Class 12 : Maths (English) – Chapter 5: Continuity and Differentiability
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌟 Introduction
The chapter Continuity and Differentiability builds upon the concept of limits and explains how smoothly a function behaves.
A function is continuous if its graph has no breaks or jumps, and differentiable if it has a well-defined tangent or slope at every point.
This lesson includes:
Conditions for continuity and differentiability
Rules for algebra of continuous and differentiable functions
Chain rule, implicit and logarithmic differentiation
Derivatives of inverse trigonometric and parametric functions
Relationship between continuity and differentiability
🧠 1. Continuity of a Function
💡 Definition:
A function f(x) is continuous at x = a if:
f(a) is defined
limₓ→ₐ f(x) exists
limₓ→ₐ f(x) = f(a)
If all three conditions hold, the function is continuous at x = a.
✔️ Graphically: No hole, jump, or break at that point.
✏️ Note:
A function is continuous on an interval if it is continuous at every point of that interval.
🟢 2. Types of Discontinuity
Removable Discontinuity:
Limit exists, but not equal to function value.
Example: f(x) = (x² − 1)/(x − 1) has a hole at x = 1.
Jump Discontinuity:
Left-hand limit ≠ Right-hand limit.
Example: Step functions.
Infinite Discontinuity:
Limit tends to ±∞, graph shoots upward or downward.
🟡 3. Continuity of Standard Functions
✔️ Always Continuous in Their Domains:
Polynomials — continuous ∀ x ∈ ℝ
Rational functions — continuous where denominator ≠ 0
Trigonometric, exponential, logarithmic, inverse trigonometric — continuous in their domains
🔵 4. Algebra of Continuous Functions
If f and g are continuous at x = a, then:
f ± g is continuous at a
f·g is continuous at a
f/g is continuous at a, if g(a) ≠ 0
Composition f(g(x)) is continuous at a if f is continuous at g(a)
🧠 5. Differentiability of a Function
💡 Definition:
A function f(x) is differentiable at x = a if both left-hand derivative (LHD) and right-hand derivative (RHD) exist and are equal.f′(a) = limₕ→0 [ f(a + h) − f(a) ] / h
✔️ If the above limit exists and is finite, f is differentiable at x = a.
✅ Differentiable ⇒ Continuous
❌ Continuous ↛ Differentiable (e.g., f(x) = |x| at x = 0)
🧠 6. Points of Non-Differentiability
A function fails to be differentiable when:
It is not continuous
Graph has a corner or cusp
It has a vertical tangent
Example:
f(x) = |x|
At x = 0, LHD = −1, RHD = +1 ⇒ Not differentiable.
🟢 7. Algebra of Differentiable Functions
If f and g are differentiable at a, then:
f ± g, f·g, f/g (if g(a) ≠ 0) are differentiable
k·f(x) is differentiable (k = constant)
Composition f(g(x)) is differentiable (Chain Rule)
💡 8. Chain Rule
If y = f(u) and u = g(x),
thendy/dx = (dy/du) × (du/dx)
Example:
Find dy/dx if y = sin(3x²)
➡️ Let u = 3x², then du/dx = 6x
➡️ dy/du = cos(u)
✔️ dy/dx = cos(3x²) × 6x
🧠 9. Standard Derivatives
🔹 (xⁿ)’ = n·xⁿ⁻¹
🔹 (eˣ)’ = eˣ
🔹 (aˣ)’ = aˣ·ln(a)
🔹 (ln x)’ = 1/x
🔹 (sin x)’ = cos x
🔹 (cos x)’ = −sin x
🔹 (tan x)’ = sec²x
🔹 (cot x)’ = −csc²x
🔹 (sec x)’ = sec x·tan x
🔹 (csc x)’ = −csc x·cot x
🧠 10. Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Function
Derivative
(d/dx)(sin⁻¹x) = 1 / √(1 − x²)
(d/dx)(cos⁻¹x) = −1 / √(1 − x²)
(d/dx)(tan⁻¹x) = 1 / (1 + x²)
(d/dx)(cot⁻¹x) = −1 / (1 + x²)
(d/dx)(sec⁻¹x) = 1 / ( |x| · √(x² − 1) )
(d/dx)(csc⁻¹x) = −1 / ( |x| · √(x² − 1) )
💡 Always consider domain restrictions when applying these formulas.
🧠 11. Implicit Differentiation
When y is not explicitly expressed in terms of x, differentiate both sides with respect to x.
Example:
x² + y² = r²
➡️ Differentiate: 2x + 2y(dy/dx) = 0
✔️ dy/dx = −x / y
🧠 12. Logarithmic Differentiation
Useful when both base and exponent depend on x.
If y = u(x)ᵛ⁽ˣ⁾,
take log both sides:ln y = v(x)·ln u(x)
Differentiate:(1/y)·(dy/dx) = v′(x)·ln u(x) + v(x)·(u′(x)/u(x))
✔️ Multiply by y to get dy/dx
🧠 13. Parametric Differentiation
If x = f(t), y = g(t), thendy/dx = (dy/dt) / (dx/dt)
Example:
x = a·cos t, y = a·sin t
➡️ dy/dt = a·cos t, dx/dt = −a·sin t
✔️ dy/dx = −cot t
🧠 14. Second-Order Derivative
If y′ = dy/dx, theny″ = d²y/dx² = d(y′)/dx
Or using parameter t:d²y/dx² = [d/dt(dy/dx)] / (dx/dt)
🧠 15. Relationship Between Continuity and Differentiability
✔️ Differentiable ⇒ Continuous
❌ Continuous ↛ Differentiable
Example:
f(x) = |x| is continuous at x = 0 but not differentiable.
🧠 16. Important Theorems
✔️ Every polynomial function is continuous and differentiable ∀ x ∈ ℝ.
✔️ Sum/product/quotient of continuous/differentiable functions → same property holds.
✔️ Composite of continuous/differentiable functions → same property holds.
🌿 17. Real-Life Applications
Smooth physical motions (no jumps) → continuity
Rate of change (velocity, acceleration) → differentiability
Used in physics, economics, biology for modeling change.
🟣 Summary (~300 words)
🔹 Continuity:
f(x) is continuous at x = a if:
limₓ→ₐ f(x) = f(a)
✔️ No breaks or holes.
🔹 Differentiability:
f(x) is differentiable at x = a if:f′(a) = limₕ→0 [ f(a + h) − f(a) ] / h
✔️ Left-hand and right-hand derivatives exist and are equal.
🔹 Relationship:
Differentiable ⇒ Continuous
Continuous ↛ Differentiable
🔹 Algebra Rules:
Sum, product, quotient of continuous/differentiable functions are continuous/differentiable (if defined).
🔹 Chain Rule:
dy/dx = (dy/du) × (du/dx)
🔹 Implicit Differentiation:
Differentiate both sides; treat y as dependent variable.
🔹 Logarithmic Differentiation:
Use log to simplify exponentials.
🔹 Parametric Differentiation:
dy/dx = (dy/dt)/(dx/dt)
🔹 Standard Derivatives:
xⁿ → n·xⁿ⁻¹, eˣ → eˣ, sin x → cos x, tan x → sec²x, etc.
🔹 Inverse Trig Derivatives:
sin⁻¹x → 1/√(1−x²), tan⁻¹x → 1/(1+x²)
📝 Quick Recap
✔️ Continuity: limₓ→ₐ f(x) = f(a)
✔️ Differentiability: LHD = RHD = f′(a)
✔️ Differentiable ⇒ Continuous
✔️ Chain Rule, Implicit, Logarithmic, Parametric methods
✔️ Derivatives show rate of change and slope of curves
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Exercise 5.1
🔵 Question 1:
Prove that the function f(x) = 5x − 3 is continuous at x = 0, at x = −3 and at x = 5.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ f(x) = 5x − 3 is a polynomial function.
💡 Polynomial functions are continuous everywhere in ℝ.
➡️ For each point:
LHL = f(a), RHL = f(a), value = f(a)
✔️ Hence, continuous at x = 0, −3, and 5.
✅ Conclusion: f(x) is continuous ∀x ∈ ℝ.
🔵 Question 2:
Examine the continuity of the function f(x) = 2x² − 1 at x = 3.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ f(x) = 2x² − 1 is a polynomial ⇒ continuous ∀x ∈ ℝ.
➡️ Check at x = 3:
f(3) = 2(3)² − 1 = 18 − 1 = 17
LHL = f(3) = 17, RHL = f(3) = 17
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(3)
✅ Conclusion: Continuous at x = 3.
🔵 Question 3 (a):
Examine f(x) = x − 5 for continuity.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Linear function ⇒ continuous ∀x ∈ ℝ.
✅ Conclusion: Continuous everywhere.
🔵 Question 3 (b):
f(x) = 1 / (x − 5), x ≠ 5
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Rational function ⇒ continuous at all points except where denominator = 0.
➡️ Denominator zero at x = 5 ⇒ discontinuous at x = 5.
✅ Conclusion: Continuous ∀x ≠ 5.
🔵 Question 3 (c):
f(x) = (x² − 25)/(x + 5), x ≠ −5
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Simplify: f(x) = (x − 5), x ≠ −5
➡️ Linear ⇒ continuous ∀x ≠ −5
➡️ At x = −5, function not defined ⇒ discontinuous there.
✅ Conclusion: Continuous ∀x ≠ −5.
🔵 Question 3 (d):
f(x) = |x − 5|
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Modulus function ⇒ continuous ∀x.
✅ Conclusion: Continuous everywhere.
🔵 Question 4:
Prove that f(x) = xⁿ is continuous at x = n, where n is a positive integer.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ f(x) = xⁿ is polynomial ⇒ continuous everywhere.
➡️ At x = n:
LHL = f(n), RHL = f(n), Value = f(n)
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(n)
✅ Conclusion: Continuous at x = n.
🔵 Question 5:
Is the function f defined by
f(x) = { x, if x ≤ 1
5, if x > 1 }
continuous at x = 0? x = 1? x = 2?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ For x < 1 → f(x) = x (continuous)
✔️ For x > 1 → f(x) = 5 (constant, continuous)
➡️ At x = 0: lies in x ≤ 1 → continuous ✅
➡️ At x = 2: lies in x > 1 → continuous ✅
➡️ At x = 1:
LHL = f(1) = 1
RHL = 5
f(1) = 1
LHL ≠ RHL ⇒ discontinuous ❌
✅ Conclusion: Continuous at 0 & 2, not continuous at 1.
🔵 Question 6:
Find points of discontinuity if
f(x) = { 2x + 3, if x ≤ 2
2x − 3, if x > 2 }
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Check at x = 2:
LHL = 2(2) + 3 = 7
RHL = 2(2) − 3 = 1
f(2) = 7
LHL ≠ RHL ⇒ discontinuous at x = 2 ❌
✅ Conclusion: Discontinuous only at x = 2.
🔵 Question 7:
f(x) = { |x| + 3, if x ≤ −3
−2x, if −3 < x < 3
6x + 2, if x ≥ 3 }
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuous in each interval.
Check at x = −3:
LHL = |−3| + 3 = 6
RHL = −2(−3) = 6
f(−3) = 6 ✅
➡️ Check at x = 3:
LHL = −2(3) = −6
RHL = 6(3) + 2 = 20
f(3) = 20
LHL ≠ RHL ⇒ discontinuous at x = 3 ❌
✅ Conclusion: Continuous ∀x ≠ 3, discontinuous at x = 3.
🔵 Question 8:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = |x| / x, if x ≠ 0
0, if x = 0
🟢 Answer:
➡️ For x ≠ 0,
f(x) = |x| / x
🔹 When x > 0 → |x| = x → f(x) = x/x = 1
🔹 When x < 0 → |x| = −x → f(x) = (−x)/x = −1
➡️ At x = 0,
f(0) = 0
💡 Check continuity at x = 0:
Left-hand limit (LHL) = limₓ→0⁻ f(x) = −1
Right-hand limit (RHL) = limₓ→0⁺ f(x) = 1
f(0) = 0
Since LHL ≠ RHL ≠ f(0),
🔴 f(x) is discontinuous at x = 0.
✔️ Continuous everywhere else.
🔵 Question 9:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = x / |x|, if x < 0
−1, if x ≥ 0
🟢 Answer:
➡️ For x < 0,
|x| = −x → f(x) = x / (−x) = −1
➡️ For x ≥ 0,
f(x) = −1
Therefore,
f(x) = −1 for all x
🟢 LHL = RHL = f(0) = −1
✔️ Hence f(x) is continuous everywhere.
🔵 Question 10:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = x + 1, if x ≥ 1
x² + 1, if x < 1
🟢 Answer:
💡 Possible point: x = 1
➡️ LHL = limₓ→1⁻ f(x) = 1² + 1 = 2
➡️ RHL = limₓ→1⁺ f(x) = 1 + 1 = 2
➡️ f(1) = 1 + 1 = 2
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(1) → continuous at x = 1
✔️ Hence f(x) is continuous everywhere.
🔵 Question 11:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = x³ − 3, if x ≤ 2
x² + 1, if x > 2
🟢 Answer:
💡 Possible point: x = 2
➡️ LHL = limₓ→2⁻ f(x) = 2³ − 3 = 8 − 3 = 5
➡️ RHL = limₓ→2⁺ f(x) = 2² + 1 = 4 + 1 = 5
➡️ f(2) = 2³ − 3 = 5
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(2) → continuous at x = 2
✔️ Hence f(x) is continuous everywhere.
🔵 Question 12:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = x¹⁰ − 1, if x ≤ 1
x², if x > 1
🟢 Answer:
💡 Possible point: x = 1
➡️ LHL = limₓ→1⁻ f(x) = 1¹⁰ − 1 = 0
➡️ RHL = limₓ→1⁺ f(x) = 1² = 1
➡️ f(1) = 1¹⁰ − 1 = 0
🔴 LHL ≠ RHL → discontinuous at x = 1
✔️ Continuous everywhere else.
🔵 Question 13:
Is the function defined by
f(x) = x + 5, if x ≤ 1
x − 5, if x > 1
a continuous function?
🟢 Answer:
💡 Possible point: x = 1
➡️ LHL = limₓ→1⁻ f(x) = 1 + 5 = 6
➡️ RHL = limₓ→1⁺ f(x) = 1 − 5 = −4
➡️ f(1) = 1 + 5 = 6
🔴 LHL ≠ RHL → discontinuous at x = 1
✔️ Continuous everywhere else.
🔵 Question 14:
Discuss the continuity of the function f, where f is defined by
f(x) = { 3, if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
4, if 1 < x < 3
5, if 3 ≤ x ≤ 10 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ On each open interval, the function is constant ⇒ continuous.
➡️ Check at x = 1: LHL = 3, RHL = 4, f(1) = 3.
➡️ Since LHL ≠ RHL, f is discontinuous at x = 1.
➡️ Check at x = 3: LHL = 4, RHL = 5, f(3) = 5.
➡️ Since LHL ≠ RHL, f is discontinuous at x = 3.
➡️ Endpoints x = 0 and x = 10 have one-sided limits equal to the function values.
✔️ Final: f is continuous on [0,1), (1,3), (3,10] and discontinuous at x = 1 and x = 3.
🔵 Question 15:
f(x) = { 2x, if x < 0
0, if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
4x, if x > 1 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ On each region (x < 0), (0 ≤ x ≤ 1), (x > 1) the function is linear/constant ⇒ continuous.
➡️ At x = 0: LHL = 2·0 = 0, RHL = 0, f(0) = 0 ⇒ continuous.
➡️ At x = 1: LHL = 0, RHL = 4·1 = 4, f(1) = 0 ⇒ discontinuous (jump).
✔️ Final: Continuous ∀x ≠ 1; discontinuous at x = 1.
🔵 Question 16:
f(x) = { −2, if x ≤ −1
2x, if −1 < x ≤ 1
2, if x > 1 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ At x = −1: LHL = −2, RHL = 2(−1) = −2, f(−1) = −2 ⇒ continuous.
➡️ At x = 1: LHL = 2(1) = 2, RHL = 2, f(1) = 2 ⇒ continuous.
➡️ Elsewhere each piece is constant/linear ⇒ continuous.
✔️ Final: f is continuous for all real x.
🔵 Question 17:
Find the relationship between a and b so that the function f defined by
f(x) = { ax + 1, if x ≤ 3
bx + 3, if x > 3 }
is continuous at x = 3.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuity at x = 3 requires LHL = RHL = f(3).
➡️ LHL = 3a + 1.
➡️ RHL = 3b + 3.
➡️ Set equal: 3a + 1 = 3b + 3.
➡️ Rearrange: 3a − 3b = 2 ⇒ a − b = 2/3.
✔️ Final: a − b = 2/3.
🔵 Question 18:
For what value of λ is the function defined by
f(x) = { λ(x² − 2x), if x ≤ 0
4x + 1, if x > 0 }
continuous at x = 0? What about continuity at x = 1?
🟢 Answer:
➡️ At x = 0:
LHL = limₓ→0⁻ λ(x² − 2x) = λ·0 = 0, and f(0) = 0.
RHL = limₓ→0⁺ (4x + 1) = 1.
➡️ For continuity at 0, need 0 = 1 — impossible.
✔️ No value of λ makes f continuous at x = 0.
➡️ At x = 1 (> 0), f(x) = 4x + 1 near 1 (both sides in the same branch).
✔️ Therefore f is continuous at x = 1 for all λ.
🔵 Question 19:
Show that the function defined by g(x) = x − ⌊x⌋ is discontinuous at all integral points. Here ⌊x⌋ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ For any integer n, consider x → n⁻:
⌊x⌋ = n − 1 ⇒ g(x) = x − (n − 1) → n − (n − 1) = 1.
➡️ For x → n⁺:
⌊x⌋ = n ⇒ g(x) = x − n → 0.
➡️ g(n) = n − ⌊n⌋ = n − n = 0.
➡️ Since LHL = 1 and RHL = 0 at every integer n, LHL ≠ RHL.
✔️ Final: g(x) is discontinuous at every integer; continuous on each open interval (n, n+1).
🔵 Question 20:
Is the function defined by f(x) = x² − sin x + 5 continuous at x = π?
🟢 Answer:
💡 Step 1: f(x) = x² − sin x + 5 is composed of:
➡️ x² → continuous ∀ x
➡️ sin x → continuous ∀ x
➡️ Constant 5 → continuous ∀ x
💡 Step 2: Sum of continuous functions ⇒ continuous function.
Therefore, f(x) is continuous ∀ x.
✔️ Conclusion: f(x) is continuous at x = π.
🔵 Question 21:
Discuss the continuity of the following functions:
(a) f(x) = sin x + cos x
(b) f(x) = sin x − cos x
(c) f(x) = sin x · cos x
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Each of sin x and cos x is continuous ∀ x.
➡️ (a) Sum → continuous.
➡️ (b) Difference → continuous.
➡️ (c) Product → continuous.
✔️ Hence all three functions (a), (b), (c) are continuous for all real x.
🔵 Question 22:
Discuss the continuity of the cosine, cosecant, secant, and cotangent functions.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ cos x → continuous ∀ x.
➡️ sec x = 1/cos x → discontinuous where cos x = 0 ⇒ x = (2n+1)π/2
➡️ csc x = 1/sin x → discontinuous where sin x = 0 ⇒ x = nπ
➡️ cot x = cos x / sin x → discontinuous where sin x = 0 ⇒ x = nπ
✔️ Summary:
🔹 cos x – continuous everywhere
🔹 sec x – discontinuous at (2n+1)π/2
🔹 csc x, cot x – discontinuous at nπ
🔵 Question 23:
Find all points of discontinuity of f, where
f(x) = { sin x / x, if x < 0
x + 1, if x ≥ 0 }
🟢 Answer:
💡 Step 1: f(x) is continuous on (−∞, 0) and [0, ∞).
💡 Step 2: Check continuity at x = 0.
➡️ LHL = limₓ→0⁻ (sin x / x) = 1
➡️ RHL = limₓ→0⁺ (x + 1) = 1
➡️ f(0) = 0 + 1 = 1
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(0) ⇒ continuous at x = 0
✔️ Final: f(x) is continuous everywhere (no discontinuity).
🔵 Question 24:
Determine if f defined by
f(x) = { x² sin(1/x), if x ≠ 0
0, if x = 0 }
is a continuous function.
🟢 Answer:
💡 Step 1: For x ≠ 0, f(x) = x² sin(1/x) → product of continuous functions ⇒ continuous.
💡 Step 2: Check at x = 0.
➡️ f(0) = 0
➡️ limₓ→0 f(x) = limₓ→0 x² sin(1/x)
Since |sin(1/x)| ≤ 1 ⇒ |x² sin(1/x)| ≤ x² → tends to 0.
✔️ Limit = 0 = f(0) ⇒ continuous at x = 0
✔️ Final: f(x) is continuous for all real x.
🔵 Question 25:
Examine the continuity of f, where f is defined by
f(x) = { sin x − cos x, if x ≠ 0
−1, if x = 0 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ For x ≠ 0, sin x − cos x is a difference of continuous functions ⇒ continuous.
➡️ At x = 0:
LHL = limₓ→0⁻(sin x − cos x) = 0 − 1 = −1
RHL = limₓ→0⁺(sin x − cos x) = 0 − 1 = −1
f(0) = −1
✔️ LHL = RHL = f(0) = −1.
✅ Final: f is continuous for all real x (including x = 0).
🔵 Question 26:
Find the value of k so that the function f is continuous at x = π/2, where
f(x) = { (k cos x)/(π − 2x), if x ≠ π/2
3, if x = π/2 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Need limₓ→π/2 (k cos x)/(π − 2x) = f(π/2) = 3.
➡️ Put x = π/2 + h, with h → 0.
cos x ≈ cos(π/2 + h) = −sin h ≈ −h
π − 2x = π − 2(π/2 + h) = −2h
➡️ Limit = k(−h)/(−2h) = k/2.
➡️ Continuity ⇒ k/2 = 3.
✔️ Final: k = 6.
🔵 Question 27:
Find the value of k so that the function f is continuous at x = 2, where
f(x) = { kx², if x ≤ 2
3, if x > 2 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuity at x = 2 ⇒ limₓ→2 kx² = 3 and f(2) = k(2)².
➡️ k·4 = 3.
✔️ Final: k = 3/4.
🔵 Question 28:
Find the value of k so that the function f is continuous at x = π, where
f(x) = { kx + 1, if x ≤ π
cos x, if x > π }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuity at x = π ⇒ kπ + 1 = cos π = −1.
➡️ kπ = −2.
✔️ Final: k = −2/π.
🔵 Question 29:
Find the value of k so that the function f is continuous at x = 5, where
f(x) = { kx + 1, if x ≤ 5
3x − 5, if x > 5 }.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuity at x = 5 ⇒ 5k + 1 = 3·5 − 5 = 10.
➡️ 5k = 9.
✔️ Final: k = 9/5.
🔵 Question 30:
Find the values of a and b such that the function defined by
f(x) = { 5, if x ≤ 2
ax + b, if 2 < x < 10
21, if x ≥ 10 }
is a continuous function.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Continuity at x = 2 ⇒ 2a + b = 5.
➡️ Continuity at x = 10 ⇒ 10a + b = 21.
➡️ Subtract: (10a + b) − (2a + b) = 21 − 5 ⇒ 8a = 16 ⇒ a = 2.
➡️ Then b = 5 − 2a = 5 − 4 = 1.
✔️ Final: a = 2, b = 1.
🔵 Question 31:
Show that the function defined by f(x) = cos(x²) is a continuous function.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ x² is continuous ∀ x.
➡️ cos t is continuous ∀ t.
➡️ Composition of continuous functions is continuous.
✔️ Final: f(x) = cos(x²) is continuous for all real x.
🔵 Question 32:
Show that the function defined by f(x) = |cos x| is a continuous function.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ cos x is continuous ∀ x.
➡️ |·| is continuous ∀ real inputs.
➡️ Composition |cos x| is continuous.
✔️ Final: f is continuous for all real x.
🔵 Question 33:
Examine that sin |x| is a continuous function.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ |x| is continuous ∀ x.
➡️ sin t is continuous ∀ t.
➡️ Composition sin(|x|) is continuous.
✔️ Final: sin|x| is continuous ∀ x ∈ ℝ.
🔵 Question 34:
Find all points of discontinuity of f defined by f(x) = |x| − |x + 1|.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ |x| and |x + 1| are continuous functions ∀ x.
➡️ Difference of continuous functions is continuous.
✔️ Final: f is continuous for all real x (no point of discontinuity).
Exercise 5.2
🔵 Question 1: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = sin(x² + 5).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let u = x² + 5.
➡️ d/dx[sin u] = cos u · du/dx.
➡️ du/dx = 2x.
✔️ Final: f′(x) = 2x · cos(x² + 5).
🔵 Question 2: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = cos(sin x).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let u = sin x.
➡️ d/dx[cos u] = −sin u · du/dx.
➡️ du/dx = cos x.
✔️ Final: f′(x) = −cos x · sin(sin x).
🔵 Question 3: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = sin(ax + b) (a, b are constants).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let u = ax + b.
➡️ d/dx[sin u] = cos u · du/dx.
➡️ du/dx = a.
✔️ Final: f′(x) = a · cos(ax + b).
🔵 Question 4: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = sec( tan(√x) ).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let u = tan(√x).
➡️ d/dx[sec u] = sec u · tan u · du/dx.
➡️ Let v = √x = x^(1/2). Then du/dx = sec²(v) · dv/dx.
➡️ dv/dx = 1/(2√x).
✔️ Final: f′(x) = [ sec(tan√x) · tan(tan√x) · sec²(√x) ] / (2√x).
🔵 Question 5: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = sin(ax + b) / cos(cx + d) (a, b, c, d are constants).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Use quotient rule: (u/v)′ = (u′v − uv′)/v².
➡️ u = sin(ax + b) ⇒ u′ = a · cos(ax + b).
➡️ v = cos(cx + d) ⇒ v′ = −c · sin(cx + d).
➡️ Substitute: f′(x) = [a cos(ax + b) · cos(cx + d) − sin(ax + b) · (−c sin(cx + d))] / cos²(cx + d).
➡️ Simplify numerator: a cos(ax + b) cos(cx + d) + c sin(ax + b) sin(cx + d).
✔️ Final:
f′(x) = [ a cos(ax + b) cos(cx + d) + c sin(ax + b) sin(cx + d) ] / cos²(cx + d).
🔵 Question 6: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = cos(x³) · sin²(x⁵).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Use product rule: (UV)′ = U′V + UV′.
➡️ U = cos(x³) ⇒ U′ = −sin(x³) · 3x².
➡️ V = [sin(x⁵)]² ⇒ V′ = 2 sin(x⁵) · cos(x⁵) · 5x⁴ = 10x⁴ sin(x⁵) cos(x⁵).
➡️ Combine: f′(x) = (−3x² sin(x³)) · sin²(x⁵) + cos(x³) · (10x⁴ sin(x⁵) cos(x⁵)).
✔️ Final:
f′(x) = −3x² sin(x³) sin²(x⁵) + 10x⁴ cos(x³) sin(x⁵) cos(x⁵).
🔵 Question 7: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = 2√(cot(x²)).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Write f(x) = 2 [cot(x²)]^(1/2).
➡️ d/dx[w^(1/2)] = (1/2) w^(−1/2) · w′.
➡️ w = cot(x²) ⇒ w′ = −csc²(x²) · 2x.
➡️ Multiply the outer 2: 2 · (1/2) · w^(−1/2) · w′ = w^(−1/2) · w′.
✔️ Final:
f′(x) = −2x · csc²(x²) / √(cot(x²)).
🔵 Question 8: Differentiate with respect to x: f(x) = cos(√x).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Let u = √x.
➡️ d/dx[cos u] = −sin u · du/dx.
➡️ du/dx = 1/(2√x).
✔️ Final: f′(x) = − sin(√x) / (2√x).
🔵 Question 9: Prove that the function f given by f(x) = |x − 1|, x ∈ ℝ is not differentiable at x = 1.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Write f(x) piecewise:
f(x) = 1 − x, if x < 1; f(x) = x − 1, if x ≥ 1.
➡️ Left derivative at 1: f′₋(1) = d/dx(1 − x) at x = 1 = −1.
➡️ Right derivative at 1: f′₊(1) = d/dx(x − 1) at x = 1 = 1.
➡️ Since f′₋(1) ≠ f′₊(1), derivative does not exist at x = 1.
✔️ Final: f is not differentiable at x = 1 (though f is continuous there).
🔵 Question 10: Prove that the greatest integer function defined by f(x) = ⌊x⌋, 0 < x < 3 is not differentiable at x = 1 and x = 2.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ The function ⌊x⌋ is constant on each open interval (n, n+1) and has jump discontinuities at every integer n.
➡️ At x = 1:
limₓ→1⁻ ⌊x⌋ = 0, limₓ→1⁺ ⌊x⌋ = 1, f(1) = 1 ⇒ discontinuous at 1.
➡️ At x = 2:
limₓ→2⁻ ⌊x⌋ = 1, limₓ→2⁺ ⌊x⌋ = 2, f(2) = 2 ⇒ discontinuous at 2.
➡️ A function must be continuous to be differentiable.
✔️ Final: f(x) is not differentiable at x = 1 and x = 2 (on 0 < x < 3).
Exercise 5.3
Find dy/dx in the following
🔵 Question 1: 2x + 3y = sin x
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: 2 + 3y′ = cos x
✔️ Final: y′ = (cos x − 2)/3
🔵 Question 2: 2x + 3y = sin y
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: 2 + 3y′ = (cos y)·y′
➡️ Rearrange: 2 = y′(cos y − 3)
✔️ Final: y′ = 2/(cos y − 3)
🔵 Question 3: a x + b y² = cos y
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: a + 2b y y′ = −(sin y)·y′
➡️ Collect y′: a = y′(−sin y − 2b y)
✔️ Final: y′ = −a/(sin y + 2b y)
🔵 Question 4: x y + y² = tan x + y
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: y + x y′ + 2y y′ = sec²x + y′
➡️ Group: y′(x + 2y − 1) = sec²x − y
✔️ Final: y′ = (sec²x − y)/(x + 2y − 1)
🔵 Question 5: x² + x y + y² = 100
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: 2x + y + x y′ + 2y y′ = 0
➡️ Group: y′(x + 2y) = −(2x + y)
✔️ Final: y′ = −(2x + y)/(x + 2y)
🔵 Question 6: x³ + x²y + x y² + y³ = 81
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate termwise: 3x² + (2x y + x² y′) + (y² + 2x y y′) + 3y² y′ = 0
➡️ Group y′: y′(x² + 2xy + 3y²) + (3x² + 2xy + y²) = 0
✔️ Final: y′ = −(3x² + 2xy + y²)/(x² + 2xy + 3y²)
🔵 Question 7: sin²y + (cos x)·y = κ
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: 2 sin y cos y · y′ + (−sin x)·y + (cos x)·y′ = 0
➡️ Group: y′(2 sin y cos y + cos x) = y sin x
✔️ Final: y′ = [y sin x]/[2 sin y cos y + cos x] (i.e., y′ = y sin x/(sin2y + cos x))
🔵 Question 8: sin²x + cos²y = 1
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Differentiate: 2 sin x cos x − 2 sin y cos y · y′ = 0
➡️ Rearrange: y′ = (sin x cos x)/(sin y cos y)
✔️ Final: y′ = (sin 2x)/(sin 2y)
🔵 Question 9: y = sin⁻¹( 2x/(1 + x²) )
🟢 Answer (set x = tan t, then −π/4 < t < π/4):
➡️ 2x/(1 + x²) = 2 tan t/(1 + tan²t) = sin 2t
➡️ y = sin⁻¹(sin 2t) = 2t
➡️ dy/dx = 2·dt/dx = 2·(1/(1 + x²))
✔️ Final: y′ = 2/(1 + x²) (valid for −1 < x < 1)
🔵 Question 10: y = tan⁻¹( (3x − x³)/(1 − 3x²) ), −1/√3 < x < 1/√3
🟢 Answer (triple-angle identity):
➡️ (3x − x³)/(1 − 3x²) = tan(3x)
➡️ y = tan⁻¹(tan 3x) = 3x
✔️ Final: y′ = 3
🔵 Question 11: y = cos⁻¹( (1 − x²)/(1 + x²) ), 0 < x < 1
🟢 Answer (let x = tan θ, 0<θ<π/4):
➡️ (1 − x²)/(1 + x²) = (1 − tan²θ)/(1 + tan²θ) = cos 2θ
➡️ y = cos⁻¹(cos 2θ) = 2θ = 2 tan⁻¹ x
✔️ Final: y′ = 2/(1 + x²)
🔵 Question 12: y = sin⁻¹( (1 − x²)/(1 + x²) ), 0 < x < 1
🟢 Answer (x = tan θ):
➡️ (1 − x²)/(1 + x²) = cos 2θ = sin(π/2 − 2θ)
➡️ y = π/2 − 2θ = π/2 − 2 tan⁻¹ x
➡️ dy/dx = −2/(1 + x²)
✔️ Final: y′ = −2/(1 + x²)
🔵 Question 13: y = cos⁻¹( 2x/(1 + x²) ), −1 < x < 1
🟢 Answer (x = tan θ):
➡️ 2x/(1 + x²) = 2 tan θ/(1 + tan²θ) = sin 2θ
➡️ y = cos⁻¹(sin 2θ) = π/2 − 2θ = π/2 − 2 tan⁻¹ x
✔️ Final: y′ = −2/(1 + x²)
🔵 Question 14: y = sin⁻¹( 2x√(1 − x²) ), −1/√2 < x < 1/√2
🟢 Answer (x = sin θ):
➡️ 2x√(1 − x²) = 2 sin θ cos θ = sin 2θ
➡️ y = sin⁻¹(sin 2θ) = 2θ = 2 sin⁻¹ x
✔️ Final: y′ = 2/√(1 − x²)
🔵 Question 15: y = sec⁻¹( 1/(2x² − 1) ), 0 < x < 1/√2
🟢 Answer (cos y = 2x² − 1 ⇒ y = cos⁻¹(2x² − 1)):
➡️ dy/dx = −(d/dx(2x² − 1))/√(1 − (2x² − 1)²)
➡️ dy/dx = −4x / √(1 − (4x⁴ − 4x² + 1))
➡️ Simplify denominator: √(4x²(1 − x²)) = 2x√(1 − x²) (since x>0)
✔️ Final: y′ = −2/√(1 − x²)
Exercise 5.4
🔵 Question 1:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = eˣ / sin x
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Using Quotient Rule:
d/dx (u/v) = (u’v − uv’) / v²
Let u = eˣ ⇒ u’ = eˣ
Let v = sin x ⇒ v’ = cos x
➡️ dy/dx = (eˣ·sin x − eˣ·cos x) / (sin x)²
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = [eˣ (sin x − cos x)] / sin²x
🔵 Question 2:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = e^(sin⁻¹x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let u = sin⁻¹x ⇒ du/dx = 1 / √(1 − x²)
➡️ dy/dx = e^(sin⁻¹x) · (1 / √(1 − x²))
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = e^(sin⁻¹x) / √(1 − x²)
🔵 Question 3:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = e^(x³)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let u = x³ ⇒ du/dx = 3x²
➡️ dy/dx = e^(x³) · 3x²
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = 3x² e^(x³)
🔵 Question 4:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = sin(tan⁻¹(e^(−x)))
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let u = tan⁻¹(e^(−x))
⇒ du/dx = [1 / (1 + e^(−2x))] · (−e^(−x)) = −e^(−x) / (1 + e^(−2x))
➡️ dy/dx = cos(u) · du/dx
💡 cos(u) = 1 / √(1 + e^(−2x))
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = −e^(−x) / (1 + e^(−2x))^(3/2)
🔵 Question 5:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = log(cos(eˣ))
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let v = cos(eˣ) ⇒ dv/dx = −sin(eˣ) · eˣ
➡️ dy/dx = (1 / v) · dv/dx = [−sin(eˣ) · eˣ] / cos(eˣ)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = −eˣ · tan(eˣ)
🔵 Question 6:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = eˣ + e^(x²) + e^(x³) + … + e^(xʳ)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ dy/dx = eˣ + 2x e^(x²) + 3x² e^(x³) + … + r x^(r−1) e^(xʳ)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = eˣ + 2x e^(x²) + 3x² e^(x³) + … + r x^(r−1) e^(xʳ)
🔵 Question 7:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = √(e^(√x)), x > 0
🟢 Answer:
✏️ y = e^(√x / 2)
➡️ dy/dx = e^(√x / 2) · (1/2) · (1 / (2√x))
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = e^(√x / 2) / (4√x)
🔵 Question 8:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = log(log x), x > 1
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let v = log x ⇒ dv/dx = 1/x
➡️ dy/dx = (1 / log x) · (1 / x)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = 1 / (x log x)
🔵 Question 9:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = cos x / log x, x > 0
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Using Quotient Rule:
u = cos x ⇒ u’ = −sin x
v = log x ⇒ v’ = 1/x
➡️ dy/dx = (u’v − uv’) / v²
= [−sin x · log x − cos x · (1/x)] / (log x)²
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = [−sin x · log x − (cos x)/x] / (log x)²
🔵 Question 10:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = cos(log x + eˣ), x > 0
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let u = log x + eˣ ⇒ du/dx = 1/x + eˣ
➡️ dy/dx = −sin(u) · du/dx
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = −sin(log x + eˣ) · (1/x + eˣ)
Exercise 5.5
🔵 Question 1:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = cos x · cos 2x · cos 3x
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = ln(cos x) + ln(cos 2x) + ln(cos 3x)
➡️ Differentiate both sides:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = −tan x − 2 tan 2x − 3 tan 3x
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = y · (−tan x − 2 tan 2x − 3 tan 3x)
➡️ dy/dx = cos x · cos 2x · cos 3x · (−tan x − 2 tan 2x − 3 tan 3x)
🔵 Question 2:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = √[ (x − 1)(x − 2) / (x − 3)(x − 4)(x − 5) ]
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Rewrite in power form:
y = [(x − 1)(x − 2)]^(1/2) · [(x − 3)(x − 4)(x − 5)]^(−1/2)
➡️ Take log both sides:
ln y = (1/2)[ ln(x − 1) + ln(x − 2) − ln(x − 3) − ln(x − 4) − ln(x − 5) ]
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = (1/2)[ 1/(x − 1) + 1/(x − 2) − 1/(x − 3) − 1/(x − 4) − 1/(x − 5) ]
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (1/2) · y · [ 1/(x − 1) + 1/(x − 2) − 1/(x − 3) − 1/(x − 4) − 1/(x − 5) ]
🔵 Question 3:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (log x)^(cos x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = cos x · ln(log x)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = (−sin x) · ln(log x) + cos x · [1 / (log x)] · (1 / x)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (log x)^(cos x) · [ −sin x · ln(log x) + (cos x) / (x · log x) ]
🔵 Question 4:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = xʳ − 2^(sin x)
🟢 Answer:
➡️ d/dx(xʳ) = r · x^(r−1)
➡️ d/dx(2^(sin x)) = 2^(sin x) · ln 2 · cos x
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = r · x^(r−1) − 2^(sin x) · ln 2 · cos x
🔵 Question 5:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x + 3)² · (x + 4)³ · (x + 5)⁴
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = 2 ln(x + 3) + 3 ln(x + 4) + 4 ln(x + 5)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = 2 / (x + 3) + 3 / (x + 4) + 4 / (x + 5)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = y · [ 2/(x + 3) + 3/(x + 4) + 4/(x + 5) ]
➡️ dy/dx = (x + 3)² · (x + 4)³ · (x + 5)⁴ · [ 2/(x + 3) + 3/(x + 4) + 4/(x + 5) ]
🔵 Question 6:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x + 1/x)ˣ + x^(1/x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Let y₁ = (x + 1/x)ˣ
ln y₁ = x · ln(x + 1/x)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y₁) · dy₁/dx = ln(x + 1/x) + x · (1 − 1/x²) / (x + 1/x)
✔️ dy₁/dx = y₁ · [ ln(x + 1/x) + (x − 1/x) / (x + 1/x) ]
✏️ Let y₂ = x^(1/x)
ln y₂ = (1/x) · ln x
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y₂) · dy₂/dx = (1 − ln x) / x²
✔️ dy₂/dx = y₂ · (1 − ln x) / x²
📘 Combine both:
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (x + 1/x)ˣ · [ ln(x + 1/x) + (x − 1/x) / (x + 1/x) ] + x^(1/x) · (1 − ln x) / x²
🔵 Question 7:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (log x)ˣ + x^(log x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Term 1: y₁ = (log x)ˣ
➡️ ln y₁ = x · ln(log x)
➡️ (1/y₁)·dy₁/dx = ln(log x) + 1/(log x)
✔️ dy₁/dx = (log x)ˣ · [ ln(log x) + 1/(log x) ]
✏️ Term 2: y₂ = x^(log x)
➡️ ln y₂ = (log x) · log x = (log x)²
➡️ (1/y₂)·dy₂/dx = 2 (log x) · (1/x)
✔️ dy₂/dx = x^(log x) · [ 2 (log x)/x ]
✅ Final derivative:
dy/dx = (log x)ˣ [ ln(log x) + 1/(log x) ] + x^(log x) [ 2 (log x)/x ]
🔵 Question 8:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (sin x)ˣ + sin⁻¹(√x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Term 1: y₁ = (sin x)ˣ
➡️ ln y₁ = x · ln(sin x)
➡️ (1/y₁)·dy₁/dx = ln(sin x) + x · (cos x/sin x) = ln(sin x) + x cot x
✔️ dy₁/dx = (sin x)ˣ [ ln(sin x) + x cot x ]
✏️ Term 2: y₂ = sin⁻¹(√x) (0 ≤ x ≤ 1)
➡️ dy₂/dx = 1 / √(1 − (√x)²) · d(√x)/dx
➡️ dy₂/dx = 1 / √(1 − x) · (1/(2√x)) = 1 / [ 2√x √(1 − x) ]
✅ Final derivative:
dy/dx = (sin x)ˣ [ ln(sin x) + x cot x ] + 1 / [ 2√x √(1 − x) ]
🔵 Question 9:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = x^(sin x) + (sin x)^(cos x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Term 1: y₁ = x^(sin x)
➡️ ln y₁ = sin x · log x
➡️ (1/y₁)·dy₁/dx = cos x · log x + (sin x)/x
✔️ dy₁/dx = x^(sin x) [ cos x · log x + (sin x)/x ]
✏️ Term 2: y₂ = (sin x)^(cos x)
➡️ ln y₂ = cos x · ln(sin x)
➡️ (1/y₂)·dy₂/dx = (−sin x) · ln(sin x) + cos x · (cos x/sin x)
✔️ dy₂/dx = (sin x)^(cos x) [ −sin x · ln(sin x) + cos x · cot x ]
✅ Final derivative:
dy/dx = x^(sin x) [ cos x · log x + (sin x)/x ] + (sin x)^(cos x) [ −sin x · ln(sin x) + cos x · cot x ]
🔵 Question 10:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = x^(cos x) + (x² + 1)/(x² − 1)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Term 1: y₁ = x^(cos x)
➡️ ln y₁ = cos x · log x
➡️ (1/y₁)·dy₁/dx = (−sin x) · log x + (cos x)/x
✔️ dy₁/dx = x^(cos x) [ −sin x · log x + (cos x)/x ]
✏️ Term 2: y₂ = (x² + 1)/(x² − 1)
➡️ dy₂/dx = [ (2x)(x² − 1) − (x² + 1)(2x) ] / (x² − 1)²
➡️ dy₂/dx = −4x / (x² − 1)²
✅ Final derivative:
dy/dx = x^(cos x) [ −sin x · log x + (cos x)/x ] − 4x / (x² − 1)²
🔵 Question 11:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x cos x)ˣ + (x sin x)ˣ
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Term 1: A = (x cos x)ˣ
➡️ ln A = x · ln(x cos x)
➡️ (1/A)·dA/dx = ln(x cos x) + x · (cos x − x sin x)/(x cos x)
✔️ dA/dx = A [ ln(x cos x) + 1 − x tan x ]
✏️ Term 2: B = (x sin x)ˣ
➡️ ln B = x · ln(x sin x)
➡️ (1/B)·dB/dx = ln(x sin x) + x · (sin x + x cos x)/(x sin x)
✔️ dB/dx = B [ ln(x sin x) + 1 + x cot x ]
✅ Final derivative:
dy/dx = (x cos x)ˣ [ ln(x cos x) + 1 − x tan x ] + (x sin x)ˣ [ ln(x sin x) + 1 + x cot x ]
🔵 Question 12:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x² + 1)^(x² − 1)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = (x² − 1) · ln(x² + 1)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = 2x · ln(x² + 1) + (x² − 1) · (1 / (x² + 1)) · 2x
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (x² + 1)^(x² − 1) · [ 2x · ln(x² + 1) + (2x(x² − 1)) / (x² + 1) ]
🔵 Question 13:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (tan x)^(cot x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = cot x · ln(tan x)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = (−cosec²x) · ln(tan x) + cot x · (sec²x / tan x)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (tan x)^(cot x) · [ −cosec²x · ln(tan x) + (cot x · sec²x) / tan x ]
🔵 Question 14:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (sin x)^(sin x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = sin x · ln(sin x)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = cos x · ln(sin x) + sin x · (cos x / sin x)
➡️ (1 / y) · dy/dx = cos x [ ln(sin x) + 1 ]
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (sin x)^(sin x) · cos x [ ln(sin x) + 1 ]
🔵 Question 15:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x² + 3x + 5)^(x²)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = x² · ln(x² + 3x + 5)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = 2x · ln(x² + 3x + 5) + x² · [ (2x + 3) / (x² + 3x + 5) ]
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (x² + 3x + 5)^(x²) · [ 2x · ln(x² + 3x + 5) + x²(2x + 3) / (x² + 3x + 5) ]
🔵 Question 16:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x³ − 1)^(1/x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = (1 / x) · ln(x³ − 1)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = (−1 / x²) · ln(x³ − 1) + (1 / x) · (3x² / (x³ − 1))
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (x³ − 1)^(1/x) · [ −(ln(x³ − 1) / x²) + 3x / (x³ − 1) ]
🔵 Question 17:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (1 + log x)^(1 / log x)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = (1 / log x) · ln(1 + log x)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = [ −1 / (x (log x)²) ] · ln(1 + log x) + (1 / log x) · [ 1 / (1 + log x) ] · (1 / x)
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (1 + log x)^(1 / log x) · [ − ln(1 + log x) / (x (log x)²) + 1 / (x log x (1 + log x)) ]
🔵 Question 18:
Differentiate with respect to x:
y = (x² + 1)^(x² + 2)
🟢 Answer:
✏️ Take log both sides:
ln y = (x² + 2) · ln(x² + 1)
➡️ Differentiate:
(1 / y) · dy/dx = 2x · ln(x² + 1) + (x² + 2) · (1 / (x² + 1)) · 2x
✔️ Final Answer:
dy/dx = (x² + 1)^(x² + 2) · [ 2x ln(x² + 1) + (2x(x² + 2)) / (x² + 1) ]
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🧭 Section A: 18 MCQs (conceptual + quick applications)
Each has 4 options with a single correct answer.
🔵 Question 1
If f(x) = (x² − 1)/(x − 1) for x ≠ 1, and f(1) = k, find k for which f(x) is continuous at x = 1.
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (C) 2
💡 Reason: limₓ→1 (x² − 1)/(x − 1) = limₓ→1 (x + 1) = 2 ⇒ f(1) = 2 for continuity.
🟢 Question 2
If f and g are continuous at x = a, and g(a) ≠ 0, then which function is also continuous at x = a?
🔵 (A) f(x) + g(x)
🟢 (B) f(x) · g(x)
🟠 (C) f(x) / g(x)
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
🟡 Question 3
If f is differentiable at x = a, then
🔵 (A) f is discontinuous at a
🟢 (B) f is continuous at a
🟠 (C) f is not continuous at a
🔴 (D) None of these
Answer: (B) f is continuous at a
🔴 Question 4
For f(x) = |x − 3|, differentiability at x = 3 is
🔵 (A) Not differentiable
🟢 (B) Differentiable
🟠 (C) Continuous only
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) Not differentiable
🔵 Question 5
If f(x) = sin(x²), find f′(x).
🔵 (A) 2x·cos(x²)
🟢 (B) cos(x²)
🟠 (C) 2x·sin(x²)
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) 2x·cos(x²)
🟢 Question 6
Derivative of tan⁻¹x is
🔵 (A) 1 / √(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) 1 / (1 + x²)
🟠 (C) −1 / (1 + x²)
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) 1 / (1 + x²)
🟡 Question 7
If f(x) = eˣ·sin x, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) eˣ(sin x + cos x)
🟢 (B) eˣ(sin x − cos x)
🟠 (C) eˣ·sin x
🔴 (D) eˣ·cos x
Answer: (A) eˣ(sin x + cos x)
🔴 Question 8
If y = logₐx, then dy/dx =
🔵 (A) 1 / (x·ln a)
🟢 (B) ln a / x
🟠 (C) 1 / ln a
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (A) 1 / (x·ln a)
🔵 Question 9
If f(x) = |x|, then f(x) is
🔵 (A) Continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
🟢 (B) Not continuous at x = 0
🟠 (C) Differentiable at x = 0
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) Continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
🟢 Question 10
If f(x) = cos x, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) −sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) −cos x
Answer: (B) −sin x
🟡 Question 11
If f(x) = x², find f′(2).
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 8
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) 4
🔴 Question 12
For f(x) = eˣ, what is f′(x)?
🔵 (A) eˣ
🟢 (B) x·eˣ
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) eˣ
🔵 Question 13
The function f(x) = ln(sin x) is continuous for
🔵 (A) x ∈ (0, π)
🟢 (B) x ∈ (0, π) ∪ (2π, 3π) ∪ …
🟠 (C) x ∈ ℝ
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) x where sin x > 0
🟢 Question 14
If f(x) = xˣ, then f′(x) =
🔵 (A) xˣ
🟢 (B) xˣ·(1 + ln x)
🟠 (C) xˣ·ln x
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) xˣ·(1 + ln x)
🟡 Question 15
For y = aˣ, dy/dx =
🔵 (A) aˣ
🟢 (B) aˣ·ln a
🟠 (C) ln a
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) aˣ·ln a
🔴 Question 16
Derivative of cos⁻¹x is
🔵 (A) 1 / √(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) −1 / √(1 − x²)
🟠 (C) 1 / (1 + x²)
🔴 (D) −1 / (1 + x²)
Answer: (B) −1 / √(1 − x²)
🔵 Question 17
If y = ln x, then d²y/dx² =
🔵 (A) 1/x²
🟢 (B) −1/x²
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (B) −1/x²
🟢 Question 18
If f(x) = x³, then f″(x) =
🔵 (A) 6x
🟢 (B) 3x²
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 6x
🔵 Question 19
If f(x) = x² + 3x + 2, find f′(x).
🟢 Answer:
f′(x) = d/dx(x²) + d/dx(3x) + d/dx(2)
= 2x + 3 + 0
✅ Final: f′(x) = 2x + 3
🔵 Question 20
Check continuity of
f(x) = { x², x < 1; 2x − 1, x ≥ 1 } at x = 1.
🟢 Answer:
f(1) = 2(1) − 1 = 1
LHL = lim x→1⁻ f(x) = 1² = 1
RHL = lim x→1⁺ f(x) = 2(1) − 1 = 1
✅ LHL = RHL = f(1) ⇒ Continuous at x = 1
🔵 Question 21
Check differentiability of f(x) = |x| at x = 0.
🟢 Answer:
For x > 0, f(x) = x ⇒ f′(x) = 1
For x < 0, f(x) = −x ⇒ f′(x) = −1
Left ≠ Right ⇒ Not differentiable at x = 0
🔵 Question 22
Find derivative of f(x) = sin(3x).
🟢 Answer:
d/dx [sin(ax)] = a cos(ax)
⇒ f′(x) = 3 cos(3x)
✅ Final: f′(x) = 3 cos(3x)
🔵 Question 23
If f(x) = e(2x), find f″(x).
🟢 Answer:
f′(x) = 2 e(2x)
f″(x) = 4 e(2x)
✅ Final: f″(x) = 4 e(2x)
🔵 Question 24
Find dy/dx if y = ln(sin x).
🟢 Answer:
dy/dx = (1 / sin x) × cos x = cot x
✅ Final: dy/dx = cot x
🔵 Question 25
Find dy/dx if y = xx.
🟢 Answer:
Take log: ln y = x ln x
Differentiate: (1/y) dy/dx = ln x + 1
⇒ dy/dx = y (ln x + 1) = xx (ln x + 1)
✅ Final: dy/dx = xx (1 + ln x)
🔵 Question 26
Find dy/dx if y = sin⁻¹(x²).
🟢 Answer:
dy/dx = 1 / √(1 − (x²)²) × 2x = 2x / √(1 − x⁴)
✅ Final: dy/dx = 2x / √(1 − x⁴)
🔵 Question 27
If y = tan⁻¹(2x / (1 − x²)), show dy/dx = 2 / (1 + x²).
🟢 Answer:
Use identity tan(2θ) = 2 tan θ / (1 − tan² θ).
Let θ = tan⁻¹ x ⇒ y = tan⁻¹[tan(2θ)] = 2θ = 2 tan⁻¹ x
Differentiate: dy/dx = 2 × 1/(1 + x²)
✅ Final: dy/dx = 2 / (1 + x²)
🔵 Question 28
If f(x) = ln(x² + 1), find f′(x) and f″(x).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: f′(x) = d/dx[ln(x² + 1)] = 1 / (x² + 1) · 2x
✔️ f′(x) = 2x / (x² + 1)
➡️ Step 2: f″(x) = d/dx [2x / (x² + 1)]
➡️ Use quotient rule: (u/v)′ = (u′v − uv′)/v², u = 2x, v = x² + 1
u′ = 2, v′ = 2x
f″(x) = [2(x² + 1) − 2x·2x] / (x² + 1)²
f″(x) = [2x² + 2 − 4x²] / (x² + 1)²
f″(x) = (−2x² + 2) / (x² + 1)²
✔️ Final: f″(x) = 2(1 − x²) / (x² + 1)²
🔵 Question 29
If y = e^(x²) · sin x, find dy/dx.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: Use product rule: (u·v)′ = u′v + uv′, u = e^(x²), v = sin x
u′ = 2x e^(x²), v′ = cos x
➡️ Step 2: dy/dx = u′v + uv′ = (2x e^(x²))·sin x + e^(x²)·cos x
✔️ Final: dy/dx = 2x e^(x²) sin x + e^(x²) cos x
🔵 Question 30
Find dy/dx if x² + xy + y² = 7 (implicit differentiation).
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: Differentiate both sides w.r.t x:
d/dx(x²) + d/dx(xy) + d/dx(y²) = d/dx(7)
➡️ 2x + (x·dy/dx + y) + 2y·dy/dx = 0
➡️ Step 2: Combine dy/dx terms:
x·dy/dx + 2y·dy/dx = dy/dx(2y + x)
2x + y + dy/dx(2y + x) = 0
➡️ Step 3: Solve for dy/dx:
dy/dx = −(2x + y) / (2y + x)
✔️ Final: dy/dx = −(2x + y) / (2y + x)
🔵 Question 31
If x = t² + 1, y = t³ − t, find dy/dx in parametric form.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: dx/dt = 2t, dy/dt = 3t² − 1
➡️ Step 2: dy/dx = (dy/dt) / (dx/dt) = (3t² − 1) / (2t)
✔️ Final: dy/dx = (3t² − 1) / (2t)
🔵 Question 32 (Case/Application)
A particle moves along y = x³ − 3x. Find the slope of the tangent at x = 2 and determine if it is increasing or decreasing.
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: y′ = d/dx (x³ − 3x) = 3x² − 3
➡️ Step 2: At x = 2, slope = 3(2)² − 3 = 12 − 3 = 9
➡️ Step 3: y″ = d/dx (3x² − 3) = 6x
At x = 2, y″ = 12 > 0 → slope is increasing
✔️ Final: Tangent slope = 9, slope increasing at x = 2
🔵 Question 33 (Case/Application)
If y = x²·ln x, find dy/dx and d²y/dx².
🟢 Answer:
➡️ Step 1: dy/dx = d/dx(x²)·ln x + x²·d/dx(ln x) = 2x ln x + x²·(1/x) = 2x ln x + x
➡️ Step 2: d²y/dx² = d/dx(2x ln x + x)
= 2·(ln x + 1) + 1 = 2 ln x + 3
✔️ Final: dy/dx = 2x ln x + x, d²y/dx² = 2 ln x + 3
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
If f(x) = |x|, then f(x) is differentiable at
🟥 1️⃣ x = 0
🟩 2️⃣ x = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x = -1
🟦 4️⃣ None of these
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ x = 1
💡 Hint: f(x) = |x| is non-differentiable only at x = 0.
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2024, Shift 1)
🔵 Question 2:
If f(x) = |x – 2|, then f(x) is not differentiable at
🟥 1️⃣ x = 2
🟩 2️⃣ x = 0
🟨 3️⃣ x = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x = -2
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ x = 2
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2023, Shift 2)
🔵 Question 3:
f(x) = x² sin(1/x) for x ≠ 0 and f(0) = 0. Then f(x) is
🟥 1️⃣ Continuous but not differentiable at x = 0
🟩 2️⃣ Differentiable at x = 0
🟨 3️⃣ Discontinuous at x = 0
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ Differentiable at x = 0
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2022, Shift 1)
🔵 Question 4:
If f(x) = x² and g(x) = sin x, then (f·g)'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x sin x
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
🟨 3️⃣ x² cos x
🟦 4️⃣ 2x cos x + x² sin x
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
💡 Hint: (fg)’ = f’g + fg’
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2021, Shift 1)
🔵 Question 5:
If y = tan⁻¹(sin x + cos x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ (cos x – sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟩 2️⃣ (cos x + sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟨 3️⃣ (sin x – cos x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ (cos x – sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2020, Shift 2)
🔵 Question 6:
The derivative of f(x) = xˣ is
🟥 1️⃣ xˣ (1 + ln x)
🟩 2️⃣ xˣ⁻¹ (1 + ln x)
🟨 3️⃣ xˣ ln x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ xˣ (1 + ln x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 7:
If f(x) = e^(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x e^(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ x e^(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 2x e^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x e^(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2024, Shift 2)
🔵 Question 8:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ √(1 – x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / x²
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2023, Shift 1)
🔵 Question 9:
If f(x) = log(sin x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ tan x
🟨 3️⃣ csc x
🟦 4️⃣ sec x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 10:
If f(x) = tan⁻¹(x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / x
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (1 + tan² x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 11:
If y = log(x² + 1), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ 2 / (x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ 2 / x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 12:
If f(x) = sin x cos x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ cos²x – sin²x
🟩 2️⃣ cos²x + sin²x
🟨 3️⃣ 2 cos²x
🟦 4️⃣ sin²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cos²x – sin²x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 13:
If f(x) = sin(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ cos(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2 sin(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ sin(2x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2024)
🔵 Question 14:
If y = cos⁻¹(x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -1 / √(1 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
🟨 3️⃣ -√(1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ √(1 – x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -1 / √(1 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2023)
🔵 Question 15:
If y = e^(sin x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(cos x) sin x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(sin x) sin x
🟦 4️⃣ e^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2022)
🔵 Question 16:
If y = log(tan x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (sin x cos x)
🟩 2️⃣ sec²x
🟨 3️⃣ tan x
🟦 4️⃣ csc²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (sin x cos x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2021)
🔵 Question 17:
If f(x) = 1 / (x² + 1), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x / (x² + 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)²
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ -1 / (x² + 1)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x / (x² + 1)²
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2020)
🔵 Question 18:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(x / 2), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / √(4 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (2√(1 – (x/2)²))
🟨 3️⃣ x / √(4 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (4 – x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / √(4 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2019)
🔵 Question 19:
If f(x) = x sin x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x – x cos x
🟨 3️⃣ cos x + x sin x
🟦 4️⃣ cos x – x sin x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2018)
🔵 Question 20:
If f(x) = (log x) / x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ (1 – log x) / x²
🟩 2️⃣ (1 + log x) / x²
🟨 3️⃣ (log x – 1) / x²
🟦 4️⃣ log x / x²
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ (1 – log x) / x²
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2017)
🔵 Question 21:
If f(x) = x³, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 3x²
🟩 2️⃣ x²
🟨 3️⃣ 2x
🟦 4️⃣ x³
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3x²
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 22:
If f(x) = sin(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2 cos(2x)
🟩 2️⃣ cos(2x)
🟨 3️⃣ sin(2x)
🟦 4️⃣ 2 sin(2x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 cos(2x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2016)
🔵 Question 23:
If y = cos(3x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -3 sin(3x)
🟩 2️⃣ 3 sin(3x)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(3x)
🟦 4️⃣ -cos(3x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -3 sin(3x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 24:
If y = e^(2x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2e^(2x)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(2x)
🟨 3️⃣ 2e^x
🟦 4️⃣ e^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2e^(2x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2015)
🔵 Question 25:
If y = log₁₀(x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (x ln 10)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / x
🟨 3️⃣ ln 10 / x
🟦 4️⃣ 10^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (x ln 10)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 26:
If y = √(x² + 1), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ x / √(x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ 2x / √(x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ (x² + 1)^(1/2)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ x / √(x² + 1)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2014)
🔵 Question 27:
If y = sin⁻¹(x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / √(1 – x⁴)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x⁴)
🟨 3️⃣ 2x / (1 + x⁴)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / √(1 – x⁴)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 28:
If f(x) = tan⁻¹(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2 / (1 + 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (1 + 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2x / (1 + 4x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 4x / (1 + 4x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 / (1 + 4x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2013)
🔵 Question 29:
If y = log(sin x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ -cot x
🟨 3️⃣ tan x
🟦 4️⃣ -tan x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 30:
If y = log(cos x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -tan x
🟩 2️⃣ tan x
🟨 3️⃣ cot x
🟦 4️⃣ -cot x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -tan x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2012)
🔵 Question 31:
If y = e^(tan x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(tan x) sec²x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(tan x) tan x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(tan x)
🟦 4️⃣ sec²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(tan x) sec²x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2011)
🔵 Question 32:
If f(x) = cos⁻¹(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2 / √(1 – 4x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2011)
🔵 Question 33:
If y = tan⁻¹(√x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / [2√x (1 + x)]
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / [√x (1 + x)]
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + x)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / √x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / [2√x (1 + x)]
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2010)
🔵 Question 34:
If y = sin(x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ sin(x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2010)
🔵 Question 35:
If y = cos(x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x sin(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x sin(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2009)
🔵 Question 36:
If f(x) = e^(sin x) + cos x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x – sin x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x – sin x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x + sin x
🟦 4️⃣ e^(sin x) sin x + cos x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x – sin x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2009)
🔵 Question 37:
If f(x) = log(x² + 2), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 2)
🟩 2️⃣ 2 / (x² + 2)
🟨 3️⃣ x / (x² + 2)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (x² + 2)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 2)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2008)
🔵 Question 38:
If y = tan⁻¹(sin x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin²x)
🟩 2️⃣ -cos x / (1 + sin²x)
🟨 3️⃣ sin x / (1 + cos²x)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin²x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2008)
🔵 Question 39:
If y = √(tan x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ sec²x / (2√(tan x))
🟩 2️⃣ sec²x / √(tan x)
🟨 3️⃣ √(tan x) sec²x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ sec²x / (2√(tan x))
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2007)
🔵 Question 40:
If y = sin⁻¹(x³), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3x² / √(1 – x⁶)
🟩 2️⃣ 3x² / √(1 + x⁶)
🟨 3️⃣ x² / √(1 – x⁶)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3x² / √(1 – x⁶)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2007)
🔵 Question 41:
If y = log(x³), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / x
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / x
🟨 3️⃣ log 3x
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (3x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3 / x
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2006)
🔵 Question 42:
If f(x) = e^(2x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 4x e^(2x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x e^(2x²)
🟨 3️⃣ e^(2x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 4x e^(2x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2005)
🔵 Question 43:
If y = tan⁻¹(3x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / (1 + 9x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (1 + 3x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 3x / (1 + 9x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (1 + 9x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3 / (1 + 9x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2005)
🔵 Question 44:
If f(x) = cos⁻¹(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x / √(1 – x⁴)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x / √(1 – x⁴)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x⁴)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x / √(1 – x⁴)
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2004)
🔵 Question 45:
If f(x) = e^(log x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1
🟩 2️⃣ log x
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / x
🟦 4️⃣ e^(log x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1
📘 (Exam: JEE Main 2003)
🔵 Question 46:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2x / √(1 – 4x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
📘 (Exam: AIEEE 2002)
🔵 Question 47:
If y = tan⁻¹(1/x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -1 / (x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / x²
🟦 4️⃣ -1 / x²
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -1 / (x² + 1)
📘 (Exam: AIEEE 2002)
🔵 Question 48:
If y = log(1 + x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ x / (1 + x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 2 / (1 + x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (1 + x²)
📘 (Exam: AIEEE 2001)
🔵 Question 49:
If f(x) = e^(3x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 3e^(3x)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(3x)
🟨 3️⃣ 3x e^(3x)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3e^(3x)
📘 (Exam: AIEEE 2001)
🔵 Question 50:
If y = sin(x³), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3x² cos(x³)
🟩 2️⃣ 3x cos(x³)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(x³)
🟦 4️⃣ sin(x³)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3x² cos(x³)
📘 (Exam: AIEEE 2001)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Let f(x) = |x|. Then f(x) is differentiable at
🟥 1️⃣ x = 0
🟩 2️⃣ x = 1
🟨 3️⃣ x = -1
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ x = 1
💡 Hint: |x| is non-differentiable only at x = 0.
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2024 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 2:
If f(x) = |x – 2|, then f(x) is not differentiable at
🟥 1️⃣ x = 2
🟩 2️⃣ x = 0
🟨 3️⃣ x = 1
🟦 4️⃣ x = -2
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ x = 2
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2023 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 3:
Let f(x) = x² sin(1/x) for x ≠ 0 and f(0) = 0. Then f is
🟥 1️⃣ continuous but not differentiable at 0
🟩 2️⃣ differentiable at 0
🟨 3️⃣ discontinuous at 0
🟦 4️⃣ none of these
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ differentiable at 0
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2023 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 4:
If f(x) = x² and g(x) = sin x, then derivative of (f·g) is
🟥 1️⃣ 2x sin x
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
🟨 3️⃣ x² cos x
🟦 4️⃣ 2x cos x + x² sin x
🟡 Answer: 2️⃣ 2x sin x + x² cos x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2022 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 5:
If y = tan⁻¹(sin x + cos x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ (cos x – sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟩 2️⃣ (cos x + sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟨 3️⃣ (sin x – cos x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
🟦 4️⃣ none
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ (cos x – sin x) / [1 + (sin x + cos x)²]
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2022 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 6:
The derivative of f(x) = xˣ is
🟥 1️⃣ xˣ (1 + ln x)
🟩 2️⃣ xˣ⁻¹ (1 + ln x)
🟨 3️⃣ xˣ ln x
🟦 4️⃣ none
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ xˣ (1 + ln x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2021 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 7:
If f(x) = e^(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x e^(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ e^(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ x e^(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 2x e^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x e^(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2021 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 8:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ √(1 – x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / x²
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 9:
If f(x) = log(sin x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ cot x
🟩 2️⃣ tan x
🟨 3️⃣ csc x
🟦 4️⃣ sec x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cot x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 10:
If f(x) = tan⁻¹(x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / x
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (1 + tan² x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (1 + x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 11:
If y = log(x² + 1), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟨 3️⃣ 2 / (x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ 2 / x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 12:
If f(x) = sin x cos x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ cos²x – sin²x
🟩 2️⃣ cos²x + sin²x
🟨 3️⃣ 2 cos²x
🟦 4️⃣ sin²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cos²x – sin²x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 13:
If f(x) = sin(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ cos(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2 sin(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ sin(2x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 14:
If y = cos⁻¹(x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -1 / √(1 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x²)
🟨 3️⃣ -√(1 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ √(1 – x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -1 / √(1 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 15:
If y = e^(sin x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(cos x) sin x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(sin x) sin x
🟦 4️⃣ e^x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 16:
If y = log(tan x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / (sin x cos x)
🟩 2️⃣ sec²x
🟨 3️⃣ tan x
🟦 4️⃣ csc²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / (sin x cos x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2016 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 17:
If f(x) = 1 / (x² + 1), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x / (x² + 1)²
🟩 2️⃣ 2x / (x² + 1)²
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (x² + 1)
🟦 4️⃣ -1 / (x² + 1)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x / (x² + 1)²
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2015 | Paper: 1)
🔵 Question 18:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(x/2), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / √(4 – x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / (2√(1 – (x/2)²))
🟨 3️⃣ x / √(4 – x²)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (4 – x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / √(4 – x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2024 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 19:
If f(x) = x sin x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
🟩 2️⃣ sin x – x cos x
🟨 3️⃣ cos x + x sin x
🟦 4️⃣ cos x – x sin x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ sin x + x cos x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2023 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 20:
If f(x) = (log x)/x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ (1 – log x)/x²
🟩 2️⃣ (1 + log x)/x²
🟨 3️⃣ (log x – 1)/x²
🟦 4️⃣ log x / x²
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ (1 – log x)/x²
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2022 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 21:
If f(x) = e^(tan x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(tan x) sec²x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(tan x) tan x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(tan x)
🟦 4️⃣ sec²x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(tan x) sec²x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2021 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 22:
If f(x) = cos⁻¹(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2 / √(1 – 4x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2021 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 23:
If y = tan⁻¹(√x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 1 / [2√x (1 + x)]
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / [√x (1 + x)]
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / (1 + x)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / √x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 1 / [2√x (1 + x)]
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 24:
If y = sin(x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ sin(x²)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x cos(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2020 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 25:
If y = cos(x²), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x sin(x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x sin(x²)
🟨 3️⃣ cos(x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x sin(x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 26:
If f(x) = e^(sin x) + cos x, then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x – sin x
🟩 2️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x + sin x
🟨 3️⃣ e^(sin x) sin x + cos x
🟦 4️⃣ e^(cos x) sin x – cos x
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ e^(sin x) cos x – sin x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2019 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 27:
If f(x) = log(x² + 2), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 2)
🟩 2️⃣ 2 / (x² + 2)
🟨 3️⃣ x / (x² + 2)
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (x² + 2)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2x / (x² + 2)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 28:
If y = tan⁻¹(sin x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin²x)
🟩 2️⃣ -cos x / (1 + sin²x)
🟨 3️⃣ sin x / (1 + cos²x)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ cos x / (1 + sin²x)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2018 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 29:
If y = √(tan x), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ sec²x / (2√(tan x))
🟩 2️⃣ sec²x / √(tan x)
🟨 3️⃣ √(tan x) sec²x
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ sec²x / (2√(tan x))
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 30:
If y = sin⁻¹(x³), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3x² / √(1 – x⁶)
🟩 2️⃣ 3x² / √(1 + x⁶)
🟨 3️⃣ x² / √(1 – x⁶)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3x² / √(1 – x⁶)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2017 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 31:
If y = log(x³), then dy/dx =
🟥 1️⃣ 3 / x
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / x
🟨 3️⃣ log 3x
🟦 4️⃣ 1 / (3x)
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 3 / x
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2016 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 32:
If f(x) = e^(2x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 4x e^(2x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x e^(2x²)
🟨 3️⃣ e^(2x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 4x e^(2x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2015 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 33:
If f(x) = cos⁻¹(x²), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ -2x / √(1 – x⁴)
🟩 2️⃣ 2x / √(1 – x⁴)
🟨 3️⃣ 1 / √(1 – x⁴)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ -2x / √(1 – x⁴)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2015 | Paper: 2)
🔵 Question 34:
If f(x) = sin⁻¹(2x), then f'(x) =
🟥 1️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟩 2️⃣ 1 / √(1 – 4x²)
🟨 3️⃣ 2x / √(1 – 4x²)
🟦 4️⃣ None
🟡 Answer: 1️⃣ 2 / √(1 – 4x²)
📘 (Exam: JEE Advanced 2014 | Paper: 2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1–Q20 (NEET-Level)
Q1. If f(x) = (x² − 1)/(x − 1) for x ≠ 1, and f(1) = k, find k for continuity.
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (C) 2
Q2. If f and g are continuous at x = a and g(a) ≠ 0, which is continuous at x = a?
🔵 (A) f(x) + g(x)
🟢 (B) f(x) · g(x)
🟠 (C) f(x)/g(x)
🔴 (D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
Q3. Differentiable at x = a implies
🔵 (A) Not continuous
🟢 (B) Continuous
🟠 (C) May be discontinuous
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) Continuous
Q4. f(x) = |x − 3| at x = 3 is
🔵 (A) Not differentiable
🟢 (B) Differentiable
🟠 (C) Continuous only
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) Not differentiable
Q5. If f(x) = sin(x²), f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 2x·cos(x²)
🟢 (B) cos(x²)
🟠 (C) 2x·sin(x²)
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) 2x·cos(x²)
Q6. Derivative of tan⁻¹x =
🔵 (A) 1/√(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) 1/(1 + x²)
🟠 (C) −1/(1 + x²)
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) 1/(1 + x²)
Q7. f(x) = eˣ·sin x, f′(x) =
🔵 (A) eˣ(sin x + cos x)
🟢 (B) eˣ(sin x − cos x)
🟠 (C) eˣ·sin x
🔴 (D) eˣ·cos x
Answer: (A) eˣ(sin x + cos x)
Q8. y = logₐx, dy/dx =
🔵 (A) 1/(x·ln a)
🟢 (B) ln a / x
🟠 (C) 1/ln a
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (A) 1/(x·ln a)
Q9. f(x) = |x| is
🔵 (A) Continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
🟢 (B) Not continuous at x = 0
🟠 (C) Differentiable at x = 0
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (A) Continuous everywhere but not differentiable at x = 0
Q10. f(x) = cos x, f′(x) =
🔵 (A) sin x
🟢 (B) −sin x
🟠 (C) cos x
🔴 (D) −cos x
Answer: (B) −sin x
Q11. f(x) = x², f′(2) =
🔵 (A) 2
🟢 (B) 4
🟠 (C) 8
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) 4
Q12. f(x) = eˣ, f′(x) =
🔵 (A) eˣ
🟢 (B) x·eˣ
🟠 (C) 1
🔴 (D) 0
Answer: (A) eˣ
Q13. f(x) = ln(sin x), continuous for
🔵 (A) x ∈ (0, π)
🟢 (B) x ∈ (0, π) ∪ (2π, 3π) ∪ …
🟠 (C) x ∈ ℝ
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) x ∈ (0, π) ∪ (2π, 3π) ∪ …
Q14. f(x) = xˣ, f′(x) =
🔵 (A) xˣ
🟢 (B) xˣ·(1 + ln x)
🟠 (C) xˣ·ln x
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) xˣ·(1 + ln x)
Q15. f(x) = aˣ, dy/dx =
🔵 (A) aˣ
🟢 (B) aˣ·ln a
🟠 (C) ln a
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (B) aˣ·ln a
Q16. Derivative of cos⁻¹x =
🔵 (A) 1 / √(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) −1 / √(1 − x²)
🟠 (C) 1 / (1 + x²)
🔴 (D) −1 / (1 + x²)
Answer: (B) −1 / √(1 − x²)
Q17. d²/dx² ln x =
🔵 (A) 1/x²
🟢 (B) −1/x²
🟠 (C) 0
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (B) −1/x²
Q18. f″(x) for x³ =
🔵 (A) 6x
🟢 (B) 3x²
🟠 (C) 2
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 6x
Q19. f(x) = x² + 3x + 2, f′(x) =
🔵 (A) 2x + 3
🟢 (B) 2x + 2
🟠 (C) 3x + 2
🔴 (D) x² + 3
Answer: (A) 2x + 3
Q20. f(x) = { x², x < 1; 2x − 1, x ≥ 1 }, continuous at x = 1?
🔵 (A) Yes
🟢 (B) No
🟠 (C) Only from left
🔴 (D) Only from right
Answer: (A) Yes
Q21
If f(x) = ln(x² + 1), find f′(x).
🔵 (A) 2x / (x² + 1)
🟢 (B) 1 / (x² + 1)
🟠 (C) x / (x² + 1)
🔴 (D) ln(x² + 1)
Answer: (A) 2x / (x² + 1)
Q22
For f(x) = e^(3x)·cos x, find f′(x).
🔵 (A) 3e^(3x)·cos x − e^(3x)·sin x
🟢 (B) 3e^(3x)·cos x + e^(3x)·sin x
🟠 (C) e^(3x)·(cos x − sin x)
🔴 (D) e^(3x)·(cos x + sin x)
Answer: (A) 3e^(3x)·cos x − e^(3x)·sin x
Q23
y = x²·ln x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) x² ln x
🟢 (B) 2x ln x + x
🟠 (C) 2 ln x + x²
🔴 (D) ln x + 2x
Answer: (B) 2x ln x + x
Q24
y = sin⁻¹(x²), find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x / √(1 − x²)
🟢 (B) 2x / √(1 − x⁴)
🟠 (C) 1 / √(1 − x²)
🔴 (D) 1 / √(1 − x⁴)
Answer: (B) 2x / √(1 − x⁴)
Q25
y = tan⁻¹(2x / (1 − x²)), dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 1 / (1 + x²)
🟢 (B) 2 / (1 + x²)
🟠 (C) 2 / (1 − x²)
🔴 (D) 1 / (1 − x²)
Answer: (B) 2 / (1 + x²)
Q26
Check differentiability of f(x) = |x − 2| at x = 2.
🔵 (A) Differentiable
🟢 (B) Not differentiable
🟠 (C) Continuous but not differentiable
🔴 (D) None
Answer: (B) Not differentiable
Q27
If y = e^(x²)·sin x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x e^(x²) sin x + e^(x²) cos x
🟢 (B) 2 e^(x²) sin x + cos x
🟠 (C) e^(x²) (2x + cos x)
🔴 (D) e^(x²) sin x
Answer: (A) 2x e^(x²) sin x + e^(x²) cos x
Q28
y = x^x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) x^x
🟢 (B) x^x (1 + ln x)
🟠 (C) x^x ln x
🔴 (D) ln x
Answer: (B) x^x (1 + ln x)
Q29
f(x) = x³ + x² + x, find f″(x).
🔵 (A) 6x + 2
🟢 (B) 3x² + 2x
🟠 (C) 6x + 2 ?
🔴 (D) 2x + 1
Answer: (A) 6x + 2
Q30
Implicit differentiation: x² + xy + y² = 7, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) −(2x + y)/(2y + x)
🟢 (B) (2x + y)/(2y + x)
🟠 (C) −(x + 2y)/(x + 2y)
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) −(2x + y)/(2y + x)
Q31
Parametric differentiation: x = t² + 1, y = t³ − t, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) (3t² − 1)/2t
🟢 (B) (3t² + 1)/2t
🟠 (C) 2t / (3t² − 1)
🔴 (D) (3t² − 1)/t
Answer: (A) (3t² − 1)/2t
Q32
Particle moves along y = x³ − 3x. Slope of tangent at x = 2?
🔵 (A) 9, slope decreasing
🟢 (B) 9, slope increasing
🟠 (C) 3, slope increasing
🔴 (D) 3, slope decreasing
Answer: (B) 9, slope increasing
Q33
y = ln(x² + 1), find f′′(x).
🔵 (A) 2 / (x² + 1)
🟢 (B) 2(1 − x²) / (x² + 1)²
🟠 (C) 2x / (x² + 1)
🔴 (D) −2x / (x² + 1)
Answer: (B) 2(1 − x²) / (x² + 1)²
Q34
y = x² ln x, d²y/dx² = ?
🔵 (A) 2 ln x + 3
🟢 (B) 2x ln x + 1
🟠 (C) 2x + ln x
🔴 (D) 2 ln x + 1
Answer: (A) 2 ln x + 3
Q35
y = sin(x²) + cos x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x cos(x²) − sin x
🟢 (B) 2x sin(x²) − cos x
🟠 (C) cos(x²) − sin x
🔴 (D) 2x cos(x²) + cos x
Answer: (A) 2x cos(x²) − sin x
Q36
y = e^x / x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) (x e^x − e^x) / x²
🟢 (B) (x e^x + e^x) / x²
🟠 (C) e^x / x²
🔴 (D) (x − 1) e^x / x²
Answer: (A) (x e^x − e^x) / x²
Q37
y = ln(sin x²), dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 1 / sin x²
🟢 (B) 2x cot(x²)
🟠 (C) 2x / sin x²
🔴 (D) cot(x²)
Answer: (B) 2x cot(x²)
Q38
y = sec⁻¹ x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 1 / (x √(x² − 1))
🟢 (B) −1 / (x √(x² − 1))
🟠 (C) 1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
🔴 (D) −1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
Answer: (C) 1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
Q39
y = csc⁻¹ x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
🟢 (B) −1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
🟠 (C) 1 / (x √(x² − 1))
🔴 (D) −1 / (x √(x² − 1))
Answer: (B) −1 / (|x| √(x² − 1))
Q40
If f(x) = |x + 1| + |x − 1|, dy/dx at x = 0?
🔵 (A) 0
🟢 (B) 1
🟠 (C) −1
🔴 (D) Does not exist
Answer: (D) Does not exist
🔵 Q41
y = x²·ln(x² + 1), find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x·ln(x² + 1) + 2x² / (x² + 1)
🟢 (B) 2x·ln(x² + 1) + x² / (x² + 1)
🟠 (C) x·ln(x² + 1) + 2x² / (x² + 1)
🔴 (D) 2x·ln(x² + 1) + 1
Answer: (A) 2x·ln(x² + 1) + 2x² / (x² + 1)
🔵 Q42
y = tan⁻¹(x²), find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 1 / (1 + x²)
🟢 (B) 2x / (1 + x⁴)
🟠 (C) 2x / (1 + x²)
🔴 (D) 1 / (1 + x⁴)
Answer: (B) 2x / (1 + x⁴)
🔵 Q43
Implicit: x² + y² + x·y = 3, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) −(2x + y) / (2y + x)
🟢 (B) (2y + x) / (2x + y)
🟠 (C) −(x + 2y) / (x + 2y)
🔴 (D) 1
Answer: (A) −(2x + y) / (2y + x)
🔵 Q44
Parametric: x = t² − 1, y = t³ + t, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) (3t² + 1) / 2t
🟢 (B) (3t² − 1) / 2t
🟠 (C) (3t² − 1) / t
🔴 (D) 2t / (3t² − 1)
Answer: (B) (3t² − 1) / 2t
🔵 Q45
y = ln(sin(x²)) + cos x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x·cot(x²) − sin x
🟢 (B) 2x·cot(x²) + sin x
🟠 (C) 2x·cot(x²) − cos x
🔴 (D) 2x·cot(x²) + cos x
Answer: (C) 2x·cot(x²) − cos x
🔵 Q46
y = eˣ² / x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) (2x·eˣ²·x − eˣ²) / x²
🟢 (B) (2x·eˣ² − eˣ²) / x²
🟠 (C) (eˣ² − 2x·eˣ²) / x²
🔴 (D) eˣ² / x²
Answer: (B) (2x·eˣ² − eˣ²) / x²
🔵 Q47
y = x³·ln x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 3x²·ln x + x²
🟢 (B) 3x²·ln x + 3x²
🟠 (C) 3x·ln x + x²
🔴 (D) 3x·ln x + 3x²
Answer: (A) 3x²·ln x + x²
🔵 Q48
y = sec⁻¹ x + csc⁻¹ x, dy/dx = ?
🔵 (A) 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1)) − 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1))
🟢 (B) 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1)) + 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1))
🟠 (C) −1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1)) − 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1))
🔴 (D) −1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1)) + 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1))
Answer: (B) 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1)) + 1 / (|x|·√(x² − 1))
🔵 Q49
y = x²·eˣ, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) 2x·eˣ + x²·eˣ
🟢 (B) 2x·eˣ − x²·eˣ
🟠 (C) x²·eˣ
🔴 (D) eˣ·(x² − 2x)
Answer: (A) 2x·eˣ + x²·eˣ
🔵 Q50
y = ln(x² + 1) / x, find dy/dx.
🔵 (A) [2x / (x² + 1) · x − ln(x² + 1)] / x²
🟢 (B) [ln(x² + 1) − 2x / (x² + 1) · x] / x²
🟠 (C) ln(x² + 1) / x²
🔴 (D) 2x / (x² + 1)
Answer: (A) [2x / (x² + 1) · x − ln(x² + 1)] / x²
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
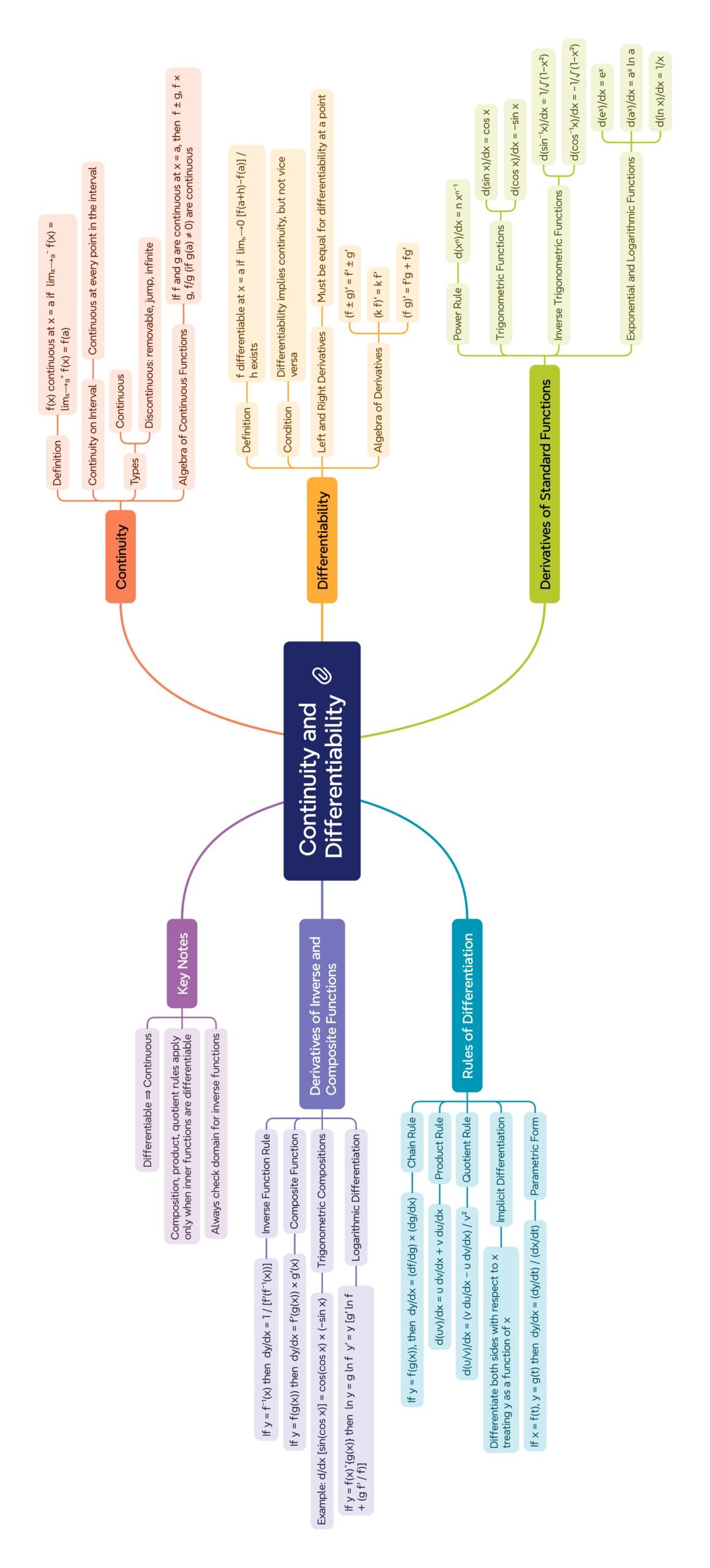
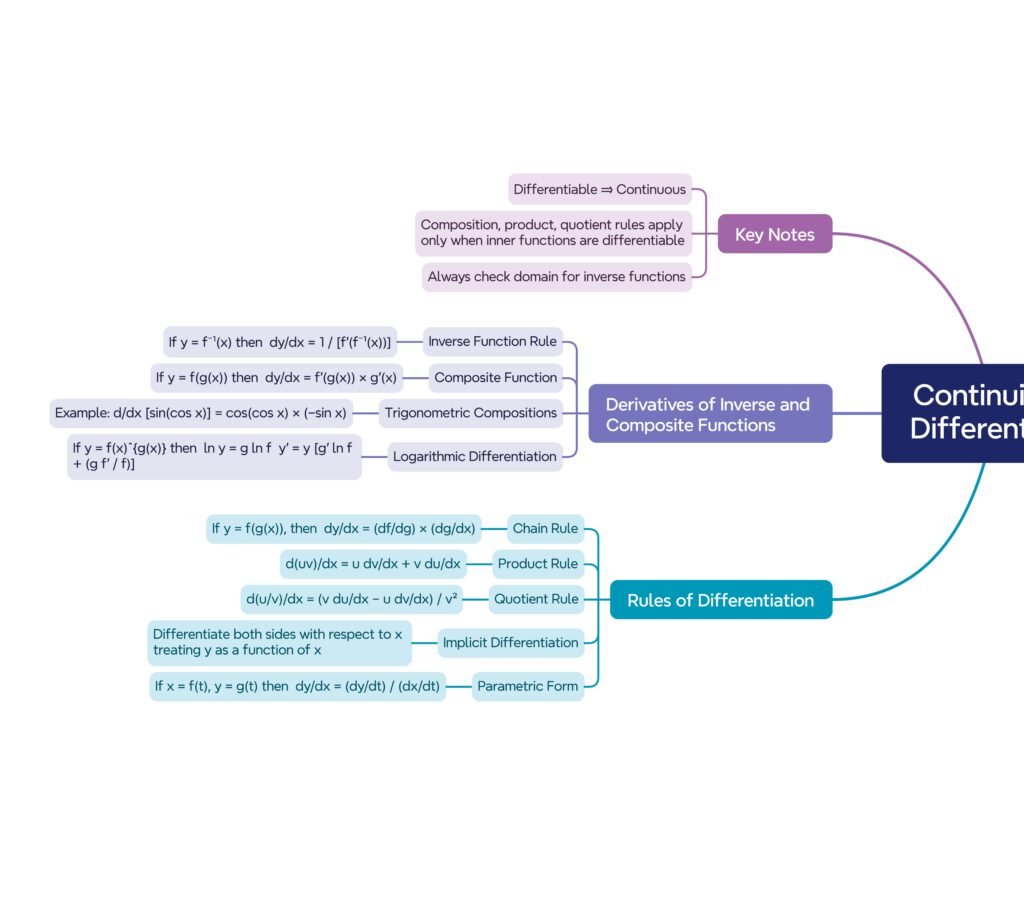
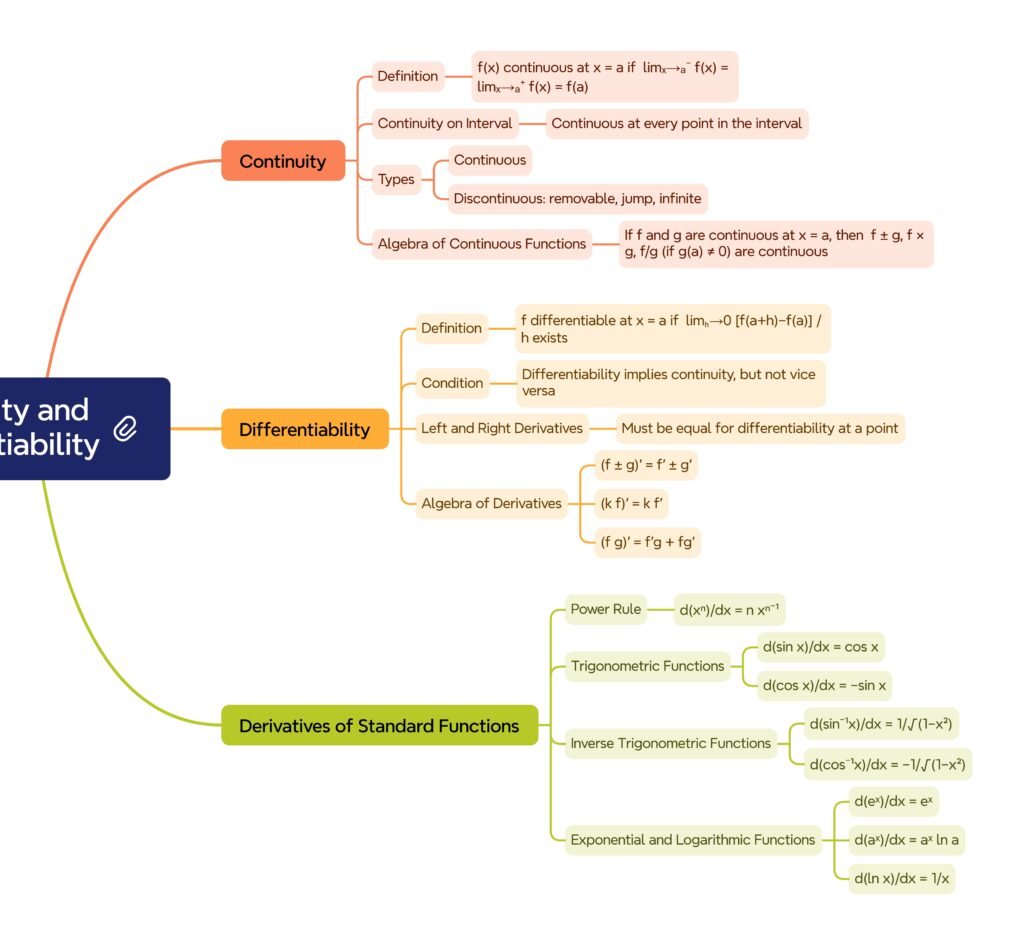
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
