Class 10 : Social Science (In English) – Lesson 14. Federalism
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔴 INTRODUCTION TO FEDERALISM
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Both levels of government enjoy their own powers independently.
In India, this system is followed to manage the vast diversity in language, culture, religion, and geography. The Indian Constitution has provided a detailed structure of this division of powers, making India a federal country.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 KEY FEATURES OF FEDERALISM
➡️ 1. Two or More Levels of Government
There are two levels of government in a federal country – one at the central level and others at the state level. Sometimes, there is a third tier (local government).
➡️ 2. Division of Powers
The powers are divided between the central and state governments through the Constitution. The Indian Constitution provides three lists – Union List, State List, and Concurrent List – to define these divisions.
➡️ 3. Independent Judiciary
The judiciary acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government. In India, the Supreme Court ensures that the division of powers is maintained.
➡️ 4. Financial Autonomy
Both the Union and the states have separate sources of revenue. This financial independence ensures that neither depends entirely on the other.
➡️ 5. Constitution is Supreme
In a federal system, the Constitution is supreme and the powers of different levels are clearly mentioned in it.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 TYPES OF FEDERALISM
☑️ 1. Coming Together Federation
Independent states come together to form a bigger unit. Power is usually equally distributed. Examples: USA, Switzerland, Australia.
☑️ 2. Holding Together Federation
A large country divides power between the central and state governments to keep the country united. Power is not equally divided. Examples: India, Spain, Belgium.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟡 HOW IS FEDERALISM PRACTISED IN INDIA?
✔️ 1. Constitutional Provisions
The Indian Constitution clearly lays out the powers of the Union and State Governments through three lists:
🔸 Union List: Subjects of national importance like defense, currency, railways.
🔸 State List: Subjects of state importance like police, trade, agriculture.
🔸 Concurrent List: Subjects of common interest like education, marriage, forests.
✔️ 2. Language Policy
India has 22 scheduled languages. The Constitution protects the rights of linguistic minorities. Hindi and English are the official languages, but states can have their own official languages.
✔️ 3. Centre-State Relations
The central government does not interfere in the matters of the states unless necessary. Over time, India’s federalism has strengthened with the rise of coalition governments and the demand for state autonomy.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟣 DECENTRALIZATION IN INDIA
🔶 1. What is Decentralization?
Decentralization means giving more powers to the lower levels of government. In India, this happened through the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments in 1992, which led to the formation of Panchayati Raj and Municipalities.
🔶 2. Importance of Decentralization
➡️ Local governments understand local problems better.
➡️ They involve people in decision-making.
➡️ They reduce the burden on higher governments.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
⚫ STRUCTURE OF LOCAL GOVERNMENTS IN INDIA
🔺 1. Rural Local Government (Panchayati Raj)
✔️ Gram Panchayat – at village level.
✔️ Panchayat Samiti – at block level.
✔️ Zilla Parishad – at district level.
🔺 2. Urban Local Government (Municipalities)
✔️ Municipal Corporations – for big cities.
✔️ Municipal Councils – for smaller cities.
✔️ Nagar Panchayats – for towns in transition.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟤 FEDERALISM IN PRACTICE: SUCCESS OF INDIAN FEDERALISM
✅ 1. Linguistic States
Creation of states on the basis of language, culture, and ethnicity strengthened federalism and promoted unity.
✅ 2. Language Policy
Respect for linguistic diversity promotes harmony.
✅ 3. Centre-State Relations
States today have more autonomy than before. Coalition politics has also made the Centre consult states on more issues.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔷 SIGNIFICANCE OF FEDERALISM IN INDIA
✴️ It maintains the unity of a diverse country.
✴️ It ensures representation of all groups.
✴️ It promotes democracy through decentralization.
✴️ It strengthens the nation’s integrity by accommodating regional identities.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟥 CHALLENGES TO FEDERALISM
🚩 Central dominance in some areas still exists.
🚩 Financial dependence of local bodies is an issue.
🚩 Conflicts between states over resources like water.
🚩 Demands for more autonomy or new states occasionally cause tension.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟩 CONCLUSION
India’s federal structure has evolved over time to accommodate the vast diversity of the nation. Through constitutional provisions, decentralization, respect for diversity, and democratic practices, India’s federalism stands strong.
It is because of federalism that India remains united despite its vast cultural, linguistic, and geographical diversities.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Q1. Mention different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q2. State different forms of communal politics with one example each.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q3. State how caste inequalities are still continuing in India.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q4. State two reasons to say that caste alone cannot determine election results in India.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. What is the status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies?
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q6. Mention any two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. When we speak of gender divisions, we usually refer to:
(A) Biological difference between men and women
(B) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
(C) Unequal child sex ratio
(D) Absence of voting rights for women in democracies
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q8. In India seats are reserved for women in:
(A) Lok Sabha
(B) State legislative assemblies
(C) Cabinets
(D) Panchayati Raj bodies
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q9. Consider the following statements on the meaning of communal politics. Communal politics is based on the belief that:
A. One religion is superior to that of others.
B. People belonging to different religions can live together happily as equal citizens.
C. Followers of a particular religion constitute one community.
D. State power cannot be used to establish the domination of one religious group over others.
Which of the statements are correct?
(A) A, B, C, and D
(B) A, B, and D
(C) A and C
(D) B and D
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q10. Which among the following statements about India’s Constitution is wrong? It:
(A) prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
(B) gives official status to one religion.
(C) provides to all individuals freedom to profess any religion.
(D) ensures equality of citizens within religious communities.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q11. Social divisions based on _ are peculiar to India.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q12. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
List I
A person who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and men
A person who says that religion is the principal basis of community
A person who thinks that caste is the principal basis of community
A person who does not discriminate others on the basis of religious beliefs
List II
A. Communalist
B. Feminist
C. Secularist
D. Castiest
Options:
(A) B C A D
(B) B A D C
(C) D C A B
(D) C A B D
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
💠💠 ANSWERS 💠💠
🔴 Answer 1:
✔ Education, employment, political participation, safety, and health are areas where women face discrimination.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 2:
✔ Everyday beliefs (prejudices)
✔ Desire for dominance (majoritarianism)
✔ Political mobilisation (religious appeals)
✔ Communal violence (riots)
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 3:
✔ Untouchability still exists.
✔ Lower castes have less access to education and jobs.
✔ Discrimination in social relations continues.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 4:
✔ No constituency is dominated by a single caste.
✔ Voters also consider party performance and leadership, not just caste.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 5:
✔ Lok Sabha: 14.36% women (2019)
✔ State Assemblies: Less than 5%
✔ Panchayati Raj: 33% reserved
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 6:
✔ India has no official religion.
✔ Freedom to practice, profess, propagate any religion is guaranteed.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 7:
✔ (B) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 8:
✔ (D) Panchayati Raj bodies
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 9:
✔ (C) A and C
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 10:
✔ (B) gives official status to one religion
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 11:
✔ Caste
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Answer 12:
✔ (B) B A D C
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. (CDS 01/2022)
❓ Which one of the following is not a feature of Indian federalism?
🅰 The federating units consented to form a union
🅱 Residuary powers vest with the Centre
🅲 Seventh Schedule of the Constitution
🅳 Dual government polity
✅ Answer: 🅰 The federating units consented to form a union
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q2. (UPSC Prelims 2021)
❓ Which one of the following in Indian polity indicates federal character?
🅰 The independence of the judiciary is safeguarded
🅱 Union Legislature has elected representatives from constituent units
🅲 Union Cabinet has members from regional parties
🅳 Fundamental Rights enforceable by Courts
✅ Answer: 🅰 The independence of the judiciary is safeguarded
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q3. (SSC CGL 2021)
❓ Which of the following states were formed in 1960?
🅰 Maharashtra & Gujarat
🅱 Punjab & Haryana
🅲 Kerala & Karnataka
🅳 None
✅ Answer: 🅰 Maharashtra & Gujarat
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q4. (Railway NTPC 2022)
❓ Who recommends measures to augment a State’s consolidated fund for local bodies?
🅰 NITI Aayog
🅱 CAG
🅲 Finance Ministry
🅳 Finance Commission
✅ Answer: 🅳 Finance Commission
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. (RRB NTPC 2023)
❓ Protection of minorities’ interests in India falls under which Article?
🅰 Article 20
🅱 Article 16
🅲 Article 15
🅳 Article 29
✅ Answer: 🅳 Article 29
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q6. (SSC GD Constable 2024)
❓ Federalism in India is inclined towards the Centre but States have powers. Which is true?
(I) Centre cannot order States.
(II) States have their own powers.
🅰 Only I
🅱 Only II
🅲 I & II
🅳 None
✅ Answer: 🅲 I & II
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. (State PCS 2019)
❓ When were Maharashtra & Gujarat states created?
🅰 1961
🅱 1960
🅲 1955
🅳 1950
✅ Answer: 🅱 1960
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q8. (Bank PO 2020)
❓ Which is NOT a State List subject?
🅰 Police
🅱 Prison
🅲 Public health
🅳 Criminal Procedure Code
✅ Answer: 🅳 Criminal Procedure Code
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q9. (UPSC Prelims 2017)
❓ Which one of the following is not a feature of Indian federalism?
🅰 Independent judiciary
🅱 Clear division of powers
🅲 Unequal representation in Rajya Sabha
🅳 Result of an agreement among federating units
✅ Answer: 🅳 Result of an agreement among federating units
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q10. (UPSC Prelims 2021)
❓ Which feature shows India’s federal character?
🅰 Independent judiciary
🅱 Elected Legislature from constituent units
🅲 Cabinet with regional parties
🅳 Fundamental Rights enforceable by Courts
✅ Answer: 🅰 Independent judiciary
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q11. (UPSC Prelims 2012)
❓ Rajya Sabha’s special power:
🅰 Change territory of State
🅱 Empower Parliament to legislate on State List, create All-India Services
🅲 Amend President’s election, pension
🅳 Determine Election Commission functions
✅ Answer: 🅱 Empower Parliament on State List, All-India Services
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q12. (UPSC Prelims 2024)
❓ North Eastern Council members include:
(1) Governor of State
(2) Chief Minister
(3) 3 nominated by President
(4) Home Minister
🅰 1, 2, 3 only
🅱 1, 3, 4 only
🅲 2, 4 only
🅳 1, 2, 3, 4
✅ Answer: 🅰 1, 2, 3 only
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q13. (UPSC Prelims 2017)
❓ What is not necessarily a consequence of President’s Rule?
(1) Dissolution of State Assembly
(2) Removal of Council of Ministers
(3) Dissolution of local bodies
🅰 1 & 2 only
🅱 1 & 3 only
🅲 2 & 3 only
🅳 1, 2 & 3
✅ Answer: 🅱 1 & 3 only
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q14. (UPSC Prelims 2023)
❓ Prisons are managed by States. They follow:
🅰 Only State rules
🅱 Only Prisons Act, 1894
🅲 Both State rules and 1894 Act
🅳 None
✅ Answer: 🅲 Both State rules and 1894 Act
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q15. (UPSC Prelims 2022)
❓ Fifth Schedule areas ensure:
🅰 No transfer of tribal lands to non-tribals
🅱 Self-governance
🅲 Conversion to Union Territory
🅳 Special Category Status
✅ Answer: 🅰 No transfer of tribal lands
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q16. (UPSC Prelims 2021)
❓ What shows Indian federalism?
🅰 Independent Judiciary
🅱 Elected legislature
🅲 Cabinet with regional parties
🅳 Courts enforce Fundamental Rights
✅ Answer: 🅰 Independent Judiciary
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q17. (UPSC Prelims 2017)
❓ Which is not a federal feature?
🅰 Independent Judiciary
🅱 Clear division of powers
🅲 Unequal representation in Rajya Sabha
🅳 Formed by agreement of units
✅ Answer: 🅳 Formed by agreement of units
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q18. (UPSC Prelims 2017)
❓ Rajya Sabha’s special role?
🅰 Territory changes
🅱 Empower Parliament on State List
🅲 Amend President’s election rules
🅳 Define Election Commission roles
✅ Answer: 🅱 Empower Parliament on State List
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q19. (UPSC Prelims Pre-2021)
❓ NOT a federal feature?
🅰 Independent Judiciary
🅱 Clear powers
🅲 Unequal representation in Rajya Sabha
🅳 Agreement among federating units
✅ Answer: 🅳 Agreement among federating units
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q20. (UPSC Prelims 2021)
❓ Cooperative federalism example:
🅰 Centre dictates States
🅱 GST Council governance
🅲 President’s Rule
🅳 Unilateral decisions by Centre
✅ Answer: 🅱 GST Council governance
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
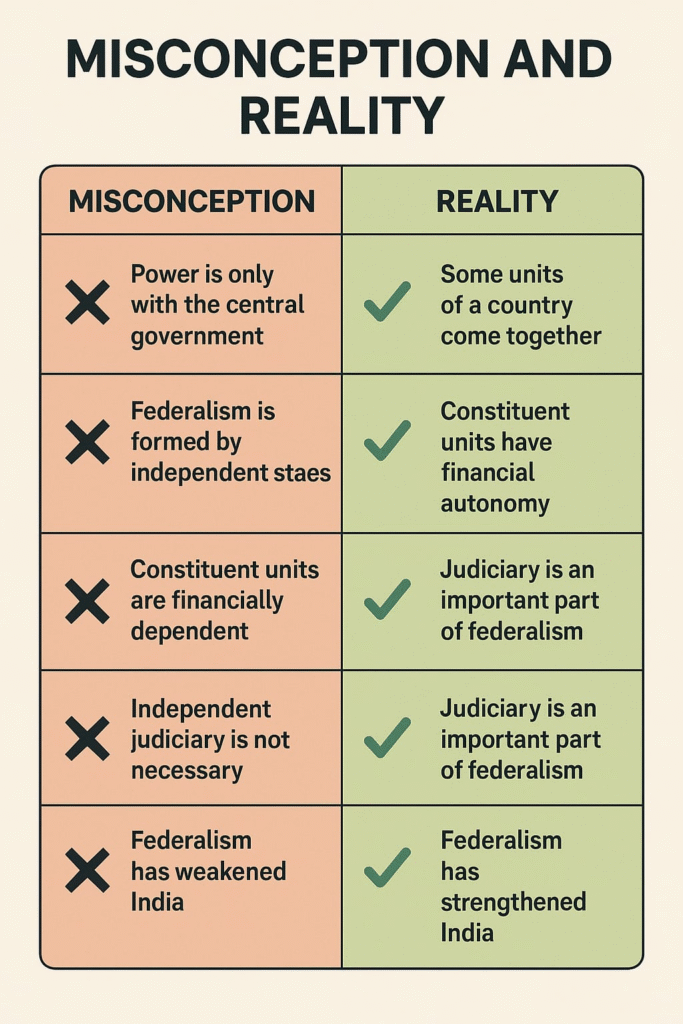
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
