Class 10 : Social Science (In English) – Lesson 10. Minerals and Energy Resources
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

Coal mines , Dhanbad, Jharkhand
🌍 1. Importance of Minerals and Energy
⛏️ Minerals are natural substances with specific chemical composition.
🏭 Backbone of industries: steel, cement, automobiles, electronics.
⚡ Energy resources are essential for transport, electricity, domestic use, and industrial growth.
🌍 Sustainable use is crucial as minerals are non-renewable in nature.
⛰️ 2. Types of Minerals
Metallic Minerals
🌟 Contain metals.
Examples: iron ore, bauxite, copper, manganese, gold.
Sub-types:
Ferrous (iron, manganese).
Non-ferrous (copper, bauxite, lead).
Non-Metallic Minerals
🌱 Do not contain metals.
Examples: mica, limestone, gypsum.
Energy Minerals
⚡ Provide energy.
Examples: coal, petroleum, natural gas, uranium.
🪨 3. Distribution of Major Minerals in India
Iron Ore
Basis of modern industry.
📍 Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Karnataka.
Manganese
Used in steelmaking.
📍 Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka.
Bauxite
Ore of aluminium.
📍 Odisha (largest), Gujarat, Maharashtra.
Copper
Electrical industry, alloys.
📍 Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand.
Mica
Used in electricals and electronics.
📍 Andhra Pradesh, Jharkhand, Rajasthan.
Limestone
Cement industry.
📍 Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan.
⚡ 4. Energy Resources
(A) Conventional Energy Sources
🔥 Coal: Major source for power, steel, chemicals.
Types: Anthracite, Bituminous, Lignite, Peat.
📍 Jharia (Jharkhand), Raniganj (West Bengal), Singrauli (MP).
🛢️ Petroleum: “Liquid gold” for transport & industries.
📍 Digboi (Assam), Bombay High (offshore), Gujarat.
💨 Natural Gas: Used in power & fertilizers.
📍 Krishna-Godavari basin, Tripura, Mumbai High.
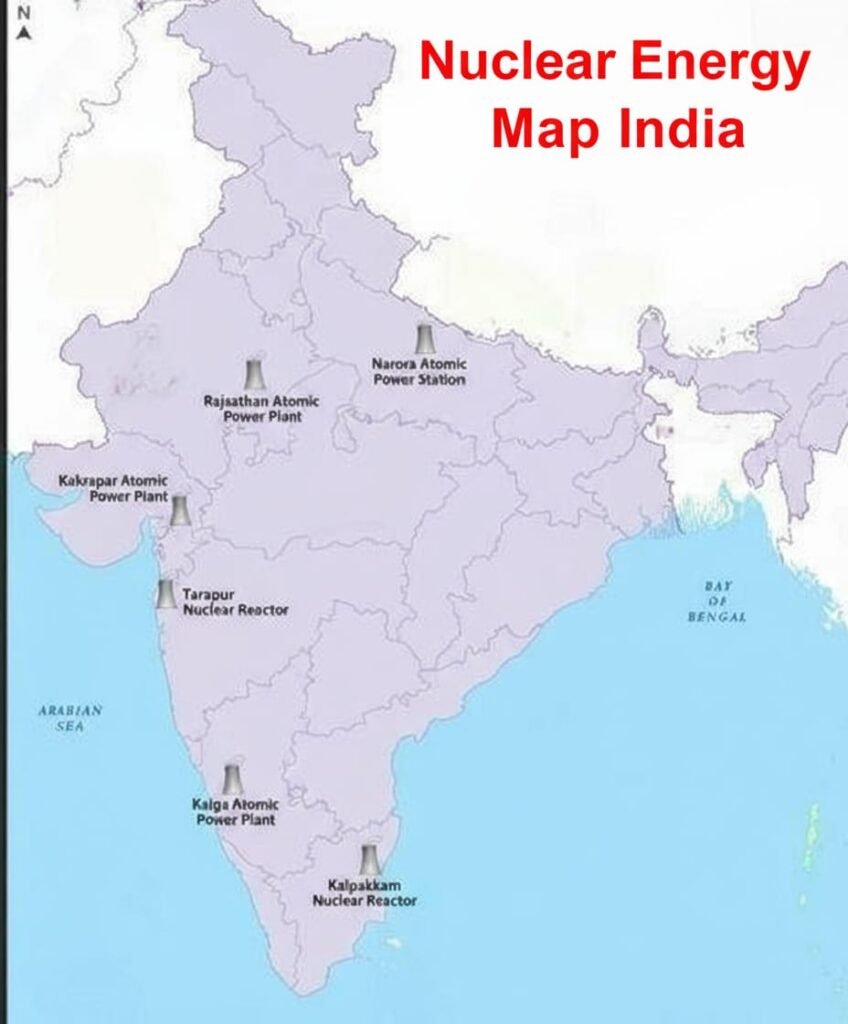
☢️ Nuclear Energy: Uses uranium, thorium.
📍 Uranium: Jharkhand, Thorium: Kerala sands.
Plants: Tarapur, Narora, Kakrapar, Kalpakkam.
(B) Non-Conventional Energy Sources
🌞 Solar Energy: Abundant in Rajasthan, Gujarat.
🌬️ Wind Energy: Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra.
💧 Tidal Energy: Gulf of Khambhat, Gulf of Kachchh.
🌱 Biogas: Rural energy, organic waste.
🌊 Geothermal Energy: Himachal Pradesh, Ladakh.
⚔️ 5. Problems of Mineral and Energy Resources
⛏️ Over-extraction → resource depletion.
🏭 Environmental pollution from mining.
🌳 Deforestation, land degradation.
🌡️ Dependence on fossil fuels → climate change.
⚔️ Regional conflicts over resource sharing.
🌱 6. Conservation of Minerals and Energy
♻️ Recycle scrap metals.
⛏️ Use low-grade ores with advanced technology.
🚜 Improve mining methods for efficiency.
🌞 Expand renewable energy (solar, wind, tidal).
👥 Promote public awareness & eco-friendly lifestyles.
📜 Implement strict laws for sustainable mining.
📝 Summary
Minerals are vital natural resources used in industries and daily life, but they are non-renewable and unevenly distributed. India has rich reserves of iron ore, bauxite, manganese, mica, and limestone. Energy resources are divided into conventional (coal, petroleum, natural gas, nuclear) and non-conventional (solar, wind, tidal, biogas, geothermal).
While conventional sources dominate today, they cause pollution and depletion. Hence, renewable sources are the future of sustainable energy. Conservation measures such as recycling, efficient mining, and adoption of renewables are essential to balance growth with sustainability.
⚡ Quick Recap
⛏️ Minerals → metallic, non-metallic, energy.
📍 Iron ore (Odisha, Jharkhand), Bauxite (Odisha), Mica (Jharkhand, Andhra), Coal (Jharkhand, Bengal).
⚡ Conventional energy → coal, petroleum, natural gas, nuclear.
🌞 Non-conventional energy → solar, wind, tidal, biogas, geothermal.
🌱 Conservation → recycling, efficiency, renewable energy promotion.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1. Multiple choice questions
(i) Which one of the following minerals is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material?
(a) coal
(b) bauxite
(c) gold
(d) zinc
Answer:
🟢 (b) Bauxite
(ii) Koderma, in Jharkhand is the leading producer of which one of the following minerals?
(a) bauxite
(b) mica
(c) iron ore
(d) copper
Answer:
🟢 (b) Mica
(iii) Minerals are deposited and accumulated in the stratas of which of the following rocks?
(a) sedimentary rocks
(b) metamorphic rocks
(c) igneous rocks
(d) none of the above
Answer:
🟢 (a) Sedimentary rocks
(iv) Which one of the following minerals is contained in the Monazite sand?
(a) oil
(b) uranium
(c) thorium
(d) coal
Answer:
🟢 (c) Thorium
Question 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Distinguish between the following in not more than 30 words:
(a) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
⛏️ Ferrous minerals: Contain iron, e.g., iron ore, manganese.
⚙️ Non-ferrous minerals: Do not contain iron but other metals, e.g., copper, bauxite.
(b) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
⚡ Conventional: Exhaustible, used for long, e.g., coal, petroleum, natural gas.
🌞 Non-conventional: Renewable, eco-friendly, e.g., solar, wind, tidal, geothermal.
(ii) What is a mineral?
Answer:
⛏️ A mineral is a naturally occurring substance with a definite chemical composition.
🪨 Found in ores, rocks, and strata; some are metals, some non-metals, some energy resources.
(iii) How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
🌋 Igneous rocks: Minerals form when molten magma cools and solidifies.
⛰️ Metamorphic rocks: Heat, pressure, and chemical activity change minerals into new forms.
(iv) Why do we need to conserve mineral resources?
Answer:
⛏️ Minerals are finite and non-renewable.
🏭 Overuse → depletion, pollution, ecological damage.
🌍 Conservation ensures resources for future generations and sustainable development.
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Describe the distribution of coal in India.
Answer:
🔥 India has rich coal deposits, mainly in Gondwana rocks (200 million years old).
📍 Major fields:
Jharia, Bokaro, Giridih (Jharkhand).
Raniganj (West Bengal).
Singrauli (Madhya Pradesh).
Korba (Chhattisgarh).
🌍 Tertiary coal deposits (55 million years old) found in Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland.
Types: Anthracite (best), Bituminous (industrial use), Lignite (Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan), Peat (low quality).
👉 Coal provides about 60% of India’s energy needs.
(ii) Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Answer:
🌞 India lies in the tropical zone → receives abundant sunlight all year.
🏜️ Desert areas (Rajasthan, Gujarat) ideal for large solar farms.
⚡ Non-polluting, renewable, reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
🏠 Useful in remote rural areas for cooking, lighting, irrigation.
🌍 Helps reduce carbon emissions and tackle climate change.
👉 With rising demand and sustainability goals, solar energy is India’s energy of the future.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Which mineral is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass?
🟡 Options:
(A) Coal
(B) Bauxite
(C) Gold
(D) Zinc
🟢 Answer: (B) Bauxite
🔵 Q2. Koderma, Jharkhand is the leading producer of:
🟡 Options:
(A) Bauxite
(B) Mica
(C) Iron ore
(D) Copper
🟢 Answer: (B) Mica
🔵 Q3. Minerals are commonly deposited in:
🟡 Options:
(A) Sedimentary rocks
(B) Igneous rocks
(C) Metamorphic rocks
(D) None of the above
🟢 Answer: (A) Sedimentary rocks
🔵 Q4. Which mineral is found in Monazite sands?
🟡 Options:
(A) Oil
(B) Uranium
(C) Thorium
(D) Coal
🟢 Answer: (C) Thorium
🔵 Q5. Which state is the largest producer of bauxite in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Odisha
(B) Jharkhand
(C) Gujarat
(D) Maharashtra
🟢 Answer: (A) Odisha
🔵 Q6. Which mineral is called the “backbone of modern industry”?
🟡 Options:
(A) Manganese
(B) Iron ore
(C) Copper
(D) Aluminium
🟢 Answer: (B) Iron ore
🔵 Q7. Which mineral is essential for making steel?
🟡 Options:
(A) Copper
(B) Manganese
(C) Bauxite
(D) Mica
🟢 Answer: (B) Manganese
🔵 Q8. Which state is the largest producer of coal in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Jharkhand
(B) Odisha
(C) Chhattisgarh
(D) West Bengal
🟢 Answer: (A) Jharkhand
🔵 Q9. Which type of coal is of the highest quality?
🟡 Options:
(A) Lignite
(B) Peat
(C) Bituminous
(D) Anthracite
🟢 Answer: (D) Anthracite
🔵 Q10. Which mineral is used in electrical and electronic industries?
🟡 Options:
(A) Copper
(B) Mica
(C) Limestone
(D) Bauxite
🟢 Answer: (B) Mica
🔵 Q11. Which region is famous for petroleum in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Jharia
(B) Raniganj
(C) Bombay High
(D) Korba
🟢 Answer: (C) Bombay High
🔵 Q12. Which state has the largest wind energy potential?
🟡 Options:
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Tamil Nadu
(C) Gujarat
(D) Maharashtra
🟢 Answer: (B) Tamil Nadu
🔵 Q13. Which nuclear mineral is abundantly available in Kerala sands?
🟡 Options:
(A) Thorium
(B) Uranium
(C) Coal
(D) Copper
🟢 Answer: (A) Thorium
🔵 Q14. Which state has the richest iron ore reserves?
🟡 Options:
(A) Odisha
(B) Rajasthan
(C) Gujarat
(D) Punjab
🟢 Answer: (A) Odisha
🔵 Q15. Which is a non-ferrous mineral?
🟡 Options:
(A) Iron
(B) Manganese
(C) Copper
(D) Chromite
🟢 Answer: (C) Copper
🔵 Q16. Which mineral is known as “liquid gold”?
🟡 Options:
(A) Natural gas
(B) Petroleum
(C) Coal
(D) Bauxite
🟢 Answer: (B) Petroleum
🔵 Q17. Which state is the leading producer of natural gas in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Gujarat
(B) Assam
(C) Maharashtra
(D) Tripura
🟢 Answer: (A) Gujarat
🔵 Q18. Which is a non-conventional source of energy?
🟡 Options:
(A) Coal
(B) Solar
(C) Petroleum
(D) Natural Gas
🟢 Answer: (B) Solar
🔵 Q19. Which dam is associated with hydroelectric power in Odisha?
🟡 Options:
(A) Hirakud Dam
(B) Bhakra Nangal Dam
(C) Sardar Sarovar Dam
(D) Tehri Dam
🟢 Answer: (A) Hirakud Dam
🔵 Q20. What is a mineral?
🟢 Answer:
⛏️ A mineral is a naturally occurring substance with a definite chemical composition.
🌍 Found in rocks, ores, and earth’s crust; may be metallic, non-metallic, or energy-giving.
🔵 Q21. Name two ferrous minerals.
🟢 Answer:
🪨 Iron ore.
⚙️ Manganese.
🔵 Q22. State two differences between conventional and non-conventional energy.
🟢 Answer:
⚡ Conventional: Exhaustible, cause pollution, e.g., coal, petroleum.
🌞 Non-conventional: Renewable, eco-friendly, e.g., solar, wind.
🔵 Q23. Mention two reasons why we must conserve minerals.
🟢 Answer:
⛏️ Minerals are finite and non-renewable.
🌍 Essential for industry, energy, and sustainable development.
🌟 SECTION C — Short Answer (3 marks each)
🔵 Q24. Differentiate between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals (any three points).
🟢 Answer:
⚙️ Ferrous → contain iron (iron ore, manganese).
🔧 Non-ferrous → do not contain iron (copper, bauxite).
🏭 Ferrous = steel industry backbone; non-ferrous = electrical, aircraft, alloys.
🔵 Q25. Explain the distribution of mica in India.
🟢 Answer:
📍 Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan.
🌟 India was once the largest producer of mica.
⚡ Widely used in electrical and electronic industries.
🔵 Q26. Mention three features of coal as an energy resource.
🟢 Answer:
🔥 Main source of power in India.
🏭 Used in steel, cement, and chemical industries.
🌍 Found in Gondwana and Tertiary deposits.
🔵 Q27. Why is petroleum called “liquid gold”?
🟢 Answer:
🛢️ Valuable, multipurpose energy resource.
🚗 Essential for transport, power, industry.
💰 High economic importance in global trade.
🔵 Q28. Mention three advantages of non-conventional energy sources.
🟢 Answer:
🌞 Renewable and inexhaustible.
🌍 Environment-friendly, low pollution.
🏡 Useful in rural/remote areas.
🌟 SECTION D — Long Answer (5 marks each)
🔵 Q29. Describe the distribution of coal in India.
🟢 Answer:
🔥 Found mainly in Gondwana rocks (200 million years old).
📍 Jharkhand → Jharia, Bokaro, Giridih.
📍 West Bengal → Raniganj.
📍 Chhattisgarh → Korba, Bilaspur.
📍 Madhya Pradesh → Singrauli.
📍 Tertiary coal → Meghalaya, Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh.
👉 Coal meets ~60% of India’s energy demand.
🔵 Q30. Explain the distribution of iron ore in India.
🟢 Answer:
📍 Odisha → Mayurbhanj, Kendujhar (largest).
📍 Jharkhand → Singhbhum, Noamundi.
📍 Chhattisgarh → Durg–Bastar–Chandrapur belt.
📍 Karnataka → Bellary, Chitradurga.
👉 India is a leading exporter of iron ore.
🔵 Q31. Explain any five measures to conserve mineral resources.
🟢 Answer:
♻️ Recycling of metals.
⛏️ Using low-grade ores with new technology.
🚜 Improving mining efficiency.
🌍 Substituting rare minerals with alternatives.
👥 Awareness and government regulation.
🔵 Q32. “Solar energy has a bright future in India.” Justify with five points.
🟢 Answer:
🌞 India lies in tropical belt → abundant sunlight.
🏜️ Desert areas (Rajasthan, Gujarat) ideal for solar farms.
🏠 Useful in rural areas for lighting, cooking, irrigation.
🌍 Eco-friendly, reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
⚡ Government promoting large-scale solar parks.
🌟 SECTION E — Case/Source-Based (4 marks each)
🔵 Q33. Case: A farmer in Rajasthan installs solar panels to pump water.
(i) Which type of energy is this? (1)
(ii) Why is it suitable for Rajasthan? (1)
(iii) State two benefits of solar energy. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🌞 Non-conventional (solar) energy.
(ii) ☀️ Rajasthan gets abundant sunlight year-round.
(iii) ♻️ Renewable, eco-friendly; ⚡ reduces cost in long term.
🔵 Q34. Case: A factory in Odisha uses bauxite as raw material.
(i) Which metal is extracted? (1)
(ii) State two uses of this metal. (2)
(iii) Name one producing state apart from Odisha. (1)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🪨 Aluminium.
(ii) ✈️ Used in aircraft; 🏭 electrical industry.
(iii) 📍 Gujarat / Maharashtra.
🔵 Q35. Source: “India has large thorium deposits in coastal sands.”
(i) Which energy resource can use thorium? (1)
(ii) Name one coastal state with such deposits. (1)
(iii) Give two advantages of nuclear energy. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) ☢️ Nuclear energy.
(ii) 📍 Kerala.
(iii) ⚡ Produces large power with small fuel; 🌍 low greenhouse gas emissions.
🌟 SECTION F — Map/Skill-Based (5 marks)
🔵 Q36. On an outline map of India, locate and label any four major coal fields.
🟢 Answer:
Jharia (Jharkhand)
Raniganj (West Bengal)
Singrauli (Madhya Pradesh)
Korba (Chhattisgarh)
🔵 Q37. For visually impaired candidates: List any four major petroleum-producing areas of India.
🟢 Answer:
Digboi (Assam)
Naharkatia (Assam)
Bombay High (offshore Maharashtra)
Ankleshwar (Gujarat)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
