Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 12. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
🌟 Introduction
🔵 Electric current produces magnetic effects, first discovered by Hans Christian Oersted in 1820.
🟢 This chapter explains how current and magnetism are interlinked, the magnetic field around conductors, right-hand rules, force on conductors, electric motor, electromagnetic induction, and electric generator.
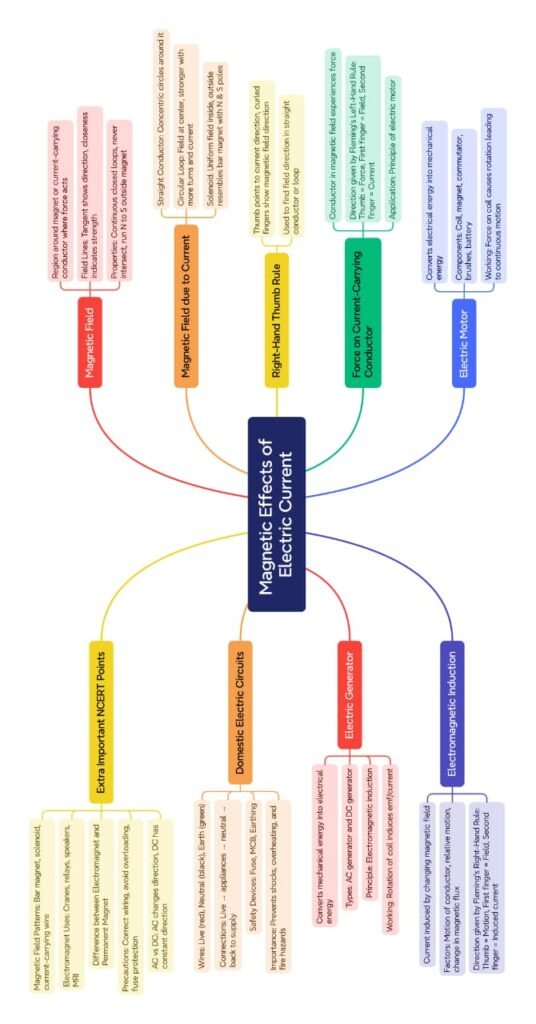
🌍 Magnetic Field and Field Lines


🌿 Magnetic field: Region around a magnet/current-carrying conductor where its influence can be felt.
🟡 Magnetic field lines: Imaginary lines drawn to represent field.
Start from North pole, end at South pole.
Inside magnet, they go from South → North.
Crowded lines = strong field.
💡 Compass needle aligns along field lines.
⚡ Oersted’s Experiment
🔵 Passing current through a conductor deflects nearby compass needle.
🟢 Concluded: current produces magnetic field.
🧠 Right-Hand Thumb Rule
🌿 If you hold current-carrying conductor with right hand, thumb along current, curled fingers show direction of magnetic field.
🟡 Helps in predicting circular field around straight conductor.
🔴 Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
🌿 Solenoid = coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire.
🟢 When current flows: behaves like a bar magnet.
🟡 Inside solenoid: field is uniform, parallel, strong.
🔵 Polarity depends on direction of current (Right-hand rule again).
💡 Applications: used in electromagnets, induction coils.
🟣 Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field
Discovered by Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule:
Stretch thumb, forefinger, middle finger mutually perpendicular.
Forefinger → field, middle → current, thumb → force (motion).
Basis of working of electric motor.
🔋 Electric Motor
Device that converts electrical energy → mechanical energy.
Components:
🔵 Coil of insulated copper wire (armature).
🟢 Permanent magnet or electromagnet.
🟡 Split-ring commutator (reverses current).
🔴 Brushes.
Principle: Force on current-carrying conductor in magnetic field.
Application: fans, mixers, machines.
🌞 Electromagnetic Induction
🔵 Discovered by Michael Faraday.
🟢 When magnetic field around conductor changes, induced current flows.
🟡 Factors: relative motion of magnet and coil, strength of magnet, number of turns.
✨ Right-Hand Rule (Fleming’s):
Forefinger → field, thumb → motion, middle finger → induced current.
⚙️ Electric Generator
Converts mechanical energy → electrical energy.
Principle: electromagnetic induction.
Components: armature coil, magnets, slip rings/commutator, brushes.
Generates AC or DC depending on arrangement.
💡 Domestic Electric Circuits
🔵 Electric power supplied at 220 V (in India).
🟢 Circuits have two wires: live and neutral.
🟡 Earth wire: safety measure.
🔴 Appliances connected in parallel for same voltage and independent operation.
🌿 Safety devices: fuse, MCB.
🟢 Summary
Current produces magnetic field (Oersted).
Direction: Right-hand thumb rule.
Solenoid acts as bar magnet with uniform field inside.
Force on conductor explained by Fleming’s Left-hand rule → basis of motor.
Electromagnetic induction → Faraday’s law, Fleming’s Right-hand rule → generator.
Household circuits: parallel connection, fuse, earth wire for safety.
📝 Quick Recap
⚡ Oersted: current produces magnetism.
👆 Right-hand thumb → direction of magnetic field.
🔄 Solenoid → bar magnet.
🖐️ Left-hand rule → motor principle.
🖖 Right-hand rule → generator principle.
🏠 Household wiring → parallel, fuse, earth wire.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
➡️Question 1
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
Answer
🔵 By right-hand thumb rule, magnetic field lines around straight current-carrying conductor form concentric circles.
✔️ Correct option: (d)
➡️Question 2
At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
(a) reduces substantially.
(b) does not change.
(c) increases heavily.
(d) vary continuously.
Answer
🟢 Short circuit → resistance drops → current becomes extremely high.
✔️ Correct option: (c)
➡️Question 3
State whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(b) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
Answer
(a) 🔵 True → inside a solenoid or circular coil, field is nearly uniform parallel lines.
(b) 🔴 False → green insulation is earth wire, live wire is red/brown.
➡️Question 4
List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Answer
🌿 Passing electric current through a straight conductor.
🌍 Using a current-carrying coil/solenoid.
➡️Question 5
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer
🟢 Force = maximum when conductor is placed perpendicular to magnetic field.
🔵 Zero when conductor is parallel to field.
➡️Question 6
Imagine you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Answer
🌿 Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule → electron current opposite to conventional.
Beam deflected to right → force to right, motion forward.
Magnetic field must be downward.
➡️Question 7
State the rule to determine the direction of –
(i) Magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current.
(ii) Force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to it.
(iii) Current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Answer
(i) 🔵 Right-hand thumb rule → thumb = current, fingers curl = field.
(ii) 🟢 Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule → thumb = force, forefinger = field, middle = current.
(iii) 🟡 Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule → thumb = motion, forefinger = field, middle = induced current.
➡️Question 8
When does an electric short circuit occur?
Answer
🔴 When live and neutral wires come into direct contact due to damaged insulation/overload.
🌍 Resistance drops, current increases abnormally → heating/fire.
➡️Question 9
What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer
🔵 Function: provides path for leakage current to ground.
🟢 Necessity: prevents electric shock if metallic body becomes live.
🟡 Ensures safety of user.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
SECTION A – (Q1–Q18 : MCQs)
Question 1: The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current is
🔵 (A) Decreasing
🟢 (B) Increasing
🟠 (C) Uniform
🔴 (D) Zero
✔️ Answer: (C) Uniform
Question 2: The direction of magnetic field lines around a straight current-carrying conductor can be found by
🔵 (A) Right-hand thumb rule
🟢 (B) Fleming’s left-hand rule
🟠 (C) Fleming’s right-hand rule
🔴 (D) Left-hand thumb rule
✔️ Answer: (A) Right-hand thumb rule
Question 3: A current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences maximum force when
🔵 (A) Parallel to field
🟢 (B) Perpendicular to field
🟠 (C) At 45° to field
🔴 (D) None of these
✔️ Answer: (B) Perpendicular to field
Question 4: Which rule gives the direction of induced current?
🔵 (A) Fleming’s left-hand rule
🟢 (B) Right-hand thumb rule
🟠 (C) Fleming’s right-hand rule
🔴 (D) Ampere’s circuital law
✔️ Answer: (C) Fleming’s right-hand rule
Question 5: Magnetic field lines inside a bar magnet run
🔵 (A) From north to south
🟢 (B) From south to north
🟠 (C) From side to side
🔴 (D) None of these
✔️ Answer: (B) From south to north
Question 6: A freely suspended bar magnet always points in
🔵 (A) East-West
🟢 (B) North-South
🟠 (C) Vertical
🔴 (D) Random
✔️ Answer: (B) North-South
Question 7: The force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field is given by
🔵 (A) F = BIL sin θ
🟢 (B) F = BIL cos θ
🟠 (C) F = BIL tan θ
🔴 (D) F = 0
✔️ Answer: (A) F = BIL sin θ
Question 8: The magnetic field due to a solenoid increases if
🔵 (A) Current decreases
🟢 (B) Number of turns decreases
🟠 (C) Current or turns increase
🔴 (D) Core is removed
✔️ Answer: (C) Current or turns increase
Question 9: In domestic appliances like electric bell, we use
🔵 (A) Permanent magnet
🟢 (B) Electromagnet
🟠 (C) Bar magnet
🔴 (D) Compass needle
✔️ Answer: (B) Electromagnet
Question 10: The device used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy is
🔵 (A) Galvanometer
🟢 (B) Electric motor
🟠 (C) Generator
🔴 (D) Battery
✔️ Answer: (B) Electric motor
Question 11: The device converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is
🔵 (A) Generator
🟢 (B) Motor
🟠 (C) Solenoid
🔴 (D) Battery
✔️ Answer: (A) Generator
Question 12: The direction of induced current in a coil opposes the change in magnetic flux. This is called
🔵 (A) Coulomb’s law
🟢 (B) Ohm’s law
🟠 (C) Lenz’s law
🔴 (D) Faraday’s law
✔️ Answer: (C) Lenz’s law
Question 13: A soft iron core increases the magnetic field in a solenoid because
🔵 (A) Reduces resistance
🟢 (B) Increases magnetic permeability
🟠 (C) Increases resistance
🔴 (D) Increases voltage
✔️ Answer: (B) Increases magnetic permeability
Question 14: In Fleming’s left-hand rule, the middle finger represents
🔵 (A) Magnetic field
🟢 (B) Motion
🟠 (C) Current
🔴 (D) Force
✔️ Answer: (C) Current
Question 15: The split ring in an electric motor is used for
🔵 (A) Continuous rotation of coil
🟢 (B) Reversing current direction
🟠 (C) Increasing voltage
🔴 (D) Both (A) and (B)
✔️ Answer: (D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 16: A current through a circular loop produces
🔵 (A) No magnetic field
🟢 (B) Magnetic field at centre
🟠 (C) Electric field
🔴 (D) None of these
✔️ Answer: (B) Magnetic field at centre
Question 17: The strength of magnetic field around a straight conductor depends on
🔵 (A) Length of wire
🟢 (B) Current magnitude
🟠 (C) Type of metal
🔴 (D) None
✔️ Answer: (B) Current magnitude
Question 18: When current through conductor increases, the magnetic field lines become
🔵 (A) Farther apart
🟢 (B) Closer together
🟠 (C) Vanish
🔴 (D) Unchanged
✔️ Answer: (B) Closer together
SECTION B – (Q19–Q27 : Short & Mid-Length Answers)
Q19. Define magnetic field and magnetic field lines.
➡️ Magnetic field is the region around a magnet or current-carrying conductor in which magnetic force can be experienced.
➡️ Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines representing the direction and strength of magnetic field.
Q20. Write two properties of magnetic field lines.
✔️ Magnetic field lines never intersect.
✔️ Closer lines → stronger field, wider → weaker field.
Q21. State the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
➡️ If the right-hand thumb points in the direction of current, the fingers encircle in direction of magnetic field lines.
Q22. What is solenoid? Draw its magnetic field pattern.
💡 A solenoid is a cylindrical coil of many turns of insulated wire. It behaves like a bar magnet when current flows.
Q23. What are electromagnets? Mention two uses.
✔️ Soft iron core wound with coil carrying current forms electromagnet.
✔️ Uses – in electric bells, cranes, electric motors.
Q24. Define electromagnetic induction.
💡 The process of generating electric current in a conductor due to changing magnetic field.
Q25. State Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
➡️ If thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of left hand are mutually perpendicular,
Forefinger → Field,
Middle → Current,
Thumb → Force (motion).
Q26. Write two differences between an electric motor and a generator.
| Motor | Generator |
| Current supplied | Current induced |
| Converts electrical → mechanical | Converts mechanical → electrical |
Q27. Explain why a current-carrying conductor experiences force in a magnetic field.
✔️ Magnetic field exerts force on moving charges in the wire, producing mechanical motion.
SECTION C – (Q28–Q30 : Long & Case-Based Answers)
Q28. Explain the working of an electric motor with a neat diagram.
💡 Principle: A current-carrying conductor in magnetic field experiences a force (Fleming’s left-hand rule).
✔️ Parts: Armature coil, commutator, brushes, field magnet, battery.
✔️ Working:
- Current enters coil → two forces act in opposite directions.
- Coil rotates continuously due to commutator reversing current every half rotation.
➡️ Converts electrical energy → mechanical energy.
Q29. Describe the principle and working of an AC generator.
💡 Principle: Electromagnetic induction – current is induced in a conductor when magnetic flux changes.
✔️ Construction: Armature coil ABCD between poles of magnet, slip rings, brushes.
✔️ Working: As coil rotates, magnetic flux changes → induced alternating current (AC).
Q30. Case Study:
A coil is moved rapidly between poles of a magnet.
(a) What happens?
(b) What type of current is produced?
(c) State any two factors on which induced current depends.
✔️ (a) Current is induced in coil.
✔️ (b) Alternating current (AC) is produced.
✔️ (c) Depends on (i) rate of change of magnetic flux and (ii) strength of magnetic field.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
