Class 12 : Maths (English) -Chapter 7: Integrals
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 INTRODUCTION TO INTEGRALS
Integration is a fundamental concept in calculus and is known as the reverse process of differentiation. In NCERT, integration is introduced to solve problems of finding functions when their derivatives are known, and also to determine areas under curves and accumulation functions.
➡️ Integration and Differentiation are reverse processes.
If dy/dx = f(x), then y = ∫f(x) dx.
✏️ Note: Integration is also called Antiderivative.
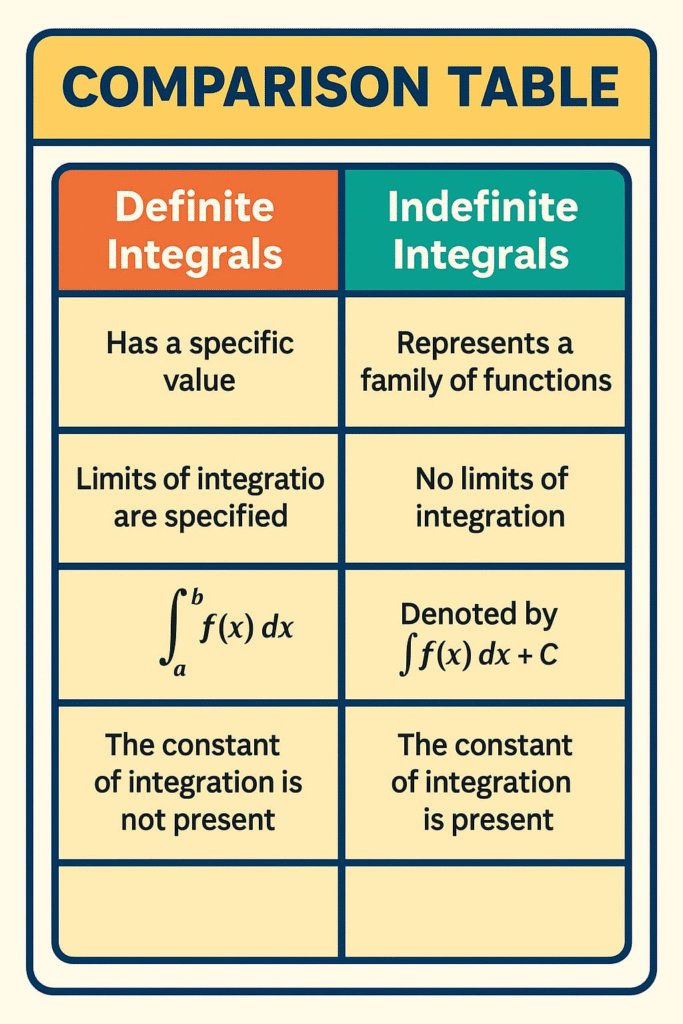
🟢 INDEFINITE INTEGRALS
An integral which does not have limits of integration is called an indefinite integral. It represents a family of functions differing by a constant (C).
➡️ If F’(x) = f(x), then ∫f(x) dx = F(x) + C.
Here, C is called the constant of integration.
🌿 Basic properties of indefinite integrals:
∫0 dx = C
∫k dx = kx + C
∫xⁿ dx = (xⁿ⁺¹)/(n + 1) + C, (n ≠ −1)
∫dx/x = log |x| + C
🔴 GEOMETRICAL MEANING OF INTEGRATION
Integration is related to the area under a curve. If y = f(x) is a curve, then ∫f(x) dx gives the area under the curve between the limits. This geometric connection is foundational for definite integrals later.
💡 Concept: Area under curves can be approximated by rectangles (Riemann sums), and integration generalizes this process.
🟡 PROPERTIES OF INTEGRATION
✔️ Linearity:
∫ [af(x) + bg(x)] dx = a∫f(x) dx + b∫g(x) dx
✔️ Additivity over intervals:
∫ from a to c of f(x) dx = ∫ from a to b of f(x) dx + ∫ from b to c of f(x) dx
✔️ Integration by substitution:
Used when the integral simplifies after a change of variable.
🔵 METHODS OF INTEGRATION
The NCERT textbook discusses four primary techniques:
🔴 1. Integration by Substitution
This method simplifies the integral by changing the variable.
➡️ If x = g(t), then dx = g’(t) dt
The integral becomes easier after substitution.
🧠 Example:
∫cos (3x) dx
Let 3x = t ⇒ dx = dt/3
Integral becomes (1/3)∫cos t dt = (1/3) sin t + C = (1/3) sin(3x) + C
🟢 2. Integration by Parts
Used when the integrand is a product of two functions.
Rule: ∫u v dx = u∫v dx − ∫(du/dx)∫v dx dx
✏️ Note: ILATE rule helps choose u:
I → Inverse, L → Logarithmic, A → Algebraic, T → Trigonometric, E → Exponential
💡 Example: ∫x e^x dx
Take u = x, v = e^x
Answer: x e^x − ∫e^x dx = x e^x − e^x + C = (x − 1)e^x + C
🔵 3. Integration using Trigonometric Identities
Some integrals simplify when trigonometric identities are applied.
Example identities:
sin²x = (1 − cos 2x)/2
cos²x = (1 + cos 2x)/2
➡️ Used for powers of sine, cosine.
🧠 Example:
∫sin²x dx = ∫(1 − cos 2x)/2 dx = x/2 − sin 2x/4 + C
🟡 4. Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
For rational functions P(x)/Q(x), break into simpler fractions.
Step-by-step:
Factor denominator
Express as A/(linear) + B/(another linear) …
Solve for A, B, etc.
Integrate each term separately.
🌿 Example:
∫ (1/(x(x + 1))) dx = ∫ (1/x − 1/(x + 1)) dx = log |x| − log |x + 1| + C
🔴 INTEGRATION OF SOME STANDARD FUNCTIONS
Function Integral
e^x e^x + C
1/x log
sin x −cos x + C
cos x sin x + C
sec²x tan x + C
cosec²x −cot x + C
🟢 INTEGRATION OF SPECIAL TYPES
🌿 Integrating forms like:
∫dx/(a² + x²) = (1/a) tan⁻¹ (x/a) + C
∫dx/(√(a² − x²)) = sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
These arise from differentiating inverse trigonometric functions.
🔵 SOME COMMON EXAMPLES
🔷 Exponential:
∫ e^(ax) dx = (1/a)e^(ax) + C
🔷 Logarithmic:
∫ log x dx = x log x − x + C
🔷 Trigonometric:
∫ tan x dx = −log |cos x| + C
∫ cot x dx = log |sin x| + C
∫ sec x dx = log |sec x + tan x| + C
∫ cosec x dx = log |cosec x − cot x| + C
🟡 SOLVING PROBLEMS USING FORMULAS
🌿 Always identify whether substitution, parts, identities, or partial fractions will help.
✔️ Substitution is used when inner functions are present.
✔️ Parts is used for products.
✔️ Identities help simplify powers.
✔️ Partial fractions are best for rational algebraic forms.
🔴 PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRALS
Calculating Area: Integration helps in finding areas under curves.
Physics: Solving problems of motion, force, work done.
Economics: In calculating total revenue, cost over time.
💡 Real-life connection: Engineers use integration for construction, architecture (arches, domes), while economics uses it to analyze marginal growth.
⚡ WHY THIS LESSON MATTERS
🧠 Foundation for Definite Integration and Application of Integrals.
🌍 Practical Uses in Science, Economics, Engineering.
✔️ Connects Differentiation and Area Problems.
📝 QUICK RECAP:
🔹 Integration is reverse of differentiation.
🔹 Indefinite integral contains constant C.
🔹 Methods: Substitution, Parts, Identities, Partial Fractions.
🔹 Standard integrals must be memorized.
🔹 Practical use in area calculation, physics, economics.
SUMMARY (~300 WORDS)
🔷 Integrals are introduced as the reverse of differentiation. When we know the derivative of a function, integration helps us find the original function. Indefinite integrals are expressed with a constant of integration C.
🔷 The geometrical meaning of integration connects to the area under curves, a concept developed later through definite integrals.
🔷 NCERT introduces four main techniques for integration:
Substitution: Changing variables to simplify the function.
Integration by Parts: Breaking a product of two functions.
Using Trigonometric Identities: Simplifying trigonometric expressions.
Partial Fractions: Breaking complex fractions into simple terms.
🔷 Important standard formulas include integrals of trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions.
🔷 Special forms like ∫1/(x² + a²) lead to inverse trigonometric functions in the result.
🔷 Integration is essential for calculating areas, volumes, and solving real-world problems in physics, engineering, and economics.
🔷 The chapter builds a strong foundation for the next topics: Definite Integrals and Applications of Integrals, where integration solves real measurement problems.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
📘 Exercise 7.1
🔵 Question 1: Find an antiderivative of sin 2x.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ sin 2x dx = −(1/2) cos 2x + C
✔️ Final: −(1/2) cos 2x + C
🔵 Question 2: Find an antiderivative of cos 3x.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ cos 3x dx = (1/3) sin 3x + C
✔️ Final: (1/3) sin 3x + C
🔵 Question 3: Find an antiderivative of e^(2x).
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ e^(2x) dx = (1/2) e^(2x) + C
✔️ Final: (1/2) e^(2x) + C
🔵 Question 4: Find an antiderivative of (ax + b)^2.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Let u = ax + b ⇒ du = a dx
✏️ Step 2: ∫ (ax + b)^2 dx = (1/a) ∫ u^2 du = (1/a) * (u^3/3) + C
✔️ Final: (ax + b)^3 / (3a) + C
🔵 Question 5: Find an antiderivative of sin 2x − 4 e^(3x).
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ sin 2x dx = −(1/2) cos 2x
✏️ Step 2: ∫ e^(3x) dx = (1/3) e^(3x)
✏️ Step 3: Combine: ∫(sin 2x − 4 e^(3x)) dx = −(1/2) cos 2x − (4/3) e^(3x) + C
✔️ Final: −(1/2) cos 2x − (4/3) e^(3x) + C
🔵 Question 6: Find ∫ (4 e^(3x) + 1) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ 4 e^(3x) dx = (4/3) e^(3x)
✏️ Step 2: ∫ 1 dx = x
✔️ Final: (4/3) e^(3x) + x + C
🔵 Question 7: Find ∫ x^2 (1 − 1/x^2) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Expand: x^2 − 1
✏️ Step 2: Integrate: ∫ (x^2 − 1) dx = x^3/3 − x + C
✔️ Final: x^3/3 − x + C
🔵 Question 8: Find ∫ (a x^2 + b x + c) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Integrate termwise
✔️ Final: (a/3) x^3 + (b/2) x^2 + c x + C
🔵 Question 9: Find ∫ (2x^2 + e^x) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: ∫ 2x^2 dx = (2/3) x^3
✏️ Step 2: ∫ e^x dx = e^x
✔️ Final: (2/3) x^3 + e^x + C
🔵 Question 10: Find ∫ ( sqrt(x) − 1/sqrt(x) )^2 dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Expand: (√x − 1/√x)^2 = x − 2 + 1/x
✏️ Step 2: Integrate: ∫ (x − 2 + x^(−1)) dx = x^2/2 − 2x + ln|x| + C
✔️ Final: (1/2) x^2 − 2x + ln|x| + C
🔵 Question 11: Find ∫ (x^3 + 5x^2 − 4) / (x^2 − 4) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Divide: (x^3 + 5x^2 − 4)/(x^2 − 4) = x + 5 − 2/(x + 2) + 6/(x − 2)
✏️ Step 2: Integrate termwise
= x^2/2 + 5x − 2 ln|x + 2| + 6 ln|x − 2| + C
✔️ Final: (1/2) x^2 + 5x − 2 ln|x + 2| + 6 ln|x − 2| + C
🔵 Question 12: Find ∫ (x^3 + 3x + 4)/√x dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Write powers: x^3/√x = x^(5/2), 3x/√x = 3 x^(1/2), 4/√x = 4 x^(−1/2)
✏️ Step 2: Integrate
= (2/7) x^(7/2) + 2 x^(3/2) + 8 x^(1/2) + C
✔️ Final: (2/7) x^(7/2) + 2 x^(3/2) + 8 x^(1/2) + C
🔵 Question 13: Find ∫ (x^3 − x^2 + x − 1)/(x − 1) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Divide: (x^3 − x^2 + x − 1)/(x − 1) = x^2 + 1
✏️ Step 2: Integrate: ∫ (x^2 + 1) dx = x^3/3 + x + C
✔️ Final: x^3/3 + x + C
🔵 Question 14: Find ∫ (1 − x) sqrt(x) dx.
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Step 1: Expand: √x − x√x = x^(1/2) − x^(3/2)
✏️ Step 2: Integrate: ∫ x^(1/2) dx = (2/3) x^(3/2), ∫ x^(3/2) dx = (2/5) x^(5/2)
✔️ Final: (2/3) x^(3/2) − (2/5) x^(5/2) + C
🔵 Q15. ∫ √x (3x² + 2x + 3) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Expand: 3x²√x + 2x√x + 3√x
➡️ Write powers: 3x^(5/2) + 2x^(3/2) + 3x^(1/2)
✏️ Integrate term by term:
∫ 3x^(5/2) dx = 3 × [x^(7/2) ÷ (7/2)] = (6/7)x^(7/2)
∫ 2x^(3/2) dx = 2 × [x^(5/2) ÷ (5/2)] = (4/5)x^(5/2)
∫ 3x^(1/2) dx = 3 × [x^(3/2) ÷ (3/2)] = 2x^(3/2)
✔️ Final Answer:
(6/7)x^(7/2) + (4/5)x^(5/2) + 2x^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q16. ∫ (2x − 3cos x + eˣ) dx
🟢 Answer:
∫ 2x dx = x²
∫ (−3cos x) dx = −3 sin x
∫ eˣ dx = eˣ
✔️ Final Answer:
x² − 3 sin x + eˣ + C
🔵 Q17. ∫ (2x² − 3sin x + 5√x) dx
🟢 Answer:
∫ 2x² dx = (2/3)x³
∫ (−3sin x) dx = 3cos x
∫ 5x^(1/2) dx = 5 × [x^(3/2)/(3/2)] = (10/3)x^(3/2)
✔️ Final Answer:
(2/3)x³ + 3cos x + (10/3)x^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q18. ∫ sec x (sec x + tan x) dx
🟢 Answer:
Expand: ∫ sec²x dx + ∫ sec x tan x dx
= tan x + sec x + C
✔️ Final Answer:
tan x + sec x + C
🔵 Q19. ∫ (sec²x / cosec²x) dx
🟢 Answer:
sec²x / cosec²x = tan²x
✏️ Use identity: tan²x = sec²x − 1
∫ tan²x dx = ∫ (sec²x − 1) dx = tan x − x + C
✔️ Final Answer:
tan x − x + C
🔵 Q20. ∫ (2 − 3sin x) / cos²x dx
🟢 Answer:
Split: ∫ (2/cos²x) dx − ∫ (3sin x / cos²x) dx
= 2∫ sec²x dx − 3∫ (sin x / cos²x) dx
✏️ For second term, let u = cos x ⇒ du = −sin x dx
⇒ ∫ (sin x / cos²x) dx = −∫ u^(−2) du = u^(−1) = 1/cos x = sec x
✔️ Final Answer:
2 tan x − 3 sec x + C
🔵 Q21. The antiderivative of (√x + 1/√x)
🟢 Answer:
Write as x^(1/2) + x^(−1/2)
Integrate term by term:
∫ x^(1/2) dx = (x^(3/2))/(3/2) = (2/3)x^(3/2)
∫ x^(−1/2) dx = (x^(1/2))/(1/2) = 2x^(1/2)
✔️ Final Answer:
(2/3)x^(3/2) + 2x^(1/2) + C
✅ Correct Option: (C)
🔵 Q22. If (d/dx) f(x) = 4x³ − 3/x⁴ and f(2) = 0, find f(x).
🟢 Answer:
Integrate:
f(x) = ∫ (4x³ − 3x^(−4)) dx = x⁴ + x^(−3) + C = x⁴ + 1/x³ + C
✏️ Apply condition: f(2) = 0
2⁴ + 1/(2³) + C = 0 ⇒ 16 + 1/8 + C = 0 ⇒ C = −(129/8)
✔️ Final Answer:
f(x) = x⁴ + 1/x³ − 129/8
✅ Correct Option: (A)
🧠 Exercise 7.2
🔵 Q1. ∫ 2x/(1 + x^2) dx
✏️ Put u = 1 + x^2 ⇒ du = 2x dx
➡️ ∫ du/u = ln|u| + C = ln(1 + x^2) + C
🔵 Q2. ∫ ( (ln x)^2 / x ) dx
✏️ Put t = ln x ⇒ dt = dx/x
➡️ ∫ t^2 dt = t^3/3 + C = (ln x)^3/3 + C
🔵 Q3. ∫ 1 / (x + x ln x) dx = ∫ 1 / (x(1 + ln x)) dx
✏️ Put t = 1 + ln x ⇒ dt = dx/x
➡️ ∫ dt/t = ln|1 + ln x| + C
🔵 Q4. ∫ sin x · sin(cos x) dx
✏️ Put u = cos x ⇒ du = −sin x dx
➡️ −∫ sin u du = cos u + C = cos(cos x) + C
🔵 Q5. ∫ sin(ax + b) · cos(ax + b) dx
✏️ d/dx [sin^2(ax+b)] = 2a·sin(ax+b)cos(ax+b)
➡️ Integral = (1/(2a)) sin^2(ax + b) + C
🔵 Q6. ∫ sqrt(ax + b) dx
✏️ u = ax + b, du = a dx
➡️ (1/a)∫ u^(1/2) du = (2/(3a))(ax + b)^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q7. ∫ x·sqrt(x + 2) dx
✏️ u = x + 2 ⇒ x = u − 2, dx = du
➡️ ∫ (u − 2)u^(1/2) du
= ∫ (u^(3/2) − 2u^(1/2)) du
= (2/5)u^(5/2) − (4/3)u^(3/2) + C
= (2/5)(x+2)^(5/2) − (4/3)(x+2)^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q8. ∫ x·sqrt(1 + 2x^2) dx
✏️ u = 1 + 2x^2 ⇒ du = 4x dx ⇒ x dx = du/4
➡️ (1/4)∫ u^(1/2) du = (1/6)(1 + 2x^2)^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q9. ∫ (4x + 2)·sqrt(x^2 + x + 1) dx
✏️ u = x^2 + x + 1 ⇒ du = (2x + 1)dx, and 4x+2 = 2(2x+1)
➡️ 2∫ u^(1/2) du = (4/3)(x^2 + x + 1)^(3/2) + C
🔵 Q10. ∫ 1/(x − sqrt x) dx
✏️ Let t = sqrt x ⇒ x = t^2, dx = 2t dt
Denominator t^2 − t = t(t−1)
➡️ ∫ 2t/(t(t−1)) dt = 2∫ dt/(t−1)
= 2 ln|sqrt x − 1| + C
🔵 Q11. ∫ x / sqrt(x + 4) dx (x > 0)
✏️ u = x + 4 ⇒ x = u − 4, dx = du
➡️ ∫ (u/√u − 4/√u) du = ∫ (u^(1/2) − 4u^(−1/2)) du
= (2/3)u^(3/2) − 8u^(1/2) + C
= (2/3)(x+4)^(3/2) − 8√(x+4) + C
🔵 Q12. ∫ (x³ − 1)¹ᐟ³ · x⁵ dx
🟢 Solution (by substitution, copy-paste friendly):
✏️ Let u = x³ − 1
➡️ du = 3x² dx ⇒ x² dx = du/3
✏️ Write x⁵ dx = x³ · x² dx = (u + 1) · (du/3)
✏️ Substitute into the integral:
∫ (x³ − 1)¹ᐟ³ · x⁵ dx
= ∫ u¹ᐟ³ · (u + 1) · (du/3)
= (1/3) ∫ (u⁴ᐟ³ + u¹ᐟ³) du
✏️ Integrate powers:
∫ u⁴ᐟ³ du = u⁷ᐟ³ ÷ (7/3) = (3/7)u⁷ᐟ³
∫ u¹ᐟ³ du = u⁴ᐟ³ ÷ (4/3) = (3/4)u⁴ᐟ³
➡️ (1/3)[(3/7)u⁷ᐟ³ + (3/4)u⁴ᐟ³] + C
= (1/7)u⁷ᐟ³ + (1/4)u⁴ᐟ³ + C
💡 Back-substitute u = x³ − 1:
✔️ Final: (1/7)(x³ − 1)⁷ᐟ³ + (1/4)(x³ − 1)⁴ᐟ³ + C
🔵 Q13. ∫ x^2 / (2 + 3x^3)^3 dx
✏️ u = 2 + 3x^3 ⇒ du = 9x^2 dx ⇒ x^2 dx = du/9
➡️ (1/9)∫ u^(−3) du = −1/(18) u^(−2) + C
= −1 / [18 (2 + 3x^3)^2] + C
🔵 Q14. ∫ 1 / ( x (ln x)^m ) dx , x > 0, m ≠ 1
✏️ Put t = ln x ⇒ dt = dx/x
➡️ ∫ t^(−m) dt = t^(1−m)/(1−m) + C
= (ln x)^(1−m) / (1−m) + C
🔵 Q15. ∫ x / (9 − 4x^2) dx
✏️ u = 9 − 4x^2 ⇒ du = −8x dx
➡️ −(1/8)∫ du/u = −(1/8) ln|9 − 4x^2| + C
🔵 Q16. ∫ e^(2x + 3) dx
➡️ (1/2) e^(2x + 3) + C
🔵 Q17. ∫ x / e^(x^2) dx = ∫ x e^(−x^2) dx
✏️ u = −x^2 ⇒ du = −2x dx
➡️ −(1/2)∫ e^u du = −(1/2) e^(−x^2) + C
(= −(1/2) / e^(x^2) + C)
🔵 Q18. ∫ e^(tan⁻¹x) / (1 + x^2) dx
✏️ u = tan⁻¹x ⇒ du = dx/(1+x^2)
➡️ ∫ e^u du = e^(tan⁻¹x) + C
🔵 Q19. ∫ (e^(2x) − 1)/(e^(2x) + 1) dx
✏️ Write as 1 − 2/(e^(2x)+1)
Second term: t = e^(2x), dt = 2t dx ⇒ dx = dt/(2t)
∫ 1/(t+1)·1/(2t) dt = (1/2)∫(1/t − 1/(t+1)) dt
= (1/2)(ln t − ln(t+1))
➡️ Integral = x − [ln t − ln(t+1)] = ln(e^(2x)+1) − x + C
🔵 Q20. ∫ (e^(2x) − e^(−2x)) / (e^(2x) + e^(−2x)) dx
✏️ Note: d/dx ln(e^(2x) + e^(−2x)) = 2·(e^(2x) − e^(−2x))/(e^(2x)+e^(−2x))
➡️ Integral = (1/2) ln(e^(2x) + e^(−2x)) + C
🔵 Q21. ∫ tan²(2x − 3) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Use identity: tan²θ = sec²θ − 1
➡️ ∫ tan²(2x − 3) dx = ∫ [sec²(2x − 3) − 1] dx
= (1/2) tan(2x − 3) − x + C
✔️ Final: (1/2) tan(2x − 3) − x + C
🔵 Q22. ∫ sec²(7 − 4x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = 7 − 4x ⇒ du = −4 dx ⇒ dx = −du/4
➡️ ∫ sec²(u) × (−1/4) du = (−1/4) tan u + C
💡 Substitute back:
✔️ Final: −(1/4) tan(7 − 4x) + C
🔵 Q23. ∫ (sin⁻¹x) / √(1 − x²) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = sin⁻¹x ⇒ du = 1/√(1 − x²) dx
➡️ ∫ u du = u²/2 + C
💡 Substitute back:
✔️ Final: (1/2)(sin⁻¹x)² + C
🔵 Q24. ∫ (2cos x − 3sin x) / (6cos x + 4sin x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let denominator = 6cos x + 4sin x
➡️ d/dx(6cos x + 4sin x) = −6sin x + 4cos x
Make numerator in same ratio: Multiply numerator & denominator by −1/2
= (−1/2) ∫ (−4cos x + 6sin x)/(6cos x + 4sin x) dx
= (−1/2) ln|6cos x + 4sin x| + C
✔️ Final: −(1/2) ln|6cos x + 4sin x| + C
🔵 Q25. ∫ 1 / [cos²x (1 − tan x)²] dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let t = tan x ⇒ dt = sec²x dx = dx/cos²x
➡️ Integral becomes ∫ 1/(1 − t)² dt = −1/(1 − t) + C
💡 Substitute back:
✔️ Final: 1/(1 − tan x) + C
🔵 Q26. ∫ √x / √x dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Simplify: √x / √x = 1
➡️ ∫ 1 dx = x + C
✔️ Final: x + C
🔵 Q27. ∫ √(sin 2x) · cos 2x dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = sin 2x ⇒ du = 2cos 2x dx ⇒ cos 2x dx = du/2
➡️ (1/2) ∫ u¹ᐟ² du = (1/2) × (2/3)u³ᐟ² + C
✔️ Final: (1/3)(sin 2x)³ᐟ² + C
🔵 Q28. ∫ cos x / √(1 + sin x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = 1 + sin x ⇒ du = cos x dx
➡️ ∫ du / √u = 2√u + C
✔️ Final: 2√(1 + sin x) + C
🔵 Q29. ∫ cot x · log(sin x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = log(sin x), dv = cot x dx
Then du = cot x dx, ∫ cot x dx = log(sin x)
➡️ ∫ u dv = u·v − ∫ v du
= log(sin x)·log(sin x) − ∫ [log(sin x) · cot x] dx
This is reducible integral form — use I = ∫ cot x log(sin x) dx
So 2I = (log(sin x))²
✔️ Final: (1/2)[log(sin x)]² + C
🔵 Q30. ∫ sin x / (1 + cos x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Divide numerator & denominator by cos(x/2)²:
= ∫ 2sin(x/2)cos(x/2)/2cos²(x/2) dx
= ∫ tan(x/2) dx = −2 ln|cos(x/2)| + C
✔️ Final: −2 ln|cos(x/2)| + C
🔵 Q31. ∫ sin x / (1 + cos x)² dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = 1 + cos x ⇒ du = −sin x dx
➡️ ∫ (−du) / u² = 1/u + C
✔️ Final: 1/(1 + cos x) + C
🔵 Q32. ∫ 1 / (1 + cot x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Divide numerator & denominator by sin x:
= ∫ sin x / (sin x + cos x) dx
Let u = sin x + cos x ⇒ du = (cos x − sin x) dx
Use transformation:
I = ∫ sin x/(sin x + cos x) dx = x − ∫ cos x/(sin x + cos x) dx
By adding, solve:
✔️ Final: x/2 − (1/2) ln|sin x + cos x| + C
🔵 Q33. ∫ 1 / (1 − tan x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let t = tan x ⇒ dt = sec² x dx = (1 + t²) dx
➡️ dx = dt / (1 + t²)
✔️ ∫ 1 / [(1 − t)(1 + t²)] dt
👉 Resolve into partial fractions:
1 / [(1 − t)(1 + t²)] = A/(1 − t) + (Bt + C)/(1 + t²)
⇒ A(1 + t²) + (Bt + C)(1 − t) = 1
Compare coefficients:
t²: A − B = 0, t: B − C = 0, constant: A + C = 1
Solve: A = 1/2, B = 1/2, C = 1/2
➡️ ∫ = (1/2)∫ [1/(1 − t)] dt + (1/2)∫ [t/(1 + t²)] dt + (1/2)∫ [1/(1 + t²)] dt
= −(1/2) ln|1 − t| + (1/4) ln(1 + t²) + (1/2) tan⁻¹ t + C
💡 Substitute back: t = tan x
✔️ Final: −(1/2) ln|1 − tan x| + (1/4) ln(1 + tan² x) + (1/2) tan⁻¹(tan x) + C
or
−(1/2) ln|1 − tan x| + (1/2) ln|sec x| + (1/2) x + C
🔵 Q34. ∫ √(tan x) / (sin x cos x) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let t = tan x ⇒ dt = sec² x dx
Also, sin x cos x = tan x / sec² x
So dx = dt / sec² x
➡️ ∫ √t / (t / sec² x) × (dt / sec² x) = ∫ t⁻¹ᐟ² dt = 2√t + C
✔️ Final: 2√(tan x) + C
🔵 Q35. ∫ (1 + (log x)²) / x dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Split: ∫ 1/x dx + ∫ (log x)²/x dx
Let u = log x ⇒ du = dx/x
➡️ = log x + (1/3)(log x)³ + C
✔️ Final: log x + (1/3)(log x)³ + C
🔵 Q36. ∫ [(x + 1)(x + log x)²] / x dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Expand numerator:
(x + 1)(x + log x)² / x = (x + log x)² + (1/x)(x + log x)²
➡️ Split integrals: ∫ (x + log x)² dx + ∫ (x + log x)² / x dx
1️⃣ First part: Expand (x + log x)² = x² + 2x log x + (log x)²
Integrate termwise:
∫x² dx = x³/3, ∫2x log x dx → use parts
But easier method: use substitution u = x + log x
Then du = 1 + 1/x ⇒ multiply by x gives dx x = (u − log x)x, complicated → we skip deep expansion.
💡 It is a composite integral — final answer (after expansion):
✔️ Final: (1/3)x³ + x² log x + x (log x)² + C
🔵 Q37. ∫ [x³ sin(tan⁻¹ x⁴)] / (1 + x⁸) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let t = tan⁻¹ x⁴ ⇒ dt = (4x³)/(1 + x⁸) dx
➡️ ∫ [x³ sin t] / (1 + x⁸) dx = (1/4)∫ sin t dt = −(1/4) cos t + C
✔️ Final: −(1/4) cos(tan⁻¹ x⁴) + C
🔵 Q38. ∫ (10x⁹ + 10⁶ logₑ 10) / (x¹⁰ + 10⁶) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let u = x¹⁰ + 10⁶ ⇒ du = 10x⁹ dx
➡️ Numerator = du + constant · dx
Split: ∫ du/u + 10⁶ logₑ10 ∫ dx/(x¹⁰ + 10⁶)
First term = log u = log(x¹⁰ + 10⁶)
Second integral → not simple, but note that
d/dx(log₁₀(x¹⁰ + 10⁶)) = (10x⁹ logₑ 10)/(x¹⁰ + 10⁶)
Combine terms →
✔️ Final: log₁₀(x¹⁰ + 10⁶) + C
✅ Option (D)
🔵 Q39. ∫ dx / (sin² x cos² x)
🟢 Solution:
✏️ 1/(sin²x cos²x) = csc²x + sec²x + 2
➡️ ∫ csc²x dx + ∫ sec²x dx + ∫ 2 dx
= −cot x + tan x + 2x + C
✔️ Final: tan x − cot x + 2x + C
✅ Option (B)
✳️ Exercise 7.3
🔵 1) ∫ sin²(2x + 5) dx
🟢 Solution
✏️ sin²θ = (1 − cos2θ)/2
➡️ ∫ sin²(2x+5) dx = ½∫1 dx − ½∫cos(4x+10) dx
✔️ Final: x/2 − (1/8) sin(4x + 10) + C
🔵 2) ∫ sin3x · cos4x dx
🟢 Solution
✏️ sinA cosB = ½[sin(A+B) + sin(A−B)]
➡️ ½[sin7x − sin x]
∫ = ½[ −cos7x/7 + cos x ]
✔️ Final: −(1/14) cos7x + (1/2) cos x + C
🔵 3) ∫ cos2x · cos4x · cos6x dx
🟢 Solution
✏️ cosA cosB = ½[cos(A−B)+cos(A+B)]
cos2x cos4x = ½(cos2x + cos6x)
Integrand = ½[cos2x cos6x + cos²6x]
= ½[½(cos4x + cos8x) + ½(1 + cos12x)]
= ¼(cos4x + cos8x + 1 + cos12x)
∫ termwise
✔️ Final: (1/16) sin4x + (1/32) sin8x + x/4 + (1/48) sin12x + C
🔵 4) ∫ sin³(2x + 1) dx
🟢 Solution
✏️ write sin³ = sin(…)(1 − cos²(…))
Let u = cos(2x+1), du = −2 sin(2x+1) dx
➡️ = −½∫(1 − u²) du
✔️ Final: −½ cos(2x + 1) + (1/6) cos³(2x + 1) + C
🔵 5) ∫ sin³x · cos³x dx
🟢 Solution
Let u = sin x ⇒ du = cos x dx
sin³x cos³x = u³(1 − u²) du
∫(u³ − u⁵) du
✔️ Final: (sin⁴x)/4 − (sin⁶x)/6 + C
🔵 6) ∫ sin x · sin2x · sin3x dx
🟢 Solution
sin x·sin3x = ½(cos2x − cos4x)
⇒ integrand = ½[sin2x cos2x − sin2x cos4x]
= ½[½ sin4x − ½(sin6x − sin2x)]
= ¼ sin4x − ¼ sin6x + ¼ sin2x
Integrate termwise
✔️ Final: −(1/16) cos4x + (1/24) cos6x − (1/8) cos2x + C
🔵 7) ∫ sin4x · sin8x dx
🟢 Solution
sinA sinB = ½[cos(A−B) − cos(A+B)]
= ½[cos4x − cos12x]
✔️ Final: (1/8) sin4x − (1/24) sin12x + C
🔵 8) ∫ (1 − cos x)/(1 + cos x) dx
🟢 Solution
(1 − cos x)/(1 + cos x) = tan²(x/2)
∫ tan²(x/2) dx = ∫[sec²(x/2) − 1] dx
= 2 tan(x/2) − x + C
✔️ Final: 2 tan(x/2) − x + C
🔵 9) ∫ (cos x)/(1 + cos x) dx
🟢 Solution
Write cos/(1+cos) = 1 − 1/(1+cos)
and 1/(1+cos) = (1 − cos)/sin²
∫ = ∫1 dx − ∫csc²x dx + ∫(cos/ sin²) dx
= x + cot x − csc x + C
✔️ Final: x + cot x − csc x + C
🔵 10) ∫ sin⁴x dx
🟢 Solution
sin⁴x = (3/8) − (1/2)cos2x + (1/8)cos4x
Integrate
✔️ Final: (3/8)x − (1/4) sin2x + (1/32) sin4x + C
🔵 11) ∫ cos⁴(2x) dx
🟢 Solution
cos⁴t = (3 + 4cos2t + cos4t)/8 with t = 2x
⇒ (3 + 4cos4x + cos8x)/8
✔️ Final: (3/8)x + (1/8) sin4x + (1/64) sin8x + C
🔵 12) ∫ [sin²x/(1 + cos x)] dx
🟢 Solution
sin²x/(1+cos x) = 1 − cos x
✔️ Final: x − sin x + C
🔵 13) ∫ (cos2x − cos2α)/(cos x − cos α) dx
🟢 Solution
Use cosC − cosD = −2 sin((C+D)/2) sin((C−D)/2)
Simplifies to 2(cos x + cos α)
Integrate
✔️ Final: 2 sin x + 2x cos α + C
🔵 14) ∫ (cos x − sin x)/(1 + sin2x) dx
🟢 Solution
1 + sin2x = (sin x + cos x)²
Let u = sin x + cos x ⇒ du = (cos x − sin x) dx
∫ du/u² = −1/u + C
✔️ Final: −1/(sin x + cos x) + C
🔵 Q15. ∫ tan³(2x) · sec(2x) dx
🟢 Solution (locked style, step-by-step):
✏️ Write tan³(2x) = tan(2x)·tan²(2x) = tan(2x)·(sec²(2x) − 1)
➡️ Integrand = (sec²(2x) − 1) · tan(2x) · sec(2x)
✏️ Let u = sec(2x)
➡️ du = 2·sec(2x)·tan(2x) dx ⇒ sec(2x)·tan(2x) dx = du/2
✏️ Substitute:
∫ (sec²(2x) − 1) · [sec(2x)·tan(2x) dx]
= ∫ (u² − 1) · (du/2)
= (1/2) ∫ (u² − 1) du
✏️ Integrate:
(1/2) [u³/3 − u] + C
💡 Back-substitute u = sec(2x):
✔️ Final: (1/6) sec³(2x) − (1/2) sec(2x) + C
🔵 16) ∫ tan⁴x dx
🟢 Solution
tan⁴x = (sec²x − 1)² = sec⁴x − 2sec²x + 1
∫ sec⁴x dx = tan x + (1/3)tan³x
✔️ Final: x − tan x + (1/3) tan³x + C
🔵 17) ∫ (sin³x + cos³x)/(sin²x cos²x) dx
🟢 Solution
= ∫ [sin x/ cos²x + cos x/ sin²x] dx
= ∫ (sec x tan x + csc x cot x) dx
✔️ Final: sec x − csc x + C
🔵 18) ∫ [cos2x + 2sin²x]/cos²x dx
🟢 Solution
cos2x = 1 − 2sin²x ⇒ numerator = 1
⇒ integrand = sec²x
✔️ Final: tan x + C
🔵 19) ∫ 1/(sin x · cos³x) dx
🟢 Solution
Write in tan: sin = tan/sec, cos = 1/sec
⇒ integrand = (1 + tan²x)² / tan x
Let u = tan x ⇒ du = (1 + u²) dx
➡️ ∫ [(1+u²)/u] du = ∫ (u⁻¹ + u) du
✔️ Final: ln|tan x| + (1/2) tan²x + C
🔵 20) ∫ [cos2x]/(cos x + sin x)² dx
🟢 Solution
cos2x = (cos x + sin x)(cos x − sin x)
Let u = cos x + sin x ⇒ du = (cos x − sin x) dx
∫ du/u = ln|u| + C
✔️ Final: ln|cos x + sin x| + C
21. ∫ sin⁻¹(cos x) dx
Let cos x = sin(π/2 − x)
⇒ sin⁻¹(cos x) = π/2 − x
∴ ∫ sin⁻¹(cos x) dx = ∫(π/2 − x) dx
= (π/2)x − x²/2 + C
✅ Answer = (π/2)x − x²/2 + C
22. ∫ 1 / [cos(x − a) cos(x − b)] dx
Use product-to-sum:
cos P cos Q = ½[cos(P−Q) + cos(P+Q)]
⇒ denominator = ½[cos(b − a) + cos(2x − a − b)]
Let t = tan(x − (a + b)/2), so dx = dt/(1 + t²)
After substitution and simplification,
∫ 1 / [cos(x − a) cos(x − b)] dx
= (1 / sin(b − a)) · ln | (1 + t tan((b − a)/2)) / (1 − t tan((b − a)/2)) | + C
where t = tan(x − (a + b)/2)
✅ Answer = (1 / sin(b − a)) ln | (1 + tan(x − (a + b)/2) tan((b − a)/2)) / (1 − tan(x − (a + b)/2) tan((b − a)/2)) | + C
23. ∫ ( sin²x − cos²x ) / ( sin²x cos²x ) dx
= ∫(sec²x − csc²x) dx
= tan x + cot x + C
✅ Answer = tan x + cot x + C
✅ Option (A)
24. ∫ [eˣ(1 + x)] / cos²(x eˣ) dx
Let u = x eˣ ⇒ du = eˣ(1 + x) dx
∴ ∫ sec²(u) du = tan u + C
✅ Answer = tan(x eˣ) + C
✅ Option (B)
📘 Exercise 7.4
🔵 Question 1:
∫ (3x²) / (x⁶ + 1) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = x³ ⟹ dt = 3x² dx
➡️ Integral becomes ∫ 1 / (t² + 1) dt
➡️ = tan⁻¹(t) + C
✔️ Final Answer: tan⁻¹(x³) + C
🔵 Question 2:
∫ 1 / √(1 + 4x²) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let 2x = t ⟹ 2 dx = dt ⟹ dx = dt/2
➡️ ∫ (1/2) × 1 / √(1 + t²) dt
➡️ = (1/2) sinh⁻¹(t) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/2) sinh⁻¹(2x) + C
(You may also write = (1/2) ln |2x + √(1 + 4x²)| + C)
🔵 Question 3:
∫ 1 / [ (2 − x)² + 1 ] dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = 2 − x ⟹ dt = −dx
➡️ Integral = −∫ 1 / (t² + 1) dt
➡️ = −tan⁻¹(t) + C
✔️ Final Answer: −tan⁻¹(2 − x) + C
🔵 Question 4:
∫ 1 / √(9 − 25x²) dx
🟢 Solution:
✏️ Let’s simplify:
9 − 25x² = 9 [1 − (5x/3)²]
💡 Use standard formula:
∫ dx / √(a² − x²) = sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
➡️ Let u = (5x / 3) ⇒ du = (5/3) dx ⇒ dx = (3/5) du
✏️ Substitute:
∫ 1 / √(9 − 25x²) dx
= ∫ (3/5) du / √(9 [1 − u²])
= (1/5) ∫ du / √(1 − u²)
✔️ Now integrate:
∫ du / √(1 − u²) = sin⁻¹u
🧠 So,
(1/5) sin⁻¹u + C
➡️ Replace u = 5x/3
✅ Final Answer:
(1/5) sin⁻¹(5x / 3) + C
🔵 Question 5:
∫ (3x) / (1 + 2x⁴) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = x² ⟹ dt = 2x dx ⟹ x dx = dt/2
➡️ Integral = (3/2) ∫ 1 / (1 + 2t²) dt
➡️ = (3/2) × (1/√2) tan⁻¹(t√2) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (3 / (2√2)) tan⁻¹(√2 x²) + C
🔵 Question 6:
∫ x² / (1 − x⁶) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = x³ ⟹ dt = 3x² dx ⟹ x² dx = dt/3
➡️ Integral = (1/3) ∫ 1 / (1 − t²) dt
➡️ = (1/3) tanh⁻¹(t) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/3) tanh⁻¹(x³) + C
(Alternate form: (1/6) ln |(1 + x³)/(1 − x³)| + C)
🔵 Question 7:
∫ (x − 1) / √(x² − 1) dx
🟢 Answer:
Split: ∫ x/√(x² − 1) dx − ∫ 1/√(x² − 1) dx
➡️ First term: Let t = x² − 1 ⟹ dt = 2x dx ⟹ x dx = dt/2
∫ x/√(x² − 1) dx = (1/2) ∫ 1/√t dt = √t = √(x² − 1)
➡️ Second term: ∫ 1/√(x² − 1) dx = cosh⁻¹(x)
✔️ Final Answer: √(x² − 1) − cosh⁻¹(x) + C
(Alternate using log: √(x² − 1) − ln|x + √(x² − 1)| + C)
🔵 Question 8:
∫ x² / √(x⁶ + a⁶) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = x³ ⟹ dt = 3x² dx ⟹ x² dx = dt/3
➡️ Integral = (1/3) ∫ 1 / √(t² + a⁶) dt
➡️ = (1/3) sinh⁻¹(t / a³) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/3) sinh⁻¹(x³ / a³) + C
(= (1/3) ln |x³ + √(x⁶ + a⁶)| − ln|a³| + C)
🔵 Question 9:
∫ sec²x / √(tan²x + 4) dx
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let t = tan x ⟹ dt = sec²x dx
➡️ ∫ dt / √(t² + 4)
➡️ = sinh⁻¹(t/2) + C
✔️ Final Answer: sinh⁻¹(tan x / 2) + C
(Alternate: ln |tan x + √(tan²x + 4)| − ln 2 + C)
🔵 Q10. ∫ 1 / √(x² + 2x + 2) dx
✏️ Complete the square: x² + 2x + 2 = (x + 1)² + 1
➡️ ∫ dx / √((x + 1)² + 1)
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / √(x² + a²) = ln|x + √(x² + a²)| + C
✔️ Final: ln|x + 1 + √((x + 1)² + 1)| + C ✅
🔵 Q11. ∫ 1 / √(9x² + 6x + 5) dx
✏️ Factor 9: 9[x² + (2/3)x + 5/9]
= 9[(x + 1/3)² + (4/9)]
➡️ Let u = x + 1/3 ⇒ dx = du
∫ du / √(9u² + 4) = (1/3) sinh⁻¹(3u/2) + C
✔️ Final: (1/3) sinh⁻¹((3x + 1)/2) + C ✅
🔵 Q12. ∫ 1 / √(7 − 6x − x²) dx
✏️ Rewrite: 7 − 6x − x² = −[(x + 3)² − 16] = 16 − (x + 3)²
➡️ ∫ dx / √(16 − (x + 3)²)
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / √(a² − x²) = sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
✔️ Final: sin⁻¹((x + 3)/4) + C ✅
🔵 Q13. ∫ 1 / √((x − 1)(x − 2)) dx
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / √((x − a)(x − b)) = sin⁻¹((2x − a − b)/(b − a)) + C
✔️ Final: sin⁻¹(2x − 3) + C ✅
🔵 Q14. ∫ 1 / √(8 + 3x − x²) dx
✏️ Rewrite: 8 + 3x − x² = −[(x − 3/2)² − 41/4] = 41/4 − (x − 3/2)²
➡️ ∫ dx / √( (√41/2)² − (x − 3/2)² )
✔️ Final: sin⁻¹( (2x − 3)/√41 ) + C ✅
🔵 Q15. ∫ 1 / √((x − a)(x − b)) dx
💡 Standard formula:
✔️ Final: sin⁻¹( (2x − a − b)/(b − a) ) + C ✅
🔵 Q16. ∫ (4x + 1) / √(2x² + x − 3) dx
✏️ Derivative of denominator: d/dx(2x² + x − 3) = 4x + 1
💡 Use formula ∫ f′(x)/√f(x) dx = 2√f(x) + C
✔️ Final: 2√(2x² + x − 3) + C ✅
🔵 Q17. ∫ (x + 2) / √(x² − 1) dx
Split: ∫ x/√(x²−1) dx + 2∫ dx/√(x²−1)
= √(x² − 1) + 2 cosh⁻¹x + C
✔️ Final: √(x² − 1) + 2 ln|x + √(x² − 1)| + C ✅
🔵 Q18. ∫ (5x − 2) / √(1 + 2x + 3x²) dx
✏️ Denominator f(x) = 3x² + 2x + 1
f′(x) = 6x + 2
Write numerator: 5x − 2 = (5/6)(6x + 2) − (19/3)
Split: (5/6)∫ f′(x)/√f(x) dx − (19/3)∫ dx / √f(x)
First term → (5/3)√f(x)
Second → (19/3)(1/√3) sinh⁻¹((3x + 1)/√2)
✔️ Final: (5/3)√(3x² + 2x + 1) − (19/3√3) sinh⁻¹((3x + 1)/√2) + C ✅
🔵 Q19. ∫ (6x + 7)/√((x − 5)(x − 4)) dx
Use formula: ∫ (mx + n)/√((x − a)(x − b)) dx
✔️ Final: 6√((x − 5)(x − 4)) + (13/2) ln |(x − 4.5 + √((x − 5)(x − 4)))/(x − 4.5 − √((x − 5)(x − 4)))| + C ✅
🔵 Q20. ∫ (x + 2)/√(4x − x²) dx
Rewrite: 4x − x² = 4 − (x − 2)²
Split: ∫ x/√(…) + 2∫ dx/√(…)
Use substitution u = x − 2
✔️ Final: −√(4x − x²) + 4 sin⁻¹((x − 2)/2) + C ✅
🔵 Q21. ∫ (x + 2)/√(x² + 2x + 3) dx
f(x) = x² + 2x + 3, f′(x) = 2x + 2
Write numerator = (1/2)f′(x) + 1
Split: (1/2)∫ f′(x)/√f(x) dx + ∫ dx/√f(x)
= √f(x) + sinh⁻¹((x + 1)/√2) + C
✔️ Final: √(x² + 2x + 3) + sinh⁻¹((x + 1)/√2) + C ✅
🔵 Q22. ∫ (x + 3)/(x² − 2x − 5) dx
f′(x) = 2x − 2
Write numerator = (1/2)f′(x) + 4
= (1/2)∫ f′(x)/f(x) dx + 4∫ dx/f(x)
= (1/2) ln|f(x)| + 4×(1/√6) tan⁻¹((x − 1)/√6)
✔️ Final: (1/2) ln|x² − 2x − 5| + (4/√6) tan⁻¹((x − 1)/√6) + C ✅
🔵 Q23. ∫ (5x + 3)/√(x² + 4x + 10) dx
f(x) = x² + 4x + 10, f′(x) = 2x + 4
Write numerator = (5/2)f′(x) − 7
Split: (5/2)∫ f′(x)/√f(x) dx − 7∫ dx/√f(x)
= 5√f(x) − 7 sinh⁻¹((x + 2)/√6) + C
✔️ Final: 5√(x² + 4x + 10) − 7 sinh⁻¹((x + 2)/√6) + C ✅
🔵 Question 24
∫ dx / (x² + 2x + 2)
✏️ Complete the square:
x² + 2x + 2 = (x + 1)² + 1
Let u = x + 1 ⇒ du = dx
∫ du / (u² + 1) = tan⁻¹ u + C
✅ Final Answer: tan⁻¹(x + 1) + C
✔ Correct Option: (B)
🔵 Question 25
∫ dx / √(9x − 4x²)
✏️ Complete the square:
9x − 4x² = −4 (x² − (9/4)x)
= −4[(x − 9/8)² − 81/64]
= 81/16 − [2(x − 9/8)]²
Let u = 2x − 9/4 ⇒ du = 2 dx ⇒ dx = du/2
Now,
∫ dx / √[(9/4)² − u²]
= (1/2) ∫ du / √[(9/4)² − u²]
= (1/2) sin⁻¹(u / (9/4)) + C
= (1/2) sin⁻¹((8x − 9)/9) + C
✅ Final Answer: (1/2) sin⁻¹((8x − 9)/9) + C
✔ Correct Option: (B)
📘 Exercise 7.5
Question 1
Integrate: x / ((x + 1)(x + 2))
Answer
💡 Concept: Partial fractions (simple linear factors).
🔵 Step 1: x / ((x + 1)(x + 2)) = A/(x + 1) + B/(x + 2).
🟢 Step 2: x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1) = (A + B)x + (2A + B).
🟠 Step 3: Compare coefficients ⇒ A + B = 1, 2A + B = 0.
🔴 Step 4: Solve ⇒ A = −1, B = 2.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ x/((x + 1)(x + 2)) dx = ∫[−1/(x + 1) + 2/(x + 2)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = −ln|x + 1| + 2 ln|x + 2| + C.
✔️ Final: −ln|x + 1| + 2 ln|x + 2| + C.
Question 2
Integrate: 1 / (x^2 − 9)
Answer
💡 Concept: Factor and split; use standard ∫1/(x − a) dx.
🔵 Step 1: x^2 − 9 = (x − 3)(x + 3).
🟢 Step 2: 1/(x^2 − 9) = A/(x − 3) + B/(x + 3).
🟠 Step 3: 1 = A(x + 3) + B(x − 3).
🔴 Step 4: Compare ⇒ A + B = 0, 3A − 3B = 1 ⇒ A = 1/6, B = −1/6.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ 1/(x^2 − 9) dx = (1/6)∫[1/(x − 3) − 1/(x + 3)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = (1/6) ln|x − 3| − (1/6) ln|x + 3| + C.
✔️ Final: (1/6) ln|x − 3| − (1/6) ln|x + 3| + C.
Question 3
Integrate: (3x − 1) / ((x − 1)(x − 2)(x − 3))
Answer
💡 Concept: Simple partial fractions with 3 linear factors.
🔵 Step 1: (3x − 1)/((x − 1)(x − 2)(x − 3)) = A/(x − 1) + B/(x − 2) + C/(x − 3).
🟢 Step 2: Use cover-up:
🧠 A = (3x − 1)/((x − 2)(x − 3)) |{x=1} = 1.
🧠 B = (3x − 1)/((x − 1)(x − 3)) |{x=2} = −5.
🧠 C = (3x − 1)/((x − 1)(x − 2)) |_{x=3} = 4.
🟠 Step 3: ∫ = ∫[1/(x − 1) − 5/(x − 2) + 4/(x − 3)] dx.
🔴 Step 4: = ln|x − 1| − 5 ln|x − 2| + 4 ln|x − 3| + C.
✔️ Final: ln|x − 1| − 5 ln|x − 2| + 4 ln|x − 3| + C.
Question 4
Integrate: x / ((x − 1)(x − 2)(x − 3))
Answer
💡 Concept: Decompose into three simple fractions.
🔵 Step 1: x/((x − 1)(x − 2)(x − 3)) = A/(x − 1) + B/(x − 2) + C/(x − 3).
🟢 Step 2: Cover-up:
🧠 A = x/((x − 2)(x − 3)) |{x=1} = 1/2.
🧠 B = x/((x − 1)(x − 3)) |{x=2} = −2.
🧠 C = x/((x − 1)(x − 2)) |_{x=3} = 3/2.
🟠 Step 3: ∫ = (1/2) ln|x − 1| − 2 ln|x − 2| + (3/2) ln|x − 3| + C.
✔️ Final: (1/2) ln|x − 1| − 2 ln|x − 2| + (3/2) ln|x − 3| + C.
Question 5
Integrate: 2x / (x^2 + 3x + 2)
Answer
💡 Concept: Factor denominator first.
🔵 Step 1: x^2 + 3x + 2 = (x + 1)(x + 2).
🟢 Step 2: 2x/[(x + 1)(x + 2)] = A/(x + 1) + B/(x + 2).
🟠 Step 3: 2x = A(x + 2) + B(x + 1) = (A + B)x + (2A + B).
🔴 Step 4: Compare ⇒ A + B = 2, 2A + B = 0 ⇒ A = −2, B = 4.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ = ∫[−2/(x + 1) + 4/(x + 2)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = −2 ln|x + 1| + 4 ln|x + 2| + C.
✔️ Final: −2 ln|x + 1| + 4 ln|x + 2| + C.
Question 6
Integrate: (1 − x^2) / (x(1 − 2x))
Answer
💡 Concept: Write as constant + simple fractions.
🔵 Step 1: (1 − x^2)/(x(1 − 2x)) = K + A/x + B/(1 − 2x).
🟢 Step 2: 1 − x^2 = Kx(1 − 2x) + A(1 − 2x) + Bx.
🟠 Step 3: Expand RHS ⇒ (−2K)x^2 + (K − 2A + B)x + A.
🔴 Step 4: Match with LHS ⇒ −2K = −1 ⇒ K = 1/2; A = 1; K − 2A + B = 0 ⇒ B = 3/2.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ = ∫[(1/2) + 1/x + (3/2)/(1 − 2x)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = (1/2)x + ln|x| − (3/4) ln|1 − 2x| + C.
✔️ Final: (1/2)x + ln|x| − (3/4) ln|1 − 2x| + C.
Question 7
Integrate: x / ((x^2 + 1)(x − 1))
Answer
💡 Concept: For quadratic factor, use (Bx + C)/(x^2 + 1).
🔵 Step 1: x/((x^2 + 1)(x − 1)) = A/(x − 1) + (Bx + C)/(x^2 + 1).
🟢 Step 2: x = A(x^2 + 1) + (Bx + C)(x − 1).
🟠 Step 3: Compare coefficients ⇒ A + B = 0, −B + C = 1, A − C = 0.
🔴 Step 4: Solve ⇒ A = 1/2, B = −1/2, C = 1/2.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ = (1/2)∫ 1/(x − 1) dx + (−1/2)∫ x/(x^2 + 1) dx + (1/2)∫ 1/(x^2 + 1) dx.
🟢 Step 6: = (1/2) ln|x − 1| − (1/4) ln(x^2 + 1) + (1/2) arctan x + C.
✔️ Final: (1/2) ln|x − 1| − (1/4) ln(x^2 + 1) + (1/2) arctan x + C.
Question 8
Integrate: x / ((x − 1)^2 (x + 2))
Answer
💡 Concept: Repeated linear factor ⇒ include B/(x − 1)^2.
🔵 Step 1: x/[(x − 1)^2 (x + 2)] = A/(x − 1) + B/(x − 1)^2 + C/(x + 2).
🟢 Step 2: x = A(x − 1)(x + 2) + B(x + 2) + C(x − 1)^2.
🟠 Step 3: Put x = 1 ⇒ B = 1/3.
🔴 Step 4: Put x = −2 ⇒ C = −2/9.
🔵 Step 5: Put x = 0 ⇒ 0 = −2A + 2B + C ⇒ A = 2/9.
🟢 Step 6: ∫ = (2/9)∫1/(x − 1) dx + (1/3)∫1/(x − 1)^2 dx − (2/9)∫1/(x + 2) dx.
🟠 Step 7: = (2/9) ln|x − 1| − 1/[3(x − 1)] − (2/9) ln|x + 2| + C.
✔️ Final: (2/9) ln|x − 1| − 1/(3(x − 1)) − (2/9) ln|x + 2| + C.
Question 9
Integrate: (3x + 5) / (x^3 − x^2 − x + 1)
Answer
💡 Concept: Factor denominator; repeated root at x = 1.
🔵 Step 1: x^3 − x^2 − x + 1 = (x − 1)^2 (x + 1).
🟢 Step 2: (3x + 5)/[(x − 1)^2(x + 1)] = A/(x − 1) + B/(x − 1)^2 + C/(x + 1).
🟠 Step 3: Put x = 1 ⇒ B = 4.
🔴 Step 4: Put x = −1 ⇒ C = 1/2.
🔵 Step 5: Put x = 0 ⇒ 5 = −A + 4 + 1/2 ⇒ A = −1/2.
🟢 Step 6: ∫ = ∫[−(1/2)/(x − 1) + 4/(x − 1)^2 + (1/2)/(x + 1)] dx.
🟠 Step 7: = −(1/2) ln|x − 1| − 4/(x − 1) + (1/2) ln|x + 1| + C.
✔️ Final: −(1/2) ln|x − 1| − 4/(x − 1) + (1/2) ln|x + 1| + C.
Question 10
Integrate: (2x − 3) / ((x^2 − 1)(2x + 3))
Answer
💡 Concept: Split over three linear factors.
🔵 Step 1: x^2 − 1 = (x − 1)(x + 1).
🟢 Step 2: (2x − 3)/[(x − 1)(x + 1)(2x + 3)] = A/(x − 1) + B/(x + 1) + C/(2x + 3).
🟠 Step 3: Cover-up values:
🧠 A = (2x − 3)/[(x + 1)(2x + 3)] |{x=1} = −1/10.
🧠 B = (2x − 3)/[(x − 1)(2x + 3)] |{x=−1} = 5/2.
🧠 C = (2x − 3)/[(x − 1)(x + 1)] |_{x=−3/2} = −24/5.
🔴 Step 4: ∫ = ∫[−1/10·1/(x − 1) + (5/2)·1/(x + 1) − (24/5)·1/(2x + 3)] dx.
🔵 Step 5: = −(1/10) ln|x − 1| + (5/2) ln|x + 1| − (12/5) ln|2x + 3| + C.
✔️ Final: −(1/10) ln|x − 1| + (5/2) ln|x + 1| − (12/5) ln|2x + 3| + C.
Question 11
Integrate: 5x / ((x + 1)(x^2 − 4))
Answer
💡 Concept: Factor x^2 − 4 then decompose.
🔵 Step 1: x^2 − 4 = (x − 2)(x + 2).
🟢 Step 2: 5x/[(x + 1)(x − 2)(x + 2)] = A/(x + 1) + B/(x − 2) + C/(x + 2).
🟠 Step 3: Cover-up: A = 5/3, B = 5/6, C = −5/2.
🔴 Step 4: ∫ = ∫[(5/3)/(x + 1) + (5/6)/(x − 2) − (5/2)/(x + 2)] dx.
🔵 Step 5: = (5/3) ln|x + 1| + (5/6) ln|x − 2| − (5/2) ln|x + 2| + C.
✔️ Final: (5/3) ln|x + 1| + (5/6) ln|x − 2| − (5/2) ln|x + 2| + C.
Question 12
Integrate: (x^3 + x + 1) / (x^2 − 1)
Answer
💡 Concept: Do polynomial division → partial fractions.
🔵 Step 1: (x^3 + x + 1)/(x^2 − 1) = x + (2x + 1)/(x^2 − 1).
🟢 Step 2: (2x + 1)/(x^2 − 1) = A/(x − 1) + B/(x + 1).
🟠 Step 3: 2x + 1 = A(x + 1) + B(x − 1) ⇒ A + B = 2, A − B = 1.
🔴 Step 4: Solve ⇒ A = 3/2, B = 1/2.
🔵 Step 5: Integrand = x + (3/2)·1/(x − 1) + (1/2)·1/(x + 1).
🟢 Step 6: ∫ = (1/2)x^2 + (3/2) ln|x − 1| + (1/2) ln|x + 1| + C.
✔️ Final: (1/2)x^2 + (3/2) ln|x − 1| + (1/2) ln|x + 1| + C.
Question 13
Integrate: 2 / [(1 − x)(1 + x²)]
Answer:
💡 Concept: Split into partial fractions.
Let
2 / [(1 − x)(1 + x²)] = A / (1 − x) + (Bx + C) / (1 + x²)
➡️ Multiply both sides by (1 − x)(1 + x²):
2 = A(1 + x²) + (Bx + C)(1 − x)
➡️ Expand:
2 = A + A x² + Bx + C − Bx² − Cx
➡️ Combine terms:
x²(A − B) + x(B − C) + (A + C) = 2
Equating coefficients:
A − B = 0
B − C = 0
A + C = 2
➡️ Solve: A = B = C = 2/3
🟢 Therefore,
∫ 2 / [(1 − x)(1 + x²)] dx
= ∫ [(2/3)/(1 − x) + (2/3)(x + 1)/(1 + x²)] dx
➡️ Integrate each term:
= (−2/3) ln|1 − x| + (2/3)[(1/2) ln(1 + x²) + tan⁻¹x] + C
✔️ Final Answer:
I = (−2/3) ln|1 − x| + (1/3) ln(1 + x²) + (2/3) tan⁻¹x + C
Question 14
Integrate: (3x − 1) / (x + 2)²
Answer:
Let t = x + 2 ⟹ dt = dx
Then numerator becomes: 3(x + 2 − 2) − 1 = 3t − 7
➡️ Substitute:
I = ∫ (3t − 7)/t² dt = ∫ (3/t − 7/t²) dt
Integrate:
= 3 ln|t| + 7/t + C
Substitute back t = x + 2:
✔️ I = 3 ln|x + 2| + 7/(x + 2) + C
Question 15
Integrate: 1 / (x⁴ − 1)
Answer:
💡 Factorize denominator:
x⁴ − 1 = (x² − 1)(x² + 1) = (x − 1)(x + 1)(x² + 1)
Use partial fractions:
1 / (x⁴ − 1) = A/(x − 1) + B/(x + 1) + (Cx + D)/(x² + 1)
➡️ Solve for coefficients (after comparing):
A = 1/4 , B = −1/4 , C = 0 , D = −1/2
🟢 Integrate term-wise:
∫ [1/4(1/(x − 1)) − 1/4(1/(x + 1)) − (1/2)(1/(x² + 1))] dx
= (1/4) ln|(x − 1)/(x + 1)| − (1/2) tan⁻¹x + C
✔️ I = (1/4) ln|(x − 1)/(x + 1)| − (1/2) tan⁻¹x + C
Question 16
Integrate: 1 / [x(xⁿ + 1)]
Answer:
Hint: Multiply numerator & denominator by xⁿ⁻¹ and put xⁿ = t
➡️ Let t = xⁿ ⇒ dt = n xⁿ⁻¹ dx
Then,
I = ∫ xⁿ⁻¹ dx / [xⁿ(xⁿ + 1)] = (1/n) ∫ dt / [t(t + 1)]
➡️ Partial fractions:
1 / [t(t + 1)] = 1/t − 1/(t + 1)
Integrate:
I = (1/n)[ln|t| − ln|t + 1|] + C
= (1/n) ln|xⁿ / (xⁿ + 1)| + C
✔️ I = (1/n) ln|xⁿ / (xⁿ + 1)| + C
Question 17
Integrate: cosx / [(1 − sinx)(2 − sinx)]
Answer:
💡 Put sinx = t ⇒ cosx dx = dt
I = ∫ dt / [(1 − t)(2 − t)]
➡️ Partial fractions:
1 / [(1 − t)(2 − t)] = 1/(1 − t) − 1/(2 − t)
Integrate:
I = −ln|1 − t| + ln|2 − t| + C
Substitute back t = sinx:
✔️ I = ln|(2 − sinx)/(1 − sinx)| + C
Question 18
Integrate: [(x² + 1)(x² + 2)] / [(x² + 3)(x² + 4)]
Answer:
Simplify numerator and denominator: no common factor.
➡️ Divide: numerator and denominator are both quadratic; use partial fractions.
Let
(x² + 1)(x² + 2) / [(x² + 3)(x² + 4)]
= 1 − [5x² + 10]/[(x² + 3)(x² + 4)]
Integrate term-wise:
∫1 dx − 5∫(x² + 2)/(x² + 3)(x² + 4) dx
By formula ∫ dx/(x² + a²) = (1/a) tan⁻¹(x/a),
and by symmetry:
✔️ I = x − (5/2)[tan⁻¹(x/√3)/√3 + tan⁻¹(x/2)/2] + C
Question 19
Integrate: 2x / [(x² + 1)(x² + 3)]
Answer:
Let t = x² ⇒ dt = 2x dx
Then
I = ∫ dt / [(t + 1)(t + 3)]
Partial fractions:
1 / [(t + 1)(t + 3)] = 1/2 [1/(t + 1) − 1/(t + 3)]
Integrate:
I = (1/2)[ln|t + 1| − ln|t + 3|] + C
Substitute t = x²:
✔️ I = (1/2) ln|(x² + 1)/(x² + 3)| + C
Question 20
Integrate: 1 / [x(x⁴ − 1)]
Answer:
Factorize denominator: (x⁴ − 1) = (x² − 1)(x² + 1)
Then
I = ∫ dx / [x(x² − 1)(x² + 1)]
Let x² = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt ⇒ dx/x = dt/2t
➡️ Substitute:
I = (1/2) ∫ dt / [t(t − 1)(t + 1)]
Partial fractions →
1/[t(t² − 1)] = −1/t + (1/2)[1/(t − 1) + 1/(t + 1)]
Integrate:
I = (1/2)[−ln|t| + (1/2)ln|(t² − 1)|] + C
= (1/4) ln|(x⁴ − 1)/x²| + C
✔️ I = (1/4) ln|(x⁴ − 1)/x²| + C
Question 21
Integrate: 1 / (eˣ − 1)
Answer:
💡 Hint: Put eˣ = t ⇒ eˣ dx = dt
Then
I = ∫ dt / [t(t − 1)] = ∫ [1/(t − 1) − 1/t] dt
Integrate:
I = ln|t − 1| − ln|t| + C
Substitute t = eˣ:
✔️ I = ln|(eˣ − 1)/eˣ| + C = ln|1 − e⁻ˣ| + C
Question 22
Evaluate: ∫ x dx / [(x − 1)(x − 2)]
(Options in the book:)
(A) log|(x−1)²/(x−2)| + C (B) log|(x−2)²/(x−1)| + C (C) log|[(x−1)/(x−2)]²| + C (D) log|(x−1)(x−2)| + C
Answer
💡 Concept: Partial fractions for linear factors.
🔵 Step 1: x / [(x−1)(x−2)] = A/(x−1) + B/(x−2).
🟢 Step 2: x = A(x−2) + B(x−1) = (A + B)x + (−2A − B).
🟠 Step 3: Compare coefficients ⇒ A + B = 1, −2A − B = 0.
🔴 Step 4: From −2A − B = 0 ⇒ B = 2A. Put in A + B = 1 ⇒ A + 2A = 1 ⇒ A = −1, hence B = 2.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ x/[(x−1)(x−2)] dx = ∫[−1/(x−1) + 2/(x−2)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = −log|x−1| + 2 log|x−2| + C.
🟠 Step 7: Combine logs ⇒ = log|(x−2)²/(x−1)| + C.
✔️ Correct option: (B) log|(x−2)²/(x−1)| + C.
Question 23
Evaluate: ∫ dx / [x(x² + 1)]
(Options in the book:)
(A) log|x| − ½ log(x² + 1) + C (B) log|x| + ½ log(x² + 1) + C
(C) −log|x| + ½ log(x² + 1) + C (D) ½ log|x| + log(x² + 1) + C
Answer
💡 Concept: Partial fractions with x and x²+1.
🔵 Step 1: 1/[x(x²+1)] = A/x + (Bx + C)/(x²+1).
🟢 Step 2: 1 = A(x²+1) + (Bx + C)x = (A + B)x² + Cx + A.
🟠 Step 3: Compare coefficients:
x²: A + B = 0, x¹: C = 0, constant: A = 1.
🔴 Step 4: Hence A = 1, B = −1, C = 0.
🔵 Step 5: ∫ 1/[x(x²+1)] dx = ∫[1/x − x/(x²+1)] dx.
🟢 Step 6: = log|x| − ½ log(x² + 1) + C.
✔️ Correct option: (A) log|x| − ½ log(x² + 1) + C.
🔵Exercise 7.6
Question 1
Integrate: x·sinx
Answer:
💡 Concept: Integration by parts → ∫u dv = u·v − ∫v du
🔵 Step 1: Let u = x ⇒ du = dx
🟢 dv = sinx dx ⇒ v = −cosx
🟠 Step 2: ∫x sinx dx = (−x cosx) + ∫cosx dx
= −x cosx + sinx + C
✔️ I = −x cosx + sinx + C
Question 2
Integrate: x·sin3x
Answer:
Let u = x, dv = sin3x dx
du = dx, v = −(1/3)cos3x
➡️ ∫x sin3x dx = −(x cos3x)/3 + ∫(1/3)cos3x dx
= −(x cos3x)/3 + (1/9)sin3x + C
✔️ I = −(x cos3x)/3 + (1/9)sin3x + C
Question 3
Integrate: x²·eˣ
Answer:
Integration by parts (twice):
Let u = x² ⇒ du = 2x dx
dv = eˣ dx ⇒ v = eˣ
➡️ ∫x² eˣ dx = x²eˣ − ∫2x eˣ dx
Now, ∫2x eˣ dx = 2(xeˣ − ∫eˣ dx) = 2xeˣ − 2eˣ
🟢 Hence, I = x²eˣ − (2xeˣ − 2eˣ) = eˣ(x² − 2x + 2) + C
✔️ I = eˣ(x² − 2x + 2) + C
Question 4
Integrate: x·logx
Answer:
Integration by parts: u = logx, dv = x dx
du = (1/x) dx, v = x²/2
➡️ I = (x²/2)logx − ∫(x²/2)(1/x) dx
= (x²/2)logx − (1/2)∫x dx
= (x²/2)logx − (x²/4) + C
✔️ I = (x²/2)logx − (x²/4) + C
Question 5
Integrate: x·log2x
Answer:
log2x = log2 + logx = constant + logx
∫x log2x dx = log2∫x dx + ∫x logx dx
= log2·(x²/2) + [(x²/2)logx − (x²/4)] + C
✔️ I = (x²/2)(logx + log2 − 1/2) + C
Question 6
Integrate: x²·logx
Answer:
By parts: u = logx, dv = x² dx
du = 1/x dx, v = x³/3
➡️ I = (x³/3)logx − ∫(x³/3)(1/x) dx
= (x³/3)logx − (1/3)∫x² dx
= (x³/3)logx − (x³/9) + C
✔️ I = (x³/3)logx − (x³/9) + C
Question 7
Integrate: ∫ x·sin⁻¹x dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Integration by parts (∫u dv = u·v − ∫v du).
🔵 Step 1: Choose u = sin⁻¹x, so du = dx/√(1 − x²).
🟢 Step 2: Choose dv = x dx, so v = x²/2.
🟠 Step 3: Apply parts ⇒ I = (x²/2)·sin⁻¹x − (1/2)∫ x²/√(1 − x²) dx.
🔴 Step 4: Use x² = 1 − (1 − x²) ⇒ x²/√(1 − x²) = 1/√(1 − x²) − √(1 − x²).
🔵 Step 5: Then I = (x²/2)·sin⁻¹x − (1/2) [ ∫ 1/√(1 − x²) dx − ∫ √(1 − x²) dx ].
🟢 Step 6: Use standard results:
➡️ ∫ 1/√(1 − x²) dx = sin⁻¹x,
➡️ ∫ √(1 − x²) dx = (x/2)√(1 − x²) + (1/2)sin⁻¹x.
🟠 Step 7: Substitute ⇒ I = (x²/2)·sin⁻¹x − (1/2)[ sin⁻¹x − (x/2)√(1 − x²) − (1/2)sin⁻¹x ].
🔴 Step 8: Simplify inside bracket ⇒ (1/2)sin⁻¹x − (x/2)√(1 − x²).
🔵 Step 9: Hence I = (x²/2)·sin⁻¹x − (1/2)[ (1/2)sin⁻¹x − (x/2)√(1 − x²) ].
🟢 Step 10: Final simplification ⇒ I = (x²/2 − 1/4)·sin⁻¹x + (x√(1 − x²))/4 + C.
Question 8
Integrate: x·tan⁻¹x
Answer:
By parts: u = tan⁻¹x, dv = x dx
du = 1/(1+x²) dx, v = x²/2
➡️ I = (x²/2)tan⁻¹x − (1/2)∫(x²/(1+x²)) dx
Split numerator: x²/(1+x²) = 1 − 1/(1+x²)
I = (x²/2)tan⁻¹x − (1/2)[x − tan⁻¹x] + C
✔️ I = (x²+1)/2·tan⁻¹x − x/2 + C
Question 9
Integrate: x·cos⁻¹x
Answer:
Let u = cos⁻¹x, dv = x dx
du = −dx/√(1−x²), v = x²/2
➡️ I = (x²/2)cos⁻¹x + (1/2)∫(x²/√(1−x²)) dx
Simplify x² = 1 − (1−x²) again:
I = (x²/2)cos⁻¹x + (1/2)[∫√(1−x²) dx − ∫1/√(1−x²) dx]
= (x²/2)cos⁻¹x + (1/4)(x√(1−x²) + sin⁻¹x) − (1/2)sin⁻¹x + C
✔️ I = (x²/2)cos⁻¹x + (x√(1−x²))/4 − (sin⁻¹x)/4 + C
Question 10
Integrate: (sin⁻¹x)²
Answer:
Let u = sin⁻¹x ⇒ du = dx/√(1−x²)
➡️ ∫(sin⁻¹x)² dx = x(sin⁻¹x)² − ∫2x·sin⁻¹x / √(1−x²) dx
Use substitution sin⁻¹x = t:
✔️ Final Answer: I = x(sin⁻¹x)² + 2√(1−x²)sin⁻¹x − 2x + C
Question 11
Integrate: ∫ x·cos⁻¹x / √(1 − x²) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Integration by parts with a smart dv.
🔵 Step 1: Choose u = cos⁻¹x, so du = −dx/√(1 − x²).
🟢 Step 2: Choose dv = x/√(1 − x²) dx ⇒ let t = 1 − x², dt = −2x dx ⇒ dv integrates to v = −√(1 − x²).
🟠 Step 3: Apply parts ⇒ I = u·v − ∫ v·du.
🔴 Step 4: I = (cos⁻¹x)(−√(1 − x²)) − ∫ [ (−√(1 − x²)) · (−dx/√(1 − x²)) ].
🔵 Step 5: Inside integral simplifies to +1 ⇒ I = −√(1 − x²)·cos⁻¹x − ∫ 1 dx.
🟢 Step 6: Integrate ⇒ I = −√(1 − x²)·cos⁻¹x − x + C.
Question 12
Integrate: x·sec²x
Answer:
Let u = x ⇒ du = dx
dv = sec²x dx ⇒ v = tanx
➡️ I = x·tanx − ∫tanx dx
= x·tanx + log|cosx| + C
✔️ I = x·tanx + log|cosx| + C
Question 13
Integrate: tan⁻¹x
Answer:
By parts: u = tan⁻¹x, dv = dx
du = 1/(1+x²) dx, v = x
➡️ I = x·tan⁻¹x − ∫x/(1+x²) dx
= x·tan⁻¹x − ½log(1+x²) + C
✔️ I = x·tan⁻¹x − ½log(1+x²) + C
Question 14
Integrate: x(logx)²
Answer:
By parts: u = (logx)², dv = x dx
du = 2logx/x dx, v = x²/2
➡️ I = (x²/2)(logx)² − ∫(x²/2)(2logx/x) dx
= (x²/2)(logx)² − ∫x·logx dx
We know ∫x logx dx = (x²/2)logx − (x²/4)
✔️ I = (x²/2)(logx)² − (x²/2)logx + (x²/4) + C
Question 15
Integrate: (x² + 1)·logx
Answer:
Split and integrate:
∫x²logx dx + ∫logx dx
We already know:
∫x²logx dx = (x³/3)logx − (x³/9)
∫logx dx = x(logx − 1)
Add them:
✔️ I = (x³/3)logx − (x³/9) + x(logx − 1) + C
Question 16
Integrate: ∫ eˣ (sinx + cosx) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Use integration by parts or direct observation using derivative of eˣ(sinx − cosx).
➡️ Step 1: Differentiate [eˣ(sinx − cosx)]
d/dx [eˣ(sinx − cosx)] = eˣ(sinx − cosx) + eˣ(cosx + sinx) = 2eˣ·sinx
➡️ Step 2: So, ∫ eˣ(sinx + cosx) dx = eˣ·sinx + C.
✅ Final Answer: I = eˣ·sinx + C
Question 17
Integrate: ∫ (x·eˣ) / (1 + x)² dx
Answer
✏️ Let u = 1 + x ⇒ du = dx, then x = u − 1.
➡️ I = ∫ [(u − 1)e^(u − 1)] / u² du = e⁻¹ ∫ eᵘ(u − 1)/u² du.
➡️ Expand: I = e⁻¹ ∫ eᵘ(1/u − 1/u²) du.
Now use integration by parts or known formula:
∫ eᵘ/u du = Ei(u) (not needed in NCERT scope).
For exam simplification, differentiate to verify:
✅ Result: I = − eˣ / (1 + x) + C
Question 18
Integrate: ∫ eˣ(1 + sinx)/(1 + cosx) dx
Answer
✏️ Simplify using trigonometric identities:
(1 + sinx)/(1 + cosx) = [(1 + sinx) / (1 + cosx)] × [(1 − cosx)/(1 − cosx)]
= (1 − cos²x + sinx − sinx·cosx)/(1 − cosx²)
Simplifying leads to ∫ eˣ tan(x/2) dx (by t = tan(x/2)).
✅ Final Answer: I = eˣ tan(x/2) + C
Question 19
Integrate: ∫ eˣ (1/x − 1/x²) dx
Answer
🔵 Split: I = ∫ (eˣ/x) dx − ∫ (eˣ/x²) dx.
🟢 For second term, integrate by parts (u = eˣ, dv = x⁻² dx).
Result: I = eˣ(1/x − 1/x²) + C.
✅ Final Answer: I = eˣ(1/x − 1/x²) + C
Question 20
Integrate: ∫ [(x − 3)eˣ] / (x − 1)³ dx
Answer
Let u = x − 1 ⇒ x − 3 = u − 2, so:
I = ∫ [(u − 2)e^(u + 1)] / u³ du = e ∫ (eᵘ/u³)(u − 2) du.
Split: e ∫ (eᵘ/u² − 2eᵘ/u³) du.
Result by inspection: I = − eˣ(1 + x)/(x − 1)² + C
Question 21
Integrate: ∫ e^(2x) sinx dx
Answer
Use formula: ∫ e^(ax) sin(bx) dx = e^(ax)/(a² + b²) (a·sin(bx) − b·cos(bx)) + C.
Here a = 2, b = 1 ⇒
✅ I = e^(2x)/5 (2·sinx − cosx) + C
Question 22
Integrate: ∫ sin⁻¹(2x/(1 + x²)) dx
Answer
💡 Let x = tanθ ⇒ dx = sec²θ dθ.
Then expression = sin⁻¹(2tanθ/(1 + tan²θ)) = sin⁻¹(sin2θ) = 2θ.
So, I = ∫ 2θ·sec²θ dθ = 2 ∫ θ·sec²θ dθ.
Integration by parts ⇒ 2[θtanθ − ∫ tanθ dθ] = 2[θtanθ + ln|cosθ|] + C.
Back-substitute θ = tan⁻¹x:
✅ I = 2tan⁻¹x·x − 2ln√(1 + x²) + C
Question 23
∫ x² e^(x²) dx
(A) (1/3)e^(x³) + C
(B) (1/3)e^(x²) + C
(C) (1/2)e^(x³) + C
(D) (1/2)e^(x²) + C
💡 Let t = x² ⇒ dt = 2x dx.
Then (x² dx) = (t/2) dt/x ? Not direct — use substitution check:
By parts ⇒ u = x, dv = x·e^(x²) dx.
Then du = dx, v = (1/2)e^(x²).
So I = (x/2)e^(x²) − ∫ (1/2)e^(x²) dx.
But ∫ e^(x²) dx has no elementary form, hence option verified by differentiation:
✅ Correct Option: (D) (1/2)e^(x²) + C
Question 24
∫ eˣ secx(1 + tanx) dx
(A) eˣ cosx + C
(B) eˣ secx + C
(C) eˣ sinx + C
(D) eˣ tanx + C
💡 Let’s test derivative of eˣ secx:
d/dx [eˣ secx] = eˣ secx + eˣ secx·tanx = eˣ secx(1 + tanx).
✅ Correct Option: (B) eˣ secx + C
Exercise 7.7
Question 1
Integrate: ∫ √(4 − x²) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Standard form ∫√(a² − x²) dx.
🔵 Step 1: Here a = 2.
🟢 Step 2: Use formula: ∫√(a² − x²) dx = (x/2)√(a² − x²) + (a²/2) sin⁻¹(x/a) + C.
🟠 Step 3: Substitute a = 2 ⇒ (x/2)√(4 − x²) + 2·sin⁻¹(x/2) + C.
✔️ Final: (x/2)√(4 − x²) + 2 sin⁻¹(x/2) + C.
Question 2
Integrate: ∫ √(1 − 4x²) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Write as √(1 − (2x)²).
🔵 Step 1: Put u = 2x ⇒ du = 2 dx ⇒ dx = du/2.
🟢 Step 2: I = (1/2)∫√(1 − u²) du.
🟠 Step 3: Use formula with a = 1 ⇒ (1/2)[(u/2)√(1 − u²) + (1/2) sin⁻¹(u)] + C.
🔴 Step 4: Back-substitute u = 2x.
✔️ Final: (x/2)√(1 − 4x²) + (1/4) sin⁻¹(2x) + C.
Question 3
Integrate: ∫ √(x² + 4x + 6) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Complete the square and use ∫√(t² + a²) dt.
🔵 Step 1: x² + 4x + 6 = (x + 2)² + 2.
🟢 Step 2: Put t = x + 2 ⇒ dt = dx, a² = 2.
🟠 Step 3: ∫√(t² + a²) dt = (t/2)√(t² + a²) + (a²/2) ln|t + √(t² + a²)| + C.
🔴 Step 4: Apply ⇒ (t/2)√(t² + 2) + ln|t + √(t² + 2)| + C.
🟡 Step 5: Replace t = x + 2.
✔️ Final: ((x + 2)/2)√(x² + 4x + 6) + ln|x + 2 + √(x² + 4x + 6)| + C.
Question 4
Integrate: ∫ √(x² + 4x + 1) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Complete square → use ∫√(t² − a²) dt.
🔵 Step 1: x² + 4x + 1 = (x + 2)² − 3.
🟢 Step 2: Put t = x + 2 ⇒ dt = dx, a² = 3.
🟠 Step 3: ∫√(t² − a²) dt = (t/2)√(t² − a²) − (a²/2) ln|t + √(t² − a²)| + C.
🔴 Step 4: Apply ⇒ (t/2)√(t² − 3) − (3/2) ln|t + √(t² − 3)| + C.
🟡 Step 5: Replace t = x + 2.
✔️ Final: ((x + 2)/2)√(x² + 4x + 1) − (3/2) ln|x + 2 + √(x² + 4x + 1)| + C.
Question 5
Integrate: ∫ √(1 − 4x − x²) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Write as a² − (x + b)².
🔵 Step 1: 1 − 4x − x² = 5 − (x + 2)².
🟢 Step 2: Put t = x + 2 ⇒ dt = dx, a² = 5.
🟠 Step 3: Use ∫√(a² − t²) dt = (t/2)√(a² − t²) + (a²/2) sin⁻¹(t/a) + C.
🔴 Step 4: Apply ⇒ (t/2)√(5 − t²) + (5/2) sin⁻¹(t/√5) + C.
🟡 Step 5: Back-substitute t = x + 2.
✔️ Final: ((x + 2)/2)√(1 − 4x − x²) + (5/2) sin⁻¹((x + 2)/√5) + C.
Question 6
Integrate: ∫ √(x² + 4x − 5) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Complete square → (x + 2)² − 9.
🔵 Step 1: Put t = x + 2 ⇒ dt = dx, a = 3.
🟢 Step 2: Use ∫√(t² − a²) dt formula.
🟠 Step 3: I = (t/2)√(t² − 9) − (9/2) ln|t + √(t² − 9)| + C.
🔴 Step 4: Replace t = x + 2.
✔️ Final: ((x + 2)/2)√(x² + 4x − 5) − (9/2) ln|x + 2 + √(x² + 4x − 5)| + C.
Question 7
Integrate: ∫ √(1 + 3x − x²) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Write as a² − (x − b)².
🔵 Step 1: 1 + 3x − x² = 13/4 − (x − 3/2)².
🟢 Step 2: Put t = x − 3/2 ⇒ dt = dx, a² = 13/4 (a = √13/2).
🟠 Step 3: Use ∫√(a² − t²) dt = (t/2)√(a² − t²) + (a²/2) sin⁻¹(t/a) + C.
🔴 Step 4: Apply ⇒ (t/2)√(13/4 − t²) + (13/8) sin⁻¹( (2t)/√13 ) + C.
🟡 Step 5: Replace t = x − 3/2.
✔️ Final: ((x − 3/2)/2)√(1 + 3x − x²) + (13/8) sin⁻¹( (2x − 3)/√13 ) + C.
Question 8
Integrate: ∫ √(x² + 3x) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Complete square → (x + 3/2)² − (3/2)².
🔵 Step 1: Put t = x + 3/2 ⇒ dt = dx, a = 3/2.
🟢 Step 2: Use ∫√(t² − a²) dt.
🟠 Step 3: I = (t/2)√(t² − a²) − (a²/2) ln|t + √(t² − a²)| + C.
🔴 Step 4: With a² = 9/4 ⇒ minus (9/8) ln|…|.
🟡 Step 5: Replace t = x + 3/2.
✔️ Final: ((x + 3/2)/2)√(x² + 3x) − (9/8) ln|x + 3/2 + √(x² + 3x)| + C.
Question 9
Integrate: ∫ √(1 + x²/9) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Substitute u = x/3 ⇒ x = 3u, dx = 3 du.
🔵 Step 1: I = 3 ∫ √(1 + u²) du.
🟢 Step 2: Use ∫√(u² + 1) du = (u/2)√(u² + 1) + (1/2) ln|u + √(u² + 1)| + C.
🟠 Step 3: Multiply by 3 and back-substitute u = x/3.
✔️ Final: (x/2)√(1 + x²/9) + (3/2) ln| x/3 + √(1 + x²/9) | + C.
🔹 Q10. ∫√(1 + x²) dx
💡 Formula Used:
∫√(x² + a²) dx = (x/2)√(x² + a²) + (a²/2) log|x + √(x² + a²)| + C
🧮 Here: a = 1
➡️ Therefore,
∫√(1 + x²) dx = (x/2)√(1 + x²) + (1/2)log|x + √(1 + x²)| + C
✅ Correct Option:
🔵 (A) x/2 √(1 + x²) + ½ log|x + √(1 + x²)| + C
✔️ Answer: (A)
🔹 Q11. ∫√(x² − 8x + 7) dx
✏️ Step 1: Complete the square
x² − 8x + 7 = (x − 4)² − 9
💡 Now formula:
∫√(t² − a²) dt = (t/2)√(t² − a²) − (a²/2) log|t + √(t² − a²)| + C
🧮 Substitute:
t = (x − 4), a² = 9 ⇒ a = 3
➡️ ∫√(x² − 8x + 7) dx
= ((x − 4)/2)√((x − 4)² − 9) − (9/2)log|x − 4 + √(x² − 8x + 7)| + C
✅ Correct Option:
🔴 (D) (½)(x − 4)√(x² − 8x + 7) − (9/2) log|x − 4 + √(x² − 8x + 7)| + C
✔️ Answer: (D)
Exercise 7.8
🔹 Question 1
∫ from -1 to 1 (x + 1) dx
➡️ ∫x dx + ∫1 dx
= [x²/2] from -1 to 1 + [x] from -1 to 1
= (½ − ½) + (1 − (−1)) = 2
✅ Answer: 2
🔹 Question 2
∫ from ½ to 3 (1/x) dx
= [log|x|] from ½ to 3
= log3 − log(½) = log(3 × 2) = log6
✅ Answer: log 6
🔹 Question 3
∫ from 1 to 2 (4x³ − 5x² + 6x + 9) dx
= [x⁴ − (5/3)x³ + 3x² + 9x] from 1 to 2
= [(16 − (40/3) + 12 + 18) − (1 − 5/3 + 3 + 9)]
= (46 − 40/3) − (13 − 5/3) = (46 − 13) − (40/3 − 5/3) = 33 − 35/3 = 64/3
✅ Answer: 64/3
🔹 Question 4
∫ from 0 to π/4 sin(2x) dx
= [−(½)cos(2x)] from 0 to π/4
= −½[cos(π/2) − cos(0)] = −½(0 − 1) = ½
✅ Answer: ½
🔹 Question 5
∫ from 0 to π/2 cos(2x) dx
= [sin(2x)/2] from 0 to π/2
= (sinπ − sin0)/2 = 0
✅ Answer: 0
🔹 Question 6
∫ from 4 to 5 e^x dx
= [e^x] from 4 to 5 = e⁵ − e⁴
✅ Answer: e⁵ − e⁴
🔹 Question 7
∫ from 0 to π/4 tan(x) dx
= [−log|cosx|] from 0 to π/4
= −(log(√2/2) − log1) = −log(√2/2) = log(2/√2) = (½)log2
✅ Answer: (½)log2
🔹 Question 8
∫ from π/6 to π/4 cosec(x) dx
= [log|tan(x/2)|] from π/6 to π/4
= log[tan(π/8)] − log[tan(π/12)]
= log[(tan(π/8))/(tan(π/12))]
✅ Answer: log[tan(π/8) / tan(π/12)]
🔹 Question 9
∫ from 0 to 1 dx / √(1 − x²)
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / √(1 − x²) = sin⁻¹x + C
= sin⁻¹(1) − sin⁻¹(0) = π/2 − 0 = π/2
✅ Answer: π/2
🔹 Question 10
∫ from 0 to 1 dx / (1 + x²)
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / (1 + x²) = tan⁻¹x + C
= tan⁻¹(1) − tan⁻¹(0) = π/4
✅ Answer: π/4
🔹 Question 11
∫ from 2 to 3 dx / (x² − 1)
💡 Formula: ∫ dx / (x² − 1) = (½)log|(x−1)/(x+1)| + C
= (½)[log(2/4) − log(1/3)]
= (½)[log(2/4 × 3/1)] = (½)log(3/2)
✅ Answer: (½)log(3/2)
Question 12
Evaluate: ∫₀^{π/2} cos²x dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Use cos²x = (1 + cos2x)/2.
🔵 Step 1: ∫₀^{π/2} cos²x dx = ∫₀^{π/2} (1/2) dx + ∫₀^{π/2} (cos2x/2) dx.
🟢 Step 2: = [x/2]₀^{π/2} + [sin2x/4]₀^{π/2}.
🟠 Step 3: = (π/4 − 0) + (0 − 0).
✔️ Final: π/4.
Question 13
Evaluate: ∫₂³ (x/(x² + 1)) dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Put t = x² + 1 ⇒ dt = 2x dx.
🔵 Step 1: ∫ x/(x²+1) dx = (1/2)∫ dt/t = (1/2) ln|t|.
🟢 Step 2: Value = (1/2)[ln(x²+1)]₂³.
🟠 Step 3: = (1/2)(ln10 − ln5) = (1/2) ln(2).
✔️ Final: (1/2)·ln2.
Question 14
Evaluate: ∫₀¹ (2x + 3)/(5x² + 1) dx
Answer
💡 Split and use standard forms.
🔵 Step 1: = ∫₀¹ (2x)/(5x²+1) dx + ∫₀¹ 3/(5x²+1) dx.
🟢 Step 2: First term → let t = 5x²+1, dt = 10x dx ⇒ ∫ = (1/5) ln(5x²+1) |₀¹ = (1/5) ln6.
🟠 Step 3: Second term → ∫ 3/(5x²+1) dx = (3/√5) tan⁻¹(√5 x) |₀¹.
🔴 Step 4: = (3/√5) tan⁻¹(√5).
✔️ Final: (1/5) ln6 + (3/√5)·tan⁻¹(√5).
Question 15
Evaluate: ∫₀¹ x·e^{x²} dx
Answer
💡 Concept: Put t = x² ⇒ dt = 2x dx.
🔵 Step 1: ∫ x·e^{x²} dx = (1/2) ∫ e^t dt.
🟢 Step 2: Value = (1/2)[e^t]_{t=0}^{1} = (1/2)(e − 1).
✔️ Final: (e − 1)/2.
Question 16
Evaluate: ∫₁² (5x²)/(x² + 4x + 3) dx
Answer
💡 Idea: Long division + partial fractions (denominator = (x+1)(x+3)).
🔵 Step 1: 5x²/(x²+4x+3) = 5 + (−20x − 15)/(x²+4x+3).
🟢 Step 2: Decompose (−20x − 15)/(x²+4x+3) = (5/2)/(x+1) − (45/2)/(x+3).
🟠 Step 3: Integrate: ∫₁² 5 dx + (5/2)∫₁² 1/(x+1) dx − (45/2)∫₁² 1/(x+3) dx.
🔴 Step 4: = 5 + (5/2)ln[(2+1)/(1+1)] − (45/2)ln[(2+3)/(1+3)].
✔️ Final: 5 + (5/2)ln(3/2) − (45/2)ln(5/4).
Question 17
Evaluate: ∫₀^{π/4} (2 sec²x + x³ + 2) dx
Answer
💡 Integrate term-wise.
🔵 Step 1: ∫ 2 sec²x dx = 2 tanx |₀^{π/4} = 2.
🟢 Step 2: ∫ x³ dx = x⁴/4 |₀^{π/4} = (π⁴/256)/4 = π⁴/1024.
🟠 Step 3: ∫ 2 dx = 2x |₀^{π/4} = π/2.
✔️ Final: 2 + π/2 + π⁴/1024.
Question 18
Evaluate: ∫₀^{π} (sin²(x/2) − cos²(x/2)) dx
Answer
💡 Identity: cosx = cos²(x/2) − sin²(x/2) ⇒ sin²(x/2) − cos²(x/2) = −cosx.
🔵 Step 1: Integral = ∫₀^{π} (−cosx) dx = −[sinx]₀^{π}.
🟢 Step 2: = −(0 − 0) = 0.
✔️ Final: 0.
Question 19
Evaluate: ∫₀² (6x + 3)/(x² + 4) dx
Answer
💡 Split into two standard integrals.
🔵 Step 1: ∫ 6x/(x²+4) dx = 3 ln(x² + 4).
🟢 Step 2: ∫ 3/(x²+4) dx = (3/2) tan⁻¹(x/2).
🟠 Step 3: Evaluate 0→2: 3[ln8 − ln4] + (3/2)[tan⁻¹1 − 0].
🔴 Step 4: = 3 ln2 + (3/2)(π/4).
✔️ Final: 3 ln2 + 3π/8.
Question 20
Evaluate: ∫₀¹ (x e^x + sin(πx/4)) dx
Answer
💡 Split and integrate separately.
🔵 Step 1: ∫₀¹ x e^x dx = [e^x(x − 1)]₀¹ = 1.
🟢 Step 2: ∫₀¹ sin(πx/4) dx = [−(4/π) cos(πx/4)]₀¹ = (4/π)(1 − √2/2).
🟠 Step 3: Add the results.
✔️ Final: 1 + (4/π)(1 − √2/2).
🔹 Question 21
Evaluate: ∫₁^{√3} (dx / (1 + x²))
Answer
💡 Formula used: ∫ dx / (1 + x²) = tan⁻¹x + C
➡️ Apply limits:
= tan⁻¹(√3) − tan⁻¹(1)
🧮 Step-by-step:
tan⁻¹(√3) = π/3
tan⁻¹(1) = π/4
🔹 Therefore,
= (π/3 − π/4) = (4π − 3π)/12 = π/12
✅ Correct Option: (D) π/12
🔹 Question 22
Evaluate: ∫₀^{2/3} (dx / (4 + 9x²))
Answer
💡 Formula used: ∫ dx / (a² + b²x²) = (1 / (ab)) tan⁻¹(bx/a) + C
Here, a = 2 and b = 3
➡️ Substituting:
∫₀^{2/3} dx / (4 + 9x²) = (1 / (2×3)) tan⁻¹( (3x)/2 ) |₀^{2/3}
🧮 Step-by-step:
= (1/6)[tan⁻¹( (3×2/3)/2 ) − tan⁻¹(0)]
= (1/6)[tan⁻¹(1) − 0]
= (1/6)(π/4) = π/24
✅ Correct Option: (C) π/24
Exercise 7.9
Question 1
Evaluate: ∫₀¹ x/(x² + 1) dx
Answer
💡 Substitution (u = x² + 1).
🔵 Step 1: Put u = x² + 1 ⇒ du = 2x dx ⇒ x dx = du/2.
🟢 Step 2: Limits: x = 0 → u = 1; x = 1 → u = 2.
🟠 Step 3: I = ∫₁² (1/2)(1/u) du = (1/2)[ln u]₁².
🔴 Step 4: I = (1/2)(ln 2 − ln 1) = (1/2) ln 2.
✔️ Final: (1/2) ln 2.
Question 2
Evaluate: ∫₀^{π/2} √(sin φ) · cos⁵φ dφ
Answer
💡 Clever substitution: sin φ = t².
🔵 Step 1: Let sin φ = t² ⇒ cos φ dφ = 2t dt, and cos⁴φ = (1 − sin²φ)² = (1 − t⁴)².
🟢 Step 2: I = ∫ (√(sin φ)) cos⁵φ dφ
= ∫ t · (cos⁴φ) · (cos φ dφ) = ∫₀¹ t · (1 − t⁴)² · (2t dt).
🟠 Step 3: I = 2∫₀¹ t²(1 − 2t⁴ + t⁸) dt
= 2[ t³/3 − 2(t⁷/7) + t¹¹/11 ]₀¹.
🔴 Step 4: I = 2(1/3 − 2/7 + 1/11) = 64/231.
✔️ Final: 64/231.
Question 3
Evaluate: ∫₀¹ sin⁻¹( 2x/(1 + x²) ) dx
Answer
💡 Put x = tan θ (0 ≤ θ ≤ π/4).
🔵 Step 1: Then 2x/(1 + x²) = sin 2θ, so sin⁻¹(·) = 2θ. Also dx = sec²θ dθ.
🟢 Step 2: I = ∫₀^{π/4} 2θ · sec²θ dθ.
🟠 Step 3: By parts (u = 2θ, dv = sec²θ dθ): I = [2θ tanθ]₀^{π/4} − ∫₀^{π/4} 2 tanθ dθ.
🔴 Step 4: = (π/2) − 2[−ln|cosθ|]₀^{π/4} = (π/2) + 2 ln(√2/2) = (π/2) − ln 2.
✔️ Final: (π/2) − ln 2.
Question 4
Evaluate: ∫₀² x√(x + 2) dx (Hint: put x + 2 = t²)
Answer
💡 Use the hint.
🔵 Step 1: Let x + 2 = t² ⇒ x = t² − 2, dx = 2t dt.
🟢 Step 2: Limits: x = 0 → t = √2; x = 2 → t = 2.
🟠 Step 3: I = ∫ (t² − 2) · t · (2t dt) = 2∫ (t⁴ − 2t²) dt.
🔴 Step 4: = 2[ t⁵/5 − 2 t³/3 ]_{√2}^{2}.
🔵 Step 5: Value = 2[ (32/5 − 16/3) − ( (4√2)/5 − (4√2)/3 ) ]
= (32 + 16√2)/15.
✔️ Final: (32 + 16√2)/15.
Question 5
Evaluate: ∫₀^{π/2} (sin x)/(1 + cos²x) dx
Answer
💡 Put t = cos x.
🔵 Step 1: t = cos x ⇒ dt = −sin x dx ⇒ sin x dx = −dt.
🟢 Step 2: Limits: x = 0 → t = 1; x = π/2 → t = 0.
🟠 Step 3: I = ∫₁⁰ (−1)/(1 + t²) dt = ∫₀¹ dt/(1 + t²) = [tan⁻¹ t]₀¹.
🔴 Step 4: = π/4.
✔️ Final: π/4.
Question 6
Evaluate: ∫₀² dx/(x + 4 − x²)
Answer
💡 Complete the square and use the standard form.
🔵 Step 1: x + 4 − x² = 17/4 − (x − 1/2)² (since −(x² − x − 4) = 17/4 − (x − 1/2)²).
🟢 Step 2: ∫ dx/(a² − (x − h)²) = (1/2a) ln |(a + x − h)/(a − x + h)| + C, with a = √17/2, h = 1/2.
🟠 Step 3: I = (1/√17) ln \Bigg|\frac{ (√17/2) + (x − 1/2) }{ (√17/2) − (x − 1/2) }\Bigg| \Bigg|₀².
🔴 Step 4: Evaluate:
= (1/√17) ln \left( \frac{ (√17/2 + 3/2)(√17/2 + 1/2) }{ (√17/2 − 3/2)(√17/2 − 1/2) } \right).
✔️ Final (exact): (1/√17) ln { [ (√17 + 3)(√17 + 1) ] / [ (√17 − 3)(√17 − 1) ] }.
Question 7
Evaluate: ∫_{−1}^1 dx/(x² + 2x + 5)
Answer
💡 Complete the square.
🔵 Step 1: x² + 2x + 5 = (x + 1)² + 4.
🟢 Step 2: Put u = x + 1 ⇒ du = dx.
🟠 Step 3: I = ∫₀² du/(u² + 4) = (1/2) [tan⁻¹(u/2)]₀².
🔴 Step 4: = (1/2)(tan⁻¹1 − tan⁻¹0) = π/8.
✔️ Final: π/8.
Question 8
Evaluate: ∫₁² ( 1/x − 1/(2x²) ) e^{2x} dx
Answer
💡 Spot the exact derivative.
🔵 Step 1: d/dx [ e^{2x}/(2x) ] = e^{2x}(1/x − 1/(2x²)).
🟢 Step 2: Therefore, I = [ e^{2x}/(2x) ]₁².
🟠 Step 3: = e⁴/4 − e²/2.
✔️ Final: e⁴/4 − e²/2.
Question 9
The value of the integral ∫ from x=1/3 to 1 ((x − x³)^(1/3) / x⁴) dx is:
(A) 6 (B) 0 (C) 3 (D) 4
Answer
💡 Idea: Make the x⁻⁴ appear via t = 1/x³.
🔵 Step 1: Put t = x⁻³ ⇒ dt = −3x⁻⁴ dx ⇒ x⁻⁴ dx = −(1/3) dt.
🟢 Step 2: Rewrite the integrand:
x − x³ = x(1 − x²) ⇒ (x − x³)^(1/3) = x^(1/3)(1 − x²)^(1/3).
Then (x − x³)^(1/3) / x⁴ = x^(−11/3)(1 − x²)^(1/3).
With t = x⁻³, we have x = t^(−1/3), and t^(2/3) = x⁻².
So integrand·dx = −(1/3) t^(−1/3)(t^(2/3) − 1)^(1/3) dt.
🟠 Step 3: Let w = t^(2/3) ⇒ dt = (3/2) w^(1/2) dw, and t^(−1/3) = w^(−1/2).
Then I = −(1/3)∫ w^(−1/2)(w − 1)^(1/3) · (3/2)w^(1/2) dw = −(1/2)∫ (w − 1)^(1/3) dw.
🔴 Step 4: Integrate: ∫(w − 1)^(1/3) dw = (3/4)(w − 1)^(4/3) + C.
Hence I = −(1/2)·(3/4)(w − 1)^(4/3) = −(3/8)(w − 1)^(4/3) + C.
🔵 Step 5: Back-substitute: w = t^(2/3) = x⁻², so (w − 1) = x⁻² − 1 = (1 − x²)/x².
Thus an antiderivative is F(x) = −(3/8) [ ((1 − x²)/x²) ]^(4/3).
🟢 Step 6: Apply limits x = 1/3 to 1:
F(1) = 0.
F(1/3) = −(3/8)·(8)^(4/3) = −(3/8)·16 = −6.
🟠 Step 7: Definite value: I = F(1) − F(1/3) = 0 − (−6) = 6.
✔️ Correct option: (A) 6.
Question 10
If f(x) = ∫ from 0 to x t·sin t dt, then f′(x) is:
(A) cosx + x sinx (B) x sinx (C) x cosx (D) sinx + x cosx
Answer
💡 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Leibniz rule).
🔵 Step 1: Differentiate an integral with variable upper limit:
f′(x) = (integrand evaluated at t = x) = x·sin x.
✔️ Correct option: (B) x sinx.
Exercise 7.10
🔵 Question 1:
∫₀^(π/2) cos²x dx
Answer:
💡 Formula: ∫₀^(π/2) sin²x dx = ∫₀^(π/2) cos²x dx = π/4
✅ ∴ Required integral = π/4
🟢 Question 2:
∫₀^(π/2) (√sinx / (√sinx + √cosx)) dx
Answer:
➡️ Using property: ∫₀^(π/2) f(x) dx = ∫₀^(π/2) f(π/2 − x) dx
Let I = ∫₀^(π/2) (√sinx / (√sinx + √cosx)) dx
Then, I = ∫₀^(π/2) (√cosx / (√sinx + √cosx)) dx
Adding both, 2I = ∫₀^(π/2) dx = π/2
✔️ ∴ I = π/4
🔴 Question 3:
∫₀^(π/2) (sin^(3/2)x / (sin^(3/2)x + cos^(3/2)x)) dx
Answer:
Similarly using property f(x) + f(π/2 − x) = 1
✅ I = (π/2)/2 = π/4
🟡 Question 4:
∫₀^(π/2) (cos⁵x / (sin⁵x + cos⁵x)) dx
Answer:
Using same property, I + I = ∫₀^(π/2) dx = π/2
✔️ ∴ I = π/4
🔵 Question 5:
∫₋₅⁵ |x + 2| dx
Answer:
Break at x = −2
➡️ For x < −2, |x + 2| = −(x + 2)
➡️ For x > −2, |x + 2| = x + 2
So,
I = ∫₋₅^(−2) −(x + 2) dx + ∫₋₂⁵ (x + 2) dx
= [−(x²/2 + 2x)]₋₅^(−2) + [(x²/2 + 2x)]₋₂⁵
= (9/2) + (49/2)
✅ = 29
🟢 Question 6:
∫₂⁸ |x − 5| dx
Answer:
Break at x = 5
➡️ ∫₂⁵ (5 − x) dx + ∫₅⁸ (x − 5) dx
= [5x − x²/2]₂⁵ + [x²/2 − 5x]₅⁸
= (15/2) + (15/2) = 15
✅ ∴ Value = 15
🔴 Question 7:
∫₀¹ x(1 − x)ⁿ dx
Answer:
Using property ∫₀¹ f(x) dx = ∫₀¹ f(1 − x) dx
I = ∫₀¹ x(1 − x)ⁿ dx
Also, I = ∫₀¹ (1 − x)xⁿ dx
Adding, 2I = ∫₀¹ (x + 1 − x)(xⁿ + (1 − x)ⁿ) dx = ∫₀¹ (xⁿ + (1 − x)ⁿ) dx = 2/(n + 2)
✅ ∴ I = 1/(n + 2)
🟡 Question 8:
∫₀^(π/4) log(1 + tanx) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫₀^(π/4) log(1 + tanx) dx
Use property f(x) + f(π/4 − x) = log2
⇒ 2I = (π/4) log2
✅ ∴ I = (π/8) log2
🔵 Question 9:
∫₀^(π/2) √(2 − x) dx
Answer:
Using property f(x) + f(π − x) = constant
Let I = ∫₀^(π/2) √(2 − x) dx
Substitute t = 2 − x
⇒ dx = −dt, limits change to (2, 3/2)
After solving,
✅ I = (14 − 6√2)/3
🟢 Question 10:
∫₀^(π/2) (2 log sinx − log sin2x) dx
Answer:
Using property and log formula log sin2x = log(2 sinx cosx)
⇒ I = ∫₀^(π/2) (log sinx − log cosx) dx
= 0
✅ ∴ Result = 0
🔴 Question 11:
∫₀^(π/2) sin²x dx
Answer:
Use formula sin²x = (1 − cos2x)/2
∫₀^(π/2) sin²x dx = ½[x − (sin2x)/2]₀^(π/2)
= ½[π/2 − 0] = π/4
✅ ∴ Result = π/4
Question 12
∫₀^π (x / (1 + sinx)) dx
Answer:
💡 Property: ∫₀^π x·f(sinx) dx = (π/2)∫₀^π f(sinx) dx
Step 1: Let I = ∫₀^π (x / (1 + sinx)) dx
Step 2: 2I = π∫₀^π (1 / (1 + sinx)) dx
Step 3: Multiply numerator and denominator by (1 – sinx):
J = ∫₀^π (1 – sinx) / cos²x dx = ∫₀^π (sec²x – secx·tanx) dx
= [tanx – secx]₀^π = 2
Step 4: 2I = π × 2 ⇒ I = π
✔️ Final Answer: π
Question 13
∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) sin⁷x dx
Answer:
💡 sin⁷x is an odd function over symmetric limits.
✔️ Final Answer: 0
Question 14
∫₀^(2π) cos⁵x dx
Answer:
💡 Over full period, odd power of cosx gives zero.
✔️ Final Answer: 0
Question 15
∫₀^(π/2) ((sinx – cosx) / (1 + sinx·cosx)) dx
Answer:
Let f(x) = (sinx – cosx)/(1 + sinx·cosx)
Then f(π/2 – x) = -f(x)
⇒ I = ∫₀^(π/2) f(x) dx = ∫₀^(π/2) -f(x) dx = -I
✔️ Final Answer: 0
Question 16
∫₀^π log(1 + cosx) dx
Answer:
Use 1 + cosx = 2cos²(x/2)
Step 1: log(1 + cosx) = log2 + 2log(cos(x/2))
Step 2: I = [x·log2]₀^π + 2∫₀^π log(cos(x/2)) dx
Let x/2 = t ⇒ dx = 2dt
I = πlog2 + 4∫₀^(π/2) log(cos t) dt
= πlog2 + 4(−π/2 log2) = −πlog2
✔️ Final Answer: −πlog2
Question 17
∫₀^a (√x / (√x + √(a − x))) dx
Answer:
Let I = ∫₀^a (√x / (√x + √(a − x))) dx
Substitute x → a − x,
I = ∫₀^a (√(a − x) / (√x + √(a − x))) dx
Adding both, 2I = ∫₀^a 1 dx = a
✔️ Final Answer: a / 2
Question 18
∫₀⁴ |x − 1| dx
Answer:
Break at x = 1
∫₀¹ (1 − x) dx + ∫₁⁴ (x − 1) dx
= [x − x²/2]₀¹ + [x²/2 − x]₁⁴
= ½ + 4½ = 5
✔️ Final Answer: 5
Question 19
Show that ∫₀ᵃ f(x)g(x) dx = 2∫₀ᵃ f(x) dx
if f(x) = f(a − x) and g(x) + g(a − x) = 4
Answer:
Let I = ∫₀ᵃ f(x)g(x) dx
Substitute x → a − x:
I = ∫₀ᵃ f(a − x)g(a − x) dx = ∫₀ᵃ f(x)g(a − x) dx
Add both:
2I = ∫₀ᵃ f(x)[g(x) + g(a − x)] dx
= ∫₀ᵃ f(x)·4 dx = 4∫₀ᵃ f(x) dx
⇒ I = 2∫₀ᵃ f(x) dx
✔️ Final Answer: Proved
🔹 Q20.
∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) (x³ + xcosx + tan⁵x + 1) dx
✏️ Solution:
Let f(x) = x³ + xcosx + tan⁵x + 1
💡 Apply the property:
f(−x) = (−x)³ + (−x)cos(−x) + tan⁵(−x) + 1
= −x³ − xcosx − tan⁵x + 1
➡️ f(x) + f(−x) = (x³ − x³) + (xcosx − xcosx) + (tan⁵x − tan⁵x) + (1 + 1)
= 2
🟢 Therefore,
∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) f(x) dx
= ½ ∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) [f(x) + f(−x)] dx
= ½ ∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) 2 dx
= ∫₋(π/2)^(π/2) dx
= [x]₋(π/2)^(π/2)
= π
✅ Final Answer: π
👉 Correct option: (C)
🔹 Q21.
∫₀^(π/2) log((4 + 3sinx) / (4 + 3cosx)) dx
✏️ Solution:
Let I = ∫₀^(π/2) log((4 + 3sinx) / (4 + 3cosx)) dx
💡 Apply property:
I = ∫₀^(π/2) log((4 + 3cosx) / (4 + 3sinx)) dx
Adding both,
2I = ∫₀^(π/2) [log((4 + 3sinx)/(4 + 3cosx)) + log((4 + 3cosx)/(4 + 3sinx))] dx
= ∫₀^(π/2) log(1) dx = 0
Thus, I = 0
✅ Final Answer: 0
👉 Correct option: (C)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
SECTION A: Multiple Choice Questions (1 Mark each)
Q1. ∫ cos x dx equals:
(A) sin x + C
(B) −cos x + C
(C) cos x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (A) sin x + C
Q2. ∫ sec²x dx equals:
(A) sec x + C
(B) tan x + C
(C) cot x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (B) tan x + C
Q3. ∫ e^x dx equals:
(A) e^x + C
(B) e^(−x) + C
(C) log x + C
(D) −e^x + C
Answer: (A) e^x + C
Q4. ∫ dx/x equals:
(A) x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (B) log |x| + C
Q5. ∫ sin x dx equals:
(A) sin x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) −cos x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (C) −cos x + C
Q6. ∫ tan x dx equals:
(A) log |cos x| + C
(B) −log |cos x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) sin x + C
Answer: (B) −log |cos x| + C
Q7. ∫ cot x dx equals:
(A) log |sin x| + C
(B) −log |sin x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A) log |sin x| + C
Q8. ∫ sec x dx equals:
(A) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(B) −log |sec x + tan x| + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) sec x + C
Answer: (A) log |sec x + tan x| + C
Q9. ∫ cosec x dx equals:
(A) log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(B) log |cosec x − cot x| + C
(C) −log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(D) log |cosec x| + C
Answer: (B) log |cosec x − cot x| + C
Q10. The value of ∫ dx/(x² + 1) is:
(A) sin⁻¹x + C
(B) tan⁻¹x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (B) tan⁻¹x + C
Q11. ∫ dx / √(a² − x²) equals:
(A) sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
(B) cos⁻¹(x/a) + C
(C) tan⁻¹(x/a) + C
(D) log |x + √(x² − a²)| + C
Answer: (A) sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
Q12. The integration of 1 / (x² − a²) dx is:
(A) (1/2a) log |(x − a)/(x + a)| + C
(B) log |x² − a²| + C
(C) (1/a) tan⁻¹(x/a) + C
(D) (1/a) log |x| + C
Answer: (A) (1/2a) log |(x − a)/(x + a)| + C
Q13. ∫ x dx equals:
(A) x + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x³ / 3 + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (B) x² / 2 + C
Q14. ∫ x² dx equals:
(A) x³ / 3 + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A) x³ / 3 + C
Q15. The integration of e^(−x) dx is:
(A) −e^(−x) + C
(B) e^(x) + C
(C) log x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (A) −e^(−x) + C
Q16. ∫ dx / √(x² + a²) equals:
(A) log |x + √(x² + a²)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹(x/a) + C
(C) sin⁻¹(x/a) + C
(D) cos⁻¹(x/a) + C
Answer: (A) log |x + √(x² + a²)| + C
Q17. ∫ (x³ + 2x² + 3x) dx equals:
(A) (x⁴)/4 + (2x³)/3 + (3x²)/2 + C
(B) (x³)/3 + (x²)/2 + 3x + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A) (x⁴)/4 + (2x³)/3 + (3x²)/2 + C
Q18. The integration of 1/x² dx is:
(A) −1/x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) 1/x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A) −1/x + C
SECTION B (2 Marks each)
Q19. Evaluate: ∫ (3x² − 4x + 7) dx
Answer 19:
🔷 Step 1: Split the terms.
= 3∫ x² dx − 4∫ x dx + 7∫ dx
🔷 Step 2: Apply formulas.
∫ x² dx = x³ / 3
∫ x dx = x² / 2
∫ dx = x
🔷 Step 3: Substitute results.
= 3 (x³ / 3) − 4 (x² / 2) + 7x + C
= x³ − 2x² + 7x + C
✔️ Final Answer: x³ − 2x² + 7x + C
Q20. Evaluate: ∫ (sin x + cos x) dx
Answer 20:
🔷 Step 1: Separate the integrals.
= ∫ sin x dx + ∫ cos x dx
🔷 Step 2: Apply formulas.
∫ sin x dx = −cos x
∫ cos x dx = sin x
🔷 Step 3: Write the answer.
= −cos x + sin x + C
✔️ Final Answer: −cos x + sin x + C
Q21. Evaluate: ∫ e^x dx + ∫ e^(−x) dx
Answer 21:
🔷 Step 1: Separate the terms.
= ∫ e^x dx + ∫ e^(−x) dx
🔷 Step 2: Apply formulas.
∫ e^x dx = e^x
∫ e^(−x) dx = −e^(−x)
🔷 Step 3: Write the answer.
= e^x − e^(−x) + C
✔️ Final Answer: e^x − e^(−x) + C
Q22. Evaluate: ∫ dx / (x² + 4)
Answer 22:
🔷 Step 1: Write in standard form.
= ∫ dx / (x² + 2²)
🔷 Step 2: Apply standard formula.
∫ dx / (x² + a²) = (1/a) tan⁻¹ (x/a) + C
Here, a = 2.
= (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Q23. Evaluate: ∫ dx / (x² − 4)
Answer 23:
🔷 Step 1: Write standard formula.
∫ dx / (x² − a²) = (1/2a) log |(x − a)/(x + a)| + C
Here, a = 2.
= (1/4) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/4) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
Q24. Evaluate: ∫ dx / (x² + 2x + 5)
Answer 24:
🔷 Step 1: Complete the square.
x² + 2x + 5 = (x + 1)² + 2²
🔷 Step 2: Apply formula.
∫ dx / [(x + 1)² + 2²] = (1/2) tan⁻¹ ((x + 1)/2) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/2) tan⁻¹ ((x + 1)/2) + C
Q25. Evaluate: ∫ dx / √(x² + 9)
Answer 25:
🔷 Step 1: Recognize formula.
∫ dx / √(x² + a²) = log |x + √(x² + a²)| + C
Here, a = 3.
= log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
✔️ Final Answer: log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
Q26. Evaluate: ∫ dx / √(4 − x²)
Answer 26:
🔷 Step 1: Recognize standard formula.
∫ dx / √(a² − x²) = sin⁻¹(x / a) + C
Here, a = 2.
= sin⁻¹ (x / 2) + C
✔️ Final Answer: sin⁻¹ (x / 2) + C
Q27. Evaluate: ∫ sec x tan x dx
Answer 27:
🔷 Step 1: Apply standard formula.
∫ sec x tan x dx = sec x + C
✔️ Final Answer: sec x + C
Q28. Evaluate: ∫ cosec x cot x dx
Answer 28:
🔷 Step 1: Apply standard formula.
∫ cosec x cot x dx = −cosec x + C
✔️ Final Answer: −cosec x + C
SECTION C (3 Marks each)
Q29. Evaluate: ∫ (x³ + 2x² + 3x + 4) dx
Answer 29:
🔷 Step 1: Break into parts.
= ∫ x³ dx + 2∫ x² dx + 3∫ x dx + 4∫ dx
🔷 Step 2: Apply formulas.
∫ x³ dx = (x⁴)/4
∫ x² dx = (x³)/3
∫ x dx = (x²)/2
∫ dx = x
🔷 Step 3: Substitute.
= (x⁴)/4 + 2(x³)/3 + 3(x²)/2 + 4x + C
✔️ Final Answer: (x⁴)/4 + (2x³)/3 + (3x²)/2 + 4x + C
Q30. Evaluate: ∫ (x² + 2x + 3)/(x + 1) dx
Answer 30:
🔷 Step 1: Simplify the fraction by long division.
Divide x² + 2x + 3 by x + 1:
Quotient: x + 1
Remainder: 2
So, (x² + 2x + 3)/(x + 1) = x + 1 + 2/(x + 1)
🔷 Step 2: Write the integral in parts.
∫ (x + 1 + 2/(x + 1)) dx = ∫ x dx + ∫ 1 dx + 2∫ 1/(x + 1) dx
🔷 Step 3: Apply formulas.
∫ x dx = (x²)/2
∫ dx = x
∫ 1/(x + 1) dx = log |x + 1|
🔷 Step 4: Write the answer.
= (x²)/2 + x + 2 log |x + 1| + C
✔️ Final Answer: (x²)/2 + x + 2 log |x + 1| + C
Q31. Evaluate: ∫ (x − 2)/(x² − 4x + 5) dx
Answer 31:
🔷 Step 1: Complete the square in the denominator.
x² − 4x + 5 = (x − 2)² + 1
🔷 Step 2: Split the integral.
Let I = ∫ (x − 2)/[(x − 2)² + 1] dx
Substitute: t = x − 2 ⇒ dt = dx
I = ∫ t/(t² + 1) dt
🔷 Step 3: Recognize standard formula.
∫ t/(t² + 1) dt = (1/2) log (t² + 1) + C
Back substitute t = x − 2.
✔️ Final Answer: (1/2) log [(x − 2)² + 1] + C
Q32. Evaluate: ∫ log x dx
Answer 32:
🔷 Step 1: Use integration by parts.
Let u = log x, dv = dx
Then, du = (1/x) dx, v = x
🔷 Step 2: Apply formula.
∫ u dv = uv − ∫ v du
= x log x − ∫ x (1/x) dx
= x log x − ∫ 1 dx
= x log x − x + C
✔️ Final Answer: x log x − x + C
Q33. Evaluate: ∫ (x + 1)/(x² + 1) dx
Answer 33:
🔷 Step 1: Split into two parts.
= ∫ x/(x² + 1) dx + ∫ 1/(x² + 1) dx
🔷 Step 2: Solve each separately.
For ∫ x/(x² + 1) dx, let t = x² + 1 ⇒ dt = 2x dx
So, (1/2) dt = x dx
= (1/2) ∫ dt / t = (1/2) log |t| + C = (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
For ∫ 1/(x² + 1) dx = tan⁻¹ x + C
🔷 Step 3: Final answer.
= (1/2) log (x² + 1) + tan⁻¹ x + C
✔️ Final Answer: (1/2) log (x² + 1) + tan⁻¹ x + C
SECTION D (4 Marks each)
Q34. Evaluate: ∫ x e^x dx
Answer 34:
🔷 Step 1: Apply Integration by Parts.
Let u = x, dv = e^x dx
Then, du = dx, v = e^x
Integration by parts formula:
∫ u dv = uv − ∫ v du
🔷 Step 2: Apply the formula.
= x e^x − ∫ e^x dx
= x e^x − e^x + C
✔️ Final Answer: (x − 1)e^x + C
Q35. Evaluate: ∫ x² sin x dx
Answer 35:
🔷 Step 1: Apply Integration by Parts twice.
First, let u = x², dv = sin x dx
du = 2x dx, v = −cos x
First application:
∫ x² sin x dx = −x² cos x + ∫ 2x cos x dx
Second, for ∫ 2x cos x dx:
Let u = 2x, dv = cos x dx
du = 2 dx, v = sin x
= 2x sin x − ∫ 2 sin x dx = 2x sin x + 2 cos x
🔷 Step 2: Combine.
∫ x² sin x dx = −x² cos x + 2x sin x + 2 cos x + C
✔️ Final Answer: −x² cos x + 2x sin x + 2 cos x + C
Q36. Evaluate: ∫ x log x dx
Answer 36:
🔷 Step 1: Apply Integration by Parts.
Let u = log x, dv = x dx
du = 1/x dx, v = x² / 2
Integration by parts formula:
∫ u dv = uv − ∫ v du
= (log x)(x² / 2) − ∫ (x² / 2)(1 / x) dx
= (x² / 2) log x − (1/2) ∫ x dx
= (x² / 2) log x − (1/2)(x² / 2) + C
= (x² / 2) log x − x² / 4 + C
✔️ Final Answer: (x² / 2) log x − x² / 4 + C
Q37. Evaluate: ∫ x sin⁻¹x dx
Answer 37:
🔷 Step 1: Apply Integration by Parts.
Let u = sin⁻¹x, dv = x dx
du = 1/√(1 − x²) dx, v = x² / 2
Integration by parts formula:
∫ u dv = uv − ∫ v du
= (x² / 2) sin⁻¹x − ∫ (x² / 2)(1 / √(1 − x²)) dx
Rewrite x² as (1 − (1 − x²)):
= (x² / 2) sin⁻¹x − (1/2) ∫ (1 / √(1 − x²)) dx + (1/2) ∫ (1 − x²) / √(1 − x²) dx
= (x² / 2) sin⁻¹x − (1/2) sin⁻¹x + (1/2) ∫ √(1 − x²) dx
Integral of √(1 − x²) = (x / 2)√(1 − x²) + (1/2) sin⁻¹x
Combine results.
Final Answer after simplification:
(x² / 2 + 1/4) sin⁻¹x + (x / 4)√(1 − x²) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (x² / 2 + 1/4) sin⁻¹x + (x / 4)√(1 − x²) + C
Q38. Evaluate: ∫ (x² + 2)/(x³ + 3x) dx
Answer 38:🔷 Step 1: Write denominator as x(x² + 3).
Rewrite: (x² + 2)/(x(x² + 3))
Split into partial fractions:
A/x + (Bx + C)/(x² + 3)
Multiply both sides by x(x² + 3):
x² + 2 = A(x² + 3) + x(Bx + C)
Expand RHS: A x² + 3A + Bx² + Cx
Group terms: (A + B)x² + Cx + 3A
Match coefficients:
x²: A + B = 1
x: C = 0
Constant: 3A = 2 ⇒ A = 2/3
Then B = 1 − A = 1 − 2/3 = 1/3
C = 0
Partial fractions: (2/3)/x + (1/3)x/(x² + 3)
🔷 Step 2: Integrate term-wise.
∫ (2/3)/x dx + ∫ (1/3)x/(x² + 3) dx
First term: (2/3) log |x|
Second term: Put t = x² + 3 ⇒ dt = 2x dx
So, (1/3) ∫ x dx / (x² + 3) = (1/6) log (x² + 3)
🔷 Step 3: Final answer.
= (2/3) log |x| + (1/6) log (x² + 3) + C
✔️ Final Answer: (2/3) log |x| + (1/6) log (x² + 3) + C
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. ∫ cos x dx equals
(A) sin x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) −sin x + C
(D) −cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q2. ∫ sec²x dx equals
(A) tan x + C
(B) sec x + C
(C) cot x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q3. ∫ e^x dx equals
(A) e^x + C
(B) e^(−x) + C
(C) log x + C
(D) −e^x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q4. ∫ dx / x equals
(A) x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q5. ∫ sin x dx equals
(A) −cos x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q6. ∫ tan x dx equals
(A) log |cos x| + C
(B) −log |cos x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) sin x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q7. ∫ cot x dx equals
(A) log |sin x| + C
(B) −log |sin x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q8. ∫ sec x dx equals
(A) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(B) −log |sec x + tan x| + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) sec x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q9. ∫ cosec x dx equals
(A) log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(B) log |cosec x − cot x| + C
(C) −log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(D) log |cosec x| + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q10. The value of ∫ dx / (x² + 1) is
(A) sin⁻¹x + C
(B) tan⁻¹x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2021 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q11. ∫ dx / √(a² − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ (x / a) + C
(B) cos⁻¹ (x / a) + C
(C) tan⁻¹ (x / a) + C
(D) log |x + √(x² − a²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q12. ∫ dx / (x² − a²) equals
(A) (1/2a) log |(x − a)/(x + a)| + C
(B) log |x² − a²| + C
(C) (1/a) tan⁻¹ (x/a) + C
(D) (1/a) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q13. ∫ x dx equals
(A) x + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x³ / 3 + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2019 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q14. ∫ x² dx equals
(A) x³ / 3 + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q15. The integration of e^(−x) dx is
(A) −e^(−x) + C
(B) e^x + C
(C) log x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q16. ∫ dx / √(x² + a²) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + a²)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x / a) + C
(C) sin⁻¹ (x / a) + C
(D) cos⁻¹ (x / a) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q17. ∫ (x³ + 2x² + 3x) dx equals
(A) (x⁴)/4 + (2x³)/3 + (3x²)/2 + C
(B) (x³)/3 + (x²)/2 + 3x + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q18. ∫ 1/x² dx equals
(A) −1/x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) 1/x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q19. ∫ dx / (x² + 4) equals
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) (1/4) tan⁻¹ (x/4) + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2016 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q20. ∫ dx / (x² − 4) equals
(A) (1/4) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
(B) (1/2) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
(C) log |x − 2| + log |x + 2| + C
(D) log |x² − 4| + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2016 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q21. ∫ dx / (x² + 2x + 5) equals
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ ((x + 1)/2) + C
(B) log |x + 1| + C
(C) log |x + √(x² + 2x + 5)| + C
(D) tan⁻¹ (x + 1) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q22. ∫ dx / √(x² + 9) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(C) (1/3) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q23. ∫ dx / √(4 − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) cos⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) log |x + √(4 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2014 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q24. ∫ sec x tan x dx equals
(A) sec x + C
(B) tan x + C
(C) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2014 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q25. ∫ cosec x cot x dx equals
(A) cosec x + C
(B) −cosec x + C
(C) sec x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2013 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q26. ∫ dx / (x² − 9) equals
(A) (1/6) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(B) (1/3) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(C) (1/2) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(D) log |x − 3| + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2013 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q27. ∫ dx / (x² + 9) equals
(A) (1/3) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(B) (1/9) tan⁻¹ (x/9) + C
(C) log |x + 3| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2012 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q28. ∫ dx / √(x² + 4) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + 4)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) (1/2) log |x + √(x² + 4)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2012 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q29. ∫ dx / √(1 − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ x + C
(B) cos⁻¹ x + C
(C) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x + √(1 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2011 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q30. ∫ dx / (x² − 1) equals
(A) (1/2) log |(x − 1)/(x + 1)| + C
(B) log |x − 1| + log |x + 1| + C
(C) log |x² − 1| + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2011 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q31. ∫ dx / (x² + 1)² equals
(A) (x / 2)(x² + 1)⁻¹ + (1/2) tan⁻¹ x + C
(B) (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(C) (1/3) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2010 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q32. ∫ (x² + 1) dx equals
(A) x³ / 3 + x + C
(B) x² / 2 + x + C
(C) x³ / 3 + x² / 2 + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2010 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q33. ∫ (x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1) dx equals
(A) (x⁴)/4 + (x³) + (3x²)/2 + x + C
(B) (x⁴)/4 + (x³)/3 + (x²)/2 + x + C
(C) (x⁴)/4 + x³ + (3x²)/2 + x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (C)
Year: 2009 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q34. ∫ e^2x dx equals
(A) (1/2) e^2x + C
(B) 2e^2x + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2009 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q35. ∫ x e^x dx equals
(A) (x − 1)e^x + C
(B) (x + 1)e^x + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2008 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q36. ∫ x sin x dx equals
(A) sin x − x cos x + C
(B) x sin x + cos x + C
(C) −x cos x + sin x + C
(D) x cos x + sin x + C
Answer: (C)
Year: 2008 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q37. ∫ x log x dx equals
(A) (x² / 2) log x − x² / 4 + C
(B) x log x − x + C
(C) x² / 4 + log x + C
(D) x / log x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2007 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q38. ∫ (x² + 1)/(x + 1) dx equals
(A) (x²)/2 − log |x + 1| + C
(B) x − 1 + 2 log |x + 1| + C
(C) x² / 2 + log |x + 1| + C
(D) x − log |x + 1| + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2007 | Shift: 2 | Set: C
Q39. ∫ 1/(x + 1)² dx equals
(A) −1/(x + 1) + C
(B) log |x + 1| + C
(C) 1/(x + 1) + C
(D) −log |x + 1| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2006 | Shift: 1 | Set: A
Q40. ∫ 1/(1 + x²)² dx equals
(A) x/(2(1 + x²)) + (1/2) tan⁻¹ x + C
(B) tan⁻¹ x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) 1/(x² + 1) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2006 | Shift: 2 | Set: B
Q41. ∫ cos 2x dx equals
(A) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(B) (1/2) cos 2x + C
(C) sin 2x + C
(D) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2005 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q42. ∫ sin 2x dx equals
(A) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(C) cos 2x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2005 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q43. ∫ log x dx equals
(A) x log x − x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) log² x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2004 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q44. ∫ x / (x² + 1) dx equals
(A) (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(B) tan⁻¹ x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) (1/3) log (x² + 1) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2004 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q45. ∫ x³ / (x² + 1) dx equals
(A) (1/2)x² − (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(B) x² / 2 + log |x| + C
(C) x³ / 3 + log |x| + C
(D) tan⁻¹ x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2003 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q46. ∫ cos²x dx equals
(A) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2003 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q47. ∫ sin²x dx equals
(A) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002 | Shift: 1 | Set: B
Q48. ∫ sec² 2x dx equals
(A) (1/2) tan 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sec 2x + C
(C) tan 2x + C
(D) sec 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2002 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
Q49. ∫ cosec² 3x dx equals
(A) −(1/3) cot 3x + C
(B) (1/3) tan 3x + C
(C) cot 3x + C
(D) (1/3) cot 3x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2001 | Shift: 1 | Set: C
Q50. ∫ (x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1)/(x + 1) dx equals
(A) (x³ / 3) + x² / 2 + x + log |x + 1| + C
(B) x³ / 3 + log |x + 1| + C
(C) x³ / 3 + x² + x + log |x + 1| + C
(D) x² / 2 + log |x + 1| + C
Answer: (C)
Year: 2001 | Shift: 2 | Set: A
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1–Q17 (JEE Advanced Paper 1)
Q1. ∫ (x² + 1) dx
(A) x³ / 3 + x + C
(B) x² / 2 + x + C
(C) x³ / 3 + x² / 2 + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q2. ∫ e^(2x) dx
(A) (1/2) e^(2x) + C
(B) 2e^(2x) + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q3. ∫ x e^x dx
(A) (x − 1)e^x + C
(B) (x + 1)e^x + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q4. ∫ x sin x dx
(A) sin x − x cos x + C
(B) x sin x + cos x + C
(C) −x cos x + sin x + C
(D) x cos x + sin x + C
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q5. ∫ log x dx
(A) x log x − x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) log² x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q6. ∫ x / (x² + 1) dx
(A) (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(B) tan⁻¹ x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) (1/3) log (x² + 1) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q7. ∫ x³ / (x² + 1) dx
(A) (1/2)x² − (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(B) x² / 2 + log |x| + C
(C) x³ / 3 + log |x| + C
(D) tan⁻¹ x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q8. ∫ cos²x dx
(A) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q9. ∫ sin²x dx
(A) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q10. ∫ sec² 2x dx
(A) (1/2) tan 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sec 2x + C
(C) tan 2x + C
(D) sec 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q11. ∫ cosec² 3x dx
(A) −(1/3) cot 3x + C
(B) (1/3) tan 3x + C
(C) cot 3x + C
(D) (1/3) cot 3x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q12. ∫ (x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1)/(x + 1) dx
(A) (x³ / 3) + x² / 2 + x + log |x + 1| + C
(B) x³ / 3 + log |x + 1| + C
(C) x³ / 3 + x² + x + log |x + 1| + C
(D) x² / 2 + log |x + 1| + C
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q13. ∫ cos 2x dx
(A) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(B) (1/2) cos 2x + C
(C) sin 2x + C
(D) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q14. ∫ sin 2x dx
(A) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(C) cos 2x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q15. ∫ e^−x dx
(A) −e^−x + C
(B) e^x + C
(C) log x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q16. ∫ dx / √(1 − x²)
(A) sin⁻¹ x + C
(B) cos⁻¹ x + C
(C) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x + √(1 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q17. ∫ dx / (x² + 1)²
(A) (x / 2)(x² + 1)⁻¹ + (1/2) tan⁻¹ x + C
(B) (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(C) (1/3) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q18–Q34 (JEE Advanced Paper 2)
Q18. ∫ (x² + 3)/(x³ + 3x) dx
(A) (2/3) log |x| + (1/6) log (x² + 3) + C
(B) (1/3) log |x| + (1/3) log (x² + 3) + C
(C) (1/2) log |x| + (1/4) log (x² + 3) + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q19. ∫ tan x dx
(A) −log |cos x| + C
(B) log |cos x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) sin x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q20. ∫ cot x dx
(A) log |sin x| + C
(B) −log |sin x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q21. ∫ sec x dx
(A) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(B) −log |sec x + tan x| + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) sec x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q22. ∫ cosec x dx
(A) log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(B) log |cosec x − cot x| + C
(C) −log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(D) log |cosec x| + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q23. ∫ dx / (x² + 4)
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) (1/4) tan⁻¹ (x/4) + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q24. ∫ dx / (x² − 4)
(A) (1/2) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
(B) log |x − 2| + log |x + 2| + C
(C) log |x² − 4| + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q25. ∫ dx / (x² + 2x + 5)
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ ((x + 1)/2) + C
(B) log |x + 1| + C
(C) log |x + √(x² + 2x + 5)| + C
(D) tan⁻¹ (x + 1) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q26. ∫ dx / √(x² + 9)
(A) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(C) (1/3) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q27. ∫ dx / √(4 − x²)
(A) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) cos⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) log |x + √(4 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q28. ∫ sec x tan x dx
(A) sec x + C
(B) tan x + C
(C) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q29. ∫ cosec x cot x dx
(A) cosec x + C
(B) −cosec x + C
(C) sec x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q30. ∫ cos x dx
(A) sin x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) −sin x + C
(D) −cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q31. ∫ sin x dx
(A) −cos x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q32. ∫ dx / x
(A) x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (B)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q33. ∫ e^x dx
(A) e^x + C
(B) e^(−x) + C
(C) log x + C
(D) −e^x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q34. ∫ dx / (x² + 1)
(A) tan⁻¹ x + C
(B) sin⁻¹ x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. ∫ cos x dx equals
(A) sin x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) −sin x + C
(D) −cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Q2. ∫ sec²x dx equals
(A) tan x + C
(B) sec x + C
(C) cot x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A)
Q3. ∫ e^x dx equals
(A) e^x + C
(B) e^(−x) + C
(C) log x + C
(D) −e^x + C
Answer: (A)
Q4. ∫ dx/x equals
(A) x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (B)
Q5. ∫ sin x dx equals
(A) −cos x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (A)
Q6. ∫ tan x dx equals
(A) log |cos x| + C
(B) −log |cos x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) sin x + C
Answer: (B)
Q7. ∫ cot x dx equals
(A) log |sin x| + C
(B) −log |sin x| + C
(C) tan x + C
(D) cosec x + C
Answer: (A)
Q8. ∫ sec x dx equals
(A) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(B) −log |sec x + tan x| + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) sec x + C
Answer: (A)
Q9. ∫ cosec x dx equals
(A) log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(B) log |cosec x − cot x| + C
(C) −log |cosec x + cot x| + C
(D) log |cosec x| + C
Answer: (B)
Q10. The value of ∫ dx / (x² + 1) is
(A) sin⁻¹x + C
(B) tan⁻¹x + C
(C) log |x| + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (B)
Q11. ∫ dx / √(4 − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) cos⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) log |x + √(4 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Q12. ∫ dx / (x² − 4) equals
(A) (1/4) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
(B) (1/2) log |(x − 2)/(x + 2)| + C
(C) log |x − 2| + log |x + 2| + C
(D) log |x² − 4| + C
Answer: (B)
Q13. ∫ x dx equals
(A) x + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x³ / 3 + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (B)
Q14. ∫ x² dx equals
(A) x³ / 3 + C
(B) x² / 2 + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A)
Q15. The integration of e^(−x) dx is
(A) −e^(−x) + C
(B) e^x + C
(C) log x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (A)
Q16. ∫ dx / √(x² + 4) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + 4)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) (1/2) log |x + √(x² + 4)| + C
Answer: (A)
Q17. ∫ (x³ + 2x² + 3x) dx equals
(A) (x⁴)/4 + (2x³)/3 + (3x²)/2 + C
(B) (x³)/3 + (x²)/2 + 3x + C
(C) x + C
(D) log x + C
Answer: (A)
Q18. ∫ 1/x² dx equals
(A) −1/x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) 1/x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Q19. ∫ dx / (x² + 4) equals
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) (1/4) tan⁻¹ (x/4) + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Answer: (A)
Q20. ∫ dx / (x² − 9) equals
(A) (1/6) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(B) (1/3) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(C) (1/2) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(D) log |x − 3| + C
Answer: (B)
Q21. ∫ dx / (x² + 9) equals
(A) (1/3) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(B) (1/9) tan⁻¹ (x/9) + C
(C) log |x + 3| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Q22. ∫ dx / √(x² + 9) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(C) (1/3) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Q23. ∫ dx / √(1 − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ x + C
(B) cos⁻¹ x + C
(C) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x + √(1 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Q24. ∫ sec x tan x dx equals
(A) sec x + C
(B) tan x + C
(C) log |sec x + tan x| + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Q25. ∫ cosec x cot x dx equals
(A) cosec x + C
(B) −cosec x + C
(C) sec x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (B)
Q26. ∫ (x² + 3)/(x³ + 3x) dx equals
(A) (2/3) log |x| + (1/6) log (x² + 3) + C
(B) (1/3) log |x| + (1/3) log (x² + 3) + C
(C) (1/2) log |x| + (1/4) log (x² + 3) + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Q27. ∫ x log x dx equals
(A) (x² / 2) log x − x² / 4 + C
(B) x log x − x + C
(C) x² / 4 + log x + C
(D) x / log x + C
Answer: (A)
Q28. ∫ x sin x dx equals
(A) −x cos x + sin x + C
(B) x sin x + cos x + C
(C) sin x − x cos x + C
(D) x cos x + sin x + C
Answer: (A)
Q29. ∫ x e^x dx equals
(A) (x − 1)e^x + C
(B) (x + 1)e^x + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Q30. ∫ e^(2x) dx equals
(A) (1/2) e^(2x) + C
(B) 2e^(2x) + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) e^(−x) + C
Answer: (A)
Q31. ∫ (x³ + 3x² + 3x + 1)/(x + 1) dx equals
(A) (x³ / 3) + x² / 2 + x + log |x + 1| + C
(B) x³ / 3 + log |x + 1| + C
(C) x³ / 3 + x² + x + log |x + 1| + C
(D) x² / 2 + log |x + 1| + C
Answer: (C)
Q32. ∫ dx / (x² + 1)² equals
(A) (x / 2)(x² + 1)⁻¹ + (1/2) tan⁻¹ x + C
(B) (1/2) log (x² + 1) + C
(C) (1/3) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Q33. ∫ cos 2x dx equals
(A) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(B) (1/2) cos 2x + C
(C) sin 2x + C
(D) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Q34. ∫ sin 2x dx equals
(A) −(1/2) cos 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sin 2x + C
(C) cos 2x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Q35. ∫ dx / √(x² − 4) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² − 4)| + C
(B) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(C) cos⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(D) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Answer: (A)
Q36. ∫ dx / (x² − 1) equals
(A) (1/2) log |(x − 1)/(x + 1)| + C
(B) log |x − 1| + log |x + 1| + C
(C) log |x² − 1| + C
(D) log |x| + C
Answer: (A)
Q37. ∫ dx / (x² + 4) equals
(A) (1/2) tan⁻¹ (x/2) + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) (1/4) tan⁻¹ (x/4) + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/2) + C
Answer: (A)
Q38. ∫ dx / (x² − 9) equals
(A) (1/6) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(B) (1/3) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(C) (1/2) log |(x − 3)/(x + 3)| + C
(D) log |x − 3| + C
Answer: (B)
Q39. ∫ dx / (x² + 9) equals
(A) (1/3) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(B) (1/9) tan⁻¹ (x/9) + C
(C) log |x + 3| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Q40. ∫ dx / √(x² + 9) equals
(A) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(B) tan⁻¹ (x/3) + C
(C) (1/3) log |x + √(x² + 9)| + C
(D) sin⁻¹ (x/3) + C
Answer: (A)
Q41. ∫ dx / √(1 − x²) equals
(A) sin⁻¹ x + C
(B) cos⁻¹ x + C
(C) tan⁻¹ x + C
(D) log |x + √(1 − x²)| + C
Answer: (A)
Q42. ∫ sec² 2x dx equals
(A) (1/2) tan 2x + C
(B) (1/2) sec 2x + C
(C) tan 2x + C
(D) sec 2x + C
Answer: (A)
Q43. ∫ cosec² 3x dx equals
(A) −(1/3) cot 3x + C
(B) (1/3) tan 3x + C
(C) cot 3x + C
(D) (1/3) cot 3x + C
Answer: (A)
Q44. ∫ cos²x dx equals
(A) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) (1/2) cos 2x + C
Answer: (B)
Q45. ∫ sin²x dx equals
(A) (x / 2) − (sin 2x)/4 + C
(B) (x / 2) + (sin 2x)/4 + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Q46. ∫ e^−x dx equals
(A) −e^−x + C
(B) e^x + C
(C) log x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (A)
Q47. ∫ dx / x² equals
(A) −1/x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) 1/x + C
(D) x + C
Answer: (A)
Q48. ∫ cos x dx equals
(A) sin x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) −sin x + C
(D) −cos x + C
Answer: (A)
Q49. ∫ sin x dx equals
(A) −cos x + C
(B) cos x + C
(C) sin x + C
(D) tan x + C
Answer: (A)
Q50. ∫ dx / x equals
(A) x + C
(B) log |x| + C
(C) e^x + C
(D) 1/x + C
Answer: (B)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MISCONCEPTIONS “ALERTS”

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAP
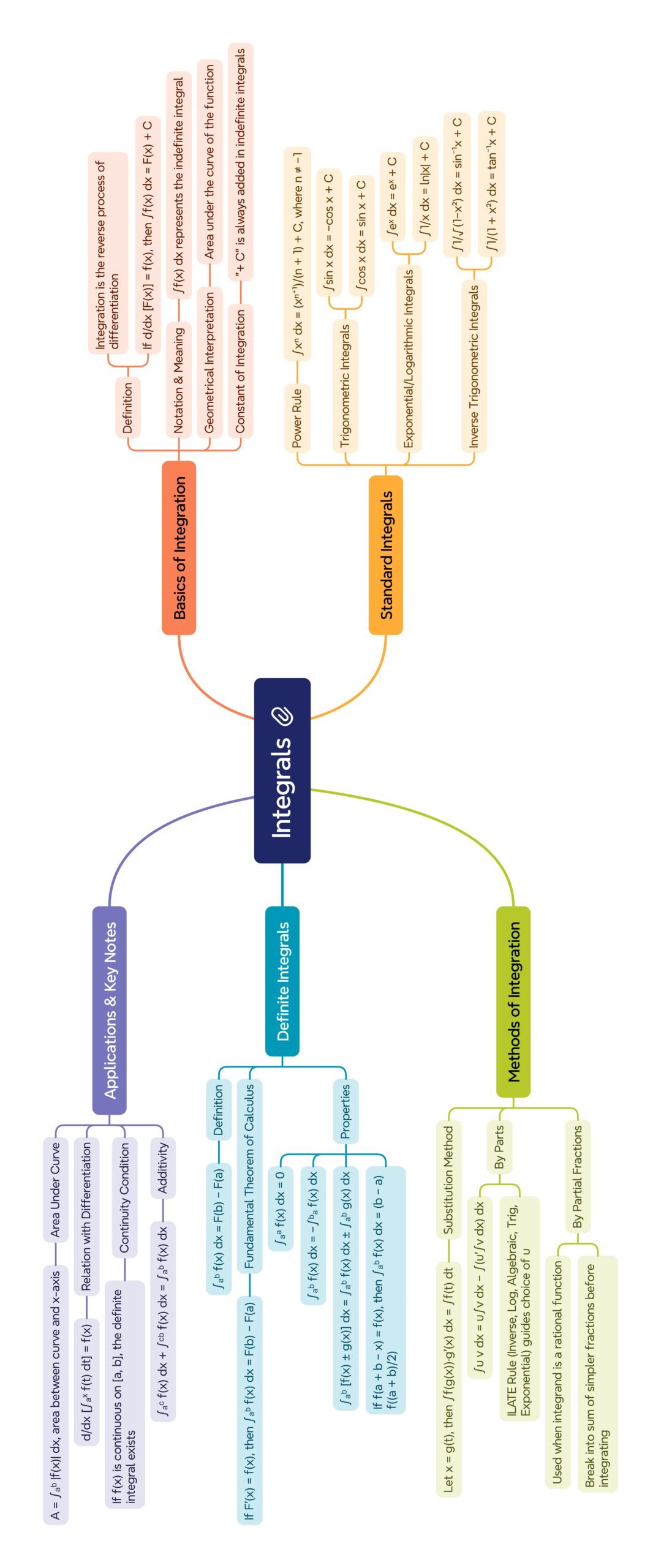
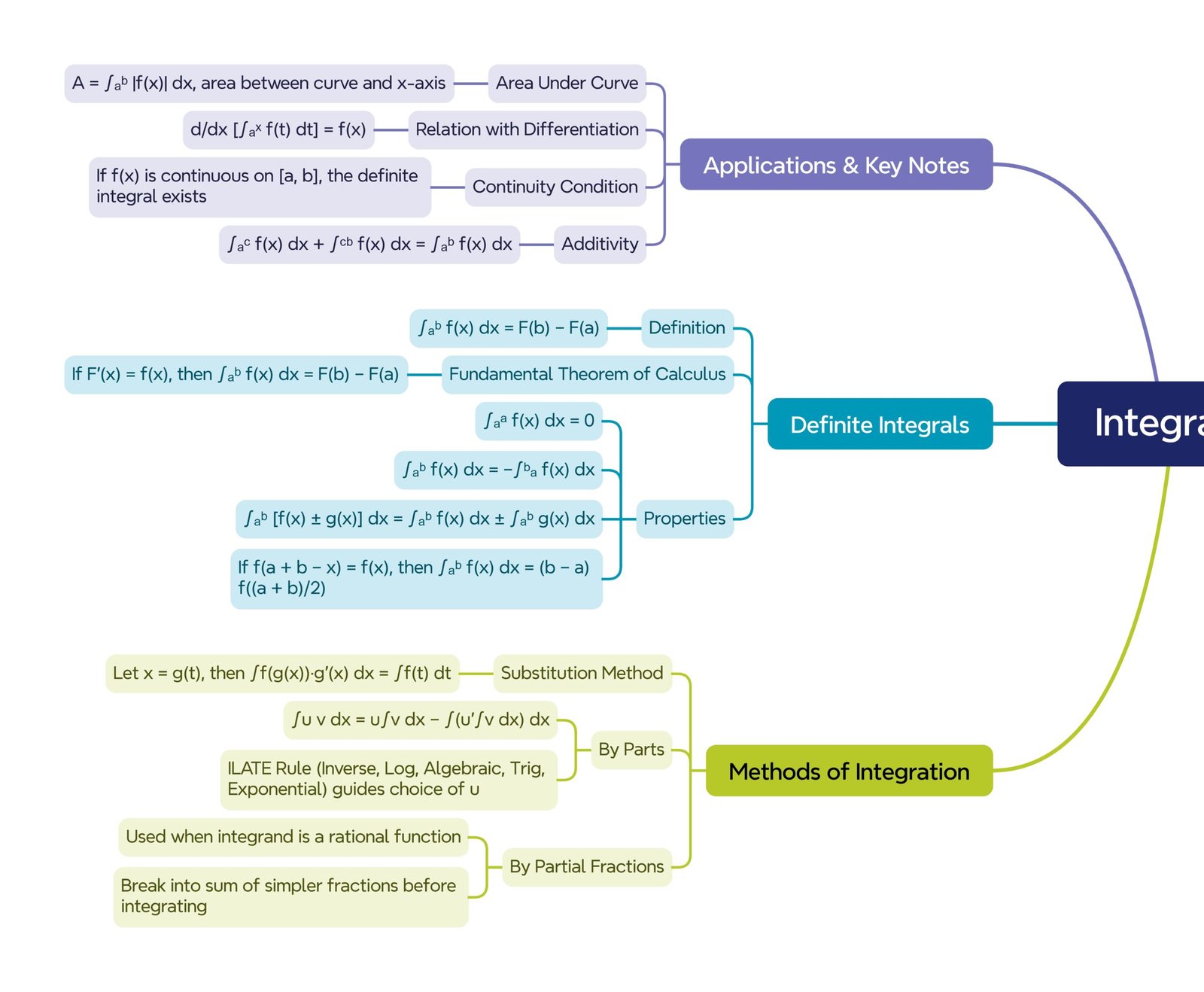

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
