Class 10 : Social Science (In English) – Lesson 12. Lifelines of National Economy
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
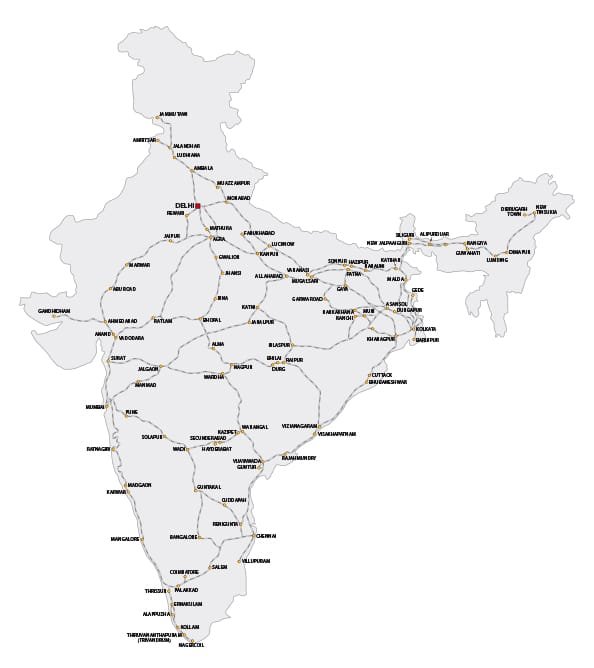
Indian rail network
🌍 1. Importance of Lifelines of Economy
🚆 Roads, railways, waterways, airways, and communication are called lifelines because they connect producers and consumers.
📦 Help in the movement of goods, services, ideas, and people.
🌍 Facilitate national integration and link India with the rest of the world.
🛣️ 2. Roadways
🚗 Provide door-to-door service; most flexible transport.
🛣️ Types:
Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: Delhi–Mumbai–Chennai–Kolkata (plus diagonals Delhi–Chennai & Mumbai–Kolkata).
National Highways (NHs): Connect major cities. NH-44 = longest (Srinagar–Kanyakumari).
State Highways, District Roads, Rural Roads (PMGSY).
🌍 Advantages: cheaper for short distances, easy construction.
⚔️ Challenges: traffic congestion, pollution.
🚆 3. Railways
🛤️ Largest public sector enterprise in India.
📍 Dense network in northern plains; difficult in Himalayan and desert regions.
🌾 Carries bulk goods: coal, iron ore, foodgrains.
👥 Provides affordable passenger transport.
⚔️ Challenges: old infrastructure, accidents, delays.
🚢 4. Waterways
🌊 Cheapest means of transport for heavy/bulky goods.
Inland waterways: Ganga (NW-1), Brahmaputra (NW-2), Godavari–Krishna rivers.
Sea routes: 95% of India’s foreign trade by volume via sea.
📍 Major ports: Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kochi, Paradip, Kandla.
🌍 International trade → connected through Suez Canal, Cape of Good Hope.
✈️ 5. Airways
🛫 Fastest, most modern transport.
✈️ Essential in hilly, desert, remote areas (Northeast, J&K, Andaman & Nicobar).
Domestic airlines + Air India for international routes.
Pawan Hans helicopters → used in oil exploration, North-East services.
⚔️ Expensive → not affordable for common people.
📡 6. Communication
📞 Essential for economic growth & governance.
Personal communication: Phones, mobiles, internet.
Mass communication: Newspapers, radio, television, cinema.
🌍 India → one of the largest telecom networks globally.
📡 Satellites (INSAT, GSAT) → help in telecommunication, broadcasting, weather, resource mapping.
📦 7. International Trade
🌍 Exchange of goods/services between countries.
📈 India’s exports: agricultural products (tea, coffee, rice, spices), minerals (iron ore, mica), manufactured goods (textiles, gems, engineering goods), software.
📉 Imports: petroleum, fertilizers, machinery, chemicals, pearls.
💰 Trade balance = Exports – Imports (India often faces trade deficit).
🏛️ WTO regulates international trade.
🌱 8. Tourism as a Trade
🕌 India → rich heritage, culture, nature.
👥 Provides jobs to 15 million people.
💰 Earns valuable foreign exchange.
📍 Hotspots: Rajasthan, Kerala, Goa, Himachal, Kashmir, Delhi, Agra.
🌍 Medical & IT tourism also rising.
⚔️ 9. Challenges
🚧 Poor infrastructure in some areas.
🏭 Overloaded networks (rail, road).
🌳 Environmental impact (pollution, deforestation).
🌍 Need for modernisation, digitalisation, and expansion.
🌱 10. Way Forward
🌐 Invest in modern railways, highways, renewable-powered transport.
📡 Expand digital infrastructure to rural areas.
🚢 Strengthen inland waterways and ports.
✈️ Make air travel affordable and widespread.
🌍 Promote eco-friendly tourism and balanced trade.
📝 Summary
The lifelines of national economy include transport (roads, railways, waterways, airways), communication, and trade. They ensure the smooth flow of goods, services, people, and information. Roads and railways are crucial for domestic connectivity, while waterways and airways connect remote areas and handle foreign trade.
Communication, both personal and mass, strengthens democracy and development. International trade and tourism boost India’s economy and global presence. However, challenges like congestion, pollution, and trade deficit exist. The future lies in sustainable transport, digital connectivity, and eco-friendly tourism.
⚡ Quick Recap
🛣️ Roads: Golden Quadrilateral + National Highways.
🚆 Railways: bulk goods + passenger transport.
🚢 Waterways: cheapest, 95% foreign trade by sea.
✈️ Airways: fastest, vital for remote areas.
📡 Communication: phones, internet, satellites, mass media.
📦 Trade: exports = tea, rice, textiles; imports = petroleum, machinery.
🕌 Tourism: jobs + foreign exchange.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1. Multiple choice questions
(i) Which two of the following extreme locations are connected by the east–west corridor?
(a) Mumbai and Nagpur
(b) Silchar and Porbandar
(c) Mumbai and Kolkata
(d) Nagpur and Siligudi
Answer:
🟢 (b) Silchar and Porbandar
(ii) Which mode of transportation reduces trans-shipment losses and delays?
(a) Railways
(b) Roadways
(c) Pipeline
(d) Waterways
Answer:
🟢 (c) Pipeline
(iii) Which one of the following states is not connected with the H.V.J. pipeline?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Gujarat
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer:
🟢 (b) Maharashtra
(iv) Which one of the following ports is the deepest land-locked and well-protected port along the east coast?
(a) Chennai
(b) Paradwip
(c) V.O. Chidambaranar (Tuticorin)
(d) Vishakhapatnam
Answer:
🟢 (d) Vishakhapatnam
(v) Which one of the following is the most important modes of transportation in India?
(a) Pipeline
(b) Railways
(c) Roadways
(d) Airways
Answer:
🟢 (c) Roadways
(vi) Which one of the following terms is used to describe trade between two or more countries?
(a) Internal trade
(b) International trade
(c) External trade
(d) Local trade
Answer:
🟢 (b) International trade
Question 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) State any three merits of roadways.
Answer:
🛣️ Provide door-to-door service.
🚗 Most flexible transport → connects rural and urban areas.
📦 Cheaper for short distances and small loads.
(ii) Where and why is rail transport the most convenient means of transportation?
Answer:
🚆 Rail transport is most convenient in northern plains.
🌾 Reasons: level land, high population density, fertile agriculture, and industries generating heavy traffic.
(iii) What is the significance of the border roads?
Answer:
🚧 Constructed in frontier areas → improve accessibility in hilly/remote areas.
⚔️ Crucial for defense and strategic needs.
🌍 Promote trade and tourism in border regions.
(iv) What is meant by trade? What is the difference between international and local trade?
Answer:
📦 Trade: Exchange of goods and services.
Local trade: Within towns/cities.
International trade: Between countries, across borders.
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Why are the means of transportation and communication called the lifelines of a nation and its economy?
Answer:
🚆 They connect production centres with markets.
🚗 Facilitate movement of goods, services, and people.
📡 Strengthen unity and integration.
🌍 Link India globally for trade, tourism, IT.
📦 Without them, no development in agriculture, industry, or services is possible.
👉 Hence, they are rightly called the lifelines of economy.
(ii) Write a note on the changing nature of international trade in the last fifteen years.
Answer:
📦 India’s trade shifted from mainly agricultural products → manufactured goods, engineering, chemicals, IT services.
🚢 Exports include gems, jewellery, textiles, engineering goods, software.
🛢️ Imports dominated by petroleum, machinery, fertilizers, gold.
🌍 Trade partners diversified → not only UK/USA but also Asian and African nations.
📈 Growth of service exports like IT, BPO, and tourism.
👉 Trade now reflects India’s transformation into a global economic player.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Which two places are connected by the East–West Corridor?
🟡 Options:
(A) Mumbai–Nagpur
(B) Silchar–Porbandar
(C) Mumbai–Kolkata
(D) Nagpur–Siliguri
🟢 Answer: (B) Silchar–Porbandar
🔵 Q2. Which mode of transport reduces trans-shipment losses?
🟡 Options:
(A) Railways
(B) Roadways
(C) Pipelines
(D) Waterways
🟢 Answer: (C) Pipelines
🔵 Q3. Which state is not connected with the HVJ pipeline?
🟡 Options:
(A) Madhya Pradesh
(B) Maharashtra
(C) Gujarat
(D) Uttar Pradesh
🟢 Answer: (B) Maharashtra
🔵 Q4. The deepest land-locked and well-protected port on the east coast is:
🟡 Options:
(A) Chennai
(B) Paradwip
(C) V.O. Chidambaranar (Tuticorin)
(D) Vishakhapatnam
🟢 Answer: (D) Vishakhapatnam
🔵 Q5. Which is the most important mode of transport in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Roadways
(B) Railways
(C) Pipelines
(D) Airways
🟢 Answer: (A) Roadways
🔵 Q6. Which term describes trade between two or more countries?
🟡 Options:
(A) Internal trade
(B) International trade
(C) Local trade
(D) Regional trade
🟢 Answer: (B) International trade
🔵 Q7. The Golden Quadrilateral connects:
🟡 Options:
(A) Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata
(B) Srinagar, Kanyakumari, Porbandar, Silchar
(C) Delhi, Jaipur, Bengaluru, Lucknow
(D) Mumbai, Pune, Hyderabad, Chennai
🟢 Answer: (A) Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata
🔵 Q8. Which is the cheapest mode of transport for heavy goods?
🟡 Options:
(A) Airways
(B) Railways
(C) Roadways
(D) Waterways
🟢 Answer: (D) Waterways
🔵 Q9. Which state has the largest road network in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Maharashtra
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) Tamil Nadu
🟢 Answer: (C) Uttar Pradesh
🔵 Q10. Which fuel is transported by the Hazira–Vijaipur–Jagdishpur pipeline?
🟡 Options:
(A) Petroleum
(B) Natural Gas
(C) Coal
(D) Diesel
🟢 Answer: (B) Natural Gas
🔵 Q11. Which organisation manages the largest postal network in the world?
🟡 Options:
(A) Indian Post
(B) BSNL
(C) MTNL
(D) ITDC
🟢 Answer: (A) Indian Post
🔵 Q12. Which city has the busiest international airport in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Chennai
(B) Delhi (IGI)
(C) Mumbai (Chhatrapati Shivaji)
(D) Bengaluru (Kempegowda)
🟢 Answer: (C) Mumbai (Chhatrapati Shivaji)
🔵 Q13. Which Indian seaport handles the maximum cargo volume?
🟡 Options:
(A) Kandla
(B) Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Nhava Sheva)
(C) Paradwip
(D) Mumbai
🟢 Answer: (B) Jawaharlal Nehru Port
🔵 Q14. Which is the largest inland waterway in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) NW–1 (Ganga)
(B) NW–2 (Brahmaputra)
(C) NW–3 (Kerala)
(D) NW–4 (Andhra Pradesh)
🟢 Answer: (A) NW–1 (Ganga)
🔵 Q15. Which Indian state has the highest density of railways?
🟡 Options:
(A) Punjab
(B) West Bengal
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) Delhi
🟢 Answer: (B) West Bengal
🔵 Q16. Which port was developed as a tidal port and is now a major hub in Gujarat?
🟡 Options:
(A) Mumbai
(B) Kandla
(C) Kochi
(D) Haldia
🟢 Answer: (B) Kandla
🔵 Q17. Which of the following is a mass communication medium?
🟡 Options:
(A) Mobile phones
(B) Television
(C) Letters
(D) Telephones
🟢 Answer: (B) Television
🔵 Q18. Which of these is India’s largest software exporting destination?
🟡 Options:
(A) Africa
(B) Europe
(C) USA
(D) Middle East
🟢 Answer: (C) USA
🔵 Q19. Which sector earns India the highest foreign exchange today?
🟡 Options:
(A) Tourism
(B) Software and IT services
(C) Agriculture
(D) Gems and jewellery
🟢 Answer: (B) Software and IT services
🔵 Q20. State any three merits of roadways.
🟢 Answer:
🚗 Provide door-to-door service.
🛣️ Easy to construct and maintain even in difficult terrains.
📦 Cheaper and flexible for short distances and small loads.
🔵 Q21. Where and why is rail transport the most convenient means of transportation?
🟢 Answer:
🚆 Northern Plains.
🌾 Reasons: level land, dense population, rich agriculture, and industries generating heavy traffic.
🔵 Q22. What is the significance of border roads?
🟢 Answer:
🚧 Provide connectivity in frontier areas.
⚔️ Important for defense and security.
🌍 Promote trade and tourism in remote border regions.
🔵 Q23. What is meant by trade? Distinguish between international and local trade.
🟢 Answer:
📦 Trade = exchange of goods and services.
🏙️ Local trade: within towns/cities.
🌍 International trade: across countries.
🌟 SECTION C — Short Answer (3 marks each)
🔵 Q24. Mention three advantages of pipelines.
🟢 Answer:
⚡ Safe and reliable for petroleum/natural gas transport.
📦 Reduce trans-shipment losses.
🛣️ Reduce pressure on road and rail transport.
🔵 Q25. Explain the importance of waterways in India.
🟢 Answer:
🌊 Cheapest transport for heavy/bulky goods.
🚢 Eco-friendly, fuel-efficient.
📍 Important inland waterways: Ganga (NW-1), Brahmaputra (NW-2), Kerala backwaters (NW-3).
🔵 Q26. Write three advantages of airways.
🟢 Answer:
✈️ Fastest means of transport.
🗻 Useful in difficult terrain (Himalayas, deserts, islands).
⚡ Vital during natural disasters and emergencies.
🔵 Q27. Why is international trade considered the economic barometer for a nation?
🟢 Answer:
📈 Reflects level of development and progress.
💰 Brings foreign exchange.
🌍 Shows integration with global economy.
🔵 Q28. Mention three modern developments in communication.
🟢 Answer:
📡 Satellite-based communication (INSAT, GSAT).
📱 Mobile phones, internet.
📺 Television, digital media.
🌟 SECTION D — Long Answer (5 marks each)
🔵 Q29. Explain the importance of railways in India.
🟢 Answer:
🚆 Backbone of bulk transport.
🌾 Carry agricultural products, minerals, industrial goods.
👥 Affordable passenger transport.
🌍 Connects far-flung regions → promotes national integration.
📦 Facilitates trade and commerce.
🔵 Q30. “Roadways have preceded railways in India.” Explain.
🟢 Answer:
🚗 Roads easier and cheaper to build.
🛣️ Can negotiate higher gradients and narrow terrain.
📦 Suitable for short distances and flexible movement.
🏔️ Accessible to hilly/remote areas where rails cannot reach.
🌍 Provide door-to-door service.
🔵 Q31. Discuss the changing nature of India’s international trade in the last 15 years.
🟢 Answer:
📦 Earlier → export of agriculture-based goods.
🏭 Now → engineering goods, chemicals, IT software, petroleum products.
🛢️ Imports → petroleum, fertilizers, gold, machinery.
🌍 Trade partners diversified → Asia, Africa, Europe, USA.
💻 Rise of service exports → IT, BPO, medical tourism.
🔵 Q32. Why are transport and communication called lifelines of the national economy?
🟢 Answer:
🚆 Transport links production with markets.
📡 Communication spreads information quickly.
🌍 Enable trade and tourism.
📦 Help agriculture, industry, services to grow.
🤝 Promote unity and integration.
🌟 SECTION E — Case/Source-Based (4 marks each)
🔵 Q33. Case: A farmer in Assam exports tea to London.
(i) Which type of trade is this? (1)
(ii) Which means of transport is used? (1)
(iii) Mention two benefits of such trade. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🌍 International trade.
(ii) 🚢 Sea route.
(iii) 💰 Earns foreign exchange; 📦 Expands India’s global market.
🔵 Q34. Case: A refinery in Gujarat sends petroleum to Delhi via pipelines.
(i) Which transport is used? (1)
(ii) Why is this transport chosen? (1)
(iii) Mention two advantages of this system. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) ⚡ Pipelines.
(ii) Safe and efficient for liquid fuels.
(iii) Reduce road congestion; minimise losses and delays.
🔵 Q35. Source: “India has the largest telecom network in Asia.”
(i) Which type of communication does telecom represent? (1)
(ii) Mention two benefits of mobile phones. (2)
(iii) Name one satellite communication system of India. (1)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 📡 Personal communication.
(ii) Instant connectivity, internet-based services.
(iii) INSAT/GSAT.
🌟 SECTION F — Map/Skill-Based (5 marks)
🔵 Q36. On an outline map of India, locate and label:
🟢 Answer:
📍 Mumbai Port
📍 Vishakhapatnam Port
📍 Chennai Port
📍 Kolkata Port
🔵 Q37. For visually impaired candidates: Write names of any four international airports in India.
🟢 Answer:
Indira Gandhi International (Delhi).
Chhatrapati Shivaji International (Mumbai).
Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose International (Kolkata).
Chennai International Airport (Chennai).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
