Class 10 : Maths (In English) – Lesson 2. Polynomials
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
🔵 1) Introduction 🌿
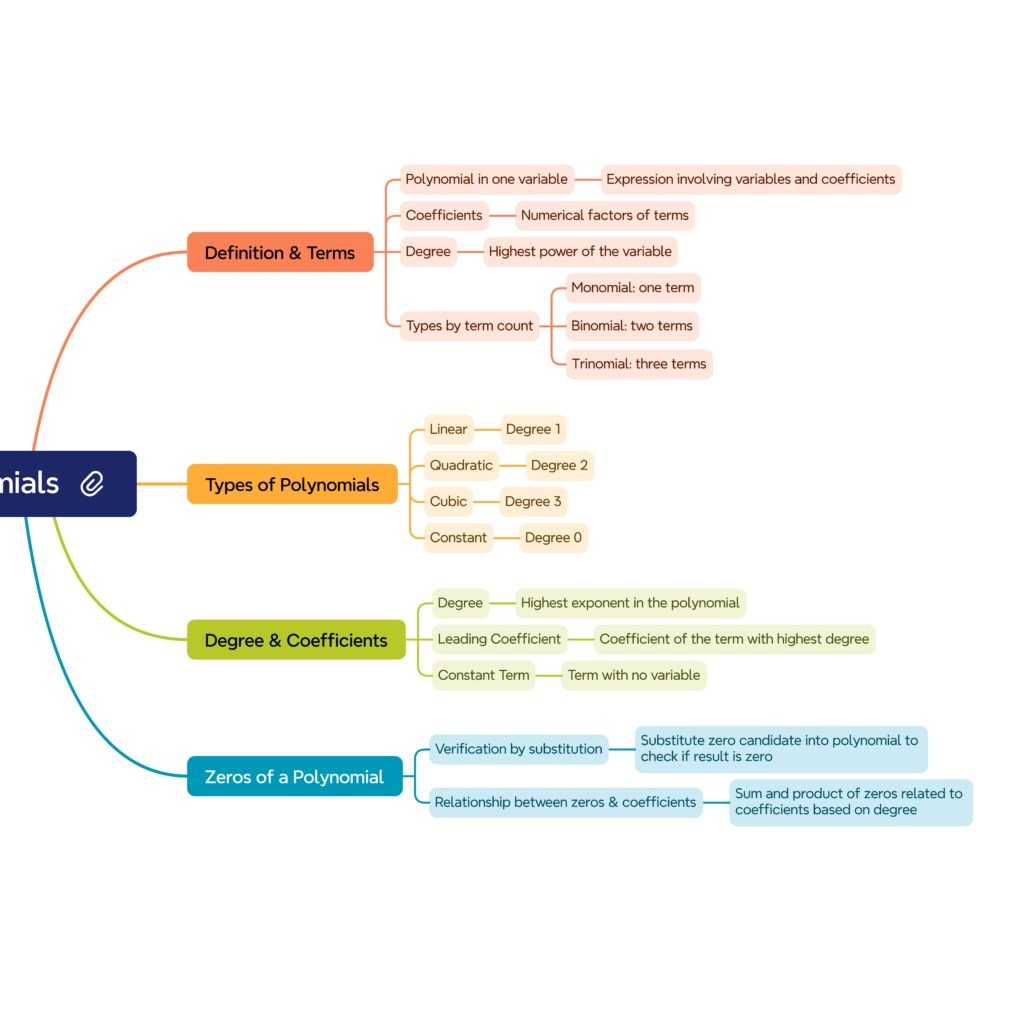
• A polynomial is an algebraic expression of the form p(x)=a₀+a₁x+a₂x²+…+aₙxⁿ where coefficients aᵢ ∈ ℝ and exponents are non-negative integers.
• Degree: highest exponent of x.
• Examples: 3x³−2x²+x−7 (cubic), x²+5x+6 (quadratic).
• Non-examples: 3/x+5 (division by variable), x⁻²+1 (negative exponent).
🟢 2) Classification ⚡
• Linear: degree 1 (ax+b).
• Quadratic: degree 2 (ax²+bx+c).
• Cubic: degree 3.
• Zero polynomial: coefficients all 0, degree undefined.
• Constant: degree 0.
🟡 3) Zeros of a Polynomial ➡️
• A zero of p(x) is a value α where p(α)=0.
• Linear polynomials: exactly one zero.
• Quadratic: at most two zeros.
• Cubic: at most three zeros.
💡 Concept: Graphically, zeros are x-intercepts of y=p(x).
🔴 4) Relationship Between Zeros and Coefficients ✔️
• For quadratic ax²+bx+c:
Sum of zeros (α+β)=−b/a.
Product of zeros (αβ)=c/a.
• For cubic ax³+bx²+cx+d:
Sum of zeros=−b/a.
Sum of products of zeros two at a time= c/a.
Product of zeros=−d/a.
✏️ Note: These relationships let you reconstruct polynomials.
🔵 5) Division Algorithm for Polynomials 🌿
For polynomials p(x),g(x) (g≠0), ∃ unique q(x), r(x) such that
p(x)=g(x)×q(x)+r(x), deg(r)<deg(g).
Example: Divide 2x³+3x²+2x+5 by x²+1:
Step 1: 2x³/x²=2x ⇒ multiply:2x³+2x.
Step 2: Subtract:3x²+5.
Step 3: 3x²/x²=3 ⇒ multiply:3x²+3.
Step 4: Subtract:2 ⇒ remainder.
✅ Result: p(x)=(x²+1)(2x+3)+2.
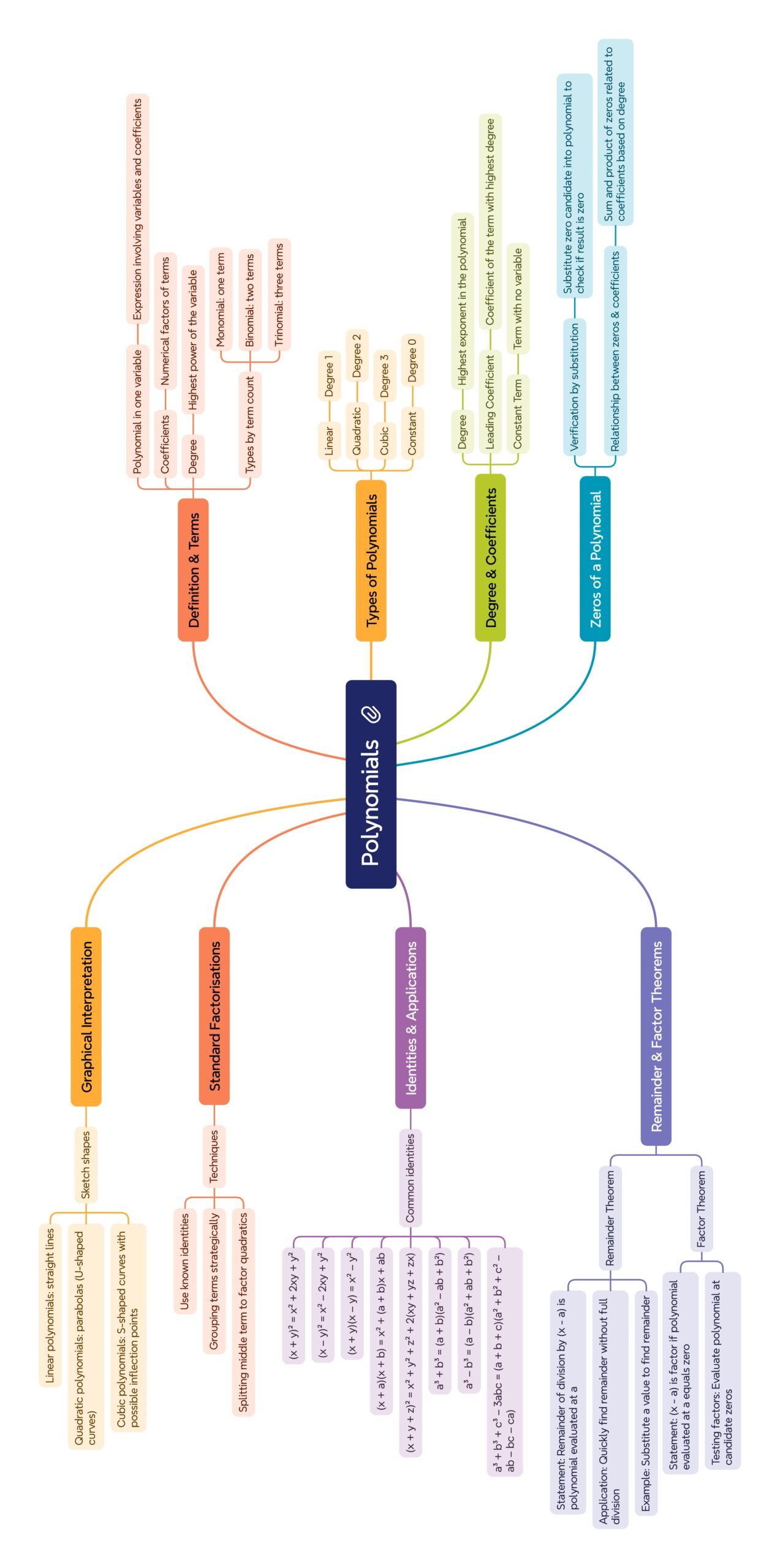
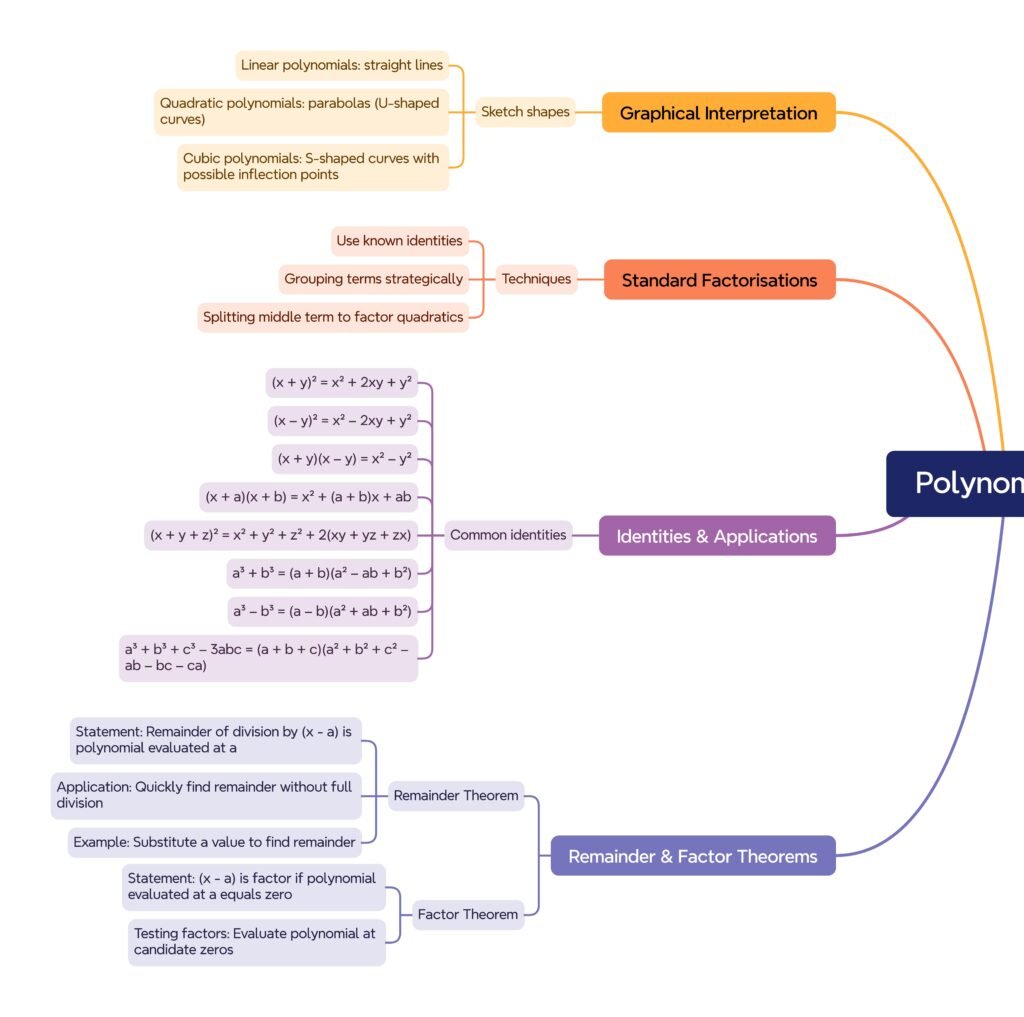
🟢 6) Factorisation of Polynomials 🧠
• Use Remainder & Factor Theorems: if p(a)=0, then x−a is a factor.
• Splitting middle term: x²+5x+6=(x+2)(x+3).
• Using identities: x³+8=(x+2)(x²−2x+4).
• Grouping: ax+ay+bx+by=(a+b)(x+y).
🟡 7) Graphical Meaning 🌿
• Linear: straight line crosses x-axis once.
• Quadratic: parabola crosses up to 2 points.
• Cubic: smooth curve crosses up to 3 points.
• ✏️ Points where graph cuts x-axis are zeros.
🔴 8) Remainder & Factor Theorem ✔️
• Remainder Theorem: Remainder of p(x) ÷ (x−a)=p(a).
• Factor Theorem: If p(a)=0, then x−a is factor of p(x).
Example: p(x)=x³−2x²−x+2. Test x=2: p(2)=8−8−2+2=0 ⇒ x−2 is factor.
🔵 9) Constructing Polynomials 🌿
Given zeros, build polynomials:
Example: Zeros 2, −3: p(x)=(x−2)(x+3)=x²+x−6.
Given zeros 1,2,3: p(x)=(x−1)(x−2)(x−3).
🟢 10) Applications ✔️
• Motion modeling (position polynomials).
• Economics: profit/cost curves.
• Graphics: Bézier curves.
• Engineering design and signal processing.
🟡 11) Common Mistakes 🔴
• Forgetting sign of coefficients when forming polynomials.
• Misusing remainder theorem with wrong divisor.
• Failing to arrange descending powers before division.
• Forgetting deg(r)<deg(g).
🔴 12) Practice Examples 🌿
1️⃣ Find zeros of x²−5x+6.
2️⃣ Divide x³−4x²+5x−2 by x−2.
3️⃣ If α,β are zeros of 2x²−3x+1, verify α+β=3/2.
4️⃣ Construct cubic polynomial with zeros −1,0,2.
5️⃣ Use factor theorem to check x+1 for x³+3x²+3x+1.
🔵 13) Higher Order Insights ⚡
• Fundamental Theorem of Algebra: every polynomial has at least one zero in ℂ.
• Real-world interpolation uses polynomials for curve fitting.
• Polynomials form a ring under addition and multiplication.
🟣 Summary (~300 words)
Definition & Types:
• p(x)=a₀+a₁x+a₂x²+…+aₙxⁿ with integer exponents ≥0.
• Classified by degree: linear(1), quadratic(2), cubic(3).
Zeros & Coefficients:
• Zeros: roots where p(x)=0.
• Quadratic: α+β=−b/a, αβ=c/a.
• Cubic: α+β+γ=−b/a; αβ+βγ+γα=c/a; αβγ=−d/a.
Division Algorithm:
• p(x)=g(x)q(x)+r(x), deg(r)<deg(g).
Factorisation:
• Use Remainder and Factor Theorems, splitting middle term, identities, or grouping.
Graphical Meaning:
• Zeros are x-intercepts of y=p(x).
• Degree indicates max crossings with x-axis.
Applications:
• Modeling, economics, engineering, graphics.
Common Errors:
• Forgetting descending order of powers.
• Incorrect sign handling.
Mastering these builds skills for solving equations, analyzing curves, and applying polynomials in science and engineering.
📝 Quick Recap
🔵 Polynomial form: a₀+a₁x+a₂x²+…+aₙxⁿ.
🟢 Zeros ↔ coefficients: quadratic/cubic relationships.
🟡 Division Algorithm: p(x)=g(x)q(x)+r(x).
🔴 Factor Theorem: p(a)=0 ⇒ x−a factor.
🔵 Graph meaning: zeros=x-intercepts.
✨ Applications: motion, economics, CAD, graphics.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
TEXT BOOK QUESTIONS
🔵 Question 1
Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
(i) 4x² – 3x + 7
(ii) y² + √2
(iii) 3√t + t√2
(iv) y + 2/y
(v) x¹⁰ + y³ + z⁵⁰
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1: Check exponents and variables.
🟢 (i) 4x²–3x+7 → powers are non-negative integers of x only → ✔ polynomial in one variable.
🟢 (ii) y²+√2 → powers are non-negative integers of y → ✔ polynomial in one variable.
🟢 (iii) 3√t+t√2 → √t = t^(1/2) → exponent 1/2 not integer → ✖ not a polynomial.
🟢 (iv) y+2/y → 2/y = y^(–1) negative exponent → ✖ not a polynomial.
🟢 (v) x¹⁰+y³+z⁵⁰ → involves three variables → ✖ not a polynomial in one variable (it’s multivariable).
✔ Final: (i),(ii) are polynomials in one variable; (iii),(iv),(v) are not.
🔵 Question 2
Write the coefficients of x² in each of the following:
(i) 2 + x² + x
(ii) 2 – x² + x³
(iii) (π/2)x² + x
(iv) √2 x – 1
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1: Identify x² term coefficient.
🟢 (i) Coefficient = 1.
🟢 (ii) Coefficient = –1.
🟢 (iii) Coefficient = π/2.
🟢 (iv) No x² term → coefficient = 0.
✔ Final: 1, –1, π/2, 0.
🔵 Question 3
Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and a monomial of degree 100.
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1: Binomial = 2 terms, degree = highest exponent.
🟢 Example: p(x) = x³⁵ + 5. (Two terms, degree 35).
🔵 Step 2: Monomial = 1 term, degree 100.
🟢 Example: q(x) = 7x¹⁰⁰. (One term, degree 100).
✔ Final: x³⁵+5 and 7x¹⁰⁰.
🔵 Question 4
Write the degree of each of the following polynomials:
(i) 5x³ + 4x² + 7x
(ii) 4 – y²
(iii) 5t – √7
(iv) 3
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1: Degree = highest power.
🟢 (i) Highest power = 3 → degree 3.
🟢 (ii) Highest power = 2 → degree 2.
🟢 (iii) Highest power = 1 → degree 1.
🟢 (iv) Constant → degree 0.
✔ Final: 3, 2, 1, 0.
🔵 Question 5
Classify the following as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials:
(i) x² + x
(ii) x – x³
(iii) x² + 4
(iv) 1 + x
(v) 3t
(vi) r²
(vii) 7x³
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1: Identify degree.
🟢 (i) Degree 2 → Quadratic.
🟢 (ii) Degree 3 → Cubic.
🟢 (iii) Degree 2 → Quadratic.
🟢 (iv) Degree 1 → Linear.
🟢 (v) Degree 1 → Linear.
🟢 (vi) Degree 2 → Quadratic.
🟢 (vii) Degree 3 → Cubic.
✔ Final:
• Quadratic: (i), (iii), (vi)
• Cubic: (ii), (vii)
• Linear: (iv), (v)
Exercise 2.2
🔵 Question 1
Find the value of the polynomial 5x – 4x² + 3 at
(i) x = 0 (ii) x = –1 (iii) x = 2
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1 (i): 5×0 – 4×0² + 3 = 0 – 0 + 3 = 3
✔ Final (i): 3
🔵 Step 2 (ii): 5×(–1) – 4×(–1)² + 3 = –5 – 4×1 + 3 = –5 – 4 + 3 = –6
✔ Final (ii): –6
🔵 Step 3 (iii): 5×2 – 4×2² + 3 = 10 – 16 + 3 = –3
✔ Final (iii): –3
🔵 Question 2
Find p(0), p(1) and p(2) for each of the following polynomials:
(i) p(y) = y² – y + 1
(ii) p(t) = 2 + t + 2t² – t³
(iii) p(x) = x³
(iv) p(x) = (x – 1)(x + 1)
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step 1 (i):
p(0) = 0² – 0 + 1 = 1
p(1) = 1² – 1 + 1 = 1
p(2) = 2² – 2 + 1 = 4 – 2 + 1 = 3
✔ Final (i): p₀ = 1, p₁ = 1, p₂ = 3
🔵 Step 2 (ii):
p(0) = 2 + 0 + 2×0² – 0³ = 2
p(1) = 2 + 1 + 2×1² – 1³ = 2 + 1 + 2 – 1 = 4
p(2) = 2 + 2 + 2×4 – 8 = 4 + 8 – 8 = 4
✔ Final (ii): p₀ = 2, p₁ = 4, p₂ = 4
🔵 Step 3 (iii):
p(0) = 0³ = 0
p(1) = 1³ = 1
p(2) = 2³ = 8
✔ Final (iii): p₀ = 0, p₁ = 1, p₂ = 8
🔵 Step 4 (iv):
p(0) = (0 – 1)(0 + 1) = (–1)(1) = –1
p(1) = (1 – 1)(1 + 1) = 0×2 = 0
p(2) = (2 – 1)(2 + 1) = 1×3 = 3
✔ Final (iv): p₀ = –1, p₁ = 0, p₂ = 3
🔵 Question 3
Verify whether the following are zeroes of the polynomial, indicated against them.
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) p(x)=3x+1, x=–¹⁄₃ → 3(–¹⁄₃)+1=–1+1=0 ✔ Yes
🔵 (ii) p(x)=5x–π, x=⁴⁄₅ → 5×(⁴⁄₅)–π=4–π≠0 ✖ No
🔵 (iii) p(x)=x²–1, x=1,–1 → 1–1=0 and 1–1=0 ✔ Both yes
🔵 (iv) p(x)=(x+1)(x–2), x=–1,2 → 0 and 0 ✔ Both yes
🔵 (v) p(x)=x², x=0 → 0 ✔ Yes
🔵 (vi) p(x)=lx+m, x=–m/l → l(–m/l)+m=–m+m=0 ✔ Yes
🔵 (vii) p(x)=3x²–1, x=1/√3, 2/√3 → 3×(1/3)–1=1–1=0 ✔ Yes; 3×(4/3)–1=4–1=3≠0 ✖ No
🔵 (viii) p(x)=2x+1, x=½ → 2×½+1=1+1=2≠0 ✖ No
🔵 Question 4
Find the zero of the polynomial in each of the following cases:
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) x+5=0 → x=–5 ✔ Final (i): –5
🔵 (ii) x–5=0 → x=5 ✔ Final (ii): 5
🔵 (iii) 2x+5=0 → 2x=–5 → x=–5/2 ✔ Final (iii): –5/2
🔵 (iv) 3x–2=0 → 3x=2 → x=2/3 ✔ Final (iv): 2/3
🔵 (v) 3x=0 → x=0 ✔ Final (v): 0
🔵 (vi) ax=0 (a≠0) → x=0 ✔ Final (vi): 0
🔵 (vii) cx+d=0 (c≠0) → x=–d/c ✔ Final (vii): –d/c
Exercise 2.3
🔵 Question 1
Determine which of the following polynomials has (x + 1) a factor :
(i) x³ + x² + x + 1
(ii) x⁴ + x³ + x² + x + 1
(iii) x⁴ + 3x³ + 3x² + x + 1
(iv) x³ − x² − (2 + √2) x + √2
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: (x + 1) is a factor ⇔ p(−1) = 0 (Factor Theorem).
🔵 Step (i): p(−1) = (−1)³ + (−1)² + (−1) + 1 = −1 + 1 − 1 + 1 = 0 → ✔ factor.
🔵 Step (ii): p(−1) = 1 − 1 + 1 − 1 + 1 = 1 ≠ 0 → ✖ not a factor.
🔵 Step (iii): p(−1) = 1 − 3 + 3 − 1 + 1 = 1 ≠ 0 → ✖ not a factor.
🔵 Step (iv): p(−1) = (−1)³ − (−1)² − (2 + √2)(−1) + √2 = −1 − 1 + 2 + √2 + √2 = 2√2 ≠ 0 → ✖ not a factor.
✔ Final: Only (i) has (x + 1) as a factor.
🔵 Question 2
Use the Factor Theorem to determine whether g(x) is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = 2x³ + x² − 2x − 1, g(x) = x + 1
(ii) p(x) = x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1, g(x) = x + 2
(iii) p(x) = x³ − 4x² + x + 6, g(x) = x − 3
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: g(x) = x − a is a factor ⇔ p(a) = 0. For g(x) = x + b, test p(−b).
🔵 Step (i): Test at x = −1.
p(−1) = 2(−1)³ + (−1)² − 2(−1) − 1 = −2 + 1 + 2 − 1 = 0 → ✔ factor.
🔵 Step (ii): Test at x = −2.
p(−2) = (−8) + 12 − 6 + 1 = −1 ≠ 0 → ✖ not a factor.
🔵 Step (iii): Test at x = 3.
p(3) = 27 − 36 + 3 + 6 = 0 → ✔ factor.
✔ Final: (i) factor, (ii) not a factor, (iii) factor.
🔵 Question 3
Find the value of k, if x − 1 is a factor of p(x) in each of the following cases:
(i) p(x) = x² + x + k
(ii) p(x) = 2x² + kx + √2
(iii) p(x) = kx² − √2 x + 1
(iv) p(x) = kx² − 3x + k
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: If (x − 1) is a factor, then p(1) = 0.
🔵 Step (i): p(1) = 1² + 1 + k = 2 + k = 0 → k = −2.
🔵 Step (ii): p(1) = 2(1)² + k(1) + √2 = 2 + k + √2 = 0 → k = −2 − √2.
🔵 Step (iii): p(1) = k(1)² − √2(1) + 1 = k − √2 + 1 = 0 → k = √2 − 1.
🔵 Step (iv): p(1) = k(1)² − 3(1) + k = 2k − 3 = 0 → k = 3/2.
✔ Final: k = −2; −2 − √2; √2 − 1; 3/2.
🔵 Question 4
Factorise :
(i) 12x² − 7x + 1
(ii) 2x² + 7x + 3
(iii) 6x² + 5x − 6
(iv) 3x² − x − 4
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step (i): 12x² − 7x + 1 = (3x − 1)(4x − 1) ✔
🔵 Step (ii): 2x² + 7x + 3 = (2x + 1)(x + 3) ✔
🔵 Step (iii): 6x² + 5x − 6 = (3x − 2)(2x + 3) ✔
🔵 Step (iv): 3x² − x − 4 = (3x − 4)(x + 1) ✔
✔ Final: Factors as above.
🔵 Question 5
Factorise :
(i) x³ − 2x² − x + 2
(ii) x³ − 3x² − 9x − 5
(iii) x³ + 13x² + 32x + 20
(iv) 2y³ + y² − 2y − 1
🟢 Answer
🔵 Step (i): Grouping → x²(x − 2) − 1(x − 2) = (x − 2)(x² − 1) = (x − 2)(x − 1)(x + 1).
✔ Final (i): (x − 2)(x − 1)(x + 1)
🔵 Step (ii): Trial root x = 5 → 125 − 75 − 45 − 5 = 0 ⇒ (x − 5) factor.
Quotient = x² + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)².
✔ Final (ii): (x − 5)(x + 1)²
🔵 Step (iii): Trial root x = −1 → 0 ⇒ (x + 1) factor.
Quotient = x² + 12x + 20 = (x + 10)(x + 2).
✔ Final (iii): (x + 1)(x + 10)(x + 2)
🔵 Step (iv): Grouping → y²(2y + 1) − 1(2y + 1) = (2y + 1)(y² − 1) = (2y + 1)(y − 1)(y + 1).
✔ Final (iv): (2y + 1)(y − 1)(y + 1)
Exercise 2.4
🔵 Question 1
Use suitable identities to find the following products:
(i) (x + 4)(x + 10) (ii) (x + 8)(x − 10) (iii) (3x + 4)(3x − 5) (iv) (y² + 3/2)(y² − 3/2) (v) (3 − 2x)(3 + 2x)
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: (x + a)(x + b) = x² + (a + b)x + ab; (A + B)(A − B) = A² − B².
🔵 (i) x² + (4 + 10)x + 4×10 = x² + 14x + 40
✔ Final (i): x² + 14x + 40
🔵 (ii) x² + (8 − 10)x + 8×(−10) = x² − 2x − 80
✔ Final (ii): x² − 2x − 80
🔵 (iii) 9x² − 15x + 12x − 20 = 9x² − 3x − 20
✔ Final (iii): 9x² − 3x − 20
🔵 (iv) (y²)² − (3/2)² = y⁴ − 9/4
✔ Final (iv): y⁴ − 9/4
🔵 (v) 3² − (2x)² = 9 − 4x²
✔ Final (v): 9 − 4x²
🔵 Question 2
Evaluate the following products without multiplying directly:
(i) 103 × 107 (ii) 95 × 96 (iii) 104 × 96
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: (a + b)(a + c) = a² + a(b + c) + bc; (a + d)(a − d) = a² − d².
🔵 (i) (100 + 3)(100 + 7) = 100² + 100(3 + 7) + 3×7 = 10000 + 1000 + 21 = 11021
✔ Final (i): 11021
🔵 (ii) (100 − 5)(100 − 4) = 100² − 100(5 + 4) + (−5)(−4) = 10000 − 900 + 20 = 9120
✔ Final (ii): 9120
🔵 (iii) (100 + 4)(100 − 4) = 100² − 4² = 10000 − 16 = 9984
✔ Final (iii): 9984
🔵 Question 3
Factorise the following using appropriate identities:
(i) 9x² + 6xy + y² (ii) 4y² − 4y + 1 (iii) x² − y²/100
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) (3x)² + 2(3x)(y) + y² = (3x + y)²
✔ Final (i): (3x + y)²
🔵 (ii) (2y)² − 2(2y)(1) + 1² = (2y − 1)²
✔ Final (ii): (2y − 1)²
🔵 (iii) x² − (y/10)² = (x − y/10)(x + y/10)
✔ Final (iii): (x − y/10)(x + y/10)
🔵 Question 4
Expand each of the following, using suitable identities:
(i) (x + 2y + 4z)² (ii) (2x − y + z)² (iii) (−2x + 3y + 2z)² (iv) (3a − 7b − c)² (v) (−2x + 5y − 3z)² (vi) [ (1/4)a − (1/2)b + 1 ]²
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: (p + q + r)² = p² + q² + r² + 2pq + 2qr + 2rp.
🔵 (i) x² + (2y)² + (4z)² + 2x(2y) + 2(2y)(4z) + 2x(4z)
➡ x² + 4y² + 16z² + 4xy + 16yz + 8xz
✔ Final (i): x² + 4y² + 16z² + 4xy + 16yz + 8xz
🔵 (ii) (2x)² + (−y)² + z² + 2(2x)(−y) + 2(−y)z + 2(2x)z
➡ 4x² + y² + z² − 4xy − 2yz + 4xz
✔ Final (ii): 4x² + y² + z² − 4xy − 2yz + 4xz
🔵 (iii) (−2x)² + (3y)² + (2z)² + 2(−2x)(3y) + 2(3y)(2z) + 2(−2x)(2z)
➡ 4x² + 9y² + 4z² − 12xy + 12yz − 8xz
✔ Final (iii): 4x² + 9y² + 4z² − 12xy + 12yz − 8xz
🔵 (iv) (3a)² + (−7b)² + (−c)² + 2(3a)(−7b) + 2(−7b)(−c) + 2(3a)(−c)
➡ 9a² + 49b² + c² − 42ab + 14bc − 6ac
✔ Final (iv): 9a² + 49b² + c² − 42ab + 14bc − 6ac
🔵 (v) (−2x)² + (5y)² + (−3z)² + 2(−2x)(5y) + 2(5y)(−3z) + 2(−2x)(−3z)
➡ 4x² + 25y² + 9z² − 20xy − 30yz + 12xz
✔ Final (v): 4x² + 25y² + 9z² − 20xy − 30yz + 12xz
🔵 (vi) (a/4)² + (−b/2)² + 1² + 2(a/4)(−b/2) + 2(−b/2)·1 + 2(a/4)·1
➡ a²/16 + b²/4 + 1 − ab/4 − b + a/2
✔ Final (vi): a²/16 + b²/4 + 1 − (ab)/4 − b + a/2
🔵 Question 5
Factorise:
(i) 4x² + 9y² + 16z² + 12xy − 24yz − 16xz
(ii) 2x² + y² + 8z² − 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz − 8xz
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) Recognise perfect square of (2x + 3y − 4z):
(2x + 3y − 4z)² = 4x² + 9y² + 16z² + 12xy − 24yz − 16xz
✔ Final (i): (2x + 3y − 4z)²
🔵 (ii) Try (√2 x − y − 2√2 z)²:
(√2 x)² + (−y)² + (−2√2 z)² + 2(√2 x)(−y) + 2(−y)(−2√2 z) + 2(√2 x)(−2√2 z)
= 2x² + y² + 8z² − 2√2 xy + 4√2 yz − 8xz
✔ Final (ii): (√2 x − y − 2√2 z)²
🔵 Question 6
Write the following cubes in expanded form:
(i) (2x + 1)³ (ii) (2a − 3b)³ (iii) [ (3/2)x + 1 ]³ (iv) (x − (2/3)y)³
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: (p + q)³ = p³ + 3p²q + 3pq² + q³; (p − q)³ = p³ − 3p²q + 3pq² − q³.
🔵 (i) 8x³ + 12x² + 6x + 1
✔ Final (i): 8x³ + 12x² + 6x + 1
🔵 (ii) 8a³ − 36a²b + 54ab² − 27b³
✔ Final (ii): 8a³ − 36a²b + 54ab² − 27b³
🔵 (iii) (27/8)x³ + (27/4)x² + (9/2)x + 1
✔ Final (iii): (27/8)x³ + (27/4)x² + (9/2)x + 1
🔵 (iv) x³ − 2x²y + (4/3)xy² − (8/27)y³
✔ Final (iv): x³ − 2x²y + (4/3)xy² − (8/27)y³
🔵 Question 7
Evaluate the following using suitable identities:
(i) (99)³ (ii) (102)³ (iii) (998)³
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) (100 − 1)³ = 100³ − 3·100²·1 + 3·100·1² − 1
➡ 1,000,000 − 30,000 + 300 − 1 = 970,299
✔ Final (i): 970,299
🔵 (ii) (100 + 2)³ = 100³ + 3·100²·2 + 3·100·2² + 2³
➡ 1,000,000 + 60,000 + 1,200 + 8 = 1,061,208
✔ Final (ii): 1,061,208
🔵 (iii) (1000 − 2)³ = 1000³ − 3·1000²·2 + 3·1000·2² − 2³
➡ 1,000,000,000 − 6,000,000 + 12,000 − 8 = 994,011,992
✔ Final (iii): 994,011,992
🔵 Question 8
Factorise each of the following:
(i) 8a³ + b³ + 12a²b + 6ab²
(ii) 8a³ − b³ − 12a²b + 6ab²
(iii) 27 − 125a³ − 135a + 225a²
(iv) 64a³ − 27b³ − 144a²b + 108ab²
(v) 27p³ − 1/216 − (9/2)p² + (1/4)p
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) (2a + b)³
✔ Final (i): (2a + b)³
🔵 (ii) (2a − b)³
✔ Final (ii): (2a − b)³
🔵 (iii) (3 − 5a)³
✔ Final (iii): (3 − 5a)³
🔵 (iv) (4a − 3b)³
✔ Final (iv): (4a − 3b)³
🔵 (v) (3p − 1/6)³
✔ Final (v): (3p − 1/6)³
🔵 Question 9
Verify: (i) x³ + y³ = (x + y)(x² − xy + y²) (ii) x³ − y³ = (x − y)(x² + xy + y²)
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) RHS = (x + y)(x² − xy + y²) = x³ − x²y + xy² + x²y − xy² + y³ = x³ + y³
✔ Final (i): Verified
🔵 (ii) RHS = (x − y)(x² + xy + y²) = x³ + x²y + xy² − x²y − xy² − y³ = x³ − y³
✔ Final (ii): Verified
🔵 Question 10
Factorise each of the following:
(i) 27y³ + 125z³ (ii) 64m³ − 343n³ [Hint: See Question 9.]
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) Sum of cubes: (3y + 5z)(9y² − 15yz + 25z²)
✔ Final (i): (3y + 5z)(9y² − 15yz + 25z²)
🔵 (ii) Difference of cubes: (4m − 7n)(16m² + 28mn + 49n²)
✔ Final (ii): (4m − 7n)(16m² + 28mn + 49n²)
🔵 Question 11
Factorise : 27x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: a³ + b³ + c³ − 3abc = (a + b + c)(a² + b² + c² − ab − bc − ca).
🔵 Take a = 3x, b = y, c = z.
➡ 27x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz = (3x + y + z)(9x² + y² + z² − 3xy − yz − 3xz)
✔ Final: (3x + y + z)(9x² + y² + z² − 3xy − yz − 3xz)
🔵 Question 12
Verify that
x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz = (1/2)(x + y + z)[(x − y)² + (y − z)² + (z − x)²]
🟢 Answer
🔵 Start from RHS.
➡ (1/2)(x + y + z)[(x² − 2xy + y²) + (y² − 2yz + z²) + (z² − 2zx + x²)]
➡ (1/2)(x + y + z)[2(x² + y² + z² − xy − yz − zx)]
➡ (x + y + z)(x² + y² + z² − xy − yz − zx)
➡ Using identity in Q11: equals x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz
✔ Final: Verified
🔵 Question 13
If x + y + z = 0, show that x³ + y³ + z³ = 3xyz.
🟢 Answer
🔵 From Q11 identity: x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz = (x + y + z)(x² + y² + z² − xy − yz − zx)
➡ Since x + y + z = 0, LHS = 0
➡ Therefore x³ + y³ + z³ − 3xyz = 0
✔ Final: x³ + y³ + z³ = 3xyz
🔵 Question 14
Without actually calculating the cubes, find the value of each of the following:
(i) (−12)³ + (7)³ + (5)³ (ii) (28)³ + (−15)³ + (−13)³
🟢 Answer
💡 Concept: If a + b + c = 0, then a³ + b³ + c³ = 3abc.
🔵 (i) −12 + 7 + 5 = 0 ⇒ value = 3(−12)(7)(5) = −1260
✔ Final (i): −1260
🔵 (ii) 28 + (−15) + (−13) = 0 ⇒ value = 3·28·(−15)·(−13) = 3·28·195 = 16380
✔ Final (ii): 16380
🔵 Question 15
Give possible expressions for the length and breadth of each of the following rectangles, in which their areas are given:
(i) Area : 25a² − 35a + 12 (ii) Area : 35y² + 13y − 12
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) 25a² − 35a + 12 = (5a − 3)(5a − 4)
✔ Final (i): length = 5a − 3, breadth = 5a − 4 (or vice-versa)
🔵 (ii) 35y² + 13y − 12 = (5y + 4)(7y − 3)
✔ Final (ii): length = 5y + 4, breadth = 7y − 3 (or vice-versa)
🔵 Question 16
What are the possible expressions for the dimensions of the cuboids whose volumes are given below?
(i) Volume : 3x² − 12x (ii) Volume : 12ky² + 8ky − 20k
🟢 Answer
🔵 (i) 3x² − 12x = 3x(x − 4)
✔ Final (i): dimensions = 3, x, (x − 4) (any order; e.g., 3x, (x − 4), 1)
🔵 (ii) 12ky² + 8ky − 20k = 4k(3y² + 2y − 5) = 4k(3y + 5)(y − 1)
✔ Final (ii): dimensions = 4k, (3y + 5), (y − 1) (any order)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Section A (1 mark each)
🔵 Question 1
State the degree of polynomial 7x³ – 4x² + 5x – 6.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Highest power of x is 3.
✳️ ➤ Degree = 3.
🔵 Question 2
Find the zero of the linear polynomial p(x) = 5x – 20.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Set p(x) = 0 ⇒ 5x – 20 = 0.
✳️ ➤ 5x = 20 ⇒ x = 4.
🔵 Question 3
Write a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are –3 and 2.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Standard form: p(x) = (x – α)(x – β).
✳️ ➤ p(x) = (x + 3)(x – 2) = x² + x – 6.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: x² + x – 6.
🔵 Question 4
If one zero of 2x² + 5x – 3 is –3, find the other zero.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes = –b/a = –5/2.
✳️ ➤ If one zero = –3 ⇒ other = –5/2 – (–3) = –5/2 + 3 = (–5 + 6)/2 = 1/2.
🔵 Question 5
Find the value of k if x + 1 is a factor of kx³ + 3x² + kx – 3.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Use remainder theorem: Substitute x = –1.
✳️ ➤ k(–1)³ + 3(–1)² + k(–1) – 3 = –k + 3 – k – 3 = –2k.
✳️ ➤ Set = 0 ⇒ –2k = 0 ⇒ k = 0.
🔵 Question 6
Write the relationship between coefficients and zeroes for quadratic polynomial ax² + bx + c.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes (α + β) = –b/a.
✳️ ➤ Product of zeroes (αβ) = c/a.
🟢 Section B (2 marks each)
🟢 Question 7
Verify that 2 and –3 are zeroes of p(x) = x² + x – 6.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ p(2) = (2)² + (2) – 6 = 4 + 2 – 6 = 0. ✔️
✳️ ➤ p(–3) = (–3)² + (–3) – 6 = 9 – 3 – 6 = 0. ✔️
✳️ ➤ Verified.
🟢 Question 8
Find a cubic polynomial whose zeroes are –1, 0, and 2.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ p(x) = (x + 1)(x)(x – 2).
✳️ ➤ Multiply: (x + 1)(x) = x² + x.
✳️ ➤ (x² + x)(x – 2) = x³ – 2x² + x² – 2x = x³ – x² – 2x.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: x³ – x² – 2x.
🟢 Question 9
Find the remainder when x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 is divided by x + 1.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ Use remainder theorem: substitute x = –1.
✳️ ➤ p(–1) = (–1)³ + 3(–1)² + 3(–1) + 1 = –1 + 3 – 3 + 1 = 0.
✳️ ➤ Remainder = 0.
🟢 Question 10
The zeroes of a quadratic polynomial are 2 and –5. Write the polynomial in standard form.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ p(x) = (x – 2)(x + 5) = x² + 5x – 2x – 10 = x² + 3x – 10.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: x² + 3x – 10.
🟢 Question 11
Divide 2x³ + 3x² – 5x + 6 by x – 2 and write quotient and remainder.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ Synthetic division: Substitute x = 2 for remainder.
✳️ ➤ Long division:
2x³ ÷ x = 2x² ⇒ Multiply: 2x²(x – 2) = 2x³ – 4x². Subtract: 3x² – (–4x²) = 7x².
Bring down –5x ⇒ 7x² ÷ x = 7x ⇒ Multiply: 7x(x – 2) = 7x² – 14x. Subtract: –5x – (–14x) = 9x.
Bring down +6 ⇒ 9x ÷ x = 9 ⇒ Multiply: 9(x – 2) = 9x – 18. Subtract: 6 – (–18) = 24.
✳️ ➤ Quotient: 2x² + 7x + 9, Remainder: 24.
🟢 Question 12
If the zeroes of a quadratic polynomial are –4 and –1, verify the relationship between coefficients and zeroes.
🔴 Answer
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes α + β = –4 + (–1) = –5.
✳️ ➤ Product αβ = (–4)(–1) = 4.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: p(x) = (x + 4)(x + 1) = x² + 5x + 4.
✳️ ➤ Coefficients: a = 1, b = 5, c = 4.
✳️ ➤ –b/a = –5, matches sum. ✔️
✳️ ➤ c/a = 4, matches product. ✔️
✳️ ➤ Verified.
🟡 Section C (3 marks each)
🟡 Question 13
Find the zeroes of p(x) = x² – 5x + 6 and verify the relationship between coefficients and zeroes.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Factorise: x² – 5x + 6 = (x – 2)(x – 3).
✳️ ➤ Zeroes: 2 and 3.
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes: 2 + 3 = 5 = –b/a = –(–5)/1 = 5 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Product: 2 × 3 = 6 = c/a = 6/1 = 6 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Verified.
🟡 Question 14
Divide x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1 by x + 1.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Using long division:
x³ ÷ x = x² ⇒ x²(x + 1) = x³ + x². Subtract: (3x² – x²) = 2x².
Bring down +3x ⇒ 2x² ÷ x = 2x ⇒ 2x(x + 1) = 2x² + 2x. Subtract: 3x – 2x = x.
Bring down +1 ⇒ x ÷ x = 1 ⇒ 1(x + 1) = x + 1. Subtract: remainder = 0.
✳️ ➤ Quotient: x² + 2x + 1, Remainder: 0.
🟡 Question 15
Find a cubic polynomial with sum of zeroes = 2, product = –4, and one zero = –1.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Let zeroes be –1, α, β. Sum: –1 + α + β = 2 ⇒ α + β = 3.
✳️ ➤ Product: (–1)(α)(β) = –4 ⇒ αβ = 4.
✳️ ➤ Quadratic factor: x² – (sum) x + product = x² – 3x + 4.
✳️ ➤ Full polynomial: (x + 1)(x² – 3x + 4) = x³ – 3x² + 4x + x² – 3x + 4 = x³ – 2x² + x + 4.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: x³ – 2x² + x + 4.
🟡 Question 16
OR
If (x – 1) is a factor of x³ – 3x² + x + k, find k and the other factors.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Substitute x = 1 ⇒ 1 – 3 + 1 + k = –1 + k = 0 ⇒ k = 1.
✳️ ➤ Divide x³ – 3x² + x + 1 by (x – 1):
x³ ÷ x = x² ⇒ x²(x – 1) = x³ – x². Subtract: –3x² – (–x²) = –2x².
Bring down +x ⇒ –2x² ÷ x = –2x ⇒ –2x(x – 1) = –2x² + 2x. Subtract: x – 2x = –x.
Bring down +1 ⇒ –x ÷ x = –1 ⇒ –1(x – 1) = –x + 1. Subtract: remainder 0.
✳️ ➤ Factors: (x – 1)(x² – 2x – 1).
🟡 Question 17
Find the remainder when x³ + 2x² – 3x + 4 is divided by x – 2.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Use remainder theorem: substitute x = 2.
p(2) = (2)³ + 2(2)² – 3(2) + 4 = 8 + 8 – 6 + 4 = 14.
✳️ ➤ Remainder = 14.
🟡 Question 18
Construct a quadratic polynomial with zeroes 4 and –5. Verify coefficients–zeroes relationship.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: (x – 4)(x + 5) = x² + 5x – 4x – 20 = x² + x – 20.
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes = 4 + (–5) = –1 = –b/a = –1 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Product = 4 × (–5) = –20 = c/a = –20 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Verified.
🟡 Question 19
Using division algorithm, show that x³ – 2x² – x + 2 is divisible by x – 2.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Substitute x = 2: p(2) = 8 – 8 – 2 + 2 = 0 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Long division: x³ ÷ x = x² ⇒ x²(x – 2) = x³ – 2x². Subtract: –2x² – (–2x²) = 0. Bring down –x + 2 ⇒ –x ÷ x = –1 ⇒ –1(x – 2) = –x + 2. Subtract: 2 – 2 = 0.
✳️ ➤ Hence divisible.
🟡 Question 20
OR
Find the zeroes of 2x² – 7x + 3 and verify the relationship.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Discriminant Δ = (–7)² – 4(2)(3) = 49 – 24 = 25.
✳️ ➤ x = [7 ± √25]/4 = [7 ± 5]/4.
✳️ ➤ Zeroes: (7 + 5)/4 = 12/4 = 3, and (7 – 5)/4 = 2/4 = 1/2.
✳️ ➤ Sum = 3 + 1/2 = 3.5 = 7/2 = –b/a ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Product = 3 × 1/2 = 3/2 = c/a = 3/2 ✔️.
🟡 Question 21
Find a polynomial p(x) of degree 3 such that p(–1) = 0, p(2) = 0, p(3) = 0 and p(1) = 24.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Roots: –1, 2, 3 ⇒ p(x) = k(x + 1)(x – 2)(x – 3).
✳️ ➤ Use p(1) = 24:
24 = k(1 + 1)(1 – 2)(1 – 3) = k(2)(–1)(–2) = k(4).
✳️ ➤ k = 6.
✳️ ➤ Polynomial: 6(x + 1)(x – 2)(x – 3).
🟡 Question 22
A motorboat, after travelling 40 km downstream in 5 h, returns upstream in 8 h. Find the speed of the boat in still water and speed of the stream using polynomials.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Downstream speed = 40/5 = 8 km/h.
✳️ ➤ Upstream speed = 40/8 = 5 km/h.
✳️ ➤ Let boat speed = x, stream speed = y.
x + y = 8, x – y = 5.
✳️ ➤ Add ⇒ 2x = 13 ⇒ x = 6.5.
✳️ ➤ Subtract ⇒ 2y = 3 ⇒ y = 1.5.
✳️ ➤ Boat speed: 6.5 km/h, Stream speed: 1.5 km/h.
🔴 Section D (4 marks each)
🔴 Question 23
Use division algorithm to divide p(x) = x⁴ – 3x³ + 5x² – x + 6 by g(x) = x² – 2x + 3. Find the quotient and remainder.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ x⁴ ÷ x² = x² ⇒ Multiply: x²(x² – 2x + 3) = x⁴ – 2x³ + 3x².
✳️ ➤ Subtract: (–3x³ – (–2x³)) = –x³; (5x² – 3x²) = 2x² ⇒ –x³ + 2x² – x + 6.
✳️ ➤ –x³ ÷ x² = –x ⇒ Multiply: –x(x² – 2x + 3) = –x³ + 2x² – 3x.
✳️ ➤ Subtract: (–x³ cancel) 2x² – 2x² = 0; (–x – (–3x)) = 2x ⇒ 2x + 6.
✳️ ➤ 2x ÷ x² = 0 ⇒ Multiply remainder step: remainder = 2x + 6, quotient = x² – x.
🔴 Question 24
A bus covers a distance of 90 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 15 km/h more, it would have taken 30 min less. Find the original speed of the bus.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Let speed = x km/h.
➤ Time = 90/x. New speed = x + 15 ⇒ time = 90/(x + 15).
✳️ ➤ Given: 90/x – 90/(x + 15) = 1/2 (30 min = 1/2 h).
✳️ ➤ Multiply by x(x + 15): 90(x + 15) – 90x = (1/2)(x(x + 15)).
✳️ ➤ 90x + 1350 – 90x = (1/2)(x² + 15x).
✳️ ➤ 1350 = (1/2)(x² + 15x).
✳️ ➤ Multiply 2: 2700 = x² + 15x ⇒ x² + 15x – 2700 = 0.
✳️ ➤ Factorise: x² + 60x – 45x – 2700 = 0 ⇒ x(x + 60) – 45(x + 60) = 0 ⇒ (x – 45)(x + 60) = 0.
✳️ ➤ x = 45 (speed positive).
✳️ ➤ Original speed = 45 km/h.
🔴 Question 25
Find the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = x³ – 4x² – x + 4 and verify the relationship among coefficients and zeroes.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Trial: Substitute x = 1 ⇒ 1 – 4 – 1 + 4 = 0 ⇒ x = 1 is a zero.
✳️ ➤ Divide by (x – 1):
x³ ÷ x = x² ⇒ x²(x – 1) = x³ – x². Subtract: –4x² – (–x²) = –3x². Bring down –x.
–3x² ÷ x = –3x ⇒ –3x(x – 1) = –3x² + 3x. Subtract: –x – 3x = –4x. Bring down +4.
–4x ÷ x = –4 ⇒ –4(x – 1) = –4x + 4. Subtract remainder = 0.
✳️ ➤ Quotient: x² – 3x – 4 ⇒ factor = (x – 4)(x + 1).
✳️ ➤ Zeroes: 1, 4, –1.
✳️ ➤ Sum of zeroes = 1 + 4 –1 = 4 = –(–4)/1 ✔️.
✳️ ➤ Product = (1)(4)(–1) = –4 = –constant term/leading coefficient ✔️.
🔴 Question 26
OR
A dealer buys a number of items at ₹450 each. He sells some at a profit of 10% and the rest at a loss of 5%. On the whole, he neither gains nor loses. Find the ratio of the number of items sold at a profit to those sold at a loss.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Let items sold at profit = x, at loss = y.
✳️ ➤ Selling prices: Profit items: 450 × 110/100 = 495. Loss items: 450 × 95/100 = 427.5.
✳️ ➤ Total cost = 450(x + y). Total revenue = 495x + 427.5y.
✳️ ➤ Break-even: 495x + 427.5y = 450(x + y).
✳️ ➤ Expand: 495x + 427.5y = 450x + 450y ⇒ 495x – 450x = 450y – 427.5y ⇒ 45x = 22.5y.
✳️ ➤ Ratio: x/y = 22.5/45 = 1/2.
✳️ ➤ Required ratio = 1:2.
🔴 Question 27
Two water taps can fill a tank in 12 min and 15 min respectively. A waste pipe can empty it in 20 min. If all are opened together, how long will it take to fill the tank?
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Fill rates: 1/12, 1/15; empty rate: –1/20.
✳️ ➤ Combined rate = 1/12 + 1/15 – 1/20.
LCM 60 ⇒ 5 + 4 – 3 = 6/60 = 1/10.
✳️ ➤ Time = 10 min.
🔴 Question 28
The sum of the reciprocals of Reema’s age (in years) three years ago and five years from now is 1/3. Find her present age.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Let present age = x.
✳️ ➤ Condition: 1/(x – 3) + 1/(x + 5) = 1/3.
✳️ ➤ LCM: (x – 3)(x + 5) ⇒ (x + 5 + x – 3)/((x – 3)(x + 5)) = 1/3 ⇒ (2x + 2)/(x² + 5x – 3x –15) = 1/3 ⇒ (2(x +1))/(x² + 2x –15) = 1/3.
✳️ ➤ Cross-multiply: 6(x + 1) = x² + 2x –15.
✳️ ➤ Expand: 6x + 6 = x² + 2x –15 ⇒ 0 = x² + 2x –15 –6x –6 ⇒ x² –4x –21 = 0.
✳️ ➤ Factor: x² –7x +3x –21 = (x –7)(x +3) = 0 ⇒ x =7 or –3.
✳️ ➤ Age positive: 7 years.
🔴 Question 29
OR
Divide 3x³ – 5x² + 7x – 2 by x – 2 and verify using division algorithm.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Use synthetic division: Substitute x=2 for remainder: p(2)=24–20+14–2=16.
✳️ ➤ Long division: 3x³ ÷ x = 3x² ⇒ 3x²(x –2)=3x³–6x². Subtract: –5x²–(–6x²)=x². Bring down +7x.
x² ÷ x = x ⇒ x(x–2)=x²–2x. Subtract: 7x–(–2x)=9x. Bring down –2.
9x ÷ x =9 ⇒9(x–2)=9x–18. Subtract: –2–(–18)=16. Quotient=3x²+x+9,Remainder=16.
✳️ ➤ Verify: (x–2)(3x²+x+9)+16=3x³–6x²+x²–2x+9x–18+16=3x³–5x²+7x–2 ✔️.
🔴 Question 30
Solve by elimination: 0.2x + 0.3y = 1.3 and 0.4x – 0.5y = –1.6.
🟢 Answer
✳️ ➤ Multiply first by 5: x + 1.5y = 6.5. Multiply second by 5: 2x – 2.5y = –8.
✳️ ➤ Multiply first by 2: 2x + 3y = 13. Subtract second: (2x +3y) – (2x –2.5y) =13–(–8)=21 ⇒ 5.5y=21 ⇒ y=21/5.5=3.818.
✳️ ➤ Substitute: x+1.5(3.818)=6.5 ⇒ x+5.727=6.5 ⇒ x=0.773.
✳️ ➤ Solution: (0.773, 3.818).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
MIND MAP
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
