Blood pressure × Stroke volume
🟡 C. Heart rate ÷ Stroke volume
🟡 D. Vital capacity × Heart rate
🟢 Answer: A. Stroke volume × Heart rate
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q39. The normal diastolic pressure in humans is
🟡 A. 60 mmHg
🟡 B. 80 mmHg
🟡 C. 100 mmHg
🟡 D. 120 mmHg
🟢 Answer: B. 80 mmHg
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q40. Which blood group has both A and B antigens but no antibodies?
🟡 A. AB
🟡 B. O
🟡 C. B
🟡 D. A
🟢 Answer: A. AB
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q41. The pacemaker of the heart is
🟡 A. AV node
🟡 B. SA node
🟡 C. Bundle of His
🟡 D. Purkinje fibres
🟢 Answer: B. SA node
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q42. The duct that drains lymph into venous blood is
🟡 A. Coronary sinus
🟡 B. Thoracic duct
🟡 C. Hepatic portal vein
🟡 D. Pulmonary vein
🟢 Answer: B. Thoracic duct
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q43. Which blood vessel has the thickest muscular wall?
🟡 A. Veins
🟡 B. Venules
🟡 C. Arteries
🟡 D. Capillaries
🟢 Answer: C. Arteries
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q44. The condition where the blood clot inside a blood vessel obstructs circulation is called
🟡 A. Embolism
🟡 B. Thrombosis
🟡 C. Atherosclerosis
🟡 D. Hypertension
🟢 Answer: B. Thrombosis
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q45. The pulmonary circulation begins in
🟡 A. Left ventricle
🟡 B. Right atrium
🟡 C. Right ventricle
🟡 D. Left atrium
🟢 Answer: C. Right ventricle
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q46. Lymph differs from blood in lacking
🟡 A. Plasma proteins
🟡 B. RBCs and platelets
🟡 C. WBCs
🟡 D. Water
🟢 Answer: B. RBCs and platelets
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q47. The closing of atrioventricular valves corresponds to
🟡 A. Ventricular systole
🟡 B. Ventricular diastole
🟡 C. Atrial systole
🟡 D. Atrial diastole
🟢 Answer: A. Ventricular systole
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q48. Coronary circulation supplies blood to
🟡 A. Lungs
🟡 B. Heart muscles
🟡 C. Kidneys
🟡 D. Brain
🟢 Answer: B. Heart muscles
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q49. Which cells in the blood release histamine during allergic reactions?
🟡 A. Neutrophils
🟡 B. Lymphocytes
🟡 C. Basophils
🟡 D. Monocytes
🟢 Answer: C. Basophils
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q50. Pulmonary veins carry blood to
🟡 A. Lungs
🟡 B. Right atrium
🟡 C. Left atrium
🟡 D. Left ventricle
🟢 Answer: C. Left atrium
📅 NEET 2016
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
The fluid connective tissue is:
🔴 1️⃣ Blood
🟢 2️⃣ Lymph
🟡 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 4️⃣ Plasma only
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Both 1 and 2
🔵 Question 2:
Plasma constitutes about __ of total blood volume:
🔴 1️⃣ 35%
🟢 2️⃣ 45%
🟡 3️⃣ 55%
🔵 4️⃣ 65%
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 55%
🔵 Question 3:
Which component of blood helps in clotting?
🔴 1️⃣ RBC
🟢 2️⃣ WBC
🟡 3️⃣ Platelets
🔵 4️⃣ Plasma
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Platelets
🔵 Question 4:
The oxygen-carrying pigment in blood is:
🔴 1️⃣ Haemocyanin
🟢 2️⃣ Haemoglobin
🟡 3️⃣ Myoglobin
🔵 4️⃣ Chlorocruorin
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Haemoglobin
🔵 Question 5:
Life span of RBC is:
🔴 1️⃣ 60 days
🟢 2️⃣ 90 days
🟡 3️⃣ 120 days
🔵 4️⃣ 180 days
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ 120 days
🔵 Question 6:
The process of formation of RBC is called:
🔴 1️⃣ Erythrolysis
🟢 2️⃣ Erythropoiesis
🟡 3️⃣ Haemopoiesis
🔵 4️⃣ Leucopoiesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Erythropoiesis
🔵 Question 7:
Which organ destroys old RBCs?
🔴 1️⃣ Kidney
🟢 2️⃣ Liver
🟡 3️⃣ Spleen
🔵 4️⃣ Bone marrow
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Spleen
🔵 Question 8:
Universal donor blood group is:
🔴 1️⃣ A
🟢 2️⃣ B
🟡 3️⃣ AB
🔵 4️⃣ O
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ O
🔵 Question 9:
Universal recipient blood group is:
🔴 1️⃣ A
🟢 2️⃣ B
🟡 3️⃣ AB
🔵 4️⃣ O
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ AB
🔵 Question 10:
Rh factor was discovered in:
🔴 1️⃣ Rabbit
🟢 2️⃣ Monkey
🟡 3️⃣ Human
🔵 4️⃣ Cat
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Monkey
🔵 Question 11:
Erythroblastosis foetalis occurs when:
🔴 1️⃣ Mother is Rh⁺ and foetus is Rh⁻
🟢 2️⃣ Mother is Rh⁻ and foetus is Rh⁺
🟡 3️⃣ Both are Rh⁺
🔵 4️⃣ Both are Rh⁻
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mother is Rh⁻ and foetus is Rh⁺
🔵 Question 12:
Which blood vessel carries oxygenated blood from lungs to heart?
🔴 1️⃣ Pulmonary artery
🟢 2️⃣ Pulmonary vein
🟡 3️⃣ Aorta
🔵 4️⃣ Vena cava
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pulmonary vein
🔵 Question 13:
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs?
🔴 1️⃣ Pulmonary vein
🟢 2️⃣ Pulmonary artery
🟡 3️⃣ Aorta
🔵 4️⃣ Vena cava
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pulmonary artery
🔵 Question 14:
The heart of human is:
🔴 1️⃣ Two-chambered
🟢 2️⃣ Three-chambered
🟡 3️⃣ Four-chambered
🔵 4️⃣ Five-chambered
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Four-chambered
🔵 Question 15:
The valve between right atrium and right ventricle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Mitral valve
🟢 2️⃣ Tricuspid valve
🟡 3️⃣ Bicuspid valve
🔵 4️⃣ Semilunar valve
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Tricuspid valve
🔵 Question 16:
The valve between left atrium and left ventricle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Tricuspid valve
🟢 2️⃣ Bicuspid valve
🟡 3️⃣ Semilunar valve
🔵 4️⃣ Pulmonary valve
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bicuspid valve
🔵 Question 17:
Heart sound “lub” is produced by:
🔴 1️⃣ Closing of semilunar valves
🟢 2️⃣ Closing of AV valves
🟡 3️⃣ Opening of semilunar valves
🔵 4️⃣ Opening of AV valves
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Closing of AV valves
🔵 Question 18:
Heart sound “dub” is produced by:
🔴 1️⃣ Opening of AV valves
🟢 2️⃣ Closing of semilunar valves
🟡 3️⃣ Opening of semilunar valves
🔵 4️⃣ Opening of AV valves
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Closing of semilunar valves
🔵 Question 19:
Normal heart rate in adults is:
🔴 1️⃣ 60 beats/min
🟢 2️⃣ 72 beats/min
🟡 3️⃣ 90 beats/min
🔵 4️⃣ 120 beats/min
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 72 beats/min
🔵 Question 20:
Cardiac cycle duration is:
🔴 1️⃣ 0.5 sec
🟢 2️⃣ 0.8 sec
🟡 3️⃣ 1.0 sec
🔵 4️⃣ 1.2 sec
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 0.8 sec
🔵 Question 21:
SA node is known as:
🔴 1️⃣ Pacemaker
🟢 2️⃣ Pace setter
🟡 3️⃣ Conductor
🔵 4️⃣ Moderator band
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Pacemaker
🔵 Question 22:
AV node passes impulse to:
🔴 1️⃣ SA node
🟢 2️⃣ Bundle of His
🟡 3️⃣ Purkinje fibers
🔵 4️⃣ Ventricle
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bundle of His
🔵 Question 23:
ECG is used to study:
🔴 1️⃣ Heart sounds
🟢 2️⃣ Heart beat
🟡 3️⃣ Electrical activity of heart
🔵 4️⃣ Blood pressure
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Electrical activity of heart
🔵 Question 24:
Which wave in ECG represents atrial depolarization?
🔴 1️⃣ P wave
🟢 2️⃣ QRS complex
🟡 3️⃣ T wave
🔵 4️⃣ PR interval
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ P wave
🔵 Question 25:
Which wave in ECG represents ventricular repolarization?
🔴 1️⃣ P wave
🟢 2️⃣ QRS complex
🟡 3️⃣ T wave
🔵 4️⃣ PR interval
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ T wave
🔵 Question 26:
Which blood vessel carries blood from organs to the heart?
🔴 1️⃣ Arteries
🟢 2️⃣ Veins
🟡 3️⃣ Capillaries
🔵 4️⃣ Arterioles
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Veins
🔵 Question 27:
Which blood vessel has valves?
🔴 1️⃣ Arteries
🟢 2️⃣ Veins
🟡 3️⃣ Capillaries
🔵 4️⃣ Arterioles
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Veins
🔵 Question 28:
Which blood vessel has thick muscular walls?
🔴 1️⃣ Veins
🟢 2️⃣ Arteries
🟡 3️⃣ Capillaries
🔵 4️⃣ Venules
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Arteries
🔵 Question 29:
Which blood vessel has no muscular wall?
🔴 1️⃣ Arteries
🟢 2️⃣ Capillaries
🟡 3️⃣ Veins
🔵 4️⃣ Arterioles
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Capillaries
🔵 Question 30:
Systemic circulation begins from:
🔴 1️⃣ Left atrium
🟢 2️⃣ Left ventricle
🟡 3️⃣ Right atrium
🔵 4️⃣ Right ventricle
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Left ventricle
🔵 Question 31:
Pulmonary circulation starts from:
🔴 1️⃣ Right atrium
🟢 2️⃣ Right ventricle
🟡 3️⃣ Left atrium
🔵 4️⃣ Left ventricle
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Right ventricle
🔵 Question 32:
Blood pressure is measured by:
🔴 1️⃣ ECG
🟢 2️⃣ Sphygmomanometer
🟡 3️⃣ Stethoscope
🔵 4️⃣ Barometer
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Sphygmomanometer
🔵 Question 33:
Normal blood pressure is:
🔴 1️⃣ 80/120 mmHg
🟢 2️⃣ 120/80 mmHg
🟡 3️⃣ 140/90 mmHg
🔵 4️⃣ 100/60 mmHg
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 120/80 mmHg
🔵 Question 34:
High blood pressure is called:
🔴 1️⃣ Hypotension
🟢 2️⃣ Hypertension
🟡 3️⃣ Tachycardia
🔵 4️⃣ Bradycardia
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hypertension
🔵 Question 35:
Which of the following is not a formed element of blood?
🔴 1️⃣ RBC
🟢 2️⃣ WBC
🟡 3️⃣ Platelets
🔵 4️⃣ Plasma
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Plasma
🔵 Question 36:
Which blood component helps in defense?
🔴 1️⃣ RBC
🟢 2️⃣ WBC
🟡 3️⃣ Platelets
🔵 4️⃣ Plasma
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ WBC
🔵 Question 37:
Which type of WBC is phagocytic?
🔴 1️⃣ Neutrophil
🟢 2️⃣ Basophil
🟡 3️⃣ Eosinophil
🔵 4️⃣ Lymphocyte
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Neutrophil
🔵 Question 38:
Which WBC secretes histamine?
🔴 1️⃣ Neutrophil
🟢 2️⃣ Basophil
🟡 3️⃣ Eosinophil
🔵 4️⃣ Monocyte
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Basophil
🔵 Question 39:
The largest WBC is:
🔴 1️⃣ Neutrophil
🟢 2️⃣ Monocyte
🟡 3️⃣ Lymphocyte
🔵 4️⃣ Basophil
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Monocyte
🔵 Question 40:
Which blood component forms antibodies?
🔴 1️⃣ Monocyte
🟢 2️⃣ Lymphocyte
🟡 3️⃣ Platelet
🔵 4️⃣ Eosinophil
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lymphocyte
🔵 Question 41:
Blood clotting requires:
🔴 1️⃣ Vitamin A
🟢 2️⃣ Vitamin K
🟡 3️⃣ Vitamin D
🔵 4️⃣ Vitamin E
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Vitamin K
🔵 Question 42:
Clotting of blood occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ 1 second
🟢 2️⃣ 3–6 minutes
🟡 3️⃣ 10 minutes
🔵 4️⃣ 1 minute
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 3–6 minutes
🔵 Question 43:
Which ion is essential for blood clotting?
🔴 1️⃣ Na⁺
🟢 2️⃣ Ca²⁺
🟡 3️⃣ K⁺
🔵 4️⃣ Mg²⁺
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ca²⁺
🔵 Question 44:
Heart beat is initiated by:
🔴 1️⃣ AV node
🟢 2️⃣ SA node
🟡 3️⃣ Bundle of His
🔵 4️⃣ Purkinje fibres
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ SA node
🔵 Question 45:
Purkinje fibres are present in:
🔴 1️⃣ Atrium
🟢 2️⃣ Ventricle walls
🟡 3️⃣ SA node
🔵 4️⃣ Aorta
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ventricle walls
🔵 Question 46:
Double circulation means:
🔴 1️⃣ Blood passes twice through heart per cycle
🟢 2️⃣ Blood passes once through heart
🟡 3️⃣ Two hearts in human
🔵 4️⃣ Blood circulates in double direction
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Blood passes twice through heart per cycle
🔵 Question 47:
Which one carries blood from intestine to liver?
🔴 1️⃣ Hepatic vein
🟢 2️⃣ Hepatic portal vein
🟡 3️⃣ Hepatic artery
🔵 4️⃣ Vena cava
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Hepatic portal vein
🔵 Question 48:
The lymphatic system carries:
🔴 1️⃣ Plasma
🟢 2️⃣ Tissue fluid
🟡 3️⃣ Lymph
🔵 4️⃣ Serum
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Lymph
🔵 Question 49:
Which of the following lacks RBC?
🔴 1️⃣ Blood
🟢 2️⃣ Lymph
🟡 3️⃣ Both
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lymph
🔵 Question 50:
The lymphatic system is important for:
🔴 1️⃣ Digestion
🟢 2️⃣ Transport of fatty acids
🟡 3️⃣ Excretion
🔵 4️⃣ Respiration
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Transport of fatty acids
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
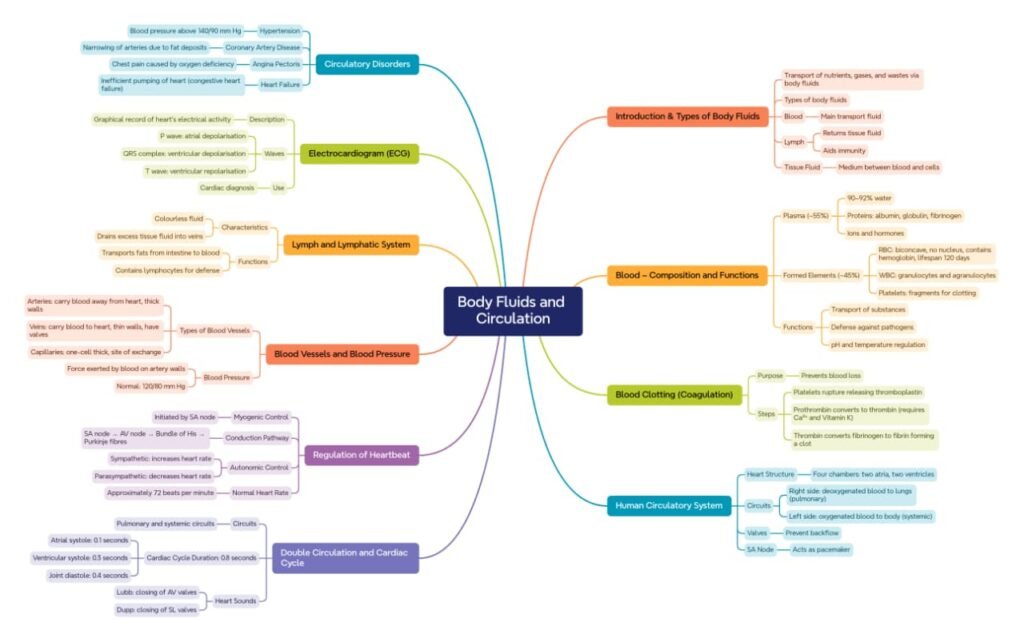
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
