Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 2. Acids, Bases and Salts
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 1. Introduction to Acids, Bases, and Salts
Chemistry deals with substances and their transformations. Among all the substances we use daily, acids, bases, and salts form the foundation of chemical behavior.
➡️ The sourness of lemon, the bitterness of soap, and the taste of table salt are all linked to these substances.
✏️ Note: Every acid, base, and salt has its own physical and chemical characteristics that define its behavior in reactions.
- Acids taste sour and turn blue litmus red.
- Bases taste bitter and turn red litmus blue.
- Salts are formed when acids react with bases, undergoing neutralization.
💡 Concept: The study of acids, bases, and salts helps us understand natural processes (like digestion and soil pH), industrial applications (fertilizers, cleaning agents, bleaching powder), and environmental aspects (acid rain, neutralization in agriculture).
🟢 2. What are Acids?
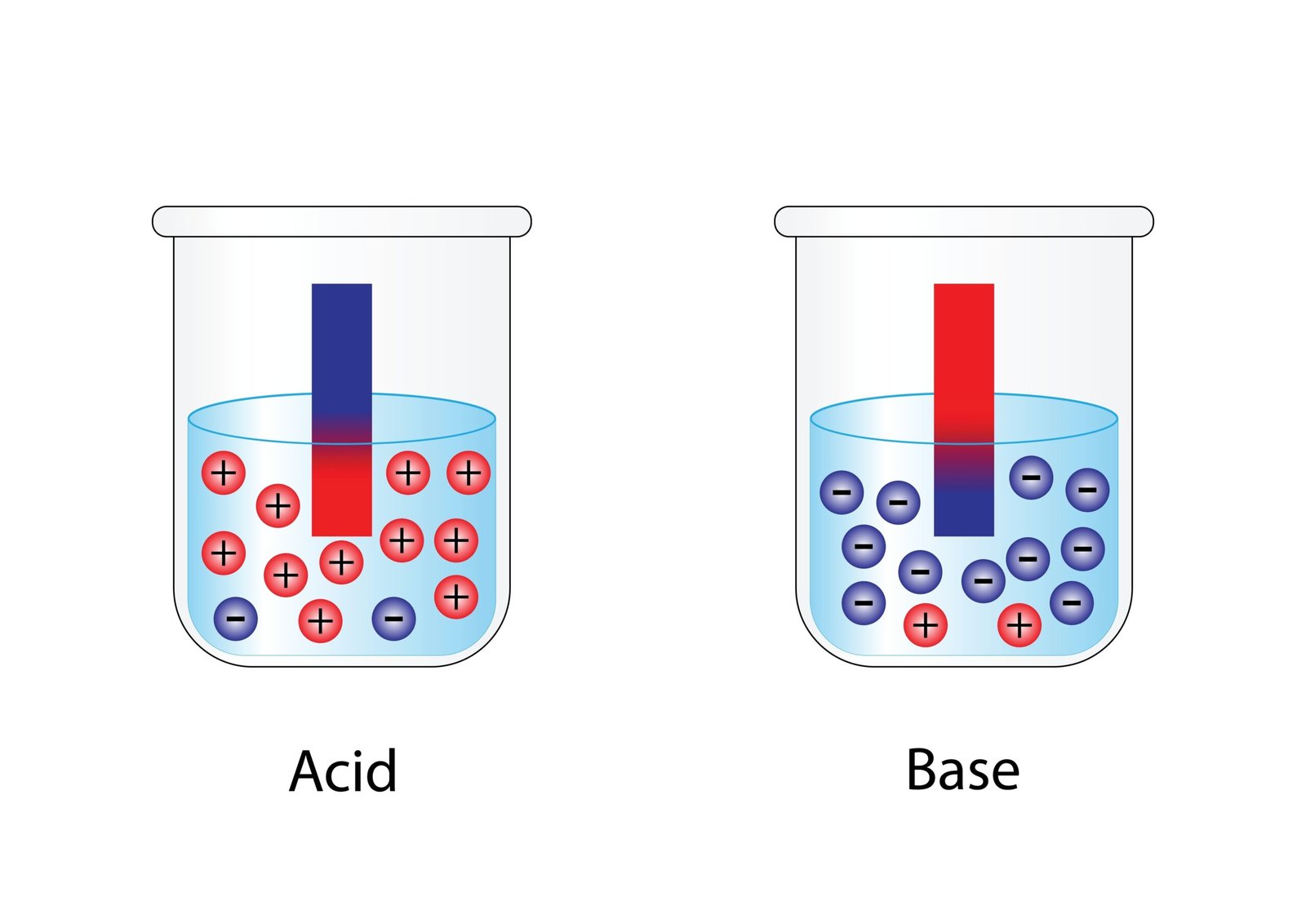
Acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) when dissolved in water.
🔵 General Properties:
- Sour in taste.
- Turn blue litmus → red.
- Conduct electricity in aqueous solution (due to free ions).
- React with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
🔵 Examples:
➡️ Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
➡️ Sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄)
➡️ Nitric acid (HNO₃)
➡️ Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
✏️ Note: The strength of an acid depends on the number of H⁺ ions produced in solution.
💡 Types of Acids:
1️⃣ Strong acids – completely ionize in water (HCl, H₂SO₄, HNO₃).
2️⃣ Weak acids – partially ionize (CH₃COOH, H₂CO₃).
🔴 Chemical Test for Acids: Add a few drops of blue litmus → it turns red, confirming acid presence.
🟡 3. What are Bases?
Bases are substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in water.
🔵 General Properties:
- Bitter in taste.
- Soapy/slippery to touch.
- Turn red litmus → blue.
- Conduct electricity in aqueous form.
🧠 Examples:
➡️ Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
➡️ Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
➡️ Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂)
➡️ Ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH)
💡 Types of Bases:
1️⃣ Strong bases – NaOH, KOH (completely ionize).
2️⃣ Weak bases – NH₄OH (partially ionizes).
✏️ Note: All alkalis are bases, but not all bases are alkalis.
➡️ Alkalis are water-soluble bases.
🔴 4. Indicators – Identifying Acids and Bases
Indicators are substances that change colour in the presence of an acid or a base.
🔵 Natural Indicators:
- Litmus (blue/red)
- Turmeric
- China rose (Hibiscus)
🟢 Synthetic Indicators:
- Phenolphthalein → colourless in acid, pink in base.
- Methyl orange → red in acid, yellow in base.
🟡 Olfactory Indicators:
➡️ Some natural substances change odour with pH:
- Onion smell disappears in base, present in acid.
- Vanilla and clove also show similar behaviour.
💡 Concept: Indicators work due to pH changes (hydrogen ion concentration) in the medium.
🔵 5. Reaction of Acids and Bases with Metals
Acids react with active metals to form salt and hydrogen gas.
➡️ Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂↑
🟢 Bases also react with certain metals (like Zn, Al) to give hydrogen gas.
➡️ 2NaOH + Zn → Na₂ZnO₂ + H₂↑
✏️ Note: Hydrogen gas can be confirmed by the “pop sound test” when a burning matchstick is brought near.
🟢 6. Reaction of Metal Carbonates and Metal Bicarbonates with Acids
These reactions produce salt, water, and carbon dioxide.
➡️ Na₂CO₃ + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H₂O + CO₂
➡️ NaHCO₃ + HCl → NaCl + H₂O + CO₂
✔️ The effervescence observed is due to carbon dioxide gas.
💡 Concept: CO₂ turns lime water milky because of CaCO₃ formation.
➡️ Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
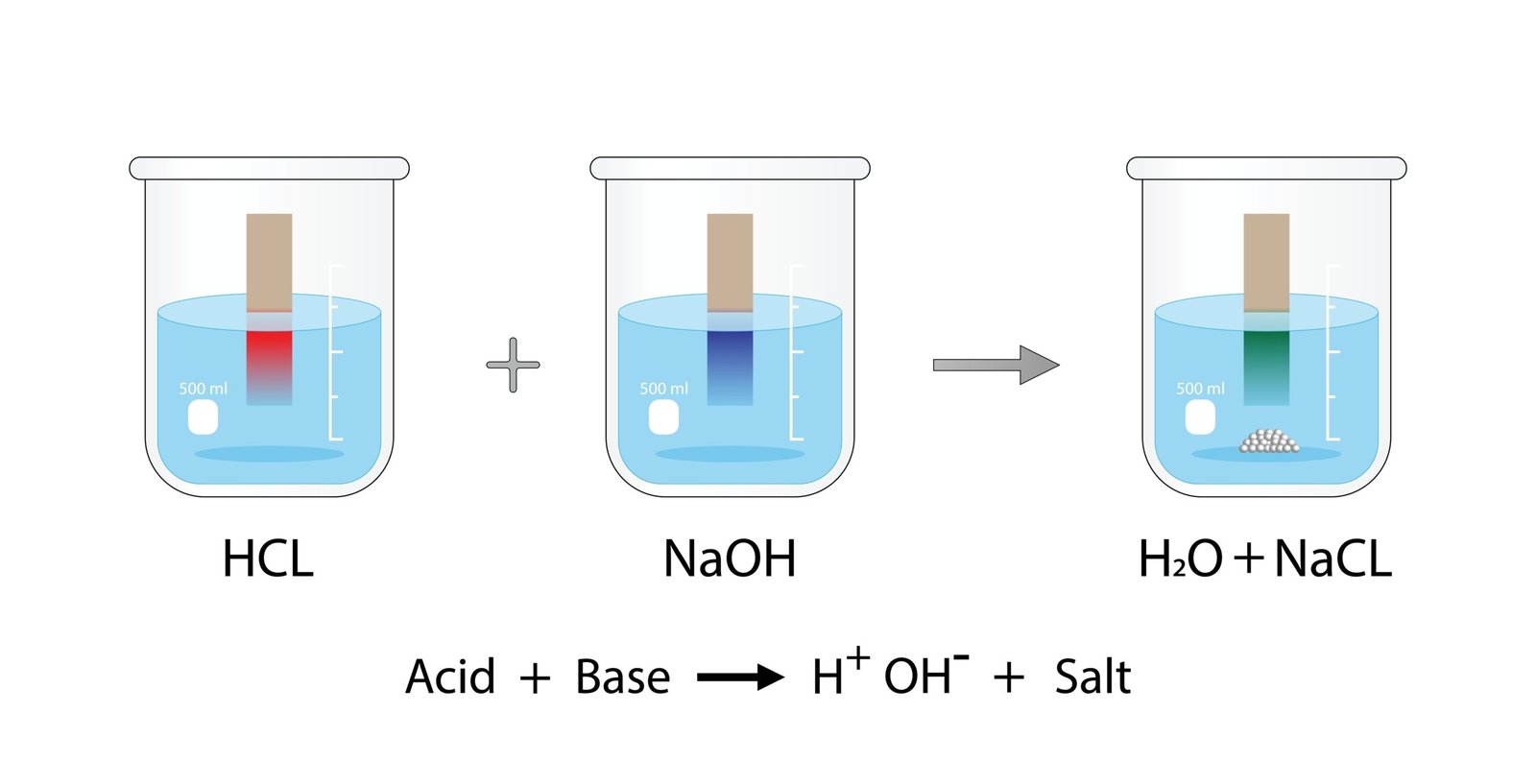
🟡 7. Reaction of Acids and Bases with Each Other – Neutralization
When an acid reacts with a base, both neutralize each other forming salt and water.
➡️ HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
✔️ Heat is released in this reaction — it’s an exothermic reaction.
💡 Concept: Neutralization helps maintain pH balance in our body, soil, and environment.
🔴 8. Reaction of Metallic Oxides and Non-Metallic Oxides
🧠 Metallic oxides (like CuO, MgO) are basic.
➡️ CuO + H₂SO₄ → CuSO₄ + H₂O
💡 Non-metallic oxides (like CO₂, SO₂) are acidic.
➡️ CO₂ + Ca(OH)₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
✏️ Note: These reactions show how oxides behave like acids or bases.
🟢 9. Acids, Bases, and Salts in Aqueous Solution
When acids or bases dissolve in water, they produce ions responsible for their properties.
🔵 Example 1 – Acid in water:
➡️ HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
🔵 Example 2 – Base in water:
➡️ NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
💡 Concept: The strength of an acid or base depends on the concentration of H⁺ or OH⁻ ions.
✏️ Note: Always add acid to water slowly (never the other way) to avoid splashing due to heat released.
🟡 10. The pH Scale (Power of Hydrogen)
The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution.
Range: 0 – 14

🔵 pH < 7 → Acidic
🟢 pH = 7 → Neutral
🔴 pH > 7 → Basic
💡 Example Values:
- Stomach acid ≈ pH 1–2
- Pure water ≈ pH 7
- Soap solution ≈ pH 9–10
✏️ Note: pH helps in biological and environmental balance (e.g., soil testing, acid rain study).
🔴 11. Importance of pH in Everyday Life
1️⃣ Human body: Blood pH ≈ 7.4; imbalance leads to health issues.
2️⃣ Plants: Soil pH affects nutrient absorption.
3️⃣ Animals: Aquatic life survives only in specific pH ranges.
4️⃣ Tooth decay: Occurs when mouth pH falls below 5.5 due to acid-producing bacteria.
5️⃣ Antacids: Neutralize stomach acidity (Mg(OH)₂, NaHCO₃).
6️⃣ Acid rain: Damages monuments, aquatic life; caused by SO₂ and NO₂ gases forming acids.
🟢 12. Common Salts and Their Uses
🔹 (a) Sodium Chloride (NaCl)

💡 Common salt — used in food and as raw material for various chemicals.
➡️ NaCl → basis for NaOH, Na₂CO₃, NaHCO₃, bleaching powder, etc.
🔹 (b) Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) – Caustic Soda

🧪 Prepared by electrolysis of brine (salt solution).
➡️ 2NaCl + 2H₂O → 2NaOH + Cl₂ + H₂
✔️ Uses: Soaps, detergents, paper, artificial fibres.
🔹 (c) Bleaching Powder (CaOCl₂)
➡️ Prepared by reacting chlorine with dry slaked lime.
Ca(OH)₂ + Cl₂ → CaOCl₂ + H₂O
✔️ Used for disinfecting water, bleaching cotton, removing stains.
🔹 (d) Baking Soda (NaHCO₃)

➡️ Produced using ammonia, CO₂, and brine (Solvay process).
✔️ Uses: Baking, antacid, fire extinguisher (CO₂ release).
🔹 (e) Washing Soda (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O)
➡️ Made from sodium carbonate crystals.
✔️ Uses: Softening water, glass industry, cleaning agent.
🔹 (f) Plaster of Paris (CaSO₄·½H₂O)
💡 Formed by heating gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O):
➡️ CaSO₄·2H₂O → CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O
✔️ Used for casts, moulds, and wall finishing.
✏️ Note: When mixed with water, Plaster of Paris sets into hard gypsum again.
🔵 13. Importance of Salts in Daily Life
- Maintain body’s electrolyte balance.
- Used in fertilizers, medicines, cleaning agents.
- Industrial raw materials for numerous chemical products.
💡 Concept: The neutralization reactions of acids and bases in industry produce various salts.
🟡 14. Crystals of Salts and Water of Crystallization
Some salts contain water molecules inside their structure. This is called water of crystallization.
➡️ Example: CuSO₄·5H₂O (blue vitriol)
➡️ Na₂CO₃·10H₂O (washing soda)
➡️ CaSO₄·2H₂O (gypsum)
✏️ Note: When heated, these salts lose water and change colour.
💡 Example: Blue CuSO₄·5H₂O becomes white CuSO₄ on heating.
🔴 15. Reactions Showing Formation of Important Salts
🔵 Formation of NaCl (neutralization):
➡️ HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O

🔵 Formation of Na₂CO₃ (from NaCl):
➡️ 2NaCl + CaCO₃ → Na₂CO₃ + CaCl₂
🔵 Formation of NaHCO₃ (baking soda):
➡️ NaCl + CO₂ + NH₃ + H₂O → NaHCO₃ + NH₄Cl
✔️ Each of these salts has important industrial applications.
🟢 16. Environmental and Safety Aspects
1️⃣ Acid rain: formed when SO₂/NO₂ dissolve in water — harmful to monuments, soil, and aquatic life.
2️⃣ Handling acids/bases: always dilute carefully, use protective gear.
3️⃣ Neutralization in agriculture: lime (Ca(OH)₂) added to acidic soil.
4️⃣ Waste management: basic wastes neutralize acidic effluents.
💡 Concept: Neutralization maintains ecological and chemical balance.
🟡 17. Key Chemical Reactions Summary
➡️ Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂↑
➡️ Na₂CO₃ + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H₂O + CO₂
➡️ HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
➡️ Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
➡️ CuO + H₂SO₄ → CuSO₄ + H₂O
➡️ CaSO₄·2H₂O → CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O
✔️ These equations represent the essence of acid–base–salt interactions.
⚡ Summary (~300 words)
🔵 Acids: Produce H⁺ ions in water, taste sour, turn blue litmus red. Examples: HCl, H₂SO₄, CH₃COOH.
🟢 Bases: Produce OH⁻ ions, feel slippery, turn red litmus blue. Examples: NaOH, Ca(OH)₂, NH₄OH.
🟡 Indicators: Help identify acids and bases through colour change — litmus, methyl orange, phenolphthalein.
🔴 Reactions of Acids & Bases:
1️⃣ With metals → hydrogen gas.
2️⃣ With carbonates → CO₂ gas.
3️⃣ With each other → salt + water (neutralization).
4️⃣ Metallic oxides → act as bases; non-metallic oxides → act as acids.
💡 pH Scale: Measures hydrogen ion concentration.
pH < 7 → Acidic; pH > 7 → Basic; pH = 7 → Neutral.
🌿 Uses of pH: Vital in digestion, soil treatment, acid rain study, tooth care, and medical balance.
🧠 Common Salts: NaCl, NaOH, Na₂CO₃, NaHCO₃, CaOCl₂, CaSO₄·½H₂O.
✔️ Formed via neutralization and used in soap, glass, paper, cement, and medical products.
💧 Water of Crystallization: Water molecules in salt structure (e.g., CuSO₄·5H₂O).
🌎 Environmental Impact: Acid rain, rusting, and corrosion controlled via neutralization. Waste neutralization protects soil and water quality.
✔️ In essence: Acids, bases, and salts are interlinked through neutralization reactions forming the chemical foundation of life and industry.
📝 Quick Recap
1️⃣ Acids → release H⁺ ions; sour; blue → red.
2️⃣ Bases → release OH⁻ ions; bitter; red → blue.
3️⃣ Neutralization → acid + base → salt + water.
4️⃣ pH → measures acidity/basicity (0–14 scale).
5️⃣ Salts → products of neutralization; used in industries and daily life.
6️⃣ Safety → dilute acids carefully, handle bases with gloves, store salts dry.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question
- A solution turns red litmus blue, its pH is likely to be
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept:
🔵 If a solution turns red litmus blue, it is basic / alkaline.
🔵 Basic solutions have pH > 7.
🟢 Now check options:
(a) 1 → strongly acidic
(b) 4 → acidic
(c) 5 → weakly acidic
(d) 10 → basic / alkaline
✔️ Final: The correct answer is (d) 10.
✔️ Correct option: (d)
🔵 Question
2. A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime-water milky. The solution contains
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl
🟢 Answer
💡 Fact: Egg-shells contain calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
🔵 Step 1: Acid + CaCO₃ → salt + water + carbon dioxide gas.
🟢 The CO₂ gas turns lime water milky due to CaCO₃ formation.
➡️ Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O (milkiness in lime water)
🔵 Strong clue: Only an acid will react like this.
Now check options:
(a) NaCl → neutral salt, will not release CO₂ with egg-shells
(b) HCl → acid, reacts with CaCO₃ to form CO₂
(c) LiCl → neutral salt
(d) KCl → neutral salt
✔️ Final: The correct answer is (b) HCl.
✔️ Correct option: (b)
🔵 Question
3. 10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL
🟢 Answer
💡 Neutralisation idea: Acid reacts with base in fixed ratio.
✏️ Note: If we double the NaOH volume, we must double the HCl volume to keep the same neutralisation.
🔵 Step 1: 10 mL NaOH needs 8 mL HCl.
🔵 Step 2: 20 mL NaOH is double of 10 mL.
🟡 Therefore HCl needed = 8 mL × 2.
➡️ 8 × 2 = 16.
✔️ Final: The correct answer is (d) 16 mL.
✔️ Correct option: (d)
🔵 Question
4. Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept:
🔵 Indigestion is caused by excess acid in the stomach.
🟢 Substances which neutralise excess acid are called antacids.
Now match:
(a) Antibiotic → kills bacteria
(b) Analgesic → pain killer
(c) Antacid → neutralises acid
(d) Antiseptic → kills germs on wounds
✔️ Final: The correct answer is (c) Antacid.
✔️ Correct option: (c)
🔵 Question
5. Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when –
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
🟢 Answer
💡 General concept for (a), (b), (c), (d):
🔵 Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
✔️ Hydrogen gas can be tested by pop sound.
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
🔵 Word equation:
➡️ Zinc + dilute sulphuric acid → zinc sulphate + hydrogen
🔵 Balanced chemical equation:
➡️ Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂↑
✔️ Final: Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
🔵 Word equation:
➡️ Magnesium + dilute hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
🔵 Balanced chemical equation:
➡️ Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂↑
✔️ Final: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
🔵 Word equation:
➡️ Aluminium + dilute sulphuric acid → aluminium sulphate + hydrogen
🔵 Balanced chemical equation (careful):
➡️ 2Al + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂↑
✔️ Final: 2Al + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
🔵 Word equation:
➡️ Iron + dilute hydrochloric acid → iron(II) chloride + hydrogen
🔵 Balanced chemical equation:
➡️ Fe + 2HCl → FeCl₂ + H₂↑
✔️ Final: Fe + 2HCl → FeCl₂ + H₂
✏️ Note: In all four reactions, hydrogen gas is released.
🔵 Question
6. Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an Activity to prove it.
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: An acid is not just “anything with hydrogen.”
🔵 Acids release H⁺ ions in water.
🟢 Alcohol and glucose contain hydrogen but they do not release H⁺ in water like acids do.
🔵 Activity (as done in lab / NCERT style):
1️⃣ Take two beakers.
2️⃣ Beaker A: dilute HCl solution in water.
3️⃣ Beaker B: glucose solution or alcohol solution in water.
4️⃣ Insert two clean inert electrodes (like graphite rods) in each beaker.
5️⃣ Connect both setups to a battery and a bulb.
🟡 Observation:
🔵 Bulb glows in beaker with HCl.
🟢 Bulb does not glow in beaker with glucose or alcohol.
💡 Explanation:
🔵 HCl in water forms ions (H⁺, Cl⁻) that conduct electricity.
🟢 Glucose / alcohol solutions do not form ions that carry current.
✔️ Final: Alcohols and glucose are not classified as acids because they do not produce H⁺ ions in aqueous solution and they do not conduct electricity like acids in water.
🔵 Question
7. Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
🟢 Answer
💡 Idea: Electrical conduction in liquids happens due to ions.
🔵 Step 1: Distilled water is pure H₂O.
🟢 It has almost no dissolved salts, so almost no ions.
🟡 With no ions, it does not conduct electricity.
🔵 Step 2: Rain water is not pure.
➡️ When rain falls through the atmosphere, it dissolves gases like CO₂ and other substances forming ions (for example, H⁺, HCO₃⁻ etc.).
🟢 These ions allow current to pass.
✔️ Final:
🔵 Distilled water = no ions = does not conduct.
🟢 Rain water = contains dissolved ionic substances = conducts electricity.
🔵 Question
8. Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
🟢 Answer
💡 Acidic behaviour means “ability to produce H⁺ ions.”
🔵 Step 1: Acids like HCl release H⁺ ions only when dissolved in water.
➡️ HCl (gas) + H₂O → H₃O⁺ + Cl⁻
🟡 Here, water helps form ions.
🔵 Step 2: In the absence of water, acids are not ionised.
🟢 If there are no free H⁺ (or H₃O⁺) ions, then the substance will not show acidic properties such as conductivity, sour taste, or turning blue litmus red.
✔️ Final:
Acids need water to ionise and produce H⁺ ions. Without water, they cannot exhibit acidic behaviour.
🔵 Question
9. Five solutions A, B, C, D and E when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9, respectively. Which solution is
(a) neutral?
(b) strongly alkaline?
(c) strongly acidic?
(d) weakly acidic?
(e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
🟢 Answer
💡 pH facts:
🔵 pH < 7 → acidic
🟢 pH = 7 → neutral
🔴 pH > 7 → basic / alkaline
💡 Smaller pH → stronger acid.
💡 Larger pH → stronger base.
Given:
A → pH 4
B → pH 1
C → pH 11
D → pH 7
E → pH 9
Now answer each part:
(a) neutral?
➡️ D (pH 7)
(b) strongly alkaline?
➡️ C (pH 11)
(c) strongly acidic?
➡️ B (pH 1)
(d) weakly acidic?
➡️ A (pH 4)
(e) weakly alkaline?
➡️ E (pH 9)
🟡 Second part: Arrange pH values in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
✏️ Note: More hydrogen ion (H⁺) means stronger acid → lower pH.
So highest [H⁺] corresponds to lowest pH.
Order from lowest [H⁺] to highest [H⁺] OR from basic to very acidic?
The question says “in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.”
➡️ Start with lowest H⁺ (strongest base) and go to highest H⁺ (strongest acid).
🔵 pH 11 (C) → least H⁺
🔵 pH 9 (E)
🔵 pH 7 (D)
🔵 pH 4 (A)
🔵 pH 1 (B) → most H⁺
✔️ Final order: C (11), E (9), D (7), A (4), B (1)
🔵 Question
10. Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A, while acetic acid (CH₃COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: Fizzing is due to hydrogen gas being released.
🔵 Faster fizzing = faster rate of gas formation.
🔵 Step 1: Both acids react with magnesium to form salt + hydrogen gas.
➡️ Mg + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂↑
➡️ Mg + 2CH₃COOH → (CH₃COO)₂Mg + H₂↑
🔵 Step 2: HCl is a strong acid.
🟢 It ionises completely in water and produces a high concentration of H⁺ ions.
🔵 Step 3: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH) is a weak acid.
🟡 It ionises only partially, so it produces fewer H⁺ ions.
✔️ Final:
Fizzing is more vigorous in test tube A (HCl) because HCl releases H⁺ ions more readily than acetic acid, so it reacts faster with magnesium to produce hydrogen gas.
🔵 Question
11. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
🟢 Answer
💡 Fact: Curd is more acidic than fresh milk.
🔵 Step 1: When milk turns to curd, bacteria convert lactose (milk sugar) into lactic acid.
🔵 Step 2: Formation of lactic acid increases acidity.
🟡 Higher acidity means lower pH.
✔️ Final:
The pH will decrease from 6 to a value less than 6 as milk turns into curd, because acids are produced during curd formation.
🔵 Question
12. A milkman adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
🟢 Answer
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline?
💡 Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO₃), which is mildly basic.
🔵 Step 1: Adding baking soda neutralises some natural acids in milk.
🔵 Step 2: This raises the pH above 7 (towards alkaline).
✔️ Final: He makes the milk slightly alkaline so it does not turn sour quickly.
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd?
🔵 Step 1: For curd to set, bacteria must produce enough lactic acid to bring pH down.
🟢 Step 2: If milk starts already alkaline, it takes longer for acidity to build up.
✔️ Final: The milk takes longer to curdle because extra acid must first neutralise the added baking soda before the milk can become acidic enough to turn into curd.
🔵 Question
13. Plaster of Paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
🟢 Answer
💡 Plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaSO₄·½H₂O).
🔵 Step 1: Plaster of Paris reacts with water to form gypsum (a hard solid).
➡️ CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O → CaSO₄·2H₂O
🔵 Step 2: If it absorbs moisture from air during storage, it will slowly convert to gypsum.
🟡 Then it will set / harden in the container and become useless.
✔️ Final:
It must be stored in moisture-proof containers to prevent it from reacting with water vapour in air and becoming hard.
🔵 Question
14. What is a neutralisation reaction? Give two examples.
🟢 Answer
💡 Definition:
🔵 A neutralisation reaction is a reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
🔵 Example 1:
➡️ HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
🟡 Here HCl (acid) reacts with NaOH (base) to form sodium chloride and water.
🔵 Example 2:
➡️ H₂SO₄ + Ca(OH)₂ → CaSO₄ + 2H₂O
🟡 Sulphuric acid reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium sulphate and water.
✔️ Final:
Neutralisation is acid + base → salt + water, often with release of heat (exothermic).
🔵 Question
15. Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
🟢 Answer
💡 Part 1: Washing soda
🔵 Washing soda is sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O).
🟢 Uses:
1️⃣ It is used for softening hard water.
2️⃣ It is used in the manufacture of glass, soaps, and detergents.
💡 Part 2: Baking soda
🔵 Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO₃).
🟢 Uses:
1️⃣ It is used in baking as a leavening agent to make cakes and bread soft and fluffy (releases CO₂ on heating).
2️⃣ It is used as an antacid to neutralise excess acid in the stomach.
✔️ Final summary for Q15:
🟡 Washing soda → cleaning / water softening / glass industry.
🟡 Baking soda → baking / antacid / fire extinguisher role.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
[CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER]
ESPECIALLY MAKE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔵 Section A – Very Short / Objective Type Questions (1 mark each)
Question 1:
Which of the following has a pH less than 7?
🔵 (A) Soap solution
🟢 (B) Milk
🟠 (C) Sodium hydroxide solution
🔴 (D) Lime water
Answer:
✔️ (B) Milk — It is slightly acidic, so its pH is below 7.
Question 2:
Which acid is present in lemon juice?
🔵 (A) Citric acid
🟢 (B) Lactic acid
🟠 (C) Acetic acid
🔴 (D) Formic acid
Answer:
✔️ (A) Citric acid — gives lemon its sour taste.
Question 3:
The chemical name of baking soda is:
🔵 (A) Sodium carbonate
🟢 (B) Sodium bicarbonate
🟠 (C) Calcium bicarbonate
🔴 (D) Sodium sulphate
Answer:
✔️ (B) Sodium bicarbonate — formula NaHCO₃.
Question 4:
Which of the following statements is true for bases?
🔵 (A) They turn blue litmus red
🟢 (B) They have a pH less than 7
🟠 (C) They release hydroxide ions in solution
🔴 (D) They taste sour
Answer:
✔️ (C) They release OH⁻ ions in solution — property of bases.
Question 5:
Which of the following is an example of a neutralisation reaction?
🔵 (A) HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
🟢 (B) 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
🟠 (C) Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂
🔴 (D) 2KClO₃ → 2KCl + 3O₂
Answer:
✔️ (A) HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O — acid reacts with base to form salt and water.
Question 6:
Which of these substances can be used to reduce acidity in the stomach?
🔵 (A) Common salt
🟢 (B) Antacid tablet
🟠 (C) Vinegar
🔴 (D) Lemon juice
Answer:
✔️ (B) Antacid tablet — contains basic compounds like magnesium hydroxide that neutralise excess acid.
🟢 Section B – Short Answer Type Questions (2 marks each)
Question 7:
Define acids and bases according to the Arrhenius concept. Give one example of each.
Answer:
💡 Concept:
🔵 Acids are substances which release hydrogen ions (H⁺) in aqueous solution.
➡️ Example: HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
🟢 Bases are substances which release hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in aqueous solution.
➡️ Example: NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻
✔️ Example acids: H₂SO₄, HCl
✔️ Example bases: NaOH, KOH
Question 8:
State the reason why dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
Answer:
✏️ Note: For a substance to show acidic behaviour, it must produce H⁺ ions in water.
💡 Dry HCl gas contains hydrogen chloride molecules, not ions.
➡️ In the absence of water, no ionisation occurs.
✔️ Hence, dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
Question 9:
Write the chemical formula for Plaster of Paris. How is it obtained from gypsum?
Answer:
🔵 Formula: CaSO₄·½H₂O (Calcium sulphate hemihydrate)
💡 Obtained by:
➡️ Heating gypsum (CaSO₄·2H₂O) at 100°C–150°C
🔵 Reaction:
CaSO₄·2H₂O → CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O
✔️ Plaster of Paris is formed by partial dehydration of gypsum.
Question 10:
Why should Plaster of Paris be stored in moisture-proof containers?
Answer:
💡 Concept: POP reacts with moisture to form gypsum, losing its setting property.
➡️ CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O → CaSO₄·2H₂O
🟢 Thus, to prevent this reaction, it must be stored in airtight, moisture-proof containers.
✔️ Otherwise, it becomes hard and unusable.
Question 11:
What is a neutralisation reaction? Write one example with balanced equation.
Answer:
💡 Concept: A neutralisation reaction occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
🔵 Example:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
✔️ Acid: HCl Base: NaOH Product: NaCl (salt) + Water
Question 12:
Explain why an aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity.
Answer:
💡 Concept: Acids ionise in water to produce H⁺ (or H₃O⁺) and other ions which conduct electricity.
➡️ HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
✔️ The movement of these ions carries electric current through the solution.
🟢 Hence, only aqueous (not dry) acids conduct electricity.
🟡 Section C – Short Answer Type-II Questions (3 marks each)
Question 13:
What are olfactory indicators? Give two examples and explain their action with acids and bases.
Answer:
💡 Concept: Olfactory indicators are substances whose smell changes in acidic or basic media.
🔵 Example 1: Vanilla essence
➡️ Its smell is recognised in acidic medium but not in basic medium.
🔵 Example 2: Clove oil
➡️ Its smell persists in acidic medium but disappears in basic medium.
✔️ These indicators work due to the effect of pH on volatile organic compounds.
Question 14:
Write the chemical equations to show the reaction of zinc with the following:
(a) Hydrochloric acid (b) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
✏️ For (a):
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
💡 Hydrogen gas is evolved; zinc chloride is formed.
✏️ For (b):
2NaOH + Zn → Na₂ZnO₂ + H₂
💡 Zinc reacts with base to form sodium zincate and hydrogen gas.
✔️ Thus, zinc reacts with both acids and bases.
Question 15:
What is meant by the term “pH of a solution”? How does the pH of a solution change when the concentration of hydrogen ions increases?
Answer:
💡 Concept: pH = –log₁₀[H⁺]
🔵 It represents the acidity or basicity of a solution.
➡️ When [H⁺] increases, pH decreases.
✔️ Hence, the solution becomes more acidic as the concentration of hydrogen ions rises.
Question 16:
A solution turns red litmus blue. Predict its nature and pH value.
Answer:
💡 Red litmus turns blue in basic solutions.
➡️ Therefore, the solution is basic.
🟢 Basic solutions have pH > 7.
✔️ Example: pH around 8–10.
Question 17:
Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5?
Answer:
💡 Concept: Tooth enamel (calcium phosphate) dissolves in acid.
➡️ When pH < 5.5, acid-producing bacteria form lactic acid.
🔵 Acid reacts with enamel:
Ca₅(PO₄)₃OH + acid → soluble salts + water
✔️ This causes corrosion and tooth decay.
Question 18:
Explain why sodium hydroxide is called a strong base and acetic acid is a weak acid.
Answer:
💡 Strong bases and acids completely ionise in water; weak ones ionise partially.
➡️ NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻ (complete ionisation)
➡️ CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺ (partial ionisation)
✔️ Therefore, NaOH is a strong base, while acetic acid is weak.
Question 19:
A few drops of universal indicator were added to a solution. It turned orange. What does this indicate about the nature and approximate pH of the solution?
Answer:
💡 Universal indicator colour orange corresponds to pH ≈ 4–5.
➡️ Hence, the solution is slightly acidic.
✔️ Example: Vinegar or tomato juice has similar pH.
Question 20:
Write the chemical name and formula of the compound formed when Plaster of Paris reacts with water.
Answer:
🔵 Reaction:
CaSO₄·½H₂O + 1½H₂O → CaSO₄·2H₂O
💡 The compound formed is Gypsum (Calcium sulphate dihydrate).
✔️ Chemical formula: CaSO₄·2H₂O.
Question 21:
What is a neutral salt? Give two examples and mention the acids and bases from which they are formed.
Answer:
💡 Concept: Neutral salts are formed when a strong acid reacts with a strong base.
➡️ Example 1: NaCl — from HCl and NaOH
➡️ Example 2: KNO₃ — from HNO₃ and KOH
✔️ These salts have pH ≈ 7 and do not hydrolyse in water.
Question 22:
What is meant by the water of crystallisation? Give two examples of salts containing water of crystallisation and mention their uses.
Answer:
💡 Definition: Water of crystallisation is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt.
🔵 Example 1: CuSO₄·5H₂O — Blue vitriol (used in electroplating)
🟢 Example 2: Na₂CO₁₀·10H₂O — Washing soda (used in softening hard water)
✔️ Heating removes water of crystallisation, changing the colour of crystals.
🔴 Section D – Long Answer Type Questions (4 marks each)
Question 23:
Explain the importance of pH in our daily life with suitable examples.
Answer:
💡 Concept: pH affects many biological and chemical processes in everyday life.
🔵 (a) pH in our digestive system:
➡️ The stomach produces hydrochloric acid (pH ≈ 1.5–3.5) which helps in digestion.
➡️ Excess acid causes indigestion or acidity.
➡️ Antacids like magnesium hydroxide neutralise excess acid.
🟢 (b) pH in tooth decay:
➡️ Bacteria in the mouth produce acids that lower pH below 5.5.
➡️ Enamel (calcium phosphate) dissolves in acid → tooth decay.
✔️ Brushing with basic toothpaste neutralises acid.
🟡 (c) pH and plants/soil:
➡️ Plants grow best in soil with pH 6–7.
➡️ If soil is too acidic, use slaked lime (Ca(OH)₂) to neutralise it.
🔴 (d) pH and aquatic life:
➡️ pH changes in water (due to acid rain) harm fish and aquatic organisms.
✔️ Therefore, maintaining correct pH is essential for survival of living organisms.
Question 24:
Describe how acids and bases react with metals, metal carbonates, and metal oxides, giving examples and balanced equations.
Answer:
💡 (a) Acids with metals:
➡️ Acids react with metals to form salt and hydrogen gas.
🔵 Example: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
💡 (b) Acids with metal carbonates:
➡️ They form salt, water, and carbon dioxide.
🟢 Example: Na₂CO₃ + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H₂O + CO₂
💡 (c) Bases with metals:
➡️ Active metals like zinc react with strong bases to form salt and hydrogen.
🟡 Example: 2NaOH + Zn → Na₂ZnO₂ + H₂
💡 (d) Metal oxides as bases:
➡️ They react with acids to form salt and water.
🔴 Example: CuO + 2HCl → CuCl₂ + H₂O
✔️ These reactions show that acids and bases have opposite chemical behaviour.
Question 25:
What are the various chemical compounds present in common salts? Write their uses.
Answer:
💡 Concept: Salts are ionic compounds formed by neutralisation of acids and bases.
🔵 1️⃣ Sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
➡️ Used in soap, paper, and textile industries.
🟢 2️⃣ Bleaching powder (CaOCl₂):
➡️ Used for disinfecting drinking water and bleaching cotton/fabrics.
🟡 3️⃣ Baking soda (NaHCO₃):
➡️ Used in baking, as antacid, and in fire extinguishers.
🔴 4️⃣ Washing soda (Na₂CO₃·10H₂O):
➡️ Used in softening hard water and glass manufacturing.
✳️ 5️⃣ Plaster of Paris (CaSO₄·½H₂O):
➡️ Used for making statues, models, and in orthopaedics.
✔️ All these compounds are derived from common salt NaCl through different reactions.
Question 26:
State reasons for the following observations:
(a) Dry HCl gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
(b) Acidic solutions conduct electricity.
(c) Antacid tablets are used by people suffering from acidity.
Answer:
🔵 (a) Dry HCl gas cannot ionise without water; hence, no H⁺ ions → no colour change.
🟢 (b) Acidic solutions have free H⁺ and other ions which conduct electricity.
🟡 (c) Antacids contain weak bases like Mg(OH)₂ that neutralise excess stomach acid.
✔️ These are direct consequences of acid-base reactions and ionisation in aqueous medium.
Question 27:
List and explain three important industrial applications of neutralisation reactions.
Answer:
💡 Concept: Neutralisation is the reaction of acid and base producing salt and water.
🔵 (a) Manufacture of fertilisers:
➡️ Ammonia gas (base) is neutralised with nitric acid to form ammonium nitrate (fertiliser).
NH₃ + HNO₃ → NH₄NO₃
🟢 (b) Treatment of acidic soil:
➡️ Farmers add quicklime (CaO) or slaked lime (Ca(OH)₂) to neutralise acidic soil.
🟡 (c) Industrial waste treatment:
➡️ Effluents from chemical industries often contain acids or alkalis.
➡️ Neutralising agents like Ca(OH)₂ or H₂SO₄ are added to make them harmless.
✔️ Thus, neutralisation plays a key role in environmental and industrial management.
Question 28:
Explain the preparation of bleaching powder. Write the balanced chemical equation and mention two uses.
Answer:
💡 Preparation:
➡️ Bleaching powder (CaOCl₂) is produced by passing chlorine gas over dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)₂].
🔵 Reaction:
Ca(OH)₂ + Cl₂ → CaOCl₂ + H₂O
🟢 Uses:
1️⃣ Used as a disinfectant for water and public places.
2️⃣ Used for bleaching cotton and linen in textile industry.
✔️ Bleaching powder is also used in paper and laundry industries.
Question 29:
Describe an activity to show that acid and base react to form salt and water (neutralisation reaction).
Answer:
💡 Activity:
1️⃣ Take dilute HCl in a beaker and measure its pH using universal indicator. (pH ≈ 1–2)
2️⃣ Add dilute NaOH slowly while stirring.
3️⃣ After each addition, check pH until it reaches 7 (neutral).
🔵 Observation:
➡️ pH gradually increases from acidic to neutral.
➡️ Heat is evolved — reaction is exothermic.
🟢 Equation:
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O
✔️ This shows that acids react with bases to form salt and water.
Question 30:
(OR) Explain with an activity how carbon dioxide is evolved when acid reacts with metal carbonates.
Answer:
💡 Activity:
1️⃣ Take marble chips (CaCO₃) in a flask.
2️⃣ Add dilute HCl through a funnel.
3️⃣ Gas bubbles evolve and pass through lime water.
🟢 Observation:
➡️ Lime water turns milky due to formation of calcium carbonate.
➡️ The milkiness disappears on excess CO₂.
🔵 Reactions:
CaCO₃ + 2HCl → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂
Ca(OH)₂ + CO₂ → CaCO₃ + H₂O
CaCO₃ + CO₂ + H₂O → Ca(HCO₃)₂
✔️ This proves that acids react with carbonates to evolve carbon dioxide gas.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
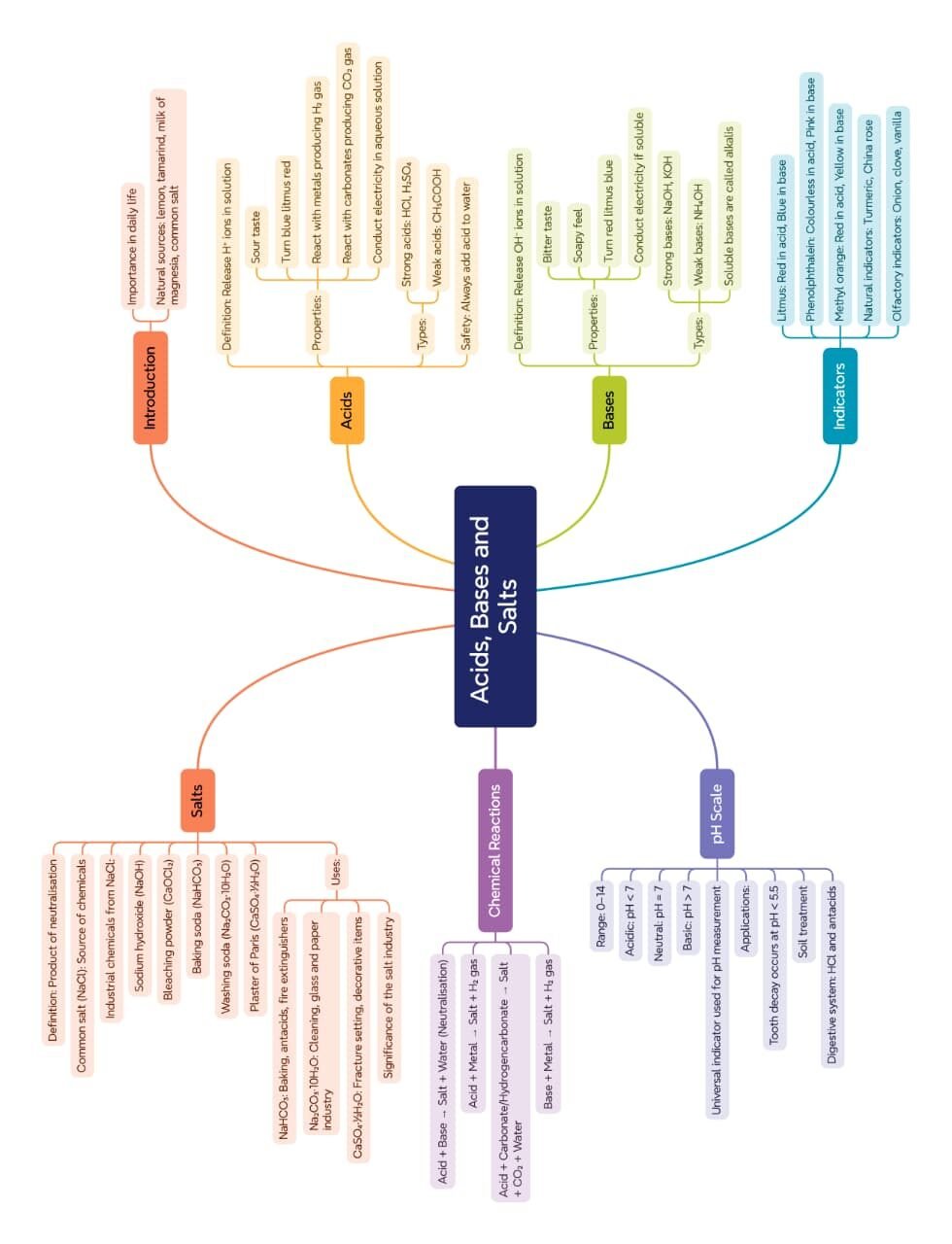
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
