Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 11: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
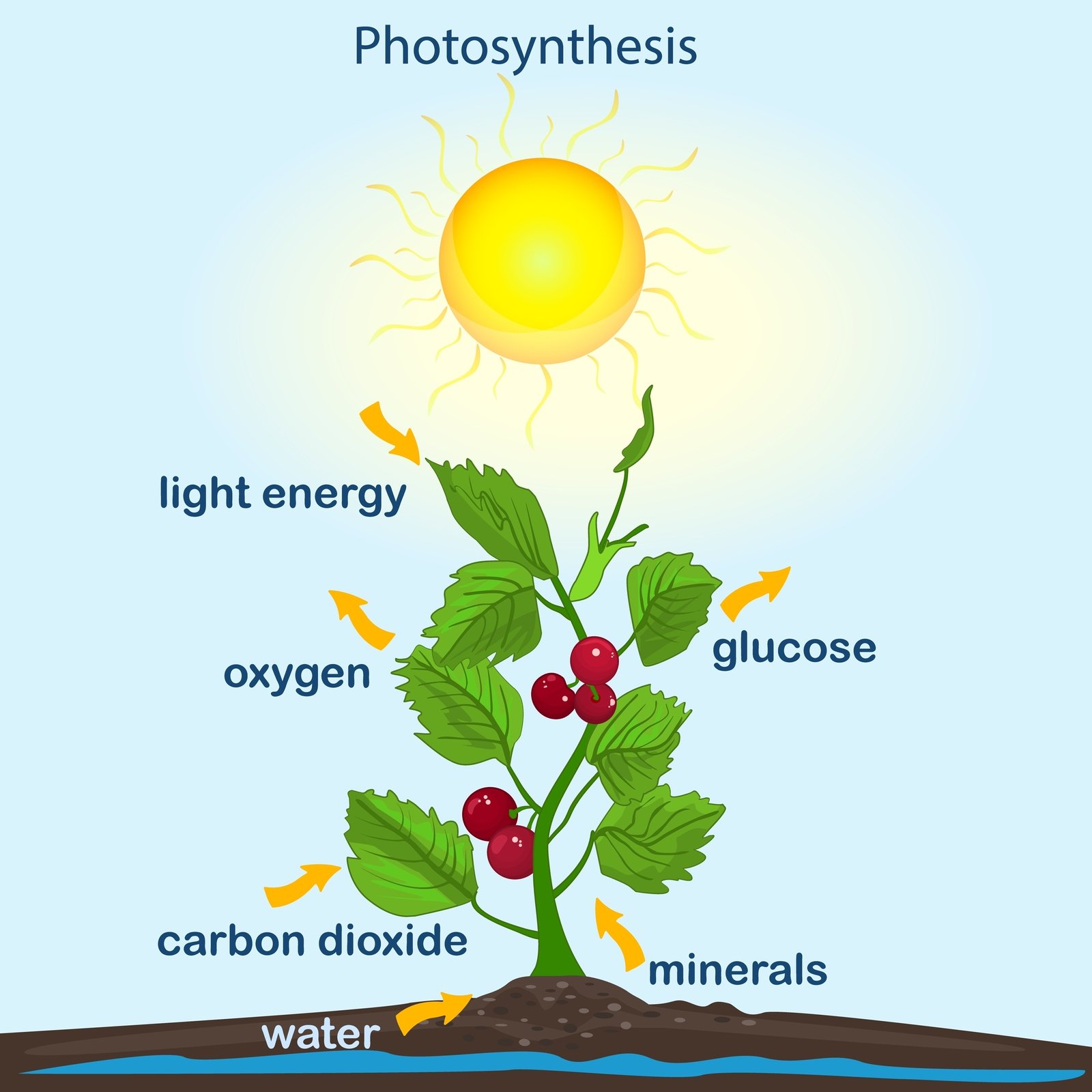
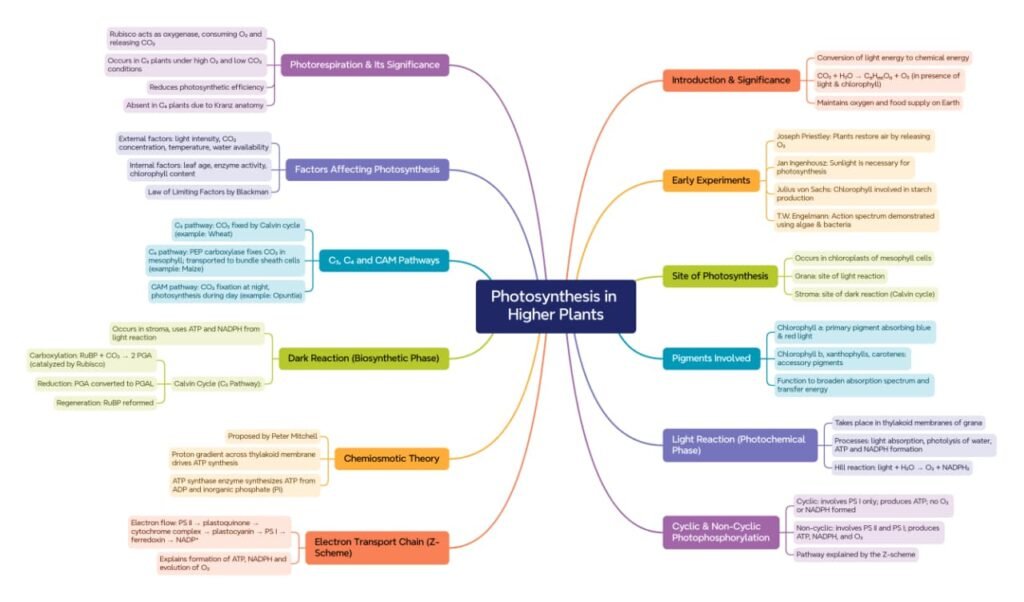
🌱✨ Introduction
🧠 Photosynthesis is the physicochemical process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose).
🌿 It is the foundation of life on Earth — providing food and oxygen for all living beings.
💡 Concept:
☀️ Light energy → stored as chemical energy in bonds of organic molecules.
🌍 Photosynthesis = Energy gateway for the biosphere.
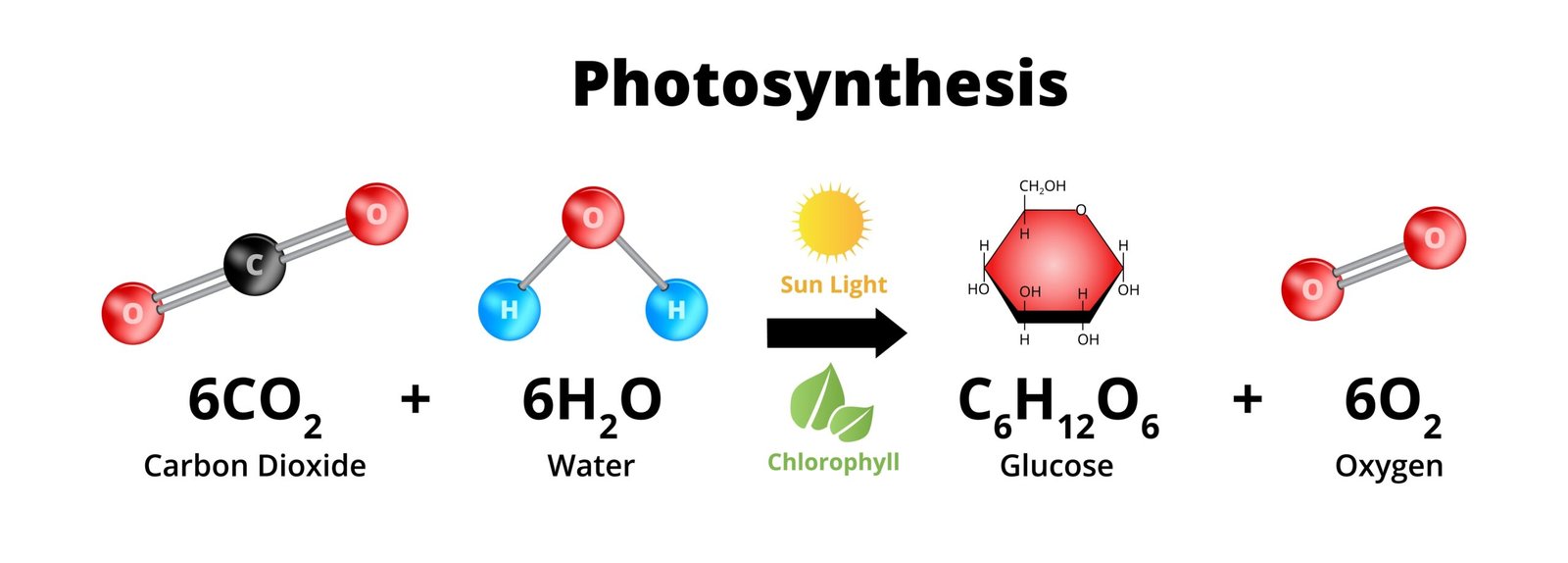
🧬 Equation:
6 CO₂ + 12 H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ + 6 H₂O (in presence of light & chlorophyll)
🌾 Historical Background

1️⃣ Priestley (1770): Discovered that plants release oxygen — candle relit experiment.
2️⃣ Ingenhousz (1779): Light essential; only green parts produce oxygen.
3️⃣ Jan Senebier: CO₂ is used in photosynthesis.
4️⃣ Sachs: Confirmed chlorophyll and light needed; product is starch.
5️⃣ Blackman (1905): Gave Law of Limiting Factors — photosynthesis controlled by light, CO₂, temperature.
💡 Concept: Photosynthesis = light-dependent & enzymatic reactions.
🌿 Site of Photosynthesis
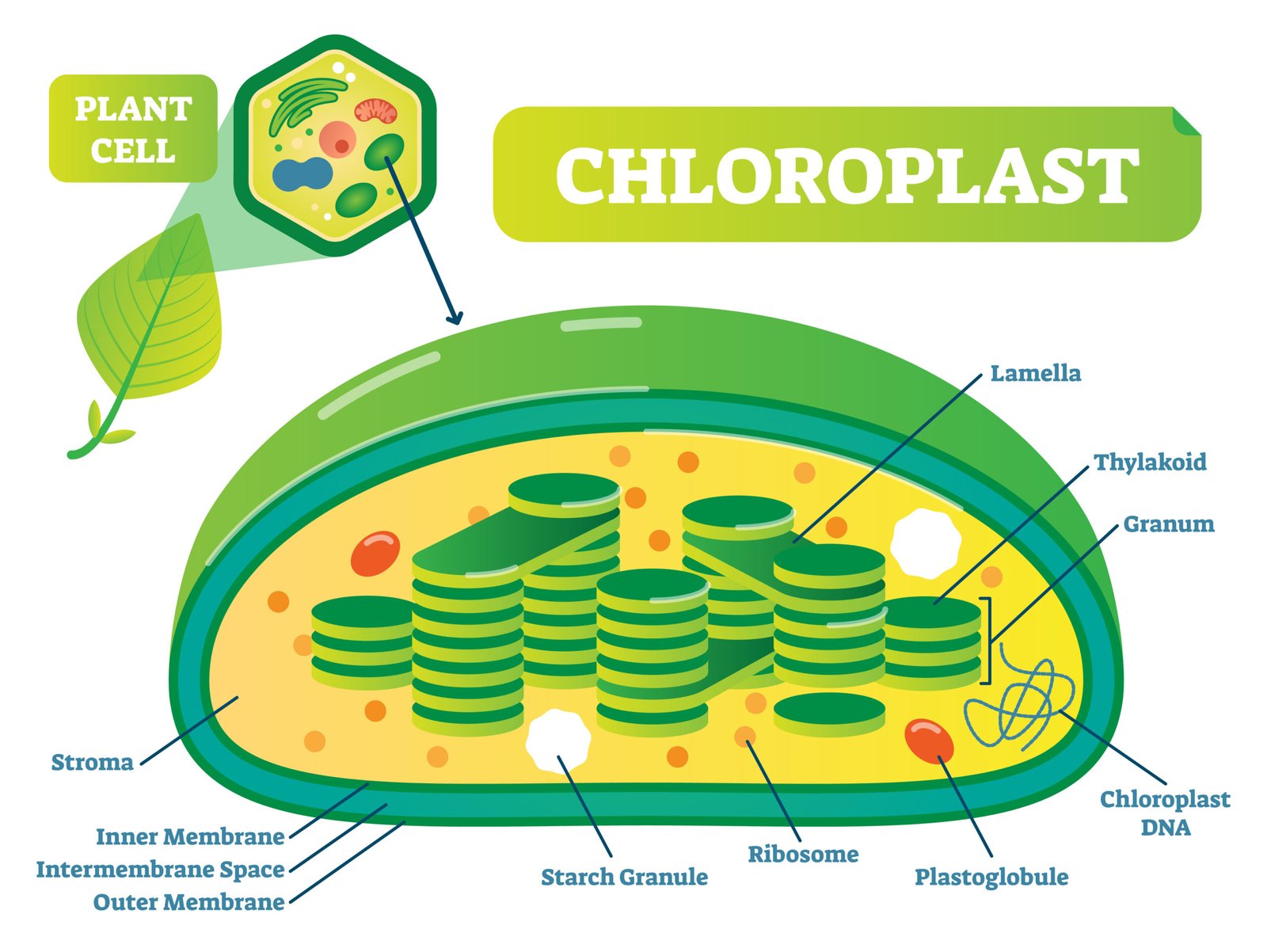
🪴 Chloroplasts — double-membrane organelles in mesophyll cells.
Contains:
🌱 Grana: stacks of thylakoids (light reactions)
🍃 Stroma: fluid matrix (dark reactions)
💚 Chlorophyll pigments in thylakoid membranes capture light energy.
🌸 Pigments Involved
1️⃣ Chlorophyll a – primary pigment
2️⃣ Chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, carotenes – accessory pigments
💡 Absorb different wavelengths → broader absorption spectrum
🌈 Absorption & Action Spectrum
Absorption spectrum: Light wavelengths absorbed by pigments.
Action spectrum: Photosynthetic rate vs light wavelength (max in blue & red regions).
🧠 Engelmann’s experiment: Demonstrated O₂ evolution maximum under blue & red light using algae and bacteria.
🌞 Light Reaction (Photochemical Phase)
⚙️ Occurs in thylakoid membranes of chloroplast.
Requires light and water; produces ATP, NADPH, O₂.
🧪 Major Steps
1️⃣ Light absorption by pigments
2️⃣ Excitation of electrons in chlorophyll
3️⃣ Photophosphorylation – formation of ATP
4️⃣ Photoreduction – NADP⁺ → NADPH
5️⃣ Photolysis of water – splits water into O₂, H⁺, e⁻
💡 Equation:
2 H₂O → 4 H⁺ + 4 e⁻ + O₂
🧬 Oxygen released is from water (Hill reaction confirmed).
⚡ Types of Photophosphorylation
🌿 1. Cyclic
Electrons return to PS I
ATP only formed, no NADPH/O₂
Occurs when NADP⁺ low or light intense
🌾 2. Non-Cyclic
Uses PS II and PS I
Electrons move linearly: H₂O → PS II → PS I → NADP⁺
ATP, NADPH, O₂ formed
💡 Concept: Light reaction provides energy currency (ATP) and reducing power (NADPH) for the next phase.
🌿 Dark Reaction (Biosynthetic Phase)
🧠 Takes place in stroma; independent of light but uses ATP and NADPH from light reaction.
🌱 Main process: CO₂ fixation → glucose synthesis.
🌸 Calvin Cycle (C₃ Pathway)
Discovered by Melvin Calvin using radioactive carbon.
Occurs in C₃ plants (wheat, rice, beans).
🌀 Three phases:
1️⃣ Carboxylation
CO₂ + RuBP (Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate) → 2 molecules of 3-PGA
(Enzyme: RuBisCO)
2️⃣ Reduction
3-PGA + ATP + NADPH → G3P (PGAL) → forms glucose
3️⃣ Regeneration
Some G3P regenerates RuBP using ATP
💡 Net Result:
6 CO₂ + 18 ATP + 12 NADPH → 1 glucose
🧬 C₄ Pathway (Hatch & Slack Pathway)
🌿 Found in tropical grasses (maize, sugarcane).
Adaptation to high light and low CO₂.
🧩 Key features:
Two cell types: mesophyll & bundle sheath
First product: 4-carbon oxaloacetic acid (OAA)
Enzyme: PEP carboxylase (no affinity for O₂)
CO₂ released in bundle sheath → enters Calvin cycle
⚙️ Result: Avoids photorespiration, increases efficiency.
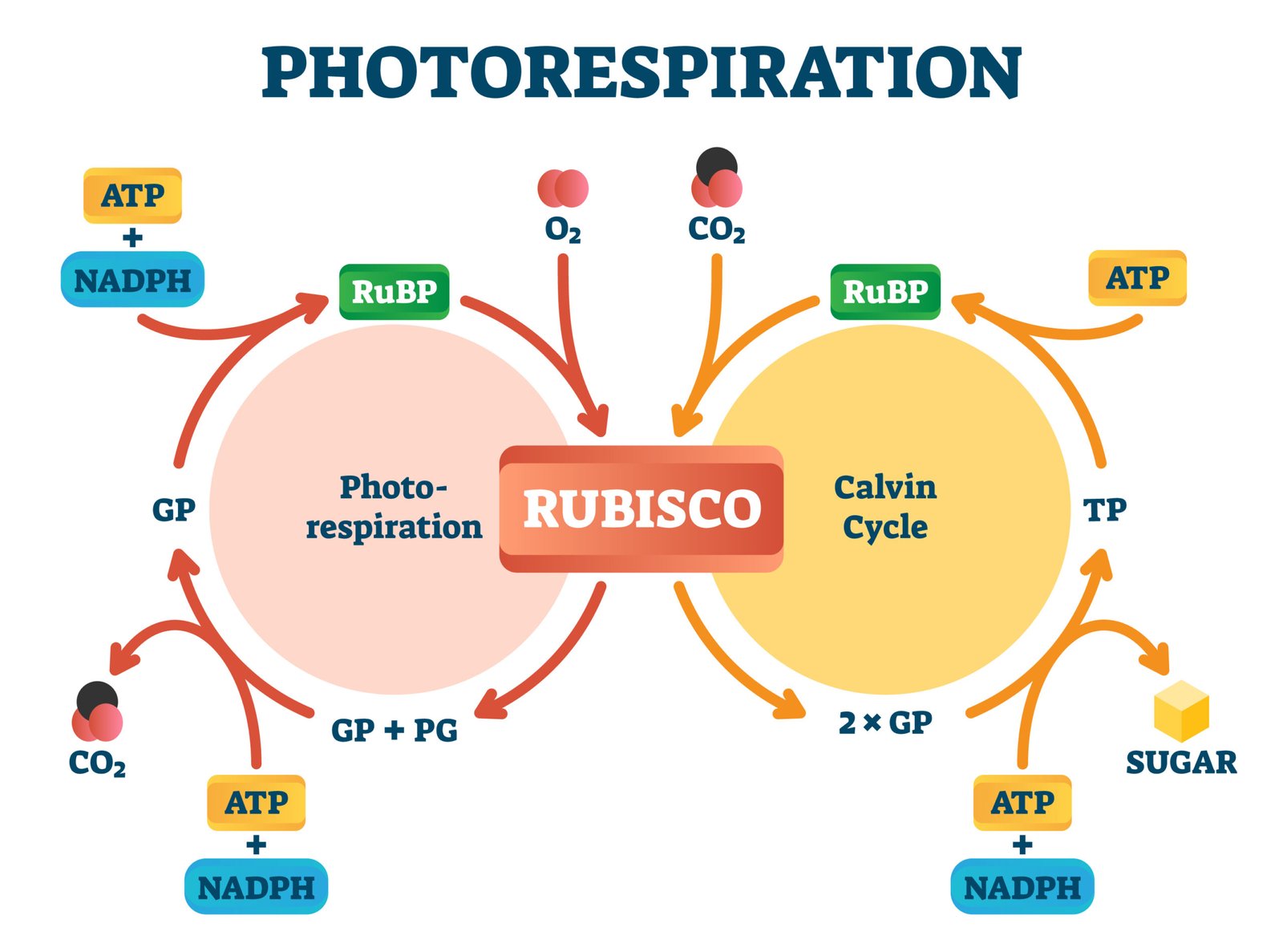
💨 Photorespiration (C₂ Cycle)
🧠 Occurs when RuBisCO binds O₂ instead of CO₂.
Leads to CO₂ loss; no ATP/glucose produced.
Significant in C₃ plants, absent in C₄ plants.
💡 C₄ pathway = evolutionary adaptation to reduce photorespiration.
🌳 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
1️⃣ Light: intensity, quality, duration
2️⃣ CO₂ concentration: directly affects rate
3️⃣ Temperature: optimum 25–35°C
4️⃣ Water: deficiency closes stomata
5️⃣ Internal factors: chlorophyll content, protoplasmic condition
📘 Blackman’s Law of Limiting Factors:
When a process is conditioned by several factors, the rate is limited by the slowest factor.
🧠 Significance of Photosynthesis
🌿 Source of food and energy
💨 Releases O₂ for respiration
🧪 Maintains CO₂–O₂ balance
⚡ Forms base of food chain
🌱 Provides fossil fuels (stored solar energy)
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🧬 Explains primary energy process on Earth
🌿 Essential for agriculture and ecology
🧠 Basis for understanding plant physiology
⚡ Important for climate balance and sustainability
📝 Quick Recap
☀️ Photosynthesis = light energy → chemical energy
🧪 Light reaction (thylakoid): ATP, NADPH, O₂
🧬 Dark reaction (stroma): CO₂ → glucose
🌾 C₃ plants use Calvin cycle; C₄ plants use Hatch–Slack
💨 Photorespiration wastes energy; absent in C₄
⚙️ Factors: light, CO₂, temperature
🌍 Provides food, oxygen, and energy for biosphere
📘 Summary
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process converting solar energy into chemical form.
The light reaction captures sunlight to form ATP and NADPH, while the dark reaction (Calvin cycle) fixes CO₂ into carbohydrates.
C₄ plants possess adaptations for higher efficiency by minimising photorespiration.
Environmental factors such as light, CO₂, and temperature regulate the rate.
This process sustains life, balancing gases and supporting all ecosystems.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. By looking at a plant externally, can you tell whether a plant is C₃ or C₄? Why and how?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 No, it is not possible to identify a C₃ or C₄ plant externally by appearance.
💡 The difference lies in their internal anatomy and biochemical pathways.
✔️ Reason:
C₃ and C₄ plants have similar external morphology.
The difference is in photosynthetic mechanism and leaf anatomy (Kranz anatomy in C₄).
➡️ Hence, microscopic observation is needed to distinguish them.
🔵 Question 2. By looking at which internal structure of a plant can you tell whether a plant is C₃ or C₄? Explain.
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Examine the leaf anatomy:
🌿 C₄ plants show Kranz anatomy:
Vascular bundles surrounded by bundle sheath cells (large, chloroplast-rich).
Presence of dimorphic chloroplasts (granal in mesophyll, agranal in bundle sheath).
🌸 C₃ plants:
No Kranz anatomy.
Only mesophyll cells perform photosynthesis.
✔️ Thus, presence of Kranz anatomy = C₄ plant.
🔵 Question 3. Even though a very few cells in a C₄ plant carry out the biosynthetic Calvin pathway, yet they are highly productive. Can you discuss why?
🟢 Answer:
🧬 C₄ plants are more productive due to:
🌿 Efficient CO₂ fixation — minimal photorespiration.
⚡ Spatial separation of initial CO₂ fixation (mesophyll) and Calvin cycle (bundle sheath).
🌸 High CO₂ concentration in bundle sheath enhances RuBisCO efficiency.
🌱 Better water-use efficiency.
✔️ Result: More biomass produced per unit time → high productivity.
🔵 Question 4. RuBisCO is an enzyme that acts both as a carboxylase and oxygenase. Why do you think RuBisCO carries out more carboxylation in C₄ plants?
🟢 Answer:
🧪 In C₄ plants, RuBisCO is located in bundle sheath cells, where CO₂ concentration is high due to C₄ cycle.
➡️ High CO₂ / O₂ ratio favours carboxylase activity and suppresses oxygenase activity.
➡️ Thus, photorespiration is negligible.
✔️ Therefore, RuBisCO performs more carboxylation in C₄ plants.
🔵 Question 5. Suppose there were plants that had a high concentration of Chlorophyll b, but lacked Chlorophyll a, would it carry out photosynthesis? Then why do plants have Chlorophyll b and other accessory pigments?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 No, photosynthesis would not occur with only chlorophyll b.
💡 Reason:
Chlorophyll a is the reaction centre pigment that converts light energy into chemical energy.
Chlorophyll b and accessory pigments (carotenoids, xanthophylls) absorb additional wavelengths and transfer energy to chlorophyll a.
✔️ Hence, accessory pigments broaden the absorption spectrum but cannot replace chlorophyll a.
🔵 Question 6. Why is the colour of a leaf kept in the dark frequently yellow or pale green? Which pigment do you think is more stable?
🟢 Answer:
🌱 In darkness, chlorophyll is degraded, but carotenoids remain intact.
💡 Result: Leaf becomes yellow/pale green.
➡️ Carotenoids are more stable than chlorophyll.
✔️ Reason: Carotenoids resist photo-oxidation and persist longer.
🔵 Question 7. Look at leaves of the same plant on the shady side and compare it with the leaves on the sunny side. Or, compare the potted plants kept in sunlight with those in the shade. Which of them has leaves that are darker green? Why?
🟢 Answer:
🌿 Shady-side leaves are darker green.
💡 Reason:
Shade leaves have more chlorophyll to capture limited light.
Sun-exposed leaves have less chlorophyll but thicker cuticle.
✔️ Adaptation ensures optimum photosynthesis in varying light conditions.
🔵 Question 8. Figure 11.10 shows the effect of light on the rate of photosynthesis. Based on the graph, answer the following questions:
(a) At which point/s (A, B or C) in the curve light is a limiting factor?
(b) What could be the limiting factor/s in region A?
(c) What do C and D represent on the curve?
🟢 Answer:
🧠 (a) Region A — light is limiting factor (rate increases with light intensity).
(b) Limiting factors in A: Light intensity and CO₂ concentration.
(c) C and D:
➡️ C — light saturation point (rate no longer increases)
➡️ D — plateau region; another factor (CO₂ or temperature) becomes limiting.
✔️ Photosynthesis rate depends on interacting limiting factors.
🔵 Question 9. Give comparison between the following:
🟢 (a) C₃ and C₄ pathways
Feature C₃ Pathway C₄ Pathway
First stable product 3C (PGA) 4C (OAA)
Site Mesophyll cells Mesophyll + bundle sheath
Enzyme RuBisCO PEP carboxylase + RuBisCO
Photorespiration High Negligible
Productivity Moderate High
🟢 (b) Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
Feature Cyclic Non-cyclic
Pathway Electrons cycle back to PS I Electrons move PS II → PS I
Product ATP only ATP + NADPH
Water splitting Absent Present
O₂ evolution No Yes
🟢 (c) Anatomy of leaf in C₃ and C₄ plants
Feature C₃ Leaf C₄ Leaf
Anatomy No Kranz anatomy Kranz anatomy present
Bundle sheath Small, few chloroplasts Large, many chloroplasts
Chloroplasts Only mesophyll Both mesophyll and bundle sheath
Photorespiration High Absent
✔️ C₄ plants are more efficient in hot, dry climates.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
The site of light-dependent reactions is —
🔴1️⃣ Stroma
🟢2️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🟡3️⃣ Matrix
🔵4️⃣ Inner membrane
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🔴 Question 2:
The dark reactions occur in —
🔴1️⃣ Grana
🟢2️⃣ Stroma
🟡3️⃣ Thylakoid lumen
🔵4️⃣ Inter-membrane space
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Stroma
🔴 Question 3:
The oxygen released in photosynthesis originates from —
🔴1️⃣ CO₂
🟢2️⃣ H₂O
🟡3️⃣ Glucose
🔵4️⃣ Chlorophyll
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ H₂O
🔴 Question 4:
Who discovered that plants release oxygen in sunlight?
🔴1️⃣ Priestley
🟢2️⃣ Ingenhousz
🟡3️⃣ Blackman
🔵4️⃣ Calvin
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Ingenhousz
🔴 Question 5:
The first stable product of C₃ cycle is —
🔴1️⃣ OAA
🟢2️⃣ 3-PGA
🟡3️⃣ PEP
🔵4️⃣ RuBP
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ 3-PGA
🔴 Question 6:
Primary CO₂ acceptor in C₄ plants is —
🔴1️⃣ RuBP
🟢2️⃣ PEP
🟡3️⃣ 3-PGA
🔵4️⃣ OAA
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ PEP
🔴 Question 7:
RUBISCO enzyme shows —
🔴1️⃣ Only carboxylase activity
🟢2️⃣ Only oxygenase activity
🟡3️⃣ Both carboxylase and oxygenase activity
🔵4️⃣ None
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Both activities
🔴 Question 8:
Which statement is true for cyclic photophosphorylation?
🔴1️⃣ Involves both PS I & PS II
🟢2️⃣ Involves only PS I
🟡3️⃣ Produces O₂
🔵4️⃣ Produces NADPH
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Involves only PS I
🔴 Question 9:
Light reaction results in formation of —
🔴1️⃣ ATP + NADPH + O₂
🟢2️⃣ Glucose
🟡3️⃣ 3-PGA
🔵4️⃣ CO₂
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ ATP + NADPH + O₂
🔴 Question 10:
Name the scientist who proposed the Calvin cycle.
🔴1️⃣ Blackman
🟢2️⃣ Calvin
🟡3️⃣ Hatch
🔵4️⃣ Hill
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Calvin
🔴 Question 11:
Define photophosphorylation.
🟢 Answer: Formation of ATP from ADP + Pi using light energy during light reaction ⚡
🔴 Question 12:
Give one difference between C₃ and C₄ plants.
🟢 Answer:
C₃: First product = 3-PGA; occurs in mesophyll only 🌿
C₄: First product = OAA; occurs in mesophyll + bundle-sheath 🌾
🔴 Question 13:
Define photosynthesis and give its overall equation.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Process by which green plants synthesize food using sunlight, CO₂ and water.
Equation:
6CO₂ + 12H₂O —(light & chlorophyll)→ C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O ☀️🌿
Significance: Converts solar energy into chemical energy.
🔴 Question 14:
Describe the main phases of photosynthesis.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Light Reaction: Occurs in thylakoid membranes; forms ATP, NADPH, O₂.
2️⃣ Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle): Occurs in stroma; uses ATP & NADPH to fix CO₂.
3️⃣ Photolysis of Water: Splits H₂O into H⁺, e⁻, and O₂ gas.
🔴 Question 15:
Explain the major events of light reaction.
🟢 Answer:
Photon absorption by chlorophyll in PS II and PS I ☀️
Electron transport chain produces ATP (photophosphorylation) ⚡
Formation of NADPH from electrons of PS I 💡
Photolysis of water releases O₂ 💧
🔴 Question 16:
Differentiate between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Cyclic Non-cyclic
Photosystems Only PS I PS II + PS I
Products ATP only ATP, NADPH, O₂
O₂ Release Absent Present
Pathway Circular Linear
💡 Cyclic: Used when ATP demand is high.
Non-cyclic: Main pathway.
🔴 Question 17:
Describe the steps of Calvin cycle.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Carboxylation: CO₂ fixed to RuBP → 3-PGA formed.
2️⃣ Reduction: ATP & NADPH convert 3-PGA → Triose phosphate.
3️⃣ Regeneration: RuBP regenerated for continuation.
✅ End product: Glucose 🍞
🔴 Question 18:
What are C₄ plants? Mention their advantages.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Plants where first stable product is 4-carbon OAA (e.g. Maize 🌾).
Advantages:
1️⃣ High photosynthetic efficiency.
2️⃣ No photorespiration.
3️⃣ Adapted to high light & temperature.
🔴 Question 19:
Explain photorespiration and its consequences.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Process using O₂ and releasing CO₂ without ATP or sugar gain.
Occurs when: O₂ > CO₂; RUBISCO acts as oxygenase.
Consequences:
1️⃣ Energy waste.
2️⃣ Reduced productivity.
3️⃣ Absent in C₄ plants.
🔴 Question 20:
Write the differences between light and dark reactions.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Light Reaction Dark Reaction
Site Thylakoid Stroma
Requirement Light No direct light
Products ATP, NADPH, O₂ Glucose
Function Energy capture CO₂ fixation
🌿 Both are interdependent.
🔴 Question 21:
Explain the role of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and accessory pigments.
🟢 Answer:
Chlorophyll a: Main pigment, absorbs blue & red light, converts to chemical energy.
Chlorophyll b: Accessory, absorbs additional wavelengths, transfers energy.
Carotenoids & xanthophylls: Protect chlorophyll, broaden absorption spectrum. 🌈
🔴 Question 22:
List the factors affecting photosynthesis.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Light: Intensity, wavelength, duration ☀️
2️⃣ CO₂ concentration: Higher = more rate till saturation.
3️⃣ Temperature: Optimum around 25–35°C 🌡️
4️⃣ Water: Deficiency reduces photosynthesis.
🔴 Question 23:
Explain the mechanism of light reaction in photosynthesis.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Thylakoid membrane of chloroplast 🌿
Steps:
1️⃣ Excitation of electrons: Light absorbed by pigments in PS II → electrons energized ☀️
2️⃣ Electron transport: Electrons move through ETC → ATP formed (photophosphorylation) ⚡
3️⃣ PS I activity: Electrons re-energized, reduce NADP⁺ → NADPH 💡
4️⃣ Photolysis of water: 2H₂O → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ + O₂ ↑
Products: ATP, NADPH, O₂
✅ Purpose: Provide energy & reducing power for CO₂ fixation.
🔴 Question 24:
Describe the Calvin cycle in detail.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Stroma of chloroplast 🌱
Enzyme: RUBISCO
Phases:
1️⃣ Carboxylation: CO₂ + RuBP → 3-PGA
2️⃣ Reduction: 3-PGA → Triose phosphate using ATP & NADPH
3️⃣ Regeneration: RuBP regenerated using ATP
Products: One glucose molecule after 6 turns 🍞
Significance: Converts inorganic CO₂ into organic food.
🔴 Question 25:
Describe the pathway of C₄ photosynthesis.
🟢 Answer:
Site: Mesophyll + bundle sheath cells 🌾
Steps:
1️⃣ CO₂ fixation: CO₂ + PEP → OAA (C₄ compound) by PEP carboxylase.
2️⃣ Transport: OAA → Malic acid → moves to bundle sheath.
3️⃣ Decarboxylation: CO₂ released → enters Calvin cycle.
4️⃣ Regeneration: PEP regenerated in mesophyll.
Advantages:
✔️ No photorespiration
✔️ High efficiency in hot, bright conditions ☀️
🔴 Question 26:
Compare C₃ and C₄ plants.
🟢 Answer:
Feature C₃ Plants C₄ Plants
First product 3-PGA (3C) OAA (4C)
Enzyme RUBISCO PEP carboxylase & RUBISCO
Site Mesophyll only Mesophyll + bundle sheath
Photorespiration Present Absent
Examples Wheat, Rice 🌾 Maize, Sugarcane 🌿
💡 C₄ plants more efficient under high light & temperature.
🔴 Question 27:
Explain Blackman’s law of limiting factors with example.
🟢 Answer:
Statement: When a process is governed by several factors, the rate is determined by the factor in least supply.
Example:
– If CO₂ is low, increasing light intensity won’t increase photosynthesis.
– If CO₂ increased, rate rises till another factor becomes limiting.
Graph: Shows plateau when one factor becomes limiting.
✅ Conclusion: All factors must be optimum for maximum photosynthesis.
🔴 Question 28:
What is photorespiration? Describe its pathway.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Wasteful process where RUBISCO fixes O₂ instead of CO₂.
Pathway:
1️⃣ In chloroplast: RuBP + O₂ → PGA + Phosphoglycolate
2️⃣ In peroxisome: Phosphoglycolate → Glycolate → Glycine
3️⃣ In mitochondria: Glycine → Serine + CO₂ released
Result: No ATP gain, CO₂ lost.
❌ Not in C₄ plants.
🔴 Question 29:
Explain the significance of light and dark reactions.
🟢 Answer:
Light Reaction:
– Converts solar energy → ATP & NADPH ⚡
– Releases O₂ for life 🌬️
Dark Reaction:
– Fixes CO₂ into carbohydrates 🍞
– Uses ATP & NADPH from light reaction
✅ Together: Ensure energy transformation and food synthesis.
🔴 Question 30:
Write notes on photolysis of water and its importance.
🟢 Answer:
Reaction:
2H₂O → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ + O₂ ↑
Site: PS II of thylakoid membrane 💧
Catalysts: Mn²⁺, Cl⁻, Ca²⁺
Importance:
1️⃣ Provides electrons to PS II.
2️⃣ Supplies protons for NADPH formation.
3️⃣ Releases O₂ used by all living organisms 🌍.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The first stable product of C₃ cycle is
🟡 A. Oxaloacetic acid (OAA)
🟡 B. Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
🟡 C. Malic acid
🟡 D. Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP)
🟢 Answer: B. Phosphoglyceric acid (PGA)
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q2. Chlorophyll-a shows maximum absorption of light in
🟡 A. Blue and red regions
🟡 B. Green and yellow regions
🟡 C. Violet and orange regions
🟡 D. Yellow and green regions
🟢 Answer: A. Blue and red regions
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q3. Emerson’s enhancement effect demonstrates the existence of
🟡 A. C₃ cycle
🟡 B. Two photosystems
🟡 C. Cyclic photophosphorylation
🟡 D. Kranz anatomy
🟢 Answer: B. Two photosystems
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q4. The site of light reaction in chloroplast is
🟡 A. Stroma
🟡 B. Grana thylakoids
🟡 C. Inner envelope membrane
🟡 D. Cytoplasm
🟢 Answer: B. Grana thylakoids
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q5. The primary CO₂ acceptor in C₄ plants is
🟡 A. PEP (Phosphoenol pyruvate)
🟡 B. RuBP
🟡 C. OAA
🟡 D. PGA
🟢 Answer: A. PEP (Phosphoenol pyruvate)
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q6. The chemiosmotic hypothesis was proposed by
🟡 A. Blackman
🟡 B. Calvin
🟡 C. Hatch and Slack
🟡 D. Peter Mitchell
🟢 Answer: D. Peter Mitchell
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q7. Kranz anatomy is a characteristic feature of
🟡 A. CAM plants
🟡 B. C₃ plants
🟡 C. C₄ plants
🟡 D. Algae
🟢 Answer: C. C₄ plants
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q8. In photosynthesis, photolysis of water occurs in
🟡 A. Photosystem I
🟡 B. Photosystem II
🟡 C. Calvin cycle
🟡 D. Cyclic photophosphorylation
🟢 Answer: B. Photosystem II
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q9. Photorespiration is significant because it
🟡 A. Consumes oxygen and releases CO₂ without ATP gain
🟡 B. Fixes carbon efficiently
🟡 C. Increases sugar production
🟡 D. Requires only Photosystem I
🟢 Answer: A. Consumes oxygen and releases CO₂ without ATP gain
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q10. The oxygen released during photosynthesis comes from
🟡 A. Carbon dioxide
🟡 B. Water
🟡 C. Glucose
🟡 D. Oxygen in air
🟢 Answer: B. Water
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q11. Cyclic photophosphorylation involves
🟡 A. Both Photosystem I and II
🟡 B. Photosystem I only
🟡 C. Photosystem II only
🟡 D. Calvin cycle only
🟢 Answer: B. Photosystem I only
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q12. Hatch and Slack pathway is another name for
🟡 A. C₃ cycle
🟡 B. C₄ cycle
🟡 C. CAM pathway
🟡 D. Photorespiration
🟢 Answer: B. C₄ cycle
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q13. The enzyme RuBisCO is located in
🟡 A. Thylakoid lumen
🟡 B. Grana
🟡 C. Stroma
🟡 D. Intermembrane space
🟢 Answer: C. Stroma
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q14. ATP and NADPH produced in light reaction are used in
🟡 A. Photolysis of water
🟡 B. Calvin cycle (dark reaction)
🟡 C. Cyclic photophosphorylation
🟡 D. Electron transport chain
🟢 Answer: B. Calvin cycle (dark reaction)
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q15. Blackman’s law of limiting factors is related to
🟡 A. Respiration
🟡 B. Photosynthesis
🟡 C. Transpiration
🟡 D. Mineral absorption
🟢 Answer: B. Photosynthesis
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q16. During photorespiration, the organelles involved are
🟡 A. Chloroplast and mitochondria only
🟡 B. Chloroplast, mitochondria, and peroxisome
🟡 C. Chloroplast and cytoplasm
🟡 D. Mitochondria and ribosome
🟢 Answer: B. Chloroplast, mitochondria, and peroxisome
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q17. Light-harvesting complexes are made of
🟡 A. Chlorophyll and lipids
🟡 B. Proteins and pigments
🟡 C. Nucleic acids and pigments
🟡 D. Carbohydrates only
🟢 Answer: B. Proteins and pigments
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q18. The compensation point for C₃ plants is
🟡 A. High CO₂ concentration
🟡 B. Low CO₂ concentration
🟡 C. High O₂ concentration
🟡 D. Equal CO₂ and O₂ exchange
🟢 Answer: D. Equal CO₂ and O₂ exchange
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q19. The special leaf anatomy in C₄ plants reduces photorespiration by
🟡 A. Storing CO₂ as malate in mesophyll cells
🟡 B. Isolating Calvin cycle in bundle sheath cells
🟡 C. Closing stomata permanently
🟡 D. Using only Photosystem I
🟢 Answer: B. Isolating Calvin cycle in bundle sheath cells
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q20. The energy-rich compound generated during cyclic photophosphorylation is
🟡 A. ATP
🟡 B. NADPH
🟡 C. Both ATP and NADPH
🟡 D. FADH₂
🟢 Answer: A. ATP
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q21. Photophosphorylation that involves both Photosystem I and II is called
🟡 A. Cyclic photophosphorylation
🟡 B. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
🟡 C. Chemiosmosis
🟡 D. Calvin cycle
🟢 Answer: B. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q22. CO₂ fixation in CAM plants occurs
🟡 A. During the day
🟡 B. During the night
🟡 C. At sunset
🟡 D. Throughout the day and night equally
🟢 Answer: B. During the night
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q23. The primary pigment involved in photosynthesis is
🟡 A. Chlorophyll a
🟡 B. Chlorophyll b
🟡 C. Xanthophyll
🟡 D. Carotene
🟢 Answer: A. Chlorophyll a
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q24. The assimilatory power for the Calvin cycle is provided by
🟡 A. NADH and ATP
🟡 B. NADPH and ATP
🟡 C. FADH₂ and ATP
🟡 D. NADPH and GTP
🟢 Answer: B. NADPH and ATP
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q25. The site of Calvin cycle in chloroplast is
🟡 A. Grana
🟡 B. Stroma
🟡 C. Thylakoid lumen
🟡 D. Intermembrane space
🟢 Answer: B. Stroma
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q26. The action spectrum of photosynthesis closely resembles the absorption spectrum of
🟡 A. Chlorophyll a
🟡 B. Chlorophyll b
🟡 C. Carotenoids
🟡 D. Xanthophyll
🟢 Answer: A. Chlorophyll a
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q27. In C₄ plants, the Calvin cycle occurs in
🟡 A. Mesophyll cells
🟡 B. Bundle sheath cells
🟡 C. Guard cells
🟡 D. Epidermal cells
🟢 Answer: B. Bundle sheath cells
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q28. The dark reaction of photosynthesis is so called because it
🟡 A. Occurs at night only
🟡 B. Does not require light directly
🟡 C. Takes place in the darkened grana
🟡 D. Requires darkness for activation
🟢 Answer: B. Does not require light directly
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q29. Which scientist demonstrated that oxygen released during photosynthesis comes from water?
🟡 A. Blackman
🟡 B. Priestley
🟡 C. Ruben and Kamen
🟡 D. Ingenhousz
🟢 Answer: C. Ruben and Kamen
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q30. CAM plants minimize photorespiration by
🟡 A. Temporal separation of steps
🟡 B. Spatial separation of steps
🟡 C. Using only Photosystem I
🟡 D. Reducing stomatal density
🟢 Answer: A. Temporal separation of steps
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q31. The wavelength of light most effective in photosynthesis is
🟡 A. Green
🟡 B. Red
🟡 C. Yellow
🟡 D. Infrared
🟢 Answer: B. Red
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q32. The primary electron acceptor in Photosystem II is
🟡 A. Plastocyanin
🟡 B. Pheophytin
🟡 C. Ferredoxin
🟡 D. Cytochrome
🟢 Answer: B. Pheophytin
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q33. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, the electrons lost by P700 are replaced by electrons from
🟡 A. Water via Photosystem II
🟡 B. NADPH
🟡 C. Carbon dioxide
🟡 D. ATP hydrolysis
🟢 Answer: A. Water via Photosystem II
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q34. The process of photophosphorylation results in
🟡 A. Formation of NADH
🟡 B. Formation of ATP
🟡 C. Formation of glucose directly
🟡 D. Fixation of carbon dioxide
🟢 Answer: B. Formation of ATP
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q35. The photochemical splitting of water is associated with
🟡 A. Photosystem I
🟡 B. Photosystem II
🟡 C. Calvin cycle
🟡 D. Cyclic photophosphorylation
🟢 Answer: B. Photosystem II
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q36. The first step of Calvin cycle is
🟡 A. Reduction of PGA
🟡 B. Carboxylation of RuBP
🟡 C. Regeneration of RuBP
🟡 D. Formation of PEP
🟢 Answer: B. Carboxylation of RuBP
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q37. During photorespiration, O₂ binds to
🟡 A. RuBP
🟡 B. PEP
🟡 C. PGA
🟡 D. NADPH
🟢 Answer: A. RuBP
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q38. Non-cyclic photophosphorylation produces
🟡 A. ATP and NADPH
🟡 B. ATP only
🟡 C. NADPH only
🟡 D. ATP and FADH₂
🟢 Answer: A. ATP and NADPH
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q39. The enzyme responsible for carbon fixation in C₃ plants is
🟡 A. PEP carboxylase
🟡 B. RuBisCO
🟡 C. Malate dehydrogenase
🟡 D. Cytochrome oxidase
🟢 Answer: B. RuBisCO
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q40. The process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy is called
🟡 A. Photorespiration
🟡 B. Photosynthesis
🟡 C. Photolysis
🟡 D. Phototropism
🟢 Answer: B. Photosynthesis
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q41. During photosynthesis, the proton gradient is created across
🟡 A. Thylakoid lumen and stroma
🟡 B. Inner and outer chloroplast membranes
🟡 C. Cytoplasm and thylakoid
🟡 D. Plasma membrane
🟢 Answer: A. Thylakoid lumen and stroma
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q42. The Hatch and Slack pathway helps plants
🟡 A. Survive in low light conditions
🟡 B. Avoid photorespiration
🟡 C. Perform cyclic photophosphorylation
🟡 D. Fix nitrogen
🟢 Answer: B. Avoid photorespiration
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q43. Blackman’s law of limiting factors explains
🟡 A. The influence of light and CO₂ on photosynthesis
🟡 B. The effect of temperature on enzymes
🟡 C. The effect of water potential on osmosis
🟡 D. The regulation of stomata
🟢 Answer: A. The influence of light and CO₂ on photosynthesis
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q44. The direct product of carboxylation in the Calvin cycle is
🟡 A. PGA
🟡 B. PEP
🟡 C. OAA
🟡 D. Malate
🟢 Answer: A. PGA
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q45. The photochemical reactions of photosynthesis occur in the
🟡 A. Stroma
🟡 B. Thylakoid membranes
🟡 C. Inner membrane of mitochondria
🟡 D. Cytoplasm
🟢 Answer: B. Thylakoid membranes
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q46. The ultimate source of electrons for photosynthesis is
🟡 A. NADPH
🟡 B. ATP
🟡 C. Water
🟡 D. Glucose
🟢 Answer: C. Water
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q47. The Calvin cycle occurs in the
🟡 A. Thylakoid lumen
🟡 B. Grana
🟡 C. Stroma of chloroplast
🟡 D. Cytoplasm
🟢 Answer: C. Stroma of chloroplast
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q48. Which pigment acts as a reaction centre in Photosystem II?
🟡 A. P680
🟡 B. P700
🟡 C. Chlorophyll b
🟡 D. Carotenoid
🟢 Answer: A. P680
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q49. In CAM plants, CO₂ fixation occurs at
🟡 A. Day only
🟡 B. Night only
🟡 C. Both day and night equally
🟡 D. Evening only
🟢 Answer: B. Night only
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q50. The primary electron acceptor of Photosystem I is
🟡 A. Plastocyanin
🟡 B. Ferredoxin
🟡 C. Quinone
🟡 D. A₀ (special chlorophyll)
🟢 Answer: D. A₀ (special chlorophyll)
📅 NEET 2018
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Photosynthesis is a process by which:
🔴 1️⃣ Light energy is converted into heat energy
🟢 2️⃣ Light energy is converted into chemical energy
🟡 3️⃣ Chemical energy is converted into light energy
🔵 4️⃣ ATP is hydrolysed
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Light energy is converted into chemical energy
🔵 Question 2:
Who discovered photosynthesis?
🔴 1️⃣ Priestley
🟢 2️⃣ Ingenhousz
🟡 3️⃣ Calvin
🔵 4️⃣ Mayer
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Mayer
🔵 Question 3:
Which gas is evolved during photosynthesis?
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ O₂
🟡 3️⃣ H₂
🔵 4️⃣ N₂
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ O₂
🔵 Question 4:
In which cell organelle does photosynthesis occur?
🔴 1️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢 2️⃣ Chloroplast
🟡 3️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleus
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Chloroplast
🔵 Question 5:
Site of light reaction is:
🔴 1️⃣ Stroma
🟢 2️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🟡 3️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔵 4️⃣ Outer membrane
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🔵 Question 6:
Site of dark reaction is:
🔴 1️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🟢 2️⃣ Stroma
🟡 3️⃣ Grana
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Stroma
🔵 Question 7:
The first stable product of C₃ cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
🟢 2️⃣ Oxaloacetate
🟡 3️⃣ Pyruvate
🔵 4️⃣ Malate
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Phosphoglycerate (PGA)
🔵 Question 8:
The first stable product of C₄ cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ PGA
🟢 2️⃣ OAA (Oxaloacetic acid)
🟡 3️⃣ Malate
🔵 4️⃣ Pyruvate
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ OAA (Oxaloacetic acid)
🔵 Question 9:
Which pigment acts as the reaction centre in PS-II?
🔴 1️⃣ Chlorophyll a (P700)
🟢 2️⃣ Chlorophyll a (P680)
🟡 3️⃣ Chlorophyll b
🔵 4️⃣ Carotenoid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Chlorophyll a (P680)
🔵 Question 10:
Which pigment acts as the reaction centre in PS-I?
🔴 1️⃣ P680
🟢 2️⃣ P700
🟡 3️⃣ Chlorophyll b
🔵 4️⃣ Xanthophyll
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ P700
🔵 Question 11:
Photolysis of water occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ PS-I
🟢 2️⃣ PS-II
🟡 3️⃣ Stroma
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ PS-II
🔵 Question 12:
The O₂ evolved in photosynthesis comes from:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ H₂O
🟡 3️⃣ Glucose
🔵 4️⃣ Air
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ H₂O
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following is not required for photosynthesis?
🔴 1️⃣ Light
🟢 2️⃣ Chlorophyll
🟡 3️⃣ Oxygen
🔵 4️⃣ CO₂
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Oxygen
🔵 Question 14:
In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are transferred from:
🔴 1️⃣ PS-I to PS-II
🟢 2️⃣ PS-II to PS-I
🟡 3️⃣ PS-I to PS-I
🔵 4️⃣ Water to NADP⁺
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ PS-II to PS-I
🔵 Question 15:
Cyclic photophosphorylation produces:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP and NADPH
🟢 2️⃣ ATP only
🟡 3️⃣ NADPH only
🔵 4️⃣ ATP and O₂
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ ATP only
🔵 Question 16:
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation produces:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP only
🟢 2️⃣ ATP, NADPH, O₂
🟡 3️⃣ ATP and O₂
🔵 4️⃣ NADPH only
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ ATP, NADPH, O₂
🔵 Question 17:
The enzyme Rubisco is responsible for:
🔴 1️⃣ Oxidation
🟢 2️⃣ CO₂ fixation
🟡 3️⃣ Reduction
🔵 4️⃣ Carboxylation only in C₄
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ CO₂ fixation
🔵 Question 18:
In Calvin cycle, CO₂ is fixed during:
🔴 1️⃣ Reduction
🟢 2️⃣ Carboxylation
🟡 3️⃣ Regeneration
🔵 4️⃣ Oxidation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Carboxylation
🔵 Question 19:
The acceptor molecule of CO₂ in Calvin cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ PGA
🟢 2️⃣ RuBP
🟡 3️⃣ OAA
🔵 4️⃣ PEP
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ RuBP
🔵 Question 20:
Which cell type is the site of Calvin cycle in C₄ plants?
🔴 1️⃣ Mesophyll
🟢 2️⃣ Bundle sheath
🟡 3️⃣ Guard cell
🔵 4️⃣ Companion cell
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bundle sheath
🔵 Question 21:
In C₄ plants, the first CO₂ fixation occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Mesophyll cells
🟢 2️⃣ Bundle sheath cells
🟡 3️⃣ Stomata
🔵 4️⃣ Chloroplast stroma
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Mesophyll cells
🔵 Question 22:
Which of the following is a C₄ plant?
🔴 1️⃣ Rice
🟢 2️⃣ Maize
🟡 3️⃣ Wheat
🔵 4️⃣ Potato
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Maize
🔵 Question 23:
Kranz anatomy is a characteristic of:
🔴 1️⃣ C₃ plants
🟢 2️⃣ C₄ plants
🟡 3️⃣ CAM plants
🔵 4️⃣ All
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ C₄ plants
🔵 Question 24:
PEP carboxylase is present in:
🔴 1️⃣ C₃ plants
🟢 2️⃣ C₄ plants
🟡 3️⃣ CAM plants
🔵 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
🔵 Question 25:
The final product of Calvin cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Glucose
🟢 2️⃣ Fructose
🟡 3️⃣ G3P (Triose phosphate)
🔵 4️⃣ Pyruvate
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ G3P (Triose phosphate)
🔵 Question 26:
During light reaction, photolysis of water occurs at:
🔴 1️⃣ PS-I
🟢 2️⃣ PS-II
🟡 3️⃣ Both PS-I and PS-II
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ PS-II
🔵 Question 27:
In C₃ plants, photorespiration occurs in:
🔴 1️⃣ Mitochondria only
🟢 2️⃣ Chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ Chloroplast only
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria
🔵 Question 28:
Photorespiration is favoured by:
🔴 1️⃣ Low temperature
🟢 2️⃣ High O₂ concentration
🟡 3️⃣ Low O₂ concentration
🔵 4️⃣ High CO₂ concentration
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ High O₂ concentration
🔵 Question 29:
Which pigment absorbs red and blue light most effectively?
🔴 1️⃣ Chlorophyll a
🟢 2️⃣ Chlorophyll b
🟡 3️⃣ Carotene
🔵 4️⃣ Xanthophyll
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Chlorophyll a
🔵 Question 30:
The dark reaction does not require:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP
🟢 2️⃣ NADPH
🟡 3️⃣ Light
🔵 4️⃣ CO₂
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Light
🔵 Question 31:
The number of ATP molecules required to fix one molecule of CO₂ in Calvin cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ 2
🟢 2️⃣ 3
🟡 3️⃣ 4
🔵 4️⃣ 6
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 3
🔵 Question 32:
The number of NADPH molecules required to fix one molecule of CO₂ is:
🔴 1️⃣ 1
🟢 2️⃣ 2
🟡 3️⃣ 3
🔵 4️⃣ 4
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 2
🔵 Question 33:
The primary electron acceptor in PS-II is:
🔴 1️⃣ Ferredoxin
🟢 2️⃣ Pheophytin
🟡 3️⃣ Plastoquinone
🔵 4️⃣ Cytochrome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Pheophytin
🔵 Question 34:
The first step of photosynthesis is:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂ fixation
🟢 2️⃣ Light absorption
🟡 3️⃣ Formation of glucose
🔵 4️⃣ ATP synthesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Light absorption
🔵 Question 35:
In which part of chloroplast does Calvin cycle occur?
🔴 1️⃣ Grana
🟢 2️⃣ Stroma
🟡 3️⃣ Thylakoid membrane
🔵 4️⃣ Intermembrane space
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Stroma
🔵 Question 36:
Hill reaction involves:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂ reduction
🟢 2️⃣ Photolysis of water
🟡 3️⃣ Formation of glucose
🔵 4️⃣ ATP hydrolysis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Photolysis of water
🔵 Question 37:
Which element is essential for photolysis of water?
🔴 1️⃣ Magnesium
🟢 2️⃣ Manganese
🟡 3️⃣ Copper
🔵 4️⃣ Zinc
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Manganese
🔵 Question 38:
The product of carboxylation in C₃ cycle is:
🔴 1️⃣ Pyruvate
🟢 2️⃣ 3-PGA
🟡 3️⃣ Malate
🔵 4️⃣ PEP
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ 3-PGA
🔵 Question 39:
During photorespiration, which compound is produced in chloroplast?
🔴 1️⃣ Glycolate
🟢 2️⃣ Glycine
🟡 3️⃣ Serine
🔵 4️⃣ Glycerate
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Glycolate
🔵 Question 40:
Which of the following shows least photorespiration?
🔴 1️⃣ C₃ plants
🟢 2️⃣ C₄ plants
🟡 3️⃣ CAM plants
🔵 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Both 2 and 3
🔵 Question 41:
The enzyme Rubisco exhibits oxygenase activity under:
🔴 1️⃣ High CO₂ concentration
🟢 2️⃣ High O₂ concentration
🟡 3️⃣ Low O₂ concentration
🔵 4️⃣ Absence of O₂
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ High O₂ concentration
🔵 Question 42:
The end product of light reaction is:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP and NADPH
🟢 2️⃣ Glucose
🟡 3️⃣ Pyruvate
🔵 4️⃣ CO₂
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ ATP and NADPH
🔵 Question 43:
Which law is applicable to photosynthesis?
🔴 1️⃣ Blackman’s law of limiting factors
🟢 2️⃣ Mendel’s law
🟡 3️⃣ Boyle’s law
🔵 4️⃣ Dalton’s law
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Blackman’s law of limiting factors
🔵 Question 44:
The assimilation number represents:
🔴 1️⃣ CO₂ used per gram chlorophyll
🟢 2️⃣ O₂ evolved per gram chlorophyll per hour
🟡 3️⃣ ATP produced per gram chlorophyll
🔵 4️⃣ CO₂ absorbed per leaf
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ O₂ evolved per gram chlorophyll per hour
🔵 Question 45:
The overall equation of photosynthesis is:
🔴 1️⃣ 6CO₂ + 12H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O
🟢 2️⃣ 6CO₂ + 6H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
🟡 3️⃣ CO₂ + H₂O → CH₂O + O₂
🔵 4️⃣ 12CO₂ + 12H₂O → C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ + 12O₂
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ 6CO₂ + 12H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O
🔵 Question 46:
Which pigment protects chlorophyll from photo-oxidation?
🔴 1️⃣ Chlorophyll b
🟢 2️⃣ Carotenoids
🟡 3️⃣ Phycocyanin
🔵 4️⃣ Xanthophyll
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Carotenoids
🔵 Question 47:
During photosynthesis, NADPH is formed in:
🔴 1️⃣ PS-I
🟢 2️⃣ PS-II
🟡 3️⃣ Both PS-I and PS-II
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ PS-I
🔵 Question 48:
Photophosphorylation means:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP synthesis using light energy
🟢 2️⃣ ATP hydrolysis using light
🟡 3️⃣ ADP breakdown
🔵 4️⃣ NADPH formation
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ ATP synthesis using light energy
🔵 Question 49:
Z-scheme represents:
🔴 1️⃣ Flow of CO₂
🟢 2️⃣ Movement of electrons
🟡 3️⃣ ATP synthesis
🔵 4️⃣ Carbon fixation
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Movement of electrons
🔵 Question 50:
In C₄ plants, CO₂ fixation and Calvin cycle occur in:
🔴 1️⃣ Same cells
🟢 2️⃣ Different cells
🟡 3️⃣ Different chloroplasts of same cell
🔵 4️⃣ Mitochondria
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Different cells
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
